⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-03 更新
MILo: Mesh-In-the-Loop Gaussian Splatting for Detailed and Efficient Surface Reconstruction
Authors:Antoine Guédon, Diego Gomez, Nissim Maruani, Bingchen Gong, George Drettakis, Maks Ovsjanikov
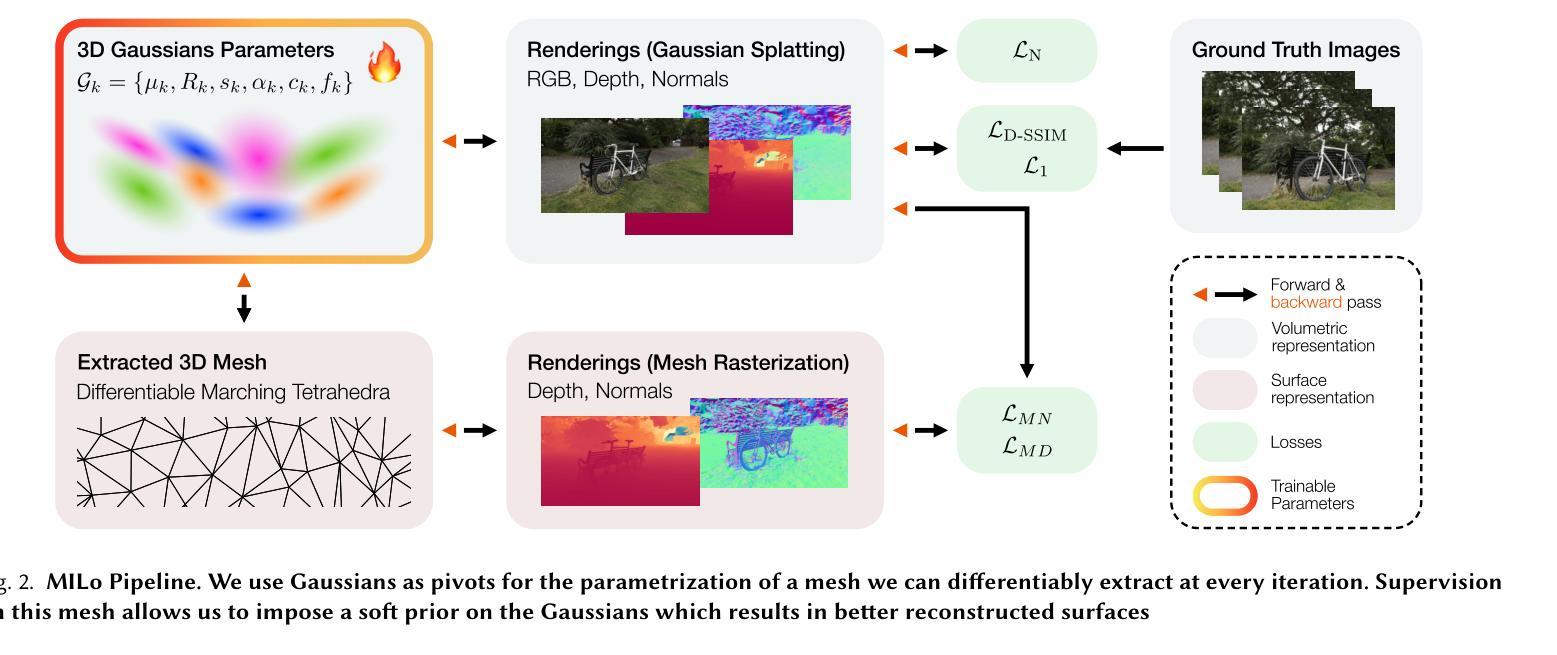
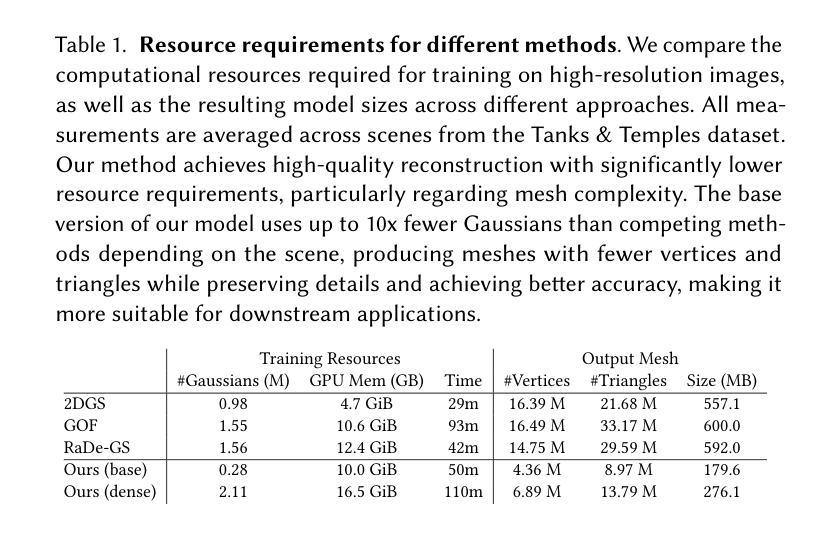
While recent advances in Gaussian Splatting have enabled fast reconstruction of high-quality 3D scenes from images, extracting accurate surface meshes remains a challenge. Current approaches extract the surface through costly post-processing steps, resulting in the loss of fine geometric details or requiring significant time and leading to very dense meshes with millions of vertices. More fundamentally, the a posteriori conversion from a volumetric to a surface representation limits the ability of the final mesh to preserve all geometric structures captured during training. We present MILo, a novel Gaussian Splatting framework that bridges the gap between volumetric and surface representations by differentiably extracting a mesh from the 3D Gaussians. We design a fully differentiable procedure that constructs the mesh-including both vertex locations and connectivity-at every iteration directly from the parameters of the Gaussians, which are the only quantities optimized during training. Our method introduces three key technical contributions: a bidirectional consistency framework ensuring both representations-Gaussians and the extracted mesh-capture the same underlying geometry during training; an adaptive mesh extraction process performed at each training iteration, which uses Gaussians as differentiable pivots for Delaunay triangulation; a novel method for computing signed distance values from the 3D Gaussians that enables precise surface extraction while avoiding geometric erosion. Our approach can reconstruct complete scenes, including backgrounds, with state-of-the-art quality while requiring an order of magnitude fewer mesh vertices than previous methods. Due to their light weight and empty interior, our meshes are well suited for downstream applications such as physics simulations or animation.
虽然高斯涂抹(Gaussian Splatting)的近期进展已经实现了从图像快速重建高质量的三维场景,但提取精确的表面网格仍然是一个挑战。当前的方法通过昂贵的后处理步骤提取表面,导致丢失了精细的几何细节,或者需要花费大量时间,并产生非常密集的网格,包含数百万个顶点。更根本的是,从体积表示到表面表示的后期转换限制了最终网格保留在训练过程中捕获的所有几何结构的能力。我们提出了MILo,这是一种新型的高斯涂抹框架,它通过从三维高斯中可微提取网格来弥合体积表示和表面表示之间的差距。我们设计了一种完全可微的程序,该程序可以直接从高斯参数(在训练过程中唯一优化的量)中,在每次迭代时构建网格,包括顶点的位置和连接。我们的方法引入了三个关键的技术贡献:一种双向一致性框架,确保高斯和提取的网格在训练过程中捕获相同的底层几何;一种在每个训练迭代中进行的自适应网格提取过程,它使用高斯作为Delaunay三角剖分的可微支点;一种从三维高斯计算带符号距离值的新方法,该方法可实现精确的表面提取,同时避免几何侵蚀。我们的方法可以重建包括背景在内的完整场景,达到最先进的品质,同时所需的网格顶点比以前的方法少一个数量级。由于我们的网格轻便且内部为空,因此非常适合用于物理模拟或动画等下游应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages. A presentation video of our approach is available at https://youtu.be/_SGNhhNz0fE
Summary
本文介绍了基于高斯拼贴的新方法MILO,该方法能够在训练过程中直接从高斯参数构建网格,实现了从体积表示到表面表示的桥梁。该方法具有三个关键技术贡献:双向一致性框架、自适应网格提取过程和计算高斯的三维带符号距离值的方法。该方法能够重建高质量的场景,包括背景,且生成的网格具有轻量级和空心的特点,适用于物理模拟和动画等下游应用。
Key Takeaways
- MILO是一种基于高斯拼贴的新方法,能够在训练过程中直接从高斯参数构建网格。
- 双向一致性框架确保高斯和提取的网格在训练过程中捕捉相同的底层几何结构。
- 自适应网格提取过程在每个训练迭代中进行,使用高斯作为可微分的Delaunay三角剖分的支点。
- 计算从三维高斯中得到的带符号距离值,实现精确的表面提取,避免几何侵蚀。
- 该方法能够重建高质量的场景,包括背景,且生成的网格具有轻量级和空心的特点。
- MILO生成的网格适用于物理模拟和动画等下游应用。
点此查看论文截图

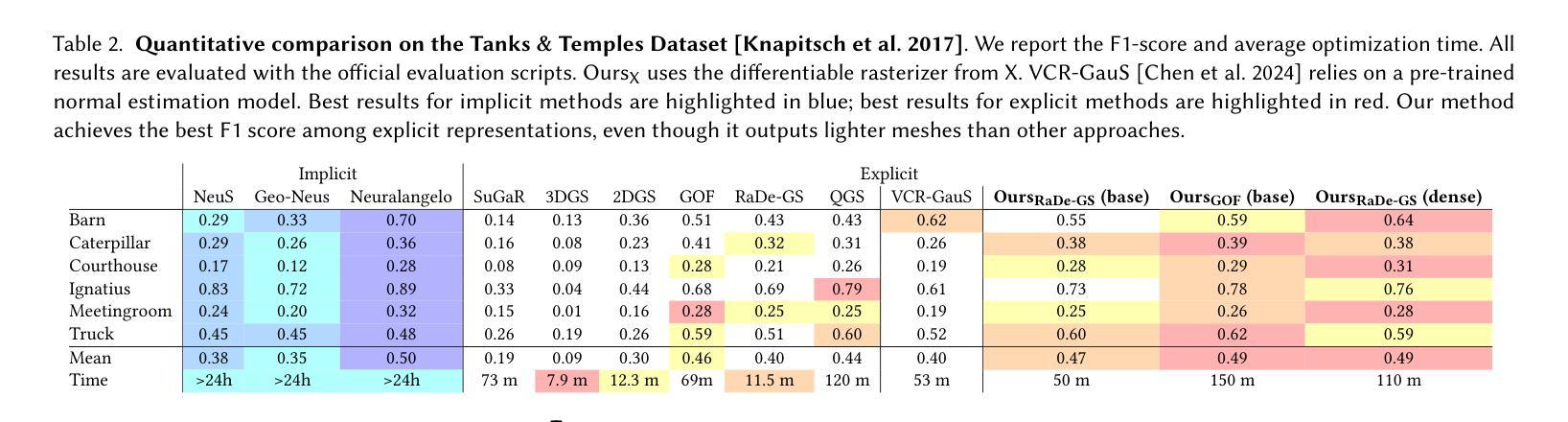

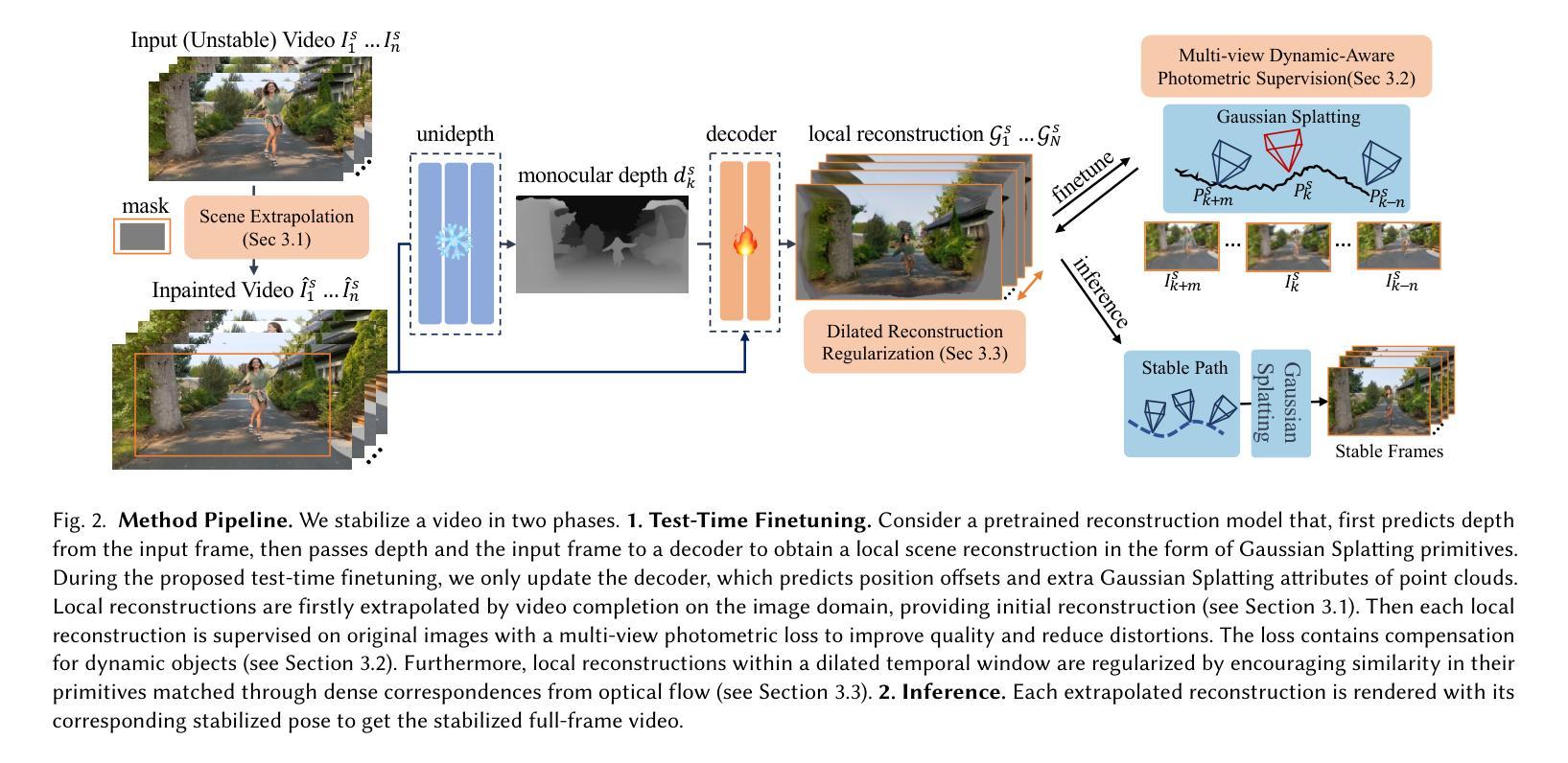
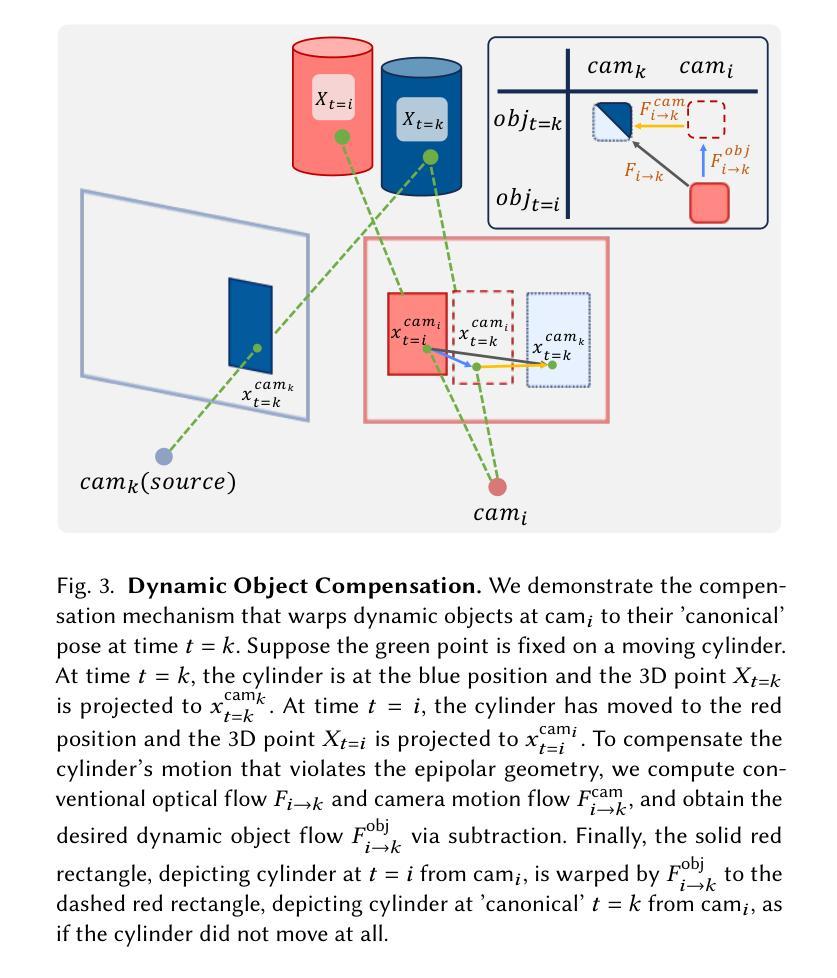
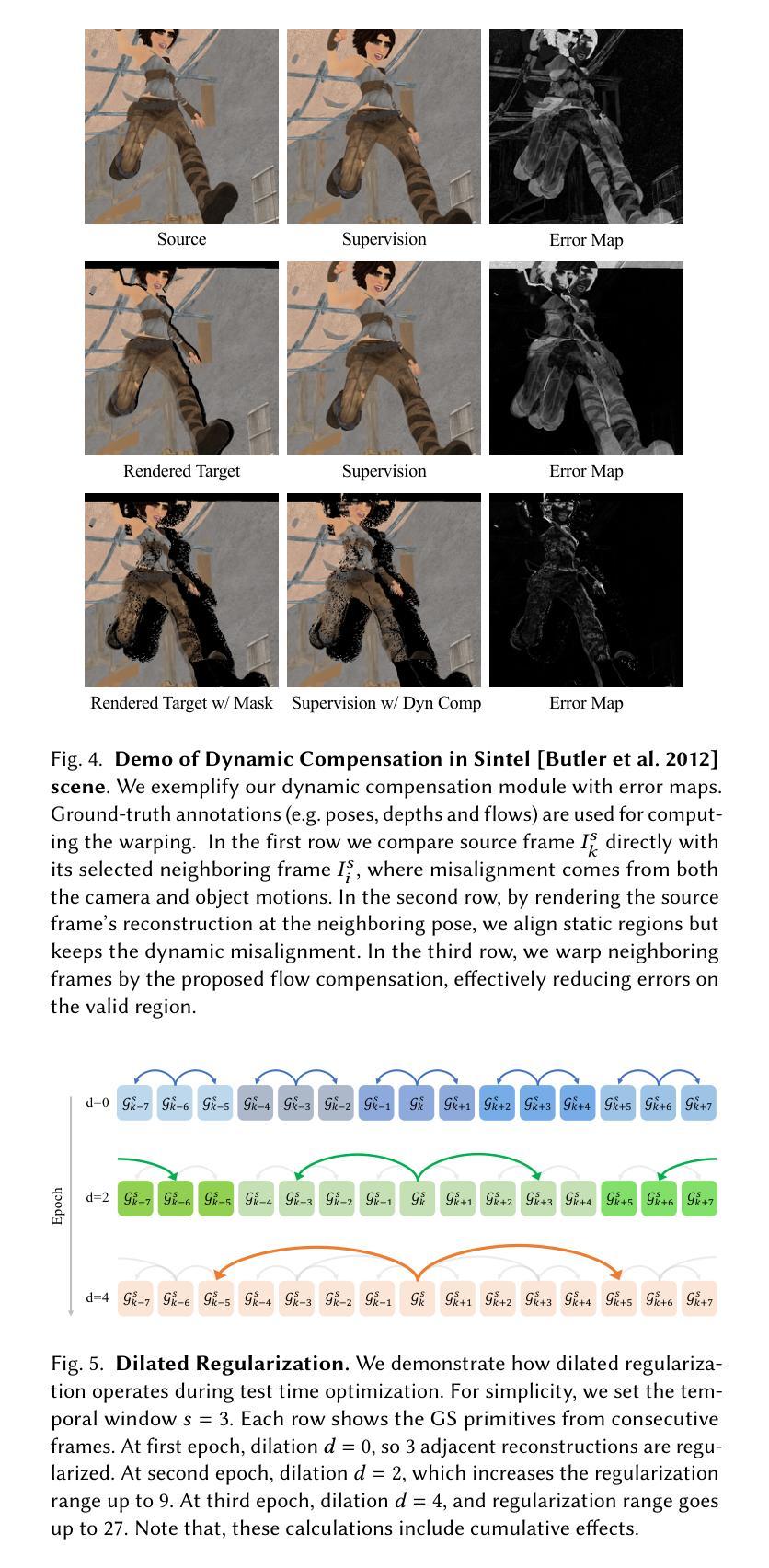
GaVS: 3D-Grounded Video Stabilization via Temporally-Consistent Local Reconstruction and Rendering
Authors:Zinuo You, Stamatios Georgoulis, Anpei Chen, Siyu Tang, Dengxin Dai
Video stabilization is pivotal for video processing, as it removes unwanted shakiness while preserving the original user motion intent. Existing approaches, depending on the domain they operate, suffer from several issues (e.g. geometric distortions, excessive cropping, poor generalization) that degrade the user experience. To address these issues, we introduce \textbf{GaVS}, a novel 3D-grounded approach that reformulates video stabilization as a temporally-consistent `local reconstruction and rendering’ paradigm. Given 3D camera poses, we augment a reconstruction model to predict Gaussian Splatting primitives, and finetune it at test-time, with multi-view dynamics-aware photometric supervision and cross-frame regularization, to produce temporally-consistent local reconstructions. The model are then used to render each stabilized frame. We utilize a scene extrapolation module to avoid frame cropping. Our method is evaluated on a repurposed dataset, instilled with 3D-grounded information, covering samples with diverse camera motions and scene dynamics. Quantitatively, our method is competitive with or superior to state-of-the-art 2D and 2.5D approaches in terms of conventional task metrics and new geometry consistency. Qualitatively, our method produces noticeably better results compared to alternatives, validated by the user study.
视频稳定对视频处理至关重要,它能消除不必要的抖动,同时保留用户原始的运动意图。现有方法根据其应用领域存在多种问题(例如几何失真、过度裁剪、泛化能力差等),这些问题会降低用户体验。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了\textbf{GaVS},这是一种新型基于3D的视频稳定方法,它将视频稳定重新定义为时间一致的“局部重建和渲染”范式。给定3D相机姿态,我们增强重建模型以预测高斯Splatting原始数据,并在测试时对其进行微调,利用多视角动态的光度监督和跨帧正则化,以产生时间一致的局部重建。然后,这些模型被用来渲染每个稳定的帧。我们使用场景外推模块来避免帧裁剪。我们的方法是在一个重新整理的数据集上进行评估的,该数据集包含了基于三维信息的数据样本,涵盖了多种相机运动和场景动态。从定量角度看,我们的方法在常规任务指标和新几何一致性方面与最先进的二维和二维半方法相当或更优越。从定性角度看,我们的方法与替代方案相比产生了明显更好的结果,得到了用户研究的验证。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF siggraph 2025, project website: https://sinoyou.github.io/gavs
Summary
本文介绍了视频稳定化的重要性,针对现有方法存在的问题,提出了一种新型的基于三维重建的局部重建和渲染的视频稳定化方法,即GaVS。该方法使用重建模型预测高斯拼贴(Gaussian Splatting)原始形态,并在测试时进行微调,以获得时间上一致的局部重建。通过场景外推模块避免帧裁剪,在具有不同相机运动和场景动态性的数据集上进行了评估,并在任务指标和几何一致性方面与现有的二维和二维半方法相比具有竞争力或更优越的表现。用户研究验证了其显著优于其他方法的结果。
Key Takeaways
- 视频稳定化对于视频处理至关重要,可消除不必要的抖动并保持原始用户运动意图。
- 现有方法存在几何失真、过度裁剪和泛化能力差等问题。
- GaVS是一种基于三维重建的视频稳定化新方法,采用局部重建和渲染模式。
- 利用重建模型预测高斯拼贴原始形态,并通过测试时的微调获得时间上一致的局部重建。
- 通过场景外推模块避免帧裁剪。
- GaVS在多种数据集上表现良好,在任务指标和几何一致性方面与现有方法相比具有竞争力或更优越。
点此查看论文截图

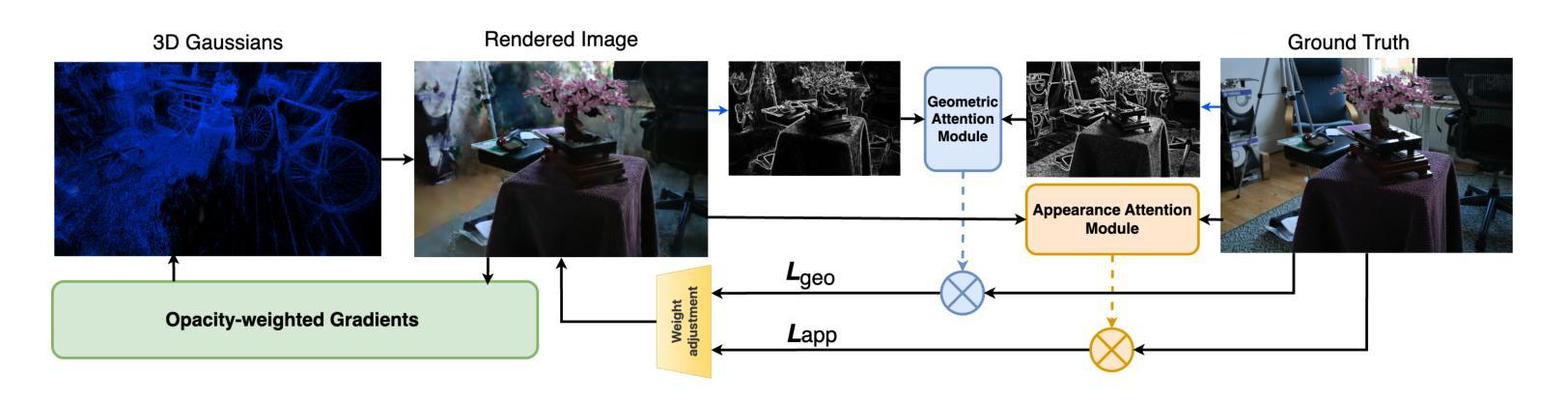
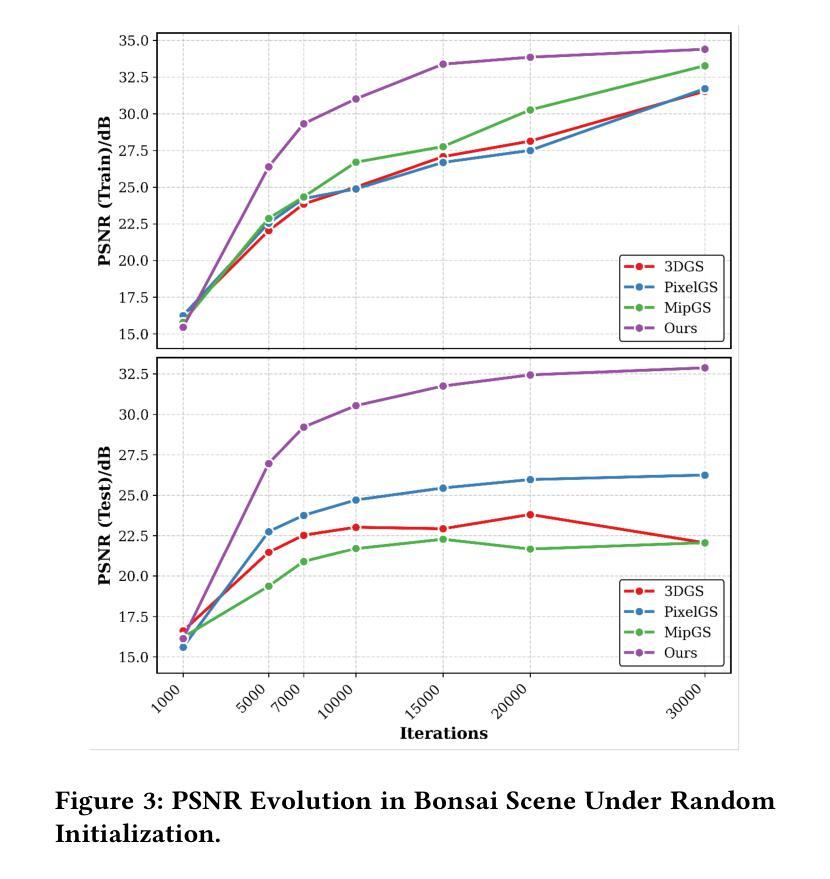
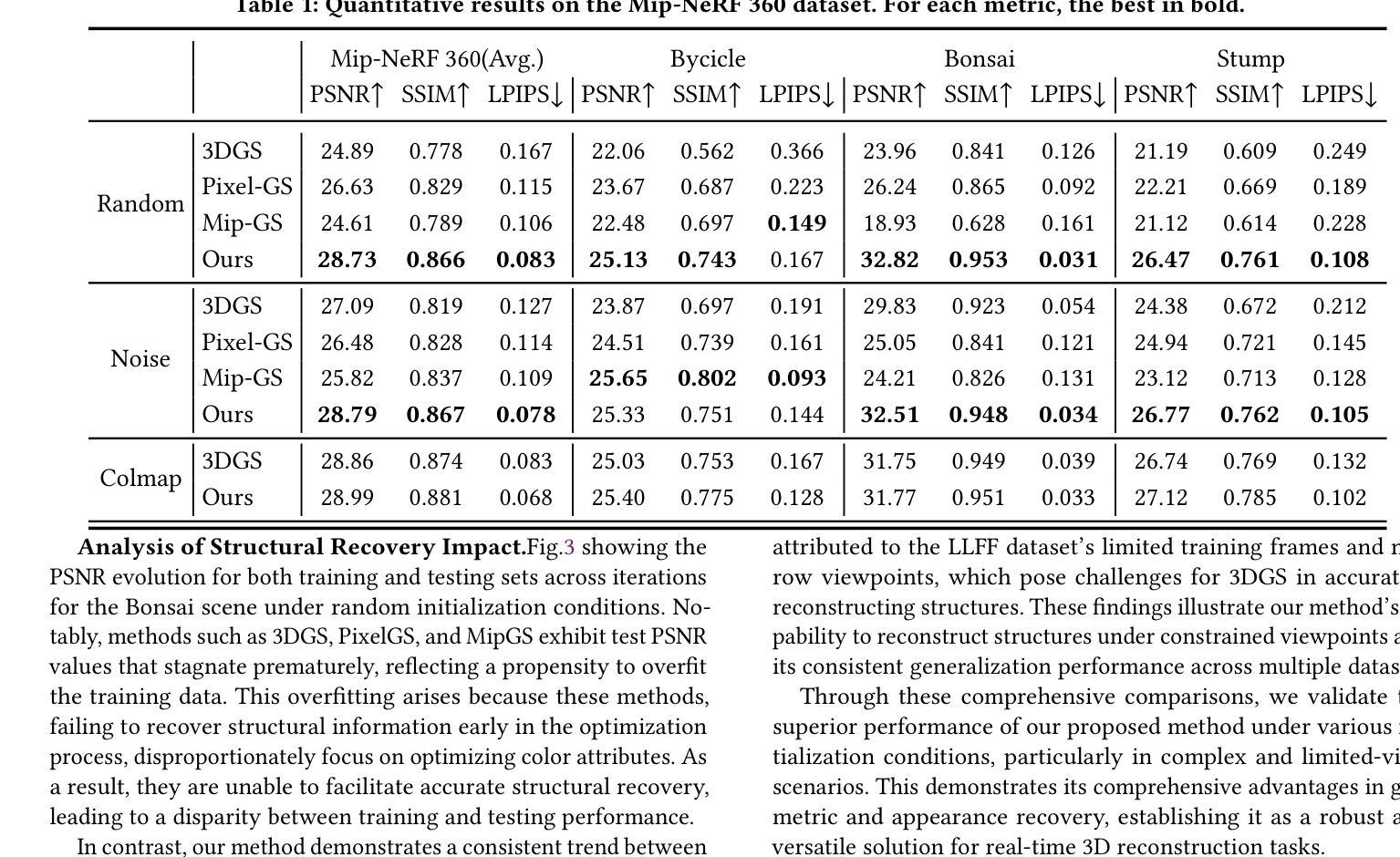
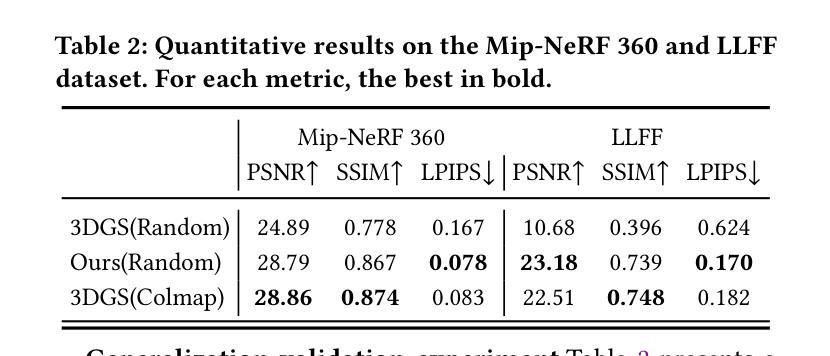
AttentionGS: Towards Initialization-Free 3D Gaussian Splatting via Structural Attention
Authors:Ziao Liu, Zhenjia Li, Yifeng Shi, Xiangang Li
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) is a powerful alternative to Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF), excelling in complex scene reconstruction and efficient rendering. However, it relies on high-quality point clouds from Structure-from-Motion (SfM), limiting its applicability. SfM also fails in texture-deficient or constrained-view scenarios, causing severe degradation in 3DGS reconstruction. To address this limitation, we propose AttentionGS, a novel framework that eliminates the dependency on high-quality initial point clouds by leveraging structural attention for direct 3D reconstruction from randomly initialization. In the early training stage, we introduce geometric attention to rapidly recover the global scene structure. As training progresses, we incorporate texture attention to refine fine-grained details and enhance rendering quality. Furthermore, we employ opacity-weighted gradients to guide Gaussian densification, leading to improved surface reconstruction. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmark datasets demonstrate that AttentionGS significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods, particularly in scenarios where point cloud initialization is unreliable. Our approach paves the way for more robust and flexible 3D Gaussian Splatting in real-world applications.
3D高斯摊铺(3DGS)是神经辐射场(NeRF)的有力替代方案,在复杂场景重建和高效渲染方面表现出色。然而,它依赖于运动结构(SfM)的高质量点云,限制了其应用范围。SfM在纹理缺失或视角受限的场景中也会失效,导致3DGS重建严重退化。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了AttentionGS这一新型框架,通过利用结构注意力来直接从随机初始化进行3D重建,从而消除了对高质量初始点云的依赖。在训练初期,我们引入几何注意力来快速恢复全局场景结构。随着训练的进行,我们结合纹理注意力来细化细节并增强渲染质量。此外,我们还采用不透明度加权梯度来指导高斯稠密化,从而改进表面重建。在多个基准数据集上的大量实验表明,AttentionGS显著优于最新方法,特别是在点云初始化不可靠的场景中。我们的方法为更稳健和灵活的3D高斯摊铺在现实世界应用中的使用铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了3D Gaussian Splatting(3DGS)技术及其在复杂场景重建和高效渲染方面的优势。然而,它依赖于高质量的点云数据,这在某些场景下存在局限性。为此,提出了一种新型框架AttentionGS,利用结构注意力机制实现从随机初始化直接进行3D重建。该框架在训练初期通过几何注意力快速恢复全局场景结构,随着训练进展,结合纹理注意力细化细节并提高渲染质量。此外,还采用基于不透明度的梯度引导高斯稠密化,改善表面重建效果。实验证明,AttentionGS在多个基准数据集上显著优于现有方法,特别是在点云初始化不可靠的场景下表现更优秀。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS是一种强大的NeRF替代技术,擅长复杂场景重建和高效渲染。
- 3DGS依赖于高质量点云数据,这在某些场景中是一个限制。
- AttentionGS框架通过利用结构注意力机制消除对高质量初始点云的依赖,实现从随机初始化直接进行3D重建。
- AttentionGS在训练初期通过几何注意力恢复全局场景结构,随后结合纹理注意力细化细节,提高渲染质量。
- 采用基于不透明度的梯度引导高斯稠密化,改善表面重建效果。
- AttentionGS在多个数据集上表现优异,特别是在点云初始化不可靠的场景中。
点此查看论文截图

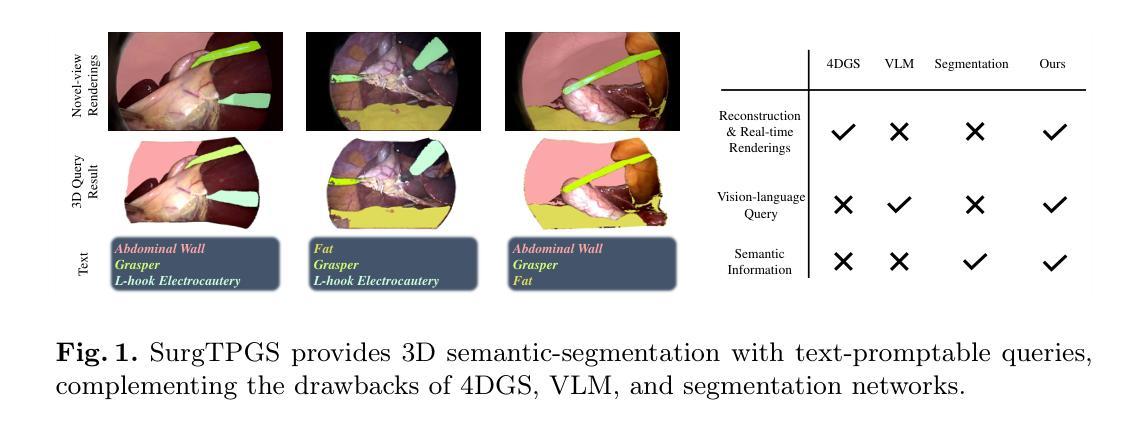
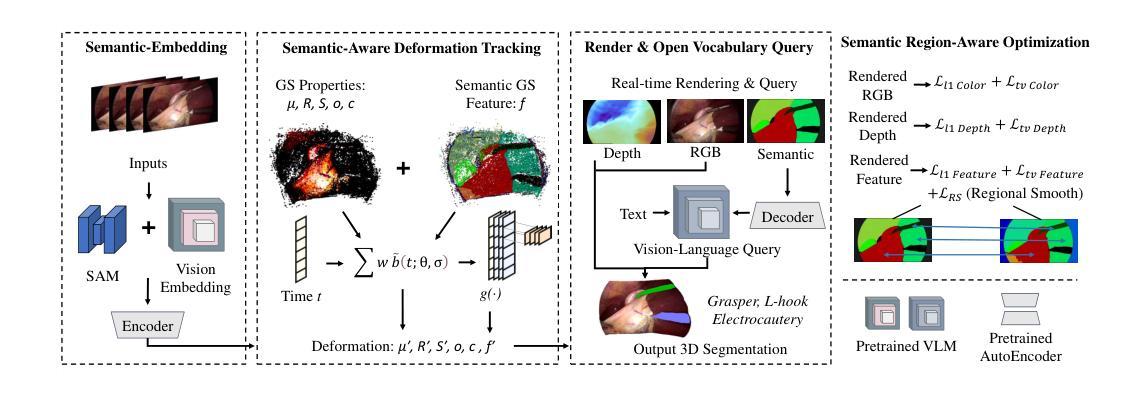
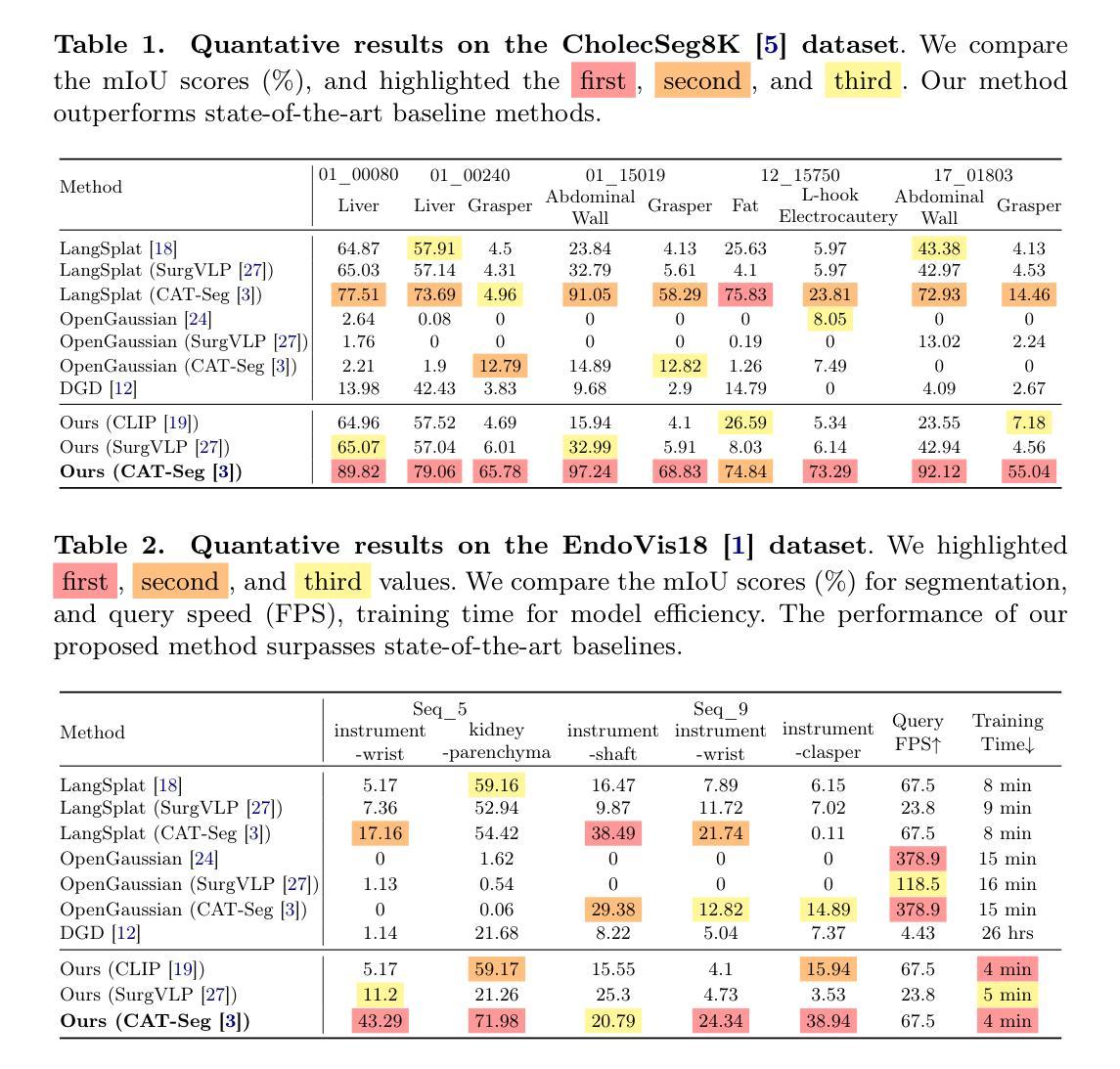
SurgTPGS: Semantic 3D Surgical Scene Understanding with Text Promptable Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Yiming Huang, Long Bai, Beilei Cui, Kun Yuan, Guankun Wang, Mobarak I. Hoque, Nicolas Padoy, Nassir Navab, Hongliang Ren
In contemporary surgical research and practice, accurately comprehending 3D surgical scenes with text-promptable capabilities is particularly crucial for surgical planning and real-time intra-operative guidance, where precisely identifying and interacting with surgical tools and anatomical structures is paramount. However, existing works focus on surgical vision-language model (VLM), 3D reconstruction, and segmentation separately, lacking support for real-time text-promptable 3D queries. In this paper, we present SurgTPGS, a novel text-promptable Gaussian Splatting method to fill this gap. We introduce a 3D semantics feature learning strategy incorporating the Segment Anything model and state-of-the-art vision-language models. We extract the segmented language features for 3D surgical scene reconstruction, enabling a more in-depth understanding of the complex surgical environment. We also propose semantic-aware deformation tracking to capture the seamless deformation of semantic features, providing a more precise reconstruction for both texture and semantic features. Furthermore, we present semantic region-aware optimization, which utilizes regional-based semantic information to supervise the training, particularly promoting the reconstruction quality and semantic smoothness. We conduct comprehensive experiments on two real-world surgical datasets to demonstrate the superiority of SurgTPGS over state-of-the-art methods, highlighting its potential to revolutionize surgical practices. SurgTPGS paves the way for developing next-generation intelligent surgical systems by enhancing surgical precision and safety. Our code is available at: https://github.com/lastbasket/SurgTPGS.
在当代的医学研究和实践中,能够使用文本提示功能准确地理解三维手术场景对于手术规划和实时手术过程中的指导尤为关键。在这种环境下,精确地识别并与手术工具和解剖结构进行交互是极其重要的。然而,现有的工作主要集中在手术视觉语言模型(VLM)、三维重建和分割上,缺乏支持实时文本提示的三维查询功能。在本文中,我们提出了SurgTPGS,这是一种新的文本提示高斯Splatting方法,以填补这一空白。我们介绍了一种三维语义特征学习策略,融合了任何分段模型和最先进的视觉语言模型。我们提取了用于三维手术场景重建的分割语言特征,以便更深入地理解复杂的手术环境。我们还提出了语义感知变形跟踪技术,以捕捉语义特征的无缝变形,为纹理和语义特征提供更精确的重建。此外,我们还提出了语义区域感知优化方法,该方法利用基于区域的语义信息来监督训练,尤其能提高重建质量和语义平滑度。我们在两个真实世界的手术数据集上进行了全面的实验,证明了SurgTPGS相较于最先进的方法具有优越性,突出了其在手术实践中进行革命性改进的巨大潜力。SurgTPGS为开发下一代智能手术系统铺平了道路,通过提高手术的精确性和安全性来推动医学技术的进步。我们的代码可在:https://github.com/lastbasket/SurgTPGS获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025. Project Page: https://lastbasket.github.io/MICCAI-2025-SurgTPGS/
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于文本提示的3D手术场景重建方法SurgTPGS,该方法采用高斯扩展技术,填补实时文本提示3D查询的空白。通过结合先进的视觉语言模型和语义分割技术,SurgTPGS能够更好地理解复杂的手术环境,提供精确的语义特征重建。此外,该技术还具备语义感知变形跟踪和区域感知优化功能,提高了重建质量和语义平滑度。实验证明,SurgTPGS在真实手术数据集上的表现优于现有方法,为开发下一代智能手术系统提供了潜力。
Key Takeaways
- SurgTPGS填补了在手术规划和实时手术过程中实现实时文本提示的空白。
- 通过结合视觉语言模型和语义分割技术,SurgTPGS能更好地理解复杂的手术环境。
- SurgTPGS具备语义感知变形跟踪功能,能无缝捕捉语义特征的变形。
- 通过区域感知优化技术,SurgTPGS提高了重建质量和语义平滑度。
- 实验证明,SurgTPGS在真实手术数据集上的表现优于其他现有方法。
- SurgTPGS有助于开发下一代智能手术系统,提高手术的精确性和安全性。
点此查看论文截图

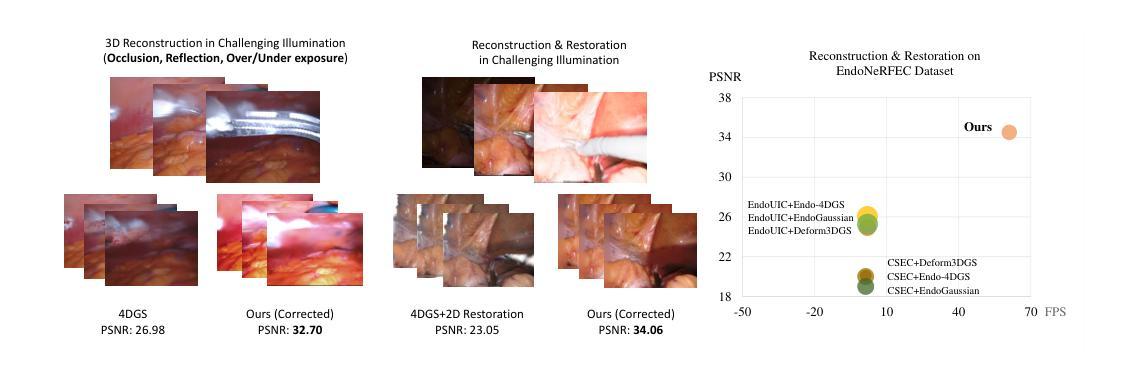
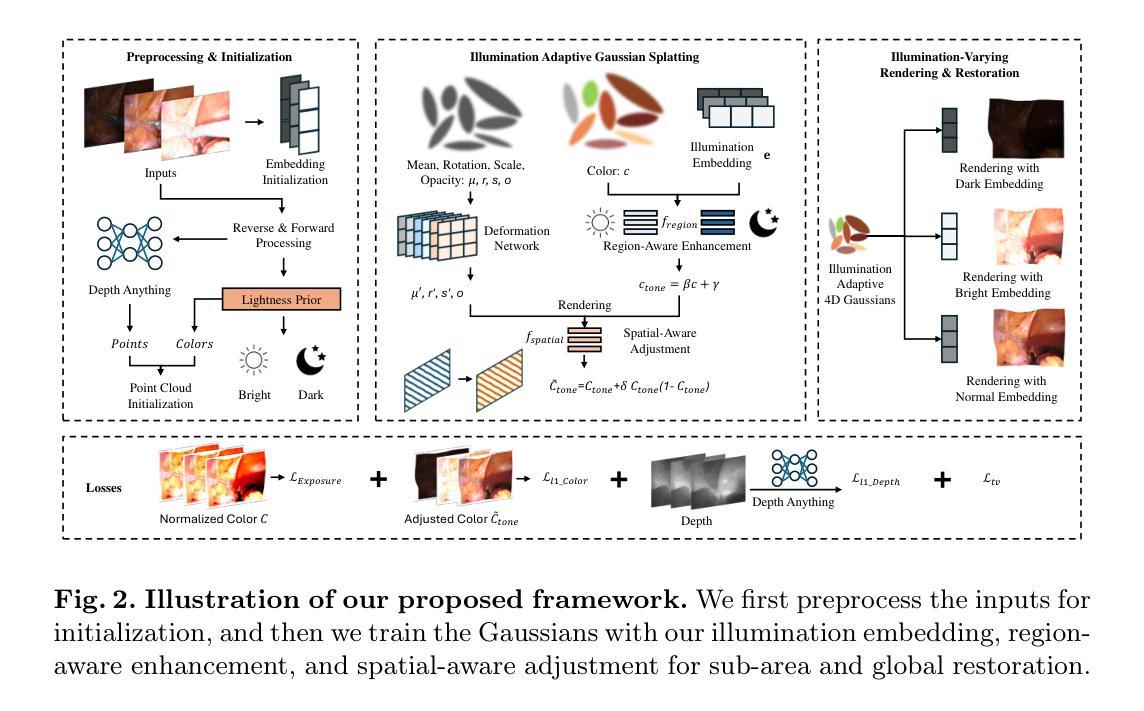
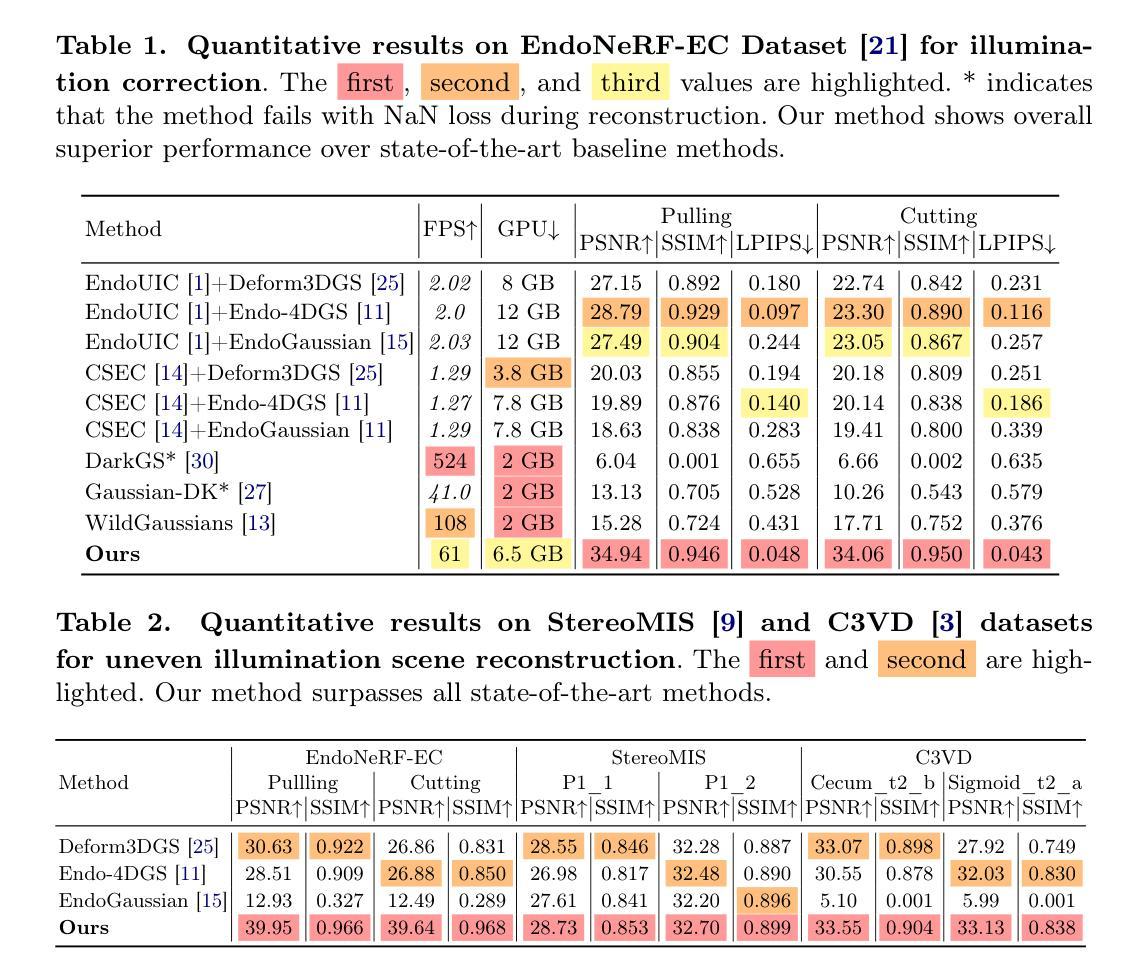
Endo-4DGX: Robust Endoscopic Scene Reconstruction and Illumination Correction with Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Yiming Huang, Long Bai, Beilei Cui, Yanheng Li, Tong Chen, Jie Wang, Jinlin Wu, Zhen Lei, Hongbin Liu, Hongliang Ren
Accurate reconstruction of soft tissue is crucial for advancing automation in image-guided robotic surgery. The recent 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) techniques and their variants, 4DGS, achieve high-quality renderings of dynamic surgical scenes in real-time. However, 3D-GS-based methods still struggle in scenarios with varying illumination, such as low light and over-exposure. Training 3D-GS in such extreme light conditions leads to severe optimization problems and devastating rendering quality. To address these challenges, we present Endo-4DGX, a novel reconstruction method with illumination-adaptive Gaussian Splatting designed specifically for endoscopic scenes with uneven lighting. By incorporating illumination embeddings, our method effectively models view-dependent brightness variations. We introduce a region-aware enhancement module to model the sub-area lightness at the Gaussian level and a spatial-aware adjustment module to learn the view-consistent brightness adjustment. With the illumination adaptive design, Endo-4DGX achieves superior rendering performance under both low-light and over-exposure conditions while maintaining geometric accuracy. Additionally, we employ an exposure control loss to restore the appearance from adverse exposure to the normal level for illumination-adaptive optimization. Experimental results demonstrate that Endo-4DGX significantly outperforms combinations of state-of-the-art reconstruction and restoration methods in challenging lighting environments, underscoring its potential to advance robot-assisted surgical applications. Our code is available at https://github.com/lastbasket/Endo-4DGX.
软组织重建的准确性对于推动图像引导机器人手术的自动化至关重要。最近出现的3D高斯渲染(3DGS)技术及其变体(如四维渲染)可以实时高质量渲染动态手术场景。然而,基于高斯球算法的方法在光照条件不同的场景中仍面临挑战,如低光和过度曝光环境。在这种极端光照条件下训练三维GS会导致严重的优化问题和灾难性的渲染质量。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种名为Endo-4DGX的新型重建方法,它采用自适应光照高斯渲染技术,专为内窥镜场景设计,场景中存在不均匀照明。通过引入光照嵌入技术,我们的方法可以有效地模拟依赖于视图的亮度变化。我们引入了区域感知增强模块,在高斯层次对子区域亮度进行建模,以及空间感知调整模块,学习视图一致的亮度调整方法。通过自适应光照设计,Endo-4DGX在低光和过度曝光条件下实现了出色的渲染性能,同时保持了几何精度。此外,我们还采用曝光控制损失恢复从不良曝光到正常水平的外观数据用于光照自适应优化。实验结果表明,在充满挑战的光照环境中,Endo-4DGX显著优于最先进组合的重构和恢复方法的应用潜能巨大。我们的代码可在https://github.com/lastbasket/Endo-4DGX找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025. Project Page: https://lastbasket.github.io/MICCAI-2025-Endo-4DGX/
摘要
本文介绍了在图像引导机器人手术中自动化软组织重建的重要性。针对最新的三维高斯散斑技术及其变体,在实时动态手术场景渲染中取得了高质量的效果。然而,基于三维高斯散斑的方法在光照变化场景,如低光和过曝光场景中,仍然存在挑战。本文提出一种新型的重建方法——Endo-4DGX,具有自适应光照的高斯散斑设计,专为光照不均匀的内窥镜场景设计。通过融入光照嵌入技术,该方法可有效模拟视觉亮度变化。同时介绍了一个区域感知增强模块,对高斯水平上的子区域亮度进行建模,以及一个空间感知调整模块,学习一致的亮度调整。凭借自适应光照设计,Endo-4DGX在低光和过曝光条件下均实现了卓越的渲染性能,同时保持了几何精度。此外,本文还采用曝光控制损失,将不良曝光下的外观恢复到正常水平,以实现自适应光照优化。实验结果表明,Endo-4DGX在具有挑战性的光照环境中显著优于最先进的重建和恢复方法组合,突显其在机器人辅助手术应用中的潜力。代码可通过https://github.com/lastbasket/Endo-4DGX 获取。
要点分析
点此查看论文截图

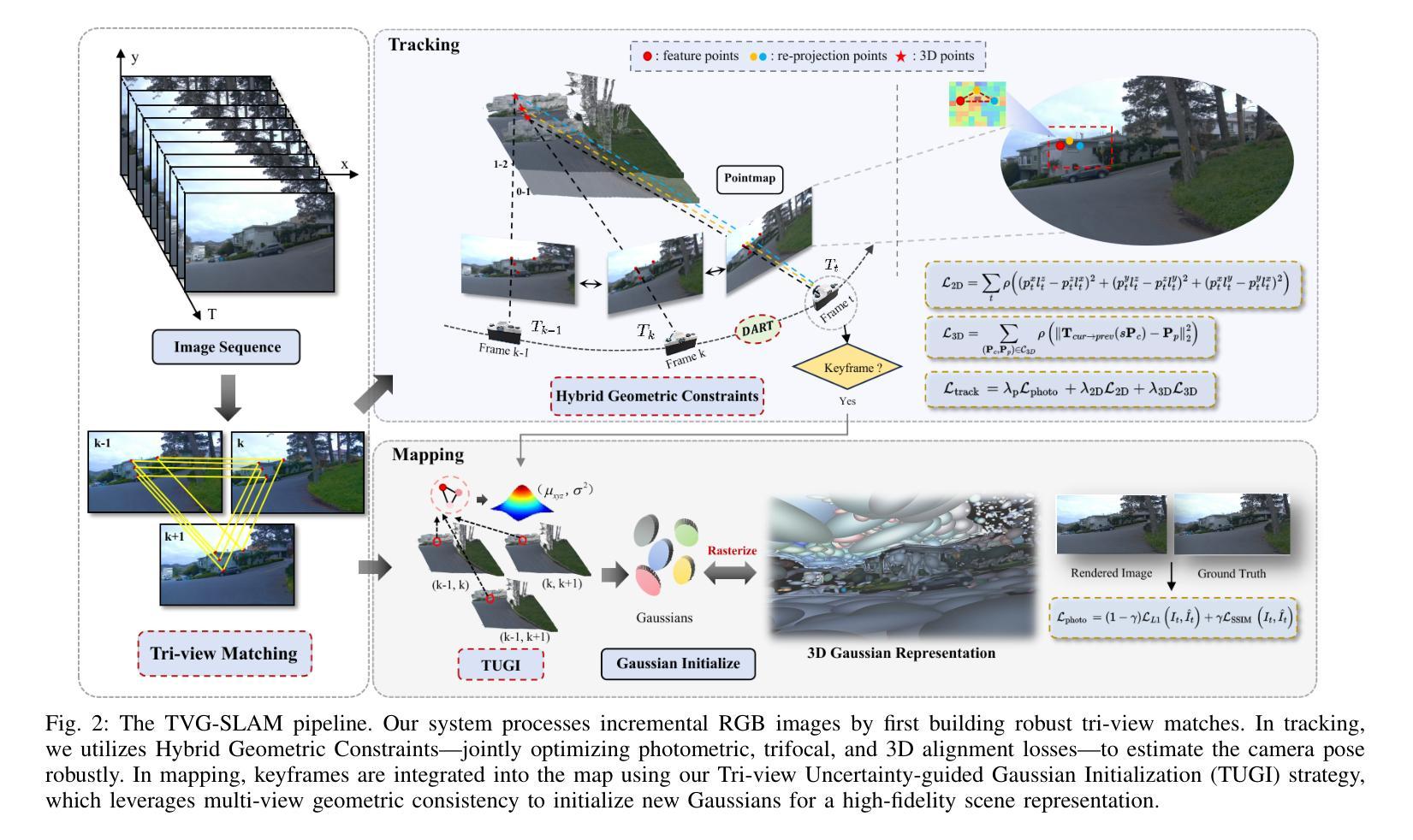
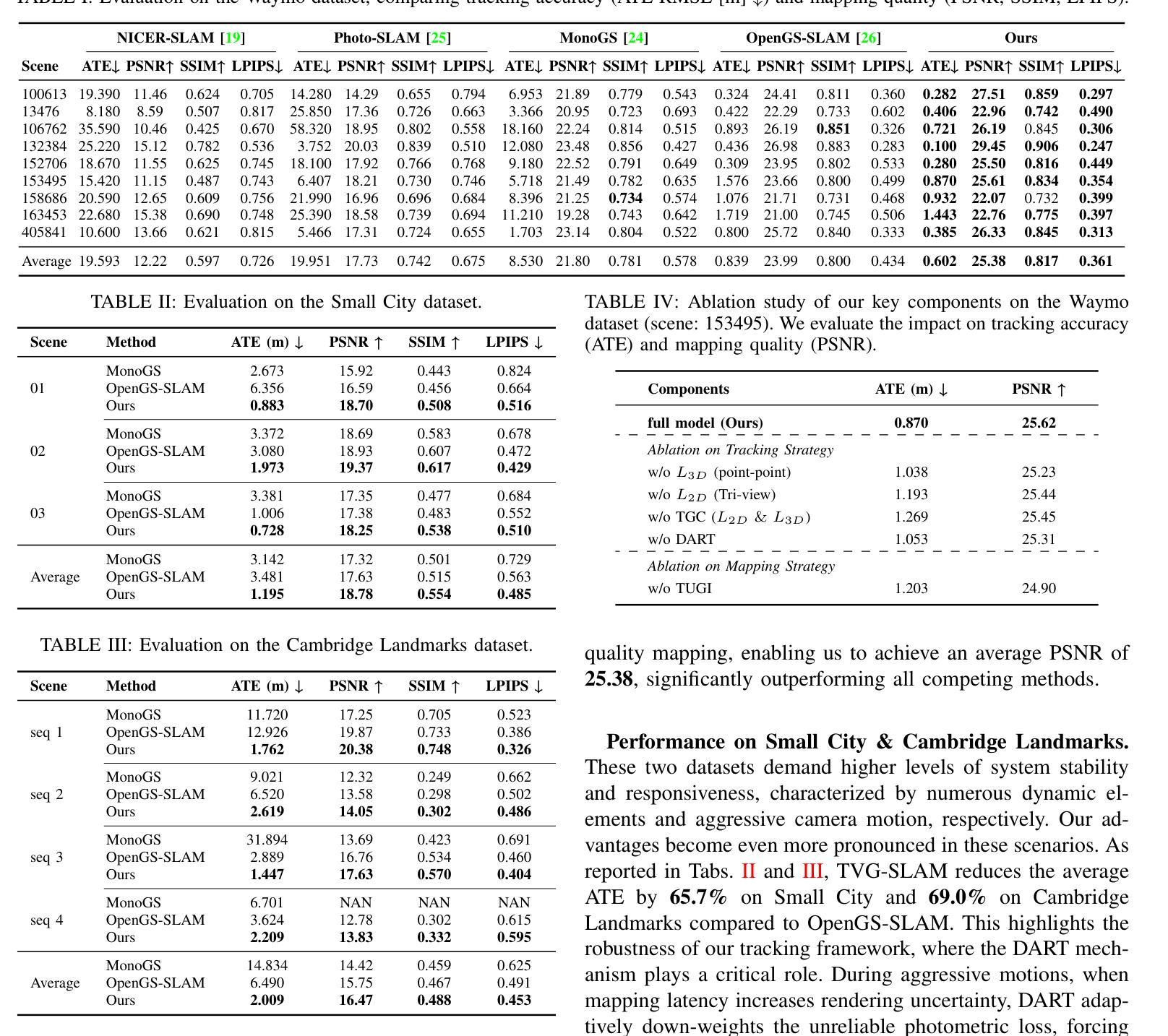
TVG-SLAM: Robust Gaussian Splatting SLAM with Tri-view Geometric Constraints
Authors:Zhen Tan, Xieyuanli Chen, Lei Feng, Yangbing Ge, Shuaifeng Zhi, Jiaxiong Liu, Dewen Hu
Recent advances in 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) have enabled RGB-only SLAM systems to achieve high-fidelity scene representation. However, the heavy reliance of existing systems on photometric rendering loss for camera tracking undermines their robustness, especially in unbounded outdoor environments with severe viewpoint and illumination changes. To address these challenges, we propose TVG-SLAM, a robust RGB-only 3DGS SLAM system that leverages a novel tri-view geometry paradigm to ensure consistent tracking and high-quality mapping. We introduce a dense tri-view matching module that aggregates reliable pairwise correspondences into consistent tri-view matches, forming robust geometric constraints across frames. For tracking, we propose Hybrid Geometric Constraints, which leverage tri-view matches to construct complementary geometric cues alongside photometric loss, ensuring accurate and stable pose estimation even under drastic viewpoint shifts and lighting variations. For mapping, we propose a new probabilistic initialization strategy that encodes geometric uncertainty from tri-view correspondences into newly initialized Gaussians. Additionally, we design a Dynamic Attenuation of Rendering Trust mechanism to mitigate tracking drift caused by mapping latency. Experiments on multiple public outdoor datasets show that our TVG-SLAM outperforms prior RGB-only 3DGS-based SLAM systems. Notably, in the most challenging dataset, our method improves tracking robustness, reducing the average Absolute Trajectory Error (ATE) by 69.0% while achieving state-of-the-art rendering quality. The implementation of our method will be released as open-source.
近期三维高斯摊铺(3DGS)的进展使得仅使用RGB的SLAM系统能够实现高保真场景表示。然而,现有系统对基于光度渲染损失进行相机跟踪的过度依赖,损害了其在场景下的稳健性,特别是在无边界的室外环境中,视角和光照变化剧烈。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了TVG-SLAM,这是一个稳健的仅使用RGB的3DGS SLAM系统,它采用新颖的三视图几何范式确保一致的跟踪和高质量的映射。我们引入了一个密集的三视图匹配模块,该模块将可靠的成对对应关系聚集为一致的三视图匹配,在帧之间形成稳健的几何约束。在跟踪方面,我们提出了混合几何约束,利用三视图匹配来构建与光度损失相辅相成的几何线索,即使在视角变化和光照变化剧烈的情况下,也能确保准确稳定的姿态估计。对于映射,我们提出了一种新的概率初始化策略,它将三视图对应关系中的几何不确定性编码到初始化的高斯分布中。此外,我们还设计了一种动态衰减渲染信任机制,以减轻由映射延迟引起的跟踪漂移。在多个公共室外数据集上的实验表明,我们的TVG-SLAM优于先前的仅使用RGB的基于3DGS的SLAM系统。值得注意的是,在最具挑战性的数据集上,我们的方法提高了跟踪的稳健性,平均绝对轨迹误差(ATE)降低了69.0%,同时实现了最先进的渲染质量。我们的方法实现将作为开源发布。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
最近,三维高斯涂抹(3DGS)技术的进展使得仅使用RGB的SLAM系统能够实现高保真场景表示。然而,现有系统对光度渲染损失的严重依赖影响了其在面对场景时的稳健性,特别是在视点无边界的户外环境中和光照条件发生改变时。为解决这些挑战,我们提出了TVG-SLAM,一个稳健的仅使用RGB的3DGS SLAM系统。该系统采用新型的三视图几何模式确保一致的跟踪和高质量映射。我们引入密集三视图匹配模块,将可靠的配对对应物聚合为一致的三视图匹配,在帧之间形成稳健的几何约束。对于跟踪,我们提出混合几何约束,利用三视图匹配构建与光度损失相辅相成的几何线索,确保即使在视点剧烈变化和光照变化的情况下也能进行准确稳定的姿态估计。对于映射,我们提出了一种新的概率初始化策略,将三视图对应的几何不确定性编码到初始化后的高斯分布中。此外,我们还设计了一种动态衰减渲染信任机制,以减轻由映射延迟引起的跟踪漂移。在多个公共户外数据集上的实验表明,我们的TVG-SLAM优于先前的仅使用RGB的基于3DGS的SLAM系统。特别是在最具挑战性的数据集中,我们的方法提高了跟踪的稳健性,将平均绝对轨迹误差(ATE)降低了69.0%,同时实现了最先进的渲染质量。我们的方法将作为开源发布。
要点归纳
- RGB-only SLAM系统借助最近发展的3DGS技术实现高保真场景表示。
- 现有系统依赖光度渲染损失进行相机跟踪,但在户外环境中存在视角和光照变化的挑战。
- TVG-SLAM通过引入三视图几何模式来提高RGB-only 3DGS SLAM系统的稳健性。
- 提出密集三视图匹配模块和三视图几何约束以增强跟踪的准确性及稳定性。
- 新颖的概率初始化策略和动态衰减渲染信任机制改善映射并降低跟踪漂移。
- 在公共户外数据集上的实验证明TVG-SLAM的性能超越现有方法。
点此查看论文截图


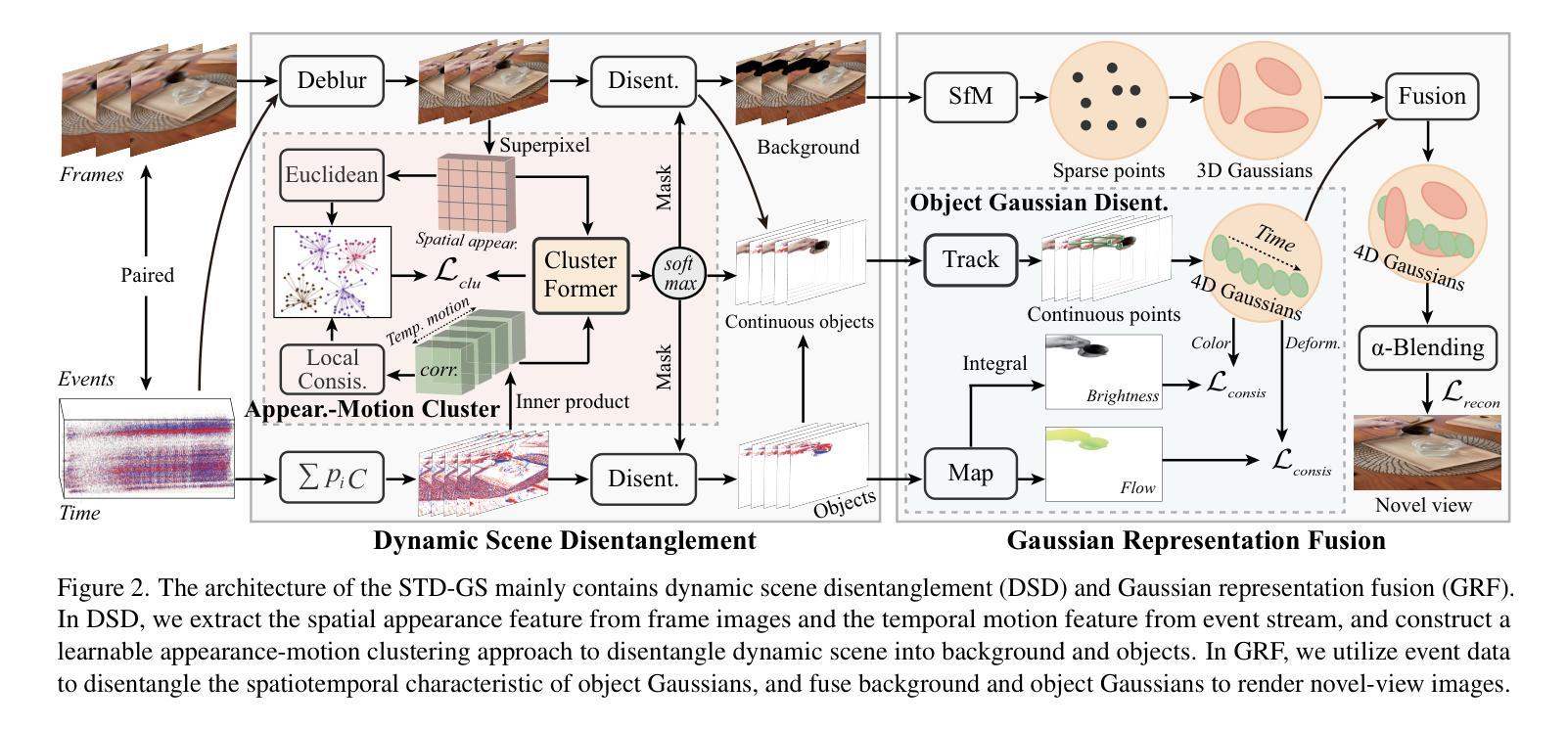
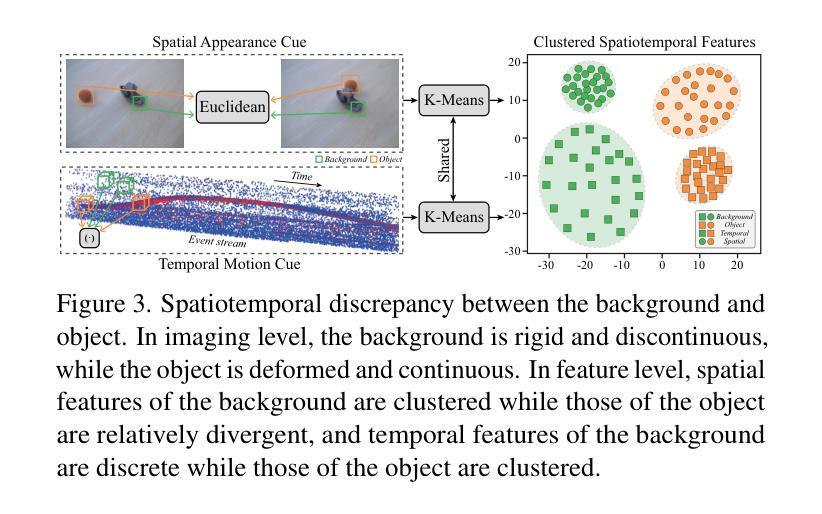
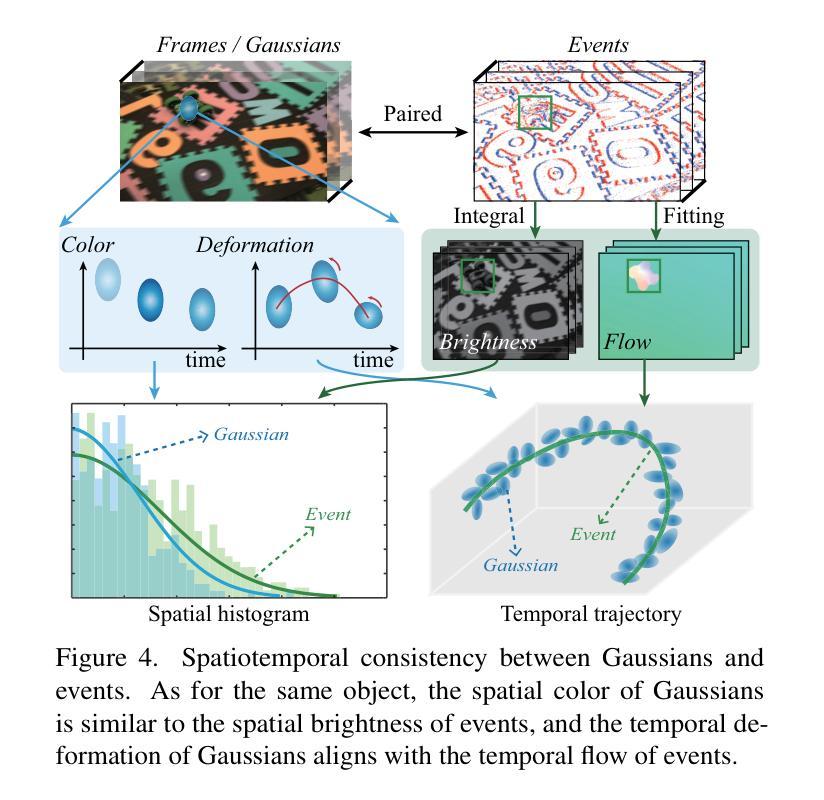
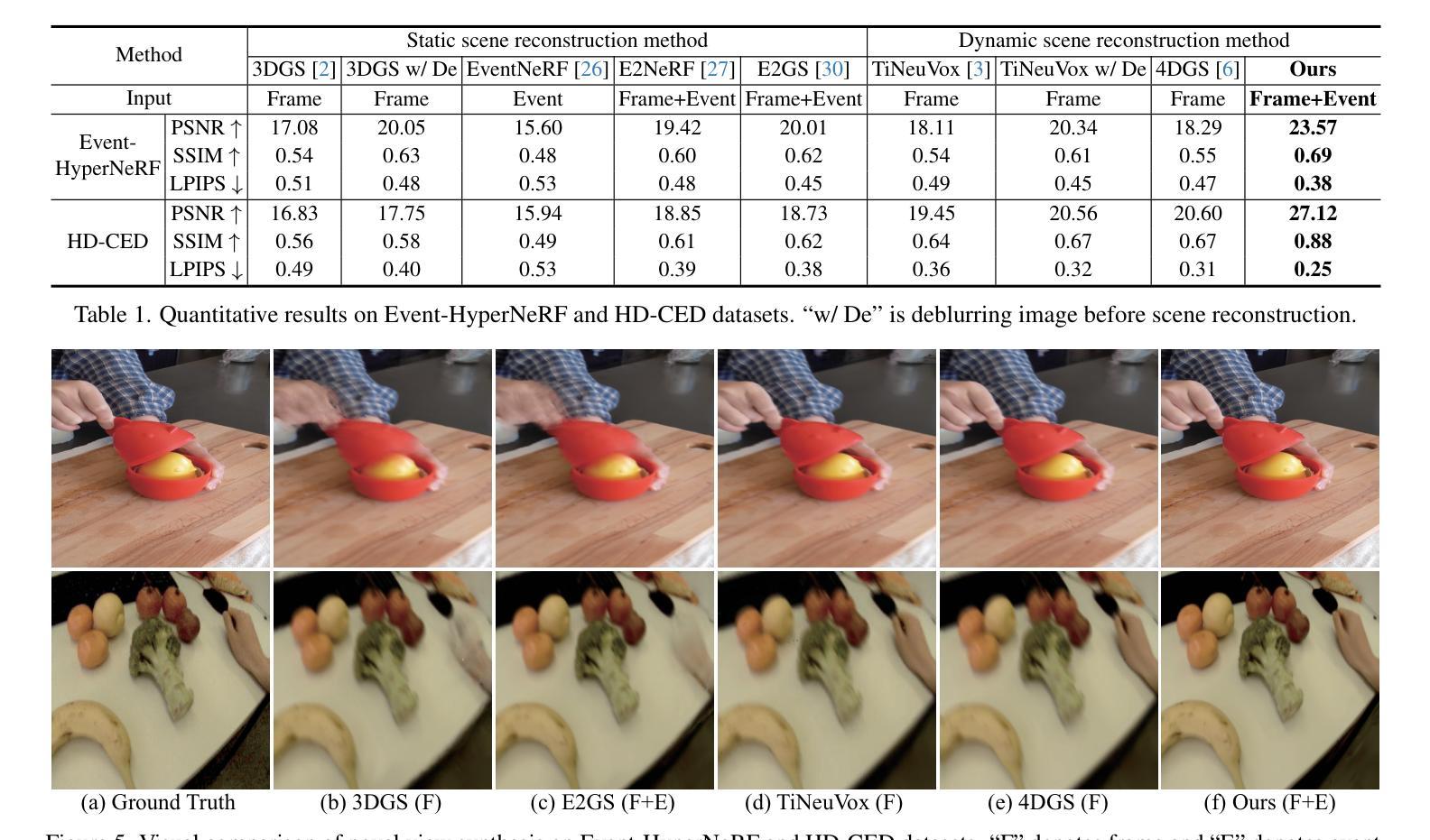
STD-GS: Exploring Frame-Event Interaction for SpatioTemporal-Disentangled Gaussian Splatting to Reconstruct High-Dynamic Scene
Authors:Hanyu Zhou, Haonan Wang, Haoyue Liu, Yuxing Duan, Luxin Yan, Gim Hee Lee
High-dynamic scene reconstruction aims to represent static background with rigid spatial features and dynamic objects with deformed continuous spatiotemporal features. Typically, existing methods adopt unified representation model (e.g., Gaussian) to directly match the spatiotemporal features of dynamic scene from frame camera. However, this unified paradigm fails in the potential discontinuous temporal features of objects due to frame imaging and the heterogeneous spatial features between background and objects. To address this issue, we disentangle the spatiotemporal features into various latent representations to alleviate the spatiotemporal mismatching between background and objects. In this work, we introduce event camera to compensate for frame camera, and propose a spatiotemporal-disentangled Gaussian splatting framework for high-dynamic scene reconstruction. As for dynamic scene, we figure out that background and objects have appearance discrepancy in frame-based spatial features and motion discrepancy in event-based temporal features, which motivates us to distinguish the spatiotemporal features between background and objects via clustering. As for dynamic object, we discover that Gaussian representations and event data share the consistent spatiotemporal characteristic, which could serve as a prior to guide the spatiotemporal disentanglement of object Gaussians. Within Gaussian splatting framework, the cumulative scene-object disentanglement can improve the spatiotemporal discrimination between background and objects to render the time-continuous dynamic scene. Extensive experiments have been performed to verify the superiority of the proposed method.
动态场景重建旨在表示具有刚体空间特征的静态背景和具有变形连续时空特征的动态对象。通常,现有方法采用统一表示模型(例如高斯模型)来直接匹配动态场景的时空特征。然而,由于帧成像的潜在不连续时间特征和背景与对象之间的异构图空间特征,这种统一的方法并不奏效。为了解决这个问题,我们将时空特征分解成各种潜在表现形式,以减轻背景和对象之间的时空不匹配问题。在这项工作中,我们引入事件相机来补偿帧相机,并提出一种时空分离的基于高斯贴图的高动态场景重建框架。对于动态场景,我们发现背景和对象在基于帧的空间特征和基于事件的时序特征方面存在外观和运动差异,这促使我们通过聚类来区分背景和对象之间的时空特征。对于动态对象,我们发现高斯表示和事件数据具有一致的时空特性,可作为引导对象高斯时空分离的先验信息。在高斯贴图框架内,累积的场景对象分离可以提高背景和对象之间的时空鉴别能力,以呈现连续的时间动态场景。已经进行了大量实验来验证所提出方法的优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
高动态场景重建中,传统统一模型在时空特征表达上表现不足。为解决这个问题,本文提出将时空特征分离成多种潜在表达,引入事件相机补偿帧相机,构建时空分离的Gaussian splatting框架。通过聚类区分背景和对象的时空特征,并利用Gaussian表达和事件数据的时空一致性,提高动态物体的时空分离效果。实验验证所提方法优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 高动态场景重建需区分静态背景与动态对象的时空特征。
- 传统统一模型在表达时空特征时存在潜在不连续性和异质性问题。
- 引入事件相机补偿帧相机,构建时空分离的Gaussian splatting框架。
- 通过聚类区分背景和对象的时空特征。
- Gaussian表达和事件数据在时空特征上具有一致性,可作为时空分离的先验信息。
- 在Gaussian splatting框架下,场景与物体的时空分离能提高背景与物体的区分度。
点此查看论文截图

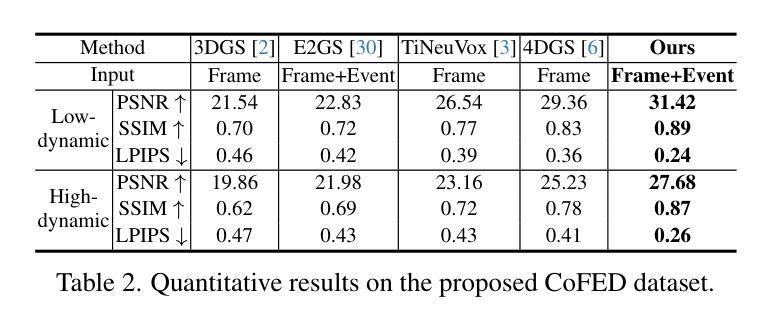
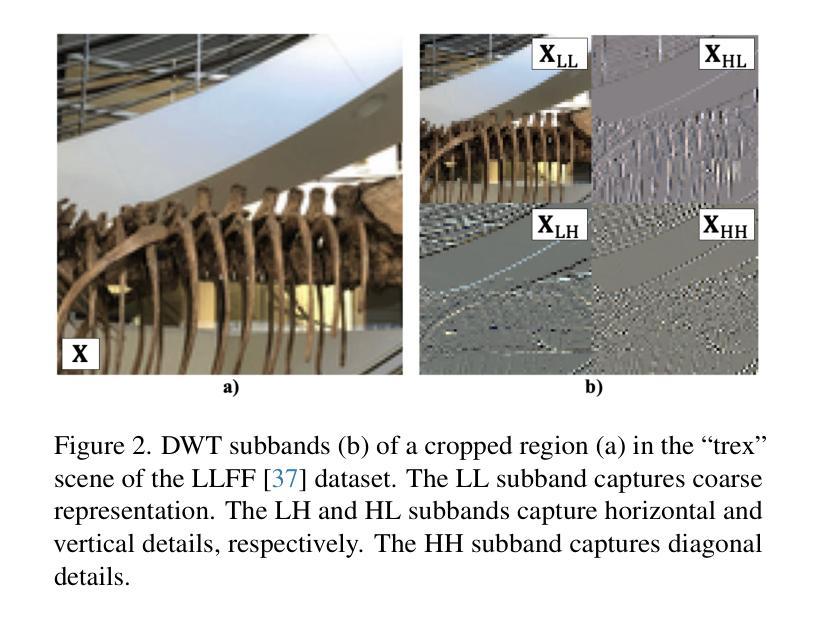
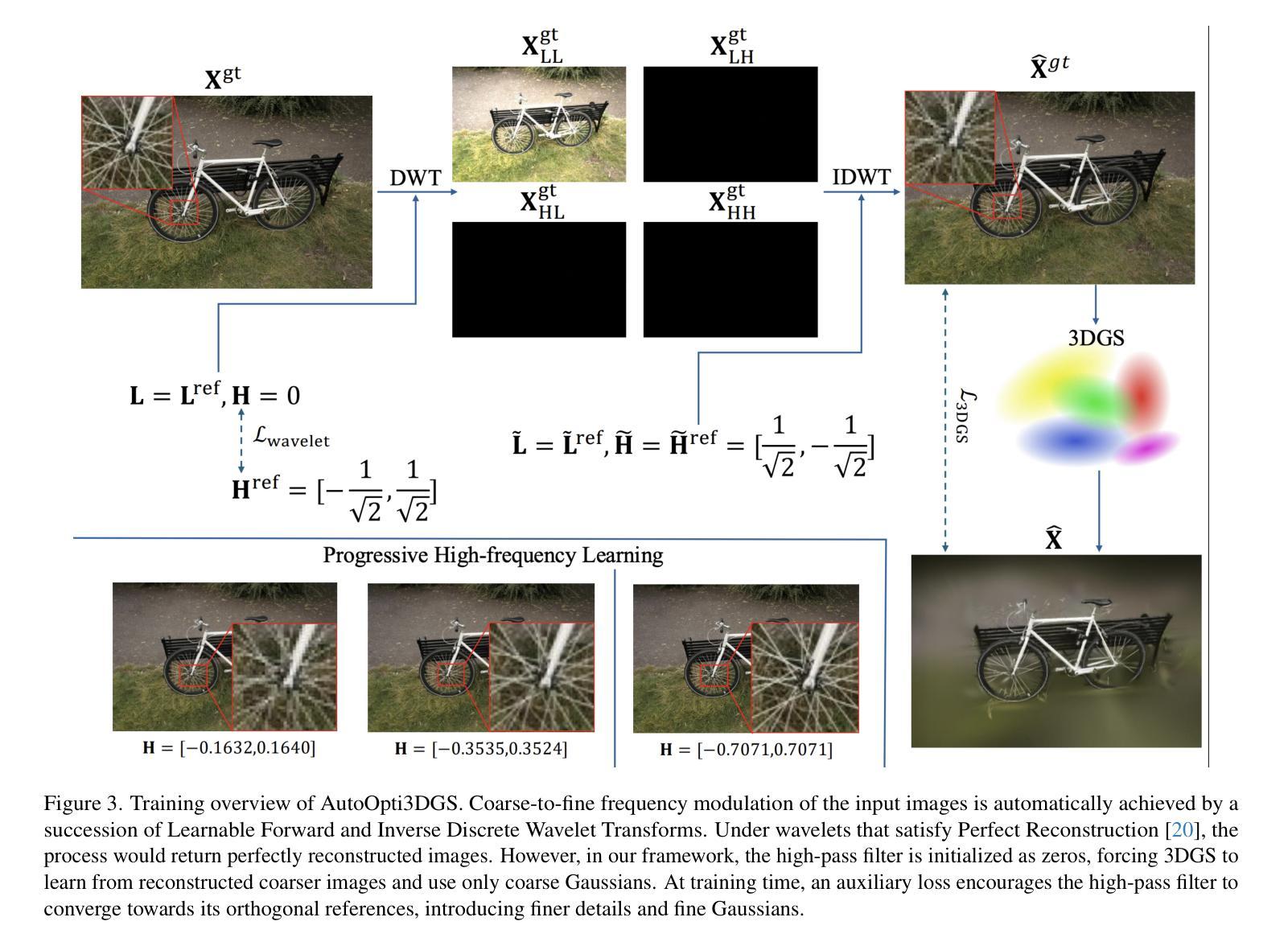
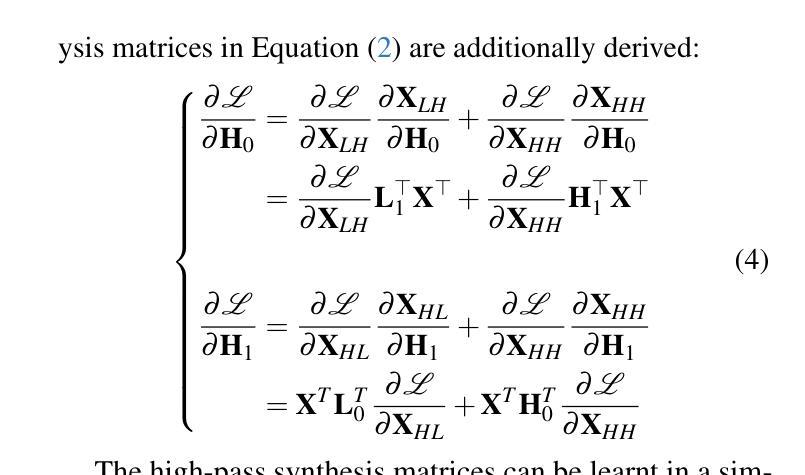
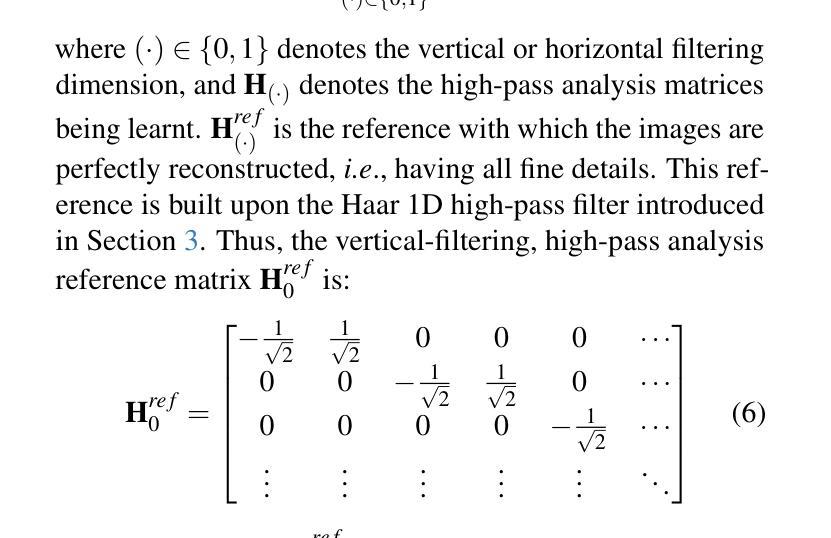
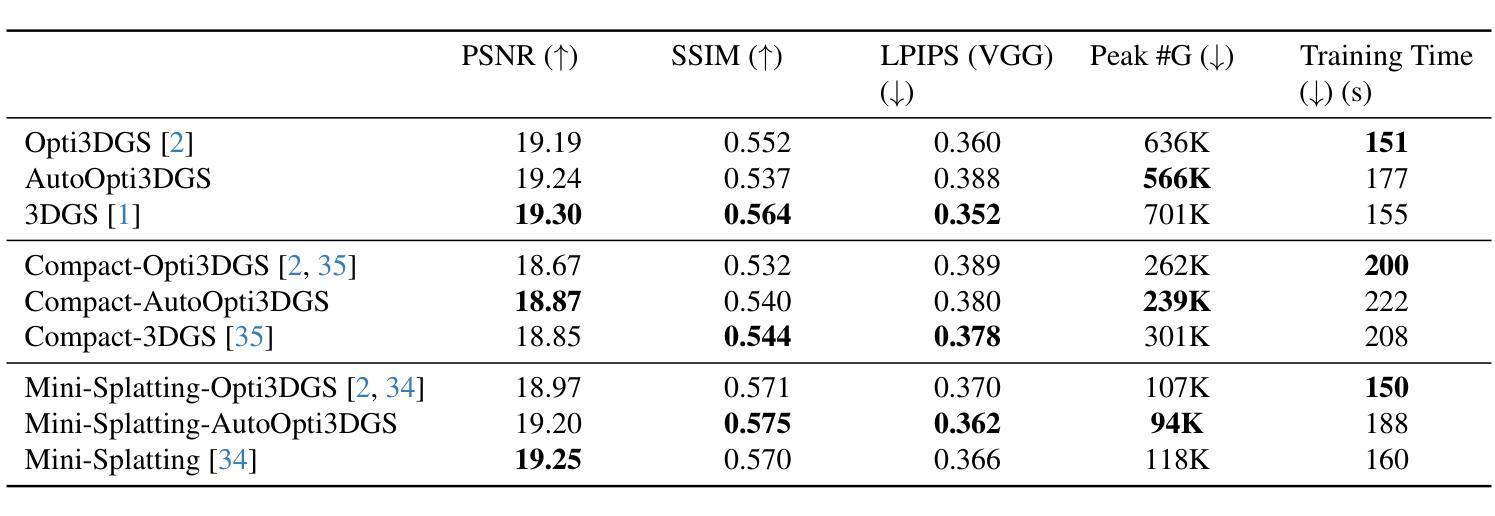
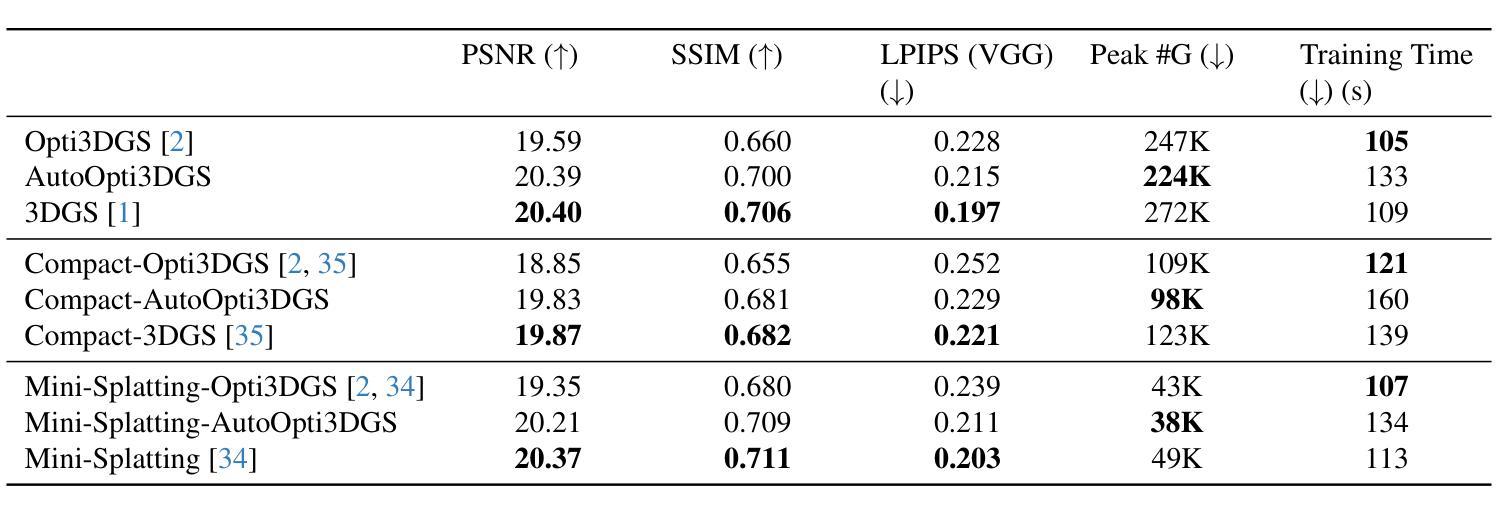
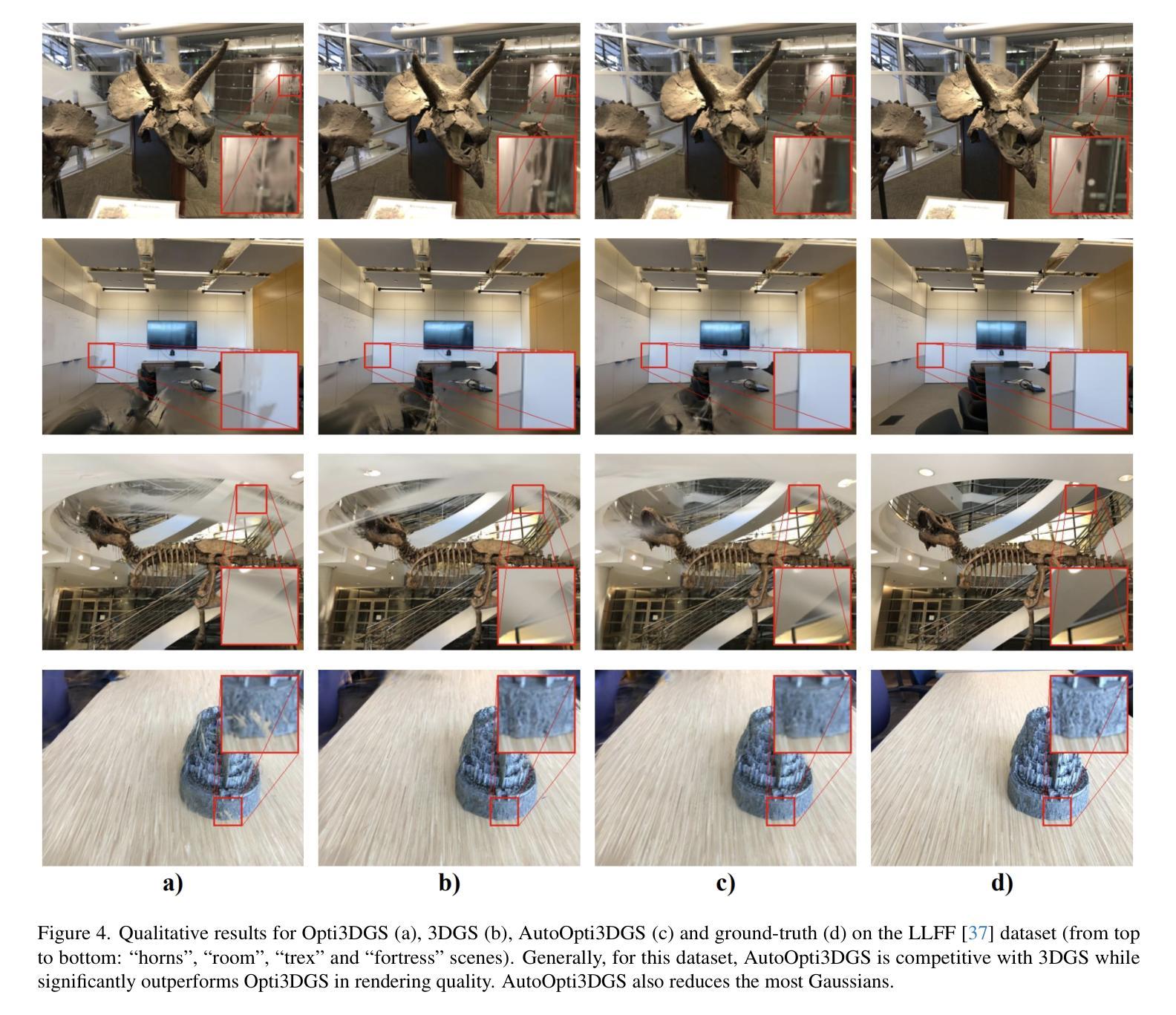
From Coarse to Fine: Learnable Discrete Wavelet Transforms for Efficient 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Hung Nguyen, An Le, Runfa Li, Truong Nguyen
3D Gaussian Splatting has emerged as a powerful approach in novel view synthesis, delivering rapid training and rendering but at the cost of an ever-growing set of Gaussian primitives that strains memory and bandwidth. We introduce AutoOpti3DGS, a training-time framework that automatically restrains Gaussian proliferation without sacrificing visual fidelity. The key idea is to feed the input images to a sequence of learnable Forward and Inverse Discrete Wavelet Transforms, where low-pass filters are kept fixed, high-pass filters are learnable and initialized to zero, and an auxiliary orthogonality loss gradually activates fine frequencies. This wavelet-driven, coarse-to-fine process delays the formation of redundant fine Gaussians, allowing 3DGS to capture global structure first and refine detail only when necessary. Through extensive experiments, AutoOpti3DGS requires just a single filter learning-rate hyper-parameter, integrates seamlessly with existing efficient 3DGS frameworks, and consistently produces sparser scene representations more compatible with memory or storage-constrained hardware.
3D高斯展开作为一种新型视图合成中的强大方法,虽然可以实现快速训练和渲染,但其代价是不断增加的高斯基本元素集,这会给内存和带宽带来压力。我们引入了AutoOpti3DGS,这是一个训练时框架,能够自动抑制高斯基本元素的增殖,同时不牺牲视觉保真度。主要思想是将输入图像输入到一系列可学习的前向和反向离散小波变换中,其中低通滤波器保持不变,高通滤波器可学习并初始化为零,一个辅助正交性损失逐渐激活精细频率。这种小波驱动的由粗到细的过程延迟了冗余精细高斯的形成,使得3DGS可以先捕捉全局结构,只在必要时进行细节优化。通过广泛的实验,AutoOpti3DGS只需要一个单一滤波器学习率超参数,可以与现有的高效3DGS框架无缝集成,并且始终产生更稀疏的场景表示,与内存或存储受限的硬件更兼容。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICCV Workshop
Summary
在三维高斯变形(3DGS)技术中,随着视角合成(Novel View Synthesis)的快速训练与渲染过程的需求,一种名为AutoOpti3DGS的训练时间框架应运而生。该框架能够自动抑制高斯基元(Gaussian primitives)的过度增长,同时不损失视觉保真度。其核心思想是通过引入离散小波变换,先学习场景的低频结构信息,逐渐添加高频细节。此方法既满足了快速的训练和渲染需求,又能避免由于高斯基元的增多而引发的内存和带宽问题。
Key Takeaways
- AutoOpti3DGS框架通过引入离散小波变换来抑制高斯基元的过度增长。
点此查看论文截图

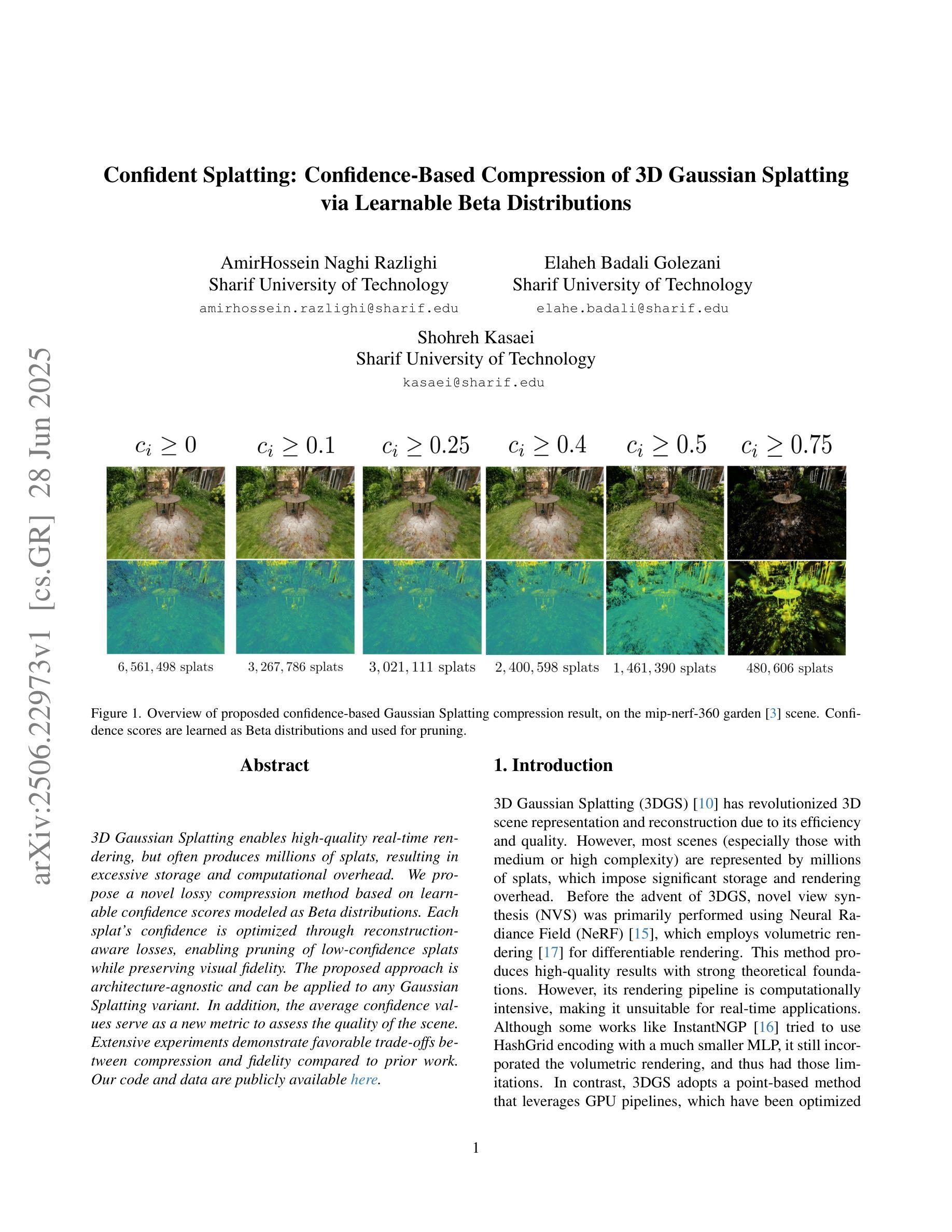
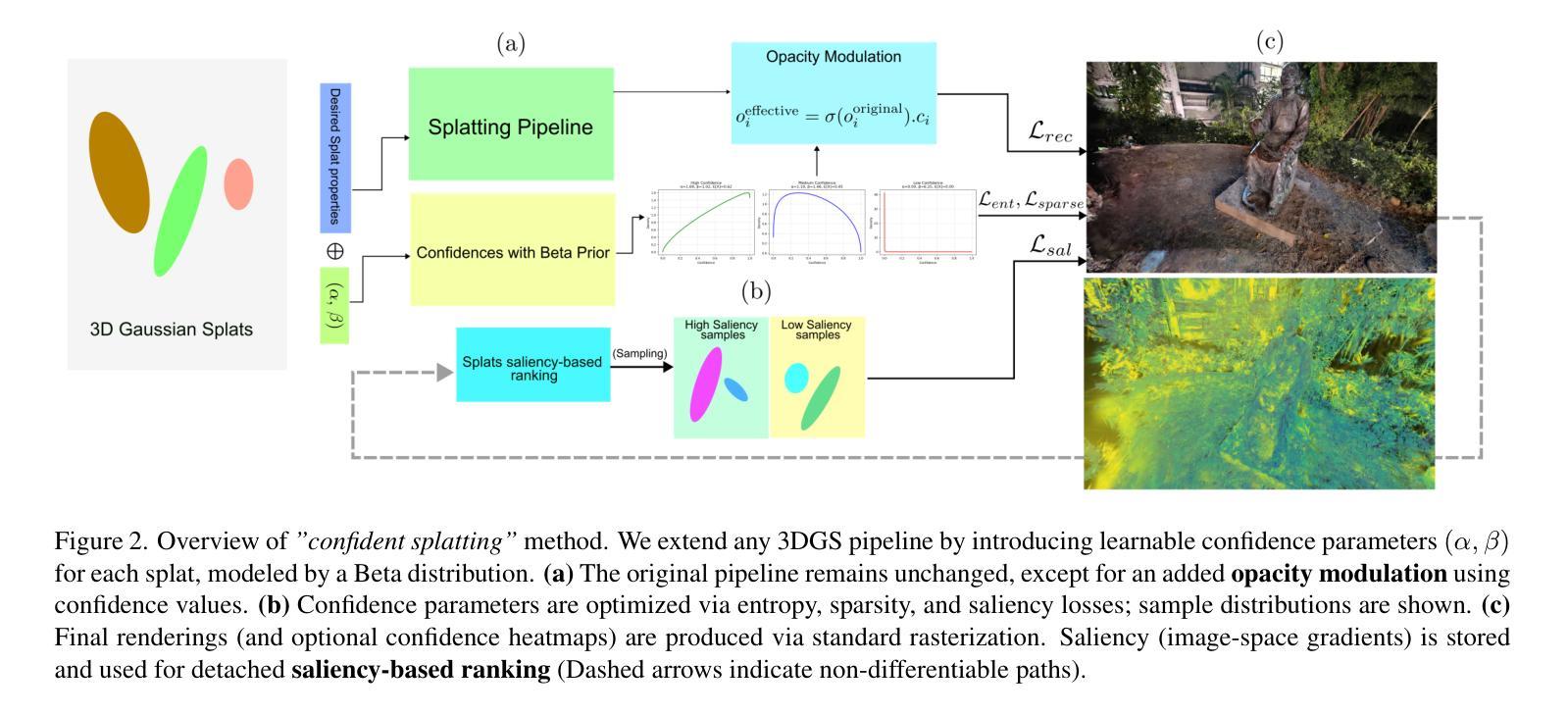
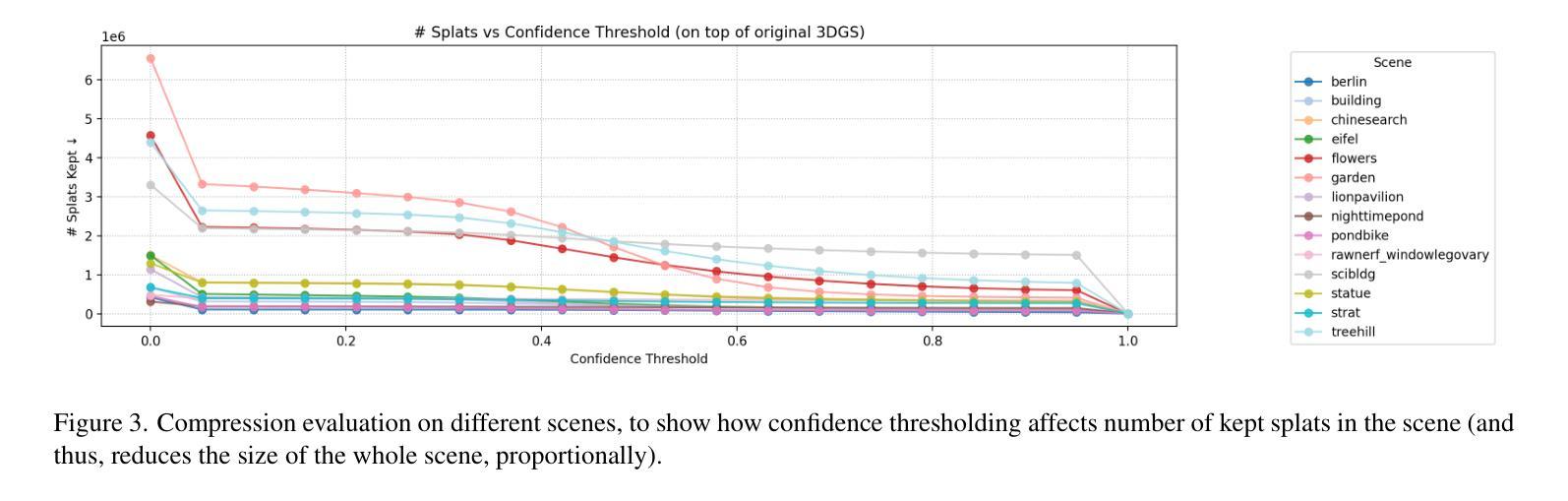
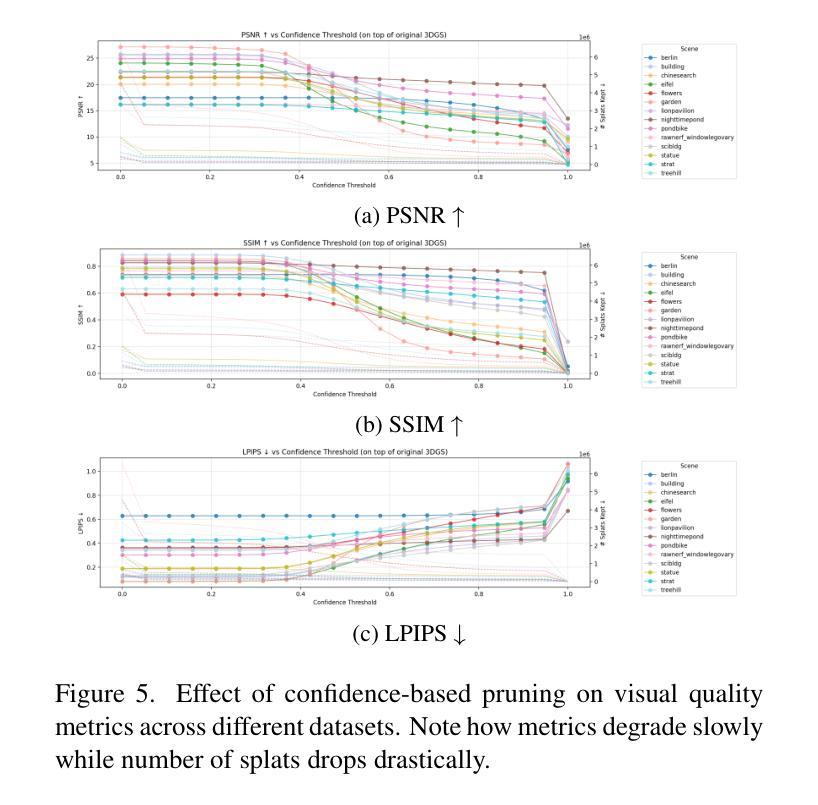
Confident Splatting: Confidence-Based Compression of 3D Gaussian Splatting via Learnable Beta Distributions
Authors:AmirHossein Naghi Razlighi, Elaheh Badali Golezani, Shohreh Kasaei
3D Gaussian Splatting enables high-quality real-time rendering but often produces millions of splats, resulting in excessive storage and computational overhead. We propose a novel lossy compression method based on learnable confidence scores modeled as Beta distributions. Each splat’s confidence is optimized through reconstruction-aware losses, enabling pruning of low-confidence splats while preserving visual fidelity. The proposed approach is architecture-agnostic and can be applied to any Gaussian Splatting variant. In addition, the average confidence values serve as a new metric to assess the quality of the scene. Extensive experiments demonstrate favorable trade-offs between compression and fidelity compared to prior work. Our code and data are publicly available at https://github.com/amirhossein-razlighi/Confident-Splatting
3D高斯延展技术能够实现高质量实时渲染,但通常会产生数百万个展点,导致存储和计算开销过大。我们提出了一种基于可学习置信度分数的有损压缩方法,这些置信度分数被建模为Beta分布。每个展点的置信度通过重建感知损失进行优化,能够在保持视觉保真度的同时剔除低置信度展点。所提出的方法不依赖于特定架构,可应用于任何高斯延展技术变体。此外,平均置信值可作为评估场景质量的新指标。大量实验证明,与先前的工作相比,该方法在压缩和保真度之间取得了有利的权衡。我们的代码和数据公开在https://github.com/amirhossein-razlighi/Confident-Splatting。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了基于可学习的置信度分数模型的损失压缩方法,用于优化3D高斯喷溅渲染。该方法通过重建感知损失优化每个喷溅的置信度,能够在保留视觉保真度的同时删除低置信度的喷溅。此方法具有通用性,可应用于任何高斯喷溅变体。同时,平均置信值作为评估场景质量的新指标。实验证明,与先前的工作相比,该方法在压缩和保真度之间取得了有利的权衡。
Key Takeaways
- 3D高斯喷溅实时渲染质量高,但产生大量喷溅数据,导致存储和计算开销大。
- 提出了一种基于可学习置信度分数的损失压缩方法,优化每个喷溅的置信度。
- 通过重建感知损失优化置信度,能在保留视觉保真度的同时删除低置信度的喷溅。
- 该方法具有通用性,适用于任何高斯喷溅变体。
- 平均置信值可作为评估场景质量的新指标。
- 实验显示,与以前的方法相比,该方法在压缩和保真度之间取得了更好的平衡。
点此查看论文截图
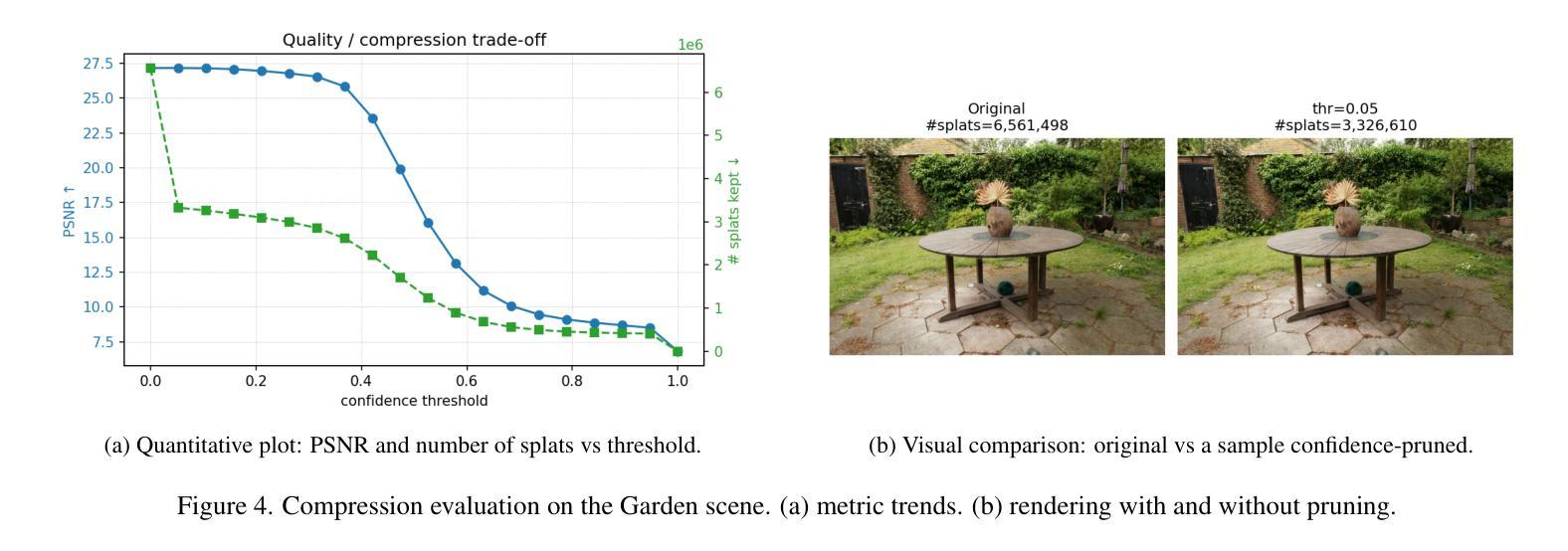
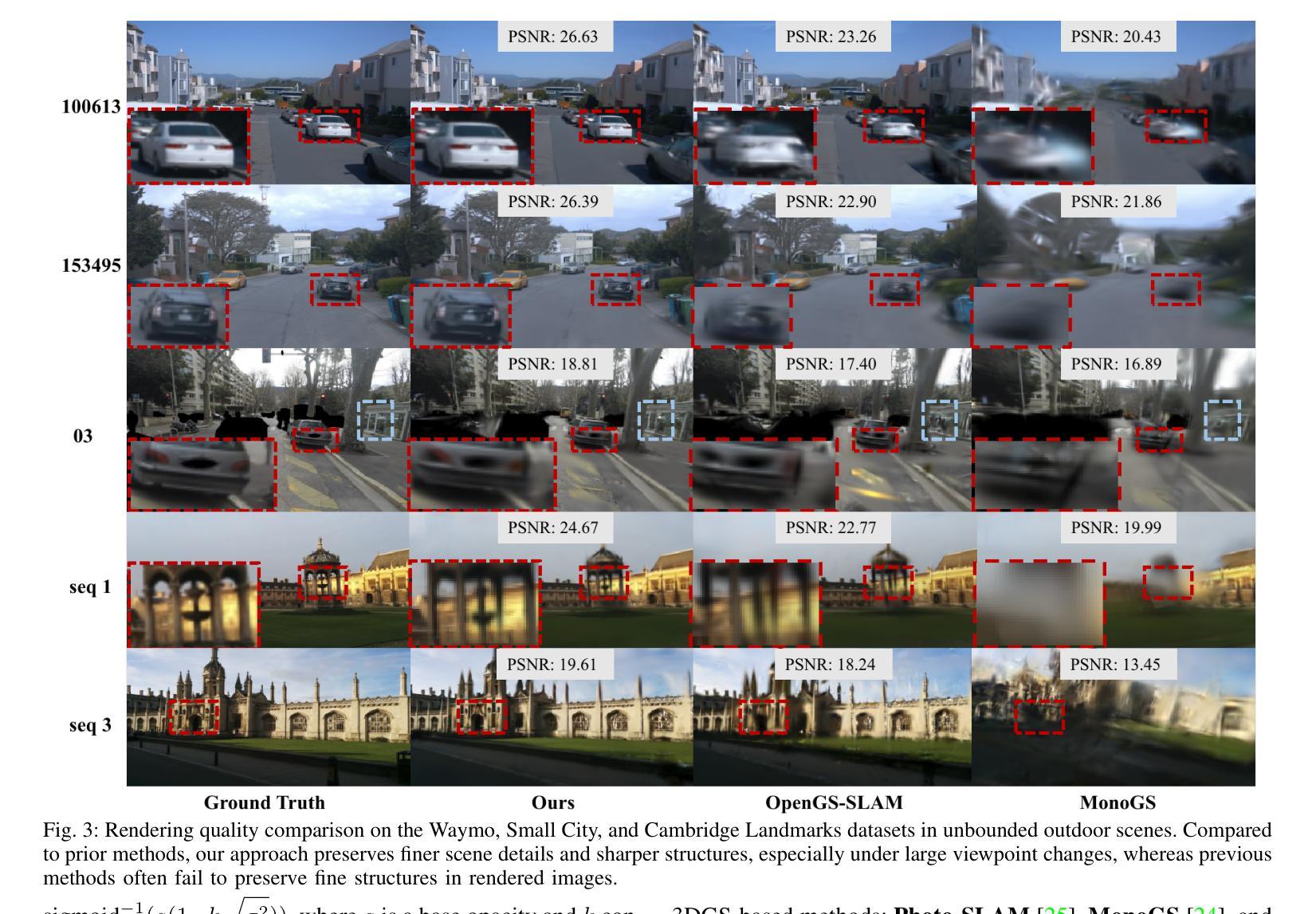
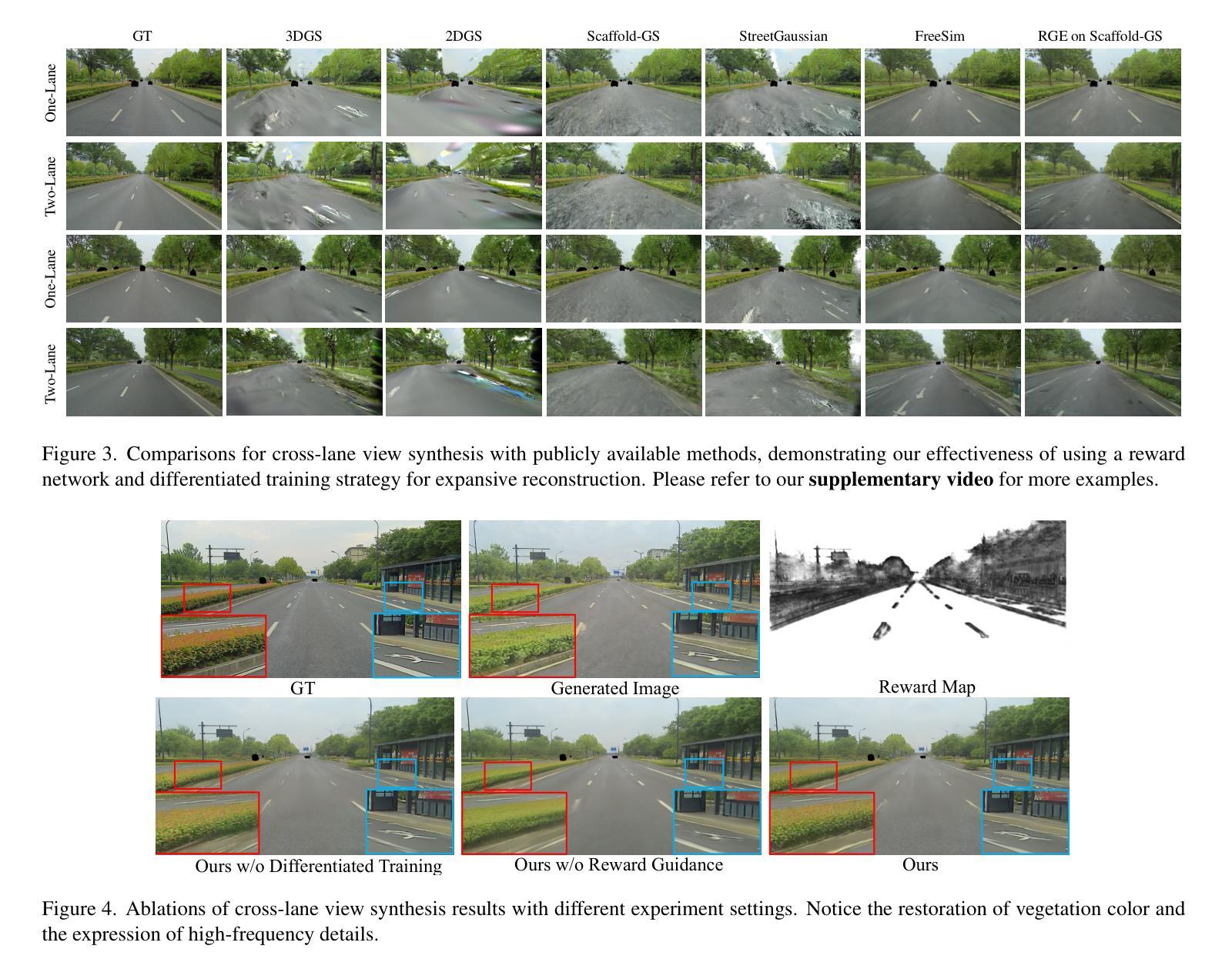
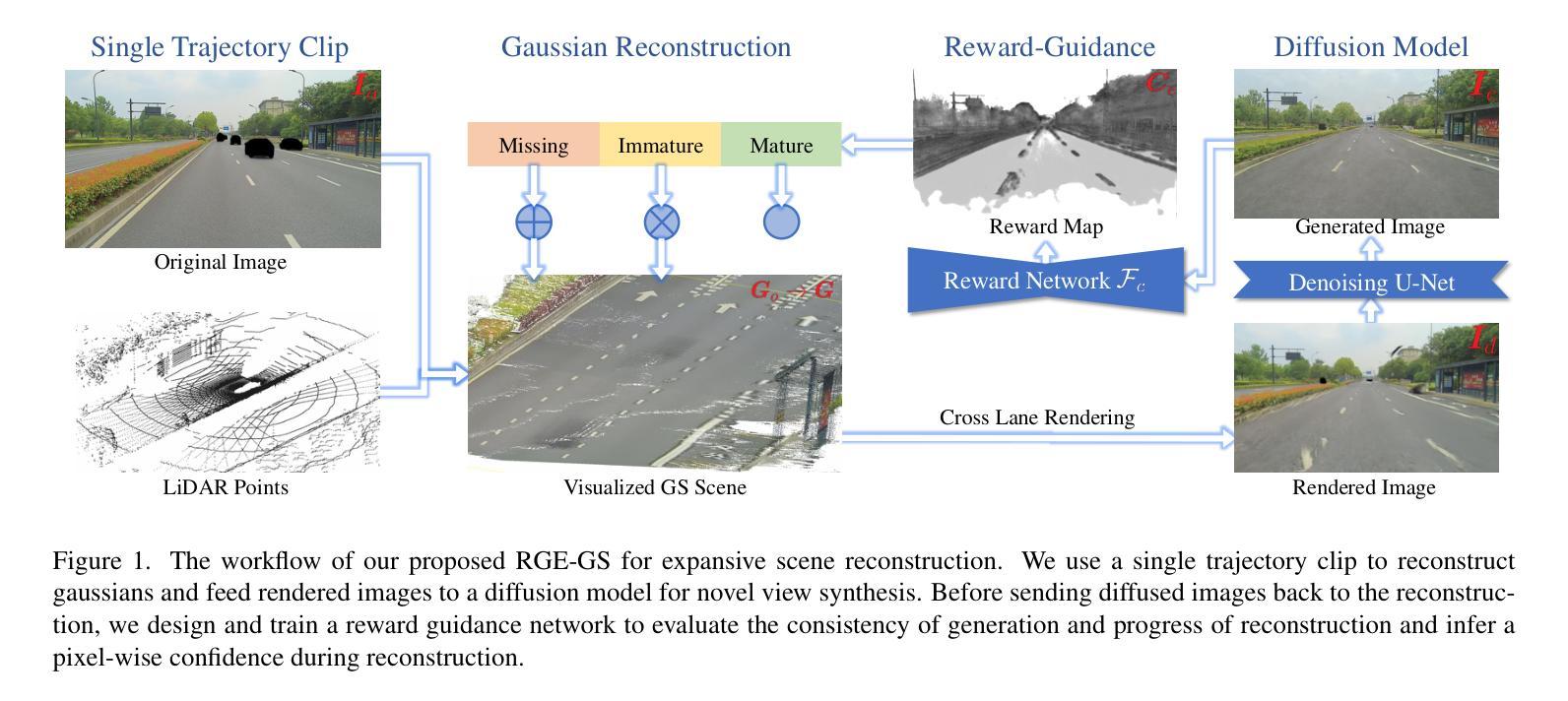
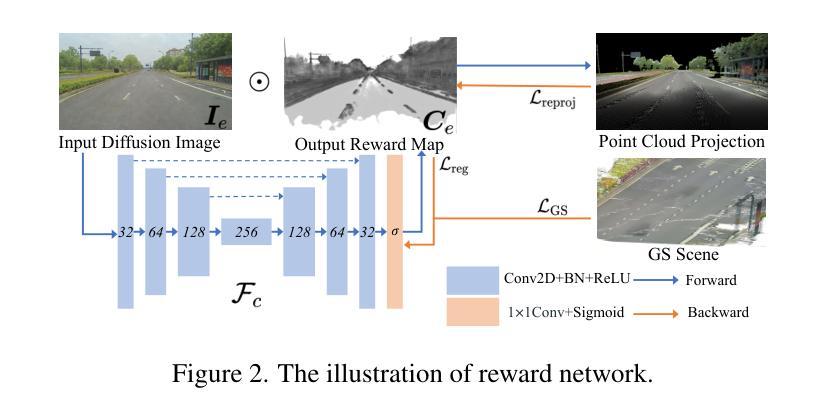
RGE-GS: Reward-Guided Expansive Driving Scene Reconstruction via Diffusion Priors
Authors:Sicong Du, Jiarun Liu, Qifeng Chen, Hao-Xiang Chen, Tai-Jiang Mu, Sheng Yang
A single-pass driving clip frequently results in incomplete scanning of the road structure, making reconstructed scene expanding a critical requirement for sensor simulators to effectively regress driving actions. Although contemporary 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) techniques achieve remarkable reconstruction quality, their direct extension through the integration of diffusion priors often introduces cumulative physical inconsistencies and compromises training efficiency. To address these limitations, we present RGE-GS, a novel expansive reconstruction framework that synergizes diffusion-based generation with reward-guided Gaussian integration. The RGE-GS framework incorporates two key innovations: First, we propose a reward network that learns to identify and prioritize consistently generated patterns prior to reconstruction phases, thereby enabling selective retention of diffusion outputs for spatial stability. Second, during the reconstruction process, we devise a differentiated training strategy that automatically adjust Gaussian optimization progress according to scene converge metrics, which achieving better convergence than baseline methods. Extensive evaluations of publicly available datasets demonstrate that RGE-GS achieves state-of-the-art performance in reconstruction quality. Our source-code will be made publicly available at https://github.com/CN-ADLab/RGE-GS. (Camera-ready version incorporating reviewer suggestions will be updated soon.)
使用单通道驾驶视频片段经常导致对道路结构的不完全扫描,这使得重建场景对于传感器模拟器有效地回归驾驶动作至关重要。尽管当前的3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)技术实现了令人印象深刻的重建质量,但它们通过集成扩散先验的直接扩展经常引入累积的物理不一致性并损害训练效率。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了RGE-GS,这是一种新型扩展重建框架,它协同基于扩散的生成与奖励引导的高斯积分。RGE-GS框架包含两个关键创新点:首先,我们提出了一种奖励网络,该网络在重建阶段之前学习识别和优先生成一致的模式,从而能够有选择地保留扩散输出以实现空间稳定性。其次,在重建过程中,我们设计了一种差异化的训练策略,该策略能够根据场景收敛指标自动调整高斯优化进度,从而实现比基线方法更好的收敛。对公开可用数据集的广泛评估表明,RGE-GS在重建质量方面达到了最新技术水平。我们的源代码将在https://github.com/CN-ADLab/RGE-GS上公开。(包含审稿人建议的最终版本将很快更新。)。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了一种名为RGE-GS的新型重建框架,该框架结合了扩散生成和奖励引导的高斯积分,用于解决单通道驾驶视频中的道路结构扫描不完整问题。RGE-GS通过引入奖励网络和差异化训练策略,提高了重建质量和训练效率,达到业界领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- 当代3D Gaussian Splatting(3DGS)技术在重建质量上表现出色,但其通过集成扩散先验的直接扩展经常引入累积的物理不一致性并影响训练效率。
- RGE-GS框架提出了一种奖励网络,用于在重建阶段前识别和优先处理一致生成的图案,从而实现选择性保留扩散输出以提高空间稳定性。
- RGE-GS在重建过程中采用差异化训练策略,根据场景收敛指标自动调整高斯优化进度,实现比基线方法更好的收敛效果。
- RGE-GS框架解决了单通道驾驶视频中的道路结构扫描不完整问题,适用于传感器模拟器的有效回归驾驶动作。
- 公开数据集的大量评估表明,RGE-GS在重建质量方面达到了业界领先水平。
- 该研究的源代码将公开发布在https://github.com/CN-ADLab/RGE-GS。
点此查看论文截图

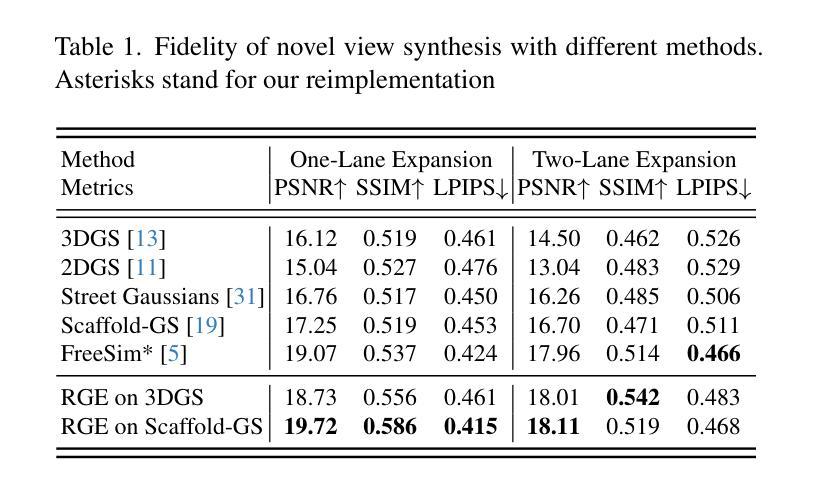

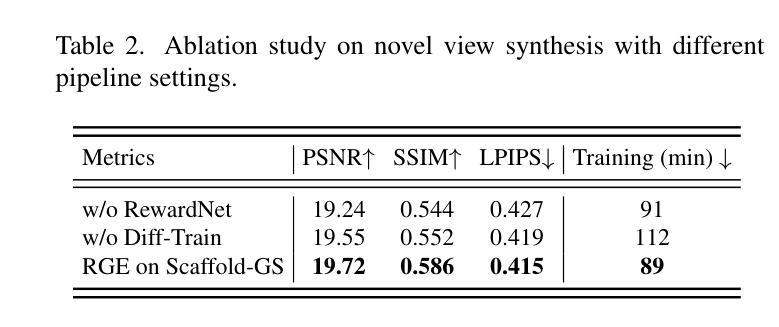
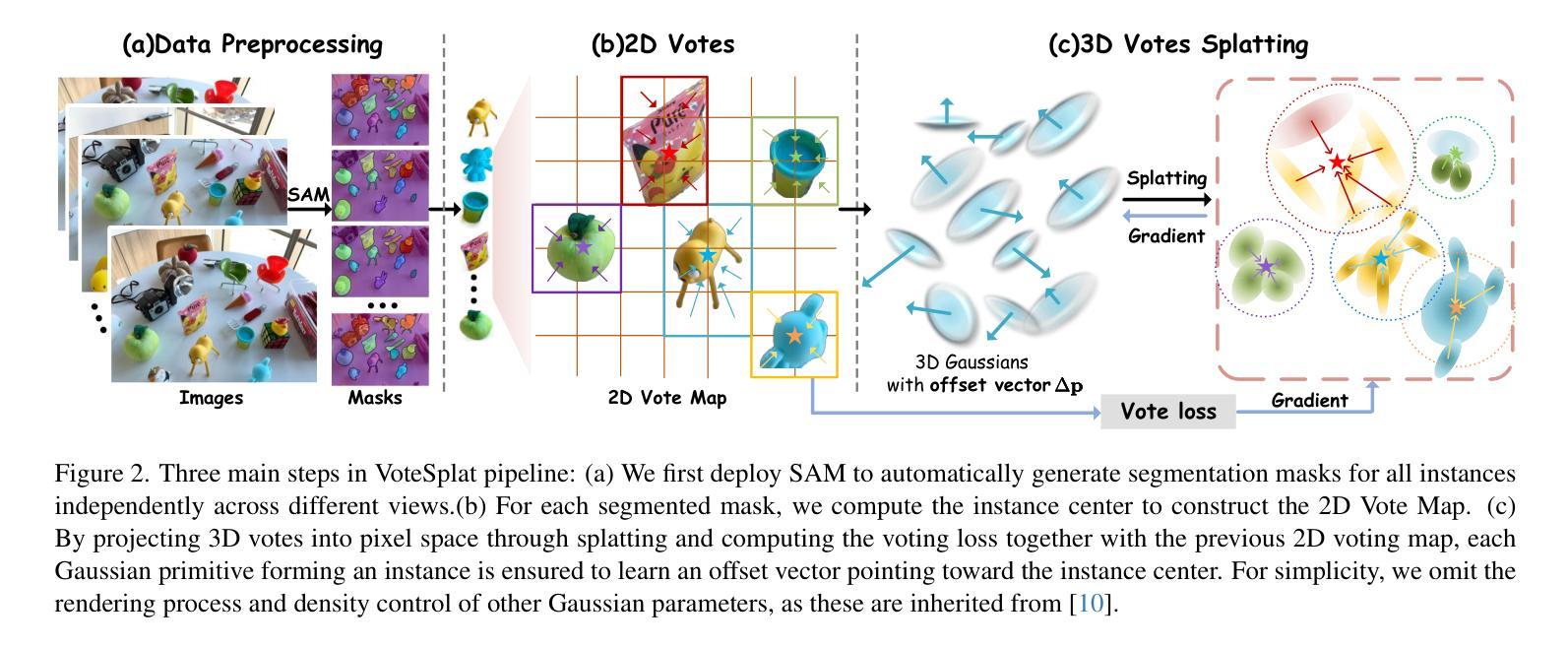
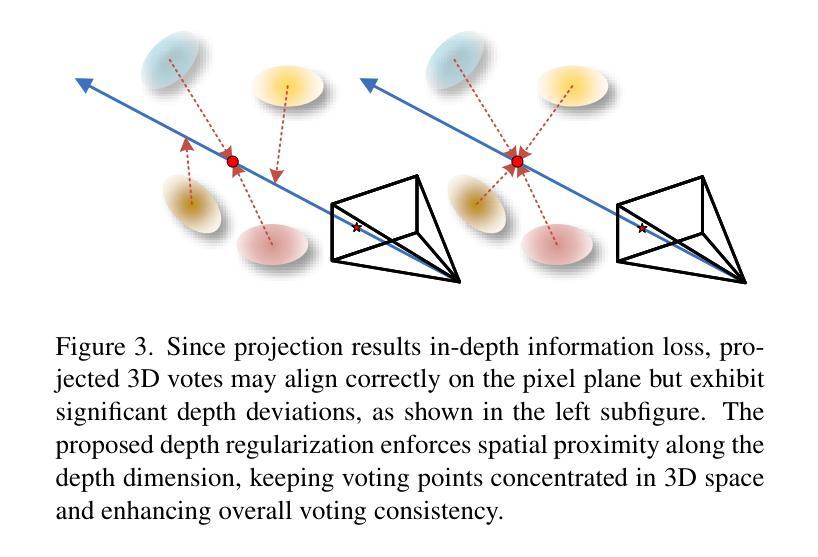
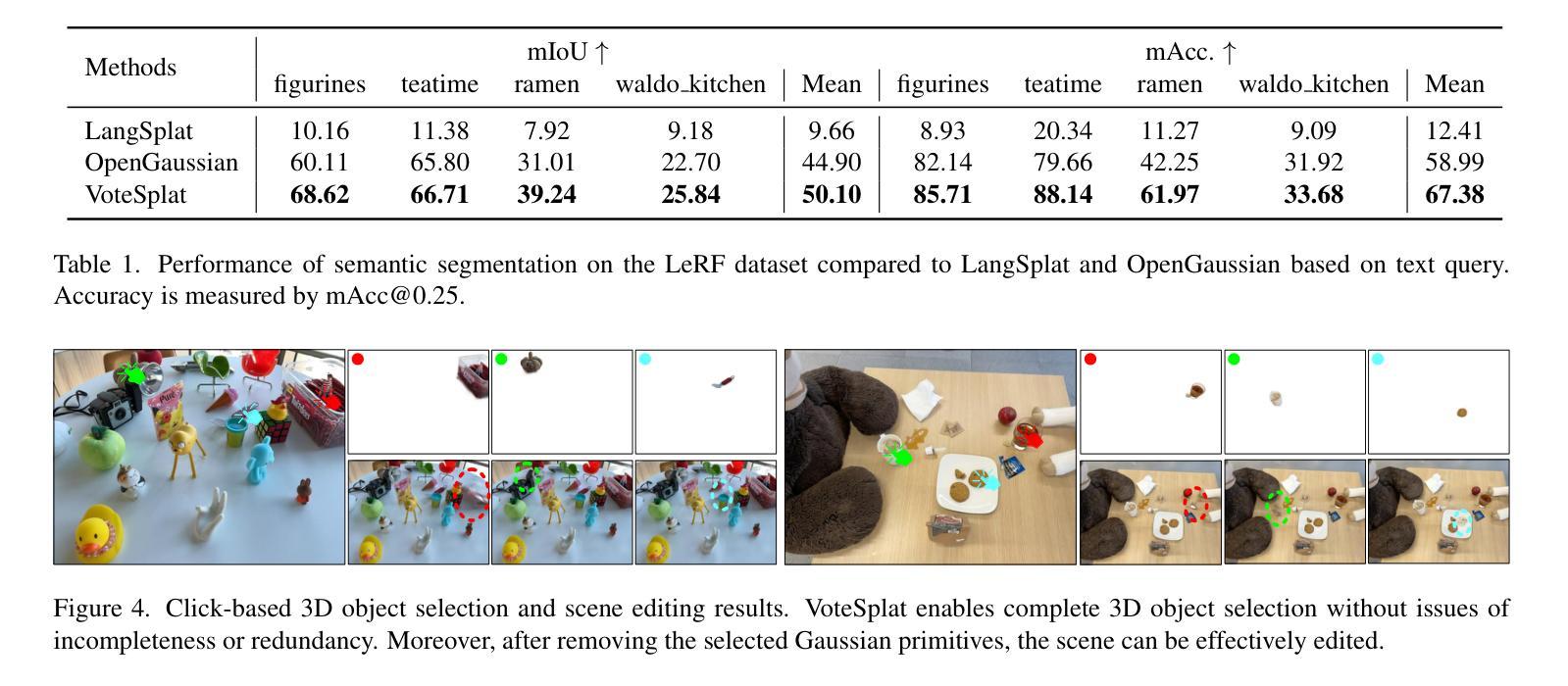
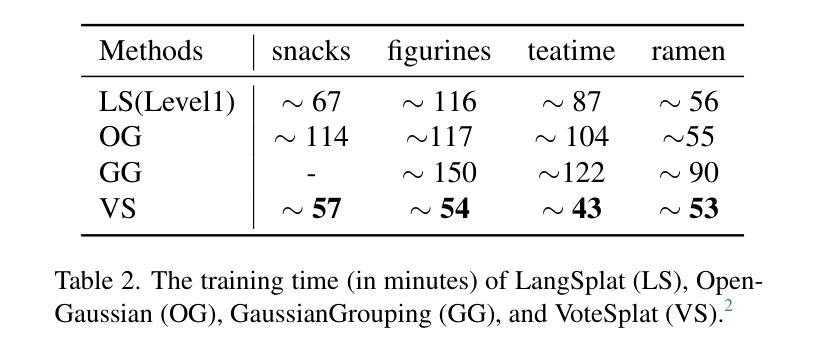
VoteSplat: Hough Voting Gaussian Splatting for 3D Scene Understanding
Authors:Minchao Jiang, Shunyu Jia, Jiaming Gu, Xiaoyuan Lu, Guangming Zhu, Anqi Dong, Liang Zhang
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has become horsepower in high-quality, real-time rendering for novel view synthesis of 3D scenes. However, existing methods focus primarily on geometric and appearance modeling, lacking deeper scene understanding while also incurring high training costs that complicate the originally streamlined differentiable rendering pipeline. To this end, we propose VoteSplat, a novel 3D scene understanding framework that integrates Hough voting with 3DGS. Specifically, Segment Anything Model (SAM) is utilized for instance segmentation, extracting objects, and generating 2D vote maps. We then embed spatial offset vectors into Gaussian primitives. These offsets construct 3D spatial votes by associating them with 2D image votes, while depth distortion constraints refine localization along the depth axis. For open-vocabulary object localization, VoteSplat maps 2D image semantics to 3D point clouds via voting points, reducing training costs associated with high-dimensional CLIP features while preserving semantic unambiguity. Extensive experiments demonstrate effectiveness of VoteSplat in open-vocabulary 3D instance localization, 3D point cloud understanding, click-based 3D object localization, hierarchical segmentation, and ablation studies. Our code is available at https://sy-ja.github.io/votesplat/
三维高斯Splatting(3DGS)已经成为高质量实时渲染中三维场景新型视角合成的核心动力。然而,现有方法主要集中在几何和外观建模上,缺乏更深层次的场景理解,同时产生了高昂的训练成本,这复杂化了原本流程化的可微分渲染管线。为此,我们提出了VoteSplat,这是一种新型的三维场景理解框架,它将霍夫投票与3DGS相结合。具体来说,我们使用Segment Anything Model(SAM)进行实例分割,提取对象并生成二维投票图。然后我们将空间偏移向量嵌入到高斯基元中。这些偏移量通过与二维图像投票相关联来构建三维空间投票,而深度失真约束则沿深度轴完善定位。对于开放词汇对象定位,VoteSplat通过投票点将二维图像语义映射到三维点云,降低了与高维CLIP特征相关的训练成本,同时保持语义清晰。大量实验证明了VoteSplat在开放词汇三维实例定位、三维点云理解、基于点击的三维对象定位、层次分割和消融研究中的有效性。我们的代码可在[https://sy-ja.github.io/votesplat/]上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICCV 2025
Summary
本文介绍了名为VoteSplat的新型三维场景理解框架,该框架结合了霍夫投票与高斯喷涂技术,并使用了名为SAM的模型实现实例分割,提升了三维场景渲染中对场景的深入理解与训练效率的提升。投票技术帮助进行物体定位和三维点云解析,简化了复杂的训练过程。VoteSplat框架对于开放词汇表的三维物体定位、三维点云理解、点击式三维物体定位以及层次分割等任务展现出显著效果。
Key Takeaways
- VoteSplat是一个新型的三维场景理解框架,结合了霍夫投票与三维高斯喷涂技术(3DGS)。
- 使用Segment Anything Model(SAM)进行实例分割,提取对象并生成二维投票图。
- 通过嵌入空间偏移向量到高斯基本体中,构建三维空间投票。
- 深度扭曲约束用于沿深度轴改进定位精度。
- VoteSplat通过投票点将二维图像语义映射到三维点云中,降低高维CLIP特征的训练成本,同时保持语义明确性。
点此查看论文截图

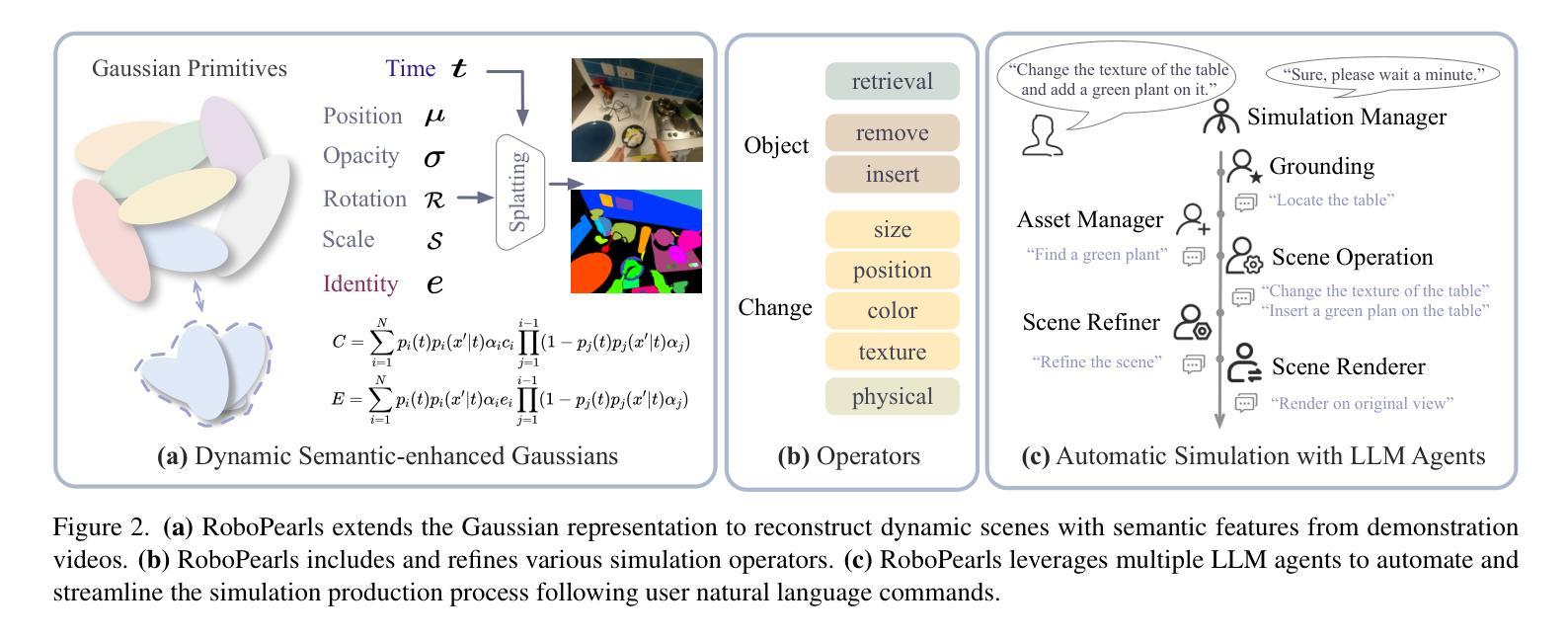
RoboPearls: Editable Video Simulation for Robot Manipulation
Authors:Tao Tang, Likui Zhang, Youpeng Wen, Kaidong Zhang, Jia-Wang Bian, xia zhou, Tianyi Yan, Kun Zhan, Peng Jia, Hefeng Wu, Liang Lin, Xiaodan Liang
The development of generalist robot manipulation policies has seen significant progress, driven by large-scale demonstration data across diverse environments. However, the high cost and inefficiency of collecting real-world demonstrations hinder the scalability of data acquisition. While existing simulation platforms enable controlled environments for robotic learning, the challenge of bridging the sim-to-real gap remains. To address these challenges, we propose RoboPearls, an editable video simulation framework for robotic manipulation. Built on 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), RoboPearls enables the construction of photo-realistic, view-consistent simulations from demonstration videos, and supports a wide range of simulation operators, including various object manipulations, powered by advanced modules like Incremental Semantic Distillation (ISD) and 3D regularized NNFM Loss (3D-NNFM). Moreover, by incorporating large language models (LLMs), RoboPearls automates the simulation production process in a user-friendly manner through flexible command interpretation and execution. Furthermore, RoboPearls employs a vision-language model (VLM) to analyze robotic learning issues to close the simulation loop for performance enhancement. To demonstrate the effectiveness of RoboPearls, we conduct extensive experiments on multiple datasets and scenes, including RLBench, COLOSSEUM, Ego4D, Open X-Embodiment, and a real-world robot, which demonstrate our satisfactory simulation performance.
通用机器人操作策略的发展已经取得了显著的进步,这得益于在多种环境中收集的大规模演示数据。然而,收集真实世界演示的高成本和不效率阻碍了数据获取的扩展性。现有的仿真平台为机器人学习提供了受控环境,但弥合仿真与真实之间的差距的挑战仍然存在。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了RoboPearls,这是一个用于机器人操作的编辑视频仿真框架。它建立在三维高斯拼贴(3DGS)的基础上,使得能够从演示视频中构建逼真的、视图一致的仿真,并支持广泛的仿真操作,包括各种对象操作,这得益于增量语义蒸馏(ISD)和三维正则化NNFM损失(3D-NNFM)等先进模块的支持。此外,通过融入大型语言模型(LLM),RoboPearls以用户友好的方式通过灵活的解释和执行命令自动化仿真生产过程。而且,RoboPearls还采用视觉语言模型(VLM)来分析机器人学习问题,以完善仿真循环,从而提高性能。为了证明RoboPearls的有效性,我们在多个数据集和场景上进行了广泛实验,包括RLBench、COLOSSEUM、Ego4D、Open X-Embodiment和真实世界机器人,实验结果证明了我们的仿真性能令人满意。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025
Summary
基于大规模演示数据的机器人通用操作策略开发取得显著进展,但仍面临真实世界数据采集的高成本和低效问题。仿真平台虽能为机器人学习提供受控环境,但模拟到现实的差距仍是挑战。我们提出RoboPearls,一个基于3D高斯拼贴技术的可编辑视频仿真框架,用于机器人操作。它支持从演示视频构建逼真的模拟环境,涵盖广泛的模拟操作,借助增量语义蒸馏和3D正则化NNFM损失等高级模块推动模拟发展。此外,RoboPearls借助大型语言模型自动化仿真生产流程,并引入视觉语言模型分析机器人学习问题,以改进模拟性能。通过实验验证,RoboPearls在多个数据集和场景上表现出良好的模拟性能。
Key Takeaways
- 基于大规模演示数据的机器人通用操作策略开发已取得显著进展。
- 真实世界数据采集的高成本和低效性仍是面临的挑战。
- 仿真平台为机器人学习提供受控环境,但模拟到现实的差距仍需解决。
- RoboPearls是一个基于3DGS的视频仿真框架,支持从演示视频构建逼真的模拟环境。
- RoboPearls具有广泛的模拟操作能力,包括各种对象操作。
- RoboPearls借助高级模块(如ISD和3D-NNFM Loss)推动模拟发展。
点此查看论文截图

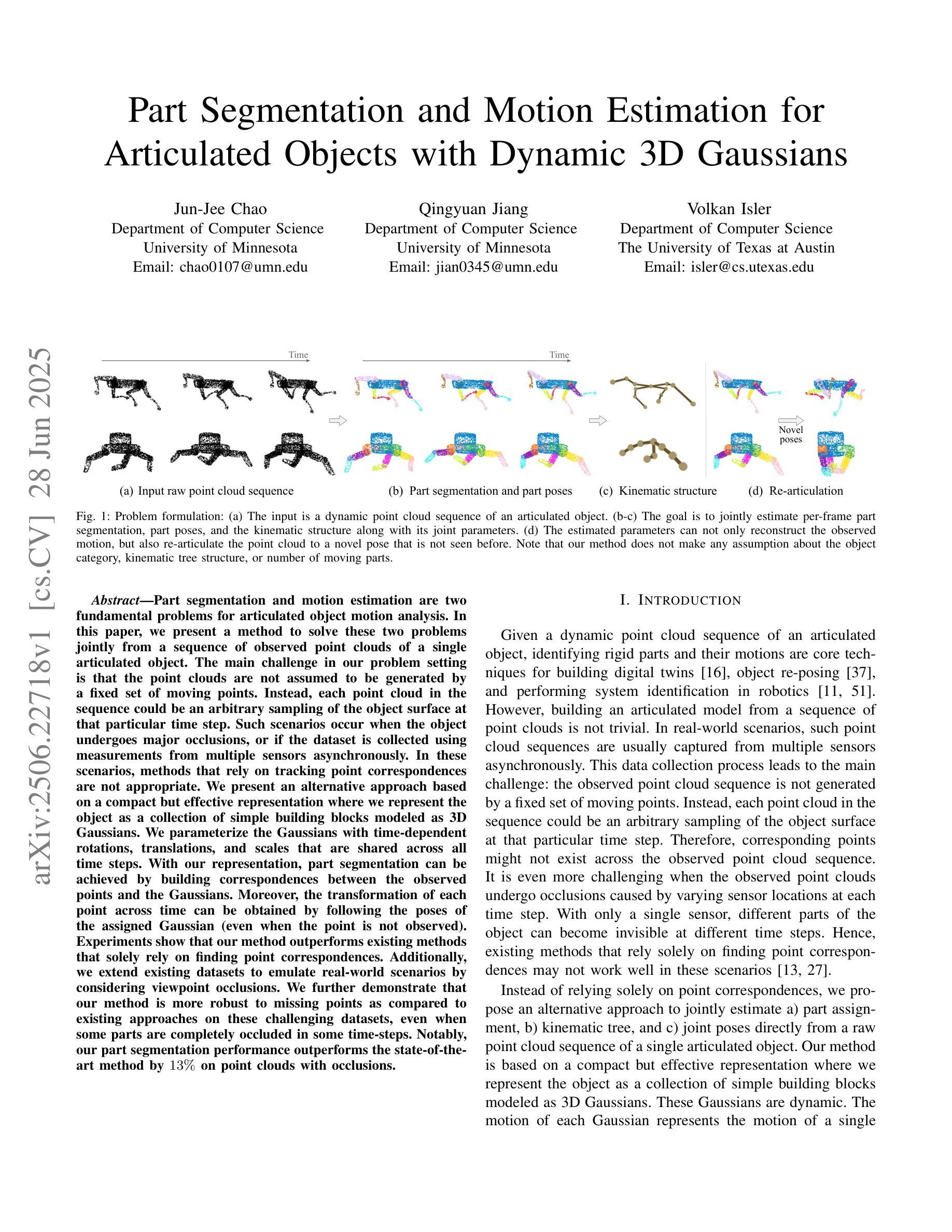
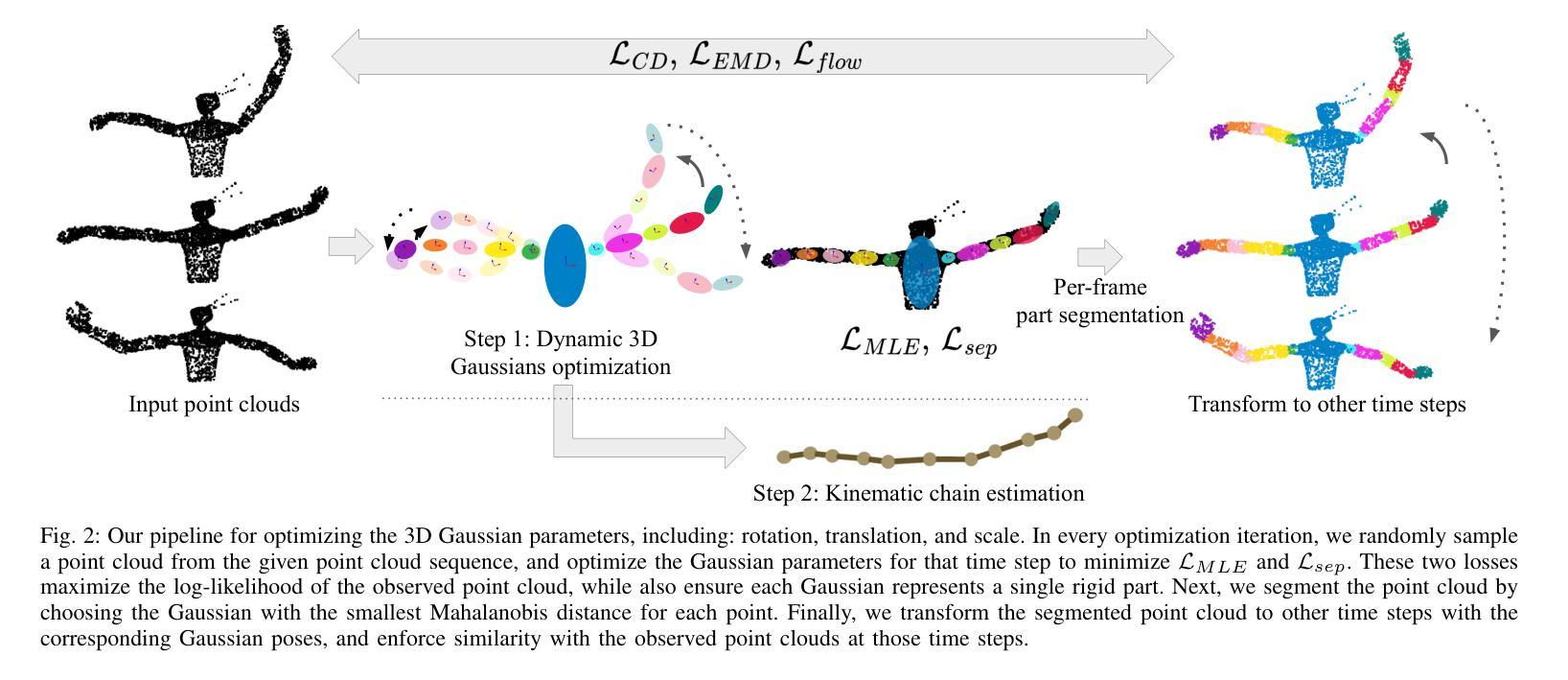
Part Segmentation and Motion Estimation for Articulated Objects with Dynamic 3D Gaussians
Authors:Jun-Jee Chao, Qingyuan Jiang, Volkan Isler
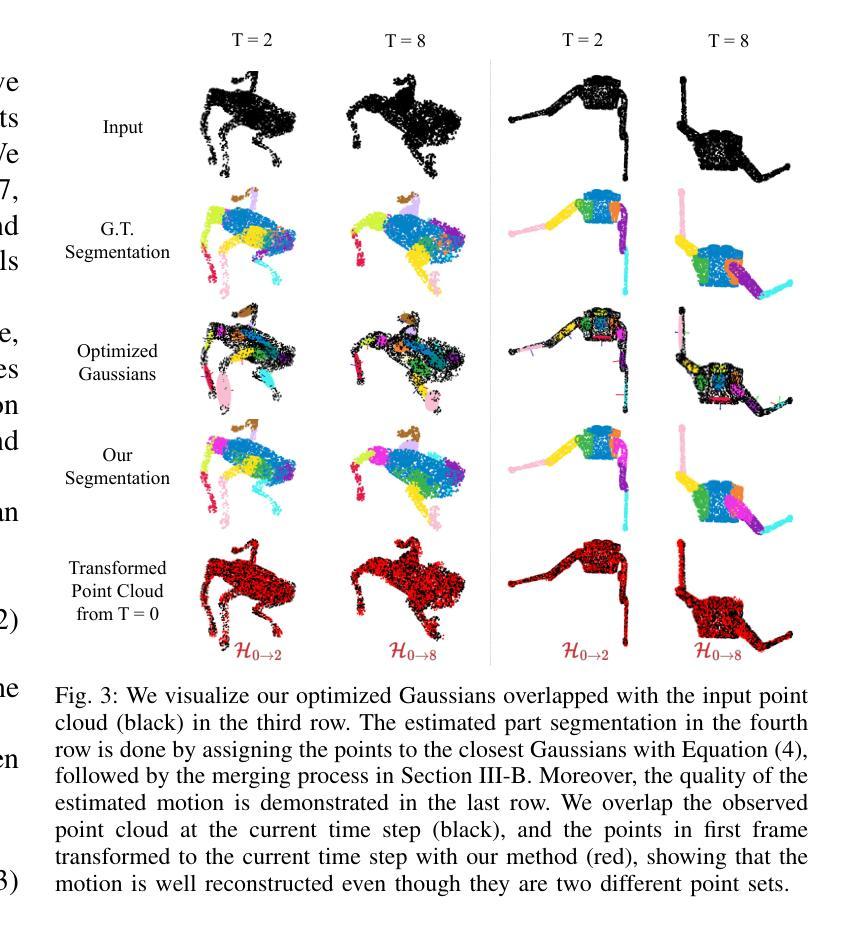
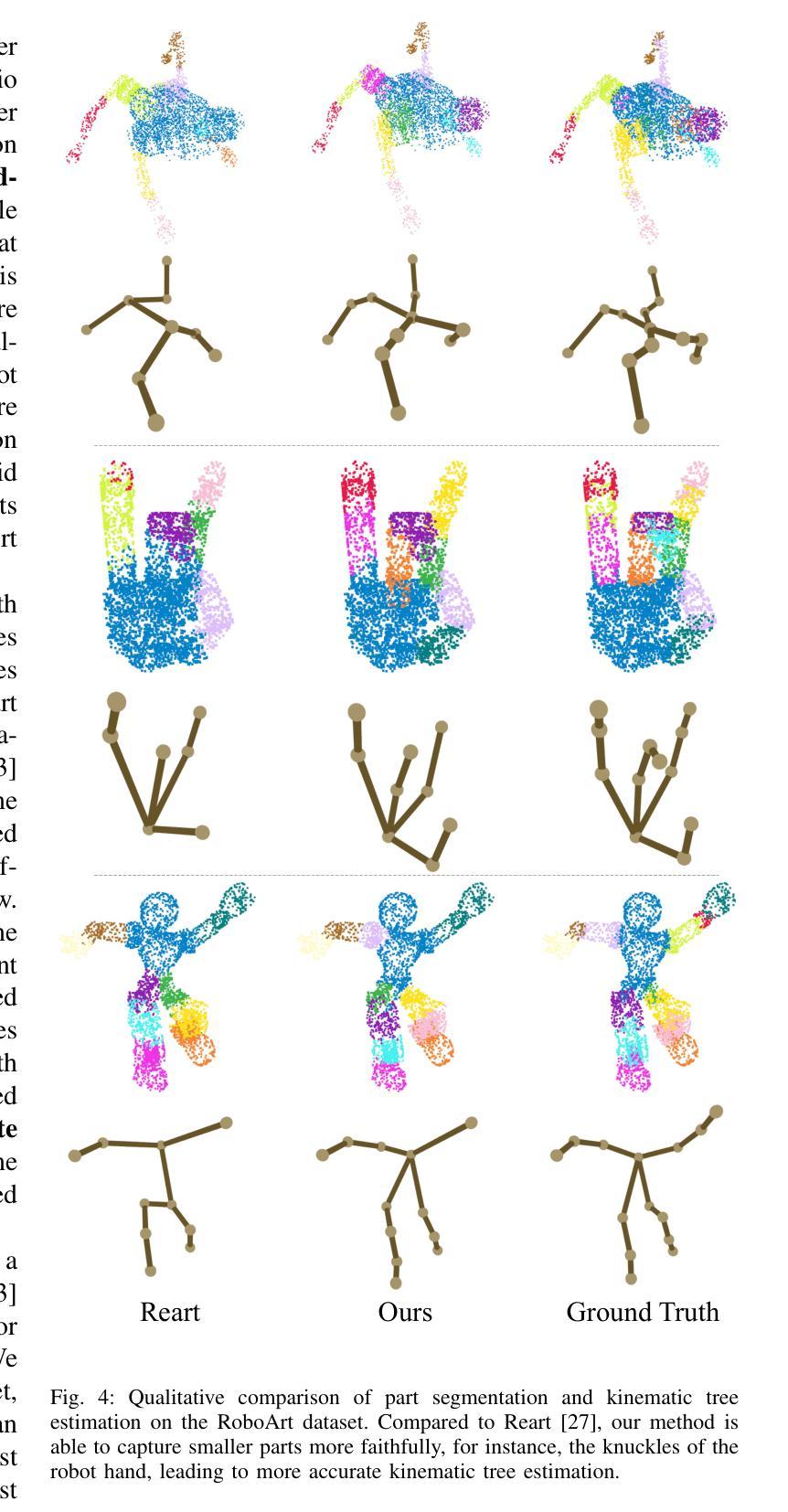
Part segmentation and motion estimation are two fundamental problems for articulated object motion analysis. In this paper, we present a method to solve these two problems jointly from a sequence of observed point clouds of a single articulated object. The main challenge in our problem setting is that the point clouds are not assumed to be generated by a fixed set of moving points. Instead, each point cloud in the sequence could be an arbitrary sampling of the object surface at that particular time step. Such scenarios occur when the object undergoes major occlusions, or if the dataset is collected using measurements from multiple sensors asynchronously. In these scenarios, methods that rely on tracking point correspondences are not appropriate. We present an alternative approach based on a compact but effective representation where we represent the object as a collection of simple building blocks modeled as 3D Gaussians. We parameterize the Gaussians with time-dependent rotations, translations, and scales that are shared across all time steps. With our representation, part segmentation can be achieved by building correspondences between the observed points and the Gaussians. Moreover, the transformation of each point across time can be obtained by following the poses of the assigned Gaussian (even when the point is not observed). Experiments show that our method outperforms existing methods that solely rely on finding point correspondences. Additionally, we extend existing datasets to emulate real-world scenarios by considering viewpoint occlusions. We further demonstrate that our method is more robust to missing points as compared to existing approaches on these challenging datasets, even when some parts are completely occluded in some time-steps. Notably, our part segmentation performance outperforms the state-of-the-art method by 13% on point clouds with occlusions.
针对关节对象运动分析,部件分割和运动估计是两个基本问题。本文提出了一种方法,可以从单个关节对象的点云序列中联合解决这两个问题。我们面临的问题的主要挑战在于,点云并不是由一组固定的移动点生成的。相反,序列中的每个点云都可能是该对象表面在特定时间步长的任意采样。当对象遭受主要遮挡或数据集是使用多个异步传感器收集的测量值时,就会出现这种情况。在这些场景中,依赖跟踪点对应的的方法并不适用。我们提出了一种基于紧凑而有效的表示方法的替代方案,我们将对象表示为作为三维高斯模型的简单构建块的集合。我们用时间相关的旋转、平移和缩放参数化高斯,这些参数在所有时间步长中都是共享的。通过我们的表示方法,可以通过在观察到的点和高斯之间建立对应关系来实现部件分割。此外,每个点随时间变化的变化可以通过跟随指定的高斯姿态来获得(即使点没有被观察到)。实验表明,我们的方法在仅依赖于寻找点对应的方法上表现更好。此外,我们通过考虑视点遮挡来模拟现实世界场景,对现有数据集进行了扩展。我们进一步证明,我们的方法在缺失点上相比这些具有挑战性的数据集上的现有方法更具鲁棒性,即使在某些时间步长中某些部分被完全遮挡也是如此。值得注意的是,我们的部件分割性能在带有遮挡的点云上比最新技术高出13%。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出一种方法,从单个可动对象的点云序列中联合解决部分分割和运动估计这两个基本问题。该方法不假定点云由固定的一组移动点生成,而是认为每个点云可能是对象表面在该时间步的任意采样。在对象遭受主要遮挡或使用多个异步传感器进行测量的情况下,依赖跟踪点对应的方法不适用。相反,本文采用紧凑有效的表示方法,将对象表示为由时间依赖的旋转、平移和缩放参数化的三维高斯简单构建块集合。通过构建观察到的点与高斯之间的对应关系,可以实现部分分割。此外,可以通过追踪指定高斯的状态获得各点随时间的变化(即使该点未被观察到)。实验表明,该方法优于仅依赖找点对应的方法。此外,通过考虑视角遮挡来模拟现实场景,扩展现有数据集。进一步证明该方法在具有挑战性的数据集上比现有方法更稳健地处理缺失点,即使在某些时间步中某些部分被完全遮挡的情况下,本文的部分分割性能也比最新技术高出13%。
要点掌握
- 本文解决了可动对象的点云序列中的部分分割和运动估计问题。
- 提出一种基于三维高斯简单构建块的表示方法,适用于对象表面的任意采样。
- 方法不依赖固定的点对应跟踪,而是通过构建观察到的点与高斯之间的对应关系实现部分分割。
- 可以追踪指定高斯的状态获得各点随时间的变化。
- 方法在实验中表现出优于现有方法的性能,特别是在处理遮挡和缺失点的现实场景中。
- 对现有数据集进行了扩展,以模拟现实世界的遮挡情况。
点此查看论文截图
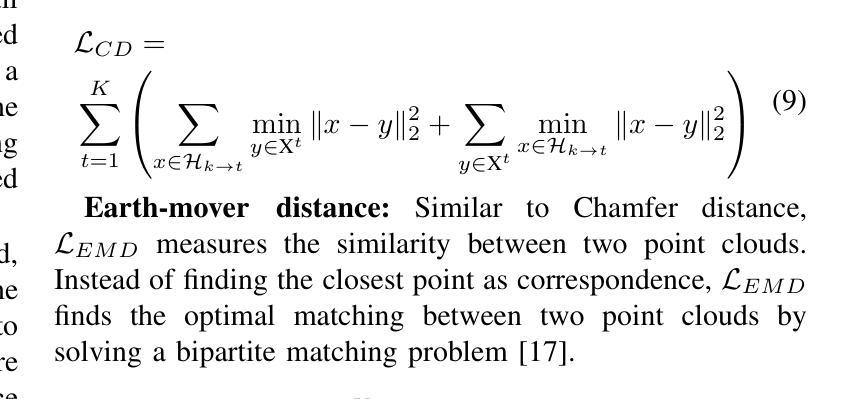
DIGS: Dynamic CBCT Reconstruction using Deformation-Informed 4D Gaussian Splatting and a Low-Rank Free-Form Deformation Model
Authors:Yuliang Huang, Imraj Singh, Thomas Joyce, Kris Thielemans, Jamie R. McClelland
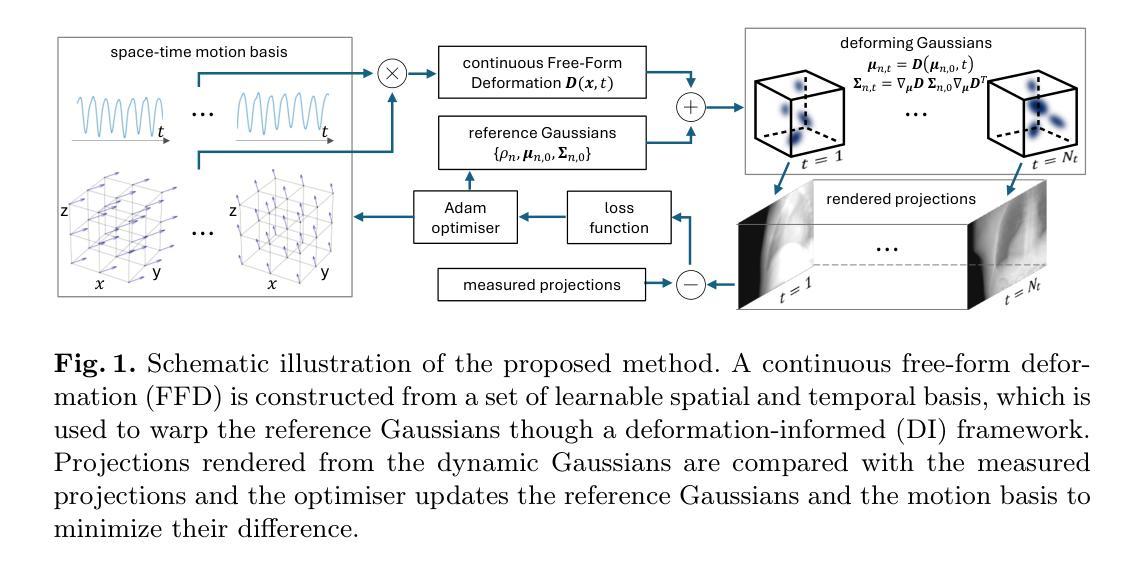
3D Cone-Beam CT (CBCT) is widely used in radiotherapy but suffers from motion artifacts due to breathing. A common clinical approach mitigates this by sorting projections into respiratory phases and reconstructing images per phase, but this does not account for breathing variability. Dynamic CBCT instead reconstructs images at each projection, capturing continuous motion without phase sorting. Recent advancements in 4D Gaussian Splatting (4DGS) offer powerful tools for modeling dynamic scenes, yet their application to dynamic CBCT remains underexplored. Existing 4DGS methods, such as HexPlane, use implicit motion representations, which are computationally expensive. While explicit low-rank motion models have been proposed, they lack spatial regularization, leading to inconsistencies in Gaussian motion. To address these limitations, we introduce a free-form deformation (FFD)-based spatial basis function and a deformation-informed framework that enforces consistency by coupling the temporal evolution of Gaussian’s mean position, scale, and rotation under a unified deformation field. We evaluate our approach on six CBCT datasets, demonstrating superior image quality with a 6x speedup over HexPlane. These results highlight the potential of deformation-informed 4DGS for efficient, motion-compensated CBCT reconstruction. The code is available at https://github.com/Yuliang-Huang/DIGS.
三维锥形束CT(CBCT)在放射治疗中得到广泛应用,但由于呼吸产生的运动伪影而受到影响。一种常见的临床方法是按呼吸阶段对投影进行排序,并按阶段重建图像,但这并没有考虑到呼吸变化。动态CBCT则会在每个投影时重建图像,捕捉连续运动而无需进行阶段排序。最近,四维高斯描画(4DGS)在模拟动态场景方面的进展提供了强大的工具,但其应用于动态CBCT仍被探索不足。现有的4DGS方法(如HexPlane)使用隐式运动表示,计算成本高昂。虽然已提出显式的低秩运动模型,但它们缺乏空间正则化,导致高斯运动的不一致性。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入基于自由形式变形(FFD)的空间基函数和变形信息框架,通过耦合高斯均值位置、尺度和旋转的暂时演变,在统一变形场下强制执行一致性。我们在六个CBCT数据集上评估了我们的方法,证明其图像质量优越,相对于HexPlane有6倍的加速效果。这些结果突出了变形信息4DGS在高效、运动补偿CBCT重建中的潜力。代码可在https://github.com/Yuliang-Huang/DIGS找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by MICCAI 2025
Summary
本文介绍了动态三维锥形束计算机断层扫描(CBCT)技术中的运动补偿问题。文章提出了一种基于自由变形(FFD)的空间基函数和变形信息框架,用于解决现有四维高斯喷绘(4DGS)方法在动态CBCT重建中的局限性。新方法通过统一变形场耦合高斯均值位置、尺度和旋转的暂时演变,实现了运动补偿,提高了图像质量,并在六个CBCT数据集上进行了验证。
Key Takeaways
- 3D Cone-Beam CT (CBCT) 在放射治疗中的广泛应用及其因呼吸运动产生的运动伪影问题。
- 现有临床方法通过按呼吸阶段排序投影并对每个阶段进行图像重建来减轻运动伪影,但不考虑呼吸变化性。
- 动态CBCT技术能够在每个投影时重建图像,捕捉连续运动,无需阶段排序。
- 四维高斯喷绘(4DGS)在建模动态场景方面的最新进展及其在动态CBCT中的应用尚未得到充分探索。
- 现有4DGS方法(如HexPlane)使用隐式运动表示,计算成本高。
- 显式低秩运动模型虽提出,但缺乏空间正则化,导致高斯运动不一致。
- 本文介绍了一种基于自由形式变形(FFD)的空间基函数和变形信息框架,以解决上述问题。
- 该方法在六个CBCT数据集上进行了评估,显示出图像质量优势,相对于HexPlane有6倍的速度提升。
- 变形信息框架通过耦合高斯的均值位置、尺度和旋转的暂时演变,在统一变形场下实现运动补偿。
点此查看论文截图

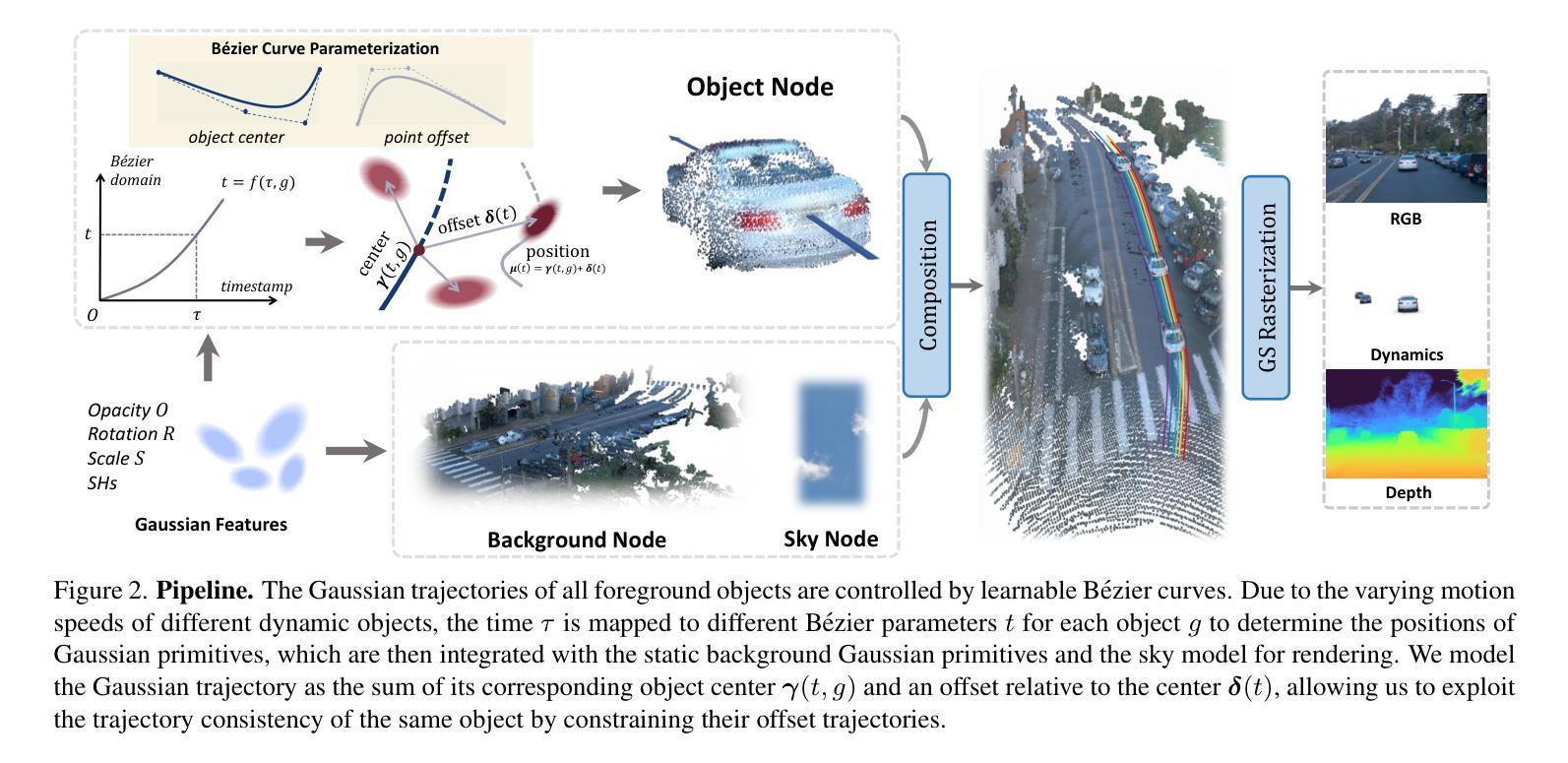
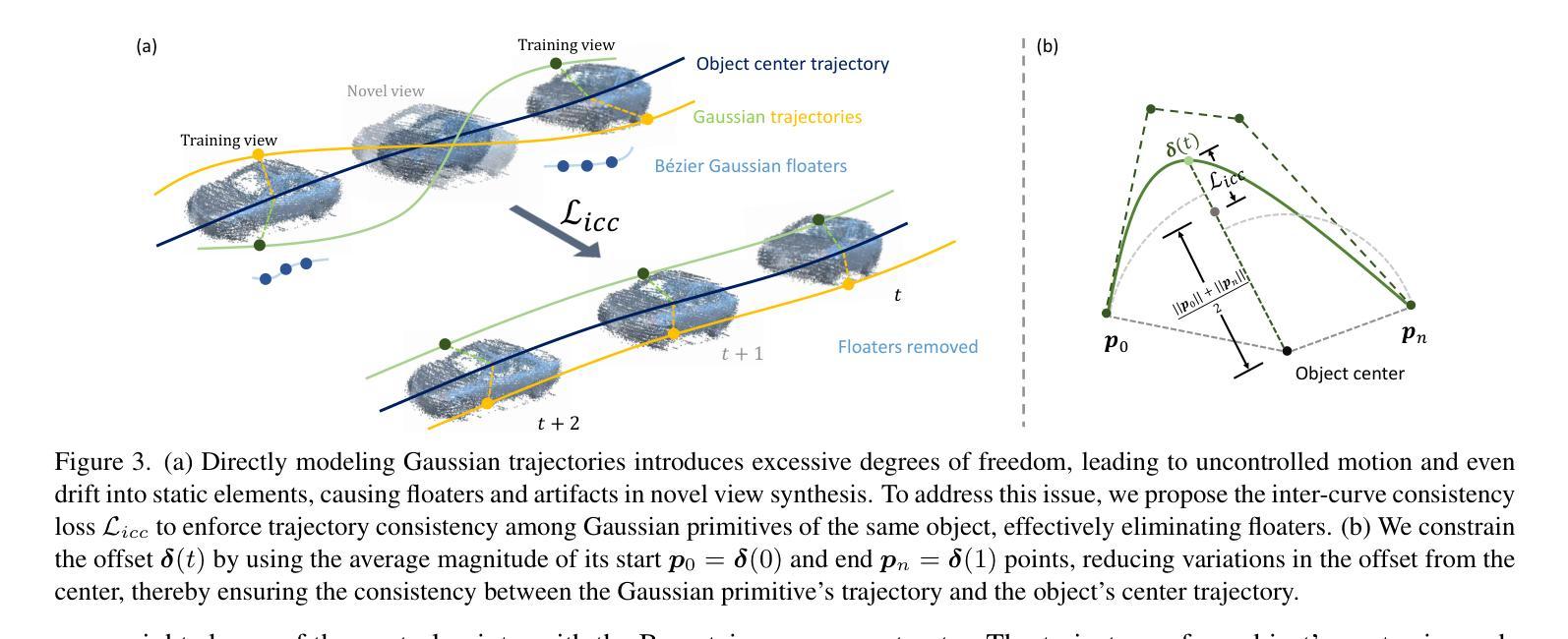
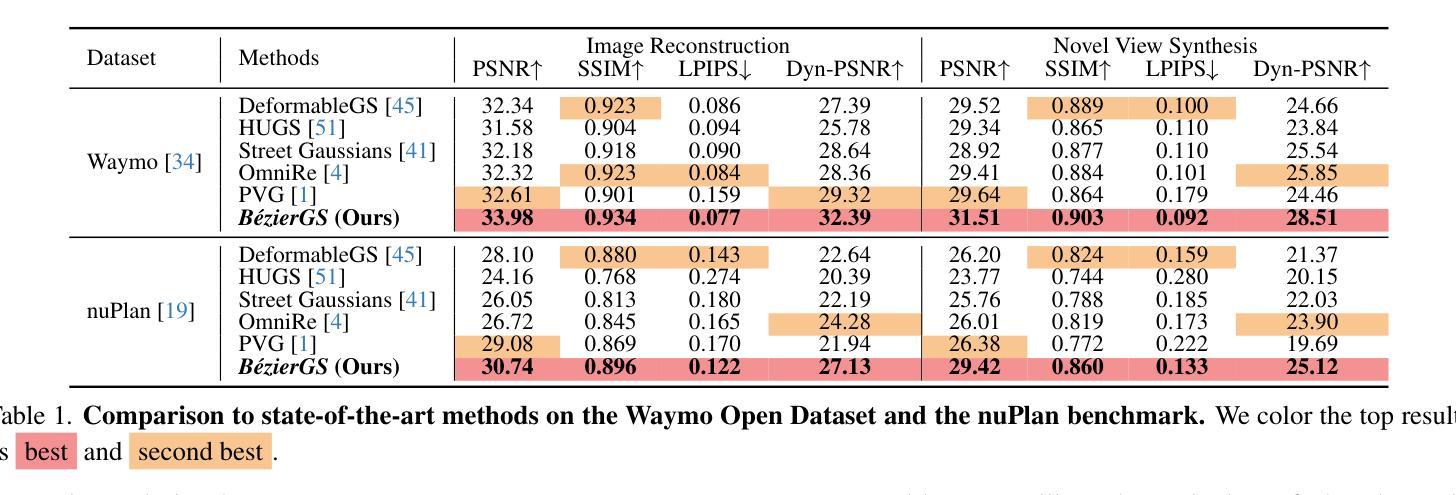
BézierGS: Dynamic Urban Scene Reconstruction with Bézier Curve Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Zipei Ma, Junzhe Jiang, Yurui Chen, Li Zhang
The realistic reconstruction of street scenes is critical for developing real-world simulators in autonomous driving. Most existing methods rely on object pose annotations, using these poses to reconstruct dynamic objects and move them during the rendering process. This dependence on high-precision object annotations limits large-scale and extensive scene reconstruction. To address this challenge, we propose B'ezier curve Gaussian splatting (B'ezierGS), which represents the motion trajectories of dynamic objects using learnable B'ezier curves. This approach fully leverages the temporal information of dynamic objects and, through learnable curve modeling, automatically corrects pose errors. By introducing additional supervision on dynamic object rendering and inter-curve consistency constraints, we achieve reasonable and accurate separation and reconstruction of scene elements. Extensive experiments on the Waymo Open Dataset and the nuPlan benchmark demonstrate that B'ezierGS outperforms state-of-the-art alternatives in both dynamic and static scene components reconstruction and novel view synthesis.
在现实世界中重建街道场景对于开发自动驾驶模拟器至关重要。现有的大多数方法都依赖于物体姿态标注,利用这些姿态来重建动态物体并在渲染过程中移动它们。对高精度物体标注的依赖限制了大规模和广泛的场景重建。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了使用Bezier曲线高斯拼贴(BezierGS)的方法,该方法使用可学习的Bezier曲线表示动态物体的运动轨迹。这种方法充分利用了动态物体的时间信息,并通过可学习的曲线模型自动校正姿态误差。通过对动态对象渲染引入额外的监督以及曲线间一致性约束,我们实现了场景元素的合理准确分离和重建。在Waymo Open Dataset和nuPlan基准测试的大量实验表明,BezierGS在动态和静态场景组件的重建以及新视角合成方面均优于最新替代方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICCV 2025, Project Page: https://github.com/fudan-zvg/BezierGS
Summary
本文提出了利用Bézier曲线高斯喷涂技术(BézierGS)来解决自主驾驶模拟器中的大规模场景重建问题。该方法利用可学习的Bézier曲线表示动态物体的运动轨迹,并利用时间信息自动校正姿态误差。通过引入动态对象渲染的附加监督以及曲线间的一致性约束,实现了场景元素的合理准确分离和重建。在Waymo公开数据集和nuPlan基准测试中,BézierGS在动态和静态场景组件重建以及新颖视图合成方面均优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 真实街道场景的重建对于自主驾驶模拟器的发展至关重要。
- 当前方法依赖于高精度对象姿态注释,这限制了大规模场景重建。
- Bézier曲线高斯喷涂技术(BézierGS)被提出用于解决这一问题。
- BézierGS利用可学习的Bézier曲线表示动态物体的运动轨迹。
- BézierGS充分利用动态物体的时间信息,并自动校正姿态误差。
- 通过引入附加监督和曲线间一致性约束,实现了场景元素的准确分离和重建。
点此查看论文截图

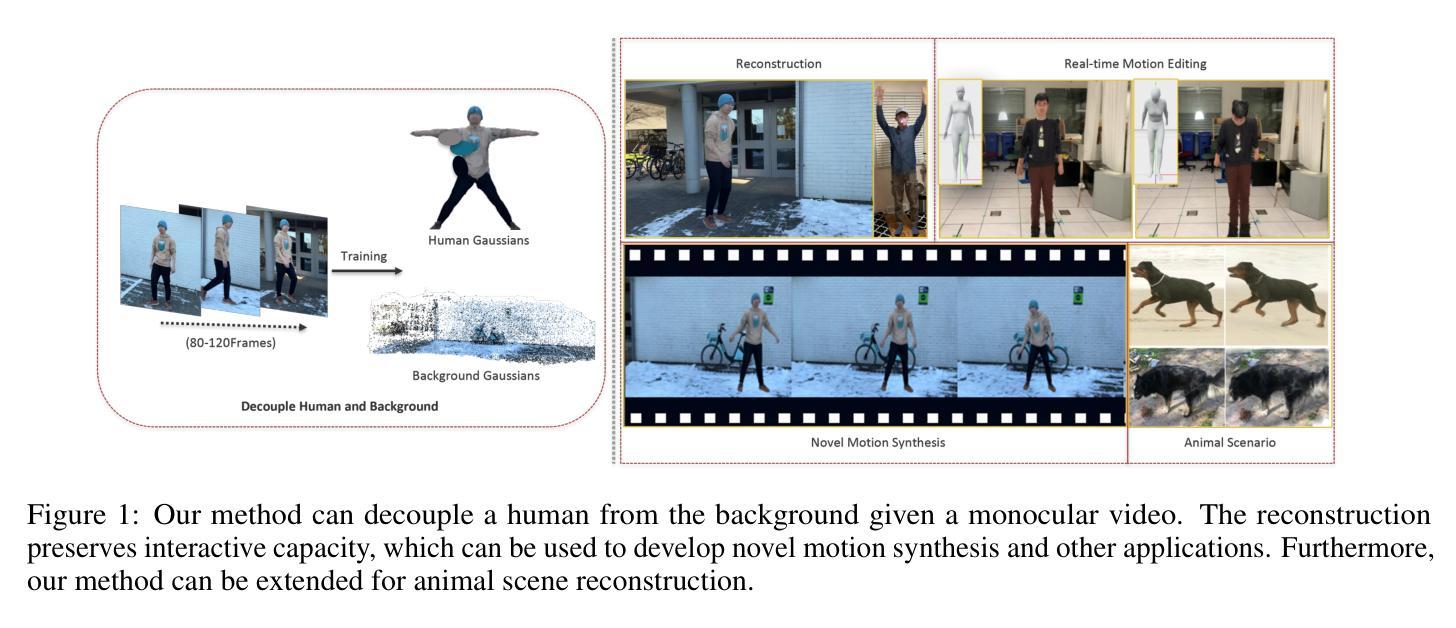
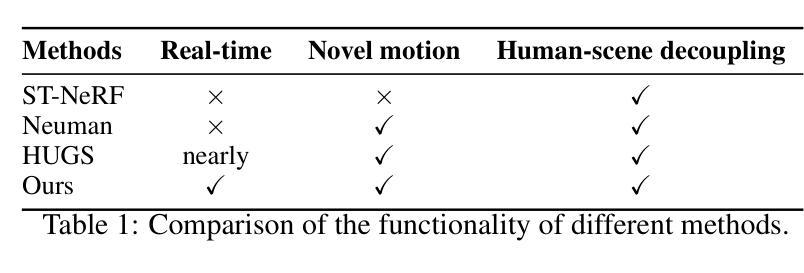
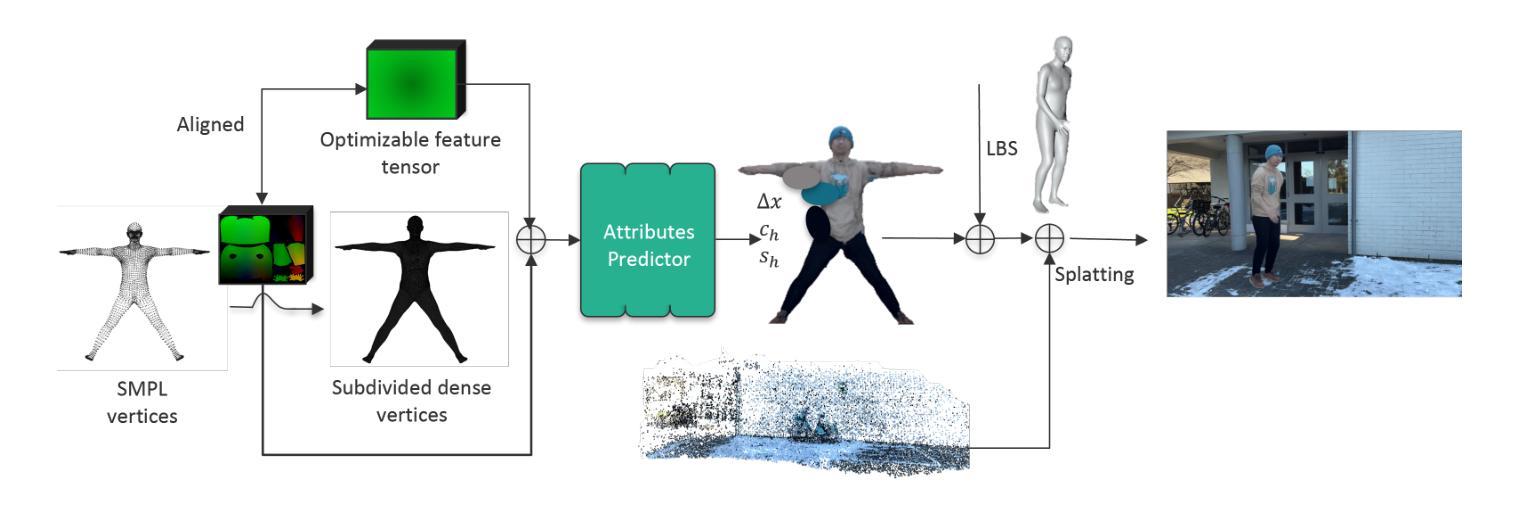
SkinningGS: Editable Dynamic Human Scene Reconstruction Using Gaussian Splatting Based on a Skinning Model
Authors:Da Li, Donggang Jia, Markus Hadwiger, Ivan Viola
Reconstructing an interactive human avatar and the background from a monocular video of a dynamic human scene is highly challenging. In this work we adopt a strategy of point cloud decoupling and joint optimization to achieve the decoupled reconstruction of backgrounds and human bodies while preserving the interactivity of human motion. We introduce a position texture to subdivide the Skinned Multi-Person Linear (SMPL) body model’s surface and grow the human point cloud. To capture fine details of human dynamics and deformations, we incorporate a convolutional neural network structure to predict human body point cloud features based on texture. This strategy makes our approach free of hyperparameter tuning for densification and efficiently represents human points with half the point cloud of HUGS. This approach ensures high-quality human reconstruction and reduces GPU resource consumption during training. As a result, our method surpasses the previous state-of-the-art HUGS in reconstruction metrics while maintaining the ability to generalize to novel poses and views. Furthermore, our technique achieves real-time rendering at over 100 FPS, $\sim$6$\times$ the HUGS speed using only Linear Blend Skinning (LBS) weights for human transformation. Additionally, this work demonstrates that this framework can be extended to animal scene reconstruction when an accurately-posed model of an animal is available.
从动态人体场景的单目视频中重建一个交互式的虚拟人物和其背景是一项非常大的挑战。在这项工作中,我们采用了点云解耦和联合优化的策略,实现了背景和人体之间的解耦重建,同时保留了人体运动的交互性。我们引入了一种位置纹理,以细分皮肤多人线性(SMPL)人体模型的表面并扩大人体点云。为了捕捉人体动态和变形的细节,我们采用了一种卷积神经网络结构,基于纹理预测人体点云特征。这一策略使我们的方法免去了对稠化的超参数调整,并使用一半的点云高效地表示了人体点。这种方法保证了高质量的人体重建,并降低了训练过程中的GPU资源消耗。因此,我们的方法在重建指标上超越了之前的先进HUGS技术,同时保持了对新型姿势和视角的泛化能力。此外,我们的技术实现了超过100FPS的实时渲染,仅使用线性混合蒙皮(LBS)权重进行人类变换,大约是HUGS速度的6倍。另外,这项工作证明,当提供准确的动物模型时,该框架可以扩展到动物场景的重建。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文介绍了一种基于点云解耦和联合优化的策略,实现从动态人类场景的单目视频中重建交互式人类角色和背景。通过引入位置纹理和卷积神经网络结构,实现了高质量的人类重建,同时降低了GPU资源消耗,并超越了现有技术。此外,该方法可实现实时渲染,速度远超现有技术,并可扩展至动物场景重建。
Key Takeaways
- 采用点云解耦和联合优化策略,实现背景和人体角色的解耦重建,同时保持人类动作的交互性。
- 引入位置纹理技术,用于细分SMPL人体模型的表面并扩展人体点云,捕捉人类动态和变形的细节。
- 结合卷积神经网络结构,基于纹理预测人体点云特征,使方法摆脱了对密集化的超参数调整需求。
- 该方法实现了高质量的人类重建,减少了GPU资源消耗,并超越了现有技术(HUGS)在重建指标上的表现。
- 方法能够推广到新型姿态和视角的泛化能力。
- 实现实时渲染,速度超过100 FPS,是使用线性混合皮肤权重(LBS)进行人类转换的HUGS速度的约6倍。
点此查看论文截图

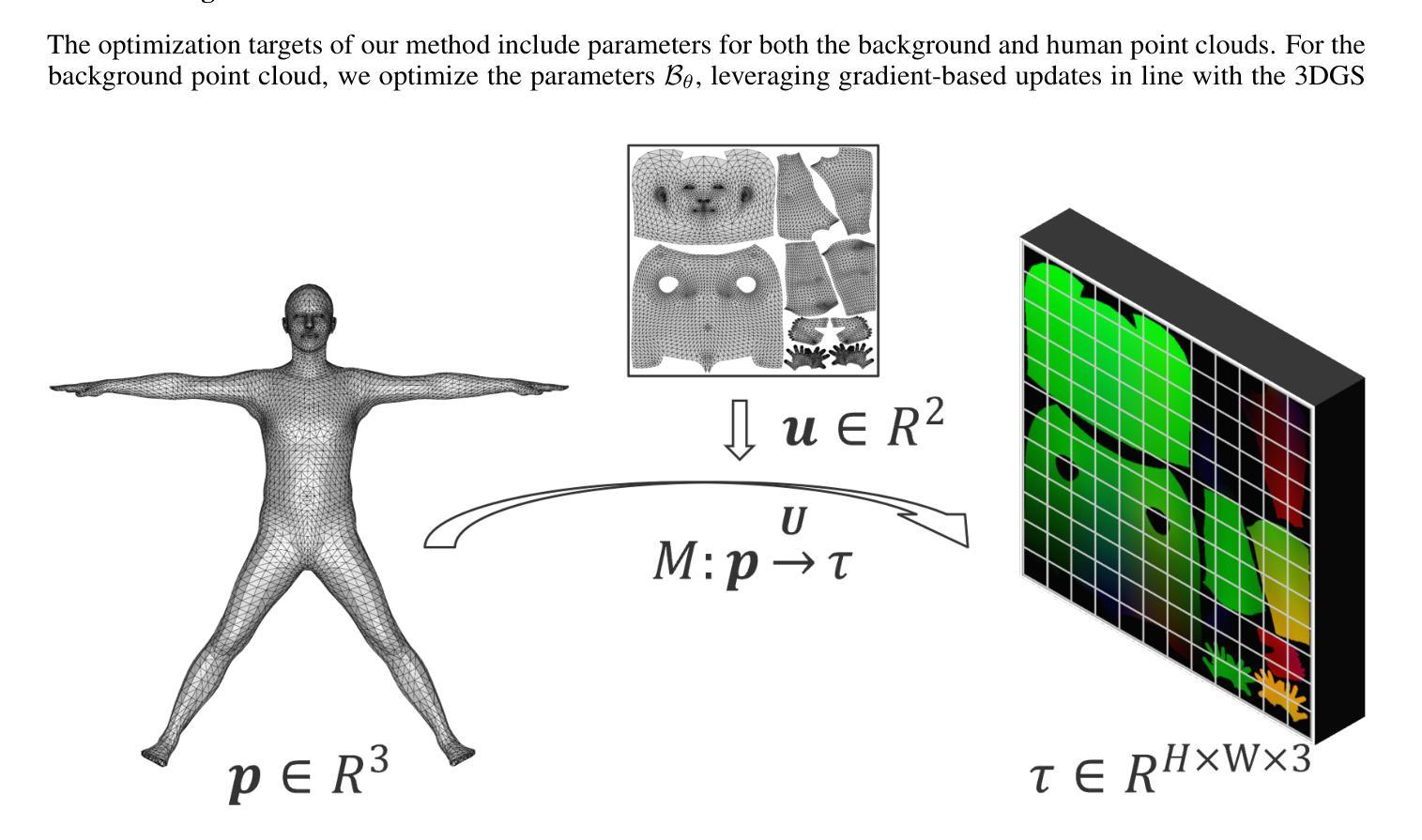
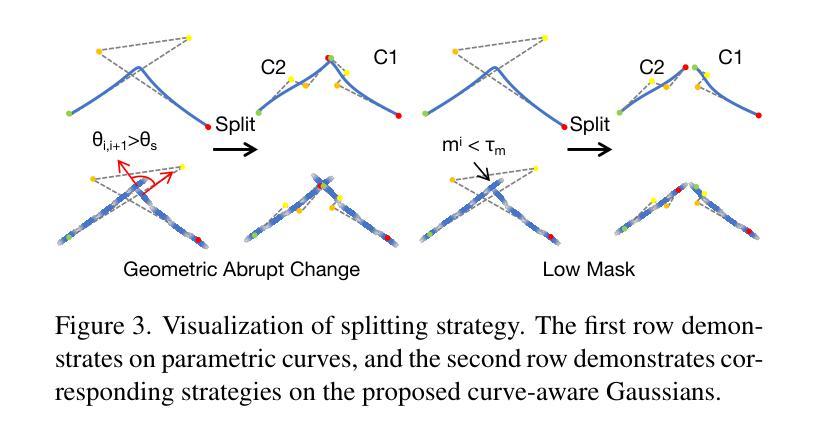
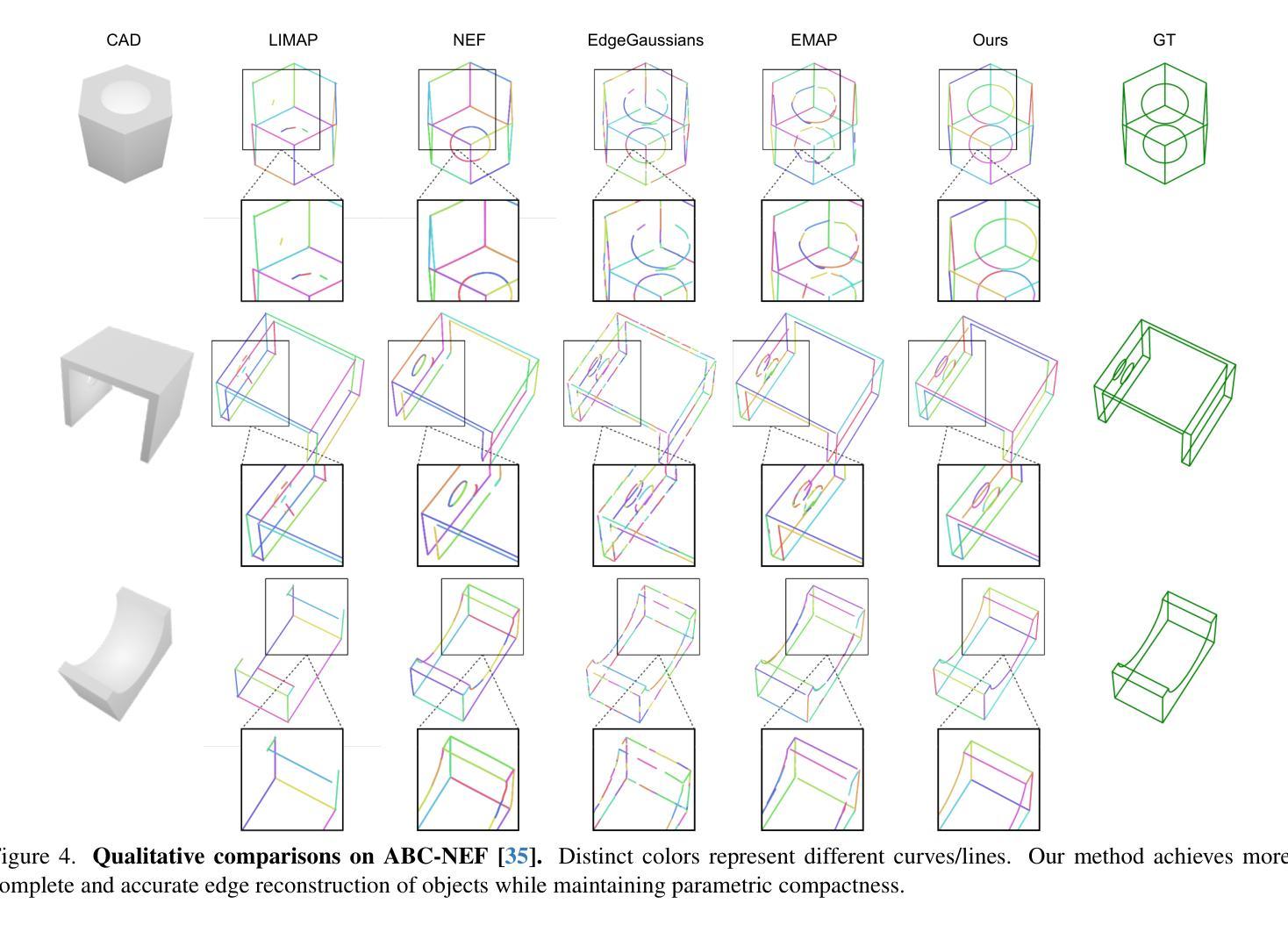
Curve-Aware Gaussian Splatting for 3D Parametric Curve Reconstruction
Authors:Zhirui Gao, Renjiao Yi, Yaqiao Dai, Xuening Zhu, Wei Chen, Chenyang Zhu, Kai Xu
This paper presents an end-to-end framework for reconstructing 3D parametric curves directly from multi-view edge maps. Contrasting with existing two-stage methods that follow a sequential ``edge point cloud reconstruction and parametric curve fitting’’ pipeline, our one-stage approach optimizes 3D parametric curves directly from 2D edge maps, eliminating error accumulation caused by the inherent optimization gap between disconnected stages. However, parametric curves inherently lack suitability for rendering-based multi-view optimization, necessitating a complementary representation that preserves their geometric properties while enabling differentiable rendering. We propose a novel bi-directional coupling mechanism between parametric curves and edge-oriented Gaussian components. This tight correspondence formulates a curve-aware Gaussian representation, \textbf{CurveGaussian}, that enables differentiable rendering of 3D curves, allowing direct optimization guided by multi-view evidence. Furthermore, we introduce a dynamically adaptive topology optimization framework during training to refine curve structures through linearization, merging, splitting, and pruning operations. Comprehensive evaluations on the ABC dataset and real-world benchmarks demonstrate our one-stage method’s superiority over two-stage alternatives, particularly in producing cleaner and more robust reconstructions. Additionally, by directly optimizing parametric curves, our method significantly reduces the parameter count during training, achieving both higher efficiency and superior performance compared to existing approaches.
本文提出了一种端到端的框架,可直接从多视角边缘地图重建3D参数曲线。与现有的两阶段方法(遵循“边缘点云重建和参数曲线拟合”的流水线)形成对比,我们的单阶段方法直接从二维边缘地图优化三维参数曲线,消除了由于不同阶段之间固有的优化间隔所导致的误差累积。然而,参数曲线在基于渲染的多视角优化方面存在固有的局限性,因此需要一种能够保留其几何属性同时实现可微分渲染的互补表示。我们提出了参数曲线和边缘定向高斯组件之间的新型双向耦合机制。这种紧密对应关系形成了一种曲线感知高斯表示(CurveGaussian),它能够实现三维曲线的可微分渲染,允许直接优化以多视角证据为指导。此外,我们在训练过程中引入了一个动态自适应拓扑优化框架,通过线性化、合并、分割和修剪操作来完善曲线结构。在ABC数据集和现实世界基准测试上的综合评估表明,我们的单阶段方法在多个方面优于两阶段方法,尤其是在生成更干净、更稳健的重建方面表现优越。此外,通过直接优化参数曲线,我们的方法在训练期间大大减少了参数计数,与现有方法相比实现了更高的效率和性能提升。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025 Code: https://github.com/zhirui-gao/Curve-Gaussian
Summary
该论文提出一种端到端的框架,能够从多视角边缘地图直接重建3D参数曲线。不同于现有的两阶段方法(依次进行边缘点云重建和参数曲线拟合),我们的单阶段方法直接从2D边缘地图优化3D参数曲线,避免了因阶段间优化差距导致的误差累积。为克服参数曲线在基于渲染的多视角优化中的不适用性问题,我们提出了一种新型的双向耦合机制,将参数曲线与边缘定向高斯组件相结合。这种紧密对应关系形成了一种曲线感知的高斯表示(CurveGaussian),能够实现3D曲线的可微渲染,并可直接由多视角证据进行优化指导。此外,我们还引入了一个动态自适应拓扑优化框架,在训练过程中通过线性化、合并、拆分和修剪操作来优化曲线结构。在ABC数据集和真实世界基准测试上的综合评估表明,我们的单阶段方法优于两阶段方法,特别是在产生更干净、更稳健的重建结果方面。此外,通过直接优化参数曲线,我们的方法在训练过程中减少了参数数量,提高了效率并超越了现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种端到端的框架,直接从多视角边缘地图重建3D参数曲线。
- 与两阶段方法相比,减少了误差累积。
- 引入了参数曲线和边缘定向高斯组件的双向耦合机制,形成了曲线感知的高斯表示(CurveGaussian)。
- 实现了3D曲线的可微渲染,可直接由多视角证据进行优化指导。
- 提出了动态自适应拓扑优化框架,在训练过程中优化曲线结构。
- 在ABC数据集和真实世界基准测试上表现出优越性能。
点此查看论文截图

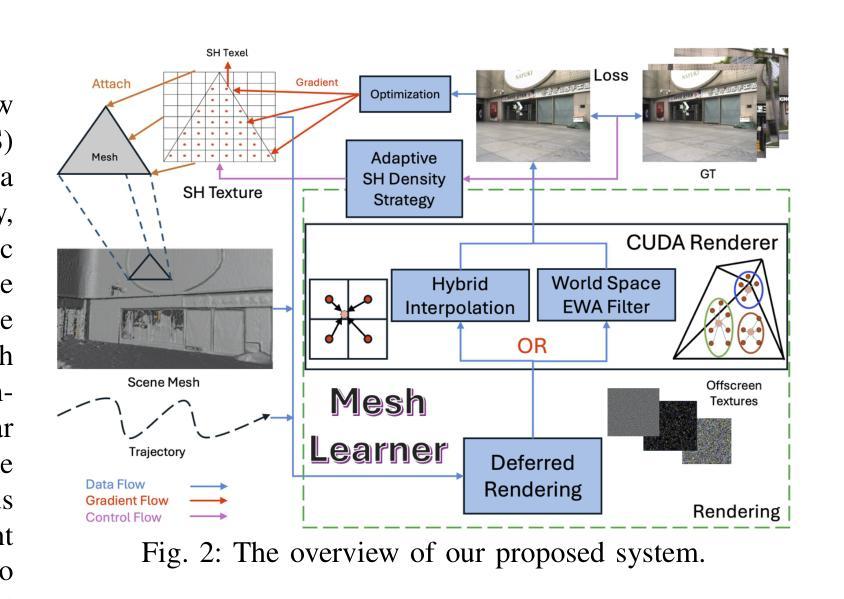
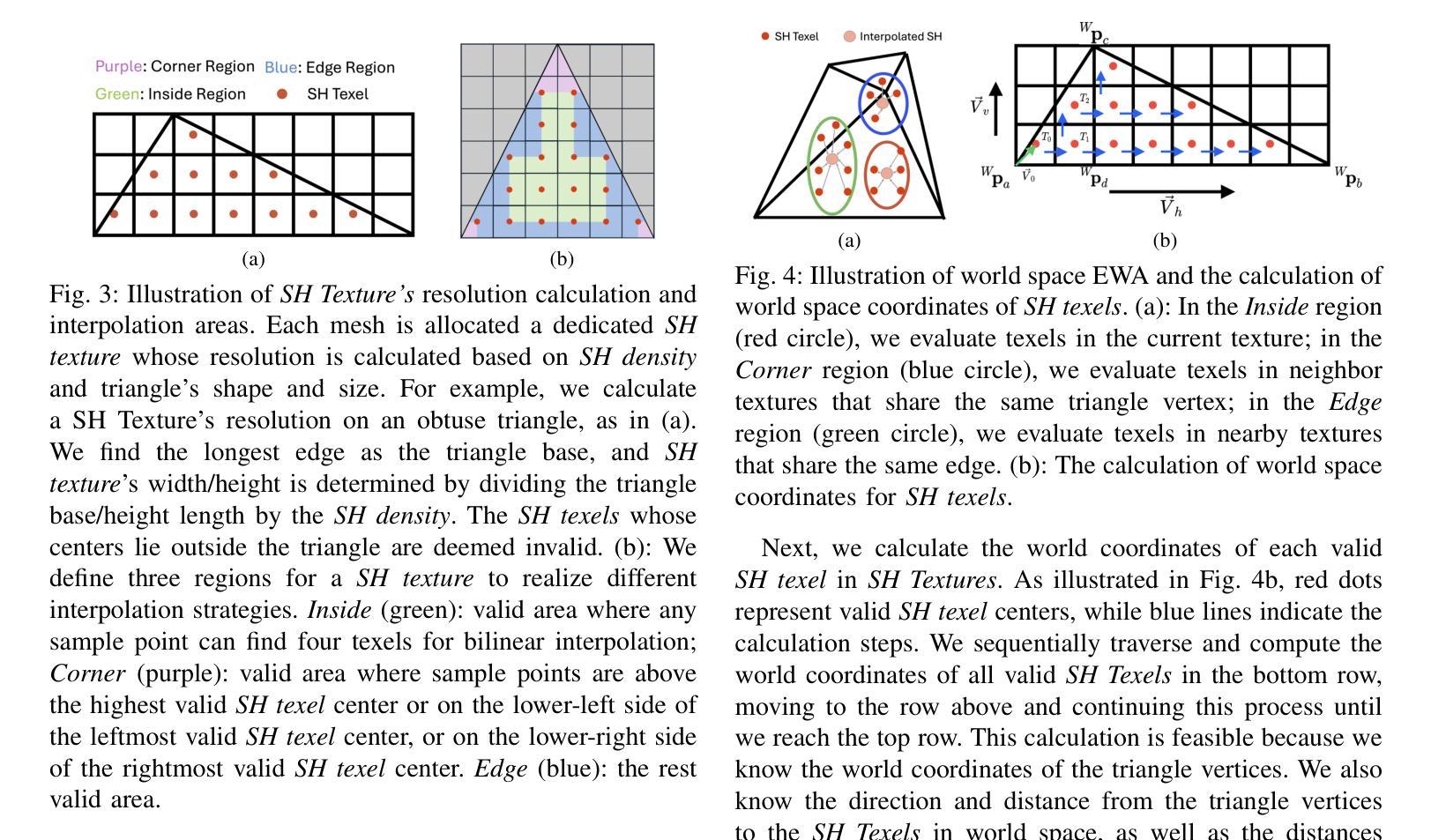
Mesh-Learner: Texturing Mesh with Spherical Harmonics
Authors:Yunfei Wan, Jianheng Liu, Chunran Zheng, Jiarong Lin, Fu Zhang
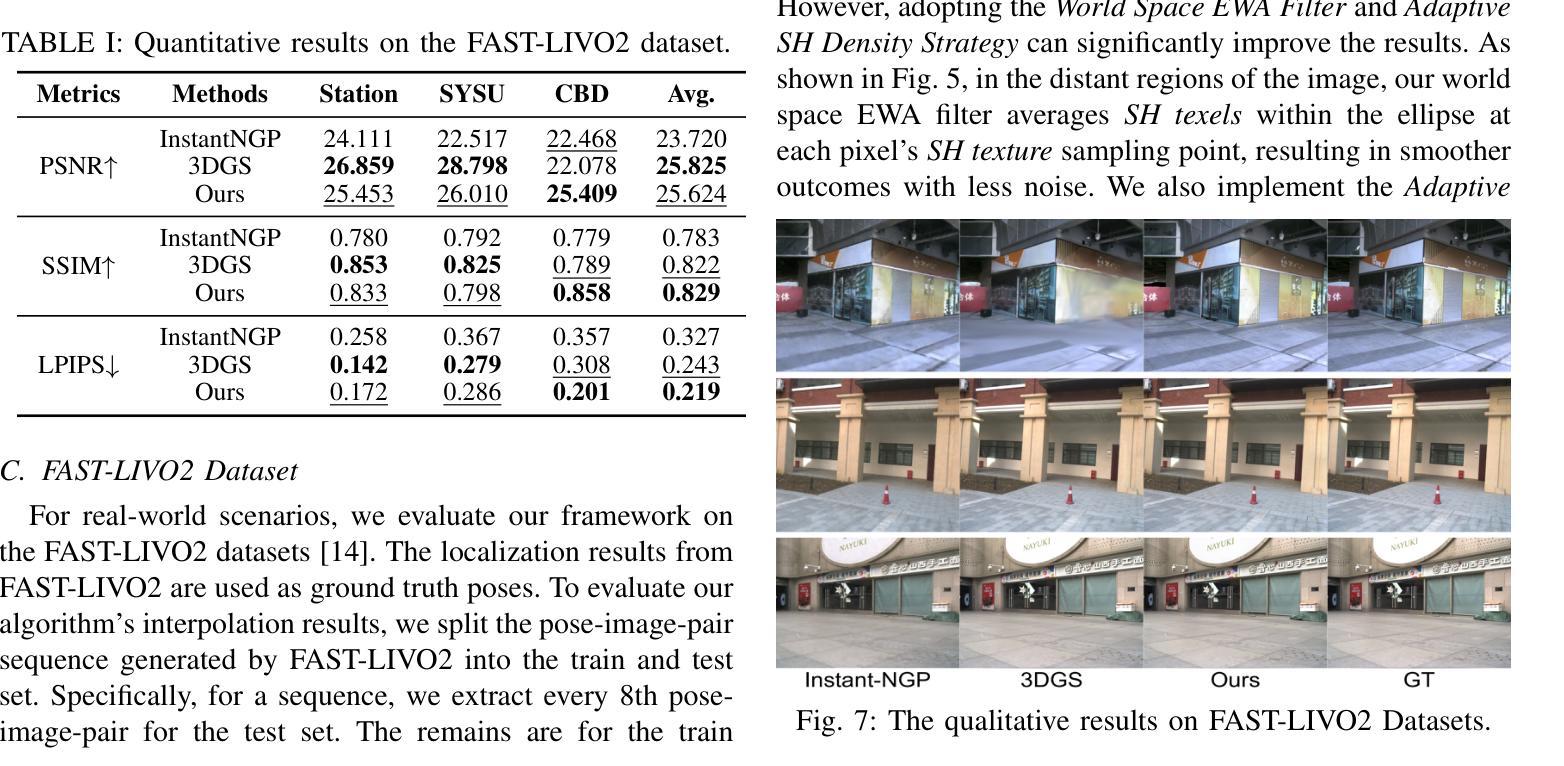
In this paper, we present a 3D reconstruction and rendering framework termed Mesh-Learner that is natively compatible with traditional rasterization pipelines. It integrates mesh and spherical harmonic (SH) texture (i.e., texture filled with SH coefficients) into the learning process to learn each mesh s view-dependent radiance end-to-end. Images are rendered by interpolating surrounding SH Texels at each pixel s sampling point using a novel interpolation method. Conversely, gradients from each pixel are back-propagated to the related SH Texels in SH textures. Mesh-Learner exploits graphic features of rasterization pipeline (texture sampling, deferred rendering) to render, which makes Mesh-Learner naturally compatible with tools (e.g., Blender) and tasks (e.g., 3D reconstruction, scene rendering, reinforcement learning for robotics) that are based on rasterization pipelines. Our system can train vast, unlimited scenes because we transfer only the SH textures within the frustum to the GPU for training. At other times, the SH textures are stored in CPU RAM, which results in moderate GPU memory usage. The rendering results on interpolation and extrapolation sequences in the Replica and FAST-LIVO2 datasets achieve state-of-the-art performance compared to existing state-of-the-art methods (e.g., 3D Gaussian Splatting and M2-Mapping). To benefit the society, the code will be available at https://github.com/hku-mars/Mesh-Learner.
本文介绍了一个名为Mesh-Learner的3D重建和渲染框架,它与传统光栅化流水线兼容。它集成了网格和球面谐波(SH)纹理(即填充SH系数的纹理)到学习过程中,以端到端的方式学习每个网格的视差相关辐射率。图像是通过一种新型插值方法,在每个像素采样点插值周围的SH纹理元素来呈现的。相反,每个像素的梯度会反向传播到相关的SH纹理中的SH纹理元素。Mesh-Learner利用光栅化流水线(纹理采样、延迟渲染)的图形特征进行渲染,这使得Mesh-Learner自然地与基于光栅化流水线的工具(例如Blender)和任务(例如3D重建、场景渲染、机器人强化学习)兼容。我们的系统可以训练大量无限的场景,因为我们将仅将视锥体内的SH纹理传输到GPU进行训练。在其他时间,SH纹理存储在CPU RAM中,这导致GPU内存使用适中。在Replica和FAST-LIVO2数据集上的插值和外推序列的渲染结果达到了与现有最先进方法(例如3D高斯溅射和M2-Mapping)相比的先进性能。为了造福社会,代码将在https://github.com/hku-mars/Mesh-Learner上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IROS2025 Accepted
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为Mesh-Learner的3D重建和渲染框架,该框架与传统的光线追踪渲染管线兼容。它通过整合网格和球面谐波纹理,实现了端到端的视图相关辐射率学习。采用新型插值方法为像素采样点插值渲染图像,同时梯度反向传播至相关的SH纹理。Mesh-Learner利用光线追踪渲染管线(纹理采样、延迟渲染)的特性进行渲染,使其自然地与基于光线追踪的工具和任务兼容。由于其仅传输视锥体内的SH纹理到GPU进行训练,因此可训练大规模无限场景。此外,它在Replica和FAST-LIVO2数据集上的渲染结果达到或超越了现有先进方法。相关代码将在https://github.com/hku-mars/Mesh-Learner上公开。
Key Takeaways
- Mesh-Learner框架融合了网格技术与球面谐波纹理,支持端到端的视图相关辐射率学习。
- 采用了新颖的像素插值方法和梯度反向传播技术。
- Mesh-Learner天然兼容传统光线追踪渲染管线,可融入现有工具和任务。
- 该框架能高效训练大规模、无限场景,通过仅传输视锥体内的SH纹理至GPU进行训练。
- SH纹理可存储在CPU RAM中,降低GPU内存使用。
- 在标准数据集上的渲染结果达到了先进水准。
点此查看论文截图




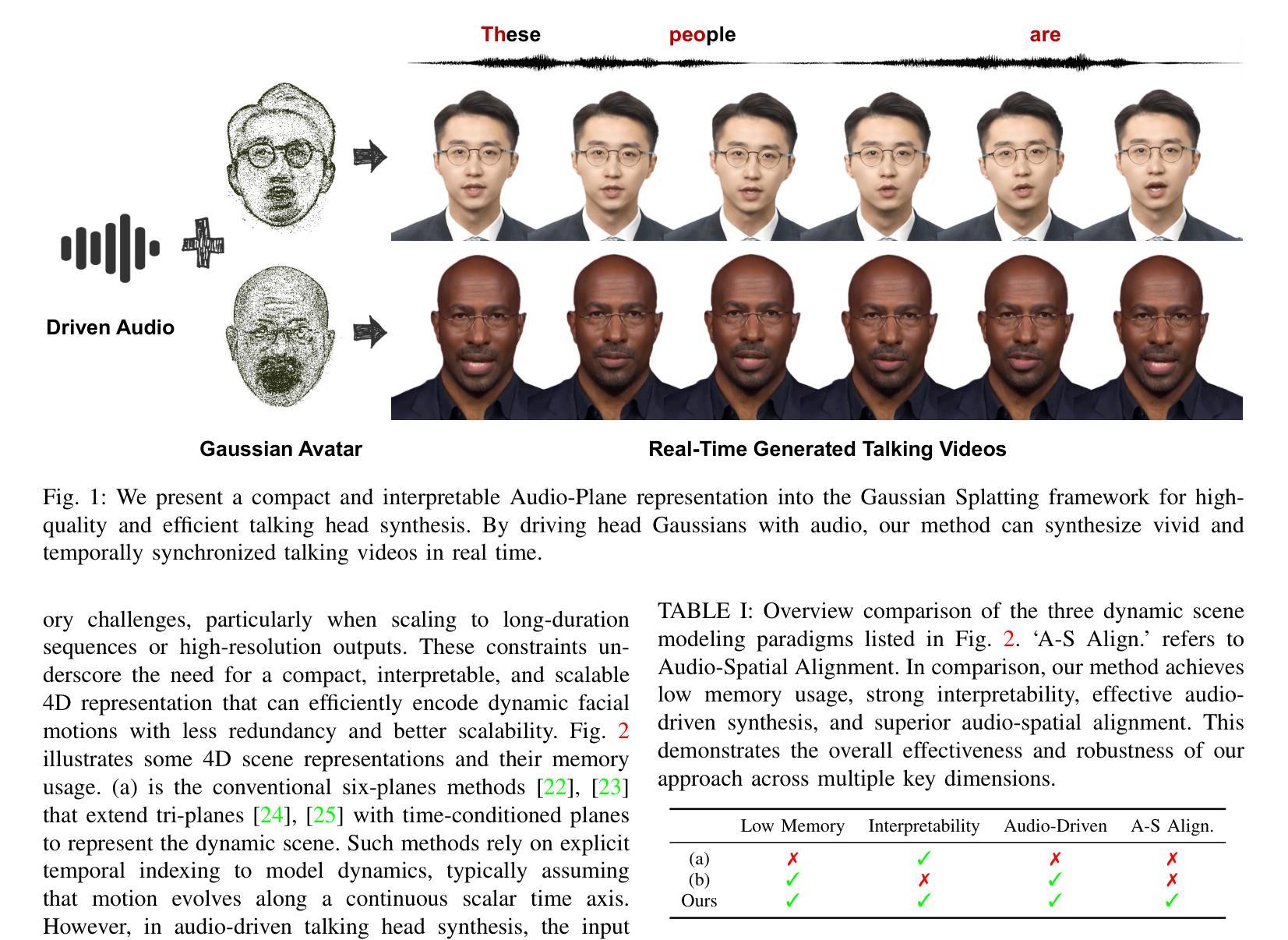
Audio-Plane: Audio Factorization Plane Gaussian Splatting for Real-Time Talking Head Synthesis
Authors:Shuai Shen, Wanhua Li, Yunpeng Zhang, Yap-Peng Tan, Jiwen Lu
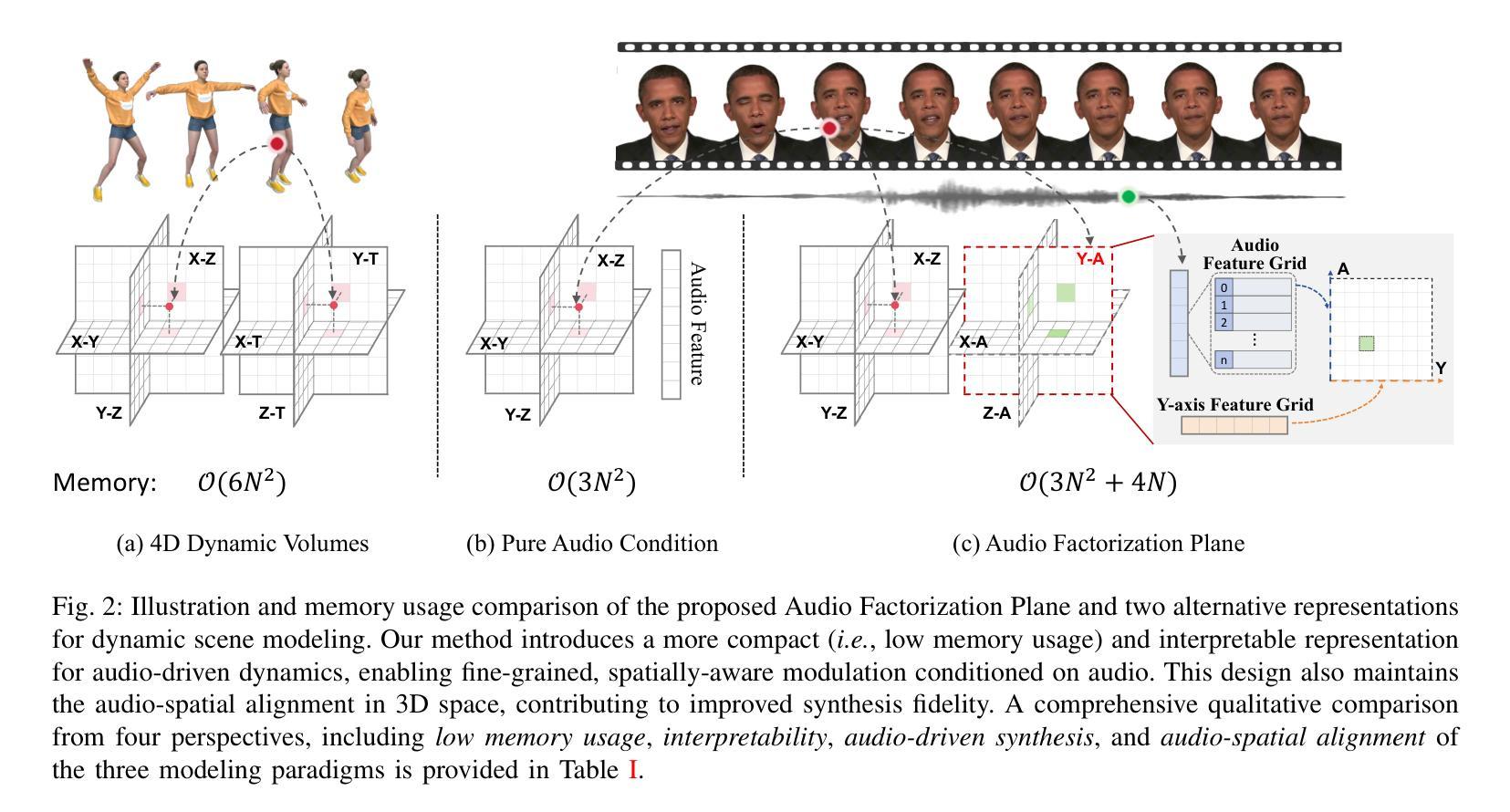
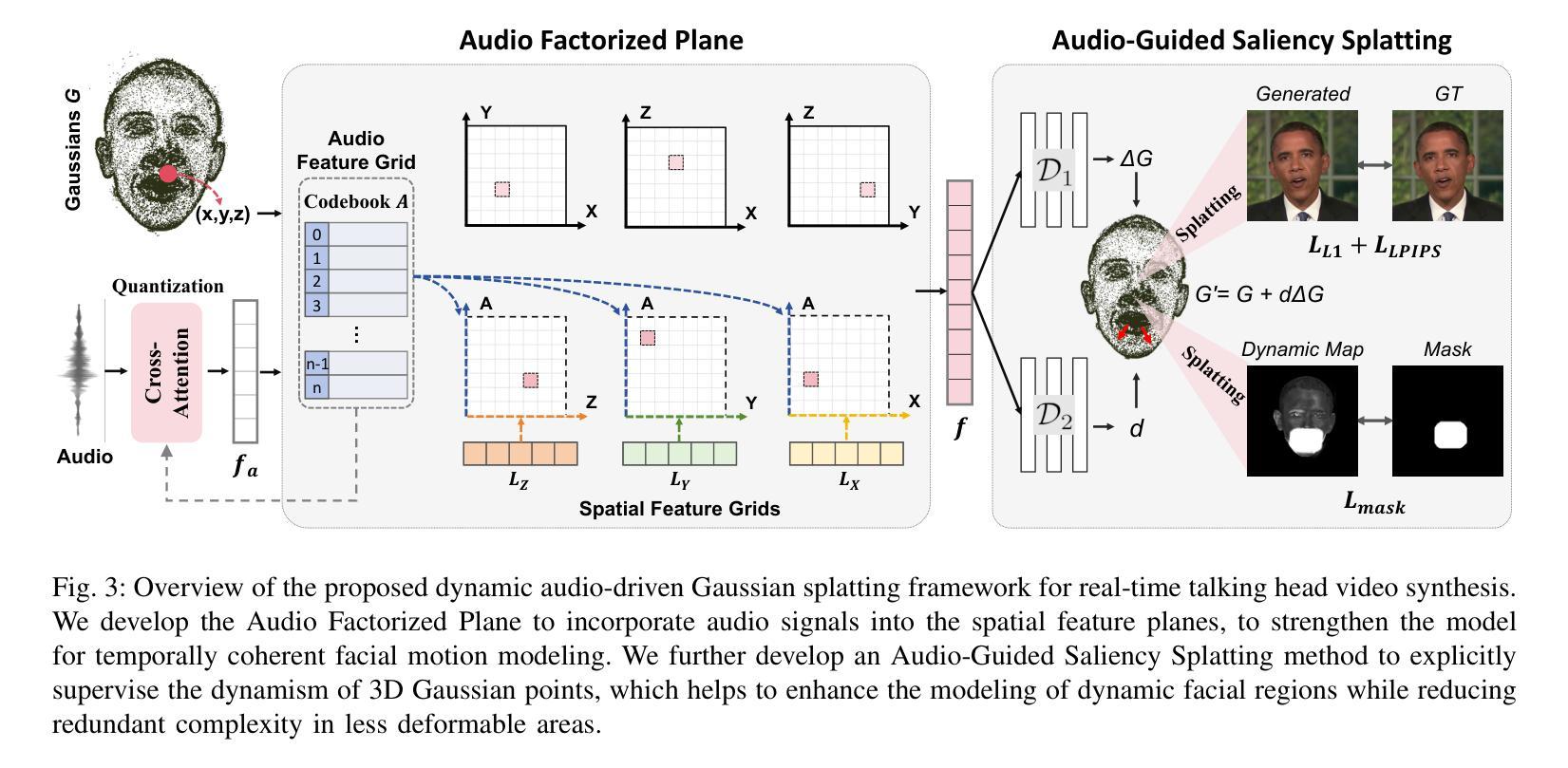
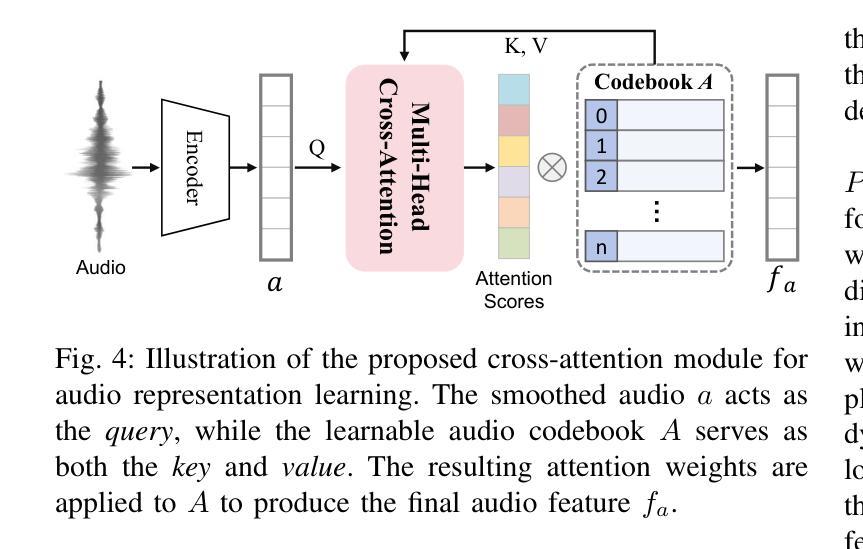
Talking head synthesis has emerged as a prominent research topic in computer graphics and multimedia, yet most existing methods often struggle to strike a balance between generation quality and computational efficiency, particularly under real-time constraints. In this paper, we propose a novel framework that integrates Gaussian Splatting with a structured Audio Factorization Plane (Audio-Plane) to enable high-quality, audio-synchronized, and real-time talking head generation. For modeling a dynamic talking head, a 4D volume representation, which consists of three axes in 3D space and one temporal axis aligned with audio progression, is typically required. However, directly storing and processing a dense 4D grid is impractical due to the high memory and computation cost, and lack of scalability for longer durations. We address this challenge by decomposing the 4D volume representation into a set of audio-independent spatial planes and audio-dependent planes, forming a compact and interpretable representation for talking head modeling that we refer to as the Audio-Plane. This factorized design allows for efficient and fine-grained audio-aware spatial encoding, and significantly enhances the model’s ability to capture complex lip dynamics driven by speech signals. To further improve region-specific motion modeling, we introduce an audio-guided saliency splatting mechanism based on region-aware modulation, which adaptively emphasizes highly dynamic regions such as the mouth area. This allows the model to focus its learning capacity on where it matters most for accurate speech-driven animation. Extensive experiments on both the self-driven and the cross-driven settings demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art visual quality, precise audio-lip synchronization, and real-time performance, outperforming prior approaches across both 2D- and 3D-based paradigms.
谈话头合成已成为计算机图形学和多媒体领域的一个重要研究课题,然而,大多数现有方法往往难以在生成质量和计算效率之间取得平衡,特别是在实时约束下。在本文中,我们提出了一个结合高斯Splatting和结构化的音频因子平面(Audio-Plane)的新型框架,以实现高质量、音频同步和实时的谈话头生成。为了模拟动态的谈话头,通常需要一个4D体积表示,该表示由三个空间轴和一个与音频进展对齐的时间轴组成。然而,由于直接存储和处理密集的4D网格存在内存和计算成本高以及长期缺乏可扩展性的问题,因此并不实用。我们通过将4D体积表示分解为一系列音频独立的平面和音频依赖的平面来解决这一挑战,形成了一种紧凑且可解释的谈话头模型表示,我们称之为Audio-Plane。这种因子化的设计允许高效且精细的音频感知空间编码,并显着提高了模型捕捉由语音信号驱动的复杂嘴唇动态的能力. 为了进一步改进特定区域的运动建模,我们引入了基于区域感知调制的音频引导显著性Splatting机制,该机制可自适应地强调高度动态的区域,如嘴巴区域。这使模型能够专注于最关键的区域,以实现精确的语言驱动动画。在自驱动和交叉驱动设置上的大量实验表明,我们的方法达到了最先进的视觉质量、精确的音频-嘴唇同步和实时性能,在2D和3D基于范式的方法中都优于先前的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Demo video at \url{https://sstzal.github.io/Audio-Plane/}
Summary
本文提出一种结合高斯涂斑技术和结构化音频因子平面(Audio-Plane)的新框架,实现了高质量、音频同步的实时头部生成。为解决直接处理密集4D网格带来的高内存和计算成本问题,采用音频独立的空间平面和音频依赖平面构成紧凑、可解释的头部模型表示。引入音频引导显著性涂斑机制,自适应强调高度动态区域,如口部区域,进一步提高区域特定运动建模。实验表明,该方法在自驱动和跨驱动设置中均实现最佳视觉质量、精确的音频-唇部同步和实时性能。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了结合高斯涂斑与结构化音频因子平面(Audio-Plane)的框架,实现高质量实时头部生成。
- 解决直接处理密集4D网格导致的高内存和计算成本问题。
- 采用音频独立的空间平面和音频依赖平面构成紧凑的头部模型表示,即Audio-Plane。
- 引入音频引导显著性涂斑机制,强调高度动态区域如口部区域。
- 方法实现了精确的音频-唇部同步。
- 在自驱动和跨驱动设置中均表现出优异的视觉质量和实时性能。
点此查看论文截图


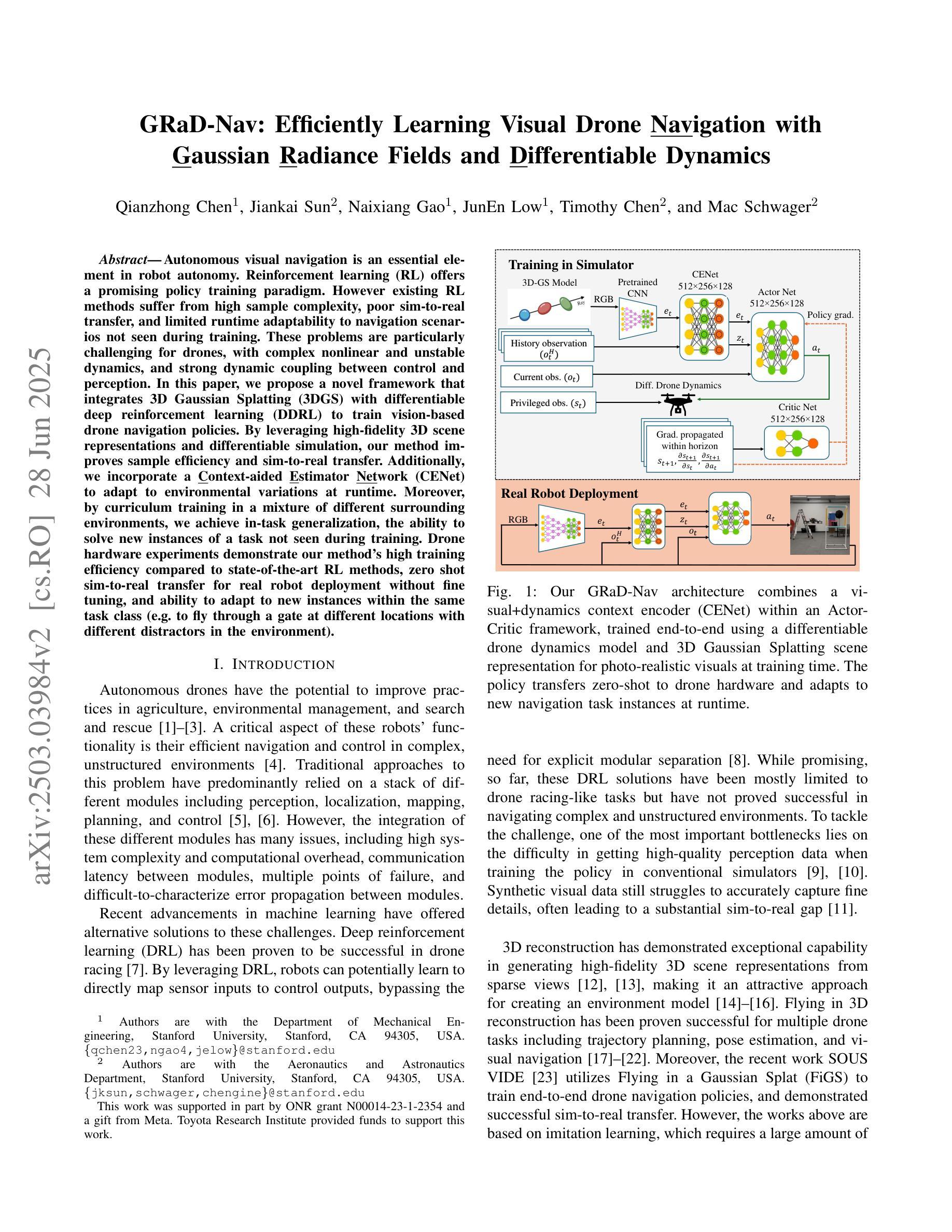
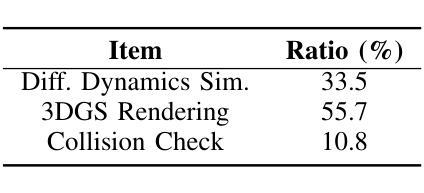
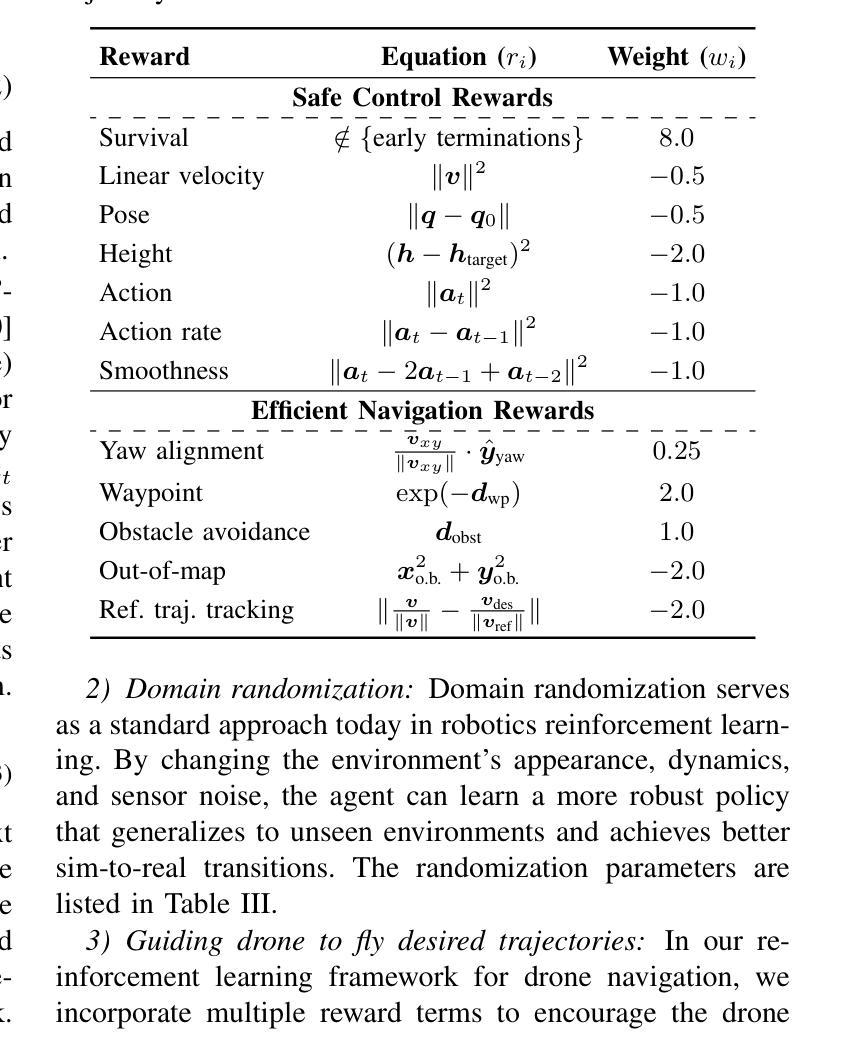
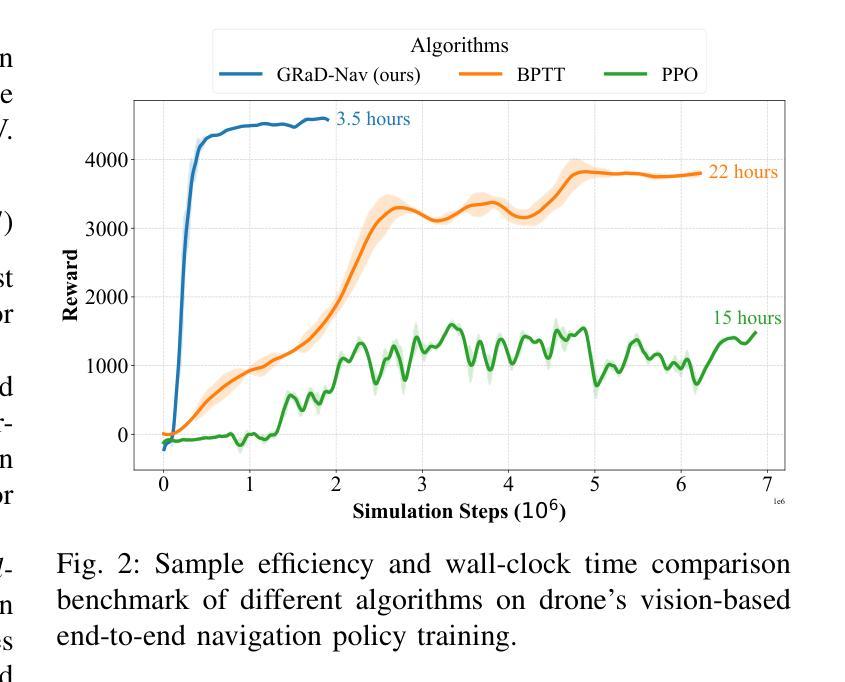
GRaD-Nav: Efficiently Learning Visual Drone Navigation with Gaussian Radiance Fields and Differentiable Dynamics
Authors:Qianzhong Chen, Jiankai Sun, Naixiang Gao, JunEn Low, Timothy Chen, Mac Schwager
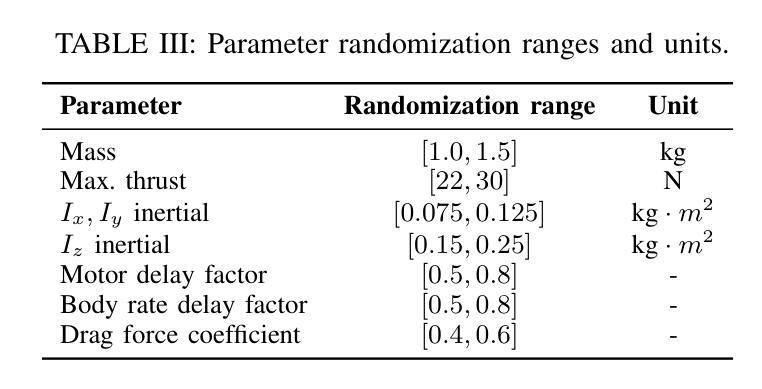
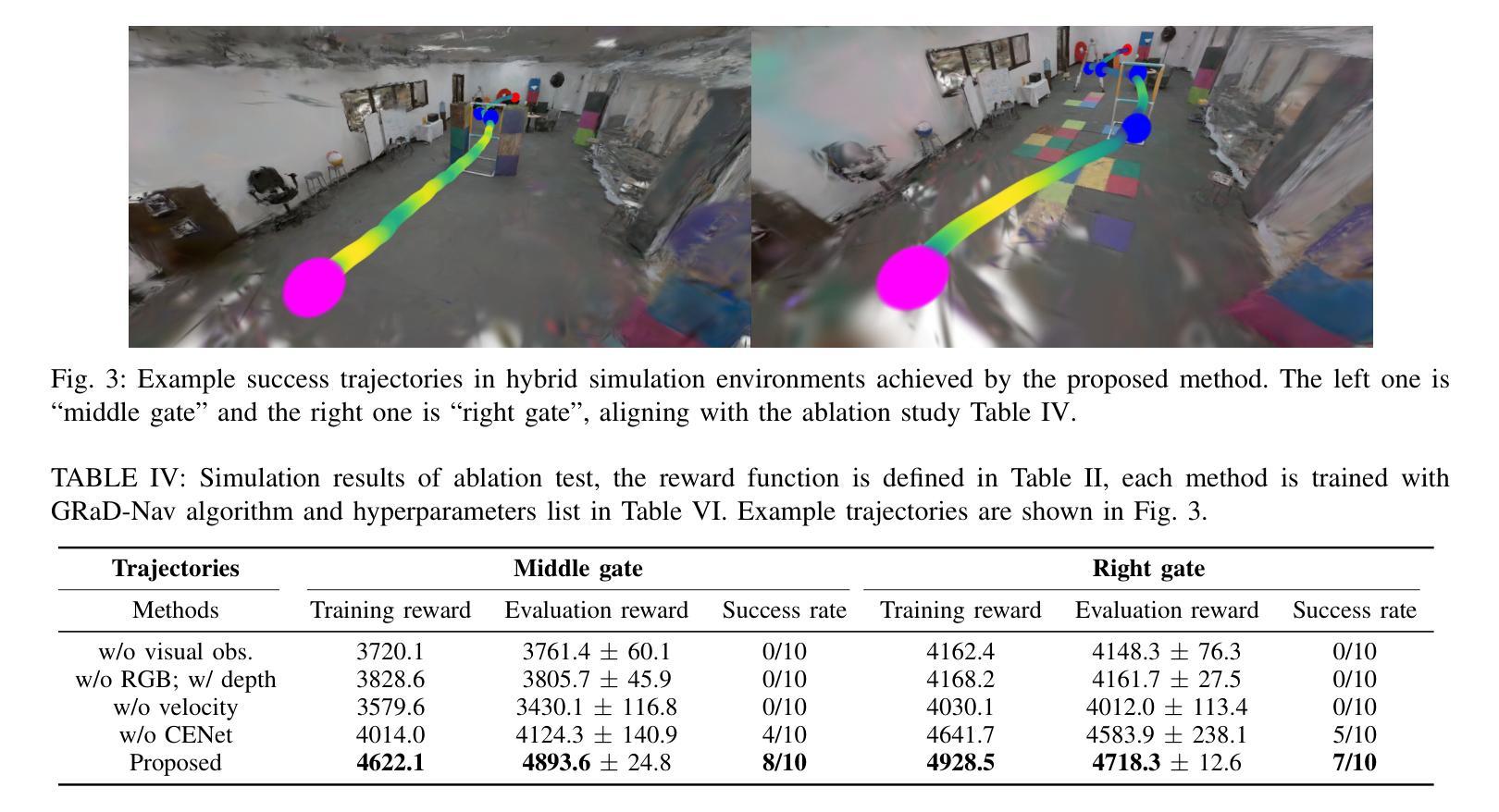
Autonomous visual navigation is an essential element in robot autonomy. Reinforcement learning (RL) offers a promising policy training paradigm. However existing RL methods suffer from high sample complexity, poor sim-to-real transfer, and limited runtime adaptability to navigation scenarios not seen during training. These problems are particularly challenging for drones, with complex nonlinear and unstable dynamics, and strong dynamic coupling between control and perception. In this paper, we propose a novel framework that integrates 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) with differentiable deep reinforcement learning (DDRL) to train vision-based drone navigation policies. By leveraging high-fidelity 3D scene representations and differentiable simulation, our method improves sample efficiency and sim-to-real transfer. Additionally, we incorporate a Context-aided Estimator Network (CENet) to adapt to environmental variations at runtime. Moreover, by curriculum training in a mixture of different surrounding environments, we achieve in-task generalization, the ability to solve new instances of a task not seen during training. Drone hardware experiments demonstrate our method’s high training efficiency compared to state-of-the-art RL methods, zero shot sim-to-real transfer for real robot deployment without fine tuning, and ability to adapt to new instances within the same task class (e.g. to fly through a gate at different locations with different distractors in the environment). Our simulator and training framework are open-sourced at: https://github.com/Qianzhong-Chen/grad_nav.
自主视觉导航是机器人自主性的一个重要组成部分。强化学习(RL)提供了一个有前景的策略训练范式。然而,现有的强化学习方法存在样本复杂度高、模拟到现实的转移性能差以及在训练期间对未见过的导航场景的实时适应能力有限等问题。对于具有复杂非线性、不稳定动力学以及控制和感知之间强动态耦合的无人机来说,这些问题更具挑战性。在本文中,我们提出了一种新颖框架,该框架将三维高斯喷涂(3DGS)与可微深度学习强化学习(DDRL)相结合,以训练基于视觉的无人机导航策略。通过利用高保真三维场景表示和可微分模拟,我们的方法提高了样本效率和模拟到现实的转移能力。此外,我们引入了上下文辅助估计网络(CENet)以在运行时适应环境变化。而且,通过在不同周围环境的混合中进行课程训练,我们实现了任务内泛化,即解决在训练期间未见的新任务实例的能力。无人机硬件实验证明,与最新强化学习方法相比,我们的方法具有高效率的训练能力、无需微调即可实现模拟到现实场景的零射转移能力以及在同类任务中适应新实例的能力(例如,在环境中有不同干扰物的情况下在不同的位置穿越栅门)。我们的模拟器和训练框架在 https://github.com/Qianzhong-Chen/grad_nav 上开源。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种结合3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)与可微分深度强化学习(DDRL)的框架,用于训练基于视觉的无人机导航策略。该框架利用高保真3D场景表示和可微分模拟,提高了样本效率和模拟到现实的转移能力。此外,还融入了上下文辅助估计网络(CENet)以适应环境变化的运行时的需求。通过在不同环境混合中的课程训练,实现了任务内泛化,即解决训练期间未见的新任务实例的能力。无人机硬件实验证明了该方法的高效训练、无需微调即可实现模拟到现实的零射击转移,以及适应新任务实例的能力。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了结合3DGS和DDRL的框架,用于训练无人机视觉导航策略。
- 利用高保真3D场景表示和可微分模拟提高样本效率和模拟到现实的转移能力。
- 融入CENet以适应环境变化,增强运行时的适应能力。
- 通过课程训练实现任务内泛化,解决未见的新任务实例。
- 无人机硬件实验证明了方法的高效训练、模拟到现实的零射击转移能力。
- 公开了模拟器与训练框架,便于他人使用与贡献。
点此查看论文截图