⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-04 更新
TD-MPC-Opt: Distilling Model-Based Multi-Task Reinforcement Learning Agents
Authors:Dmytro Kuzmenko, Nadiya Shvai
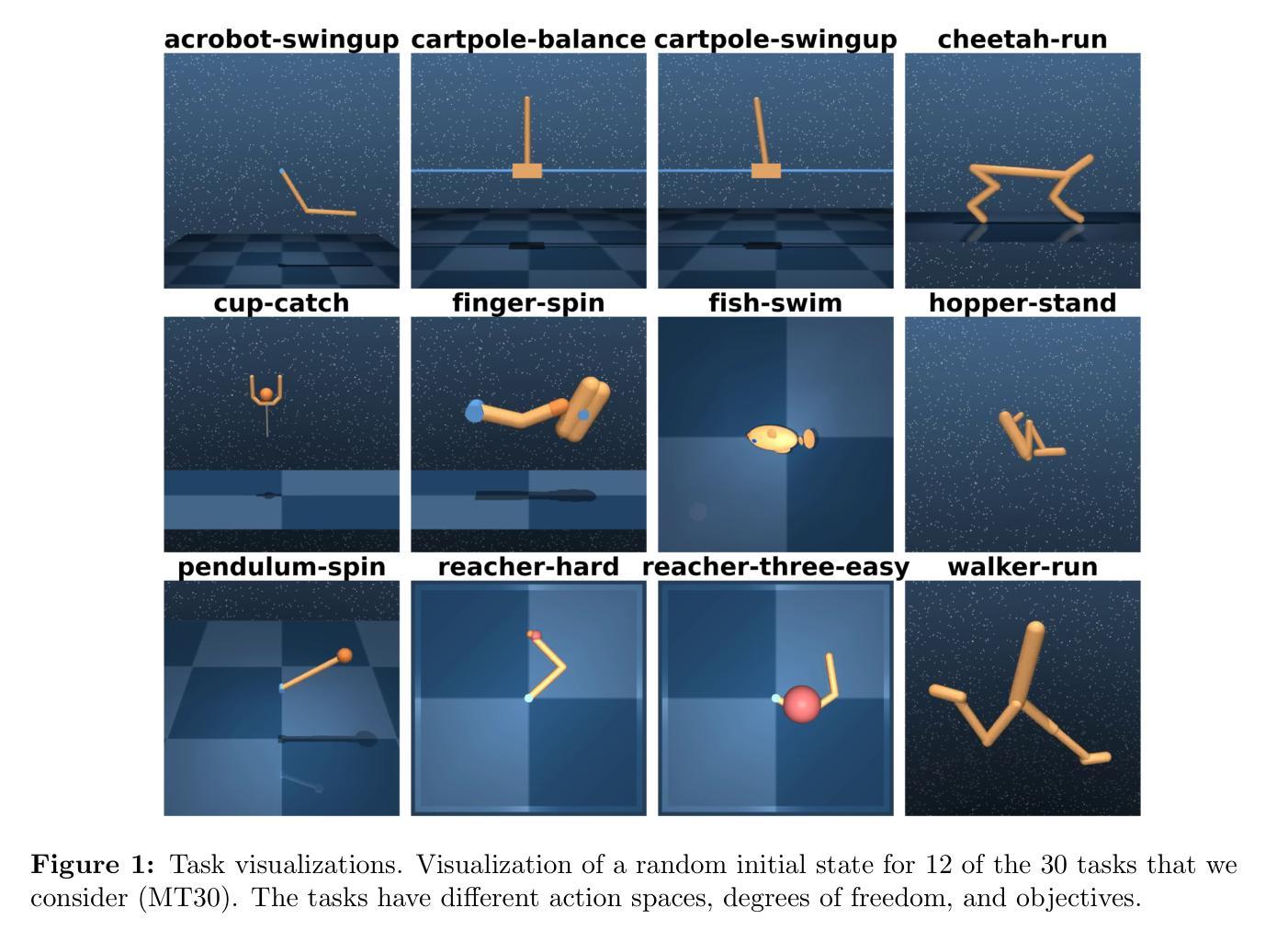
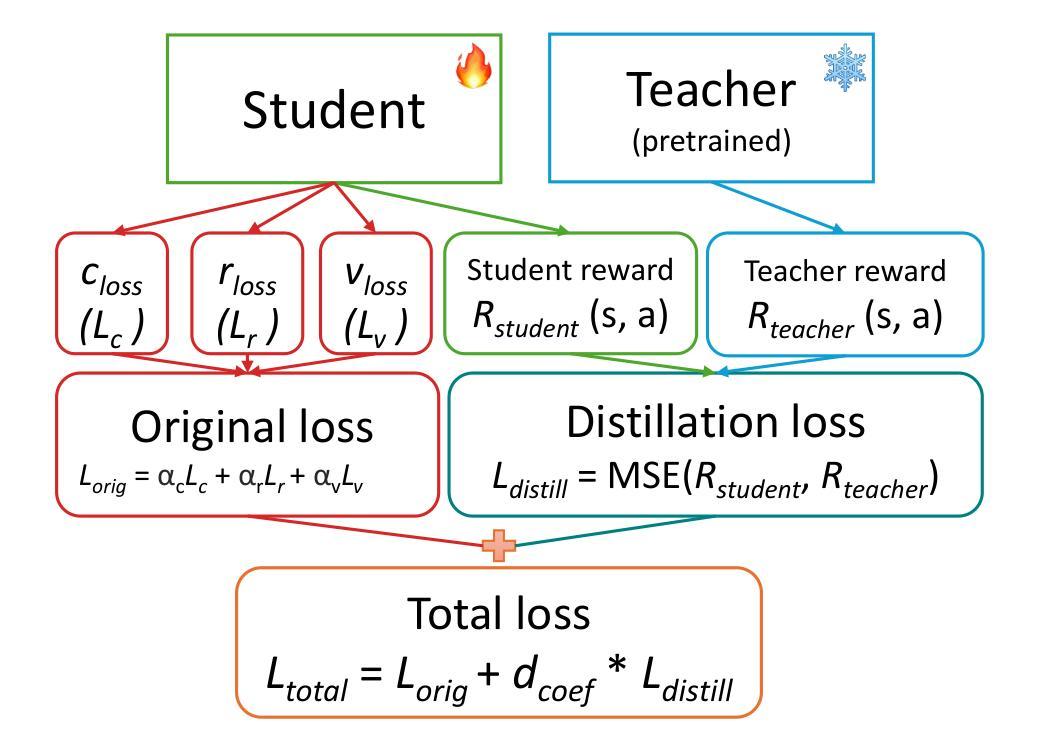
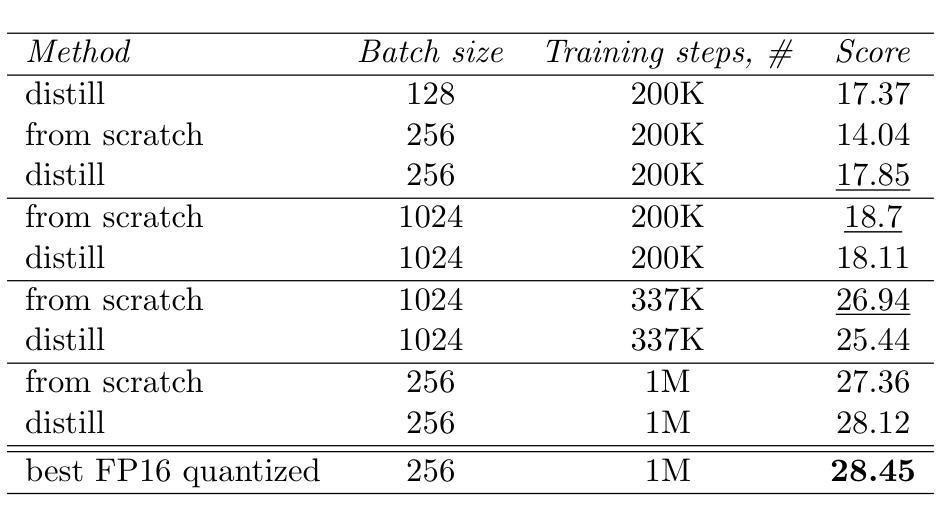
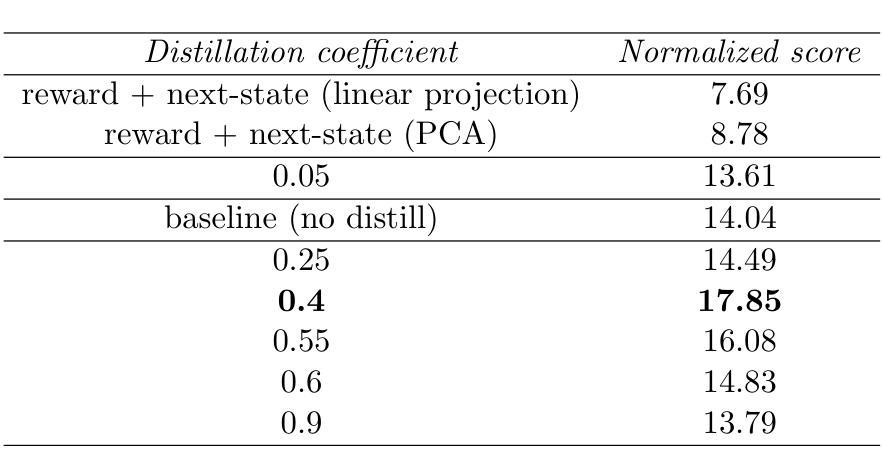
We present a novel approach to knowledge transfer in model-based reinforcement learning, addressing the critical challenge of deploying large world models in resource-constrained environments. Our method efficiently distills a high-capacity multi-task agent (317M parameters) into a compact model (1M parameters) on the MT30 benchmark, significantly improving performance across diverse tasks. Our distilled model achieves a state-of-the-art normalized score of 28.45, surpassing the original 1M parameter model score of 18.93. This improvement demonstrates the ability of our distillation technique to capture and consolidate complex multi-task knowledge. We further optimize the distilled model through FP16 post-training quantization, reducing its size by $\sim$50%. Our approach addresses practical deployment limitations and offers insights into knowledge representation in large world models, paving the way for more efficient and accessible multi-task reinforcement learning systems in robotics and other resource-constrained applications. Code available at https://github.com/dmytro-kuzmenko/td-mpc-opt.
我们提出了一种基于模型强化学习中的知识迁移的新方法,解决了在资源受限环境中部署大型世界模型的重大挑战。我们的方法在MT30基准测试上,能够有效地将高容量的多任务代理(3.17亿参数)蒸馏成紧凑模型(1百万参数),在多种任务上的性能得到显著提高。我们提炼的模型达到了最先进的归一化得分28.45,超过了原始1百万参数模型的得分18.93。这一改进证明了我们提炼技术捕捉和巩固复杂多任务知识的能力。我们进一步通过FP16后训练量化优化提炼的模型,将其大小减少了约50%。我们的方法解决了实际部署的限制,为大型世界模型中的知识表示提供了见解,为机器人和其他资源受限应用中的更高效、更便捷的多任务强化学习系统铺平了道路。代码可通过https://github.com/dmytro-kuzmenko/td-mpc-opt获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint of a manuscript submitted for peer review
Summary
大型世界模型在资源受限环境中的部署面临挑战。本研究提出了一种新颖的模型蒸馏方法,将多任务高容量模型(3.17亿参数)高效蒸馏成紧凑模型(仅含百万参数),并在MT30基准测试中表现出优异性能。此外,通过对蒸馏模型进行FP16训练后量化优化,其体积缩小约50%,取得了行业领先水平并有助于应对实际部署挑战,在机器人和其他资源受限应用中将构建更为高效且可靠的多任务强化学习系统。同时研究有助于对大型世界模型中的知识表示提供深入见解。代码可在GitHub上找到。
Key Takeaways
- 研究解决了大型世界模型在资源受限环境中的部署问题。
- 提出了一种新颖的模型蒸馏方法,实现了从多任务高容量模型到紧凑模型的转化。
- 在MT30基准测试中,蒸馏模型表现出卓越性能,超过了原有模型的得分。
- 通过FP16训练后量化优化,进一步减小了蒸馏模型的体积。
- 方法有助于应对实际部署挑战,对机器人和其他资源受限应用中的多任务强化学习系统构建具有积极影响。
- 研究提供了对大型世界模型中知识表示的深入见解。
点此查看论文截图

Agent Ideate: A Framework for Product Idea Generation from Patents Using Agentic AI
Authors:Gopichand Kanumolu, Ashok Urlana, Charaka Vinayak Kumar, Bala Mallikarjunarao Garlapati
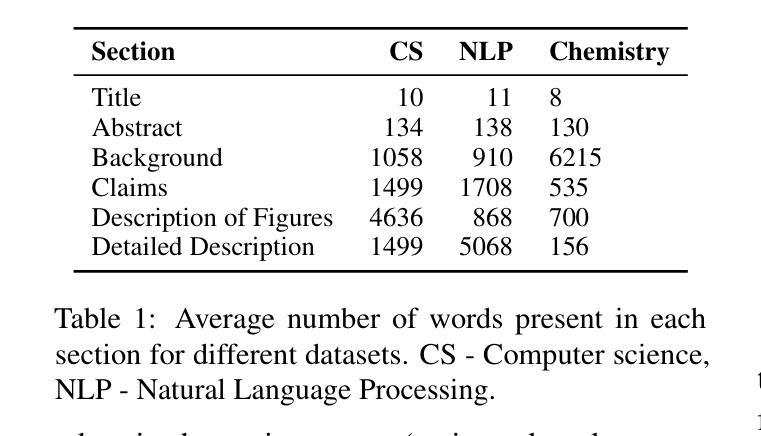
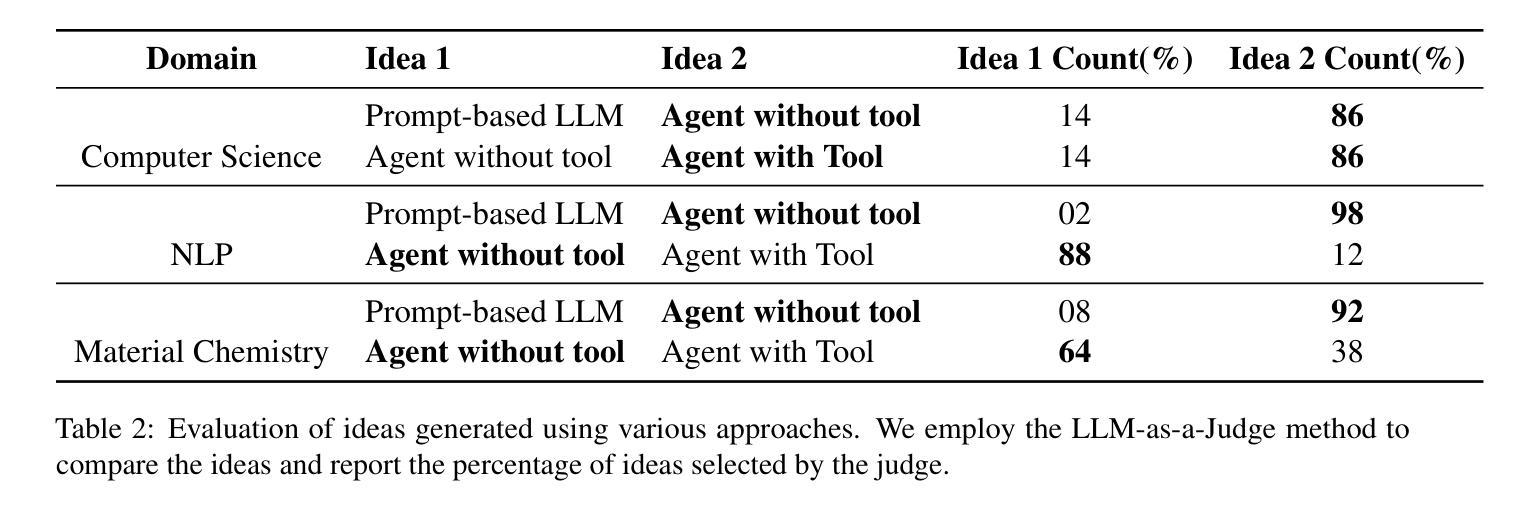
Patents contain rich technical knowledge that can inspire innovative product ideas, yet accessing and interpreting this information remains a challenge. This work explores the use of Large Language Models (LLMs) and autonomous agents to mine and generate product concepts from a given patent. In this work, we design Agent Ideate, a framework for automatically generating product-based business ideas from patents. We experimented with open-source LLMs and agent-based architectures across three domains: Computer Science, Natural Language Processing, and Material Chemistry. Evaluation results show that the agentic approach consistently outperformed standalone LLMs in terms of idea quality, relevance, and novelty. These findings suggest that combining LLMs with agentic workflows can significantly enhance the innovation pipeline by unlocking the untapped potential of business idea generation from patent data.
专利蕴含着丰富的技术知识,能够激发创新产品的灵感,然而访问和解读这些信息仍然是一个挑战。本研究探索了使用大型语言模型(LLM)和自主代理来从给定专利中挖掘和生成产品概念。在这项工作中,我们设计了Agent Ideate,这是一个从专利中自动生成基于产品的商业想法的框架。我们在计算机科学、自然语言处理和材料化学三个领域尝试了开源LLM和基于代理的架构。评估结果表明,在思想质量、相关性和新颖性方面,代理方法始终优于单独的LLM。这些发现表明,通过将LLM与代理工作流程相结合,可以显著增强创新管道,通过解锁来自专利数据的商业想法生成的未开发潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF AgentScen Workshop, IJCAI 2025
Summary
专利蕴含丰富的技术知识,可激发创新产品灵感,但访问和解读这些信息仍然具有挑战性。本研究探索使用大型语言模型(LLMs)和自主代理来从给定专利中挖掘和生成产品概念。我们设计了Agent Ideate框架,可自动从专利中生成基于产品的商业想法。我们在计算机科学、自然语言处理和材料化学三个领域进行了开源LLMs和基于代理的架构的实验。评估结果表明,代理方法在创意质量、相关性和新颖性方面始终优于单独的LLMs。这表明将LLMs与代理工作流程相结合,可以从专利数据中显著增强创新管道,挖掘出未充分利用的潜力,促进商业想法的产生。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)和自主代理可用于从专利中挖掘和生成产品概念。
- Agent Ideate框架可自动从专利中生成基于产品的商业想法。
- 在计算机、NLP和材料化学领域进行实验表明,代理方法生成的产品创意在质量、相关性和新颖性方面优于单独的LLMs。
- 结合LLMs和代理工作流程能显著增强创新管道。
- 专利数据蕴含丰富的技术知识,可作为激发创新灵感的宝库。
- 通过使用LLMs和自主代理技术,能够解锁专利数据中未开发的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

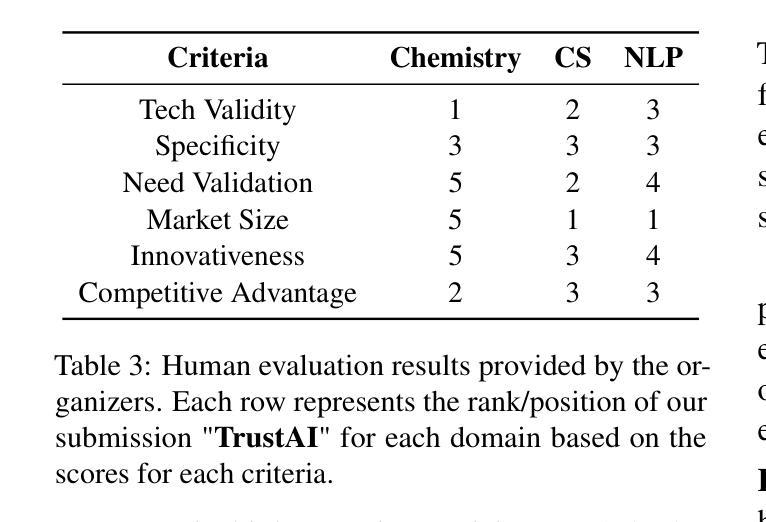
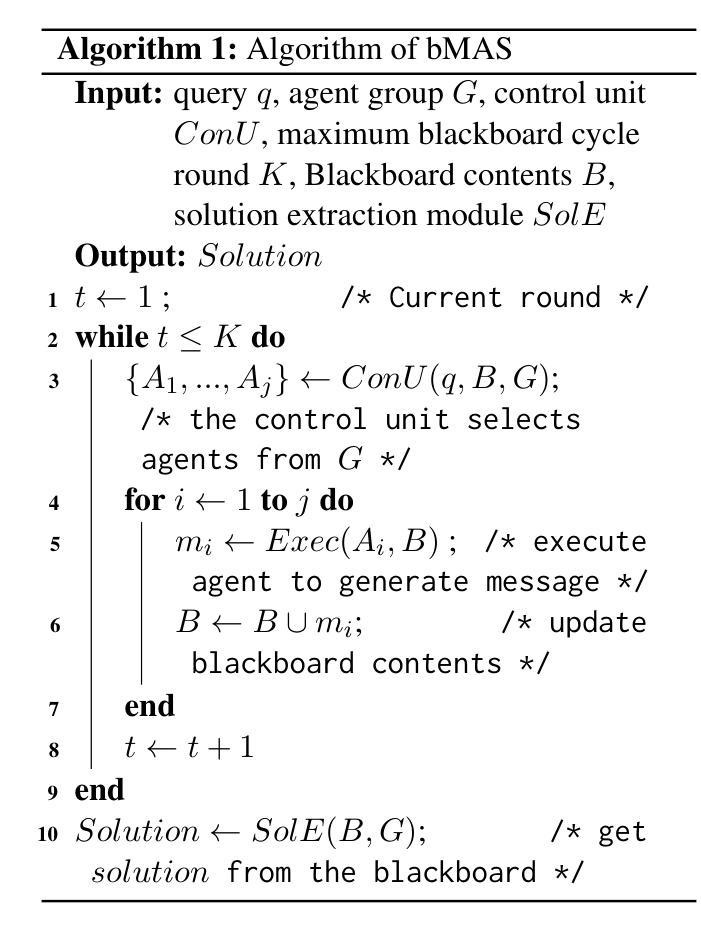
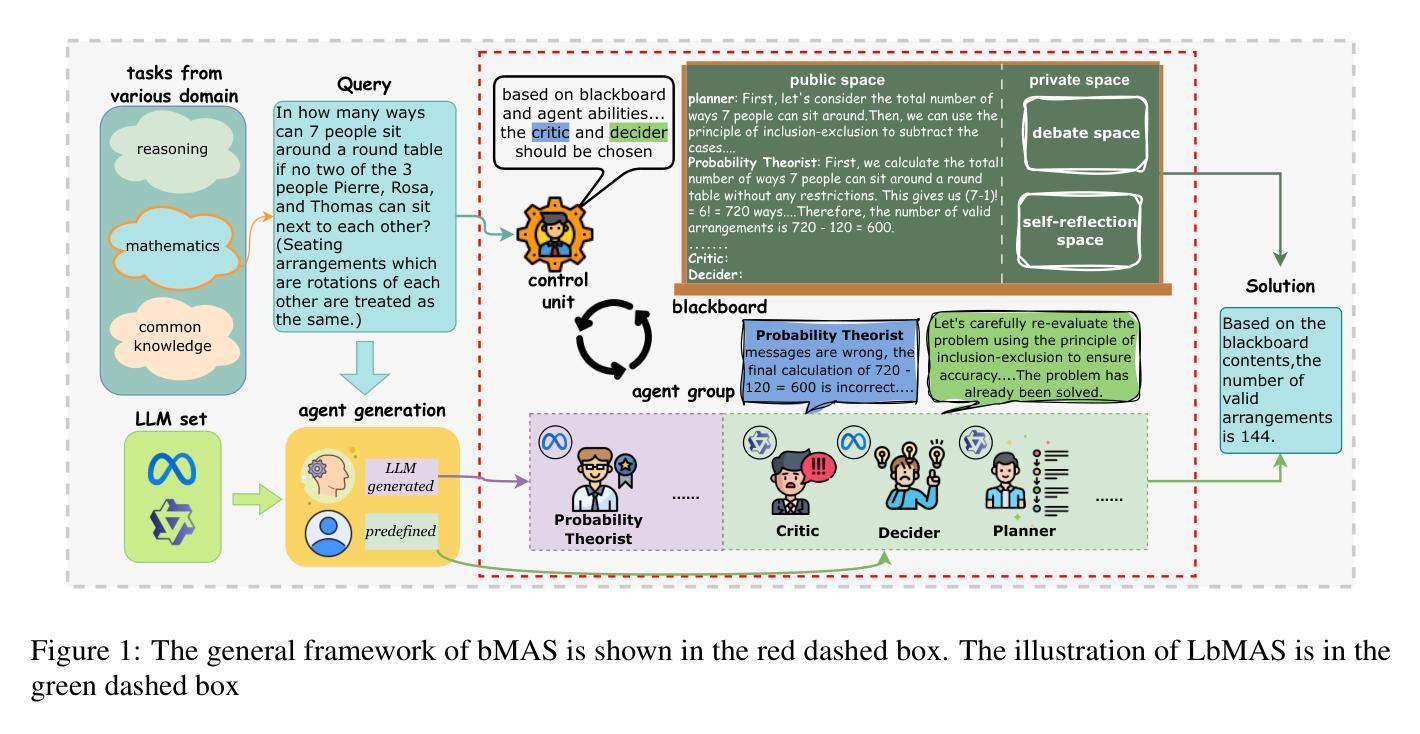
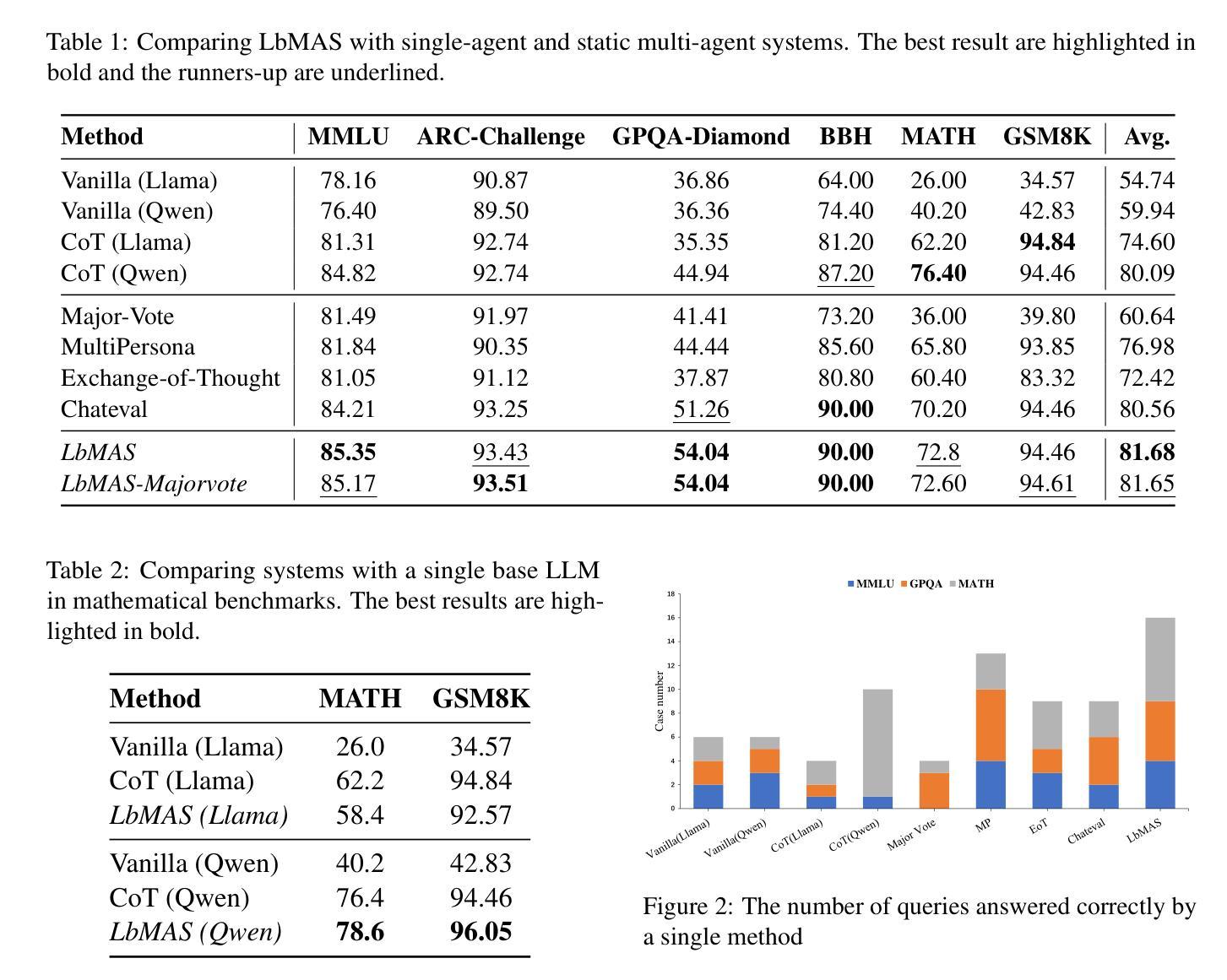
Exploring Advanced LLM Multi-Agent Systems Based on Blackboard Architecture
Authors:Bochen Han, Songmao Zhang
In this paper, we propose to incorporate the blackboard architecture into LLM multi-agent systems (MASs) so that (1) agents with various roles can share all the information and others’ messages during the whole problem-solving process, (2) agents that will take actions are selected based on the current content of the blackboard, and (3) the selection and execution round is repeated until a consensus is reached on the blackboard. We develop the first implementation of this proposal and conduct experiments on commonsense knowledge, reasoning and mathematical datasets. The results show that our system can be competitive with the SOTA static and dynamic MASs by achieving the best average performance, and at the same time manage to spend less tokens. Our proposal has the potential to enable complex and dynamic problem-solving where well-defined structures or workflows are unavailable.
在这篇论文中,我们提议将黑板架构融入到大型语言模型多智能体系统(MASs)中,以实现以下几点目标:(1)不同角色的智能体在整个问题解决过程中可以共享所有信息和他人消息;(2)根据当前黑板内容选择将采取行动的智能体;(3)重复选择和执行回合,直到黑板上达成共识。我们首次实现了这一提议,并在常识知识、推理和数学数据集上进行了实验。结果表明,我们的系统可以通过获得最佳平均性能与最先进(SOTA)的静态和动态MASs竞争,同时减少令牌消耗。我们的提议具有在结构或工作流程不明确的情况下实现复杂和动态问题解决的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文提出将黑板架构融入大型语言模型多智能体系统(MASs),使不同角色的智能体在解决问题过程中共享信息和相互沟通。智能体的行动选择基于当前黑板内容,并重复选择和执行过程直至黑板达成共识。实验结果显示,该系统在常识知识、推理和数学数据集上的表现具有竞争力,相较于现有最佳静态和动态MASs,本系统性能更佳且消耗令牌更少。此提议有望在没有明确结构或工作流程的复杂动态问题求解中得到应用。
Key Takeaways:
- 论文提出将黑板架构融入大型语言模型多智能体系统(MASs)。
- 智能体通过黑板共享信息,促进问题解决过程中的沟通。
- 智能体的行动选择基于黑板当前内容。
- 系统通过重复选择和执行过程直至黑板达成共识。
- 论文提供了该系统的初步实现并进行实验验证。
- 实验结果显示,该系统在多个数据集上的性能具有竞争力,且相较于其他系统性能更佳,消耗资源更少。
- 该提议有望应用于复杂动态问题求解场景,特别是在没有明确结构或工作流程的情况下。
点此查看论文截图

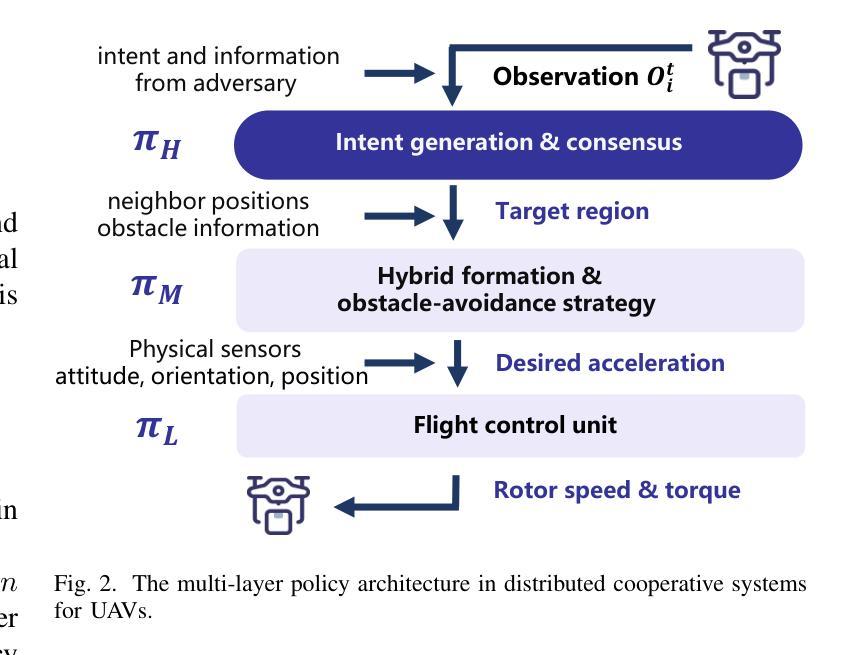
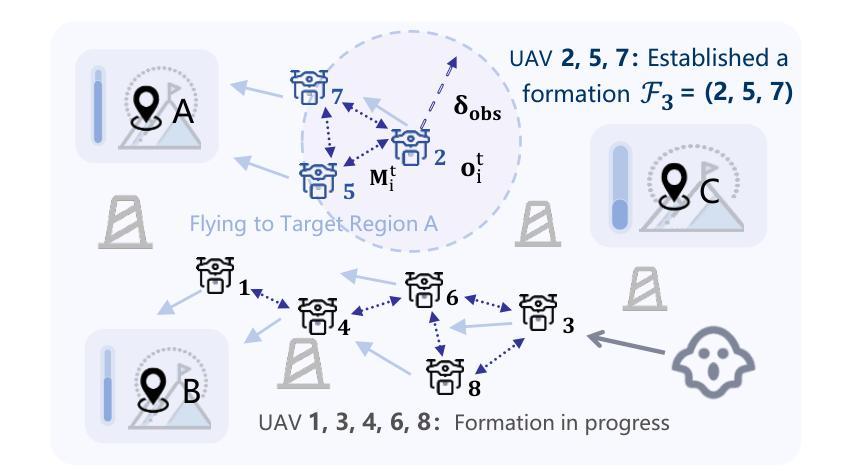
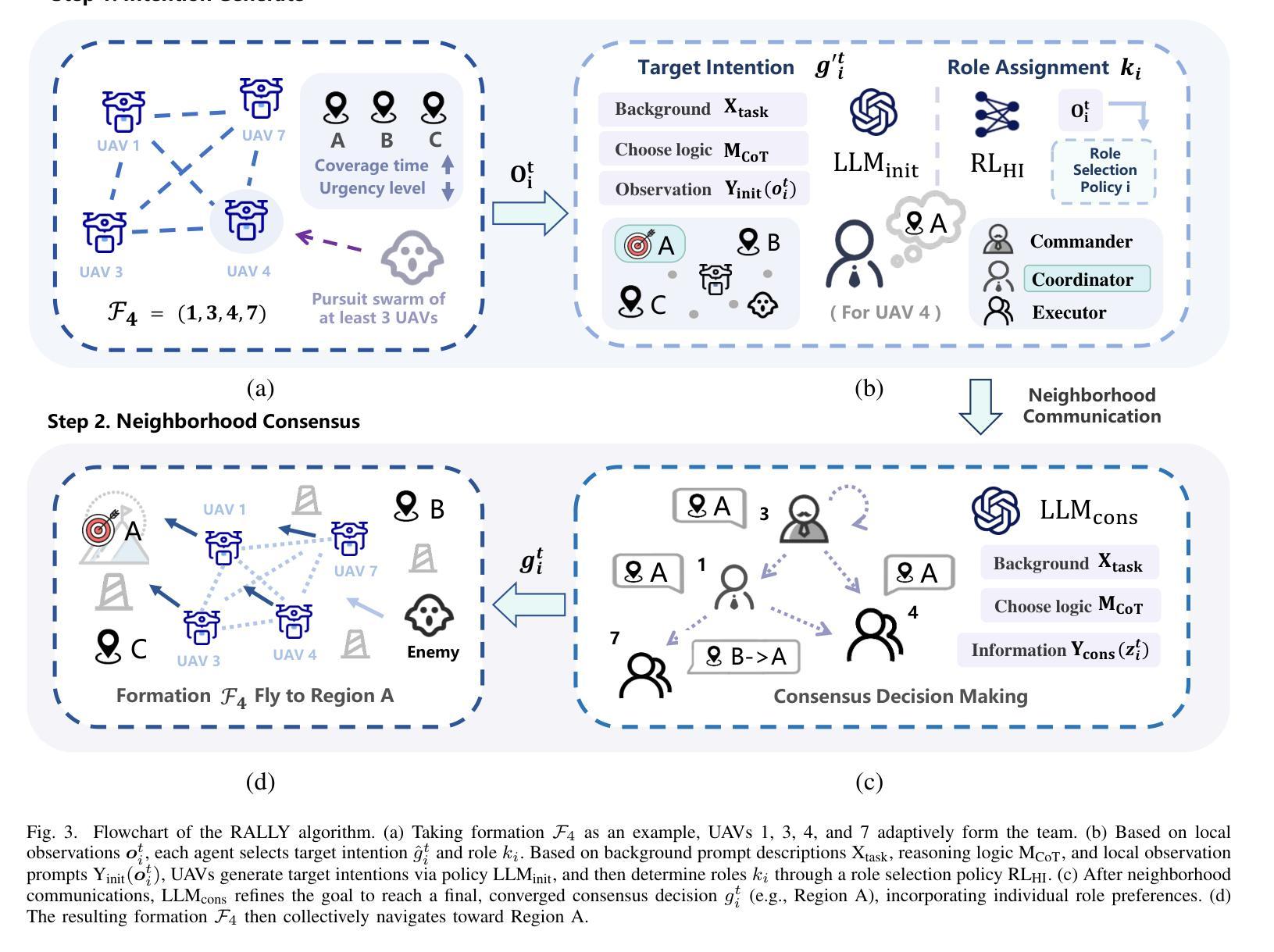
RALLY: Role-Adaptive LLM-Driven Yoked Navigation for Agentic UAV Swarms
Authors:Ziyao Wang, Rongpeng Li, Sizhao Li, Yuming Xiang, Haiping Wang, Zhifeng Zhao, Honggang Zhang
Intelligent control of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) swarms has emerged as a critical research focus, and it typically requires the swarm to navigate effectively while avoiding obstacles and achieving continuous coverage over multiple mission targets. Although traditional Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) approaches offer dynamic adaptability, they are hindered by the semantic gap in numerical communication and the rigidity of homogeneous role structures, resulting in poor generalization and limited task scalability. Recent advances in Large Language Model (LLM)-based control frameworks demonstrate strong semantic reasoning capabilities by leveraging extensive prior knowledge. However, due to the lack of online learning and over-reliance on static priors, these works often struggle with effective exploration, leading to reduced individual potential and overall system performance. To address these limitations, we propose a Role-Adaptive LLM-Driven Yoked navigation algorithm RALLY. Specifically, we first develop an LLM-driven semantic decision framework that uses structured natural language for efficient semantic communication and collaborative reasoning. Afterward, we introduce a dynamic role-heterogeneity mechanism for adaptive role switching and personalized decision-making. Furthermore, we propose a Role-value Mixing Network (RMIX)-based assignment strategy that integrates LLM offline priors with MARL online policies to enable semi-offline training of role selection strategies. Experiments in the Multi-Agent Particle Environment (MPE) environment and a Software-In-The-Loop (SITL) platform demonstrate that RALLY outperforms conventional approaches in terms of task coverage, convergence speed, and generalization, highlighting its strong potential for collaborative navigation in agentic multi-UAV systems.
无人机集群的智能控制已成为关键的研究焦点,通常需要集群进行有效导航,同时避开障碍物,实现对多个任务目标的连续覆盖。尽管传统的多智能体强化学习(MARL)方法提供了动态适应性,但它们受到数字通信中的语义差距和同质角色结构的限制,导致泛化能力较差和任务可扩展性有限。最近基于大型语言模型(LLM)的控制框架的进展,通过利用丰富的先验知识,展示了强大的语义推理能力。然而,由于缺乏在线学习和对静态先验的过度依赖,这些工作在有效探索方面往往面临挑战,降低了个体潜力和整体系统性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本主要介绍了无人机集群的智能控制研究。传统的多智能体强化学习(MARL)方法存在语义鸿沟和角色结构僵化的问题,导致任务泛化能力和可扩展性有限。最近的大型语言模型(LLM)控制框架具有强大的语义推理能力,但缺乏在线学习和过度依赖静态先验知识,导致探索效果不佳。针对这些问题,提出了一种基于自适应角色的大型语言模型驱动导航算法RALLY。它结合了LLM的语义决策框架、动态角色异质性和角色价值混合网络,提高了任务覆盖、收敛速度和泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 无人机集群的智能控制是当前的热门研究领域。
- 传统MARL方法存在语义鸿沟和角色结构僵化的问题。
- LLM控制框架具有强大的语义推理能力,但缺乏在线学习和过度依赖静态先验知识。
- RALLY算法结合了LLM的语义决策框架和动态角色异质性机制,以提高无人机集群的导航效率。
- RALLY使用角色价值混合网络来整合离线先验知识和在线策略,实现半离线角色选择策略训练。
- 实验表明,RALLY在任务覆盖、收敛速度和泛化能力方面优于传统方法。
点此查看论文截图

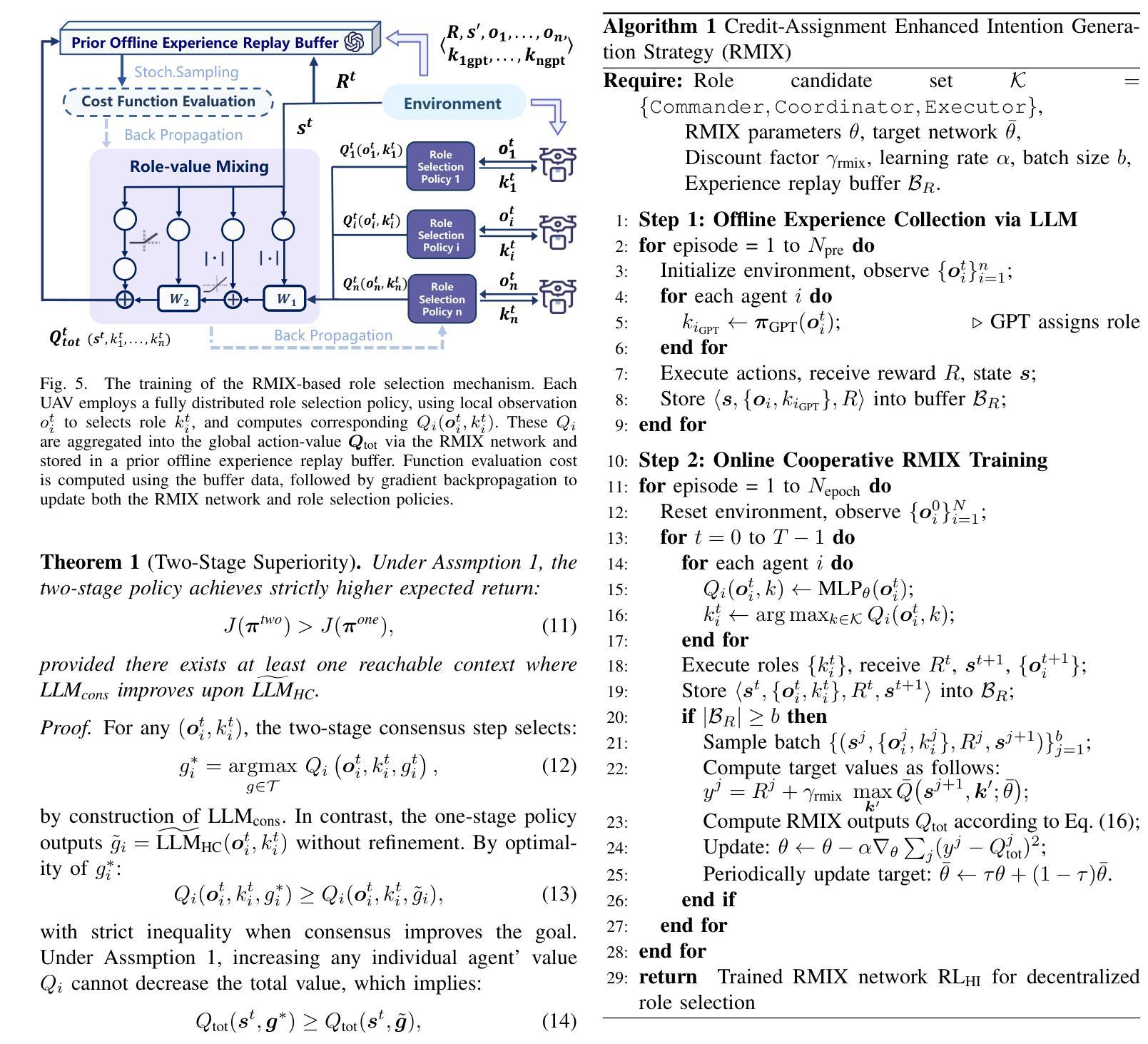
WebArXiv: Evaluating Multimodal Agents on Time-Invariant arXiv Tasks
Authors:Zihao Sun, Meng Fang, Ling Chen
Recent progress in large language models (LLMs) has enabled the development of autonomous web agents capable of navigating and interacting with real websites. However, evaluating such agents remains challenging due to the instability and inconsistency of existing benchmarks, which often rely on dynamic content or oversimplified simulations. In this work, we introduce WebArXiv, a static and time-invariant benchmark comprising 275 web-based tasks grounded in the arXiv platform. WebArXiv ensures reproducible and reliable evaluation by anchoring tasks in fixed web snapshots with deterministic ground truths and standardized action trajectories. Through behavioral analysis, we identify a common failure mode, Rigid History Reflection, where agents over-rely on fixed interaction histories. To address this, we propose a lightweight dynamic reflection mechanism that allows agents to selectively retrieve relevant past steps during decision-making. We evaluate ten state-of-the-art web agents on WebArXiv. Results demonstrate clear performance differences across agents and validate the effectiveness of our proposed reflection strategy.
最近,大型语言模型(LLM)的进展为能够导航和与现实网站进行交互的自主网络代理的发展提供了可能。然而,由于现有基准测试的不稳定性和不一致性,评估此类代理仍然具有挑战性,这些基准测试通常依赖于动态内容或过于简化的模拟。在这项工作中,我们介绍了WebArXiv,这是一个静态且时间不变的基准测试,包含基于arXiv平台的275个网络任务。WebArXiv通过锚定任务在具有确定性地面真实和标准化行动轨迹的固定网络快照上,确保可重复和可靠的评估。通过行为分析,我们发现了一种常见的失败模式,即刚性历史反射,其中代理过度依赖于固定的交互历史。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种轻量级的动态反射机制,允许代理在决策过程中有选择地检索相关的过去步骤。我们在WebArXiv上评估了十个最先进的网络代理。结果表明,各代理之间的性能差异明显,并验证了我们所提出的反射策略的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 9 figures, 4 tables
Summary
WebArXiv是一个基于arXiv平台的静态、时间不变的基准测试平台,用于评估自主网页代理在真实网站上的表现。它通过固定网页快照和标准化行为轨迹来确保评估的可重复性和可靠性。研究发现了一种常见的问题模式——Rigid History Reflection,并提出了一个轻量级的动态反射机制来解决这一问题。通过对十个顶尖的网络代理进行评估,验证了WebArXiv的效果和提出的反射策略的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- WebArXiv是一个基于arXiv平台的静态、时间不变的基准测试平台,旨在评估自主网页代理在真实网站上的表现。
- WebArXiv通过固定网页快照和标准化行为轨迹确保评估的可重复性和可靠性。
- 存在一种常见的问题模式——Rigid History Reflection,即代理过度依赖固定的交互历史。
- 为了解决这一问题,提出了一种轻量级的动态反射机制,允许代理在决策过程中有选择地检索相关的过去步骤。
- 在WebArXiv上评估了十个顶尖的网络代理,结果显示不同代理之间的性能差异明显。
- 评估结果验证了提出的反射策略的有效性。
- WebArXiv为评估自主网页代理提供了一个新的可靠基准。
点此查看论文截图


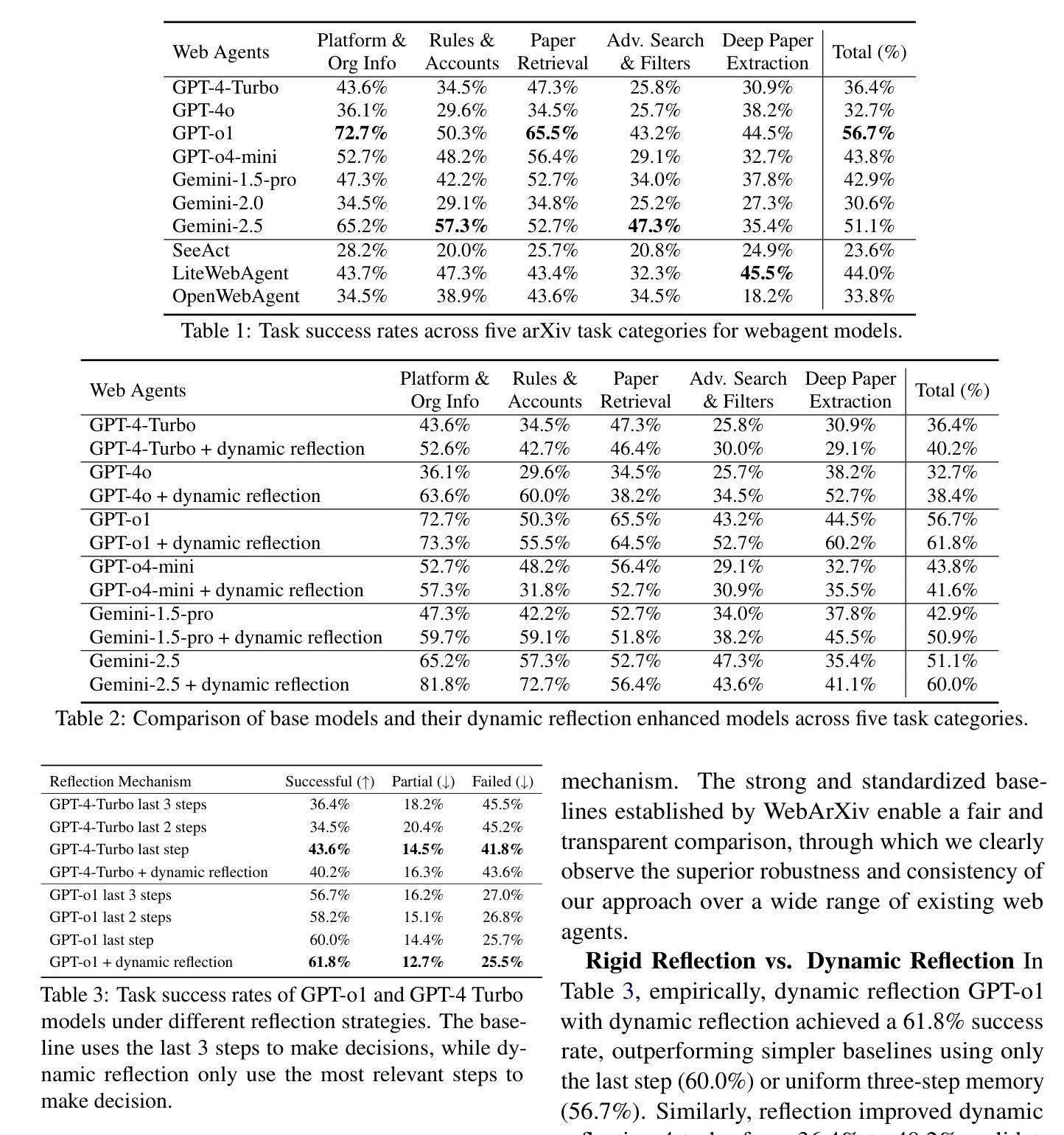
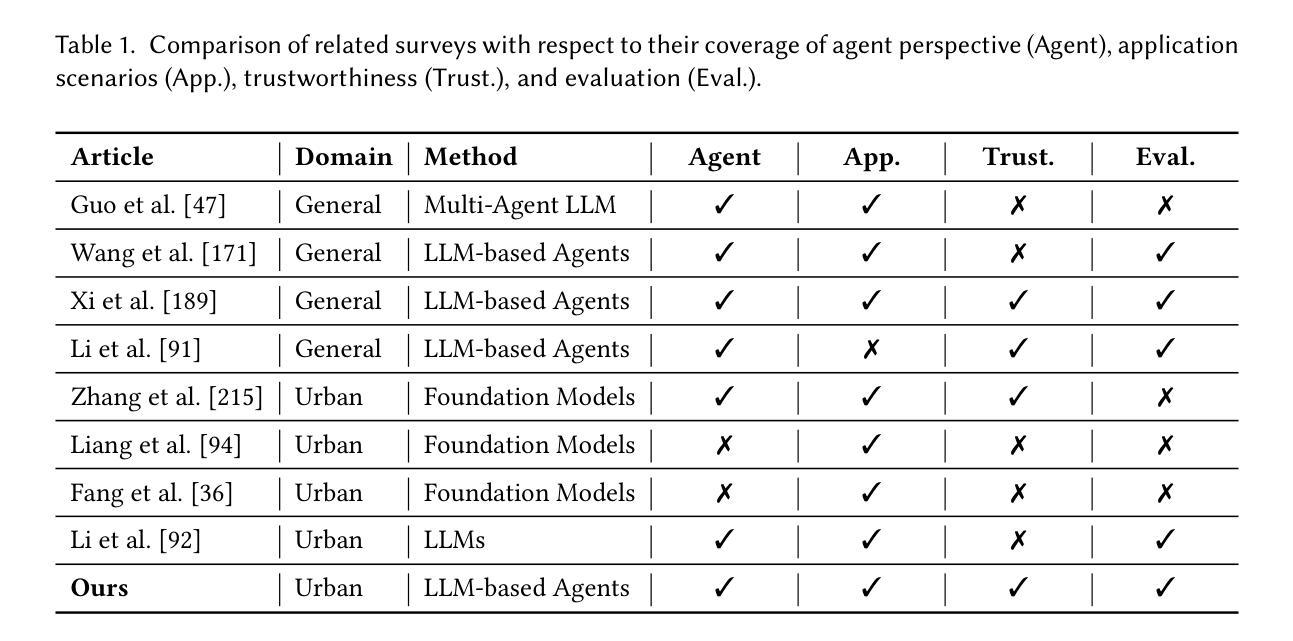
Large Language Model Powered Intelligent Urban Agents: Concepts, Capabilities, and Applications
Authors:Jindong Han, Yansong Ning, Zirui Yuan, Hang Ni, Fan Liu, Tengfei Lyu, Hao Liu
The long-standing vision of intelligent cities is to create efficient, livable, and sustainable urban environments using big data and artificial intelligence technologies. Recently, the advent of Large Language Models (LLMs) has opened new ways toward realizing this vision. With powerful semantic understanding and reasoning capabilities, LLMs can be deployed as intelligent agents capable of autonomously solving complex problems across domains. In this article, we focus on Urban LLM Agents, which are LLM-powered agents that are semi-embodied within the hybrid cyber-physical-social space of cities and used for system-level urban decision-making. First, we introduce the concept of urban LLM agents, discussing their unique capabilities and features. Second, we survey the current research landscape from the perspective of agent workflows, encompassing urban sensing, memory management, reasoning, execution, and learning. Third, we categorize the application domains of urban LLM agents into five groups: urban planning, transportation, environment, public safety, and urban society, presenting representative works in each group. Finally, we discuss trustworthiness and evaluation issues that are critical for real-world deployment, and identify several open problems for future research. This survey aims to establish a foundation for the emerging field of urban LLM agents and to provide a roadmap for advancing the intersection of LLMs and urban intelligence. A curated list of relevant papers and open-source resources is maintained and continuously updated at https://github.com/usail-hkust/Awesome-Urban-LLM-Agents.
智能城市的长期愿景是借助大数据和人工智能技术开发高效、宜居和可持续的城市环境。最近,大型语言模型(LLM)的出现为实现这一愿景提供了新的途径。凭借强大的语义理解和推理能力,LLM可以被部署为智能代理,能够在各个领域自主解决复杂问题。本文重点关注城市LLM代理,这些代理在城市混合的赛博物理社会空间内半实体化,用于系统级的城市决策。首先,我们介绍城市LLM代理的概念,讨论其独特的能力和特点。其次,我们从代理工作流的视角审视当前的研究状况,包括城市感知、内存管理、推理、执行和学习。第三,我们将城市LLM代理的应用领域分为五组:城市规划、交通、环境、公共安全和城市社会,每组都介绍了代表性的工作。最后,我们讨论了现实世界部署中至关重要的可信度和评估问题,并指出了未来研究的一些开放性问题。本文旨在建立城市LLM代理这一新兴领域的基石,为LLM和城市智能的交叉点提供发展路线图。相关论文和开源资源的精选列表持续维护并更新在https://github.com/usail-hkust/Awesome-Urban-LLM-Agents上。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了智能城市的长远愿景以及大型语言模型(LLMs)如何助力实现这一愿景。重点介绍了城市LLM代理的概念及其在五个应用领域(城市规划、交通、环境、公共安全以及城市社会)中的代表性工作。同时,文章还讨论了其在现实世界中部署的信任度和评估问题,并指出了未来研究的几个开放性问题。
Key Takeaways
- 智能城市的愿景是利用大数据和人工智能技术创建高效、宜居和可持续的城市环境。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)的出现在实现智能城市愿景方面开启了新途径。
- 城市LLM代理是具有自主解决复杂问题能力的智能代理,半融入城市的混合物理社会空间,用于系统级的城市决策。
- 城市LLM代理的应用领域包括城市规划、交通、环境、公共安全以及城市社会等五个领域。
- 在实现城市LLM代理的现实世界部署时,信任度和评估问题至关重要。
- 目前该领域仍存在一些开放性问题需要未来进一步研究。
点此查看论文截图

Fair Algorithms with Probing for Multi-Agent Multi-Armed Bandits
Authors:Tianyi Xu, Jiaxin Liu, Zizhan Zheng
We propose a multi-agent multi-armed bandit (MA-MAB) framework aimed at ensuring fair outcomes across agents while maximizing overall system performance. A key challenge in this setting is decision-making under limited information about arm rewards. To address this, we introduce a novel probing framework that strategically gathers information about selected arms before allocation. In the offline setting, where reward distributions are known, we leverage submodular properties to design a greedy probing algorithm with a provable performance bound. For the more complex online setting, we develop an algorithm that achieves sublinear regret while maintaining fairness. Extensive experiments on synthetic and real-world datasets show that our approach outperforms baseline methods, achieving better fairness and efficiency.
我们提出了一种多智能体多臂老虎机(MA-MAB)框架,旨在确保智能体之间的公平结果,同时最大限度地提高整体系统性能。在此环境中,关键挑战是在有限的奖励信息下做出决策。为解决这一问题,我们引入了一种新型的探测框架,该框架在分配前会针对选定的手臂进行战略性的信息收集。在奖励分布已知的情况下,我们利用子模块属性设计了一种贪婪探测算法,该算法具有可证明的性能界限。对于更复杂的在线环境,我们开发了一种算法,它在保持公平性的同时实现了次线性遗憾。在合成数据集和真实数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法优于基线方法,实现了更好的公平性和效率。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
提出一种多智能体多臂老虎机(MA-MAB)框架,旨在确保智能体之间的公平结果,同时最大限度地提高整体系统性能。针对在有限的奖励信息下决策的关键挑战,引入了一种新型的探测框架,对选定臂进行战略性的信息收集。在奖励分布已知的离线场景下,利用子模块属性设计贪婪探测算法,具有可证明的性能界限。针对更复杂的在线场景,开发了一种算法,在保持公平性的同时实现次线性后悔。在合成和真实数据集上的广泛实验表明,该方法优于基线方法,实现了更好的公平性和效率。
Key Takeaways:
- 提出了一种多智能体多臂老虎机(MA-MAB)框架,旨在确保智能体间的公平结果并优化系统性能。
- 面临的关键挑战是在有限的奖励信息下做出决策。
- 为了解决此挑战,引入了一种新型的探测框架,用于战略性地对选定臂进行信息收集。
- 在离线场景下,利用子模块属性设计贪婪探测算法,具有可证明的性能界限。
- 对于在线场景,开发了一种算法,能在保持公平性的同时实现次线性后悔。
- 通过广泛的实验验证,该框架在合成和真实数据集上的表现均优于基线方法。
点此查看论文截图


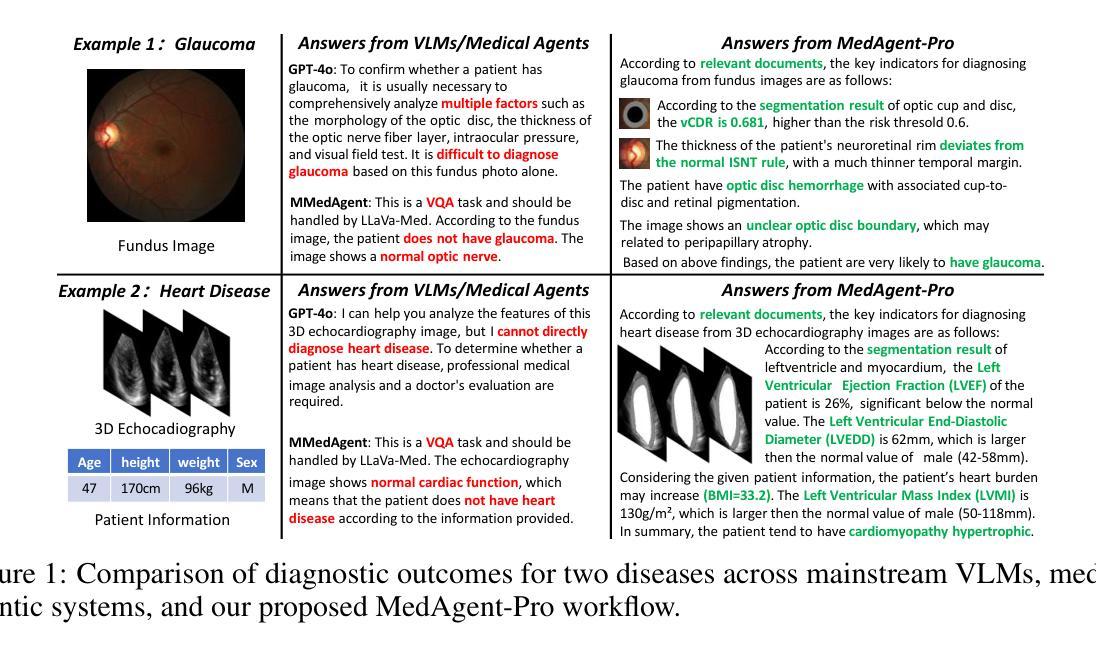
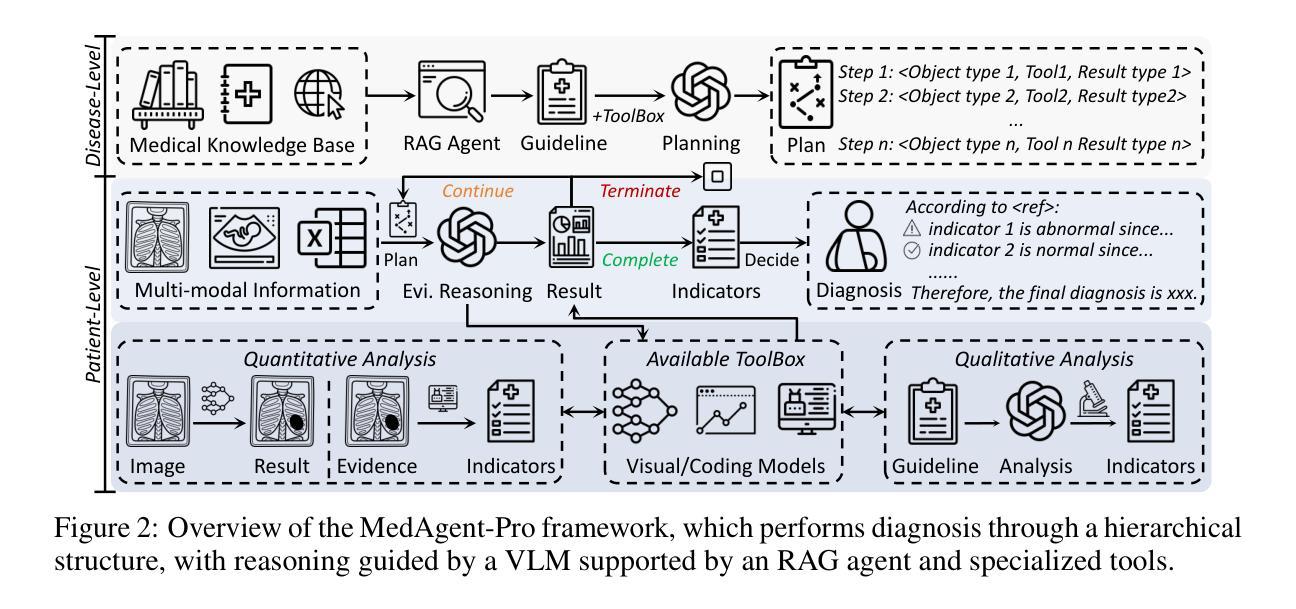
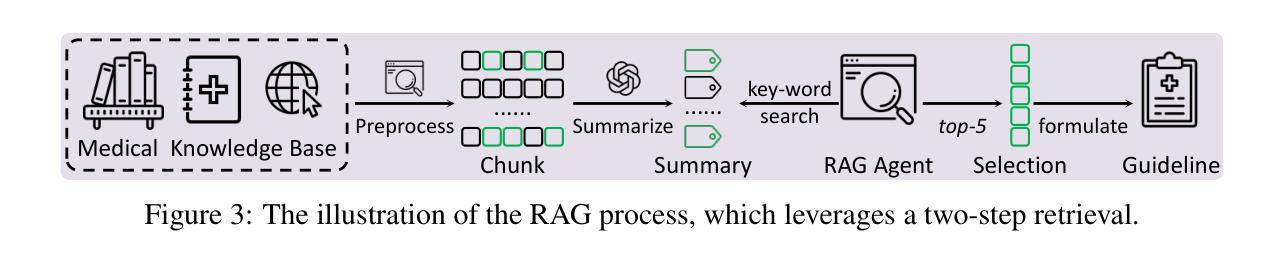
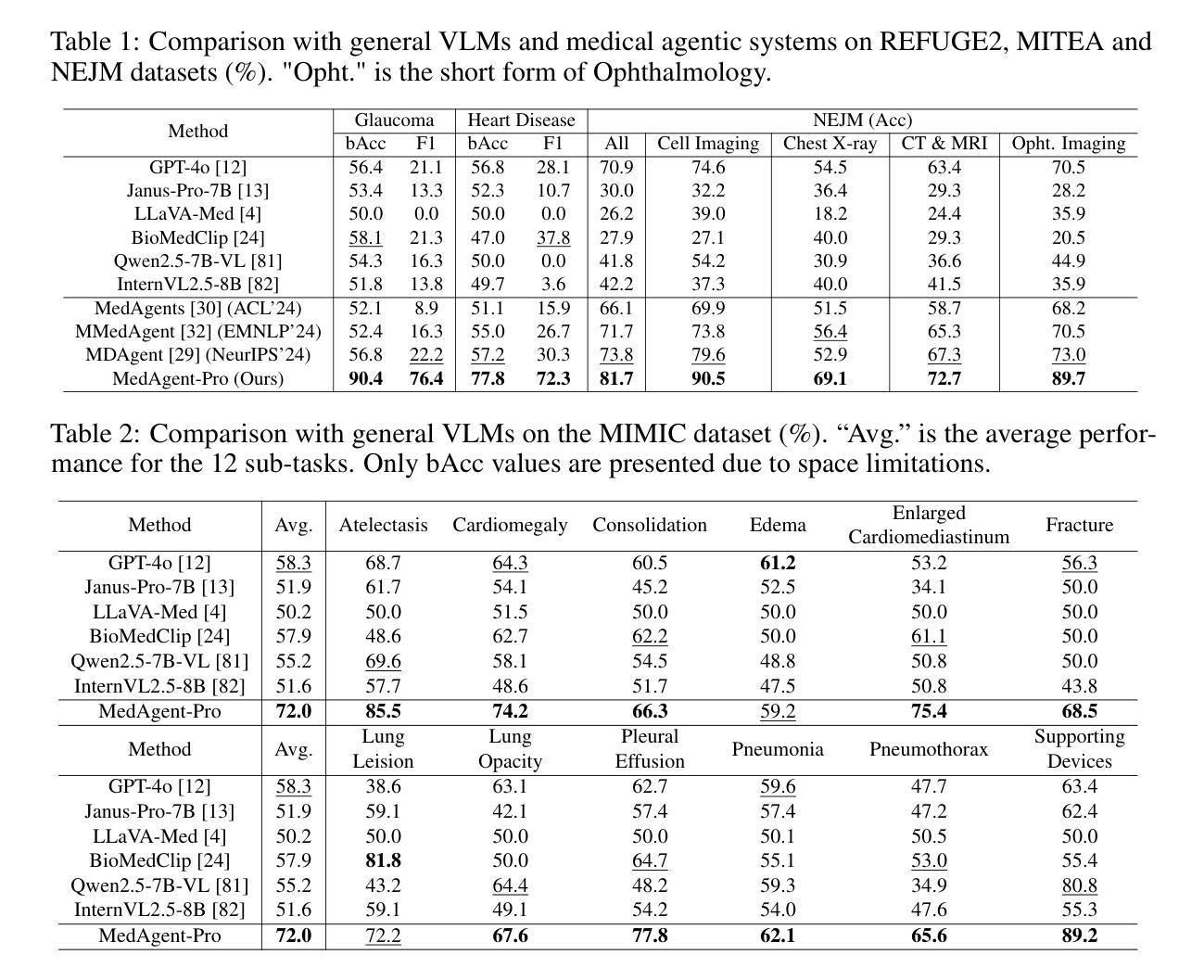
MedAgent-Pro: Towards Evidence-based Multi-modal Medical Diagnosis via Reasoning Agentic Workflow
Authors:Ziyue Wang, Junde Wu, Linghan Cai, Chang Han Low, Xihong Yang, Qiaxuan Li, Yueming Jin
In modern medicine, clinical diagnosis relies on the comprehensive analysis of primarily textual and visual data, drawing on medical expertise to ensure systematic and rigorous reasoning. Recent advances in large Vision-Language Models (VLMs) and agent-based methods hold great potential for medical diagnosis, thanks to the ability to effectively integrate multi-modal patient data. However, they often provide direct answers and draw empirical-driven conclusions without quantitative analysis, which reduces their reliability and clinical usability. We propose MedAgent-Pro, a new agentic reasoning paradigm that follows the diagnosis principle in modern medicine, to decouple the process into sequential components for step-by-step, evidence-based reasoning. Our MedAgent-Pro workflow presents a hierarchical diagnostic structure to mirror this principle, consisting of disease-level standardized plan generation and patient-level personalized step-by-step reasoning. To support disease-level planning, an RAG-based agent is designed to retrieve medical guidelines to ensure alignment with clinical standards. For patient-level reasoning, we propose to integrate professional tools such as visual models to enable quantitative assessments. Meanwhile, we propose to verify the reliability of each step to achieve evidence-based diagnosis, enforcing rigorous logical reasoning and a well-founded conclusion. Extensive experiments across a wide range of anatomical regions, imaging modalities, and diseases demonstrate the superiority of MedAgent-Pro to mainstream VLMs, agentic systems and state-of-the-art expert models. Ablation studies and human evaluation by clinical experts further validate its robustness and clinical relevance. Code is available at https://github.com/jinlab-imvr/MedAgent-Pro.
在现代医学中,临床诊断依赖于对主要是文本和视觉数据的综合分析,并借助医学专业知识确保系统且严谨推理。由于大型视觉语言模型(VLMs)和基于代理的方法的最新进展能够有效整合多模式患者数据,因此它们在医学诊断方面具有巨大潜力。然而,它们通常提供直接答案并基于经验得出结论,但没有进行定量分析,这降低了它们的可靠性和临床实用性。我们提出了MedAgent-Pro,这是一种新的代理推理范式,遵循现代医学的诊断原则,将过程分解为顺序组件,以进行基于证据的逐步推理。我们的MedAgent-Pro工作流程呈现了一个层次化的诊断结构来反映这一原则,包括疾病级别的标准化计划生成和患者级别的个性化逐步推理。为了支持疾病级别的规划,我们设计了一个基于RAG的代理来检索医学指南,以确保与临床标准的对齐。对于患者级别的推理,我们提议整合专业工具,如视觉模型,以实现定量评估。同时,我们提议验证每一步的可靠性,以实现基于证据的诊断,并强制执行严谨的逻辑推理和合理的结论。在广泛的解剖区域、成像模式和疾病方面的实验表明,MedAgent-Pro优于主流的VLMs、代理系统和最先进的专家模型。通过临床专家的消融研究和他评进一步验证了其稳健性和临床相关性。代码可在https://github.com/jinlab-imvr/MedAgent-Pro获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
现代医学临床诊断依赖于文本和视觉数据的综合分析,以及医学专业的系统严谨推理。最近的大型视觉语言模型和基于代理的方法为医学诊断提供了巨大潜力,但它们缺乏定量分析和可靠性验证。我们提出MedAgent-Pro,一种遵循现代医学诊断原则的新代理推理范式,将诊断过程分解为连续步骤进行证据基础的推理。其展现了一个层次化的诊断结构,包括疾病级别的标准化计划生成和患者级别的个性化逐步推理。代码已发布在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 现代医学诊断依赖于文本和视觉数据的综合分析。
- 大型视觉语言模型和基于代理的方法在医学诊断中具有潜力。
- 现有方法缺乏定量分析和可靠性验证,可能影响临床使用。
- MedAgent-Pro遵循现代医学诊断原则,将诊断过程分解为连续步骤进行证据基础的推理。
- MedAgent-Pro展现了一个层次化的诊断结构,包括疾病级别标准化计划生成和患者级别个性化推理。
- MedAgent-Pro通过RAG-based agent确保与临床标准的对齐,并通过集成专业工具进行定量评估。
点此查看论文截图