⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-04 更新
ADAptation: Reconstruction-based Unsupervised Active Learning for Breast Ultrasound Diagnosis
Authors:Yaofei Duan, Yuhao Huang, Xin Yang, Luyi Han, Xinyu Xie, Zhiyuan Zhu, Ping He, Ka-Hou Chan, Ligang Cui, Sio-Kei Im, Dong Ni, Tao Tan
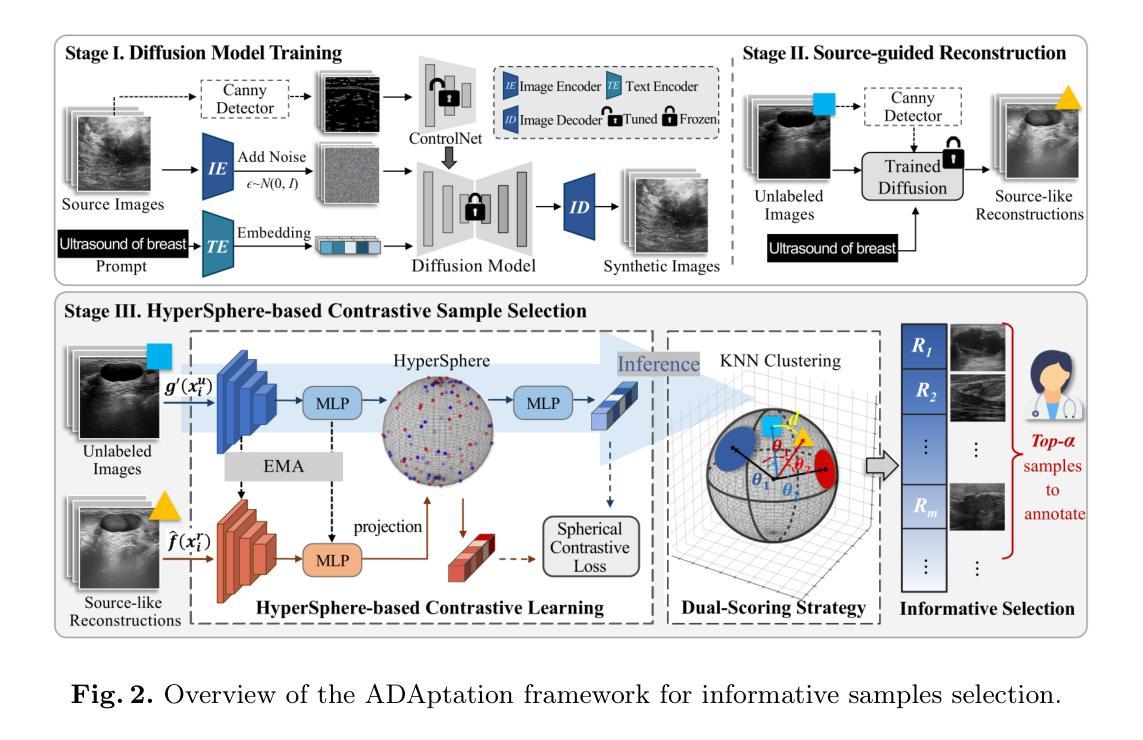
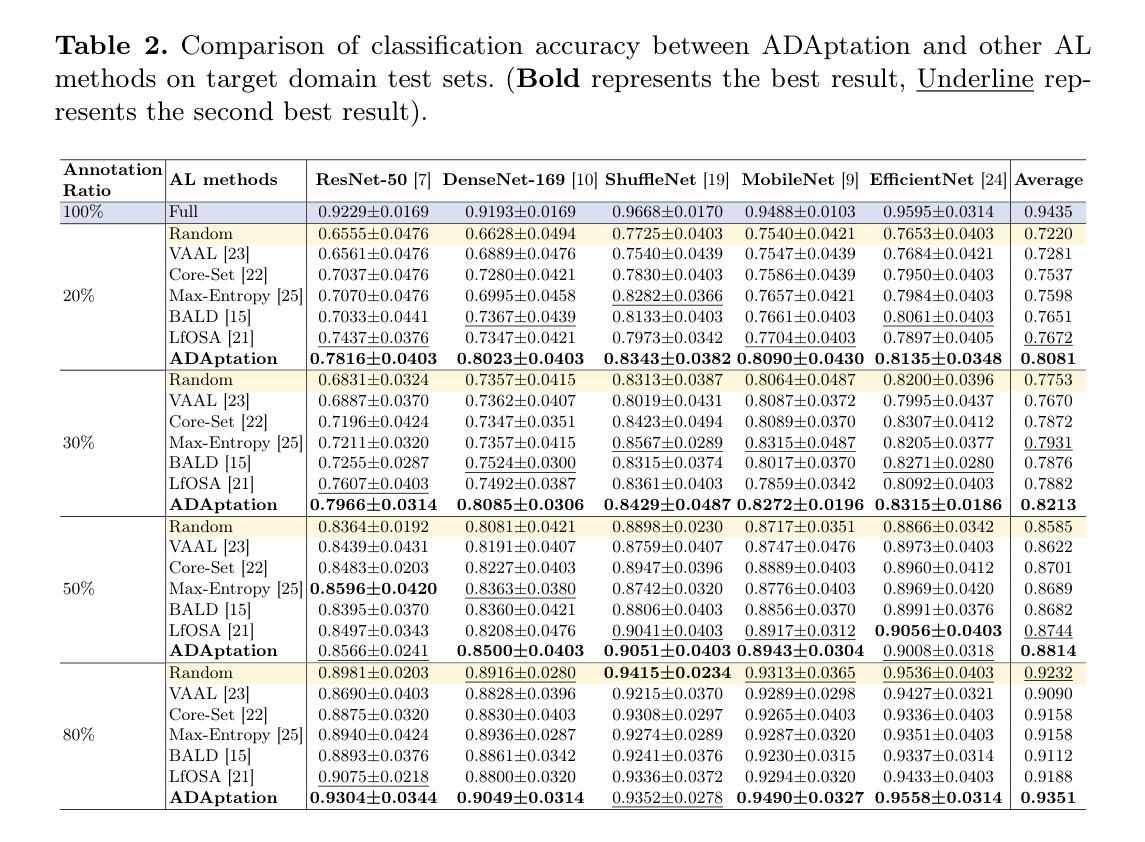
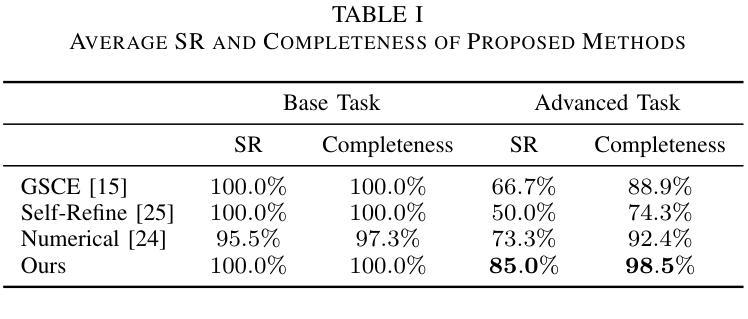
Deep learning-based diagnostic models often suffer performance drops due to distribution shifts between training (source) and test (target) domains. Collecting and labeling sufficient target domain data for model retraining represents an optimal solution, yet is limited by time and scarce resources. Active learning (AL) offers an efficient approach to reduce annotation costs while maintaining performance, but struggles to handle the challenge posed by distribution variations across different datasets. In this study, we propose a novel unsupervised Active learning framework for Domain Adaptation, named ADAptation, which efficiently selects informative samples from multi-domain data pools under limited annotation budget. As a fundamental step, our method first utilizes the distribution homogenization capabilities of diffusion models to bridge cross-dataset gaps by translating target images into source-domain style. We then introduce two key innovations: (a) a hypersphere-constrained contrastive learning network for compact feature clustering, and (b) a dual-scoring mechanism that quantifies and balances sample uncertainty and representativeness. Extensive experiments on four breast ultrasound datasets (three public and one in-house/multi-center) across five common deep classifiers demonstrate that our method surpasses existing strong AL-based competitors, validating its effectiveness and generalization for clinical domain adaptation. The code is available at the anonymized link: https://github.com/miccai25-966/ADAptation.
基于深度学习的诊断模型由于训练(源)和测试(目标)域之间的分布变化,常常会出现性能下降的情况。为模型重新训练收集并标注足够的目标域数据是一种最佳解决方案,然而这受到时间和资源的限制。主动学习(AL)提供了一种有效的方法来降低标注成本,同时保持性能,但难以处理不同数据集分布变化带来的挑战。在这项研究中,我们提出了一种用于域适应的无监督主动学习框架,名为ADAptation,它能够在有限的标注预算下,从多域数据池中有效地选择信息样本。作为基本步骤,我们的方法首先利用扩散模型的分布均化能力,通过转换目标图像到源域风格来弥补跨数据集之间的差距。然后我们引入了两个关键创新点:(a)一个超球约束的对比学习网络,用于紧凑特征聚类,(b)一个量化并平衡样本不确定性和代表性的双评分机制。在四个乳腺超声数据集(三个公开和一个内部/多中心)上进行的广泛实验表明,我们的方法在五个常见的深度分类器上的表现超过了现有的强大基于AL的竞争对手,验证了其在临床域适应中的有效性和通用性。代码可在匿名链接中找到:https://github.com/miccai25-966/ADAptation。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 4 figures, 4 tables. Accepted by conference MICCAI2025
Summary
本文提出了一种名为ADAptation的新型无监督主动学习方法,用于解决深度学习模型在不同数据集间分布变化的问题。该方法通过利用扩散模型的分布均衡能力,将目标图像转化为源域风格,缩小跨数据集差距。同时引入超球约束对比学习网络和双重评分机制,量化并平衡样本不确定性和代表性。在四个乳腺超声数据集上的实验表明,该方法在临床医学领域优于现有主动学习方法。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习模型在训练和测试数据分布不一致时性能会下降。
- 目标域数据的重新标注和收集是优化模型的方法之一,但受限于时间和资源。
- 主动学习方法可减少标注成本同时保持性能,但难以处理不同数据集间的分布变化。
- 本研究提出了一种名为ADAptation的新型无监督主动学习方法,用于域适应。
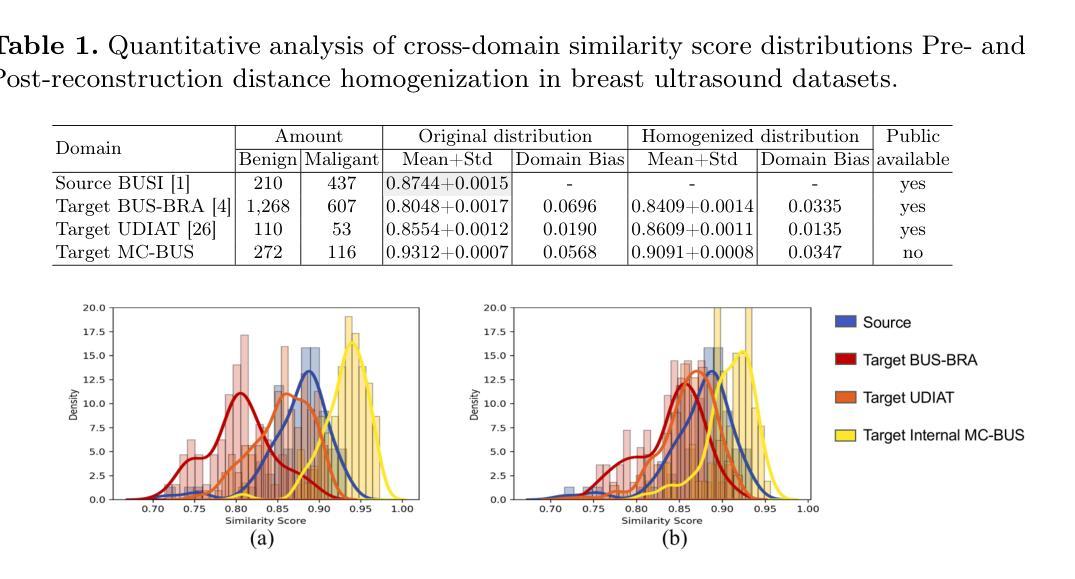
5.ADAptation利用扩散模型的分布均衡能力,将目标图像转化为源域风格。 - 引入超球约束对比学习网络和双重评分机制来量化并平衡样本的不确定性和代表性。
点此查看论文截图