⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-03 更新
Imagine for Me: Creative Conceptual Blending of Real Images and Text via Blended Attention
Authors:Wonwoong Cho, Yanxia Zhang, Yan-Ying Chen, David I. Inouye
Blending visual and textual concepts into a new visual concept is a unique and powerful trait of human beings that can fuel creativity. However, in practice, cross-modal conceptual blending for humans is prone to cognitive biases, like design fixation, which leads to local minima in the design space. In this paper, we propose a T2I diffusion adapter “IT-Blender” that can automate the blending process to enhance human creativity. Prior works related to cross-modal conceptual blending are limited in encoding a real image without loss of details or in disentangling the image and text inputs. To address these gaps, IT-Blender leverages pretrained diffusion models (SD and FLUX) to blend the latent representations of a clean reference image with those of the noisy generated image. Combined with our novel blended attention, IT-Blender encodes the real reference image without loss of details and blends the visual concept with the object specified by the text in a disentangled way. Our experiment results show that IT-Blender outperforms the baselines by a large margin in blending visual and textual concepts, shedding light on the new application of image generative models to augment human creativity.
将视觉和文本概念融合为一个新的视觉概念是人类独特且强大的特质,能够激发创造力。然而,在实践中,人类的跨模态概念融合容易受到认知偏见的影响,如设计僵化,这会导致设计空间中出现局部最小值。在本文中,我们提出了一种T2I扩散适配器“IT-Blender”,可以自动化融合过程以增强人类的创造力。以往与跨模态概念融合相关的工作在编码真实图像时要么会损失细节,要么无法解开图像和文本输入。为了解决这些缺陷,IT-Blender利用预训练的扩散模型(SD和FLUX)来融合干净参考图像和噪声生成图像的潜在表示。结合我们新颖的融合注意力机制,IT-Blender能够编码真实参考图像而不损失细节,并以解开的方式将视觉概念与文本指定的对象融合在一起。我们的实验结果表明,在融合视觉和文本概念方面,IT-Blender大幅度超越了基线方法,为图像生成模型在增强人类创造力方面的新应用提供了启示。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project website is available at https://imagineforme.github.io/
摘要
人类融合视觉和文本概念形成新的视觉概念是一个独特而强大的特质,能够激发创造力。然而,在实践中,人类的跨模态概念融合容易受到认知偏见的影响,如设计僵化症,这会导致设计空间的局部最小值。本文提出了一种T2I扩散适配器IT-Blender,可以自动化融合过程以增强人类的创造力。先前与跨模态概念融合相关的工作在编码真实图像时存在细节损失或在分离图像和文本输入方面的局限性。为了解决这些问题,IT-Blender利用预训练的扩散模型(SD和FLUX)将干净参考图像的潜在表示与噪声生成图像的潜在表示相融合。结合我们新颖的融合注意力机制,IT-Blender能够无损编码真实参考图像,并以分离的方式将视觉概念与文本指定的对象相融合。实验结果表明,IT-Blender在融合视觉和文本概念方面大大优于基线方法,为图像生成模型在增强人类创造力方面的新应用提供了新的启示。
关键见解
- 人类融合视觉和文本概念的能力是独特且强大的,能够激发创造力。
- 跨模态概念融合在实践中易受到认知偏见的影响,如设计僵化症。
- IT-Blender是一种T2I扩散适配器,旨在自动化跨模态概念融合过程以增强人类创造力。
- IT-Blender利用预训练的扩散模型和新颖的融合注意力机制进行图像和文本的融合。
- IT-Blender能够在编码真实图像时保持细节无损。
- IT-Blender将视觉概念与文本指定的对象以分离的方式融合。
点此查看论文截图


Supervised Diffusion-Model-Based PET Image Reconstruction
Authors:George Webber, Alexander Hammers, Andrew P King, Andrew J Reader
Diffusion models (DMs) have recently been introduced as a regularizing prior for PET image reconstruction, integrating DMs trained on high-quality PET images with unsupervised schemes that condition on measured data. While these approaches have potential generalization advantages due to their independence from the scanner geometry and the injected activity level, they forgo the opportunity to explicitly model the interaction between the DM prior and noisy measurement data, potentially limiting reconstruction accuracy. To address this, we propose a supervised DM-based algorithm for PET reconstruction. Our method enforces the non-negativity of PET’s Poisson likelihood model and accommodates the wide intensity range of PET images. Through experiments on realistic brain PET phantoms, we demonstrate that our approach outperforms or matches state-of-the-art deep learning-based methods quantitatively across a range of dose levels. We further conduct ablation studies to demonstrate the benefits of the proposed components in our model, as well as its dependence on training data, parameter count, and number of diffusion steps. Additionally, we show that our approach enables more accurate posterior sampling than unsupervised DM-based methods, suggesting improved uncertainty estimation. Finally, we extend our methodology to a practical approach for fully 3D PET and present example results from real [$^{18}$F]FDG brain PET data.
扩散模型(DMs)最近被引入为正电子发射断层扫描(PET)图像重建的正则化先验,将经过高质量PET图像训练的扩散模型与基于测量数据的无监督方案相结合。尽管这些方法由于独立于扫描器几何和注射活度水平而具有潜在的泛化优势,但它们放弃了显式建模扩散模型先验与噪声测量数据之间交互的机会,可能会限制重建的准确性。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种基于扩散模型的PET重建监督算法。我们的方法强制实施PET的Poisson似然模型的非负性,并适应PET图像的广泛强度范围。通过对现实的大脑PET幻影进行实验,我们证明了我们的方法在高剂量水平范围内定量地优于或匹配了基于最新深度学习的技术。我们进一步进行消融研究,以展示我们模型中提出的组件的优势,以及其依赖于训练数据、参数数量和扩散步骤数量的程度。此外,我们还表明,我们的方法能够比无监督的扩散模型方法提供更准确的后验采样,这表明不确定性估计有所提高。最后,我们将我们的方法论扩展为完全实用的3D PET方法,并展示了来自实际使用的${}^{18}$FDG大脑PET数据的示例结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 6 figures. Submitted to MICCAI 2025, not peer-reviewed
摘要
扩散模型(DMs)作为PET图像重建的正则化先验最近已被引入,通过将训练于高质量PET图像的DMs与基于测量数据的无监督方案相结合。虽然这些方法由于独立于扫描器几何和注入活度水平而具有潜在的优势,但它们没有显式建模DM先验与噪声测量数据之间的相互作用,可能限制了重建的准确性。针对这一问题,我们提出了一种基于扩散模型的监督式PET重建算法。我们的方法强制实施PET的Poisson似然模型的非负性,并适应PET图像的宽强度范围。在真实脑PET Phantom上的实验表明,我们的方法在多个剂量水平上定量优于或匹配最先进基于深度学习的方法。我们还进行了消融研究,以展示我们模型中提议组件的优势,以及其依赖于训练数据、参数计数和扩散步骤数量的程度。此外,我们显示我们的方法比无监督的DM方法能更准确地估计后验分布,这暗示了改进的不确定性估计。最后,我们将方法论扩展到用于全3D PET的实际方法,并展示了来自真实脑PET数据的示例结果。
关键见解
- 扩散模型(DMs)已作为PET图像重建的正则化先验引入。
- DMs结合了无监督方案和基于测量数据的方案。
- 虽然DMs具有潜在优势,但它们未显式建模与噪声测量数据的相互作用,可能限制了重建准确性。
- 提出了一种基于扩散模型的监督式PET重建算法,该算法强制实施PET的Poisson似然模型的非负性,适应PET图像的宽强度范围。
- 在真实脑PET Phantom上的实验显示新方法优于或匹配现有方法。
- 消融研究展示了模型中各组件的优势及其依赖性。
点此查看论文截图

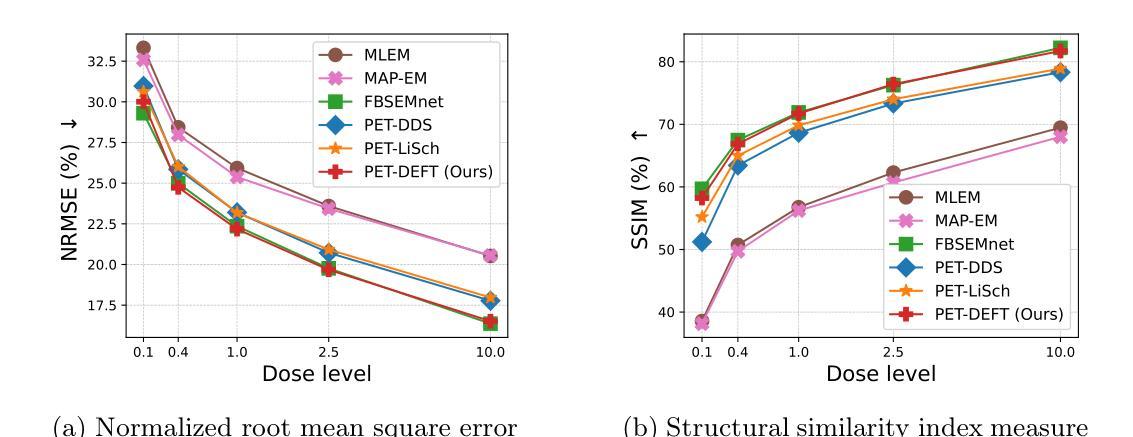
Controllable Reference-Based Real-World Remote Sensing Image Super-Resolution with Generative Diffusion Priors
Authors:Ce Wang, Wanjie Sun
Super-resolution (SR) techniques can enhance the spatial resolution of remote sensing images by utilizing low-resolution (LR) images to reconstruct high-resolution (HR) images, enabling more efficient large-scale earth observation applications. While single-image super-resolution (SISR) methods have shown progress, reference-based super-resolution (RefSR) offers superior performance by incorporating historical HR images alongside current LR observations. However, existing RefSR methods struggle with real-world complexities, such as cross-sensor resolution gap and significant land cover changes, often leading to under-generation or over-reliance on reference image. To address these challenges, we propose CRefDiff, a novel controllable reference-based diffusion model for real-world remote sensing image SR. To address the under-generation problem, CRefDiff is built upon the pretrained Stable Diffusion model, leveraging its powerful generative prior to produce accurate structures and textures. To mitigate over-reliance on the reference, we introduce a dual-branch fusion mechanism that adaptively integrates both local and global information from the reference image. Moreover, this novel dual-branch design enables reference strength control during inference, enhancing interactivity and flexibility of the model. Finally, a strategy named Better Start is proposed to significantly reduce the number of denoising steps, thereby accelerating the inference process. To support further research, we introduce Real-RefRSSRD, a new real-world RefSR dataset for remote sensing images, consisting of HR NAIP and LR Sentinel-2 image pairs with diverse land cover changes and significant temporal gaps. Extensive experiments on Real-RefRSSRD show that CRefDiff achieves state-of-the-art performance across various metrics and improves downstream tasks such as scene classification and semantic segmentation.
超分辨率(SR)技术可以利用低分辨率(LR)图像重建高分辨率(HR)图像,从而提高遥感图像的空间分辨率,使大规模地球观测应用更加高效。虽然单图像超分辨率(SISR)方法已经取得了进展,但基于参考的超分辨率(RefSR)方法通过结合历史高分辨率图像和当前低分辨率观测,表现出更优越的性能。然而,现有的RefSR方法面临现实世界的复杂性挑战,如跨传感器分辨率差距和土地覆盖变化显著等问题,这常常导致生成不足或过度依赖参考图像。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了CRefDiff,这是一种基于可控参考的新型遥感图像超分辨率的扩散模型。为解决生成不足的问题,CRefDiff建立在预训练的Stable Diffusion模型之上,利用强大的生成先验来产生准确的结构和纹理。为了减轻对参考图像的过度依赖,我们引入了一种双分支融合机制,该机制能够自适应地集成参考图像的局部和全局信息。此外,这种新型的双分支设计使得在推理过程中能够进行参考强度控制,增强了模型的交互性和灵活性。最后,我们提出了一种名为“更好开始”的策略,以大大减少去噪步骤的数量,从而加快推理过程。为了支持进一步研究,我们引入了Real-RefRSSRD,这是一个新的遥感图像现实世界的RefSR数据集,由高分辨率的NAIP和低分辨率的Sentinel-2图像对组成,具有多样化的土地覆盖变化和显著的时间间隔。在Real-RefRSSRD上的广泛实验表明,CRefDiff在各种指标上达到了最先进的性能,并改进了下游任务,如场景分类和语义分割。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于预训练的Stable Diffusion模型,我们提出了一种可控的参考基础扩散模型CRefDiff,用于解决真实遥感图像SR中的分辨率提升问题。CRefDiff通过引入双分支融合机制和Better Start策略,解决了现有RefSR方法面临的参考图像依赖过度和生成不足的问题,提高了模型的交互性和灵活性。此外,我们还引入了新的真实遥感图像RefSR数据集Real-RefRSSRD,实验表明CRefDiff在各项指标上均达到最新水平,并提高了场景分类和语义分割等下游任务的效果。
Key Takeaways
- CRefDiff模型利用预训练的Stable Diffusion模型的强大生成先验,解决真实遥感图像SR中的生成问题。
- 通过引入双分支融合机制,CRefDiff减轻了过度依赖参考图像的问题,并自适应地融合了局部和全局信息。
- CRefDiff首次实现了参考强度的可控性,增强了模型的交互性和灵活性。
- 提出的Better Start策略显著减少了去噪步骤的数量,从而加速了推理过程。
- 引入了新的真实遥感图像RefSR数据集Real-RefRSSRD,包含具有各种土地覆盖变化和显著时间间隔的HR NAIP和LR Sentinel-2图像对。
- 实验证明,CRefDiff在各种指标上实现了卓越的性能。
点此查看论文截图


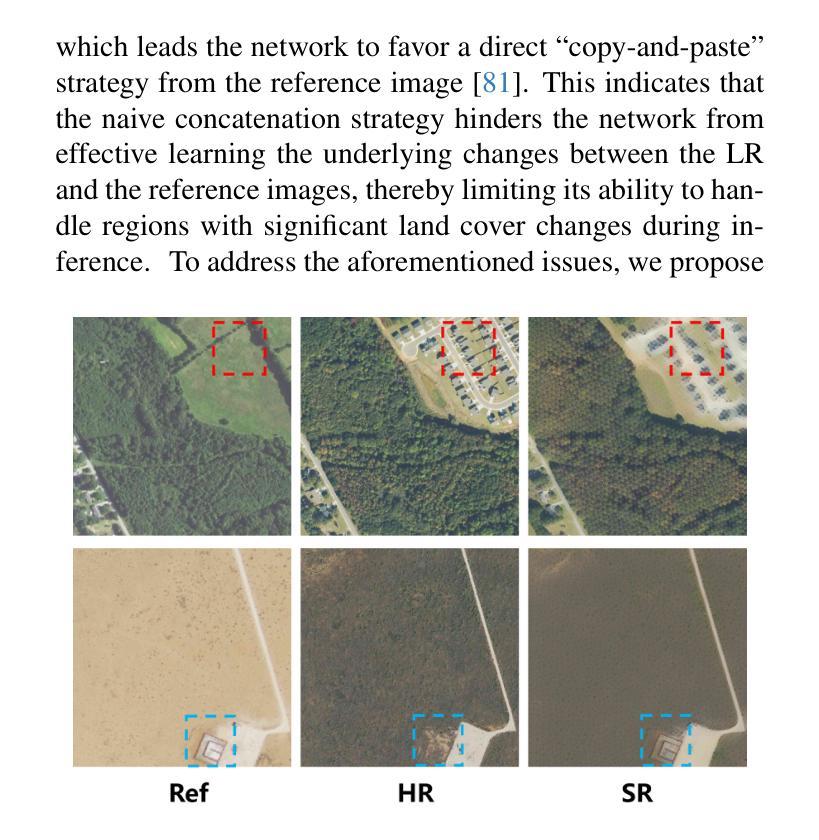
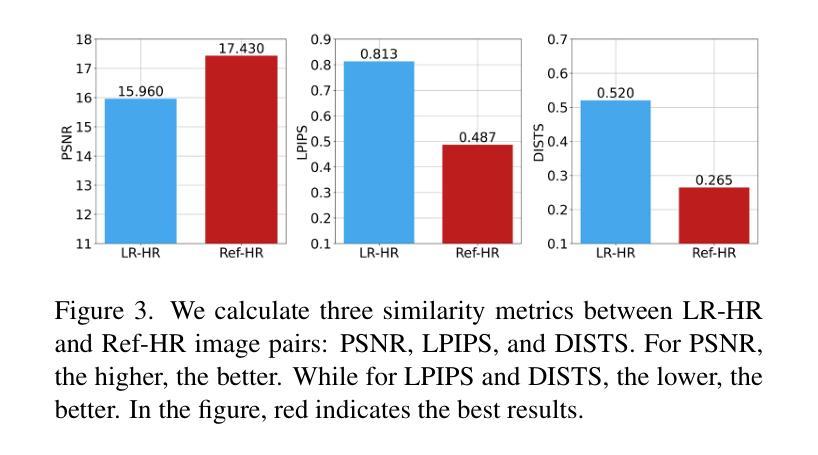
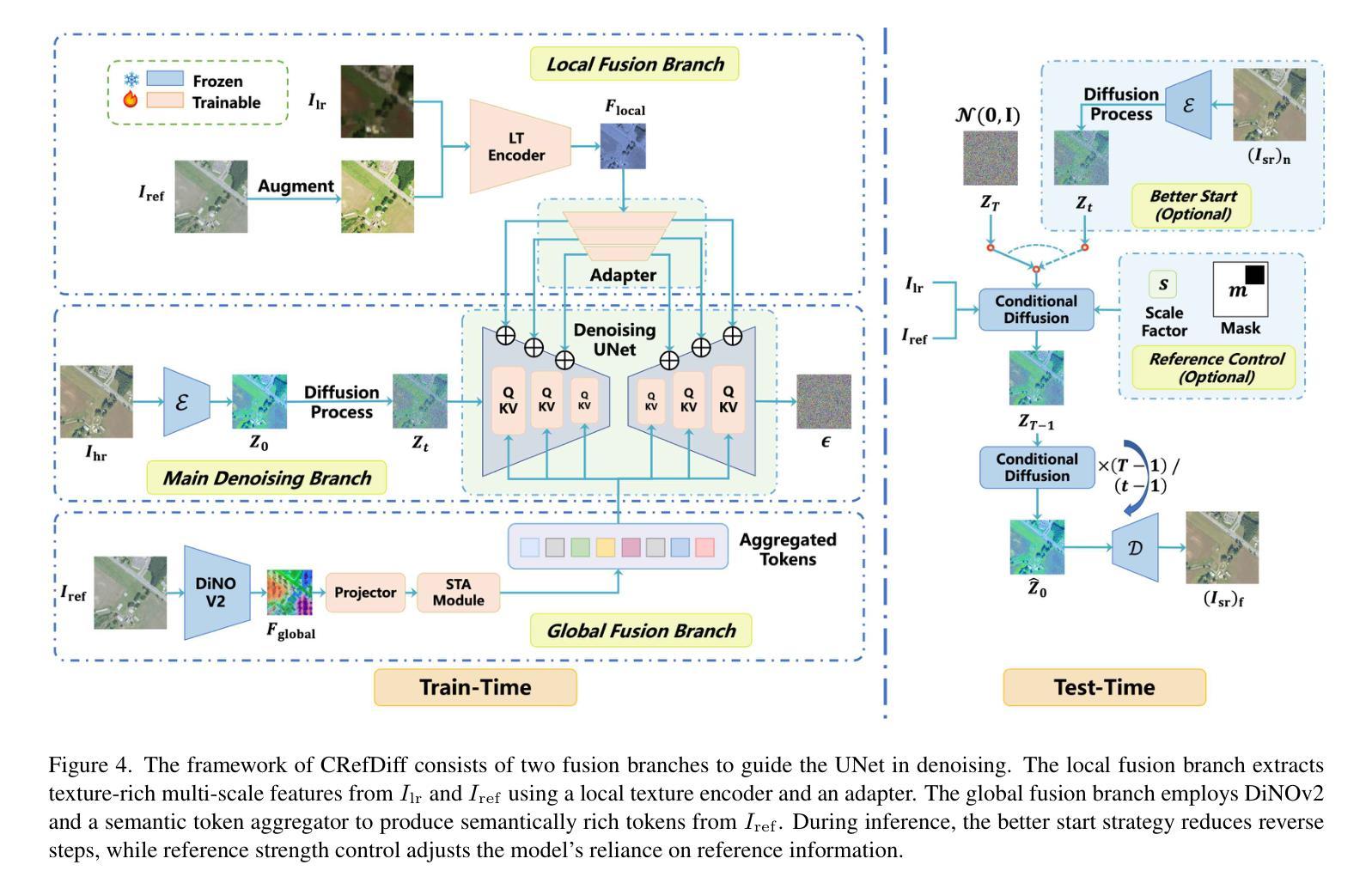
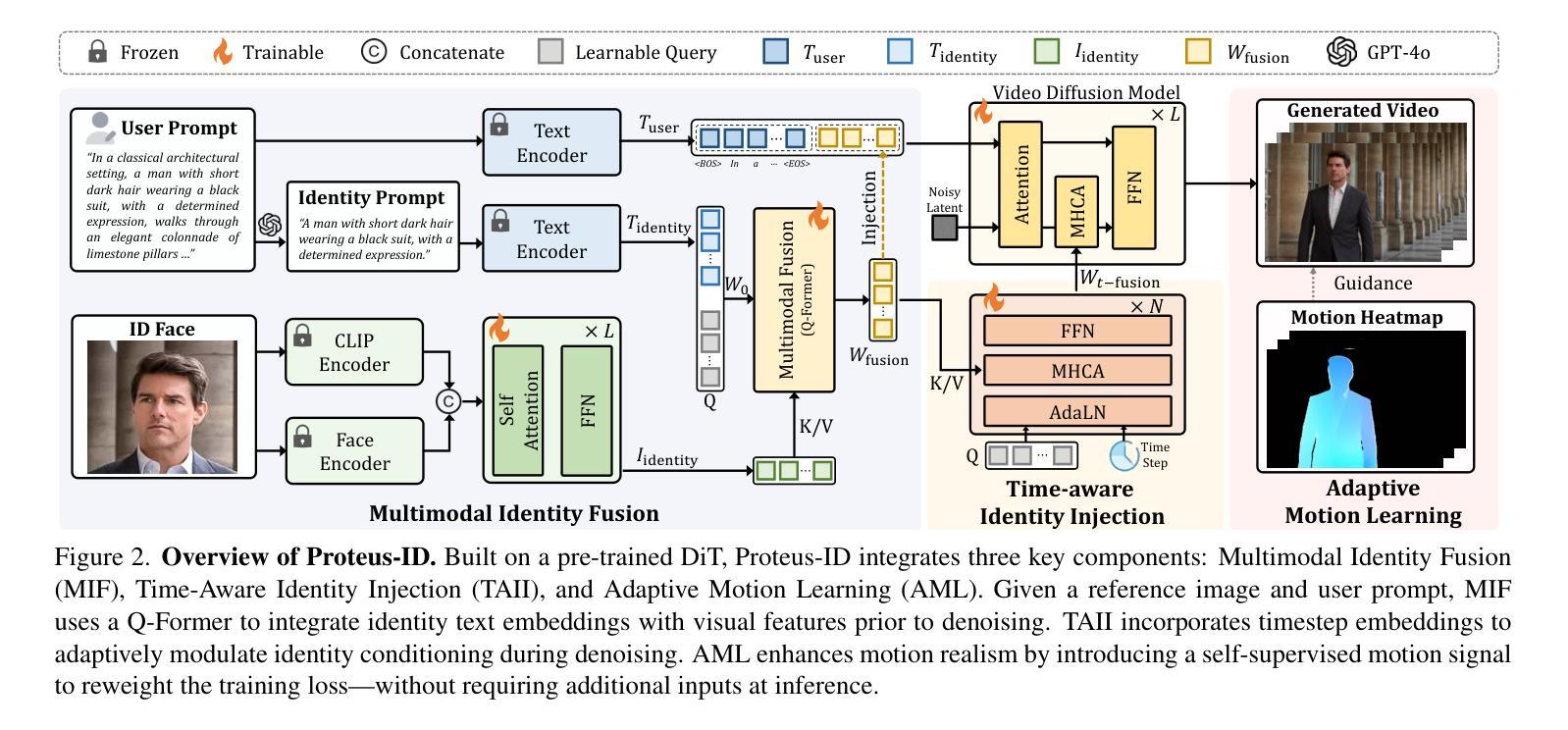
Proteus-ID: ID-Consistent and Motion-Coherent Video Customization
Authors:Guiyu Zhang, Chen Shi, Zijian Jiang, Xunzhi Xiang, Jingjing Qian, Shaoshuai Shi, Li Jiang
Video identity customization seeks to synthesize realistic, temporally coherent videos of a specific subject, given a single reference image and a text prompt. This task presents two core challenges: (1) maintaining identity consistency while aligning with the described appearance and actions, and (2) generating natural, fluid motion without unrealistic stiffness. To address these challenges, we introduce Proteus-ID, a novel diffusion-based framework for identity-consistent and motion-coherent video customization. First, we propose a Multimodal Identity Fusion (MIF) module that unifies visual and textual cues into a joint identity representation using a Q-Former, providing coherent guidance to the diffusion model and eliminating modality imbalance. Second, we present a Time-Aware Identity Injection (TAII) mechanism that dynamically modulates identity conditioning across denoising steps, improving fine-detail reconstruction. Third, we propose Adaptive Motion Learning (AML), a self-supervised strategy that reweights the training loss based on optical-flow-derived motion heatmaps, enhancing motion realism without requiring additional inputs. To support this task, we construct Proteus-Bench, a high-quality dataset comprising 200K curated clips for training and 150 individuals from diverse professions and ethnicities for evaluation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Proteus-ID outperforms prior methods in identity preservation, text alignment, and motion quality, establishing a new benchmark for video identity customization. Codes and data are publicly available at https://grenoble-zhang.github.io/Proteus-ID/.
视频身份定制旨在根据单张参考图像和文本提示合成特定主体的现实且时间上连贯的视频。此任务面临两个核心挑战:(1)在符合描述的外貌和行为的同时保持身份一致性;(2)生成自然流畅的动作,避免不现实的僵硬。为解决这些挑战,我们推出了Proteus-ID,这是一种基于扩散的身份一致且运动连贯的视频定制新型框架。首先,我们提出了多模态身份融合(MIF)模块,该模块使用Q-Former将视觉和文本线索统一为联合身份表示,为扩散模型提供连贯的指导,并消除模态不平衡。其次,我们提出了时间感知身份注入(TAII)机制,该机制动态调节去噪步骤中的身份条件,改进了精细细节的重构。第三,我们提出了自适应运动学习(AML)策略,这是一种自监督策略,根据光学流动派生的运动热图重新训练损失权重,增强运动真实感,而无需额外的输入。为了支持这项任务,我们构建了Proteus-Bench数据集,包含20万个高质量精选片段用于训练和来自不同职业和种族背景的150个个体用于评估。大量实验表明,Proteus-ID在身份保留、文本对齐和运动质量方面优于先前的方法,为视频身份定制树立了新基准。相关代码和数据已公开在https://grenoble-zhang.github.io/Proteus-ID/上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint. Work in progress
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于扩散模型的新型视频身份定制框架Proteus-ID,用于合成与给定参考图像和文本提示一致的视频。它面临的主要挑战是保持身份一致性并生成自然、流畅的运动。通过引入Multimodal Identity Fusion(MIF)模块、Time-Aware Identity Injection(TAII)机制和Adaptive Motion Learning(AML)策略,Proteus-ID在身份保留、文本对齐和运动质量方面均表现出优异性能。同时,本文还构建了Proteus-Bench数据集以支持此任务,实验结果证明了其性能优越性。该方法的代码和数据已在网上公开。
Key Takeaways
以下是文中涉及的关键点概览:
- 视频身份定制的目标是合成与给定参考图像和文本提示一致的视频。
- 主要挑战在于保持身份一致性并生成自然、流畅的运动。
- Proteus-ID是一种基于扩散模型的新型视频身份定制框架,通过引入多种策略解决上述挑战。
- MIF模块结合了视觉和文本线索,形成联合身份表示,为扩散模型提供连贯指导并消除模态不平衡问题。
- TAII机制动态调节身份条件在降噪步骤中的应用,改进了精细细节的重建。
- AML是一种自监督策略,基于光学流衍生的运动热图重新训练损失权重,提高运动真实感。
- 为支持此任务,构建了Proteus-Bench数据集,包含大量高质量视频剪辑用于训练和评估。
点此查看论文截图


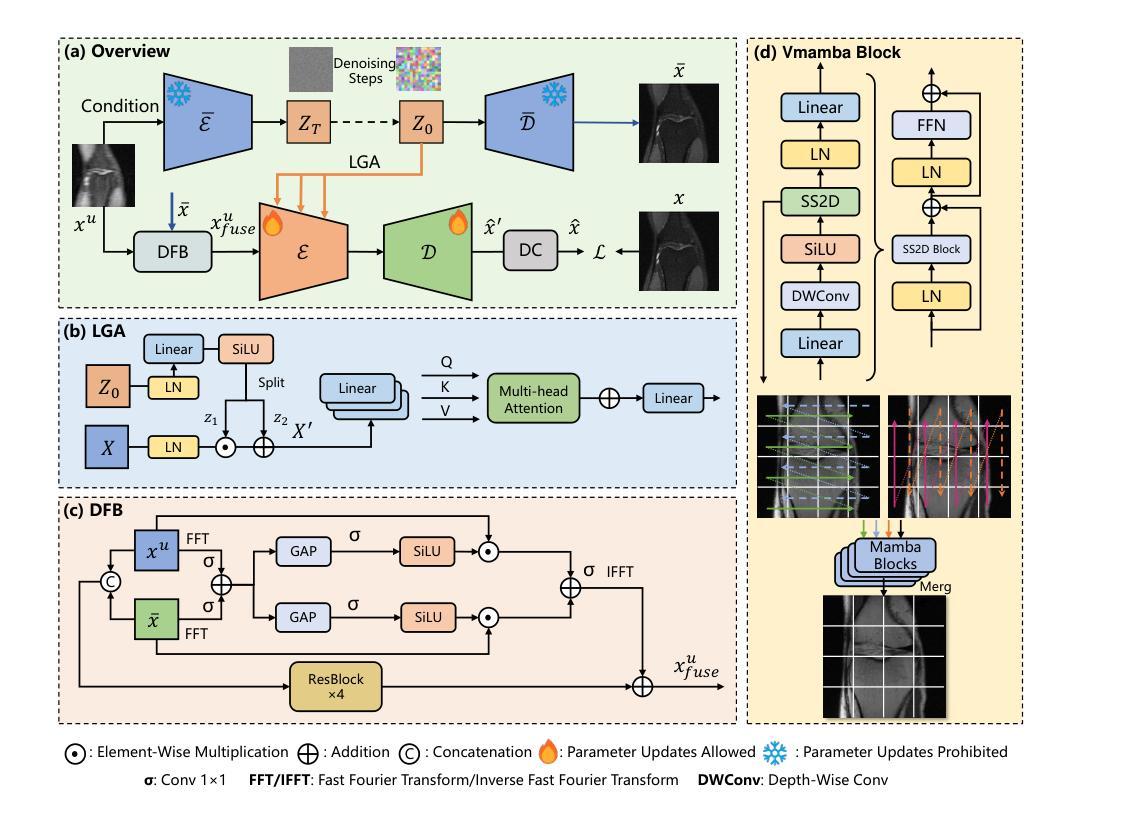
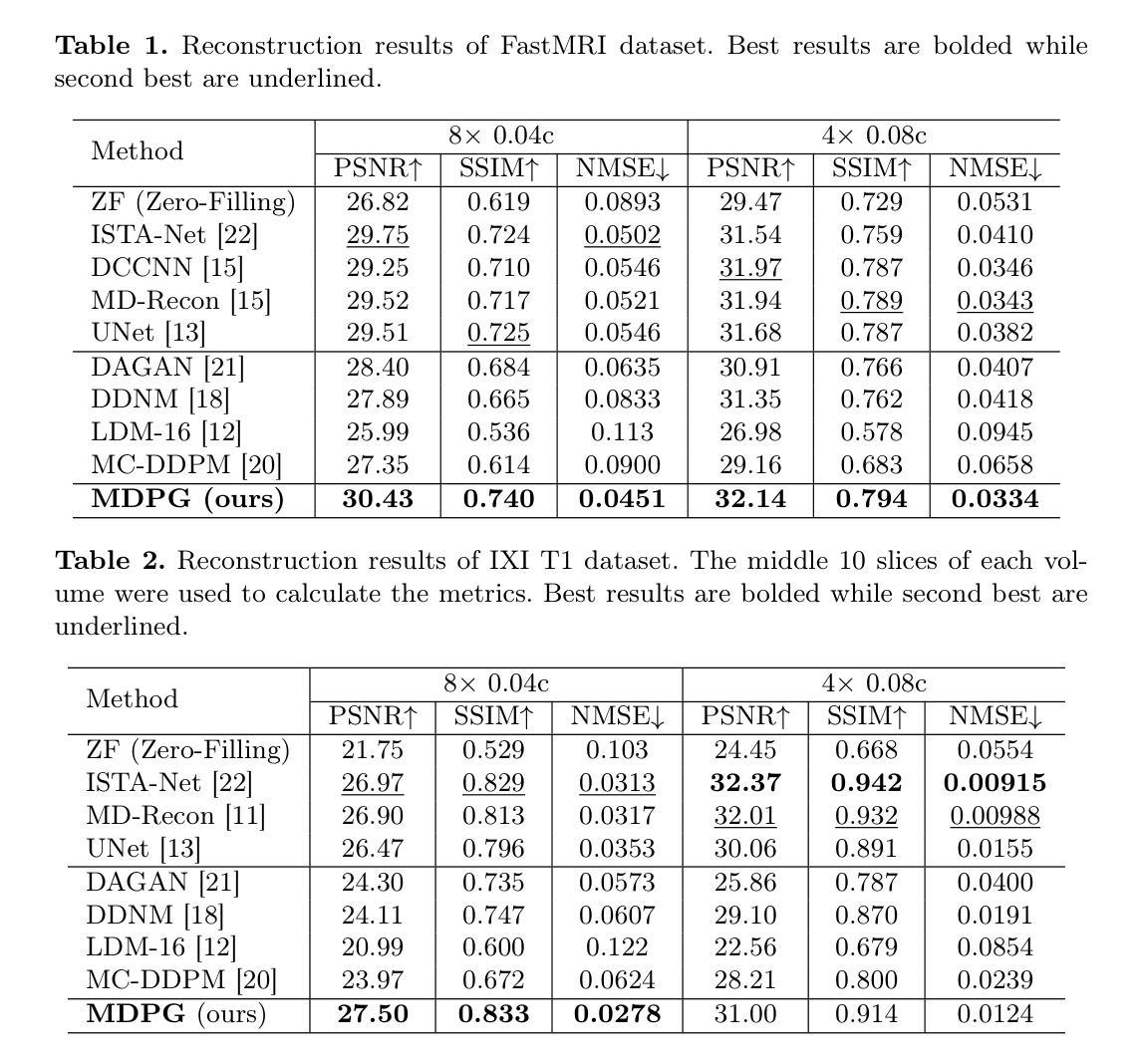
MDPG: Multi-domain Diffusion Prior Guidance for MRI Reconstruction
Authors:Lingtong Zhang, Mengdie Song, Xiaohan Hao, Huayu Mai, Bensheng Qiu
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) reconstruction is essential in medical diagnostics. As the latest generative models, diffusion models (DMs) have struggled to produce high-fidelity images due to their stochastic nature in image domains. Latent diffusion models (LDMs) yield both compact and detailed prior knowledge in latent domains, which could effectively guide the model towards more effective learning of the original data distribution. Inspired by this, we propose Multi-domain Diffusion Prior Guidance (MDPG) provided by pre-trained LDMs to enhance data consistency in MRI reconstruction tasks. Specifically, we first construct a Visual-Mamba-based backbone, which enables efficient encoding and reconstruction of under-sampled images. Then pre-trained LDMs are integrated to provide conditional priors in both latent and image domains. A novel Latent Guided Attention (LGA) is proposed for efficient fusion in multi-level latent domains. Simultaneously, to effectively utilize a prior in both the k-space and image domain, under-sampled images are fused with generated full-sampled images by the Dual-domain Fusion Branch (DFB) for self-adaption guidance. Lastly, to further enhance the data consistency, we propose a k-space regularization strategy based on the non-auto-calibration signal (NACS) set. Extensive experiments on two public MRI datasets fully demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed methodology. The code is available at https://github.com/Zolento/MDPG.
磁共振成像(MRI)重建在医学诊断中至关重要。作为最新的生成模型,扩散模型(DMs)由于其在图像域中的随机性,难以产生高保真图像。潜在扩散模型(LDMs)在潜在域中产生紧凑且详细的先验知识,这可以有效地引导模型更有效地学习原始数据分布。受此启发,我们提出了由预训练的LDMs提供的多域扩散先验指导(MDPG),以增强MRI重建任务中的数据一致性。具体来说,我们首先构建了一个基于Visual-Mamba的骨干网,该骨干网能够实现欠采样图像的有效编码和重建。然后,将预训练的LDMs集成到潜在域和图像域中,以提供条件先验。提出了一种新型的潜在引导注意力(LGA),用于在多层次潜在域中进行有效融合。同时,为了有效利用k空间和图像域中的先验信息,欠采样图像通过双域融合分支(DFB)与生成的完整采样图像融合,以实现自适应引导。最后,为了进一步增强数据一致性,我们提出了一种基于非自动校准信号(NACS)集的k空间正则化策略。在两个公共MRI数据集上的大量实验充分证明了所提出方法的有效性。代码可在https://github.com/Zolento/MDPG找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accept by MICCAI2025
Summary
本文提出一种基于多域扩散先验指导(MDPG)的磁共振成像(MRI)重建方法。该方法利用预训练的潜在扩散模型(LDM)提供条件先验,通过视觉玛珈(Visual-Mamba)为基础的后备架构实现高效编码和重建。同时,引入潜在引导注意力(LGA)实现多级潜在域的有效融合,并通过双域融合分支(DFB)进行自适应指导。此外,还提出了一种基于非自动校准信号(NACS)集的k-空间正则化策略,进一步提高数据一致性。该方法在公共MRI数据集上的实验验证了其有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型(DMs)在生成高保真图像方面存在挑战,尤其在图像域的随机性影响其表现。
- 潜在扩散模型(LDMs)在潜在域提供紧凑和详细的先验知识,能有效指导模型学习原始数据分布。
- 提出了一种基于预训练LDMs的多域扩散先验指导(MDPG)方法,用于增强MRI重建任务中的数据一致性。
- 利用视觉玛珈为基础的后备架构实现高效编码和重建。
- 引入潜在引导注意力(LGA)实现多级别潜在域的有效融合。
- 通过双域融合分支(DFB)进行自适应指导,利用k-空间和非自动校准信号(NACS)的先验信息。
点此查看论文截图

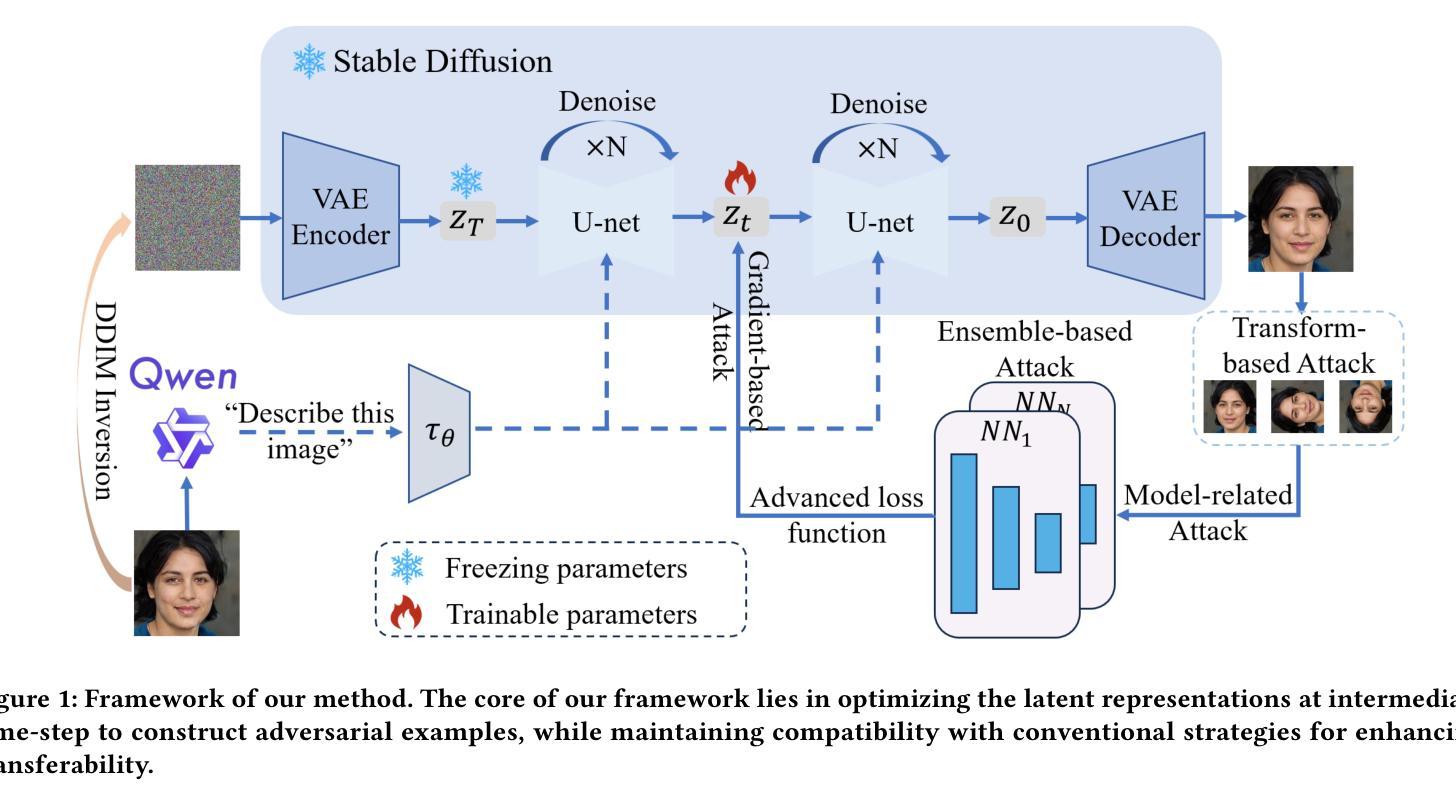
A Unified Framework for Stealthy Adversarial Generation via Latent Optimization and Transferability Enhancement
Authors:Gaozheng Pei, Ke Ma, Dongpeng Zhang, Chengzhi Sun, Qianqian Xu, Qingming Huang
Due to their powerful image generation capabilities, diffusion-based adversarial example generation methods through image editing are rapidly gaining popularity. However, due to reliance on the discriminative capability of the diffusion model, these diffusion-based methods often struggle to generalize beyond conventional image classification tasks, such as in Deepfake detection. Moreover, traditional strategies for enhancing adversarial example transferability are challenging to adapt to these methods. To address these challenges, we propose a unified framework that seamlessly incorporates traditional transferability enhancement strategies into diffusion model-based adversarial example generation via image editing, enabling their application across a wider range of downstream tasks. Our method won first place in the “1st Adversarial Attacks on Deepfake Detectors: A Challenge in the Era of AI-Generated Media” competition at ACM MM25, which validates the effectiveness of our approach.
由于基于扩散模型的对抗样本生成方法通过图像编辑具备强大的图像生成能力,它们正迅速流行起来。然而,由于这些基于扩散的方法依赖于扩散模型的判别能力,它们往往在超越传统图像分类任务时遇到难题,例如在深度伪造检测中。此外,将传统增强对抗样本迁移性的策略应用于这些方法是一个挑战。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一个统一框架,通过图像编辑将传统迁移增强策略无缝纳入基于扩散模型的对抗样本生成方法中,使它们能够广泛应用于更广泛的下游任务。我们的方法在ACM MM25举办的“首个针对深度伪造检测器的对抗性攻击:人工智能媒体时代的新挑战”竞赛中获得第一名,验证了我们的方法的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型基于图像编辑的对抗样本生成方法因其强大的图像生成能力而迅速流行。然而,由于依赖于扩散模型的判别能力,这些方法在深度伪造检测等非常规图像分类任务上往往难以推广。为了克服这些挑战,我们提出了一个统一的框架,通过图像编辑将传统的可转移性增强策略无缝地融入到扩散模型为基础的对抗样本生成中,使它们能够应用于更广泛的下游任务。我们的方法在ACM MM25的“第一届针对深度伪造检测器的对抗性攻击:人工智能生成媒体时代的挑战”竞赛中荣获第一名,验证了我们的方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型基于图像编辑的对抗样本生成方法具有强大的图像生成能力,因此受到广泛关注。
- 由于依赖扩散模型的判别能力,这些方法在非常规图像分类任务上的推广存在挑战。
- 为了克服这些挑战,提出了一个统一的框架,将传统可转移性增强策略融入扩散模型对抗样本生成中。
- 该框架通过图像编辑实现传统与扩散模型方法的结合,提高了方法的适用性。
- 该方法在ACM MM25竞赛中荣获第一名,验证了其有效性。
- 此方法有助于提高扩散模型在非常规图像分类任务上的性能,为深度伪造检测等领域提供了新的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图


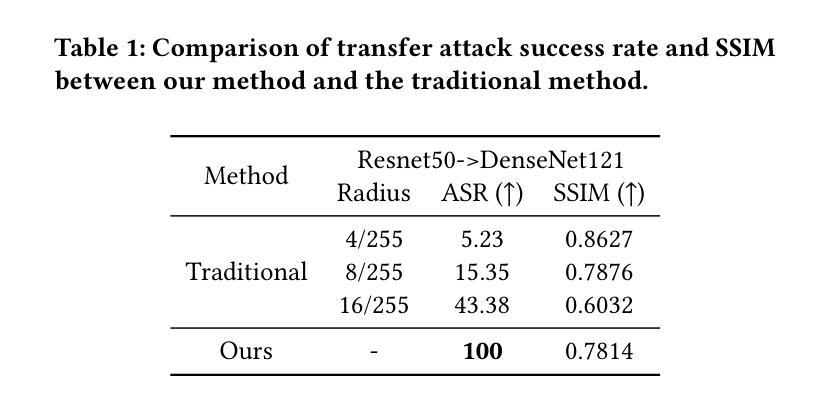


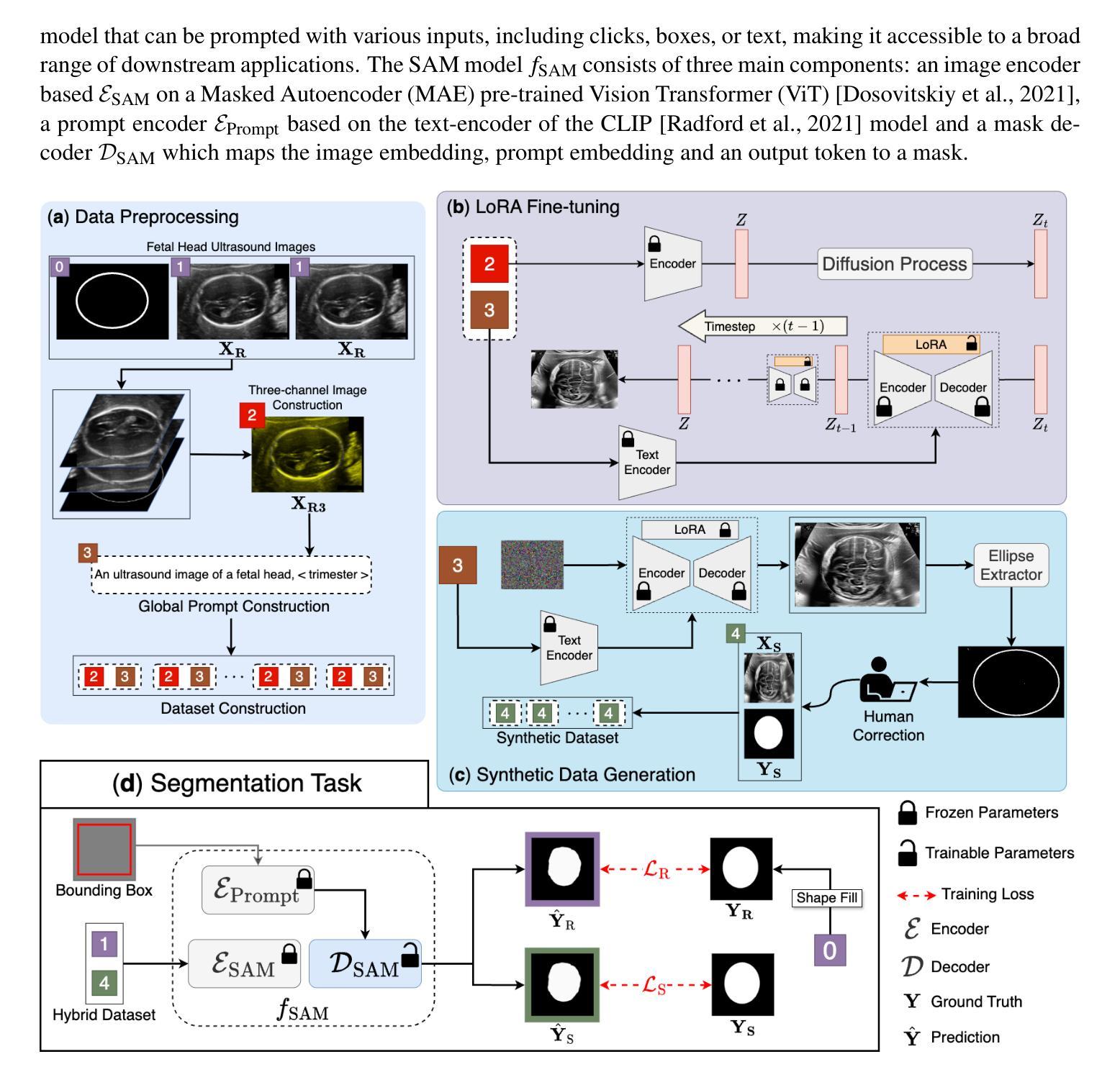
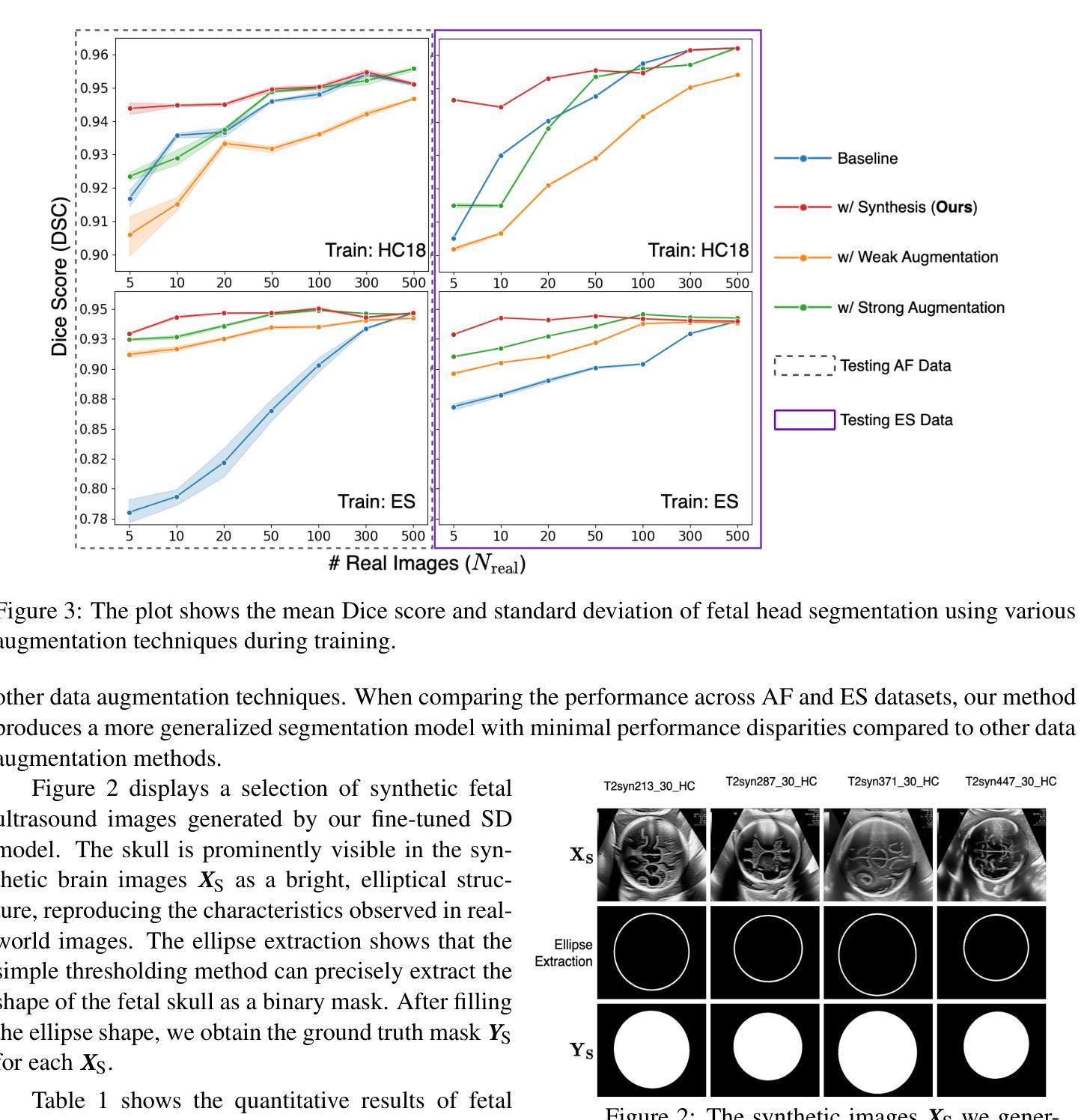
Diffusion Model-based Data Augmentation Method for Fetal Head Ultrasound Segmentation
Authors:Fangyijie Wang, Kevin Whelan, Félix Balado, Guénolé Silvestre, Kathleen M. Curran
Medical image data is less accessible than in other domains due to privacy and regulatory constraints. In addition, labeling requires costly, time-intensive manual image annotation by clinical experts. To overcome these challenges, synthetic medical data generation offers a promising solution. Generative AI (GenAI), employing generative deep learning models, has proven effective at producing realistic synthetic images. This study proposes a novel mask-guided GenAI approach using diffusion models to generate synthetic fetal head ultrasound images paired with segmentation masks. These synthetic pairs augment real datasets for supervised fine-tuning of the Segment Anything Model (SAM). Our results show that the synthetic data captures real image features effectively, and this approach reaches state-of-the-art fetal head segmentation, especially when trained with a limited number of real image-mask pairs. In particular, the segmentation reaches Dice Scores of 94.66% and 94.38% using a handful of ultrasound images from the Spanish and African cohorts, respectively. Our code, models, and data are available on GitHub.
医疗图像数据由于隐私和监管限制,相较于其他领域更难以获取。此外,标注需要临床专家进行昂贵且耗时的手动图像注释。为了克服这些挑战,合成医疗数据生成提供了一个有前景的解决方案。采用生成式深度学习模型的生成人工智能(GenAI)已被证明在生成逼真的合成图像方面非常有效。本研究提出了一种使用扩散模型的新型掩膜引导GenAI方法,生成合成胎儿头部超声图像及其分割掩膜配对。这些合成配对数据增强了真实数据集,用于监督微调Segment Anything Model(SAM)。我们的结果表明,合成数据有效地捕捉了真实图像的特征,特别是在使用有限数量的真实图像-掩膜配对进行训练时,该方法达到了最先进的胎儿头部分割效果。特别是,使用来自西班牙和非洲队列的少量超声图像,分割率达到Dice Score的94.66%和94.38%。我们的代码、模型和数据可在GitHub上获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究提出一种使用扩散模型生成带有分割掩膜合成胎儿头部超声图像的方法。合成数据用于增强真实数据集,以监督微调分割任何模型(SAM)。结果显示,合成数据能有效捕捉真实图像特征,特别是在使用少量真实图像-掩膜对进行训练时,达到先进的胎儿头部分割效果。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像数据由于隐私和监管限制而难以获取。
- 医学图像标注需要临床专家耗时耗力的手动标注。
- 生成式人工智能(GenAI)使用生成式深度学习模型,能有效生成逼真的合成图像。
- 本研究提出一种新颖的基于扩散模型的mask-guided GenAI方法,用于生成合成胎儿头部超声图像及其分割掩膜。
- 合成数据对真实数据集进行增强,用于监督微调SAM模型。
- 合成数据能有效捕捉真实图像特征。
点此查看论文截图

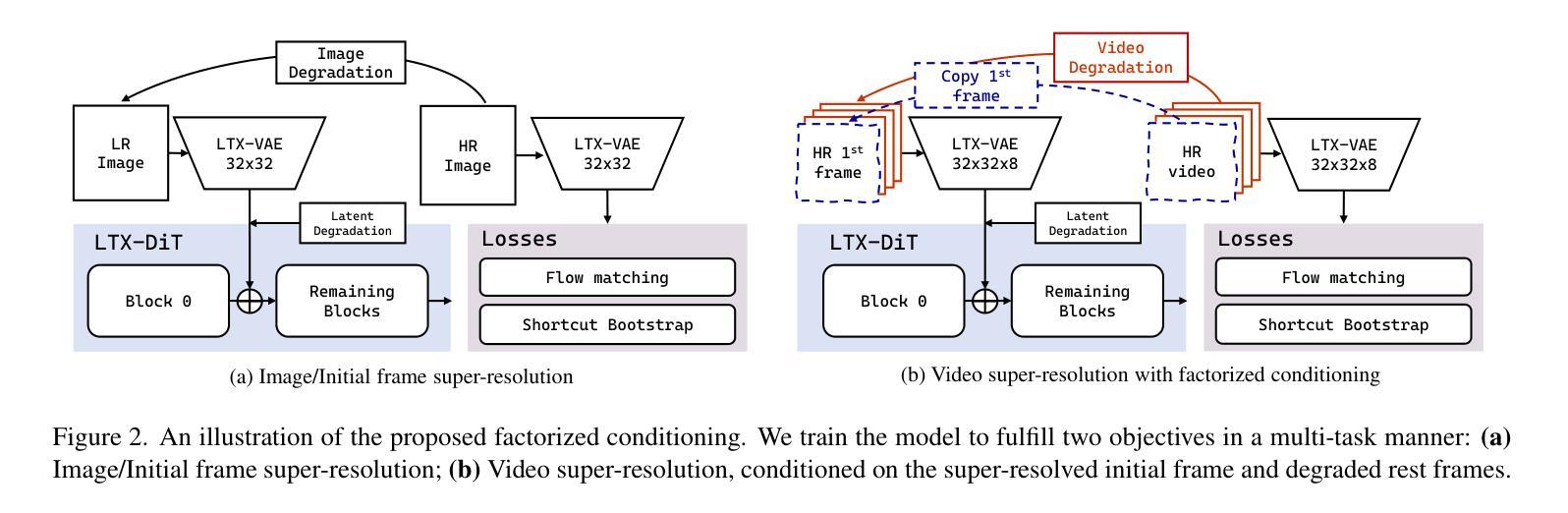
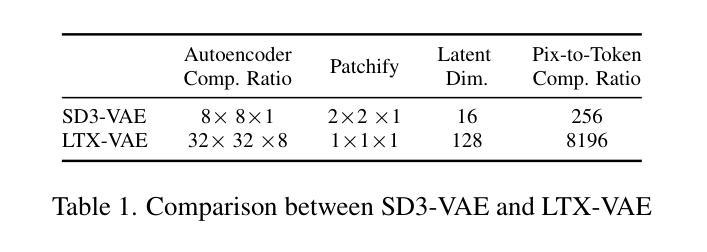
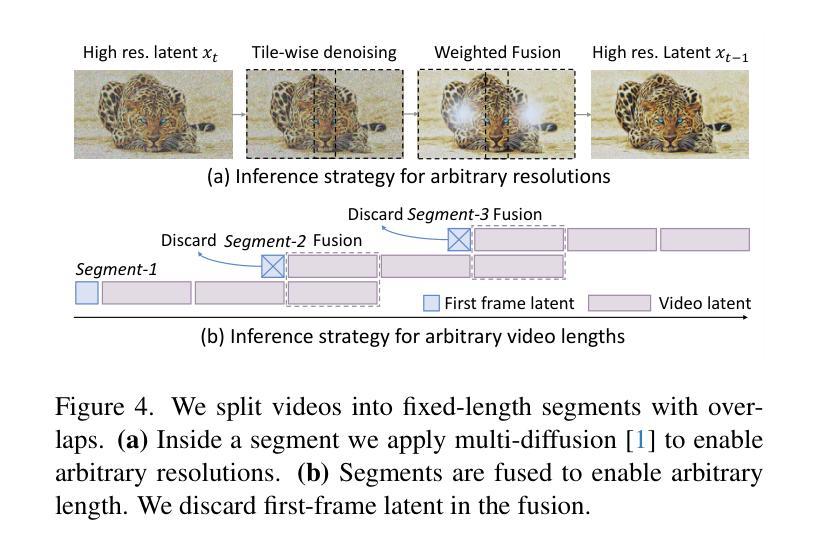
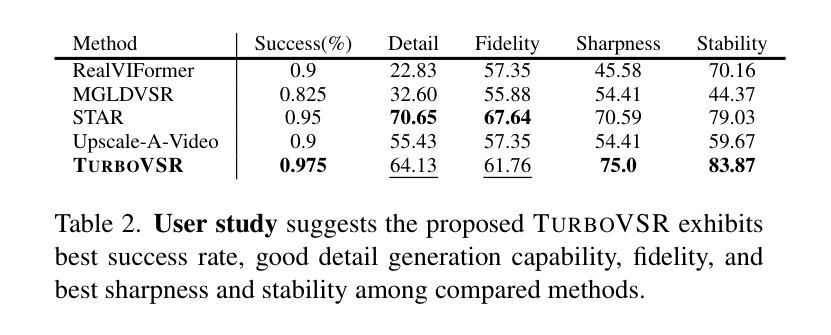
TurboVSR: Fantastic Video Upscalers and Where to Find Them
Authors:Zhongdao Wang, Guodongfang Zhao, Jingjing Ren, Bailan Feng, Shifeng Zhang, Wenbo Li
Diffusion-based generative models have demonstrated exceptional promise in the video super-resolution (VSR) task, achieving a substantial advancement in detail generation relative to prior methods. However, these approaches face significant computational efficiency challenges. For instance, current techniques may require tens of minutes to super-resolve a mere 2-second, 1080p video. In this paper, we present TurboVSR, an ultra-efficient diffusion-based video super-resolution model. Our core design comprises three key aspects: (1) We employ an autoencoder with a high compression ratio of 32$\times$32$\times$8 to reduce the number of tokens. (2) Highly compressed latents pose substantial challenges for training. We introduce factorized conditioning to mitigate the learning complexity: we first learn to super-resolve the initial frame; subsequently, we condition the super-resolution of the remaining frames on the high-resolution initial frame and the low-resolution subsequent frames. (3) We convert the pre-trained diffusion model to a shortcut model to enable fewer sampling steps, further accelerating inference. As a result, TurboVSR performs on par with state-of-the-art VSR methods, while being 100+ times faster, taking only 7 seconds to process a 2-second long 1080p video. TurboVSR also supports image resolution by considering image as a one-frame video. Our efficient design makes SR beyond 1080p possible, results on 4K (3648$\times$2048) image SR show surprising fine details.
基于扩散的生成模型在视频超分辨率(VSR)任务中表现出巨大的潜力,相对于传统方法,在细节生成方面取得了实质性的进展。然而,这些方法面临着计算效率的重大挑战。例如,当前的技术可能需要数分钟来对一个仅2秒、1080p的视频进行超分辨率处理。在本文中,我们提出了TurboVSR,一种高效的基于扩散的视频超分辨率模型。我们的核心设计包括三个方面:(1)我们采用压缩比为32×32×8的自编码器来减少令牌数量。(2)高度压缩的潜在空间给训练带来了巨大挑战。我们引入了因子化条件来减轻学习复杂性:我们首先学习对初始帧进行超分辨率处理,然后将其余帧的超分辨率条件设置为高分辨率初始帧和低分辨率后续帧。(3)我们将预训练的扩散模型转换为快捷方式模型,以减少采样步骤,从而进一步加速推理。因此,TurboVSR的性能与最先进的VSR方法相当,但速度提高了100倍以上,仅需7秒即可处理一个2秒的1080p视频。TurboVSR还支持将图像视为单帧视频进行分辨率提升。我们高效的设计使得超过1080p的SR成为可能,在4K(3648×2048)图像SR的结果显示出惊人的细节。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV, 2025
摘要
扩散模型在视频超分辨率(VSR)任务中展现出巨大潜力,相比传统方法,在细节生成方面取得了显著进展。然而,这些方法在计算效率上面临挑战。例如,现有技术可能需要数分钟才能对仅2秒、1080p的视频进行超分辨率处理。本文提出TurboVSR,一种高效的扩散模型视频超分辨率方法。其核心设计包括三个方面:首先,采用压缩比为32×32×8的自编码器减少令牌数量。其次,针对高度压缩的潜在问题,我们引入因子化条件来减轻学习复杂性:首先学习超分辨率初始帧,然后以其高分辨率初始帧和低分辨率后续帧为条件进行剩余帧的超分辨率处理。最后,我们将预训练的扩散模型转换为快捷方式模型,以减少采样步骤,进一步加速推理。因此,TurboVSR性能与最先进的VSR方法相当,但速度提高了100倍以上,仅需7秒即可处理2秒长的1080p视频。此外,TurboVSR通过将图像视为单帧视频来支持图像分辨率提升,其高效设计使得超过1080p的SR成为可能,在4K(3648×2048)图像SR的结果显示出惊人的细节。
关键见解
- 扩散模型在视频超分辨率任务中具有显著优势,在细节生成方面取得重大进展。
- 当前扩散模型在计算效率方面面临挑战,需要优化。
- TurboVSR通过采用高效设计提高扩散模型的计算效率,包括使用自编码器、因子化条件和快捷方式模型转换。
- TurboVSR性能与最先进的VSR方法相当,但处理速度显著提高。
- TurboVSR能够在短时间内处理高分辨率视频,例如仅需7秒即可处理2秒长的1080p视频。
- TurboVSR支持图像分辨率提升,可将图像视为单帧视频进行处理。
- TurboVSR在4K图像超分辨率方面的表现令人印象深刻,显示出惊人的细节。
点此查看论文截图

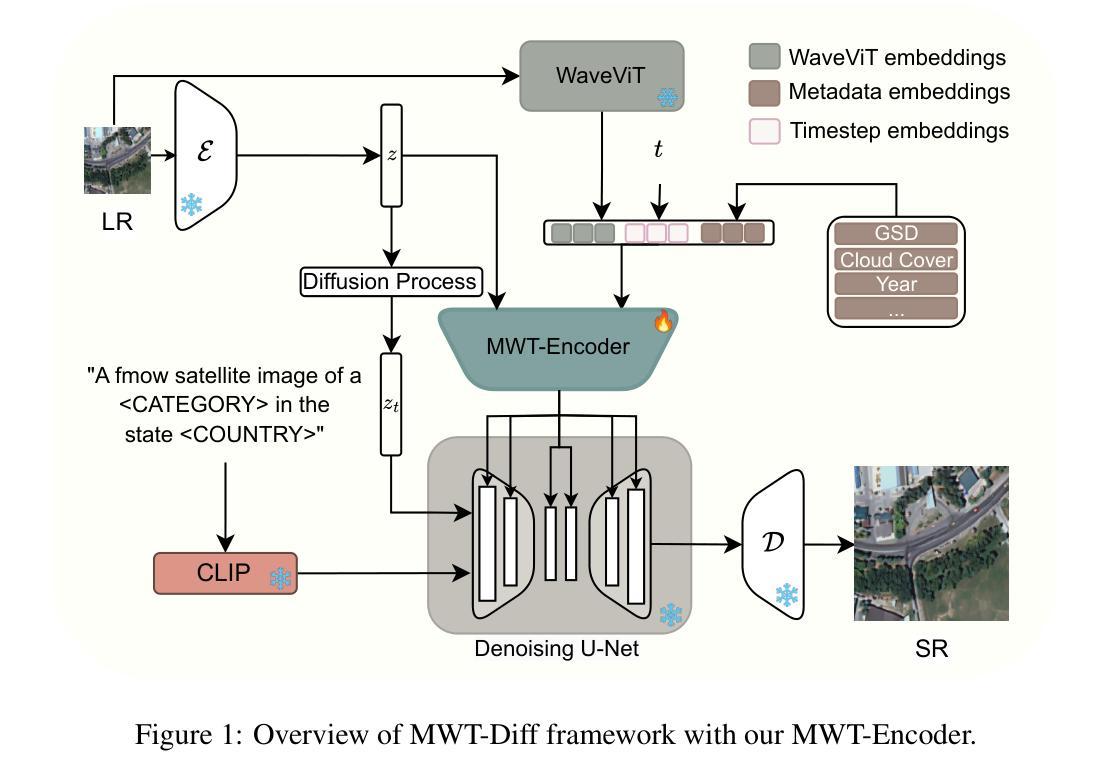
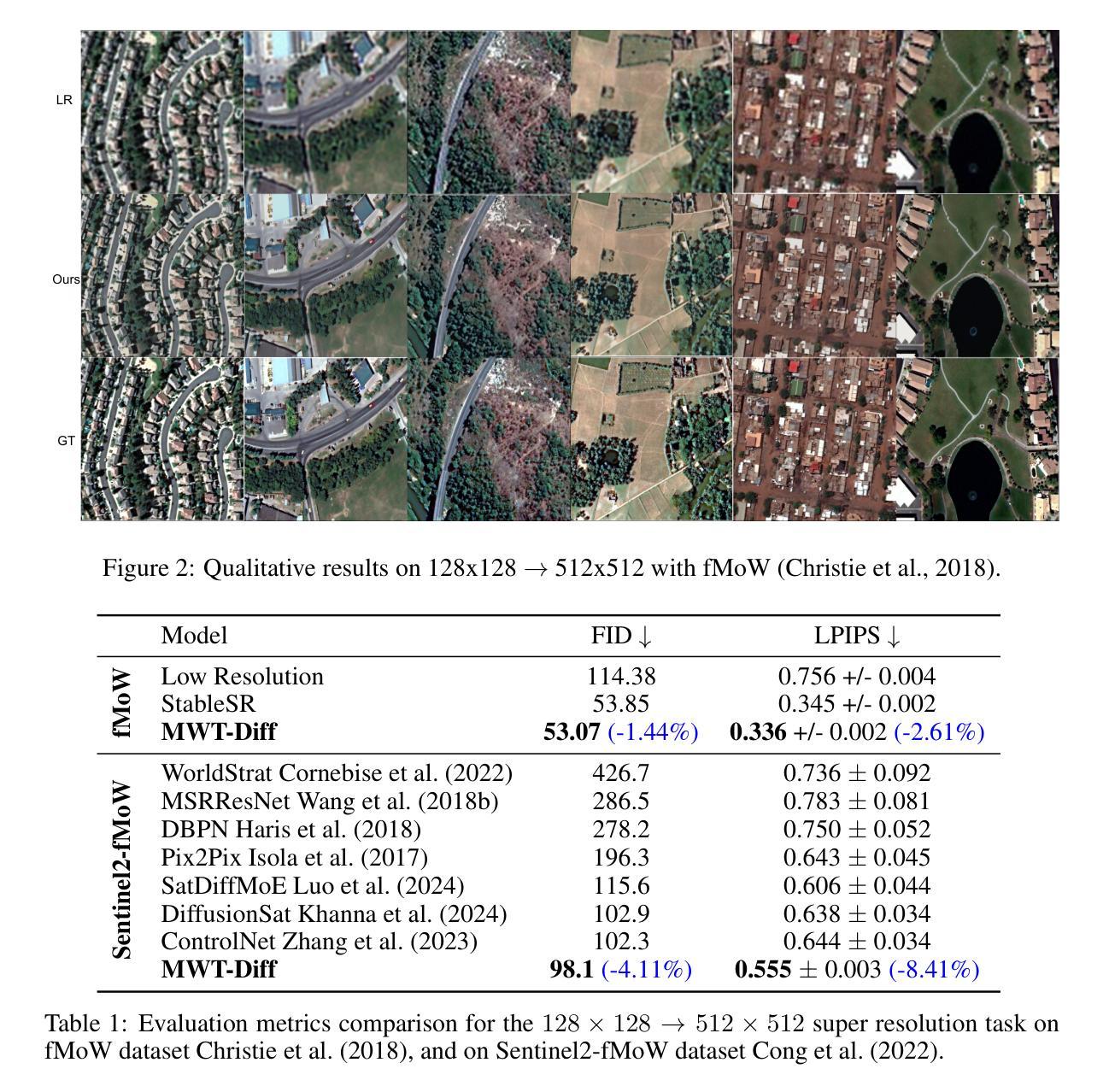
Metadata, Wavelet, and Time Aware Diffusion Models for Satellite Image Super Resolution
Authors:Luigi Sigillo, Renato Giamba, Danilo Comminiello
The acquisition of high-resolution satellite imagery is often constrained by the spatial and temporal limitations of satellite sensors, as well as the high costs associated with frequent observations. These challenges hinder applications such as environmental monitoring, disaster response, and agricultural management, which require fine-grained and high-resolution data. In this paper, we propose MWT-Diff, an innovative framework for satellite image super-resolution (SR) that combines latent diffusion models with wavelet transforms to address these challenges. At the core of the framework is a novel metadata-, wavelet-, and time-aware encoder (MWT-Encoder), which generates embeddings that capture metadata attributes, multi-scale frequency information, and temporal relationships. The embedded feature representations steer the hierarchical diffusion dynamics, through which the model progressively reconstructs high-resolution satellite imagery from low-resolution inputs. This process preserves critical spatial characteristics including textural patterns, boundary discontinuities, and high-frequency spectral components essential for detailed remote sensing analysis. The comparative analysis of MWT-Diff across multiple datasets demonstrated favorable performance compared to recent approaches, as measured by standard perceptual quality metrics including FID and LPIPS.
获取高分辨率卫星图像通常受到卫星传感器空间和时间上的限制以及频繁观测带来的高成本的影响。这些挑战阻碍了环境监控、灾害响应和农业管理等应用,这些应用需要精细的、高分辨率的数据。在本文中,我们提出了MWT-Diff,这是一个创新的卫星图像超分辨率(SR)框架,它将潜在扩散模型与小波变换相结合,以解决这些挑战。该框架的核心是一个新颖的金属数据、小波和时间感知编码器(MWT-Encoder),它生成嵌入,捕获金属数据属性、多尺度频率信息和时间关系。嵌入式特征表示引导分层扩散动力学,通过该模型从低分辨率输入逐步重建高分辨率卫星图像。这一过程保留了重要的空间特征,包括纹理模式、边界不连续性和高频谱成分,对于详细的遥感分析至关重要。MWT-Diff在多数据集上的比较分析表明,与最近的方法相比,其在FID和LPIPS等标准感知质量指标上的表现较为优越。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025 Workshop on Machine Learning for Remote Sensing (ML4RS)
摘要
本文提出了MWT-Diff框架,该框架结合潜在扩散模型和小波变换,旨在解决高分辨率卫星图像获取所面临的挑战。该框架通过元数据、小波和时序感知编码器(MWT-Encoder)生成嵌入特征,捕捉元数据属性、多尺度频率信息和时序关系。嵌入特征表示引导层次扩散动力学,模型从低分辨率输入逐步重建高分辨率卫星图像。这一过程保留了关键的空间特征,包括纹理模式、边界不连续性和高频光谱成分,适用于详细的遥感分析。对比多个数据集上的MWT-Diff分析显示,与最新方法相比,其性能表现优异,通过标准感知质量指标FID和LPIPS进行评估。
关键见解
- MWT-Diff框架结合了潜在扩散模型和小波变换,旨在解决卫星图像超分辨率(SR)中的挑战。
- 框架核心在于元数据、小波和时序感知编码器(MWT-Encoder),能生成捕捉多种信息的嵌入特征。
- 嵌入特征引导层次扩散动力学,从低分辨率输入重建高分辨率卫星图像。
- 该过程保留了空间特征,包括纹理模式、边界不连续性和高频光谱成分。
- MWT-Diff在多个数据集上的表现优于其他最新方法。
- 性能评估采用标准感知质量指标,如FID和LPIPS。
- 该框架在环境监控、灾害响应和农业管理等应用中具有潜在应用价值。
点此查看论文截图

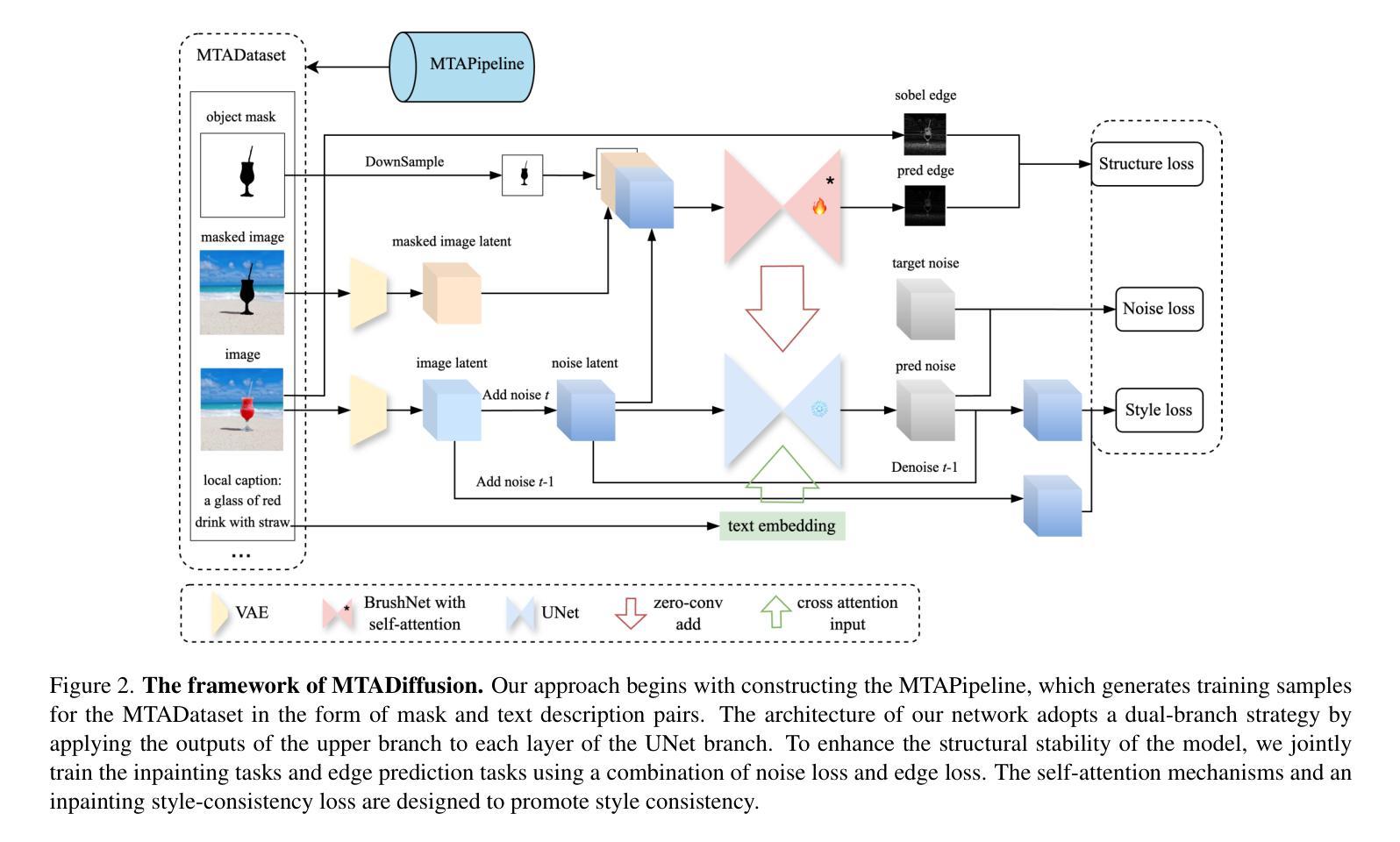
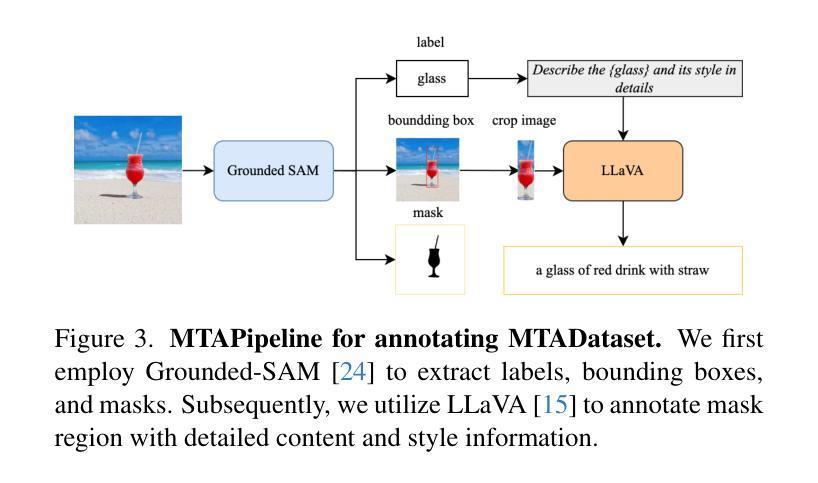
MTADiffusion: Mask Text Alignment Diffusion Model for Object Inpainting
Authors:Jun Huang, Ting Liu, Yihang Wu, Xiaochao Qu, Luoqi Liu, Xiaolin Hu
Advancements in generative models have enabled image inpainting models to generate content within specific regions of an image based on provided prompts and masks. However, existing inpainting methods often suffer from problems such as semantic misalignment, structural distortion, and style inconsistency. In this work, we present MTADiffusion, a Mask-Text Alignment diffusion model designed for object inpainting. To enhance the semantic capabilities of the inpainting model, we introduce MTAPipeline, an automatic solution for annotating masks with detailed descriptions. Based on the MTAPipeline, we construct a new MTADataset comprising 5 million images and 25 million mask-text pairs. Furthermore, we propose a multi-task training strategy that integrates both inpainting and edge prediction tasks to improve structural stability. To promote style consistency, we present a novel inpainting style-consistency loss using a pre-trained VGG network and the Gram matrix. Comprehensive evaluations on BrushBench and EditBench demonstrate that MTADiffusion achieves state-of-the-art performance compared to other methods.
生成模型的进步使得图像填充模型能够根据提供的提示和蒙版,在图像特定区域内生成内容。然而,现有的填充方法常常存在语义不匹配、结构失真和风格不一致等问题。在这项工作中,我们提出了MTADiffusion,这是一个为对象填充设计的Mask-Text对齐扩散模型。为了增强填充模型的语义能力,我们引入了MTAPipeline,这是一个自动解决方案,用于对蒙版进行详细的描述标注。基于MTAPipeline,我们构建了一个新的MTADataset,包含500万张图像和2500万个蒙版文本对。此外,我们提出了一种多任务训练策略,将填充和边缘预测任务结合起来,以提高结构稳定性。为了促进风格的一致性,我们利用预训练的VGG网络和Gram矩阵,提出了一种新的填充风格一致性损失。在BrushBench和EditBench上的综合评估表明,与其他方法相比,MTADiffusion达到了最先进的表现。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了MTADiffusion,一种用于目标补全的遮罩文本对齐扩散模型。为提高补全模型的语义能力,引入了MTAPipeline,可自动为遮罩提供详细描述的解决方案,并基于此构建了新的MTADataset数据集。同时,采用多任务训练策略,结合补全和边缘预测任务,以提高结构稳定性。通过预训练的VGG网络和Gram矩阵,提出了一种新的补全风格一致性损失。在BrushBench和EditBench上的综合评估表明,MTADiffusion相较于其他方法取得了最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- MTADiffusion是一个用于目标补全的遮罩文本对齐扩散模型,解决了现有补全方法中的语义不对齐、结构扭曲和风格不一致等问题。
- 引入MTAPipeline自动为遮罩提供详细描述的解决方案,增强模型的语义能力。
- 构建新的MTADataset数据集,包含5百万图像和2千5百万个遮罩文本对,用于模型训练。
- 采用多任务训练策略,结合补全和边缘预测任务,以提高模型的结构稳定性。
- 借助预训练的VGG网络和Gram矩阵,提出了一个新颖的补全风格一致性损失,确保补全内容的风格与原始图像一致。
- 在BrushBench和EditBench上的综合评估显示MTADiffusion性能卓越,达到了当前的最佳水平。
点此查看论文截图

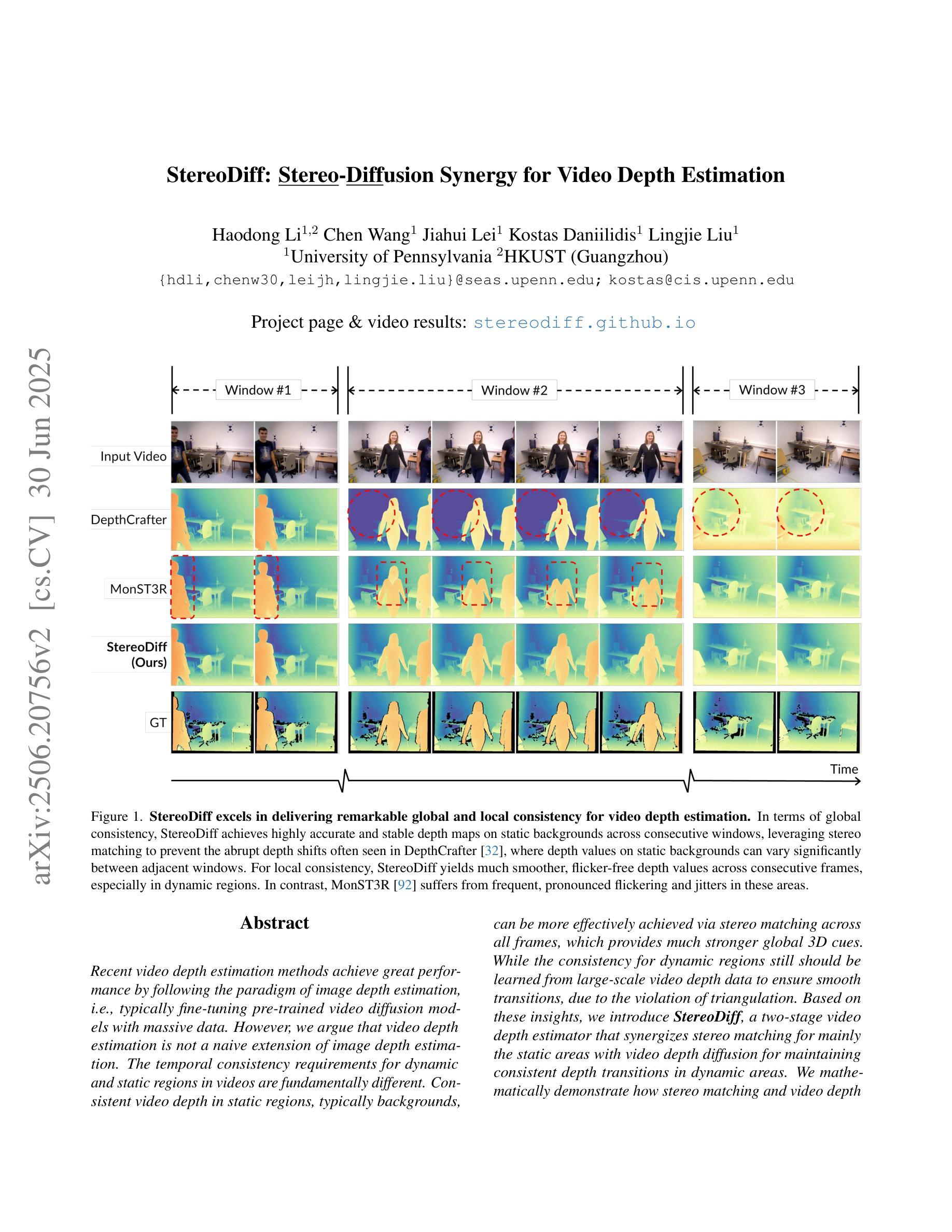
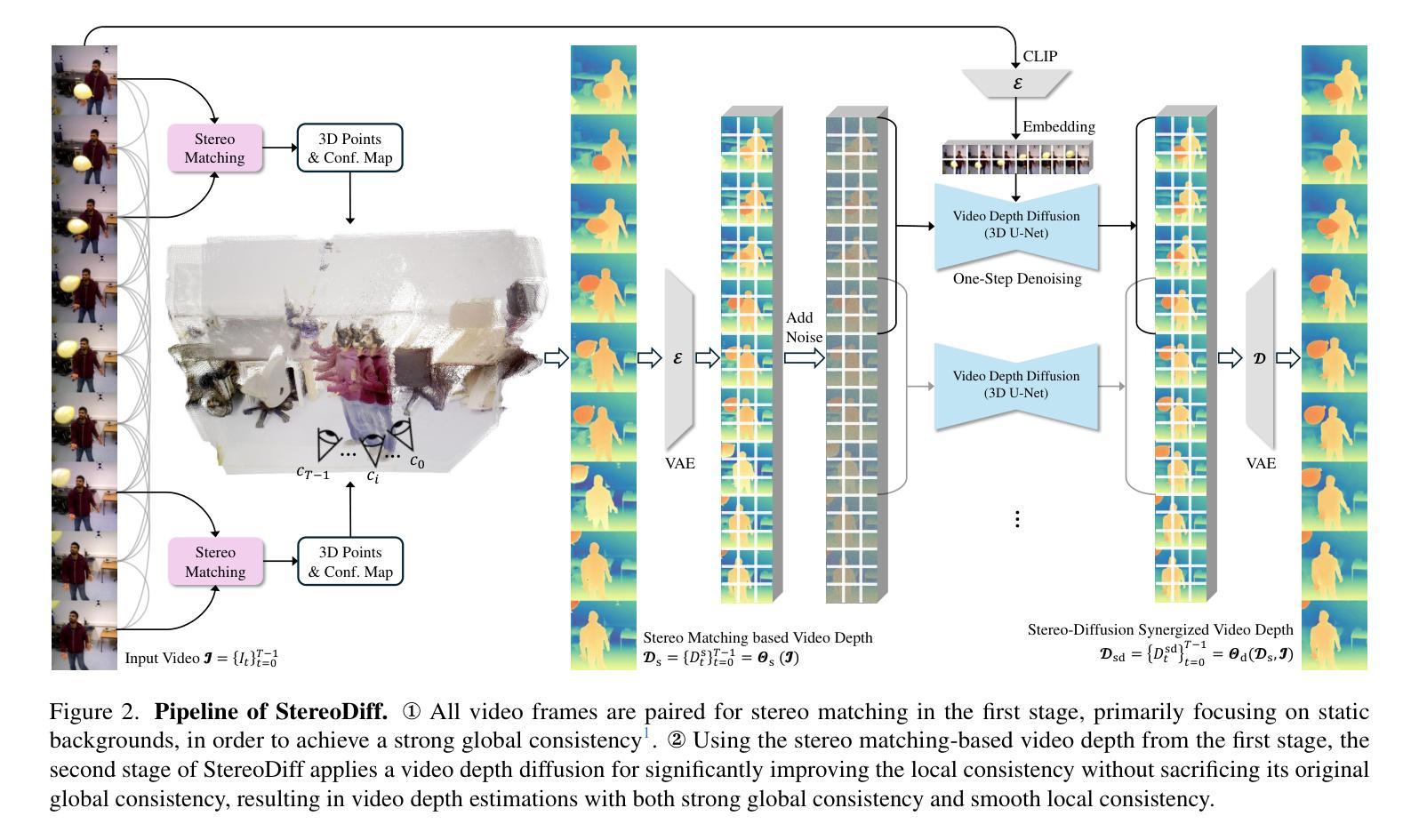
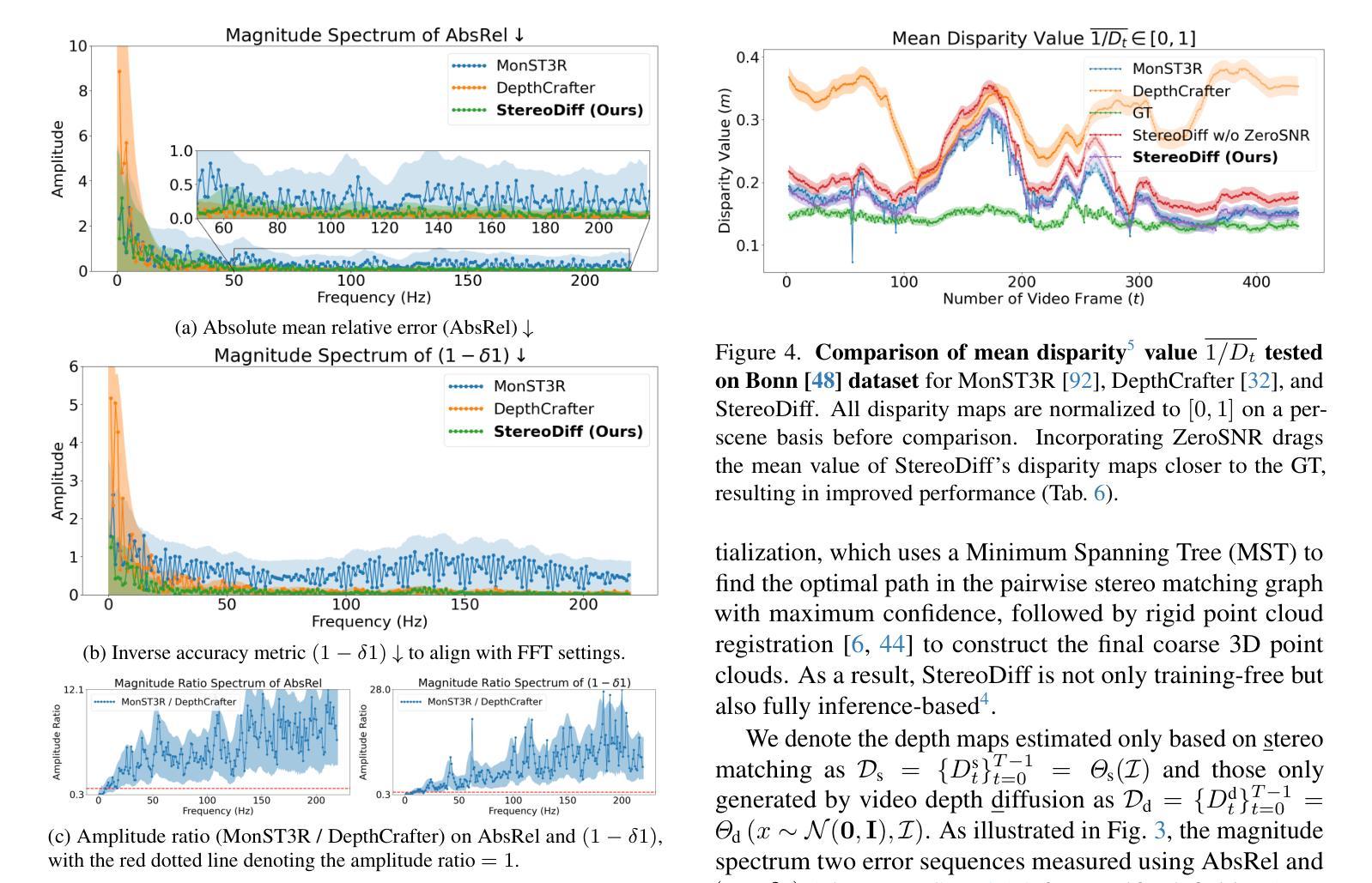
StereoDiff: Stereo-Diffusion Synergy for Video Depth Estimation
Authors:Haodong Li, Chen Wang, Jiahui Lei, Kostas Daniilidis, Lingjie Liu
Recent video depth estimation methods achieve great performance by following the paradigm of image depth estimation, i.e., typically fine-tuning pre-trained video diffusion models with massive data. However, we argue that video depth estimation is not a naive extension of image depth estimation. The temporal consistency requirements for dynamic and static regions in videos are fundamentally different. Consistent video depth in static regions, typically backgrounds, can be more effectively achieved via stereo matching across all frames, which provides much stronger global 3D cues. While the consistency for dynamic regions still should be learned from large-scale video depth data to ensure smooth transitions, due to the violation of triangulation constraints. Based on these insights, we introduce StereoDiff, a two-stage video depth estimator that synergizes stereo matching for mainly the static areas with video depth diffusion for maintaining consistent depth transitions in dynamic areas. We mathematically demonstrate how stereo matching and video depth diffusion offer complementary strengths through frequency domain analysis, highlighting the effectiveness of their synergy in capturing the advantages of both. Experimental results on zero-shot, real-world, dynamic video depth benchmarks, both indoor and outdoor, demonstrate StereoDiff’s SoTA performance, showcasing its superior consistency and accuracy in video depth estimation.
最近的视频深度估计方法遵循图像深度估计的模式,即通常通过对大量数据进行预训练的视频扩散模型进行微调,取得了很好的性能。然而,我们认为视频深度估计并不是图像深度估计的简单扩展。视频中的动态和静态区域的时序一致性要求存在根本差异。对于通常是背景等的静态区域的视频深度一致性,可以通过所有帧的立体匹配更有效地实现,这提供了更强的全局三维线索。而对于动态区域的一致性仍然需要从大规模视频深度数据中学习,以确保平滑过渡,这违反了三角约束。基于这些见解,我们引入了StereoDiff,这是一种两阶段的视频深度估计器,它将主要用于静态区域的立体匹配与用于保持动态区域中一致深度过渡的视频深度扩散相结合。我们通过频域分析从数学上证明了立体匹配和视频深度扩散如何提供互补优势,突显了它们在捕捉两者优势方面的协同有效性。在零样本、现实世界、室内和室外的动态视频深度基准测试上的实验结果表明,StereoDiff的性能达到了最新水平,展示了其在视频深度估计中的卓越一致性和准确性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Work done in Nov 2024, during an internship at the University of Pennsylvania. Project page: https://stereodiff.github.io/
Summary
本文介绍了视频深度估计的新方法StereoDiff,该方法结合立体匹配和视频深度扩散技术,针对静态和动态区域的不同要求,实现了视频深度的一致性估计。立体匹配主要用于静态区域,而视频深度扩散则用于保持动态区域的深度过渡一致性。实验结果表明,StereoDiff在零样本、真实世界、室内和室外动态视频深度评估标准上均表现出卓越的性能,具有领先的准确性和一致性。
Key Takeaways
- 视频深度估计不是图像深度估计的简单扩展,因为视频中的动态和静态区域对时间一致性的要求根本不同。
- 立体匹配技术在静态区域(如背景)的视频深度估计中更有效,能提供更强的全局3D线索。
- 动态区域的一致性需要从大规模视频深度数据中学习,以确保平滑过渡,违反三角约束。
- StereoDiff是一个两阶段的视频深度估计器,结合立体匹配和视频深度扩散技术。
- 立体匹配和视频深度扩散在频率域分析中表现出互补的优势,有效地结合了两者的优点。
- 实验结果表明,StereoDiff在视频深度估计的零样本、真实世界、室内和室外动态视频上具有最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图
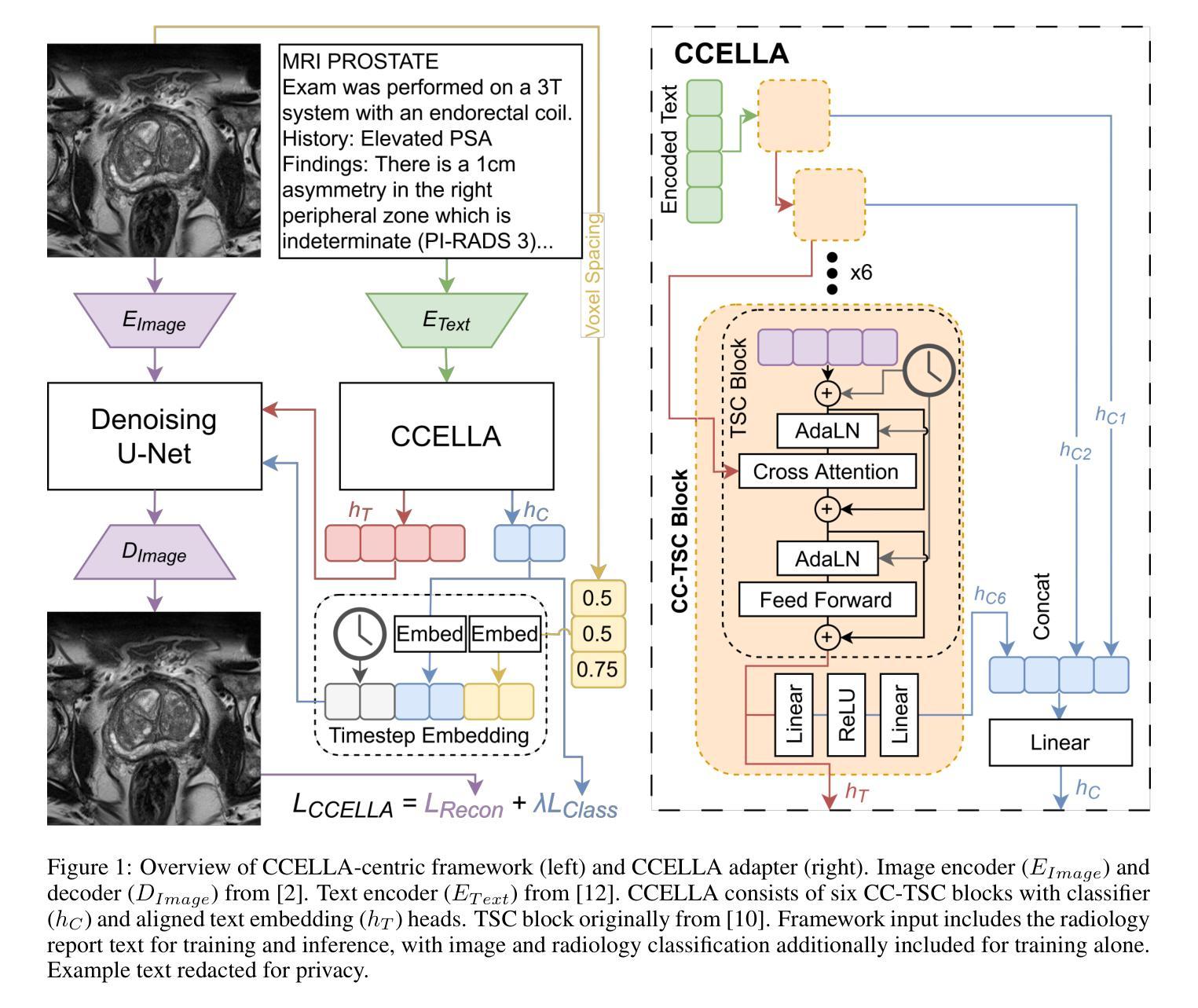
Prompt-Guided Latent Diffusion with Predictive Class Conditioning for 3D Prostate MRI Generation
Authors:Emerson P. Grabke, Masoom A. Haider, Babak Taati
Objective: Latent diffusion models (LDM) could alleviate data scarcity challenges affecting machine learning development for medical imaging. However, medical LDM strategies typically rely on short-prompt text encoders, non-medical LDMs, or large data volumes. These strategies can limit performance and scientific accessibility. We propose a novel LDM conditioning approach to address these limitations. Methods: We propose Class-Conditioned Efficient Large Language model Adapter (CCELLA), a novel dual-head conditioning approach that simultaneously conditions the LDM U-Net with free-text clinical reports and radiology classification. We also propose a data-efficient LDM framework centered around CCELLA and a proposed joint loss function. We first evaluate our method on 3D prostate MRI against state-of-the-art. We then augment a downstream classifier model training dataset with synthetic images from our method. Results: Our method achieves a 3D FID score of 0.025 on a size-limited 3D prostate MRI dataset, significantly outperforming a recent foundation model with FID 0.071. When training a classifier for prostate cancer prediction, adding synthetic images generated by our method during training improves classifier accuracy from 69% to 74%. Training a classifier solely on our method’s synthetic images achieved comparable performance to training on real images alone. Conclusion: We show that our method improved both synthetic image quality and downstream classifier performance using limited data and minimal human annotation. Significance: The proposed CCELLA-centric framework enables radiology report and class-conditioned LDM training for high-quality medical image synthesis given limited data volume and human data annotation, improving LDM performance and scientific accessibility. Code from this study will be available at https://github.com/grabkeem/CCELLA
目标:潜在扩散模型(Latent Diffusion Models,LDM)可以缓解医学成像领域机器学习开发中的数据稀缺挑战。然而,医学LDM策略通常依赖于短提示文本编码器、非医学LDMs或大量数据。这些策略可能会限制性能和科学可及性。我们提出了一种新的LDM条件处理方法来解决这些限制。方法:我们提出了Class-Conditioned Efficient Large Language model Adapter(CCELLA),这是一种新的双头条件处理方法,可以同时使用自由文本临床报告和放射学分类对LDM U-Net进行条件处理。我们还以CCELLA为核心,围绕其构建了一个高效数据LDM框架,并设计了一个联合损失函数。我们首先在最先进的3D前列腺MRI上评估了我们的方法。然后,我们使用该方法生成的合成图像增强下游分类器模型的训练数据集。结果:我们的方法在规模有限的三维前列腺MRI数据集上达到了0.025的3DFID分数,显著优于最近的基础模型的FID 0.071。在训练前列腺癌预测分类器时,在训练过程中添加我们方法生成的合成图像将分类器的准确度从69%提高到74%。仅在我们的方法生成的合成图像上训练分类器可实现与仅在真实图像上训练分类器相当的性能。结论:我们证明,使用有限的数据和最少的人工标注,我们的方法可以提高合成图像的质量和下游分类器的性能。意义:以CCELLA为核心的框架实现了以放射学报告和类别为条件的LDM训练,可在数据量和人工标注有限的情况下进行高质量医学图像合成,提高了LDM的性能和科学可及性。本研究的代码将在https://github.com/grabkeem/CCELLA上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MAH and BT are co-senior authors on the work. This work has been submitted to the IEEE for possible publication
Summary
本文提出一种名为CCELLA的新型LDM条件化方法,用于解决医学影像机器学习中的数据稀缺挑战。通过同时结合自由文本临床报告和放射学分类,CCELLA能够在有限数据和无需大量人工标注的情况下生成高质量医学图像,并提升下游分类器的性能。实验结果显示,该方法在3D前列腺MRI数据集上表现优异,并可有效提高前列腺癌预测分类器的准确性。
Key Takeaways
- LDM可以缓解医学影像机器学习中的数据稀缺问题。
- 现有LDM策略在医学领域应用时存在局限。
- 提出新型LDM条件化方法CCELLA,结合自由文本临床报告和放射学分类。
- CCELLA方法能够在有限数据和无需大量人工标注的情况下生成高质量医学图像。
- 在3D前列腺MRI数据集上,CCELLA方法表现优异,3D FID分数达到0.025,优于其他模型。
- 使用CCELLA生成的合成图像训练下游分类器,可提高分类器准确性。
- CCELLA框架可提高LDM在医学领域的性能及科学可及性。
点此查看论文截图

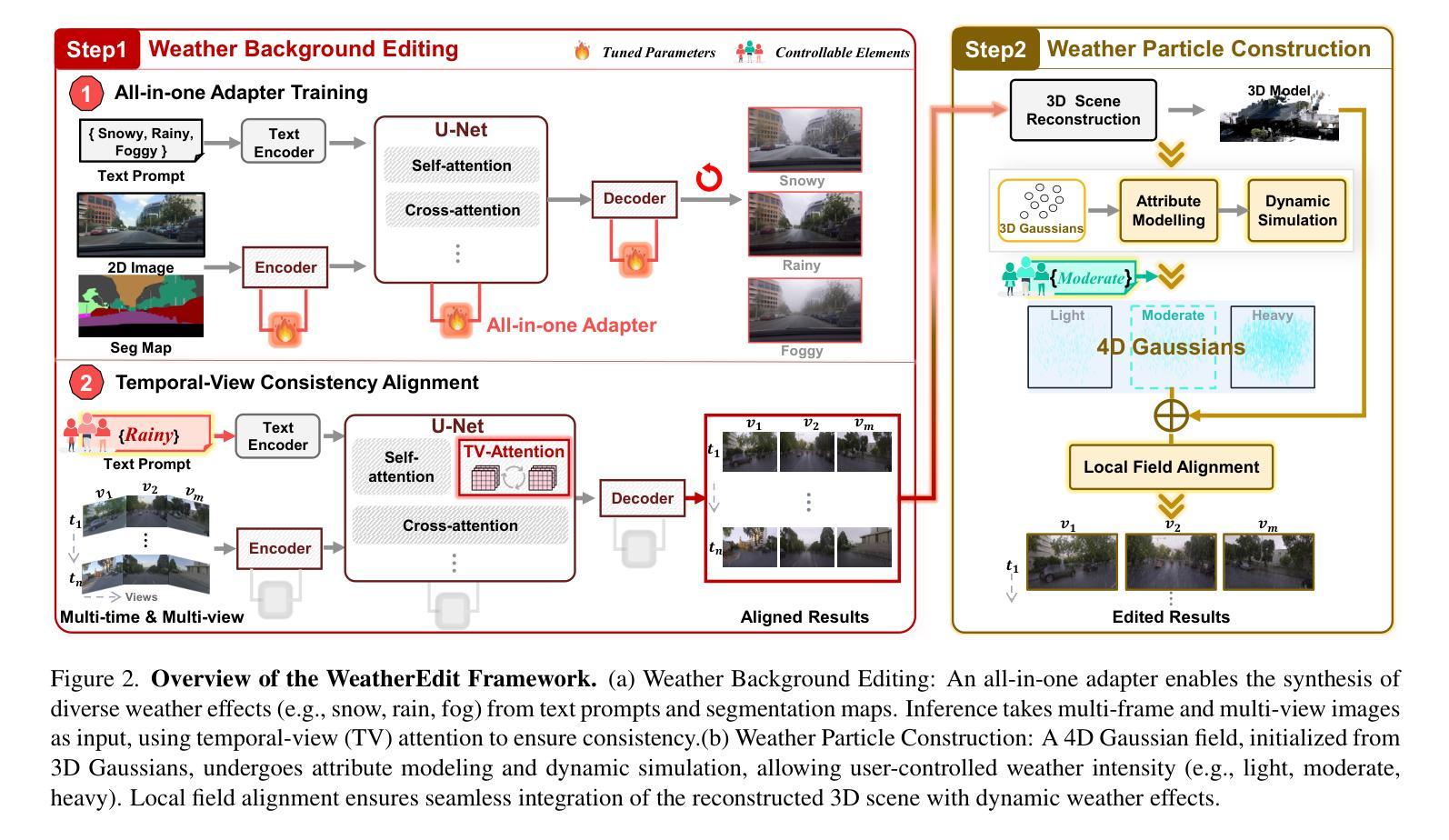
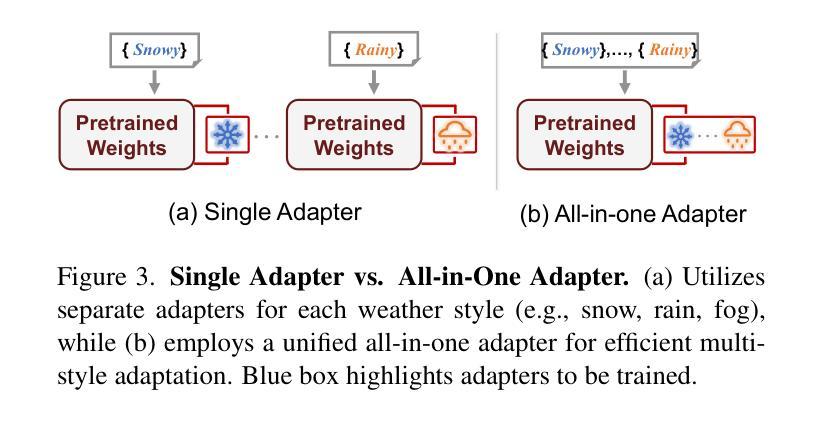
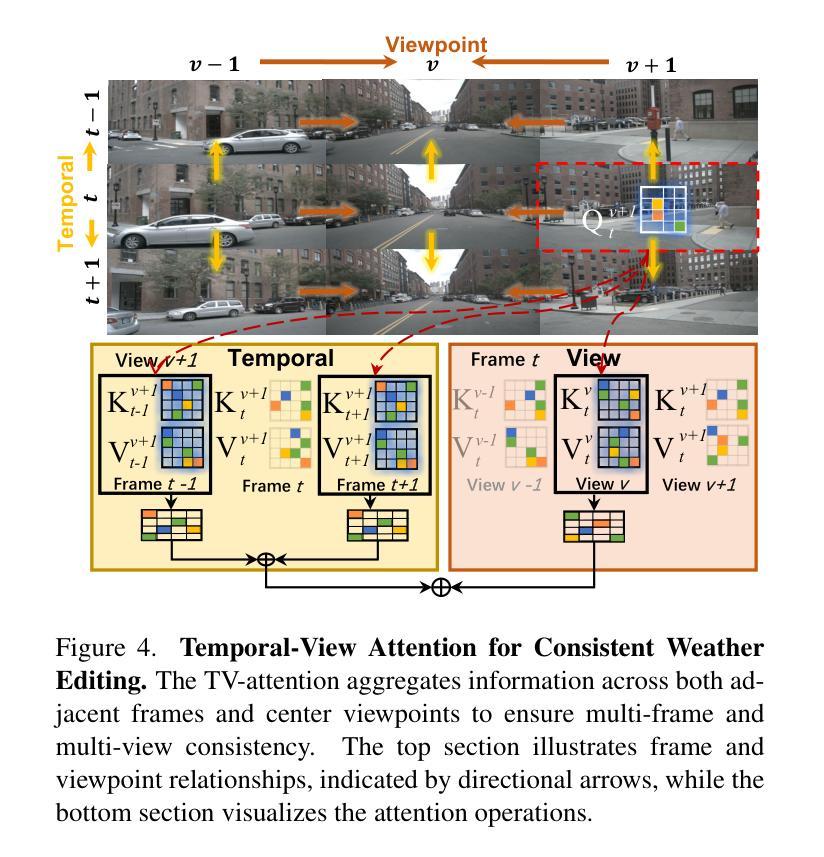
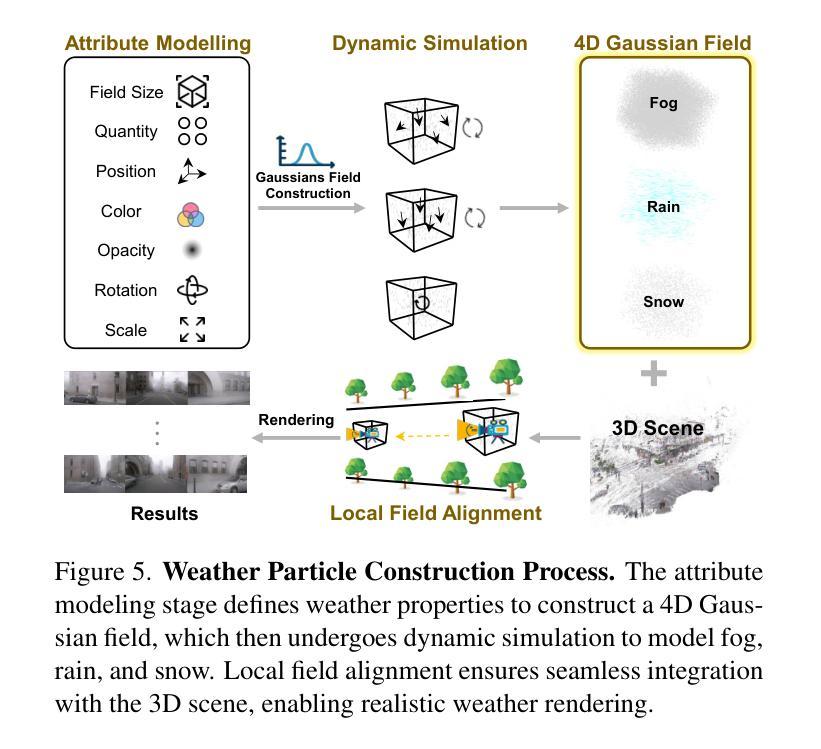
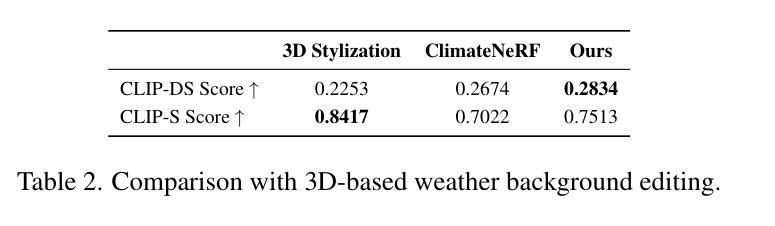
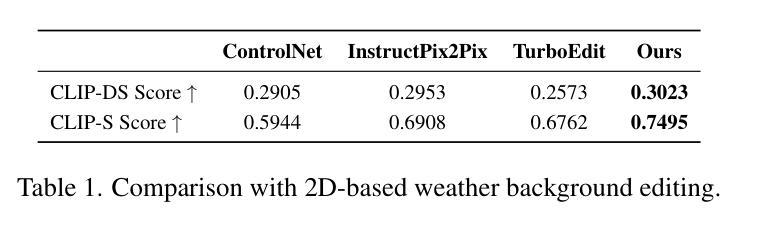
WeatherEdit: Controllable Weather Editing with 4D Gaussian Field
Authors:Chenghao Qian, Wenjing Li, Yuhu Guo, Gustav Markkula
In this work, we present WeatherEdit, a novel weather editing pipeline for generating realistic weather effects with controllable types and severity in 3D scenes. Our approach is structured into two key components: weather background editing and weather particle construction. For weather background editing, we introduce an all-in-one adapter that integrates multiple weather styles into a single pretrained diffusion model, enabling the generation of diverse weather effects in 2D image backgrounds. During inference, we design a Temporal-View (TV-) attention mechanism that follows a specific order to aggregate temporal and spatial information, ensuring consistent editing across multi-frame and multi-view images. To construct the weather particles, we first reconstruct a 3D scene using the edited images and then introduce a dynamic 4D Gaussian field to generate snowflakes, raindrops and fog in the scene. The attributes and dynamics of these particles are precisely controlled through physical-based modelling and simulation, ensuring realistic weather representation and flexible severity adjustments. Finally, we integrate the 4D Gaussian field with the 3D scene to render consistent and highly realistic weather effects. Experiments on multiple driving datasets demonstrate that WeatherEdit can generate diverse weather effects with controllable condition severity, highlighting its potential for autonomous driving simulation in adverse weather. See project page: https://jumponthemoon.github.io/w-edit
在这项工作中,我们提出了WeatherEdit,这是一个新的天气编辑管道,用于在3D场景生成具有可控类型和严重程度的现实天气效果。我们的方法分为两个关键组成部分:天气背景编辑和天气粒子构建。对于天气背景编辑,我们引入了一个全能适配器,将多种天气风格集成到一个预训练的扩散模型中,从而在2D图像背景中生成多种天气效果。在推理过程中,我们设计了一种时间视图(TV)注意力机制,按照特定顺序聚合时间和空间信息,确保跨多帧和多视图图像的一致编辑。为了构建天气粒子,我们首先使用编辑后的图像重建3D场景,然后引入动态4D高斯场来在场景中生成雪花、雨滴和雾。这些粒子的属性和动态通过基于物理的建模和模拟进行精确控制,确保现实的天气表现和灵活的严重程度调整。最后,我们将4D高斯场与3D场景相结合,呈现一致且高度现实的天气效果。在多个驾驶数据集上的实验表明,WeatherEdit可以生成具有可控条件严重程度的多种天气效果,突显其在恶劣天气条件下自动驾驶模拟的潜力。更多详情见项目页面:https://jumponthemoon.github.io/w-edit。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本工作提出了WeatherEdit,一个用于在3D场景中生成具有可控类型和严重程度的逼真天气效果的新型天气编辑管道。它包含两个关键组件:天气背景编辑和天气粒子构建。通过引入全合一适配器,将多种天气风格集成到一个预训练的扩散模型中,实现2D图像背景中多种天气效果的生成。设计了一种时间视图(TV)注意力机制,以特定顺序聚合时间和空间信息,确保跨多帧和多视图图像的一致编辑。通过重建3D场景并引入动态4D高斯场来构建天气粒子,通过基于物理的建模和模拟精确控制这些粒子的属性和动态,确保天气表示的真实性和灵活调整严重程度。最终,将4D高斯场与3D场景集成,呈现一致且高度逼真的天气效果。
Key Takeaways
- WeatherEdit是一个用于生成逼真天气效果的天气编辑管道,支持可控的天气类型和严重程度。
- 包含两个关键组件:天气背景编辑和天气粒子构建。
- 通过全合一适配器集成多种天气风格到预训练扩散模型中,实现2D图像背景多样天气效果的生成。
- 设计了时间视图(TV)注意力机制,确保跨多帧和多视图图像的一致编辑。
- 通过重建3D场景并引入动态4D高斯场来生成天气粒子,保证天气表示的真实性和灵活调整其严重程度。
- 实验证明,WeatherEdit能在多个驾驶数据集中生成具有可控条件的多样天气效果。
点此查看论文截图


Object detection in adverse weather conditions for autonomous vehicles using Instruct Pix2Pix
Authors:Unai Gurbindo, Axel Brando, Jaume Abella, Caroline König
Enhancing the robustness of object detection systems under adverse weather conditions is crucial for the advancement of autonomous driving technology. This study presents a novel approach leveraging the diffusion model Instruct Pix2Pix to develop prompting methodologies that generate realistic datasets with weather-based augmentations aiming to mitigate the impact of adverse weather on the perception capabilities of state-of-the-art object detection models, including Faster R-CNN and YOLOv10. Experiments were conducted in two environments, in the CARLA simulator where an initial evaluation of the proposed data augmentation was provided, and then on the real-world image data sets BDD100K and ACDC demonstrating the effectiveness of the approach in real environments. The key contributions of this work are twofold: (1) identifying and quantifying the performance gap in object detection models under challenging weather conditions, and (2) demonstrating how tailored data augmentation strategies can significantly enhance the robustness of these models. This research establishes a solid foundation for improving the reliability of perception systems in demanding environmental scenarios, and provides a pathway for future advancements in autonomous driving.
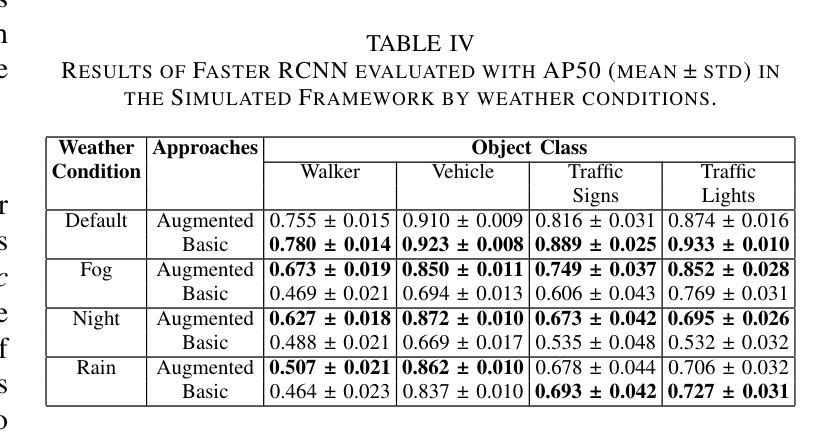
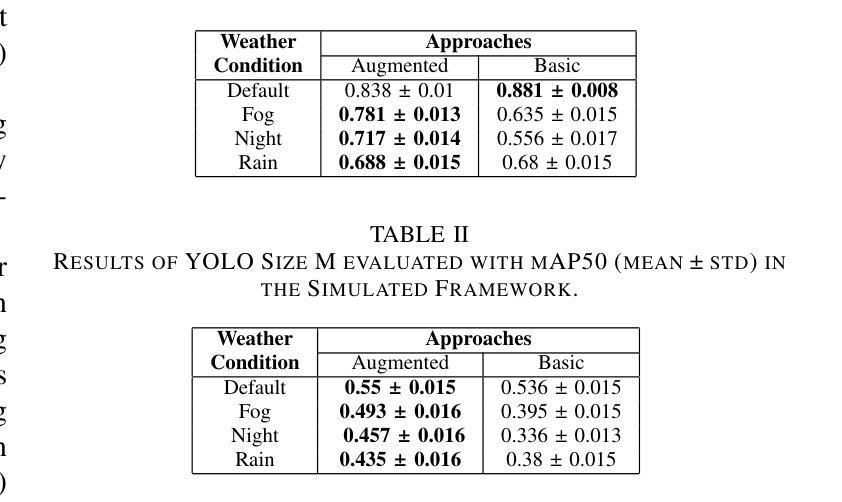
增强恶劣天气条件下物体检测系统稳健性对于自动驾驶技术的发展至关重要。本研究提出了一种利用扩散模型Instruct Pix2Pix开发提示方法的新方法,生成具有天气增强的现实数据集,旨在减轻恶劣天气对最新物体检测模型感知能力的影响,包括Faster R-CNN和YOLOv10。实验在两个环境中进行,包括CARLA模拟器,该模拟器提供了所提出的数据增强的初步评估,以及在BDD100K和ACDC真实世界图像数据集上的实验,证明了该方法在真实环境中的有效性。这项工作的关键贡献有两方面:(1)识别和量化物体检测模型在恶劣天气条件下的性能差距;(2)展示针对性的数据增强策略如何显着提高这些模型的稳健性。该研究为提高需求环境场景中感知系统的可靠性奠定了坚实基础,并为自动驾驶技术的未来发展提供了途径。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 5 figures. Accepted at the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN) 2025 (to appear)
摘要
本研究利用扩散模型Instruct Pix2Pix发展出一种新型提示方法,生成具有天气增强的现实数据集,旨在减轻恶劣天气对先进目标检测模型感知能力的影响。在CARLA模拟器及BDD100K和ACDC真实图像数据集上的实验证明该方法在真实环境中的有效性。本研究的关键贡献在于:一、识别和量化目标检测模型在恶劣条件下的性能差距;二、证明定制的数据增强策略能显著提高这些模型的稳健性。这为改善环境需求下的感知系统可靠性奠定了基础,并为自动驾驶的未来发展提供了路径。
关键见解
- 利用扩散模型Instruct Pix2Pix发展新型提示方法,生成现实数据集以模拟恶劣天气条件。
- 数据增强策略旨在减轻恶劣天气对目标检测模型感知能力的影响。
- 在CARLA模拟器上初步评估数据增强的有效性。
- 在BDD100K和ACDC真实图像数据集上验证了方法的有效性。
- 研究识别和量化目标检测模型在恶劣条件下的性能差距。
- 定制的数据增强策略能显著提高目标检测模型的稳健性。
点此查看论文截图




Towards Generalized and Training-Free Text-Guided Semantic Manipulation
Authors:Yu Hong, Xiao Cai, Pengpeng Zeng, Shuai Zhang, Jingkuan Song, Lianli Gao, Heng Tao Shen
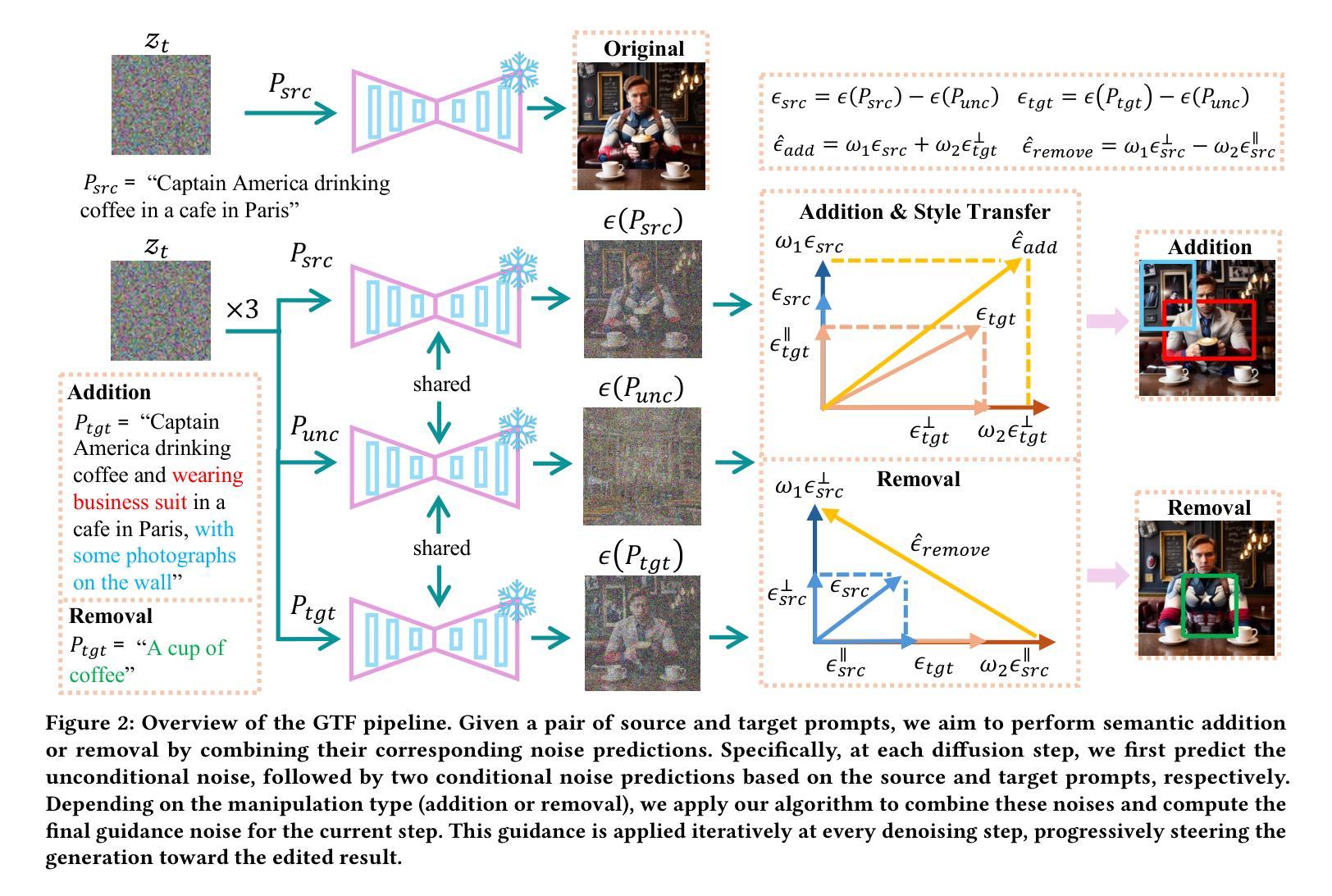
Text-guided semantic manipulation refers to semantically editing an image generated from a source prompt to match a target prompt, enabling the desired semantic changes (e.g., addition, removal, and style transfer) while preserving irrelevant contents. With the powerful generative capabilities of the diffusion model, the task has shown the potential to generate high-fidelity visual content. Nevertheless, existing methods either typically require time-consuming fine-tuning (inefficient), fail to accomplish multiple semantic manipulations (poorly extensible), and/or lack support for different modality tasks (limited generalizability). Upon further investigation, we find that the geometric properties of noises in the diffusion model are strongly correlated with the semantic changes. Motivated by this, we propose a novel $\textit{GTF}$ for text-guided semantic manipulation, which has the following attractive capabilities: 1) $\textbf{Generalized}$: our $\textit{GTF}$ supports multiple semantic manipulations (e.g., addition, removal, and style transfer) and can be seamlessly integrated into all diffusion-based methods (i.e., Plug-and-play) across different modalities (i.e., modality-agnostic); and 2) $\textbf{Training-free}$: $\textit{GTF}$ produces high-fidelity results via simply controlling the geometric relationship between noises without tuning or optimization. Our extensive experiments demonstrate the efficacy of our approach, highlighting its potential to advance the state-of-the-art in semantics manipulation.
文本引导语义操纵是指对由源提示生成的图像进行语义编辑,以匹配目标提示,实现期望的语义更改(例如添加、删除和风格转换),同时保留无关内容。扩散模型的强大生成能力使该任务有潜力生成高保真视觉内容。然而,现有方法通常需要耗时的微调(效率不高),无法完成多项语义操作(扩展性较差),并且缺乏对不同模态任务的支持(泛化能力有限)。通过进一步调查,我们发现扩散模型中的噪声几何属性与语义更改密切相关。基于此,我们提出了一种用于文本引导语义操纵的新型GTF( Guided Transformation Framework)。它具有以下吸引人的功能:1)通用性:我们的GTF支持多项语义操作(例如添加、删除和风格转换),并且可以无缝集成到所有基于扩散的方法中(即插即用),适用于不同模态(即模态无关);2)免训练:GTF通过简单控制噪声之间的几何关系即可产生高保真结果,无需调整或优化。我们的大量实验证明了该方法的有效性,突出了其在语义操纵方面领先技术的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://ayanami-yu.github.io/GTF-Project-Page/
Summary
文本引导语义操控是指对由源提示生成的图像进行语义编辑,使其匹配目标提示,实现所需语义更改(如添加、删除和风格转换),同时保留无关内容。利用扩散模型的强大生成能力,该任务有潜力生成高保真视觉内容。然而,现有方法通常需要耗时微调(效率低下)、无法完成多项语义操控(扩展性差)且缺乏不同模态任务的支持(泛化能力有限)。我们发现扩散模型中的噪声几何属性与语义更改之间存在强烈相关性。因此,我们提出了一种新型的文本引导语义操控方法GTF,具有支持多种语义操控、可无缝集成到所有扩散方法(即插即用)和不同模态中的能力,以及无需训练即可通过控制噪声之间的几何关系产生高保真结果的能力。
Key Takeaways
- 文本引导语义操控可以编辑图像以匹配目标提示,实现多种语义更改。
- 扩散模型具备强大的生成能力,可生成高保真视觉内容。
- 现有方法存在效率低下、扩展性差和泛化能力有限的问题。
- 噪声的几何属性与语义更改之间存在强烈相关性。
- GTF方法支持多种语义操控,并能无缝集成到所有扩散方法(即插即用)。
- GTF方法具有跨不同模态的能力。
点此查看论文截图


Diffusion Models for Robotic Manipulation: A Survey
Authors:Rosa Wolf, Yitian Shi, Sheng Liu, Rania Rayyes
Diffusion generative models have demonstrated remarkable success in visual domains such as image and video generation. They have also recently emerged as a promising approach in robotics, especially in robot manipulations. Diffusion models leverage a probabilistic framework, and they stand out with their ability to model multi-modal distributions and their robustness to high-dimensional input and output spaces. This survey provides a comprehensive review of state-of-the-art diffusion models in robotic manipulation, including grasp learning, trajectory planning, and data augmentation. Diffusion models for scene and image augmentation lie at the intersection of robotics and computer vision for vision-based tasks to enhance generalizability and data scarcity. This paper also presents the two main frameworks of diffusion models and their integration with imitation learning and reinforcement learning. In addition, it discusses the common architectures and benchmarks and points out the challenges and advantages of current state-of-the-art diffusion-based methods.
扩散生成模型在图像和视频生成等视觉领域取得了显著的成功。它们最近也作为机器人技术的一种有前途的方法出现,尤其是机器人操控。扩散模型利用概率框架,以其能够模拟多模态分布和对高维输入和输出空间的稳健性而脱颖而出。这篇综述对机器人操作中的最新扩散模型进行了全面回顾,包括抓取学习、轨迹规划和数据增强。场景和图像增强的扩散模型位于机器人和计算机视觉的交叉点,用于基于视觉的任务,以提高通用性和解决数据稀缺问题。本文还介绍了扩散模型的两个主要框架及其与模仿学习和强化学习的融合。此外,它还讨论了常见的架构和基准测试,并指出了当前最先进的基于扩散的方法的挑战和优势。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 28 pages, 2 figure, 9 tables
Summary
扩散生成模型在图像和视频生成等领域取得了显著的成功,最近在机器人领域,特别是在机器人操作方面展现出巨大的潜力。本文全面综述了机器人操作中的扩散模型,包括抓取学习、轨迹规划和数据增强等。扩散模型结合模仿学习和强化学习,可以提高机器人的通用性和解决数据稀缺问题。本文还介绍了扩散模型的两个主要框架、常见架构和基准测试,并指出了当前先进扩散方法的挑战和优势。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散生成模型在视觉领域如图像和视频生成上取得了显著成功。
- 扩散模型在机器人操作领域展现出巨大潜力,特别是在抓取学习、轨迹规划和数据增强方面。
- 扩散模型能结合模仿学习和强化学习,提高机器人的通用性。
- 扩散模型在解决机器人数据稀缺问题上发挥重要作用。
- 本文介绍了扩散模型的两个主要框架和常见架构。
- 当前先进扩散方法面临挑战,但也具有优势。
点此查看论文截图

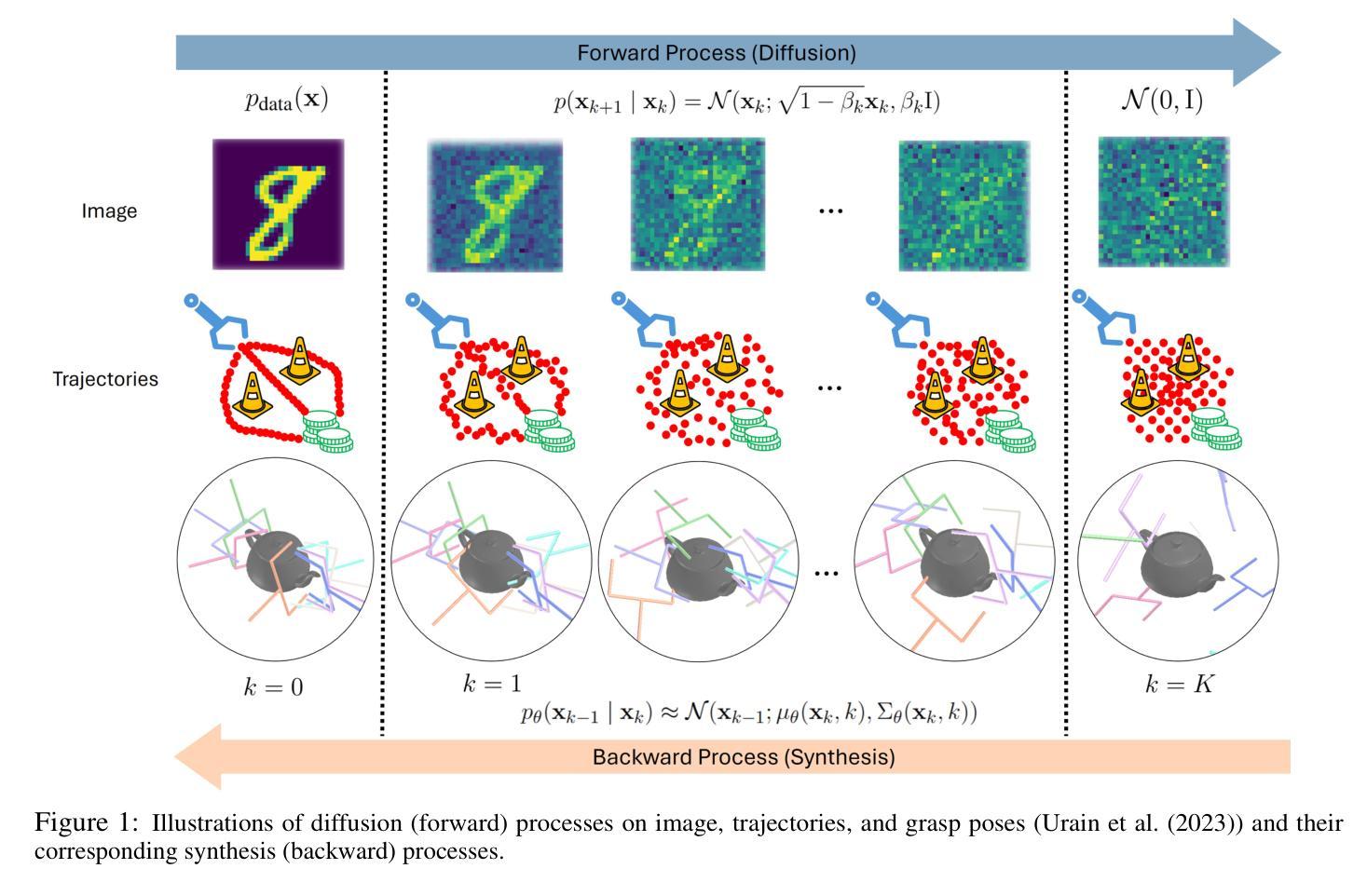
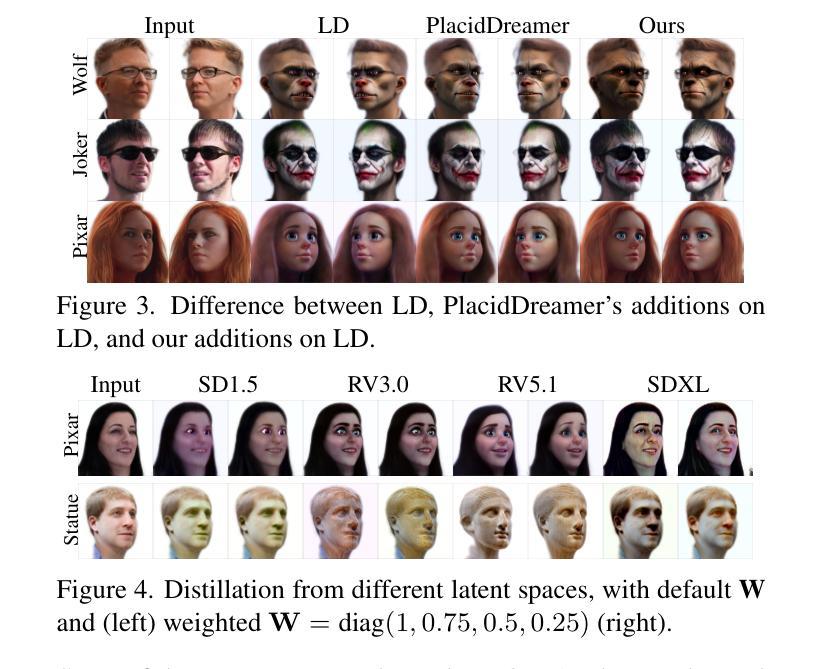
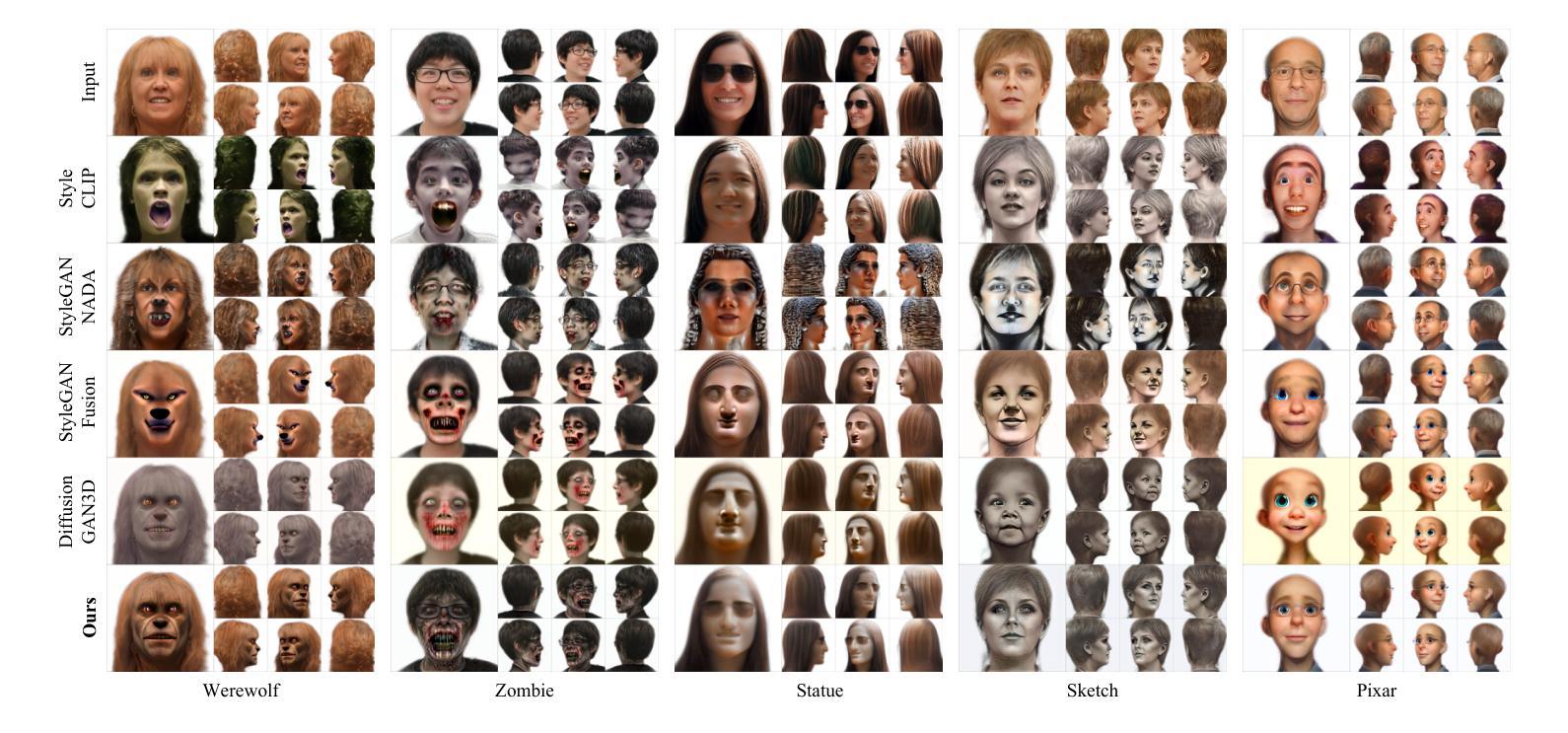
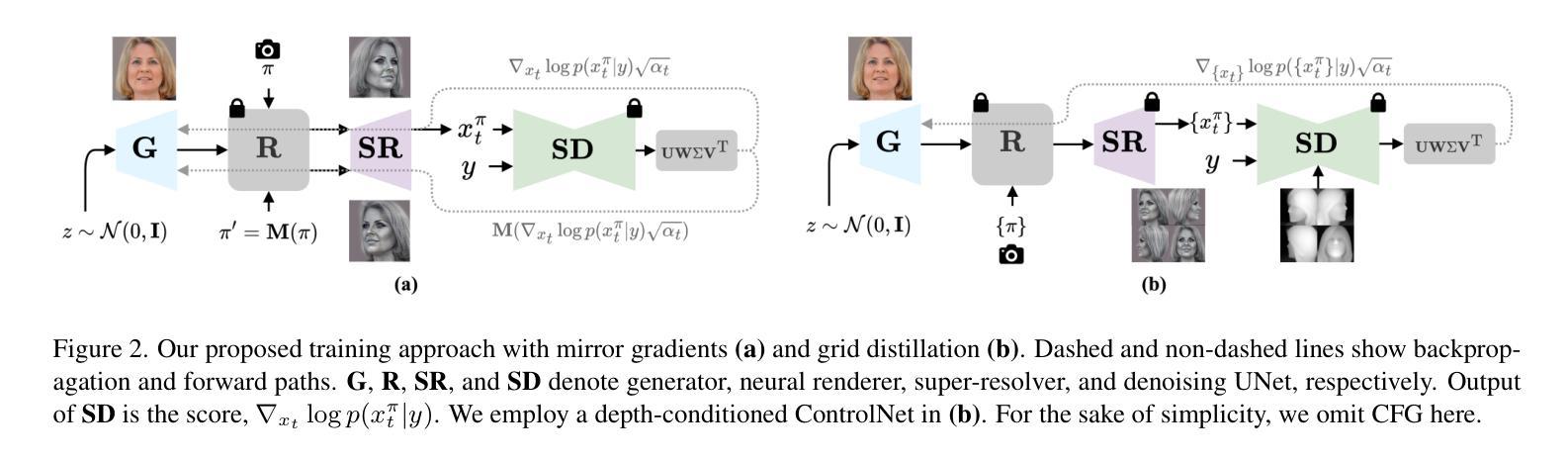
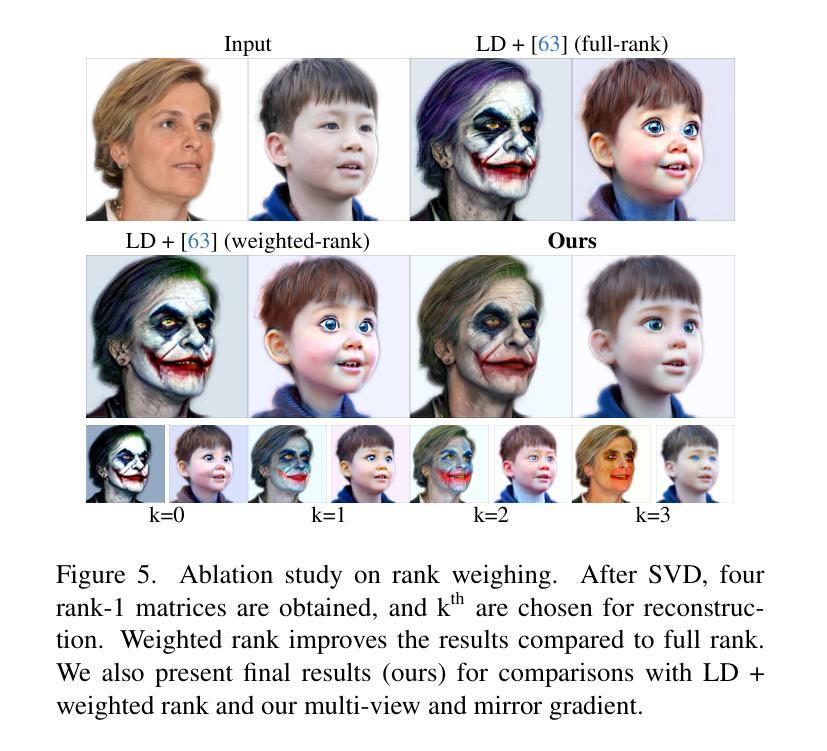
Identity Preserving 3D Head Stylization with Multiview Score Distillation
Authors:Bahri Batuhan Bilecen, Ahmet Berke Gokmen, Furkan Guzelant, Aysegul Dundar
3D head stylization transforms realistic facial features into artistic representations, enhancing user engagement across gaming and virtual reality applications. While 3D-aware generators have made significant advancements, many 3D stylization methods primarily provide near-frontal views and struggle to preserve the unique identities of original subjects, often resulting in outputs that lack diversity and individuality. This paper addresses these challenges by leveraging the PanoHead model, synthesizing images from a comprehensive 360-degree perspective. We propose a novel framework that employs negative log-likelihood distillation (LD) to enhance identity preservation and improve stylization quality. By integrating multi-view grid score and mirror gradients within the 3D GAN architecture and introducing a score rank weighing technique, our approach achieves substantial qualitative and quantitative improvements. Our findings not only advance the state of 3D head stylization but also provide valuable insights into effective distillation processes between diffusion models and GANs, focusing on the critical issue of identity preservation. Please visit the https://three-bee.github.io/head_stylization for more visuals.
3D头部风格化转换能将现实的面部特征转化为艺术表现形式,增强游戏和虚拟现实应用中的用户参与度。虽然3D感知生成器已经取得了重大进展,但许多3D风格化方法主要提供近乎正面的视角,并且在保留原始主体的独特身份方面存在困难,这往往导致输出结果缺乏多样性和个性化。本文针对这些挑战,采用PanoHead模型,从全面的360度视角合成图像。我们提出了一种采用负对数似然蒸馏(LD)的新框架,以提高身份保留和提高风格化质量。通过在3D GAN架构中整合多视图网格评分和镜像梯度,并引入评分排名加权技术,我们的方法在定性和定量方面都取得了显著的改进。我们的研究不仅推动了3D头部风格化的研究发展,而且为扩散模型和GANs之间的有效蒸馏过程提供了有价值的见解,重点关注身份保留这一关键问题。更多视觉效果请访问 https://three-bee.github.io/head_stylization。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF https://three-bee.github.io/head_stylization
Summary
基于3D头模型技术,该论文探讨了如何提升虚拟角色头部艺术风格的渲染效果和用户参与度。针对现有方法在多角度展示和个性化身份保留方面的不足,论文提出了一个全新的框架,通过负对数似然蒸馏技术(LD)和多视角网格评分与镜像梯度集成在3D GAN架构中,实现了头部风格化的实质性提升。该研究不仅推动了3D头部风格化的进展,还为扩散模型和GAN之间的有效蒸馏过程提供了宝贵见解。更多视觉展示请访问:https://three-bee.github.io/head_stylization。
Key Takeaways
点此查看论文截图



Pixel super-resolved virtual staining of label-free tissue using diffusion models
Authors:Yijie Zhang, Luzhe Huang, Nir Pillar, Yuzhu Li, Hanlong Chen, Aydogan Ozcan
Virtual staining of tissue offers a powerful tool for transforming label-free microscopy images of unstained tissue into equivalents of histochemically stained samples. This study presents a diffusion model-based super-resolution virtual staining approach utilizing a Brownian bridge process to enhance both the spatial resolution and fidelity of label-free virtual tissue staining, addressing the limitations of traditional deep learning-based methods. Our approach integrates novel sampling techniques into a diffusion model-based image inference process to significantly reduce the variance in the generated virtually stained images, resulting in more stable and accurate outputs. Blindly applied to lower-resolution auto-fluorescence images of label-free human lung tissue samples, the diffusion-based super-resolution virtual staining model consistently outperformed conventional approaches in resolution, structural similarity and perceptual accuracy, successfully achieving a super-resolution factor of 4-5x, increasing the output space-bandwidth product by 16-25-fold compared to the input label-free microscopy images. Diffusion-based super-resolved virtual tissue staining not only improves resolution and image quality but also enhances the reliability of virtual staining without traditional chemical staining, offering significant potential for clinical diagnostics.
组织虚拟染色为无标签的显微镜图像提供了一种强大的工具,将其转化为与组化染色样本相当的图像。本研究提出了一种基于扩散模型的超分辨率虚拟染色方法,利用布朗桥过程提高了无标签虚拟组织染色的空间分辨率和保真度,解决了基于传统深度学习方法的局限性。我们的方法将新型采样技术集成到基于扩散模型的图像推理过程中,显著降低了生成虚拟染色图像的方差,从而得到更稳定和准确的输出。盲目应用于无标签人肺组织样本的低分辨率自体荧光图像,基于扩散的超分辨率虚拟染色模型在分辨率、结构相似性和感知准确性方面始终优于传统方法,成功实现4-5倍的超分辨率,与无标签的显微镜图像相比,输出空间带宽积增加了16-25倍。基于扩散的超分辨率虚拟组织染色不仅提高了分辨率和图像质量,还提高了虚拟染色的可靠性,无需传统的化学染色,为临床诊断提供了巨大的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 39 Pages, 7 Figures
Summary
虚拟染色组织技术通过扩散模型实现了无标记显微镜图像向等效的免疫组织化学染色样本的转变。本研究提出了一种基于扩散模型的超分辨率虚拟染色方法,利用布朗桥过程提高了无标记虚拟组织染色的空间分辨率和保真度,解决了传统深度学习方法的局限性。该方法将新型采样技术集成到扩散模型图像推断过程中,显著降低了生成虚拟染色图像的方差,产生了更稳定、更准确的输出。应用于无标记人肺组织样本的低分辨率自体荧光图像时,基于扩散的超分辨率虚拟染色模型在分辨率、结构相似性和感知准确性方面均优于传统方法,成功实现4-5倍的超分辨率,输出空间带宽乘积比输入的无标记显微镜图像提高了16-25倍。基于扩散的超分辨率虚拟组织染色技术不仅提高了分辨率和图像质量,还提高了无传统化学染料的虚拟染色的可靠性,为临床诊断和治疗提供了巨大的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 虚拟染色技术能将无标记的显微镜图像转化为等效的免疫组织化学染色样本。
- 本研究提出了一种基于扩散模型的超分辨率虚拟染色方法。
- 通过布朗桥过程提高了无标记虚拟组织染色的空间分辨率和保真度。
- 该方法集成了新型采样技术到扩散模型图像推断中,提高了虚拟染色图像的稳定性与准确性。
- 在无标记肺组织样本上应用时,基于扩散的方法在分辨率、结构相似性和感知准确性方面超越了传统方法。
- 成功实现了4-5倍的超分辨率,大幅提升了输出图像的空间带宽乘积。
点此查看论文截图

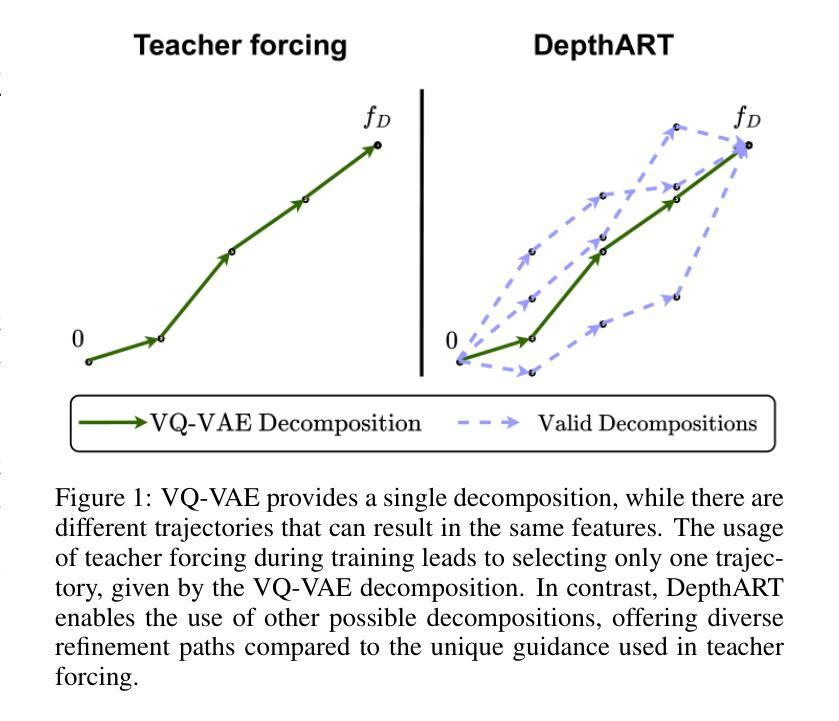
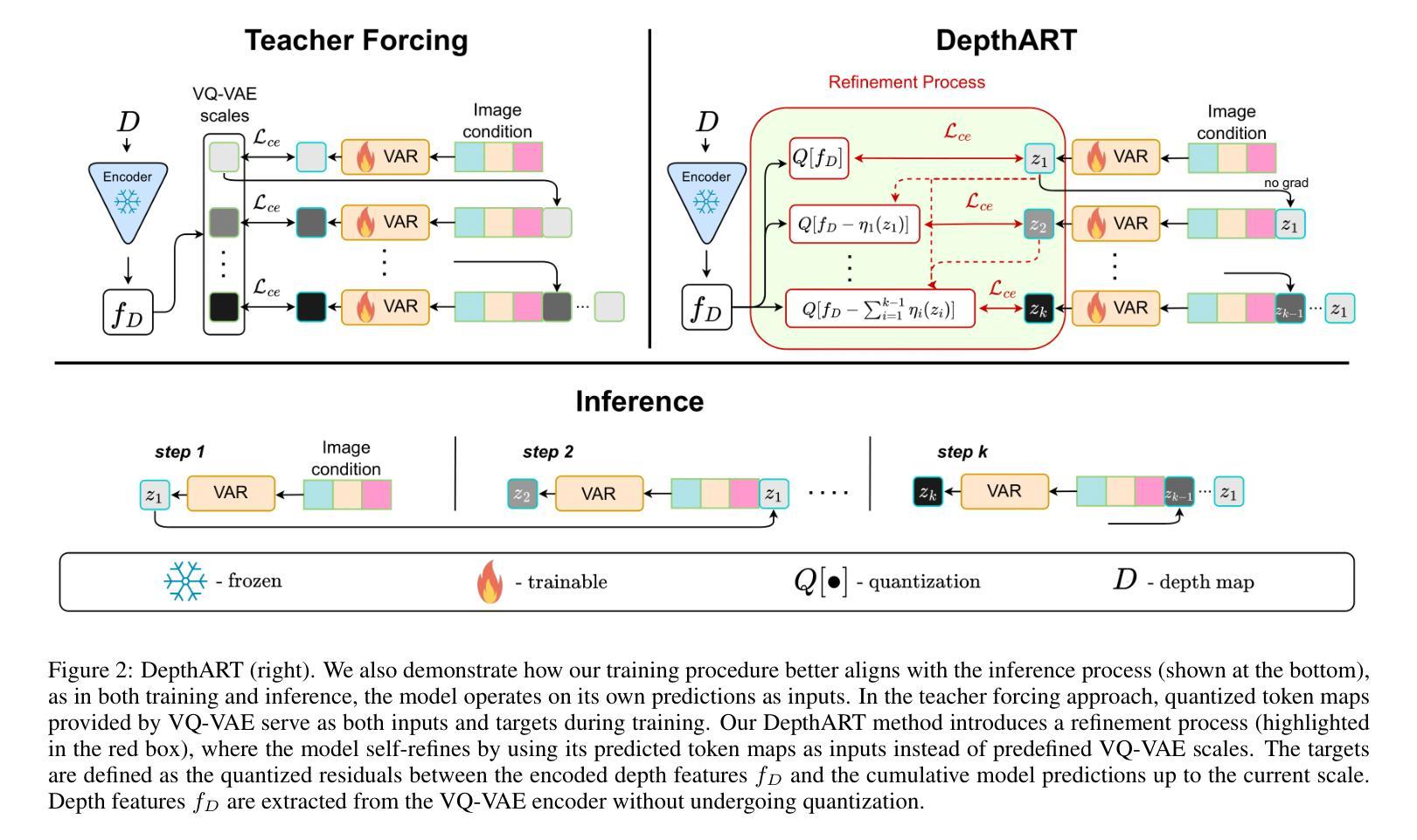
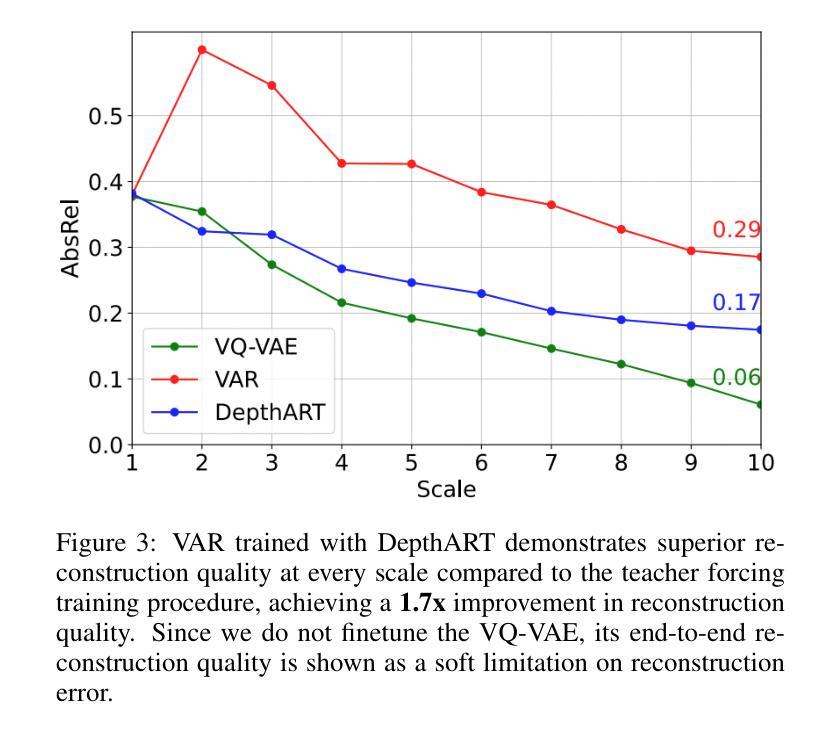
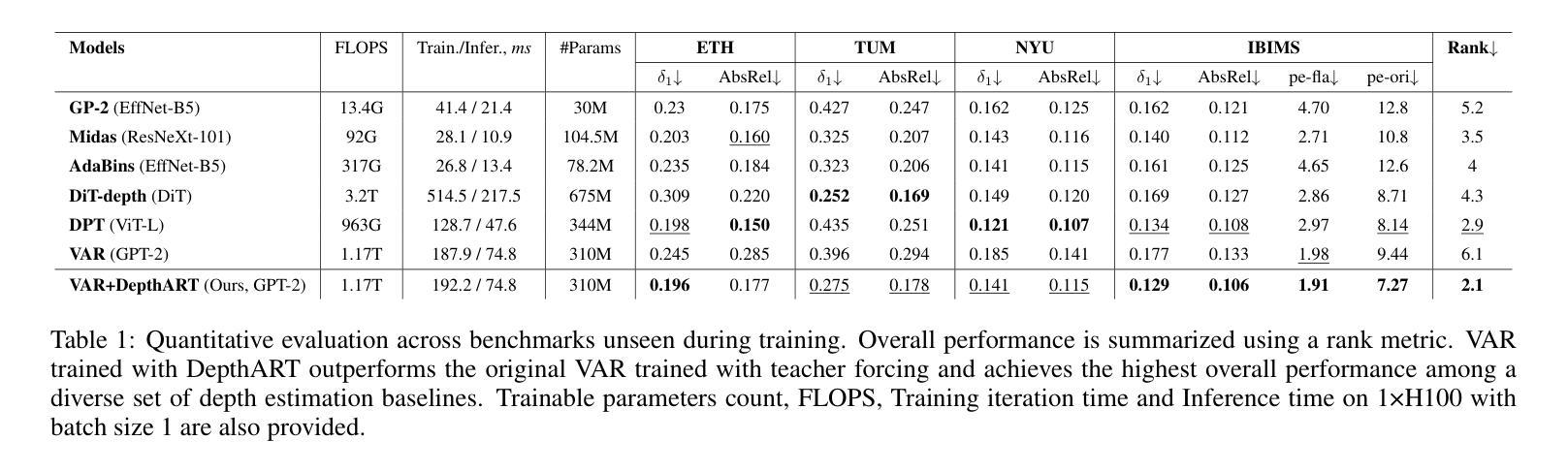
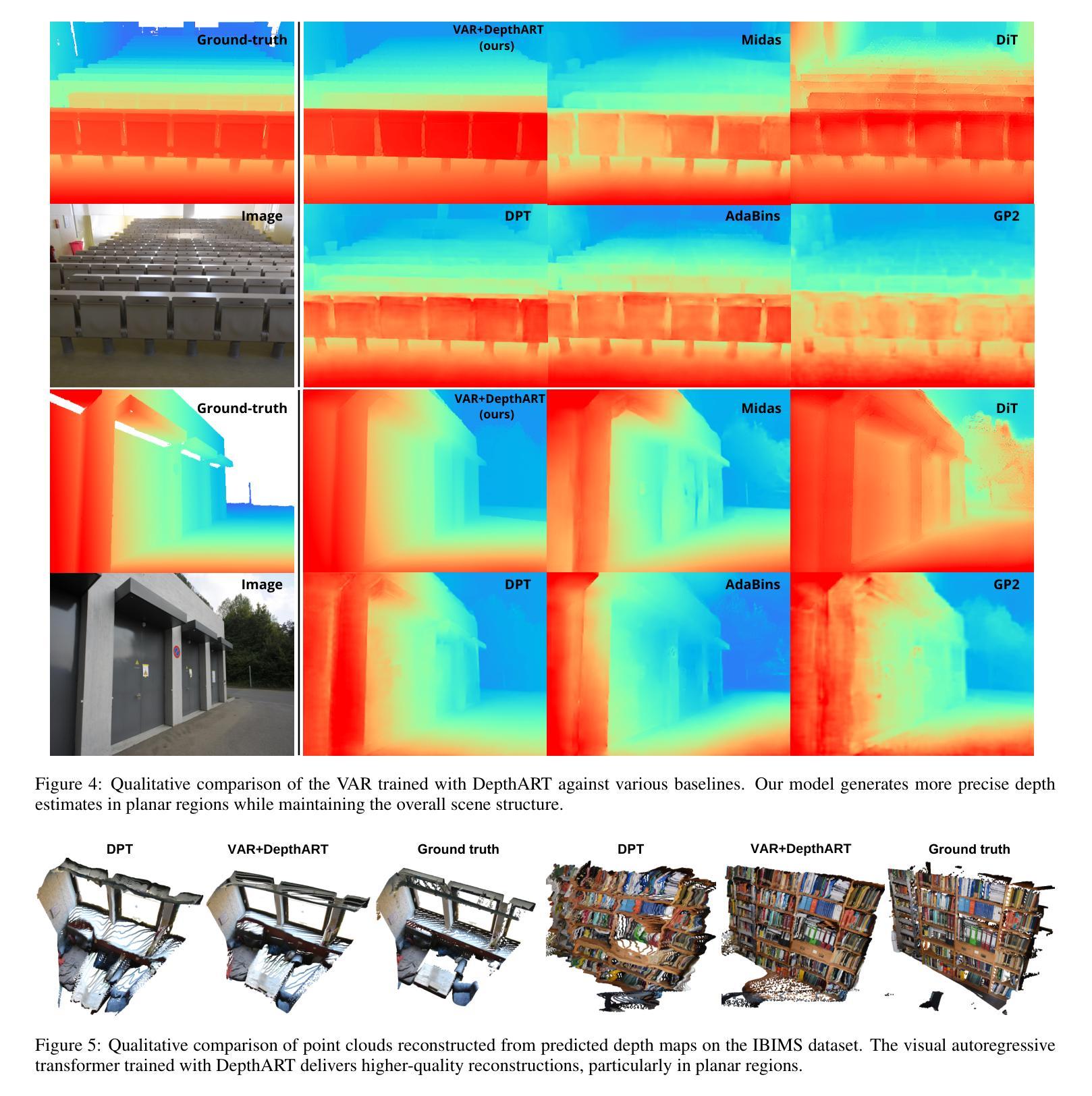
DepthART: Monocular Depth Estimation as Autoregressive Refinement Task
Authors:Bulat Gabdullin, Nina Konovalova, Nikolay Patakin, Dmitry Senushkin, Anton Konushin
Monocular depth estimation has seen significant advances through discriminative approaches, yet their performance remains constrained by the limitations of training datasets. While generative approaches have addressed this challenge by leveraging priors from internet-scale datasets, with recent studies showing state-of-the-art results using fine-tuned text-to-image diffusion models, there is still room for improvement. Notably, autoregressive generative approaches, particularly Visual AutoRegressive modeling, have demonstrated superior results compared to diffusion models in conditioned image synthesis, while offering faster inference times. In this work, we apply Visual Autoregressive Transformer (VAR) to the monocular depth estimation problem. However, the conventional GPT-2-style training procedure (teacher forcing) inherited by VAR yields suboptimal results for depth estimation. To address this limitation, we introduce DepthART - a novel training method formulated as a Depth Autoregressive Refinement Task. Unlike traditional VAR training with static inputs and targets, our method implements a dynamic target formulation based on model outputs, enabling self-refinement. By utilizing the model’s own predictions as inputs instead of ground truth token maps during training, we frame the objective as residual minimization, effectively reducing the discrepancy between training and inference procedures. Our experimental results demonstrate that the proposed training approach significantly enhances the performance of VAR in depth estimation tasks. When trained on Hypersim dataset using our approach, the model achieves superior results across multiple unseen benchmarks compared to existing generative and discriminative baselines.
单目深度估计通过判别方法取得了显著进展,但其性能仍受到训练数据集局限性的限制。虽然生成方法通过利用互联网规模数据集的先验来解决这一挑战,且近期研究使用微调文本到图像扩散模型显示出最前沿结果,但仍存在改进空间。值得注意的是,自回归生成方法,特别是视觉自回归建模,在条件图像合成方面显示出比扩散模型更优越的结果,同时提供更快的推理时间。在这项工作中,我们将视觉自回归转换器(VAR)应用于单目深度估计问题。然而,VAR继承的常规GPT-2风格训练程序(教师强制)对于深度估计产生次优结果。为了解决这一局限性,我们引入了DepthART——一种新颖的训练方法,被制定为深度自回归细化任务。与传统的使用静态输入和目标的VAR训练不同,我们的方法实现了基于模型输出的动态目标公式,实现自我完善。通过在训练过程中利用模型自己的预测作为输入,而不是使用地面真实令牌映射,我们将目标定位为残差最小化,有效减少了训练和推理过程之间的差异。我们的实验结果表明,所提出的训练方法显著提高了VAR在深度估计任务中的性能。在HyperSim数据集上采用我们的方法进行训练后,该模型在多个未见过的基准测试中取得了优于现有生成和判别基准的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本描述了使用生成模型进行单眼深度估计的挑战及进展。为提高模型性能,提出将视觉自回归转换器(VAR)应用于单眼深度估计问题,并引入DepthART训练方法。该策略使用模型的预测值而非真实标签作为训练过程中的输入,从而实现目标残余最小化并提升模型性能。经过HyperSim数据集训练的实验结果表明,相较于现有的生成和判别基准模型,该方法在多个未见过的基准测试中取得了更好的效果。
Key Takeaways
- 生成模型对单眼深度估计的性能提升受限,尽管使用判别方法已经取得进展。需要改进模型的性能和适用性。
- 利用大型互联网数据集作为先验的生成方法已经在一定程度上解决了训练数据集的问题。扩散模型已经在精细调整文本到图像的任务中取得了最先进的成果。但自回归生成模型在条件图像合成方面表现出更高的性能。
点此查看论文截图

Transformers from Diffusion: A Unified Framework for Neural Message Passing
Authors:Qitian Wu, David Wipf, Junchi Yan
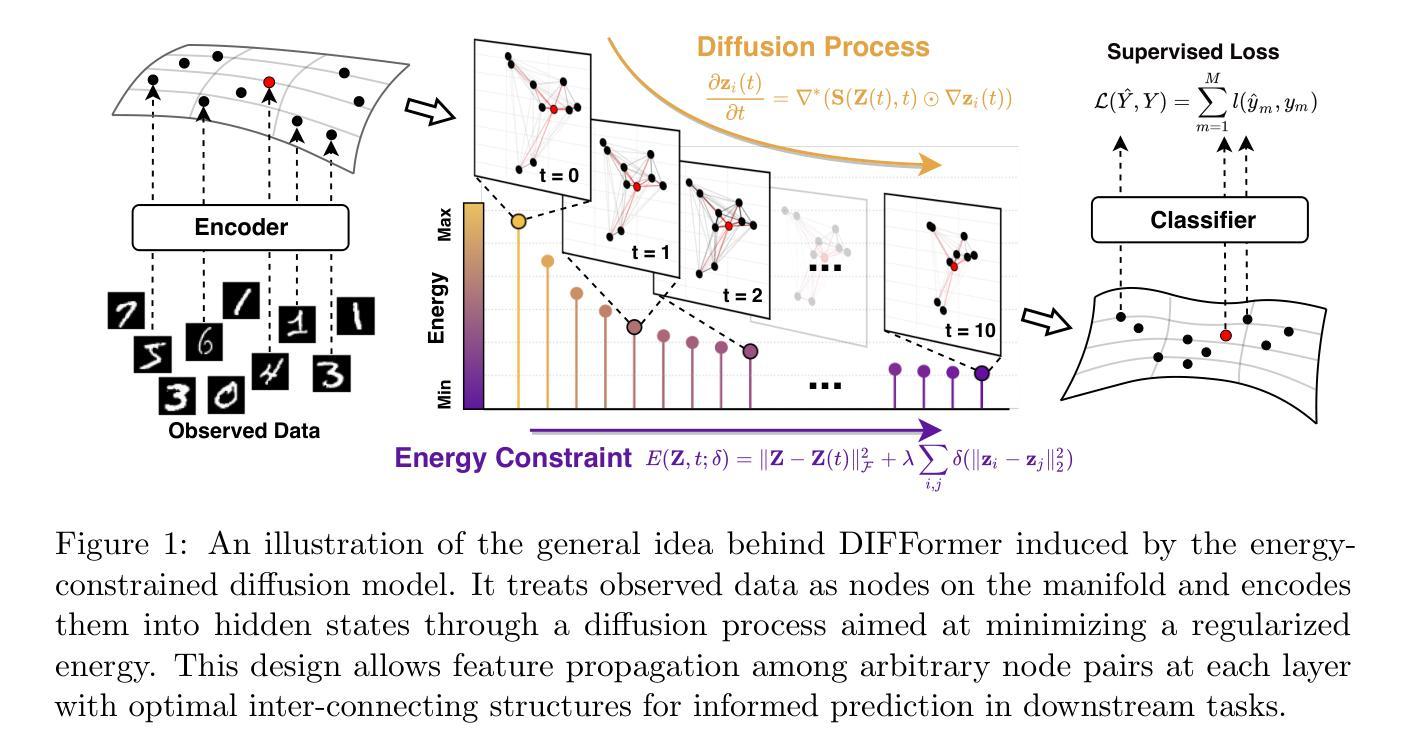
Learning representations for structured data with certain geometries (e.g., observed or unobserved) is a fundamental challenge, wherein message passing neural networks (MPNNs) have become a de facto class of model solutions. In this paper, inspired by physical systems, we propose an energy-constrained diffusion model, which integrates the inductive bias of diffusion on manifolds with layer-wise constraints of energy minimization. We identify that the diffusion operators have a one-to-one correspondence with the energy functions implicitly descended by the diffusion process, and the finite-difference iteration for solving the energy-constrained diffusion system induces the propagation layers of various types of MPNNs operating on observed or latent structures. This leads to a unified mathematical framework for common neural architectures whose computational flows can be cast as message passing (or its special case), including MLPs, GNNs, and Transformers. Building on these insights, we devise a new class of neural message passing models, dubbed diffusion-inspired Transformers (DIFFormer), whose global attention layers are derived from the principled energy-constrained diffusion framework. Across diverse datasets ranging from real-world networks to images, texts, and physical particles, we demonstrate that the new model achieves promising performance in scenarios where the data structures are observed (as a graph), partially observed, or entirely unobserved.
针对具有某些几何结构(无论是观察到的还是未观察到的)的数据学习表示是一项基本挑战,其中消息传递神经网络(MPNNs)已成为一种模型解决方案的实际类别。在本文中,我们受到物理系统的启发,提出了一个受能量约束的扩散模型,该模型结合了流形上扩散的归纳偏见与能量最小化的逐层约束。我们发现扩散算子与扩散过程隐含下降的能量函数有一一对应关系,解决能量约束扩散系统的有限差分迭代引发了操作在观测或潜在结构上的各种类型的MPNN的传播层。这为常见的神经网络架构提供了一个统一的数学框架,其计算流程可以表示为消息传递(或其特殊情况),包括MLPs、GNNs和Transformer。基于这些见解,我们设计了一种新型的神经网络消息传递模型,称为受扩散启发的Transformer(DIFFormer),其全局注意力层源于有原则的能量约束扩散框架。在涵盖从真实世界网络到图像、文本和物理粒子的各种数据集上,我们证明了该新模型在数据结构为图、部分观测或完全未观测的场景中均取得了有前景的性能表现。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in Journal of Machine Learning Research (JMLR). Extended from DIFFormer in ICLR 2023
Summary
本文提出了一个受物理系统启发的能量约束扩散模型,该模型结合了扩散流形上的归纳偏见与能量最小化的逐层约束。扩散算子与能量函数有一一对应关系,通过求解能量约束扩散系统得到的有限差分迭代,诱导了适用于观测或潜在结构的各类消息传递网络(MPNNs)的传播层。这为常见的计算流程可转换为消息传递或其特殊情况的神经网络架构提供了统一的数学框架,包括MLPs、GNNs和Transformer。基于这些见解,我们开发了一种新型的神经消息传递模型——扩散启发式Transformer(DIFFormer),其全局注意力层源于有原则的能量约束扩散框架。在多种数据集上,无论是作为图观测、部分观测还是完全未观测的数据结构,新模型均表现出良好的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 论文提出了能量约束扩散模型,该模型结合了扩散流形上的归纳偏见与能量最小化的逐层约束。
- 扩散算子与能量函数之间存在一一对应关系。
- 有限差分迭代为不同的MPNNs传播层提供了解决方案,这些网络可应用于观测或潜在结构。
- 这提供了统一的数学框架,涵盖计算流程可转换为消息传递或其特殊情况的神经网络架构,如MLPs、GNNs和Transformer。
- 基于上述见解,论文开发了一种新型的神经消息传递模型——扩散启发式Transformer(DIFFormer)。
- DIFFormer的全局注意力层是基于有原则的能量约束扩散框架推导出来的。
点此查看论文截图