⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-04 更新
A Gift from the Integration of Discriminative and Diffusion-based Generative Learning: Boundary Refinement Remote Sensing Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Hao Wang, Keyan Hu, Xin Guo, Haifeng Li, Chao Tao
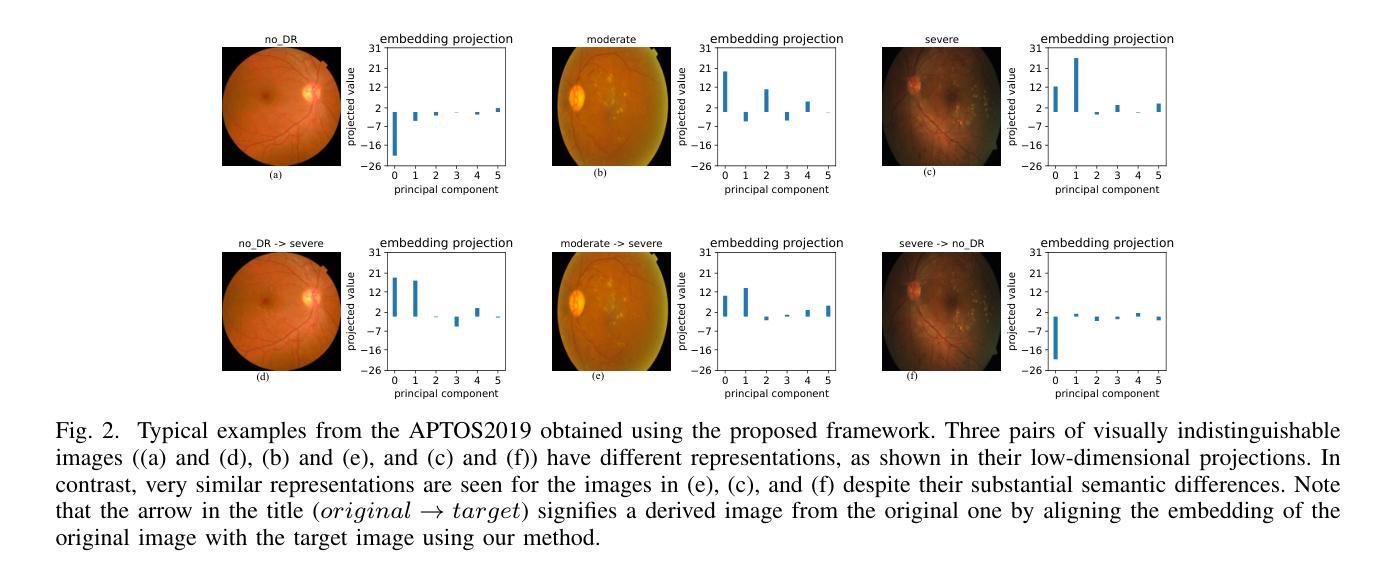
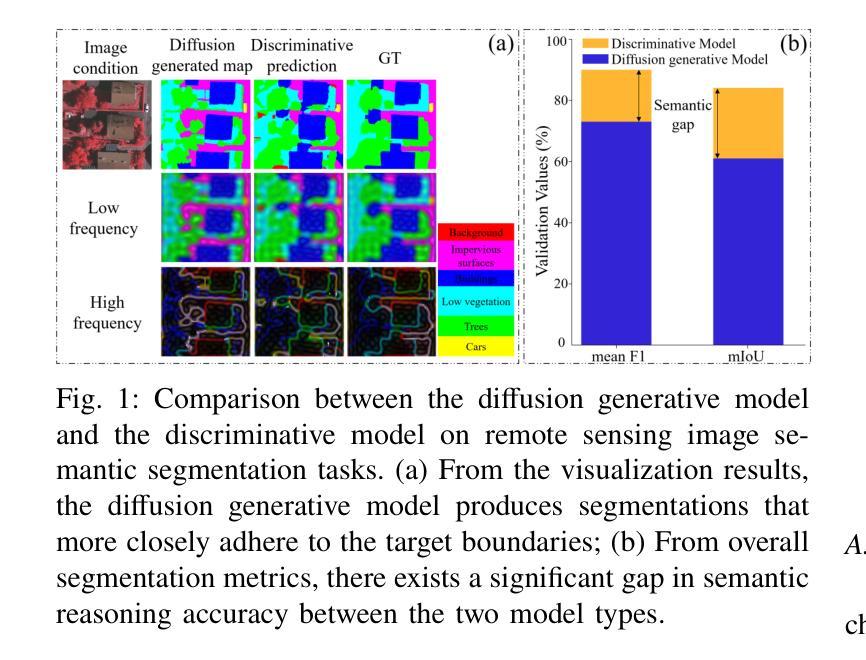
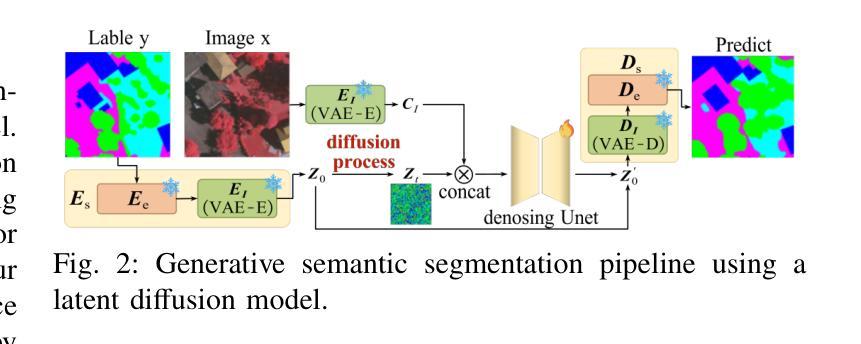
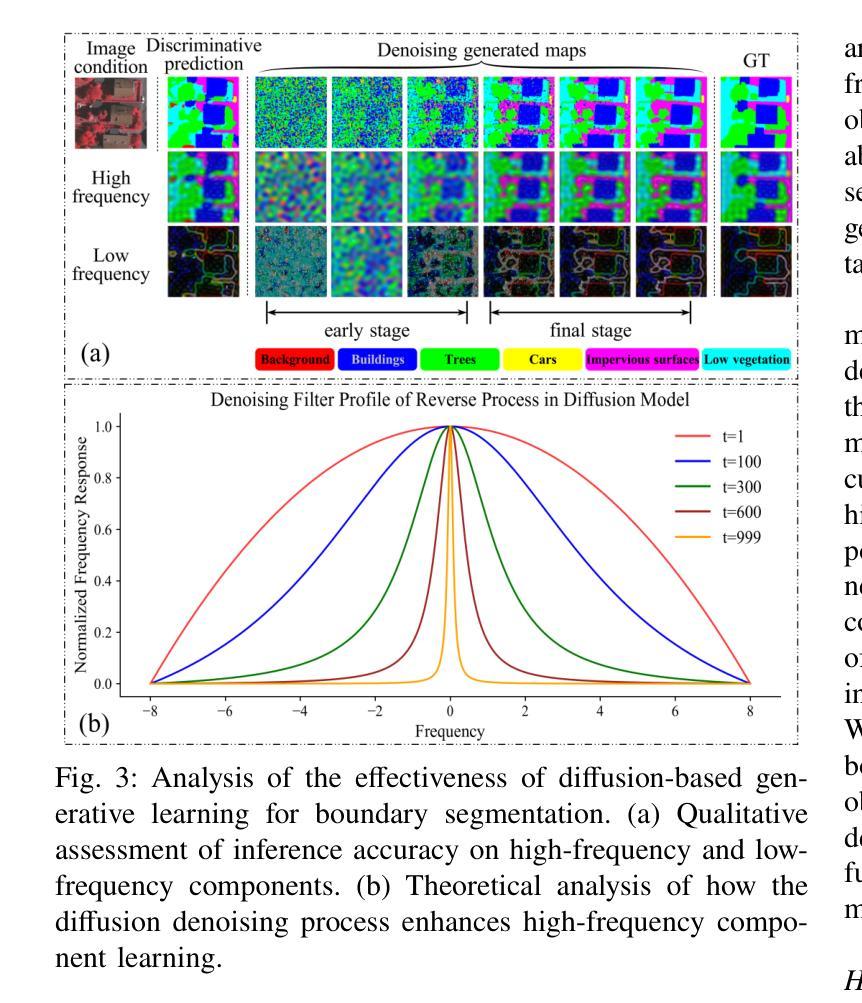
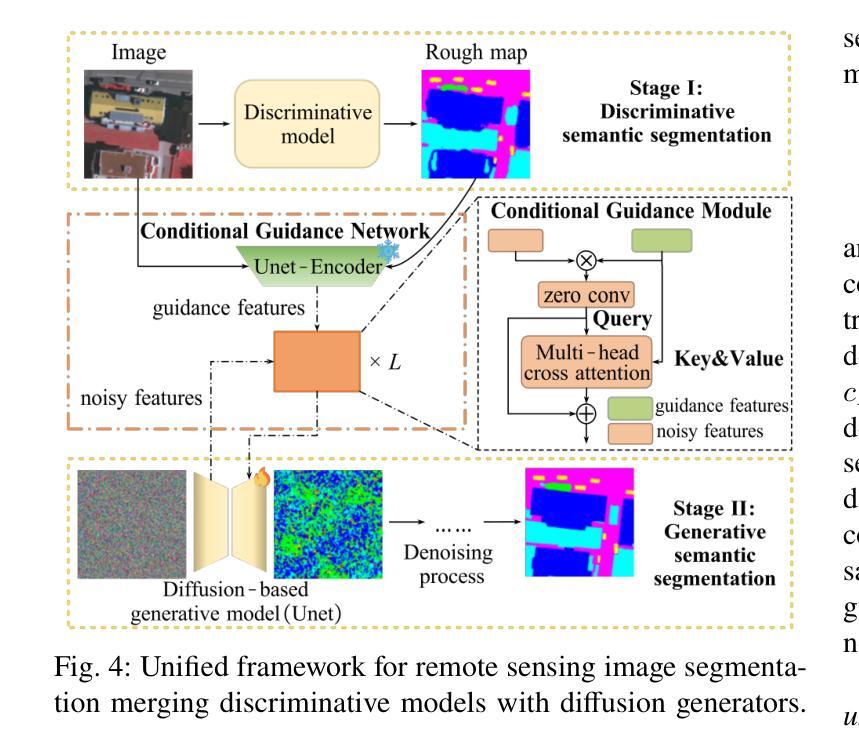
Remote sensing semantic segmentation must address both what the ground objects are within an image and where they are located. Consequently, segmentation models must ensure not only the semantic correctness of large-scale patches (low-frequency information) but also the precise localization of boundaries between patches (high-frequency information). However, most existing approaches rely heavily on discriminative learning, which excels at capturing low-frequency features, while overlooking its inherent limitations in learning high-frequency features for semantic segmentation. Recent studies have revealed that diffusion generative models excel at generating high-frequency details. Our theoretical analysis confirms that the diffusion denoising process significantly enhances the model’s ability to learn high-frequency features; however, we also observe that these models exhibit insufficient semantic inference for low-frequency features when guided solely by the original image. Therefore, we integrate the strengths of both discriminative and generative learning, proposing the Integration of Discriminative and diffusion-based Generative learning for Boundary Refinement (IDGBR) framework. The framework first generates a coarse segmentation map using a discriminative backbone model. This map and the original image are fed into a conditioning guidance network to jointly learn a guidance representation subsequently leveraged by an iterative denoising diffusion process refining the coarse segmentation. Extensive experiments across five remote sensing semantic segmentation datasets (binary and multi-class segmentation) confirm our framework’s capability of consistent boundary refinement for coarse results from diverse discriminative architectures. The source code will be available at https://github.com/KeyanHu-git/IDGBR.
遥感语义分割必须解决图像内地面对象是什么以及它们位置的问题。因此,分割模型必须确保大规模斑块(低频信息)的语义正确性,同时还要确保斑块之间边界的精确定位(高频信息)。然而,大多数现有方法都严重依赖于判别学习,这种方法在捕获低频特征方面非常出色,但却忽视了在学习语义分割高频特征方面的固有局限性。最近的研究表明,扩散生成模型在生成高频细节方面表现出色。我们的理论分析证实,扩散去噪过程显著增强了模型学习高频特征的能力;然而,我们也观察到,当仅由原始图像引导时,这些模型对低频特征的语义推断不足。因此,我们结合了判别学习和生成学习的优点,提出了融合判别和基于扩散的生成学习以进行边界细化(IDGBR)的框架。该框架首先使用判别骨干模型生成一个粗略的分割图。然后,将这个图与原始图像一起输入条件引导网络,共同学习一个引导表示,随后由迭代去噪扩散过程利用该表示来细化粗略的分割。在五个遥感语义分割数据集(二进制和多类分割)上进行的广泛实验证实,我们的框架能够对来自各种判别架构的粗略结果进行一致的边界细化。源代码将发布在https://github.com/KeyanHu-git/IDGBR。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages, 14 figures
Summary
本文探讨了遥感语义分割中面临的问题,包括既要识别地面物体的种类,又要确定其位置。现有的分割模型大多侧重于低频信息的语义正确性,而忽视了高频信息的精确边界定位。为此,本文结合了判别学习和扩散生成模型的优势,提出了IDGBR框架。该框架首先使用判别骨干模型生成粗略分割图,然后与原始图像一起输入条件引导网络,共同学习引导表示,再通过迭代去噪扩散过程对粗略分割进行细化。实验证明,该框架能够细化不同判别架构的粗略结果,提高遥感语义分割的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 遥感语义分割需同时识别地面物体的种类和位置。
- 现有模型侧重于低频信息的语义正确性,忽视了高频信息的精确边界定位。
- 扩散生成模型擅长生成高频细节。
- IDGBR框架结合了判别学习和扩散生成模型的优势。
- IDGBR框架使用判别骨干模型生成粗略分割图,并通过条件引导网络和迭代去噪扩散过程进行细化。
- 在五个遥感语义分割数据集上的实验证明了IDGBR框架的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

TrackingMiM: Efficient Mamba-in-Mamba Serialization for Real-time UAV Object Tracking
Authors:Bingxi Liu, Calvin Chen, Junhao Li, Guyang Yu, Haoqian Song, Xuchen Liu, Jinqiang Cui, Hong Zhang
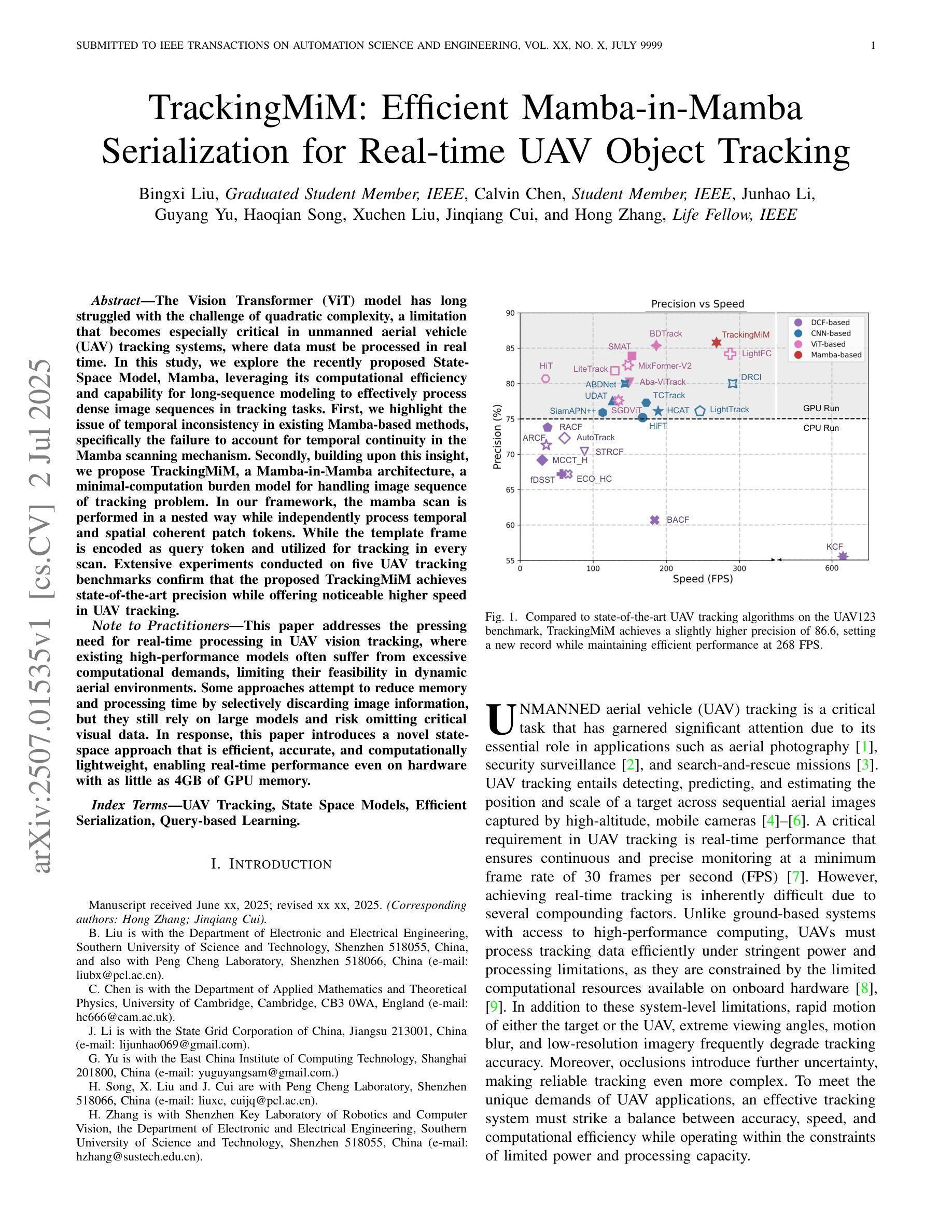
The Vision Transformer (ViT) model has long struggled with the challenge of quadratic complexity, a limitation that becomes especially critical in unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) tracking systems, where data must be processed in real time. In this study, we explore the recently proposed State-Space Model, Mamba, leveraging its computational efficiency and capability for long-sequence modeling to effectively process dense image sequences in tracking tasks. First, we highlight the issue of temporal inconsistency in existing Mamba-based methods, specifically the failure to account for temporal continuity in the Mamba scanning mechanism. Secondly, building upon this insight,we propose TrackingMiM, a Mamba-in-Mamba architecture, a minimal-computation burden model for handling image sequence of tracking problem. In our framework, the mamba scan is performed in a nested way while independently process temporal and spatial coherent patch tokens. While the template frame is encoded as query token and utilized for tracking in every scan. Extensive experiments conducted on five UAV tracking benchmarks confirm that the proposed TrackingMiM achieves state-of-the-art precision while offering noticeable higher speed in UAV tracking.
Vision Transformer(ViT)模型长期以来一直面临着二次复杂度的挑战,这一限制在无人飞行器(UAV)跟踪系统中尤其关键,因为这些系统中的数据必须实时处理。在这项研究中,我们探索了最近提出的State-Space Model(Mamba),利用它的计算效率和长序列建模能力,以有效处理跟踪任务中的密集图像序列。首先,我们强调了基于Mamba的方法中存在的时间不一致性问题,特别是Mamba扫描机制未能考虑时间连续性。其次,基于这一认识,我们提出了TrackingMiM,这是一个Mamba-in-Mamba架构,是一个用于处理跟踪问题图像序列的低计算负担模型。在我们的框架中,mamba扫描以嵌套的方式进行,同时独立处理时间和空间连贯的补丁令牌。模板帧被编码为查询令牌,并在每次扫描中用于跟踪。在五个UAV跟踪基准测试上进行的广泛实验证实,所提出的TrackingMiM实现了最先进的精度,同时在UAV跟踪中提供了明显的更高速度。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages
Summary
ViT模型在处理跟踪任务时面临二次复杂性挑战,尤其在无人机跟踪系统中。研究探讨了新近提出的Mamba状态空间模型,发现其计算效率高、适合处理长序列数据。但现有Mamba方法存在时间不一致性问题,未能充分考虑时间连续性。因此,研究提出了TrackingMiM模型,利用Mamba-in-Mamba架构处理跟踪问题的图像序列,实现了高效且高精度的无人机跟踪。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformer (ViT)模型在处理跟踪任务时面临二次复杂性挑战。
- Mamba状态空间模型具有计算效率高、适合处理长序列数据的优点。
- 现有Mamba方法存在时间不一致性问题,未能充分考虑时间连续性。
- TrackingMiM模型利用Mamba-in-Mamba架构处理跟踪问题的图像序列。
- TrackingMiM模型实现了高效且高精度的无人机跟踪。
- TrackingMiM模型在五个无人机跟踪基准测试上达到了最先进的精度。
点此查看论文截图
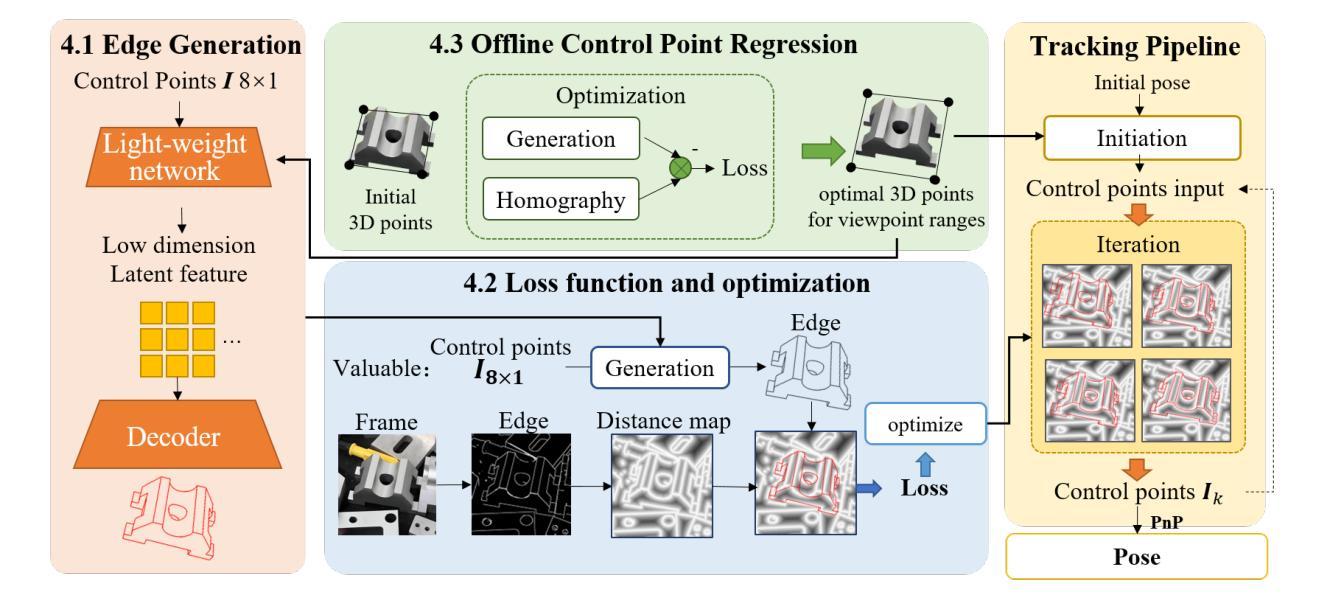
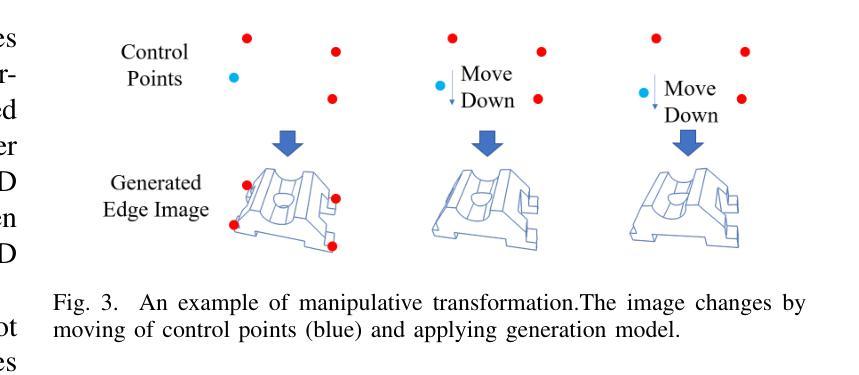
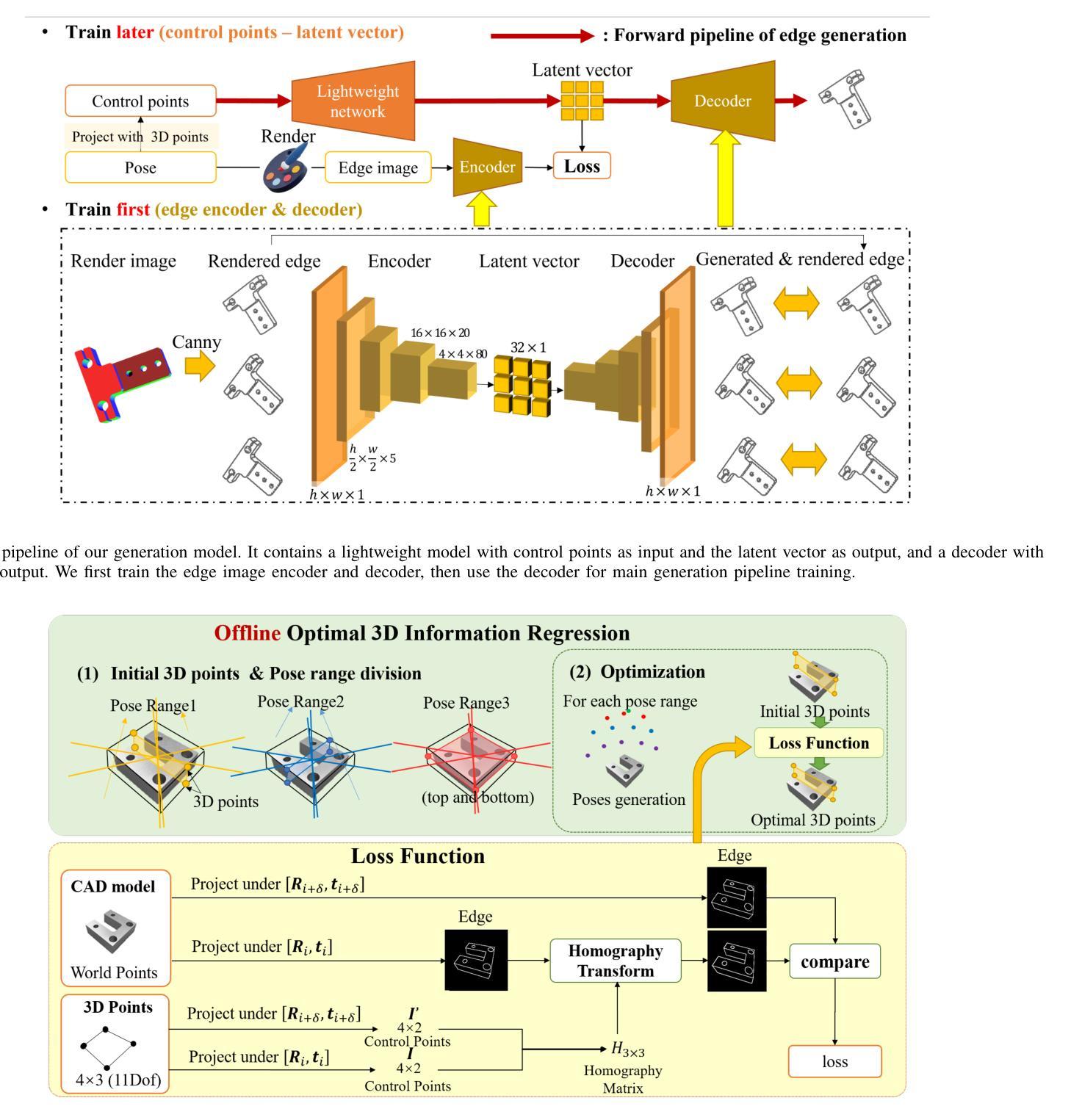
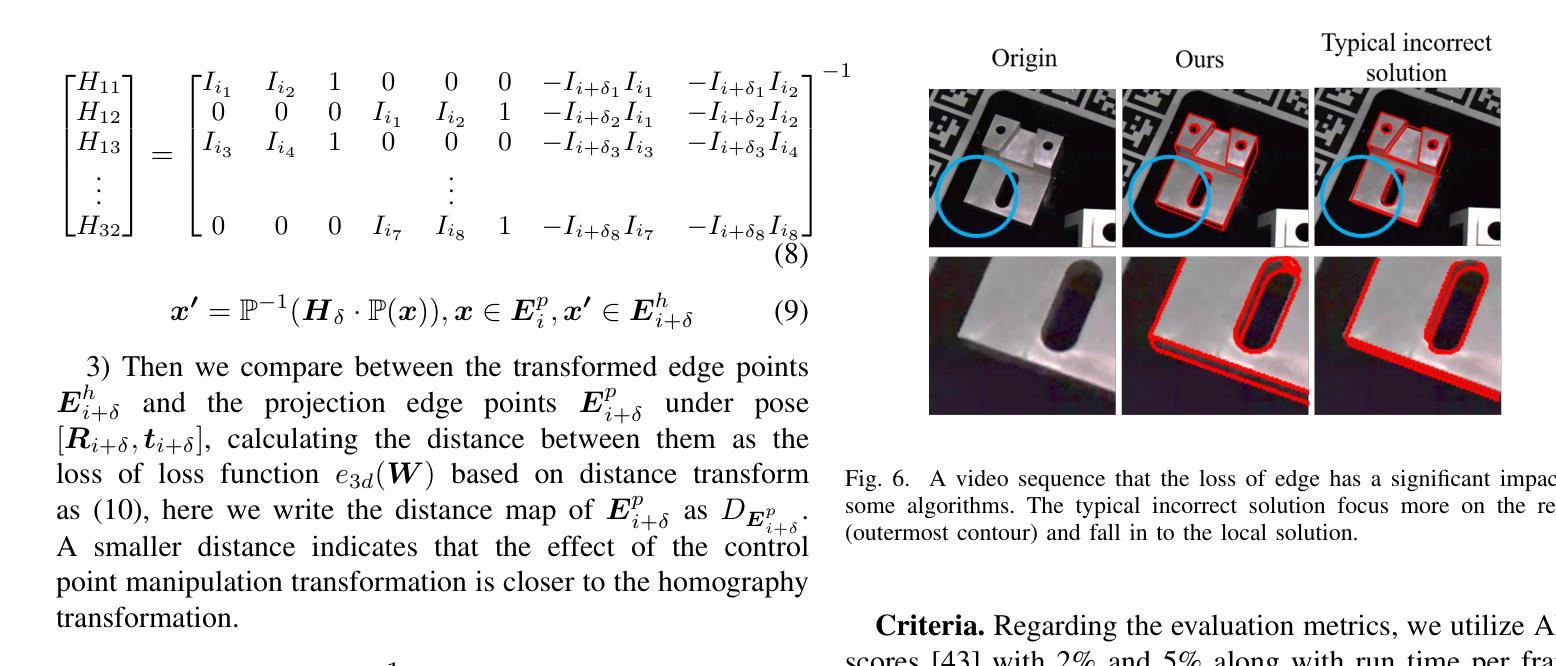
Active Control Points-based 6DoF Pose Tracking for Industrial Metal Objects
Authors:Chentao Shen, Ding Pan, Mingyu Mei, Zaixing He, Xinyue Zhao
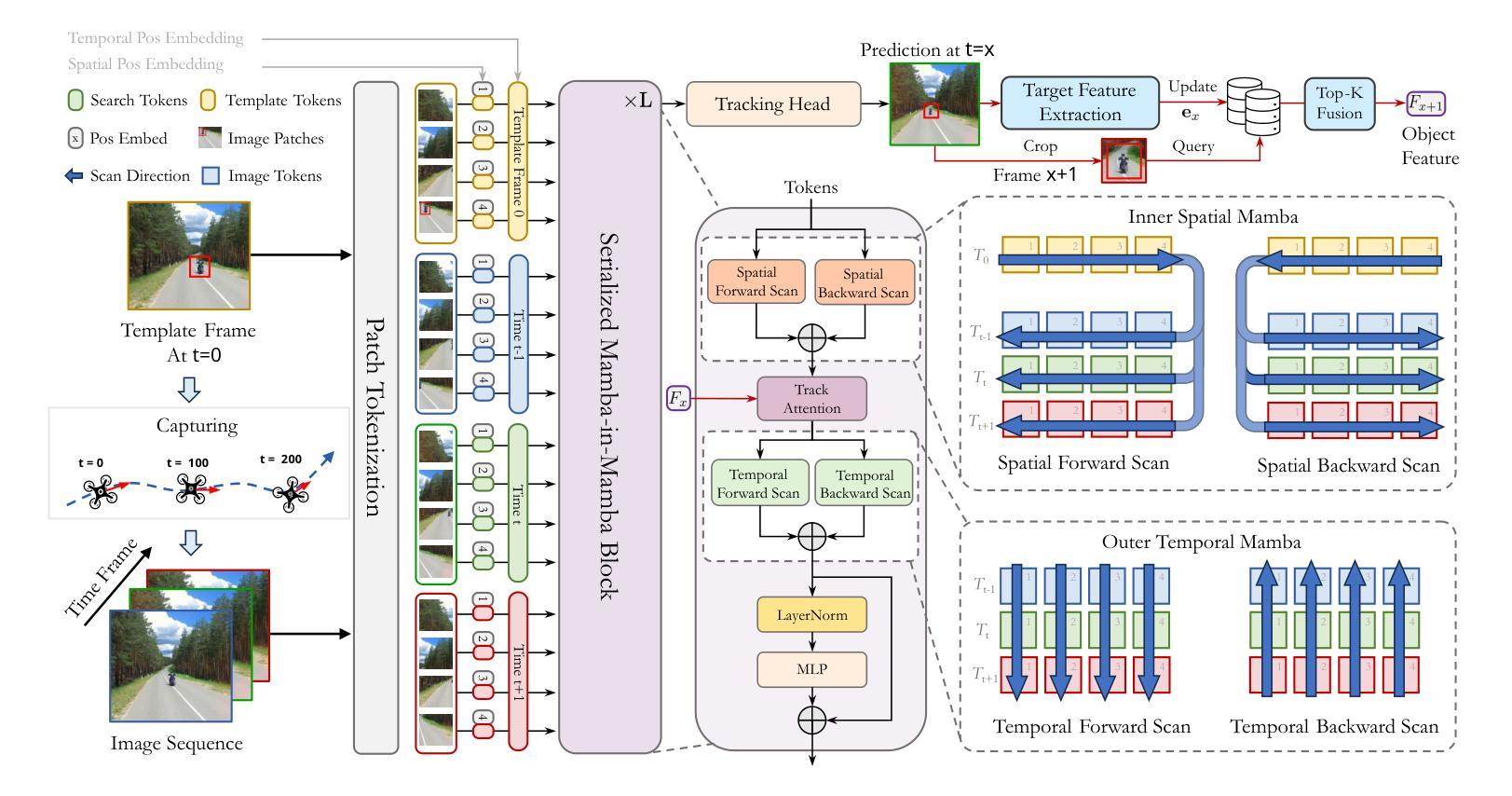
Visual pose tracking is playing an increasingly vital role in industrial contexts in recent years. However, the pose tracking for industrial metal objects remains a challenging task especially in the real world-environments, due to the reflection characteristic of metal objects. To address this issue, we propose a novel 6DoF pose tracking method based on active control points. The method uses image control points to generate edge feature for optimization actively instead of 6DoF pose-based rendering, and serve them as optimization variables. We also introduce an optimal control point regression method to improve robustness. The proposed tracking method performs effectively in both dataset evaluation and real world tasks, providing a viable solution for real-time tracking of industrial metal objects. Our source code is made publicly available at: https://github.com/tomatoma00/ACPTracking.
近年来,视觉姿态跟踪在工业领域的应用越来越重要。然而,对于工业金属物体的姿态跟踪,在真实世界环境下仍然是一项具有挑战性的任务,尤其是由于金属物体的反射特性。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种基于主动控制点的新型6DoF姿态跟踪方法。该方法使用图像控制点来主动生成边缘特征进行优化,而不是基于6DoF姿态的渲染,并将其作为优化变量。我们还引入了一种最优控制点回归方法,以提高其稳健性。所提出的跟踪方法在数据集评估和真实世界任务中都表现有效,为工业金属物体的实时跟踪提供了可行的解决方案。我们的源代码已公开在:https://github.com/tomatoma00/ACPTracking。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF preprint version
Summary
视觉姿态跟踪近年来在工业领域的作用越来越重要。然而,对于工业金属物体的姿态跟踪,尤其是在真实世界环境中,由于金属物体的反射特性,仍是一项具有挑战性的任务。为此,我们提出了一种基于主动控制点的新型6DoF姿态跟踪方法。该方法使用图像控制点来主动生成边缘特征进行优化,而不是基于6DoF姿态的渲染,并将其作为优化变量。我们还引入了一种优化控制点回归方法,以提高稳健性。所提出的方法在数据集评估和真实世界任务中都表现有效,为工业金属物体的实时跟踪提供了可行的解决方案。源代码已公开发布在:https://github.com/tomatoma00/ACPTracking。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉姿态跟踪在工业领域的重要性日益凸显。
- 工业金属物体的姿态跟踪在真实世界环境中具有挑战性,主要因为金属物体的反射特性。
- 提出了一种基于主动控制点的新型6DoF姿态跟踪方法。
- 该方法通过图像控制点生成边缘特征并进行优化。
- 所提出的方法不仅适用于数据集评估,也在真实世界任务中表现良好。
- 引入优化控制点回归方法以提高稳健性。
点此查看论文截图
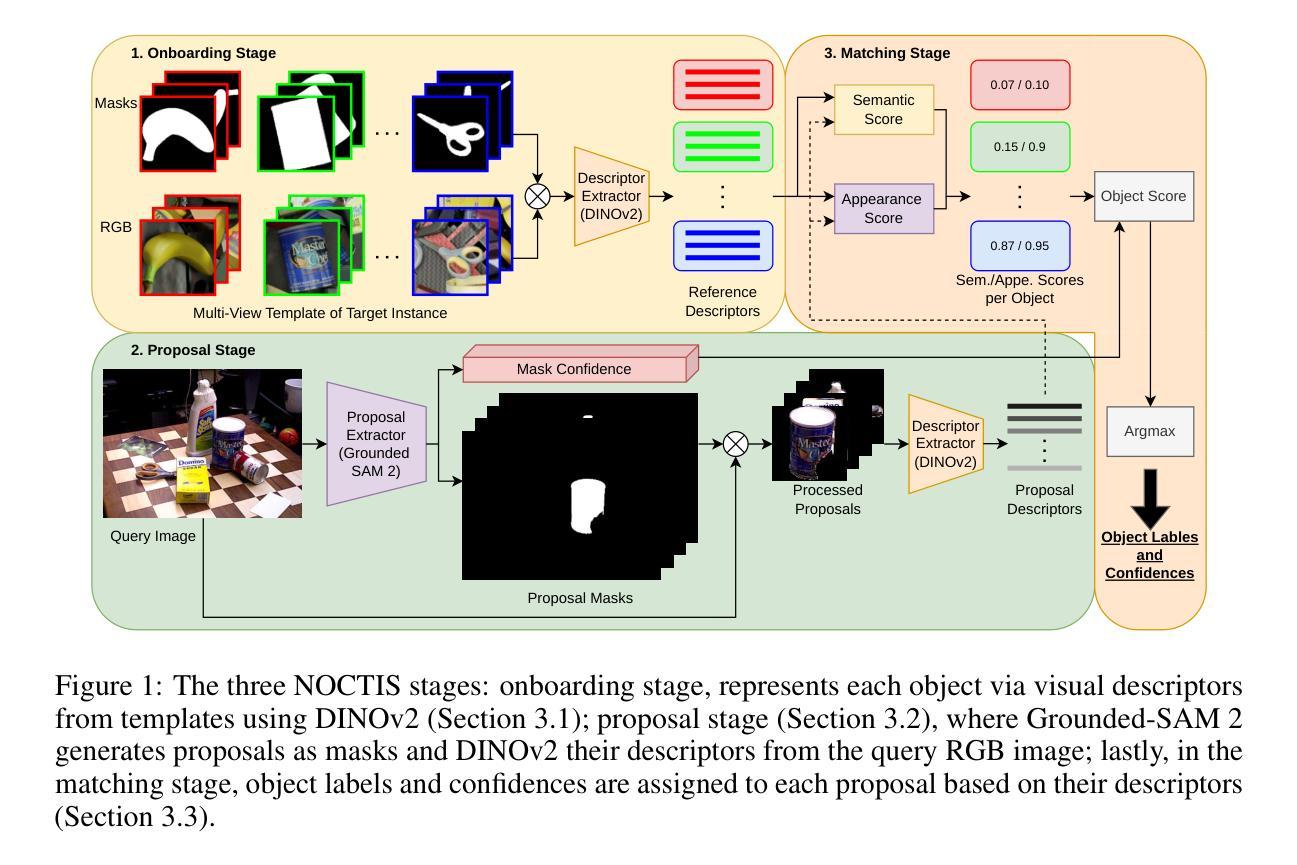
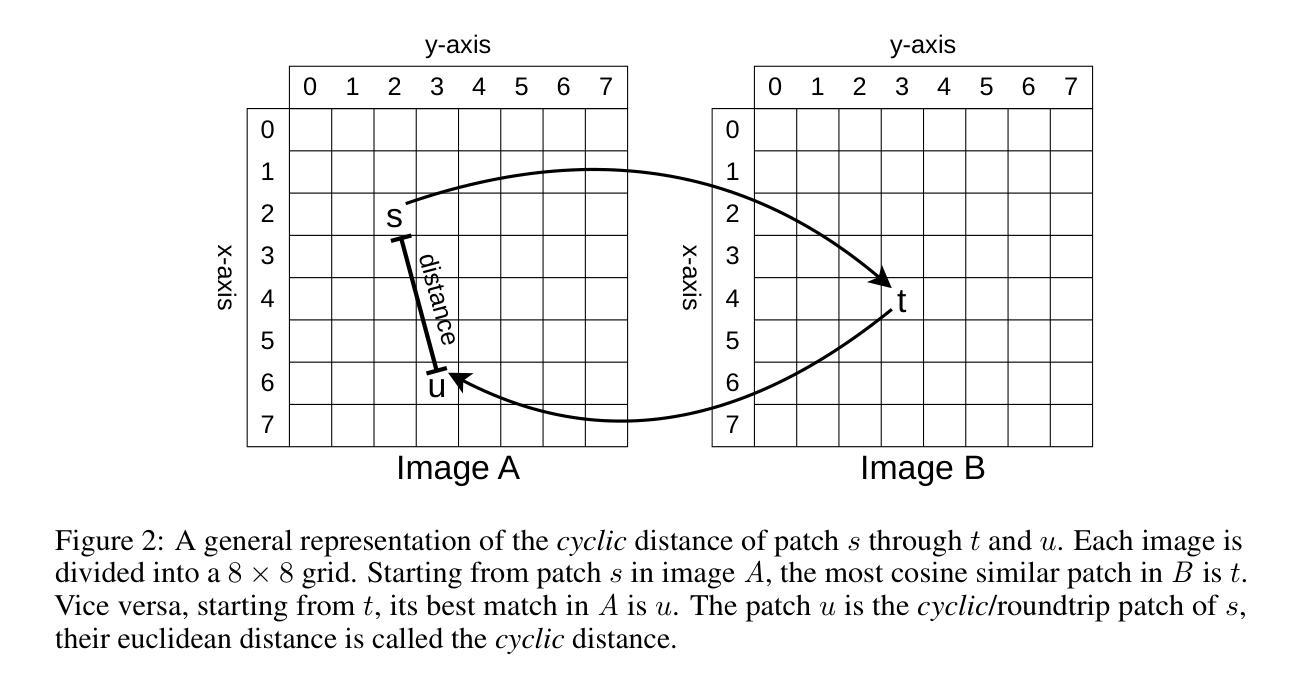
NOCTIS: Novel Object Cyclic Threshold based Instance Segmentation
Authors:Max Gandyra, Alessandro Santonicola, Michael Beetz
Instance segmentation of novel objects instances in RGB images, given some example images for each object, is a well known problem in computer vision. Designing a model general enough to be employed, for all kinds of novel objects, without (re-) training, has proven to be a difficult task. To handle this, we propose a simple, yet powerful, framework, called: Novel Object Cyclic Threshold based Instance Segmentation (NOCTIS). This work stems from and improves upon previous ones like CNOS, SAM-6D and NIDS-Net; thus, it also leverages on recent vision foundation models, namely: Grounded-SAM 2 and DINOv2. It utilises Grounded-SAM 2 to obtain object proposals with precise bounding boxes and their corresponding segmentation masks; while DINOv2’s zero-shot capabilities are employed to generate the image embeddings. The quality of those masks, together with their embeddings, is of vital importance to our approach; as the proposal-object matching is realized by determining an object matching score based on the similarity of the class embeddings and the average maximum similarity of the patch embeddings. Differently to SAM-6D, calculating the latter involves a prior patch filtering based on the distance between each patch and its corresponding cyclic/roundtrip patch in the image grid. Furthermore, the average confidence of the proposals’ bounding box and mask is used as an additional weighting factor for the object matching score. We empirically show that NOCTIS, without further training/fine tuning, outperforms the best RGB and RGB-D methods on the seven core datasets of the BOP 2023 challenge for the “Model-based 2D segmentation of unseen objects” task.
在RGB图像中对新型物体实例进行实例分割是一个众所周知的计算机视觉问题。给定每个物体的示例图像,设计一种足够通用的模型,能够应用于所有新型物体,而无需(重新)训练,已被证明是一项艰巨的任务。为了处理这个问题,我们提出了一种简单而强大的框架,称为:基于新型物体循环阈值的实例分割(NOCTIS)。这项工作源于并改进了先前的CNOS、SAM-6D和NIDS-Net等研究;因此,它也依赖于最近的视觉基础模型,即Grounded-SAM 2和DINOv2。它利用Grounded-SAM 2获得精确的对象提议边界框及其相应的分割掩模;而DINOv2的零样本能力则用于生成图像嵌入。这些掩模的质量以及它们的嵌入对我们的方法至关重要;因为提议对象匹配是通过确定基于类别嵌入的相似性以及与补丁嵌入的平均最大相似性的对象匹配分数来实现的。与SAM-6D不同,计算后者涉及基于每个补丁与其在图像网格中的循环/往返补丁之间的距离的先验补丁过滤。此外,提案边界框和掩模的平均置信度被用作对象匹配分数的附加加权因子。我们通过实验证明,NOCTIS无需进一步的训练或微调,在BOP 2023挑战的七个核心数据集上,对于“未见过物体的基于模型的2D分割”任务,表现优于最佳的RGB和RGB-D方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 3 figures, 3 tables, NeurIPS 2025 preprint
Summary
该文本介绍了一种处理RGB图像中新型对象实例实例分割问题的简单而强大的框架——基于循环阈值的新型对象实例分割(NOCTIS)。该框架借助了之前的模型如CNOS、SAM-6D和NIDS-Net,并借助了最近的视觉基础模型Grounded-SAM 2和DINOv2。NOCTIS利用Grounded-SAM 2获得精确的目标提案及其对应的分割掩码,并利用DINOv2的零样本能力生成图像嵌入。通过计算类别嵌入和补丁嵌入的平均最大相似性的对象匹配分数,实现提案对象匹配。与SAM-6D不同,计算后者涉及基于每个补丁与其在图像网格中的循环对应补丁之间的距离的先验补丁过滤。此外,提案边界框和掩模的平均置信度被用作对象匹配分数的附加加权因子。实证结果表明,无需进一步训练或微调,NOCTIS在BOP 2023挑战的七个核心数据集上的“基于模型的未见对象二维分割”任务中表现优于最佳RGB和RGB-D方法。
Key Takeaways
- NOCTIS框架是一个用于处理RGB图像中新型对象实例分割的模型,可在不同类型的未见对象上应用而无需重新训练。
- 该框架利用Grounded-SAM 2模型获得精确的目标提案和对应的分割掩码。
- DINOv2模型的零样本能力被用于生成图像嵌入,对于目标匹配至关重要。
- NOCTIS通过计算类别嵌入和补丁嵌入的相似性来确定对象匹配分数,实现提案对象匹配。
- 与SAM-6D相比,NOCTIS在计算对象匹配分数时考虑了补丁过滤的先验信息。
- 提案的边界框和掩模的平均置信度作为对象匹配分数的附加加权因子。
点此查看论文截图

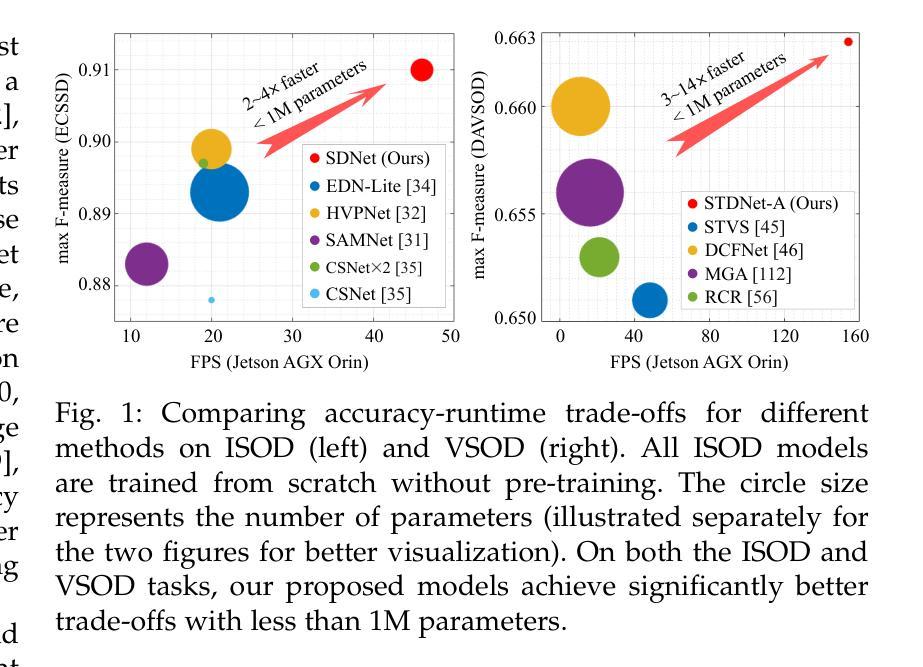
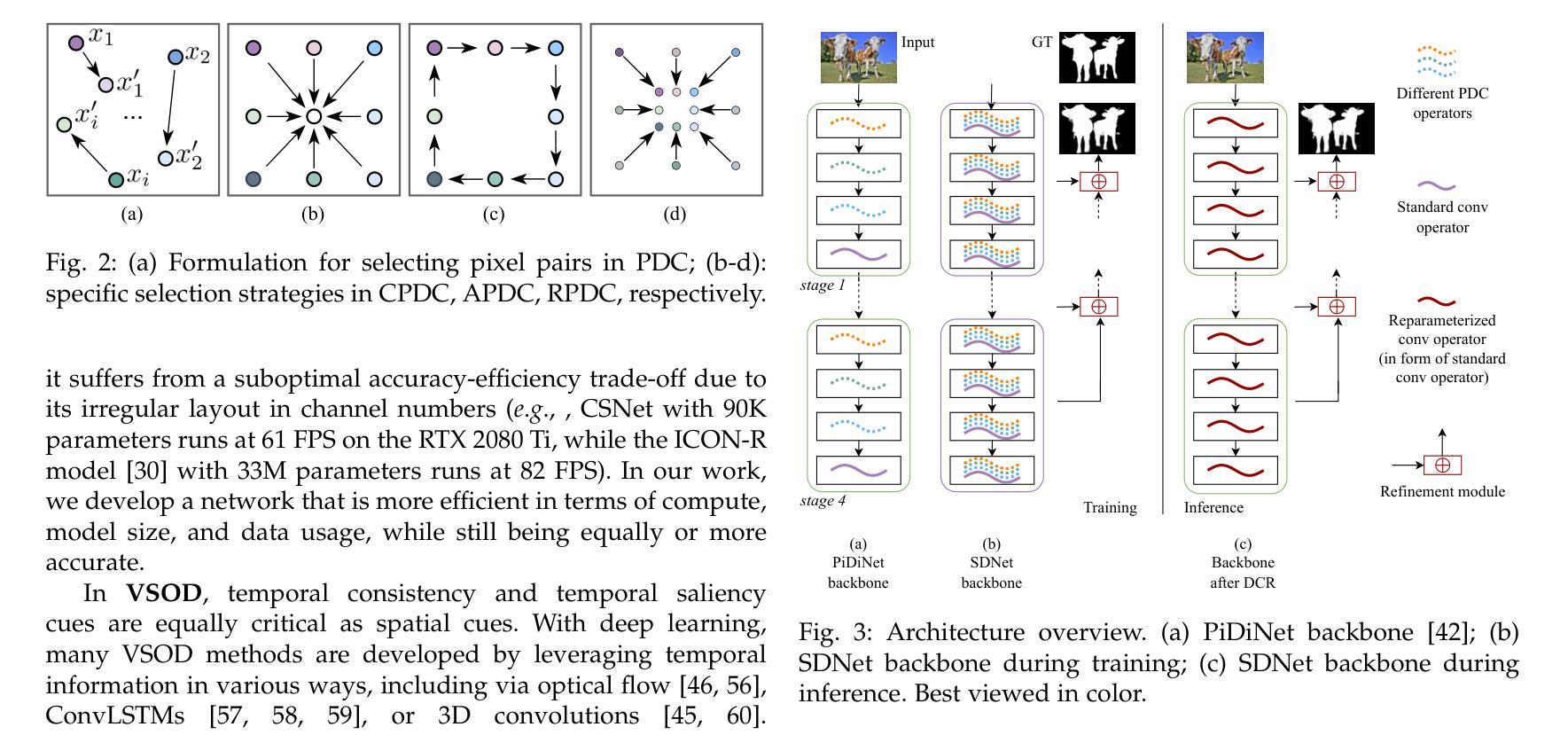
Rapid Salient Object Detection with Difference Convolutional Neural Networks
Authors:Zhuo Su, Li Liu, Matthias Müller, Jiehua Zhang, Diana Wofk, Ming-Ming Cheng, Matti Pietikäinen
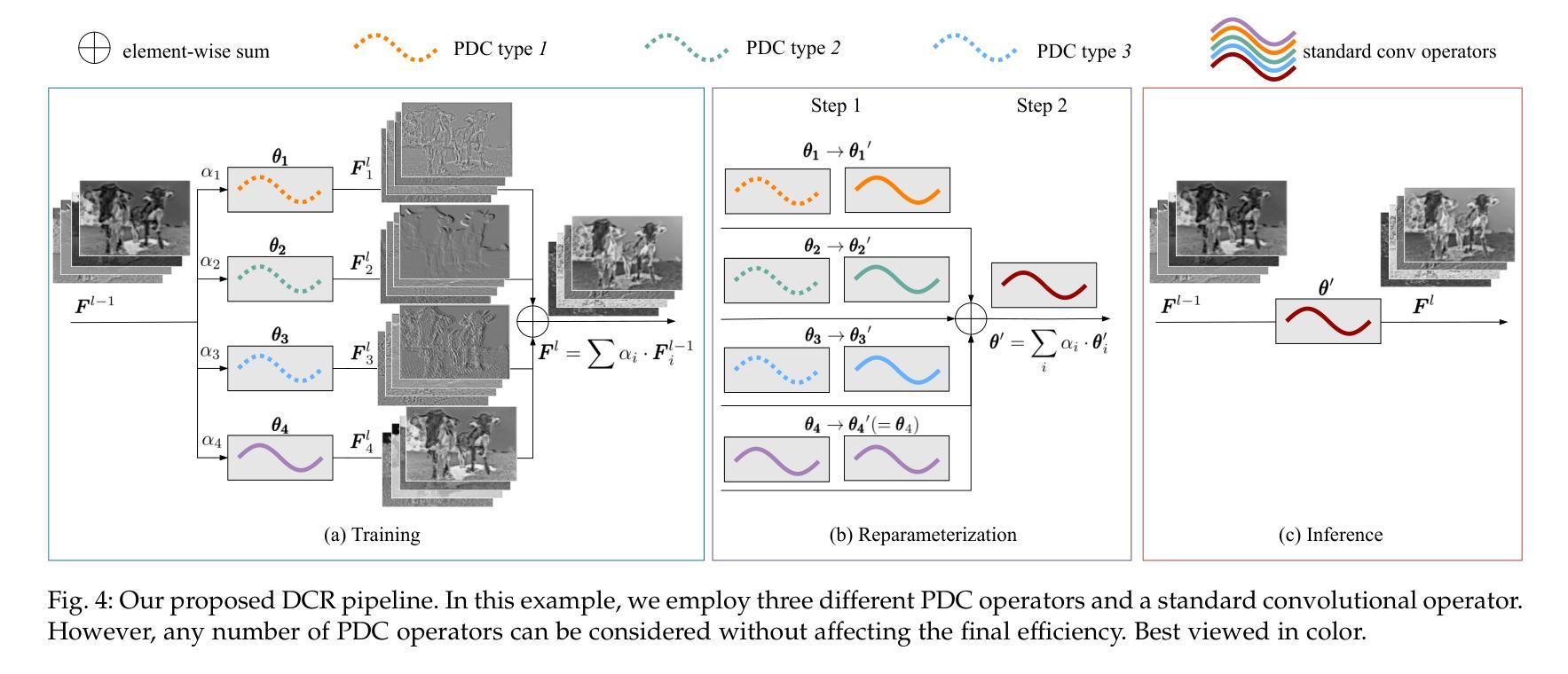
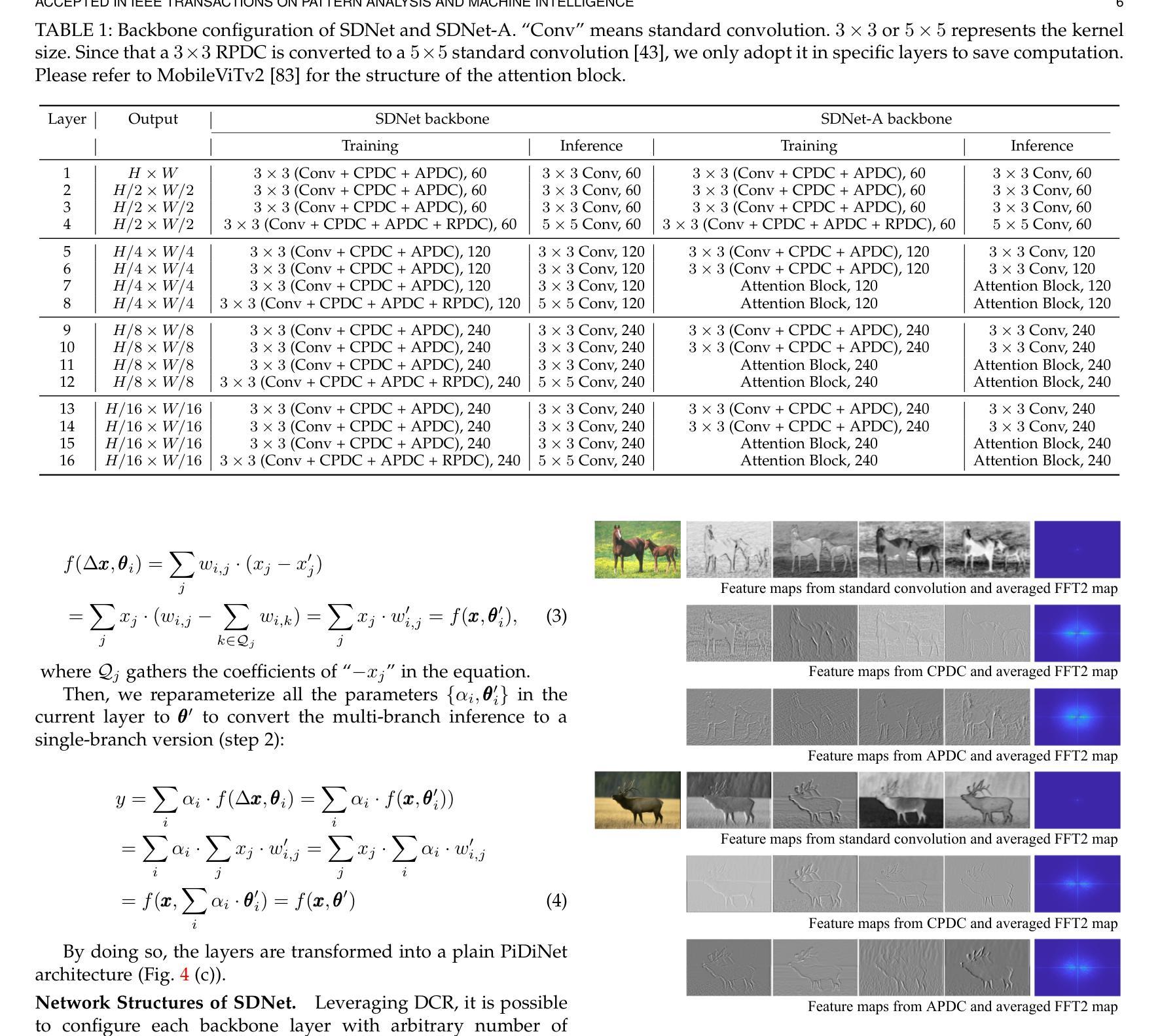
This paper addresses the challenge of deploying salient object detection (SOD) on resource-constrained devices with real-time performance. While recent advances in deep neural networks have improved SOD, existing top-leading models are computationally expensive. We propose an efficient network design that combines traditional wisdom on SOD and the representation power of modern CNNs. Like biologically-inspired classical SOD methods relying on computing contrast cues to determine saliency of image regions, our model leverages Pixel Difference Convolutions (PDCs) to encode the feature contrasts. Differently, PDCs are incorporated in a CNN architecture so that the valuable contrast cues are extracted from rich feature maps. For efficiency, we introduce a difference convolution reparameterization (DCR) strategy that embeds PDCs into standard convolutions, eliminating computation and parameters at inference. Additionally, we introduce SpatioTemporal Difference Convolution (STDC) for video SOD, enhancing the standard 3D convolution with spatiotemporal contrast capture. Our models, SDNet for image SOD and STDNet for video SOD, achieve significant improvements in efficiency-accuracy trade-offs. On a Jetson Orin device, our models with $<$ 1M parameters operate at 46 FPS and 150 FPS on streamed images and videos, surpassing the second-best lightweight models in our experiments by more than $2\times$ and $3\times$ in speed with superior accuracy. Code will be available at https://github.com/hellozhuo/stdnet.git.
本文旨在应对在资源受限设备上以实时性能执行显著性目标检测(SOD)的挑战。尽管深度神经网络领域的最新进展改进了SOD,但现有的顶尖模型计算成本高昂。我们提出了一种有效的网络设计,它将传统的SOD智慧和现代CNN的表示能力相结合。我们的模型借鉴了生物学启发的经典SOD方法,依靠计算对比线索来确定图像区域的显著性,利用像素差异卷积(PDC)对特征对比进行编码。不同之处在于,PDC被集成到CNN架构中,以便从丰富的特征图中提取有价值的对比线索。为了提高效率,我们引入了差异卷积重新参数化(DCR)策略,将PDC嵌入到标准卷积中,从而在推理过程中消除了计算和参数。此外,我们为视频SOD引入了时空差异卷积(STDC),通过时空对比捕获增强标准3D卷积。我们的模型SDNet用于图像SOD,STDNet用于视频SOD,在效率与准确性之间取得了显著改进。在Jetson Orin设备上,我们的模型使用<1M参数在流式图像和视频上分别以46FPS和150FPS运行,在我们的实验中,其速度超过第二好的轻量级模型2倍以上,同时保持更高的准确性。代码将在https://github.com/hellozhuo/stdnet.git上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, accepted in TPAMI
Summary
本文解决的是在资源受限设备上部署显著目标检测(SOD)的挑战,同时实现实时性能。文章结合传统显著目标检测的智慧和现代卷积神经网络(CNN)的表征能力,提出了有效的网络设计。模型利用像素差异卷积(PDC)编码特征对比,并通过时空差异卷积(STDC)提高视频SOD的效能。所提出的方法实现了高效率与准确性的良好平衡,可在Jetson Orin设备上实现高帧率运行。
Key Takeaways
- 文章主要解决资源受限设备上的实时显著目标检测(SOD)挑战。
- 结合传统显著目标检测方法和现代卷积神经网络(CNN)的表征能力,提出高效网络设计。
- 引入像素差异卷积(PDC)编码特征对比,并将其融入CNN架构中。
- 通过差异卷积重参数化(DCR)策略提高模型效率,减少推理时的计算和参数。
- 引入时空差异卷积(STDC)以提高视频SOD性能,结合3D卷积进行时空对比捕捉。
- 提出SDNet和STDNet模型分别用于图像和视频SOD,实现了效率和准确性的良好平衡。
点此查看论文截图

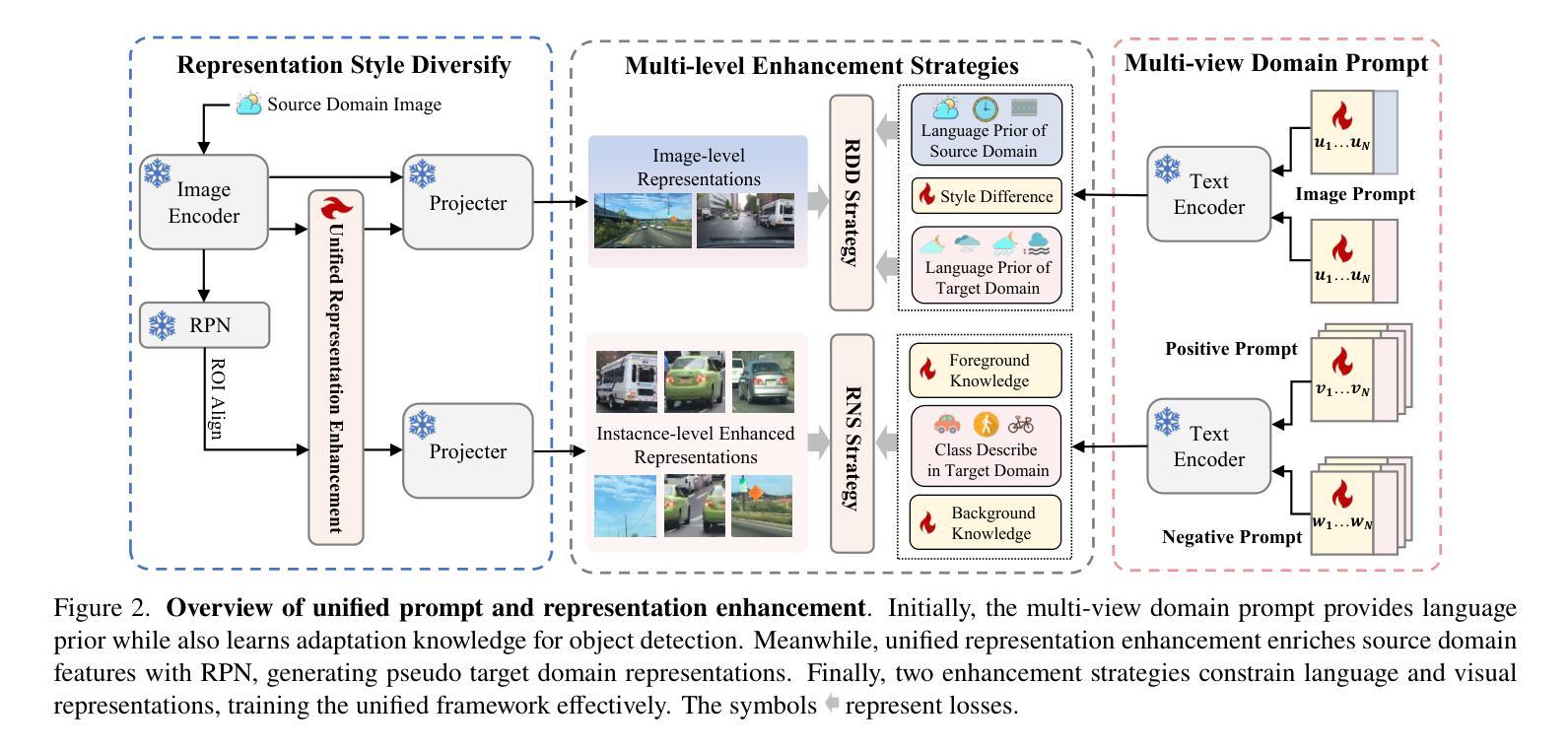
UPRE: Zero-Shot Domain Adaptation for Object Detection via Unified Prompt and Representation Enhancement
Authors:Xiao Zhang, Fei Wei, Yong Wang, Wenda Zhao, Feiyi Li, Xiangxiang Chu
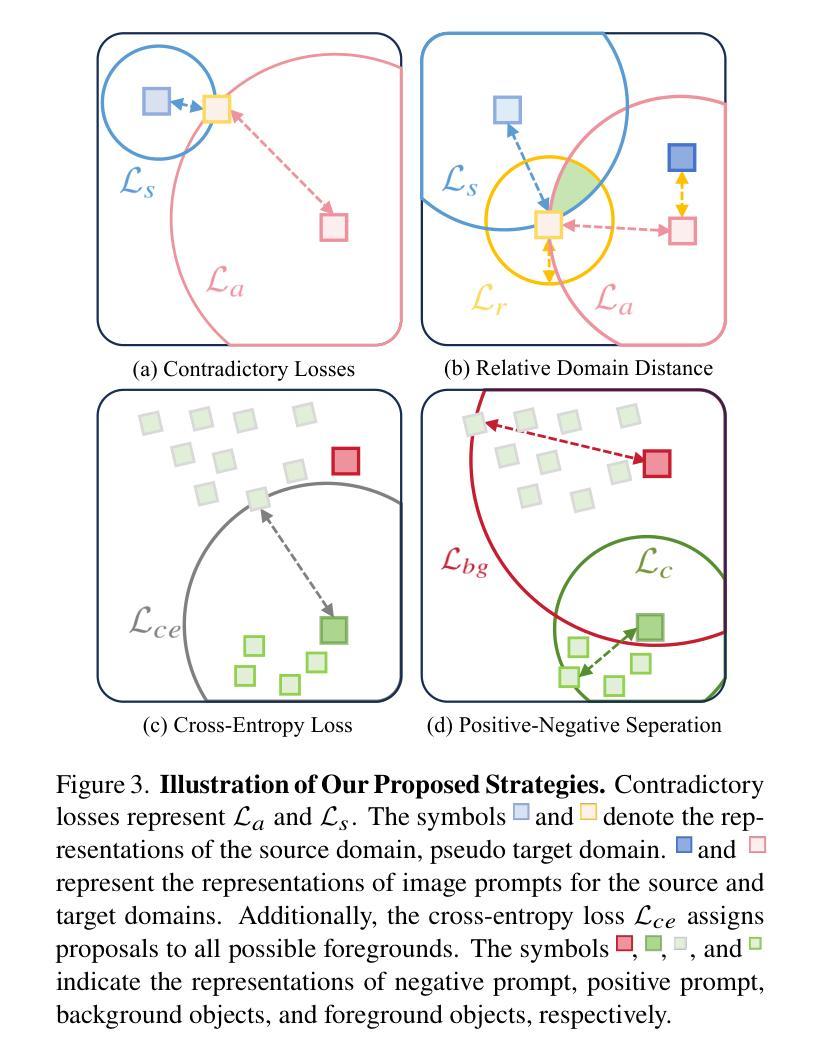
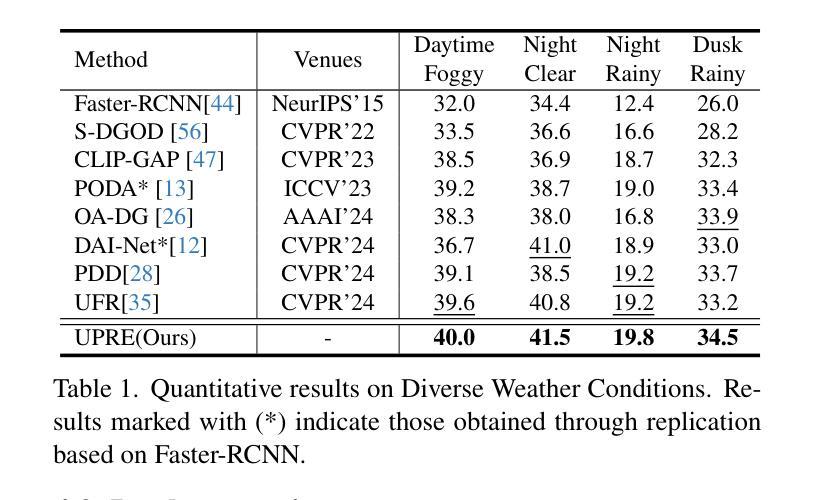
Zero-shot domain adaptation (ZSDA) presents substantial challenges due to the lack of images in the target domain. Previous approaches leverage Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to tackle this challenge, exploiting their zero-shot learning capabilities. However, these methods primarily address domain distribution shifts and overlook the misalignment between the detection task and VLMs, which rely on manually crafted prompts. To overcome these limitations, we propose the unified prompt and representation enhancement (UPRE) framework, which jointly optimizes both textual prompts and visual representations. Specifically, our approach introduces a multi-view domain prompt that combines linguistic domain priors with detection-specific knowledge, and a visual representation enhancement module that produces domain style variations. Furthermore, we introduce multi-level enhancement strategies, including relative domain distance and positive-negative separation, which align multi-modal representations at the image level and capture diverse visual representations at the instance level, respectively. Extensive experiments conducted on nine benchmark datasets demonstrate the superior performance of our framework in ZSDA detection scenarios. Code is available at https://github.com/AMAP-ML/UPRE.
零样本域自适应(ZSDA)由于缺乏目标域的图像而面临巨大挑战。之前的方法利用视觉语言模型(VLMs)来解决这一挑战,发挥它们的零样本学习能力。然而,这些方法主要解决域分布偏移问题,忽视了检测任务和依赖于手工制作的提示的VLM之间的不匹配。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了统一提示和表示增强(UPRE)框架,该框架联合优化文本提示和视觉表示。具体来说,我们的方法引入了一种多视角域提示,它将语言域先验知识与检测特定知识相结合,以及一个视觉表示增强模块,用于生成域风格变化。此外,我们引入了多层次增强策略,包括相对域距离和正负分离,分别在图像层面实现对多模态表示的对齐和在实例层面捕获多样化的视觉表示。在九个基准数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,我们的框架在ZSDA检测场景中具有卓越的性能。代码可访问https://github.com/AMAP-ML/UPRE。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV2025
Summary
零样本领域自适应(ZSDA)面临缺乏目标域图像的挑战。先前的方法利用视觉语言模型(VLMs)解决此挑战,但主要关注领域分布转移,忽略了检测任务与依赖手工提示的VLMs之间的不匹配。为克服这些限制,我们提出了统一提示和表示增强(UPRE)框架,联合优化文本提示和视觉表示。通过引入结合语言领域先验知识和检测特定知识的多视图领域提示,以及生成领域风格变化的视觉表示增强模块,该框架提高了性能。此外,我们介绍了多层次增强策略,包括相对领域距离和正负分离,分别对齐图像级别的多模态表示并捕获实例级别的多样视觉表示。在九个基准数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的框架在ZSDA检测场景中表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- ZSDA面临缺乏目标域图像的挑战。
- 之前的解决方案主要利用VLMs处理领域分布转移,但忽略了检测任务与VLMs之间的不匹配。
- UPRE框架通过联合优化文本提示和视觉表示来提高性能。
- UPRE引入多视图领域提示,结合语言领域知识和检测特定知识。
- 视觉表示增强模块生成领域风格变化。
- 多层次增强策略包括相对领域距离和正负分离,提高多模态表示的对齐和实例级别的视觉表示捕获。
点此查看论文截图