⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-03 更新
Visual Textualization for Image Prompted Object Detection
Authors:Yongjian Wu, Yang Zhou, Jiya Saiyin, Bingzheng Wei, Yan Xu
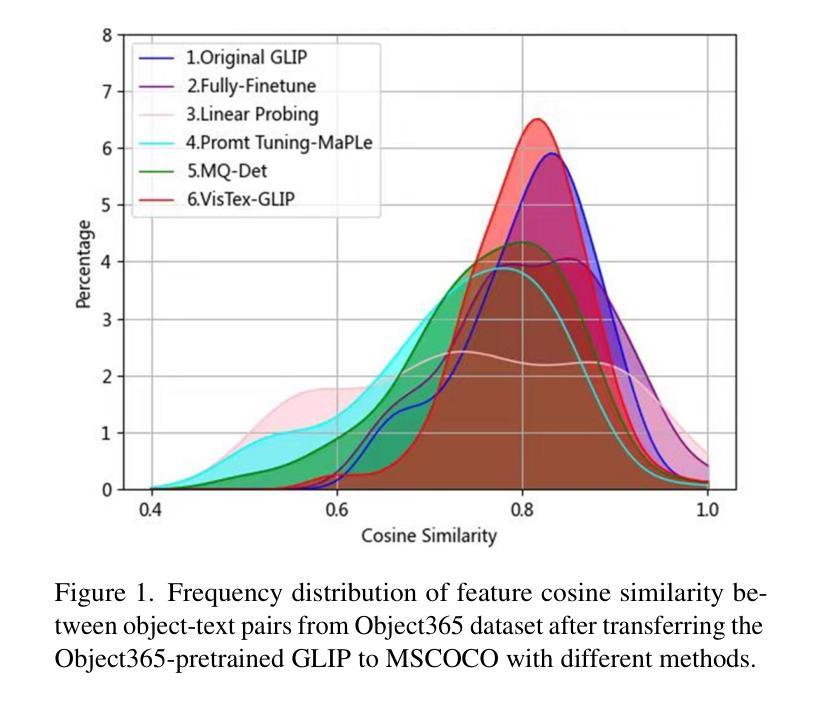
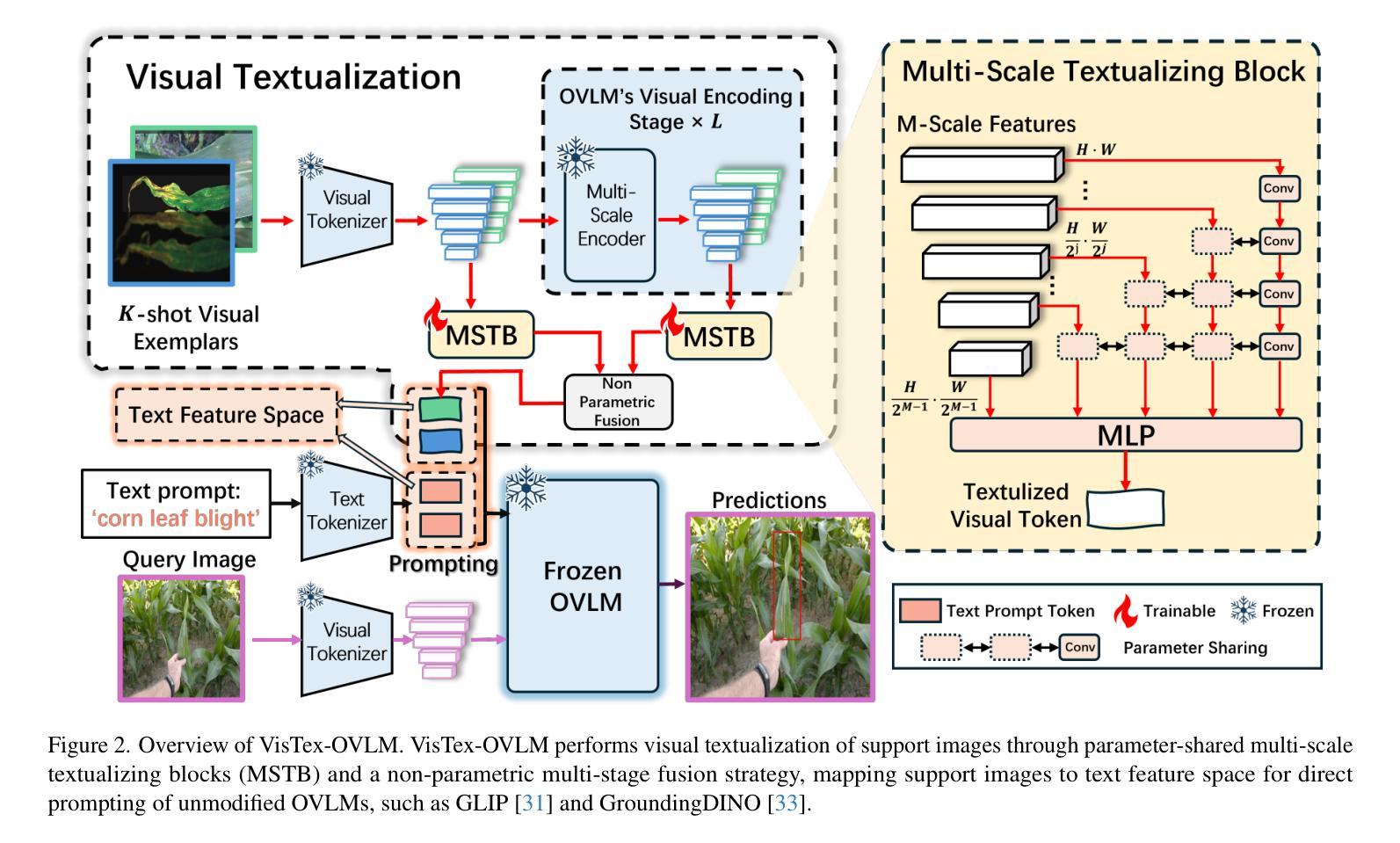
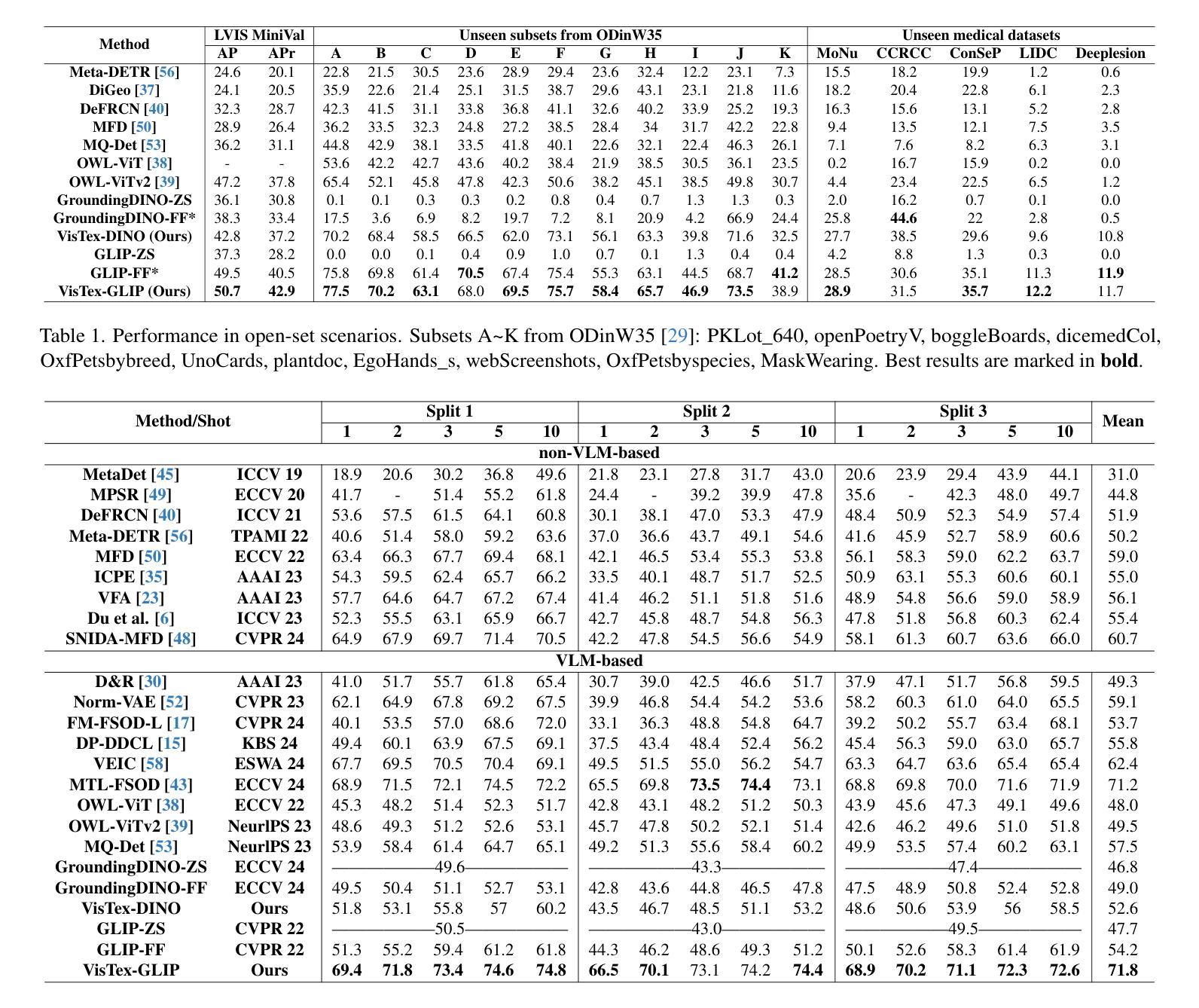
We propose VisTex-OVLM, a novel image prompted object detection method that introduces visual textualization – a process that projects a few visual exemplars into the text feature space to enhance Object-level Vision-Language Models’ (OVLMs) capability in detecting rare categories that are difficult to describe textually and nearly absent from their pre-training data, while preserving their pre-trained object-text alignment. Specifically, VisTex-OVLM leverages multi-scale textualizing blocks and a multi-stage fusion strategy to integrate visual information from visual exemplars, generating textualized visual tokens that effectively guide OVLMs alongside text prompts. Unlike previous methods, our method maintains the original architecture of OVLM, maintaining its generalization capabilities while enhancing performance in few-shot settings. VisTex-OVLM demonstrates superior performance across open-set datasets which have minimal overlap with OVLM’s pre-training data and achieves state-of-the-art results on few-shot benchmarks PASCAL VOC and MSCOCO. The code will be released at https://github.com/WitGotFlg/VisTex-OVLM.
我们提出了VisTex-OVLM,这是一种新型的图片引导目标检测法。它通过视觉文本化这一流程——将少量视觉样本投射到文本特征空间来增强对象级别的视觉语言模型(OVLMs)检测那些难以用文字描述、几乎不存在于他们的预训练数据中的稀有类别的能力,同时保持它们预先训练的对象文本对齐方式。具体来说,VisTex-OVLM利用多尺度文本化块和多阶段融合策略整合来自视觉样本的视觉信息,生成带有文本的视觉令牌,有效地指导OVLM与文本提示一起发挥作用。与之前的方法不同,我们的方法保持了OVLM的原始架构,保持了其泛化能力,同时在少样本环境中增强了性能。VisTex-OVLM在开放数据集上表现出卓越的性能,与OVLM的预训练数据重叠极小,并在PASCAL VOC和MSCOCO的少样本基准测试中取得了最新成果。代码将在https://github.com/WitGotFlg/VisTex-OVLM发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025
Summary
VisTex-OVLM是一种新型图像提示目标检测方法,它通过视觉文本化技术增强Object-level Vision-Language Models(OVLM)在检测罕见类别目标的能力。该方法将视觉实例投影到文本特征空间,提高模型在检测难以文本描述的罕见类别目标的性能,同时保留预训练的对象文本对齐。VisTex-OVLM采用多尺度文本化块和多阶段融合策略,集成视觉信息生成文本化视觉标记,有效引导OVLM与文本提示协同工作。该方法在开放数据集上表现优越,与OVLM预训练数据重叠度极小,并在PASCAL VOC和MSCOCO少样本基准测试上达到最新水平。代码将发布在https://github.com/WitGotFlg/VisTex-OVLM。
Key Takeaways
- VisTex-OVLM是一种新型图像提示目标检测方法,通过视觉文本化技术增强模型检测罕见类别目标的能力。
- 该方法将视觉实例投影到文本特征空间,以提高模型描述和检测难以文本描述的罕见类别目标的性能。
- VisTex-OVLM保留了预训练的对象文本对齐,同时引入了多尺度文本化块和多阶段融合策略来集成视觉信息。
- 该方法生成文本化视觉标记,有效引导OVLM与文本提示协同工作,提高了模型的性能。
- VisTex-OVLM在开放数据集上的表现优越,与预训练数据的重叠度低。
- VisTex-OVLM在PASCAL VOC和MSCOCO少样本基准测试上达到了最新水平。
点此查看论文截图
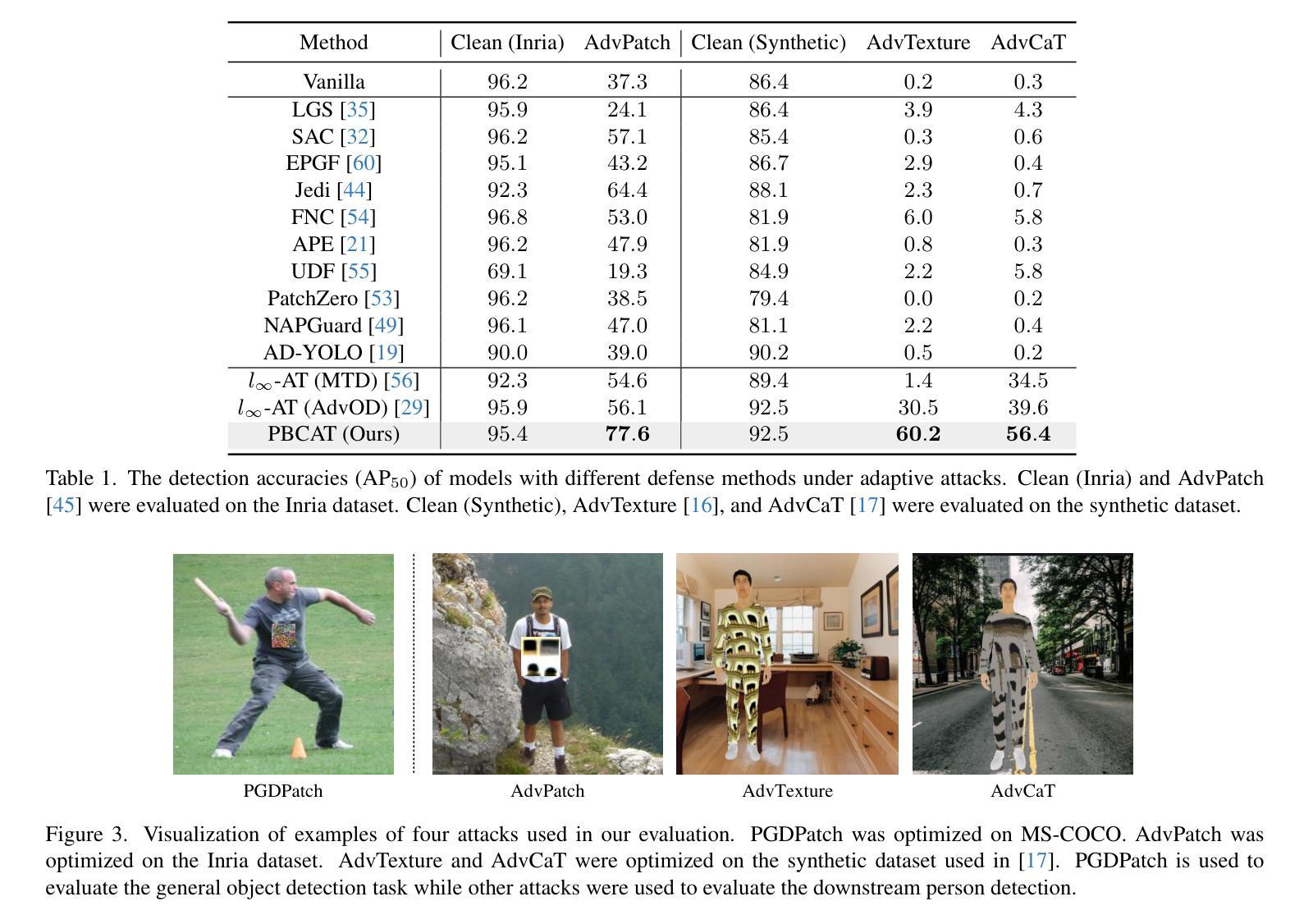
PBCAT: Patch-based composite adversarial training against physically realizable attacks on object detection
Authors:Xiao Li, Yiming Zhu, Yifan Huang, Wei Zhang, Yingzhe He, Jie Shi, Xiaolin Hu
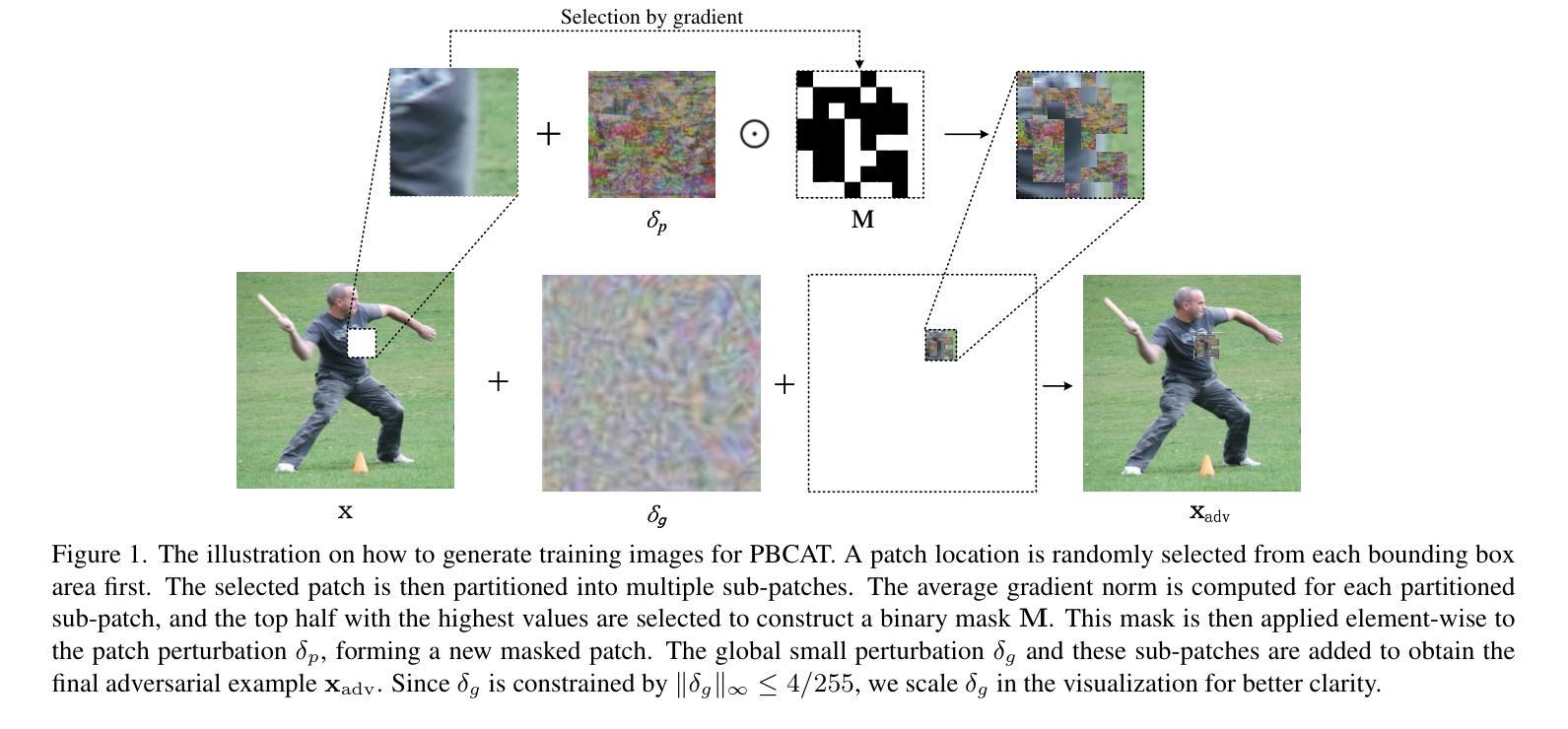
Object detection plays a crucial role in many security-sensitive applications. However, several recent studies have shown that object detectors can be easily fooled by physically realizable attacks, \eg, adversarial patches and recent adversarial textures, which pose realistic and urgent threats. Adversarial Training (AT) has been recognized as the most effective defense against adversarial attacks. While AT has been extensively studied in the $l_\infty$ attack settings on classification models, AT against physically realizable attacks on object detectors has received limited exploration. Early attempts are only performed to defend against adversarial patches, leaving AT against a wider range of physically realizable attacks under-explored. In this work, we consider defending against various physically realizable attacks with a unified AT method. We propose PBCAT, a novel Patch-Based Composite Adversarial Training strategy. PBCAT optimizes the model by incorporating the combination of small-area gradient-guided adversarial patches and imperceptible global adversarial perturbations covering the entire image. With these designs, PBCAT has the potential to defend against not only adversarial patches but also unseen physically realizable attacks such as adversarial textures. Extensive experiments in multiple settings demonstrated that PBCAT significantly improved robustness against various physically realizable attacks over state-of-the-art defense methods. Notably, it improved the detection accuracy by 29.7% over previous defense methods under one recent adversarial texture attack.
对象检测在许多安全敏感应用中扮演着至关重要的角色。然而,最近的一些研究表明,对象检测器很容易受到物理可实现攻击(例如对抗性补丁和最新的对抗性纹理)的欺骗,这些攻击带来了现实而紧迫的威胁。对抗训练(AT)已被公认为对抗对抗性攻击的最有效防御手段。虽然AT在$l_\infty$攻击分类模型的设置中已经得到了广泛的研究,但针对对象检测器的物理可实现攻击的AT却鲜有研究。早期的尝试仅用于防御对抗性补丁,而对更广泛的物理可实现攻击的AT探索不足。在这项工作中,我们考虑使用统一的AT方法来防御各种物理可实现攻击。我们提出了PBCAT,这是一种基于补丁的复合对抗训练策略。PBCAT通过结合小区域梯度引导对抗补丁和覆盖整个图像的难以察觉的全局对抗扰动来优化模型。通过这些设计,PBCAT不仅有潜力防御对抗补丁,还有潜力防御未见过的物理可实现攻击,如对抗纹理。在多个设置中的大量实验表明,与最先进的防御方法相比,PBCAT在抵抗各种物理可实现攻击方面显著提高了鲁棒性。值得注意的是,它在最近的一次对抗纹理攻击下,相较于以前的方法提高了29.7%的检测准确率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025
Summary
本文探讨了目标检测在安全性敏感应用中的挑战,特别是面临物理可实现攻击时的问题。虽然对抗训练(AT)在分类模型中的对抗攻击中已被广泛研究,但在目标检测器的物理可实现攻击上的研究仍然有限。针对此问题,本文提出了一种基于补丁的复合对抗训练策略(PBCAT),能够防御各种物理可实现攻击。实验表明,与现有方法相比,PBCAT在各种物理可实现攻击中具有更高的鲁棒性。特别是针对一种最新的对抗纹理攻击,其检测准确率提高了29.7%。
Key Takeaways
- 目标检测在安全性敏感应用中面临物理可实现攻击的挑战。
- 对抗训练(AT)是防御对抗攻击的有效手段,但在目标检测器的物理可实现攻击方面的应用仍然有限。
- 本文提出了基于补丁的复合对抗训练策略(PBCAT),用于防御多种物理可实现攻击。
- PBCAT通过结合小区域梯度引导的对抗补丁和覆盖整个图像的不易察觉的全局对抗扰动来优化模型。
- PBCAT不仅能防御对抗补丁攻击,还能防御未知的物理可实现攻击,如对抗纹理攻击。
- 实验表明,与现有方法相比,PBCAT在各种物理可实现攻击中具有更高的鲁棒性。
点此查看论文截图


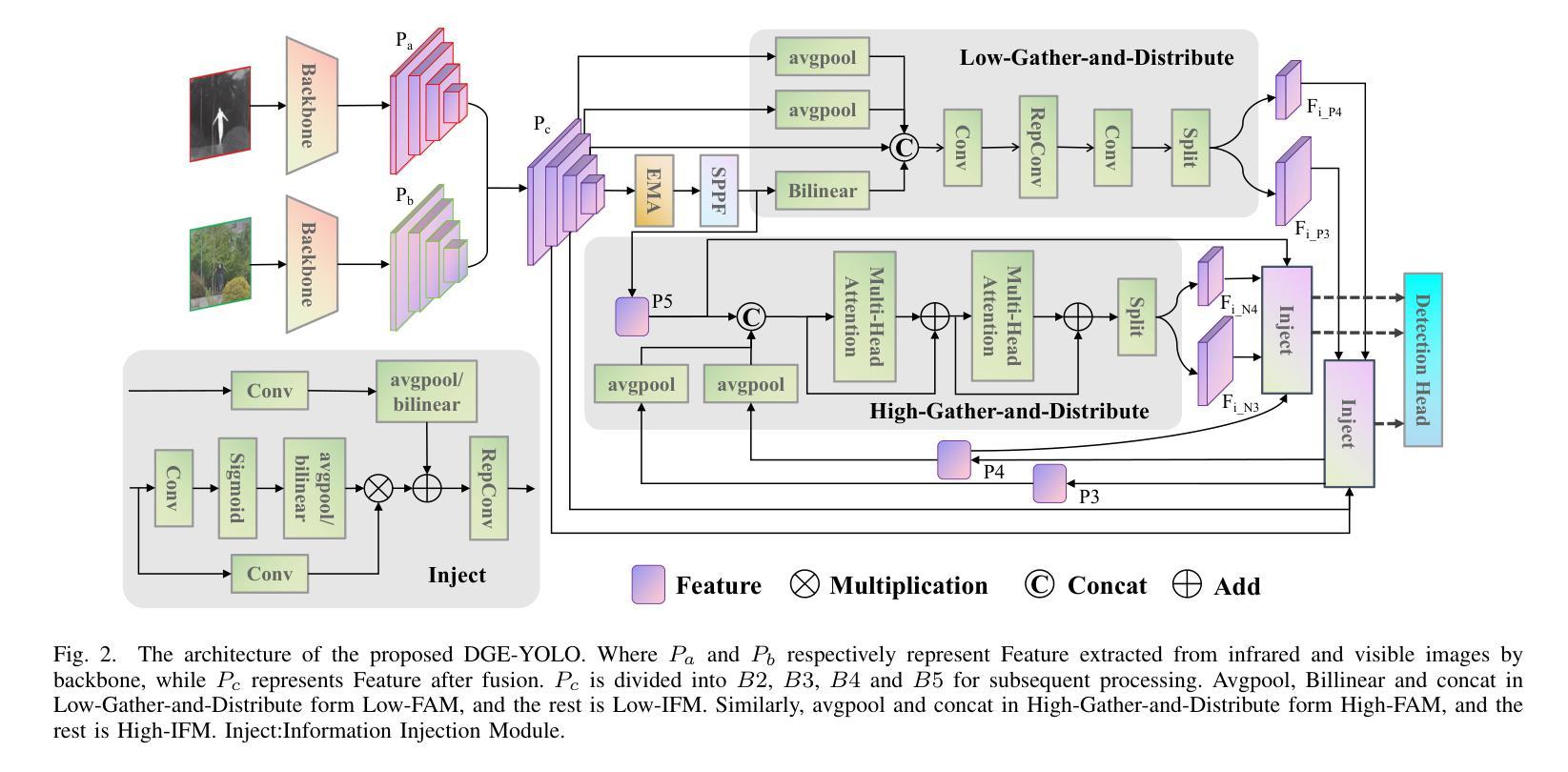
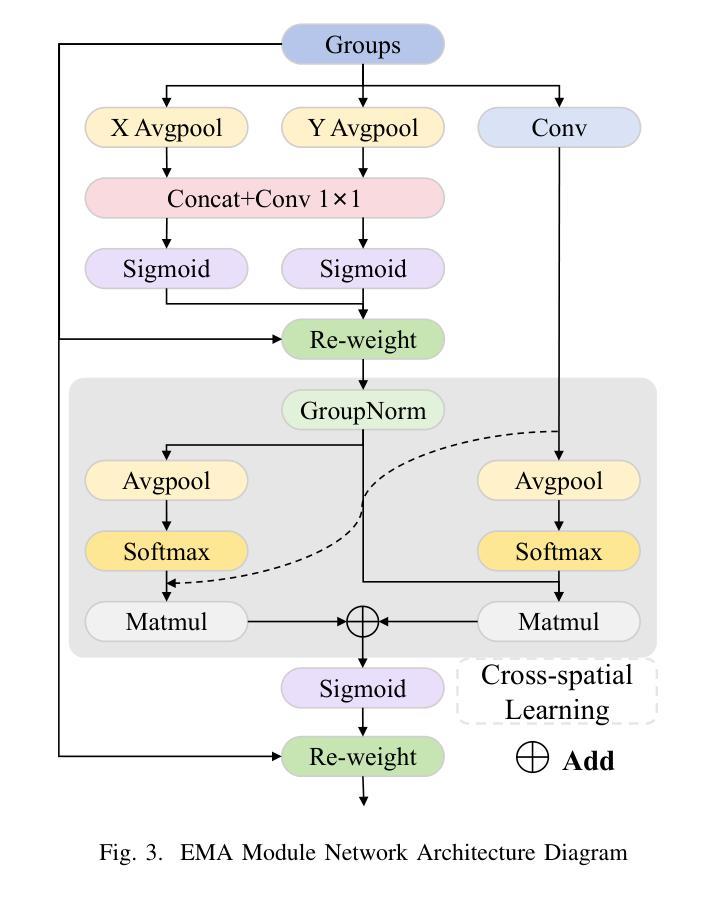
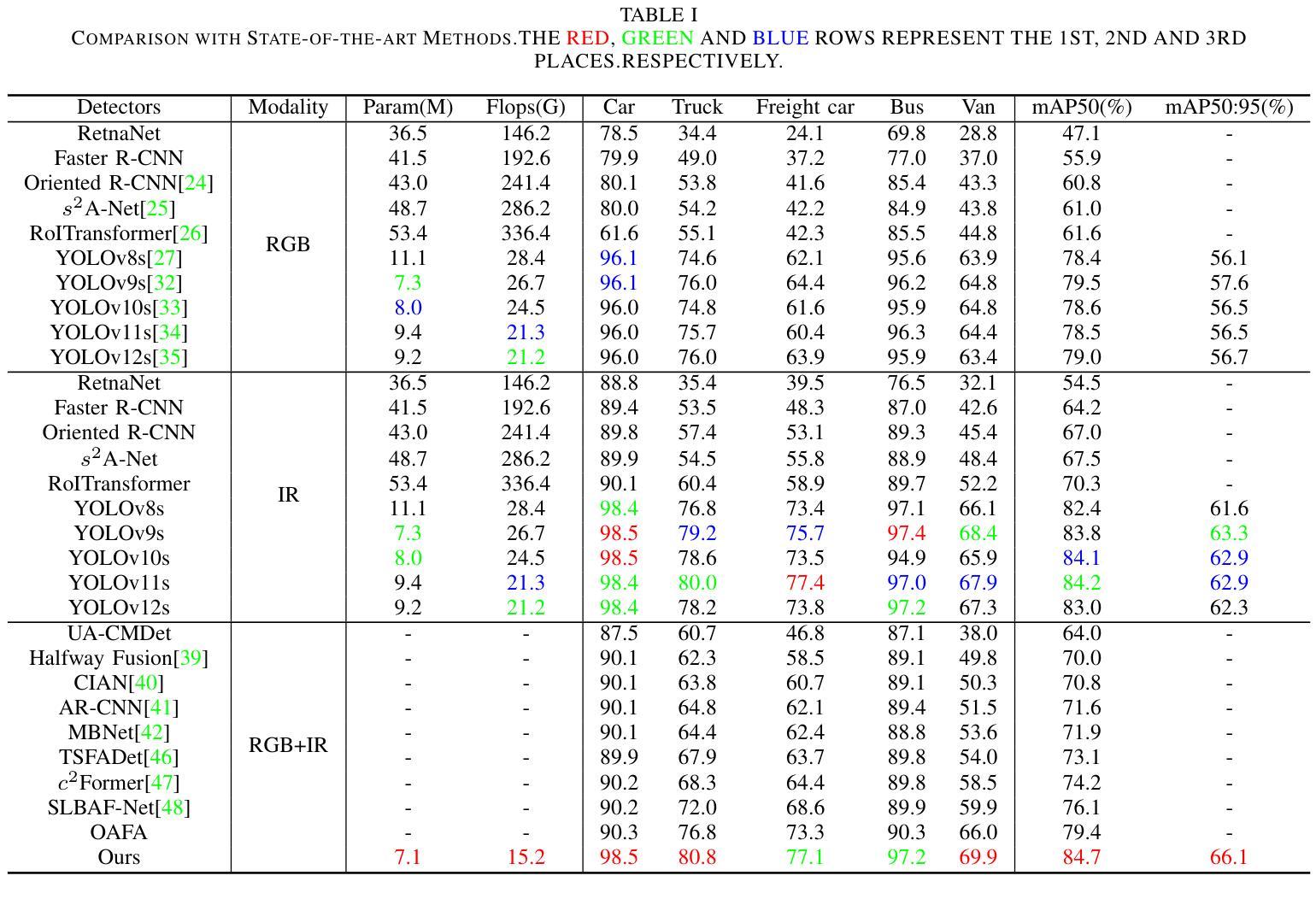
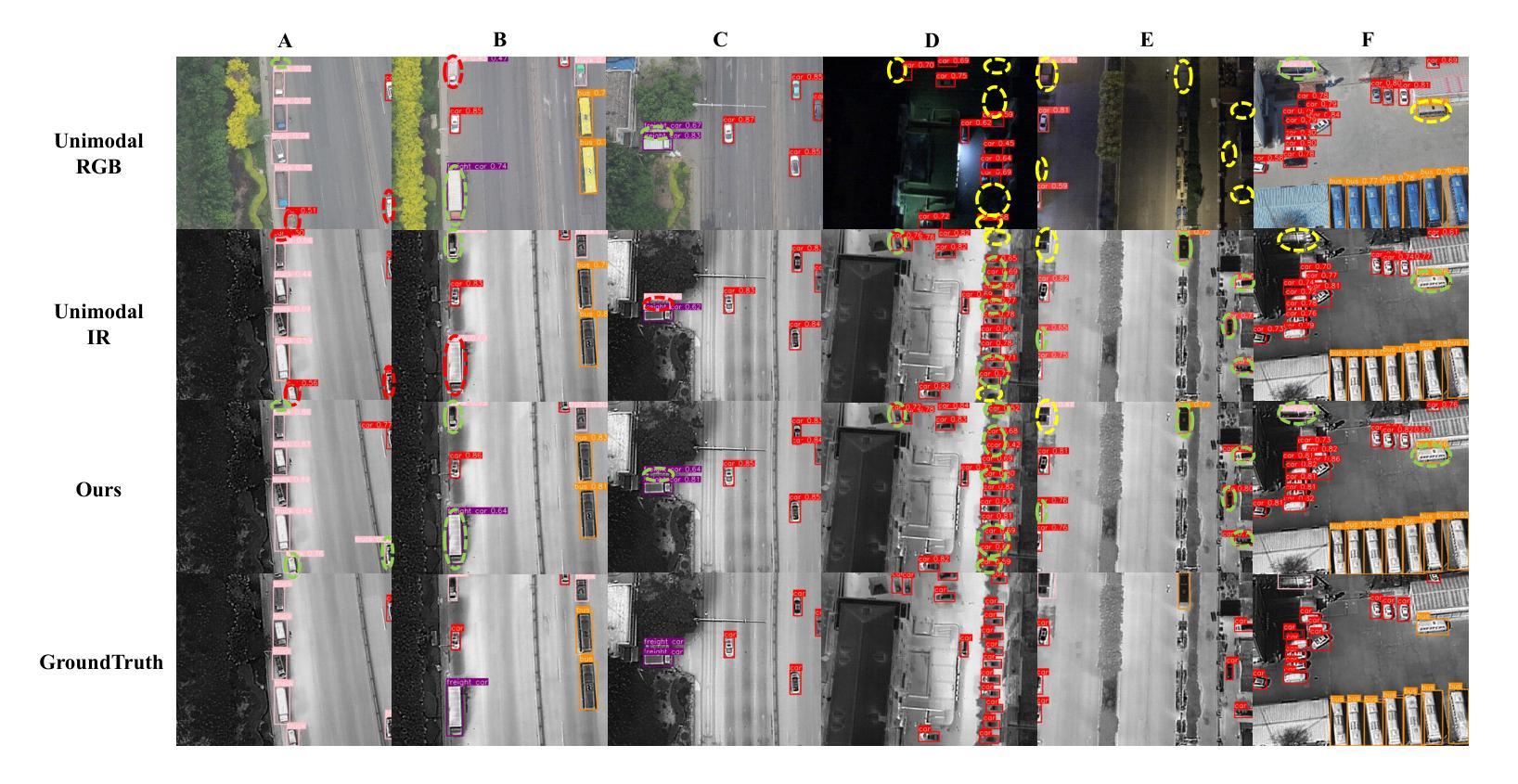
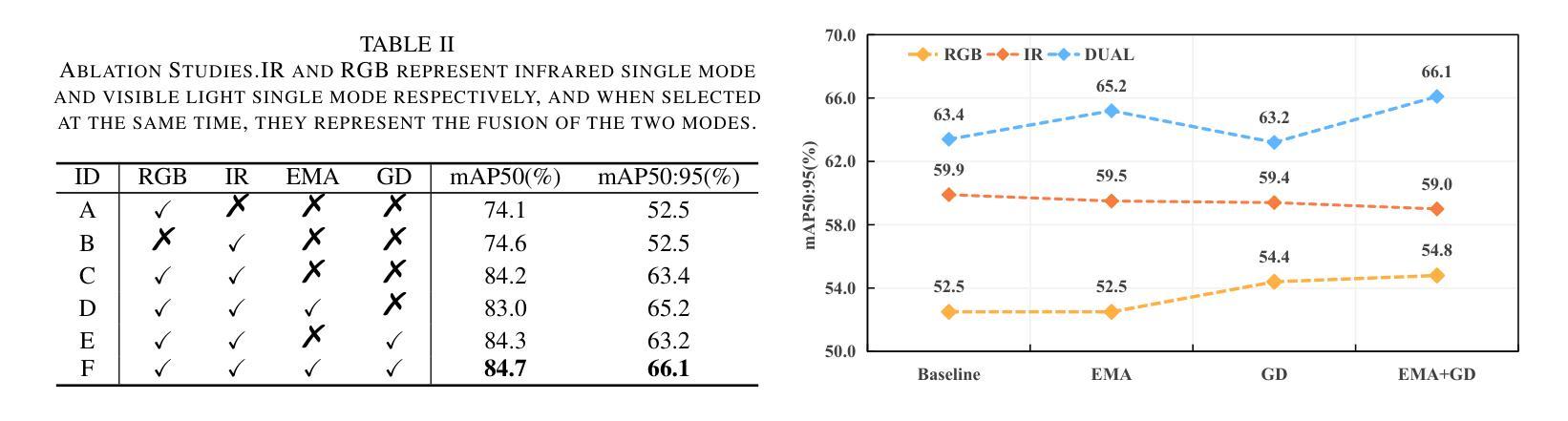
DGE-YOLO: Dual-Branch Gathering and Attention for Accurate UAV Object Detection
Authors:Kunwei Lv, Ping Lan
The rapid proliferation of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) has highlighted the importance of robust and efficient object detection in diverse aerial scenarios. Detecting small objects under complex conditions, however, remains a significant challenge. Existing approaches often prioritize inference speed, leading to degraded performance when handling multi-modal inputs. To address this, we present DGE-YOLO, an enhanced YOLO-based detection framework designed to effectively fuse multi-modal information. Specifically, we introduce a dual-branch architecture for modality-specific feature extraction, enabling the model to process both infrared and visible images. To further enrich semantic representation, we propose an Efficient Multi-scale Attention (EMA) mechanism that enhances feature learning across spatial scales. Additionally, we replace the conventional neck with a Gather-and-Distribute module to mitigate information loss during feature aggregation. Extensive experiments on the Drone Vehicle dataset demonstrate that DGE-YOLO achieves superior performance over state-of-the-art methods, validating its effectiveness in multi-modal UAV object detection tasks.
随着无人机(UAVs)的快速普及,在各种空中场景中实现稳健高效的目标检测显得尤为重要。然而,在复杂条件下检测小目标仍然是一个巨大的挑战。现有的方法往往优先注重推理速度,在处理多模态输入时性能下降。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了DGE-YOLO,这是一种基于YOLO的增强检测框架,旨在有效地融合多模态信息。具体来说,我们引入了用于特定模态特征提取的双分支架构,使模型能够处理红外和可见光图像。为了丰富语义表示,我们提出了一种有效的多尺度注意力(EMA)机制,该机制可以在不同的空间尺度上增强特征学习。此外,我们用Gather-and-Distribute模块替换了传统的颈部,以减轻特征聚合过程中的信息损失。在Drone Vehicle数据集上的大量实验表明,DGE-YOLO在无人机多模态目标检测任务上的性能优于其他先进方法,验证了其在多模态无人机目标检测任务中的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 5 figures
Summary
无人机技术的快速发展使得在多样化的空中场景下实现稳健高效的目标检测至关重要。复杂条件下的小目标检测仍是重大挑战。现有方法往往注重推理速度,在处理多模态输入时性能下降。为解决这一问题,我们提出基于YOLO增强的检测框架DGE-YOLO,有效融合多模态信息。通过引入双分支架构进行模态特定特征提取,能够处理红外和可见光图像。为丰富语义表示,我们提出高效多尺度注意力(EMA)机制,增强跨空间尺度的特征学习。此外,我们采用Gather-and-Distribute模块替代传统颈部结构,减少特征聚合过程中的信息损失。在Drone Vehicle数据集上的广泛实验表明,DGE-YOLO在多媒体无人机目标检测任务上的性能优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 无人机技术的快速发展突出了在多样化空中场景下实现稳健高效目标检测的必要性。
- 复杂条件下的小目标检测是一个重大挑战。
- 现有方法在处理多模态输入时性能下降,主要因为注重推理速度而忽视准确性。
- DGE-YOLO是一个基于YOLO的增强检测框架,旨在有效融合多模态信息。
- DGE-YOLO引入双分支架构进行模态特定特征提取,能处理红外和可见光图像。
- EMA机制用于丰富语义表示并增强跨空间尺度的特征学习。
点此查看论文截图

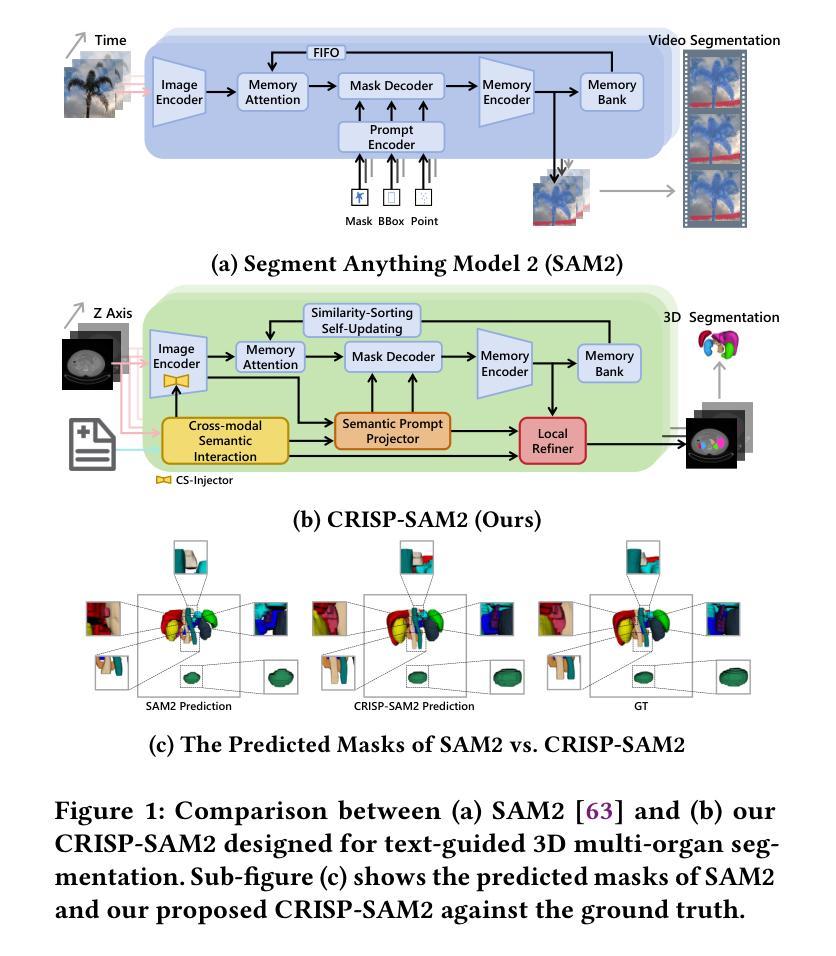
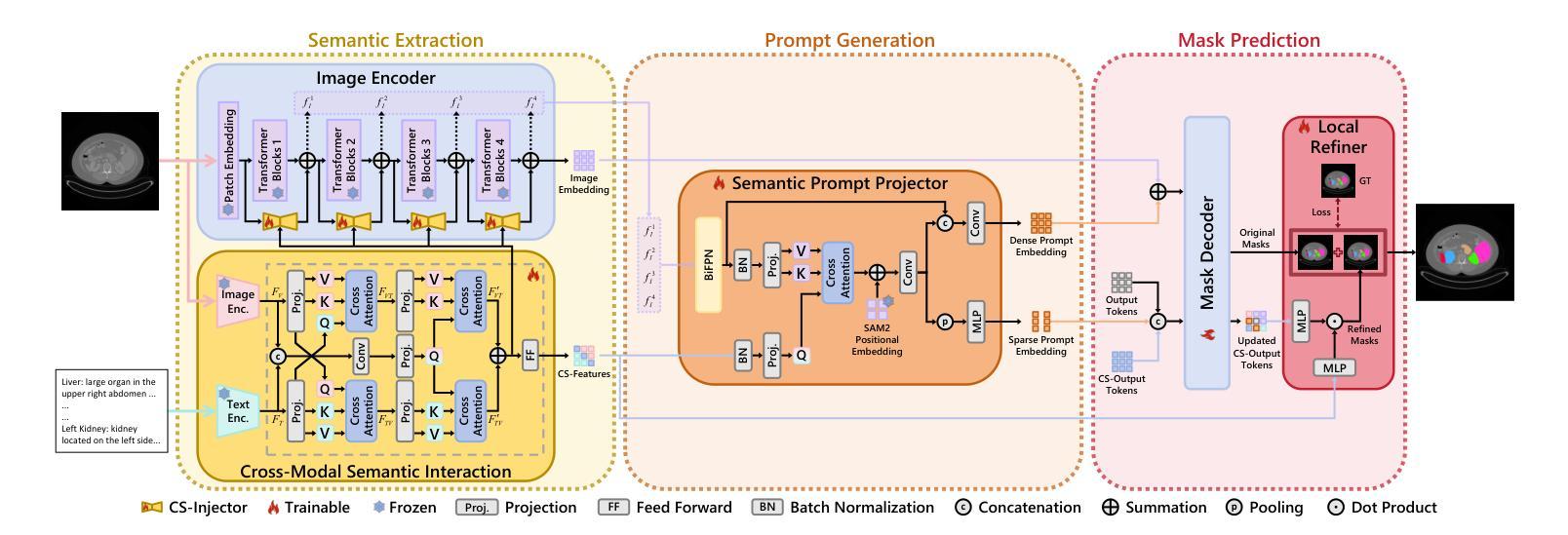
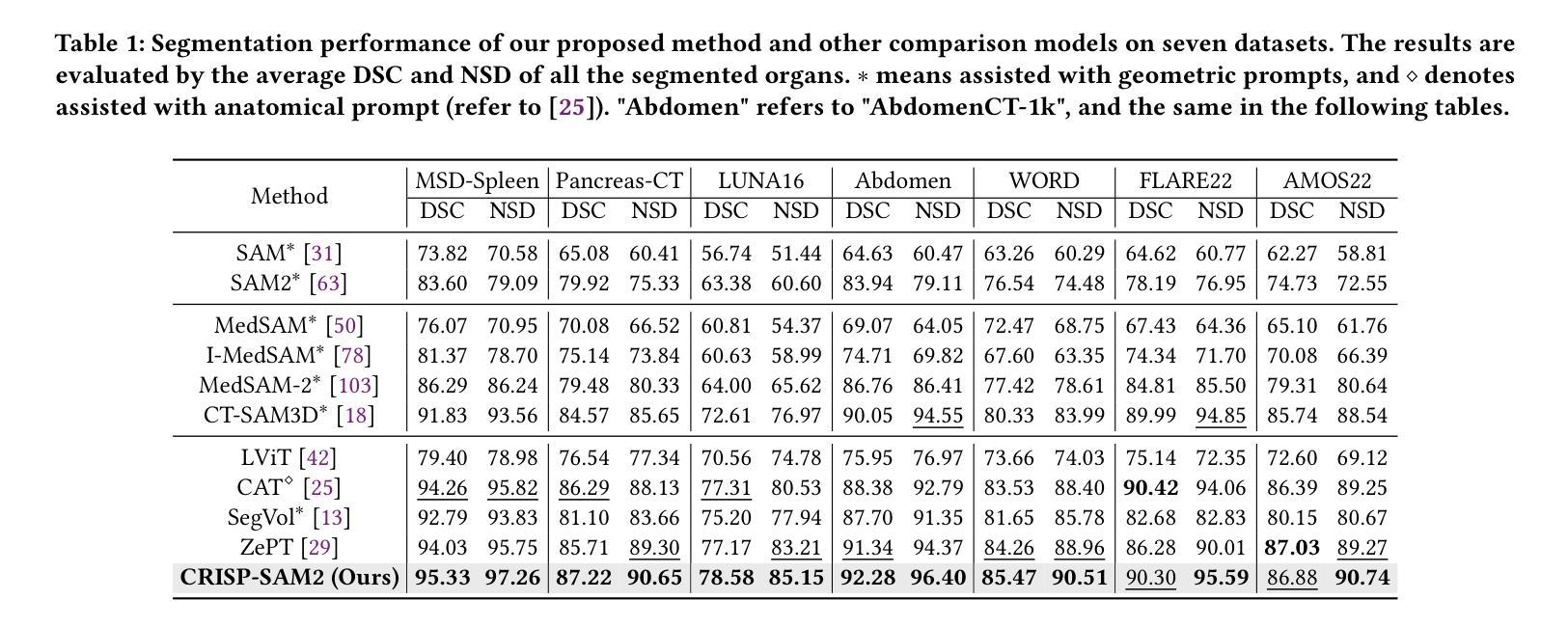
CRISP-SAM2: SAM2 with Cross-Modal Interaction and Semantic Prompting for Multi-Organ Segmentation
Authors:Xinlei Yu, Chanmiao Wang, Hui Jin, Ahmed Elazab, Gangyong Jia, Xiang Wan, Changqing Zou, Ruiquan Ge
Multi-organ medical segmentation is a crucial component of medical image processing, essential for doctors to make accurate diagnoses and develop effective treatment plans. Despite significant progress in this field, current multi-organ segmentation models often suffer from inaccurate details, dependence on geometric prompts and loss of spatial information. Addressing these challenges, we introduce a novel model named CRISP-SAM2 with CRoss-modal Interaction and Semantic Prompting based on SAM2. This model represents a promising approach to multi-organ medical segmentation guided by textual descriptions of organs. Our method begins by converting visual and textual inputs into cross-modal contextualized semantics using a progressive cross-attention interaction mechanism. These semantics are then injected into the image encoder to enhance the detailed understanding of visual information. To eliminate reliance on geometric prompts, we use a semantic prompting strategy, replacing the original prompt encoder to sharpen the perception of challenging targets. In addition, a similarity-sorting self-updating strategy for memory and a mask-refining process is applied to further adapt to medical imaging and enhance localized details. Comparative experiments conducted on seven public datasets indicate that CRISP-SAM2 outperforms existing models. Extensive analysis also demonstrates the effectiveness of our method, thereby confirming its superior performance, especially in addressing the limitations mentioned earlier. Our code is available at: https://github.com/YU-deep/CRISP\_SAM2.git.
医学多器官分割是医学图像处理的重要组成部分,对于医生进行准确诊断和制定有效治疗方案至关重要。尽管该领域已经取得了重大进展,但现有的多器官分割模型通常存在细节不准确、依赖几何提示以及空间信息丢失等问题。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了一种名为CRISP-SAM2的新模型,该模型基于SAM2具有跨模态交互和语义提示功能。该模型是一种有前途的方法,通过器官的文字描述来引导多器官医学分割。我们的方法首先通过渐进的交叉注意力交互机制将视觉和文字输入转换为跨模态上下文语义。然后,这些语义被注入图像编码器,以提高对视觉信息的详细理解。为了减少对几何提示的依赖,我们使用语义提示策略,以替代原始提示编码器,提高难以识别目标的感知能力。此外,还采用了用于记忆的相似度排序自更新策略和掩膜细化过程,以进一步适应医学影像并增强局部细节。在七个公共数据集上进行的对比实验表明,CRISP-SAM2优于现有模型。广泛的分析也证明了我们的方法的有效性,从而证实了其卓越性能,特别是在解决上述限制方面。我们的代码可通过以下链接获取:https://github.com/YU-deep/CRISP_SAM2.git。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 9 figures, 10 tables
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为CRISP-SAM2的新型多器官医学分割模型。该模型通过跨模态交互和语义提示技术,解决了当前模型在细节准确性、对几何提示的依赖以及空间信息丢失等方面的问题。CRISP-SAM2模型通过渐进式跨注意力交互机制,将视觉和文本输入转换为跨模态上下文语义,然后将其注入图像编码器,提高视觉信息的详细理解。此外,采用语义提示策略消除了对几何提示的依赖,同时采用相似度排序自更新策略和掩膜细化过程,进一步适应医学成像并增强局部细节。在七个公共数据集上的对比实验表明,CRISP-SAM2模型优于现有模型。
Key Takeaways
- 多器官医学分割是医疗图像处理中的关键部分,对医生进行准确诊断和治疗计划至关重要。
- 当前多器官分割模型存在细节不准确、依赖几何提示和空间信息丢失等挑战。
- CRISP-SAM2模型通过跨模态交互和语义提示技术解决这些问题。
- CRISP-SAM2将视觉和文本输入转换为跨模态上下文语义,提高视觉信息理解。
- 语义提示策略消除对几何提示的依赖,并采用相似度排序自更新策略和掩膜细化过程,适应医学成像并增强局部细节。
- 在七个公共数据集上的对比实验显示,CRISP-SAM2模型性能优越。
点此查看论文截图

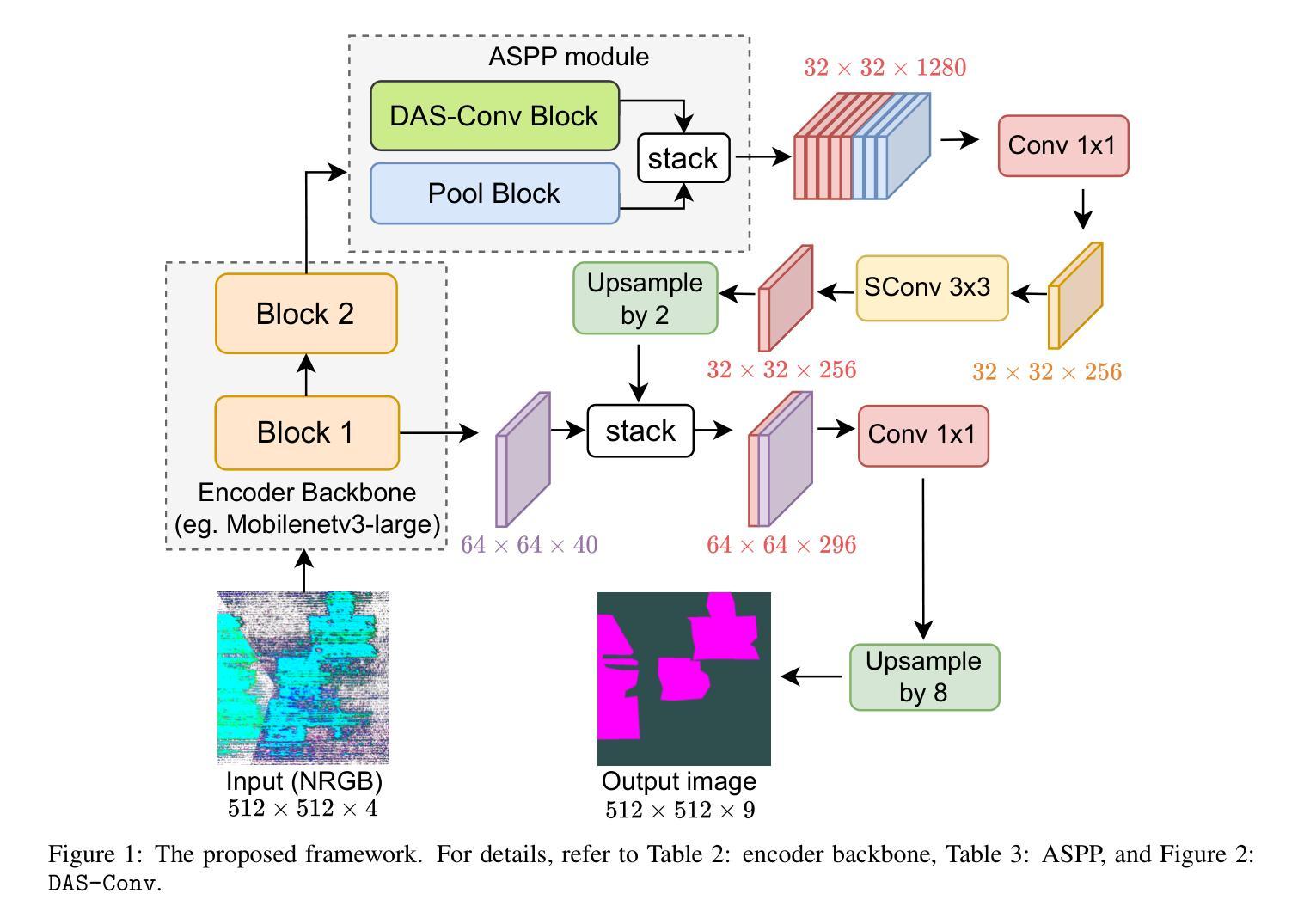
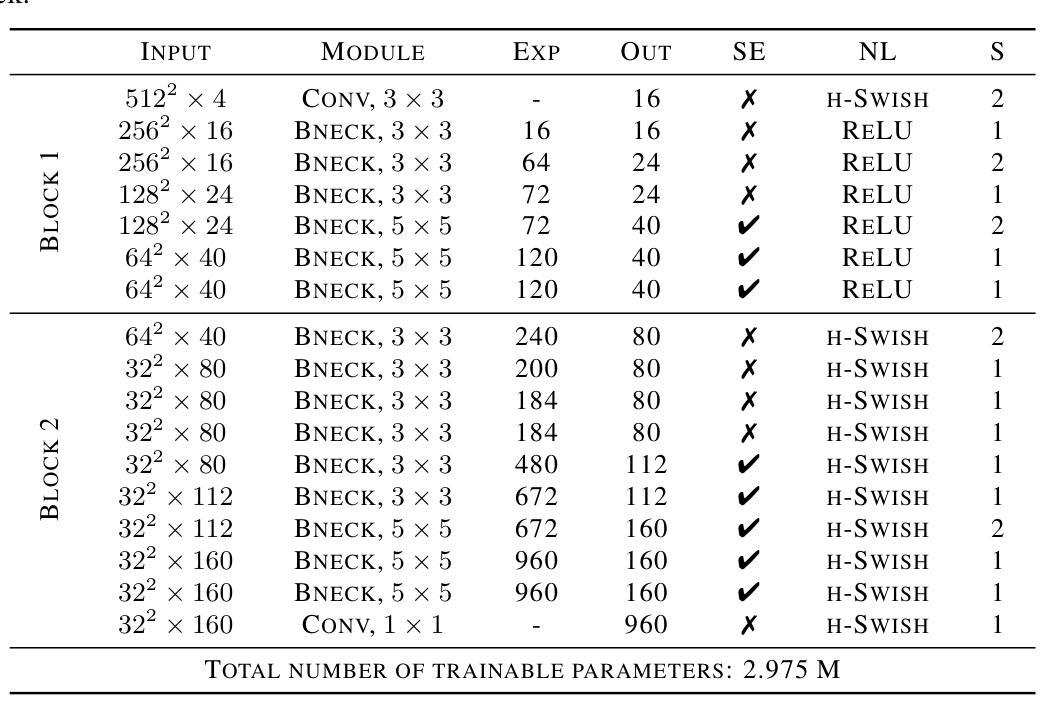
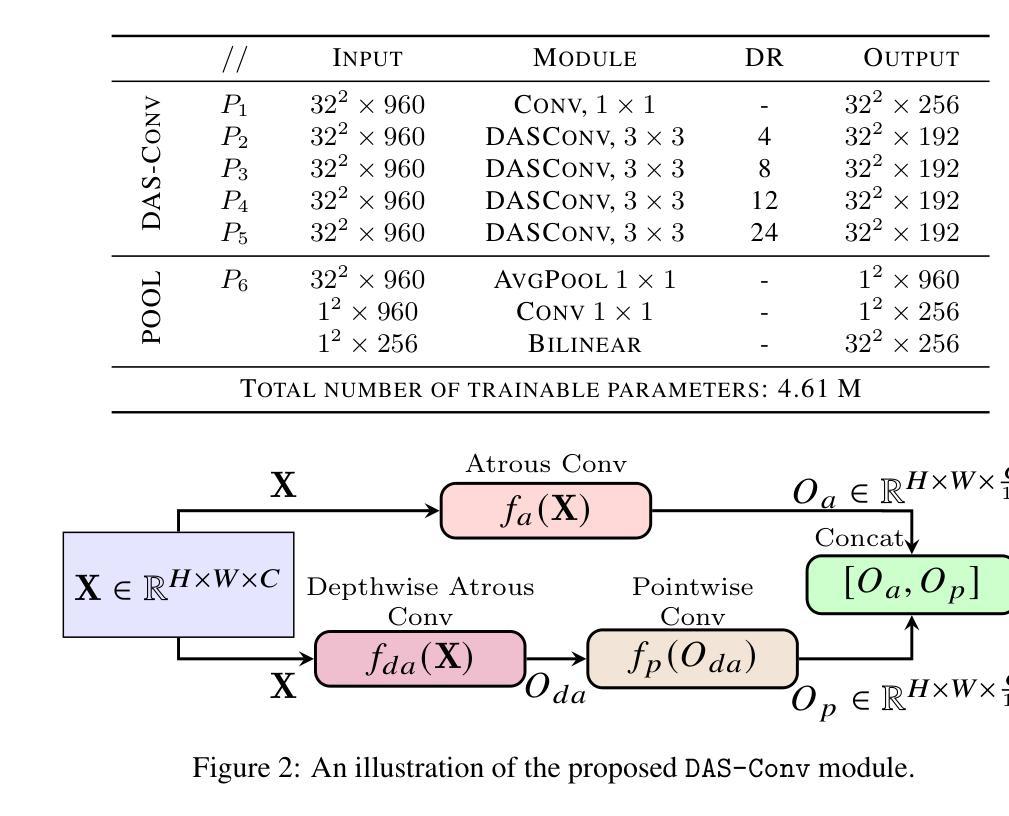
Dual Atrous Separable Convolution for Improving Agricultural Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Chee Mei Ling, Thangarajah Akilan, Aparna Ravinda Phalke
Agricultural image semantic segmentation is a pivotal component of modern agriculture, facilitating accurate visual data analysis to improve crop management, optimize resource utilization, and boost overall productivity. This study proposes an efficient image segmentation method for precision agriculture, focusing on accurately delineating farmland anomalies to support informed decision-making and proactive interventions. A novel Dual Atrous Separable Convolution (DAS Conv) module is integrated within the DeepLabV3-based segmentation framework. The DAS Conv module is meticulously designed to achieve an optimal balance between dilation rates and padding size, thereby enhancing model performance without compromising efficiency. The study also incorporates a strategic skip connection from an optimal stage in the encoder to the decoder to bolster the model’s capacity to capture fine-grained spatial features. Despite its lower computational complexity, the proposed model outperforms its baseline and achieves performance comparable to highly complex transformer-based state-of-the-art (SOTA) models on the Agriculture Vision benchmark dataset. It achieves more than 66% improvement in efficiency when considering the trade-off between model complexity and performance, compared to the SOTA model. This study highlights an efficient and effective solution for improving semantic segmentation in remote sensing applications, offering a computationally lightweight model capable of high-quality performance in agricultural imagery.
农业图像语义分割是现代农业中的关键组成部分,通过精确的视觉数据分析,有助于改善作物管理、优化资源利用,并提高整体生产力。本研究提出了一种高效的图像分割方法,旨在精准农业中准确描绘农田异常现象,以支持决策制定和主动干预。在基于DeepLabV3的分割框架中集成了新型的双膨胀可分离卷积(DAS Conv)模块。DAS Conv模块精心设计,以实现膨胀率和填充大小之间的最佳平衡,从而提高模型性能而不损失效率。该研究还从编码器的最佳阶段到解码器加入了策略性跳过连接,以增强模型捕获精细空间特征的能力。尽管计算复杂度较低,该模型在农业视觉基准数据集上的性能超过了基线模型,并达到了与基于复杂变换器的前沿模型相当的性能。与前沿模型相比,在考虑模型复杂性与性能之间的权衡时,该模型的效率提高了66%以上。本研究强调了提高遥感应用中语义分割效率的有效解决方案,提供了一个计算量轻、性能高的农业图像模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 7 figures, 6 tables
Summary
农业图像语义分割是现代农业中的关键组成部分,通过对视觉数据的精确分析,改进作物管理、优化资源配置并提高整体生产力。本研究提出了一种高效的图像分割方法,专注于精确描绘农田异常,以支持决策制定和主动干预。该研究在深LabV3分割框架中集成了新型的双膨胀可分离卷积(DAS Conv)模块,旨在实现膨胀率和填充大小之间的最佳平衡,从而提高模型性能而不损失效率。此外,研究还通过从编码器中的最佳阶段到解码器的战略跳跃连接,增强了模型捕获精细空间特征的能力。与其他高度复杂的基于转换器的最新模型相比,所提出的模型在农业视觉基准数据集上表现出色,在计算复杂性和性能之间的权衡方面实现了超过66%的效率提升。本研究为解决遥感应用中语义分割问题提供了高效且实用的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 农业图像语义分割在现代农业中至关重要,有助于视觉数据分析以提高农业生产力。
- 本研究提出了一种基于DeepLabV3的高效图像分割方法,用于精确描绘农田异常。
- 集成新型双膨胀可分离卷积(DAS Conv)模块,实现模型性能与效率的平衡。
- 通过战略跳跃连接增强模型捕获精细空间特征的能力。
- 所提出模型在农业视觉基准数据集上表现出色,实现了高效率与计算复杂度的权衡优化。
- 与当前复杂的基于转换器的最新模型相比,该研究提出的模型更具优势。
点此查看论文截图

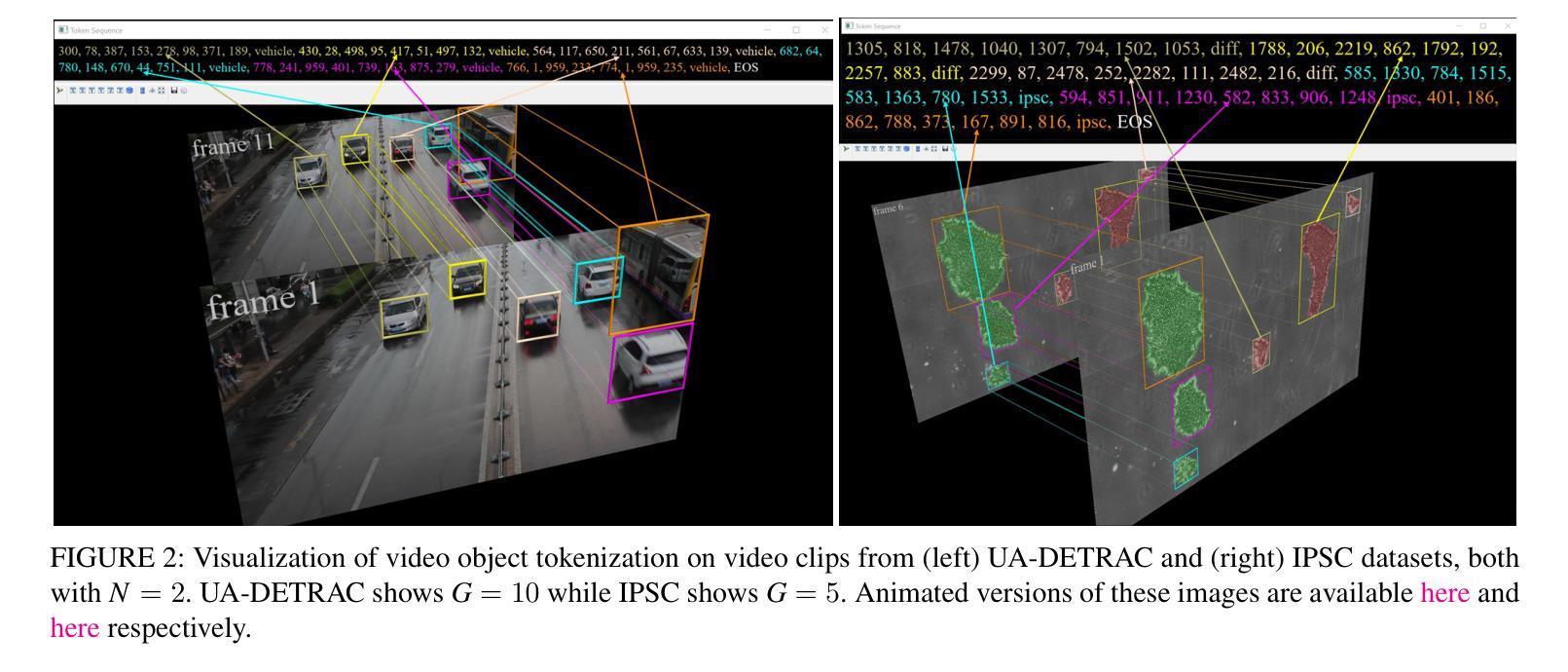
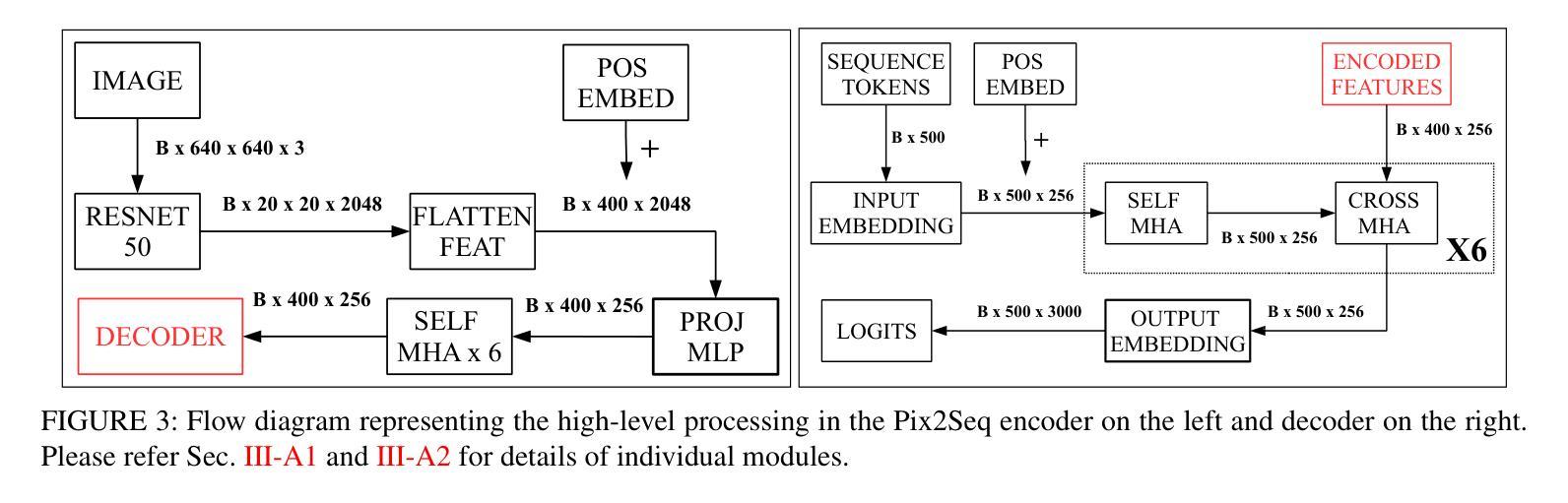
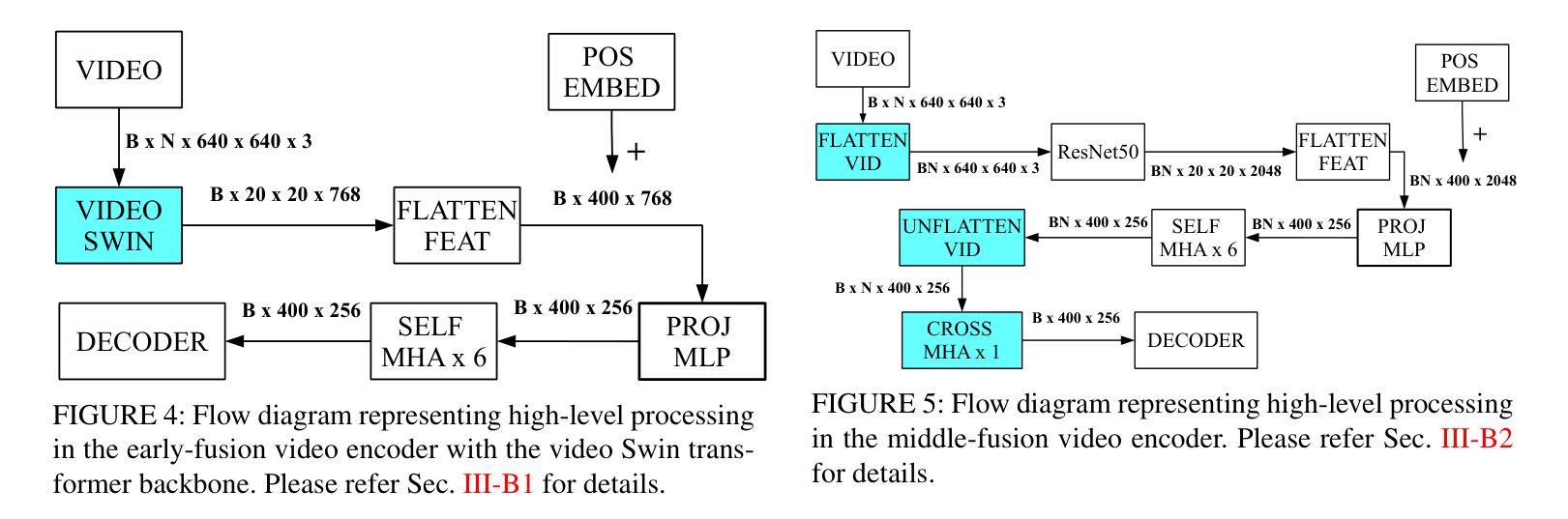
Improving Token-based Object Detection with Video
Authors:Abhineet Singh, Nilanjan Ray
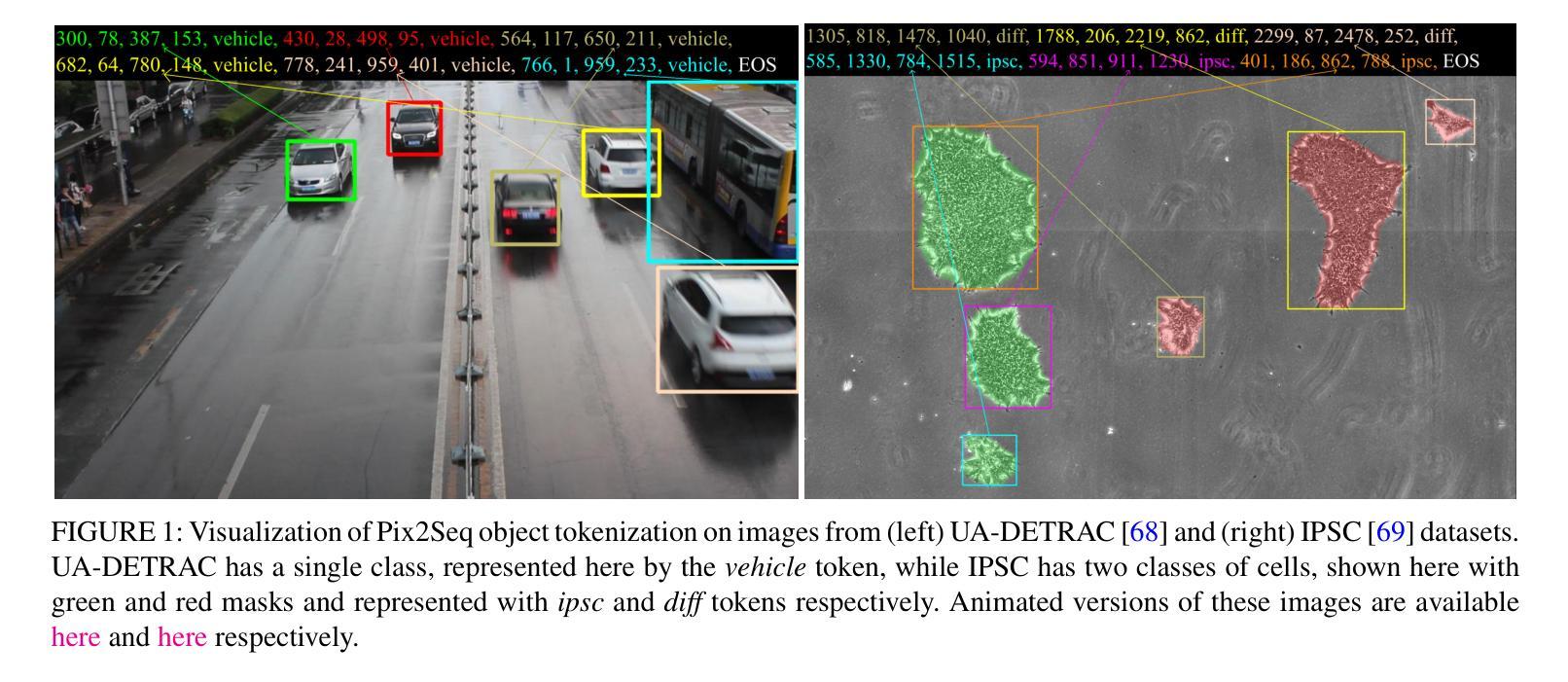
This paper improves upon the Pix2Seq object detector by extending it for videos. In the process, it introduces a new way to perform end-to-end video object detection that improves upon existing video detectors in two key ways. First, by representing objects as variable-length sequences of discrete tokens, we can succinctly represent widely varying numbers of video objects, with diverse shapes and locations, without having to inject any localization cues in the training process. This eliminates the need to sample the space of all possible boxes that constrains conventional detectors and thus solves the dual problems of loss sparsity during training and heuristics-based postprocessing during inference. Second, it conceptualizes and outputs the video objects as fully integrated and indivisible 3D boxes or tracklets instead of generating image-specific 2D boxes and linking these boxes together to construct the video object, as done in most conventional detectors. This allows it to scale effortlessly with available computational resources by simply increasing the length of the video subsequence that the network takes as input, even generalizing to multi-object tracking if the subsequence can span the entire video. We compare our video detector with the baseline Pix2Seq static detector on several datasets and demonstrate consistent improvement, although with strong signs of being bottlenecked by our limited computational resources. We also compare it with several video detectors on UA-DETRAC to show that it is competitive with the current state of the art even with the computational bottleneck. We make our code and models publicly available.
本文改进了Pix2Seq目标检测器,将其扩展至视频领域。在此过程中,它引入了一种新的端到端视频目标检测方式,在两个关键方面对现有视频检测器进行了改进。首先,通过将目标表示为离散标记的可变长度序列,我们可以简洁地表示数量众多、形状和位置各异的视频目标,而无需在训练过程中注入任何定位线索。这消除了需要对所有可能框的空间进行采样的需要,这限制了传统检测器,从而解决了训练过程中的损失稀疏性和推理过程中的基于启发式方法的后处理这两个问题。其次,它概念化并将视频目标输出为完整且不可分的3D框或轨迹,而不是生成特定的图像2D框,并将这些框连接起来构建视频目标,这是大多数传统检测器所做的事情。这允许它轻松扩展可用的计算资源,只需通过增加网络所接受的视频子序列的长度,即使子序列能跨越整个视频,也能推广到多目标跟踪。我们在多个数据集上将我们的视频检测器与基线Pix2Seq静态检测器进行了比较,并表现出了持续的改进,尽管受到我们有限计算资源的限制。我们还与UA-DETRAC上的其他视频检测器进行了比较,以证明即使在计算瓶颈的情况下,它也具有与最新技术竞争的能力。我们的代码和模型已公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review for publication in IEEE Access
Summary
本文改进了Pix2Seq目标检测器,将其扩展到视频领域。通过引入一种新的端到端视频目标检测方式,它在两个关键方面超越了现有视频检测器。首先,通过将目标表示为离散令牌的可变长度序列,可以简洁地表示数量众多、形状和位置各异的目标,而无需在训练过程中注入任何定位线索。这解决了传统检测器在训练过程中的损失稀疏问题和推理过程中的基于启发式规则的后处理。其次,它将视频目标概念化为完全集成和不可分割的3D框或轨迹,而不是生成针对图像特定的2D框并连接这些框来构建视频目标(这是大多数传统检测器所做的)。这使得它能够轻松扩展可用的计算资源,通过简单地增加网络作为输入的视频子序列的长度来进行缩放,甚至在子序列能够跨越整个视频时推广到多目标跟踪。我们在多个数据集上将我们的视频检测器与基线Pix2Seq静态检测器进行比较,表现出一致的性能改进,尽管受到了有限计算资源的限制。在UA-DETRAC上与几种视频检测器的比较表明,即使在计算瓶颈的情况下,它也是当前最先进的。我们公开提供了代码和模型。
Key Takeaways
- 改进了Pix2Seq目标检测器以应用于视频领域。
- 通过将目标表示为离散令牌的可变长度序列,解决了训练过程中的损失稀疏问题和推理过程中的启发式后处理需求。
- 引入了新的视频目标检测方式,将视频目标概念化为完全集成和不可分割的3D框或轨迹。
- 该方法能够轻松扩展计算资源,通过简单地增加网络作为输入的视频子序列的长度来进行缩放。
- 在多个数据集上与基线Pix2Seq静态检测器进行了比较,表现出性能改进。
- 在UA-DETRAC上与当前最先进的视频检测器具有竞争力,即使存在计算瓶颈。
点此查看论文截图


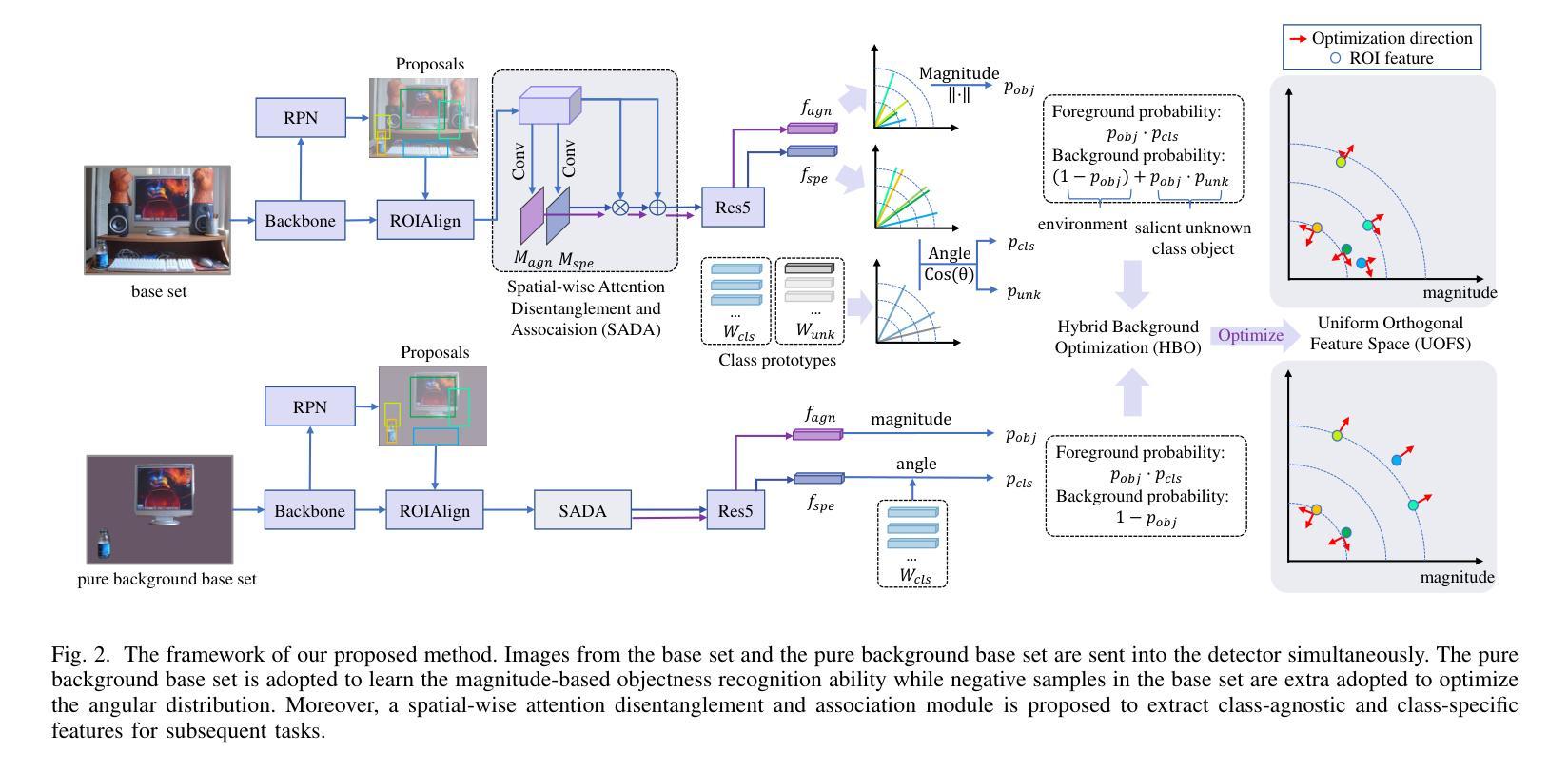
Attention-disentangled Uniform Orthogonal Feature Space Optimization for Few-shot Object Detection
Authors:Taijin Zhao, Heqian Qiu, Yu Dai, Lanxiao Wang, Fanman Meng, Qingbo Wu, Hongliang Li
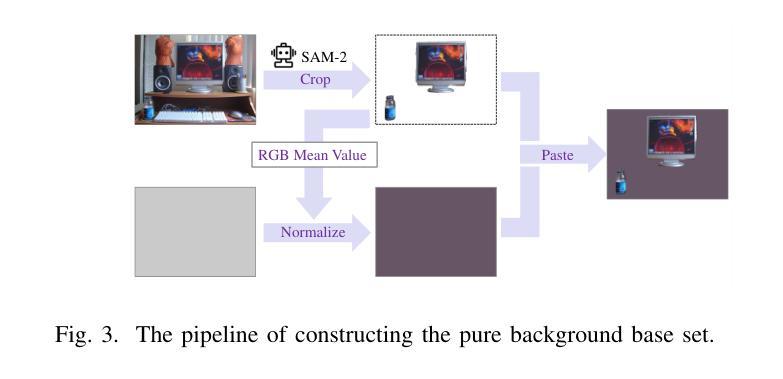
Few-shot object detection (FSOD) aims to detect objects with limited samples for novel classes, while relying on abundant data for base classes. Existing FSOD approaches, predominantly built on the Faster R-CNN detector, entangle objectness recognition and foreground classification within shared feature spaces. This paradigm inherently establishes class-specific objectness criteria and suffers from unrepresentative novel class samples. To resolve this limitation, we propose a Uniform Orthogonal Feature Space (UOFS) optimization framework. First, UOFS decouples the feature space into two orthogonal components, where magnitude encodes objectness and angle encodes classification. This decoupling enables transferring class-agnostic objectness knowledge from base classes to novel classes. Moreover, implementing the disentanglement requires careful attention to two challenges: (1) Base set images contain unlabeled foreground instances, causing confusion between potential novel class instances and backgrounds. (2) Angular optimization depends exclusively on base class foreground instances, inducing overfitting of angular distributions to base classes. To address these challenges, we propose a Hybrid Background Optimization (HBO) strategy: (1) Constructing a pure background base set by removing unlabeled instances in original images to provide unbiased magnitude-based objectness supervision. (2) Incorporating unlabeled foreground instances in the original base set into angular optimization to enhance distribution uniformity. Additionally, we propose a Spatial-wise Attention Disentanglement and Association (SADA) module to address task conflicts between class-agnostic and class-specific tasks. Experiments demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms existing approaches based on entangled feature spaces.
少量样本目标检测(Few-shot Object Detection,FSOD)旨在针对新类别使用有限样本进行目标检测,同时依赖于基本类别的丰富数据。现有的FSOD方法主要基于Faster R-CNN检测器,在共享特征空间内纠缠目标识别和前景分类。这种范式固有的建立了特定类别的目标性标准,并受到新类别样本代表性的限制。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了统一正交特征空间(Uniform Orthogonal Feature Space,UOFS)优化框架。首先,UOFS将特征空间解耦为两个正交组件,其中幅度编码目标性,角度编码分类。这种解耦使得从基本类别转移到新类别的类别无关的目标性知识成为可能。此外,实现解耦需要注意两个挑战:(1)基础集图像包含未标记的前景实例,导致潜在的新类别实例和背景之间的混淆。(2)角度优化完全依赖于基本类别的前景实例,导致角度分布对基本类别产生过度拟合。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了混合背景优化(Hybrid Background Optimization,HBO)策略:(1)通过去除原始图像中的未标记实例来构建纯净的背景基础集,以提供无偏的基于幅度的目标性监督。(2)将原始基础集中的未标记前景实例纳入角度优化,以增强分布均匀性。此外,我们提出了空间关注解耦与关联(Spatial-wise Attention Disentanglement and Association,SADA)模块,以解决类别无关和特定类别任务之间的任务冲突。实验表明,我们的方法在基于纠缠特征空间的方法上实现了显著的优势。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在有限的样本下对新型类别进行目标检测是少样本目标检测(FSOD)的任务。现有的FSOD方法主要基于Faster R-CNN检测器,在共享特征空间中纠缠目标识别和前景分类。本文提出了一个统一正交特征空间(UOFS)的优化框架,将特征空间解耦为两个正交组件:幅度编码目标性和角度编码分类。解决了类特定目标性标准的建立和不代表性新型类别样本的问题。通过混合背景优化(HBO)策略解决了解耦实现的挑战,包括构建纯背景基础集和增强分布均匀性。同时,提出了空间关注解纠缠和关联(SADA)模块来解决类通用和类特定任务之间的冲突。实验表明,该方法显著优于基于纠缠特征空间的方法。
Key Takeaways
- FSOD旨在使用有限样本对新型类别进行目标检测。
- 现有FSOD方法主要基于Faster R-CNN检测器,在共享特征空间中处理目标识别和前景分类,存在类特定目标性标准和样本不代表性挑战。
- UOFS框架将特征空间解耦为两个正交组件:幅度用于编码目标性,角度用于编码分类。
- HBO策略解决了特征解耦的两个挑战:构建纯背景基础集以提供无偏的目标性监督,并增强分布均匀性。
- SADA模块解决了类通用和类特定任务之间的冲突。
- 实验结果表明,所提出的方法在性能上显著优于基于纠缠特征空间的方法。
点此查看论文截图

Object detection in adverse weather conditions for autonomous vehicles using Instruct Pix2Pix
Authors:Unai Gurbindo, Axel Brando, Jaume Abella, Caroline König
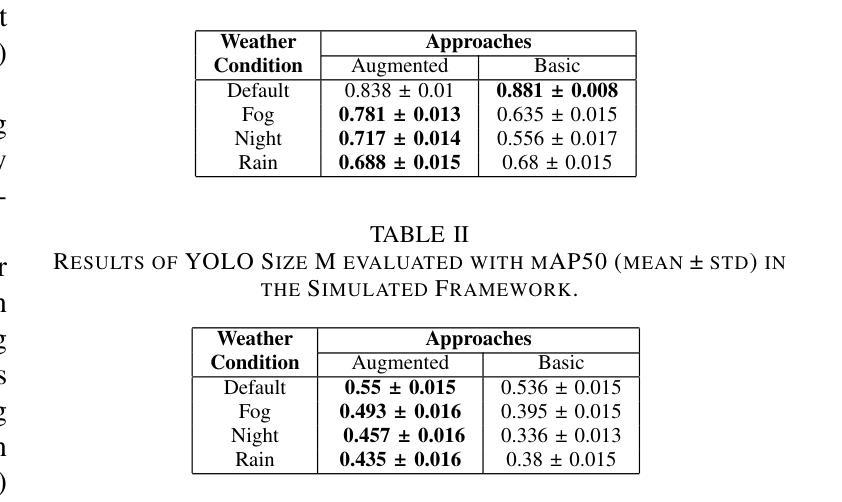
Enhancing the robustness of object detection systems under adverse weather conditions is crucial for the advancement of autonomous driving technology. This study presents a novel approach leveraging the diffusion model Instruct Pix2Pix to develop prompting methodologies that generate realistic datasets with weather-based augmentations aiming to mitigate the impact of adverse weather on the perception capabilities of state-of-the-art object detection models, including Faster R-CNN and YOLOv10. Experiments were conducted in two environments, in the CARLA simulator where an initial evaluation of the proposed data augmentation was provided, and then on the real-world image data sets BDD100K and ACDC demonstrating the effectiveness of the approach in real environments. The key contributions of this work are twofold: (1) identifying and quantifying the performance gap in object detection models under challenging weather conditions, and (2) demonstrating how tailored data augmentation strategies can significantly enhance the robustness of these models. This research establishes a solid foundation for improving the reliability of perception systems in demanding environmental scenarios, and provides a pathway for future advancements in autonomous driving.
提高恶劣天气条件下物体检测系统的稳健性对于自动驾驶技术的发展至关重要。本研究提出了一种利用扩散模型Instruct Pix2Pix开发提示方法的新方法,生成具有天气增强的现实数据集,旨在减轻恶劣天气对最新物体检测模型感知能力的影响,包括Faster R-CNN和YOLOv10。实验在两个环境中进行,在CARLA模拟器中进行所提出的数据增强的初步评估,然后在真实世界图像数据集BDD100K和ACDC上展示该方法在真实环境中的有效性。这项工作的关键贡献有两点:(1)识别和量化物体检测模型在恶劣天气条件下的性能差距;(2)展示有针对性的数据增强策略如何显著增强这些模型的稳健性。该研究为提高需求环境场景中感知系统的可靠性奠定了坚实的基础,并为自动驾驶技术的未来发展提供了途径。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 5 figures. Accepted at the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN) 2025 (to appear)
Summary
该研究利用扩散模型Instruct Pix2Pix发展出新的提示方法,生成具有天气增强的现实数据集,旨在减轻恶劣天气对最先进物体检测模型感知能力的影响,包括Faster R-CNN和YOLOv10。研究在CARLA模拟器与BDD100K及ACDC真实图像数据集上进行实验,验证了该方法的有效性。本研究关键贡献在于识别并量化物体检测模型在恶劣条件下的性能差距,并展示量身定制的数据增强策略如何显著提升模型的稳健性。该研究为改进需求环境下感知系统的可靠性奠定坚实基础,并为自动驾驶的未来发展铺平道路。
Key Takeaways
- 研究利用Instruct Pix2Pix扩散模型,提出一种新颖的方法生成带有天气增强的现实数据集。
- 该方法旨在减轻恶劣天气对物体检测模型的感知能力的影响。
- 实验在CARLA模拟器上进行初步评估,并在BDD100K及ACDC真实图像数据集上验证方法的有效性。
- 研究识别并量化物体检测模型在恶劣条件下的性能差距。
- 展示量身定制的数据增强策略能显著提升物体检测模型的稳健性。
- 本研究为改进感知系统在需求环境下的可靠性奠定坚实基础。
点此查看论文截图




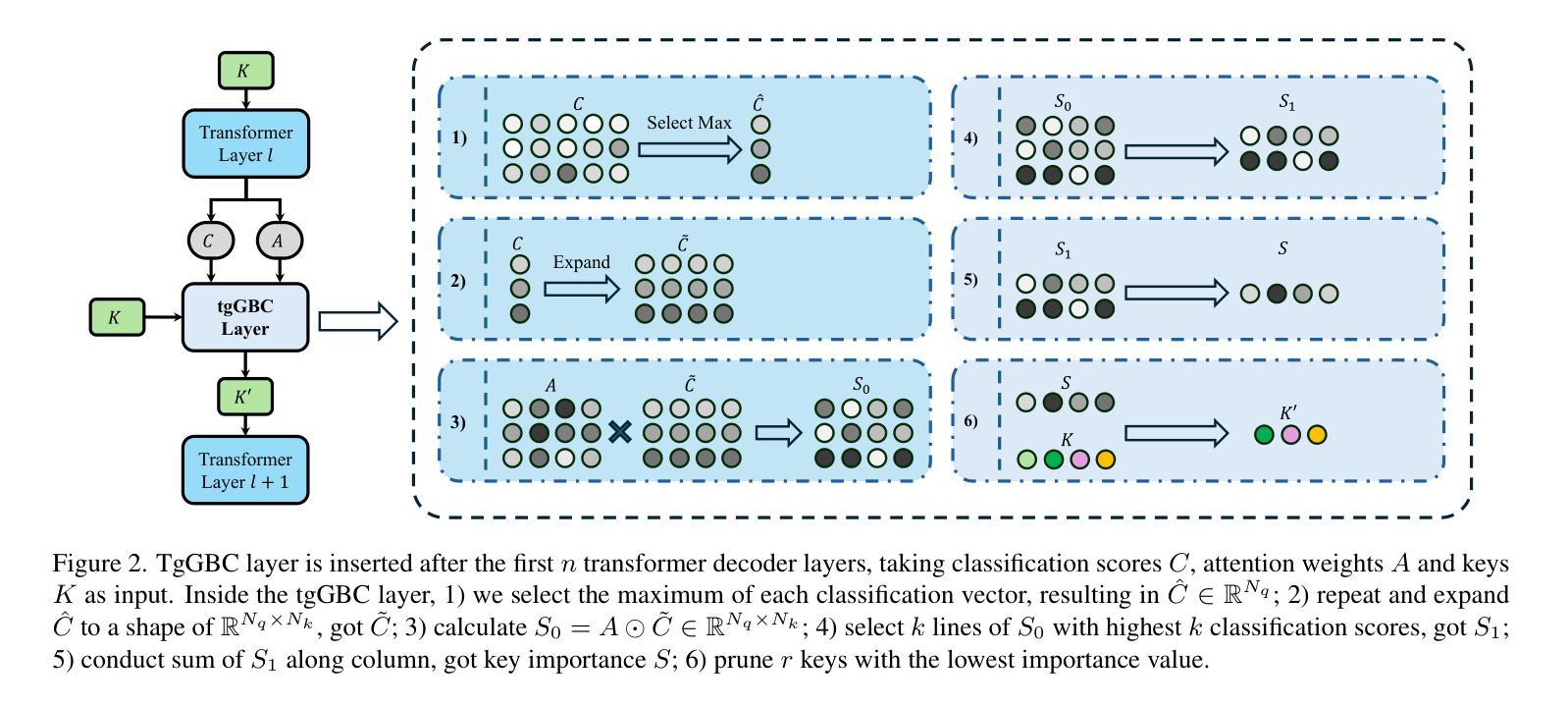
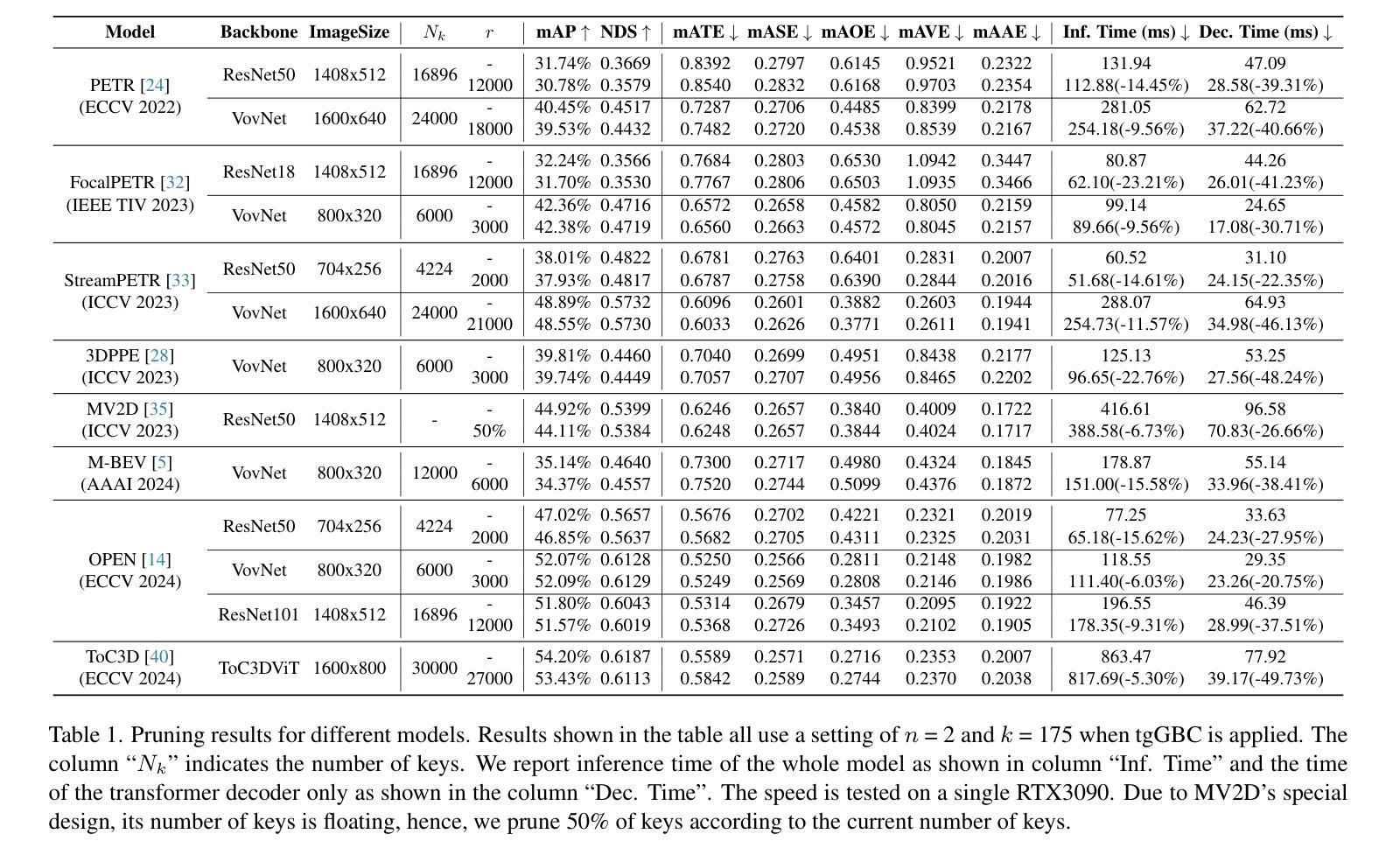
Accelerate 3D Object Detection Models via Zero-Shot Attention Key Pruning
Authors:Lizhen Xu, Xiuxiu Bai, Xiaojun Jia, Jianwu Fang, Shanmin Pang
Query-based methods with dense features have demonstrated remarkable success in 3D object detection tasks. However, the computational demands of these models, particularly with large image sizes and multiple transformer layers, pose significant challenges for efficient running on edge devices. Existing pruning and distillation methods either need retraining or are designed for ViT models, which are hard to migrate to 3D detectors. To address this issue, we propose a zero-shot runtime pruning method for transformer decoders in 3D object detection models. The method, termed tgGBC (trim keys gradually Guided By Classification scores), systematically trims keys in transformer modules based on their importance. We expand the classification score to multiply it with the attention map to get the importance score of each key and then prune certain keys after each transformer layer according to their importance scores. Our method achieves a 1.99x speedup in the transformer decoder of the latest ToC3D model, with only a minimal performance loss of less than 1%. Interestingly, for certain models, our method even enhances their performance. Moreover, we deploy 3D detectors with tgGBC on an edge device, further validating the effectiveness of our method. The code can be found at https://github.com/iseri27/tg_gbc.
基于查询的方法和密集特征在3D目标检测任务中取得了显著的成功。然而,这些模型对计算的需求,特别是在大图像尺寸和多个转换器层的情况下,对于在边缘设备上进行高效运行构成了重大挑战。现有的修剪和蒸馏方法都需要重新训练,或者针对ViT模型设计,很难迁移到3D检测器。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种用于3D目标检测模型中变压器解码器的零射击运行时修剪方法。该方法被称为tgGBC(通过分类分数逐步引导修剪关键),它根据关键的重要性系统地修剪变压器模块中的关键。我们将分类分数扩展到与注意力图相乘,以得到每个关键的重要性分数,然后根据其重要性分数在每个转换器层之后修剪某些关键。我们的方法在最新的ToC3D模型的变压器解码器中实现了1.99倍的速度提升,性能损失仅低于1%。有趣的是,对于某些模型,我们的方法甚至提高了其性能。此外,我们在边缘设备上部署了带有tgGBC的3D检测器,进一步验证了我们的方法的有效性。代码位于https://github.com/iseri27/tg_gbc。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV2025. The code can be found at https://github.com/iseri27/tg_gbc
Summary
基于查询方法和密集特征的3D对象检测任务取得了显著成功,但计算需求较高,特别是在处理大图像和多层Transformer时。为解决此问题,我们提出了一种名为tgGBC的零运行时修剪方法,该方法基于分类分数计算关键重要性,并逐层修剪Transformer模块中的关键。tgGBC在最新ToC3D模型的Transformer解码器中实现了1.99倍加速,性能损失极小(不到1%),并在某些模型中甚至提高了性能。此外,我们在边缘设备上部署了带有tgGBC的3D检测器,验证了其有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 查询方法和密集特征在3D对象检测中表现优异。
- 计算需求高,特别是对于大图像和多层Transformer。
- 提出一种零运行时修剪方法——tgGBC,针对Transformer解码器进行优化。
- tgGBC基于分类分数计算关键重要性并进行修剪。
- 在最新ToC3D模型的Transformer解码器中实现了1.99倍加速。
- 性能损失极小(不到1%),在某些模型中甚至提高了性能。
- 在边缘设备上部署了带有tgGBC的3D检测器,验证了其有效性。
点此查看论文截图


Mitigating Hallucinations in YOLO-based Object Detection Models: A Revisit to Out-of-Distribution Detection
Authors:Weicheng He, Changshun Wu, Chih-Hong Cheng, Xiaowei Huang, Saddek Bensalem
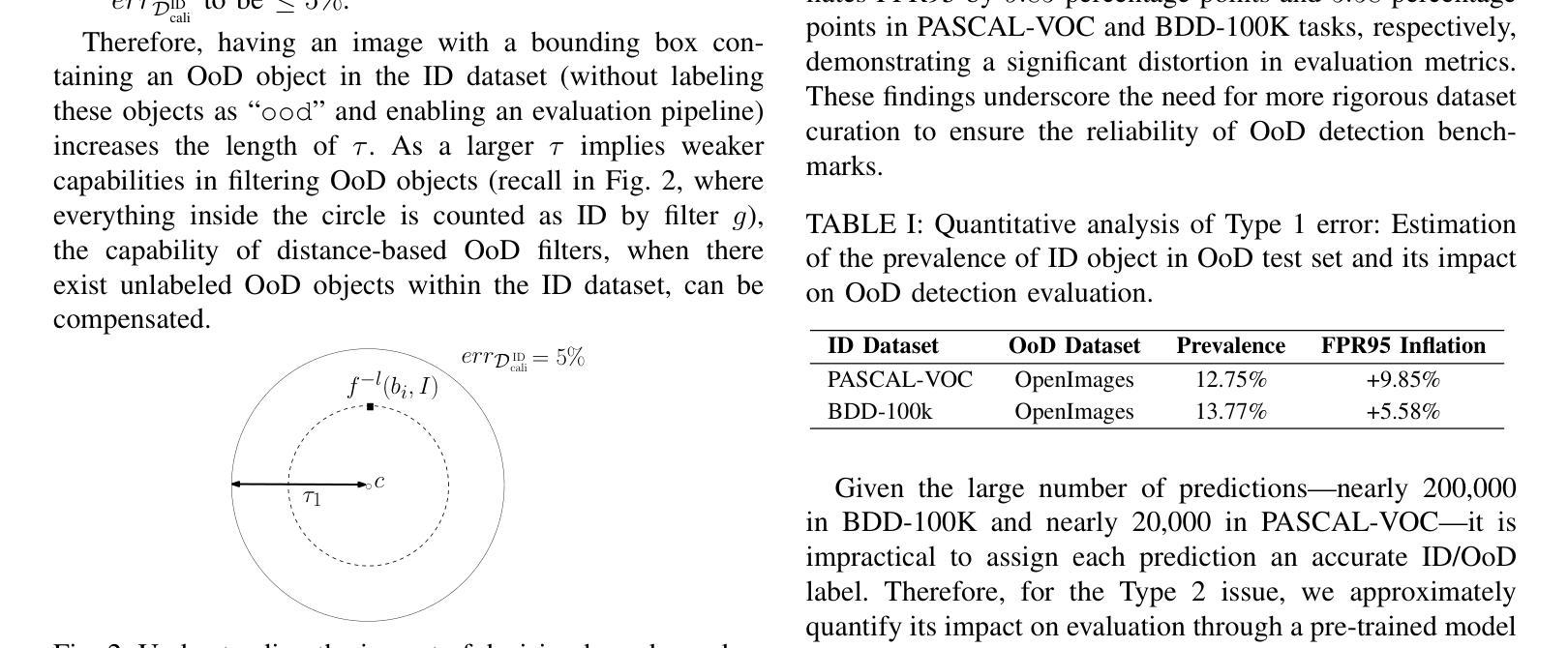
Object detection systems must reliably perceive objects of interest without being overly confident to ensure safe decision-making in dynamic environments. Filtering techniques based on out-of-distribution (OoD) detection are commonly added as an extra safeguard to filter hallucinations caused by overconfidence in novel objects. Nevertheless, evaluating YOLO-family detectors and their filters under existing OoD benchmarks often leads to unsatisfactory performance. This paper studies the underlying reasons for performance bottlenecks and proposes a methodology to improve performance fundamentally. Our first contribution is a calibration of all existing evaluation results: Although images in existing OoD benchmark datasets are claimed not to have objects within in-distribution (ID) classes (i.e., categories defined in the training dataset), around 13% of objects detected by the object detector are actually ID objects. Dually, the ID dataset containing OoD objects can also negatively impact the decision boundary of filters. These ultimately lead to a significantly imprecise performance estimation. Our second contribution is to consider the task of hallucination reduction as a joint pipeline of detectors and filters. By developing a methodology to carefully synthesize an OoD dataset that semantically resembles the objects to be detected, and using the crafted OoD dataset in the fine-tuning of YOLO detectors to suppress the objectness score, we achieve a 88% reduction in overall hallucination error with a combined fine-tuned detection and filtering system on the self-driving benchmark BDD-100K. Our code and dataset are available at: https://gricad-gitlab.univ-grenoble-alpes.fr/dnn-safety/m-hood.
对象检测系统必须可靠地感知动态环境中的感兴趣对象,同时避免过于自信,以确保做出安全决策。基于离群分布(Out-of-Distribution,OoD)检测的过滤技术通常被用作额外的安全保护措施,以过滤由于过于自信而产生的新型对象的幻觉。然而,在现有的OoD基准测试中评估YOLO系列检测器及其过滤器通常会得到令人不满意的表现。本文研究了性能瓶颈的底层原因,并提出了一种从根本上提高性能的方法。我们的第一个贡献是校准了所有现有的评估结果:尽管现有OoD基准数据集声称在内部分布(ID)类(即训练数据集中定义的类别)中没有对象,但对象检测器检测到的对象中大约有13%实际上是ID对象。同样,包含OoD对象的ID数据集也可能对过滤器的决策边界产生负面影响。这些最终导致了性能估计的严重不准确。我们的第二个贡献是将幻觉减少任务视为检测器和过滤器的联合管道。通过开发一种仔细合成在语义上类似于待检测对象的OoD数据集的方法,并使用精细调整的YOLO检测器抑制对象分数来精心制作的OoD数据集,我们在自动驾驶基准BDD-100K上实现了整体幻觉误差降低了88%,这是通过结合精细调整的检测和过滤系统实现的。我们的代码和数据集可在以下网址找到:https://gricad-gitlab.univ-grenoble-alpes.fr/dnn-safety/m-hood。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Camera-ready version for IROS 2025
摘要
对象检测系统需在动态环境中可靠识别目标对象,同时避免过度自信导致的幻觉。本文研究了基于异常值检测技术的滤波技术在YOLO系列检测器中的应用瓶颈,并提出了改进方案。研究发现现有异常值检测基准测试中存在问题,检测出的ID对象中约存在高达百分之十三的非ID对象。针对上述问题,本研究提出了新的评价标准和合成异常值数据集的方法论,通过微调YOLO检测器抑制对象得分,实现了在BDD-100K自动驾驶基准测试中幻觉误差减少百分之八十八。研究代码及数据集已公开分享。
关键见解
- 对象检测系统应避免过度自信的问题以确保决策安全性。在复杂动态环境中使用性能评估和增强滤波器是至关重要的。在现存在的系统可靠性中提高和改进稳定性更为关键。已有采用以评估函数的新开发方式对既成传感器设计和要求认识精准和理解来进行检查范例开发和设备初始化校正手段等方式来保证和提高测试精准度的问题与保障;基于此背景下实施先进解决方案具有重要的实用价值和发展前景广阔的研究领域前景展望重要性显而易见;新测试精准度将具有显著的推广价值和产业潜力及现实意义,该研究成果的应用场景极其广泛;代码和数据集已公开分享。
点此查看论文截图

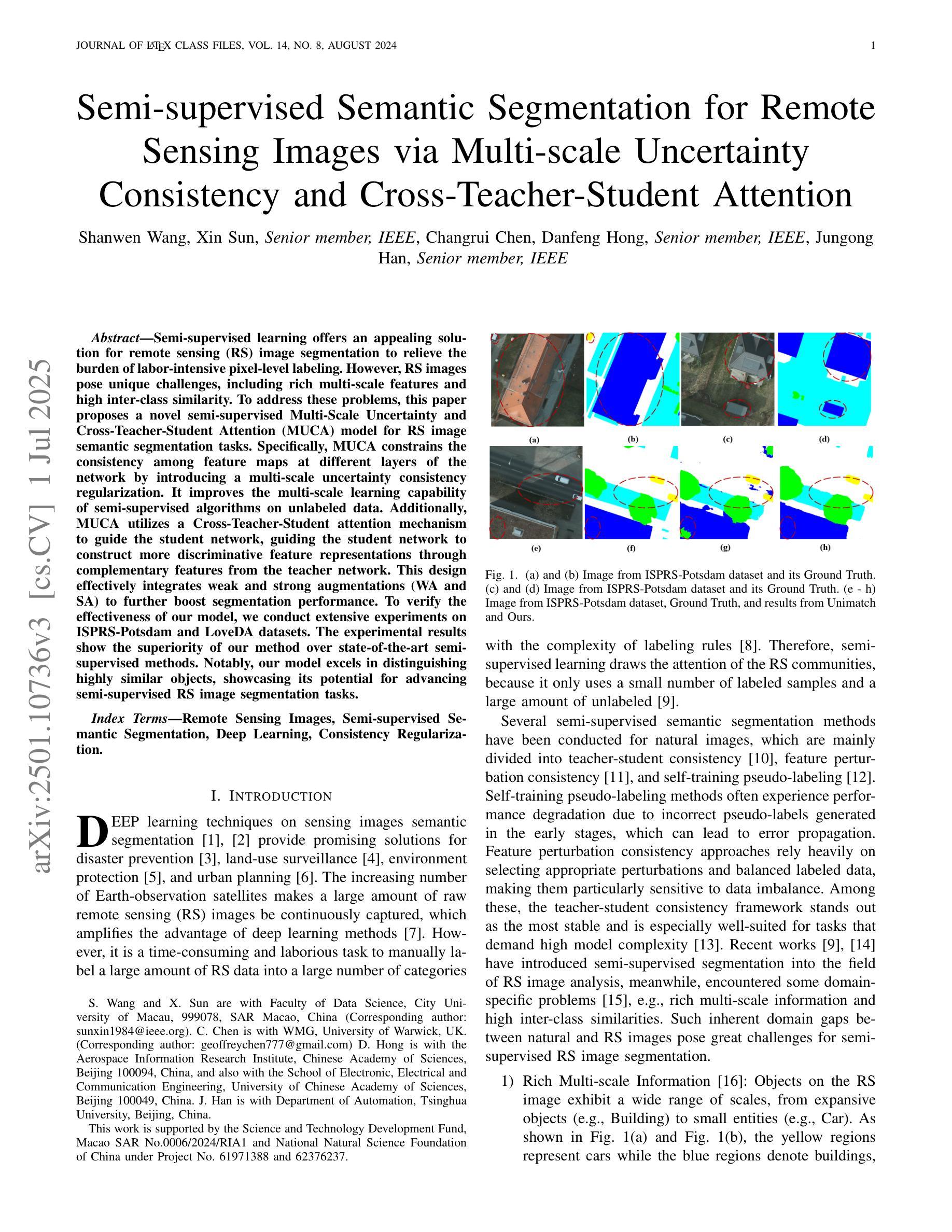
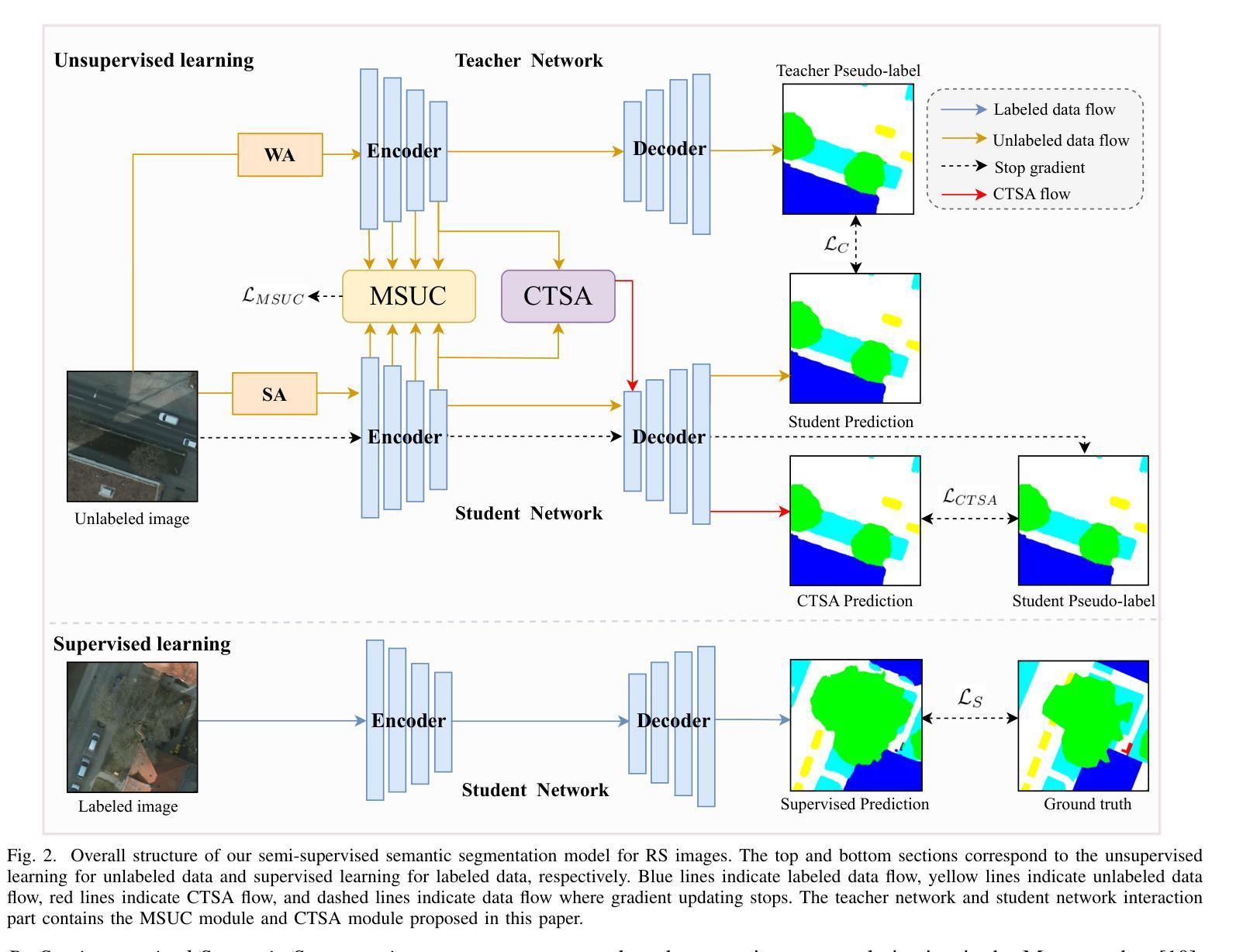
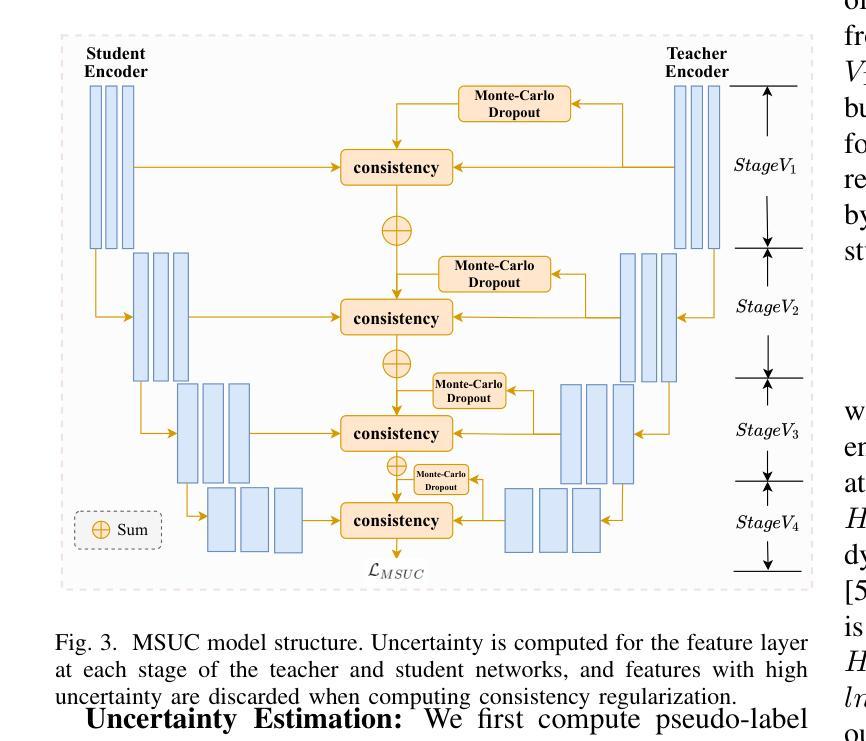
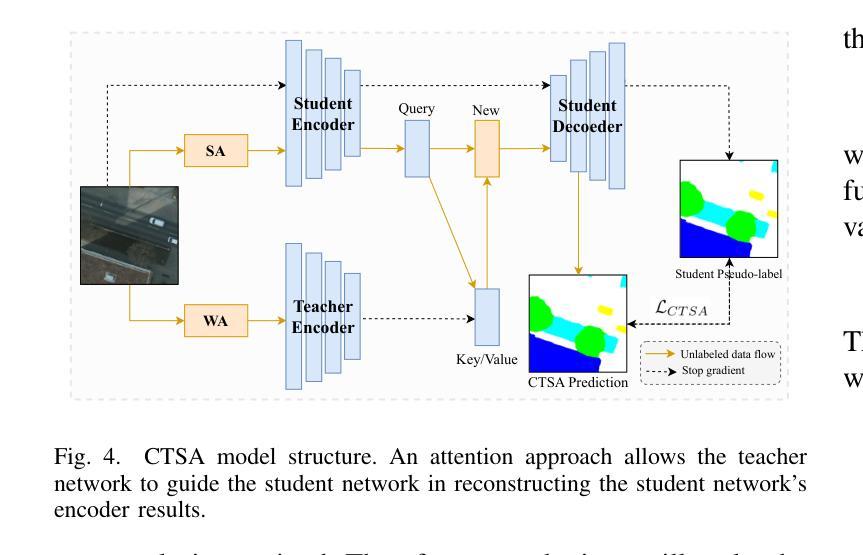
Semi-supervised Semantic Segmentation for Remote Sensing Images via Multi-scale Uncertainty Consistency and Cross-Teacher-Student Attention
Authors:Shanwen Wang, Xin Sun, Changrui Chen, Danfeng Hong, Jungong Han
Semi-supervised learning offers an appealing solution for remote sensing (RS) image segmentation to relieve the burden of labor-intensive pixel-level labeling. However, RS images pose unique challenges, including rich multi-scale features and high inter-class similarity. To address these problems, this paper proposes a novel semi-supervised Multi-Scale Uncertainty and Cross-Teacher-Student Attention (MUCA) model for RS image semantic segmentation tasks. Specifically, MUCA constrains the consistency among feature maps at different layers of the network by introducing a multi-scale uncertainty consistency regularization. It improves the multi-scale learning capability of semi-supervised algorithms on unlabeled data. Additionally, MUCA utilizes a Cross-Teacher-Student attention mechanism to guide the student network, guiding the student network to construct more discriminative feature representations through complementary features from the teacher network. This design effectively integrates weak and strong augmentations (WA and SA) to further boost segmentation performance. To verify the effectiveness of our model, we conduct extensive experiments on ISPRS-Potsdam and LoveDA datasets. The experimental results show the superiority of our method over state-of-the-art semi-supervised methods. Notably, our model excels in distinguishing highly similar objects, showcasing its potential for advancing semi-supervised RS image segmentation tasks.
半监督学习为遥感(RS)图像分割提供了一种吸引人的解决方案,减轻了劳动密集型的像素级标注的负担。然而,遥感图像带来了独特的挑战,包括丰富的多尺度特征和高的类间相似性。为了解决这些问题,本文提出了一种新型的半监督多尺度不确定性与交叉教师学生注意力(MUCA)模型,用于遥感图像语义分割任务。具体来说,MUCA通过引入多尺度不确定性一致性正则化,约束网络不同层特征图之间的一致性。它提高了半监督算法在未标记数据上的多尺度学习能力。此外,MUCA利用跨教师学生注意力机制来引导学生网络,通过教师网络的互补特征构建更具判别力的特征表示。这种设计有效地结合了弱增强和强增强(WA和SA),进一步提高了分割性能。为了验证我们模型的有效性,我们在ISPRS-Potsdam和LoveDA数据集上进行了大量实验。实验结果表明,我们的方法优于最新的半监督方法。值得注意的是,我们的模型在区分高度相似物体方面表现出色,展示了其在推进半监督遥感图像分割任务方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
半监督学习为遥感图像分割提供了一种吸引人的解决方案,减轻了劳动密集型的像素级标注负担。本文提出一种新型的半监督多尺度不确定性及交叉教师学生注意力模型(MUCA),解决遥感图像分割中特有的丰富多尺度特征和高度类别相似性挑战。MUCA通过引入多尺度不确定性一致性正则化,提高半监督算法在未标注数据上的多尺度学习能力。此外,MUCA利用交叉教师学生注意力机制引导学生网络构建更具区分性的特征表示。实验结果表明,该方法在ISPRS-Potsdam和LoveDA数据集上表现出优异的性能,尤其是在区分高度相似对象方面潜力巨大。
Key Takeaways
- 半监督学习是解决遥感图像分割中劳动密集型标注负担的有效方法。
- 本文提出的MUCA模型解决了遥感图像分割特有的丰富多尺度特征和高度类别相似性挑战。
- MUCA通过引入多尺度不确定性一致性正则化,提高半监督算法在未标注数据上的多尺度学习能力。
- MUCA利用交叉教师学生注意力机制,通过教师网络的互补特征引导学生网络构建更具区分性的特征表示。
- 模型在ISPRS-Potsdam和LoveDA数据集上进行了广泛的实验验证。
- 实验结果表明,MUCA模型在性能上优于其他先进的半监督方法。
点此查看论文截图

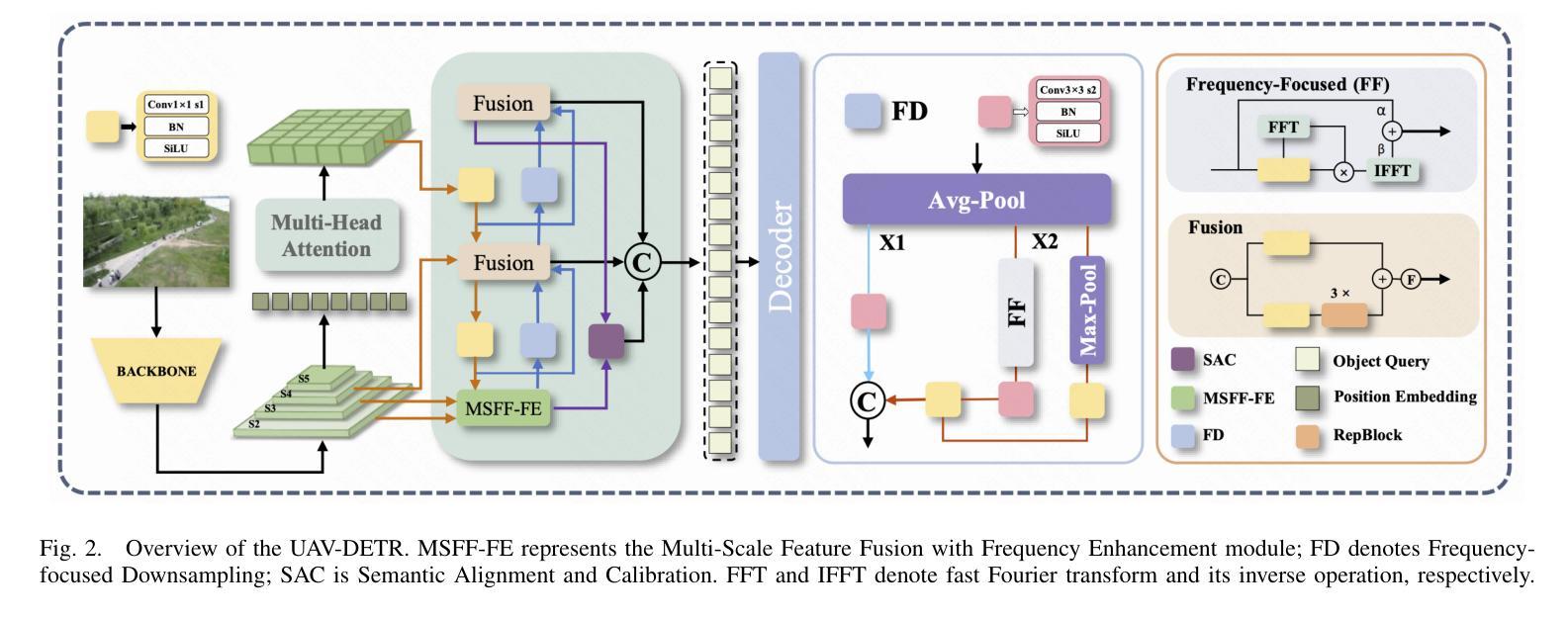
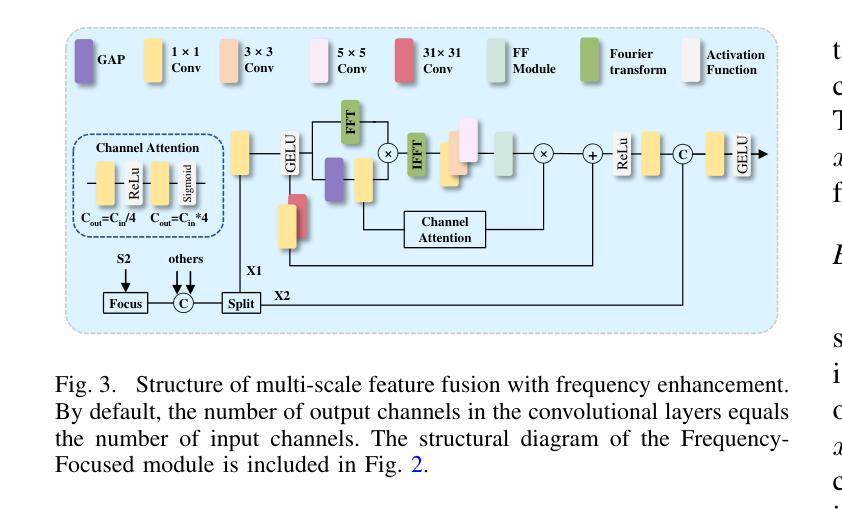
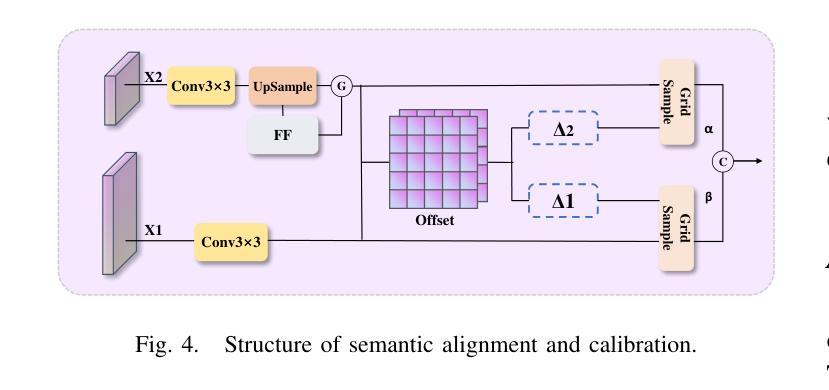
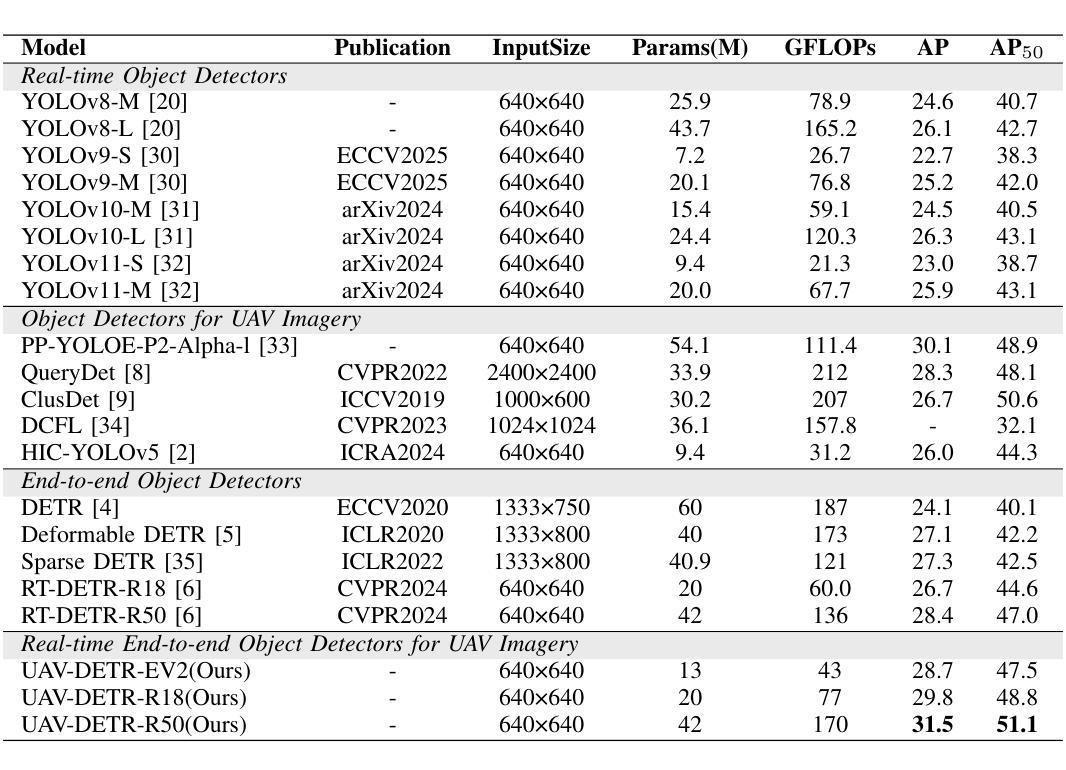
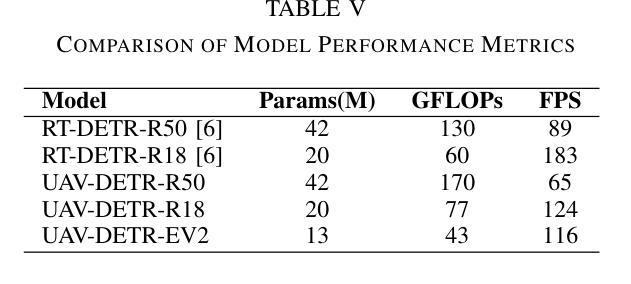
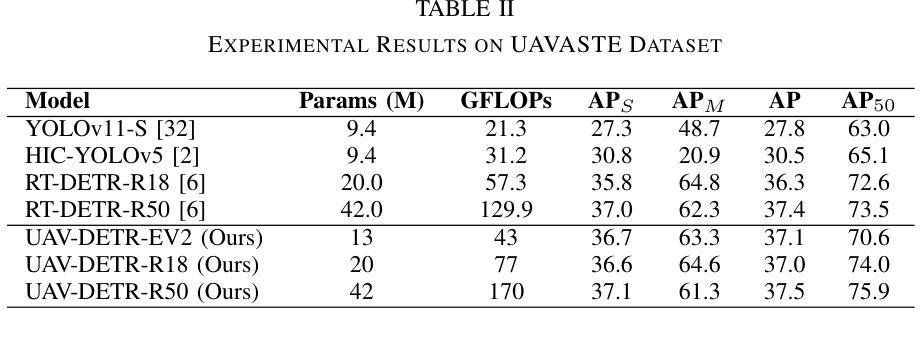
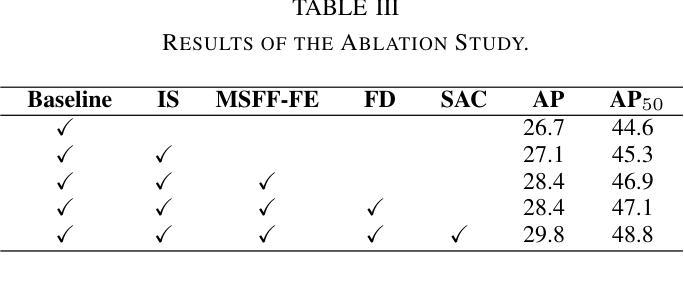
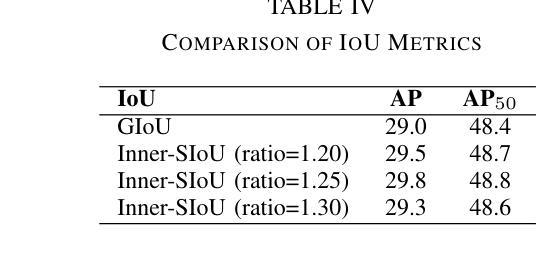
UAV-DETR: Efficient End-to-End Object Detection for Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Imagery
Authors:Huaxiang Zhang, Kai Liu, Zhongxue Gan, Guo-Niu Zhu
Unmanned aerial vehicle object detection (UAV-OD) has been widely used in various scenarios. However, most existing UAV-OD algorithms rely on manually designed components, which require extensive tuning. End-to-end models that do not depend on such manually designed components are mainly designed for natural images, which are less effective for UAV imagery. To address such challenges, this paper proposes an efficient detection transformer (DETR) framework tailored for UAV imagery, i.e., UAV-DETR. The framework includes a multi-scale feature fusion with frequency enhancement module, which captures both spatial and frequency information at different scales. In addition, a frequency-focused down-sampling module is presented to retain critical spatial details during down-sampling. A semantic alignment and calibration module is developed to align and fuse features from different fusion paths. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness and generalization of our approach across various UAV imagery datasets. On the VisDrone dataset, our method improves AP by 3.1% and $\text{AP}_{50}$ by 4.2% over the baseline. Similar enhancements are observed on the UAVVaste dataset. The project page: https://github.com/ValiantDiligent/UAV-DETR
无人机目标检测(UAV-OD)已在各种场景中得到了广泛应用。然而,大多数现有的UAV-OD算法依赖于手动设计的组件,需要大量的调整。不依赖于此类手动设计组件的端到端模型主要设计用于自然图像,但对无人机图像的效果较差。为了应对这些挑战,本文提出了一种针对无人机图像的的高效检测转换器(DETR)框架,即UAV-DETR。该框架包括具有频率增强模块的多尺度特征融合,能够捕获不同尺度的空间和信息频率。此外,还提出了频率聚焦的下采样模块,以在下采样过程中保留关键的空间细节。开发了一个语义对齐和校准模块,以对齐和融合来自不同融合路径的特征。实验结果表明,我们的方法在各种无人机图像数据集上的有效性和通用性。在VisDrone数据集上,我们的方法较基线提高了3.1%的AP和4.2%的AP50。在UAVVaste数据集上也观察到了类似的改进。项目页面:https://github.com/ValiantDiligent/UAV-DETR
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种针对无人机图像的高效检测变压器(UAV-DETR)框架,用于解决现有无人机目标检测算法依赖手动设计组件的问题。该框架包括多尺度特征融合与频率增强模块、频率聚焦下采样模块以及语义对齐与校准模块。实验结果表明,该算法在不同无人机图像数据集上具有良好的有效性和泛化能力,相较于基线方法在VisDrone数据集上的AP提高了3.1%,AP50提高了4.2%。项目页面:https://github.com/ValiantDiligent/UAV-DETR。
Key Takeaways
- UAV-OD算法广泛应用在各种场景中,但依赖手动设计组件的算法需要大量调整。
- 端到端模型在自然图像上的表现较好,但在无人机图像上的效果较差。
- 本文提出了一种针对无人机图像设计的检测变压器(DETR)框架,即UAV-DETR。
- UAV-DETR框架包括多尺度特征融合与频率增强模块,用于捕捉不同尺度的空间和频率信息。
- 无人机图像数据集中,UAV-DETR算法表现出良好的有效性和泛化能力。
- 在VisDrone数据集上,UAV-DETR相较于基线方法提高了检测性能。
点此查看论文截图

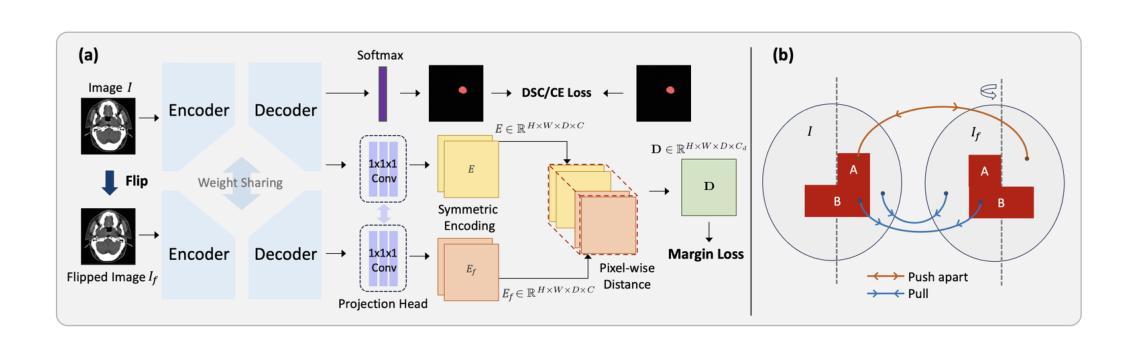
Leveraging Semantic Asymmetry for Precise Gross Tumor Volume Segmentation of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma in Planning CT
Authors:Zi Li, Ying Chen, Zeli Chen, Yanzhou Su, Tai Ma, Tony C. W. Mok, Yan-Jie Zhou, Yunhai Bai, Zhinlin Zheng, Le Lu, Yirui Wang, Jia Ge, Xianghua Ye, Senxiang Yan, Dakai Jin
In the radiation therapy of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), clinicians typically delineate the gross tumor volume (GTV) using non-contrast planning computed tomography to ensure accurate radiation dose delivery. However, the low contrast between tumors and adjacent normal tissues necessitates that radiation oncologists manually delineate the tumors, often relying on diagnostic MRI for guidance. % In this study, we propose a novel approach to directly segment NPC gross tumors on non-contrast planning CT images, circumventing potential registration errors when aligning MRI or MRI-derived tumor masks to planning CT. To address the low contrast issues between tumors and adjacent normal structures in planning CT, we introduce a 3D Semantic Asymmetry Tumor segmentation (SATs) method. Specifically, we posit that a healthy nasopharyngeal region is characteristically bilaterally symmetric, whereas the emergence of nasopharyngeal carcinoma disrupts this symmetry. Then, we propose a Siamese contrastive learning segmentation framework that minimizes the voxel-wise distance between original and flipped areas without tumor and encourages a larger distance between original and flipped areas with tumor. Thus, our approach enhances the sensitivity of features to semantic asymmetries. % Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed SATs achieves the leading NPC GTV segmentation performance in both internal and external testing, \emph{e.g.}, with at least 2% absolute Dice score improvement and 12% average distance error reduction when compared to other state-of-the-art methods in the external testing.
在鼻咽癌(NPC)的放射治疗过程中,临床医生通常使用非对比计划计算机断层扫描(planning CT)来划定大体肿瘤体积(GTV),以确保准确的辐射剂量传递。然而,肿瘤与相邻正常组织之间的对比度较低,迫使放疗科医生手动划定肿瘤,通常依赖诊断磁共振成像(MRI)进行引导。本研究提出了一种直接在非对比计划CT图像上分割鼻咽癌大体肿瘤的新方法,避免了将MRI或MRI衍生的肿瘤掩膜与计划CT对齐时可能出现的注册误差。为了解决计划CT中肿瘤与相邻正常结构之间对比度低的问题,我们引入了3D语义不对称肿瘤分割(SATs)方法。具体来说,我们认为健康的鼻咽区域具有双侧对称性,而鼻咽癌的出现会破坏这种对称性。然后,我们提出了一种Siamese对比学习分割框架,该框架通过最小化原始和翻转的无肿瘤区域的体素级距离来训练模型,同时鼓励原始和带有肿瘤的翻转区域之间的距离更大。因此,我们的方法提高了对语义不对称性的特征敏感性。大量实验表明,所提出的SATs在内部和外部测试中均实现了领先的NPC GTV分割性能,例如与外部测试中的其他最新方法相比,至少提高了2%的绝对Dice得分并降低了12%的平均距离误差。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:在鼻咽癌放射治疗过程中,肿瘤与邻近正常组织对比度低,需医生手动区分。本研究提出了一种基于非对比剂规划计算机断层扫描(CT)直接分割鼻咽癌大体肿瘤体积(GTV)的新方法,通过利用健康的鼻咽区域具有特征性双侧对称性质来区分肿瘤,并采用Siamese对比学习分割框架,提高了语义不对称的敏感性。实验表明,该方法在内外测试中均达到了领先的NPC GTV分割性能。
Key Takeaways:
- 鼻咽癌放射治疗需要准确区分肿瘤和邻近正常组织。
- 由于肿瘤与邻近组织的对比度低,通常需依赖医生手动分割肿瘤。
- 本研究提出了一种新的NPC肿瘤分割方法,基于非对比剂规划CT影像。
- 该方法利用健康的鼻咽区域具有特征性双侧对称性质来识别肿瘤。
- 采用Siamese对比学习分割框架,提高了语义不对称的敏感性。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在内外测试中表现优异,与其他最先进的方法相比,绝对Dice分数至少提高了2%,平均距离误差减少了12%。
点此查看论文截图

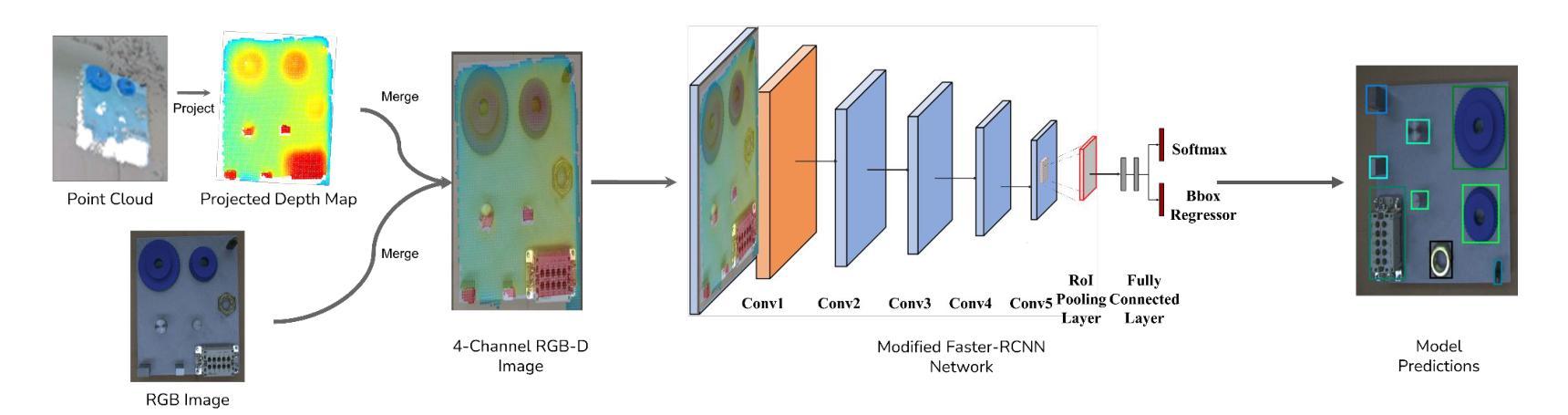
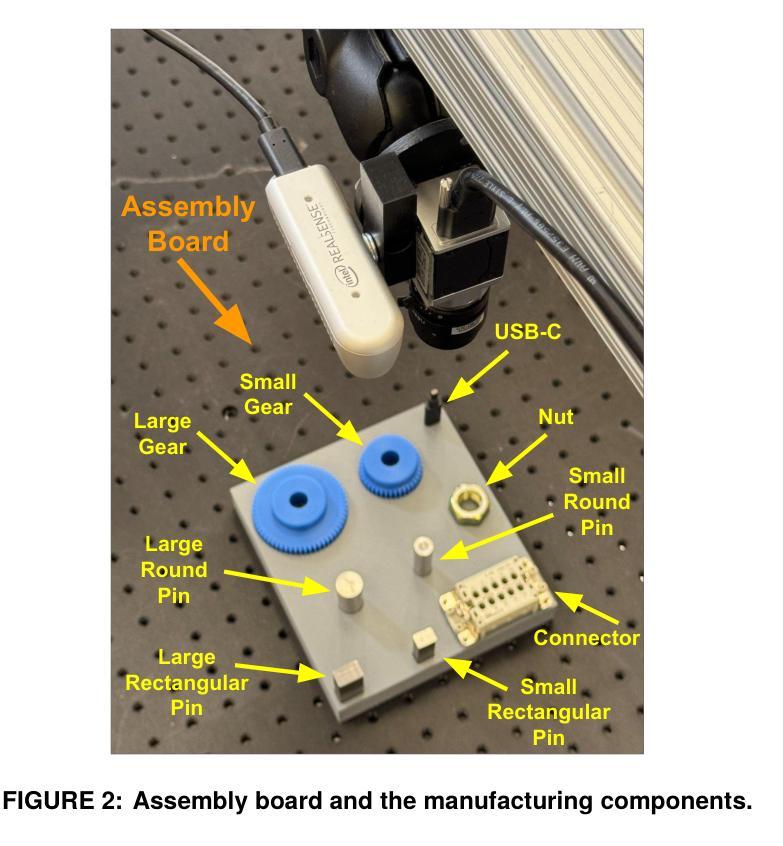
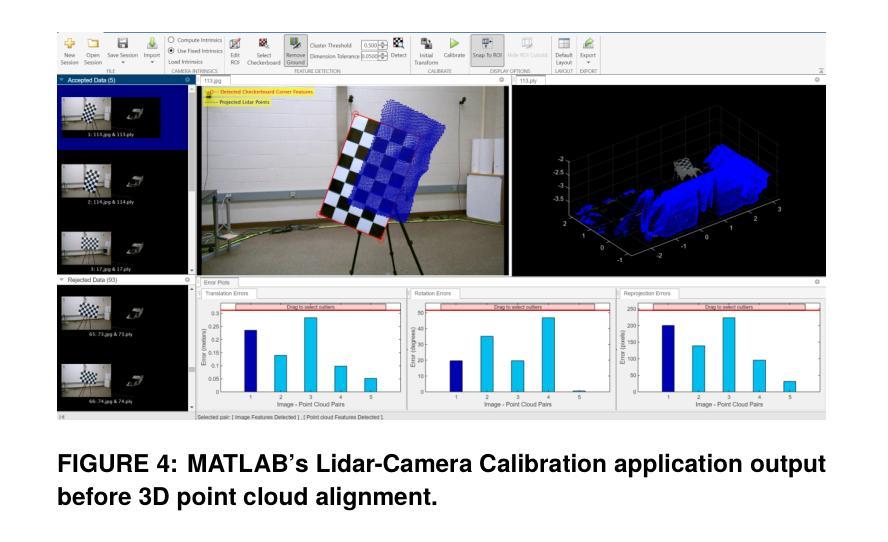
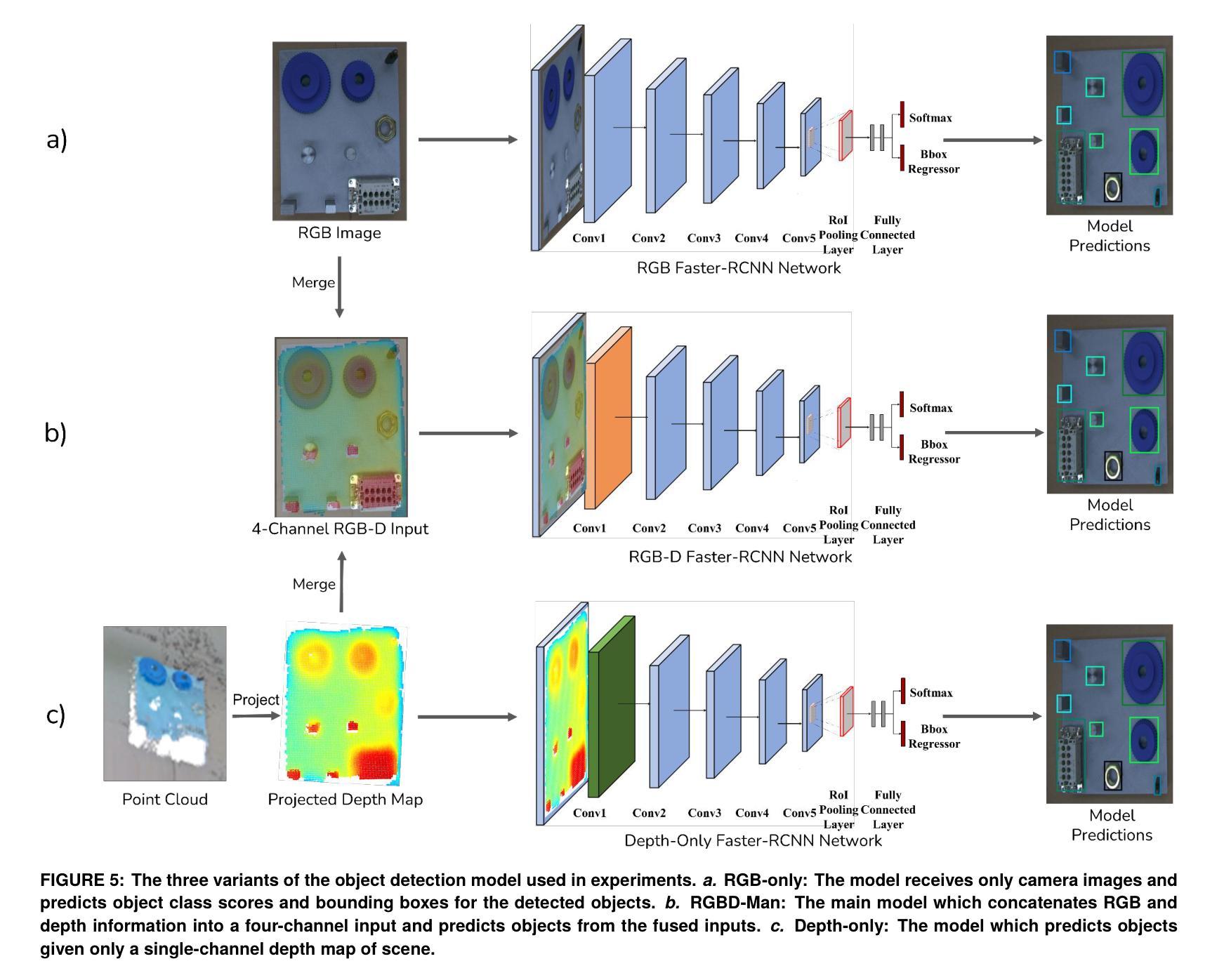
Multimodal Object Detection using Depth and Image Data for Manufacturing Parts
Authors:Nazanin Mahjourian, Vinh Nguyen
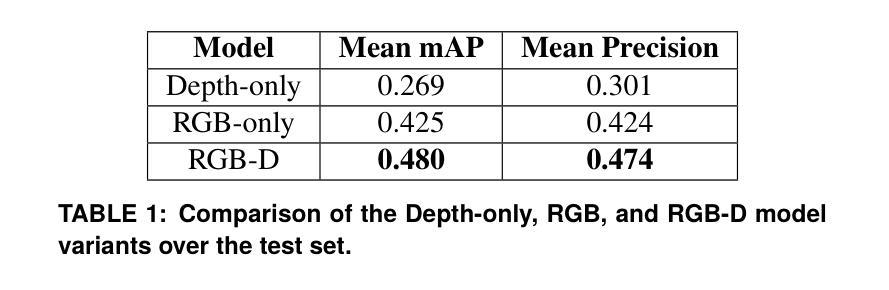
Manufacturing requires reliable object detection methods for precise picking and handling of diverse types of manufacturing parts and components. Traditional object detection methods utilize either only 2D images from cameras or 3D data from lidars or similar 3D sensors. However, each of these sensors have weaknesses and limitations. Cameras do not have depth perception and 3D sensors typically do not carry color information. These weaknesses can undermine the reliability and robustness of industrial manufacturing systems. To address these challenges, this work proposes a multi-sensor system combining an red-green-blue (RGB) camera and a 3D point cloud sensor. The two sensors are calibrated for precise alignment of the multimodal data captured from the two hardware devices. A novel multimodal object detection method is developed to process both RGB and depth data. This object detector is based on the Faster R-CNN baseline that was originally designed to process only camera images. The results show that the multimodal model significantly outperforms the depth-only and RGB-only baselines on established object detection metrics. More specifically, the multimodal model improves mAP by 13% and raises Mean Precision by 11.8% in comparison to the RGB-only baseline. Compared to the depth-only baseline, it improves mAP by 78% and raises Mean Precision by 57%. Hence, this method facilitates more reliable and robust object detection in service to smart manufacturing applications.
制造需要可靠的目标检测方法,用于精确拾取和处理各种类型的制造零部件。传统目标检测方法仅使用相机拍摄的2D图像或使用激光雷达或类似的三维传感器获取的数据。然而,每种传感器都有其缺点和局限性。摄像机没有深度感知能力,而三维传感器通常不包含颜色信息。这些缺点可能会破坏工业制造系统的可靠性和稳健性。为解决这些挑战,这项工作提出了一种结合红色绿色蓝色(RGB)相机和三维点云传感器的多传感器系统。这两个传感器经过校准,以对两个硬件设备捕获的多模态数据进行精确对齐。开发了一种新型的多模态目标检测方法,可同时处理RGB和深度数据。该目标检测器基于Faster R-CNN基线开发,最初设计仅用于处理相机图像。结果表明,在公认的目标检测指标上,多模态模型显著优于仅使用深度信息和仅使用RGB信息的基线模型。更具体地说,与仅使用RGB的基线相比,多模态模型的平均精度均值提高了13%,平均精度提高了11.8%。与仅使用深度信息的基线相比,平均精度均值提高了78%,平均精度提高了57%。因此,该方法在智能制造应用中促进了更可靠和稳健的目标检测。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
制造业需要可靠的目标检测方法,对多种制造零件和组件进行精确抓取和处理。本工作提出一种结合RGB相机和三维点云传感器的多传感器系统,克服传统目标检测方法的局限。通过开发新型的多模态目标检测方法,处理RGB和深度数据,显著提高目标检测的可靠性和鲁棒性,为智能制造应用提供服务。
要点
- 制造业中目标检测的可靠性对于精确抓取和处理各类部件至关重要。
- 传统方法依赖单一传感器(如相机或3D传感器)进行目标检测,存在局限性。
- 本工作提出一种多传感器系统,结合RGB相机和三维点云传感器,提高数据精度和可靠性。
- 新型多模态目标检测方法结合了RGB和深度数据,显著提高目标检测的准确性和鲁棒性。
- 该方法基于Faster R-CNN基线模型开发,可处理多模态数据。
- 实验结果显示,多模态模型在目标检测指标上显著优于仅使用深度或RGB的基线模型。
- 该方法对于智能制造业中的目标检测具有广泛应用前景。
点此查看论文截图