⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-03 更新
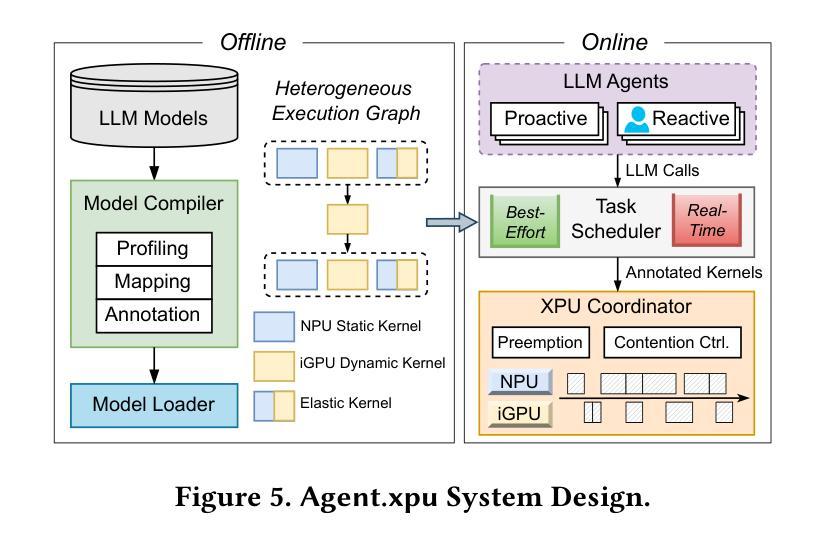
Agent.xpu: Efficient Scheduling of Agentic LLM Workloads on Heterogeneous SoC
Authors:Xinming Wei, Jiahao Zhang, Haoran Li, Jiayu Chen, Rui Qu, Maoliang Li, Xiang Chen, Guojie Luo
The proliferation of agentic Large Language Models (LLMs) on personal devices introduces a new class of workloads characterized by a dichotomy of objectives. Reactive tasks, initiated by users, demand immediate, low-latency responses, while proactive tasks operate invisibly and prioritize throughput. Existing on-device LLM engines, designed for isolated inferences, fail to efficiently manage these concurrent and conflicting requests on consumer-grade heterogeneous SoCs with CPU, integrated GPU, and NPU. This paper introduces Agent.xpu, an efficient serving system for agentic LLM workloads on memory-unified heterogeneous SoCs. With dedicated offline profiling, Agent.xpu first constructs a heterogeneous execution graph, which fuses and chunks model kernels for affinity-guided, elastic accelerator mapping with predictive kernel annotation. At runtime, its online scheduler enables fine-grained, kernel-level preemption to guarantee the responsiveness of reactive tasks. To maximize SoC utilization, it adopts slack-aware kernel backfill to opportunistically append proactive tasks, and mitigates NPU-iGPU contention via bandwidth-aware dispatch. Evaluation on an Intel Core Ultra SoC shows that Agent.xpu achieves 4.6$\times$ lower latency for reactive tasks and sustains 1.6$\times$-6.8$\times$ higher throughput for proactive tasks compared to state-of-the-art inference engines.
个人设备上代理型大规模语言模型(LLM)的激增引发了一种新的工作负载特征,表现为目标的两重性。用户发起的反应式任务需要即时、低延迟的响应,而主动任务则隐形运行并优先进行吞吐量操作。现有的用于孤立推理的片上LLM引擎无法有效管理这些并发且相互冲突的消费级异构SoC请求,这些SoC包括CPU、集成GPU和NPU。本文介绍了Agent.xpu,这是一个在内存统一异构SoC上高效运行代理型LLM工作负载的服务系统。通过专用的离线分析,Agent.xpu首先构建了一个异构执行图,该图融合了模型内核并进行分块,以实现基于亲和力的弹性加速器映射和预测内核注释。在运行时,其在线调度程序可实现精细粒度的内核级抢占,以保证反应式任务的响应能力。为了最大化SoC利用率,它采用空闲内核回填来适时追加主动任务,并通过带宽感知调度来缓解NPU-iGPU争用情况。在Intel Core Ultra SoC上的评估表明,与最新的推理引擎相比,Agent.xpu将反应式任务的延迟降低了4.6倍,并将主动任务的吞吐量提高了1.6倍至6.8倍。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文介绍了大型语言模型(LLM)在个人设备上的普及带来了一种新的工作负载类别,具有目标二元性的特征。反应性任务需要即时、低延迟的响应,而主动性任务则隐形运行并优先注重吞吐量。现有的针对孤立推理设计的LLM引擎无法有效管理这些并发且相互冲突的请求。为此,本文提出了Agent.xpu系统,该系统专为内存统一的异构SoC上的LLM工作负载服务设计。通过专用的离线分析,Agent.xpu首先构建了一个异构执行图,用于融合和分段模型内核以实现弹性加速器映射和预测内核注释。其在线调度器保证了反应性任务的响应性,并最大限度地提高了SoC的利用率。评估显示,与最新的推理引擎相比,Agent.xpu在反应性任务上实现了4.6倍的延迟降低,并在主动性任务上保持了1.6-6.8倍的吞吐量提升。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在个人设备上的普及带来了反应性和主动性并存的新工作负载类别。
- 现有LLM引擎设计无法有效处理并发且冲突的任务请求。
- Agent.xpu系统专为内存统一的异构SoC上的LLM工作负载服务设计。
- Agent.xpu通过构建异构执行图来优化任务处理。
- Agent.xpu实现了弹性加速器映射和预测内核注释以提高效率。
- Agent.xpu的在线调度器确保了反应性任务的响应性。
点此查看论文截图

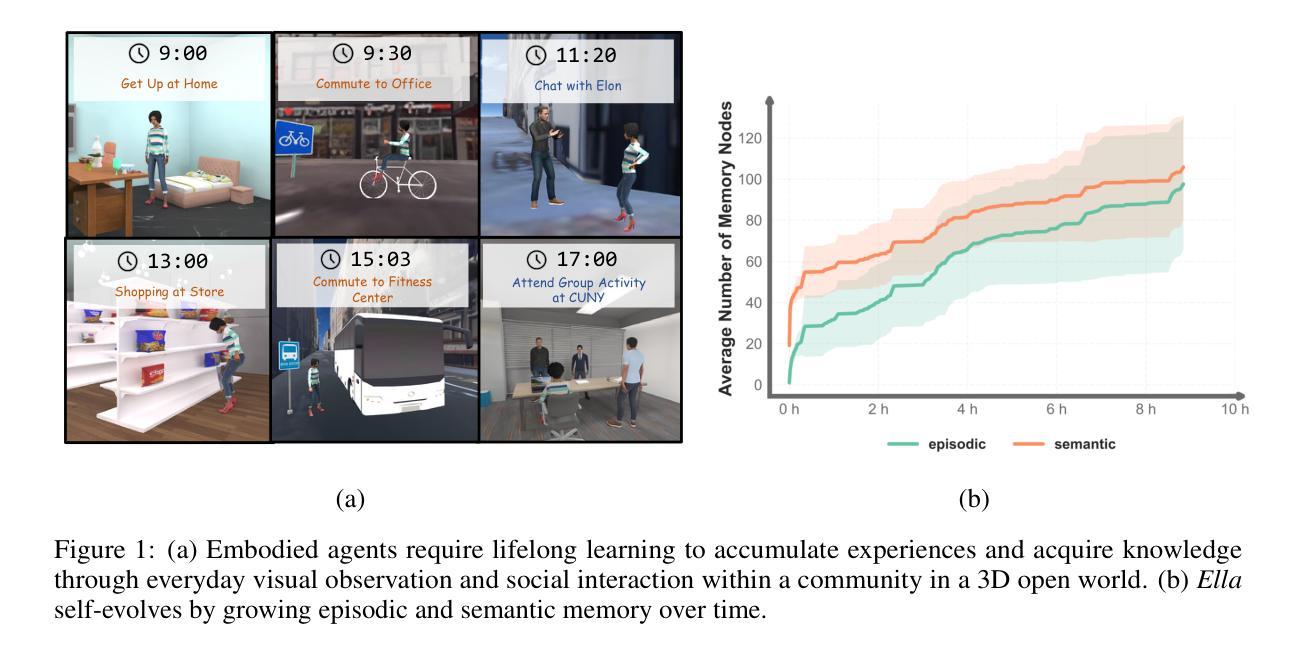
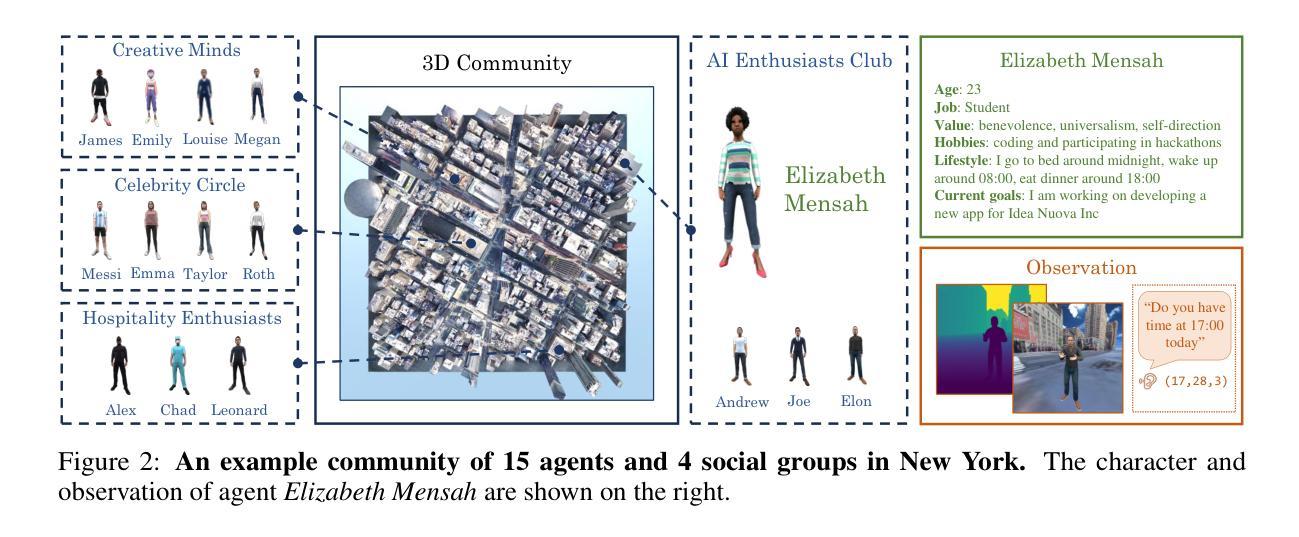
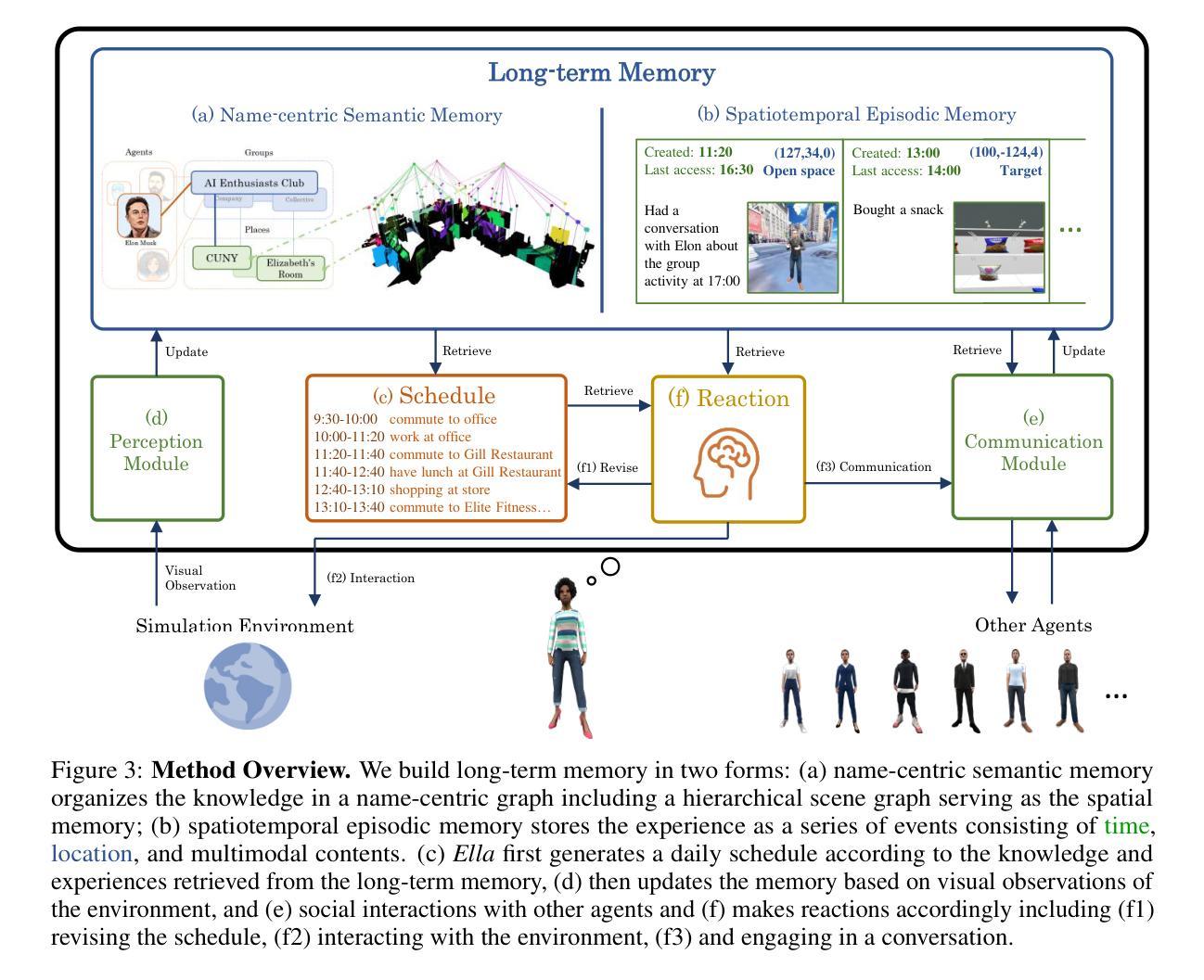
Ella: Embodied Social Agents with Lifelong Memory
Authors:Hongxin Zhang, Zheyuan Zhang, Zeyuan Wang, Zunzhe Zhang, Lixing Fang, Qinhong Zhou, Chuang Gan
We introduce Ella, an embodied social agent capable of lifelong learning within a community in a 3D open world, where agents accumulate experiences and acquire knowledge through everyday visual observations and social interactions. At the core of Ella’s capabilities is a structured, long-term multimodal memory system that stores, updates, and retrieves information effectively. It consists of a name-centric semantic memory for organizing acquired knowledge and a spatiotemporal episodic memory for capturing multimodal experiences. By integrating this lifelong memory system with foundation models, Ella retrieves relevant information for decision-making, plans daily activities, builds social relationships, and evolves autonomously while coexisting with other intelligent beings in the open world. We conduct capability-oriented evaluations in a dynamic 3D open world where 15 agents engage in social activities for days and are assessed with a suite of unseen controlled evaluations. Experimental results show that Ella can influence, lead, and cooperate with other agents well to achieve goals, showcasing its ability to learn effectively through observation and social interaction. Our findings highlight the transformative potential of combining structured memory systems with foundation models for advancing embodied intelligence. More videos can be found at https://umass-embodied-agi.github.io/Ella/.
我们介绍了Ella,这是一个能够在三维开放世界社区中进行终生学习的实体社交代理。在这个世界中,代理通过日常的视觉观察和社会互动积累经验并获取知识。Ella的核心能力是一个结构化的长期多模式记忆系统,它能有效地存储、更新和检索信息。它由一个以名字为中心的语义记忆组成,用于组织获得的知识,以及一个时空情景记忆,用于捕捉多模式经验。通过将这种终身记忆系统与基础模型相结合,Ella可以检索与决策相关的信息,规划日常活动,建立社会关系,并在与其他智能生物共存的同时自主进化。我们在一个动态的三维开放世界进行了面向能力的评估,在这里,15个代理参与社交活动数天,并通过一系列未见过的受控评估进行评估。实验结果表明,Ella能够很好地影响、带领其他代理,并与它们合作实现目标,展示了其通过观察和社交互动进行有效学习的能力。我们的研究结果突出了将结构化记忆系统与基础模型相结合在推动实体智能方面的变革潜力。更多视频可在https://umass-embodied-agi.github.io/Ella/ 找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
Ella是一款能够在三维开放世界中持续学习的实体社交代理。Ella通过日常视觉观察和社会互动积累经验和知识,其核心是一个结构化的长期多模态记忆系统,有效地存储、更新和检索信息。该记忆系统由用于组织获取知识的以名字为中心语义记忆和用于捕捉多模式经历的时空事件记忆组成。通过与基础模型的集成,Ella可以检索相关信息进行决策、规划日常活动、建立社会关系,并在开放世界中与其他智能生物共存并自主发展。实验结果表明,Ella能很好地影响、领导并与其他代理合作实现目标,展示了其通过观察和社交互动进行有效学习的能力。
Key Takeaways
- Ella是一个能在三维开放世界中进行终身学习的实体社交代理。
- Ella通过日常视觉观察和社会互动积累经验和知识。
- Ella的核心是一个结构化的长期多模态记忆系统,包括以名字为中心的语义记忆和时空事件记忆。
- Ella能够检索信息进行决策、规划日常活动并建立社会关系。
- Ella可以与其他智能生物共存并自主发展。
- Ella能够很好地影响、领导并与其他代理合作实现目标。
点此查看论文截图

Harnessing AI Agents to Advance Research on Refugee Child Mental Health
Authors:Aditya Shrivastava, Komal Gupta, Shraddha Arora
The international refugee crisis deepens, exposing millions of dis placed children to extreme psychological trauma. This research suggests a com pact, AI-based framework for processing unstructured refugee health data and distilling knowledge on child mental health. We compare two Retrieval-Aug mented Generation (RAG) pipelines, Zephyr-7B-beta and DeepSeek R1-7B, to determine how well they process challenging humanitarian datasets while avoid ing hallucination hazards. By combining cutting-edge AI methods with migration research and child psychology, this study presents a scalable strategy to assist policymakers, mental health practitioners, and humanitarian agencies to better assist displaced children and recognize their mental wellbeing. In total, both the models worked properly but significantly Deepseek R1 is superior to Zephyr with an accuracy of answer relevance 0.91
随着国际难民危机日益加剧,数百万流离失所的儿童面临着极端心理创伤。本研究提出了一种基于人工智能的紧凑框架,用于处理非结构化的难民健康数据并提炼有关儿童精神健康的知识。我们比较了两种检索增强生成(RAG)管道,Zephyr-7B-beta和DeepSeek R1-7B,以确定它们在处理具有挑战的人道主义数据集时如何避免幻视风险。本研究将最前沿的AI方法与移民研究和儿童心理学相结合,为决策者、精神健康专业人士和人道主义机构提供了一种可扩展的策略,以更好地帮助流离失所的儿童并承认他们的精神福祉。总的来说,两个模型运行正常,但Deepseek R1明显优于Zephyr,其答案的相关性准确度为0.91。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 page , 2 image , 2 tables , accepted under 5th International Conference on Innovations in Computational Intelligence and Computer Vision (ICICV-2025)
Summary
随着国际难民危机加深,数百万的流离失所儿童面临极端心理创伤。本研究提出了一种紧凑的、基于人工智能的框架,用于处理非结构化的难民健康数据并提炼关于儿童精神健康的知识。通过比较Zephyr-7B-beta和DeepSeek R1-7B两种检索增强生成(RAG)管道,研究确定它们如何处理具有挑战的人道主义数据集,同时避免虚构风险。结合前沿的AI方法、移民研究和儿童心理学,本研究为政策制定者、精神健康专业人士和人道主义机构提供了一种可伸缩的策略,以更好地帮助流离失所的儿童并关注他们的精神福祉。
Key Takeaways
- 国际难民危机正在加剧,影响数百万儿童的心理健康。
- 研究提出了一个基于AI的框架用于处理难民健康数据,聚焦于儿童精神健康方面的知识的提炼。
- 比较了两种检索增强生成(RAG)管道Zephyr-7B-beta和DeepSeek R1-7B的性能。
- DeepSeek R1在处理人道主义数据集方面表现较好,答案的准确性达到了0.91。
- 结合前沿AI方法、移民研究和儿童心理学,该研究为政策制定者和人道主义机构提供了有效帮助流离失所儿童的策略。
- 该策略可提高对儿童精神健康的关注和协助,有助于更好地满足流离失所儿童的需求。
点此查看论文截图

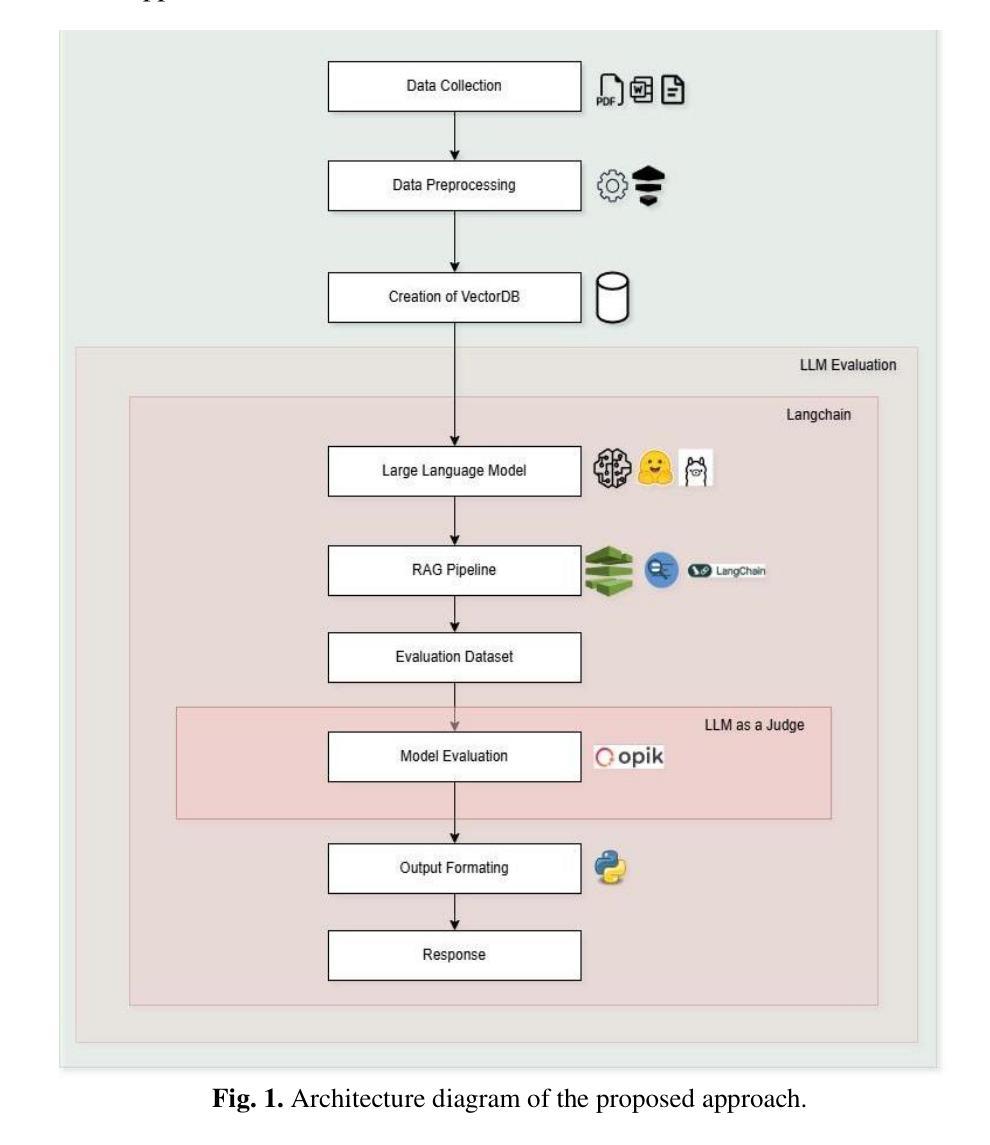
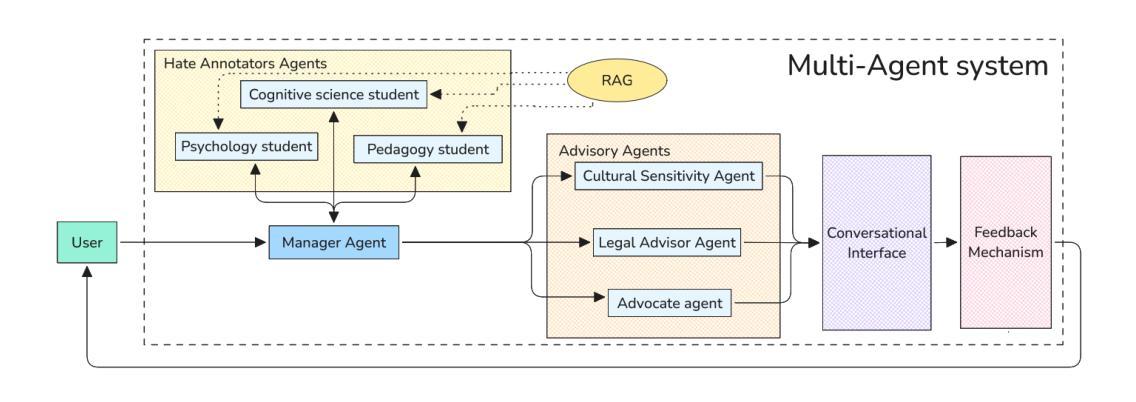
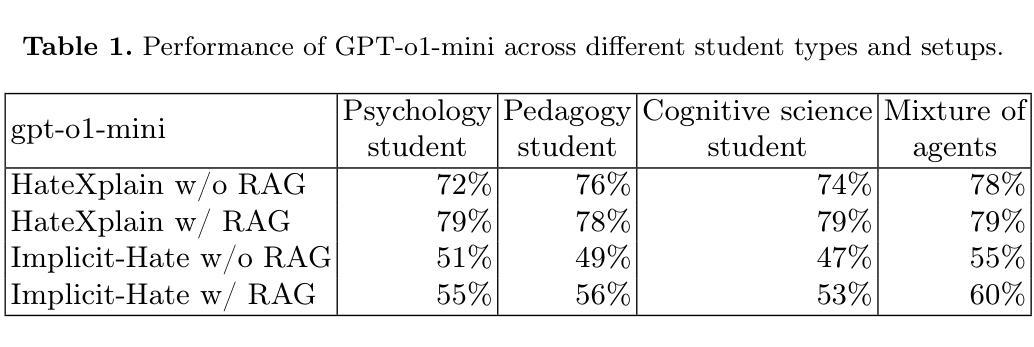
Leveraging a Multi-Agent LLM-Based System to Educate Teachers in Hate Incidents Management
Authors:Ewelina Gajewska, Michal Wawer, Katarzyna Budzynska, Jarosław A. Chudziak
Computer-aided teacher training is a state-of-the-art method designed to enhance teachers’ professional skills effectively while minimising concerns related to costs, time constraints, and geographical limitations. We investigate the potential of large language models (LLMs) in teacher education, using a case of teaching hate incidents management in schools. To this end, we create a multi-agent LLM-based system that mimics realistic situations of hate, using a combination of retrieval-augmented prompting and persona modelling. It is designed to identify and analyse hate speech patterns, predict potential escalation, and propose effective intervention strategies. By integrating persona modelling with agentic LLMs, we create contextually diverse simulations of hate incidents, mimicking real-life situations. The system allows teachers to analyse and understand the dynamics of hate incidents in a safe and controlled environment, providing valuable insights and practical knowledge to manage such situations confidently in real life. Our pilot evaluation demonstrates teachers’ enhanced understanding of the nature of annotator disagreements and the role of context in hate speech interpretation, leading to the development of more informed and effective strategies for addressing hate in classroom settings.
计算机辅助教师培训是一种先进的方法,旨在有效地提升教师的专业技能,同时最大限度地减少与成本、时间限制和地理限制相关的担忧。我们调查大型语言模型(LLM)在教师教育中的潜力,以学校仇恨事件管理教学为例。为此,我们创建了一个基于多代理的LLM系统,模拟仇恨的现实情境,结合检索增强提示和人格建模。它旨在识别和分析仇恨言论模式,预测可能的升级,并提出有效的干预策略。通过人格建模与代理LLM的结合,我们创建了仇恨事件的上下文多样模拟,模拟真实生活情境。该系统允许教师在安全可控的环境中分析仇恨事件的动力,提供有价值的见解和实用知识,以便在现实生活中自信地处理这种情况。我们的初步评估表明,教师增强了他们对注释者分歧的性质以及上下文在仇恨言论解释中的作用的理解,从而制定出更有针对性和有效的策略来解决课堂环境中的仇恨问题。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 1 figure
Summary:计算机辅助教学培训是一种先进的方法,旨在有效地提高教师的专业技能,同时最小化成本、时间限制和地理限制相关的担忧。本研究调查大型语言模型在教师教育中的潜力,以管理校园仇恨事件为例。为此,我们创建了一个基于多代理的大型语言模型的系统,模拟仇恨的真实情境,结合增强检索提示和人格建模。该系统旨在识别和分析仇恨言论模式,预测潜在升级,并提出有效的干预策略。通过人格建模与代理大型语言模型的结合,我们创建了仇恨事件的上下文多样性模拟,模拟真实生活情境。该系统允许教师在安全和受控的环境中分析仇恨事件的动态,为管理此类情况提供宝贵的见解和实用知识。教师试点评估显示,他们更深入地理解了注释者分歧的本质和在仇恨言论解读中上下文的作用,从而发展出更加明智有效的应对课堂仇恨的策略。
Key Takeaways:
- 计算机辅助教学培训旨在提高教师专业技能,同时考虑成本、时间和地理限制。
- 大型语言模型在教师教育中有巨大潜力,可应用于管理校园仇恨事件。
- 基于多代理的大型语言模型系统能模拟仇恨的真实情境。
- 该系统可识别和分析仇恨言论模式,预测潜在升级。
- 通过人格建模与代理大型语言模型的结合,创建了仇恨事件的上下文多样性模拟。
- 教师在安全和受控的环境中通过该系统能分析仇恨事件的动态。
点此查看论文截图

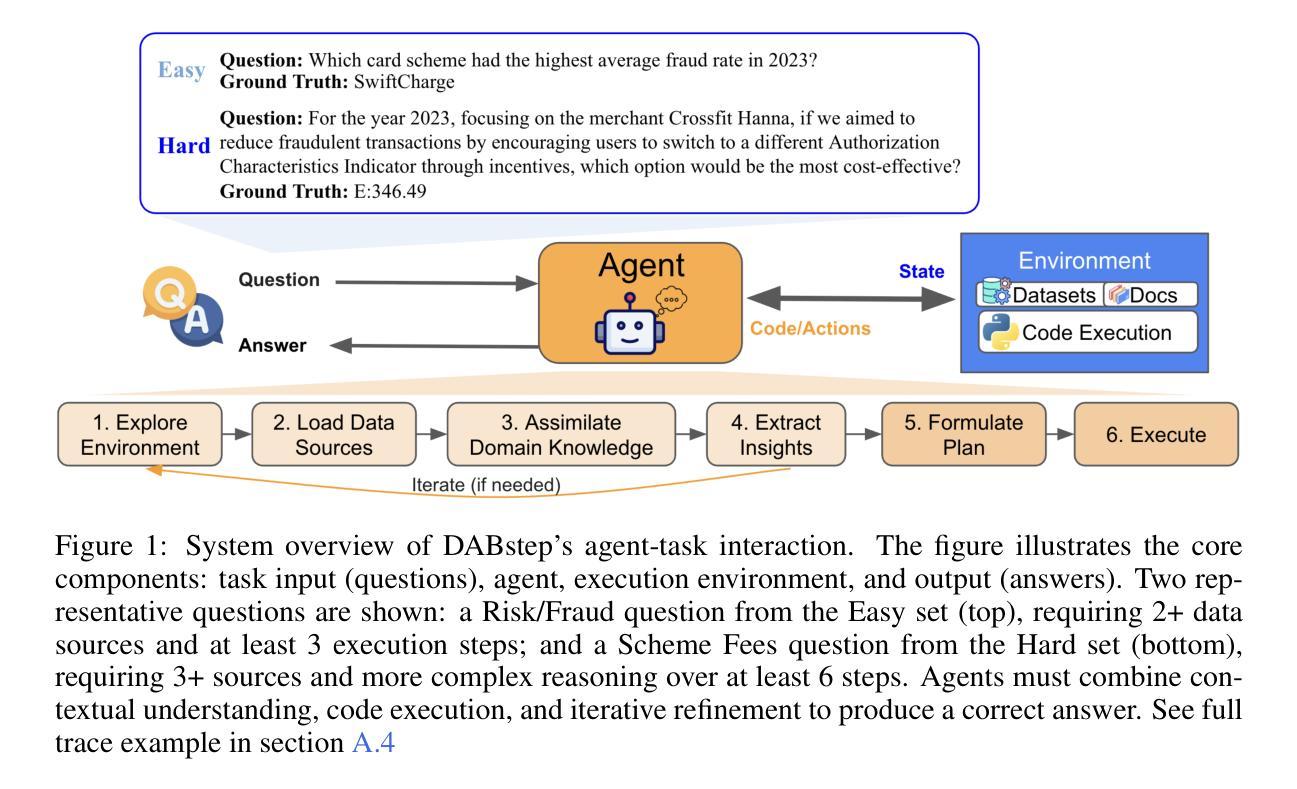
DABstep: Data Agent Benchmark for Multi-step Reasoning
Authors:Alex Egg, Martin Iglesias Goyanes, Friso Kingma, Andreu Mora, Leandro von Werra, Thomas Wolf
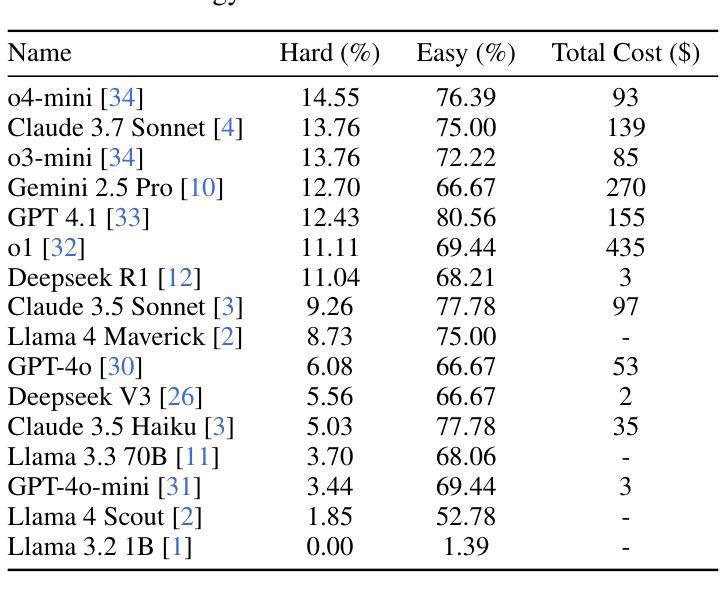
We introduce DABstep, a novel benchmark for evaluating AI agents on realistic multi-step data analysis tasks. DABstep comprises over 450 real-world challenges derived from a financial analytics platform, requiring models to combine code-based data processing with contextual reasoning over heterogeneous documentation. Each task demands an iterative, multi-step problem-solving approach, testing capabilities in data manipulation, cross-referencing multiple sources, and precise result reporting. The benchmark provides a factoid-style answer format with automatic correctness checks for objective scoring at scale. We evaluate leading LLM-based agents, revealing a substantial performance gap: even the best agent achieves only 14.55% accuracy on the hardest tasks. We detail our benchmark’s design, dataset composition, task formulation, evaluation protocol, report baseline results and analyze failure modes. DABstep is released with a public leaderboard and toolkit to accelerate research in autonomous data analysis.
我们介绍了DABstep,这是一个用于评估AI代理在现实多步骤数据分析任务上的新型基准测试。DABstep包含来自金融分析平台的450多个现实挑战,要求模型结合基于代码的数据处理和对异质文档的上下文推理。每个任务都需要迭代、多步骤的问题解决方式,测试数据操纵、跨源参照和精确结果报告的能力。该基准测试提供了一种事实型答案格式,并提供了大规模客观评分的自动正确性检查。我们评估了基于大型语言模型(LLM)的领先代理,结果显示出显著的性能差距:即使在最困难的任务上,最佳代理也只达到了14.55%的准确率。我们详细介绍了基准测试的设计、数据集组成、任务制定、评估协议、报告基线结果和分析失败模式。DABstep与公开排行榜和工具包一起发布,以加快自主数据分析的研究进程。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 5 figures
Summary
DABstep是一个新型基准测试,用于评估AI代理在真实的多步骤数据分析任务上的表现。它包含450多个来自金融分析平台的真实世界挑战,要求模型结合代码数据处理和跨异构文档进行上下文推理。此基准测试揭示了顶尖的大型语言模型代理之间的性能差距,并详细说明了其设计、数据集构成、任务制定、评估协议、基准测试结果和失败模式。DABstep已发布公开排行榜和工具包,以加速自主数据研究。
Key Takeaways
- DABstep是一个用于评估AI代理多步骤数据分析能力的基准测试。
- 它包含450多个真实世界挑战,来源于金融分析平台。
- DABstep要求模型结合代码数据处理和跨异构文档进行上下文推理。
- 基准测试要求迭代、多步骤的解决问题的方法。
- 评估协议包括数据操作、跨源参考和精确结果报告的能力测试。
- 顶尖的大型语言模型代理在DABstep上的性能存在显著差距。
点此查看论文截图

PokéAI: A Goal-Generating, Battle-Optimizing Multi-agent System for Pokemon Red
Authors:Zihao Liu, Xinhang Sui, Yueran Song, Siwen Wang
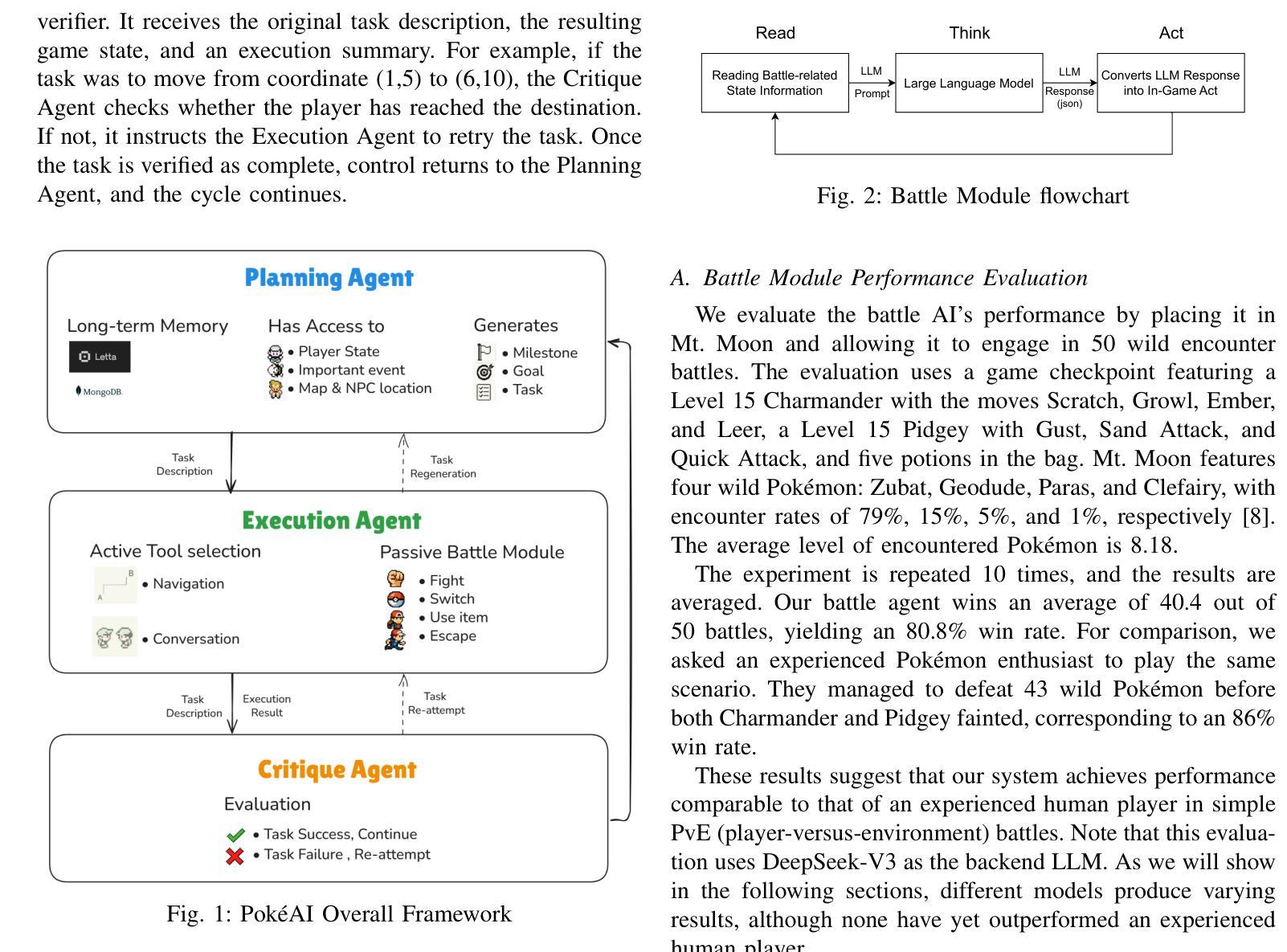
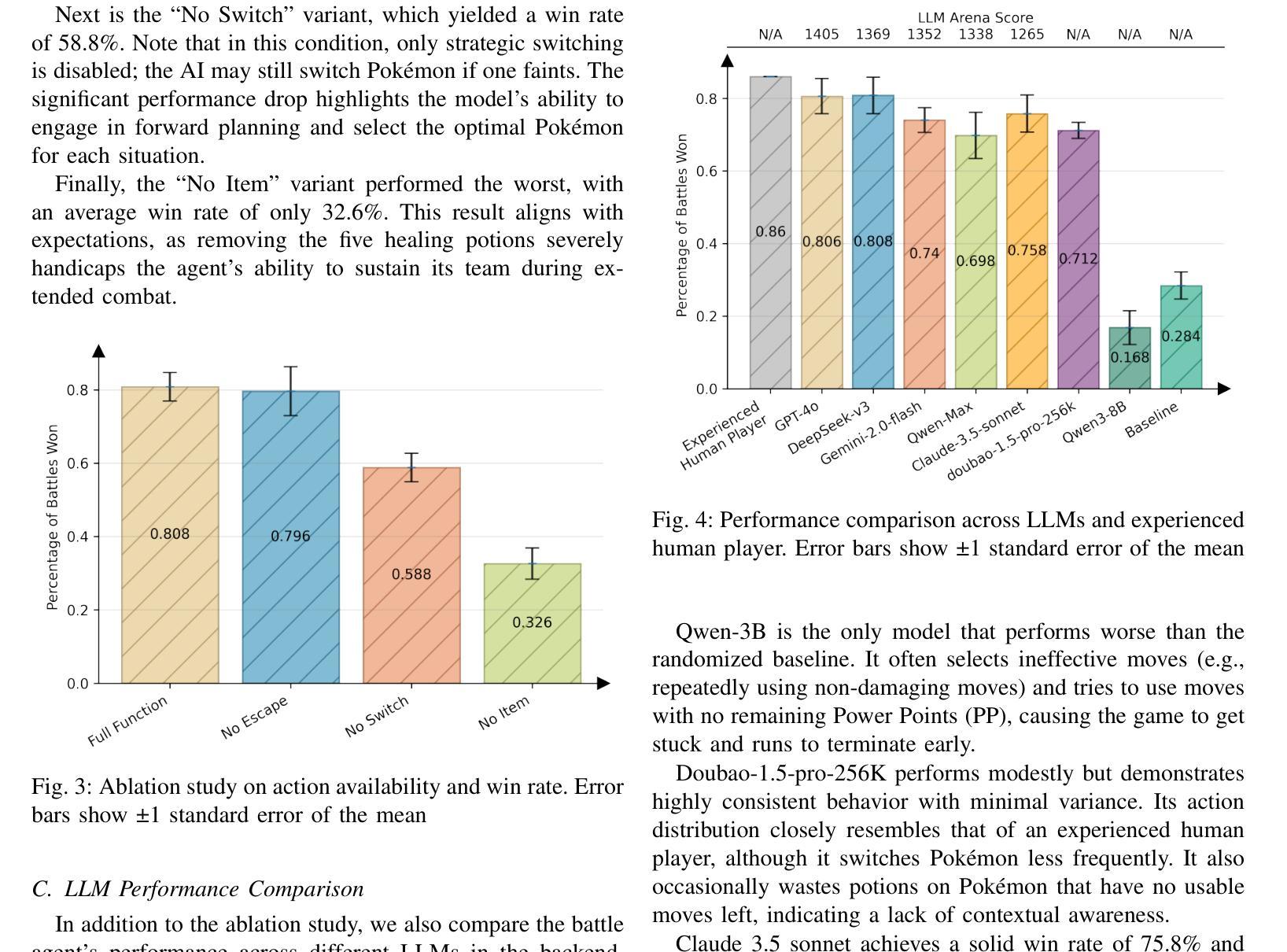
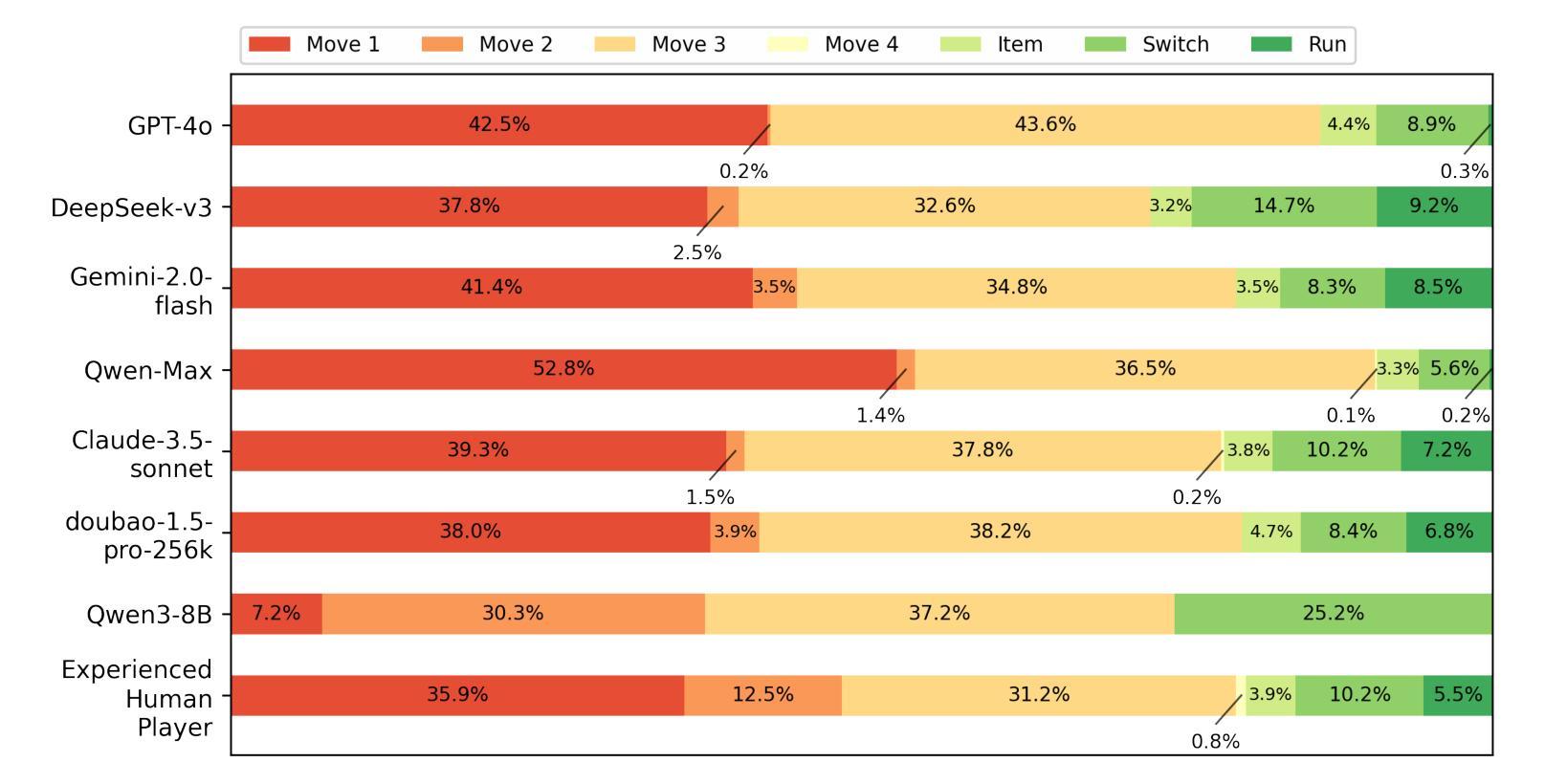
We introduce Pok'eAI, the first text-based, multi-agent large language model (LLM) framework designed to autonomously play and progress through Pok'emon Red. Our system consists of three specialized agents-Planning, Execution, and Critique-each with its own memory bank, role, and skill set. The Planning Agent functions as the central brain, generating tasks to progress through the game. These tasks are then delegated to the Execution Agent, which carries them out within the game environment. Upon task completion, the Critique Agent evaluates the outcome to determine whether the objective was successfully achieved. Once verification is complete, control returns to the Planning Agent, forming a closed-loop decision-making system. As a preliminary step, we developed a battle module within the Execution Agent. Our results show that the battle AI achieves an average win rate of 80.8% across 50 wild encounters, only 6% lower than the performance of an experienced human player. Furthermore, we find that a model’s battle performance correlates strongly with its LLM Arena score on language-related tasks, indicating a meaningful link between linguistic ability and strategic reasoning. Finally, our analysis of gameplay logs reveals that each LLM exhibits a unique playstyle, suggesting that individual models develop distinct strategic behaviors.
我们介绍了PokéAI,这是首款基于文本的多智能体大型语言模型(LLM)框架,旨在自主玩和推进Pokémon Red游戏。我们的系统由三个专业智能体组成:规划、执行和批判,每个智能体都有自己的记忆库、角色和技能集。规划智能体充当中央大脑,生成任务以推动游戏进程。这些任务然后分配给执行智能体,它在游戏环境中执行它们。任务完成后,批判智能体会评估结果,以确定目标是否成功实现。一旦验证完成,控制权将返回给规划智能体,形成一个闭环决策系统。作为初步工作,我们在执行智能体内开发了一个战斗模块。我们的结果表明,战斗人工智能在50场野生遭遇中的平均胜率为80.8%,比经验丰富的玩家低仅6%。此外,我们发现一个模型的战斗性能与其在LLM Arena上的语言相关任务的得分具有很强的相关性,表明语言能力和战略推理之间存在有意义的联系。最后,我们对游戏日志的分析表明,每个LLM都表现出独特的游戏风格,这表明个别模型会发展出不同的战略行为。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了PokéAI,首款基于文本的多智能体大型语言模型框架,旨在自主玩并推进Pokémon Red游戏。该系统包括规划、执行和评论三个智能体,每个智能体都有自己的记忆库、角色和技能集。规划智能体作为中央大脑,生成任务推进游戏。然后,执行任务被委派给执行智能体,其在游戏环境中执行任务。任务完成后,评估智能体会评估结果以确定目标是否成功实现。验证完成后,控制权返回规划智能体,形成一个闭环决策系统。初步开发了一个战斗模块在执行智能体中,战斗人工智能平均胜率为80.8%,在野外遭遇中略低于熟练人类玩家的表现。还发现模型战斗性能与其在大型语言模型竞技场上的语言任务得分密切相关,表明语言能力和战略推理之间存在联系。最后,对游戏日志的分析显示每个大型语言模型展现出独特的游戏风格。
Key Takeaways
- PokéAI是首个基于文本的多智能体大型语言模型框架,用于自主玩并推进Pokémon Red游戏。
- 系统包含三个智能体:规划、执行和评论,每个智能体有自己的记忆库、角色和技能集。
- 规划智能体生成任务推进游戏,执行智能体在游戏环境中执行任务,评论智能体评估任务结果。
- 初步开发的战斗模块在执行智能体中表现出较高的胜率。
- 模型战斗性能与其在语言任务上的表现密切相关,表明语言能力和战略推理之间的联系。
点此查看论文截图

L0: Reinforcement Learning to Become General Agents
Authors:Junjie Zhang, Jingyi Xi, Zhuoyang Song, Junyu Lu, Yuhua Ke, Ting Sun, Yukun Yang, Jiaxing Zhang, Songxin Zhang, Zejian Xie
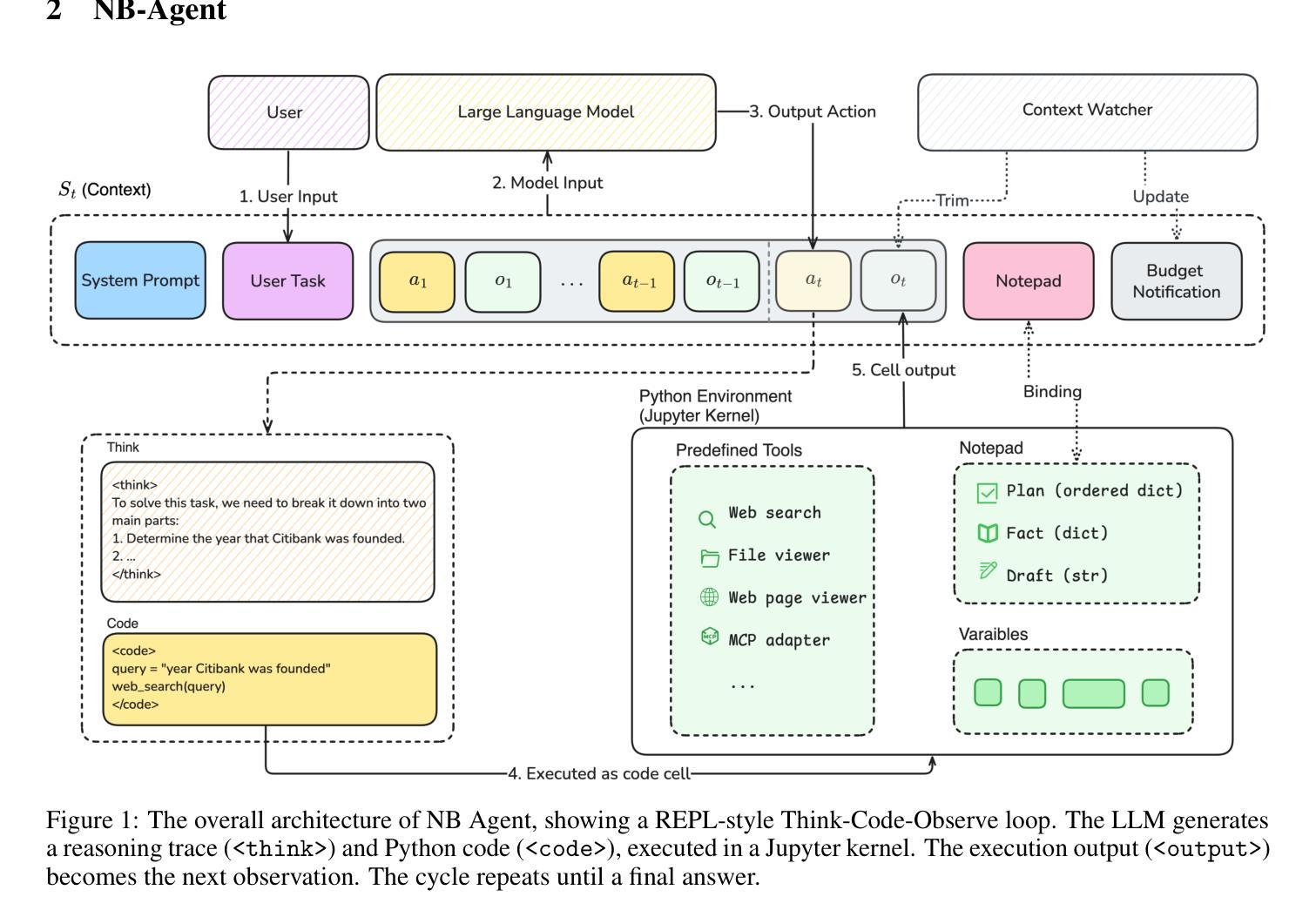
Training large language models (LLMs) to act as autonomous agents for multi-turn, long-horizon tasks remains significant challenges in scalability and training efficiency. To address this, we introduce L-Zero (L0), a scalable, end-to-end training pipeline for general-purpose agents. Featuring a low-cost, extensible, and sandboxed concurrent agent worker pool, L0 lowers the barrier for applying reinforcement learning in complex environments. We also introduce NB-Agent, the agent scaffold within L0, which operates in a “code-as-action” fashion via a Read-Eval-Print-Loop (REPL). We evaluate L0 on factuality question-answering benchmarks. Our experiments demonstrate that a base model can develop robust problem-solving skills using solely Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR). On the Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct model, our method boosts accuracy on SimpleQA from 30 % to 80 % and on HotpotQA from 22 % to 41 %. We have open-sourced the entire L0 system, including our L0 series models, the NB-Agent, a complete training pipeline, and the corresponding training recipes on (https://github.com/cmriat/l0).
训练大型语言模型(LLM)以执行多轮、长期任务作为自主代理仍然存在可扩展性和训练效率方面的重大挑战。为了解决这一问题,我们推出了L-Zero(L0),这是一个用于通用代理的可扩展端到端训练管道。L0采用低成本、可扩展和沙箱并发代理工作池的方式,降低了在复杂环境中应用强化学习的门槛。我们还介绍了L0内的代理脚手架NB-Agent,它采用“代码即行动”的方式,通过Read-Eval-Print-Loop(REPL)进行操作。我们在事实性问题回答基准测试上对L0进行了评估。实验表明,基础模型仅使用可验证奖励强化学习(RLVR)就能发展出稳健的问题解决能力。在Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct模型上,我们的方法将SimpleQA的准确率从30%提高到80%,HotpotQA的准确率从22%提高到41%。我们已公开了整个L0系统,包括我们的L0系列模型、NB-Agent、完整的训练管道和相应训练配方(https://github.com/cmriat/l0)。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
L-Zero(L0)是一个用于通用代理的可扩展端到端训练管道,解决了大型语言模型(LLM)在多轮长时间任务中的可扩展性和训练效率的挑战。它采用低成本、可扩展和沙箱化的并发代理工作者池,降低了在复杂环境中应用强化学习的门槛。通过“代码即行动”的方式,L0中的NB-Agent代理架构在Read-Eval-Print-Loop(REPL)中进行操作。评估表明,L0在事实性问题回答基准测试中表现优异,仅使用可验证奖励的强化学习,基础模型的问题解决能力就能得到显著提升。
Key Takeaways
- L-Zero(L0)是一个用于通用代理的可扩展端到端训练管道,旨在解决大型语言模型(LLM)在多轮长时间任务中的训练挑战。
- L0采用低成本、可扩展和沙箱化的并发代理工作者池,降低在复杂环境中应用强化学习的门槛。
- NB-Agent是L0中的代理架构,以“代码即行动”的方式在Read-Eval-Print-Loop(REPL)中操作。
- L0通过强化学习与可验证奖励(RLVR)提升基础模型的问题解决能力。
- 在事实性问题回答基准测试中,L0表现出色,如SimpleQA的准确率从30%提升至80%,HotpotQA的准确率从22%提升至41%。
- L0系统已开源,包括L0系列模型、NB-Agent、完整的训练管道和相应的训练配方。
- L0的开源系统为大型语言模型的训练和代理架构的发展提供了重要资源和参考。
点此查看论文截图


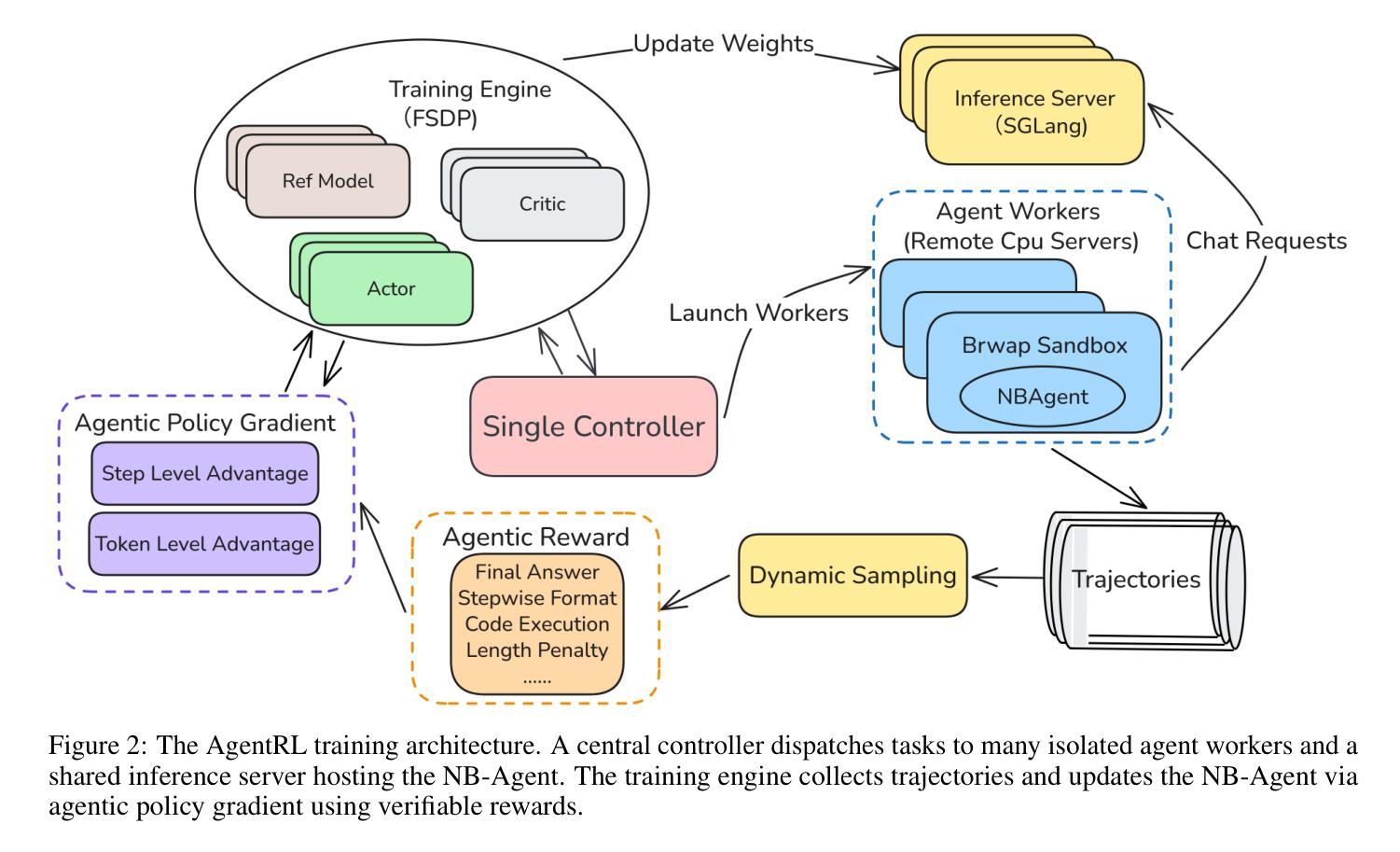
Thought-Augmented Planning for LLM-Powered Interactive Recommender Agent
Authors:Haocheng Yu, Yaxiong Wu, Hao Wang, Wei Guo, Yong Liu, Yawen Li, Yuyang Ye, Junping Du, Enhong Chen
Interactive recommendation is a typical information-seeking task that allows users to interactively express their needs through natural language and obtain personalized recommendations. Large language model-powered (LLM-powered) agents have become a new paradigm in interactive recommendations, effectively capturing users’ real-time needs and enhancing personalized experiences. However, due to limited planning and generalization capabilities, existing formulations of LLM-powered interactive recommender agents struggle to effectively address diverse and complex user intents, such as intuitive, unrefined, or occasionally ambiguous requests. To tackle this challenge, we propose a novel thought-augmented interactive recommender agent system (TAIRA) that addresses complex user intents through distilled thought patterns. Specifically, TAIRA is designed as an LLM-powered multi-agent system featuring a manager agent that orchestrates recommendation tasks by decomposing user needs and planning subtasks, with its planning capacity strengthened through Thought Pattern Distillation (TPD), a thought-augmentation method that extracts high-level thoughts from the agent’s and human experts’ experiences. Moreover, we designed a set of user simulation schemes to generate personalized queries of different difficulties and evaluate the recommendations based on specific datasets. Through comprehensive experiments conducted across multiple datasets, TAIRA exhibits significantly enhanced performance compared to existing methods. Notably, TAIRA shows a greater advantage on more challenging tasks while generalizing effectively on novel tasks, further validating its superiority in managing complex user intents within interactive recommendation systems. The code is publicly available at:https://github.com/Alcein/TAIRA.
互动推荐是一种典型的信息搜索任务,允许用户通过自然语言进行互动表达他们的需求,并获得个性化的推荐。以大型语言模型(LLM)为动力的代理已成为互动推荐的新范式,能够有效捕捉用户的实时需求并增强个性化体验。然而,由于规划和泛化能力的限制,现有的LLM驱动型互动推荐代理难以有效应对多样且复杂的用户意图,如直觉性、未完成或偶尔模糊的请求。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一种新型思想增强型互动推荐代理系统(TAIRA),它通过提炼思想模式来应对复杂的用户意图。具体来说,TAIRA被设计为一个以LLM为动力的多代理系统,具有一个管理代理,通过分解用户需求并规划子任务来协调推荐任务。其规划能力通过思想模式蒸馏(TPD)增强,这是一种思想增强方法,从代理和人类专家的经验中提取高级思想。此外,我们设计了一系列用户模拟方案,以生成不同难度的个性化查询,并根据特定数据集对推荐进行评估。通过多个数据集进行的综合实验表明,TAIRA与现有方法相比,表现出显著增强的性能。值得注意的是,TAIRA在更具挑战性的任务上显示出更大的优势,并在新型任务上实现有效泛化,进一步验证了其在互动推荐系统中管理复杂用户意图的优越性。代码公开在:https://github.com/Alcein/TAIRA。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
互动推荐是一种典型的信息检索任务,允许用户通过自然语言进行互动表达需求并获得个性化推荐。大型语言模型驱动的代理已成为互动推荐的新模式,能有效捕捉用户的实时需求并增强个性化体验。为解决现有大型语言模型驱动的互动推荐代理在应对复杂用户需求方面的局限性,我们提出了思想增强的互动推荐代理系统(TAIRA),通过提炼思想模式来应对复杂的用户需求。TAIRA被设计为一个多代理系统,通过分解用户需求并规划子任务来协调推荐任务,其规划能力通过思想模式蒸馏得到增强。实验表明,TAIRA在应对不同难度的个性化查询和特定数据集的评价方面表现出显著优势,尤其在更具挑战性的任务上表现出更大的优势并在新颖任务上实现了有效的泛化。
Key Takeaways
- 互动推荐允许用户通过自然语言互动表达需求并获得个性化推荐。
- 大型语言模型驱动的代理已成为互动推荐的新模式。
- 现有大型语言模型驱动的互动推荐代理在应对复杂用户需求方面存在挑战。
- 提出了思想增强的互动推荐代理系统(TAIRA)以应对复杂用户需求。
- TAIRA是一个多代理系统,具有分解并协调推荐任务的能力。
- TAIRA通过思想模式蒸馏增强规划能力。
点此查看论文截图


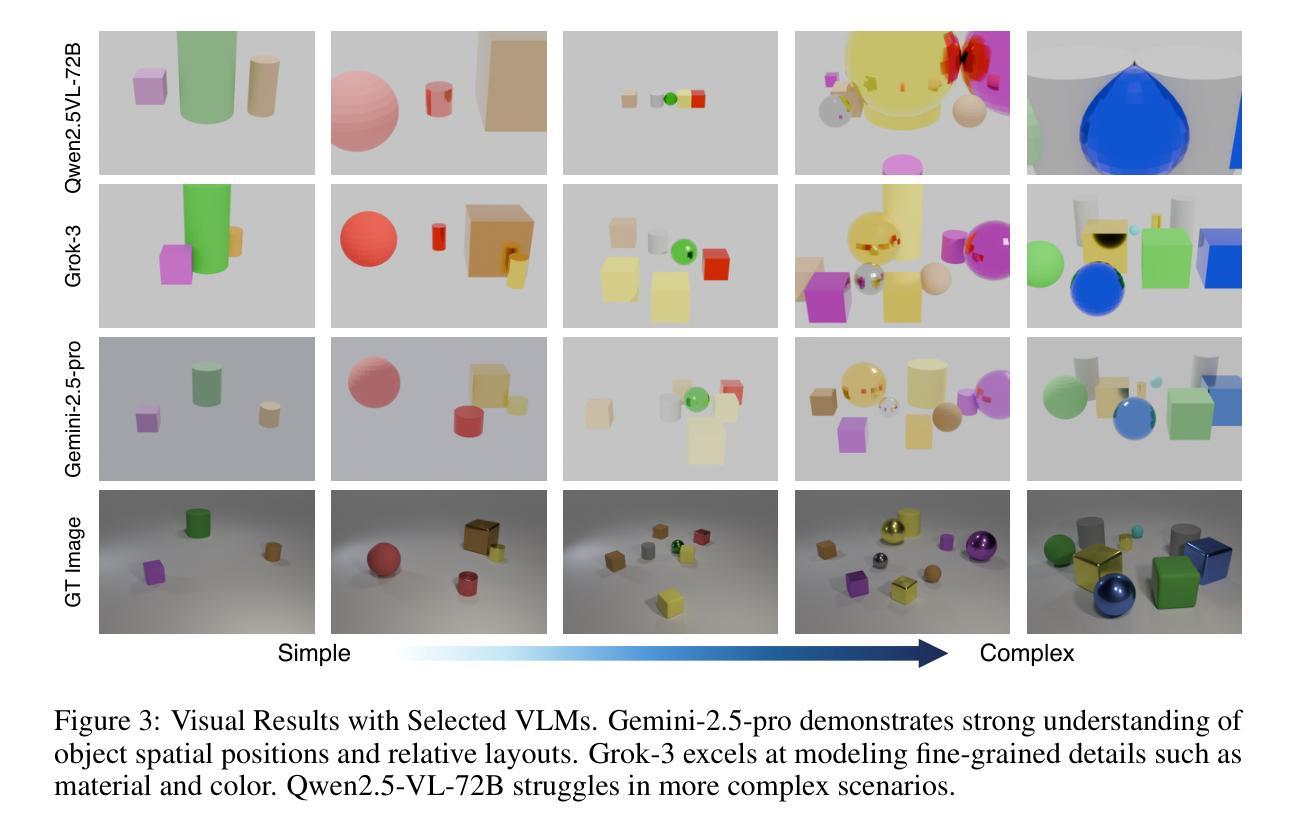
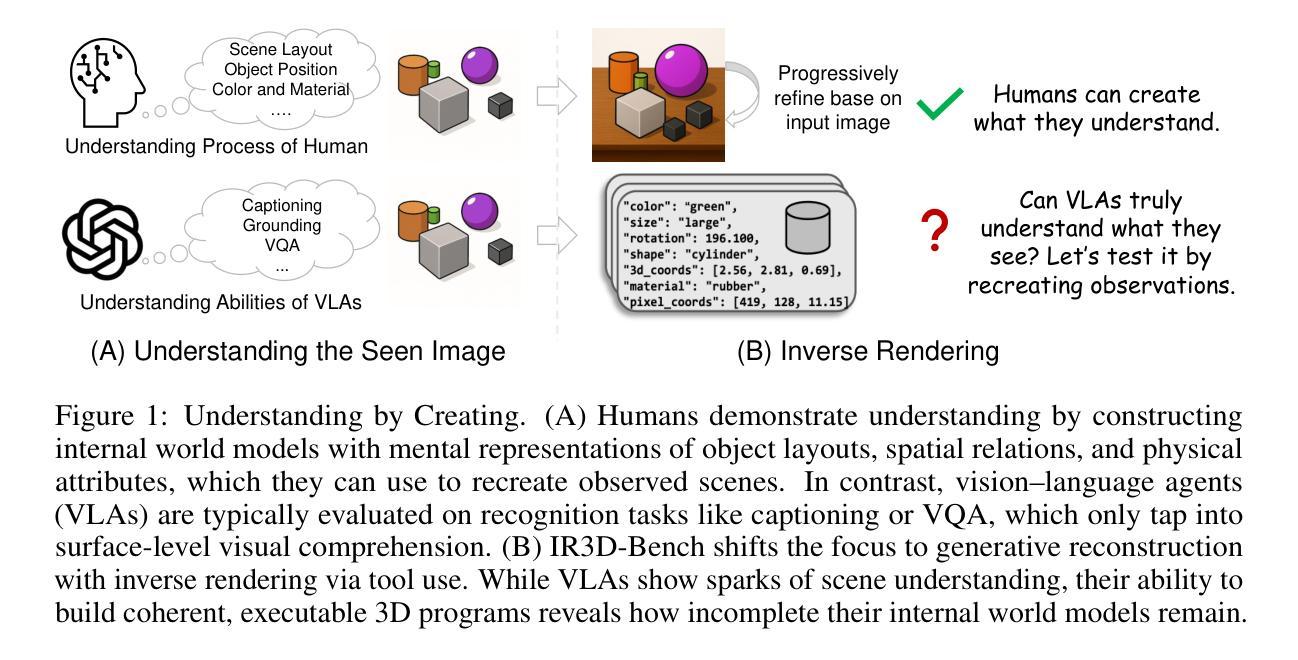
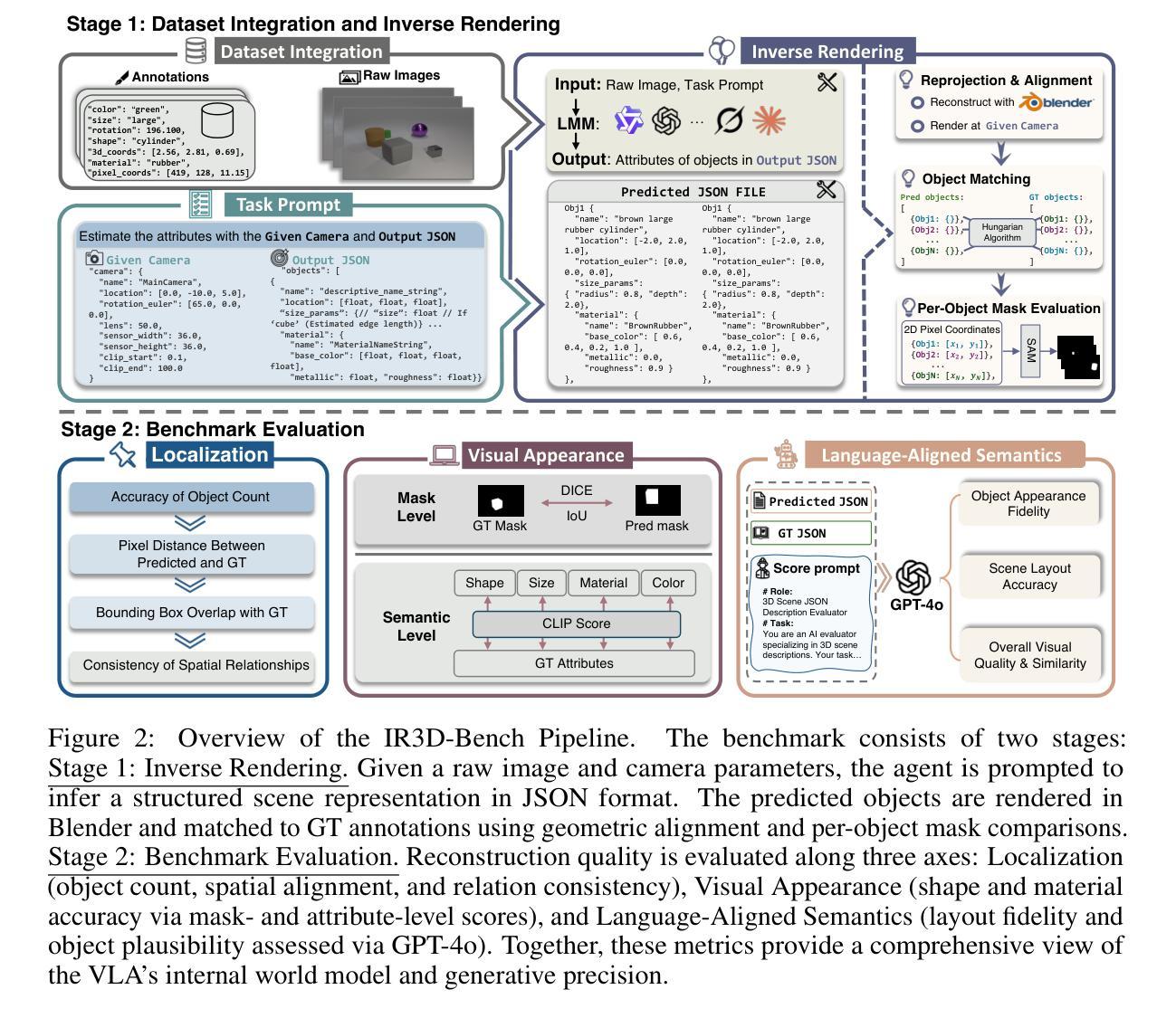
IR3D-Bench: Evaluating Vision-Language Model Scene Understanding as Agentic Inverse Rendering
Authors:Parker Liu, Chenxin Li, Zhengxin Li, Yipeng Wu, Wuyang Li, Zhiqin Yang, Zhenyuan Zhang, Yunlong Lin, Sirui Han, Brandon Y. Feng
Vision-language models (VLMs) excel at descriptive tasks, but whether they truly understand scenes from visual observations remains uncertain. We introduce IR3D-Bench, a benchmark challenging VLMs to demonstrate understanding through active creation rather than passive recognition. Grounded in the analysis-by-synthesis paradigm, IR3D-Bench tasks Vision-Language Agents (VLAs) with actively using programming and rendering tools to recreate the underlying 3D structure of an input image, achieving agentic inverse rendering through tool use. This “understanding-by-creating” approach probes the tool-using generative capacity of VLAs, moving beyond the descriptive or conversational capacity measured by traditional scene understanding benchmarks. We provide a comprehensive suite of metrics to evaluate geometric accuracy, spatial relations, appearance attributes, and overall plausibility. Initial experiments on agentic inverse rendering powered by various state-of-the-art VLMs highlight current limitations, particularly in visual precision rather than basic tool usage. IR3D-Bench, including data and evaluation protocols, is released to facilitate systematic study and development of tool-using VLAs towards genuine scene understanding by creating.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)在描述性任务方面表现出色,但它们是否真正通过视觉观察理解场景仍存在不确定性。我们引入了IR3D-Bench,这是一个挑战VLMs的基准测试,通过主动创造而非被动识别来展示理解力。基于合成分析范式,IR3D-Bench要求视觉语言代理(VLAs)积极使用编程和渲染工具来重新创建输入图像的基础3D结构,通过工具使用实现代理逆向渲染。这种“通过创造来理解”的方法探索了VLAs的工具使用生成能力,超越了传统场景理解基准测试所衡量的描述性或会话能力。我们提供了一套综合指标来评估几何精度、空间关系、外观属性和整体可行性。在各种最先进的VLMs驱动的代理逆向渲染的初步实验突出了当前的局限性,特别是在视觉精度而不是基本工具使用方面。IR3D-Bench包括数据和评估协议,旨在促进工具使用VLAs的系统研究和发展,以实现通过创造真正理解场景。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://ir3d-bench.github.io/
Summary
在视觉观察场景中,视觉语言模型(VLMs)的理解程度仍存在不确定性。为此,我们推出了IR3D-Bench基准测试,挑战VLMs通过主动创造而非被动识别来展示理解。该基准测试基于分析综合范式,要求视觉语言代理(VLAs)积极使用编程和渲染工具重新创建输入图像的底层3D结构,通过工具使用实现代理逆向渲染。这种“通过创造来理解”的方法探索了VLAs的工具使用生成能力,超越了传统场景理解基准测试所衡量的描述性或会话能力。我们提供了一套综合指标来评估几何精度、空间关系、外观属性和整体可行性。初步实验表明,当前最先进的VLMs在视觉精度方面存在局限,而非基本工具使用方面。IR3D-Bench包括数据和评估协议,旨在促进工具使用VLAs的系统研究和发展,以实现通过创造真正理解场景。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉语言模型(VLMs)在描述任务上表现出色,但它们是否真正理解从视觉观察中获得的场景仍存在疑问。
- IR3D-Bench基准测试旨在挑战VLMs通过主动创造来展示理解,而不仅仅是被动识别。
- IR3D-Bench基于分析综合范式,要求VLAs使用编程和渲染工具重新创建输入图像的底层3D结构。
- “通过创造来理解”的方法强调VLAs的工具使用生成能力。
- 初步实验揭示了当前VLMs在视觉精度方面的局限,而非基本工具使用上的问题。
- IR3D-Bench包括数据和评估协议,以推动VLAs的系统研究和发展。
点此查看论文截图


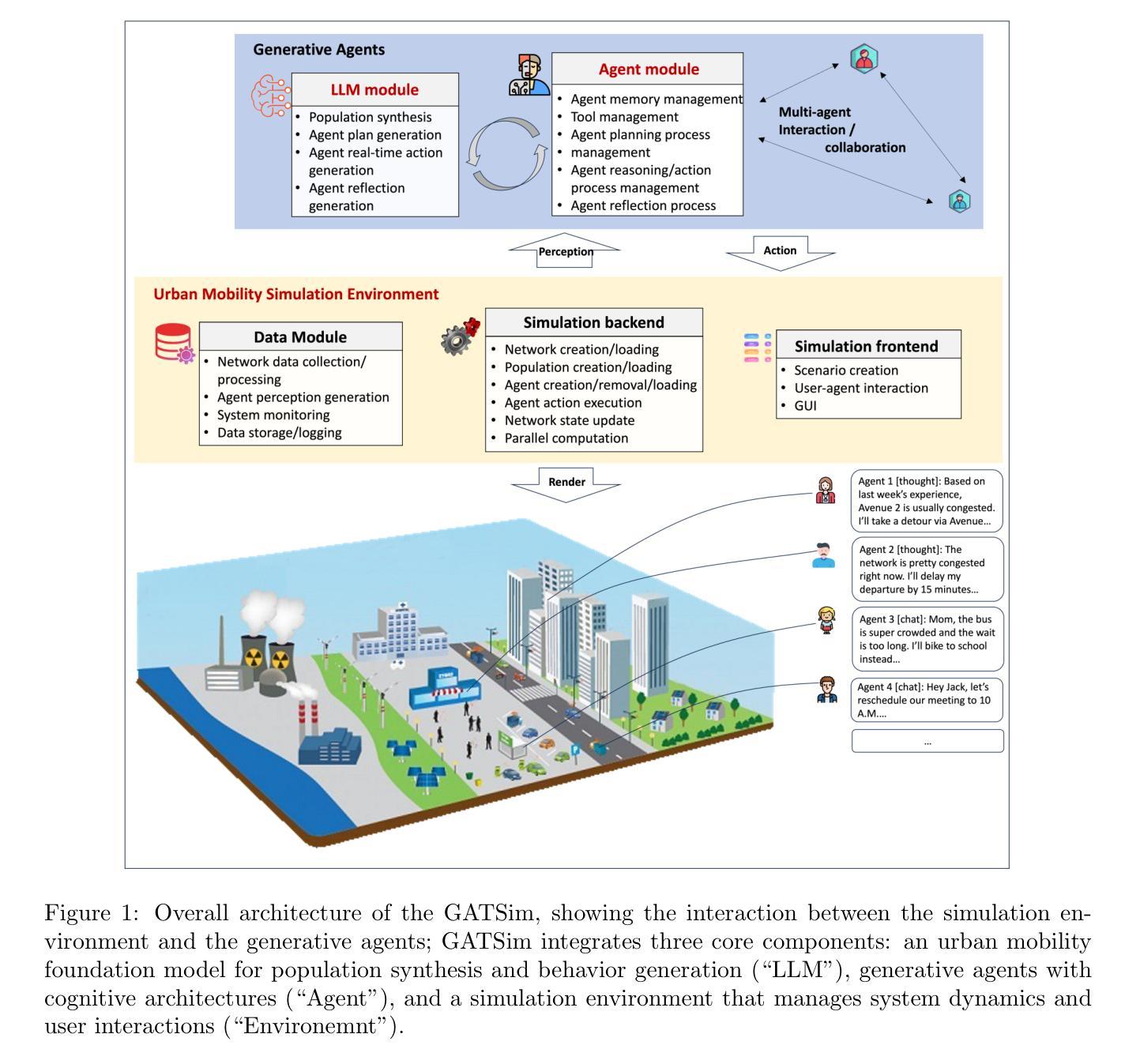
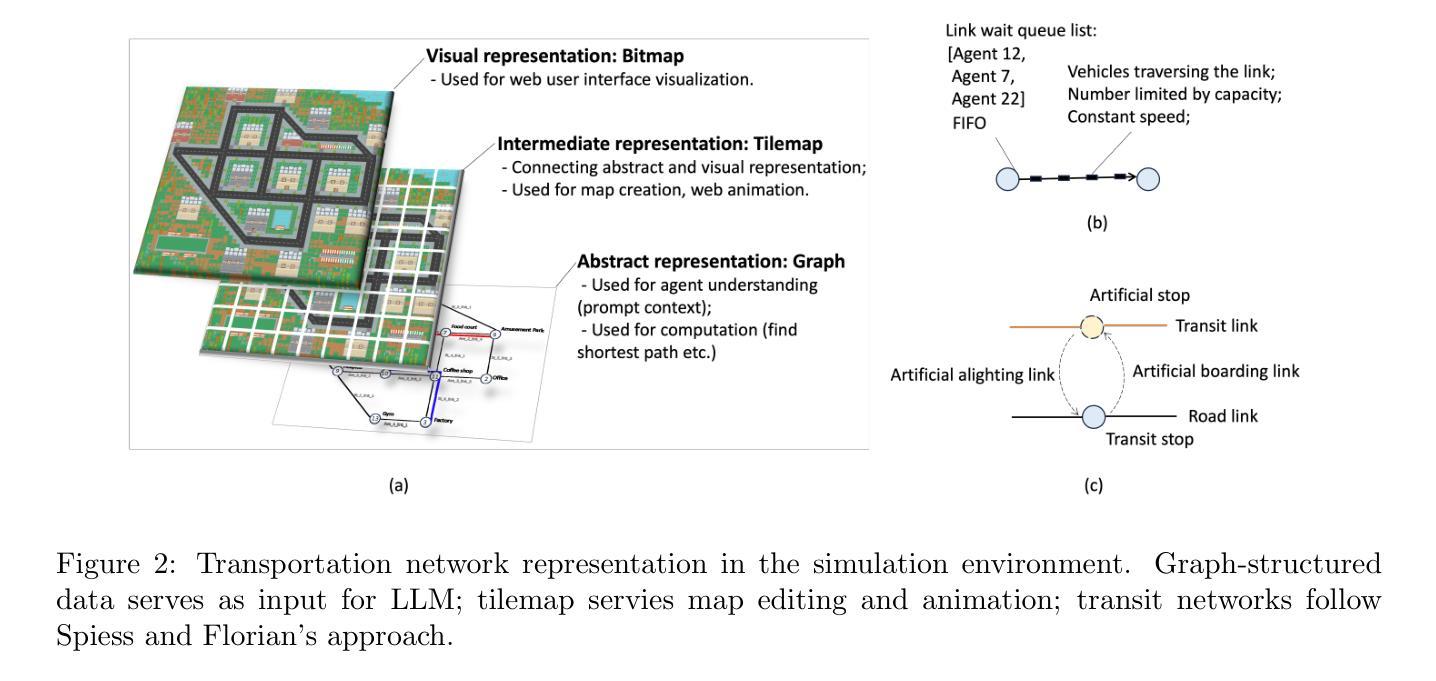
GATSim: Urban Mobility Simulation with Generative Agents
Authors:Qi Liu, Can Li, Wanjing Ma
Traditional agent-based urban mobility simulations rely on rigid rule-based systems that fail to capture the complexity, adaptability, and behavioral diversity characteristic of human travel decision-making. Recent advances in large language models and AI agent technology offer opportunities to create agents with reasoning capabilities, persistent memory, and adaptive learning mechanisms. We propose GATSim (Generative-Agent Transport Simulation), a novel framework that leverages these advances to create generative agents with rich behavioral characteristics for urban mobility simulation. Unlike conventional approaches, GATSim agents possess diverse socioeconomic attributes, individual lifestyles, and evolving preferences that shape their mobility decisions through psychologically-informed memory systems, tool usage capabilities, and lifelong learning mechanisms. The main contributions of this study include: (1) a comprehensive architecture combining an urban mobility foundation model with agent cognitive systems and transport simulation environment, (2) a fully functional prototype implementation, and (3) systematic validation demonstrating that generative agents produce believable travel behaviors. Through designed reflection processes, generative agents in this study can transform specific travel experiences into generalized insights, enabling realistic behavioral adaptation over time with specialized mechanisms for activity planning and real-time reactive behaviors tailored to urban mobility contexts. Experiments show that generative agents perform competitively with human annotators in mobility scenarios while naturally producing macroscopic traffic evolution patterns. The code for the prototype system is shared at https://github.com/qiliuchn/gatsim.
传统基于代理的城市交通模拟依赖于僵化的基于规则的系统,这些系统无法捕捉到人类出行决策特征的复杂性、适应性和行为多样性。大型语言模型和AI代理技术的最新进展提供了创建具有推理能力、持久性记忆和自适应学习机制的代理的机会。我们提出了GATSim(生成式交通模拟),这是一个利用这些技术创建具有丰富行为特征的生成式代理,用于城市交通模拟的新型框架。与传统的交通模拟方法不同,GATSim中的生成式代理拥有多样化的社会经济属性、个人生活方式和不断发展的偏好,通过心理学指导下的记忆系统、工具使用能力和终身学习机制来影响他们的出行决策。该研究的主要贡献包括:(1)一个结合了城市交通基础模型与代理认知系统和交通模拟环境的综合架构,(2)一个功能齐全的原型实现,(3)系统性验证表明生成式代理可以产生可信的出行行为。本研究中的生成式代理能够通过设计的反思过程将特定的旅行经历转化为一般性见解,实现随时间推移的实际行为适应,并具有针对城市出行环境的活动规划和实时反应行为的专门机制。实验表明,在交通场景中,生成式代理的表现与人类注释器相当,并能自然地产生宏观的交通演变模式。该原型系统的代码共享在https://github.com/qiliuchn/gatsim上。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种新的城市出行仿真框架GATSim(生成式代理交通仿真),该框架利用先进的语言模型和AI代理技术,创建具有丰富行为特征的生成式代理来进行城市出行仿真。与传统仿真方法不同,GATSim的代理拥有多样的社会经济属性、个人生活方式和不断变化的偏好,通过心理感知的记忆系统、工具使用能力和终身学习机制来影响出行决策。研究的主要贡献包括:综合性架构、原型实现和系统验证。生成式代理能够通过设计反思过程将特定出行经验转化为通用见解,实现随时间变化的现实行为适应,并具备针对城市出行环境的专门活动规划和实时反应行为机制。实验表明,生成式代理在人类出行场景中的表现具有竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- GATSim利用大型语言模型和AI技术创建生成式代理进行城市出行仿真。
- 生成式代理具有多样的社会经济属性、个人生活方式和变化的偏好,影响出行决策。
- 综合架构结合了城市出行基础模型与代理认知系统和交通仿真环境。
- 原型实现具备功能完备性。
- 系统验证显示生成式代理能展现可信的出行行为。
- 生成式代理能将特定出行经验转化为通用见解,实现行为适应和规划反应。
点此查看论文截图

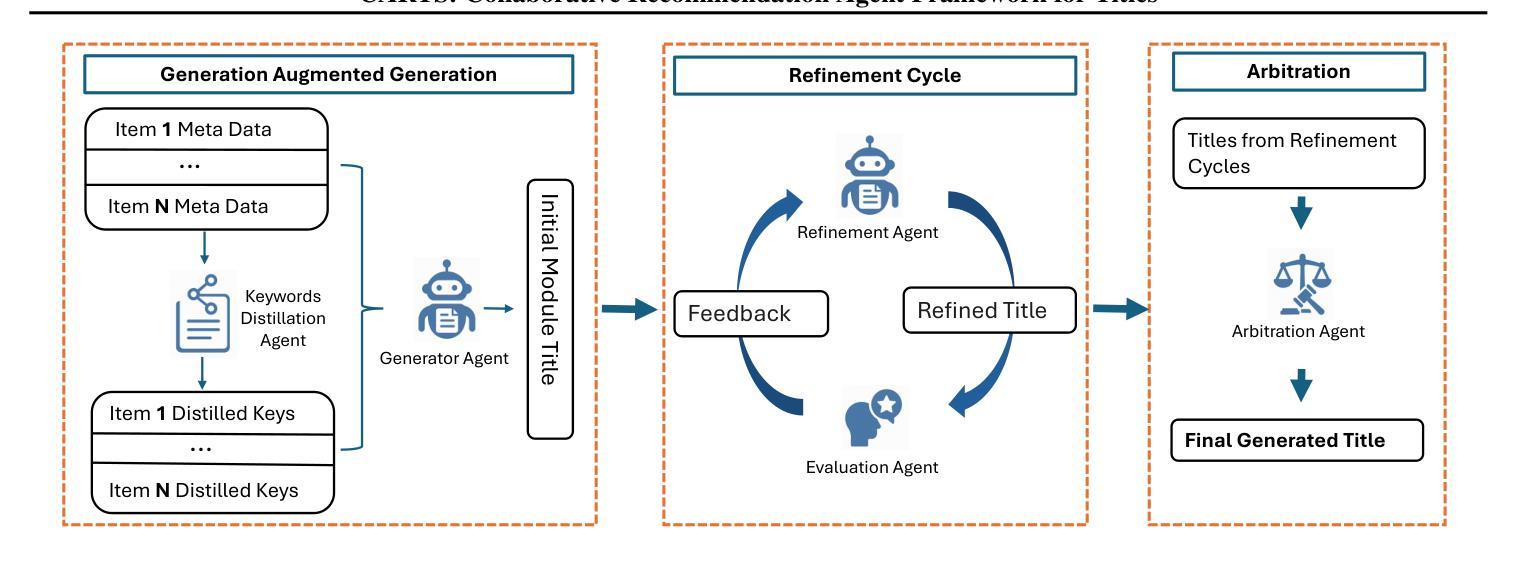
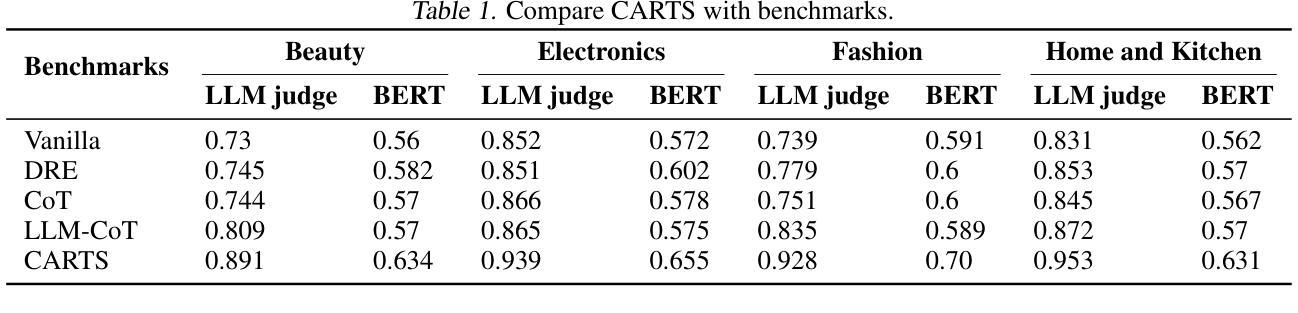
CARTS: Collaborative Agents for Recommendation Textual Summarization
Authors:Jiao Chen, Kehui Yao, Reza Yousefi Maragheh, Kai Zhao, Jianpeng Xu, Jason Cho, Evren Korpeoglu, Sushant Kumar, Kannan Achan
Current recommendation systems often require some form of textual data summarization, such as generating concise and coherent titles for product carousels or other grouped item displays. While large language models have shown promise in NLP domains for textual summarization, these approaches do not directly apply to recommendation systems, where explanations must be highly relevant to the core features of item sets, adhere to strict word limit constraints. In this paper, we propose CARTS (Collaborative Agents for Recommendation Textual Summarization), a multi-agent LLM framework designed for structured summarization in recommendation systems. CARTS decomposes the task into three stages-Generation Augmented Generation (GAG), refinement circle, and arbitration, where successive agent roles are responsible for extracting salient item features, iteratively refining candidate titles based on relevance and length feedback, and selecting the final title through a collaborative arbitration process. Experiments on large-scale e-commerce data and live A/B testing show that CARTS significantly outperforms single-pass and chain-of-thought LLM baselines, delivering higher title relevance and improved user engagement metrics.
当前推荐系统通常需要某种形式的文本数据摘要,例如为产品轮播图或其他分组项目显示生成简洁连贯的标题。虽然大型语言模型在NLP领域的文本摘要方面显示出潜力,但这些方法并不直接适用于推荐系统,因为推荐系统的解释必须高度相关于项目集的核心功能,并受到严格的字数限制约束。在本文中,我们提出了CARTS(推荐文本摘要协作代理,Collaborative Agents for Recommendation Textual Summarization),这是一个多代理LLM框架,专为推荐系统中的结构化摘要而设计。CARTS将任务分解为三个阶段:生成增强生成(GAG)、改进循环和仲裁,其中连续代理角色负责提取重要的项目特征、基于相关性和长度反馈迭代改进候选标题,并通过协作仲裁过程选择最终标题。在大型电子商务数据和实时A/B测试上的实验表明,CARTS在单通道和思维链式LLM基准测试方面表现出显著优势,提高了标题相关性和用户参与度指标。
论文及项目相关链接
总结
本论文针对推荐系统中的文本摘要问题,提出了一种名为CARTS的多智能体LLM框架。该框架通过三个阶段完成结构化摘要任务:生成增强生成阶段、精细化循环和仲裁阶段。通过连续的智能体角色负责提取重要项目特征,基于相关性和长度反馈进行迭代精炼候选标题,并通过协作仲裁过程选择最终标题。实验表明,CARTS在大型电子商务数据和实时A/B测试中显著优于单通道和链式思维LLM基线,提高了标题相关性和用户参与度指标。
关键见解
- 推荐系统需要处理文本摘要,如生成产品轮播或其他分组项目显示的简洁连贯标题。
- 大型语言模型在NLP领域的文本摘要中显示出潜力,但直接应用于推荐系统的方法并不适用。
- 推荐系统的解释必须高度相关于项目集的核心特征,并符合严格的字数限制。
- CARTS是一个多智能体LLM框架,专为推荐系统中的结构化摘要设计。
- CARTS将任务分解为三个阶段:生成增强生成、精细化循环和仲裁。
- 通过实验和实时A/B测试,CARTS显著优于其他方法,提高了标题相关性和用户参与度。
点此查看论文截图

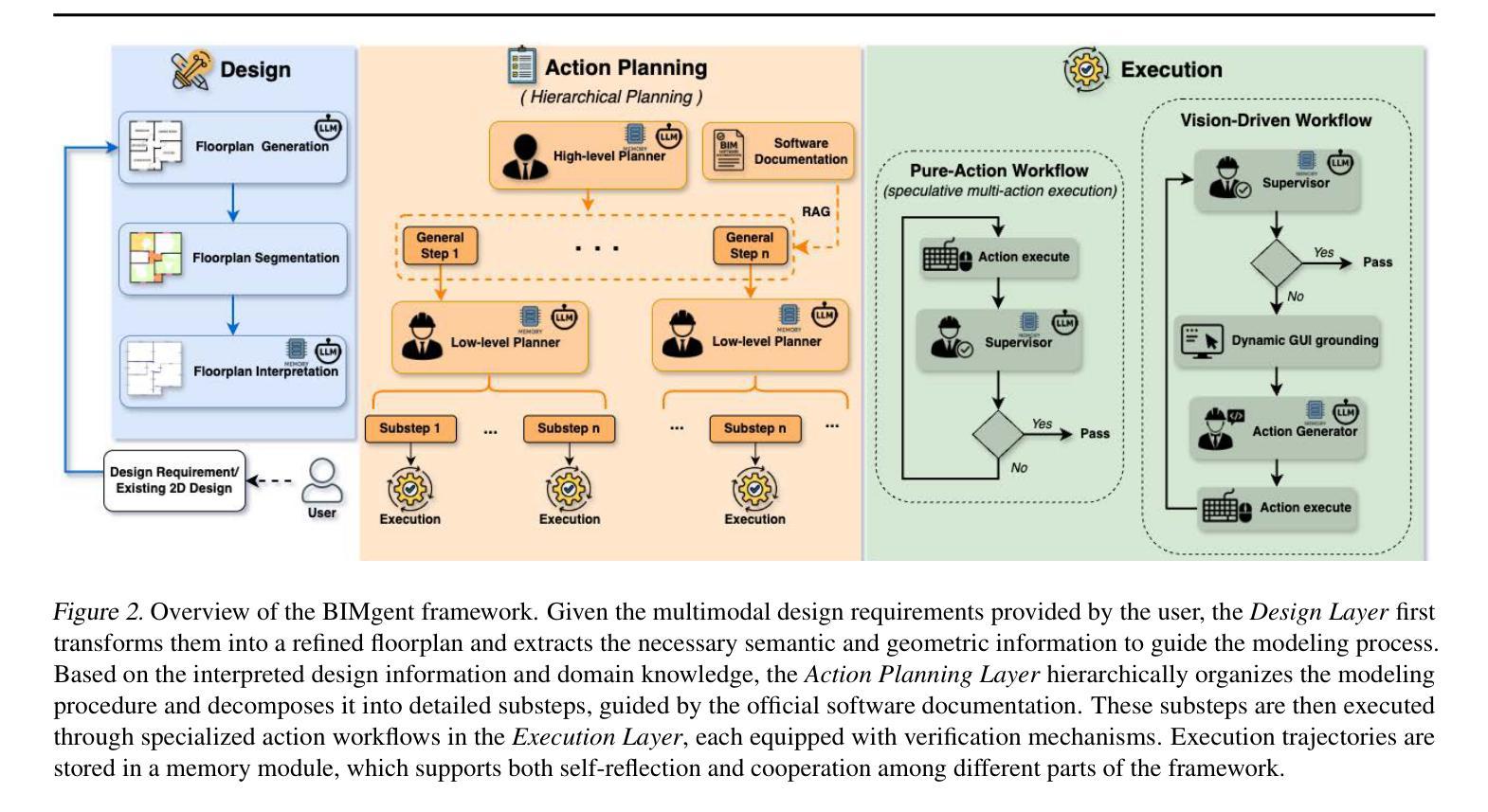
BIMgent: Towards Autonomous Building Modeling via Computer-use Agents
Authors:Zihan Deng, Changyu Du, Stavros Nousias, André Borrmann
Existing computer-use agents primarily focus on general-purpose desktop automation tasks, with limited exploration of their application in highly specialized domains. In particular, the 3D building modeling process in the Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) sector involves open-ended design tasks and complex interaction patterns within Building Information Modeling (BIM) authoring software, which has yet to be thoroughly addressed by current studies. In this paper, we propose BIMgent, an agentic framework powered by multimodal large language models (LLMs), designed to enable autonomous building model authoring via graphical user interface (GUI) operations. BIMgent automates the architectural building modeling process, including multimodal input for conceptual design, planning of software-specific workflows, and efficient execution of the authoring GUI actions. We evaluate BIMgent on real-world building modeling tasks, including both text-based conceptual design generation and reconstruction from existing building design. The design quality achieved by BIMgent was found to be reasonable. Its operations achieved a 32% success rate, whereas all baseline models failed to complete the tasks (0% success rate). Results demonstrate that BIMgent effectively reduces manual workload while preserving design intent, highlighting its potential for practical deployment in real-world architectural modeling scenarios. Project page: https://tumcms.github.io/BIMgent.github.io/
现有计算机使用代理主要关注通用桌面自动化任务,对其在高度专业化领域的应用探索有限。特别是在建筑、工程和建筑(AEC)领域的3D建筑建模过程中,涉及开放设计任务和建筑信息建模(BIM)设计软件内的复杂交互模式,尚未得到当前研究的充分解决。本文提出BIMgent,这是一个由多模态大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的代理框架,旨在通过图形用户界面(GUI)操作实现自主建筑模型创作。BIMgent自动化建筑建模过程,包括多模态输入概念设计、软件特定工作流程的规划以及作者GUI动作的有效执行。我们在现实世界建筑建模任务上评估了BIMgent,包括基于文本的概念设计生成和从现有设计中重建。BIMgent的设计质量被认为是合理的。其操作实现了32%的成功率,而所有基线模型均未能完成任务(成功率为0%)。结果表明,BIMgent在减少手动工作量的同时保持了设计意图,突显其在现实建筑建模场景中的实际应用潜力。项目页面:https://tumcms.github.io/BIMgent.github.io/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025 Workshop on Computer Use Agents
Summary
BIMgent框架利用多模态大型语言模型(LLMs)驱动,旨在通过图形用户界面(GUI)操作实现建筑模型的自主创建。该框架自动化建筑建模流程,包括概念设计的多模态输入、特定软件的工作流规划以及高效执行GUI动作。在真实建筑建模任务上的评估显示,BIMgent的设计质量良好,操作成功率达到32%,而所有基线模型均未能完成任务(成功率为0%)。这证明了BIMgent在减少手动工作量的同时,有效保持设计初衷,展现了其在真实建筑建模场景中的部署潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 当前计算机使用代理主要集中在通用桌面自动化任务上,缺乏高度专业化的应用领域的探索。特别是在建筑信息建模(BIM)软件的复杂交互模式方面尚未得到充分研究。
- BIMgent是一个基于多模态大型语言模型的代理框架,旨在通过图形用户界面(GUI)操作实现自主的建筑模型创建。
- BIMgent可以自动化建筑建模流程,包括概念设计的多模态输入、特定软件的工作流规划以及GUI动作的快速执行。
- BIMgent的设计质量良好,在实际建筑建模任务上的成功率为32%,显示出其潜力。
- 与所有基线模型相比,BIMgent是唯一能够完成任务的模型,其他模型均未能实现任何任务成功完成(成功率为0%)。
- BIMgent在减少手动工作量的同时保持了设计初衷,展现了其在真实场景中的实用性。
点此查看论文截图

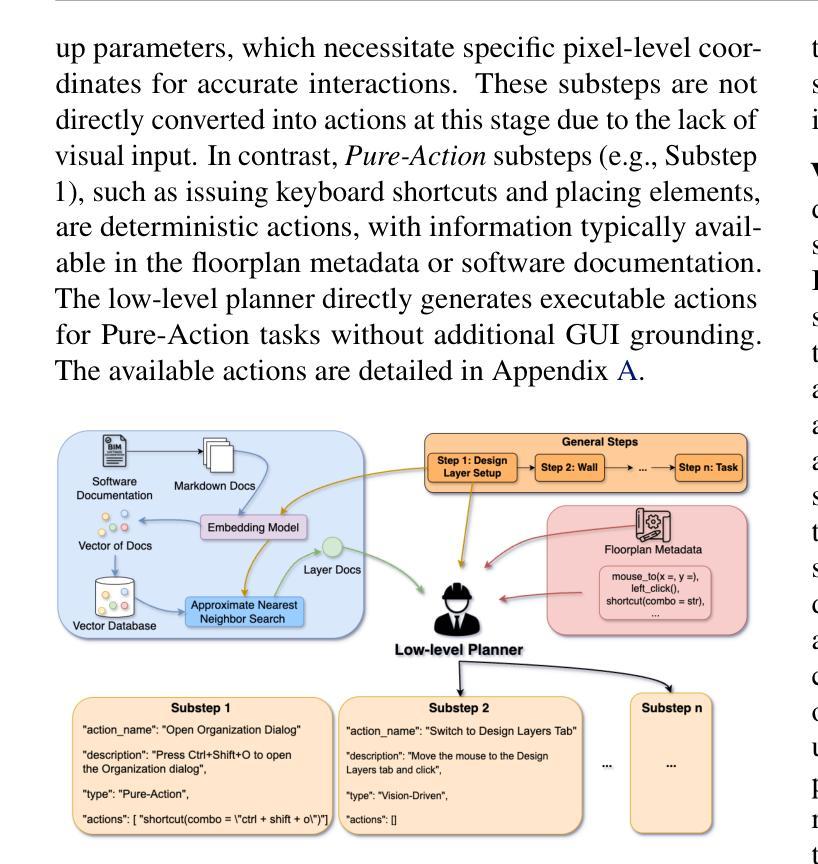
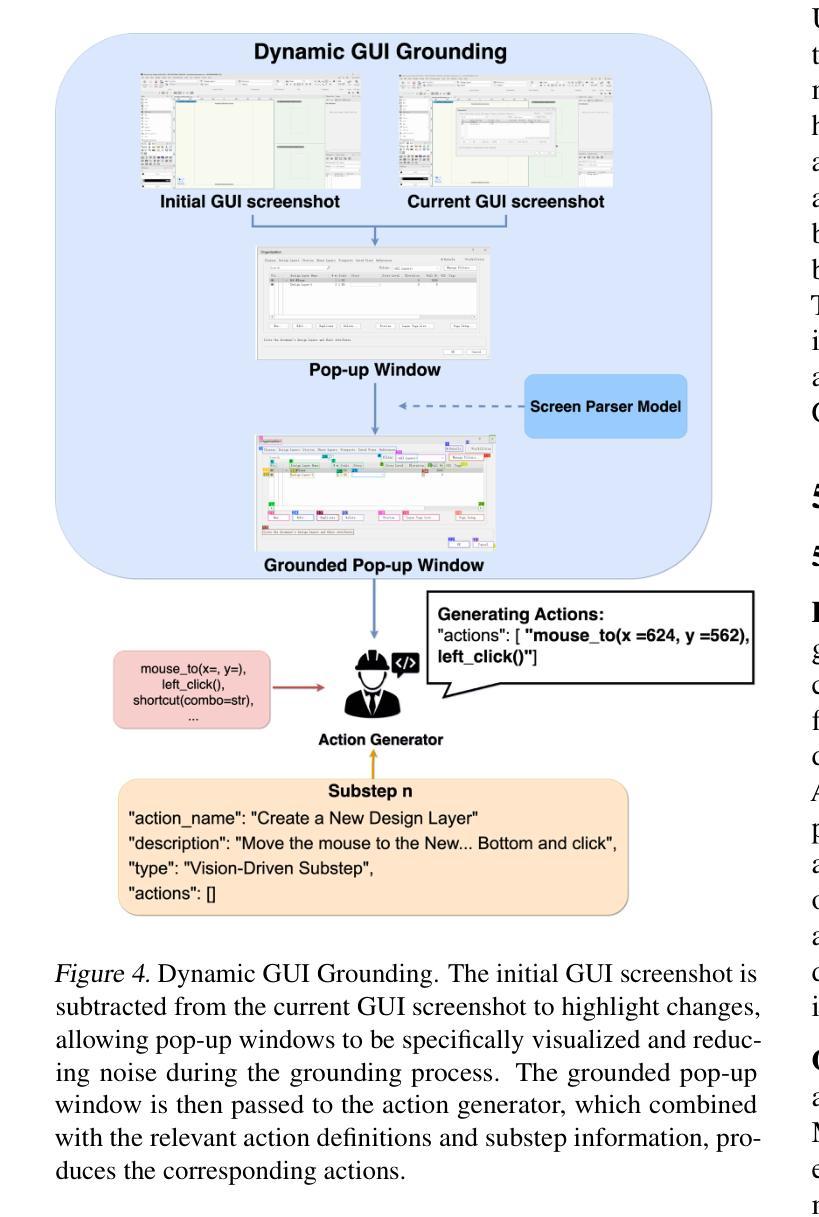
LibVulnWatch: A Deep Assessment Agent System and Leaderboard for Uncovering Hidden Vulnerabilities in Open-Source AI Libraries
Authors:Zekun Wu, Seonglae Cho, Umar Mohammed, Cristian Munoz, Kleyton Costa, Xin Guan, Theo King, Ze Wang, Emre Kazim, Adriano Koshiyama
Open-source AI libraries are foundational to modern AI systems, yet they present significant, underexamined risks spanning security, licensing, maintenance, supply chain integrity, and regulatory compliance. We introduce LibVulnWatch, a system that leverages recent advances in large language models and agentic workflows to perform deep, evidence-based evaluations of these libraries. Built on a graph-based orchestration of specialized agents, the framework extracts, verifies, and quantifies risk using information from repositories, documentation, and vulnerability databases. LibVulnWatch produces reproducible, governance-aligned scores across five critical domains, publishing results to a public leaderboard for ongoing ecosystem monitoring. Applied to 20 widely used libraries, including ML frameworks, LLM inference engines, and agent orchestration tools, our approach covers up to 88% of OpenSSF Scorecard checks while surfacing up to 19 additional risks per library, such as critical RCE vulnerabilities, missing SBOMs, and regulatory gaps. By integrating advanced language technologies with the practical demands of software risk assessment, this work demonstrates a scalable, transparent mechanism for continuous supply chain evaluation and informed library selection.
开源人工智能库是现代人工智能系统的基础,但它们带来了涵盖安全、许可、维护、供应链完整性和法规遵从性等方面的重大且尚未得到充分研究的风险。我们介绍了LibVulnWatch系统,它利用最新的人工智能语言模型和技术代理工作流程,对这些库进行深度、基于证据的评价。该系统建立在基于图的特殊代理编排之上,利用来自仓库、文档和漏洞数据库的信息提取、验证和量化风险。LibVulnWatch在五个关键领域产生可重现、符合治理的分数,并将结果发布到公共排行榜上,用于持续监控生态系统。该方法应用于20个广泛使用的库,包括机器学习框架、大型语言模型推理引擎和代理编排工具等,覆盖OpenSSF记分卡检查的88%,同时显示出每个库的另外多达19个风险,例如关键的远程代码执行漏洞、缺少SBOM和法规空白等。通过将先进的语言技术与软件风险评估的实际需求相结合,这项工作展示了一种用于持续供应链评估和知情的库选择的规模化、透明机制。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACL 2025 Student Research Workshop and ICML 2025 TAIG Workshop
Summary
本文介绍了Open-source AI库在现代AI系统中的重要性,但也指出了其存在的风险,包括安全、许可、维护、供应链完整性和法规合规性等方面的问题。为此,提出了一种名为LibVulnWatch的系统,该系统利用大型语言模型和代理工作流程的最新进展,对AI库进行深度、基于证据的评价。该框架通过图形化编排的专用代理提取、验证和量化风险,并使用来自仓库、文档和漏洞数据库的信息。LibVulnWatch在五个关键领域产生可重现、符合治理的分数,并将结果发布到公共排行榜上,用于持续监控生态系统。应用于广泛使用的库,包括机器学习框架、大型语言模型推理引擎和代理编排工具等,该系统的覆盖率高达OssF Scorecard检查的88%,同时发现每个库的额外风险高达19个,如关键远程代码执行漏洞、缺少SBOM和法规差距等。该工作将先进的语言技术与软件风险评估的实际需求相结合,展示了可扩展、透明的持续供应链评估机制和有针对性的库选择。
Key Takeaways
- Open-source AI库在现代AI系统中至关重要,但也存在多方面的风险。
- LibVulnWatch系统利用大型语言模型和代理工作流程进行深度风险评估。
- 该系统通过图形化编排的专用代理提取风险信息并进行验证和量化。
- LibVulnWatch覆盖OssF Scorecard检查的88%,并发现额外的风险如漏洞和法规差距等。
- 该系统适用于多种类型的库,包括机器学习框架和大型语言模型推理引擎等。
- LibVulnWatch采用可重现的评估方法,并通过公共排行榜进行持续监控。
点此查看论文截图

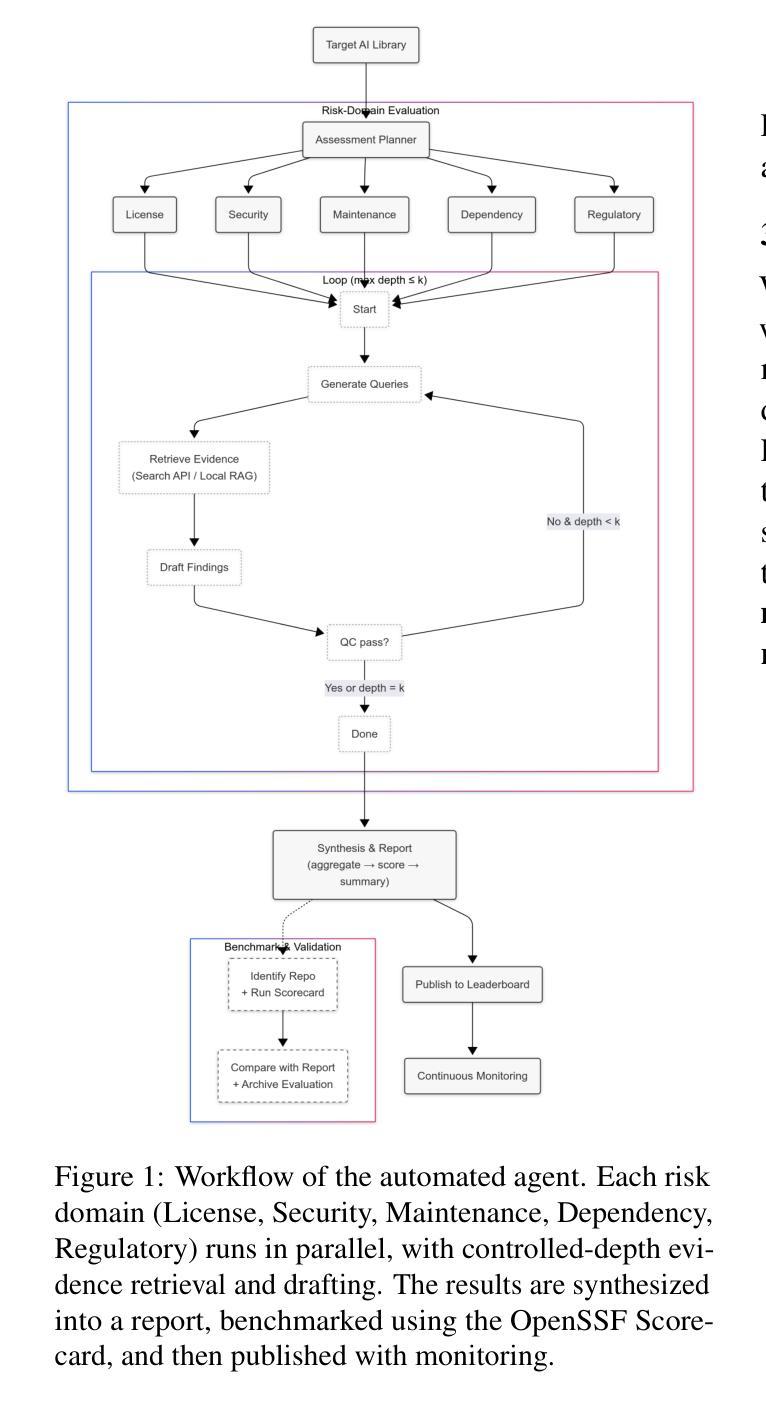
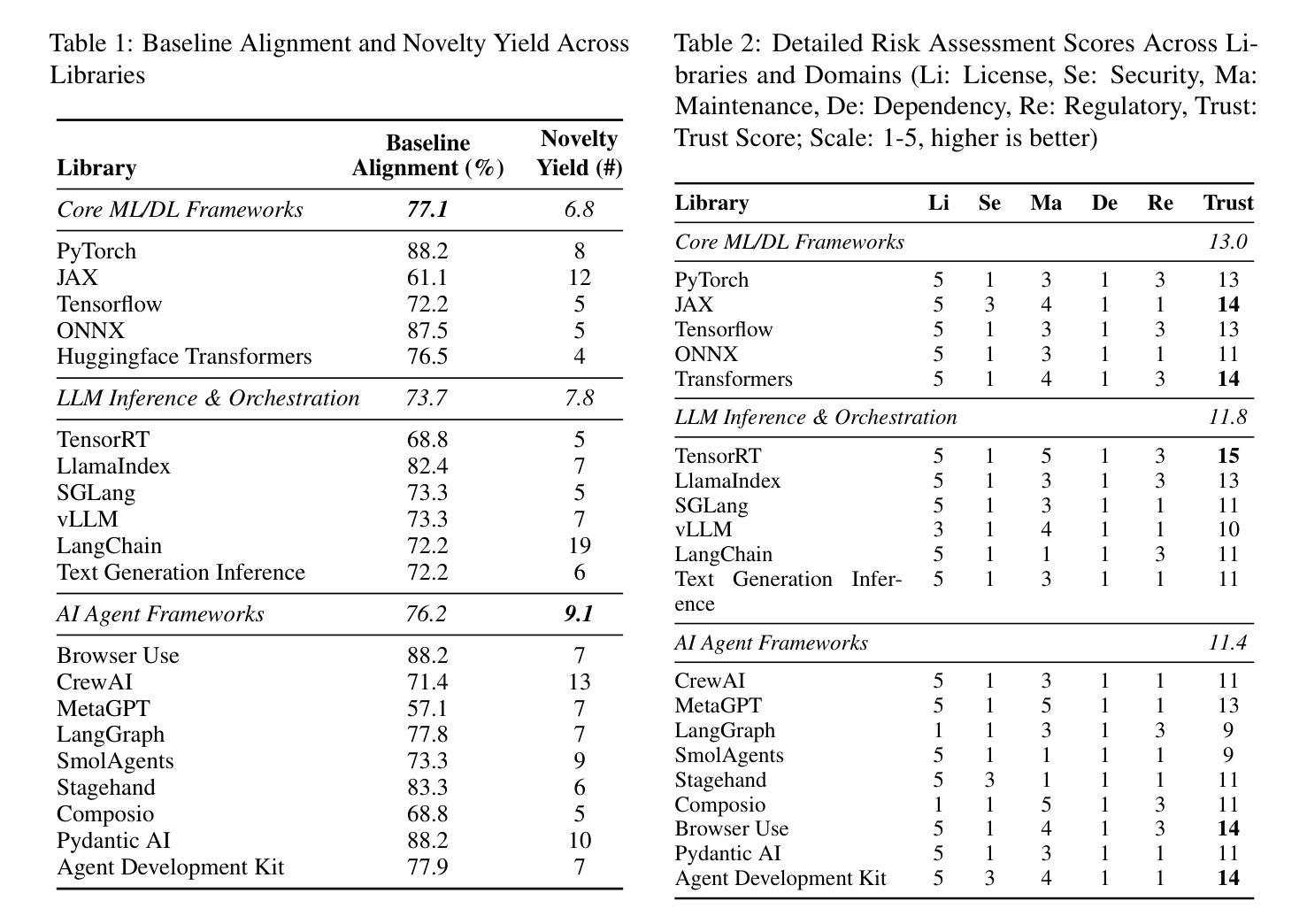
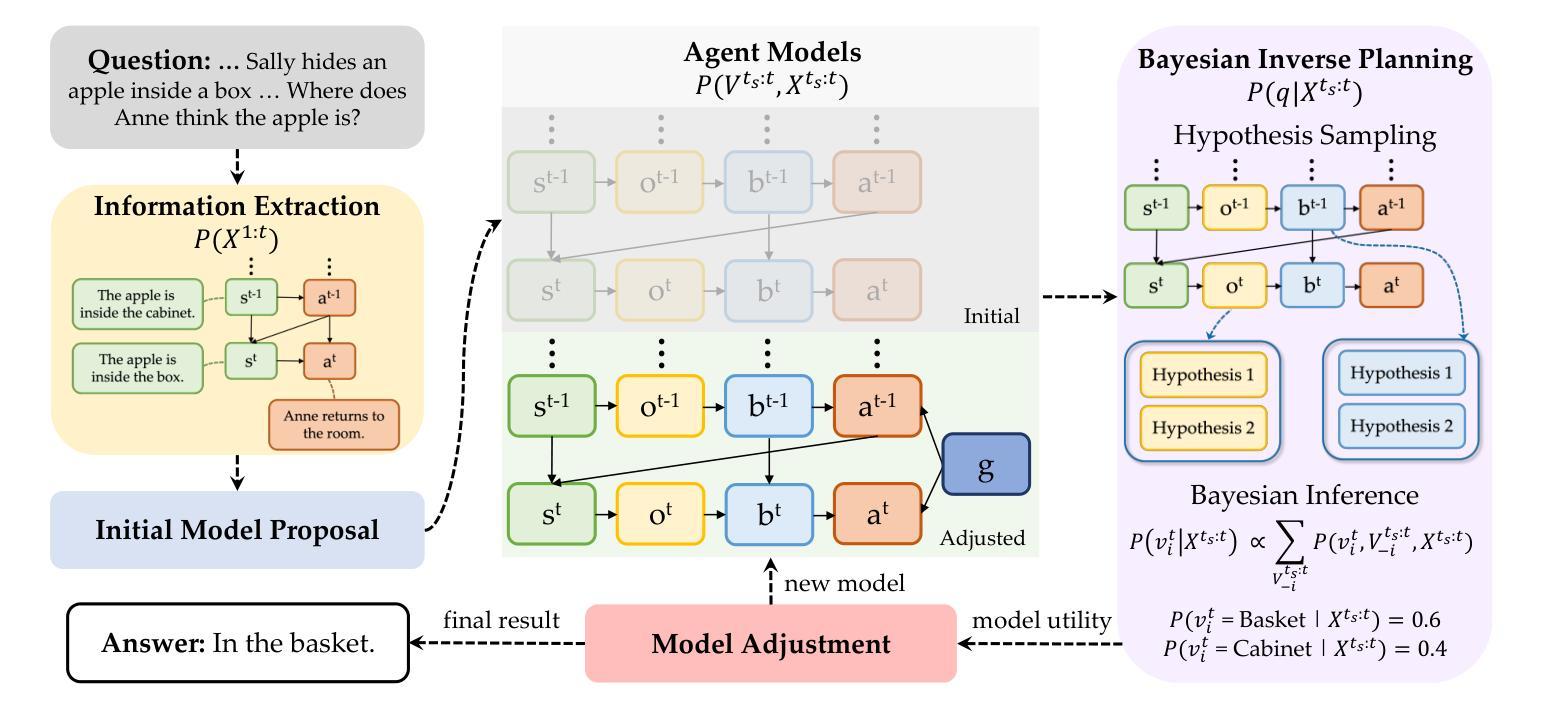
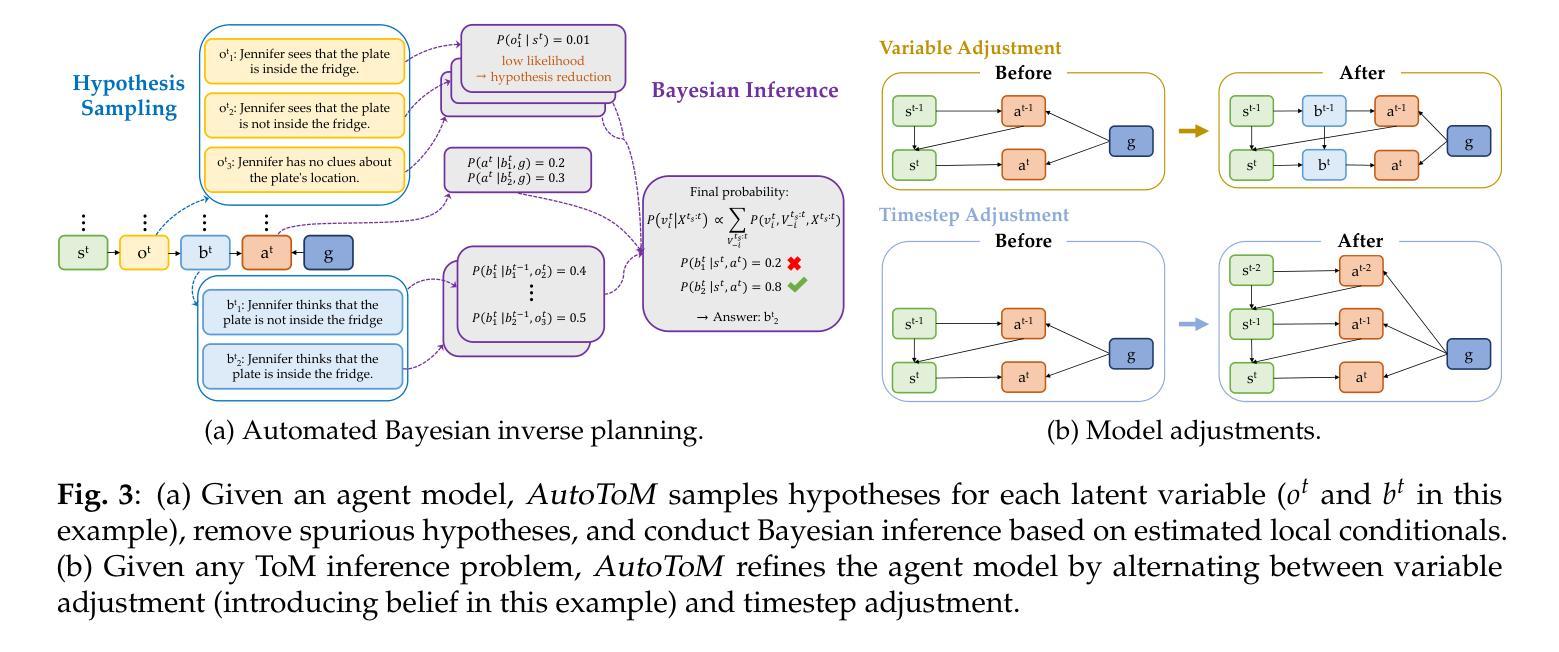
AutoToM: Scaling Model-based Mental Inference via Automated Agent Modeling
Authors:Zhining Zhang, Chuanyang Jin, Mung Yao Jia, Shunchi Zhang, Tianmin Shu
Theory of Mind (ToM), the ability to understand people’s minds based on their behavior, is key to developing socially intelligent agents. Current approaches to ToM reasoning either rely on prompting Large Language Models (LLMs), which are prone to systematic errors, or use handcrafted, rigid agent models for model-based inference, which are more robust but fail to generalize across domains. In this work, we introduce AutoToM, an automated agent modeling method for scalable, robust, and interpretable mental inference. Given a ToM problem, AutoToM first proposes an initial agent model and then performs automated Bayesian inverse planning based on this model, leveraging an LLM backend. Guided by inference uncertainty, it iteratively refines the model by introducing additional mental variables and/or incorporating more timesteps in the context. Across five diverse benchmarks, AutoToM outperforms existing ToM methods and even large reasoning models. Additionally, we show that AutoToM can produce human-like confidence estimates and enable online mental inference for embodied decision-making.
心理理论(ToM)是根据人们的行为理解他们心理的能力,是开发社会智能代理的关键。当前的心理理论推理方法要么依赖于提示大型语言模型(LLM),这容易产生系统误差,要么使用基于手工制作的僵化代理模型进行基于模型的推理,这在跨域推广时虽然更稳健但无法概括。在这项工作中,我们介绍了AutoToM,这是一种用于可扩展、稳健和可解释的心理推理的自动化代理建模方法。给定一个心理理论问题,AutoToM首先提出一个初步的代理模型,然后基于此模型进行自动化贝叶斯逆向规划,并利用LLM后端。在推理不确定性的指导下,它通过引入额外的心理变量和/或在背景下融入更多的时间步长来迭代优化模型。在五个不同的基准测试中,AutoToM的表现优于现有的心理理论方法和大型推理模型。此外,我们还展示了AutoToM能够产生类似人类的信心估计,并能够实现在线心理推理,用于实体决策制定。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 39 pages, 10 figures, 13 tables. Website at https://chuanyangjin.com/AutoToM/
Summary
本文介绍了理论思维(ToM)在开发社会智能代理中的重要性。当前的理论思维推理方法存在缺陷,要么依赖于易产生系统误差的大型语言模型(LLM),要么使用基于模型的推理的僵化代理模型,难以跨领域推广。本文提出了AutoToM这一自动化代理建模方法,用于实现可伸缩、稳健和可解释的心理推理。AutoToM针对理论思维问题首先提出初始代理模型,然后基于该模型进行自动化贝叶斯逆向规划,并利用大型语言模型后端。在五个不同的基准测试中,AutoToM的表现均优于现有的理论思维方法和大型推理模型。此外,我们还展示了AutoToM可以产生类似人类的信心估计,并用于在线心理推理和决策制定。
Key Takeaways
- 理论思维(ToM)是开发社会智能代理的关键。
- 当前的理论思维推理方法存在缺陷,需要新方法来解决。
- AutoToM是一种新的自动化代理建模方法,用于心理推理。
- AutoToM结合初始代理模型和贝叶斯逆向规划进行推理。
- AutoToM利用大型语言模型后端,通过引入心理变量和时间步长来不断优化模型。
- AutoToM在五个基准测试中表现优异,优于现有的理论思维方法和大型推理模型。
点此查看论文截图