⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-03 更新
JAM-Flow: Joint Audio-Motion Synthesis with Flow Matching
Authors:Mingi Kwon, Joonghyuk Shin, Jaeseok Jung, Jaesik Park, Youngjung Uh
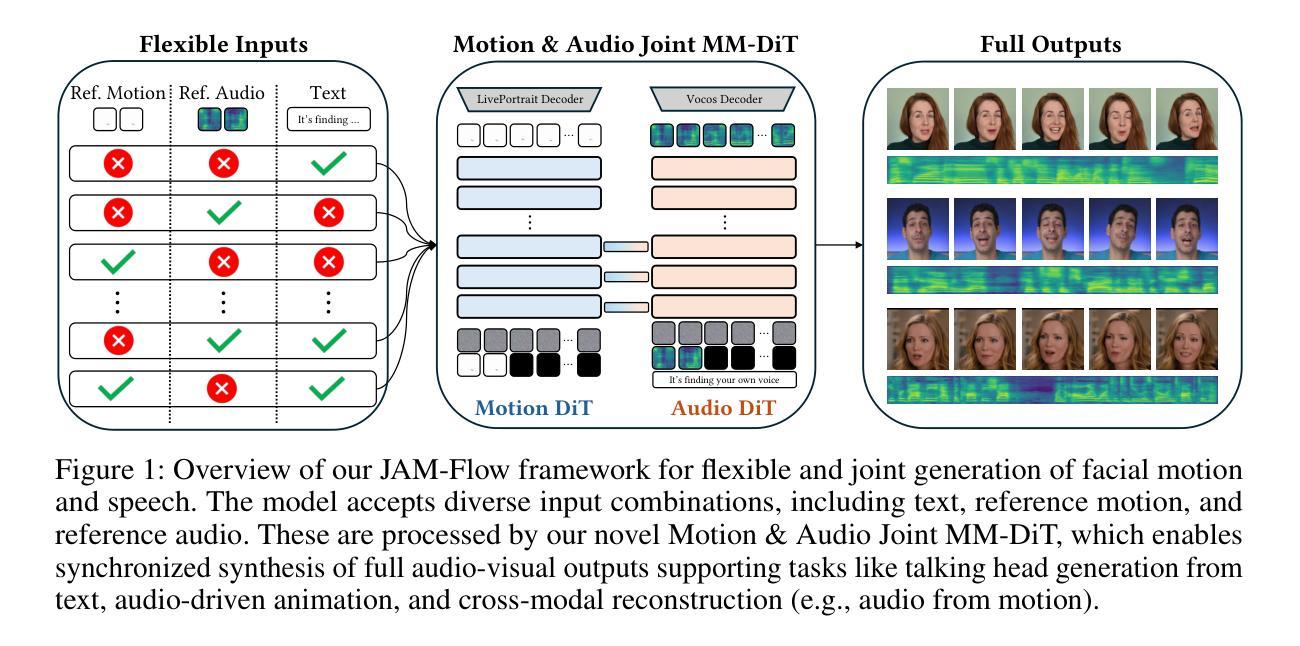
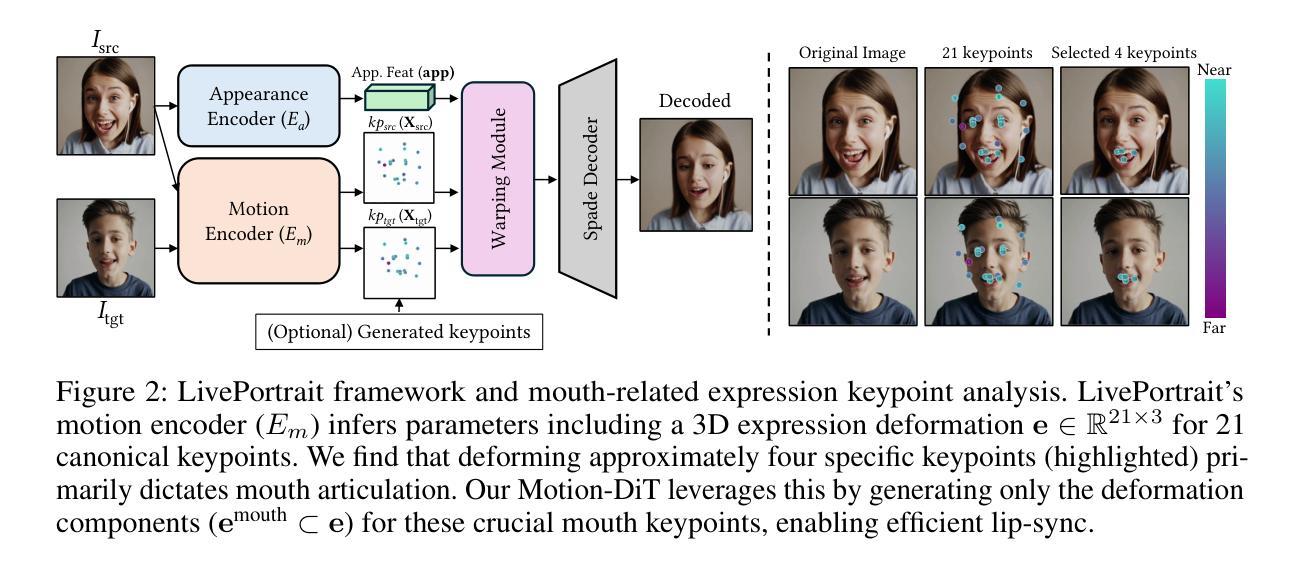
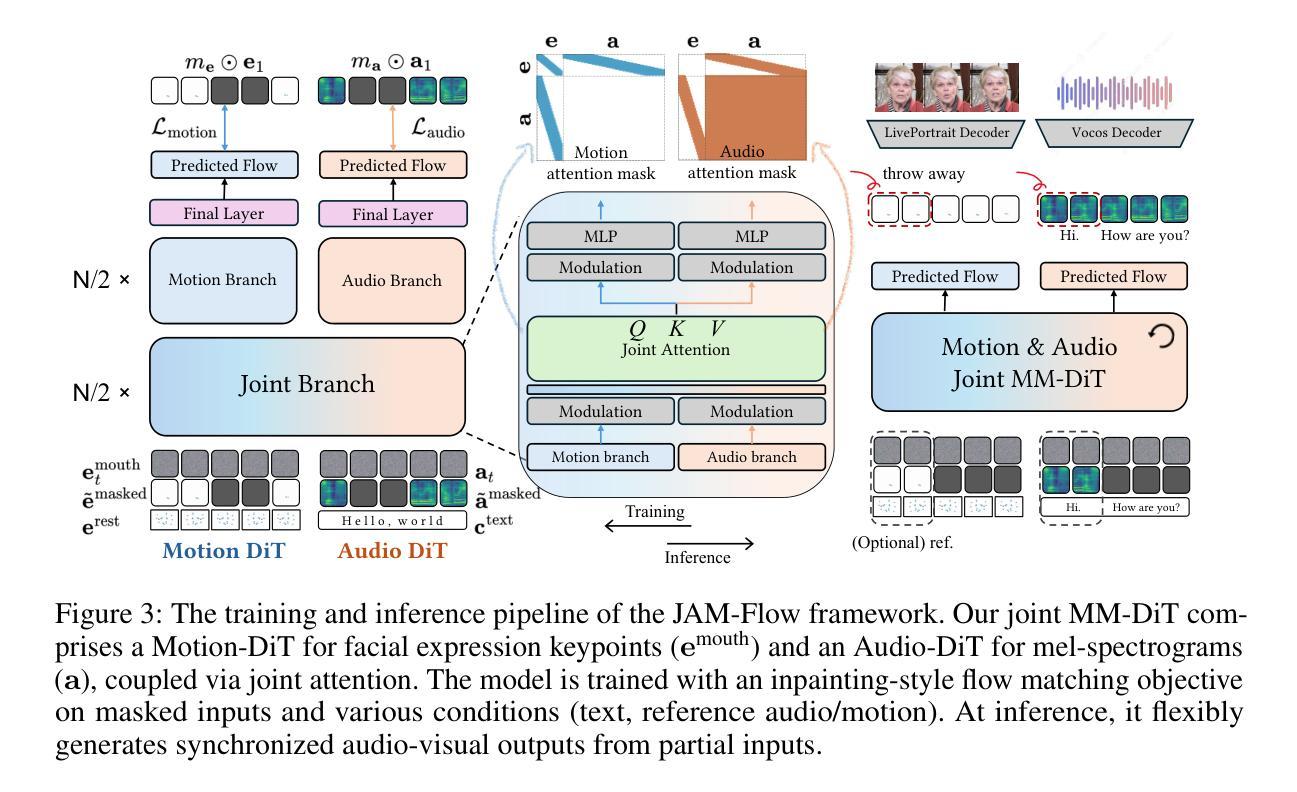
The intrinsic link between facial motion and speech is often overlooked in generative modeling, where talking head synthesis and text-to-speech (TTS) are typically addressed as separate tasks. This paper introduces JAM-Flow, a unified framework to simultaneously synthesize and condition on both facial motion and speech. Our approach leverages flow matching and a novel Multi-Modal Diffusion Transformer (MM-DiT) architecture, integrating specialized Motion-DiT and Audio-DiT modules. These are coupled via selective joint attention layers and incorporate key architectural choices, such as temporally aligned positional embeddings and localized joint attention masking, to enable effective cross-modal interaction while preserving modality-specific strengths. Trained with an inpainting-style objective, JAM-Flow supports a wide array of conditioning inputs-including text, reference audio, and reference motion-facilitating tasks such as synchronized talking head generation from text, audio-driven animation, and much more, within a single, coherent model. JAM-Flow significantly advances multi-modal generative modeling by providing a practical solution for holistic audio-visual synthesis. project page: https://joonghyuk.com/jamflow-web
面部动作与语音之间的内在联系在生成模型中经常被忽视,生成模型中通常会分别处理头部合成和文本到语音(TTS)这两个任务。本文介绍了JAM-Flow,这是一个统一框架,可以同时合成并基于面部动作和语音的条件进行建模。我们的方法利用流匹配和新颖的多模态扩散Transformer(MM-DiT)架构,集成了专门的Motion-DiT和Audio-DiT模块。它们通过选择性联合注意力层进行耦合,并融入了关键架构选择,如时间对齐位置嵌入和局部联合注意力掩码,以实现有效的跨模态交互,同时保留模态特定的优势。通过采用填充风格的目标进行训练,JAM-Flow支持广泛的条件输入,包括文本、参考音频和参考动作,便于完成诸如根据文本生成同步对话头部、音频驱动动画等任务,所有这些都在一个连贯的单一模型中实现。JAM-Flow通过为全面的视听合成提供实用解决方案,从而极大地推动了多模态生成模型的发展。项目页面:链接
论文及项目相关链接
PDF project page: https://joonghyuk.com/jamflow-web Under review. Preprint published on arXiv
Summary
本文提出了一种名为JAM-Flow的统一框架,该框架能同时合成并依赖于面部运动和语音。它利用流匹配和新型的多模态扩散转换器(MM-DiT)架构,通过选择性联合注意层将专门的运动-DiT和音频-DiT模块耦合在一起。JAM-Flow支持多种条件输入,包括文本、参考音频和参考运动,可在单个连贯的模型内完成同步说话头生成、音频驱动动画等任务。该框架为整体音视频合成提供了实用解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- JAM-Flow是一个统一框架,用于同时合成并依赖于面部运动和语音。
- 引入流匹配技术和多模态扩散转换器(MM-DiT)架构,整合运动模块和音频模块。
- 通过选择性联合注意层实现模块间的耦合。
- 架构中包含关键选择,如时间对齐位置嵌入和局部联合注意屏蔽。
- 有效实现跨模态交互同时保持模态特定优势。
- 利用填充风格的目标进行训练,支持多种条件输入,包括文本、参考音频和参考运动。
点此查看论文截图

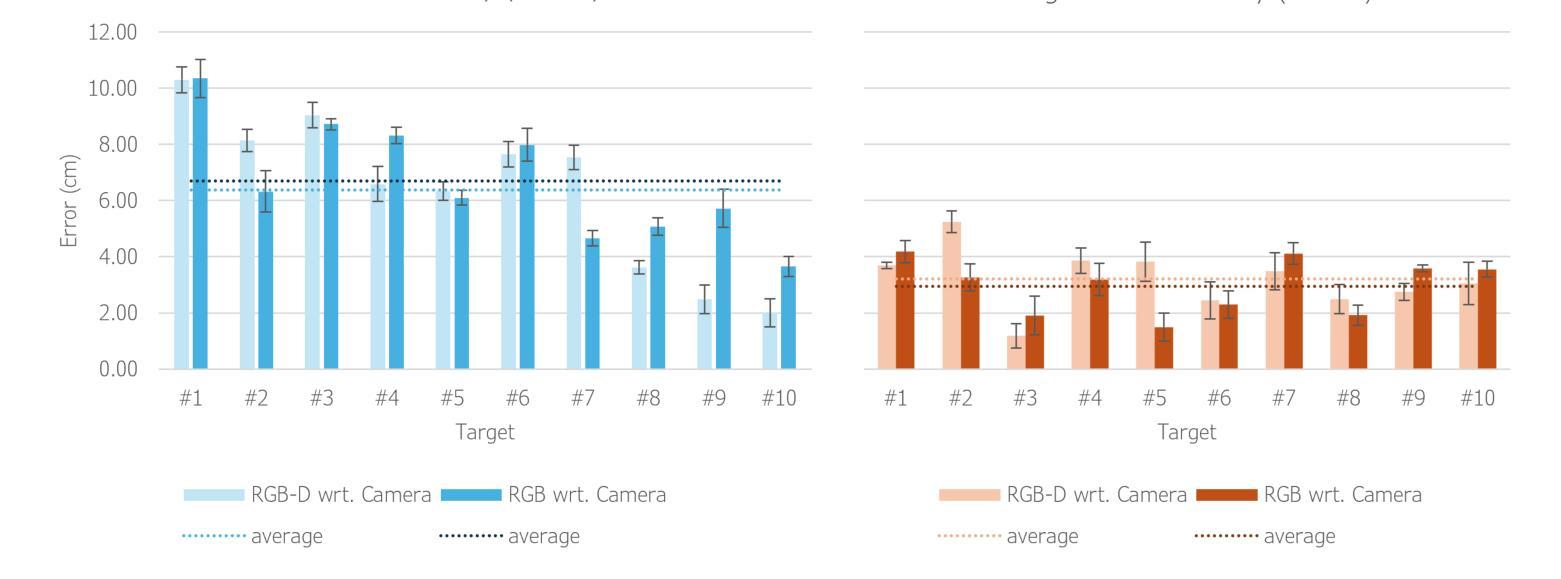
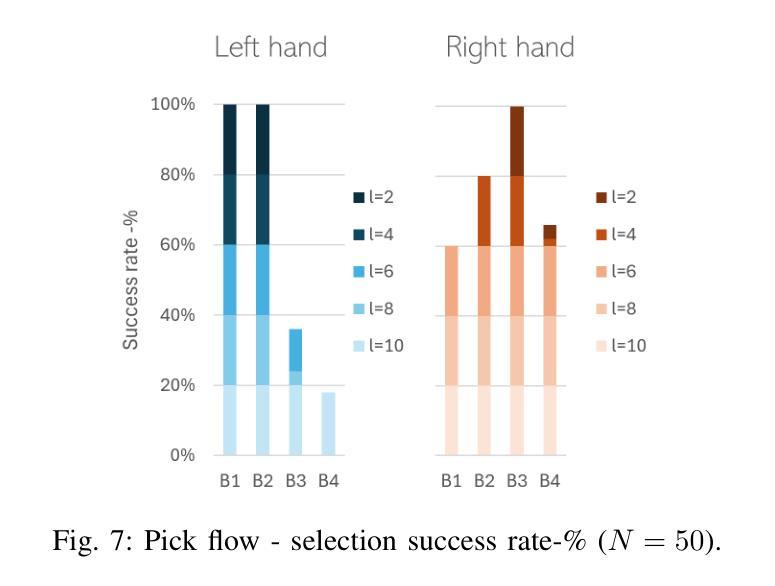
Evaluating Pointing Gestures for Target Selection in Human-Robot Collaboration
Authors:Noora Sassali, Roel Pieters
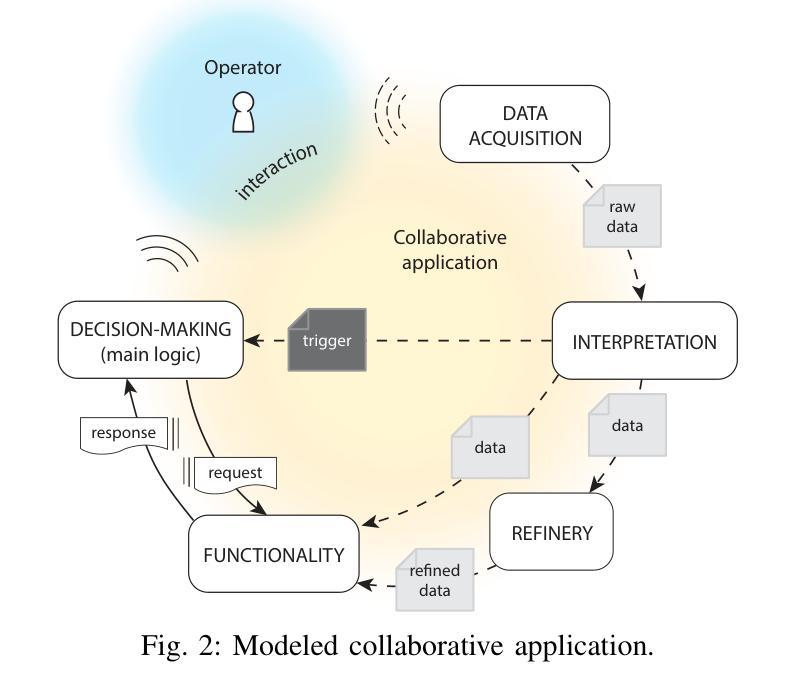
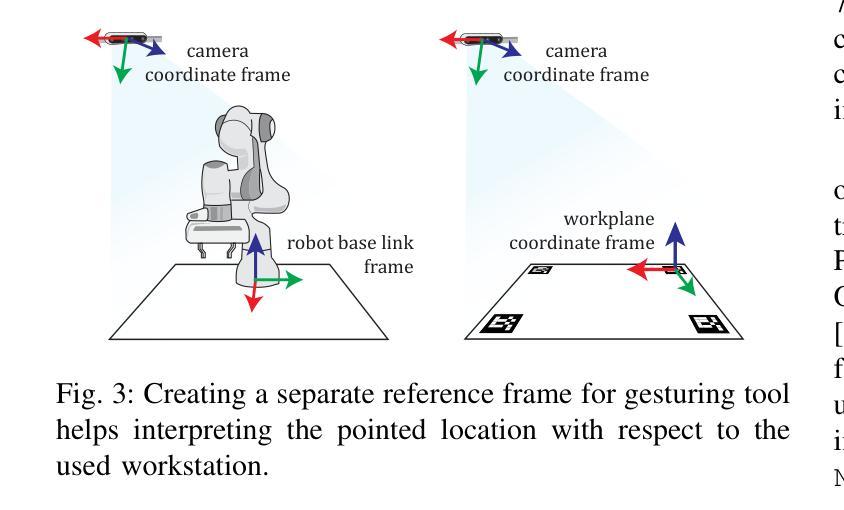
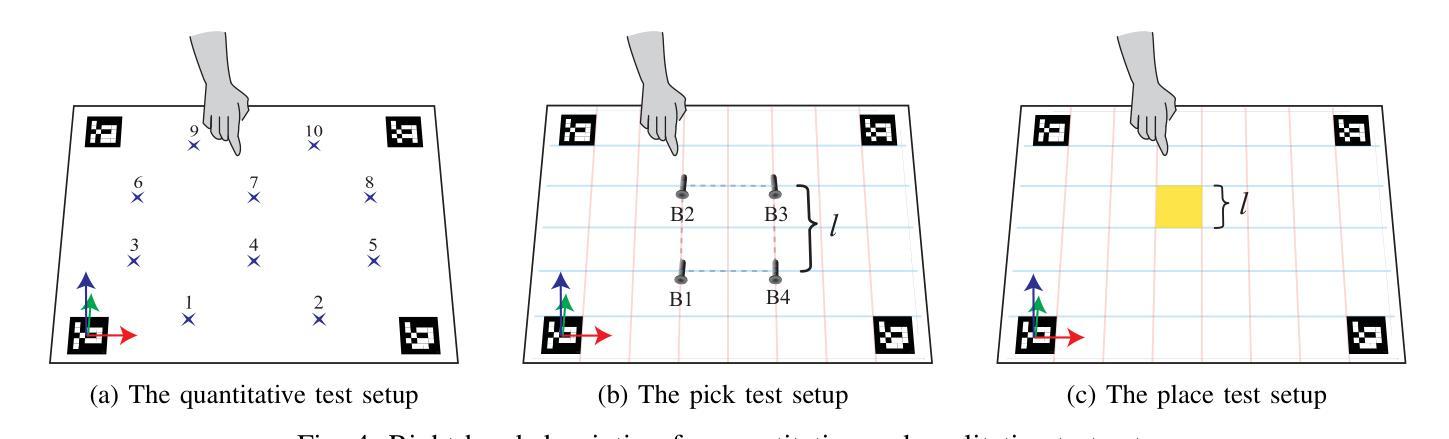
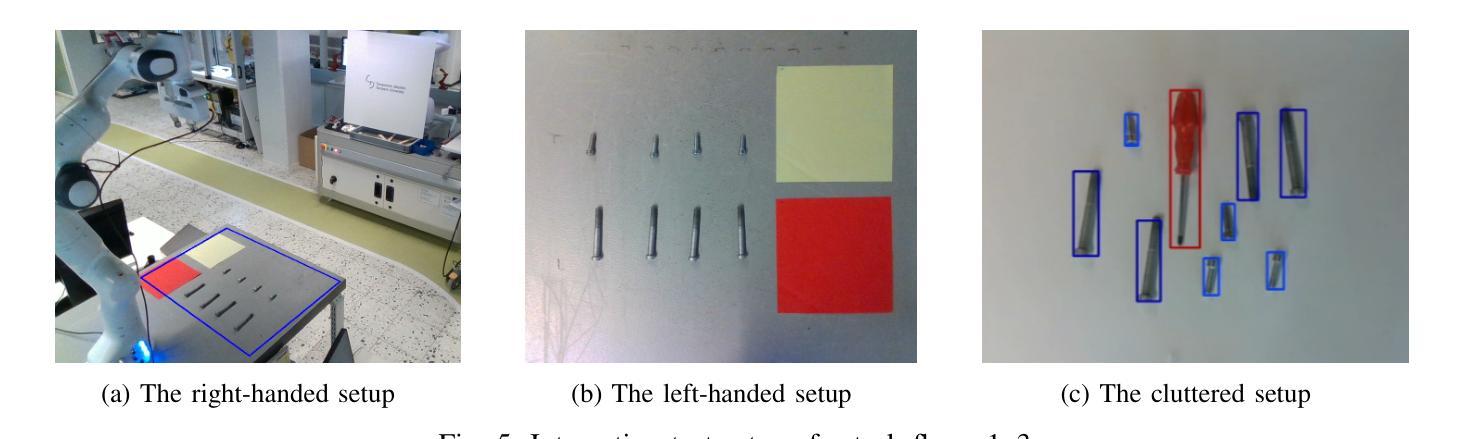
Pointing gestures are a common interaction method used in Human-Robot Collaboration for various tasks, ranging from selecting targets to guiding industrial processes. This study introduces a method for localizing pointed targets within a planar workspace. The approach employs pose estimation, and a simple geometric model based on shoulder-wrist extension to extract gesturing data from an RGB-D stream. The study proposes a rigorous methodology and comprehensive analysis for evaluating pointing gestures and target selection in typical robotic tasks. In addition to evaluating tool accuracy, the tool is integrated into a proof-of-concept robotic system, which includes object detection, speech transcription, and speech synthesis to demonstrate the integration of multiple modalities in a collaborative application. Finally, a discussion over tool limitations and performance is provided to understand its role in multimodal robotic systems. All developments are available at: https://github.com/NMKsas/gesture_pointer.git.
指向手势在人类与机器人的协作中是一种常见交互方法,用于完成各种任务,从选择目标到指导工业流程。本研究介绍了一种在平面工作空间内定位指向目标的方法。该方法采用姿态估计和基于肩腕伸展的简单几何模型,从RGB-D流中提取手势数据。研究为评估典型机器人任务中的指向手势和目标选择提出了严格的方法和综合分析。除了评估工具精度外,该工具还被集成到一个概念验证机器人系统中,该系统包括对象检测、语音转录和语音合成,以演示协作应用中多种模式的集成。最后,对工具的限制和性能进行了讨论,以了解其在多模式机器人系统中的作用。所有开发内容均可在:https://github.com/NMKsas/gesture_pointer.git上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by the 2025 34th IEEE International Conference on Robot and Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN). Preprint
Summary
本文研究了在人机协作中用于目标指向和任务选择的指向手势。研究提出了一种基于姿态估计和肩腕伸展简单几何模型的方法,从RGB-D流中提取手势数据。该研究不仅评估了工具精度,还将工具集成到一个概念验证的机器人系统中,展示了多模式的协作应用集成。文章还讨论了工具的限制和性能,以理解其在多模式机器人系统中的作用。
Key Takeaways
- 指向手势在人机协作中用于多种任务,如目标选择和工业过程指导。
- 研究采用姿态估计和肩腕伸展的几何模型进行指向目标的定位。
- 开发了一种从RGB-D流中提取手势数据的方法。
- 除工具精度评估外,还将工具集成到包含对象检测、语音转录和语音合成的机器人系统中,以展示多模式集成的协作应用。
- 工具已公开在指定链接上供公众访问。
- 文章讨论了该工具的限制和性能表现。
点此查看论文截图

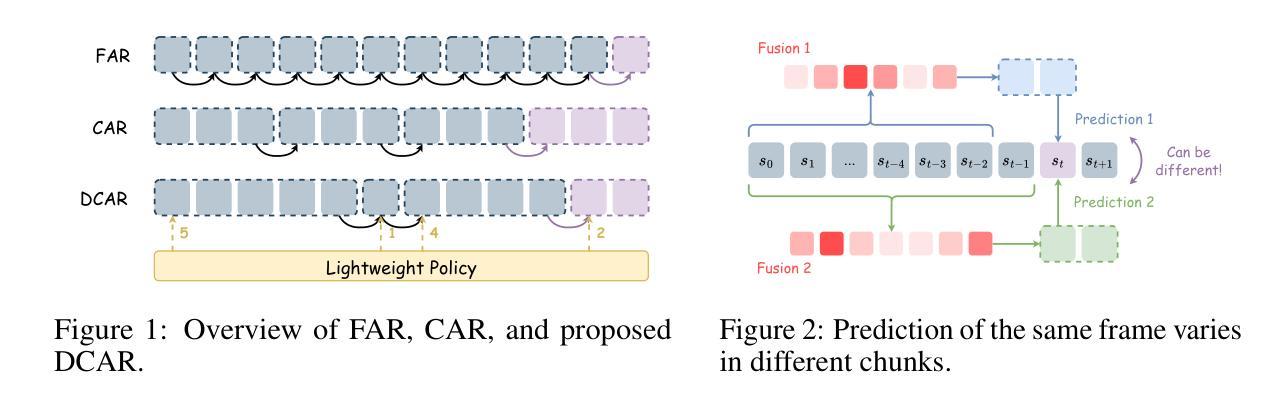
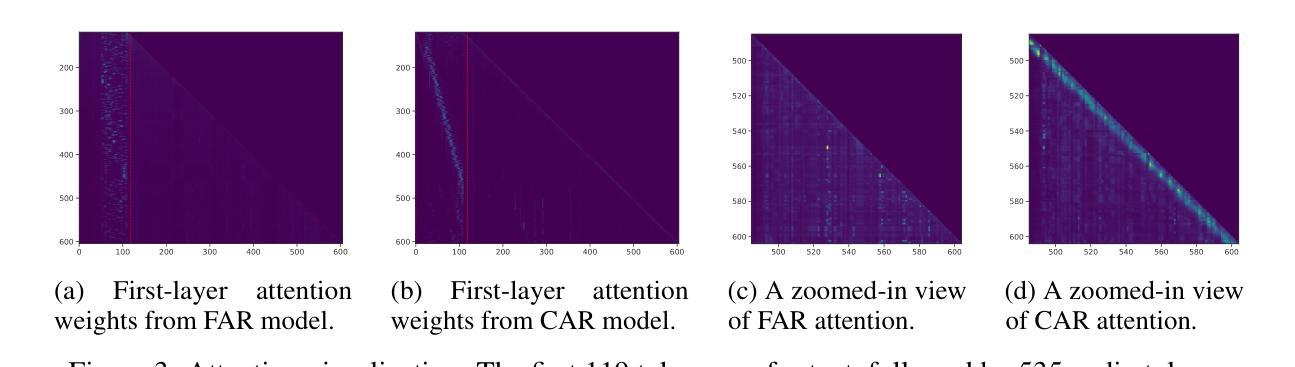
Robust and Efficient Autoregressive Speech Synthesis with Dynamic Chunk-wise Prediction Policy
Authors:Bohan Li, Zhihan Li, Haoran Wang, Hanglei Zhang, Yiwei Guo, Hankun Wang, Xie Chen, Kai Yu
Recently, autoregressive (AR) language models have emerged as a dominant approach in speech synthesis, offering expressive generation and scalable training. However, conventional AR speech synthesis models relying on the next-token prediction paradigm often encounter significant challenges when handling long speech sequences. These models often struggle to construct stable frame-to-frame attention, leading to increased latency and degraded synthesis quality, thereby limiting their feasibility for real-time applications. To address these limitations, we introduce a novel dynamic chunk-wise autoregressive synthesis framework, termed DCAR, designed to enhance both efficiency and intelligibility robustness in AR speech generation. DCAR introduces a chunk-to-frame attention mechanism through training with multi-token prediction, enabling dynamic chunk prediction in variable speech contexts using a lightweight module trained on-policy. DCAR dynamically adjusts the token prediction span, significantly reducing the sequence length dependency while obtaining high synthesis quality. Comprehensive empirical evaluations demonstrate that DCAR substantially outperforms traditional next-token prediction models, achieving up to 72.27% intelligibility improvement and 2.61x inference speedup simultaneously on the test set. Furthermore, we conduct comprehensive analysis to support it as a versatile foundation for next-generation speech synthesis systems.
最近,自回归(AR)语言模型在语音合成中脱颖而出,成为一种主流方法,提供了表达性生成和可扩展训练。然而,传统的基于下一个令牌预测范式的AR语音合成模型在处理长语音序列时经常面临重大挑战。这些模型在构建稳定的帧到帧注意力方面往往遇到困难,导致延迟增加和合成质量下降,从而限制了它们在实时应用中的可行性。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入了一种新型动态分段自回归合成框架,称为DCAR,旨在提高AR语音生成中的效率和清晰度稳健性。DCAR通过多令牌预测进行训练,引入了块到帧的注意力机制,使用轻量级模块进行策略训练,在可变语音环境中实现动态块预测。DCAR动态调整令牌预测范围,在获得高合成质量的同时,显著减少了序列长度依赖性。全面的实证评估表明,DCAR在测试集上大幅优于传统的下一个令牌预测模型,同时实现了高达72.27%的清晰度提升和2.61倍的推理速度提升。此外,我们进行了综合分析,支持其作为下一代语音合成系统的多功能基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 8 figures, 5 tables
Summary
本文介绍了在语音合成领域新兴的自回归(AR)语言模型。传统AR语音合成模型在处理长语音序列时面临挑战,如构建稳定的帧间注意力、增加延迟和降低合成质量。为解决这些问题,本文提出了一种新型动态分段自回归合成框架DCAR,旨在提高AR语音生成的效率和清晰度稳健性。DCAR引入了一个基于多令牌预测的帧间注意力机制,利用轻量级模块实现动态分段预测,在可变的语音环境下取得较高合成质量。全面评估表明,DCAR在测试集上明显优于传统单一令牌预测模型,同时实现了高达72.27%的清晰度提升和2.61倍的推理速度。这为下一代语音合成系统提供了多功能基础。
Key Takeaways
- 自回归(AR)语言模型已成为语音合成中的主流方法,具有表现力生成和可扩展训练的优势。
- 传统AR语音合成模型在处理长语音序列时面临稳定性、延迟和合成质量问题。
- DCAR框架旨在解决这些问题,通过引入动态分段预测和多令牌预测机制提高效率和清晰度稳健性。
- DCAR利用轻量级模块实现动态分段预测,适应可变语音环境。
- DCAR与传统模型相比在测试集上取得了显著优势,提高了清晰度并降低了延迟。
点此查看论文截图

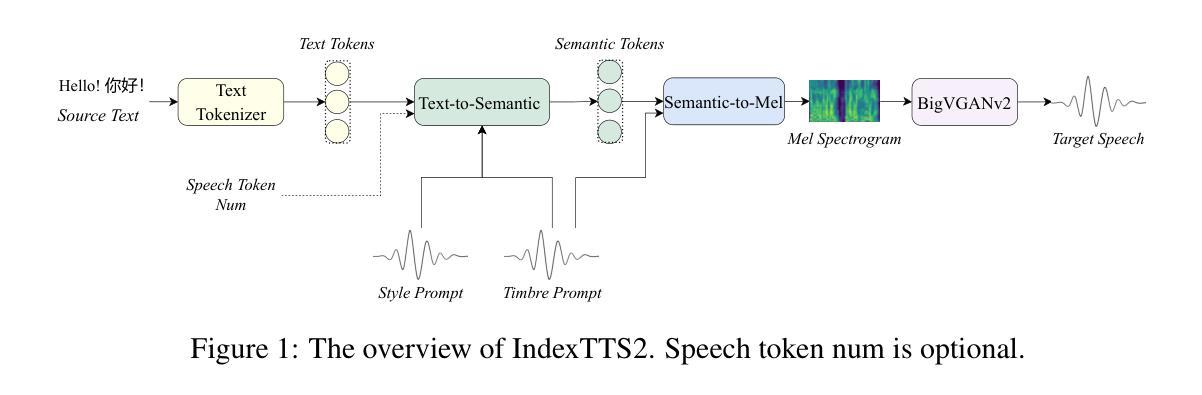
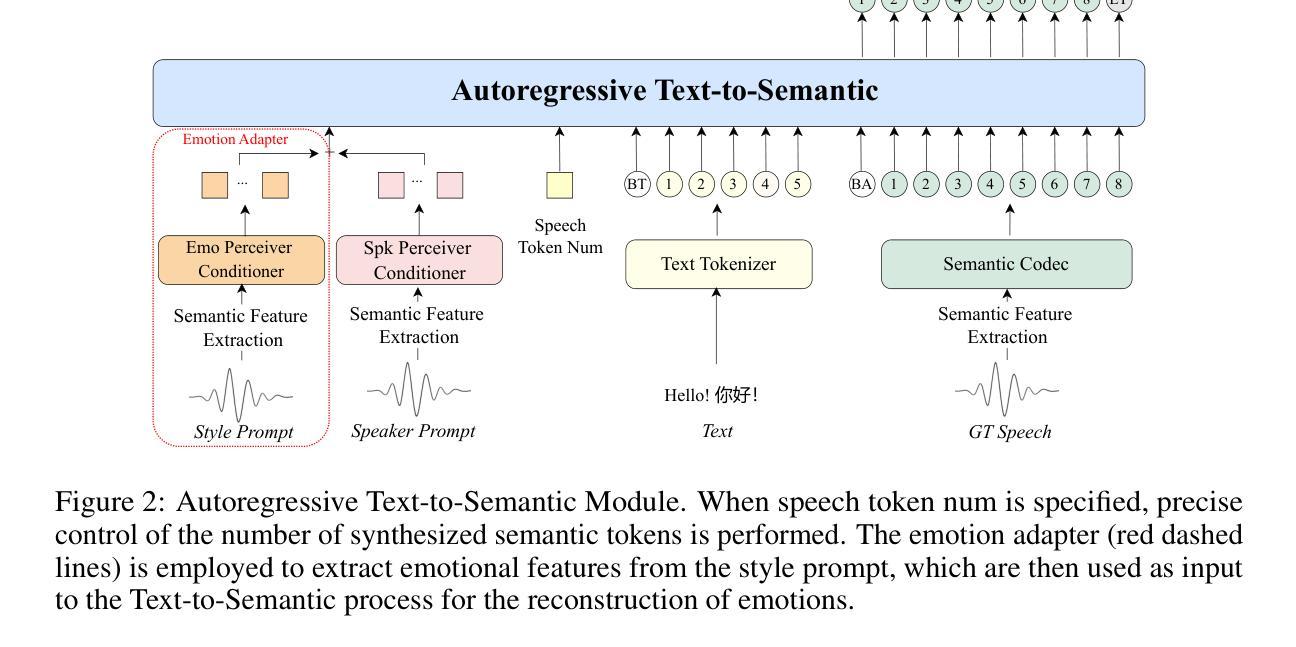
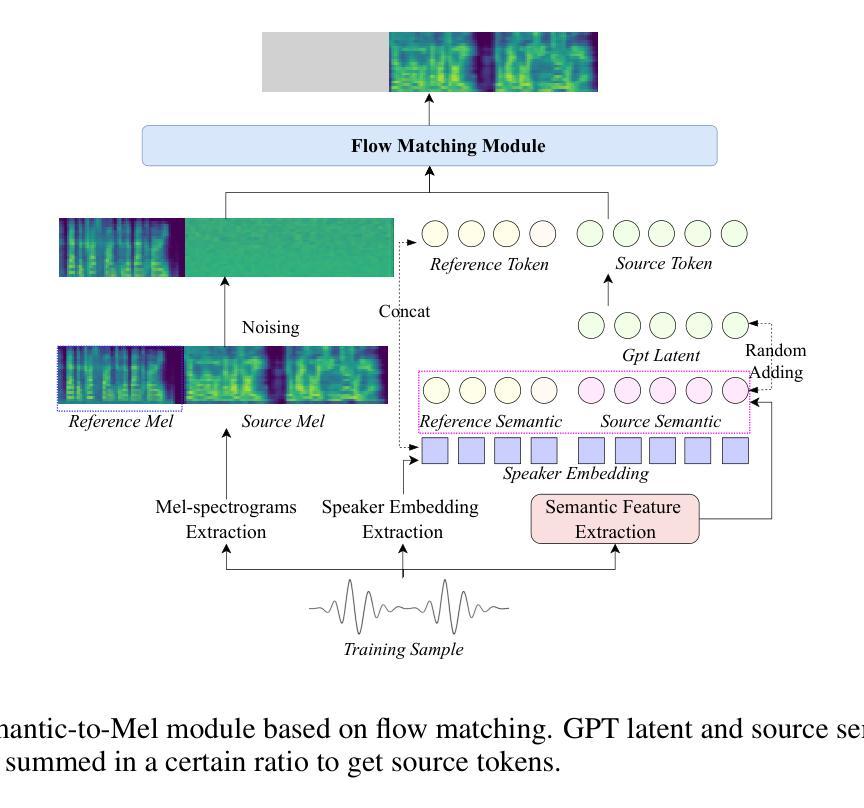
IndexTTS2: A Breakthrough in Emotionally Expressive and Duration-Controlled Auto-Regressive Zero-Shot Text-to-Speech
Authors:Siyi Zhou, Yiquan Zhou, Yi He, Xun Zhou, Jinchao Wang, Wei Deng, Jingchen Shu
Large-scale text-to-speech (TTS) models are typically categorized into autoregressive and non-autoregressive systems. Although autoregressive systems exhibit certain advantages in speech naturalness, their token-by-token generation mechanism makes it difficult to precisely control the duration of synthesized speech. This is a key limitation in applications such as video dubbing that require strict audio-visual synchronization. This paper introduces IndexTTS2, which proposes a novel and autoregressive-model-friendly method for speech duration control. The method supports two generation modes: one allows explicit specification of the number of generated tokens for precise duration control; the other does not require manual input and lets the model freely generate speech while preserving prosodic characteristics from the input prompt. Furthermore, IndexTTS2 achieves disentanglement between emotional expression and speaker identity, enabling independent control of timbre and emotion. In the zero-shot setting, the model can perfectly reproduce the emotional characteristics of the input prompt. Users may also provide a separate emotion prompt, even from a different speaker, allowing the model to reconstruct the target timbre while conveying the desired emotion. To enhance clarity during strong emotional expressions, we incorporate GPT latent representations to improve speech stability. Meanwhile, to lower the barrier for emotion control, we design a soft instruction mechanism based on textual descriptions by fine-tuning Qwen3. This enables effective guidance of speech generation with desired emotional tendencies using natural language input. Experimental results demonstrate that IndexTTS2 outperforms existing state-of-the-art zero-shot TTS models in word error rate, speaker similarity, and emotional fidelity.
大规模文本到语音(TTS)模型通常分为自回归和非自回归系统。尽管自回归系统在语音自然度方面具有一定的优势,但其逐个标记的生成机制使得难以精确控制合成语音的持续时间。这在诸如需要严格音视频同步的视频配音等应用中是一个关键限制。本文介绍了IndexTTS2,它提出了一种新颖且适用于自回归模型的语音持续时间控制方法。该方法支持两种生成模式:一种允许明确指定生成的标记数量以实现精确的持续时间控制;另一种则不需要人工输入,让模型在保留输入提示的韵律特征的同时自由生成语音。此外,IndexTTS2实现了情感表达和说话人身份的解耦,能够实现音调和情感的独立控制。在零样本设置下,模型可以完美地再现输入提示的情感特征。用户还可以提供不同的情感提示,甚至来自不同的说话人,使模型在传达期望情感的同时重建目标音调。为了提高强烈情感表达时的清晰度,我们融入了GPT的潜在表示来提高语音的稳定性。同时,为了降低情感控制的障碍,我们设计了一种基于文本描述的柔和指令机制,通过微调Qwen3来实现。这使得使用自然语言输入有效地引导具有期望情感倾向的语音生成。实验结果表明,IndexTTS2在词错误率、说话人相似度和情感保真度方面超越了现有的最先进的零样本TTS模型。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文介绍了Large-scale TTS模型的新方法——IndexTTS2。该方法解决了传统自回归模型在语音合成中难以精确控制时长的问题,特别适用于视频配音等需要严格音视频同步的应用。IndexTTS2支持两种生成模式,一种可明确指定生成的标记数量以实现精确时长控制,另一种则让模型自由生成语音,同时保留输入提示的韵律特征。此外,IndexTTS2实现了情感表达和说话人身份的解耦,可独立控制音色和情感。在零样本环境下,该模型能完美复制输入提示的情感特征。用户甚至可提供不同的情感提示,让模型在传达情感的同时重构目标音色。为增强强烈情感表达时的清晰度,我们融入了GPT潜在表征来提高语音稳定性。同时,我们设计了一种基于文本描述的软指令机制,通过微调Qwen3来降低情感控制的障碍。实验结果表明,IndexTTS2在词错误率、说话人相似度和情感保真度方面超越了现有的零样本TTS模型。
关键见解
- IndexTTS2解决了自回归TTS模型在精确控制合成语音时长方面的关键难题。
- IndexTTS2支持两种生成模式,既能够精确控制时长,又能保留输入提示的韵律。
- IndexTTS2能够独控制音色和情感,实现了情感表达和说话人身份的解耦。
- 在零样本环境下,IndexTTS2能完美复制输入提示的情感特征,并允许使用不同的情感提示。
- 通过融入GPT潜在表征,IndexTTS2增强了语音稳定性,尤其是在强烈情感表达时。
- 设计了基于文本描述的软指令机制,通过微调Qwen3以自然语言输入来有效指导语音生成。
点此查看论文截图

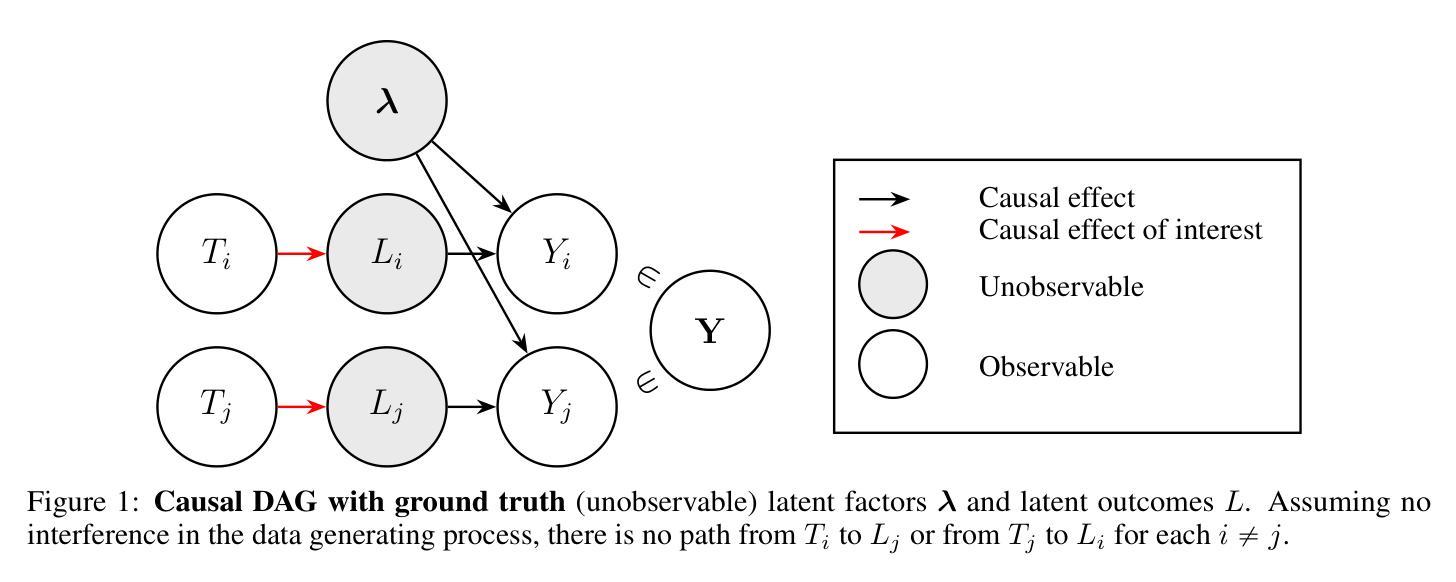
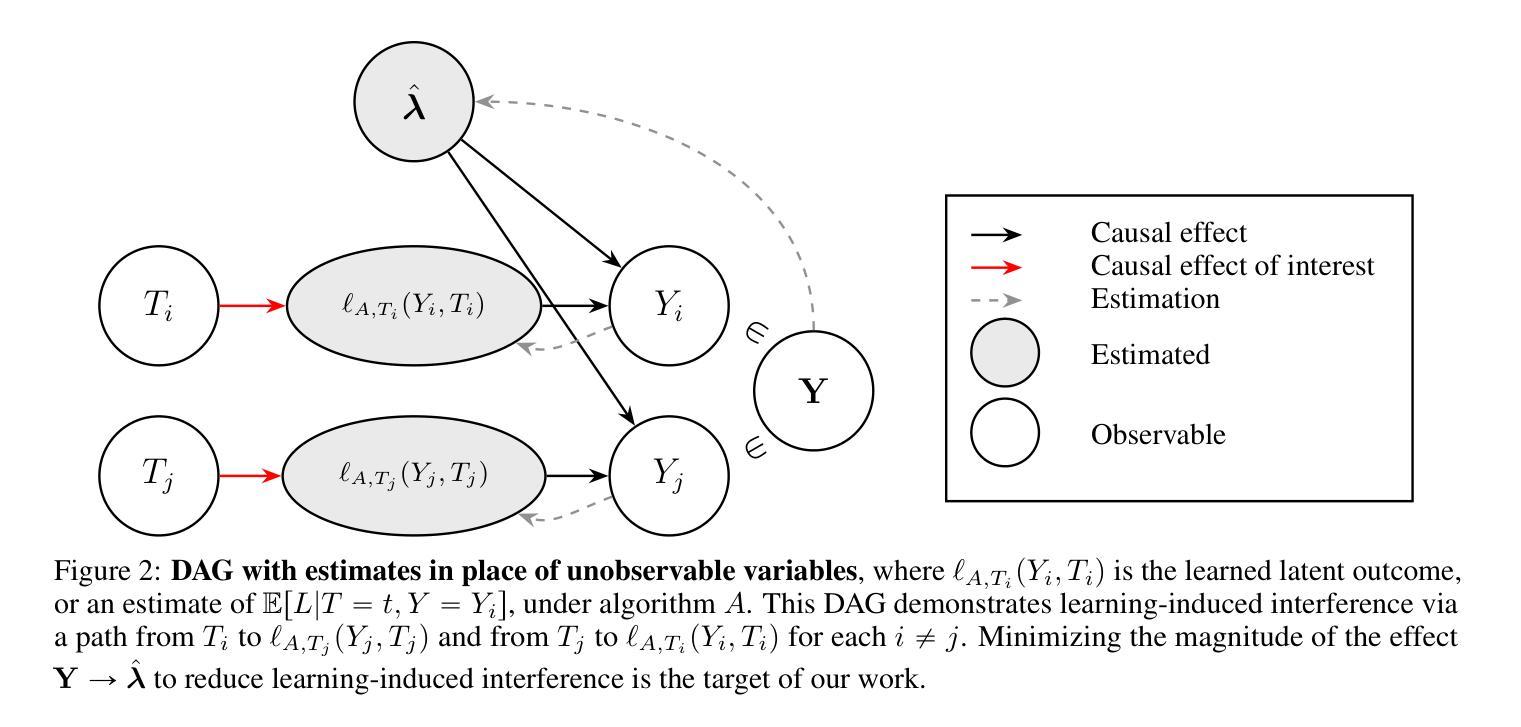
Causal Inference for Latent Outcomes Learned with Factor Models
Authors:Jenna M. Landy, Dafne Zorzetto, Roberta De Vito, Giovanni Parmigiani
In many fields$\unicode{x2013}$including genomics, epidemiology, natural language processing, social and behavioral sciences, and economics$\unicode{x2013}$it is increasingly important to address causal questions in the context of factor models or representation learning. In this work, we investigate causal effects on $\textit{latent outcomes}$ derived from high-dimensional observed data using nonnegative matrix factorization. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to formally address causal inference in this setting. A central challenge is that estimating a latent factor model can cause an individual’s learned latent outcome to depend on other individuals’ treatments, thereby violating the standard causal inference assumption of no interference. We formalize this issue as $\textit{learning-induced interference}$ and distinguish it from interference present in a data-generating process. To address this, we propose a novel, intuitive, and theoretically grounded algorithm to estimate causal effects on latent outcomes while mitigating learning-induced interference and improving estimation efficiency. We establish theoretical guarantees for the consistency of our estimator and demonstrate its practical utility through simulation studies and an application to cancer mutational signature analysis. All baseline and proposed methods are available in our open-source R package, ${\tt causalLFO}$.
在许多领域——包括基因组学、流行病学、自然语言处理、社会行为科学和经济学——在因子模型或表示学习的背景下解决因果问题变得越来越重要。在这项工作中,我们利用非负矩阵分解法研究高维观测数据衍生的潜在结果的因果关系。据我们所知,这是该领域首次正式研究因果推断。一个核心挑战在于估计潜在因子模型可能会导致个体的潜在结果与他人的处理存在依赖关系,从而违反了无干扰的标准因果推断假设。我们将这一问题形式化为“学习引起的干扰”,并将其与数据生成过程中的干扰区别开来。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种新颖、直观、理论上有依据的算法来估计潜在结果的因果关系,同时减少学习引起的干扰,提高估计效率。我们为估计器的一致性提供了理论保证,并通过模拟研究和对癌症突变签名分析的应用来展示其实用性。所有基准方法和提出的方法都可在我们的开源R包${\tt causalLFO}$中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 7 figures, 1 table (+ references and supplement). For open-source R software package, see https://github.com/jennalandy/causalLFO. For all code used in the simulation studies and data application, see https://github.com/jennalandy/causalLFO_PAPER
Summary
本文探索了在高维观测数据下,运用非负矩阵分解技术来探究潜在结果的因果效应。文章针对当前面临的一个挑战,即在学习潜在因子模型时个体的潜在结果可能会受到其他个体处理的影响,导致因果推断假设的违反,称为学习诱导干扰。为解决这一问题,文章提出了一种新的算法,旨在估计潜在结果的因果效应,同时减少学习诱导干扰并提升估计效率。该算法的理论保障已得到确立,并通过模拟研究及癌症突变特征分析的应用实例证明了其实用性。
Key Takeaways
- 研究关注多个领域(如基因组学、流行病学等)中因子模型或表示学习下的因果问题。
- 使用非负矩阵分解探索高维观测数据的潜在结果因果效应。
- 提出一个重要挑战:学习潜在因子模型时可能出现学习诱导干扰问题。
- 为解决学习诱导干扰问题,提出了一种新的算法,旨在估计潜在结果的因果效应并提升估计效率。
- 该算法具有理论保障,并通过模拟研究验证了其有效性。
- 该研究的应用实例展示了其在癌症突变特征分析中的实用性。
点此查看论文截图

TTRL: Test-Time Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Yuxin Zuo, Kaiyan Zhang, Li Sheng, Shang Qu, Ganqu Cui, Xuekai Zhu, Haozhan Li, Yuchen Zhang, Xinwei Long, Ermo Hua, Biqing Qi, Youbang Sun, Zhiyuan Ma, Lifan Yuan, Ning Ding, Bowen Zhou
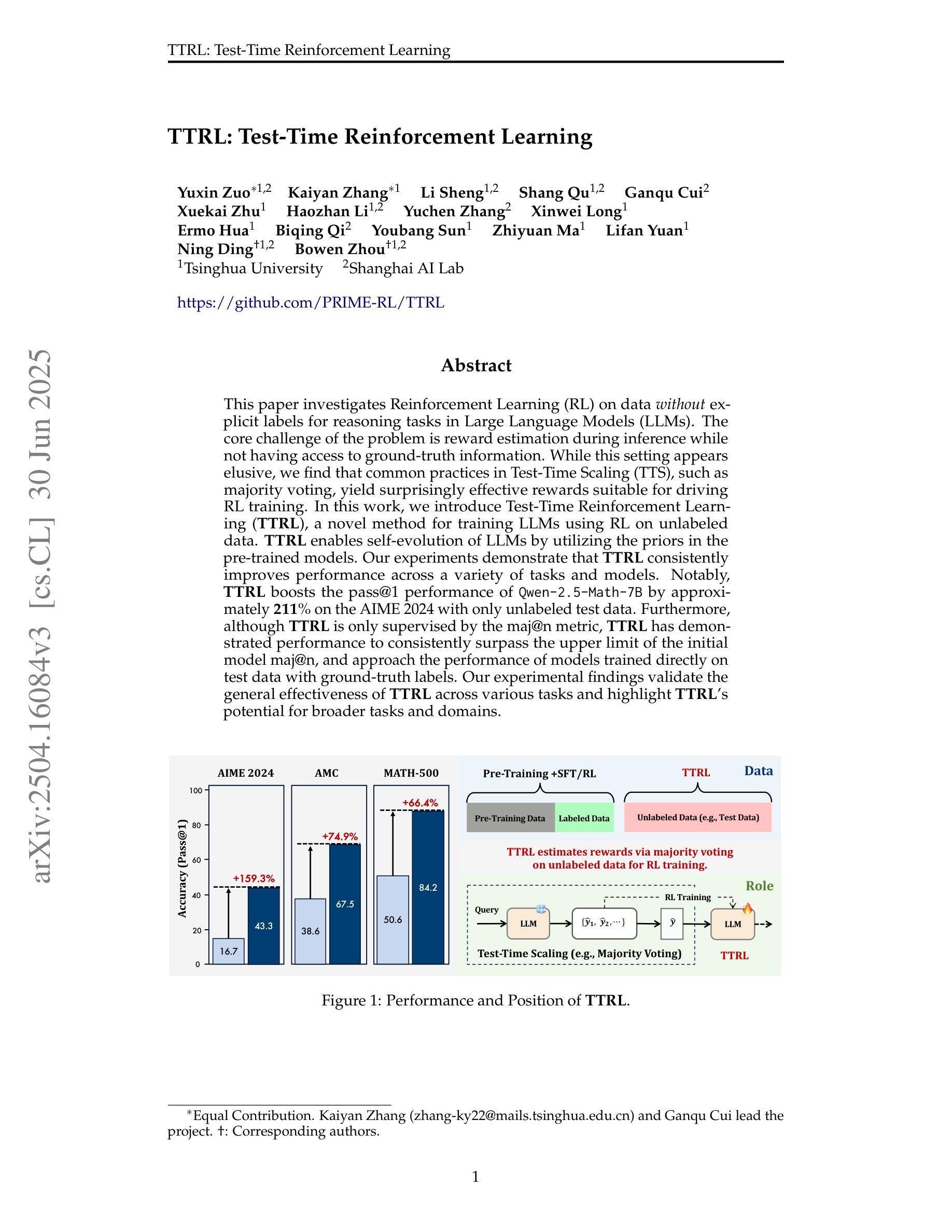
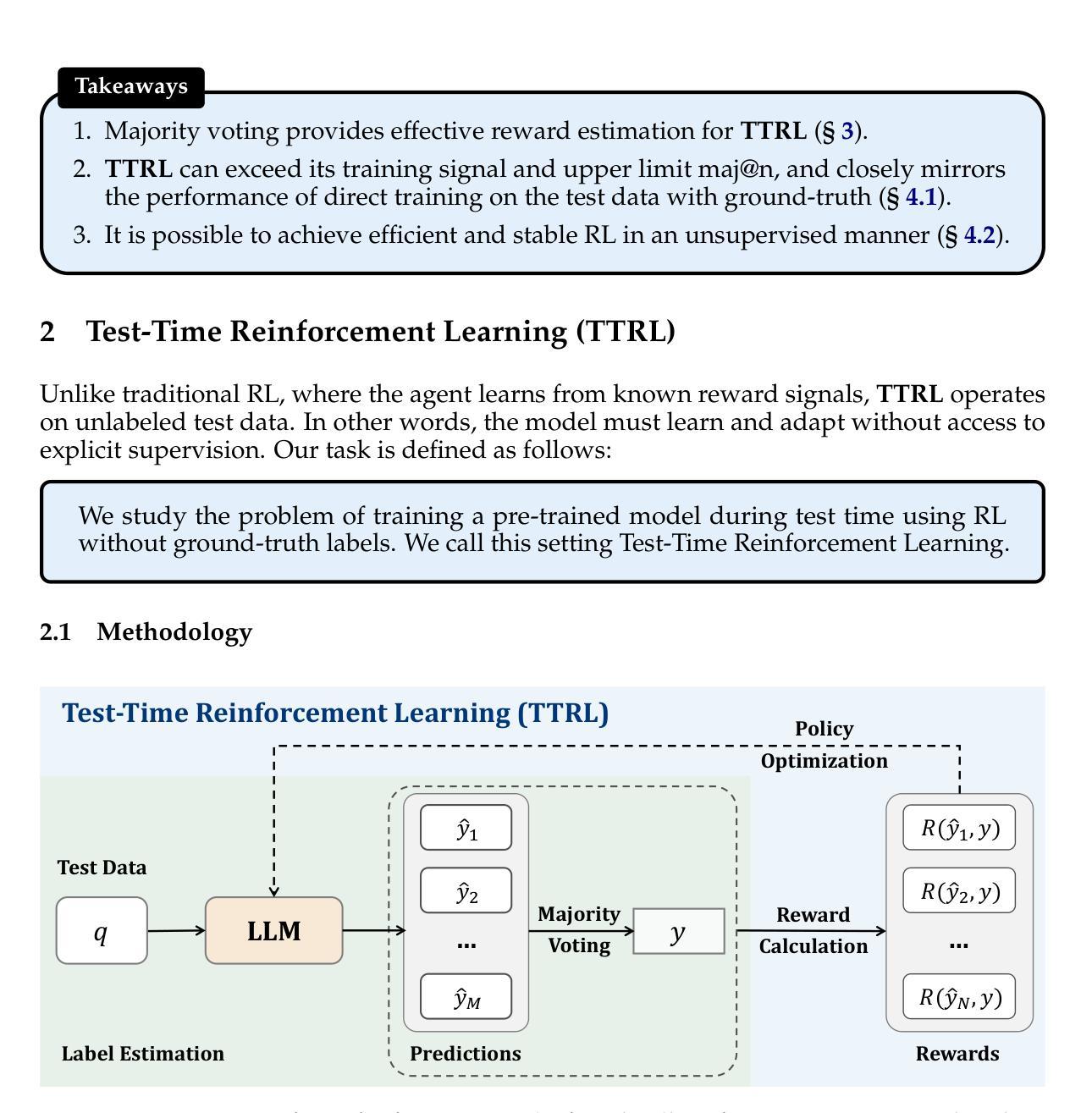
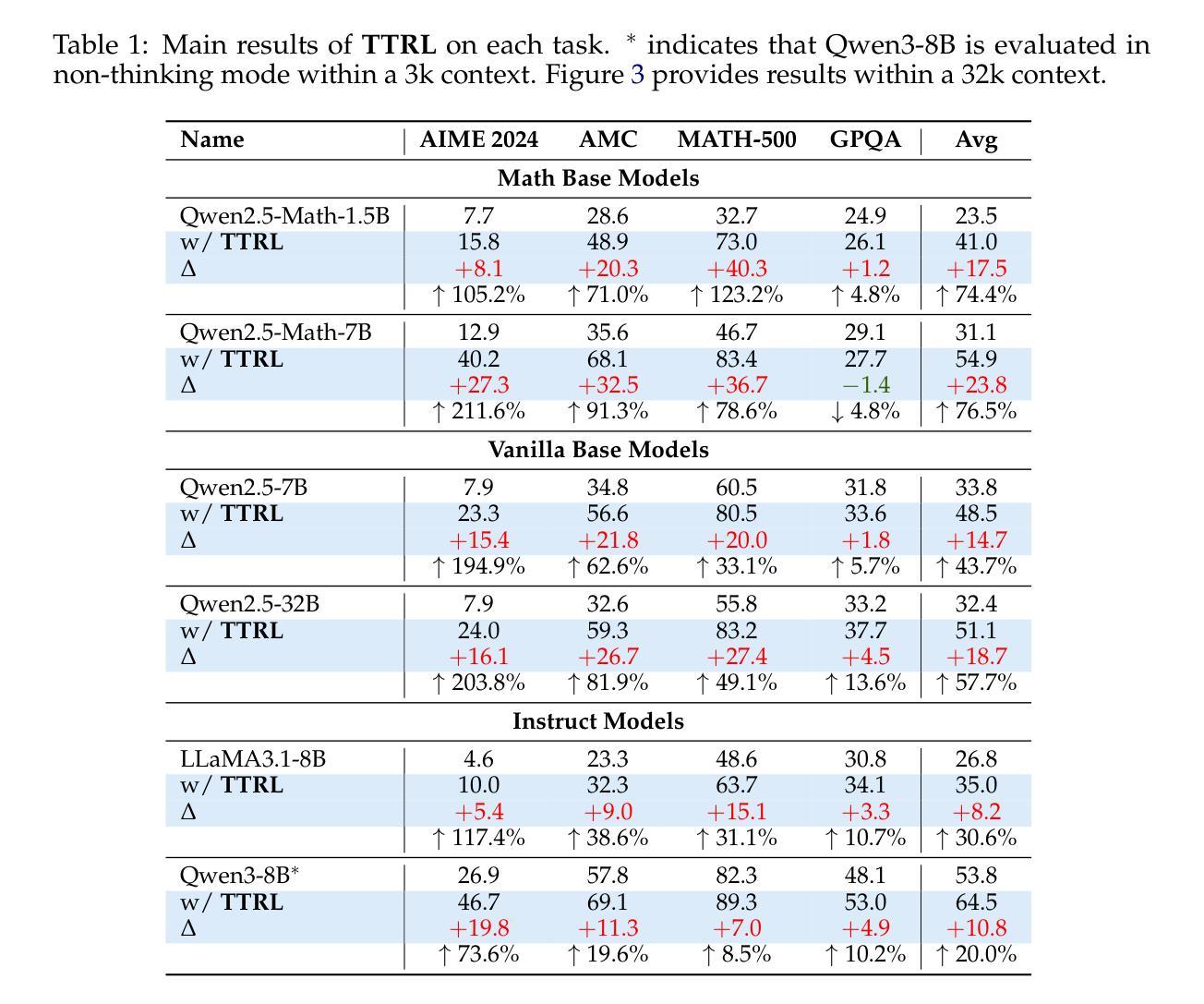
This paper investigates Reinforcement Learning (RL) on data without explicit labels for reasoning tasks in Large Language Models (LLMs). The core challenge of the problem is reward estimation during inference while not having access to ground-truth information. While this setting appears elusive, we find that common practices in Test-Time Scaling (TTS), such as majority voting, yield surprisingly effective rewards suitable for driving RL training. In this work, we introduce Test-Time Reinforcement Learning (TTRL), a novel method for training LLMs using RL on unlabeled data. TTRL enables self-evolution of LLMs by utilizing the priors in the pre-trained models. Our experiments demonstrate that TTRL consistently improves performance across a variety of tasks and models. Notably, TTRL boosts the pass@1 performance of Qwen-2.5-Math-7B by approximately 211% on the AIME 2024 with only unlabeled test data. Furthermore, although TTRL is only supervised by the maj@n metric, TTRL has demonstrated performance to consistently surpass the upper limit of the initial model maj@n, and approach the performance of models trained directly on test data with ground-truth labels. Our experimental findings validate the general effectiveness of TTRL across various tasks and highlight TTRL’s potential for broader tasks and domains. GitHub: https://github.com/PRIME-RL/TTRL
本文研究了在大语言模型(LLM)的推理任务中,在无需明确标签的数据上应用强化学习(RL)的情况。该问题的核心挑战在于推理过程中无法获得真实信息,从而无法进行奖励估算。尽管这一设置看似难以捉摸,但我们发现测试时间缩放(TTS)中的常见做法,如多数投票,会产生出人意料的有效奖励,适用于驱动RL训练。在这项工作中,我们引入了测试时间强化学习(TTRL),这是一种使用无标签数据对LLM进行RL训练的新方法。TTRL利用预训练模型中的先验知识,实现了LLM的自我进化。实验表明,TTRL在各种任务和模型上的性能持续提高。值得注意的是,在AIME 2024比赛中,TTRL将Qwen-2.5-Math-7B的pass@1性能提高了大约211%,而且这一切只在无标签的测试数据上实现。此外,尽管TTRL只受到maj@n指标的监督,但其性能已经超越了初始模型的maj@n上限,并接近直接在带有真实标签的测试数据上训练的模型性能。我们的实验结果表明了TTRL在多种任务中的普遍有效性,并突出了其在更广泛的任务和领域中的潜力。GitHub地址:https://github.com/PRIME-rl/TTRL
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
此论文探讨了在大型语言模型(LLM)的推理任务中,利用无明确标签的数据进行强化学习(RL)的方法。论文的核心挑战在于推理过程中如何估算奖励,同时无法获取真实信息。研究发现,测试时间缩放(TTS)的常见方法,如多数投票,能得出有效的奖励,适用于驱动RL训练。为此,论文提出了测试时间强化学习(TTRL)这一新方法,用于训练LLM在无标签数据上的使用。TTRL利用预训练模型中的先验知识,实现LLM的自我进化。实验表明,TTRL在各种任务和模型上的表现都有所提升。特别是在AIME 2024的Qwen-2.5-Math-7B任务中,TTRL仅使用无标签测试数据,就将pass@1性能提升了约211%。尽管TTRL只受到maj@n指标的监督,但其表现始终超过初始模型的maj@n上限,并接近直接在带有真实标签的测试数据上训练的模型性能。
Key Takeaways
- 研究解决了在大型语言模型(LLM)的推理任务中,如何在无明确标签的数据上进行强化学习(RL)的挑战。
- 提出了测试时间强化学习(TTRL)这一新方法,利用预训练模型中的先验知识,使LLM能在无标签数据上进行自我进化。
- 测试时间缩放(TTS)的常见方法,如多数投票,在TTRL中能产生有效的奖励,进而驱动RL训练。
- TTRL在各种任务上的表现都有所提升,特别是在特定任务中的性能提升显著。
- TTRL的表现超过初始模型的指标上限,并接近使用真实标签数据训练的模型性能。
- 实验结果证明了TTRL方法的有效性及其在多种任务上的潜在应用。
点此查看论文截图