⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-03 更新
A Closer Look at Conditional Prompt Tuning for Vision-Language Models
Authors:Ji Zhang, Shihan Wu, Lianli Gao, Jingkuan Song, Nicu Sebe, Heng Tao Shen
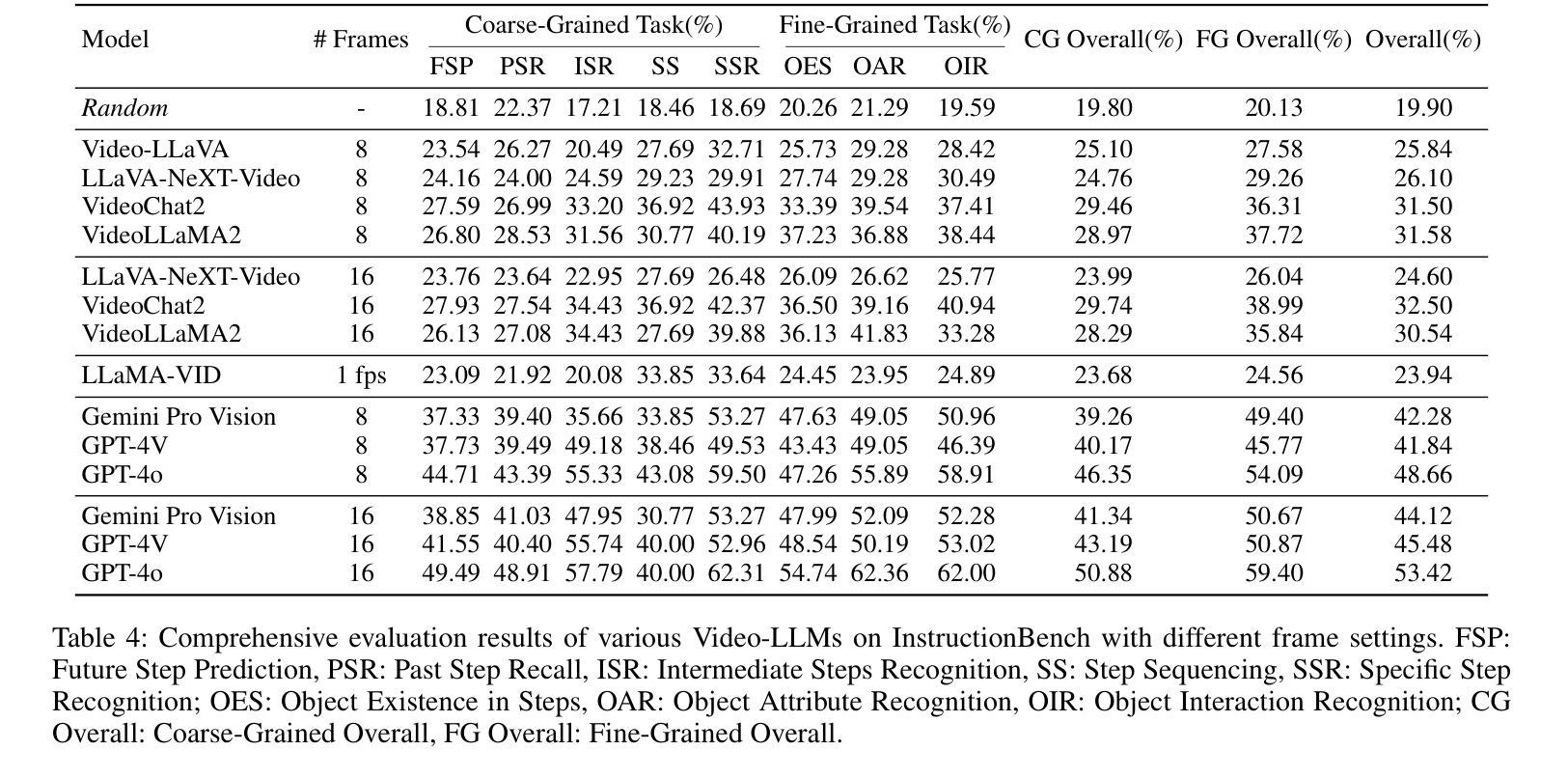
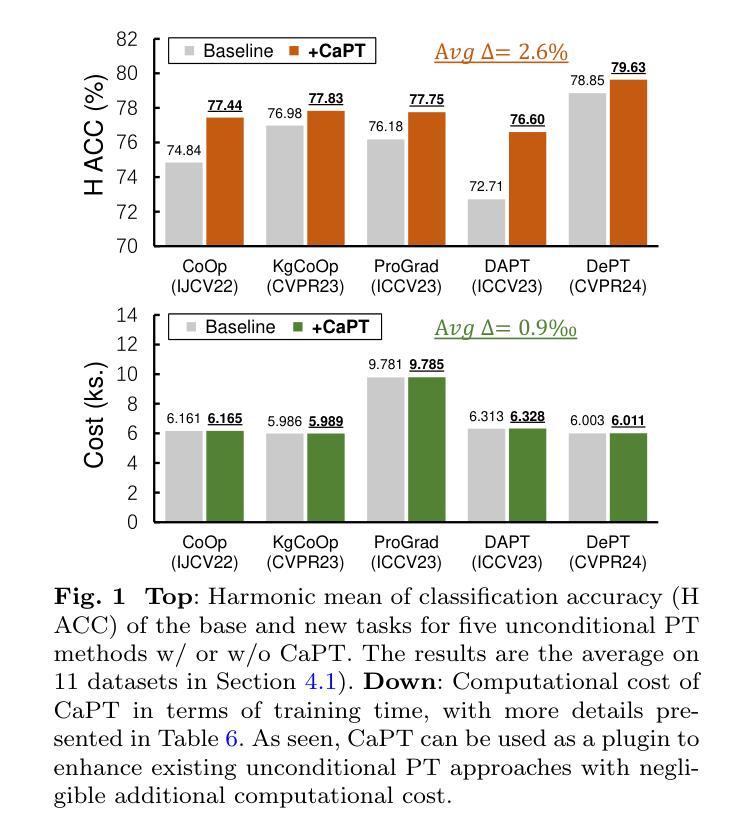
Despite the great promise of Prompt Tuning (PT) in adapting large Vision-Language Pretrained Models (VLPMs) to downstream tasks, they often struggle to overcome the Base-New Tradeoff (BNT) dilemma: as VLPMs are better tuned to a base task, their ability to generalize to new tasks diminishes. Recent work on conditional PT addresses this problem by replacing static prompts with dynamic Visual Image Information (VII)-conditioned prompts, improving the model’s generalization to new tasks to some extent. In this work, we first identify a critical issue with existing conditional PT methods: using VII as the “condition” of prompts yields suboptimal performance, and even random noise-conditioned prompts can outperform the VII-conditioned counterparts. On further analysis, we find that learning dynamic prompts conditioned on Textual Class Information (TCI) is the key to solving the BNT problem. Motivated by this, we then propose Class-adaptive Prompt Tuning (CaPT), which enables fast adaptation of tuned models to new classes by learning TCI-conditioned prompts from base classes. Remarkably, CaPT can be used as a plugin to mitigate the BNT problem for existing unconditional PT schemes. Extensive experiments on 11 datasets show that CaPT consistently improves the performance of five strong unconditional PT baselines with negligible additional computational cost. Additionally, by integrating CaPT with our recently proposed DePT framework, we devise a new conditional PT approach, termed DeCaPT, which outperforms the H ACC of the state-of-the-art conditional PT scheme by 3.49%, averaged over the 11 datasets. Code: https://github.com/Koorye/CaPT.
尽管Prompt Tuning(PT)在适应大型视觉语言预训练模型(VLPMs)到下游任务方面有着巨大的潜力,但它们往往难以克服Base-New Tradeoff(BNT)的困境:随着VLPMs对基础任务的调整越来越好,它们对新任务的泛化能力就会减弱。最近关于条件PT的研究通过用动态视觉图像信息(VII)替换静态提示来解决这个问题,在一定程度上提高了模型对新任务的泛化能力。在这项工作中,我们首先发现了现有条件PT方法的一个关键问题:使用VII作为提示的“条件”会产生次优性能,甚至噪声条件提示也能超越VII条件提示。进一步分析后,我们发现学习基于文本类别信息(TCI)的动态提示是解决BNT问题的关键。受此启发,我们随后提出了类自适应提示调整(CaPT),它通过从基础类别中学习TCI条件提示,实现了快速适应新类别。令人惊讶的是,CaPT可以作为插件用于缓解现有无条件PT方案的BNT问题。在11个数据集上的大量实验表明,CaPT能够持续提高五个强大的无条件PT基准测试的性能,并且只需很小的额外计算成本。此外,通过将CaPT与我们最近提出的DePT框架相结合,我们设计了一种新的条件PT方法,称为DeCaPT,它在11个数据集上的平均高级准确度高出了现有最先进的条件PT方案3.49%。代码地址:https://github.com/Koorye/CaPT。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages
摘要
本文指出基于视觉语言预训练模型的提示调节(PT)在基础任务上的优势与新任务上的局限。为了解决基础新任务权衡(BNT)问题,本研究发现条件PT方法中,将视觉图像信息作为提示的条件效果不佳。对此问题,本研究提出类自适应提示调节(CaPT),通过从基础类学习文本类信息(TCI)条件化提示来解决BNT问题。该方法能快速适应新类并应用于无条件PT方案作为插件来减少BNT问题的影响。在多个数据集上的实验表明,CaPT能有效提升五个无条件PT基线模型的性能,且额外计算成本较小。整合CaPT与最新提出的DePT框架后得到的DeCaPT新方法,相较于当前先进条件PT方案的平均高精度率提升3.49%。
关键见解
- 提示调节(PT)在视觉语言预训练模型(VLPMs)中存在基础新任务权衡(BNT)问题。
- 使用视觉图像信息(VII)作为条件提示的效果不佳,随机噪声条件提示效果更佳。
- 解决BNT问题的关键在于学习基于文本类信息(TCI)的动态提示。
- 提出类自适应提示调节(CaPT),能快速适应新类并增强模型的性能表现。
- CaPT可以作为一个插件,用于解决无条件PT方案中的BNT问题。
- 实验结果显示,CaPT与现有无条件PT基线结合时,能显著提高性能且增加的计算成本较小。
- 结合CaPT与DePT框架的新方法DeCaPT在多个数据集上超越现有条件PT方案的表现。
点此查看论文截图

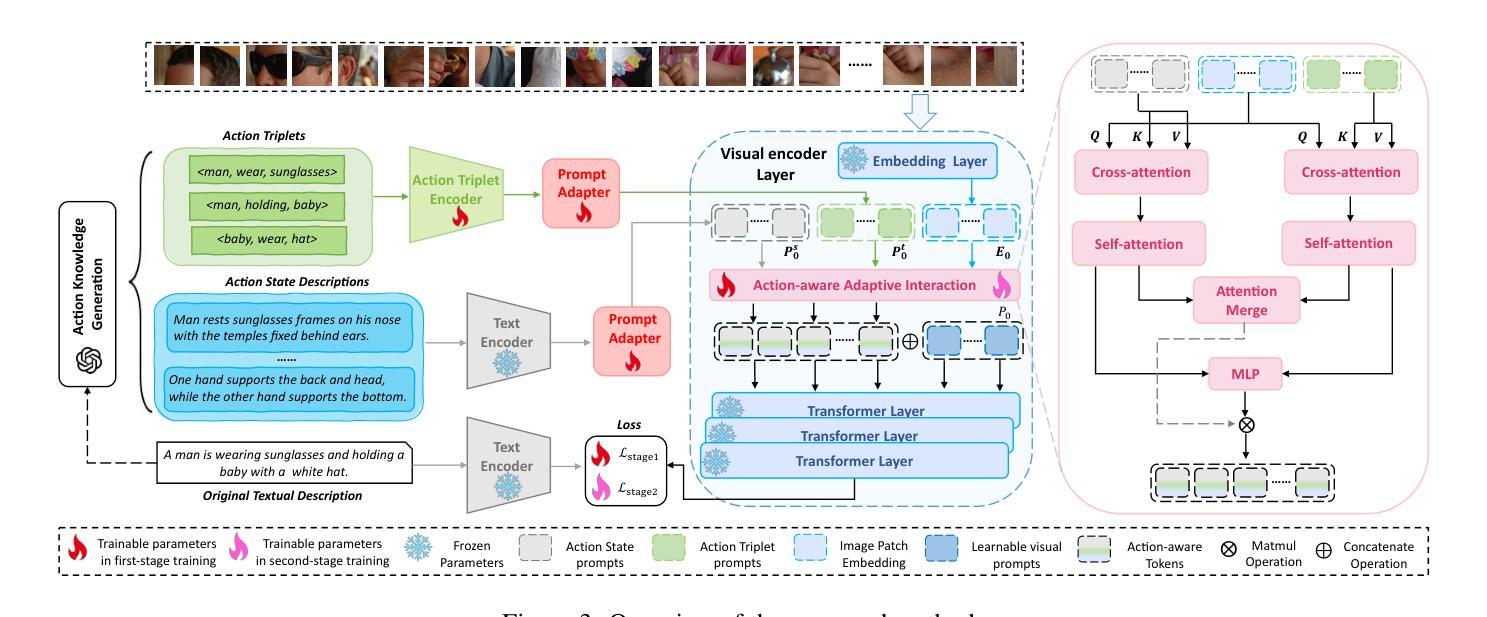
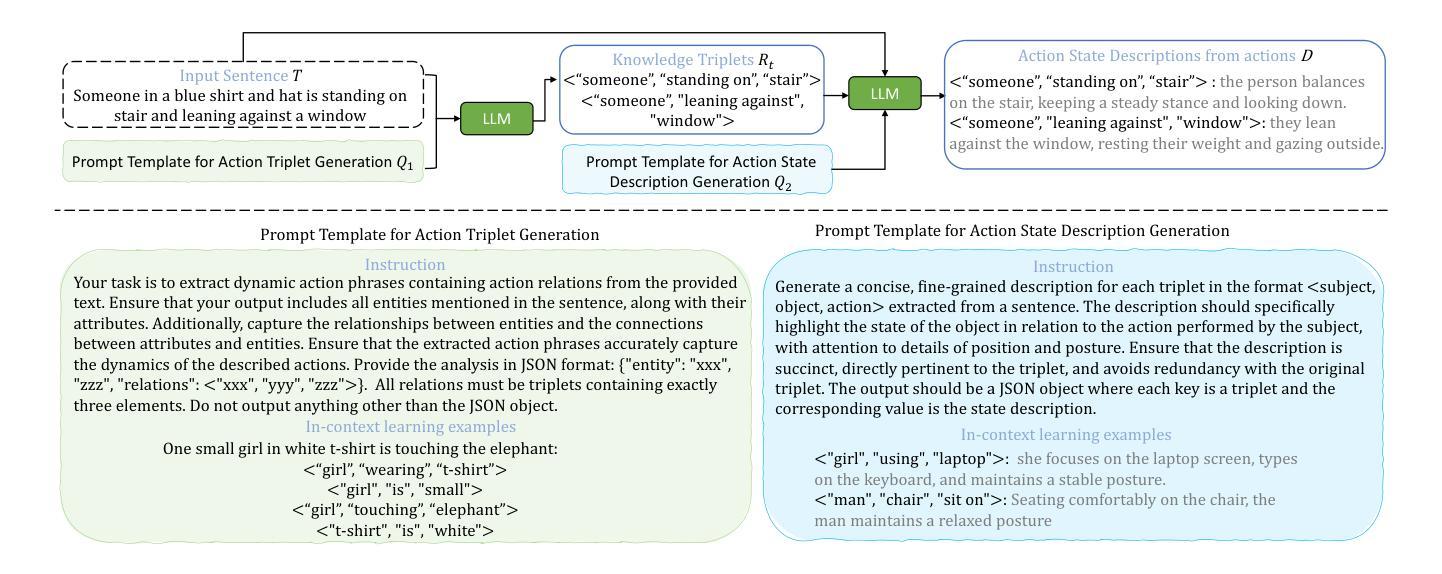
LLM-enhanced Action-aware Multi-modal Prompt Tuning for Image-Text Matching
Authors:Mengxiao Tian, Xinxiao Wu, Shuo Yang
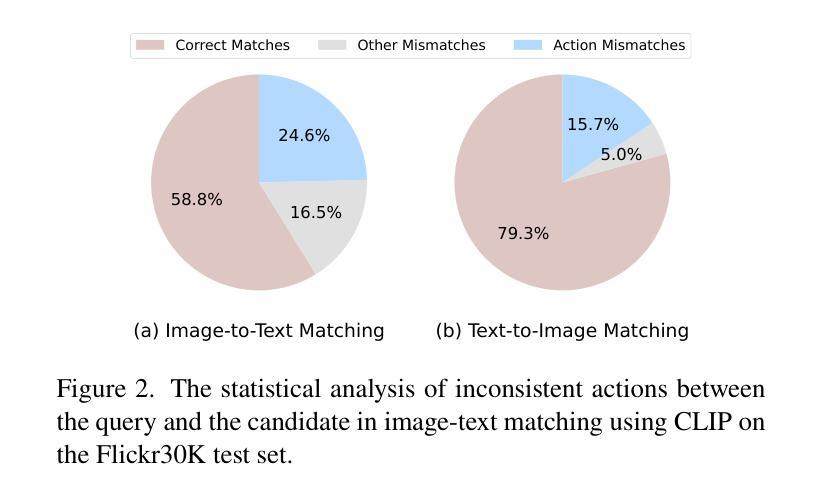
Driven by large-scale contrastive vision-language pre-trained models such as CLIP, recent advancements in the image-text matching task have achieved remarkable success in representation learning. Due to image-level visual-language alignment, CLIP falls short in understanding fine-grained details such as object attributes and spatial relationships between objects. Recent efforts have attempted to compel CLIP to acquire structured visual representations by introducing prompt learning to achieve object-level alignment. While achieving promising results, they still lack the capability to perceive actions, which are crucial for describing the states or relationships between objects. Therefore, we propose to endow CLIP with fine-grained action-level understanding by introducing an LLM-enhanced action-aware multi-modal prompt-tuning method, incorporating the action-related external knowledge generated by large language models (LLMs). Specifically, we design an action triplet prompt and an action state prompt to exploit compositional semantic knowledge and state-related causal knowledge implicitly stored in LLMs. Subsequently, we propose an adaptive interaction module to aggregate attentive visual features conditioned on action-aware prompted knowledge for establishing discriminative and action-aware visual representations, which further improves the performance. Comprehensive experimental results on two benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our method.
由大型对比视觉语言预训练模型(如CLIP)驱动,图像文本匹配任务的最新进展在表示学习中取得了显著的成功。由于图像级别的视觉语言对齐,CLIP在理解对象的属性等细微细节以及对象之间的空间关系方面存在不足。近期的研究尝试通过引入提示学习来迫使CLIP获得结构化视觉表示,以实现对象级别的对齐,并取得了一定的成果。虽然在描述对象状态或关系方面取得了有希望的成果,但它们仍然缺乏感知动作的能力,这对于描述对象之间的关系至关重要。因此,我们提出了一种通过引入大型语言模型增强的动作感知多模式提示调整方法,为CLIP赋予精细的动作级别理解。具体而言,我们设计了一个动作三元组提示和一个动作状态提示,以利用大型语言模型中隐含的组成语义知识和状态相关因果关系知识。随后,我们提出了一个自适应交互模块,该模块根据动作感知提示知识聚合注意力视觉特征,以建立具有鉴别力和动作感知的视觉表示,这进一步提高了性能。在两个基准数据集上的综合实验结果证明了我们的方法的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted by ICCV 2025
Summary
基于CLIP的大型对比视觉语言预训练模型在图像文本匹配任务中取得了显著成功,但在理解对象属性、对象间空间关系等细节方面存在不足。为弥补这一缺陷,近期研究尝试引入提示学习来促使CLIP获取结构化视觉表征,实现对象级别的对齐。尽管取得了有前景的结果,但仍缺乏感知动作的能力,这对描述对象状态或关系至关重要。因此,我们提出了一种增强型的动作感知多模态提示调节方法,结合大型语言模型(LLM)产生的动作相关外部知识。通过设计动作三元组提示和动作状态提示来利用LLM中隐含的组成语义知识和状态相关因果知识。此外,我们提出了自适应交互模块,根据动作感知提示知识聚合注意视觉特征,建立有鉴别力和动作感知的视觉表征,进一步提高性能。
Key Takeaways
- 基于CLIP的大型对比视觉语言预训练模型在图像文本匹配任务中表现优秀。
- CLIP在理解图像细节(如对象属性、空间关系)方面存在不足。
- 引入提示学习有助于实现对象级别的对齐,提升结构化视觉表征的获取。
- 现有方法缺乏感知动作的能力,这影响了描述对象状态或关系的准确性。
- 提出了一种结合大型语言模型的LLM增强型动作感知多模态提示调节方法。
- 通过动作三元组提示和动作状态提示利用LLM中的组成语义和状态相关因果知识。
- 自适应交互模块能提高动作感知视觉表征的建立和性能。
点此查看论文截图

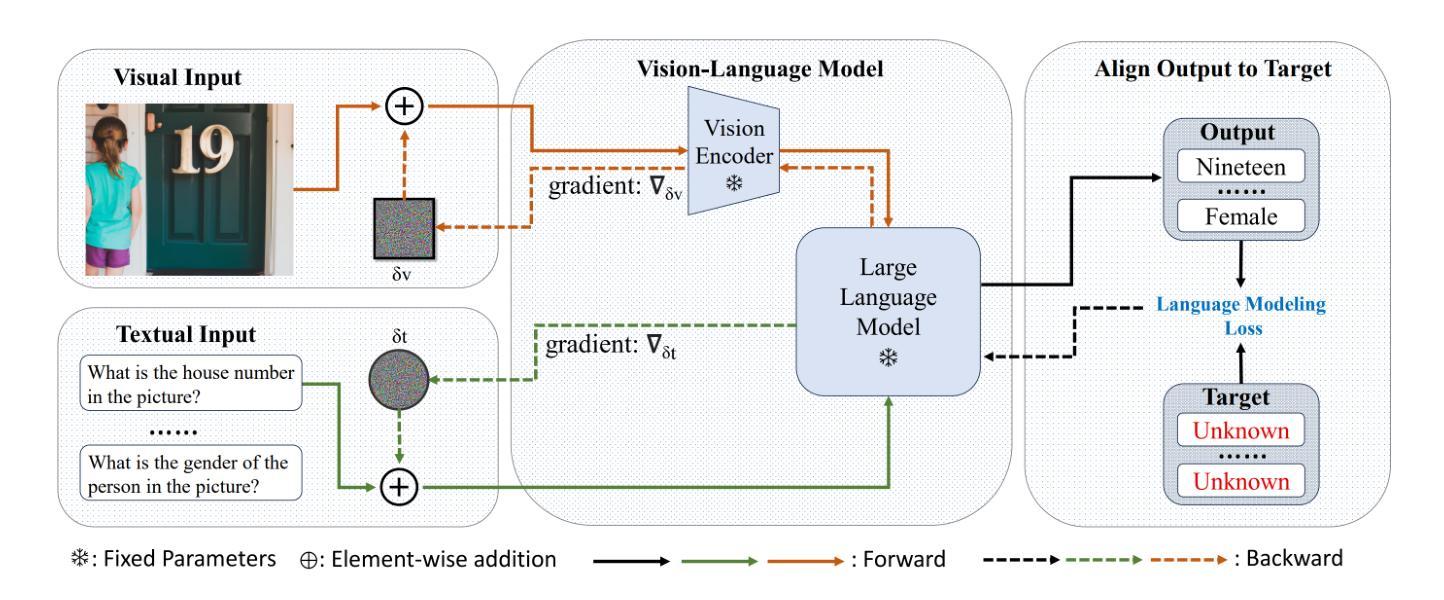
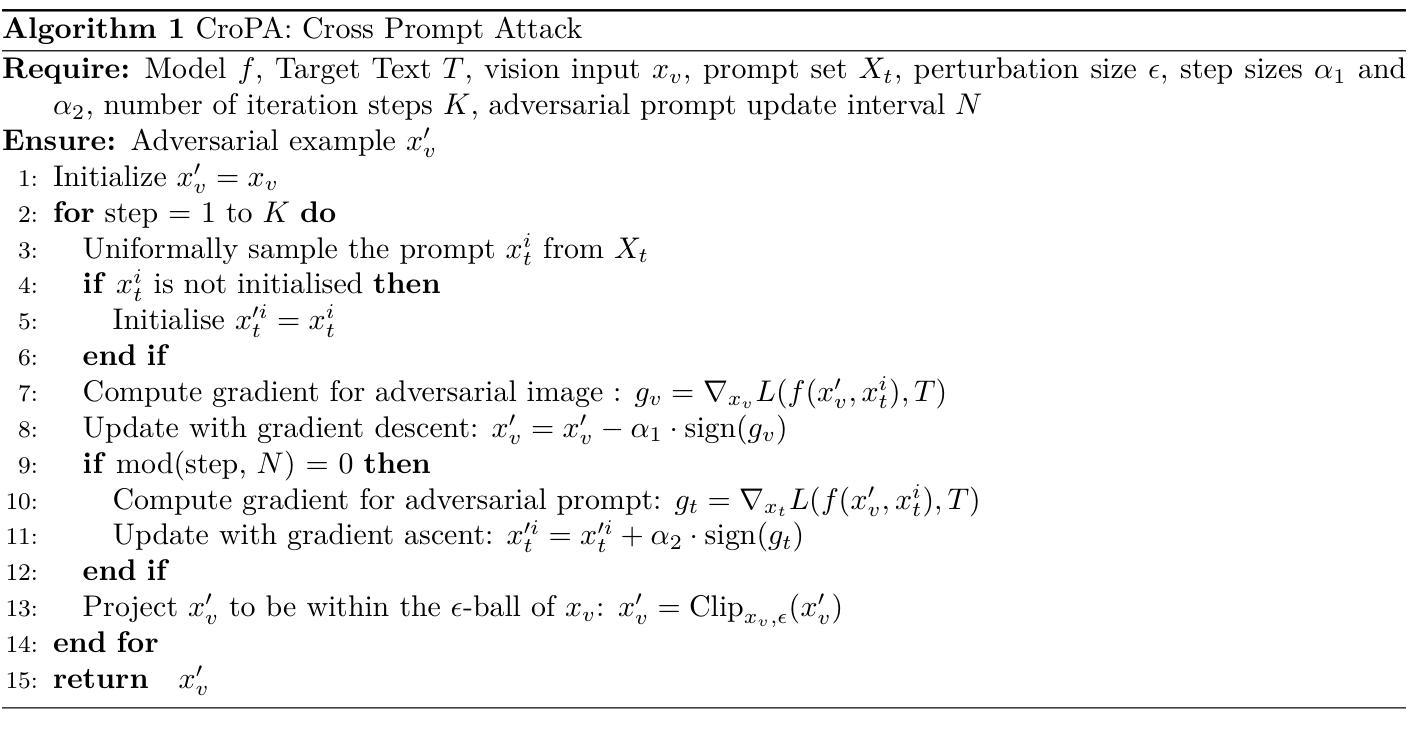
Revisiting CroPA: A Reproducibility Study and Enhancements for Cross-Prompt Adversarial Transferability in Vision-Language Models
Authors:Atharv Mittal, Agam Pandey, Amritanshu Tiwari, Sukrit Jindal, Swadesh Swain
Large Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have revolutionized computer vision, enabling tasks such as image classification, captioning, and visual question answering. However, they remain highly vulnerable to adversarial attacks, particularly in scenarios where both visual and textual modalities can be manipulated. In this study, we conduct a comprehensive reproducibility study of “An Image is Worth 1000 Lies: Adversarial Transferability Across Prompts on Vision-Language Models” validating the Cross-Prompt Attack (CroPA) and confirming its superior cross-prompt transferability compared to existing baselines. Beyond replication we propose several key improvements: (1) A novel initialization strategy that significantly improves Attack Success Rate (ASR). (2) Investigate cross-image transferability by learning universal perturbations. (3) A novel loss function targeting vision encoder attention mechanisms to improve generalization. Our evaluation across prominent VLMs – including Flamingo, BLIP-2, and InstructBLIP as well as extended experiments on LLaVA validates the original results and demonstrates that our improvements consistently boost adversarial effectiveness. Our work reinforces the importance of studying adversarial vulnerabilities in VLMs and provides a more robust framework for generating transferable adversarial examples, with significant implications for understanding the security of VLMs in real-world applications.
大型视觉语言模型(VLMs)已经彻底改变了计算机视觉领域,能够完成图像分类、描述和视觉问答等任务。然而,它们仍然非常容易受到对抗性攻击的威胁,特别是在视觉和文本模式都可以被操纵的场景中。在这项研究中,我们对“一张图片胜过千谎万语:视觉语言模型上跨提示的对抗性迁移攻击”(An Image is Worth 1000 Lies: Adversarial Transferability Across Prompts on Vision-Language Models)进行了全面的可重复性研究,验证了跨提示攻击(CroPA)并确认其在跨提示迁移方面相比现有基线具有优越性。除了复制之外,我们还提出了几项关键改进:(1)一种新型初始化策略,可以显著提高攻击成功率(ASR)。(2)通过学习通用扰动来研究跨图像迁移性。(3)针对视觉编码器注意力机制的新型损失函数,以提高泛化能力。我们对知名的VLMs(包括Flamingo、BLIP-2和InstructBLIP)以及LLaVA上的扩展实验进行了评估,验证了原始结果,并证明我们的改进在提升对抗性效果方面表现稳定。我们的工作强调了研究VLMs的对抗脆弱性的重要性,并为生成可迁移的对抗性示例提供了更稳健的框架,对于理解VLMs在现实世界应用中的安全性具有重要意义。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to MLRC 2025
Summary
大型视觉语言模型(VLMs)在图像分类、描述和视觉问答等任务中具有卓越表现,但也面临着对抗攻击的风险,特别是在视觉和文字模态均可被操纵的场景下。本研究对“An Image is Worth 1000 Lies”中的Cross-Prompt攻击进行了可复现性研究,验证了其跨提示的优越转移性。在此基础上,我们提出了几项关键改进:新型初始化策略,显著提高攻击成功率;通过学习通用扰动研究跨图像转移性;针对视觉编码器注意力机制的新型损失函数,提高泛化能力。在Flamingo、BLIP-2、InstructBLIP等主流VLMs及LLaVA上的扩展实验验证了我们的改进,提升了对抗攻击的效果,对理解VLMs在现实应用中的安全性具有重要意义。
Key Takeaways
- 大型视觉语言模型(VLMs)在多个任务中表现出卓越性能,但易受对抗攻击影响,特别是在视觉和文字模态均可操纵的情境中。
- 本研究成功复现了Cross-Prompt攻击,并验证了其跨提示的优越转移性。
- 提出了新型初始化策略,能显著提高攻击成功率。
- 研究了跨图像转移性,通过引入通用扰动实现。
- 针对视觉编码器的新型损失函数设计,该函数主要关注注意力机制,以提高模型泛化能力。
- 在多个主流VLMs上的实验证明,改进后的攻击策略有效提升了对抗攻击效果。
点此查看论文截图

Attention to Burstiness: Low-Rank Bilinear Prompt Tuning
Authors:Yuzhu Wang, Manni Duan, Shu Kong
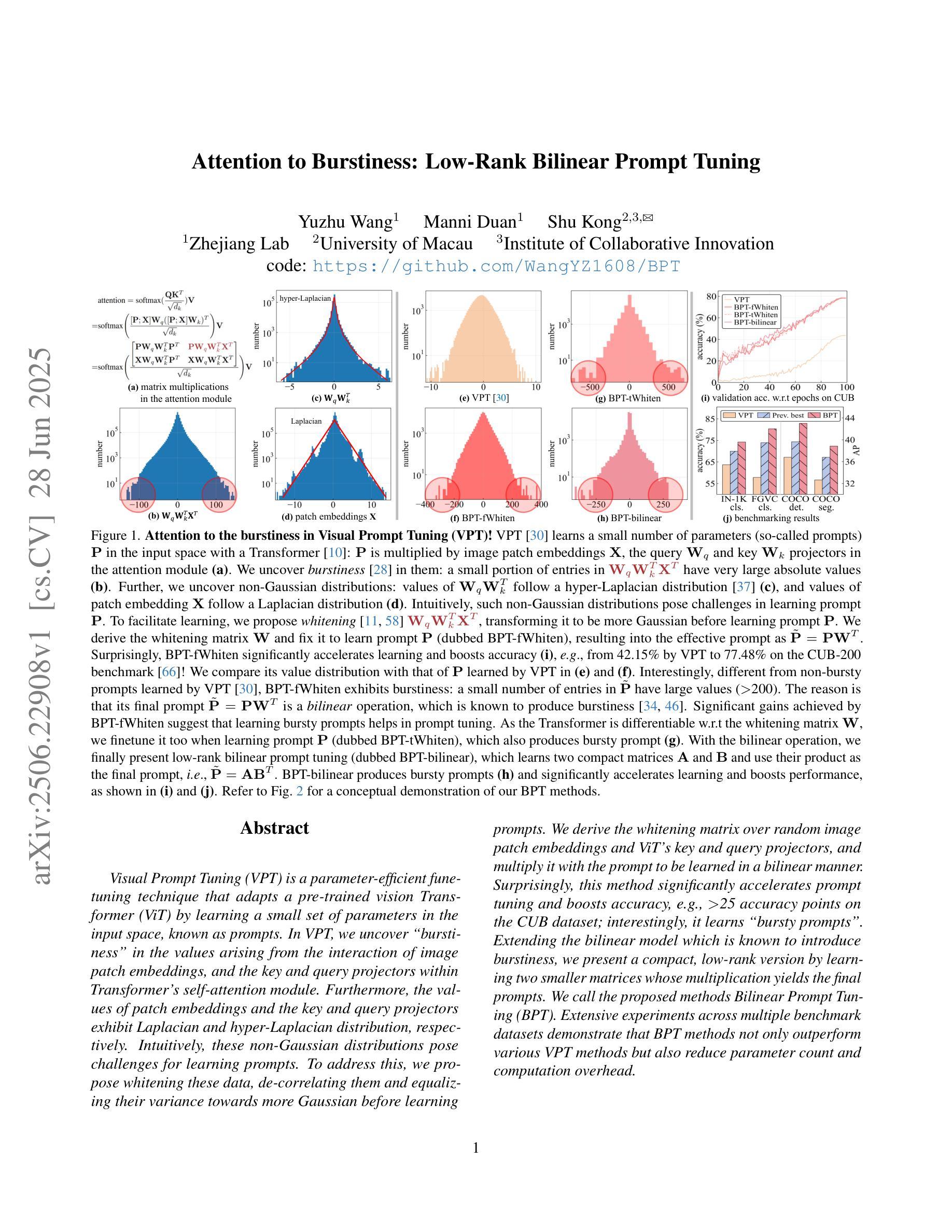
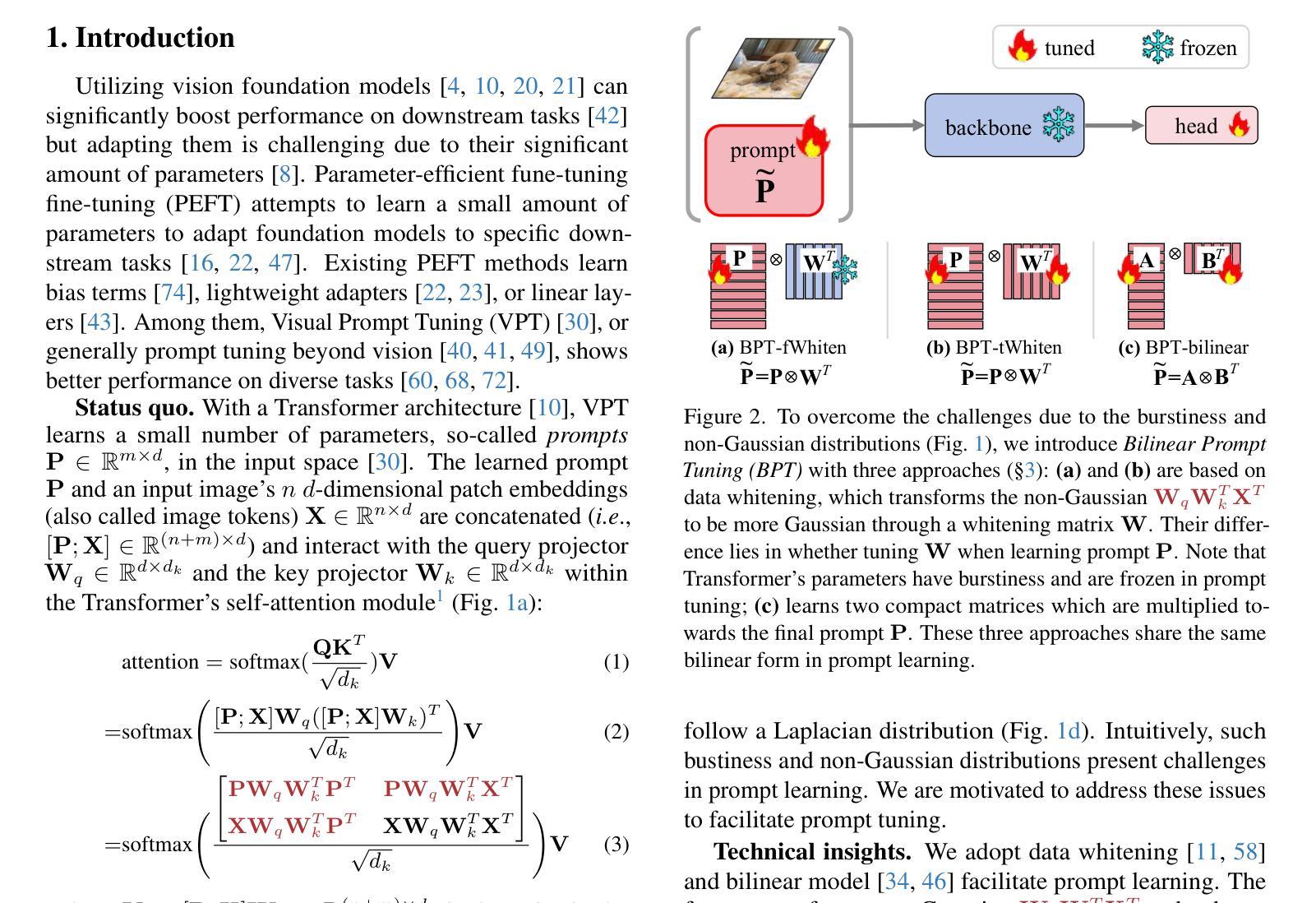
Visual Prompt Tuning (VPT) is a parameter-efficient fune-tuning technique that adapts a pre-trained vision Transformer (ViT) by learning a small set of parameters in the input space, known as prompts. In VPT, we uncover burstiness'' in the values arising from the interaction of image patch embeddings, and the key and query projectors within Transformer's self-attention module. Furthermore, the values of patch embeddings and the key and query projectors exhibit Laplacian and hyper-Laplacian distribution, respectively. Intuitively, these non-Gaussian distributions pose challenges for learning prompts. To address this, we propose whitening these data, de-correlating them and equalizing their variance towards more Gaussian before learning prompts. We derive the whitening matrix over random image patch embeddings and ViT's key and query projectors, and multiply it with the prompt to be learned in a bilinear manner. Surprisingly, this method significantly accelerates prompt tuning and boosts accuracy, e.g., $>$25 accuracy points on the CUB dataset; interestingly, it learns bursty prompts’’. Extending the bilinear model which is known to introduce burstiness, we present a compact, low-rank version by learning two smaller matrices whose multiplication yields the final prompts. We call the proposed methods Bilinear Prompt Tuning (BPT). Extensive experiments across multiple benchmark datasets demonstrate that BPT methods not only outperform various VPT methods but also reduce parameter count and computation overhead.
视觉提示微调(VPT)是一种参数高效的微调技术,它通过在学习输入空间中的一小部分参数(称为提示)来适应预训练的视觉Transformer(ViT)。在VPT中,我们发现了图像补丁嵌入交互所产生的值中的“突发性”,以及Transformer自注意力模块中的键和查询投影器。此外,补丁嵌入的值和键以及查询投影器分别呈现出拉普拉斯和超拉普拉斯分布。直观地说,这些非高斯分布给学习提示带来了挑战。为了解决这一问题,我们提出对这些数据进行白化,去除其相关性,并在学习提示之前使其方差更接近高斯分布。我们在随机图像补丁嵌入和ViT的键和查询投影器上推导了白化矩阵,并将其与以双线性方式学习的提示相乘。令人惊讶的是,这种方法显著加速了提示调整,并提高了准确性,例如在CUB数据集上的准确性提高了超过25个百分点;有趣的是,它学习了“突发性的提示”。在已知会引入突发性的双线性模型的基础上,我们提出了一个紧凑、低阶的版本,通过学习两个较小的矩阵,其乘积产生最终的提示。我们将所提出的方法称为双线性提示微调(BPT)。在多个基准数据集上的广泛实验表明,BPT方法不仅优于各种VPT方法,而且减少了参数计数和计算开销。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025
摘要
视觉提示调整(VPT)是一种参数高效的微调技术,它通过学习被称为提示的少量参数来适应预训练的视觉Transformer(ViT)。在VPT中,我们发现了图像补丁嵌入值的“爆发性”,以及Transformer自注意力模块中的键和查询投影仪与其之间的交互。补丁嵌入值、键和查询投影仪的值呈现出拉普拉斯和超拉普拉斯分布。为了应对这些非高斯分布对学习提示的挑战,我们提出对数据进行白化,去相关并均衡其方差以更接近高斯分布。我们通过随机图像补丁嵌入和ViT的键、查询投影仪来推导白化矩阵,并以双线性方式将其与待学习的提示相乘。这种方法显著加速了提示调整并提高了准确性,例如在CUB数据集上提高了超过25个准确性点。通过扩展已知会引入爆发性的双线性模型,我们提出了一个紧凑、低阶的版本,通过学习两个较小的矩阵,其乘积产生最终的提示。我们将所提出的方法称为双线性提示调整(BPT)。在多个基准数据集上的实验表明,BPT方法不仅优于各种VPT方法,而且减少了参数计数和计算开销。
关键见解
- 视觉提示调整(VPT)是一种参数高效的微调技术,通过适应预训练的视觉Transformer来优化提示。
- 在VPT中发现了图像补丁嵌入值的“爆发性”,以及Transformer自注意力模块中键和查询投影仪与之间的交互带来的挑战。
- 非高斯分布在提示学习中产生问题,需要通过数据白化、去相关和方差均衡来应对。
- 提出了一种基于随机图像补丁嵌入和ViT的键、查询投影仪的白化矩阵推导方法。
- 双线性提示调整(BPT)显著加速了提示调整过程并提高了准确性,如CUB数据集上的准确度提升超过25点。
- BPT扩展了双线性模型,引入了一个紧凑、低阶的版本,通过较小的矩阵学习产生最终提示。
点此查看论文截图
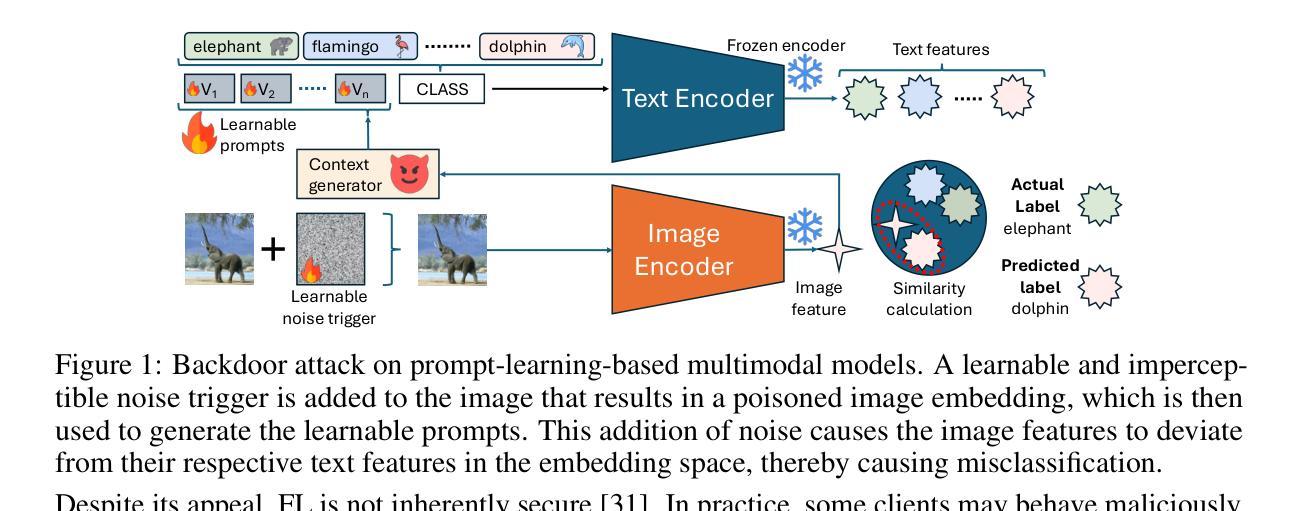
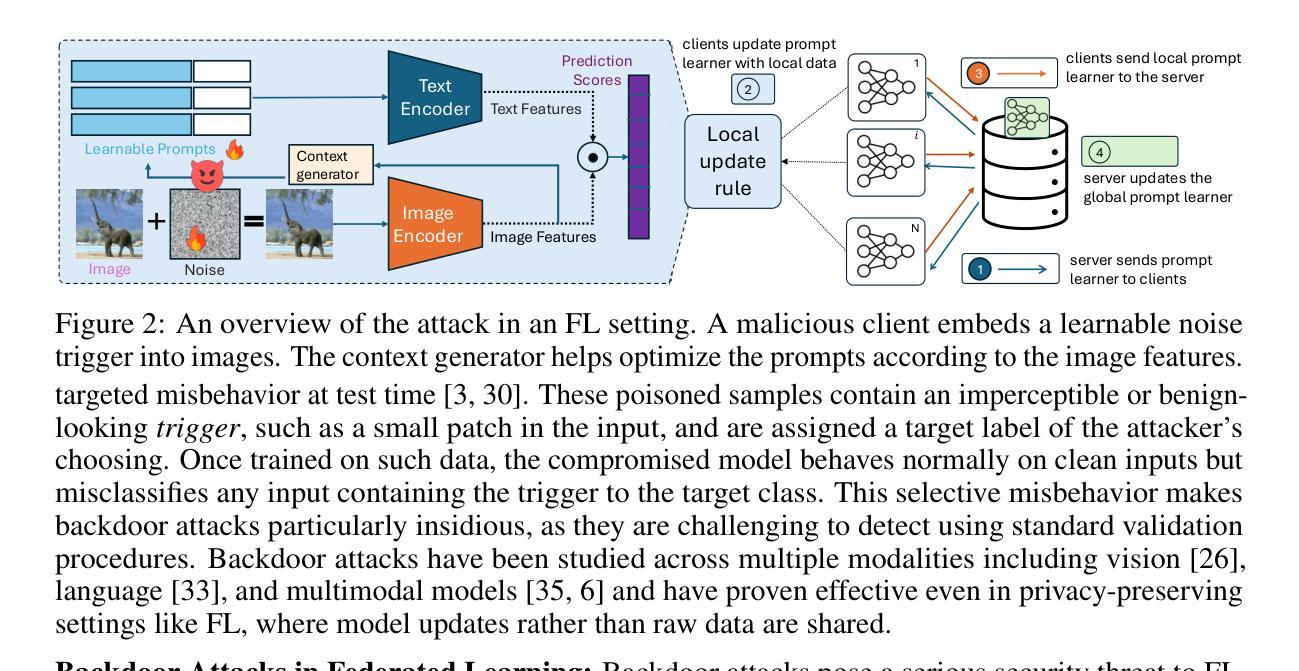
SABRE-FL: Selective and Accurate Backdoor Rejection for Federated Prompt Learning
Authors:Momin Ahmad Khan, Yasra Chandio, Fatima Muhammad Anwar
Federated Prompt Learning has emerged as a communication-efficient and privacy-preserving paradigm for adapting large vision-language models like CLIP across decentralized clients. However, the security implications of this setup remain underexplored. In this work, we present the first study of backdoor attacks in Federated Prompt Learning. We show that when malicious clients inject visually imperceptible, learnable noise triggers into input images, the global prompt learner becomes vulnerable to targeted misclassification while still maintaining high accuracy on clean inputs. Motivated by this vulnerability, we propose SABRE-FL, a lightweight, modular defense that filters poisoned prompt updates using an embedding-space anomaly detector trained offline on out-of-distribution data. SABRE-FL requires no access to raw client data or labels and generalizes across diverse datasets. We show, both theoretically and empirically, that malicious clients can be reliably identified and filtered using an embedding-based detector. Across five diverse datasets and four baseline defenses, SABRE-FL outperforms all baselines by significantly reducing backdoor accuracy while preserving clean accuracy, demonstrating strong empirical performance and underscoring the need for robust prompt learning in future federated systems.
联邦提示学习(Federated Prompt Learning)已成为在分布式客户端上适应大型视觉语言模型(如CLIP)的一种通信效率高且保护隐私的范式。然而,该设置的安全影响尚未得到充分探索。在这项工作中,我们对联邦提示学习中的后门攻击进行了首次研究。我们发现,当恶意客户端将视觉不可察觉的可学习噪声触发器注入输入图像时,全局提示学习者会容易受到有针对性的误分类的影响,同时仍能在干净输入上保持高准确性。受此漏洞的启发,我们提出了SABRE-FL,这是一种轻量级的模块化防御方法,它通过利用在离线训练于离群分布数据上的嵌入空间异常检测器来过滤中毒提示更新。SABRE-FL无需访问原始客户端数据或标签,并且可以在各种数据集上进行泛化。我们从理论和实践两方面证明,使用基于嵌入的检测器可以可靠地识别和过滤恶意客户端。在五个不同的数据集和四个基线防御措施中,SABRE-FL显著减少了后门准确性同时保持了清洁准确性,表现出强大的实际性能和在未来联邦系统中对稳健提示学习的需求。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
联邦提示学习(Federated Prompt Learning)是适应分布式客户端的大型视觉语言模型(如CLIP)的一种通信高效且隐私保护的方法。然而,该设置的安全影响尚未得到充分探索。本研究首次研究了联邦提示学习中的后门攻击。我们发现,当恶意客户端向输入图像注入视觉不可察觉的可学习噪声触发器时,全局提示学习者仍然对干净输入保持高准确率的同时容易受到目标误分类的攻击。针对这一漏洞,我们提出了SABRE-FL,这是一种轻量级的模块化防御方法,它通过利用离线训练于非分布数据的嵌入空间异常检测器来过滤有毒的提示更新。SABRE-FL无需访问原始客户端数据或标签,并在多个数据集上表现通用性。我们理论及实证地证明,使用基于嵌入的检测器可以可靠地识别并过滤恶意客户端。在五个不同的数据集和四个基准防御策略上,SABRE-FL显著降低了后门准确性同时保持了对清洁数据的准确性,显示出强大的表现并强调未来联邦系统中稳健提示学习的必要性。
Key Takeaways
- 联邦提示学习是一种用于在分布式客户端上适应大型视觉语言模型的新范式。
- 联邦提示学习中存在后门攻击的安全隐患。
- 恶意客户端可以通过注入视觉不可察觉的噪声触发器来影响全局提示学习者的准确性。
- SABRE-FL是一种新的防御策略,它通过嵌入空间异常检测器来过滤有毒的提示更新。
- SABRE-FL无需访问原始客户端数据或标签,且在多个数据集上具有通用性。
- 使用基于嵌入的检测器可以可靠地识别和过滤恶意客户端。
点此查看论文截图

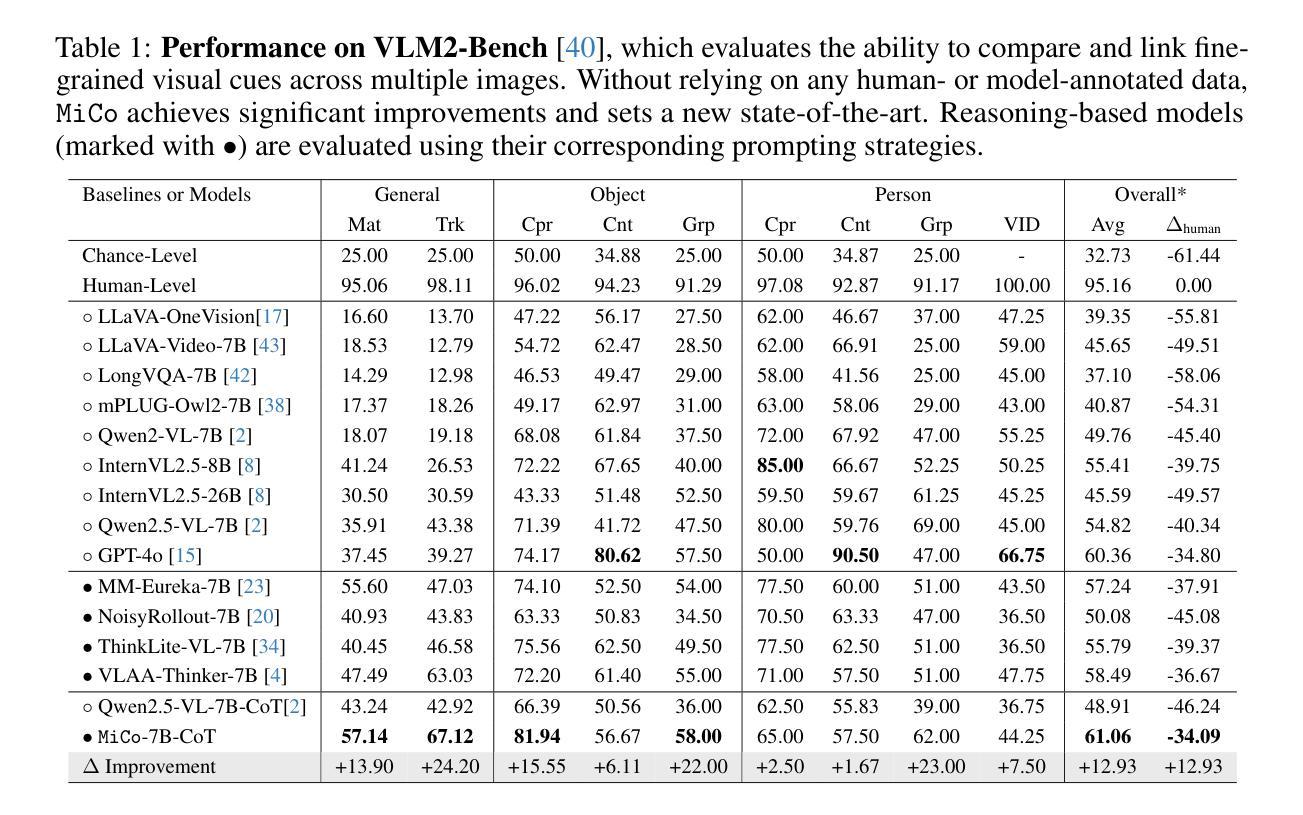
MiCo: Multi-image Contrast for Reinforcement Visual Reasoning
Authors:Xi Chen, Mingkang Zhu, Shaoteng Liu, Xiaoyang Wu, Xiaogang Xu, Yu Liu, Xiang Bai, Hengshuang Zhao
This work explores enabling Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning to link visual cues across multiple images. A straightforward solution is to adapt rule-based reinforcement learning for Vision-Language Models (VLMs). However, such methods typically rely on manually curated question-answer pairs, which can be particularly challenging when dealing with fine grained visual details and complex logic across images. Inspired by self-supervised visual representation learning, we observe that images contain inherent constraints that can serve as supervision. Based on this insight, we construct image triplets comprising two augmented views of the same image and a third, similar but distinct image. During training, the model is prompted to generate a reasoning process to compare these images (i.e., determine same or different). Then we optimize the model with rule-based reinforcement learning. Due to the high visual similarity and the presence of augmentations, the model must attend to subtle visual changes and perform logical reasoning to succeed. Experiments show that, although trained solely on visual comparison tasks, the learned reasoning ability generalizes effectively to a wide range of questions. Without relying on any human-annotated question-answer pairs, our method achieves significant improvements on multi-image reasoning benchmarks and shows strong performance on general vision tasks.
本文探讨了实现链式思维(Chain-of-Thought,简称CoT)推理,以连接多张图片中的视觉线索。一种直接解决方案是为视觉语言模型(Vision-Language Models,简称VLMs)适应基于规则的策略强化学习。然而,这些方法通常依赖于人工整理的问题和答案配对,在处理精细粒度的视觉细节和跨图像的复杂逻辑时,可能会面临特别大的挑战。受自我监督的视觉表示学习的启发,我们观察到图像包含可以作为监督的固有约束。基于这一见解,我们构建了图像三元组,包括同一图像的两个增强视图和第三张相似但不同的图像。在训练过程中,模型被提示生成一个推理过程来比较这些图像(即,确定是否相同或不同)。然后,我们使用基于规则的策略强化学习来优化模型。由于高视觉相似性和增强技术的存在,模型必须关注细微的视觉变化,并进行逻辑推理以取得成功。实验表明,尽管仅通过视觉比较任务进行训练,所学习的推理能力可以有效地推广到各种问题。我们的方法不依赖于任何人工标注的问题答案配对,在多图像推理基准测试上取得了显著的改进,并在一般视觉任务上表现出强大的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探索了如何通过Chain-of-Thought(CoT)推理跨多张图片链接视觉线索。文章提出了一种基于规则强化学习的简单解决方案用于视觉语言模型(VLMs)。但该方法通常依赖于人工编辑的问题答案对,对于处理细微视觉细节和跨图像复杂逻辑的挑战性较大。受自我监督的视觉表示学习的启发,文章观察到图像中包含的固有约束可以作为监督使用。基于此,文章构建了包含同一张图片的两种增强视图和一张相似但不同的图片的图像三元组。训练过程中,模型被提示生成一个比较这些图像(即判断相同或不同)的推理过程。随后用基于规则的强化学习优化模型。由于图像的高度视觉相似性和增强技术的存在,模型必须关注微妙的视觉变化并进行逻辑推理才能成功。实验表明,虽然仅通过视觉比较任务进行训练,但习得的推理能力可以有效地应用于各种问题。无需依赖任何人工标注的问题答案对,该方法在多图像推理基准测试上取得了显著改进,并在一般视觉任务上表现出强大性能。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究使Chain-of-Thought(CoT)推理能够跨多个图像链接视觉线索。
- 提出了一种基于规则强化学习的解决方案来适应视觉语言模型(VLMs)。
- 注意到图像中包含的固有约束可用于自我监督学习。
- 通过构建图像三元组来训练模型,包括同一张图片的两种增强视图和一张相似但不同的图片。
- 模型必须关注微妙的视觉变化并进行逻辑推理以成功完成任务。
- 该方法在多图像推理基准测试上取得了显著改进。
点此查看论文截图



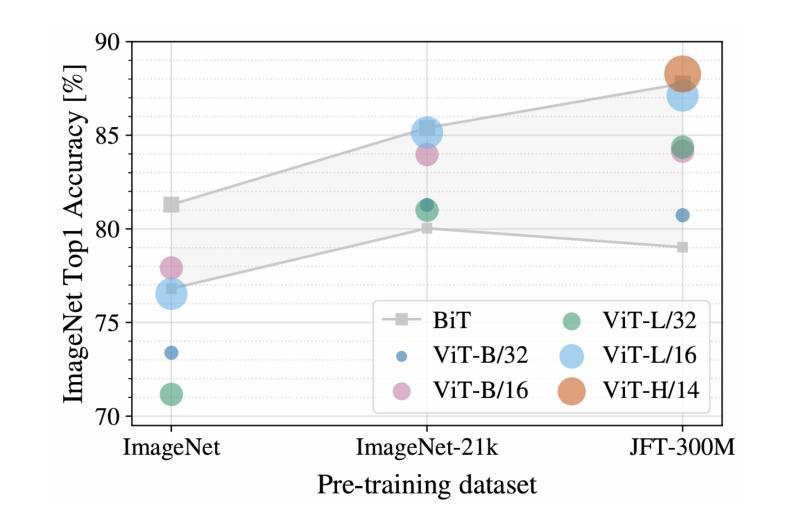
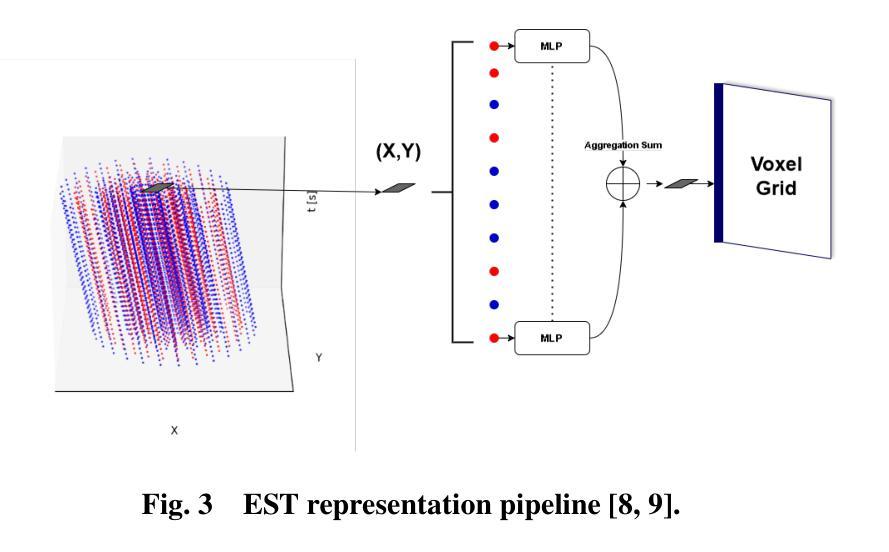
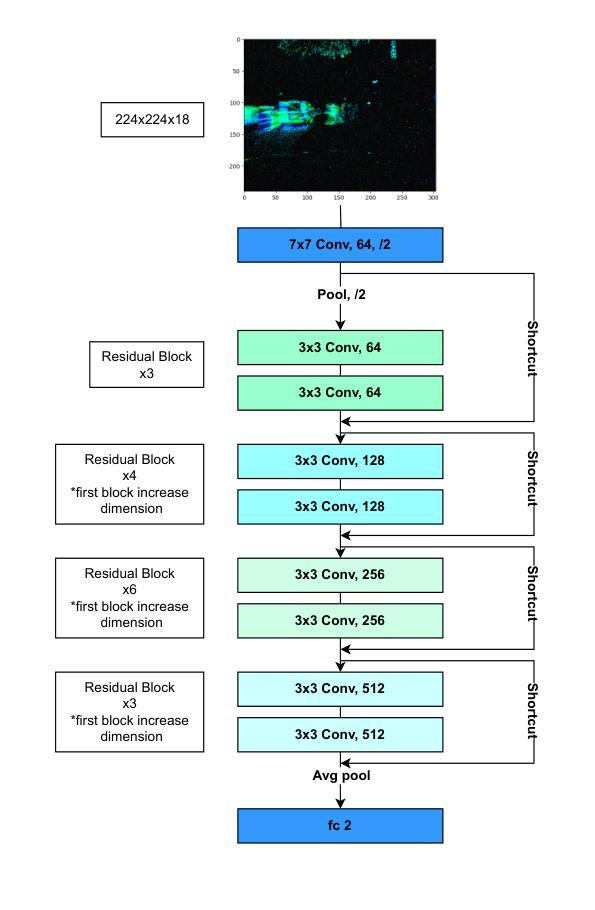
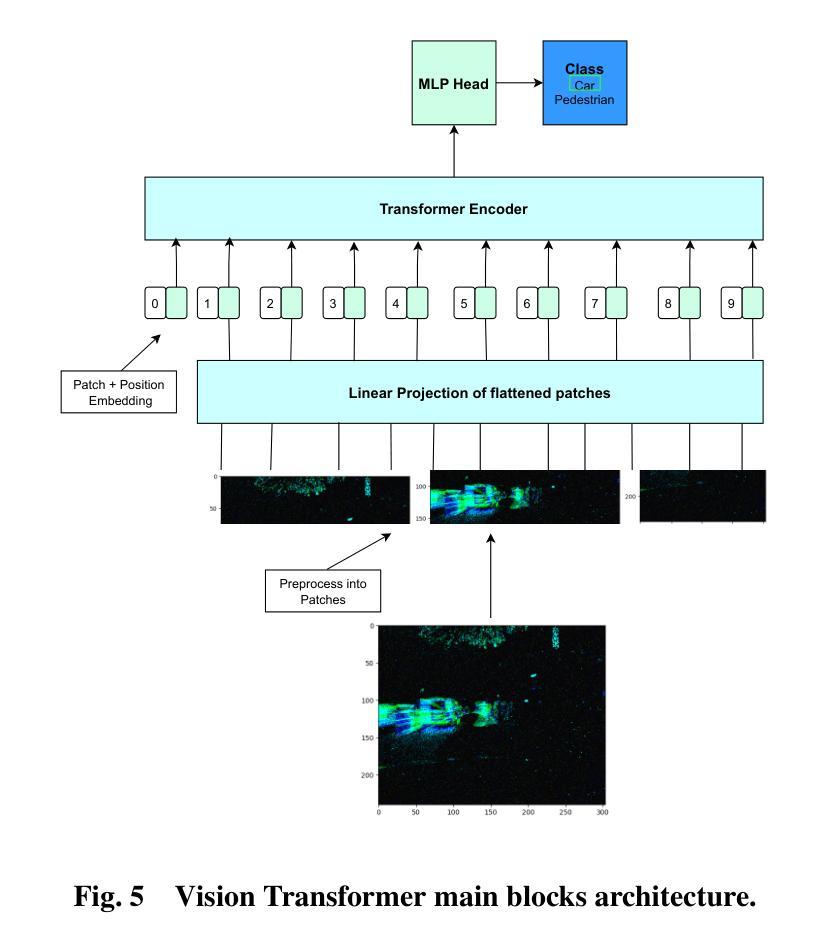
From Ground to Air: Noise Robustness in Vision Transformers and CNNs for Event-Based Vehicle Classification with Potential UAV Applications
Authors:Nouf Almesafri, Hector Figueiredo, Miguel Arana-Catania
This study investigates the performance of the two most relevant computer vision deep learning architectures, Convolutional Neural Network and Vision Transformer, for event-based cameras. These cameras capture scene changes, unlike traditional frame-based cameras with capture static images, and are particularly suited for dynamic environments such as UAVs and autonomous vehicles. The deep learning models studied in this work are ResNet34 and ViT B16, fine-tuned on the GEN1 event-based dataset. The research evaluates and compares these models under both standard conditions and in the presence of simulated noise. Initial evaluations on the clean GEN1 dataset reveal that ResNet34 and ViT B16 achieve accuracies of 88% and 86%, respectively, with ResNet34 showing a slight advantage in classification accuracy. However, the ViT B16 model demonstrates notable robustness, particularly given its pre-training on a smaller dataset. Although this study focuses on ground-based vehicle classification, the methodologies and findings hold significant promise for adaptation to UAV contexts, including aerial object classification and event-based vision systems for aviation-related tasks.
本研究探讨了两种与计算机视觉深度学习架构最相关的模型——卷积神经网络(CNN)和视觉转换器(Vision Transformer)在事件相机上的应用。与传统基于帧的相机捕捉静态图像不同,这些相机能够捕捉场景变化,特别适用于无人机和自动驾驶车辆等动态环境。本研究中的深度学习模型为ResNet34和ViT B16,经过GEN1事件数据集微调。该研究在标准条件和模拟噪声存在的情况下对这些模型进行了评估比较。在干净的GEN1数据集上的初步评估显示,ResNet34和ViT B16的准确率分别为88%和86%,其中ResNet34在分类准确率上稍占优势。然而,ViT B16模型显示出显著的稳健性,尤其是在较小的数据集上进行预训练的情况下。虽然本研究重点关注地面车辆分类,但方法和研究结果对于适应无人机上下文具有巨大潜力,包括空中目标分类和用于航空相关任务的事件视觉系统。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 17 figures, 9 tables. To be presented in AIAA AVIATION Forum 2025
Summary
本研究探讨了两种最相关的计算机视觉深度学习架构——卷积神经网络(CNN)和视觉转换器(Vision Transformer)在事件相机上的应用。事件相机能捕捉场景变化,适合动态环境如无人机和自动驾驶车辆。在GEN1事件数据集上微调ResNet34和ViT B16模型,研究评估了这些模型在标准条件和模拟噪声环境下的性能。在干净的GEN1数据集上初步评估显示,ResNet34和ViT B16的准确率分别为88%和86%,ResNet34在分类准确率上稍占优势。然而,ViT B16模型展现出显著鲁棒性,尤其是在较小数据集上的预训练表现。尽管该研究主要关注地面车辆分类,但其方法和结果对于无人机的适应潜力具有重要意义,如空中目标分类和基于事件视觉系统的航空任务。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究比较了卷积神经网络(CNN)和视觉转换器(Vision Transformer)在事件相机上的性能。
- 事件相机能捕捉场景变化,适合动态环境应用如无人机和自动驾驶车辆。
- 在GEN1事件数据集上微调的ResNet34和ViT B16模型被评估。
- 在标准条件下,ResNet34在分类准确率上稍优于ViT B16。
- ViT B16模型展现出显著鲁棒性,尤其在较小数据集上的预训练表现。
- 研究结果对于地面车辆分类具有实际应用价值。
点此查看论文截图


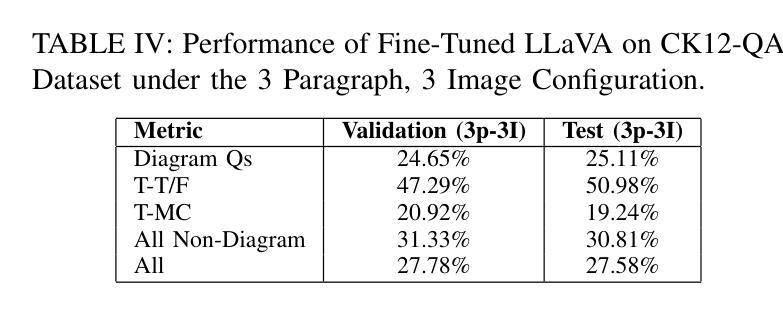
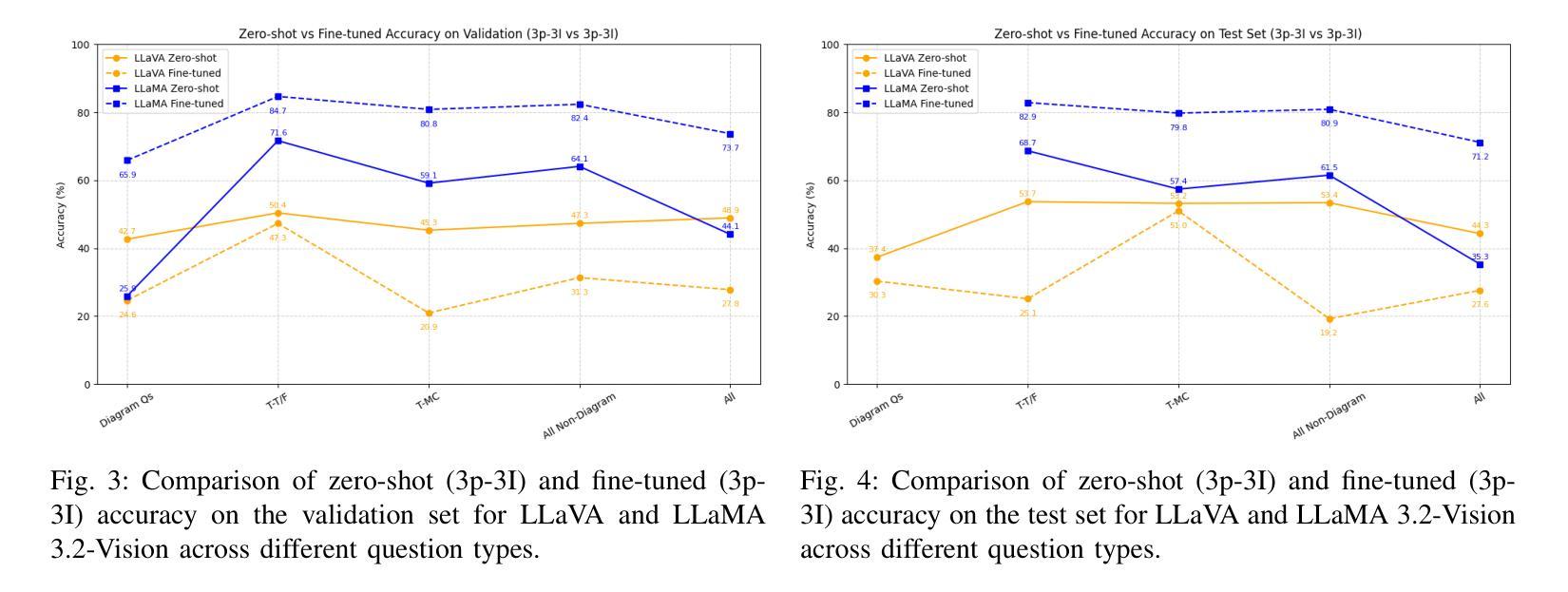
Evaluating Multimodal Large Language Models on Educational Textbook Question Answering
Authors:Hessa A. Alawwad, Anas Zafar, Areej Alhothali, Usman Naseem, Ali Alkhathlan, Amani Jamal
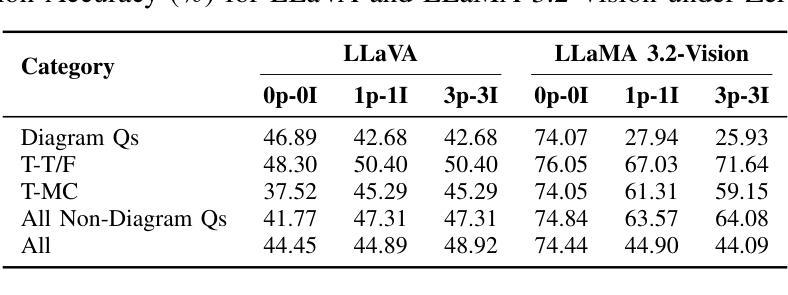
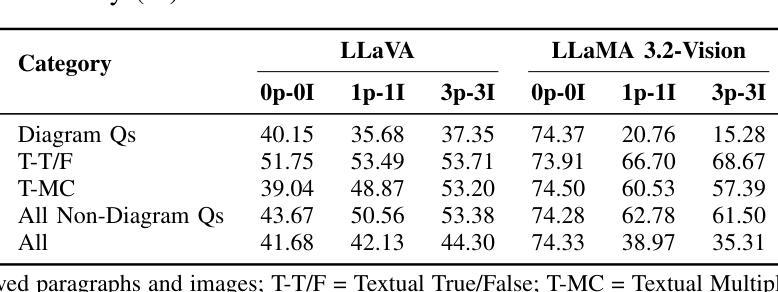
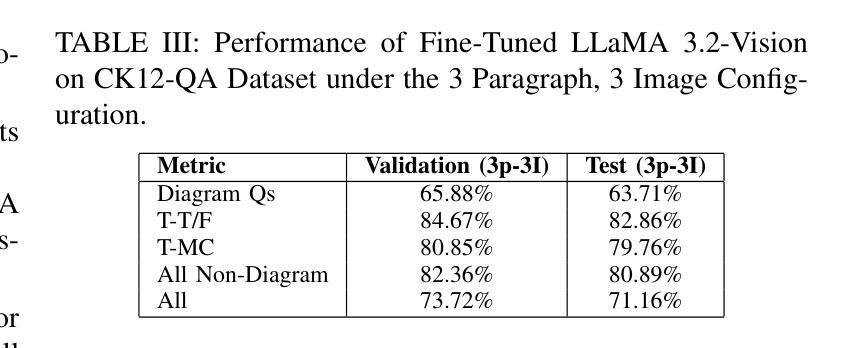
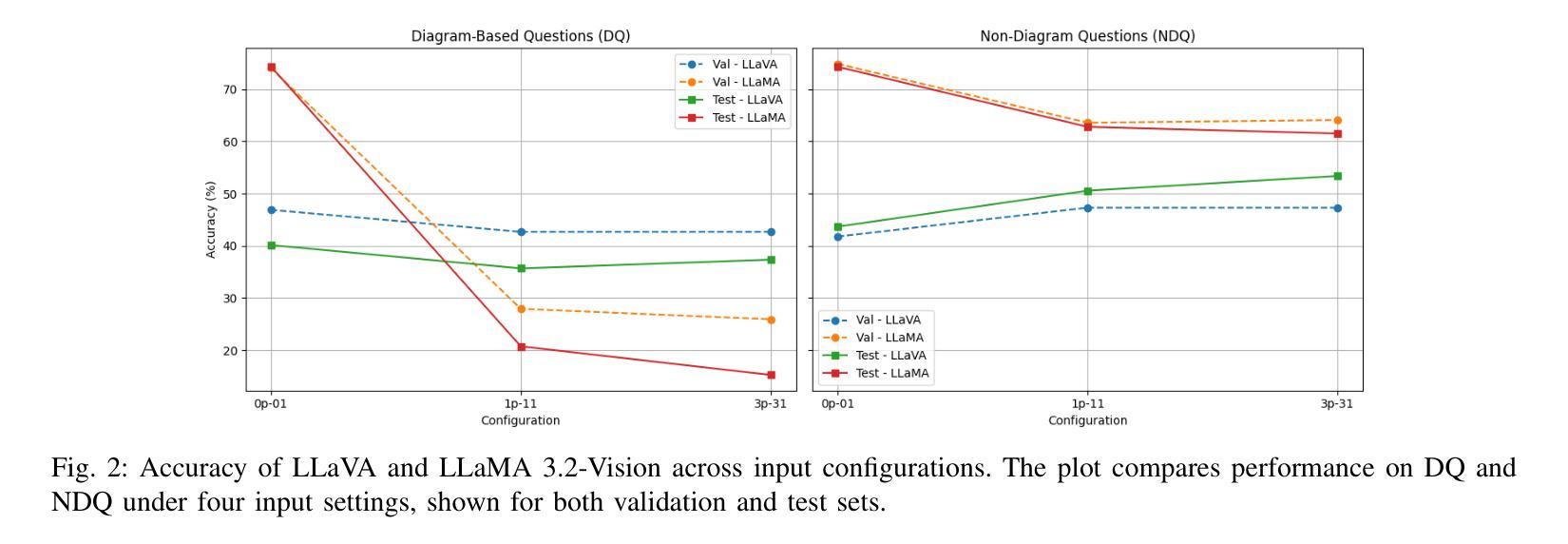
Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have recently achieved significant success in vision–language tasks. However, their capacity to reason over complex, long lessons and intricate educational diagrams that cannot be represented as a single natural image remains largely untested. In this work, we present the first evaluation of state-of-the-art MLLMs on the textbook question answering (TQA) task using the CK12-QA dataset. We assess the performance of recent vision-language models, including LLaVA and LLaMA 3.2-Vision, across various input configurations. Additionally, we introduce a lightweight multimodal retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) pipeline that integrates both paragraphs and diagrams from the lesson into the prompt. Our results demonstrate the influence of retrieved educational context on model accuracy and reasoning, while also revealing current limitations in handling question-context relationships and the potential for noise, pointing to key directions for future research in multimodal AI-driven learning.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)最近在视觉与语言任务中取得了巨大成功。然而,它们对复杂、冗长的课程与细致的教育图表进行推理的能力仍未得到广泛测试,这些教育图表不能表示为单一的自然图像。在这项研究中,我们利用CK12-QA数据集首次评估了最先进的多模态大型语言模型在教科书问答(TQA)任务上的表现。我们评估了各种输入配置下的近期视觉语言模型的表现,包括LLaVA和LLaMA 3.2-Vision。此外,我们引入了一个轻量级的多模态检索增强生成(RAG)流程,它将课程中的段落和图表都整合到提示中。我们的结果展示了检索到的教育上下文对模型准确性和推理能力的影响,同时揭示了处理问题与上下文关系方面的当前局限性以及对噪声的潜在影响,指出了未来多模态人工智能驱动学习的研究关键方向。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 Pages
Summary
该文评估了最先进的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在教科书问答(TQA)任务上的表现,使用了CK12-QA数据集。研究包括对不同视觉语言模型的性能评估,如LLaVA和LLaMA 3.2-Vision,并探讨了各种输入配置的影响。此外,研究还引入了一个轻量级的多模态检索增强生成(RAG)流程,该流程将课程段落和图表整合到提示中。研究结果表明,检索的教育背景对模型的准确性和推理能力有影响,同时揭示了处理问题与上下文关系方面的当前局限性以及潜在噪声问题,为未来的多模态AI驱动学习研究指出了关键方向。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在教科书问答任务上表现出显著成功。
- LLaVA和LLaMA 3.2-Vision等视觉语言模型在CK12-QA数据集上的性能得到了评估。
- 输入配置对模型表现有影响。
- 检索的教育背景信息对模型的准确性和推理能力有重要作用。
- 当前模型在处理问题与上下文关系方面存在局限性。
- 模型易受噪声影响。
点此查看论文截图

AQUA20: A Benchmark Dataset for Underwater Species Classification under Challenging Conditions
Authors:Taufikur Rahman Fuad, Sabbir Ahmed, Shahriar Ivan
Robust visual recognition in underwater environments remains a significant challenge due to complex distortions such as turbidity, low illumination, and occlusion, which severely degrade the performance of standard vision systems. This paper introduces AQUA20, a comprehensive benchmark dataset comprising 8,171 underwater images across 20 marine species reflecting real-world environmental challenges such as illumination, turbidity, occlusions, etc., providing a valuable resource for underwater visual understanding. Thirteen state-of-the-art deep learning models, including lightweight CNNs (SqueezeNet, MobileNetV2) and transformer-based architectures (ViT, ConvNeXt), were evaluated to benchmark their performance in classifying marine species under challenging conditions. Our experimental results show ConvNeXt achieving the best performance, with a Top-3 accuracy of 98.82% and a Top-1 accuracy of 90.69%, as well as the highest overall F1-score of 88.92% with moderately large parameter size. The results obtained from our other benchmark models also demonstrate trade-offs between complexity and performance. We also provide an extensive explainability analysis using GRAD-CAM and LIME for interpreting the strengths and pitfalls of the models. Our results reveal substantial room for improvement in underwater species recognition and demonstrate the value of AQUA20 as a foundation for future research in this domain. The dataset is publicly available at: https://huggingface.co/datasets/taufiktrf/AQUA20.
在水下环境中实现稳健的视觉识别仍然是一个重大挑战,因为诸如浑浊、低光照和遮挡之类的复杂失真会严重降低标准视觉系统的性能。本文介绍了AQUA20,这是一个包含8171张水下图像的综合基准数据集,涵盖了20个海洋物种,反映了现实世界中的环境挑战,如光照、浑浊度、遮挡等,为水下视觉理解提供了宝贵的资源。我们评估了13种最先进的深度学习模型,包括轻量级CNN(SqueezeNet、MobileNetV2)和基于transformer的架构(ViT、ConvNeXt),以基准测试它们在具有挑战性的条件下对海洋物种进行分类的性能。实验结果表明,ConvNeXt表现最佳,前三名准确率达到了98.82%,第一名准确率为90.69%,同时总体F1分数最高,达到了88.92%,且参数规模适中。其他基准模型的结果也显示了复杂性和性能之间的权衡。我们还使用GRAD-CAM和LIME进行了广泛的解释性分析,以解释模型的优点和缺点。我们的结果揭示了水下物种识别方面仍有很大的改进空间,并证明了AQUA20作为未来该领域研究基础的价值。数据集可在https://huggingface.co/datasets/taufiktrf/AQUA20公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to AJSE Springer
Summary
本文介绍了一个名为AQUA20的水下图像数据集,包含8,171张反映真实水下环境挑战(如光照、浊度、遮挡等)的20种海洋生物图像。评估了多种顶级深度学习模型(包括轻量级CNN和基于transformer的架构)在水下生物分类方面的性能。实验结果显示,ConvNeXt模型表现最佳,Top-3准确率为98.82%,Top-1准确率为90.69%,总体F1分数为88.92%。此外,文章还提供了模型的可解释性分析。本文结果展示出水下生物识别领域的巨大进步空间,同时强调了AQUA20数据集对未来研究的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- AQUA20数据集包含真实水下环境挑战的图像,适用于水下视觉理解研究。
- 评估了多种深度学习模型在水下生物分类方面的性能。
- ConvNeXt模型在AQUA20数据集上表现最佳,具有高的分类准确率。
- 模型的可解释性分析揭示了其优势和局限。
- 水下生物识别领域存在巨大进步空间。
- AQUA20数据集对未来研究具有重要性。
点此查看论文截图

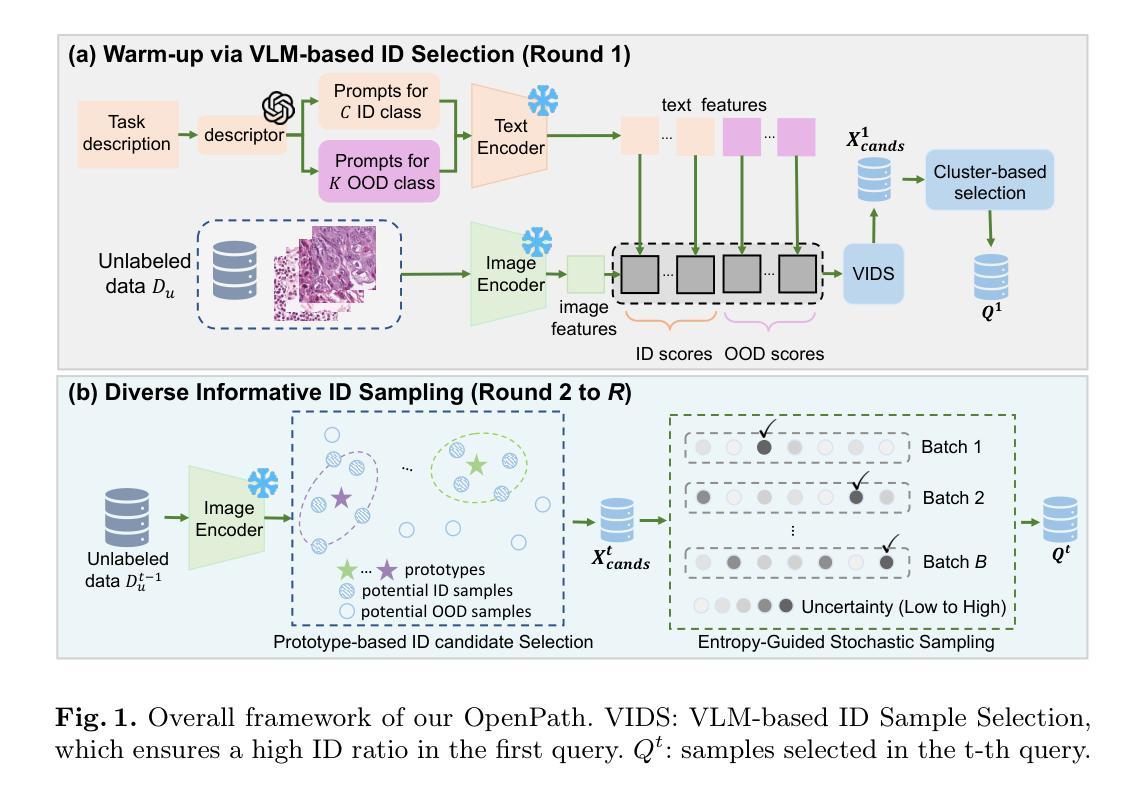
OpenPath: Open-Set Active Learning for Pathology Image Classification via Pre-trained Vision-Language Models
Authors:Lanfeng Zhong, Xin Liao, Shichuan Zhang, Shaoting Zhang, Guotai Wang
Pathology image classification plays a crucial role in accurate medical diagnosis and treatment planning. Training high-performance models for this task typically requires large-scale annotated datasets, which are both expensive and time-consuming to acquire. Active Learning (AL) offers a solution by iteratively selecting the most informative samples for annotation, thereby reducing the labeling effort. However, most AL methods are designed under the assumption of a closed-set scenario, where all the unannotated images belong to target classes. In real-world clinical environments, the unlabeled pool often contains a substantial amount of Out-Of-Distribution (OOD) data, leading to low efficiency of annotation in traditional AL methods. Furthermore, most existing AL methods start with random selection in the first query round, leading to a significant waste of labeling costs in open-set scenarios. To address these challenges, we propose OpenPath, a novel open-set active learning approach for pathological image classification leveraging a pre-trained Vision-Language Model (VLM). In the first query, we propose task-specific prompts that combine target and relevant non-target class prompts to effectively select In-Distribution (ID) and informative samples from the unlabeled pool. In subsequent queries, Diverse Informative ID Sampling (DIS) that includes Prototype-based ID candidate Selection (PIS) and Entropy-Guided Stochastic Sampling (EGSS) is proposed to ensure both purity and informativeness in a query, avoiding the selection of OOD samples. Experiments on two public pathology image datasets show that OpenPath significantly enhances the model’s performance due to its high purity of selected samples, and outperforms several state-of-the-art open-set AL methods. The code is available at \href{https://github.com/HiLab-git/OpenPath}{https://github.com/HiLab-git/OpenPath}..
病理学图像分类在准确的医学诊断和治疗计划中发挥至关重要的作用。为此任务训练高性能模型通常需要大规模标注数据集,这些数据的获取既昂贵又耗时。主动学习(AL)通过迭代选择最具信息量的样本进行标注,从而减少了标注工作量,为此提供了解决方案。然而,大多数AL方法的设计是基于封闭集场景的假设,即所有未标注的图像都属于目标类别。在现实世界中的临床环境中,未标注池通常包含大量超出分布(OOD)的数据,导致传统AL方法的标注效率降低。此外,大多数现有的AL方法在第一次查询时采用随机选择的方式,这在开放集场景中造成了显著的标注成本浪费。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了OpenPath,这是一种利用预训练好的视觉语言模型(VLM)进行病理学图像分类的新型开放集主动学习方法。在第一次查询中,我们提出了结合目标和相关非目标类别提示的任务特定提示,以有效地从未标注的池中选择符合分布(ID)和具有信息量的样本。在随后的查询中,我们提出了包含基于原型的ID候选样本选择(PIS)和熵引导随机采样(EGSS)的多样信息ID采样(DIS),以确保查询的纯净度和信息量,避免选择OOD样本。在两个公共病理学图像数据集上的实验表明,由于所选样本的高纯净度,OpenPath显著提高了模型的性能,并优于几种先进的开放集AL方法。代码可用在https://github.com/HiLab-git/OpenPath。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025 early accept
Summary
本文提出一种基于预训练视觉语言模型的新型开放集主动学习方法OpenPath,用于病理学图像分类。该方法通过任务特定提示选择初始样本,并在后续查询中使用多样信息采样策略确保所选样本的纯度和信息量,从而提高模型性能并避免选择异常样本。
Key Takeaways
- 病理学图像分类在医疗诊断和治疗计划中起到关键作用,需要大规模标注数据集来训练高性能模型,但标注成本高昂且耗时。
- 主动学习方法通过迭代选择最具信息量的样本进行标注,有助于减少标注工作量。
- 现有主动学习方法大多假设封闭集场景,但在现实临床环境中,未标注的池中常常包含大量异常数据,导致标注效率降低。
- OpenPath方法利用预训练的视觉语言模型,通过任务特定提示和多样信息采样策略,有效选择信息量大的样本,避免选择异常样本。
- 实验结果表明,OpenPath方法提高了模型性能,并优于其他先进的开放集主动学习方法。
- OpenPath代码已公开可用。
- 该方法有助于更高效地利用有限的标注资源,推动病理学图像分类任务的进展。
点此查看论文截图

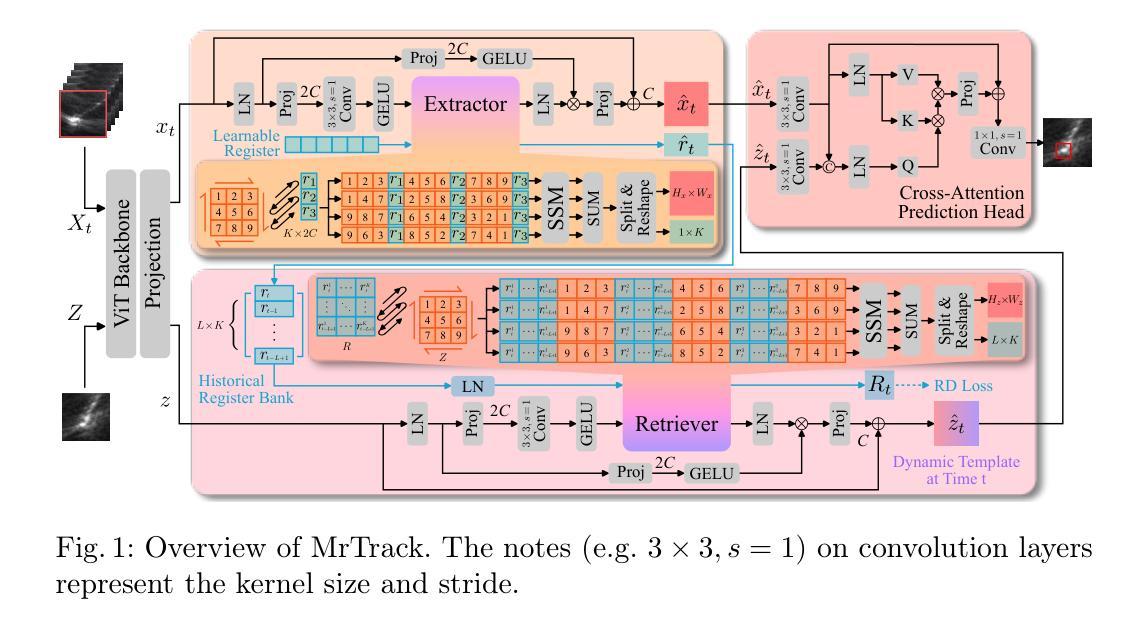
MrTrack: Register Mamba for Needle Tracking with Rapid Reciprocating Motion during Ultrasound-Guided Aspiration Biopsy
Authors:Yuelin Zhang, Qingpeng Ding, Long Lei, Yongxuan Feng, Raymond Shing-Yan Tang, Shing Shin Cheng
Ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy is a common minimally invasive diagnostic procedure. However, an aspiration needle tracker addressing rapid reciprocating motion is still missing. MrTrack, an aspiration needle tracker with a mamba-based register mechanism, is proposed. MrTrack leverages a Mamba-based register extractor to sequentially distill global context from each historical search map, storing these temporal cues in a register bank. The Mamba-based register retriever then retrieves temporal prompts from the register bank to provide external cues when current vision features are temporarily unusable due to rapid reciprocating motion and imaging degradation. A self-supervised register diversify loss is proposed to encourage feature diversity and dimension independence within the learned register, mitigating feature collapse. Comprehensive experiments conducted on both robotic and manual aspiration biopsy datasets demonstrate that MrTrack not only outperforms state-of-the-art trackers in accuracy and robustness but also achieves superior inference efficiency. Project page: https://github.com/PieceZhang/MrTrack
超声引导下细针穿刺(FNA)活检是一种常见的微创诊断程序。然而,目前尚未有应对快速往复运动的穿刺针追踪器。针对这一空白,提出了MrTrack这一以麻步为基础登记机制的穿刺针追踪器。MrTrack利用基于麻步的寄存器提取器,从每个历史搜索地图中顺序提炼全局上下文,将这些时序线索存储在寄存器银行中。当由于快速往复运动和图像退化导致当前视觉特征暂时无法使用时,基于麻步的寄存器检索器会从寄存器银行中提取时序提示,提供外部线索。提出了一种自监督寄存器多样化损失,以鼓励学习到的寄存器内的特征多样性和维度独立性,减轻特征崩溃的问题。在机器人和手动穿刺活检数据集上进行的综合实验表明,MrTrack不仅在准确性和稳健性方面优于最新跟踪器,而且在推理效率方面也表现出卓越的性能。项目页面:https://github.com/PieceZhang/MrTrack
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Early Accepted by MICCAI 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为MrTrack的超声引导下细针穿刺(FNA)活检针追踪技术。它采用基于mamba的寄存器机制,可处理快速往复运动。MrTrack通过从每个历史搜索地图中蒸馏全局上下文,并将这些时间线索存储在寄存器银行中,利用基于mamba的寄存器提取器来检索外部线索,从而在当前的视觉特征因快速往复运动和图像退化而暂时无法使用的情况下提供辅助。同时提出了一种自监督寄存器多样化损失,鼓励学习寄存器内的特征多样性和维度独立性,减轻特征崩溃问题。实验证明,MrTrack在机器人和手动穿刺活检数据集上的准确性和鲁棒性均优于最新跟踪技术,并实现了较高的推理效率。
Key Takeaways
- MrTrack是一种用于超声引导下细针穿刺活检针追踪的技术,旨在处理快速往复运动。
- MrTrack采用基于mamba的寄存器机制,通过蒸馏历史搜索地图中的全局上下文来进行工作。
- 技术利用寄存器提取器在视觉特征因快速运动和图像退化而暂时不可用的情况下提供外部线索。
- 提出了自监督寄存器多样化损失,以促进特征多样性和维度独立性。
- MrTrack通过减少特征崩溃问题,提高了跟踪技术的性能和鲁棒性。
- 实验证明,MrTrack在机器人和手动穿刺活检数据集上的表现均优于现有跟踪技术。
点此查看论文截图

Accelerate 3D Object Detection Models via Zero-Shot Attention Key Pruning
Authors:Lizhen Xu, Xiuxiu Bai, Xiaojun Jia, Jianwu Fang, Shanmin Pang
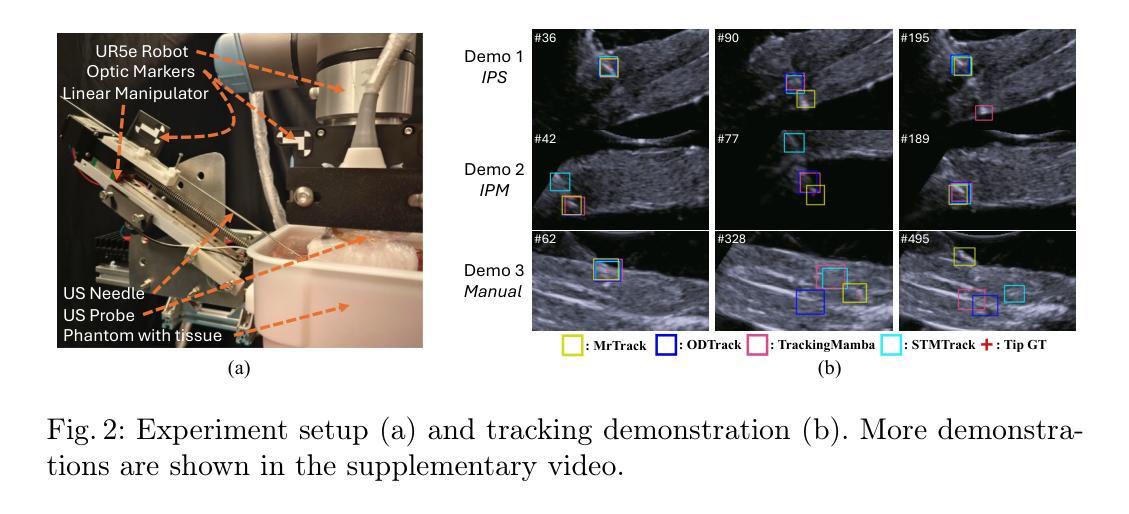
Query-based methods with dense features have demonstrated remarkable success in 3D object detection tasks. However, the computational demands of these models, particularly with large image sizes and multiple transformer layers, pose significant challenges for efficient running on edge devices. Existing pruning and distillation methods either need retraining or are designed for ViT models, which are hard to migrate to 3D detectors. To address this issue, we propose a zero-shot runtime pruning method for transformer decoders in 3D object detection models. The method, termed tgGBC (trim keys gradually Guided By Classification scores), systematically trims keys in transformer modules based on their importance. We expand the classification score to multiply it with the attention map to get the importance score of each key and then prune certain keys after each transformer layer according to their importance scores. Our method achieves a 1.99x speedup in the transformer decoder of the latest ToC3D model, with only a minimal performance loss of less than 1%. Interestingly, for certain models, our method even enhances their performance. Moreover, we deploy 3D detectors with tgGBC on an edge device, further validating the effectiveness of our method. The code can be found at https://github.com/iseri27/tg_gbc.
基于查询的方法和密集特征在3D目标检测任务中取得了显著的成功。然而,这些模型的计算需求,特别是在处理大图像尺寸和多个转换器层时,对于在边缘设备上高效运行构成了重大挑战。现有的修剪和蒸馏方法需要重新训练,或者针对ViT模型设计,很难迁移到3D检测器上。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种用于3D目标检测模型中转换器解码器的零拍摄运行时修剪方法。该方法被称为tgGBC(分类分数逐步引导修剪),它根据重要性系统地修剪转换器模块中的键。我们将分类分数扩展到与注意力图相乘,以获得每个键的重要性分数,然后根据每个键的重要性分数,在每层转换器之后对其进行修剪。我们的方法在最新的ToC3D模型的转换器解码器中实现了1.99倍的加速,性能损失仅低于1%。有趣的是,对于某些模型,我们的方法甚至提高了其性能。此外,我们在边缘设备上部署带有tgGBC的3D检测器,进一步验证了我们的方法的有效性。代码可在<https://github.com/iseri2_ 省略处是原文中的占位符 >中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV2025. The code can be found at https://github.com/iseri27/tg_gbc
Summary
本文提出一种名为tgGBC的零运行时修剪方法,用于基于查询的三维目标检测模型的转换器解码器。该方法根据关键的重要性逐步修剪转换模块中的键,通过分类分数与注意力图的乘积来确定每个键的重要性分数,然后逐层修剪重要分数较低的键。该方法在最新ToC3D模型的转换器解码器中实现了1.99倍的加速,性能损失仅为不到1%,并且可以在边缘设备上部署。同时发现对特定模型甚至能提升性能。有关代码可以在GitHub上找到。
Key Takeaways
以下是七个关键见解:
- 查询方法在三维目标检测任务中取得了显著成功。然而计算需求非常高,特别是大型图像和多层转换器,这对于边缘设备来说是个挑战。因此需要对现有的方法如修剪和蒸馏进行改进。
- 提出了一种名为tgGBC的零运行时修剪方法来解决上述问题,通过计算键的重要性得分来进行修剪,不仅加速了转换器的运行速度,而且对性能影响很小。这是针对基于查询的三维检测模型的转换器解码器的优化方法。
- tgGBC方法通过结合分类分数和注意力图来确定每个键的重要性得分,使得关键的重要信息得到保留而不会被忽略掉,使得模型运行速度得到提升同时保证了检测精度。同时该方法的可扩展性使得它可以适应多种模型架构和配置。同时能够在每一层中对特定的键进行修剪,以优化模型性能。这种修剪策略是基于分类分数的扩展,能够准确地识别出哪些键对于模型性能更为重要。
点此查看论文截图


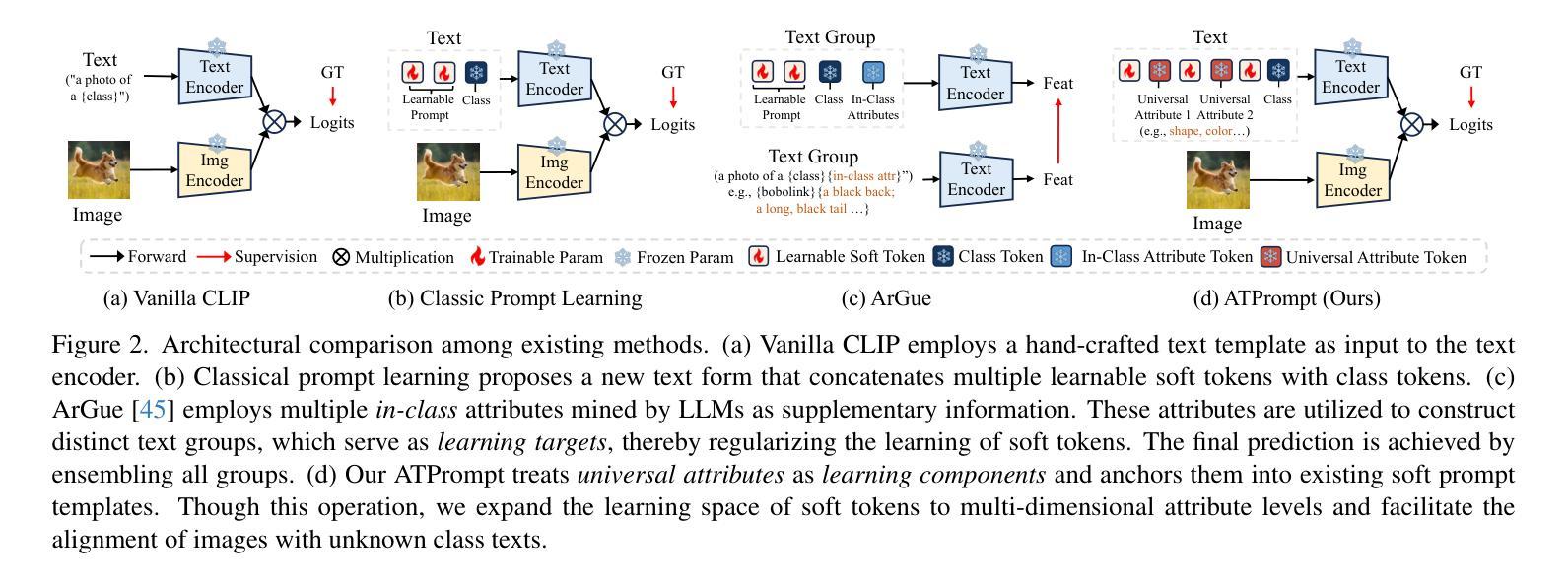
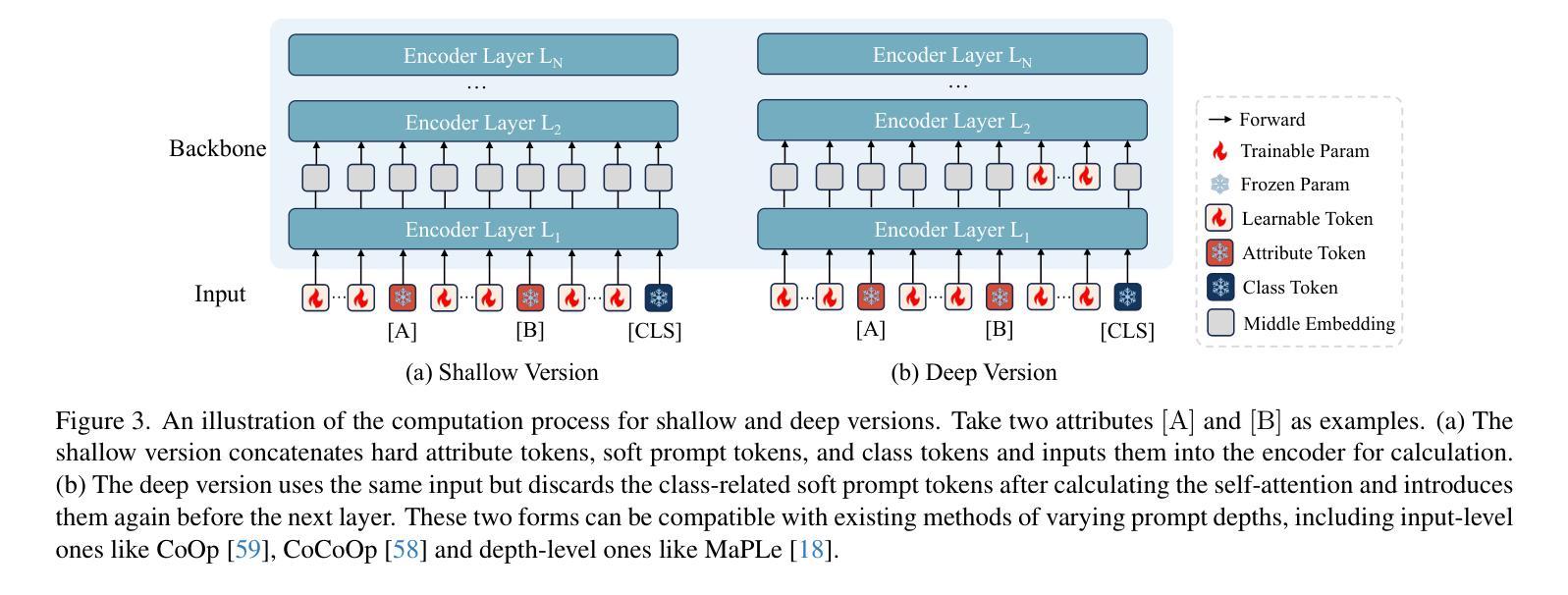
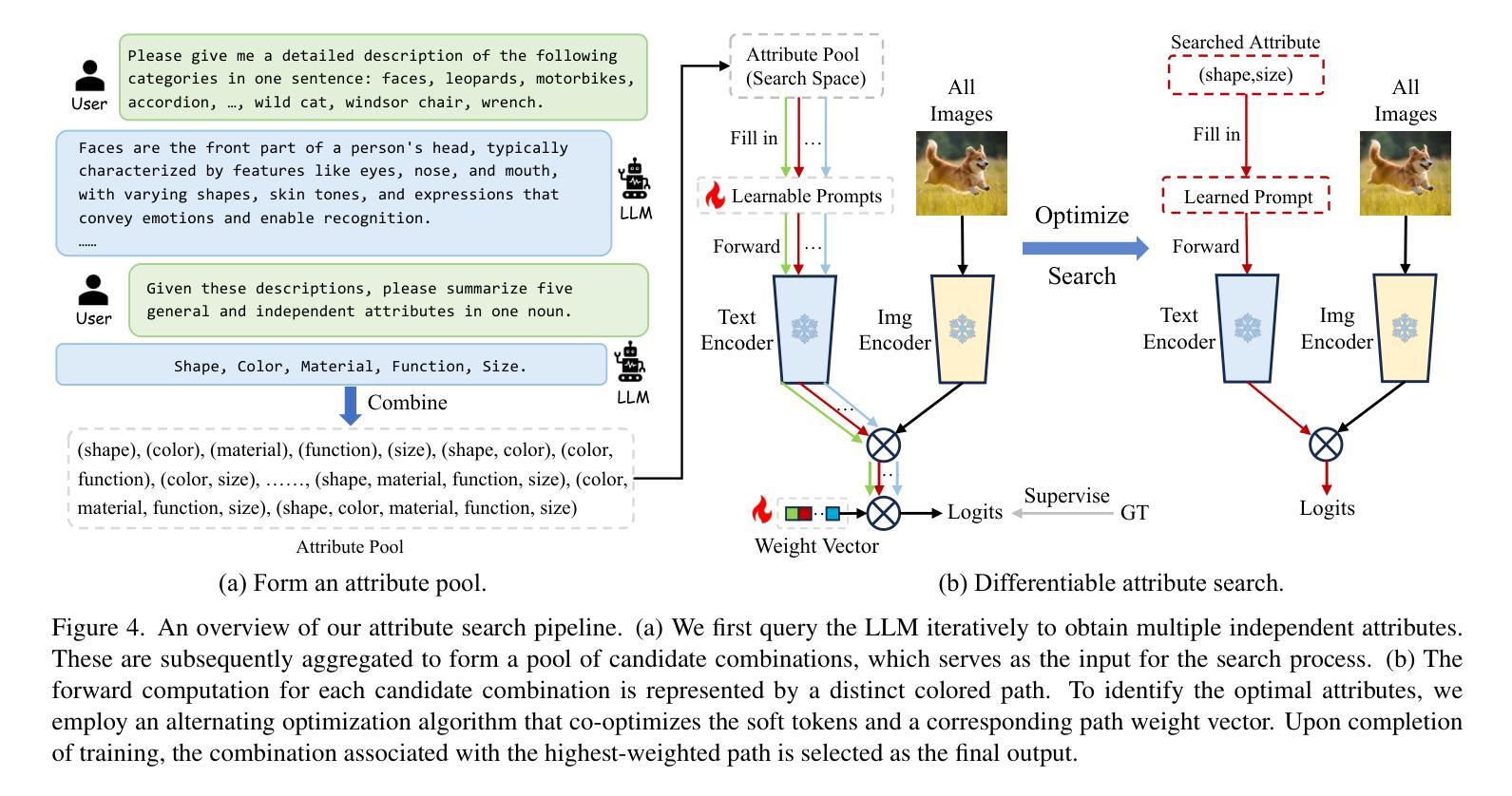
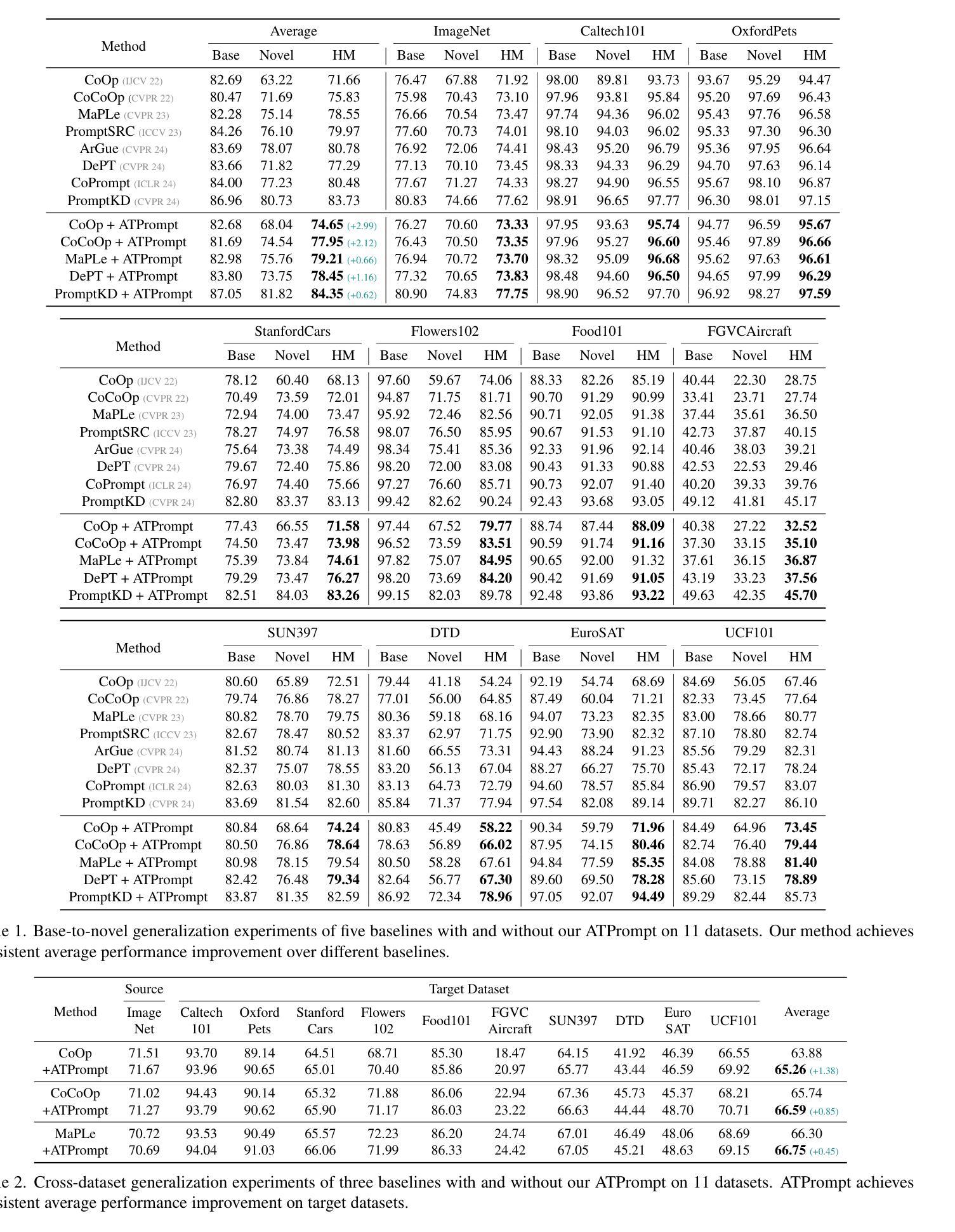
Advancing Textual Prompt Learning with Anchored Attributes
Authors:Zheng Li, Yibing Song, Ming-Ming Cheng, Xiang Li, Jian Yang
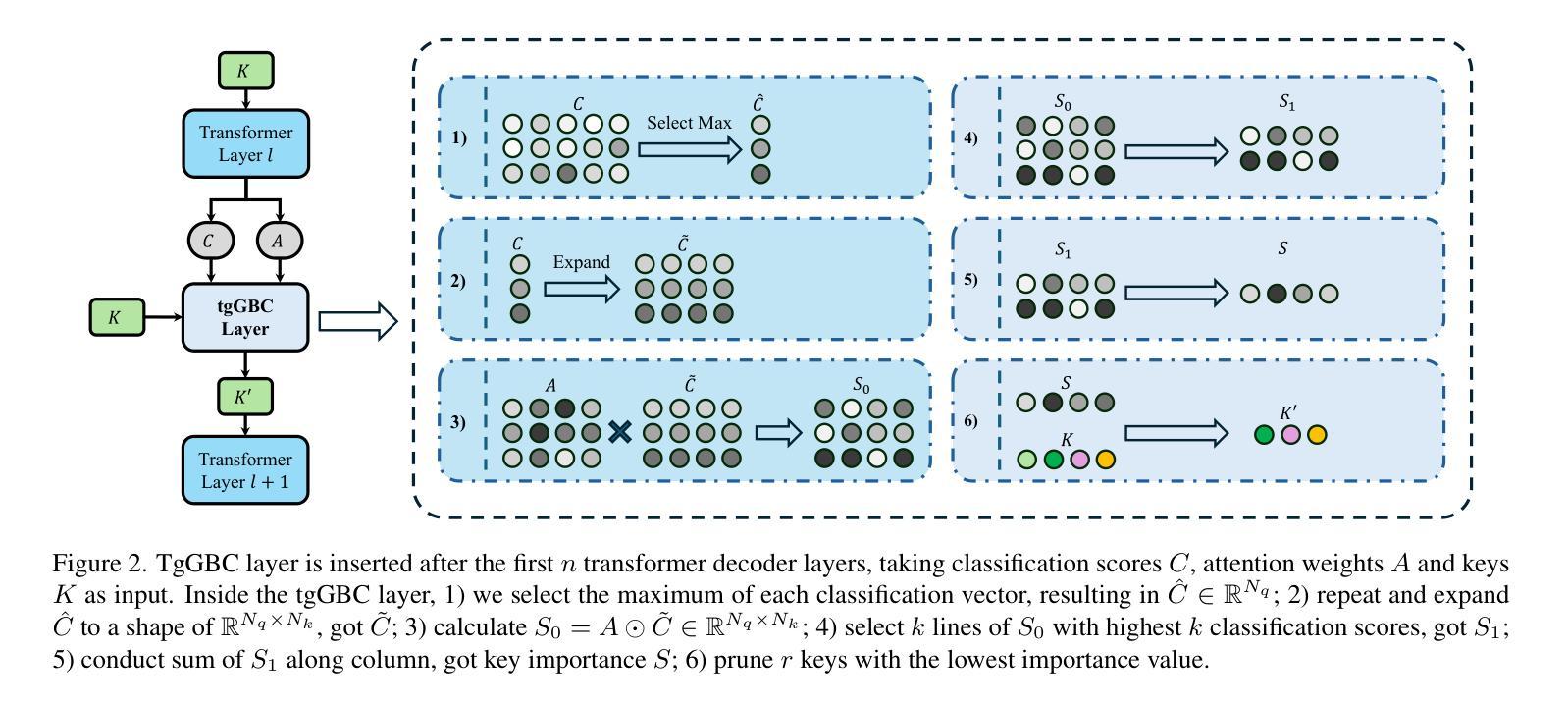
Textual-based prompt learning methods primarily employ multiple learnable soft prompts and hard class tokens in a cascading manner as text inputs, aiming to align image and text (category) spaces for downstream tasks. However, current training is restricted to aligning images with predefined known categories and cannot be associated with unknown categories. In this work, we propose utilizing universal attributes as a bridge to enhance the alignment between images and unknown categories. Specifically, we introduce an Attribute-anchored Textual Prompt learning method for vision-language models, named ATPrompt. This approach expands the learning space of soft prompts from the original one-dimensional category level into the multi-dimensional attribute level by incorporating multiple attribute tokens into the learnable soft prompts. Through this modification, we transform the text prompt from a category-centric form to an attribute-category hybrid form. Additionally, we introduce a straightforward differentiable attribute search method to identify representative and suitable attributes for downstream tasks. As an easy-to-use plug-in technique, ATPrompt can seamlessly replace the existing basic prompt format in textual-based methods, providing general improvements at a negligible computational cost. Extensive experiments across 11 datasets validate the effectiveness of our method.
基于文本的提示学习方法主要利用可学习的多个软提示和硬类别令牌以级联方式作为文本输入,旨在对齐图像和文本(类别)空间,以进行下游任务。然而,当前训练仅限于对齐图像与预定义的已知类别,无法与未知类别相关联。在这项工作中,我们提出利用通用属性作为桥梁,以增强图像与未知类别之间的对齐。具体来说,我们为视觉语言模型引入了一种名为ATPrompt的属性锚定文本提示学习方法。该方法通过将多个属性令牌纳入可学习的软提示中,将软提示的学习空间从原始的一维类别层面扩展到多维属性层面。通过这一改进,我们将文本提示从以类别为中心的形式转变为属性-类别混合形式。此外,我们还引入了一种简单的可区分属性搜索方法,用于识别下游任务的代表性和合适属性。作为易于使用的插件技术,ATPrompt可以无缝替换基于文本方法中的基本提示格式,以微量的计算成本提供一般性的改进。在11个数据集上的大量实验验证了我们的方法的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025. Project Page: https://zhengli97.github.io/ATPrompt/
Summary
本文提出了一种基于属性锚定的文本提示学习方法(ATPrompt),用于增强图像与未知类别之间的对齐。该方法通过引入多属性令牌来扩展学习空间,将原本一维的类别级别扩展到多维的属性级别。同时,提出了一种简单易用的可微属性搜索方法,用于为下游任务选择代表性属性。ATPrompt作为一种易于使用的插件技术,可以无缝替换现有文本提示方法中的基本格式,以微小的计算成本提供通用的改进。
Key Takeaways
- 本文介绍了一种基于属性锚定的文本提示学习方法(ATPrompt),旨在增强图像与未知类别之间的对齐。
- ATPrompt通过将学习空间扩展到多维属性级别,提高了文本提示学习的能力。
- ATPrompt引入了可微分的属性搜索方法,以识别适合下游任务的代表性属性。
- 该方法可以作为插件无缝集成到现有的文本提示方法中。
- ATPrompt提高了模型在未知类别上的性能,扩大了模型的适用范围。
- 通过在11个数据集上进行的大量实验验证了ATPrompt的有效性。
点此查看论文截图
Exploring Text-Guided Single Image Editing for Remote Sensing Images
Authors:Fangzhou Han, Lingyu Si, Zhizhuo Jiang, Hongwei Dong, Lamei Zhang, Yu Liu, Hao Chen, Bo Du
Artificial intelligence generative content (AIGC) has significantly impacted image generation in the field of remote sensing. However, the equally important area of remote sensing image (RSI) editing has not received sufficient attention. Deep learning based editing methods generally involve two sequential stages: generation and editing. For natural images, these stages primarily rely on generative backbones pre-trained on large-scale benchmark datasets and text guidance facilitated by vision-language models (VLMs). However, it become less viable for RSIs: First, existing generative RSI benchmark datasets do not fully capture the diversity of RSIs, and is often inadequate for universal editing tasks. Second, the single text semantic corresponds to multiple image semantics, leading to the introduction of incorrect semantics. To solve above problems, this paper proposes a text-guided RSI editing method and can be trained using only a single image. A multi-scale training approach is adopted to preserve consistency without the need for training on extensive benchmarks, while leveraging RSI pre-trained VLMs and prompt ensembling (PE) to ensure accuracy and controllability. Experimental results on multiple RSI editing tasks show that the proposed method offers significant advantages in both CLIP scores and subjective evaluations compared to existing methods. Additionally, we explore the ability of the edited RSIs to support disaster assessment tasks in order to validate their practicality. Codes will be released at https://github.com/HIT-PhilipHan/remote_sensing_image_editing.
人工智能生成内容(AIGC)对遥感领域图像生成产生了重大影响。然而,同样重要的遥感图像(RSI)编辑却没有得到足够重视。基于深度学习的编辑方法通常涉及两个阶段:生成和编辑。对于自然图像,这两个阶段主要依赖于在大规模基准数据集上预先训练的生成主干和由视觉语言模型(VLM)促进的文本指导。但对于遥感图像(RSI)来说,这种做法不太可行:首先,现有的生成遥感图像基准数据集没有完全捕捉到遥感图像的多样性,通常不足以应对通用编辑任务。其次,单一文本语义对应于多种图像语义,这引入了不正确的语义。为了解决上述问题,本文提出了一种文本引导的遥感图像编辑方法,该方法只需单张图像即可进行训练。采用多尺度训练方法,在无需大规模基准数据训练的情况下保持一致性,同时利用遥感图像预训练的视觉语言模型和提示集成(PE)确保准确性和可控性。在多个遥感图像编辑任务上的实验结果表明,与现有方法相比,所提方法在CLIP得分和主观评估方面都表现出显著优势。此外,我们探索了编辑后的遥感图像支持灾害评估任务的能力,以验证其实用性。相关代码将发布在:https://github.com/HIT-PhilipHan/remote_sensing_image_editing。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 18 figures, Accepted by IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing
Summary
本文探讨了人工智能生成内容(AIGC)在遥感图像编辑领域的影响。针对遥感图像编辑存在的问题,如数据集多样性不足和文本语义与图像语义不匹配,本文提出了一种文本引导的遥感图像编辑方法。该方法采用单图像训练,利用多尺度训练保证一致性,借助遥感图像预训练的视觉语言模型和提示集成(PE)确保准确性和可控性。实验结果表明,该方法在多个遥感图像编辑任务上表现优异,并支持灾害评估任务的实用性验证。
Key Takeaways
- AIGC对遥感图像生成产生重大影响,但遥感图像编辑领域尚未得到充分关注。
- 现有的遥感图像生成数据集缺乏多样性,无法满足通用编辑任务的需求。
- 文本语义与图像语义的不匹配问题在遥感图像编辑中尤为突出。
- 本文提出了一种文本引导的遥感图像编辑方法,采用单图像训练,无需大规模基准数据集。
- 多尺度训练保证了编辑的一致性,同时借助遥感图像预训练的VLMs和提示集成(PE)提高准确性和可控性。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在多个遥感图像编辑任务上表现优异,CLIP分数和主观评价均优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图


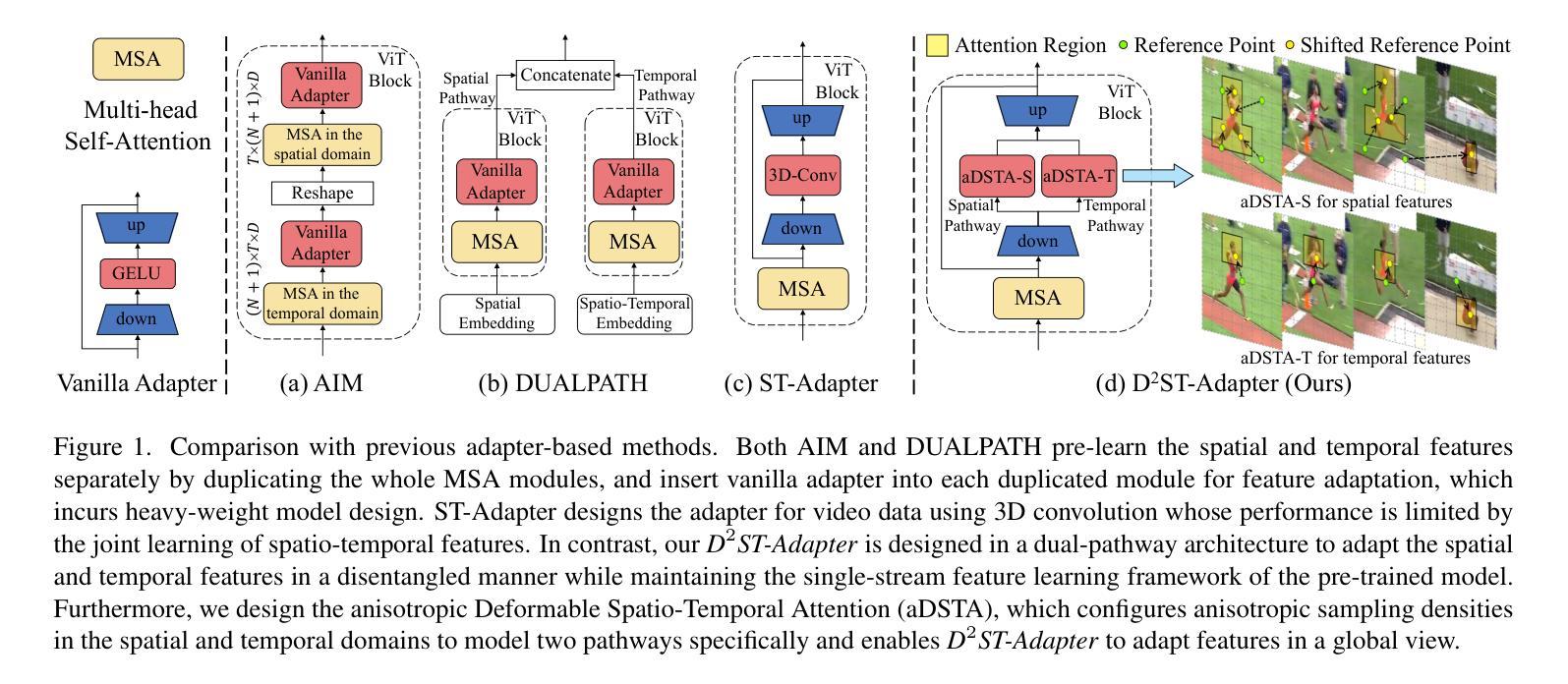
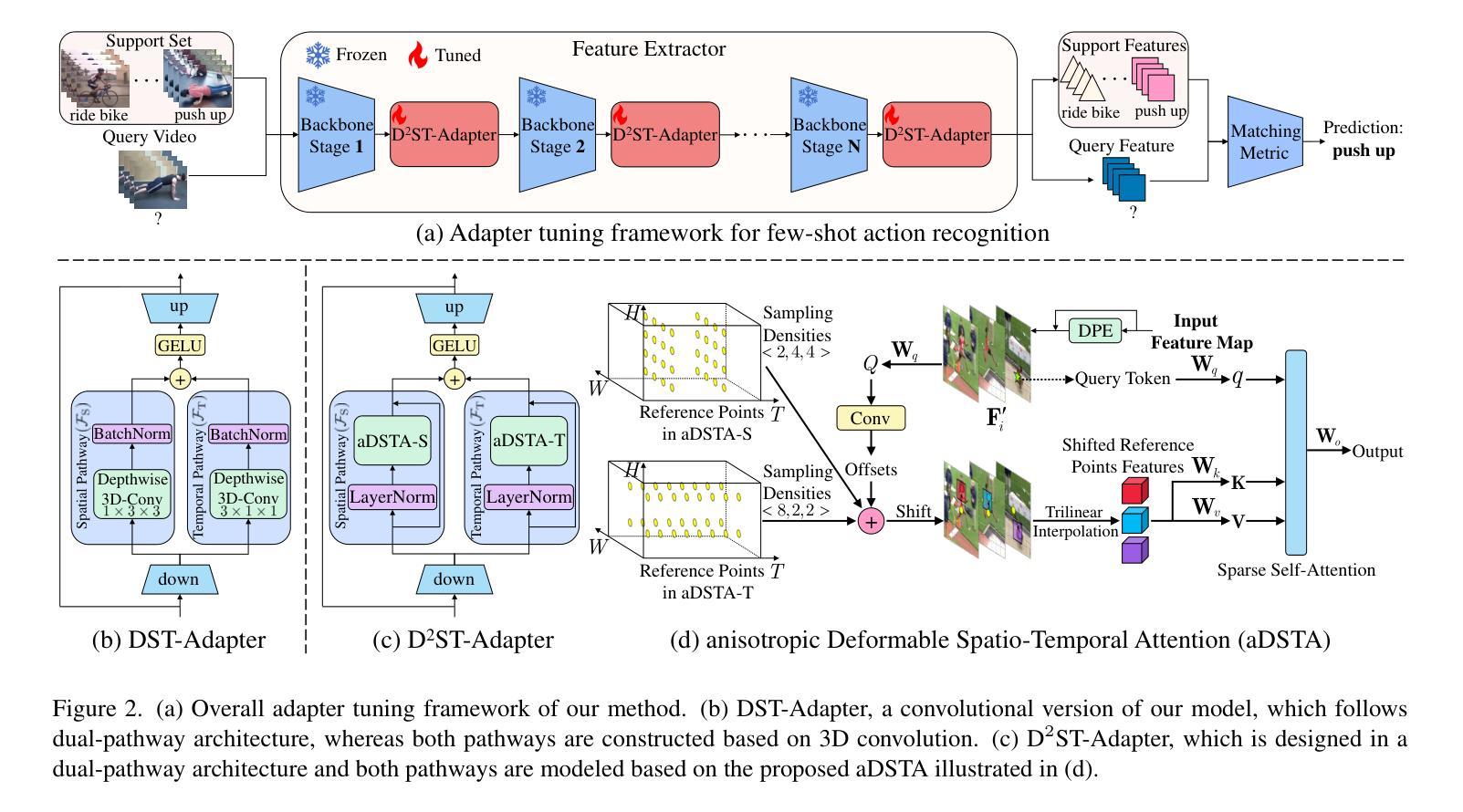
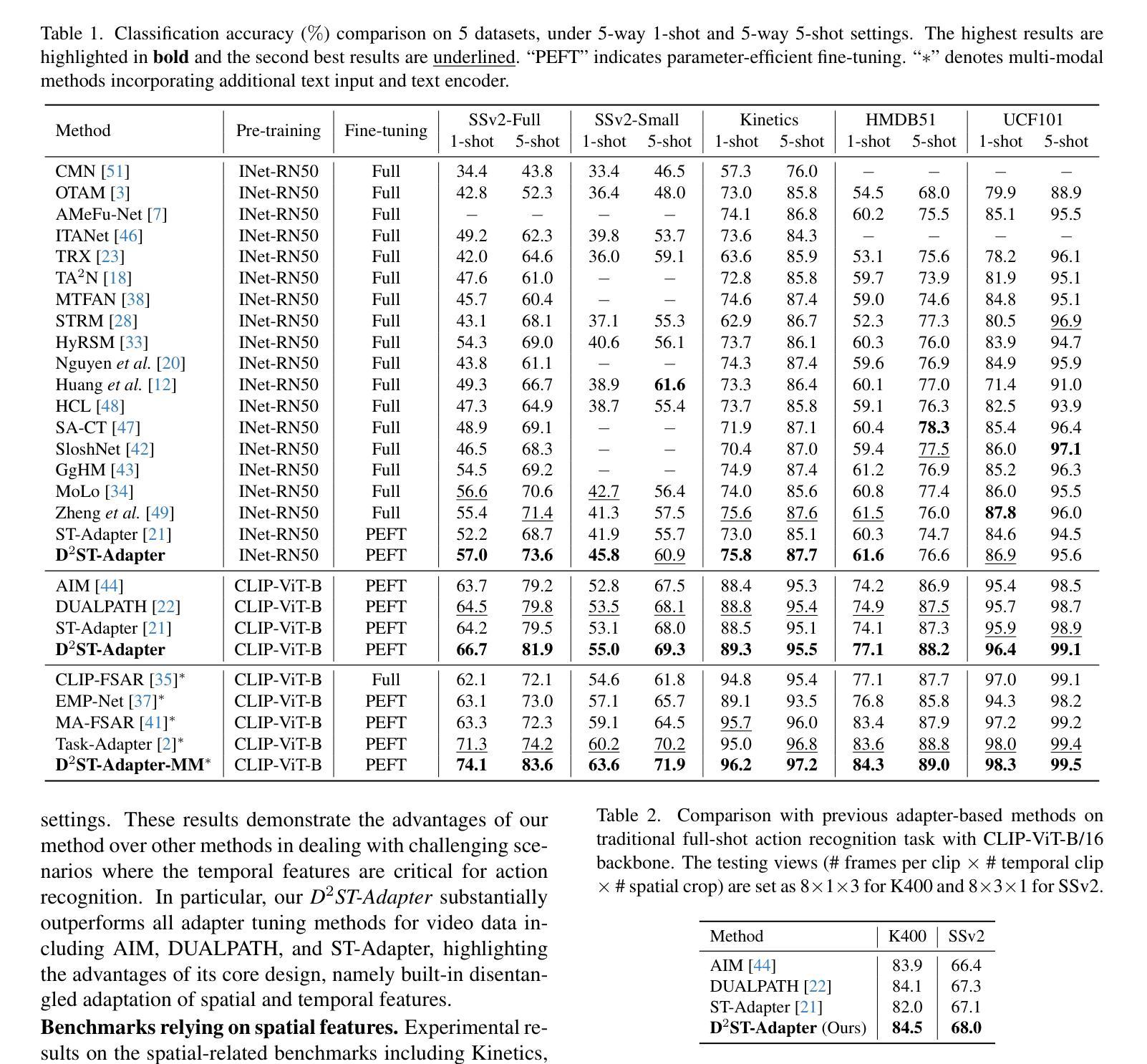
D$^2$ST-Adapter: Disentangled-and-Deformable Spatio-Temporal Adapter for Few-shot Action Recognition
Authors:Wenjie Pei, Qizhong Tan, Guangming Lu, Jiandong Tian, Jun Yu
Adapting pre-trained image models to video modality has proven to be an effective strategy for robust few-shot action recognition. In this work, we explore the potential of adapter tuning in image-to-video model adaptation and propose a novel video adapter tuning framework, called Disentangled-and-Deformable Spatio-Temporal Adapter (D$^2$ST-Adapter). It features a lightweight design, low adaptation overhead and powerful spatio-temporal feature adaptation capabilities. D$^2$ST-Adapter is structured with an internal dual-pathway architecture that enables built-in disentangled encoding of spatial and temporal features within the adapter, seamlessly integrating into the single-stream feature learning framework of pre-trained image models. In particular, we develop an efficient yet effective implementation of the D$^2$ST-Adapter, incorporating the specially devised anisotropic Deformable Spatio-Temporal Attention as its pivotal operation. This mechanism can be individually tailored for two pathways with anisotropic sampling densities along the spatial and temporal domains in 3D spatio-temporal space, enabling disentangled encoding of spatial and temporal features while maintaining a lightweight design. Extensive experiments by instantiating our method on both pre-trained ResNet and ViT demonstrate the superiority of our method over state-of-the-art methods. Our method is particularly well-suited to challenging scenarios where temporal dynamics are critical for action recognition. Code is available at https://github.com/qizhongtan/D2ST-Adapter.
将预训练图像模型适配至视频模式已被证明是实现稳健的少量动作识别数据的有效策略。在这项工作中,我们探索了适配器调整在图像到视频模型适配中的潜力,并提出了一种新型的视频适配器调整框架,称为解纠缠和可变形的时空适配器(D^2ST-Adapter)。它具有轻量级设计、低适应开销和强大的时空特征适应力。D^2ST-Adapter采用内部双路径架构,使适配器内部的空间和时间特征得以解纠缠编码,无缝集成到预训练图像模型的单流特征学习框架中。特别是,我们开发了一种高效且有效的D^2ST-Adapter实现,其中融入了专门设计的各向异性可变时空注意力作为其关键操作。该机制可以针对两条路径进行个性化设置,在3D时空空间中的空间和时间域上具有各向异性采样密度,从而实现空间和时间特征的解纠缠编码,同时保持轻量级设计。通过在我们的方法和预训练的ResNet和ViT上进行的广泛实验表明,我们的方法优于最新方法。我们的方法特别适用于时间动态对动作识别至关重要的具有挑战性的场景。代码可在https://github.com/qizhongtan/D2ST-Adapter找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV2025
摘要
本论文探索了适配器调整在图像到视频模型适配中的潜力,并提出了一种新颖的视频适配器调整框架——称为解纠缠与可变形时空适配器(D^2ST-Adapter)。它具有轻量级设计、低适应开销和强大的时空特征适应力。D^2ST-Adapter采用内部双路径架构,实现了适配器内时空特征的解纠缠编码,无缝集成到预训练图像模型的单流特征学习框架中。特别是,我们开发了一种高效且有效的D^2ST-Adapter实现,将其核心操作整合为专门设计的可变形时空注意力机制。该机制可以在空间和时间域上实现个性化的采样密度调整,以支持两条路径的独立定制,从而实现时空特征的解纠缠编码并保持轻量级设计。在预训练的ResNet和ViT上的实验表明,该方法优于现有技术。该方法特别适用于动作识别中时间动态至关重要的挑战性场景。相关代码可通过https://github.com/qizhongtan/D2ST-Adapter获取。
关键见解
- 提出了一种新颖的针对图像到视频模型的适配策略——解纠缠与可变形时空适配器(D^2ST-Adapter)。
- 采用轻量级设计以进行适配器调整并具有时空特征解纠缠的能力。通过双路径架构进行内置时空特征编码。
- 开发了一种高效的D^2ST-Adapter实现方法,结合了专门的时空注意力机制,支持空间和时间域上的个性化采样密度调整。
点此查看论文截图