⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-03 更新
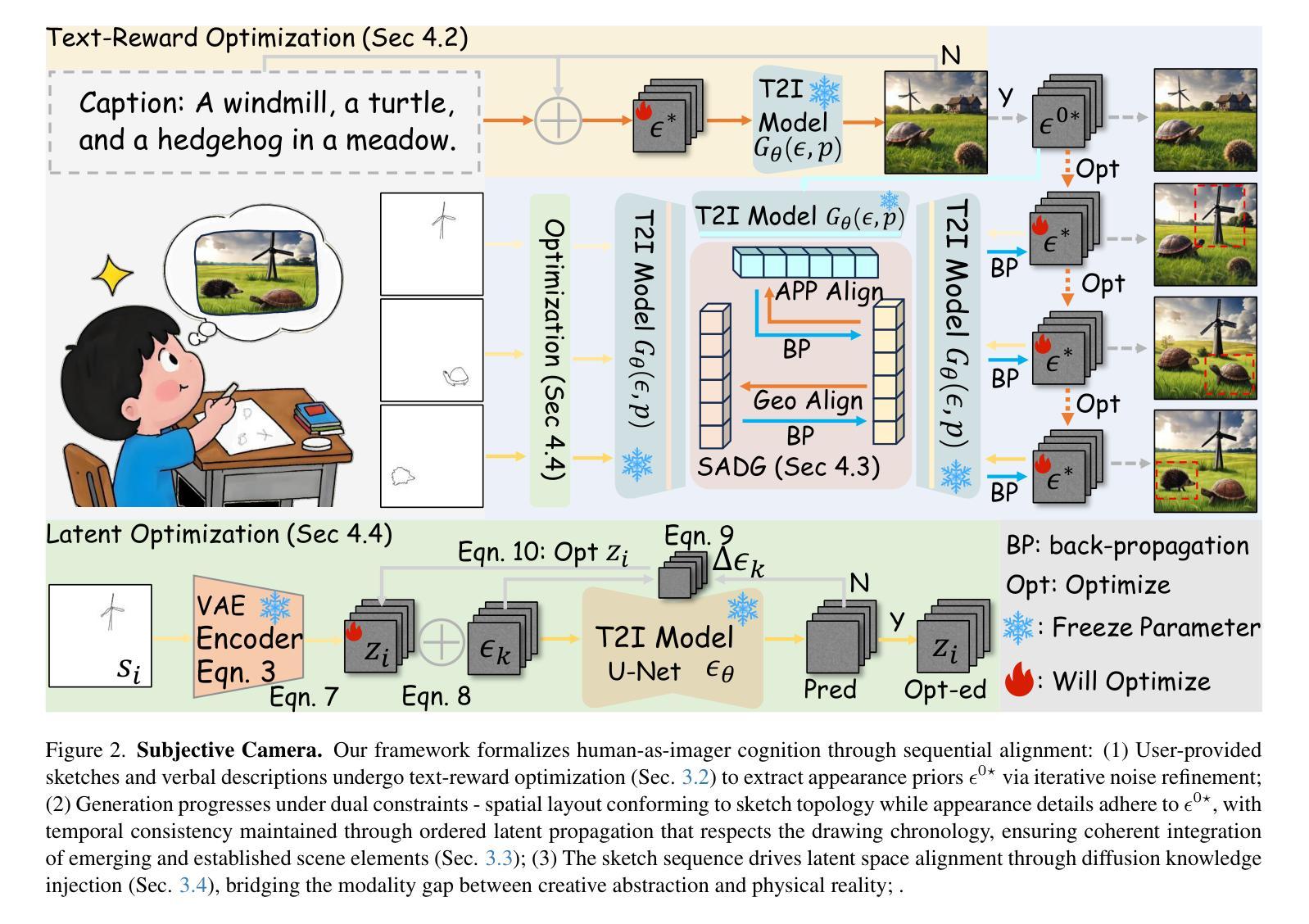
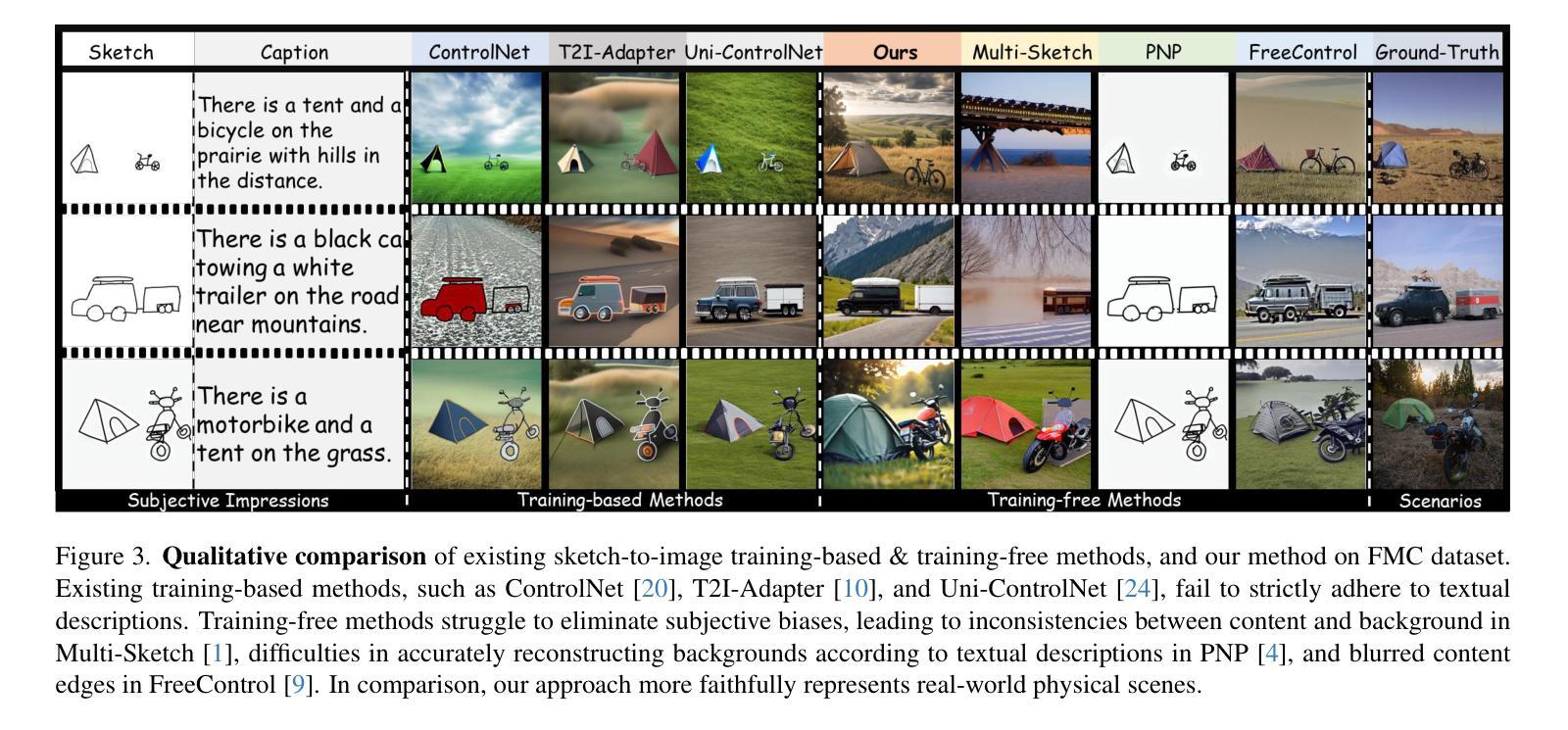
Subjective Camera: Bridging Human Cognition and Visual Reconstruction through Sequence-Aware Sketch-Guided Diffusion
Authors:Haoyang Chen, Dongfang Sun, Caoyuan Ma, Shiqin Wang, Kewei Zhang, Zheng Wang, Zhixiang Wang
We propose Subjective Camera, a human-as-imaging-device paradigm that reconstructs real-world scenes from mental impressions through synergistic use of verbal descriptions and progressive rough sketches. This approach overcomes dual limitations of language ambiguity and sketch abstraction by treating the user’s drawing sequence as priors, effectively translating subjective perceptual expectations into photorealistic images. Existing approaches face three fundamental barriers: (1) user-specific subjective input biases, (2) huge modality gap between planar sketch and 3D priors in diffusion, and (3) sketch quality-sensitive performance degradation. Current solutions either demand resource-intensive model adaptation or impose impractical requirements on sketch precision. Our framework addresses these challenges through concept-sequential generation. (1) We establish robust appearance priors through text-reward optimization, and then implement sequence-aware disentangled generation that processes concepts in sketching order; these steps accommodate user-specific subjective expectation in a train-free way. (2) We employ latent optimization that effectively bridges the modality gap between planar sketches and 3D priors in diffusion. (3) Our hierarchical reward-guided framework enables the use of rough sketches without demanding artistic expertise. Comprehensive evaluation across diverse datasets demonstrates that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance in maintaining both semantic and spatial coherence.
我们提出了主观相机(Subjective Camera)这一概念,这是一种以人为成像设备范式,通过协同使用语言描述和渐进式粗略草图,从心理印象重建真实场景。该方法通过用户的绘图序列作为先验,克服了语言模糊和草图抽象性的双重局限性,有效地将主观感知期望转化为逼真的图像。现有方法面临三大基本障碍:(1)用户特定的主观输入偏见,(2)平面草图与扩散中三维先验之间的巨大模态差距,(3)草图质量敏感的性能下降。目前的解决方案要么需要大量资源对模型进行适配,要么对草图的精确性提出不切实际的要求。我们的框架通过概念序列生成来解决这些挑战。(1)我们通过文本奖励优化建立稳健的外观先验,然后实现序列感知的分离生成,按草图顺序处理概念;这些步骤以无训练的方式容纳用户特定的主观期望。(2)我们采用潜在优化,有效地缩小了平面草图和扩散中三维先验之间的模态差距。(3)我们的分层奖励引导框架允许使用粗略草图,无需艺术专业知识。在多个数据集上的综合评估表明,我们的方法在保持语义和空间连贯性方面达到了最新性能水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
我们提出了主观相机这一人类作为成像设备的新范式,它通过协同使用言语描述和渐进的粗略草图,从心理印象重建现实世界场景。这种方法克服了语言模糊和草图抽象性的双重局限性,通过将用户的绘图序列视为先验信息,有效地将主观感知期望转化为逼真的图像。我们的框架通过概念序列生成解决现有挑战,无需特定模型适应或高要求的草图精度要求,同时实现了文本奖励优化、序列感知分离生成以及潜在优化技术。全面评估表明,我们的方法在保持语义和空间连贯性方面达到了最新技术水平。
Key Takeaways:
- 提出了Subjective Camera新范式,将人类视为成像设备,结合言语描述和草图重建现实场景。
- 克服语言模糊和草图抽象性的挑战,将用户绘图序列作为先验信息,转化为真实图像。
- 现有方法面临用户主观输入偏见、草图与3D先验间的模态差距以及草图质量敏感的性能下降等三大难题。
- 通过概念序列生成解决挑战,包括建立外观先验、序列感知分离生成等。
- 采用文本奖励优化和潜在优化技术,缩小了草图与3D先验之间的模态差距。
- 框架允许使用粗略草图,无需艺术专业技能。
点此查看论文截图

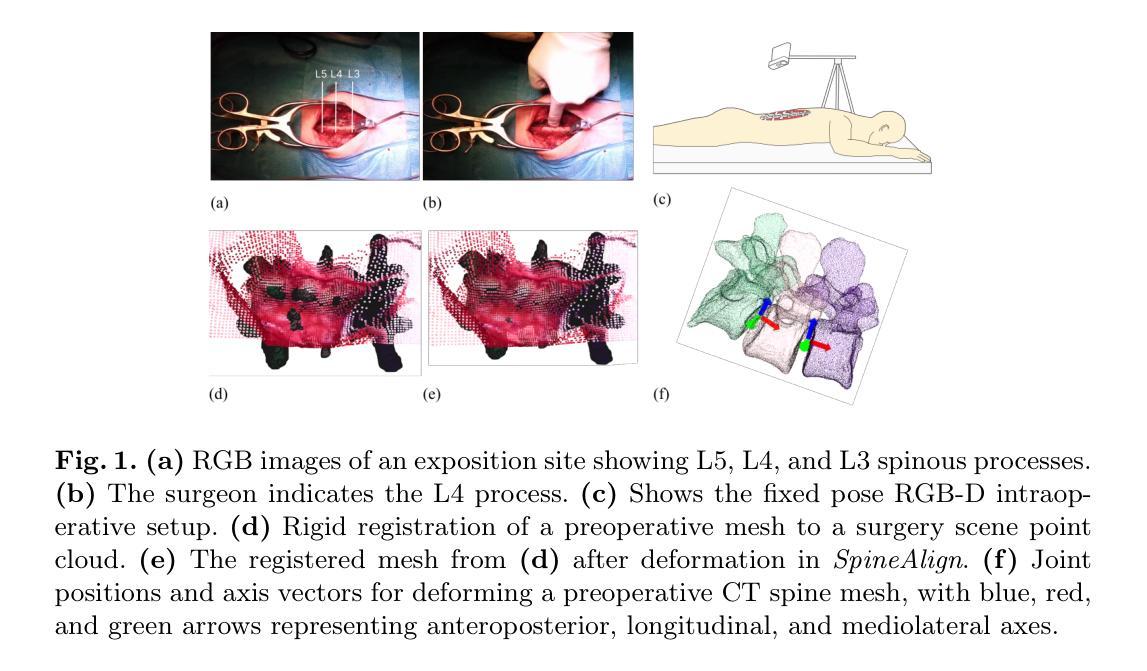
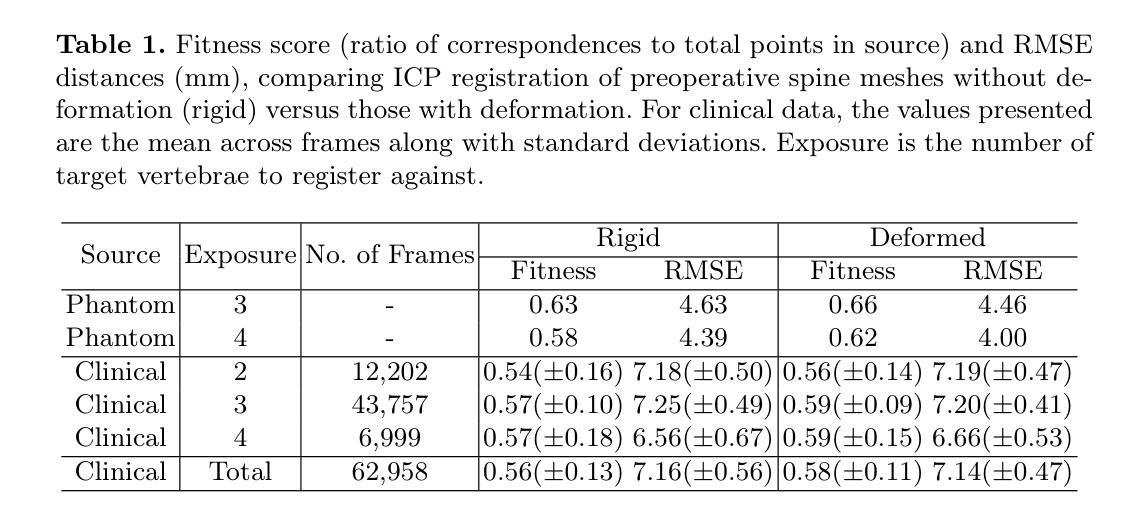
Towards Markerless Intraoperative Tracking of Deformable Spine Tissue
Authors:Connor Daly, Elettra Marconi, Marco Riva, Jinendra Ekanayake, Daniel S. Elson, Ferdinando Rodriguez y Baena
Consumer-grade RGB-D imaging for intraoperative orthopedic tissue tracking is a promising method with high translational potential. Unlike bone-mounted tracking devices, markerless tracking can reduce operating time and complexity. However, its use has been limited to cadaveric studies. This paper introduces the first real-world clinical RGB-D dataset for spine surgery and develops SpineAlign, a system for capturing deformation between preoperative and intraoperative spine states. We also present an intraoperative segmentation network trained on this data and introduce CorrespondNet, a multi-task framework for predicting key regions for registration in both intraoperative and preoperative scenes.
消费级RGB-D成像用于术中骨科组织追踪是一种具有很高应用潜力且前景光明的方法。与骨安装式追踪设备不同,无标记追踪可以减少手术时间和复杂性。然而,其应用仅限于尸体研究。本文介绍了第一个用于脊柱手术的实时临床RGB-D数据集,并开发了SpineAlign系统,用于捕获术前和术中脊柱状态之间的变形。我们还展示了基于此数据的术中分割网络,并引入了CorrespondNet多任务框架,用于预测术中情景和术前情景中的关键区域的注册。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF An improved version of this manuscript was accepted to MICCAI
Summary
消费者级RGB-D成像在术中骨科组织追踪方面展现出巨大潜力,具有高度的临床转化潜力。无标记追踪技术相较于骨头上安装的追踪设备,能够减少手术时间和复杂性。然而,其应用仅限于尸体研究。本文首次引入用于脊柱外科的真实世界临床RGB-D数据集,并开发了SpineAlign系统以捕获术前和术中脊椎状态之间的变形情况。此外,本文展示了一个基于该数据训练的术中分割网络,并引入了CorrespondNet多任务框架,用于预测术中与术前场景的注册关键区域。
Key Takeaways
- RGB-D成像在术中骨科组织追踪方面具有巨大潜力。
- 无标记追踪技术相较于骨头上安装的追踪设备能够减少手术时间和复杂性。
- RGB-D成像的应用在真实世界临床环境中仍处于初步阶段,仅限于尸体研究。
- 首次引入用于脊柱外科的真实世界临床RGB-D数据集。
- 开发了SpineAlign系统以捕捉术前和术中脊椎状态之间的变形情况。
- 展示了一个基于真实世界临床数据训练的术中分割网络。
点此查看论文截图

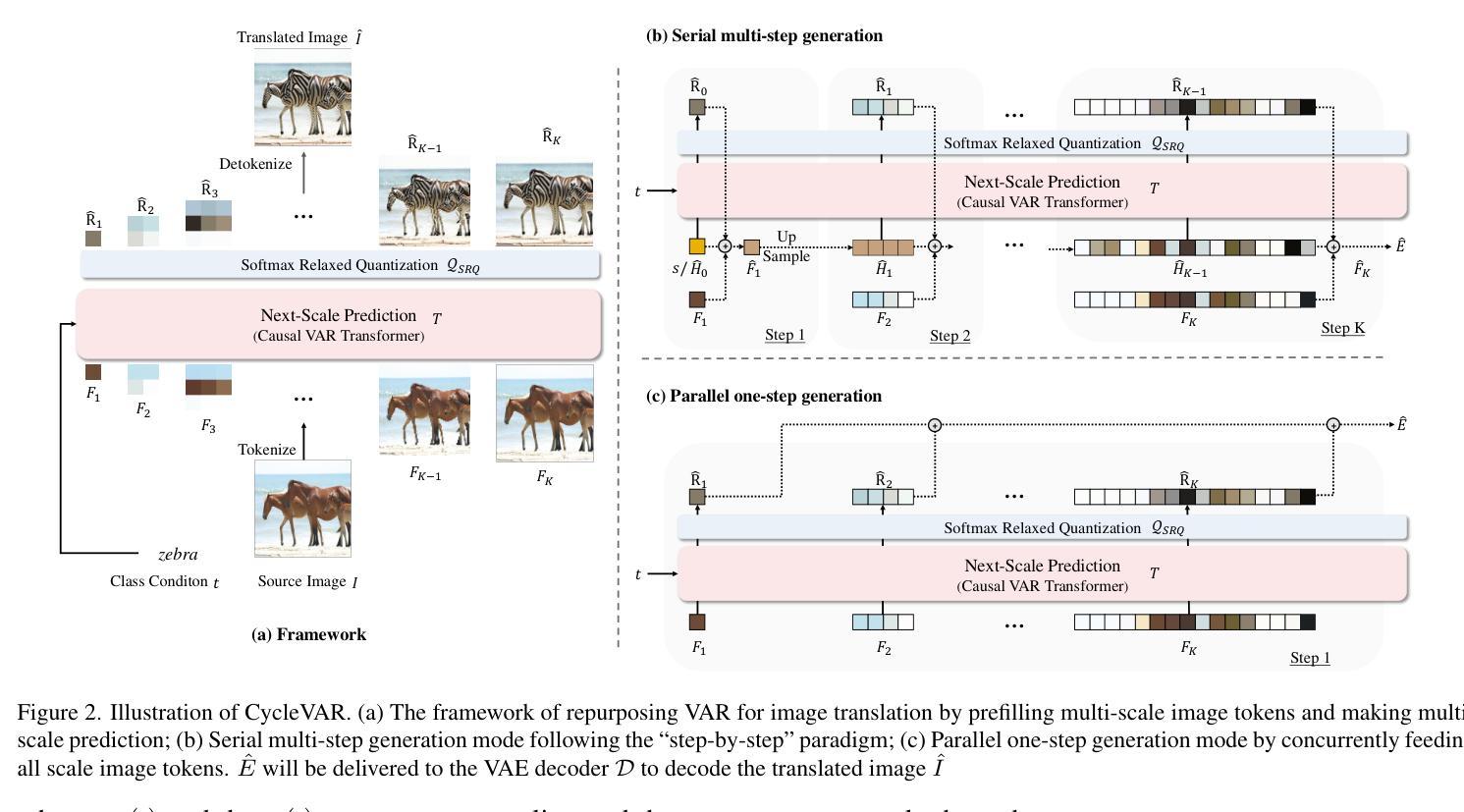
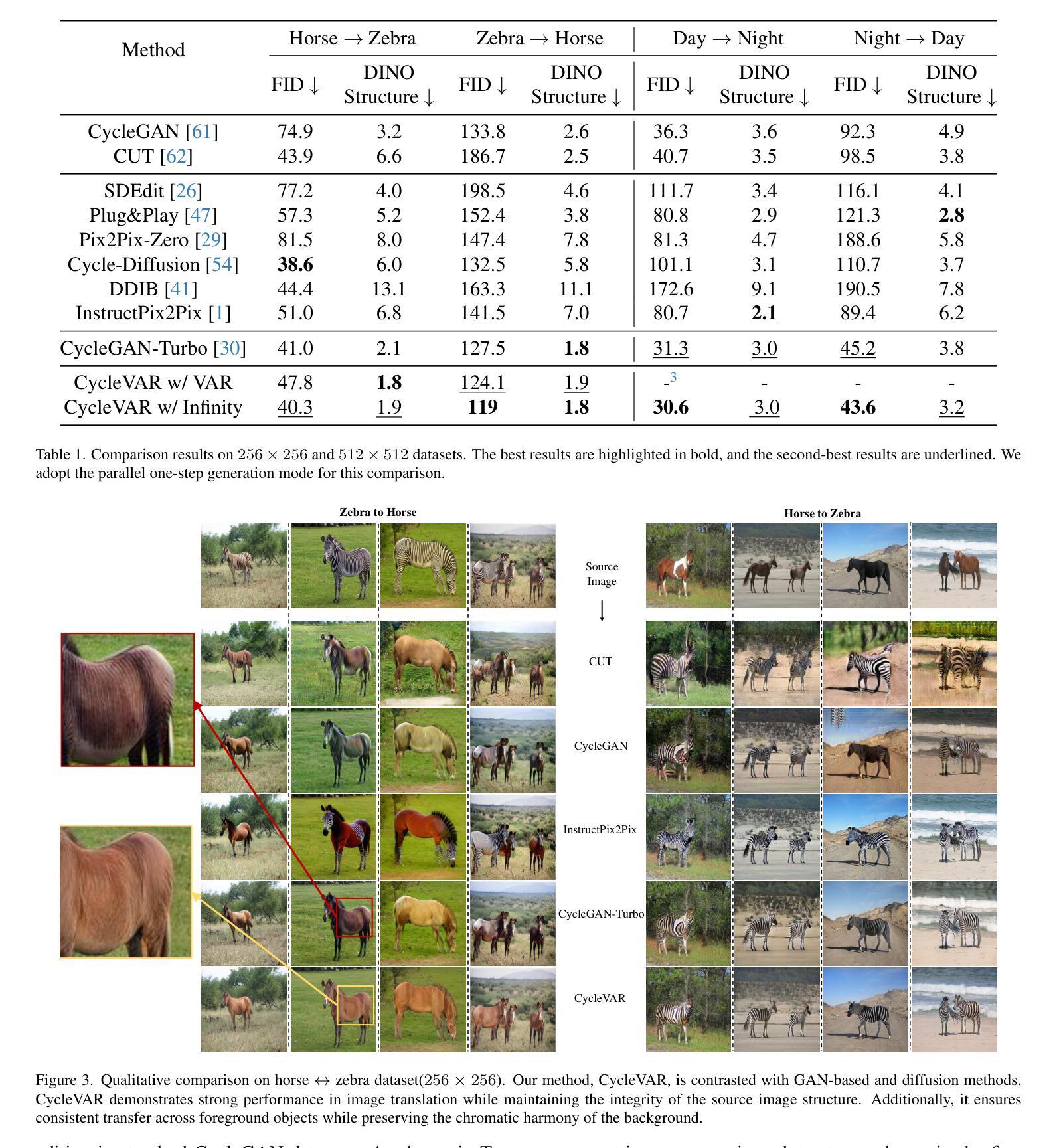
CycleVAR: Repurposing Autoregressive Model for Unsupervised One-Step Image Translation
Authors:Yi Liu, Shengqian Li, Zuzeng Lin, Feng Wang, Si Liu
The current conditional autoregressive image generation methods have shown promising results, yet their potential remains largely unexplored in the practical unsupervised image translation domain, which operates without explicit cross-domain correspondences. A critical limitation stems from the discrete quantization inherent in traditional Vector Quantization-based frameworks, which disrupts gradient flow between the Variational Autoencoder decoder and causal Transformer, impeding end-to-end optimization during adversarial training in image space. To tackle this issue, we propose using Softmax Relaxed Quantization, a novel approach that reformulates codebook selection as a continuous probability mixing process via Softmax, thereby preserving gradient propagation. Building upon this differentiable foundation, we introduce CycleVAR, which reformulates image-to-image translation as image-conditional visual autoregressive generation by injecting multi-scale source image tokens as contextual prompts, analogous to prefix-based conditioning in language models. CycleVAR exploits two modes to generate the target image tokens, including (1) serial multi-step generation, enabling iterative refinement across scales, and (2) parallel one-step generation synthesizing all resolution outputs in a single forward pass. Experimental findings indicate that the parallel one-step generation mode attains superior translation quality with quicker inference speed than the serial multi-step mode in unsupervised scenarios. Furthermore, both quantitative and qualitative results indicate that CycleVAR surpasses previous state-of-the-art unsupervised image translation models, \textit{e}.\textit{g}., CycleGAN-Turbo.
当前的条件自回归图像生成方法已经显示出有前景的结果,但在实际的无监督图像翻译领域,其潜力在很大程度上尚未被探索,这一领域的工作不需要明确的跨域对应。一个关键的局限性来自于传统基于向量量化的框架中的离散量化,它破坏了变分自编码器解码器和因果变压器之间的梯度流,阻碍了图像空间对抗训练过程中的端到端优化。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了Softmax松弛量化方法,这是一种将码本选择重新制定为一个连续的概率混合过程的新方法,通过Softmax保留梯度传播。基于这个可微分的基础,我们引入了CycleVAR,它将图像到图像的翻译重新定义为图像条件视觉自回归生成,通过注入多尺度源图像标记作为上下文提示,类似于语言模型中的前缀条件。CycleVAR利用两种模式来生成目标图像标记,包括(1)串行多步生成,实现跨尺度的迭代细化;(2)并行一步生成,在一次前向传递中合成所有分辨率的输出。实验结果表明,在无人监督的情况下,并行一步生成模式具有更高的翻译质量和更快的推理速度,优于串行多步模式。此外,定量和定性的结果都表明,CycleVAR超越了现有的最先进的无监督图像翻译模型,例如CycleGAN-Turbo。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
当前条件自回归图像生成方法已显示出有前景的结果,但在无监督图像翻译领域的应用潜力尚未得到充分探索。针对传统基于向量量化的框架中存在的离散量化问题,我们提出使用Softmax Relaxed Quantization,将码本选择重构为连续的概略混合过程,从而保留梯度传播。在此基础上,我们引入CycleVAR,将图像到图像的翻译重构为图像条件视觉自回归生成,通过注入多尺度源图像令牌作为上下文提示。实验表明,在无人监督的场景下,并行一步生成模式在翻译质量和推理速度上优于串行多步生成模式。此外,CycleVAR在定量和定性结果上都超越了之前的无监督图像翻译模型。
Key Takeaways
- 条件自回归图像生成方法在无监督图像翻译领域应用潜力巨大。
- 传统基于向量量化的框架存在离散量化问题,影响梯度流和端到端优化。
- Softmax Relaxed Quantization方法将码本选择重构为连续的概略混合过程。
- CycleVAR将图像到图像的翻译重构为图像条件视觉自回归生成。
- CycleVAR利用多尺度源图像令牌作为上下文提示,引入两种生成模式。
- 并行一步生成模式在无人监督的场景下表现优越,翻译质量和推理速度更佳。
点此查看论文截图

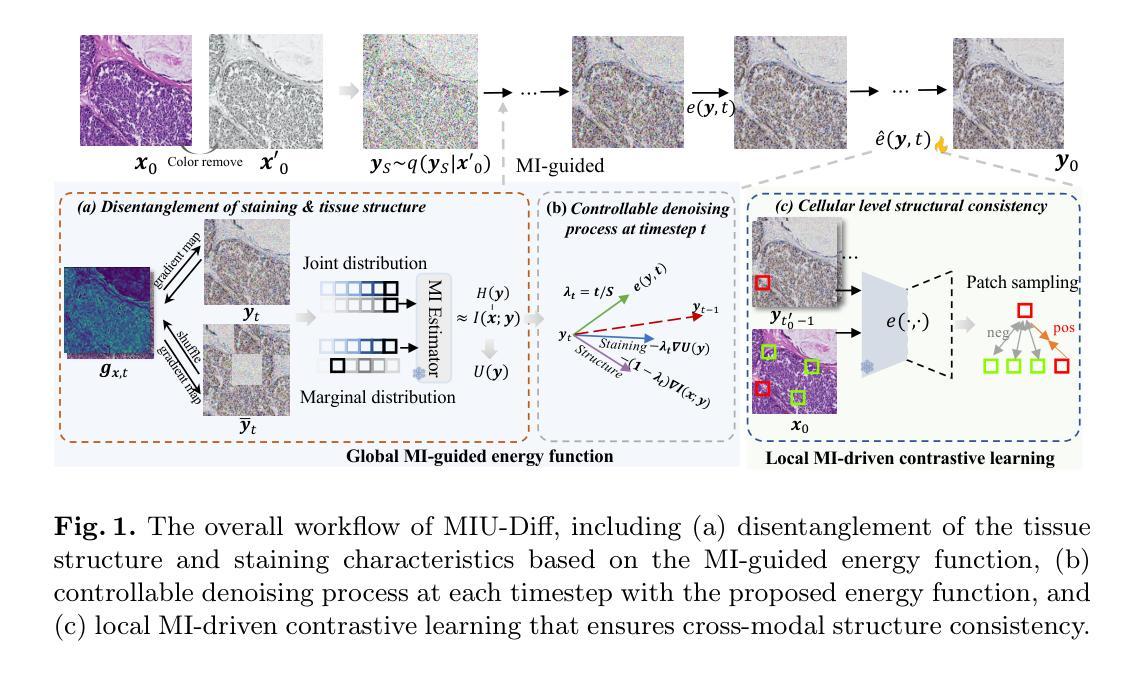
Score-based Diffusion Model for Unpaired Virtual Histology Staining
Authors:Anran Liu, Xiaofei Wang, Jing Cai, Chao Li
Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining visualizes histology but lacks specificity for diagnostic markers. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining provides protein-targeted staining but is restricted by tissue availability and antibody specificity. Virtual staining, i.e., computationally translating the H&E image to its IHC counterpart while preserving the tissue structure, is promising for efficient IHC generation. Existing virtual staining methods still face key challenges: 1) effective decomposition of staining style and tissue structure, 2) controllable staining process adaptable to diverse tissue and proteins, and 3) rigorous structural consistency modelling to handle the non-pixel-aligned nature of paired H&E and IHC images. This study proposes a mutual-information (MI)-guided score-based diffusion model for unpaired virtual staining. Specifically, we design 1) a global MI-guided energy function that disentangles the tissue structure and staining characteristics across modalities, 2) a novel timestep-customized reverse diffusion process for precise control of the staining intensity and structural reconstruction, and 3) a local MI-driven contrastive learning strategy to ensure the cellular level structural consistency between H&E-IHC images. Extensive experiments demonstrate the our superiority over state-of-the-art approaches, highlighting its biomedical potential. Codes will be open-sourced upon acceptance.
苏木精和伊红(H&E)染色能可视化组织形态学,但缺乏特异性诊断标志物。免疫组织化学(IHC)染色提供针对蛋白质的染色,但受到组织可用性和抗体特异性的限制。虚拟染色即通过计算将H&E图像翻译成其IHC对应物,同时保留组织结构,对于高效生成IHC非常有前景。现有的虚拟染色方法仍面临关键挑战:1)有效分解染色风格和组织结构;2)可控的染色过程,适应各种组织和蛋白质;3)严格的结构一致性建模,以处理成对的H&E和IHC图像的非像素对齐性质。本研究提出了一种用于非配对虚拟染色的基于互信息(MI)引导得分扩散模型。具体来说,我们设计了1)一种全局MI引导的能量函数,该函数可以解开不同模式下的组织结构和染色特性;2)一种新型的定时反向扩散过程,实现对染色强度的精确控制和结构重建;3)一种局部MI驱动的对比学习策略,以确保H&E-IHC图像在细胞水平上的结构一致性。大量实验证明,我们的方法优于最新方法,突显了其生物医学潜力。代码将在接受后开源。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 3 figures
Summary:
该研究提出一种基于互信息指导的分数扩散模型用于非配对的虚拟染色技术。通过设计全局互信息引导的能量函数,分离不同模态下的组织结构和染色特征;采用时间步长定制的逆向扩散过程,精确控制染色强度和结构重建;使用局部互信息驱动对比学习策略,确保H&E与IHC图像在细胞水平上的结构一致性。实验证明该方法优于现有技术,展现其在生物医学领域的潜力。代码接受后将开源。
Key Takeaways:
- 虚拟染色技术能够在计算上将H&E图像转化为IHC图像,同时保留组织结构。
- 现存的虚拟染色方法面临有效分解染色风格和组织结构、适应多种组织和蛋白质的可控染色过程,以及处理H&E和IHC图像非像素对齐的严格结构一致性建模等挑战。
- 该研究通过设计全局互信息引导的能量函数,实现了不同模态下组织结构和染色特征的分离。
- 采用时间步长定制的逆向扩散过程,实现对染色强度的精确控制以及结构重建。
- 通过局部互信息驱动对比学习策略,确保了H&E与IHC图像在细胞水平上的结构一致性。
- 实验证明该方法优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

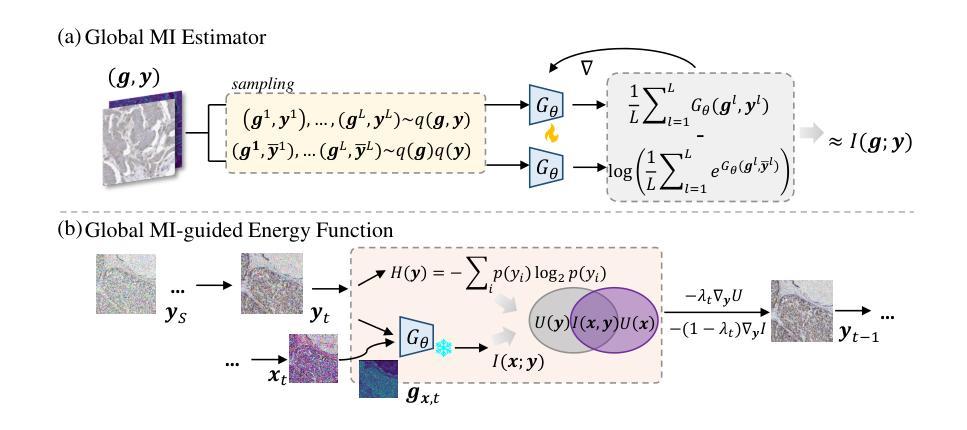
MatChA: Cross-Algorithm Matching with Feature Augmentation
Authors:Paula Carbó Cubero, Alberto Jaenal Gálvez, André Mateus, José Araújo, Patric Jensfelt
State-of-the-art methods fail to solve visual localization in scenarios where different devices use different sparse feature extraction algorithms to obtain keypoints and their corresponding descriptors. Translating feature descriptors is enough to enable matching. However, performance is drastically reduced in cross-feature detector cases, because current solutions assume common keypoints. This means that the same detector has to be used, which is rarely the case in practice when different descriptors are used. The low repeatability of keypoints, in addition to non-discriminatory and non-distinctive descriptors, make the identification of true correspondences extremely challenging. We present the first method tackling this problem, which performs feature descriptor augmentation targeting cross-detector feature matching, and then feature translation to a latent space. We show that our method significantly improves image matching and visual localization in the cross-feature scenario and evaluate the proposed method on several benchmarks.
当前先进技术的方法无法在处理视觉定位的场景中解决不同设备使用不同的稀疏特征提取算法获取关键点和其对应的描述符的问题。翻译特征描述符足以实现匹配。但在跨特征检测器的情况下,性能会大大降低,因为当前解决方案假设了共同的关键点。这意味着必须使用相同的检测器,但在实践中当使用不同的描述符时,这种情况很少见。关键点的低重复性以及非歧视性和非独特性描述符,使得识别真正的对应关系极具挑战性。我们提出了第一种解决此问题的方法,该方法针对跨检测器特征匹配进行特征描述符增强,然后将其转换为潜在空间。我们证明了该方法在跨特征场景中显著提高了图像匹配和视觉定位的能力,并在多个基准测试上对所提出的方法进行了评估。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了不同设备使用不同稀疏特征提取算法进行关键点及其对应描述符提取时,视觉定位面临的挑战。当前解决方案假设共同关键点,但在跨特征检测器情况下性能大幅降低。为此,本文提出一种解决此问题的方法,通过特征描述符增强和跨检测器特征匹配,然后将特征翻译到潜在空间。实验证明,该方法在跨特征场景中能显著提高图像匹配和视觉定位效果。
Key Takeaways
- 不同设备使用不同的稀疏特征提取算法时,视觉定位面临挑战。
- 当前解决方案假设共同关键点,导致跨特征检测器情况下性能降低。
- 特征描述符的翻译是使匹配成为可能的关键。
- 关键点低重复率以及描述符的非歧视性和非独特性使得识别真正的对应关系极具挑战性。
- 本文提出一种解决此问题的方法,通过特征描述符增强和匹配,针对跨检测器进行特征翻译至潜在空间。
- 该方法在跨特征场景中能显著提高图像匹配和视觉定位效果。
- 本文方法在多个基准测试集上进行了评估。
点此查看论文截图

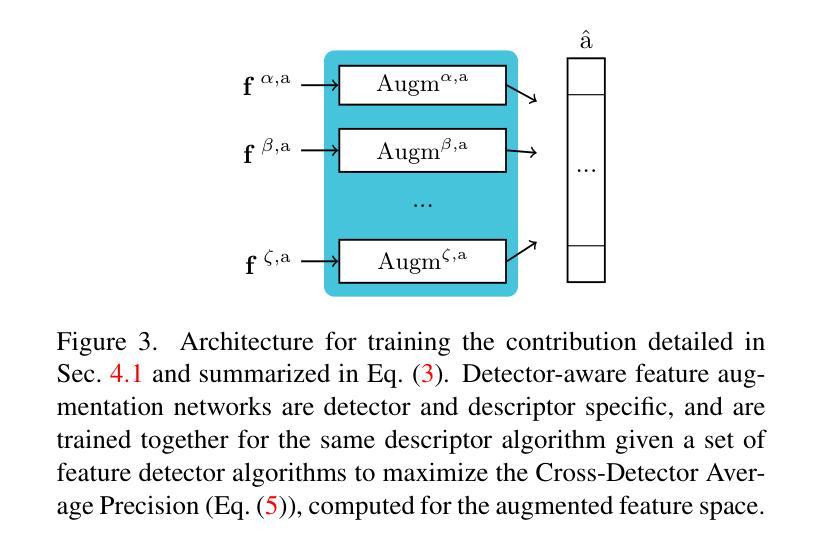
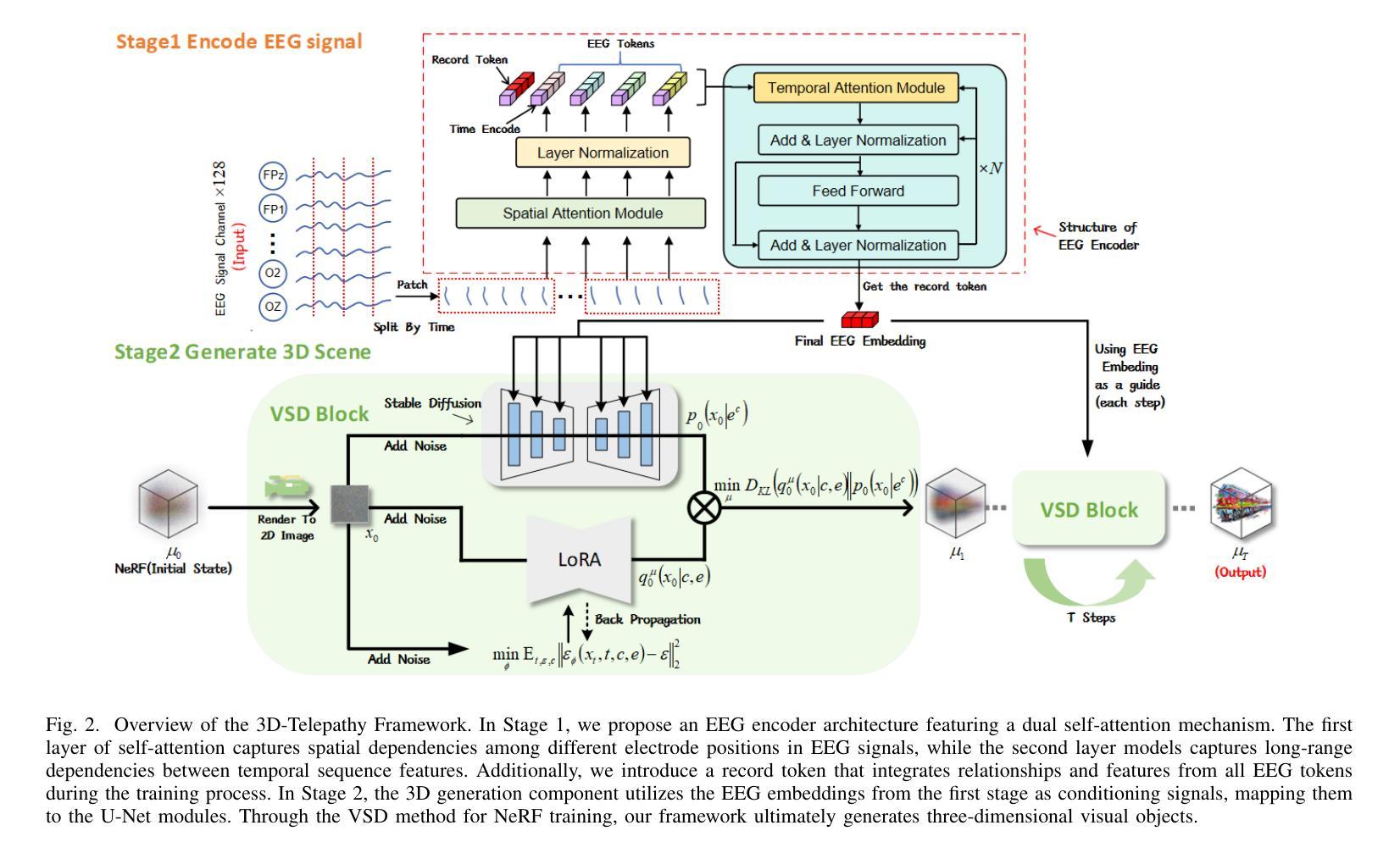
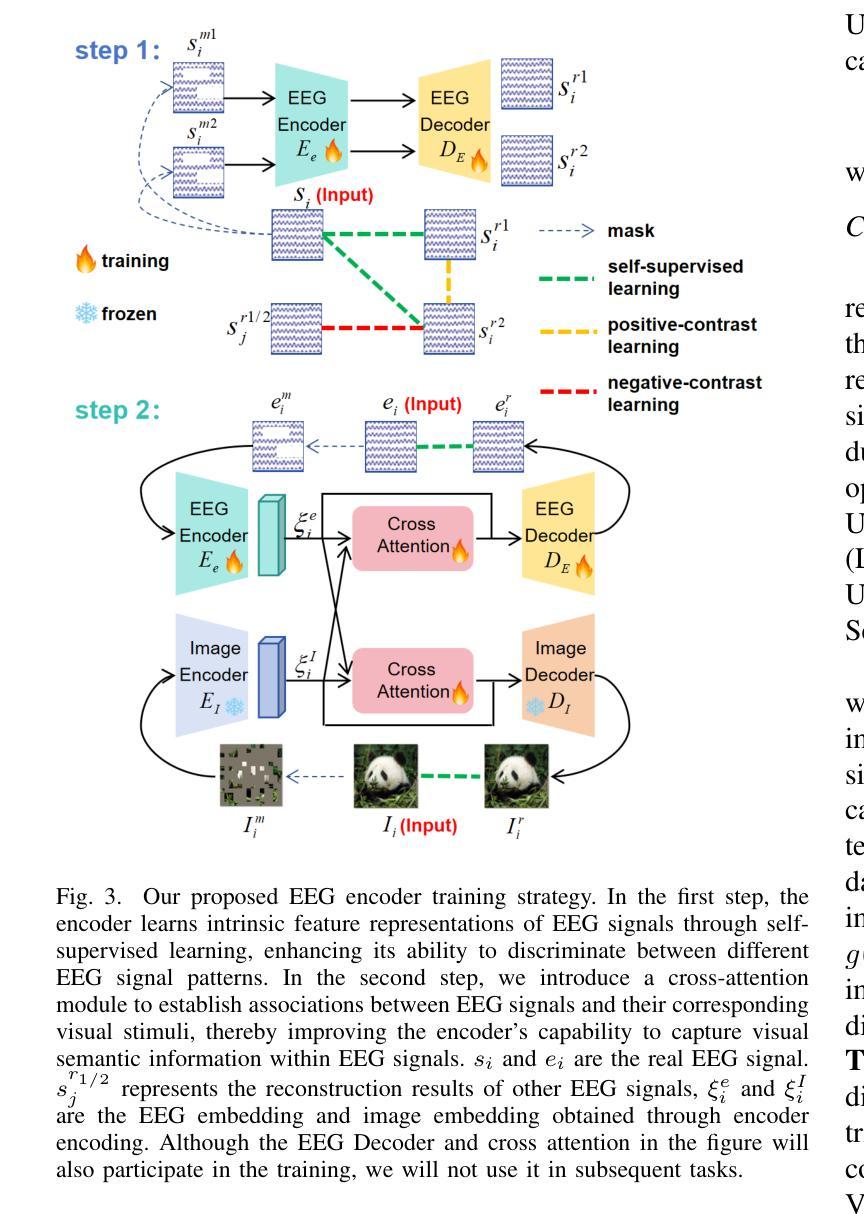
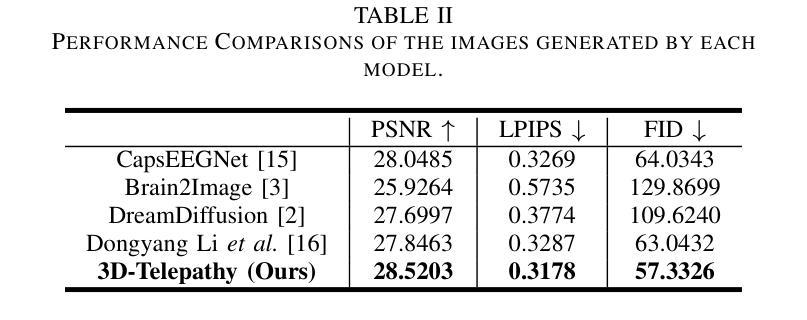
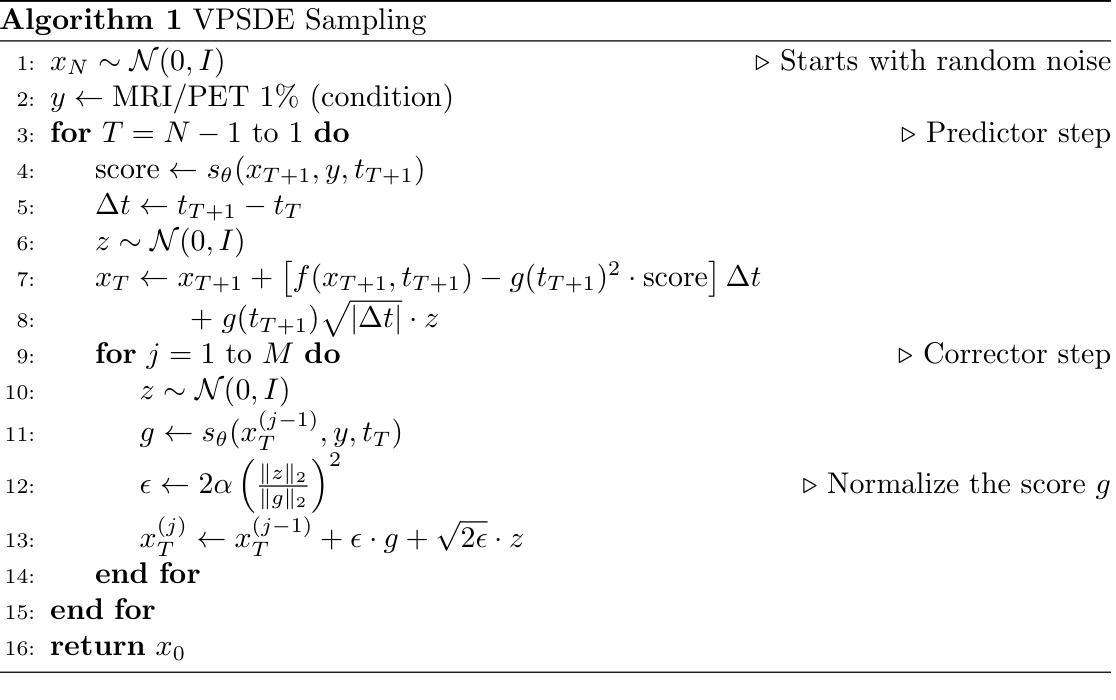
3D-Telepathy: Reconstructing 3D Objects from EEG Signals
Authors:Yuxiang Ge, Jionghao Cheng, Ruiquan Ge, Zhaojie Fang, Gangyong Jia, Xiang Wan, Nannan Li, Ahmed Elazab, Changmiao Wang
Reconstructing 3D visual stimuli from Electroencephalography (EEG) data holds significant potential for applications in Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs) and aiding individuals with communication disorders. Traditionally, efforts have focused on converting brain activity into 2D images, neglecting the translation of EEG data into 3D objects. This limitation is noteworthy, as the human brain inherently processes three-dimensional spatial information regardless of whether observing 2D images or the real world. The neural activities captured by EEG contain rich spatial information that is inevitably lost when reconstructing only 2D images, thus limiting its practical applications in BCI. The transition from EEG data to 3D object reconstruction faces considerable obstacles. These include the presence of extensive noise within EEG signals and a scarcity of datasets that include both EEG and 3D information, which complicates the extraction process of 3D visual data. Addressing this challenging task, we propose an innovative EEG encoder architecture that integrates a dual self-attention mechanism. We use a hybrid training strategy to train the EEG Encoder, which includes cross-attention, contrastive learning, and self-supervised learning techniques. Additionally, by employing stable diffusion as a prior distribution and utilizing Variational Score Distillation to train a neural radiation field, we successfully generate 3D objects with similar content and structure from EEG data.
从脑电图(EEG)数据中重建3D视觉刺激在脑机接口(BCI)应用中具有显著潜力,并能帮助有交流障碍的人。传统上,人们致力于将脑活动转化为二维图像,却忽视了将脑电图数据转化为三维物体的可能性。这种局限性值得注意,因为无论观察二维图像还是真实世界,人类大脑都内在地处理三维空间信息。脑电图捕捉到的神经活动包含丰富的空间信息,在仅重建二维图像时会不可避免地丢失,从而限制了其在脑机接口中的实际应用。从脑电图数据过渡到三维物体重建面临着相当大的障碍。其中包括脑电图信号中存在大量噪声,以及缺乏同时包含脑电图和三维信息的数据集,这使得三维视觉数据的提取过程变得复杂。为了应对这一具有挑战性的任务,我们提出了一种创新的脑电图编码器架构,该架构结合了双重自注意力机制。我们使用混合训练策略来训练脑电图编码器,包括交叉注意力、对比学习和自我监督学习技术。此外,通过采用稳定扩散作为先验分布,并利用变分分数蒸馏训练神经辐射场,我们成功地从脑电图数据中生成了具有相似内容和结构的三维物体。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:利用脑电图(EEG)数据重建三维视觉刺激在脑机接口(BCI)和辅助沟通障碍个体方面具有巨大潜力。传统上,研究主要关注将脑活动转化为二维图像,但将EEG数据翻译为三维物体的研究尚未得到足够重视。本文提出了一种创新的EEG编码器架构,采用双重自注意力机制,通过混合训练策略,成功从EEG数据中生成具有相似内容和结构的三维物体。
Key Takeaways:
- EEG数据重建三维视觉刺激在脑机接口及辅助沟通障碍领域具有显著潜力。
- 传统方法主要将脑活动转化为二维图像,忽视了从EEG数据翻译到三维物体的研究。
- EEG信号中包含丰富的空间信息,在重建过程中不可避免地会丢失部分信息。
- 从EEG数据到三维物体重建存在挑战,包括EEG信号中的大量噪声和缺乏包含EEG和三维信息的数据集。
- 创新的EEG编码器架构结合了双重自注意力机制,为应对这些挑战提供了新的方向。
- 使用混合训练策略,包括交叉注意力、对比学习和自监督学习技术来训练EEG编码器。
点此查看论文截图

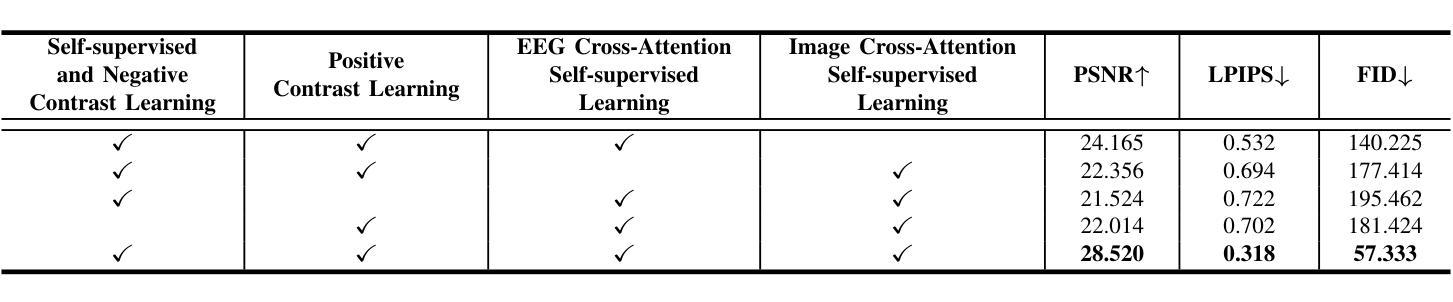
Score-based Generative Diffusion Models to Synthesize Full-dose FDG Brain PET from MRI in Epilepsy Patients
Authors:Jiaqi Wu, Jiahong Ouyang, Farshad Moradi, Mohammad Mehdi Khalighi, Greg Zaharchuk
Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET to evaluate patients with epilepsy is one of the most common applications for simultaneous PET/MRI, given the need to image both brain structure and metabolism, but is suboptimal due to the radiation dose in this young population. Little work has been done synthesizing diagnostic quality PET images from MRI data or MRI data with ultralow-dose PET using advanced generative AI methods, such as diffusion models, with attention to clinical evaluations tailored for the epilepsy population. Here we compared the performance of diffusion- and non-diffusion-based deep learning models for the MRI-to-PET image translation task for epilepsy imaging using simultaneous PET/MRI in 52 subjects (40 train/2 validate/10 hold-out test). We tested three different models: 2 score-based generative diffusion models (SGM-Karras Diffusion [SGM-KD] and SGM-variance preserving [SGM-VP]) and a Transformer-Unet. We report results on standard image processing metrics as well as clinically relevant metrics, including congruency measures (Congruence Index and Congruency Mean Absolute Error) that assess hemispheric metabolic asymmetry, which is a key part of the clinical analysis of these images. The SGM-KD produced the best qualitative and quantitative results when synthesizing PET purely from T1w and T2 FLAIR images with the least mean absolute error in whole-brain specific uptake value ratio (SUVR) and highest intraclass correlation coefficient. When 1% low-dose PET images are included in the inputs, all models improve significantly and are interchangeable for quantitative performance and visual quality. In summary, SGMs hold great potential for pure MRI-to-PET translation, while all 3 model types can synthesize full-dose FDG-PET accurately using MRI and ultralow-dose PET.
使用氟脱氧葡萄糖(FDG)PET评估癫痫患者是同时PET/MRI最常见的应用之一,由于需要同时显示大脑结构和代谢。但是由于年轻患者的辐射剂量问题,其效果并不理想。目前很少有工作使用先进的生成式人工智能方法(如扩散模型)合成具有诊断质量的PET图像或MRI数据与超低剂量PET的MRI数据,并针对癫痫人群进行临床评估。在这里,我们比较了基于扩散和非扩散深度学习模型在MRI到PET图像转换任务上的表现,使用同时PET/MRI对52名癫痫患者(40名训练/ 2名验证/ 10名保留测试)进行成像。我们测试了三种不同的模型:两种基于分数的生成扩散模型(SGM-Karras扩散[SGM-KD]和SGM-方差保留[SGM-VP])和一个Transformer-Unet。我们报告了标准图像处理指标的结果以及与临床相关的指标,包括评估半球代谢不对称性的符合度指标(符合度指数和符合度平均绝对误差)。符合度指数是这些图像临床分析的关键部分。SGM-KD在仅使用T1w和T2 FLAIR图像合成PET时产生了最佳的主观和客观结果,具有最低的全脑特异性摄取值比率(SUVR)平均绝对误差和最高的组内相关系数。当包含1%低剂量PET图像时,所有模型的定量性能和视觉质量均得到显着提高并且可以互换使用。总之,SGM在纯MRI到PET翻译方面显示出巨大潜力,而所有三种类型的模型都可以使用MRI和超低剂量PET准确合成全剂量FDG-PET图像。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了利用深度学习模型在MRI图像基础上合成PET图像的方法,对比了扩散模型与非扩散模型在癫痫病人成像中的表现。研究发现,基于扩散模型的SGM-KD在纯MRI图像上表现最佳,而所有模型在结合超低剂量PET时都能准确合成全剂量FDG-PET图像。
Key Takeaways
1.氟代脱氧葡萄糖(FDG)PET用于评估癫痫患者的应用是最常见的PET/MRI同时应用之一,但需要同时成像大脑结构和代谢。
2.由于年轻人口的辐射剂量问题,当前的应用被认为是不理想的。
3.本研究使用深度学习模型,包括扩散模型,对MRI到PET的图像转换任务进行了比较。
4.在癫痫成像方面,研究对三种模型进行了测试:基于扩散的SGM-KD和SGM-VP模型以及Transformer-Unet模型。
5.SGM-KD模型在纯MRI图像上表现出最佳的定性和定量结果,具有最小的全脑特定摄取值比率(SUVR)平均绝对误差和最高的组内相关系数。
6.当加入超低剂量PET图像时,所有模型的表现都得到了显著提高,并且在定量性能和视觉质量方面变得可互换。
点此查看论文截图

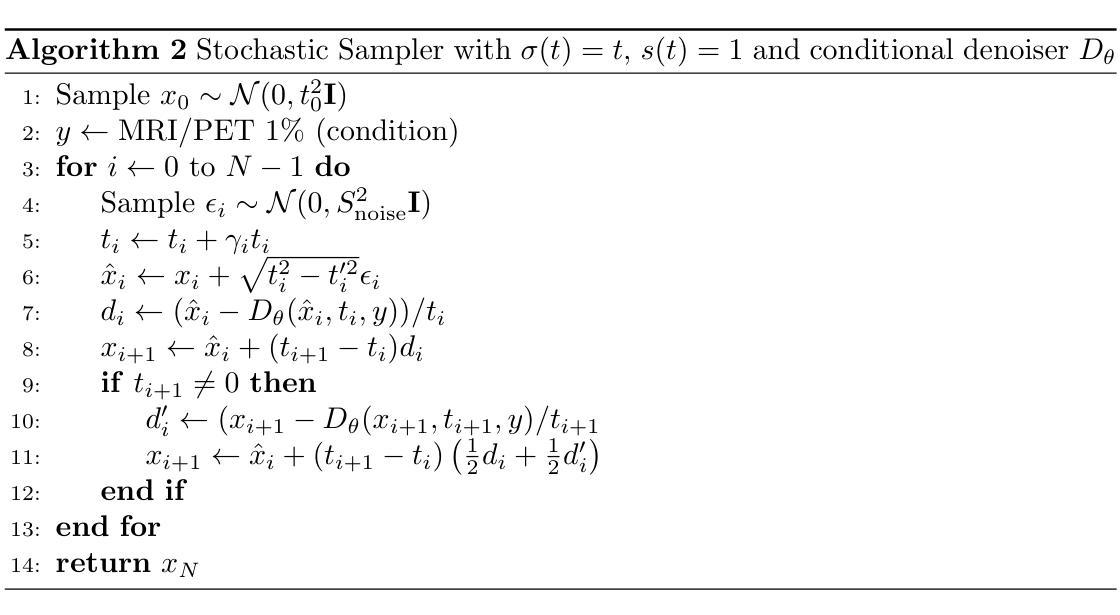
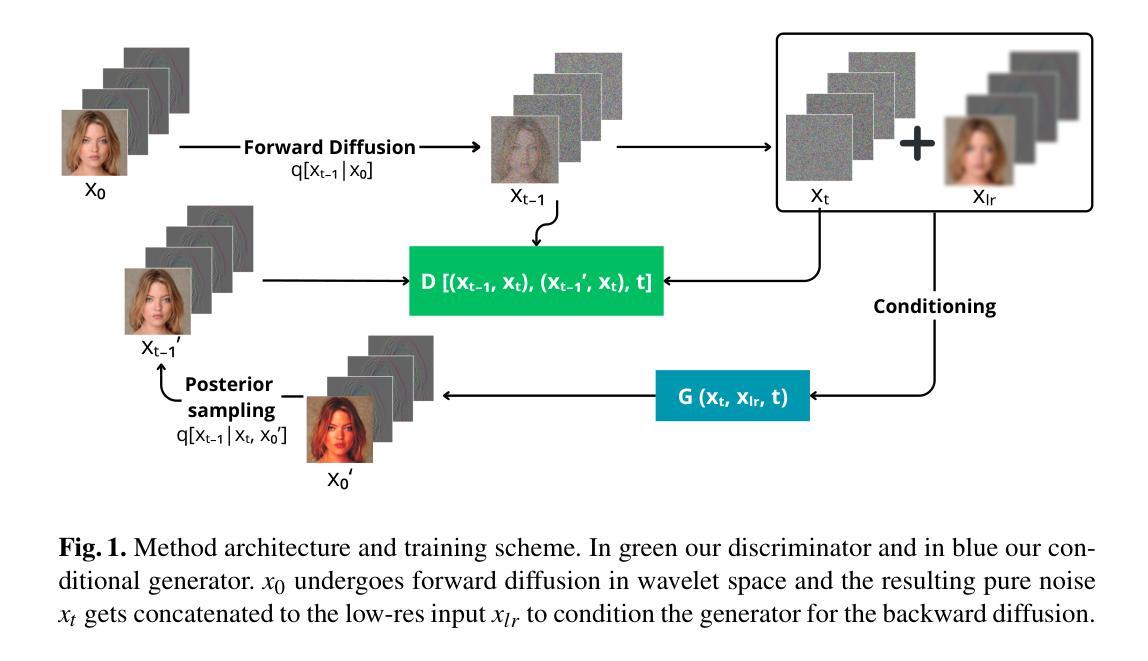
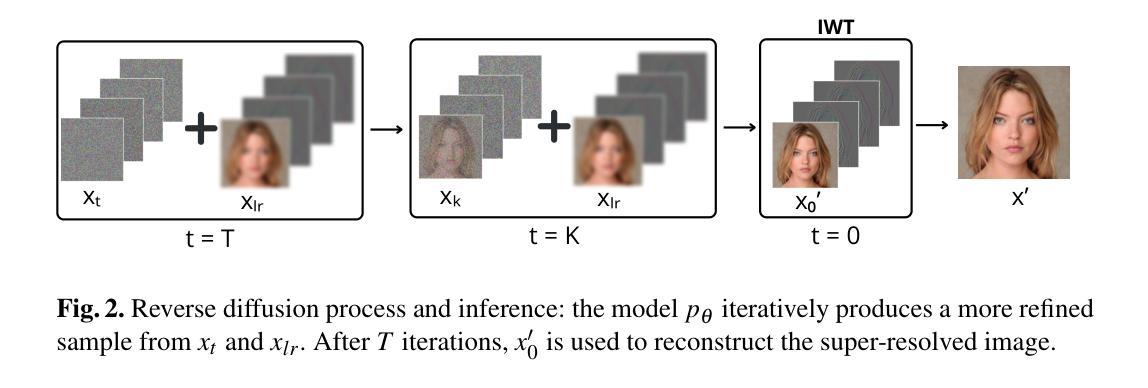
A Wavelet Diffusion GAN for Image Super-Resolution
Authors:Lorenzo Aloisi, Luigi Sigillo, Aurelio Uncini, Danilo Comminiello
In recent years, diffusion models have emerged as a superior alternative to generative adversarial networks (GANs) for high-fidelity image generation, with wide applications in text-to-image generation, image-to-image translation, and super-resolution. However, their real-time feasibility is hindered by slow training and inference speeds. This study addresses this challenge by proposing a wavelet-based conditional Diffusion GAN scheme for Single-Image Super-Resolution (SISR). Our approach utilizes the diffusion GAN paradigm to reduce the timesteps required by the reverse diffusion process and the Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) to achieve dimensionality reduction, decreasing training and inference times significantly. The results of an experimental validation on the CelebA-HQ dataset confirm the effectiveness of our proposed scheme. Our approach outperforms other state-of-the-art methodologies successfully ensuring high-fidelity output while overcoming inherent drawbacks associated with diffusion models in time-sensitive applications.
近年来,扩散模型已经作为生成对抗网络(GANs)的优质替代方案,在高保真图像生成方面展现出优势,广泛应用于文本到图像生成、图像到图像转换和超分辨率处理。然而,由于其训练和推理速度慢,实时性能受限。本研究针对这一挑战,提出一种基于小波条件的扩散GAN方案,用于单图像超分辨率(SISR)。我们的方法利用扩散GAN范式减少反向扩散过程所需的时间步长,并利用离散小波变换(DWT)实现降维,从而显著缩短训练和推理时间。在CelebA-HQ数据集上的实验验证结果证实了我们方案的有效性。我们的方法成功超越了其他最先进的方法,既保证了高保真输出,又克服了扩散模型在时间敏感应用中的固有缺陷。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The paper has been accepted at Italian Workshop on Neural Networks (WIRN) 2024
Summary
近年来,扩散模型已逐渐取代生成对抗网络(GANs),成为高保真图像生成的首选方法,广泛应用于文本到图像生成、图像到图像转换以及超分辨率等领域。然而,其实时可行性受到训练速度慢和推理速度慢的阻碍。本研究通过提出一种基于小波的条件扩散GAN方案来解决这一挑战,用于单图像超分辨率(SISR)。我们的方法利用扩散GAN范式减少了反向扩散过程所需的时间步长,并利用离散小波变换(DWT)实现降维,从而显著减少训练和推理时间。在CelebA-HQ数据集上的实验验证结果表明了本方法的有效性。本方法成功超越了其他先进的方法论,确保了高保真输出,并克服了扩散模型在时间敏感应用中的固有缺陷。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型已成为高保真图像生成的主流方法,替代了生成对抗网络(GANs)。
- 扩散模型在实时应用中面临训练和推理速度慢的难题。
- 本研究提出一种基于小波的条件扩散GAN方案,旨在解决扩散模型在实时应用中的瓶颈。
- 方法利用扩散GAN范式减少时间步长,并利用离散小波变换(DWT)实现降维。
- 实验在CelebA-HQ数据集上进行,证明了该方法的有效性。
- 该方法成功超越了其他先进的方法,保证了高保真输出。
点此查看论文截图