⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-03 更新
AttentionGS: Towards Initialization-Free 3D Gaussian Splatting via Structural Attention
Authors:Ziao Liu, Zhenjia Li, Yifeng Shi, Xiangang Li
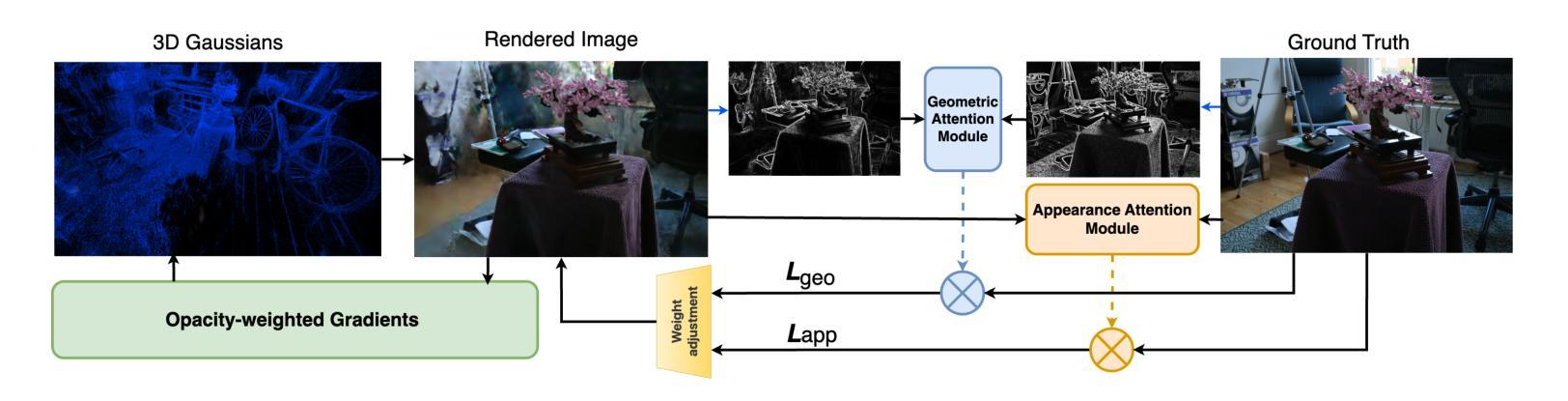
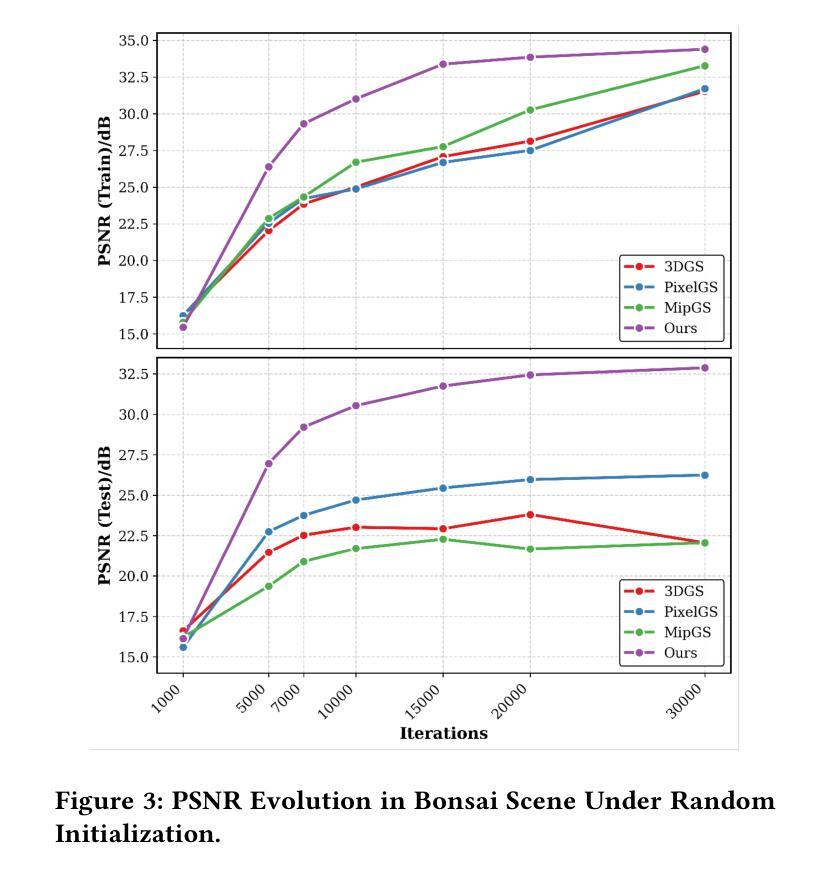
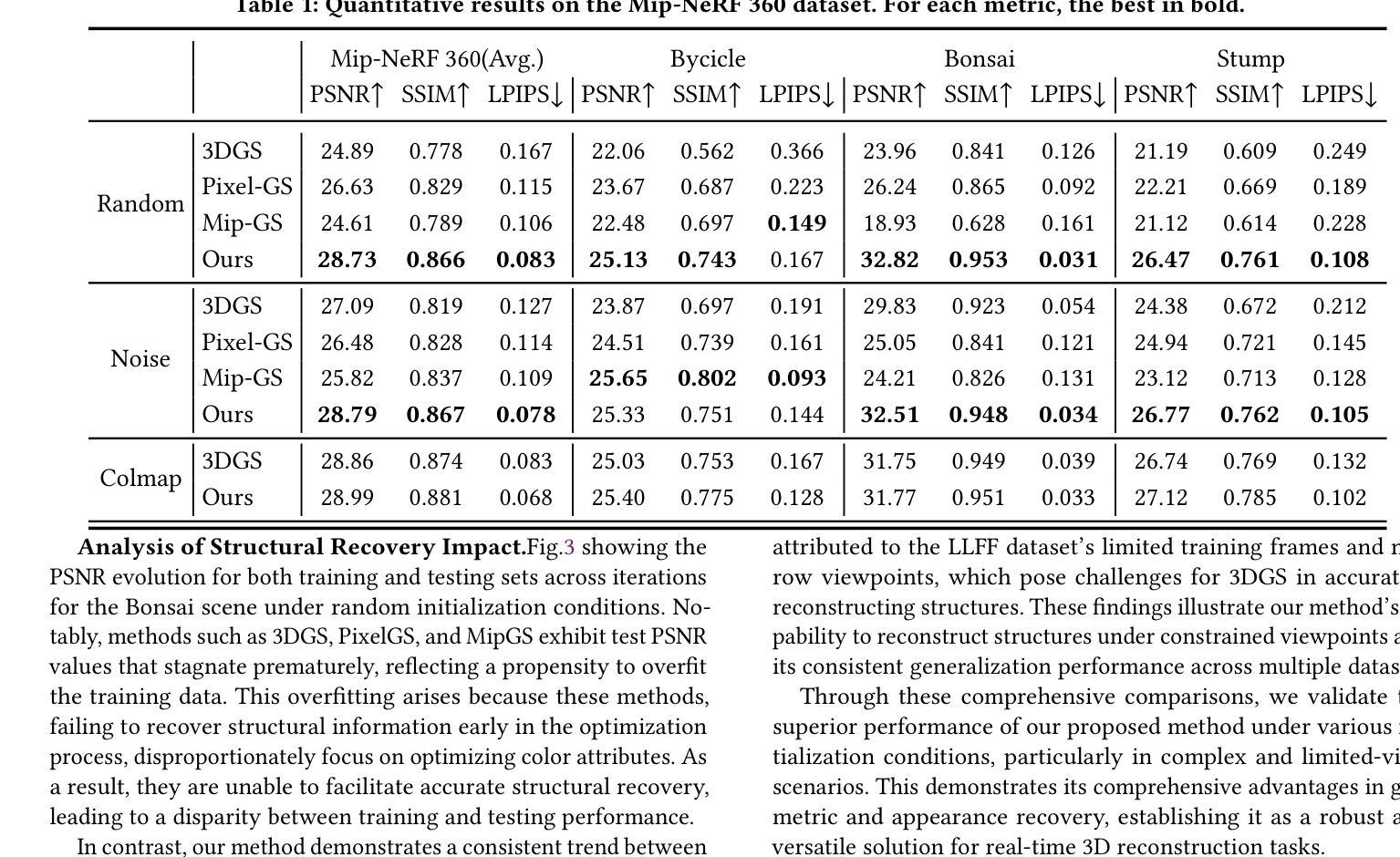
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) is a powerful alternative to Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF), excelling in complex scene reconstruction and efficient rendering. However, it relies on high-quality point clouds from Structure-from-Motion (SfM), limiting its applicability. SfM also fails in texture-deficient or constrained-view scenarios, causing severe degradation in 3DGS reconstruction. To address this limitation, we propose AttentionGS, a novel framework that eliminates the dependency on high-quality initial point clouds by leveraging structural attention for direct 3D reconstruction from randomly initialization. In the early training stage, we introduce geometric attention to rapidly recover the global scene structure. As training progresses, we incorporate texture attention to refine fine-grained details and enhance rendering quality. Furthermore, we employ opacity-weighted gradients to guide Gaussian densification, leading to improved surface reconstruction. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmark datasets demonstrate that AttentionGS significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods, particularly in scenarios where point cloud initialization is unreliable. Our approach paves the way for more robust and flexible 3D Gaussian Splatting in real-world applications.
3D高斯涂抹(3DGS)是神经辐射场(NeRF)的有力替代方案,在复杂场景重建和高效渲染方面表现出色。然而,它依赖于运动结构(SfM)的高质量点云,限制了其适用性。SfM在纹理缺失或视角受限的场景中也会失效,导致3DGS重建严重退化。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了AttentionGS这一新型框架,通过利用结构注意力,实现从随机初始化进行直接3D重建,消除了对高质量初始点云的依赖。在训练初期,我们引入几何注意力,快速恢复全局场景结构。随着训练的进行,我们结合纹理注意力,细化细节,提高渲染质量。此外,我们还采用不透明度加权梯度引导高斯稠密化,提高了表面重建效果。在多个基准数据集上的大量实验表明,AttentionGS显著优于最先进的方法,特别是在点云初始化不可靠的场景中。我们的方法为更稳健和灵活的3D高斯涂抹技术在现实世界应用奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了基于注意力机制的改进型3D高斯插值方法(AttentionGS),用于从随机初始化进行直接三维重建,解决结构从运动(SfM)对高质量初始点云的依赖问题。该方法通过引入几何注意力和纹理注意力机制,在训练初期快速恢复全局场景结构,并随着训练进展优化细节,提高渲染质量。此外,还采用基于不透明度加权的梯度引导高斯密集化技术,改善表面重建效果。实验证明,AttentionGS在点云初始化不可靠的场景中表现优于现有方法,为实际应用中更稳健灵活的3D高斯插值方法开辟道路。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了基于注意力机制的改进型三维重建方法AttentionGS。
- AttentionGS解决了对高质量初始点云的依赖问题,可以通过随机初始化进行直接三维重建。
- 该方法利用几何注意力和纹理注意力机制恢复场景结构并优化细节。
- 采用基于不透明度加权的梯度引导高斯密集化技术,提高表面重建质量。
- AttentionGS在点云初始化不可靠的场景中表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

Dynamic View Synthesis from Small Camera Motion Videos
Authors:Huiqiang Sun, Xingyi Li, Juewen Peng, Liao Shen, Zhiguo Cao, Ke Xian, Guosheng Lin
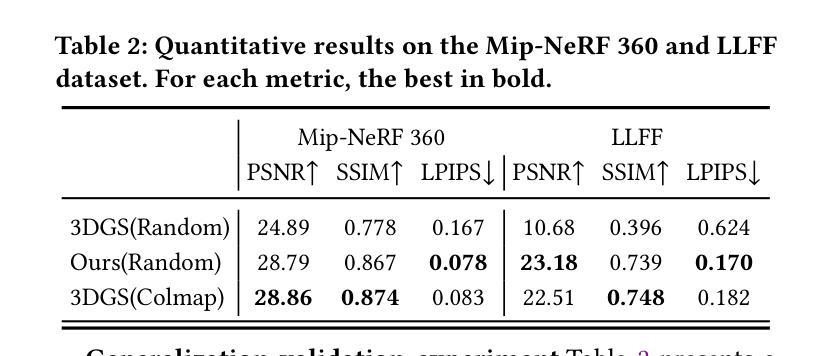
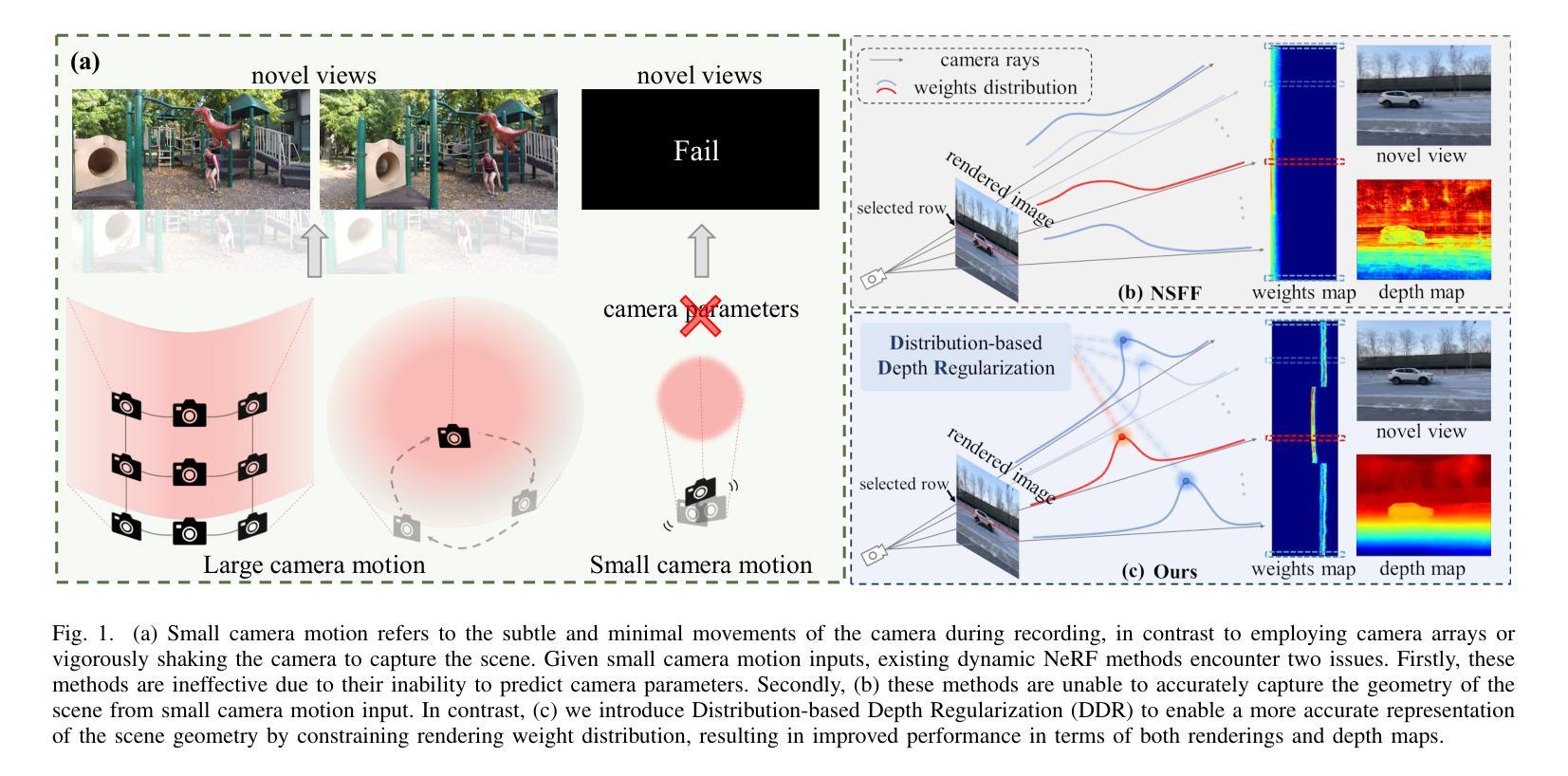
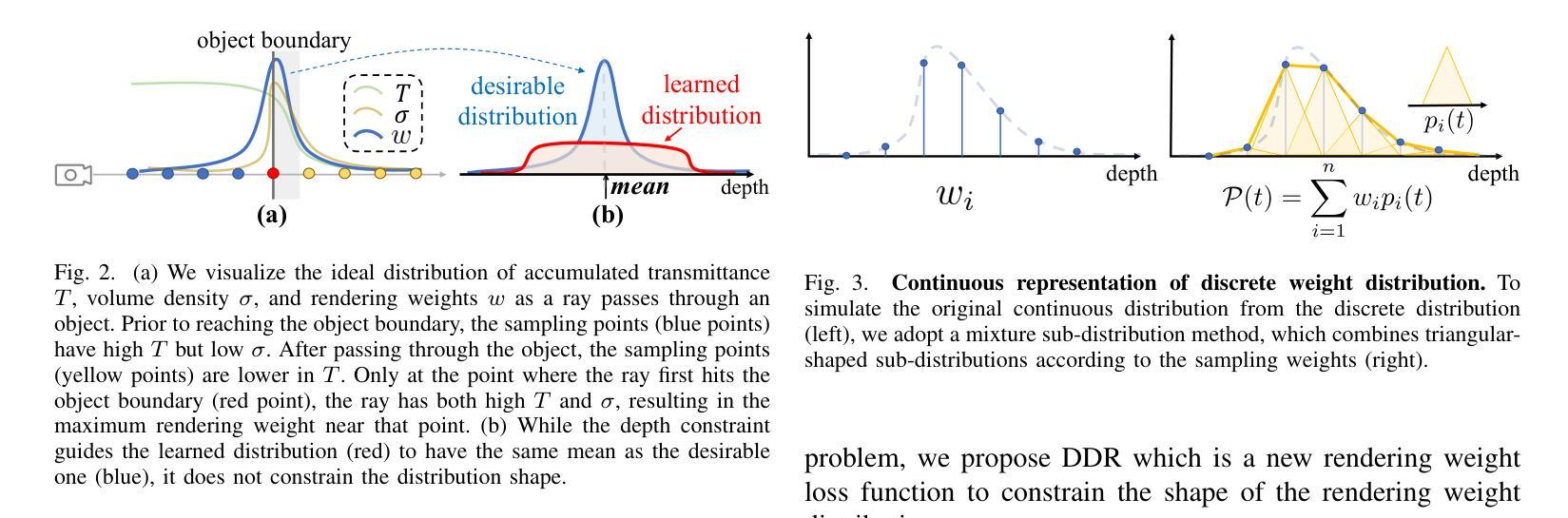
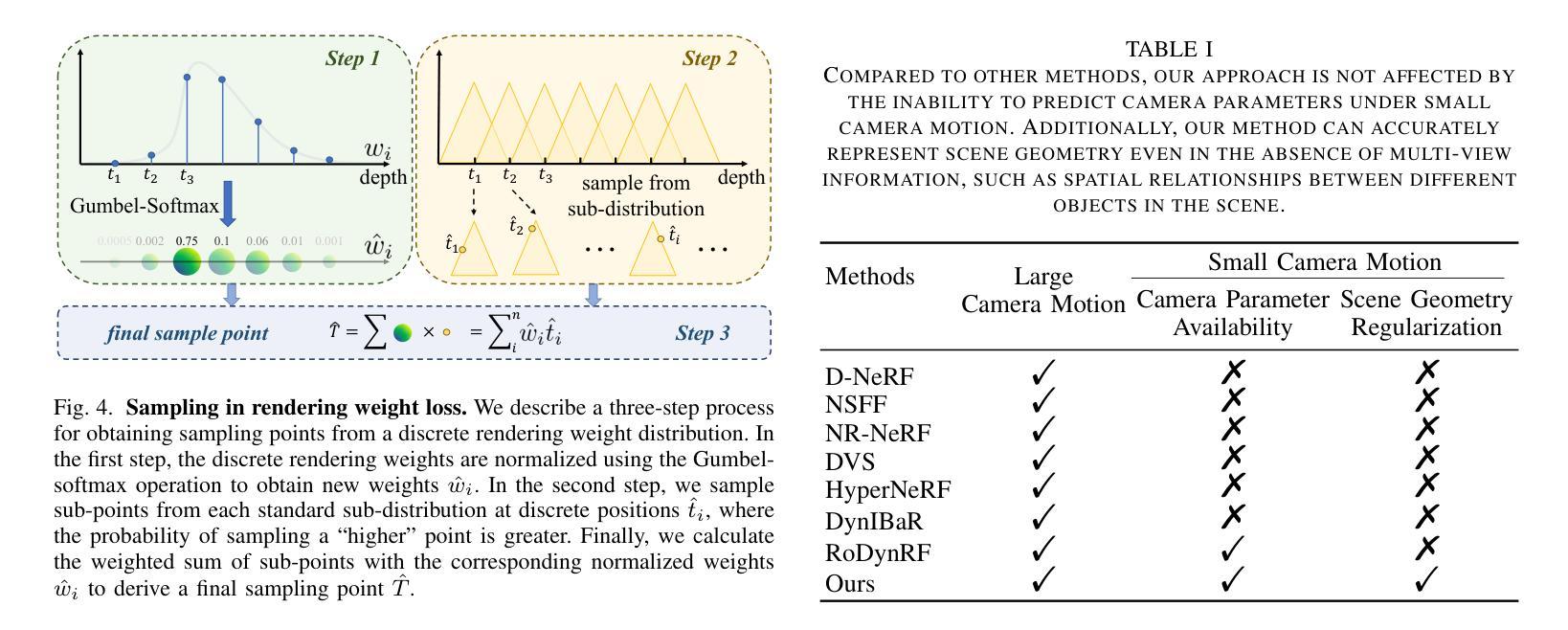
Novel view synthesis for dynamic $3$D scenes poses a significant challenge. Many notable efforts use NeRF-based approaches to address this task and yield impressive results. However, these methods rely heavily on sufficient motion parallax in the input images or videos. When the camera motion range becomes limited or even stationary (i.e., small camera motion), existing methods encounter two primary challenges: incorrect representation of scene geometry and inaccurate estimation of camera parameters. These challenges make prior methods struggle to produce satisfactory results or even become invalid. To address the first challenge, we propose a novel Distribution-based Depth Regularization (DDR) that ensures the rendering weight distribution to align with the true distribution. Specifically, unlike previous methods that use depth loss to calculate the error of the expectation, we calculate the expectation of the error by using Gumbel-softmax to differentiably sample points from discrete rendering weight distribution. Additionally, we introduce constraints that enforce the volume density of spatial points before the object boundary along the ray to be near zero, ensuring that our model learns the correct geometry of the scene. To demystify the DDR, we further propose a visualization tool that enables observing the scene geometry representation at the rendering weight level. For the second challenge, we incorporate camera parameter learning during training to enhance the robustness of our model to camera parameters. We conduct extensive experiments to demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in representing scenes with small camera motion input, and our results compare favorably to state-of-the-art methods.
动态三维场景的新型视图合成是一个巨大的挑战。许多引人注目的努力使用基于NeRF的方法来解决这项任务,并产生了令人印象深刻的结果。然而,这些方法在很大程度上依赖于输入图像或视频中的充足运动视差。当相机运动范围变得有限甚至静止(即相机运动很小)时,现有方法面临两个主要挑战:场景几何表示不正确和相机参数估计不准确。这些挑战使得现有方法难以产生令人满意的结果,甚至变得无效。为了解决第一个挑战,我们提出了一种基于分布的深度正则化(DDR)方法,确保渲染权重分布与真实分布对齐。具体来说,与以前使用深度损失来计算期望误差的方法不同,我们使用Gumbel-softmax可微采样点来计算离散渲染权重分布的误差期望。此外,我们引入了约束条件,强制沿光线方向在物体边界之前的空间点的体积密度接近零,确保我们的模型学习场景的正确几何形状。为了揭示DDR的神秘性,我们进一步开发了一个可视化工具,可以观察到渲染权重级别的场景几何表示。对于第二个挑战,我们在训练过程中加入了相机参数学习,以提高模型对相机参数的稳健性。我们进行了大量实验,证明了我们方法在表示具有小相机运动输入的场景方面的有效性,我们的结果与最先进的方法相比具有竞争力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by TVCG
Summary
该文本提出了一种针对动态三维场景的新型视图合成方法,通过基于NeRF的方法解决此任务并获得了令人印象深刻的结果。然而,现有方法在小范围相机运动的情况下面临两大挑战:场景几何的不正确表示和相机参数的不准确估计。为了解决这些问题,提出了基于分布的深度正则化(DDR)和一种新的可视化工具,能增强模型对相机参数的鲁棒性,并在场景几何表示方面取得了显著成果。
Key Takeaways
- 动态三维场景的新型视图合成是一个重大挑战,现有方法主要依赖NeRF技术解决此问题。
- 当相机运动范围有限或静止时,现有方法面临两大挑战:场景几何表示不准确和相机参数估计不准确。
- 提出了一种基于分布的深度正则化(DDR)方法,确保渲染权重分布与真实分布对齐。
- DDR通过Gumbel-softmax可微采样点来计算误差的期望值,同时引入约束以强化场景几何的正确性。
- 为了更好地理解DDR,提出了一种新的可视化工具来观察场景几何表示在渲染权重层面的信息。
- 模型在训练过程中结合了相机参数学习,提高了对相机参数的鲁棒性。
点此查看论文截图


UnMix-NeRF: Spectral Unmixing Meets Neural Radiance Fields
Authors:Fabian Perez, Sara Rojas, Carlos Hinojosa, Hoover Rueda-Chacón, Bernard Ghanem
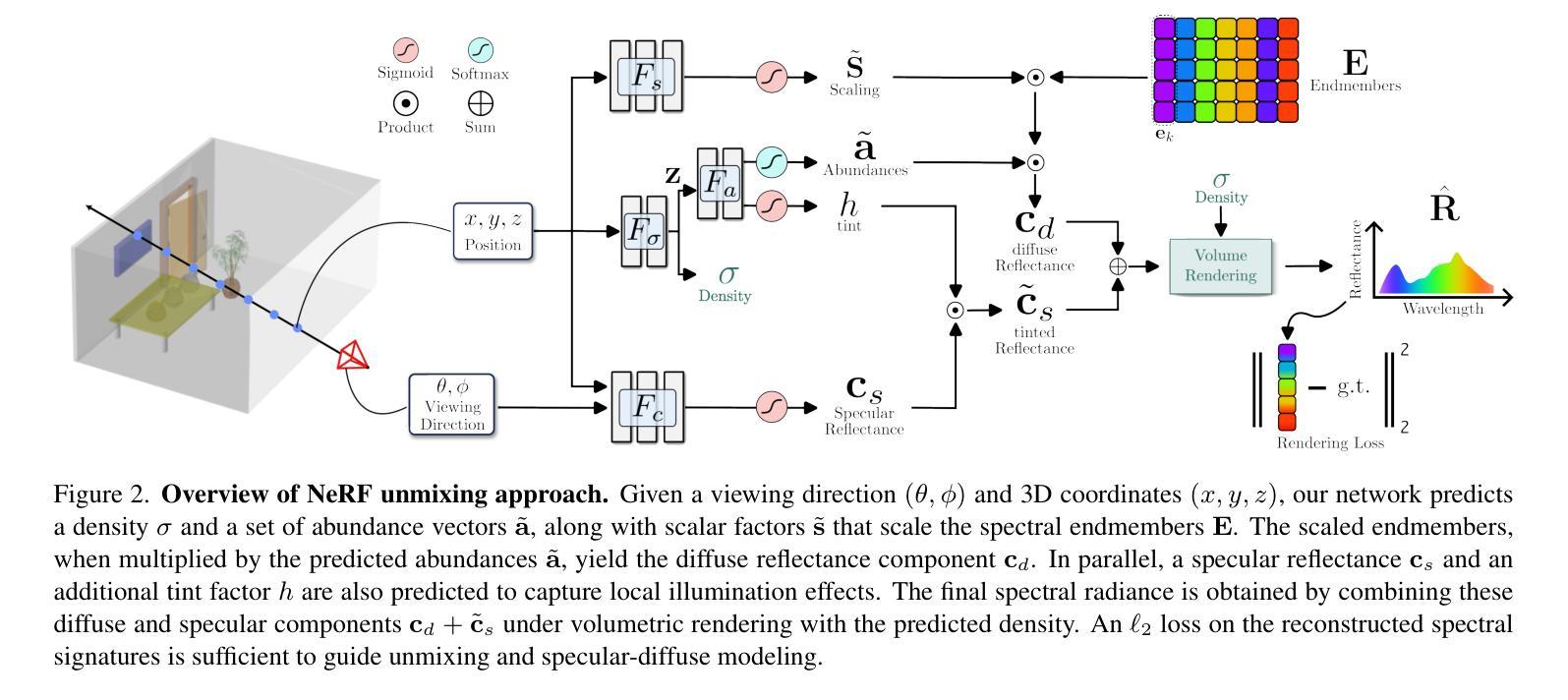
Neural Radiance Field (NeRF)-based segmentation methods focus on object semantics and rely solely on RGB data, lacking intrinsic material properties. This limitation restricts accurate material perception, which is crucial for robotics, augmented reality, simulation, and other applications. We introduce UnMix-NeRF, a framework that integrates spectral unmixing into NeRF, enabling joint hyperspectral novel view synthesis and unsupervised material segmentation. Our method models spectral reflectance via diffuse and specular components, where a learned dictionary of global endmembers represents pure material signatures, and per-point abundances capture their distribution. For material segmentation, we use spectral signature predictions along learned endmembers, allowing unsupervised material clustering. Additionally, UnMix-NeRF enables scene editing by modifying learned endmember dictionaries for flexible material-based appearance manipulation. Extensive experiments validate our approach, demonstrating superior spectral reconstruction and material segmentation to existing methods. Project page: https://www.factral.co/UnMix-NeRF.
基于神经辐射场(NeRF)的分割方法主要关注对象语义,并仅依赖于RGB数据,缺乏内在材料属性。这一局限性限制了材料感知的准确性,对于机器人、增强现实、模拟和其他应用而言,这是至关重要的。我们引入了UnMix-NeRF框架,它将光谱混合技术集成到NeRF中,实现了超光谱新视角合成和无人监督材料分割的联合处理。我们的方法通过漫反射和镜面反射成分对光谱反射进行建模,其中通过全局端元学习字典表示纯材料特征,而每点的丰度则捕捉其分布。对于材料分割,我们使用沿学习端元的谱特征预测,实现无人监督的材料聚类。此外,UnMix-NeRF通过修改学习端元字典,实现场景编辑,进行灵活的材料外观操作。大量实验验证了我们的方法,在光谱重建和材料分割方面优于现有方法。项目页面:https://www.factral.co/UnMix-NeRF。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Paper accepted at ICCV 2025 main conference
Summary
本文介绍了基于NeRF的UnMix-NeRF框架,该框架结合了光谱混合技术,实现了联合超光谱新视角合成和无监督材料分割。通过模拟材料的反射光谱,UnMix-NeRF使用全局端元组成的字典表示纯材料特征,并通过每点的丰度捕捉其分布。对于材料分割,它使用光谱特征预测和学习的端元进行无监督材料聚类。此外,UnMix-NeRF还能通过修改学习的端元字典实现场景编辑,进行灵活的材料外观操作。
Key Takeaways
- UnMix-NeRF结合了光谱混合技术,实现了NeRF在超光谱新视角合成和无监督材料分割方面的突破。
- 通过模拟材料的反射光谱,UnMix-NeRF使用全局端元字典表示纯材料特征。
- UnMix-NeRF采用每点的丰度捕捉材料分布。
- 利用光谱特征预测和学习的端元进行无监督材料聚类,实现材料分割。
- UnMix-NeRF支持场景编辑,通过修改学习的端元字典实现灵活的材料外观操作。
- 实验验证,UnMix-NeRF在光谱重建和材料分割方面优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

ICP-3DGS: SfM-free 3D Gaussian Splatting for Large-scale Unbounded Scenes
Authors:Chenhao Zhang, Yezhi Shen, Fengqing Zhu
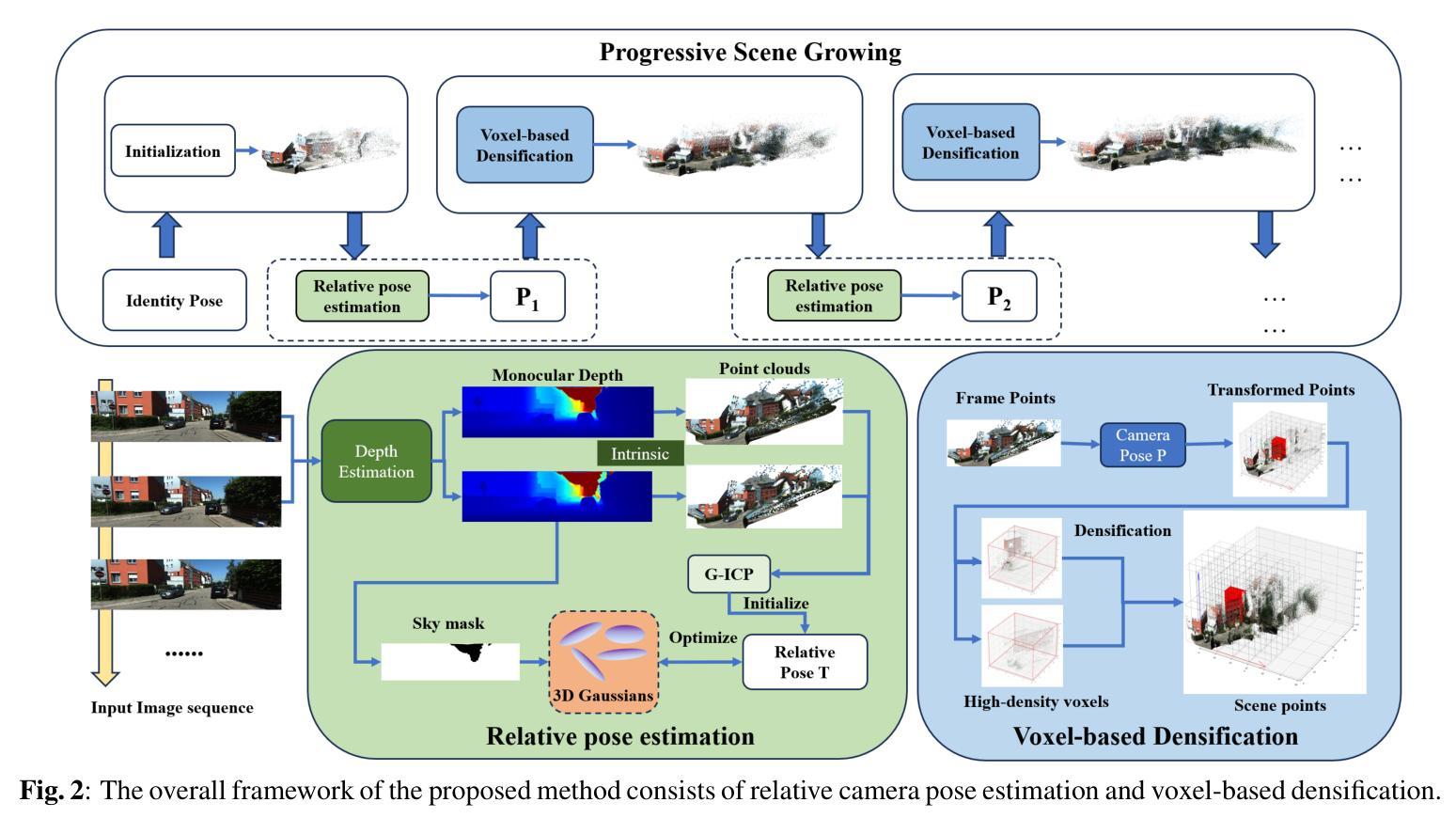
In recent years, neural rendering methods such as NeRFs and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) have made significant progress in scene reconstruction and novel view synthesis. However, they heavily rely on preprocessed camera poses and 3D structural priors from structure-from-motion (SfM), which are challenging to obtain in outdoor scenarios. To address this challenge, we propose to incorporate Iterative Closest Point (ICP) with optimization-based refinement to achieve accurate camera pose estimation under large camera movements. Additionally, we introduce a voxel-based scene densification approach to guide the reconstruction in large-scale scenes. Experiments demonstrate that our approach ICP-3DGS outperforms existing methods in both camera pose estimation and novel view synthesis across indoor and outdoor scenes of various scales. Source code is available at https://github.com/Chenhao-Z/ICP-3DGS.
近年来,神经渲染方法,如NeRF和三维高斯溅出(3DGS),在场景重建和新颖视角合成方面取得了显著进展。然而,它们严重依赖于从运动恢复结构(SfM)预处理的相机姿态和三维结构先验,这在户外场景中很难获取。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出结合迭代最近点(ICP)和优化精修方法来实现大相机运动下的准确相机姿态估计。此外,我们还介绍了一种基于体素的场景稠化方法,以指导大规模场景的重建。实验表明,我们的ICP-3DGS方法在室内外各种规模的场景的相机姿态估计和新颖视角合成方面都优于现有方法。源代码可在https://github.com/Chenhao-Z/ICP-3DGS获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, Source code is available at https://github.com/Chenhao-Z/ICP-3DGS. To appear at ICIP 2025
Summary
近年来,神经渲染方法如NeRF和3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)在场景重建和视角合成方面取得显著进展,但它们依赖于运动结构(SfM)的预处理相机姿态和3D结构先验,这在户外场景中获取具有挑战性。为应对此挑战,我们结合迭代最近点(ICP)与优化精修法,在大范围相机移动下实现准确的相机姿态估计。此外,我们引入了基于体素的场景密集化方法,以指导大规模场景的重建。实验证明,我们的ICP-3DGS方法在相机姿态估计和视角合成方面表现优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 神经渲染方法如NeRF和3DGS在场景重建和视角合成上取得进展。
- 现有方法依赖SfM的预处理数据和结构先验,这在户外场景中是挑战。
- 提出结合ICP和优化精修法,实现大移动下的准确相机姿态估计。
- 引入基于体素的场景密集化方法,用于指导大规模场景的重建。
- ICP-3DGS方法在相机姿态估计和视角合成上表现优越。
- 方法适用于室内和室外各种规模的场景。
点此查看论文截图

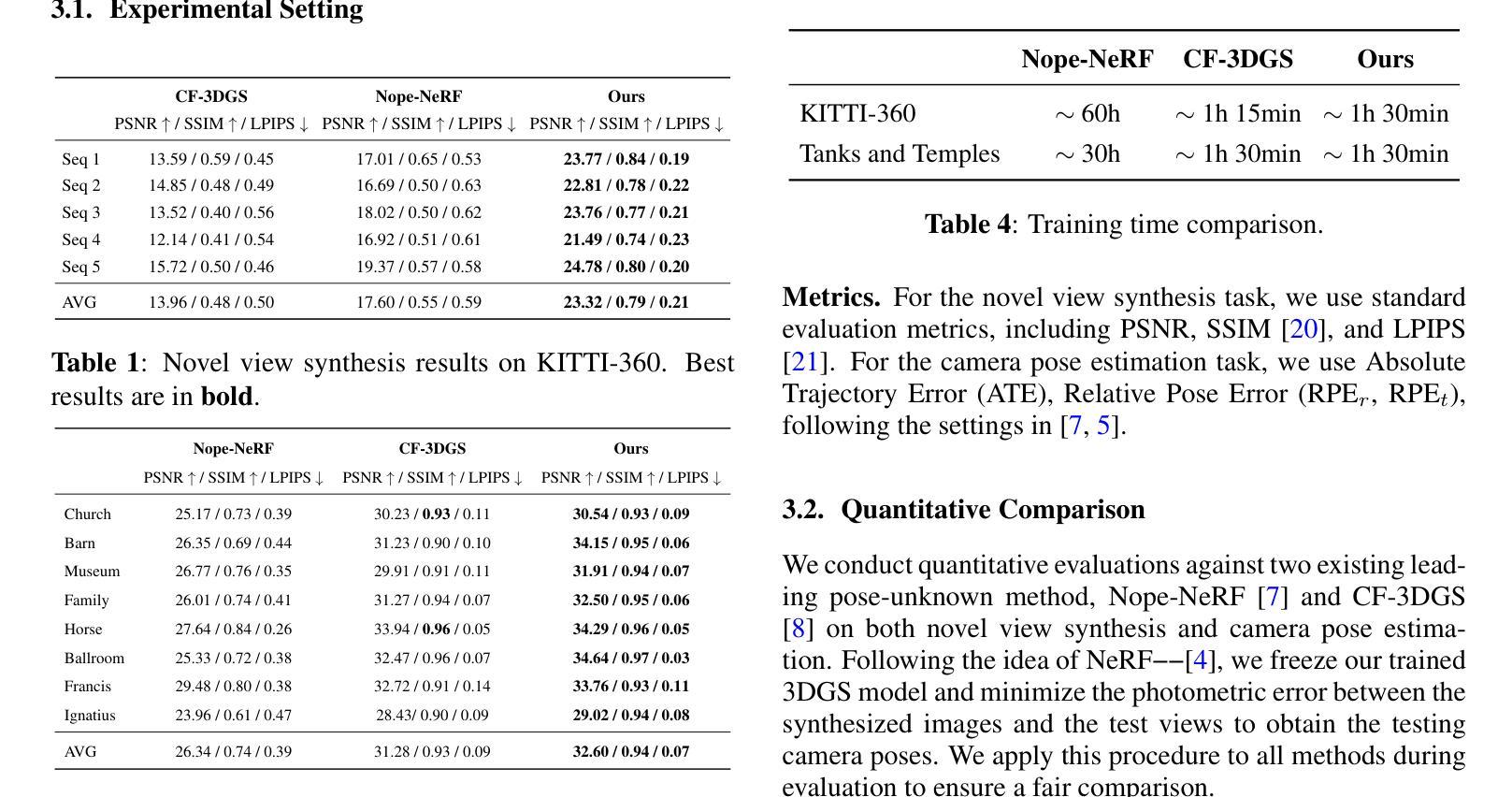
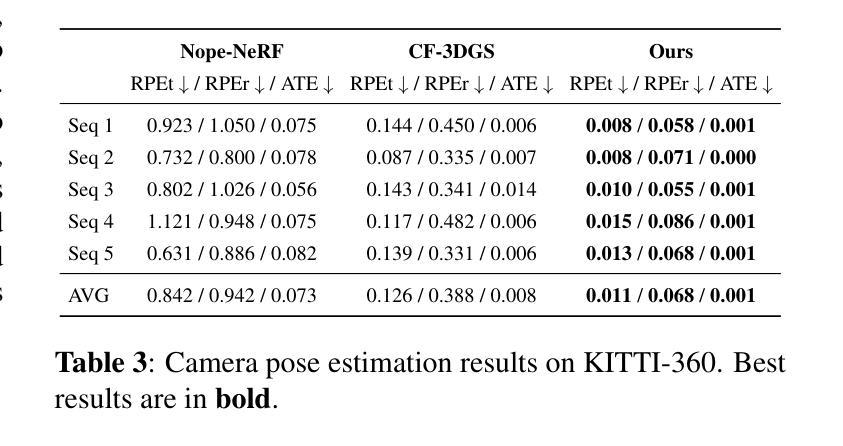


HumanGif: Single-View Human Diffusion with Generative Prior
Authors:Shoukang Hu, Takuya Narihira, Kazumi Fukuda, Ryosuke Sawata, Takashi Shibuya, Yuki Mitsufuji
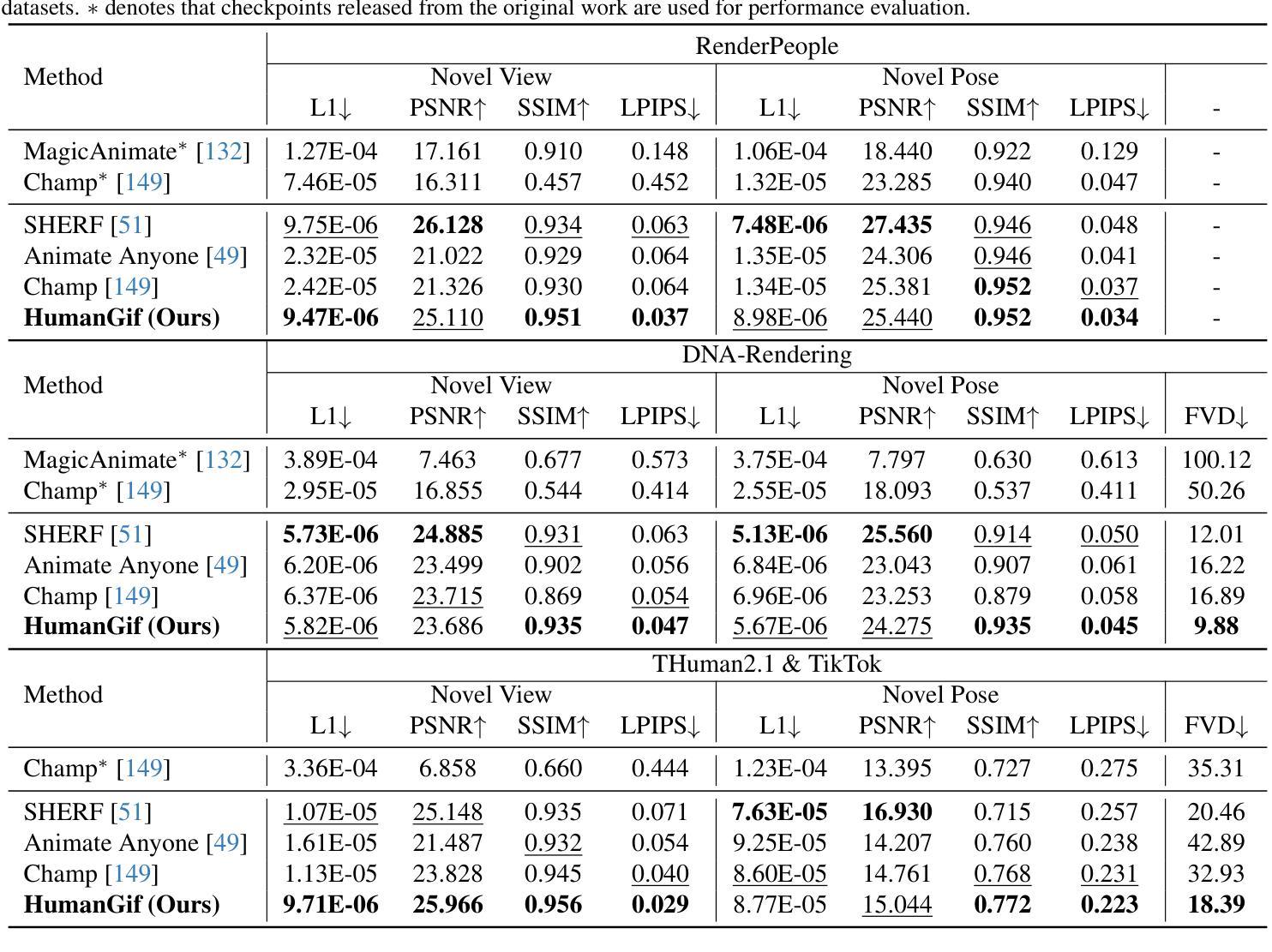
Previous 3D human creation methods have made significant progress in synthesizing view-consistent and temporally aligned results from sparse-view images or monocular videos. However, it remains challenging to produce perpetually realistic, view-consistent, and temporally coherent human avatars from a single image, as limited information is available in the single-view input setting. Motivated by the success of 2D character animation, we propose HumanGif, a single-view human diffusion model with generative prior. Specifically, we formulate the single-view-based 3D human novel view and pose synthesis as a single-view-conditioned human diffusion process, utilizing generative priors from foundational diffusion models to complement the missing information. To ensure fine-grained and consistent novel view and pose synthesis, we introduce a Human NeRF module in HumanGif to learn spatially aligned features from the input image, implicitly capturing the relative camera and human pose transformation. Furthermore, we introduce an image-level loss during optimization to bridge the gap between latent and image spaces in diffusion models. Extensive experiments on RenderPeople, DNA-Rendering, THuman 2.1, and TikTok datasets demonstrate that HumanGif achieves the best perceptual performance, with better generalizability for novel view and pose synthesis.
之前的3D人物创建方法在合成视图一致且时间上对齐的结果方面取得了显著进展,这些结果来源于稀疏视图图像或单目视频。然而,从单张图像生成永久逼真的、视图一致且时间上连贯的人物化身仍然是一个挑战,因为在单视图输入设置中可用的信息有限。受到二维角色动画成功的启发,我们提出了HumanGif,这是一个带有生成先验的单视图人类扩散模型。具体来说,我们将基于单视图的3D人物新颖视角和姿态合成制定为受单视图条件约束的人类扩散过程,利用基础扩散模型的生成先验来补充缺失的信息。为了确保精细且一致的全新视角和姿态合成,我们在HumanGif中引入了Human NeRF模块,从输入图像中学习空间对齐的特征,隐式捕获相对相机和人物姿态变换。此外,我们在优化过程中引入了图像级损失,以弥合扩散模型中的潜在空间和图像空间之间的差距。在RenderPeople、DNA-Rendering、THuman 2.1和TikTok数据集上的大量实验表明,HumanGif在感知性能上表现最佳,对于新颖视角和姿态合成具有更好的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://skhu101.github.io/HumanGif/
Summary
本文提出了一种基于单视角的扩散模型HumanGif,用于创建人类角色动画。该模型结合了二维角色动画的成功经验,通过引入生成先验信息来弥补单视角输入信息不足的问题。HumanGif使用Human NeRF模块学习从输入图像中提取的空间对齐特征,并隐式捕捉相机和人类姿势的相对变换。此外,还引入了图像级损失优化模型,缩小潜在空间和图像空间之间的差距。实验证明,HumanGif在感知性能上表现最佳,具有出色的新颖视角和姿态合成的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- HumanGif是一个基于单视角的人类扩散模型,利用生成先验信息合成新颖视角和姿态的人类角色动画。
- 该模型通过引入Human NeRF模块学习从输入图像中提取空间对齐特征,隐式捕捉相机和人类姿势的相对变换。
- HumanGif采用图像级损失优化模型,以提高对未知视角和姿态的泛化能力。
- 实验证明,HumanGif在感知性能上表现最佳,能够提供高质量的人类角色动画。
- 该模型适用于多种数据集,包括RenderPeople、DNA-Rendering、THuman 2.1和TikTok等。
- HumanGif的成功源于其结合二维角色动画经验并引入生成先验信息的创新方法。
点此查看论文截图

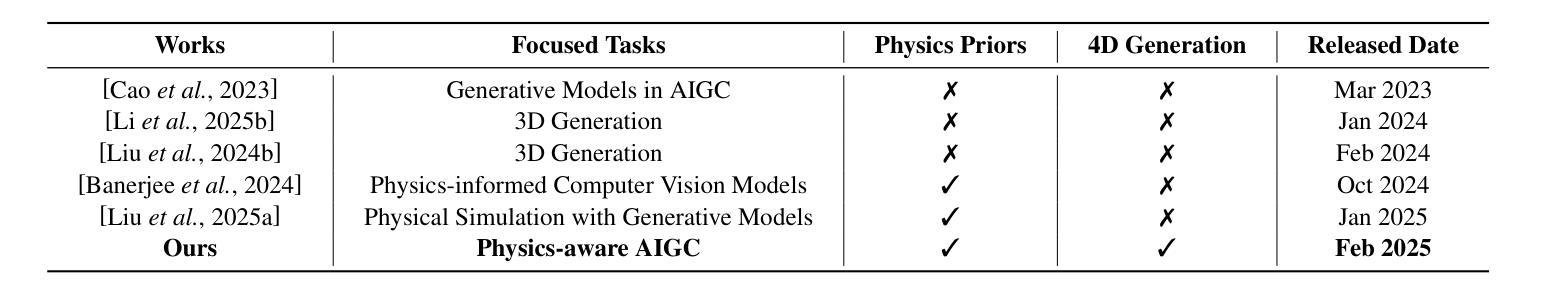
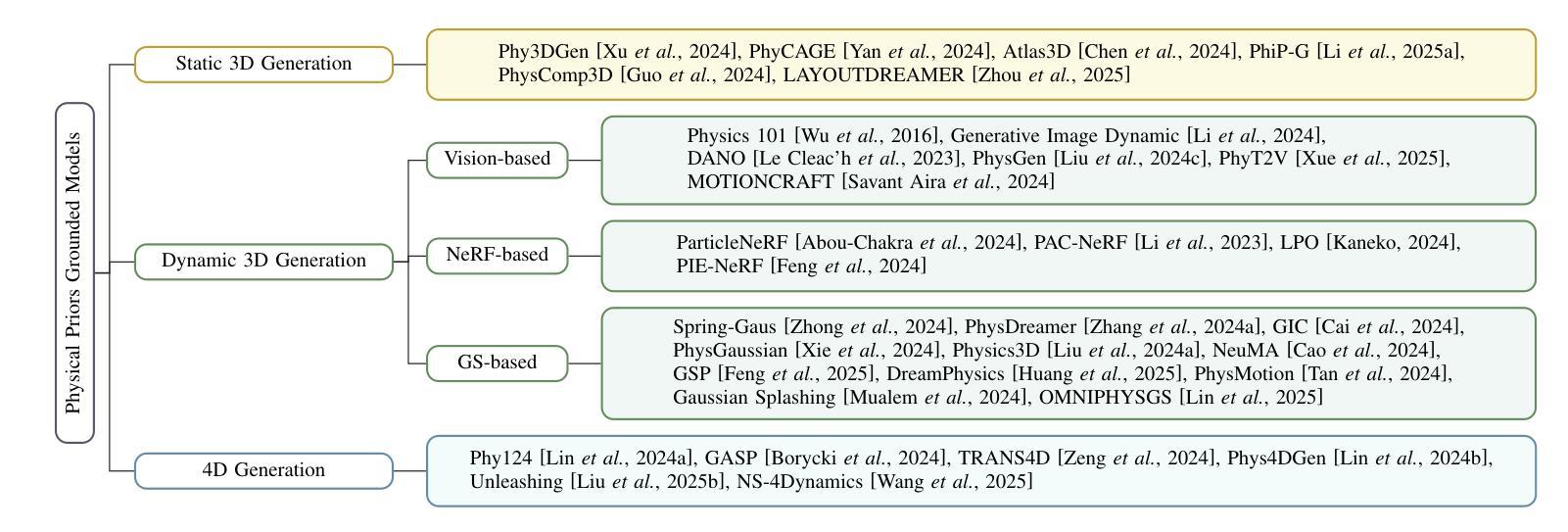
Grounding Creativity in Physics: A Brief Survey of Physical Priors in AIGC
Authors:Siwei Meng, Yawei Luo, Ping Liu
Recent advancements in AI-generated content have significantly improved the realism of 3D and 4D generation. However, most existing methods prioritize appearance consistency while neglecting underlying physical principles, leading to artifacts such as unrealistic deformations, unstable dynamics, and implausible objects interactions. Incorporating physics priors into generative models has become a crucial research direction to enhance structural integrity and motion realism. This survey provides a review of physics-aware generative methods, systematically analyzing how physical constraints are integrated into 3D and 4D generation. First, we examine recent works in incorporating physical priors into static and dynamic 3D generation, categorizing methods based on representation types, including vision-based, NeRF-based, and Gaussian Splatting-based approaches. Second, we explore emerging techniques in 4D generation, focusing on methods that model temporal dynamics with physical simulations. Finally, we conduct a comparative analysis of major methods, highlighting their strengths, limitations, and suitability for different materials and motion dynamics. By presenting an in-depth analysis of physics-grounded AIGC, this survey aims to bridge the gap between generative models and physical realism, providing insights that inspire future research in physically consistent content generation.
近年来,人工智能生成内容方面的最新进展极大地提高了3D和4D生成的逼真度。然而,大多数现有方法优先考虑外观的一致性,却忽略了基本的物理原理,导致出现不真实的变形、不稳定的动态以及不合理的物体交互等伪迹。因此,将物理先验知识融入生成模型已成为增强结构完整性和运动逼真度的关键研究方向。本文综述了物理感知生成方法,系统分析了如何将物理约束融入3D和4D生成。首先,我们研究了近期将物理先验知识融入静态和动态3D生成的工作,按表示类型对方法进行分类,包括基于视觉、基于NeRF和基于高斯拼贴的方法。其次,我们探索了4D生成的新兴技术,重点关注利用物理模拟对时间动态进行建模的方法。最后,我们对主要方法进行了比较分析,重点介绍了它们各自的优势、局限性和在不同材料和运动动力学方面的适用性。通过对基于物理原理的人工智能生成内容的深入分析,本综述旨在缩小生成模型和物理逼真度之间的差距,提供见解,为物理一致性内容生成方面的未来研究提供灵感。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IJCAI 2025 Survey Track
Summary
新一代人工智能生成内容的技术进步显著提高了三维(3D)和四维(4D)内容的逼真度。然而,现有方法往往重视外观一致性,忽视了底层物理原理,导致出现不真实的变形、动态不稳定和物体交互不合理等问题。为了增强结构完整性和动作逼真性,将物理先验知识融入生成模型成为重要研究方向。本文综述了物理感知生成方法,系统分析了如何将物理约束融入3D和4D内容生成。文章首先探讨了将物理先验知识融入静态和动态3D生成的方法,按表示类型分类,包括基于视觉、NeRF和Gaussian Splatting的方法。接着,文章探讨了用于建模时间动态的物理模拟的4D生成新兴技术。最后,对主要方法进行了比较分析,突出了其优势、局限性和在不同材料和运动动态中的适用性。本文旨在弥补生成模型和物理真实性之间的鸿沟,提供深入了解并为未来的物理一致性内容生成研究提供启示。
Key Takeaways
- AI生成的3D和4D内容在逼真度上有了显著的提升。
- 当前方法过于注重外观一致性,忽视了物理原理,导致存在不真实变形等问题。
- 将物理先验知识融入生成模型可以增强结构完整性和动作逼真性。
- 文章综述了物理感知生成方法,并系统分析了如何将物理约束融入3D和4D内容生成。
- 静态和动态3D生成方法按表示类型分类,包括基于视觉、NeRF和Gaussian Splatting的方法。
- 4D生成技术主要关注于使用物理模拟建模时间动态。
点此查看论文截图

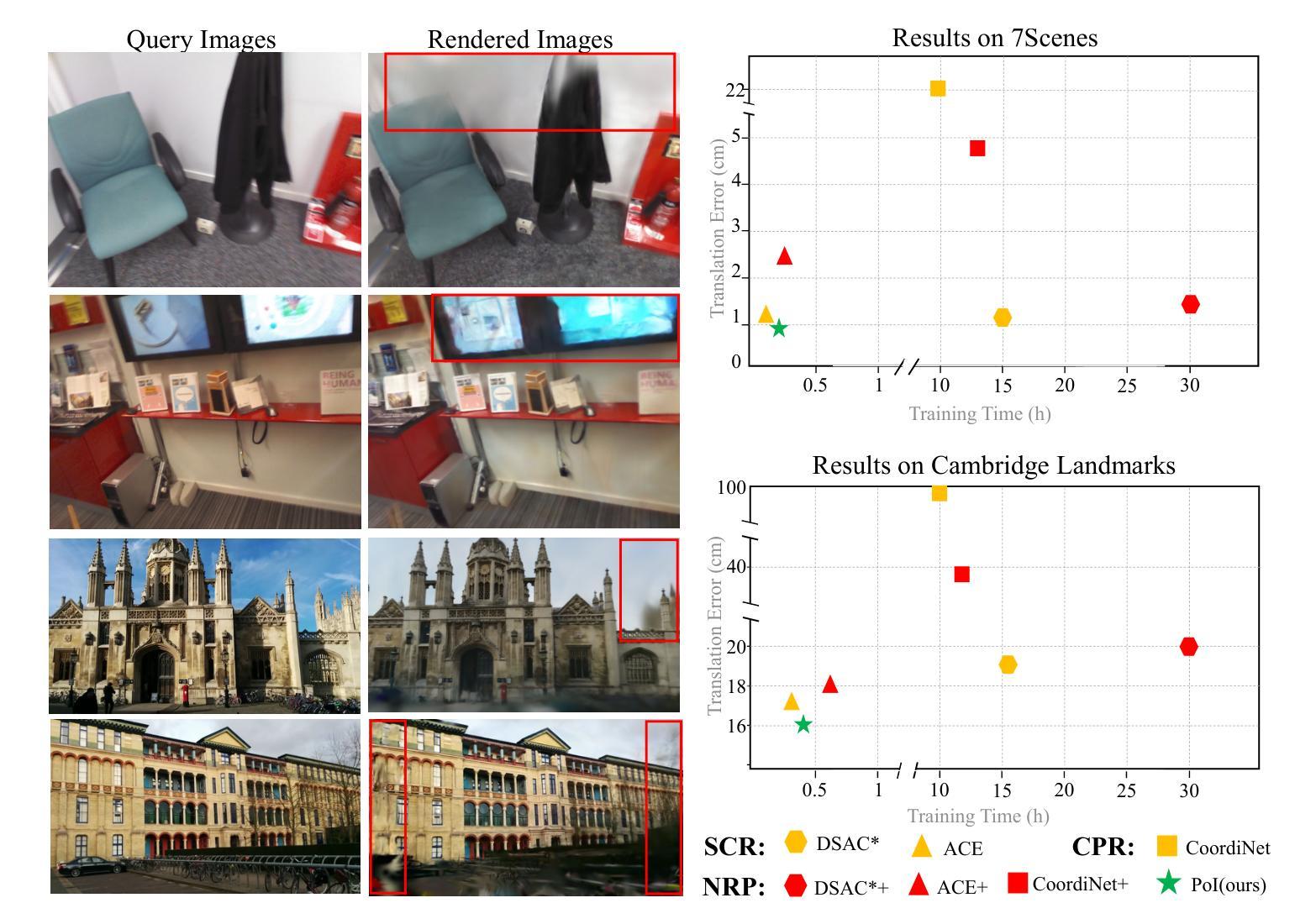
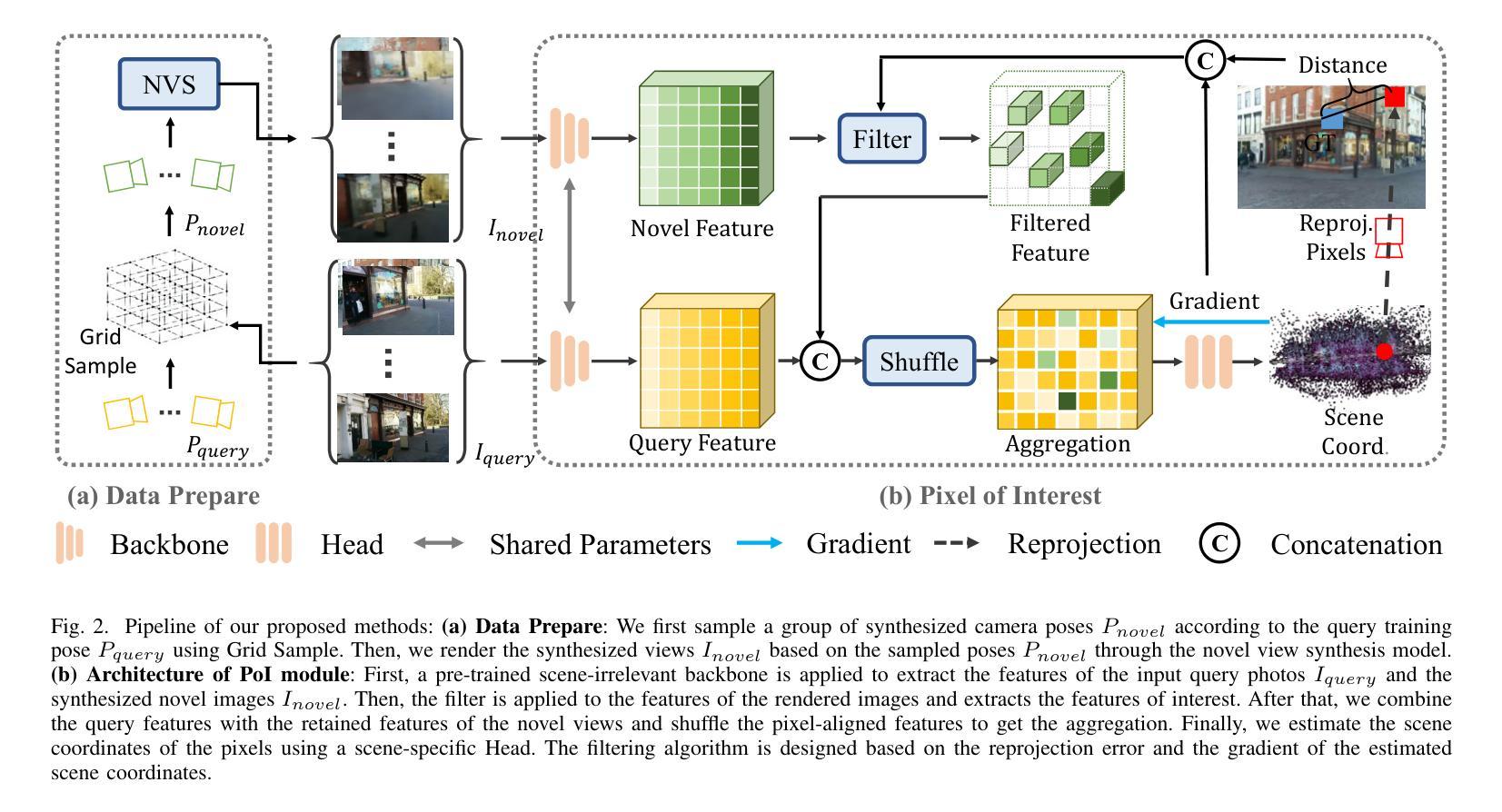
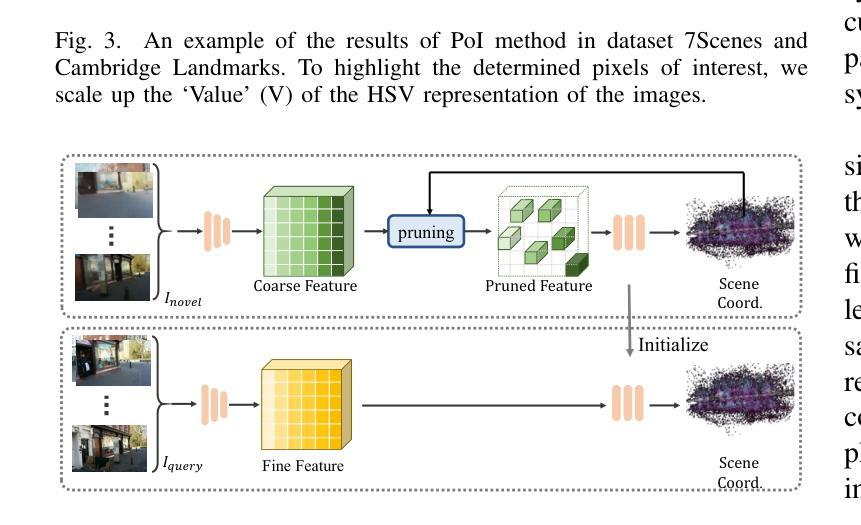
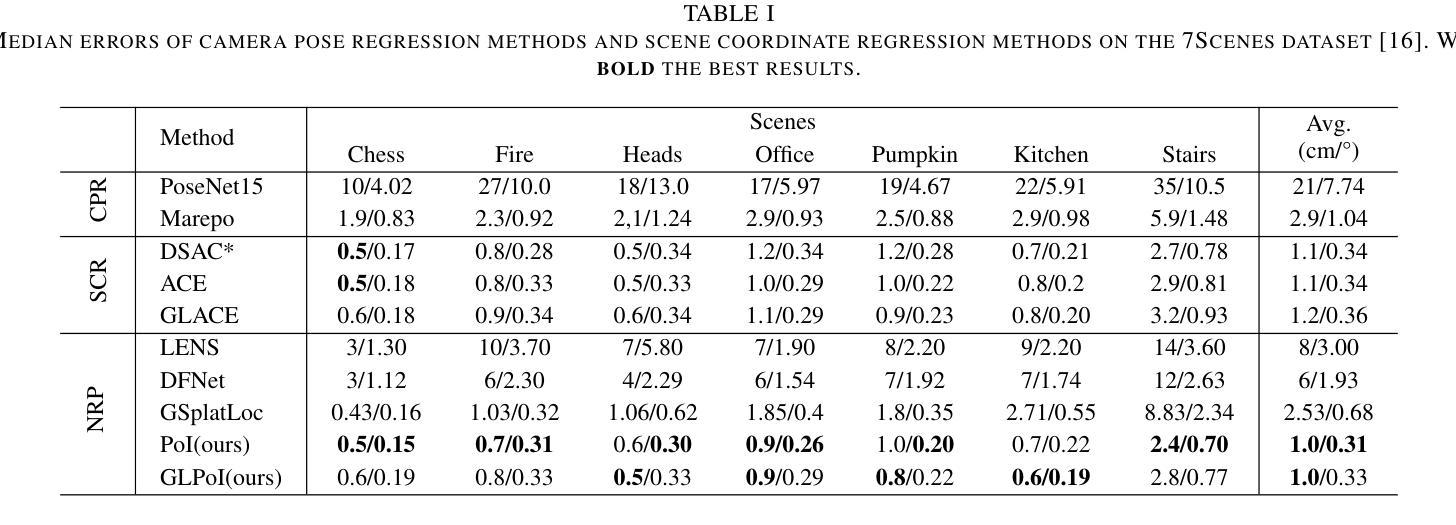
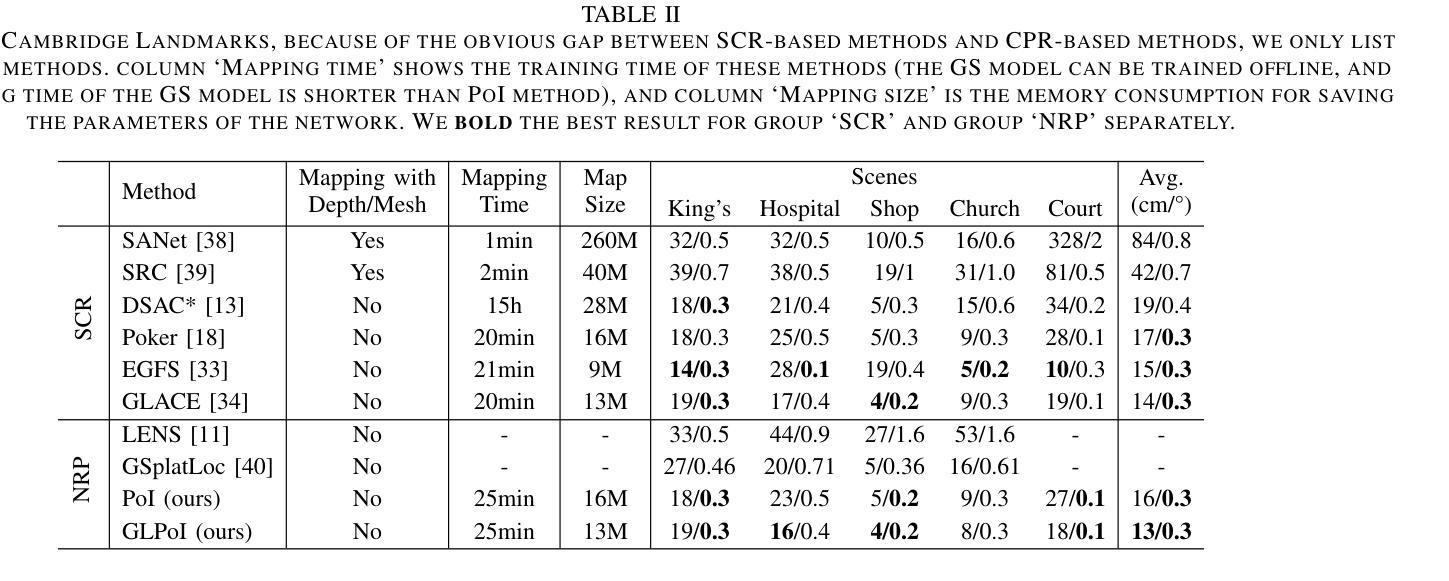
PoI: A Filter to Extract Pixel of Interest from Novel View Synthesis for Scene Coordinate Regression
Authors:Feifei Li, Qi Song, Chi Zhang, Hui Shuai, Rui Huang
Novel View Synthesis (NVS) techniques, notably Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), can augment camera pose estimation by extending and diversifying training data. However, images generated by these methods are often plagued by spatial artifacts such as blurring and ghosting, undermining their reliability as training data for camera pose estimation. This limitation is particularly critical for Scene Coordinate Regression (SCR) methods, which aim at pixel-level 3D coordinate estimation, because rendering artifacts directly lead to estimation inaccuracies. To address this challenge, we propose a dual-criteria filtering mechanism that dynamically identifies and discards suboptimal pixels during training. The dual-criteria filter evaluates two concurrent metrics: (1) real-time SCR reprojection error, and (2) gradient threshold, across the coordinate regression domain. In addition, for visual localization problems in sparse-input scenarios, it becomes even more necessary to use NVS-generated data to assist localization. We design a coarse-to-fine Points of Interest (PoI) variant using sparse-input NVS to solve this problem. Experiments across indoor and outdoor benchmarks confirm our method’s efficacy, achieving state-of-the-art localization accuracy while maintaining computational efficiency.
新颖视图合成(NVS)技术,特别是神经辐射场(NeRF)和三维高斯喷涂(3DGS),可以通过扩展和多样化训练数据来增强相机姿态估计。然而,由这些方法生成的图像往往受到空间伪影的困扰,如模糊和重影,这降低了它们作为相机姿态估计训练数据的可靠性。这一局限性对于场景坐标回归(SCR)方法尤为重要,因为这些方法旨在进行像素级别的三维坐标估计,渲染伪影直接导致估计不准确。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了一种双标准过滤机制,该机制在训练过程中动态识别并丢弃次优像素。双标准过滤器评估两个并发指标:(1)实时SCR再投影误差,(2)坐标回归域中的梯度阈值。此外,在稀疏输入的视觉定位问题中,使用NVS生成的数据辅助定位变得尤为必要。我们设计了一种从粗到细的感兴趣点(PoI)变体,使用稀疏输入的NVS来解决这个问题。室内和室外基准测试的实验结果证实了我们的方法的有效性,在保持计算效率的同时实现了最先进的定位精度。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
利用神经辐射场(NeRF)和三维高斯贴片(3DGS)等新型视图合成(NVS)技术,可以增强相机姿态估计。然而,这些方法生成的图像常存在空间伪影问题,如模糊和重影,降低了它们作为训练数据的可靠性。针对场景坐标回归(SCR)方法的渲染伪影导致估计不准确的问题,提出了基于双重标准的过滤机制,该机制在训练过程中动态识别并丢弃非优质像素。此外,针对稀疏输入场景下的视觉定位问题,使用NVS生成的数据辅助定位至关重要。设计了一种从粗到细的感兴趣点(PoI)变体来解决这一问题,并在室内和室外基准测试上进行了实验验证,实现了高定位精度和计算效率。
Key Takeaways
- NVS技术如NeRF和3DGS能增强相机姿态估计的训练数据多样性和扩展性。
- NVS生成的图像存在空间伪影问题,如模糊和重影,影响作为训练数据的可靠性。
- 双重标准的过滤机制可以动态识别并丢弃非优质像素,提高SCR方法的准确性。
- 在稀疏输入场景下,使用NVS生成的数据对于视觉定位至关重要。
- 设计了从粗到细的PoI变体来解决稀疏输入场景下的视觉定位问题。
- 实验验证了该方法在室内外基准测试上的高效性和高定位精度。
点此查看论文截图


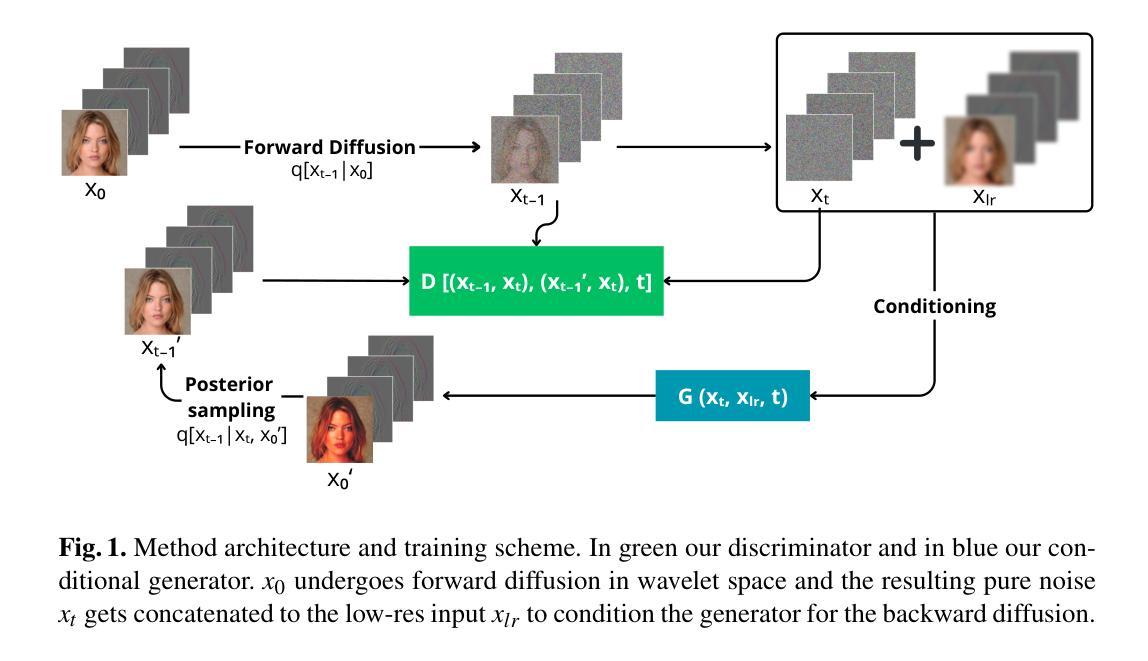
A Wavelet Diffusion GAN for Image Super-Resolution
Authors:Lorenzo Aloisi, Luigi Sigillo, Aurelio Uncini, Danilo Comminiello
In recent years, diffusion models have emerged as a superior alternative to generative adversarial networks (GANs) for high-fidelity image generation, with wide applications in text-to-image generation, image-to-image translation, and super-resolution. However, their real-time feasibility is hindered by slow training and inference speeds. This study addresses this challenge by proposing a wavelet-based conditional Diffusion GAN scheme for Single-Image Super-Resolution (SISR). Our approach utilizes the diffusion GAN paradigm to reduce the timesteps required by the reverse diffusion process and the Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) to achieve dimensionality reduction, decreasing training and inference times significantly. The results of an experimental validation on the CelebA-HQ dataset confirm the effectiveness of our proposed scheme. Our approach outperforms other state-of-the-art methodologies successfully ensuring high-fidelity output while overcoming inherent drawbacks associated with diffusion models in time-sensitive applications.
近年来,扩散模型已经作为生成对抗网络(GANs)在高保真图像生成方面的优越替代方案而出现,广泛应用于文本到图像生成、图像到图像转换和超分辨率等领域。然而,由于其训练和推理速度慢,实时可行性受到限制。本研究通过提出一种基于小波的单一图像超分辨率(SISR)条件扩散GAN方案来解决这一挑战。我们的方法利用扩散GAN范式减少反向扩散过程所需的时间步长和离散小波变换(DWT)来实现降维,从而显著减少训练和推理时间。在CelebA-HQ数据集上的实验验证结果证实了所提出方案的有效性。我们的方法成功超越了其他最先进的方法,在保证高保真输出的同时,克服了扩散模型在时间敏感应用中的固有缺点。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The paper has been accepted at Italian Workshop on Neural Networks (WIRN) 2024
Summary
扩散模型在高保真图像生成领域展现出优于生成对抗网络(GANs)的优势,广泛应用于文本转图像、图像转图像以及超分辨率等场景。但扩散模型存在训练及推理速度慢的问题。本研究提出一种基于小波变换的条件扩散GAN方案,用于单图像超分辨率(SISR)。该研究利用扩散GAN范式减少反向扩散过程所需的时间步长,并结合离散小波变换(DWT)实现降维,显著缩短训练和推理时间。在CelebA-HQ数据集上的实验验证,确认了所提方案的有效性。该研究在保证高保真输出的同时,克服了扩散模型在时间敏感性应用中的固有缺点,优于其他先进方法。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型已成为高保真图像生成领域的领先技术,替代了生成对抗网络(GANs)。
- 扩散模型广泛应用于文本转图像、图像转图像以及超分辨率等场景。
- 扩散模型存在训练和推理速度慢的问题。
- 本研究提出了一种基于小波变换的条件扩散GAN方案,用于单图像超分辨率(SISR)。
- 该方案利用扩散GAN范式减少反向扩散过程的时间步长。
- 结合离散小波变换(DWT)实现降维,提高了效率。
点此查看论文截图

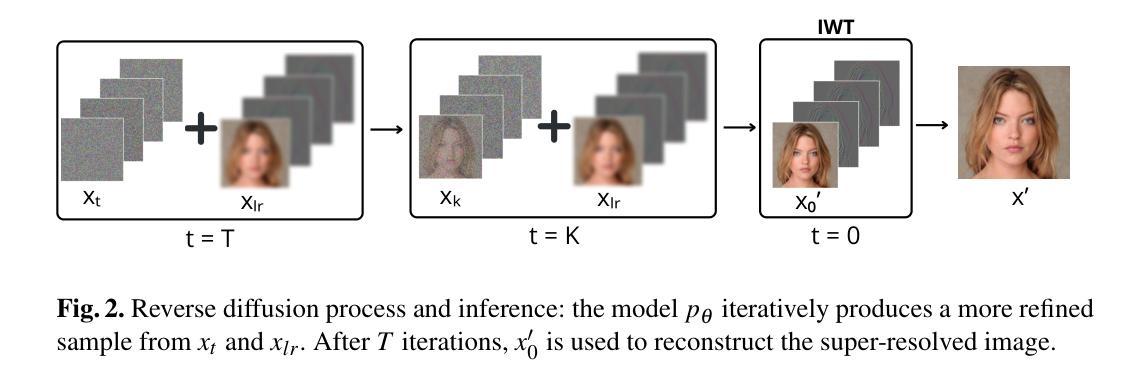
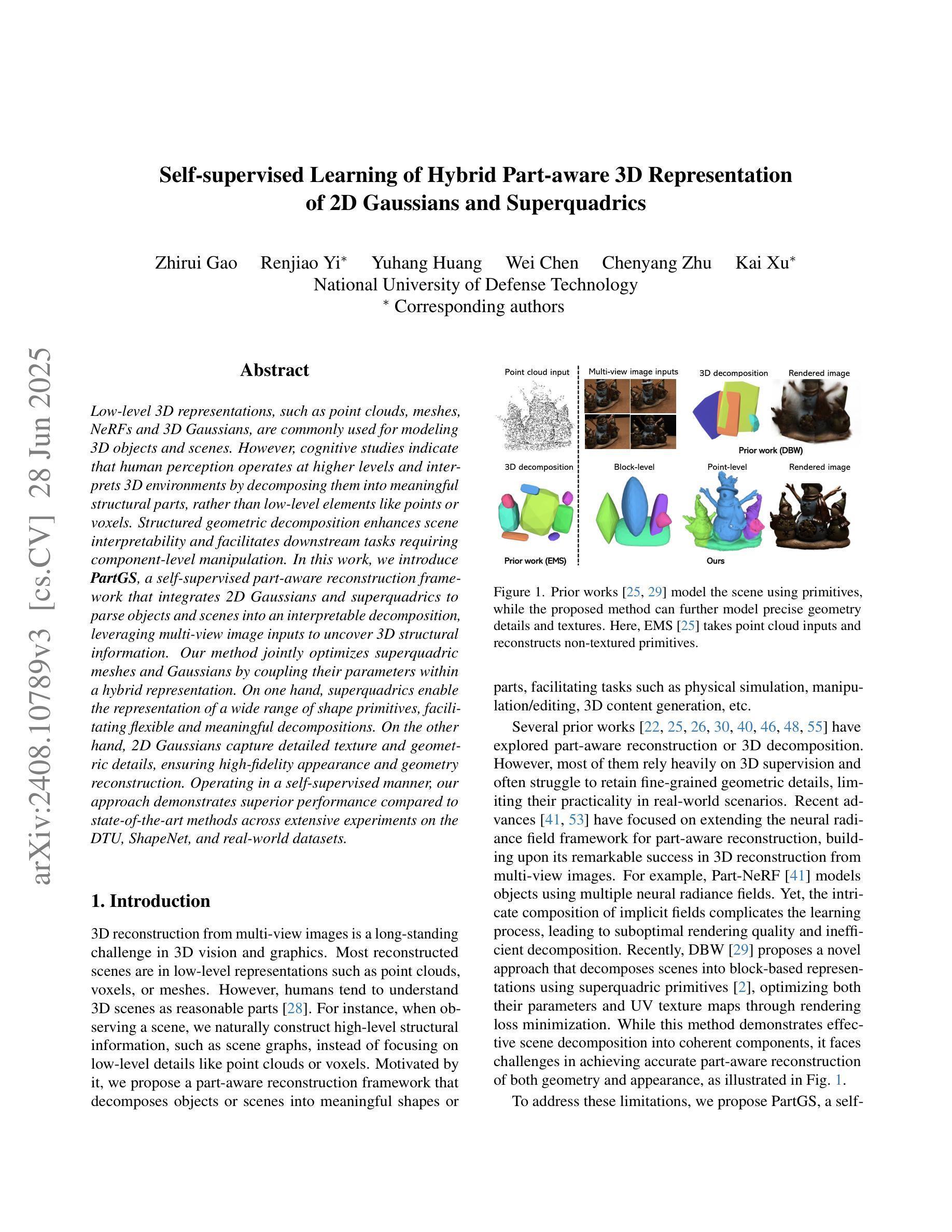
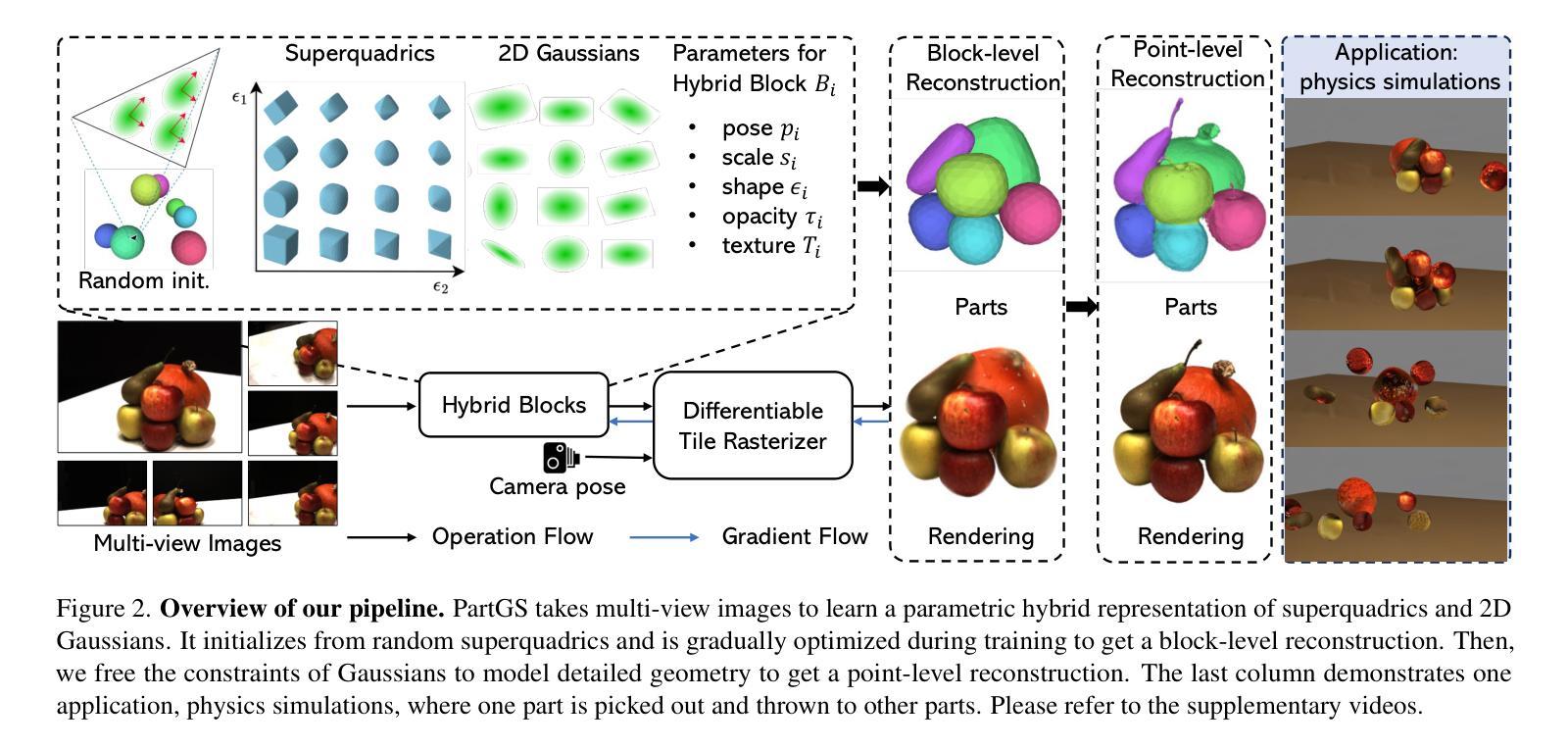
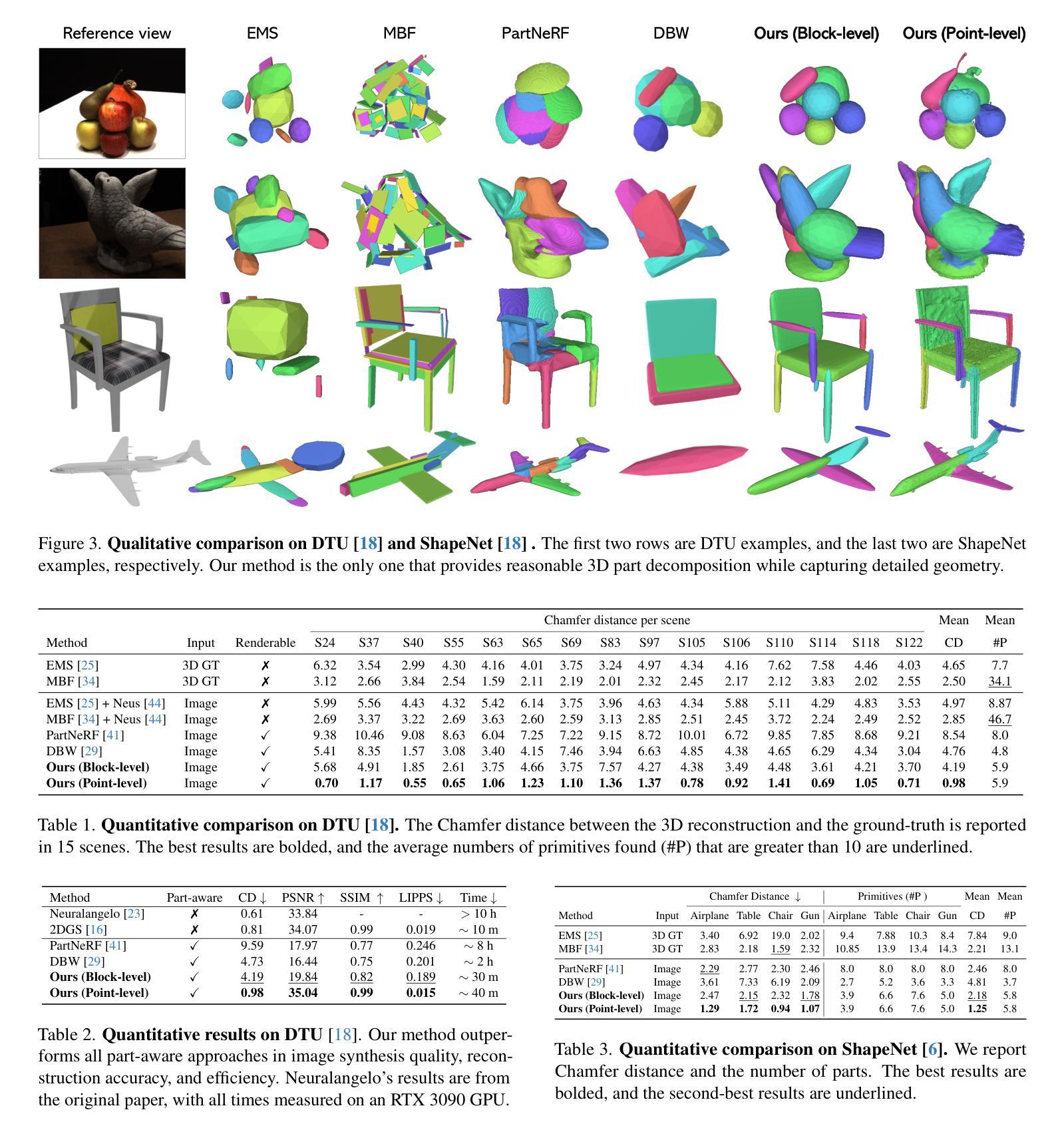
Self-supervised Learning of Hybrid Part-aware 3D Representation of 2D Gaussians and Superquadrics
Authors:Zhirui Gao, Renjiao Yi, Yuhang Huang, Wei Chen, Chenyang Zhu, Kai Xu
Low-level 3D representations, such as point clouds, meshes, NeRFs and 3D Gaussians, are commonly used for modeling 3D objects and scenes. However, cognitive studies indicate that human perception operates at higher levels and interprets 3D environments by decomposing them into meaningful structural parts, rather than low-level elements like points or voxels. Structured geometric decomposition enhances scene interpretability and facilitates downstream tasks requiring component-level manipulation. In this work, we introduce PartGS, a self-supervised part-aware reconstruction framework that integrates 2D Gaussians and superquadrics to parse objects and scenes into an interpretable decomposition, leveraging multi-view image inputs to uncover 3D structural information. Our method jointly optimizes superquadric meshes and Gaussians by coupling their parameters within a hybrid representation. On one hand, superquadrics enable the representation of a wide range of shape primitives, facilitating flexible and meaningful decompositions. On the other hand, 2D Gaussians capture detailed texture and geometric details, ensuring high-fidelity appearance and geometry reconstruction. Operating in a self-supervised manner, our approach demonstrates superior performance compared to state-of-the-art methods across extensive experiments on the DTU, ShapeNet, and real-world datasets.
低级别的三维表示,如点云、网格、NeRF和三维高斯等,通常用于对三维物体和场景进行建模。然而,认知研究表明,人类的感知是在更高层次上进行的,通过分解三维环境为有意义的结构部分来进行解读,而非低级别的元素,如点或体素。结构化几何分解增强了场景的可解释性,并促进了需要组件级操作的下游任务。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025 Code: https://github.com/zhirui-gao/PartGS
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为PartGS的自监督感知重建框架,该框架利用二维高斯和超级二次曲面来解析对象和场景,将其分解为可解释的结构。通过多视角图像输入,揭示三维结构信息。该方法通过混合表示中的参数耦合来联合优化超级二次曲面网格和高斯,从而实现灵活和有意义的分解,同时保证高保真度的外观和几何重建。
Key Takeaways
- PartGS框架结合二维高斯和超级二次曲面,实现对对象和场景的感知重建。
- 通过多视角图像输入,揭示三维结构信息。
- PartGS框架采用自监督学习方式,无需大量标注数据。
- 超级二次曲面能够表示多种形状原始,促进灵活和有意义的分解。
- 二维高斯捕捉详细的纹理和几何细节,确保高保真度的重建。
- PartGS框架在DTU、ShapeNet和真实世界数据集上的实验表现优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图
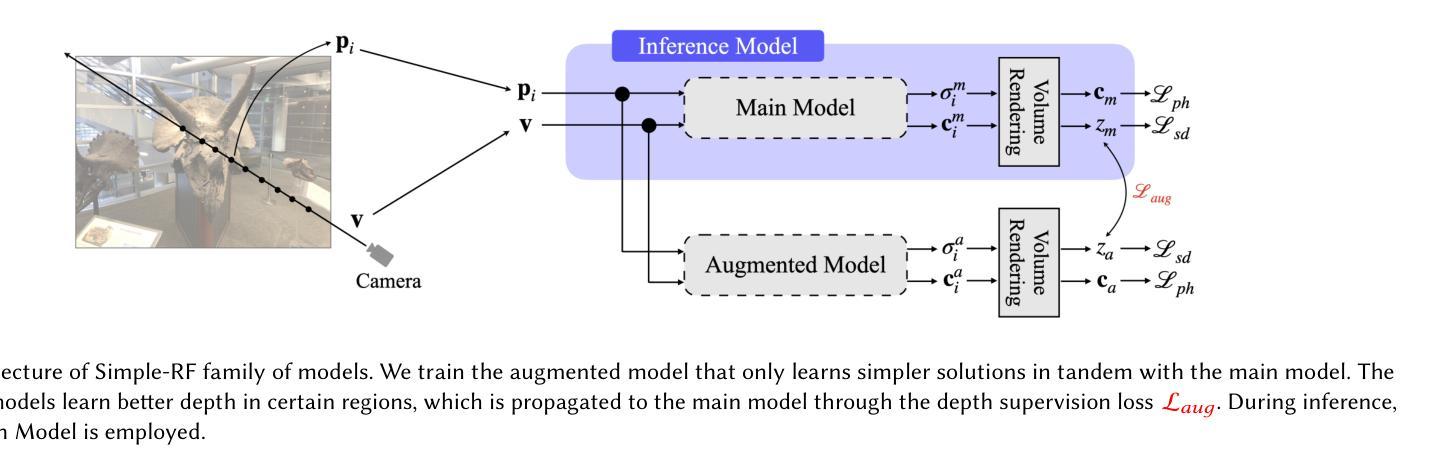
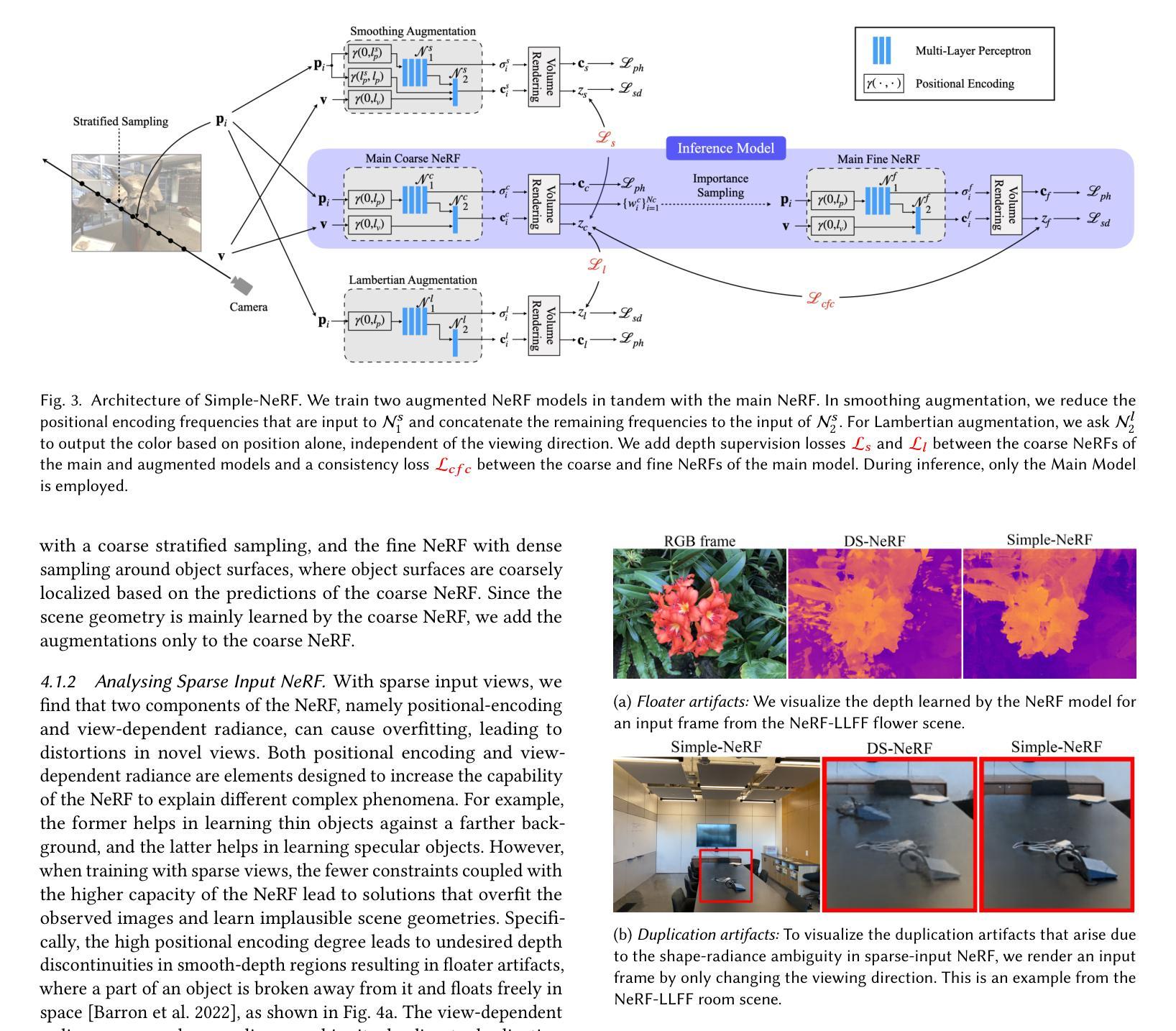
Simple-RF: Regularizing Sparse Input Radiance Fields with Simpler Solutions
Authors:Nagabhushan Somraj, Sai Harsha Mupparaju, Adithyan Karanayil, Rajiv Soundararajan
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) show impressive performance in photo-realistic free-view rendering of scenes. Recent improvements on the NeRF such as TensoRF and ZipNeRF employ explicit models for faster optimization and rendering, as compared to the NeRF that employs an implicit representation. However, both implicit and explicit radiance fields require dense sampling of images in the given scene. Their performance degrades significantly when only a sparse set of views is available. Researchers find that supervising the depth estimated by a radiance field helps train it effectively with fewer views. The depth supervision is obtained either using classical approaches or neural networks pre-trained on a large dataset. While the former may provide only sparse supervision, the latter may suffer from generalization issues. As opposed to the earlier approaches, we seek to learn the depth supervision by designing augmented models and training them along with the main radiance field. Further, we aim to design a framework of regularizations that can work across different implicit and explicit radiance fields. We observe that certain features of these radiance field models overfit to the observed images in the sparse-input scenario. Our key finding is that reducing the capability of the radiance fields with respect to positional encoding, the number of decomposed tensor components or the size of the hash table, constrains the model to learn simpler solutions, which estimate better depth in certain regions. By designing augmented models based on such reduced capabilities, we obtain better depth supervision for the main radiance field. We achieve state-of-the-art view-synthesis performance with sparse input views on popular datasets containing forward-facing and 360$^\circ$ scenes by employing the above regularizations.
神经辐射场(NeRF)在场景的光写实自由视图渲染中表现出令人印象深刻的性能。最近的NeRF改进,如TensoRF和ZipNeRF,采用显式模型进行更快的优化和渲染,与之前采用隐式表示的NeRF形成对比。然而,隐式和显式辐射场都需要对给定场景中的图像进行密集采样。当只有少量稀疏视图可用时,它们的性能会显著下降。研究人员发现,通过深度监督训练辐射场有助于使用较少的视图进行有效的训练。深度监督是通过经典方法或使用大型数据集进行预训练神经网络获得的。虽然前者可能只能提供稀疏的监督,但后者可能会遭受泛化问题。与早期的方法不同,我们试图通过设计增强模型并与主要的辐射场一起训练来学习深度监督。此外,我们旨在设计一个可以在不同隐式和显式辐射场之间工作的正则化框架。我们观察到,这些辐射场模型的某些特征在稀疏输入的情况下过度拟合观察到的图像。我们的关键发现是,通过减少辐射场相对于位置编码的能力、分解的张量组件的数量或哈希表的大小,可以约束模型学习更简单的解决方案,这在某些区域中估计出更好的深度。基于这种减少的能力设计增强模型,我们可以为主要的辐射场获得更好的深度监督。通过采用上述正则化方法,我们在包含正面和360°场景流行数据集上实现了最先进的视图合成性能,并在稀疏输入视图上表现良好。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The source code for our model can be found on our project page: https://nagabhushansn95.github.io/publications/2024/Simple-RF.html. Extension of arXiv:2309.03955
摘要
神经辐射场(NeRF)在场景的自由视角渲染中展现出令人印象深刻的表现。最近的改进方法如TensoRF和ZipNeRF采用显式模型实现更快的优化和渲染,相比于NeRF的隐式表示法。然而,隐式和显式辐射场都需要对场景进行密集的图像采样。当只有稀疏的视图可用时,它们的性能会显著下降。研究发现,通过深度监督训练辐射场,即使使用较少的视图也能有效训练。深度监督可通过传统方法或在大数据集上预训练的神经网络获得。前者可能只能提供稀疏的监督,而后者可能面临泛化问题。相反,我们寻求通过设计增强模型并与主辐射场一起训练来学习深度监督。此外,我们旨在设计一个可以在不同隐式和显式辐射场之间工作的正则化框架。我们观察到,这些辐射场模型的某些特征在稀疏输入的情况下会对观察到的图像过度拟合。我们的关键发现是,通过减少辐射场在位置编码、分解张量组件的数量或哈希表大小方面的能力,可以约束模型学习更简单的解决方案,从而在特定区域更好地估计深度。基于这种减少的能力设计增强模型,我们为主要的辐射场获得了更好的深度监督。通过采用上述正则化方法,我们在流行的数据集上实现了最先进的稀疏输入视图合成性能,包括正面和360°场景。
要点
- NeRF及其改进方法在场景的自由视角渲染中有出色表现,但稀疏视图下性能下降。
- 深度监督对于训练NeRF模型在少量视图下有效。
- 现有深度监督方法存在局限性,如稀疏监督或泛化问题。
- 提出通过设计具有约束能力的增强模型来学习深度监督,适用于隐式和显式辐射场。
- 减少辐射场模型在某些方面的能力,如位置编码、张量组件数量或哈希表大小,有助于在特定区域更好地估计深度。
- 采用正则化方法,实现了在稀疏输入视图下的先进视图合成性能。
- 在包含正面和360°场景的主流数据集上取得了最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图