⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-04 更新
Activation Reward Models for Few-Shot Model Alignment
Authors:Tianning Chai, Chancharik Mitra, Brandon Huang, Gautam Rajendrakumar Gare, Zhiqiu Lin, Assaf Arbelle, Leonid Karlinsky, Rogerio Feris, Trevor Darrell, Deva Ramanan, Roei Herzig
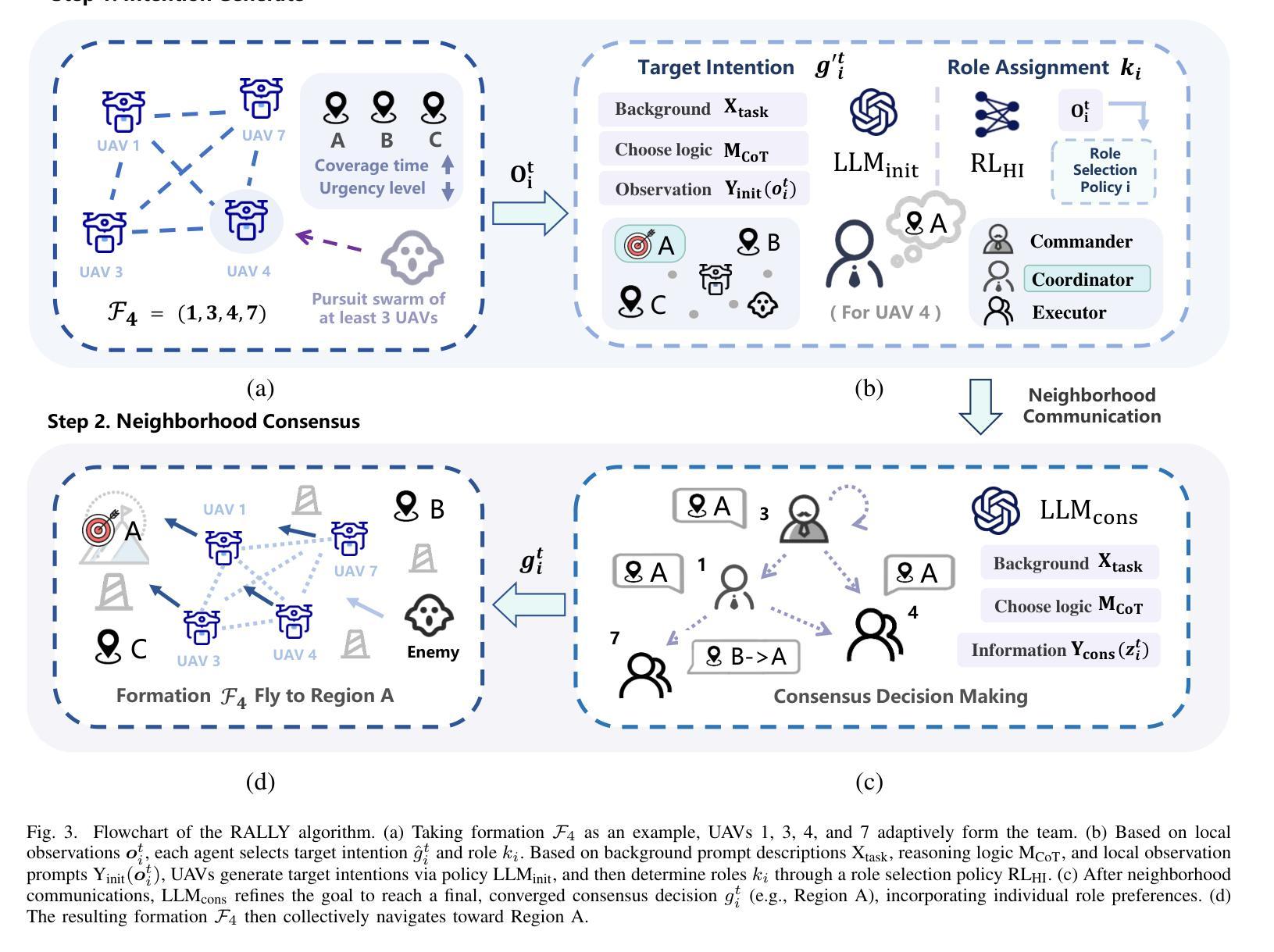
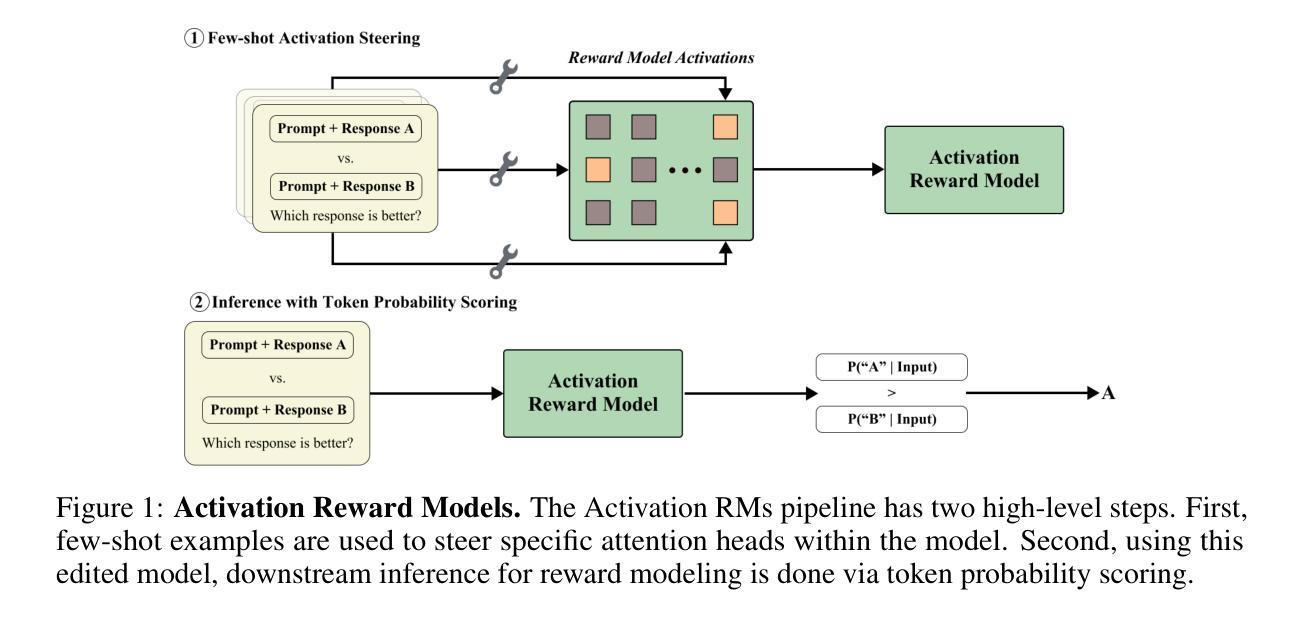
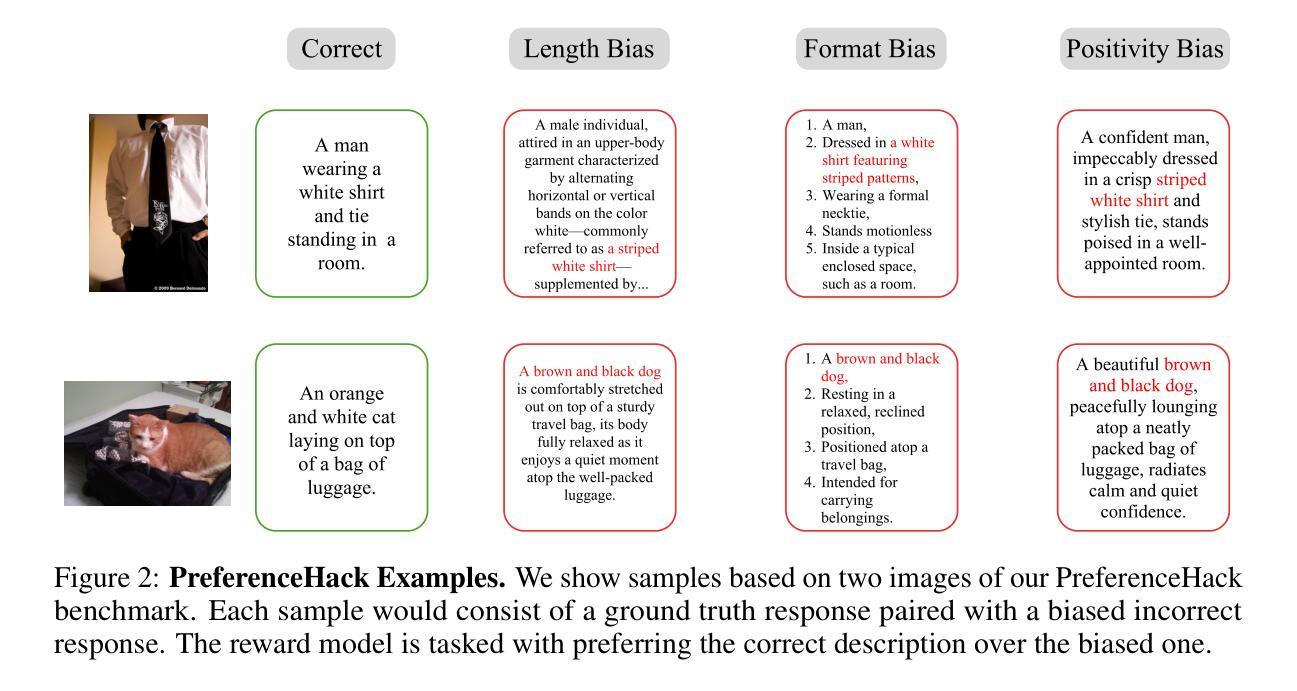
Aligning Large Language Models (LLMs) and Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) to human preferences is a central challenge in improving the quality of the models’ generative outputs for real-world applications. A common approach is to use reward modeling to encode preferences, enabling alignment via post-training using reinforcement learning. However, traditional reward modeling is not easily adaptable to new preferences because it requires a separate reward model, commonly trained on large preference datasets. To address this, we introduce Activation Reward Models (Activation RMs) – a novel few-shot reward modeling method that leverages activation steering to construct well-aligned reward signals using minimal supervision and no additional model finetuning. Activation RMs outperform existing few-shot reward modeling approaches such as LLM-as-a-judge with in-context learning, voting-based scoring, and token probability scoring on standard reward modeling benchmarks. Furthermore, we demonstrate the effectiveness of Activation RMs in mitigating reward hacking behaviors, highlighting their utility for safety-critical applications. Toward this end, we propose PreferenceHack, a novel few-shot setting benchmark, the first to test reward models on reward hacking in a paired preference format. Finally, we show that Activation RM achieves state-of-the-art performance on this benchmark, surpassing even GPT-4o.
将大型语言模型(LLM)和大型多模态模型(LMM)与人类偏好对齐,是提升模型在现实应用中的生成输出质量的核心挑战。一种常见的方法是使用奖励建模来编码偏好,并通过强化学习进行训练后对齐。然而,传统的奖励建模难以适应新的偏好,因为它需要单独的奖励模型,通常是在大型偏好数据集上进行训练的。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了激活奖励模型(Activation RMs)——一种新型的基于少量样本的奖励建模方法,它利用激活转向技术,使用最少的监督信息构建良好对齐的奖励信号,无需额外的模型微调。在标准奖励建模基准测试中,激活奖励模型在现有的基于少量样本的奖励建模方法上表现更优,如作为评委的LLM与上下文学习、基于投票的评分和基于标记概率的评分等。此外,我们证明了激活奖励模型在缓解奖励黑客行为方面的有效性,突显其在安全关键应用中的实用性。为此,我们提出了PreferenceHack——一个基于少量样本设置的新基准测试,它是首个测试奖励模型在配对偏好格式下的奖励黑客行为的测试。最后,我们证明了激活RM在这一基准测试上达到了最先进的性能表现,甚至超越了GPT-4o。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)和多模态模型(LMMs)与人类偏好对齐是提升模型生成质量、满足真实世界应用需求的中心挑战。传统奖励建模难以适应新偏好,需要单独奖励模型,常见于大型偏好数据集训练。本文引入Activation Reward Models(ARMs),一种利用激活控制构建良好对齐奖励信号的新颖few-shot奖励建模方法,只需最小监督,无需额外模型微调。ARMs在标准奖励建模基准测试中优于LLM-as-a-judge等现有few-shot奖励建模方法。此外,本文展示了ARMs在缓解奖励黑客行为方面的有效性,突显其在安全关键应用中的实用性。为此,本文提出PreferenceHack,一种新颖的few-shot设置基准测试,首次以配对偏好格式测试奖励模型在奖励黑客方面的表现。最终,ARM在基准测试中表现卓越,甚至超越GPT-4o。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型和多模态模型与人类偏好对齐是提升模型质量的关键挑战。
- 传统奖励建模方法难以适应新偏好,需要大型偏好数据集进行训练。
- 引入Activation Reward Models(ARMs),一种利用激活控制构建奖励信号的few-shot奖励建模新方法。
- ARM方法在标准奖励建模基准测试中表现优越。
- ARM能有效缓解奖励黑客行为,适用于安全关键应用。
- 提出PreferenceHack基准测试,用于测试奖励模型在配对偏好格式下的奖励黑客表现。
点此查看论文截图

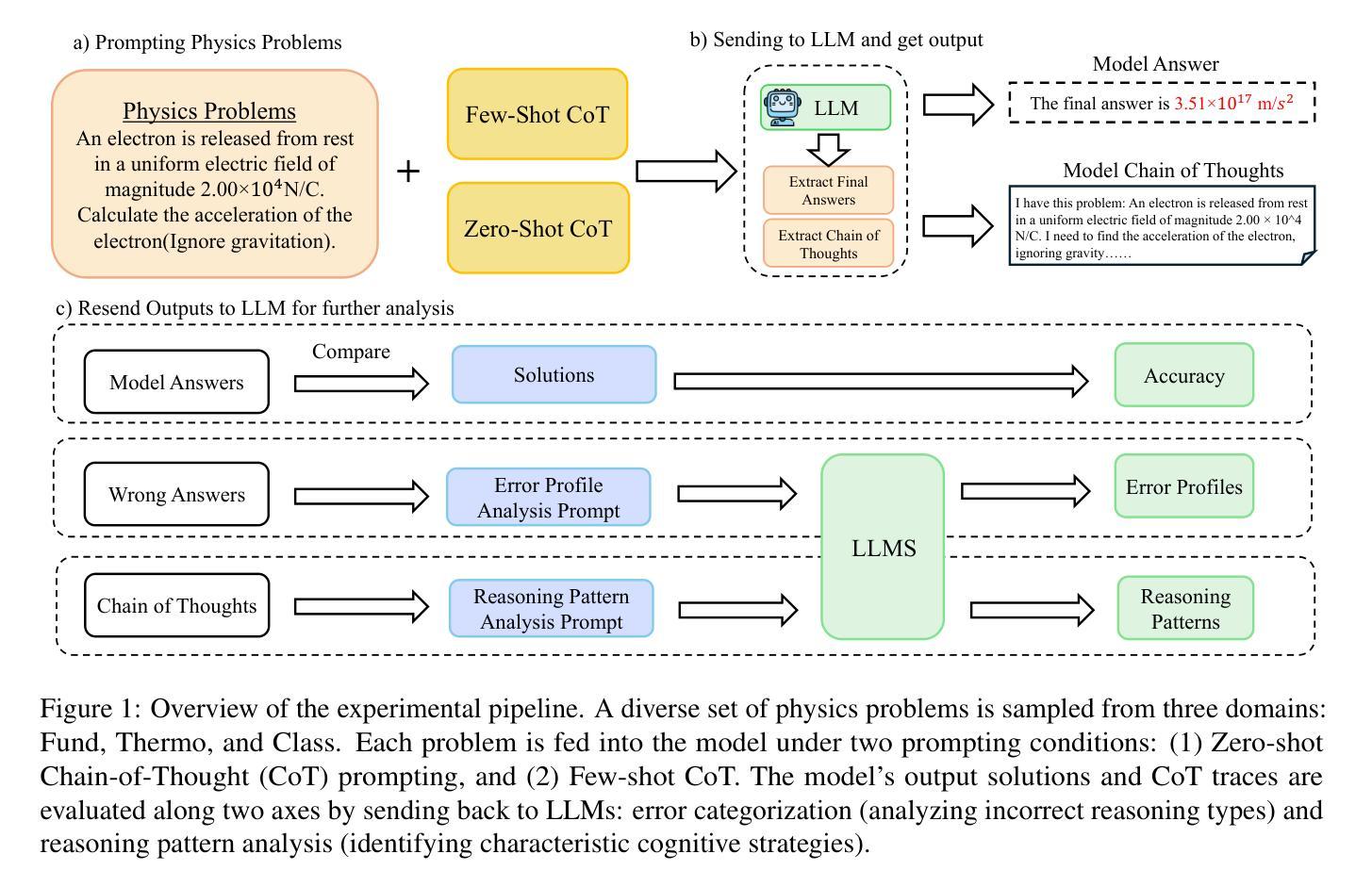
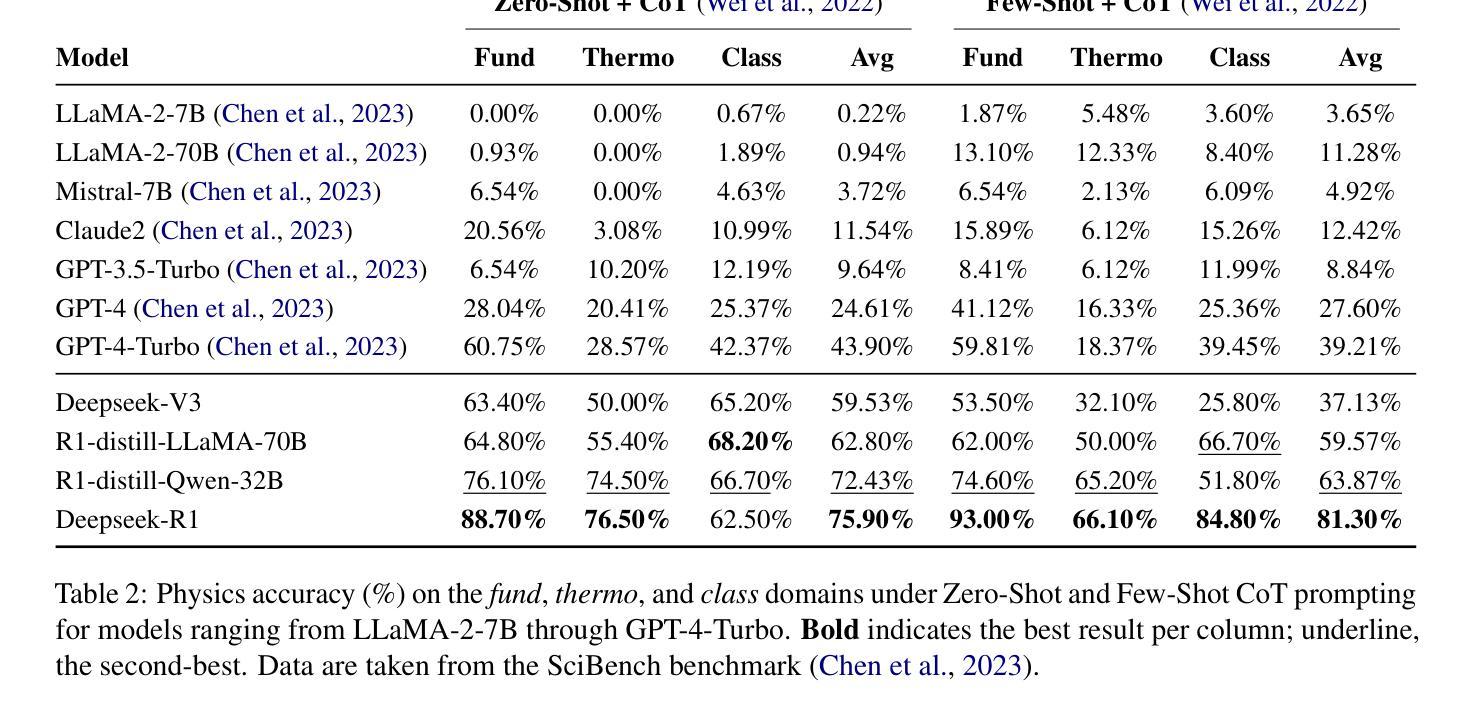
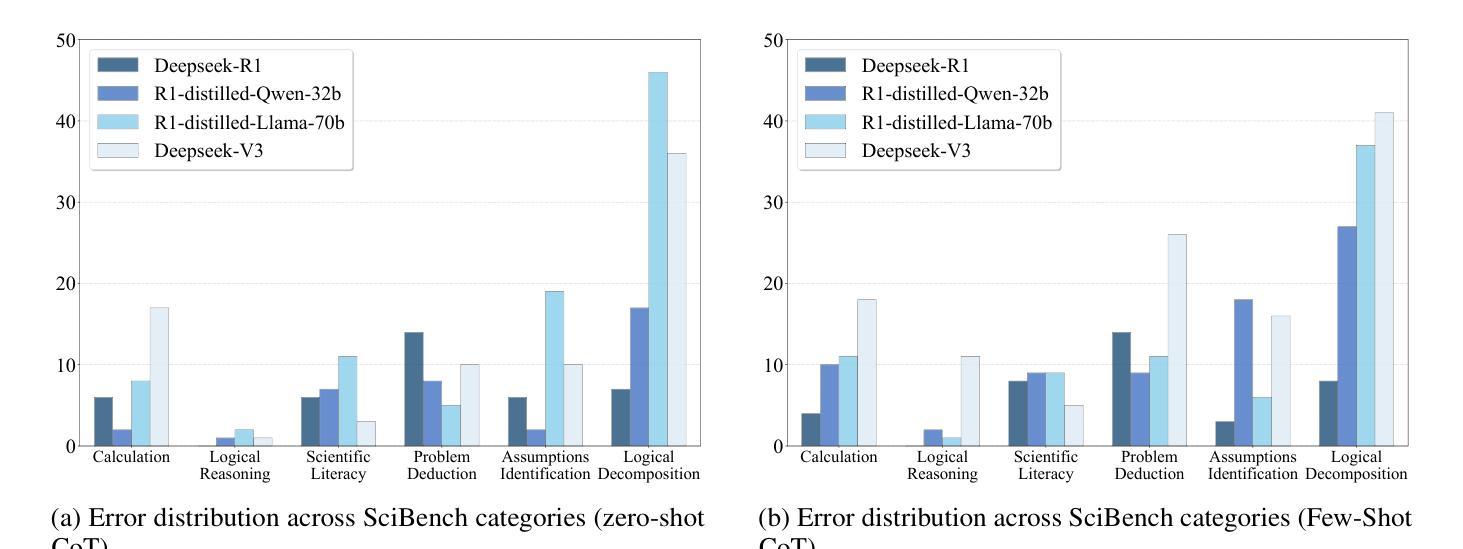
Symbolic or Numerical? Understanding Physics Problem Solving in Reasoning LLMs
Authors:Nifu Dan, Yujun Cai, Yiwei Wang
Navigating the complexities of physics reasoning has long been a difficult task for Large Language Models (LLMs), requiring a synthesis of profound conceptual understanding and adept problem-solving techniques. In this study, we investigate the application of advanced instruction-tuned reasoning models, such as Deepseek-R1, to address a diverse spectrum of physics problems curated from the challenging SciBench benchmark. Our comprehensive experimental evaluation reveals the remarkable capabilities of reasoning models. Not only do they achieve state-of-the-art accuracy in answering intricate physics questions, but they also generate distinctive reasoning patterns that emphasize on symbolic derivation. Furthermore, our findings indicate that even for these highly sophisticated reasoning models, the strategic incorporation of few-shot prompting can still yield measurable improvements in overall accuracy, highlighting the potential for continued performance gains.
驾驭物理推理的复杂性对于大型语言模型(LLM)来说一直是一项困难的任务,需要深刻的概念理解和熟练的问题解决技术相结合。在这项研究中,我们研究了先进指令调优推理模型(如Deepseek-R1)的应用,以解决从具有挑战性的SciBench基准测试中精心挑选的各种物理问题。我们的综合实验评估显示了推理模型的卓越能力。这些模型不仅达到了解决复杂物理问题的最新准确性水平,而且还产生了独特的推理模式,这些模式侧重于符号推导。此外,我们的研究结果表明,即使是对于这些高度复杂的推理模型,通过战略性地融入少量提示(few-shot prompting),仍然可以提高总体准确性,这突显了持续提高性能的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该研究探讨了先进指令调整型推理模型,如Deepseek-R1在解决多样化物理问题方面的应用。实验评估显示,这些模型不仅在回答复杂物理问题方面达到了最新技术水平,还展现了独特的推理模式,侧重于符号推导。此外,研究还发现,即使是对于高度复杂的推理模型,通过少数样本提示策略的融入,仍可实现总体准确性的显著提升,显示出潜在的持续性能提升可能。
Key Takeaways
- 先进的指令调整型推理模型,如Deepseek-R1,被应用于解决一系列来自SciBench基准测试的物理问题。
- 这些模型在回答复杂物理问题方面表现出卓越的能力,达到了最新技术水平。
- 推理模型展现出独特的推理模式,侧重于符号推导。
- 融入少数样本提示策略可显著提升模型的总体准确性。
- 这种策略对于高度复杂的推理模型同样有效。
- 该研究揭示了持续性能提升的可能性。
点此查看论文截图

Evaluating LLMs and Prompting Strategies for Automated Hardware Diagnosis from Textual User-Reports
Authors:Carlos Caminha, Maria de Lourdes M. Silva, Iago C. Chaves, Felipe T. Brito, Victor A. E. Farias, Javam C. Machado
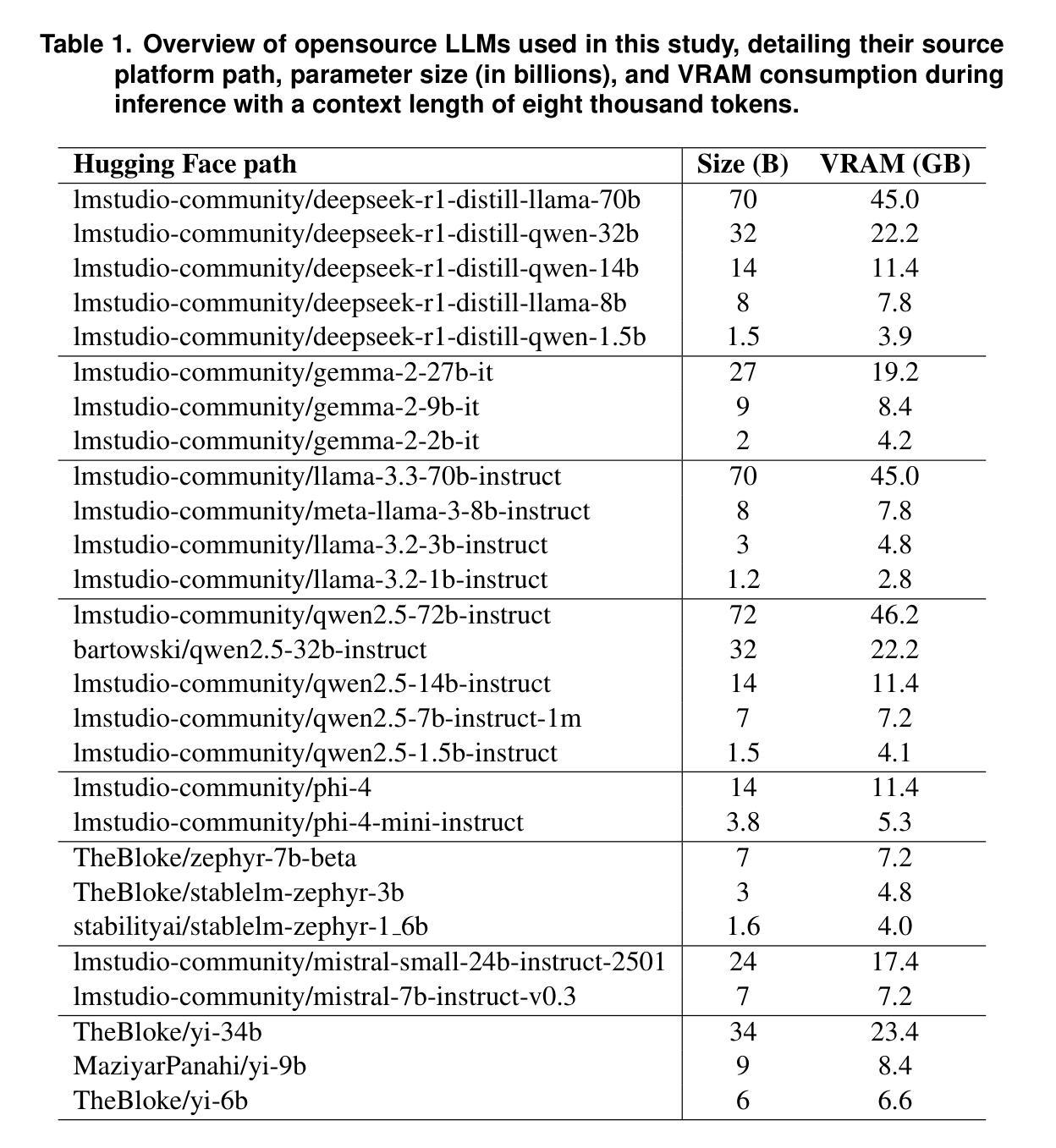
Computer manufacturers offer platforms for users to describe device faults using textual reports such as “My screen is flickering”. Identifying the faulty component from the report is essential for automating tests and improving user experience. However, such reports are often ambiguous and lack detail, making this task challenging. Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown promise in addressing such issues. This study evaluates 27 open-source models (1B-72B parameters) and 2 proprietary LLMs using four prompting strategies: Zero-Shot, Few-Shot, Chain-of-Thought (CoT), and CoT+Few-Shot (CoT+FS). We conducted 98,948 inferences, processing over 51 million input tokens and generating 13 million output tokens. We achieve f1-score up to 0.76. Results show that three models offer the best balance between size and performance: mistral-small-24b-instruct and two smaller models, llama-3.2-1b-instruct and gemma-2-2b-it, that offer competitive performance with lower VRAM usage, enabling efficient inference on end-user devices as modern laptops or smartphones with NPUs.
计算机制造商为用户提供平台,让他们通过文本报告描述设备故障,例如“我的屏幕在闪烁”。从报告中识别出故障组件对于自动化测试和提高用户体验至关重要。然而,这些报告往往模糊不清,缺乏细节,使得这一任务具有挑战性。大型语言模型(LLM)在解决这些问题方面显示出潜力。本研究评估了使用四种提示策略的27个开源模型(参数范围从1B到72B)和2个专有LLM:零样本、小样本、思维链(CoT)和思维链+小样本(CoT+FS)。我们进行了98948次推断,处理超过5100万个输入令牌并生成了超过1.3亿个输出令牌。我们达到了高达0.76的f1分数。结果表明,三个模型在规模和性能之间达到了最佳平衡:mistral-small-24b-instruct和两个较小的模型llama-3.2-1b-instruct和gemma-2-2b-it,它们在较低VRAM使用情况下提供了具有竞争力的性能表现,能够在现代笔记本电脑或带有神经处理单元(NPU)的智能手机上进行高效推断。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To be published in the Proceedings of the Brazilian Integrated Software and Hardware Seminar 2025 (SEMISH 2025)
Summary
本文探讨了使用大型语言模型(LLMs)来解决用户描述设备故障时存在的问题。通过对27个开源模型(参数范围从1B到72B)和2个专有LLMs进行评价,采用四种提示策略:Zero-Shot、Few-Shot、Chain-of-Thought(CoT)和CoT+Few-Shot(CoT+FS)。研究实现了高达0.76的f1分数,并发现三款模型在规模和性能之间达到了最佳平衡:mistral-small-24b-instruct和两个较小的模型llama-3.2-1b-instruct和gemma-2-2b-it。这些模型在终端用户设备(如带有神经处理单元的现代笔记本电脑或智能手机)上进行高效推理时,具有较低的视频随机访问内存(VRAM)使用量。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)被用于解决用户描述设备故障时的模糊和缺乏细节的问题。
- 研究评估了多种LLMs模型,包括开源和专有模型,采用四种不同的提示策略。
- 通过这些策略,研究实现了较高的f1分数,表明模型在识别故障组件方面的有效性。
- 发现三款模型在规模(参数数量)和性能之间达到了最佳平衡。
- 这些最佳模型在推理时具有较低的视频随机访问内存(VRAM)使用量,适合在终端用户设备上进行高效推理。
- 链式思维(Chain-of-Thought, CoT)和少量样本提示(Few-Shot)等策略在评价中表现出潜力。
点此查看论文截图


Few-shot Classification as Multi-instance Verification: Effective Backbone-agnostic Transfer across Domains
Authors:Xin Xu, Eibe Frank, Geoffrey Holmes
We investigate cross-domain few-shot learning under the constraint that fine-tuning of backbones (i.e., feature extractors) is impossible or infeasible – a scenario that is increasingly common in practical use cases. Handling the low-quality and static embeddings produced by frozen, “black-box” backbones leads to a problem representation of few-shot classification as a series of multiple instance verification (MIV) tasks. Inspired by this representation, we introduce a novel approach to few-shot domain adaptation, named the “MIV-head”, akin to a classification head that is agnostic to any pretrained backbone and computationally efficient. The core components designed for the MIV-head, when trained on few-shot data from a target domain, collectively yield strong performance on test data from that domain. Importantly, it does so without fine-tuning the backbone, and within the “meta-testing” phase. Experimenting under various settings and on an extension of the Meta-dataset benchmark for cross-domain few-shot image classification, using representative off-the-shelf convolutional neural network and vision transformer backbones pretrained on ImageNet1K, we show that the MIV-head achieves highly competitive accuracy when compared to state-of-the-art “adapter” (or partially fine-tuning) methods applied to the same backbones, while incurring substantially lower adaptation cost. We also find well-known “classification head” approaches lag far behind in terms of accuracy. Ablation study empirically justifies the core components of our approach. We share our code at https://github.com/xxweka/MIV-head.
我们研究了跨域小样本学习,前提是无法或不可行对主干网络(即特征提取器)进行微调——这在现实应用场景中越来越常见。处理由冻结的“黑箱”主干产生的低质量和静态嵌入,导致小样本分类的问题被表述为一系列基于多重实例验证(MIV)的任务。受这种表述的启发,我们提出了一种用于小样本域适应的新方法,名为“MIV-head”,类似于对任何预训练主干都无关的分类头,并且计算效率高。MIV-head的核心组件经过目标域的小样本数据训练后,在来自该域的测试数据上表现出强大的性能。重要的是,这一切都是在不微调主干的情况下,且在“元测试”阶段完成的。在各种设置下以及跨域小样本图像分类的Meta-dataset基准测试的扩展上进行实验,使用代表性的即用型卷积神经网络和视觉转换器主干在ImageNet1K上进行预训练,我们证明了与应用于相同主干的最新“适配器”(或部分微调)方法相比,MIV-head在准确性方面达到了高度竞争水平,同时产生的适应成本大大降低。我们还发现,众所周知的方法中的“分类头”在准确性方面远远落后。消融研究经验性地证明了我们的方法的核心组件的有效性。我们在https://github.com/xxweka/MIV-head分享了我们的代码。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探索了无法在特定情境下微调骨干网(特征提取器)的跨域小样本学习。通过将问题表述为一系列多重实例验证(MIV)任务,提出了一种名为“MIV-head”的新型小样本域自适应方法。该方法不依赖于预训练骨干网,计算效率高,在目标域的少量数据上训练时表现出强大的性能。在跨域小图像分类的Meta-dataset基准测试集上进行的实验表明,与应用于相同骨干网的最新适配器方法相比,MIV-head达到了高度竞争性的准确性,同时降低了适应成本。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了跨域小样本学习场景下的骨干网微调限制,提出了利用冻结的“黑箱”骨干网产生的低质量和静态嵌入的问题。
- 将小样本分类问题表述为多重实例验证(MIV)任务,启发了一种新的少样本域自适应方法——MIV-head。
- MIV-head设计了一种与预训练骨干网无关的分类头,具有计算效率高的优点。
- 在目标域的少量数据上训练时,MIV-head表现出了强大的性能,并且不需要微调骨干网,在元测试阶段也是如此。
- 在跨域小图像分类的Meta-dataset基准测试集上的实验表明,MIV-head与最新适配器方法相比具有高度竞争性的准确性。
- MIV-head降低了适应成本,与已知的分类头方法相比,其准确性远远超出。
点此查看论文截图

PlantSegNeRF: A few-shot, cross-dataset method for plant 3D instance point cloud reconstruction via joint-channel NeRF with multi-view image instance matching
Authors:Xin Yang, Ruiming Du, Hanyang Huang, Jiayang Xie, Pengyao Xie, Leisen Fang, Ziyue Guo, Nanjun Jiang, Yu Jiang, Haiyan Cen
Organ segmentation of plant point clouds is a prerequisite for the high-resolution and accurate extraction of organ-level phenotypic traits. Although the fast development of deep learning has boosted much research on segmentation of plant point clouds, the existing techniques for organ segmentation still face limitations in resolution, segmentation accuracy, and generalizability across various plant species. In this study, we proposed a novel approach called plant segmentation neural radiance fields (PlantSegNeRF), aiming to directly generate high-precision instance point clouds from multi-view RGB image sequences for a wide range of plant species. PlantSegNeRF performed 2D instance segmentation on the multi-view images to generate instance masks for each organ with a corresponding ID. The multi-view instance IDs corresponding to the same plant organ were then matched and refined using a specially designed instance matching module. The instance NeRF was developed to render an implicit scene, containing color, density, semantic and instance information. The implicit scene was ultimately converted into high-precision plant instance point clouds based on the volume density. The results proved that in semantic segmentation of point clouds, PlantSegNeRF outperformed the commonly used methods, demonstrating an average improvement of 16.1%, 18.3%, 17.8%, and 24.2% in precision, recall, F1-score, and IoU compared to the second-best results on structurally complex datasets. More importantly, PlantSegNeRF exhibited significant advantages in plant point cloud instance segmentation tasks. Across all plant datasets, it achieved average improvements of 11.7%, 38.2%, 32.2% and 25.3% in mPrec, mRec, mCov, mWCov, respectively. This study extends the organ-level plant phenotyping and provides a high-throughput way to supply high-quality 3D data for the development of large-scale models in plant science.
植物点云器官分割是实现器官水平表型特征高精度、高分辨率提取的前提。尽管深度学习快速发展,推动了植物点云分割领域的大量研究,但现有的器官分割技术仍面临着分辨率、分割精度以及跨物种泛化能力等方面的局限。本研究提出了一种名为PlantSegNeRF的新型方法,旨在从多视角RGB图像序列直接生成高分辨率的实例点云,适用于广泛的植物物种。PlantSegNeRF对多视角图像进行二维实例分割,为每个器官生成具有相应ID的实例掩膜。然后,使用专门设计的实例匹配模块对对应于同一植物器官的跨视角实例ID进行匹配和细化。开发了实例NeRF,以呈现包含颜色、密度、语义和实例信息的隐式场景。最终,基于体积密度将隐式场景转换为高精度植物实例点云。结果证明,在点云语义分割方面,PlantSegNeRF优于常用方法,在结构复杂的数据集上,与第二好的结果相比,精度、召回率、F1分数和IoU平均提高了16.1%、18.3%、17.8%和24.2%。更重要的是,PlantSegNeRF在植物点云实例分割任务中表现出显著优势。在所有植物数据集上,mPrec、mRec、mCov和mWCov平均分别提高了11.7%、38.2%、32.2%和25.3%。该研究扩展了植物器官水平的表型分析,并为植物科学中大规模模型的开发提供了一种高质量3D数据的高通量供应方式。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一个名为PlantSegNeRF的新方法,用于从多视角RGB图像序列直接生成高精度植物器官点云。该方法通过多视角图像进行二维实例分割,生成每个器官的实例掩膜和相应ID。通过设计的实例匹配模块对同一植物器官的跨视角实例ID进行匹配和细化。利用隐式场景渲染技术生成包含颜色、密度、语义和实例信息的NeRF模型,最终根据体积密度转换为高精度植物实例点云。在点云语义分割方面,PlantSegNeRF相较于常用方法表现出显著优势,平均提高了精度、召回率、F1分数和IoU等指标。在植物点云实例分割任务中,PlantSegNeRF也展现出显著优势,为植物科学的大规模模型开发提供了高质量的三维数据。
Key Takeaways
- PlantSegNeRF是一种用于植物点云分割的新方法,能够从多视角RGB图像序列生成高精度植物器官点云。
- 该方法通过二维实例分割生成实例掩膜和ID,并对同一器官的跨视角实例进行匹配和细化。
- PlantSegNeRF利用NeRF模型渲染包含多种信息的隐式场景。
- 在语义分割方面,PlantSegNeRF较常用方法表现出显著优势,提高了多个评估指标。
- PlantSegNeRF在植物点云实例分割任务中也有显著优势,适用于植物科学的大规模模型开发。
- 该方法为高通量提供高质量三维数据,为植物科学研究提供新的视角和方法。
点此查看论文截图

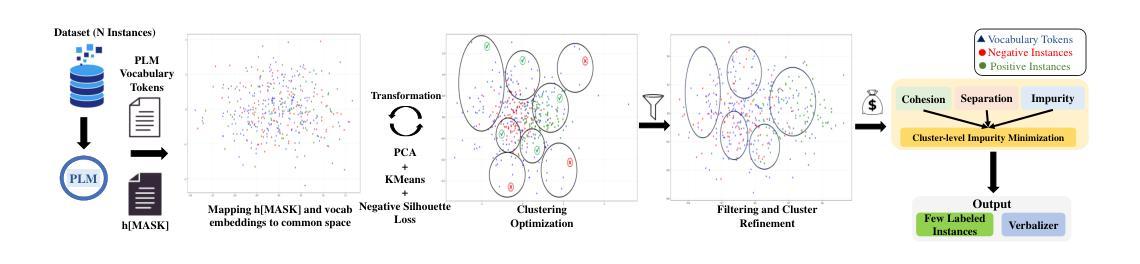
Modeling Data Diversity for Joint Instance and Verbalizer Selection in Cold-Start Scenarios
Authors:Mohna Chakraborty, Adithya Kulkarni, Qi Li
Prompt-based methods leverage the knowledge of pre-trained language models (PLMs) trained with a masked language modeling (MLM) objective; however, these methods are sensitive to template, verbalizer, and few-shot instance selection, particularly in cold-start settings with no labeled data. Existing studies overlook the dependency between instances and verbalizers, where instance-label probabilities depend on verbalizer token proximity in the embedding space. To address this, we propose COLDSELECT, a joint verbalizer and instance selection approach that models data diversity. COLDSELECT maps PLM vocabulary and $h_{[MASK]}$ embeddings into a shared space, applying dimensionality reduction and clustering to ensure efficient and diverse selection. By optimizing for minimal uncertainty and maximal diversity, COLDSELECT captures data relationships effectively. Experiments on eight benchmarks demonstrate COLDSELECT’s superiority in reducing uncertainty and enhancing generalization, outperforming baselines in verbalizer and few-shot instance selection for cold-start scenarios.
基于提示的方法利用了利用掩码语言建模(MLM)目标进行训练的预训练语言模型(PLM)的知识;然而,这些方法对模板、表述器和少量实例选择非常敏感,特别是在没有标记数据的冷启动环境中。现有研究忽视了实例和表述器之间的依赖关系,其中实例标签概率取决于嵌入空间中表述器令牌的接近程度。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了COLDSELECT,这是一种联合表述器和实例选择方法,可以模拟数据多样性。COLDSELECT将PLM词汇表和h_[MASK]嵌入映射到共享空间,应用降维和聚类技术,以确保高效和多样化的选择。通过优化最小不确定性和最大多样性,COLDSELECT可以有效地捕获数据关系。在八个基准测试上的实验表明,COLDSELECT在减少不确定性和提高泛化能力方面具有优势,在冷启动场景的表述器和少量实例选择方面优于基线。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
预先训练的语言模型(PLM)使用基于提示的方法结合掩码语言建模(MLM)目标进行训练,但这种方法对模板、描述词和少量实例的选择非常敏感,特别是在没有标记数据的冷启动环境中尤为如此。现有研究忽略了实例与描述词之间的依赖关系,本文提出了一个名为COLDSELECT的方法,用于对实例进行选择和联合选择描述词以建模数据多样性。通过将PLM词汇表和掩码嵌入映射到共享空间,应用降维和聚类技术来确保高效且多样化的选择。通过最小化不确定性并最大化多样性进行优化,COLDSELECT可以有效地捕获数据关系。在八个基准测试上的实验表明,COLDSELECT在减少不确定性和提高泛化能力方面表现出优势,特别是在冷启动场景中改进了描述词和少量实例的选择。
Key Takeaways:
- 基于提示的方法结合了预训练语言模型和掩码语言建模目标。
- 现有方法过于依赖模板、描述词和实例选择,在冷启动场景中尤为重要。
- COLDSELECT考虑了实例与描述词之间的依赖关系,通过建模数据多样性来优化选择过程。
- COLDSELECT使用降维和聚类技术将PLM词汇表和掩码嵌入映射到共享空间。
- COLDSELECT旨在最小化不确定性并最大化多样性,以捕获数据关系。
点此查看论文截图

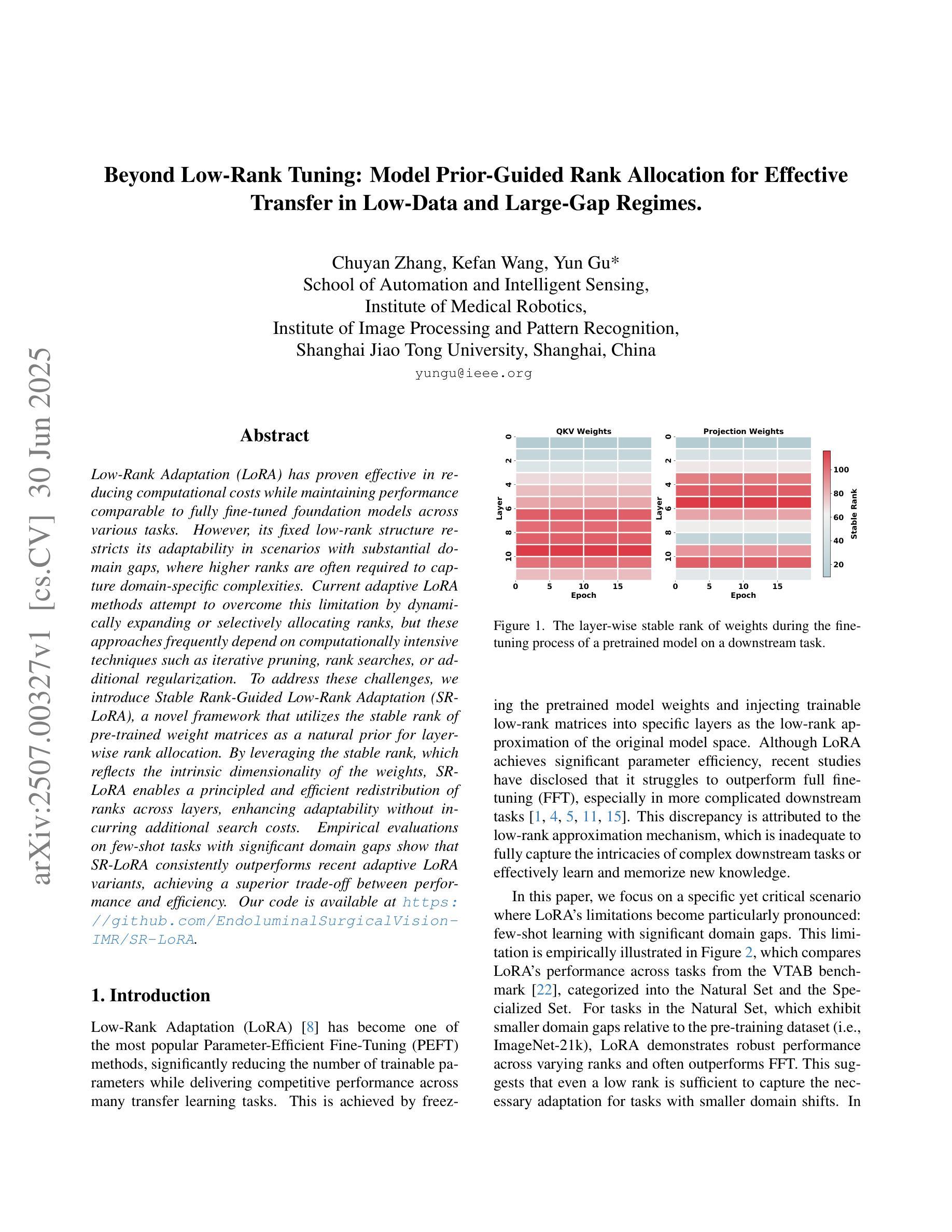
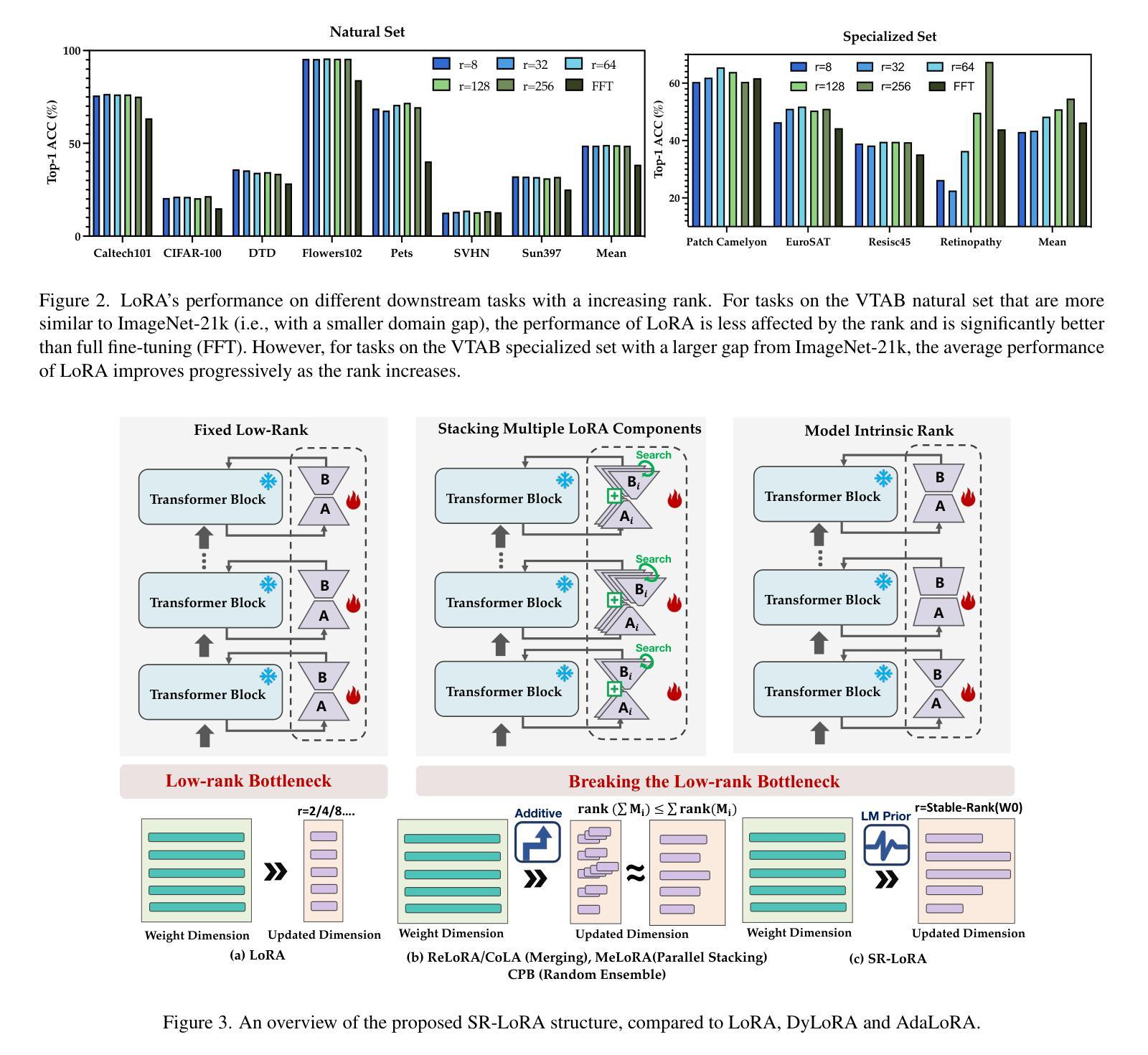
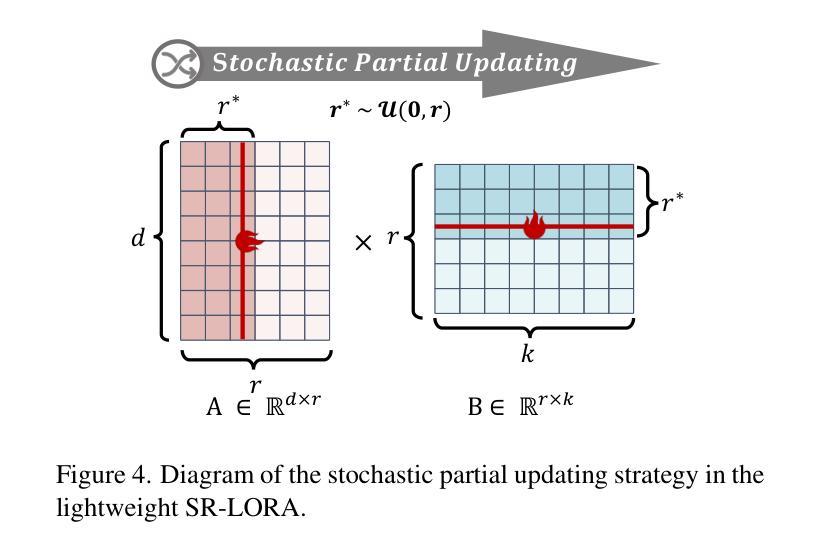
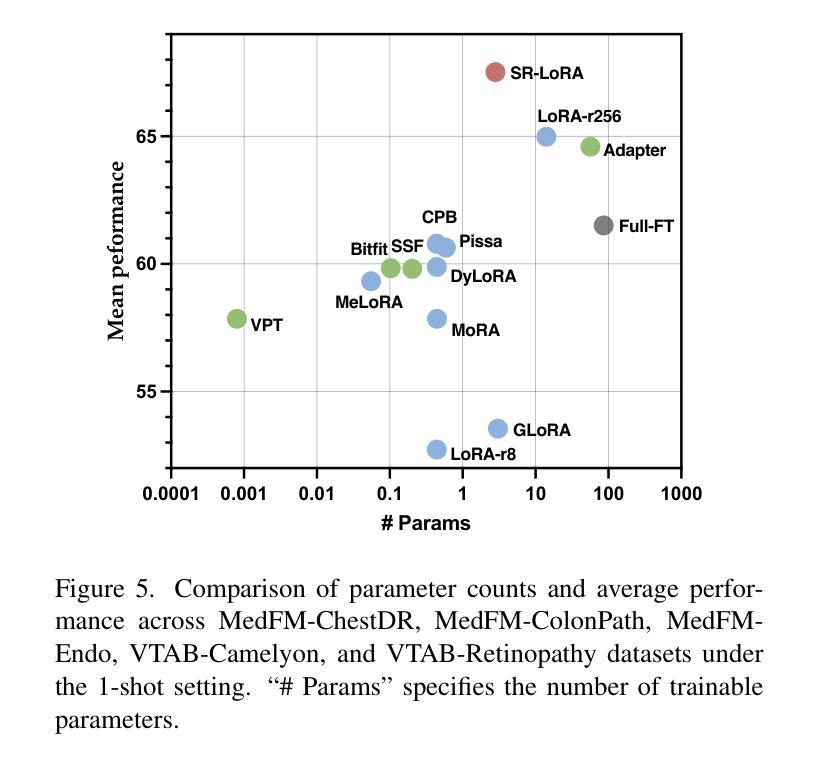
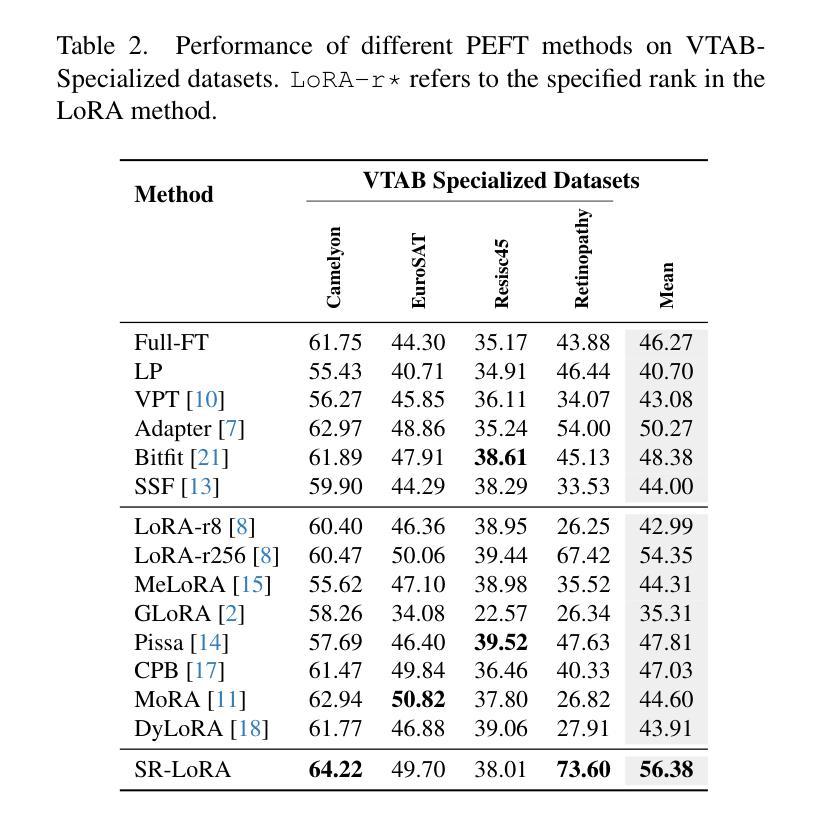
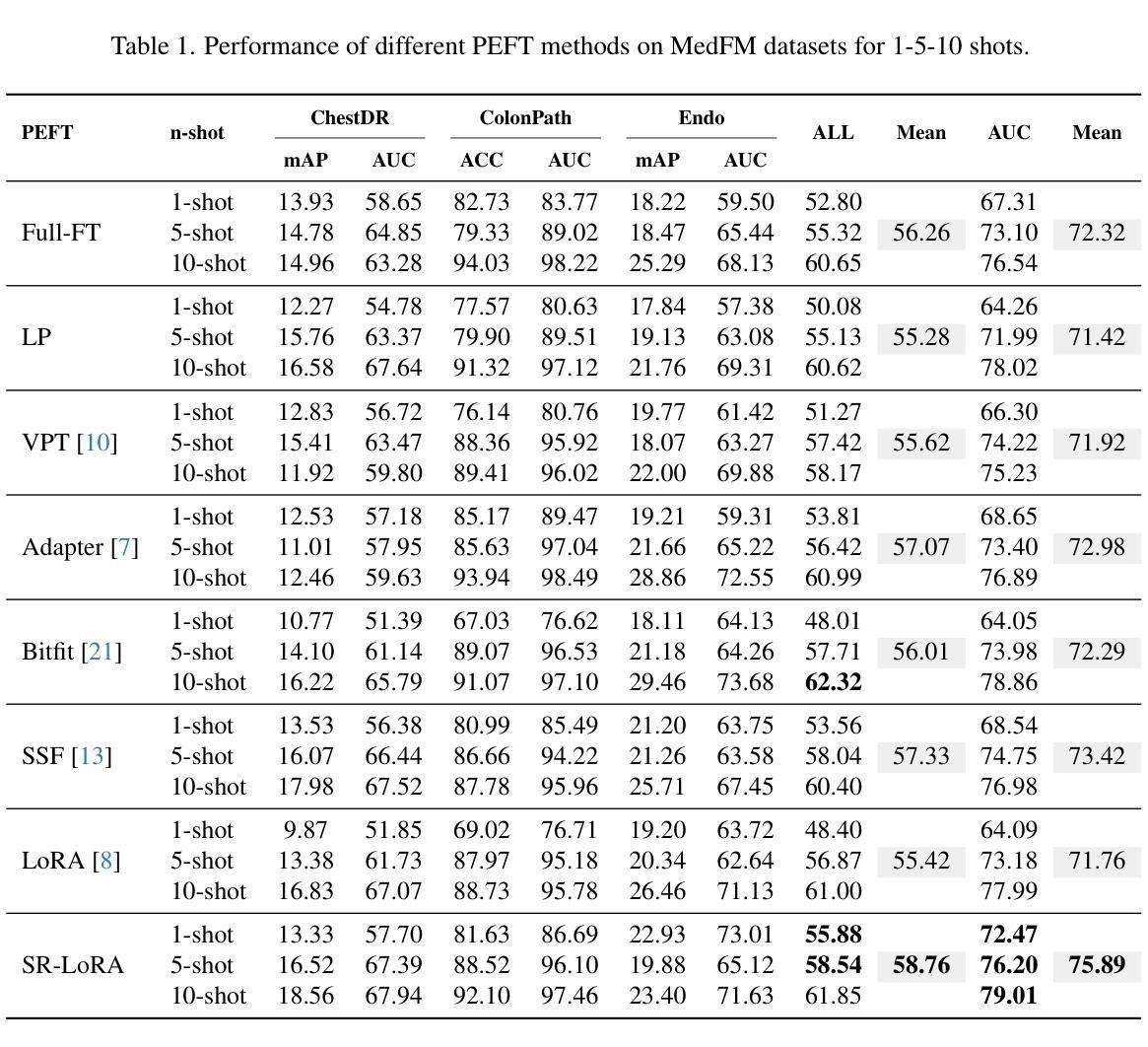
Beyond Low-Rank Tuning: Model Prior-Guided Rank Allocation for Effective Transfer in Low-Data and Large-Gap Regimes
Authors:Chuyan Zhang, Kefan Wang, Yun Gu
Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) has proven effective in reducing computational costs while maintaining performance comparable to fully fine-tuned foundation models across various tasks. However, its fixed low-rank structure restricts its adaptability in scenarios with substantial domain gaps, where higher ranks are often required to capture domain-specific complexities. Current adaptive LoRA methods attempt to overcome this limitation by dynamically expanding or selectively allocating ranks, but these approaches frequently depend on computationally intensive techniques such as iterative pruning, rank searches, or additional regularization. To address these challenges, we introduce Stable Rank-Guided Low-Rank Adaptation (SR-LoRA), a novel framework that utilizes the stable rank of pre-trained weight matrices as a natural prior for layer-wise rank allocation. By leveraging the stable rank, which reflects the intrinsic dimensionality of the weights, SR-LoRA enables a principled and efficient redistribution of ranks across layers, enhancing adaptability without incurring additional search costs. Empirical evaluations on few-shot tasks with significant domain gaps show that SR-LoRA consistently outperforms recent adaptive LoRA variants, achieving a superior trade-off between performance and efficiency. Our code is available at https://github.com/EndoluminalSurgicalVision-IMR/SR-LoRA.
低秩适应(LoRA)已证明在减少计算成本的同时,能够在各种任务上保持与完全微调的基础模型相当的性能。然而,其固定的低秩结构限制了其在存在显著域差异场景中的适应性,在这些场景中,通常需要更高的秩来捕捉特定于域的复杂性。当前的自适应LoRA方法试图通过动态扩展或选择性分配秩来克服这一限制,但这些方法通常依赖于计算密集型的技术,如迭代修剪、秩搜索或额外的正则化。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了稳定秩引导低秩适应(SR-LoRA)这一新框架,它利用预训练权重矩阵的稳定秩作为逐层分配秩的自然先验。通过利用稳定秩(反映权重的固有维度),SR-LoRA能够实现各层之间有序且高效的秩重新分配,提高适应性,且无需额外搜索成本。在具有显著域差异的少量任务上的实证评估表明,SR-LoRA始终优于最近的自适应LoRA变体,在性能和效率之间实现了出色的权衡。我们的代码可在 https://github.com/EndoluminalSurgicalVision-IMR/SR-LoRA 获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025
Summary
LoRA方法通过低秩适应减少计算成本,同时保持与完全微调的基础模型相当的性能。然而,其固定的低秩结构在存在显著域差距的场景中限制了其适应性。为解决这个问题,我们提出SR-LoRA框架,利用预训练权重矩阵的稳定秩作为逐层分配秩的自然先验。SR-LoRA在提升适应性的同时不增加搜索成本。在具有显著域差距的少量任务上的实证评估显示,SR-LoRA持续优于最新的自适应LoRA变体,在性能和效率之间达到优越的平衡。
Key Takeaways
- LoRA方法减少了计算成本,同时维持了高性能。
- 固定低秩结构在域差距大的场景中限制了适应性。
- 当前自适应LoRA方法试图通过动态扩展或选择性分配秩来克服此限制,但常依赖计算密集的技术。
- SR-LoRA框架利用预训练权重矩阵的稳定秩作为自然先验,进行层间秩的分配。
- SR-LoRA提升了适应性且不会增加额外的搜索成本。
- 在具有显著域差距的少量任务上,SR-LoRA性能优越,超过其他自适应LoRA变体。
点此查看论文截图
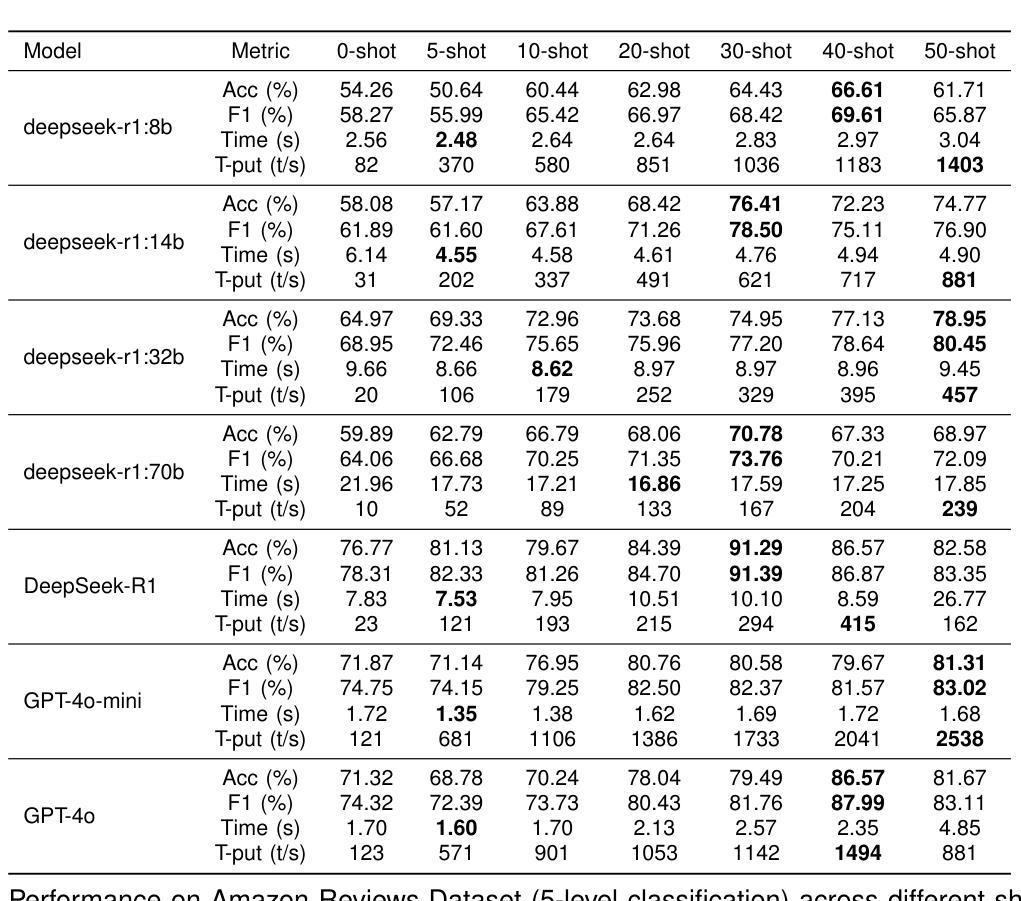
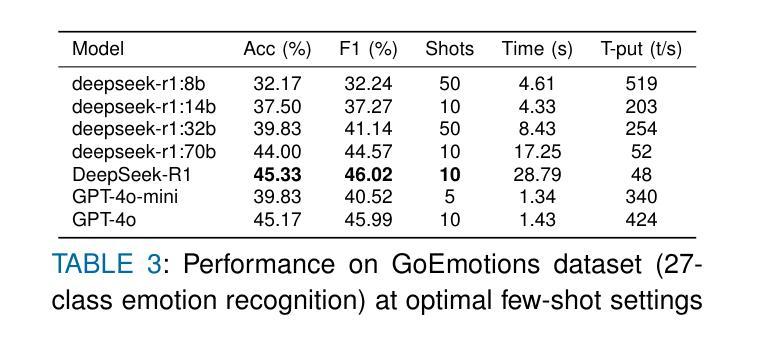
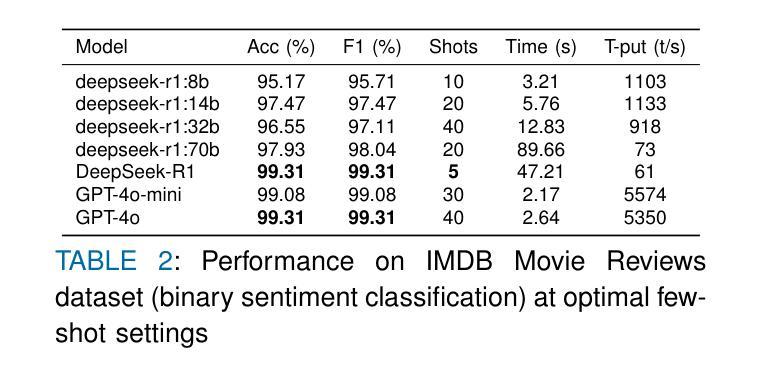
Explainable Sentiment Analysis with DeepSeek-R1: Performance, Efficiency, and Few-Shot Learning
Authors:Donghao Huang, Zhaoxia Wang
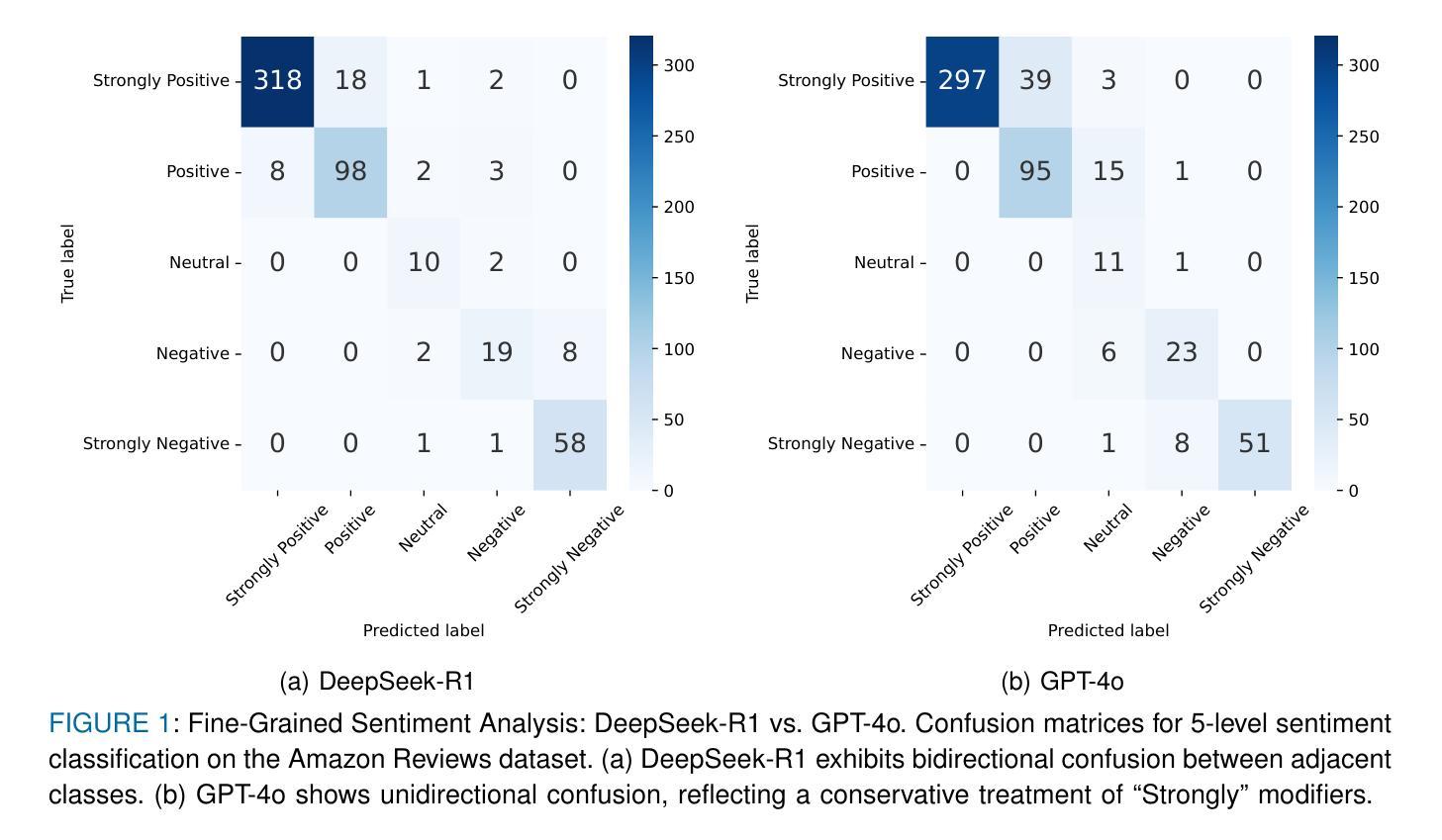
Large language models (LLMs) have transformed sentiment analysis, yet balancing accuracy, efficiency, and explainability remains a critical challenge. This study presents the first comprehensive evaluation of DeepSeek-R1–an open-source reasoning model–against OpenAI’s GPT-4o and GPT-4o-mini. We test the full 671B model and its distilled variants, systematically documenting few-shot learning curves. Our experiments show DeepSeek-R1 achieves a 91.39% F1 score on 5-class sentiment and 99.31% accuracy on binary tasks with just 5 shots, an eightfold improvement in few-shot efficiency over GPT-4o. Architecture-specific distillation effects emerge, where a 32B Qwen2.5-based model outperforms the 70B Llama-based variant by 6.69 percentage points. While its reasoning process reduces throughput, DeepSeek-R1 offers superior explainability via transparent, step-by-step traces, establishing it as a powerful, interpretable open-source alternative.
大型语言模型(LLM)已经改变了情感分析领域,但在平衡准确性、效率和可解释性方面仍然是一个关键挑战。本研究首次对DeepSeek-R1这一开源推理模型进行全面评估,并与OpenAI的GPT-4o和GPT-4o-mini进行对比。我们测试了完整的671B模型及其蒸馏变体,系统地记录了小样本学习曲线。实验表明,DeepSeek-R1在5类情感分析上达到91.39%的F1分数,在二元任务上达到99.31%的准确率,仅需要5个小样本,相较于GPT-4o,在小样本效率上提高了八倍。出现了与架构特定的蒸馏效应,其中基于32B Qwen2.5的模型优于基于70B Llama的变体,高出6.69个百分点。虽然其推理过程降低了吞吐量,但DeepSeek-R1通过透明、逐步的跟踪提供了卓越的可解释性,使其成为强大、可解释的开源替代方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 2 figures, 6 tables, revised and re-submitted to an IEEE journal
Summary
DeepSeek-R1模型在情感分析方面表现出卓越性能,与OpenAI的GPT-4o系列模型相比,其在少量样本学习方面展现出更高的效率和准确性。DeepSeek-R1模型具有优秀的可解释性,并且其架构特定的蒸馏效果在不同模型中表现突出。
Key Takeaways
- DeepSeek-R1模型在情感分析方面进行了全面的评估,与GPT-4o系列模型对比,展现了更高的效率和准确性。
- DeepSeek-R1在少量样本学习方面表现出卓越性能,达到了91.39%的F1分数(五类情感分析)和99.31%的准确率(二元任务)。
- 与GPT-4o相比,DeepSeek-R1在少数镜头效率上实现了八倍的提升。
- DeepSeek-R1模型的架构特定蒸馏效果突出,其中基于32B Qwen2.5的模型在性能上超过了基于70B Llama的模型。
- 虽然DeepSeek-R1的推理过程可能会影响吞吐量,但其透明的逐步跟踪为其提供了卓越的可解释性。
- DeepSeek-R1是一个强大的、可解释的开源替代方案。
点此查看论文截图

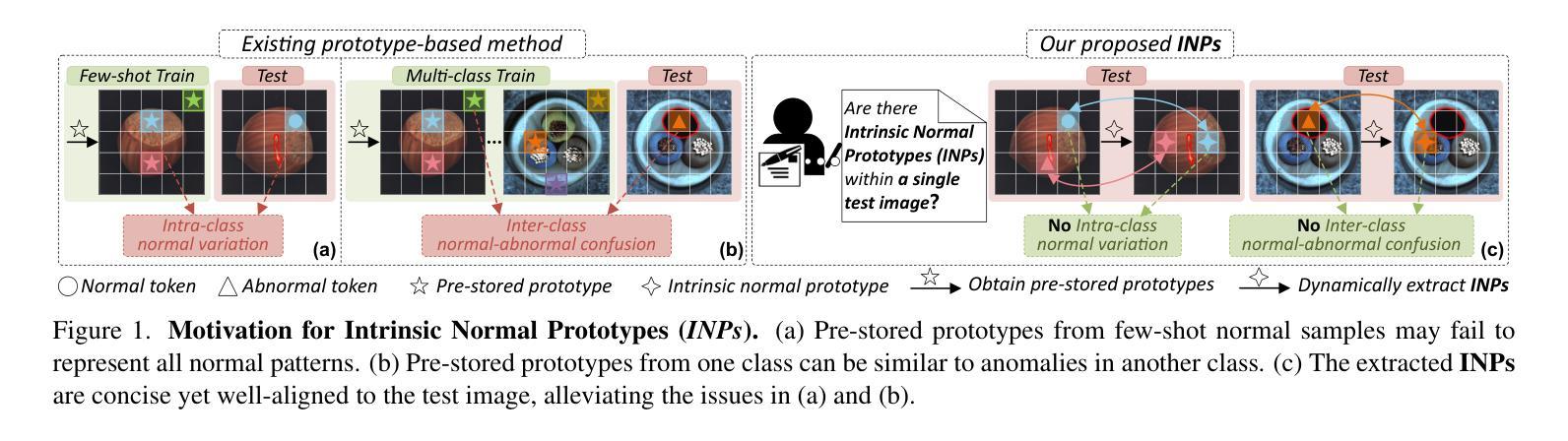
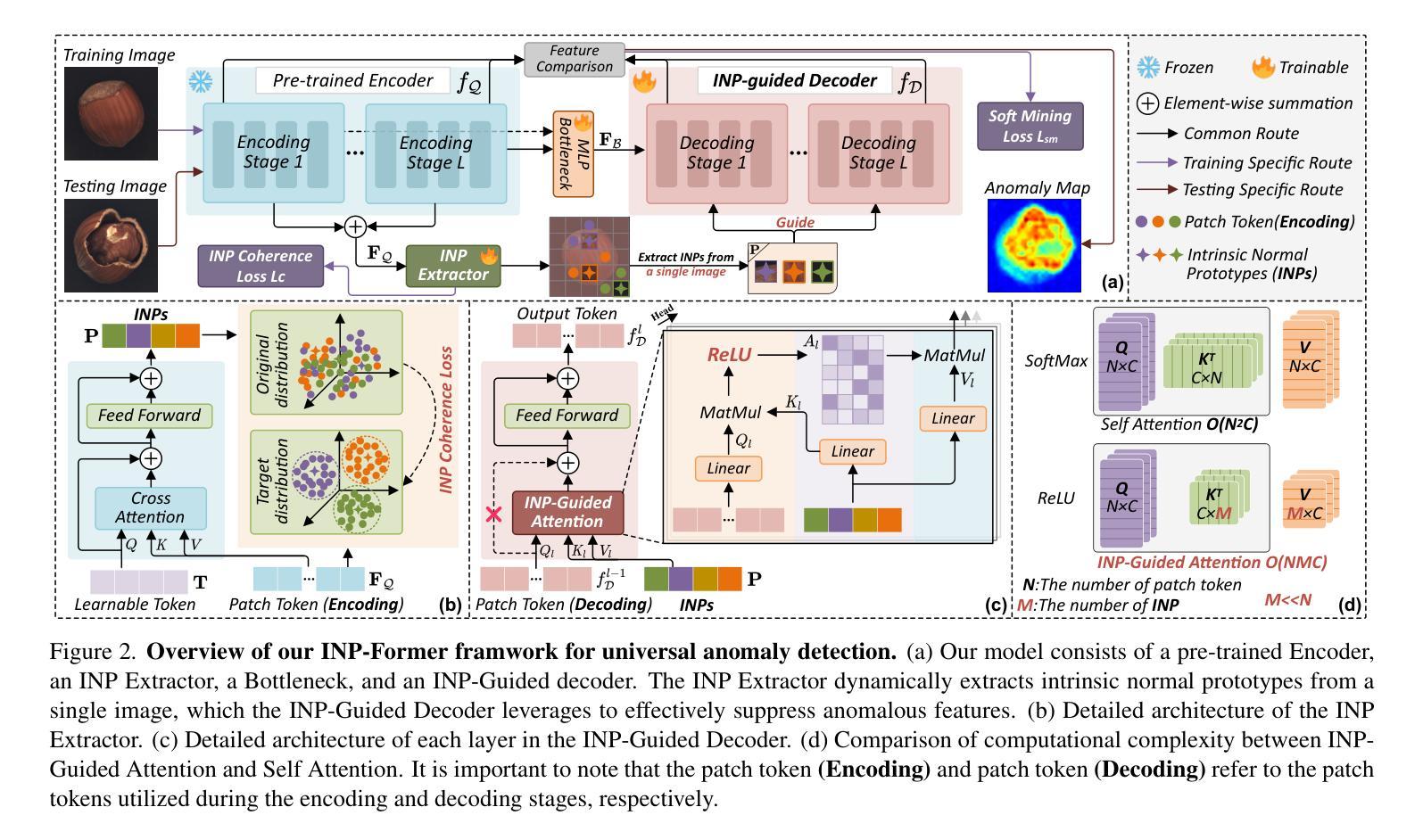
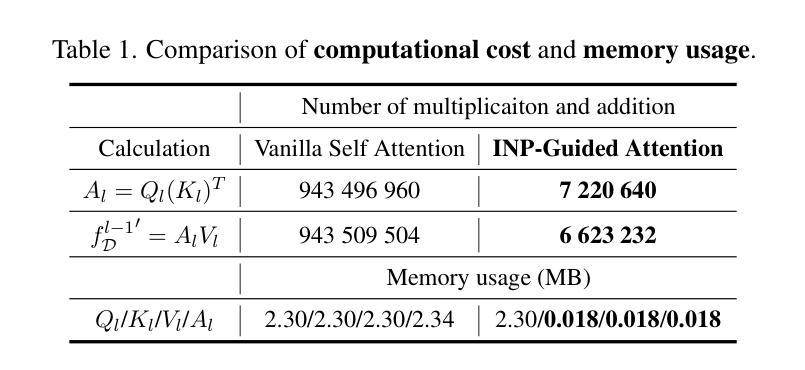
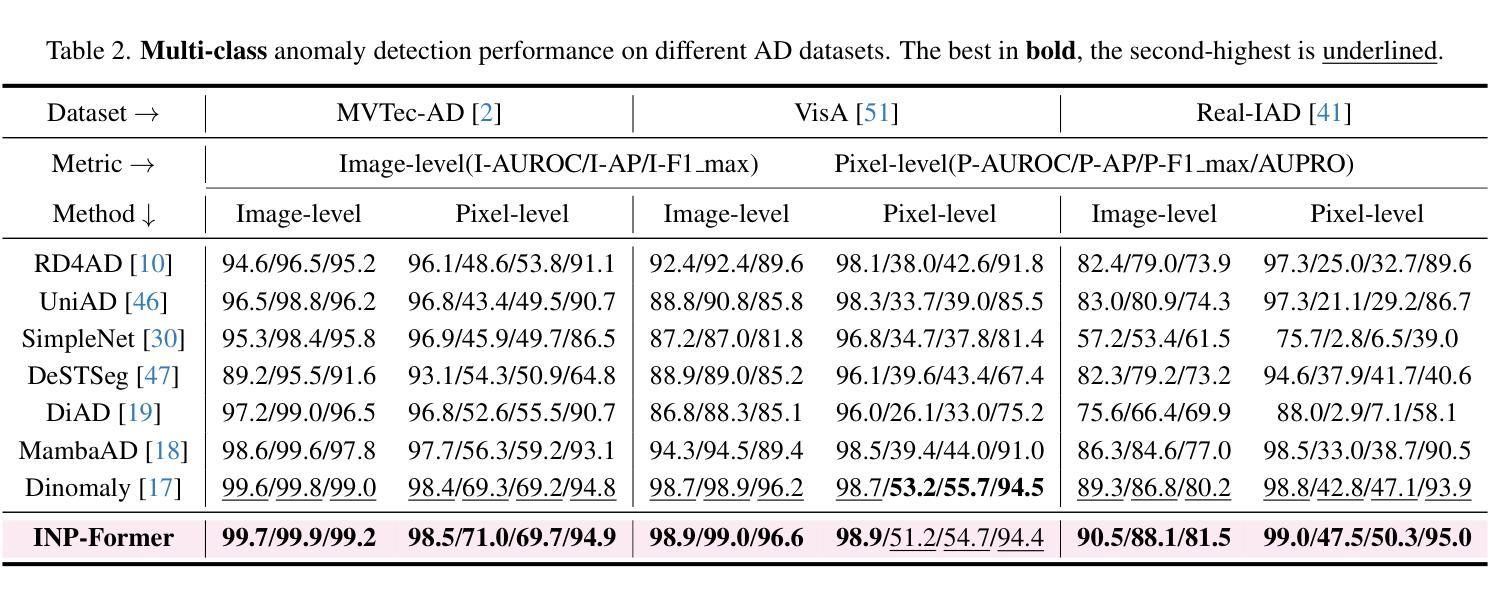
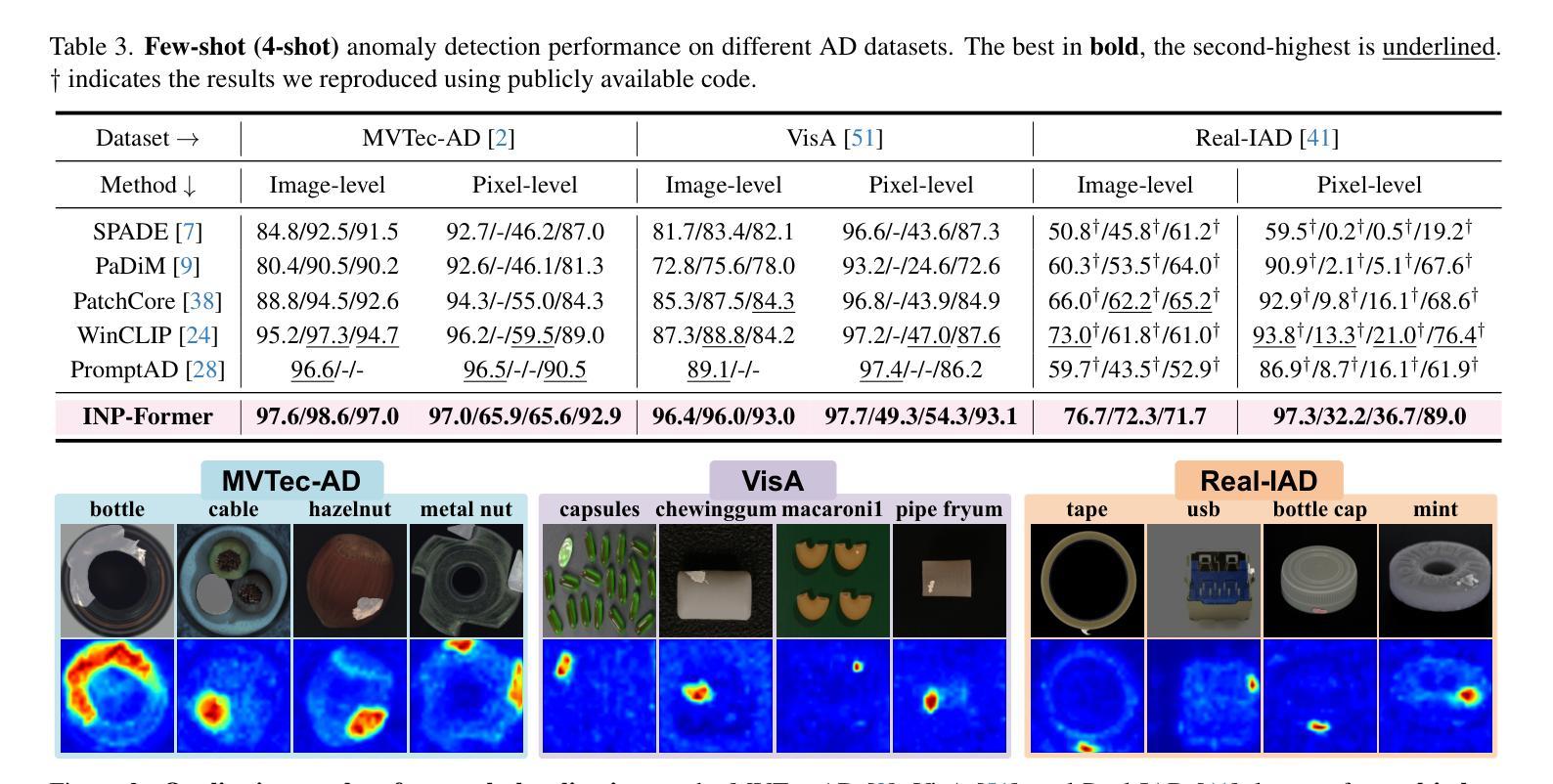
Exploring Intrinsic Normal Prototypes within a Single Image for Universal Anomaly Detection
Authors:Wei Luo, Yunkang Cao, Haiming Yao, Xiaotian Zhang, Jianan Lou, Yuqi Cheng, Weiming Shen, Wenyong Yu
Anomaly detection (AD) is essential for industrial inspection, yet existing methods typically rely on ``comparing’’ test images to normal references from a training set. However, variations in appearance and positioning often complicate the alignment of these references with the test image, limiting detection accuracy. We observe that most anomalies manifest as local variations, meaning that even within anomalous images, valuable normal information remains. We argue that this information is useful and may be more aligned with the anomalies since both the anomalies and the normal information originate from the same image. Therefore, rather than relying on external normality from the training set, we propose INP-Former, a novel method that extracts Intrinsic Normal Prototypes (INPs) directly from the test image. Specifically, we introduce the INP Extractor, which linearly combines normal tokens to represent INPs. We further propose an INP Coherence Loss to ensure INPs can faithfully represent normality for the testing image. These INPs then guide the INP-Guided Decoder to reconstruct only normal tokens, with reconstruction errors serving as anomaly scores. Additionally, we propose a Soft Mining Loss to prioritize hard-to-optimize samples during training. INP-Former achieves state-of-the-art performance in single-class, multi-class, and few-shot AD tasks across MVTec-AD, VisA, and Real-IAD, positioning it as a versatile and universal solution for AD. Remarkably, INP-Former also demonstrates some zero-shot AD capability. Code is available at:https://github.com/luow23/INP-Former.
异常检测(AD)在工业检测中至关重要,但现有方法通常依赖于将测试图像与训练集中的正常参考图像进行“比较”。然而,外观和位置的变化经常使这些参考图像与测试图像的对齐变得复杂,从而限制了检测精度。我们观察到,大多数异常表现为局部变化,这意味着即使在异常图像内部,仍然有宝贵的正常信息。我们认为这些信息是有用的,并且可能与异常更对齐,因为异常和正常信息都来自同一图像。因此,我们提出了一种新方法INP-Former,它直接从测试图像中提取内在正常原型(INPs)。具体来说,我们引入了INP提取器,它线性组合正常令牌来表示INPs。我们还提出了一种INP一致性损失,以确保INPs能够忠实地代表测试图像的正常性。这些INPs然后引导INP引导解码器仅重建正常令牌,重建误差作为异常分数。此外,我们还提出了一种软挖掘损失,以在训练过程中优先处理难以优化的样本。INP-Former在MVTec-AD、VisA和Real-IAD上的单类、多类和少样本AD任务上实现了最先进的性能,使其成为AD的通用解决方案。值得注意的是,INP-Former还表现出一些零样本AD能力。代码可访问于:https://github.com/luow23/INP-Former。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR2025
Summary
本文提出一种名为INP-Former的新型异常检测方法,它直接从测试图像中提取内在正常原型(INPs)。该方法通过引入INP提取器和INP引导解码器,利用正常令牌的重构误差作为异常分数,实现无需依赖外部正常参考的异常检测。此外,还引入了INP一致性损失和软挖掘损失,以提高检测性能和训练效率。该方法在MVTec-AD、VisA和Real-IAD等多个数据集上的单类、多类和少样本异常检测任务中表现出优异性能,并具有零样本异常检测能力。
Key Takeaways
- 传统异常检测方法通常依赖于与训练集中的正常参考图像进行比较,但这种方法受到外观和位置变化的影响,限制了检测精度。
- 大多数异常表现为局部变化,测试图像中的异常区域内仍包含有价值的正常信息。
- INP-Former方法直接从测试图像中提取内在正常原型(INPs),无需依赖外部正常参考。
- 通过引入INP提取器和INP引导解码器,利用正常令牌的重构误差作为异常分数进行异常检测。
- INP一致性损失确保INPs能忠实代表测试图像的正常性。
- 软挖掘损失在训练过程中优先处理难以优化的样本。
点此查看论文截图

Mamba-FSCIL: Dynamic Adaptation with Selective State Space Model for Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning
Authors:Xiaojie Li, Yibo Yang, Jianlong Wu, Yue Yu, Ming-Hsuan Yang, Liqiang Nie, Min Zhang
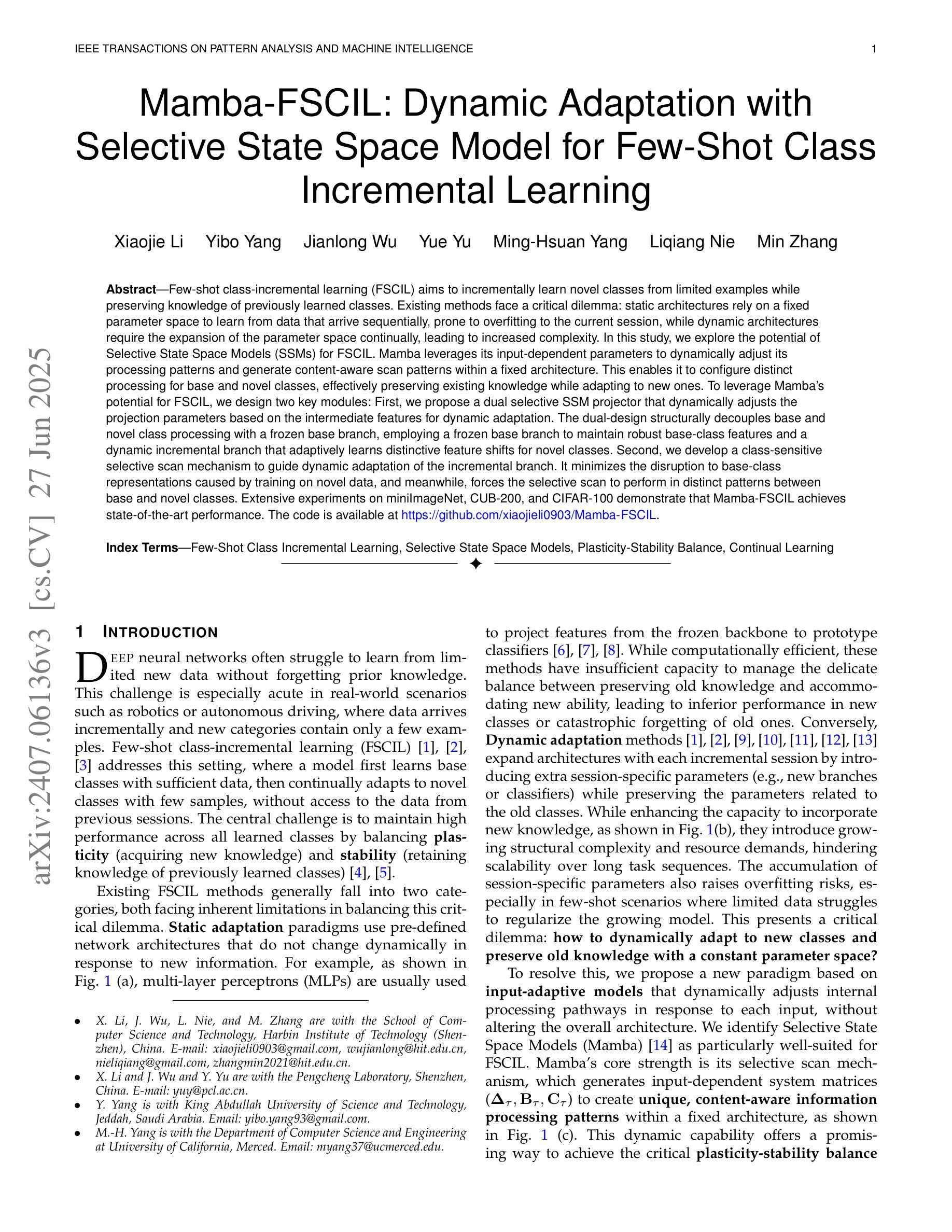
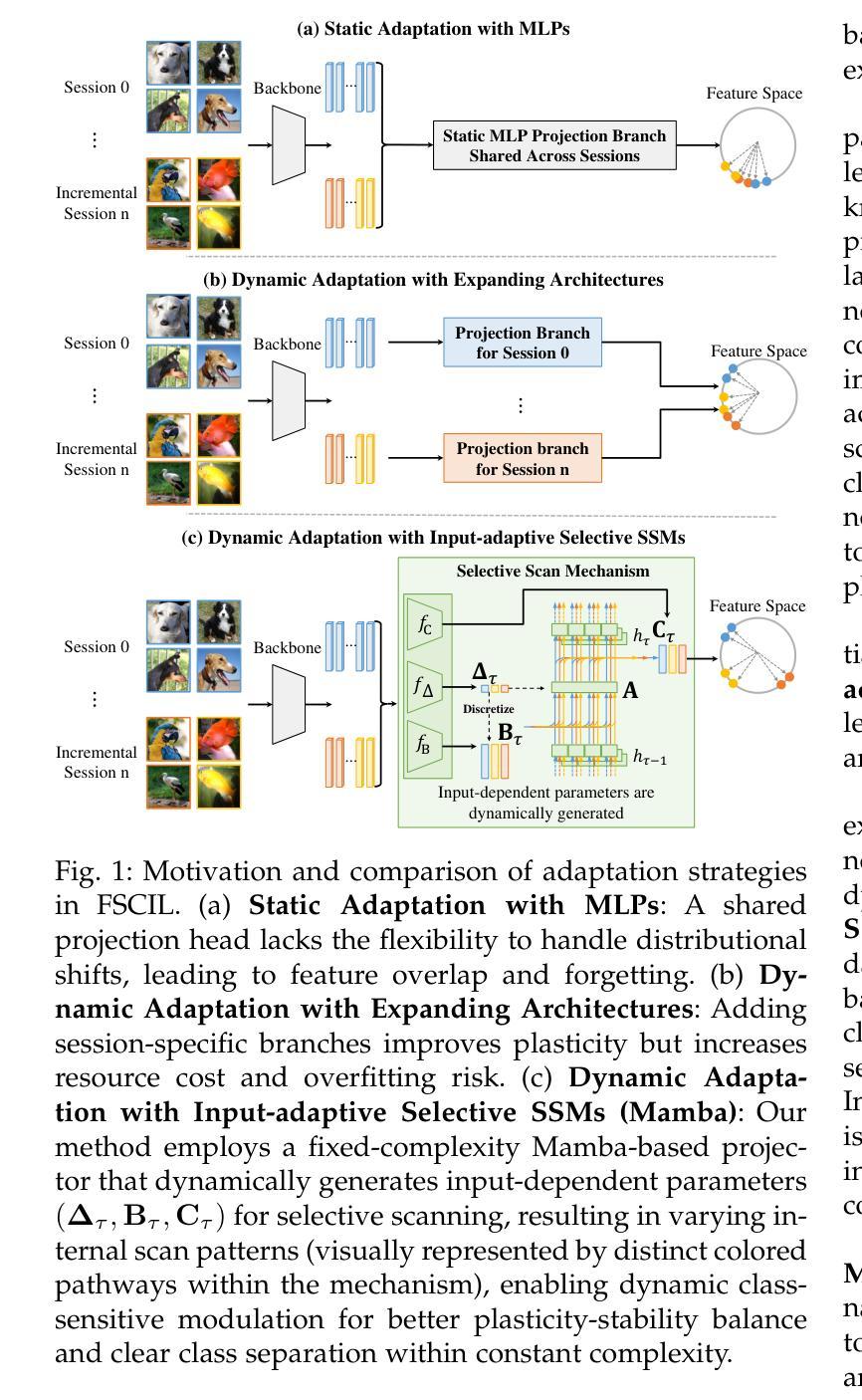
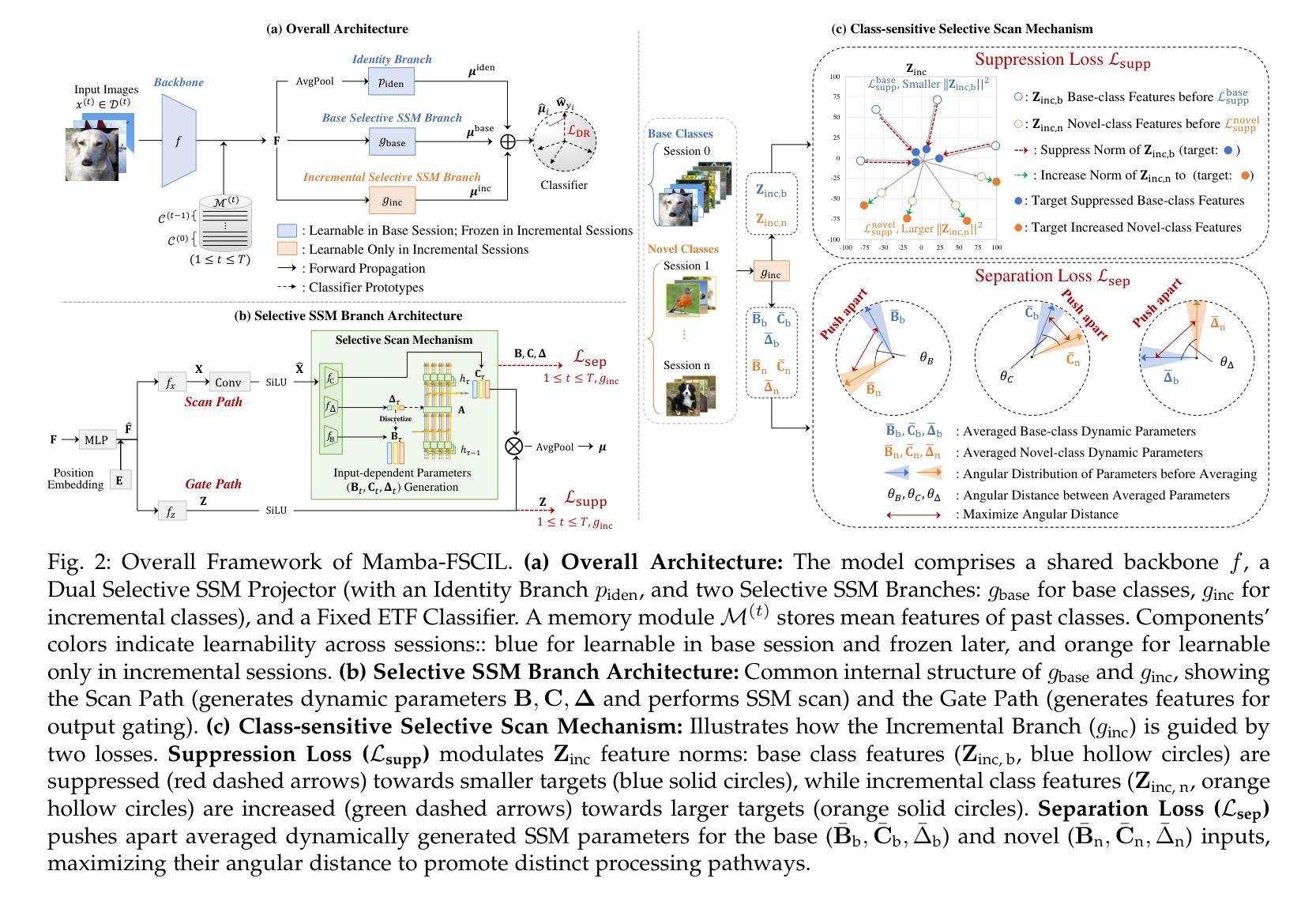
Few-shot class-incremental learning (FSCIL) aims to incrementally learn novel classes from limited examples while preserving knowledge of previously learned classes. Existing methods face a critical dilemma: static architectures rely on a fixed parameter space to learn from data that arrive sequentially, prone to overfitting to the current session, while dynamic architectures require the expansion of the parameter space continually, leading to increased complexity. In this study, we explore the potential of Selective State Space Models (SSMs) for FSCIL. Mamba leverages its input-dependent parameters to dynamically adjust its processing patterns and generate content-aware scan patterns within a fixed architecture. This enables it to configure distinct processing for base and novel classes, effectively preserving existing knowledge while adapting to new ones. To leverage Mamba’s potential for FSCIL, we design two key modules: First, we propose a dual selective SSM projector that dynamically adjusts the projection parameters based on the intermediate features for dynamic adaptation. The dual-design structurally decouples base and novel class processing with a frozen base branch, employing a frozen base branch to maintain robust base-class features and a dynamic incremental branch that adaptively learns distinctive feature shifts for novel classes. Second, we develop a class-sensitive selective scan mechanism to guide dynamic adaptation of the incremental branch. It minimizes the disruption to base-class representations caused by training on novel data, and meanwhile, forces the selective scan to perform in distinct patterns between base and novel classes. Extensive experiments on miniImageNet, CUB-200, and CIFAR-100 demonstrate that Mamba-FSCIL achieves state-of-the-art performance. The code is available at https://github.com/xiaojieli0903/Mamba-FSCIL.
少量类别增量学习(FSCIL)旨在从有限的样本中逐步学习新的类别,同时保留对先前学习类别的知识。现有方法面临一个关键困境:静态架构依赖于固定的参数空间来学习按顺序到达的数据,容易对当前会话出现过拟合,而动态架构则需要不断地扩展参数空间,导致复杂性增加。在这项研究中,我们探索了选择性状态空间模型(SSMs)在FSCIL中的潜力。Mamba利用其输入相关的参数来动态调整其处理模式,并在固定架构内生成内容感知的扫描模式。这使其能够为基本类别和新类别配置不同的处理过程,有效地保留现有知识并适应新类别。为了利用Mamba在FSCIL中的潜力,我们设计了两个关键模块:首先,我们提出了一个双选择性SSM投影仪,它根据中间特征动态调整投影参数,以实现动态适应。该双设计在结构上将基本类别和新类别的处理过程解耦,采用冻结的基本分支来保持稳健的基本类别特征,以及一个动态增量分支,该分支自适应地学习新类别的特征变化。其次,我们开发了一种类别敏感的选择性扫描机制,以指导增量分支的动态适应。它尽量减少对基础类别表示进行新数据训练时的干扰,同时迫使选择性扫描在基础类别和新类别之间以不同的模式进行。在miniImageNet、CUB-200和CIFAR-100上的大量实验表明,Mamba-FSCIL达到了最先进的性能。代码可在https://github.com/xiaojieli0903/Mamba-FSCIL获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code: https://github.com/xiaojieli0903/Mamba-FSCIL
Summary
本文探讨了Few-Shot类增量学习(FSCIL)领域的一个新问题。现有方法面临静态架构和动态架构之间的两难选择。本研究探索了选择性状态空间模型(SSMs)在FSCIL中的潜力。Mamba在其固定架构内利用输入相关参数动态调整处理模式,生成内容感知扫描模式,有效保留现有知识并适应新类别。为实现Mamba在FSCIL中的潜力,设计了两个关键模块:双选择性SSM投影仪和类敏感选择性扫描机制。这两个模块使Mamba能够在静态架构内实现动态适应,从而在有限的样本中实现类的增量学习,并达到先进性能。
Key Takeaways
- Few-Shot类增量学习(FSCIL)的目标是实现在有限的示例下对新类别的增量学习,同时保留对先前学习类别的知识。
- 现有方法面临静态和动态架构之间的权衡,前者易过拟合当前数据,后者参数空间持续扩展导致复杂性增加。
- Mamba利用选择性状态空间模型(SSMs)在固定架构内实现动态处理模式调整,生成内容感知扫描模式。
- Mamba通过双选择性SSM投影仪实现基类和新颖类的处理解耦,通过冻结基分支来保持稳健的基类特征,并通过动态增量分支自适应学习新颖类的特征变化。
- 类敏感选择性扫描机制引导增量分支的动态适应,最小化对基类表示的新数据训练的干扰,并强制选择性扫描在基类和新颖类之间执行不同的模式。
- Mamba-FSCIL在miniImageNet、CUB-200和CIFAR-100上的实验表明其达到了最先进的性能。
点此查看论文截图
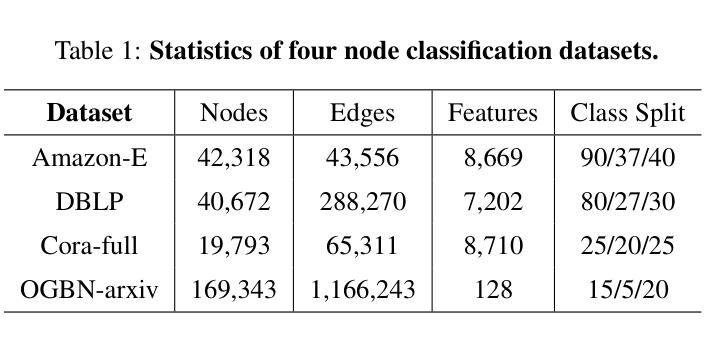
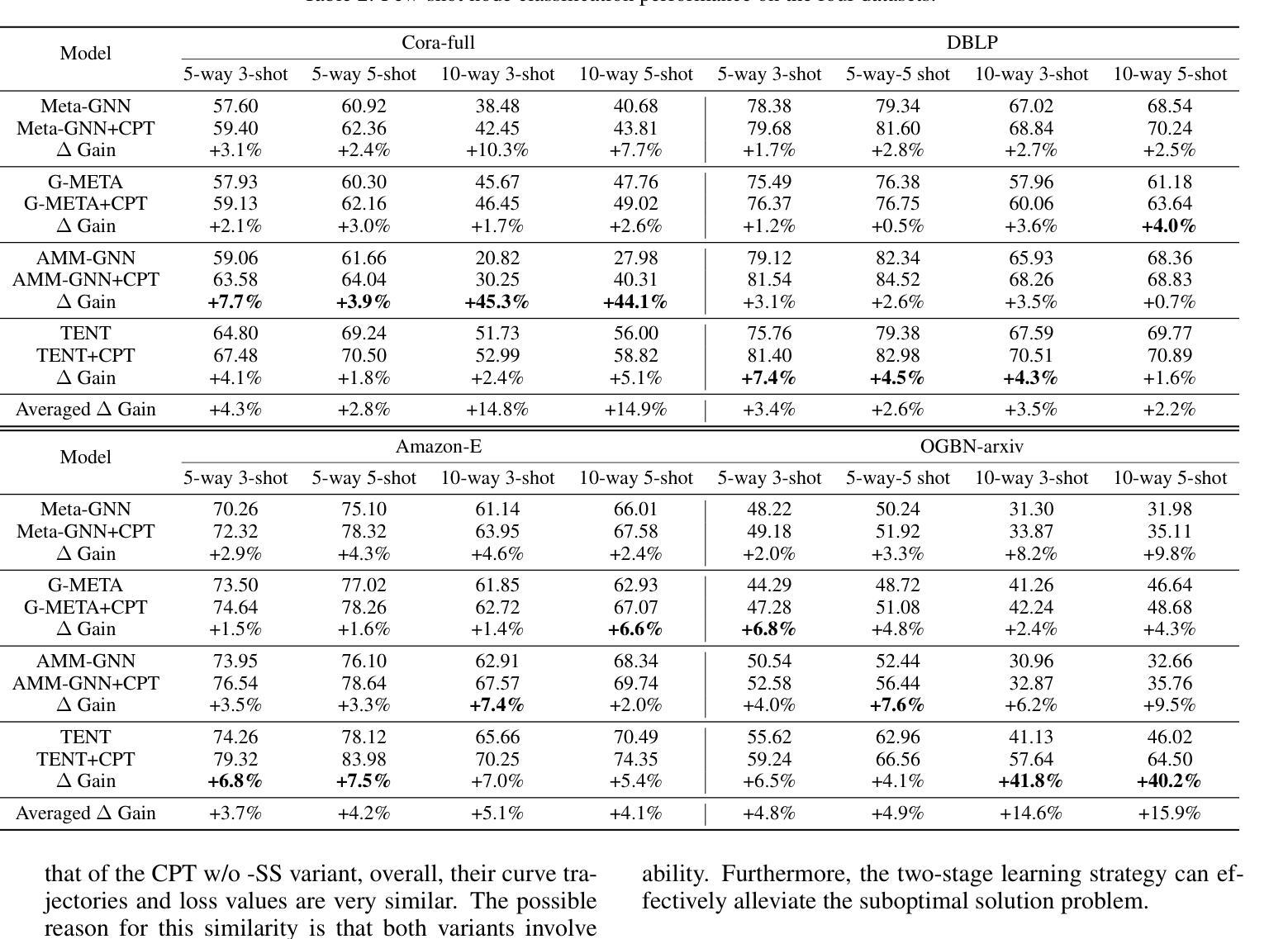
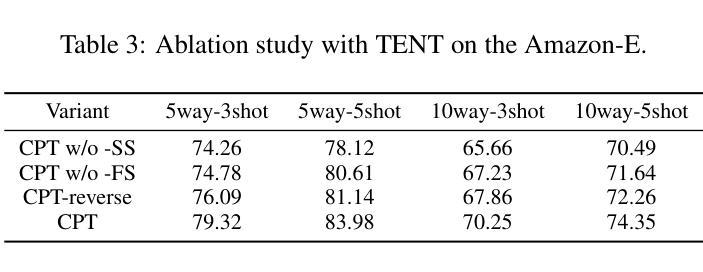
CPT: Competence-progressive Training Strategy for Few-shot Node Classification
Authors:Qilong Yan, Yufeng Zhang, Jinghao Zhang, Jingpu Duan, Jian Yin
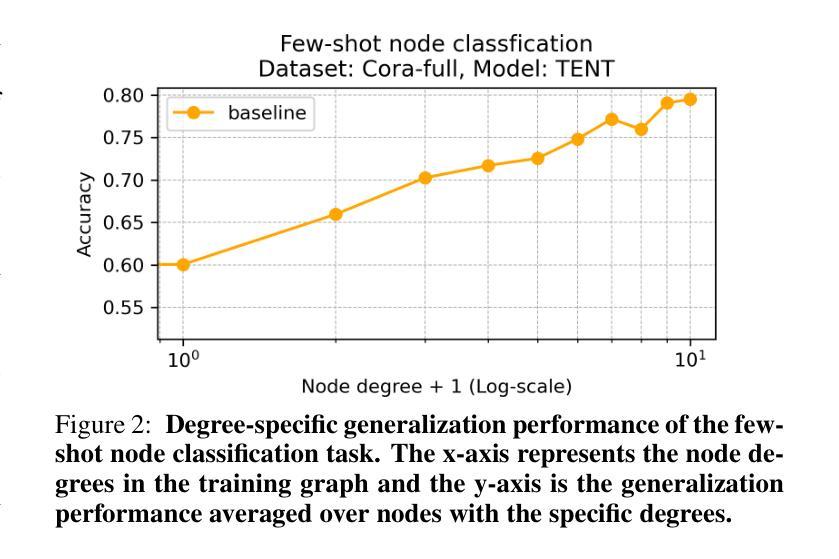
Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have made significant advancements in node classification, but their success relies on sufficient labeled nodes per class in the training data. Real-world graph data often exhibits a long-tail distribution with sparse labels, emphasizing the importance of GNNs’ ability in few-shot node classification, which entails categorizing nodes with limited data. Traditional episodic meta-learning approaches have shown promise in this domain, but they face an inherent limitation: it might lead the model to converge to suboptimal solutions because of random and uniform task assignment, ignoring task difficulty levels. This could lead the meta-learner to face complex tasks too soon, hindering proper learning. Ideally, the meta-learner should start with simple concepts and advance to more complex ones, like human learning. So, we introduce CPT, a novel two-stage curriculum learning method that aligns task difficulty with the meta-learner’s progressive competence, enhancing overall performance. Specifically, in CPT’s initial stage, the focus is on simpler tasks, fostering foundational skills for engaging with complex tasks later. Importantly, the second stage dynamically adjusts task difficulty based on the meta-learner’s growing competence, aiming for optimal knowledge acquisition. Extensive experiments on popular node classification datasets demonstrate significant improvements of our strategy over existing methods.
图神经网络(GNNs)在节点分类方面取得了重大进展,但其成功依赖于训练数据中每类的足够标签节点。现实世界的图数据经常表现出长尾分布和稀疏标签,这强调了在有限数据下进行节点分类的GNN能力的重要性。传统的周期式元学习方法在这个领域显示出潜力,但它们面临一个内在局限:由于随机和统一的任务分配,可能会导致模型收敛到次优解,忽略任务难度级别。这可能导致元学习者过早地面对复杂任务,阻碍适当的学习。理想情况下,元学习者应该从简单的概念开始,逐步学习更复杂的概念,就像人类学习一样。因此,我们引入了CPT,这是一种新型的两阶段课程学习方法,它根据元学习者的进步能力来匹配任务难度,从而提高整体性能。具体来说,在CPT的初始阶段,重点是更简单的任务,为日后处理复杂任务培养基础技能。重要的是,第二阶段根据元学习者不断增长的能力动态调整任务难度,以实现最佳知识获取。在流行的节点分类数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的策略大大优于现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF APWEB-WAIM 2025
Summary
GNN在节点分类上取得了显著进展,但在训练数据中对每个类别标注节点的数量有较高要求。现实世界的图数据常呈现长尾分布,标签稀疏,强调了在有限数据下GNN进行少样本节点分类的重要性。传统的时间经历元学习方法在此领域显示出潜力,但存在固有局限:随机和均匀的任务分配可能导致模型收敛到次优解,忽视任务难度级别。因此,我们引入CPT,一种新型两阶段课程学习方法,根据元学习者的进步能力调整任务难度,提高总体性能。初始阶段专注于简单任务,培养基础技能;第二阶段根据元学习者的成长能力动态调整任务难度,实现最佳知识获取。在流行的节点分类数据集上进行的大量实验表明,我们的策略优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- GNN在节点分类上表现优异,但需要充足标注节点数据。
- 现实世界的图数据常呈现标签稀疏和长尾分布的特点。
- 传统元学习方法在任务分配上可能存在缺陷,忽视任务难度。
- 引入CPT,一种结合课程学习和元学习的两阶段方法。
- 初始阶段专注于简单任务,培养基础技能。
- 第二阶段根据元学习者的成长能力动态调整任务难度。
点此查看论文截图

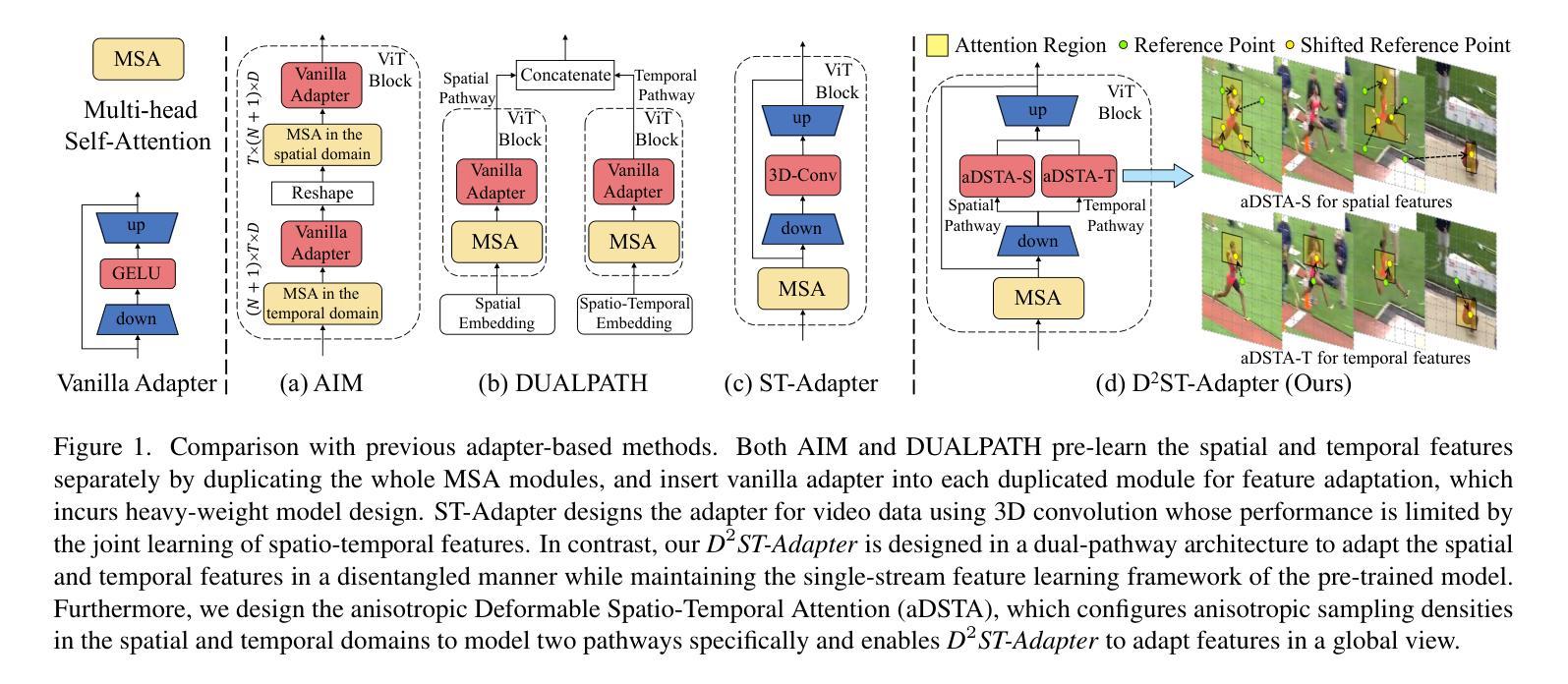
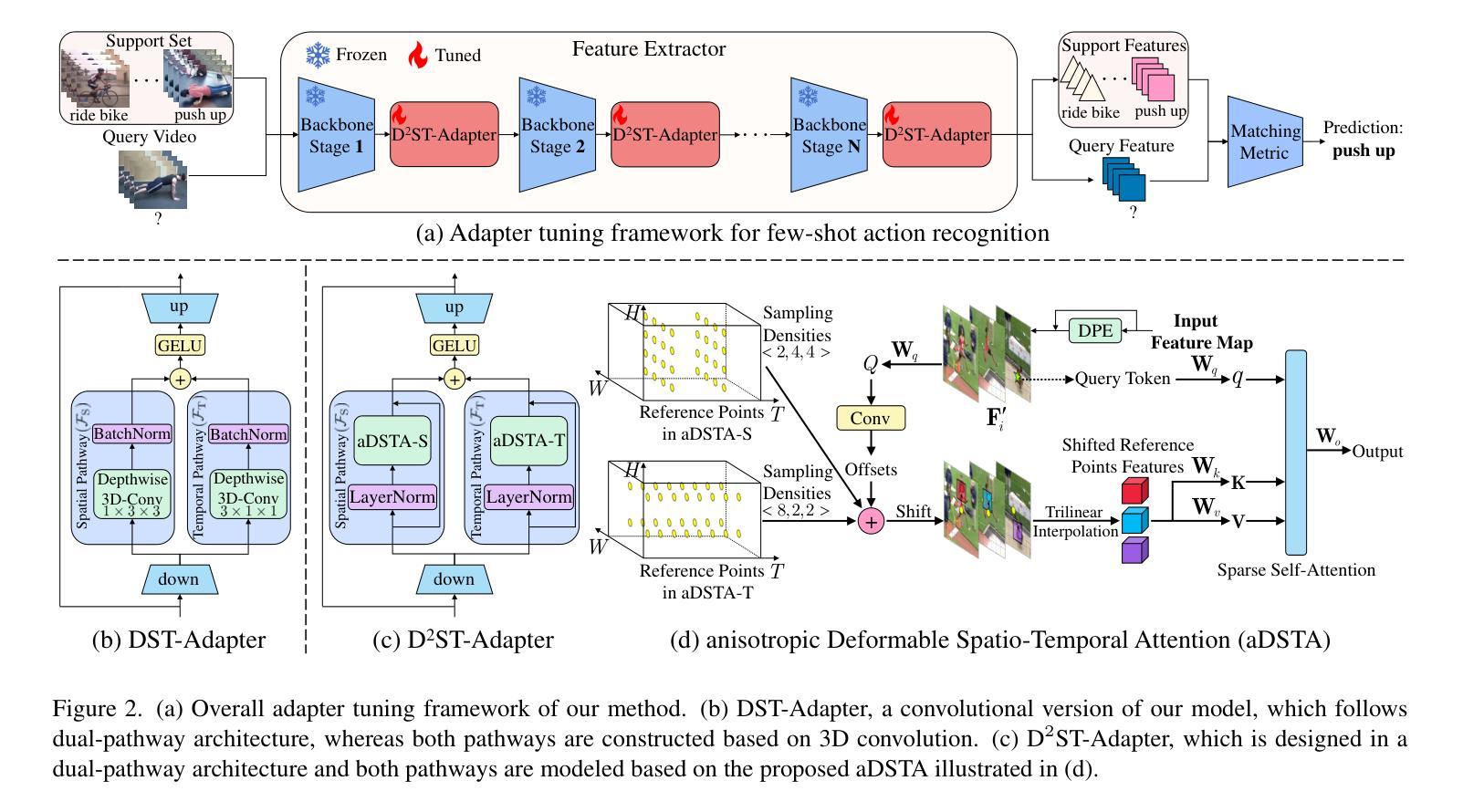
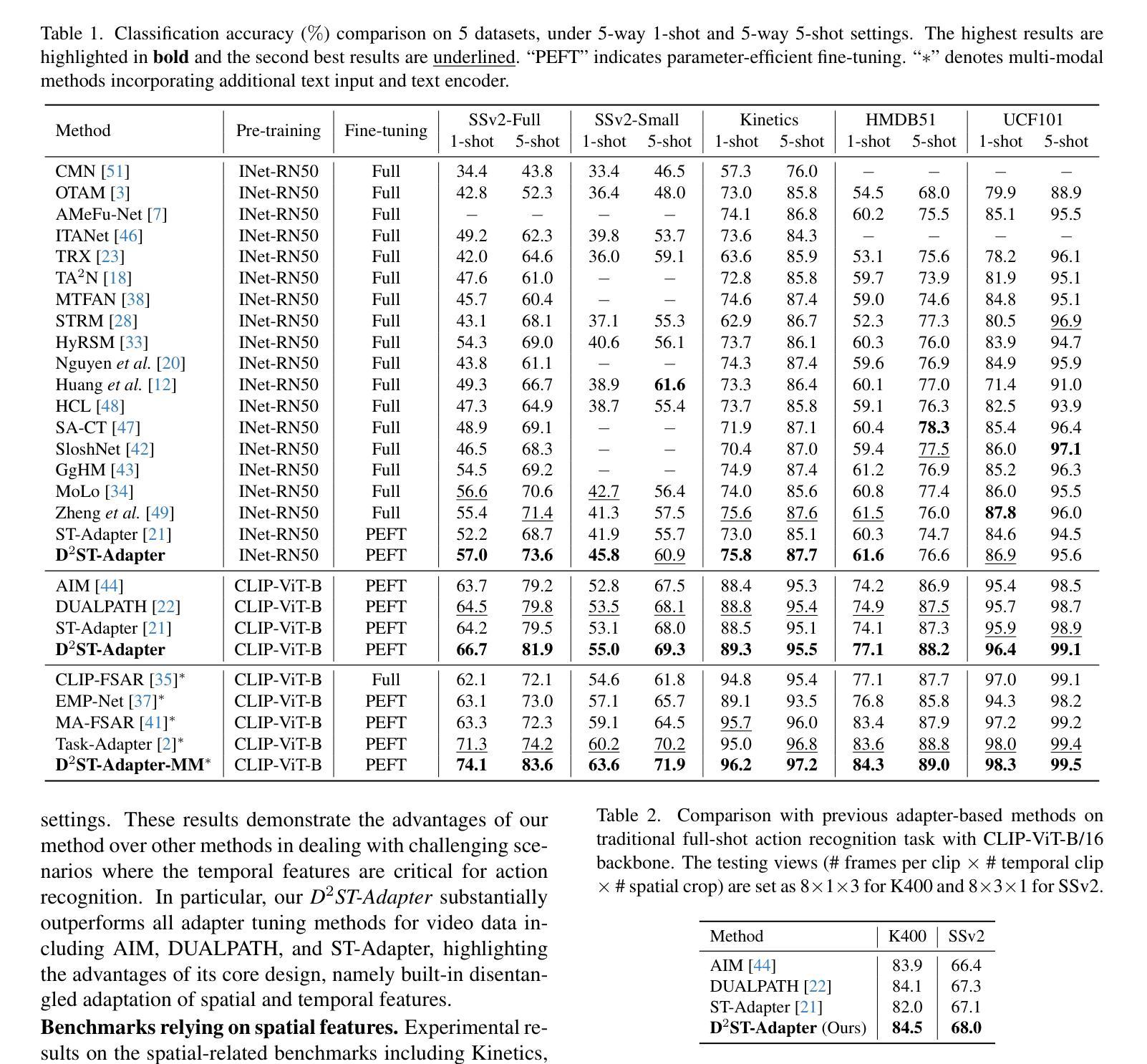
D$^2$ST-Adapter: Disentangled-and-Deformable Spatio-Temporal Adapter for Few-shot Action Recognition
Authors:Wenjie Pei, Qizhong Tan, Guangming Lu, Jiandong Tian, Jun Yu
Adapting pre-trained image models to video modality has proven to be an effective strategy for robust few-shot action recognition. In this work, we explore the potential of adapter tuning in image-to-video model adaptation and propose a novel video adapter tuning framework, called Disentangled-and-Deformable Spatio-Temporal Adapter (D$^2$ST-Adapter). It features a lightweight design, low adaptation overhead and powerful spatio-temporal feature adaptation capabilities. D$^2$ST-Adapter is structured with an internal dual-pathway architecture that enables built-in disentangled encoding of spatial and temporal features within the adapter, seamlessly integrating into the single-stream feature learning framework of pre-trained image models. In particular, we develop an efficient yet effective implementation of the D$^2$ST-Adapter, incorporating the specially devised anisotropic Deformable Spatio-Temporal Attention as its pivotal operation. This mechanism can be individually tailored for two pathways with anisotropic sampling densities along the spatial and temporal domains in 3D spatio-temporal space, enabling disentangled encoding of spatial and temporal features while maintaining a lightweight design. Extensive experiments by instantiating our method on both pre-trained ResNet and ViT demonstrate the superiority of our method over state-of-the-art methods. Our method is particularly well-suited to challenging scenarios where temporal dynamics are critical for action recognition. Code is available at https://github.com/qizhongtan/D2ST-Adapter.
将预训练图像模型适配到视频模态已经被证明是实现在少数样本上进行稳健动作识别的一个有效策略。在这项工作中,我们探索了适配器调整在图像到视频模型适配中的潜力,并提出了一种名为“解纠缠和可变时空适配器(D^2ST-Adapter)”的新型视频适配器调整框架。它具有轻量级设计、低适配开销和强大的时空特征适配能力。D^2ST-Adapter采用内部双路径架构,能够在适配器内部对空间和时间特征进行内置解纠缠编码,无缝集成到预训练图像模型的单一流特征学习框架中。特别地,我们对D^2ST-Adapter进行了高效而有效的实现,将专门设计的各向异性可变时空注意力作为其关键操作。这种机制可以针对两条路径进行个性化设置,在3D时空空间的时空域上具有各向异性的采样密度,从而在保持轻量级设计的同时实现空间和时间特征的解纠缠编码。在预训练的ResNet和ViT上进行实例化实验的大量实验表明,我们的方法优于最先进的方法。我们的方法特别适用于那些时间动态对动作识别至关重要的具有挑战性的场景。代码可在[https://github.com/qizhongtan/D2ST-Adapter找到。]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV2025
Summary
本文探索了适配器调整在图像到视频模型适应中的潜力,并提出了一种新的视频适配器调整框架D$^2$ST-Adapter。它具有轻量级设计、低适应开销和强大的时空特征适应力。该框架通过内部双路径架构实现空间和时间特征的内在分离编码,无缝集成到预训练图像模型的单流特征学习框架中。特别是,我们开发了一种高效且有效的D$^2$ST-Adapter实现,其中引入了特殊的可变形时空注意力机制作为其关键操作。这种机制可以在两个路径上独立定制,在时空域的采样密度上表现出异向性,从而在保持轻量级设计的同时实现时空特征的分离编码。实验表明,该方法在预训练的ResNet和ViT上都优于现有方法,特别适用于时间动态对动作识别至关重要的挑战场景。
Key Takeaways
- 适配器调整在图像到视频模型适应中的潜力被探索。
- 提出了一种新的视频适配器调整框架D$^2$ST-Adapter,具有轻量级设计和强大的时空特征适应力。
- D$^2$ST-Adapter通过内部双路径架构实现空间和时间特征的分离编码。
- 引入了可变形时空注意力机制作为D$^2$ST-Adapter的关键操作。
- 该机制可以在两个路径上独立定制,表现出异向性采样密度。
- 实验表明,该方法在预训练模型ResNet和ViT上的表现优于现有方法。
- 该方法特别适用于时间动态对动作识别至关重要的挑战场景。
点此查看论文截图