⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-04 更新
Kwai Keye-VL Technical Report
Authors: Kwai Keye Team, Biao Yang, Bin Wen, Changyi Liu, Chenglong Chu, Chengru Song, Chongling Rao, Chuan Yi, Da Li, Dunju Zang, Fan Yang, Guorui Zhou, Hao Peng, Haojie Ding, Jiaming Huang, Jiangxia Cao, Jiankang Chen, Jingyun Hua, Jin Ouyang, Kaibing Chen, Kaiyu Jiang, Kaiyu Tang, Kun Gai, Shengnan Zhang, Siyang Mao, Sui Huang, Tianke Zhang, Tingting Gao, Wei Chen, Wei Yuan, Xiangyu Wu, Xiao Hu, Xingyu Lu, Yang Zhou, Yi-Fan Zhang, Yiping Yang, Yulong Chen, Zhenhua Wu, Zhenyu Li, Zhixin Ling, Ziming Li, Dehua Ma, Di Xu, Haixuan Gao, Hang Li, Jiawei Guo, Jing Wang, Lejian Ren, Muhao Wei, Qianqian Wang, Qigen Hu, Shiyao Wang, Tao Yu, Xinchen Luo, Yan Li, Yiming Liang, Yuhang Hu, Zeyi Lu, Zhuoran Yang, Zixing Zhang
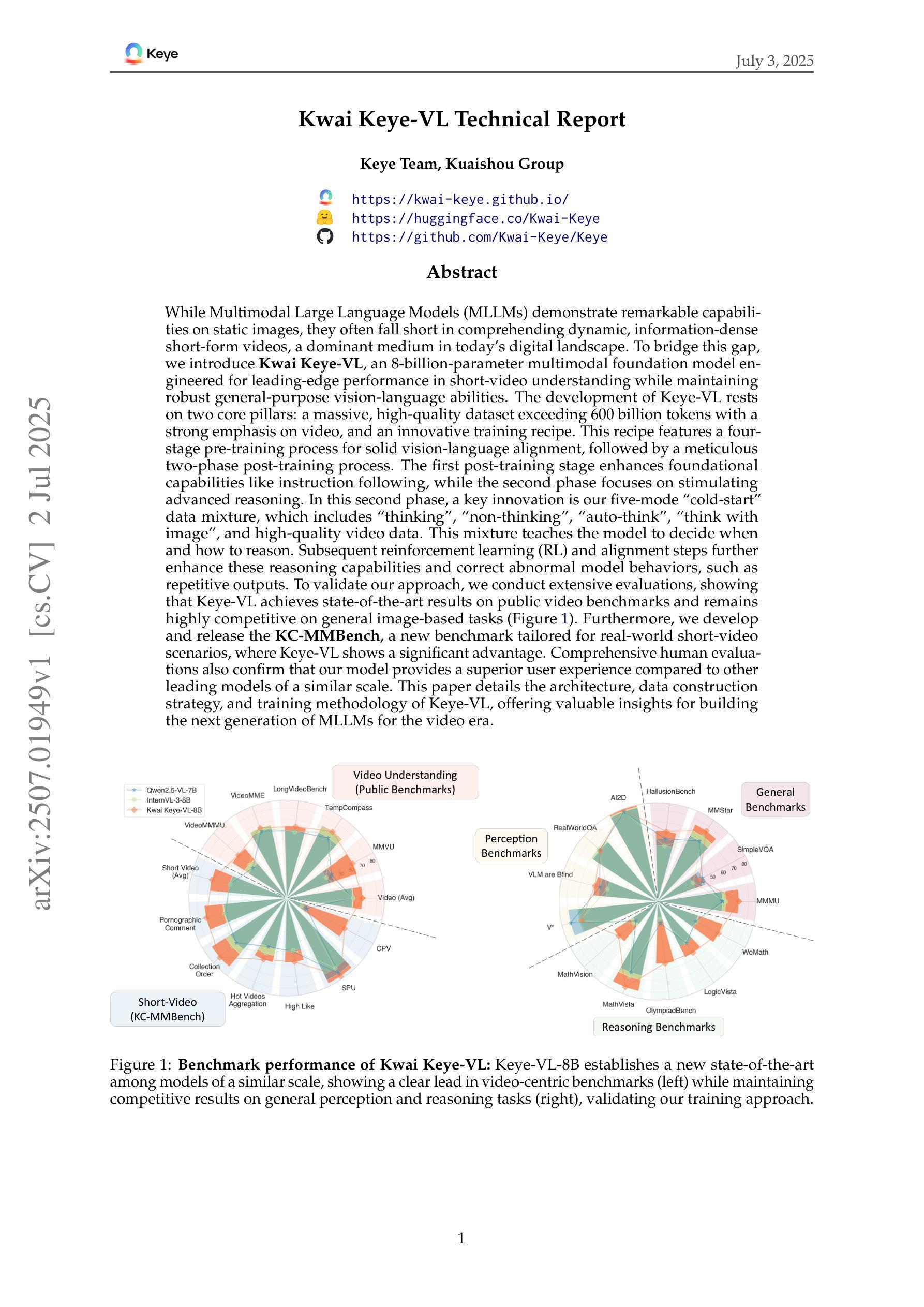
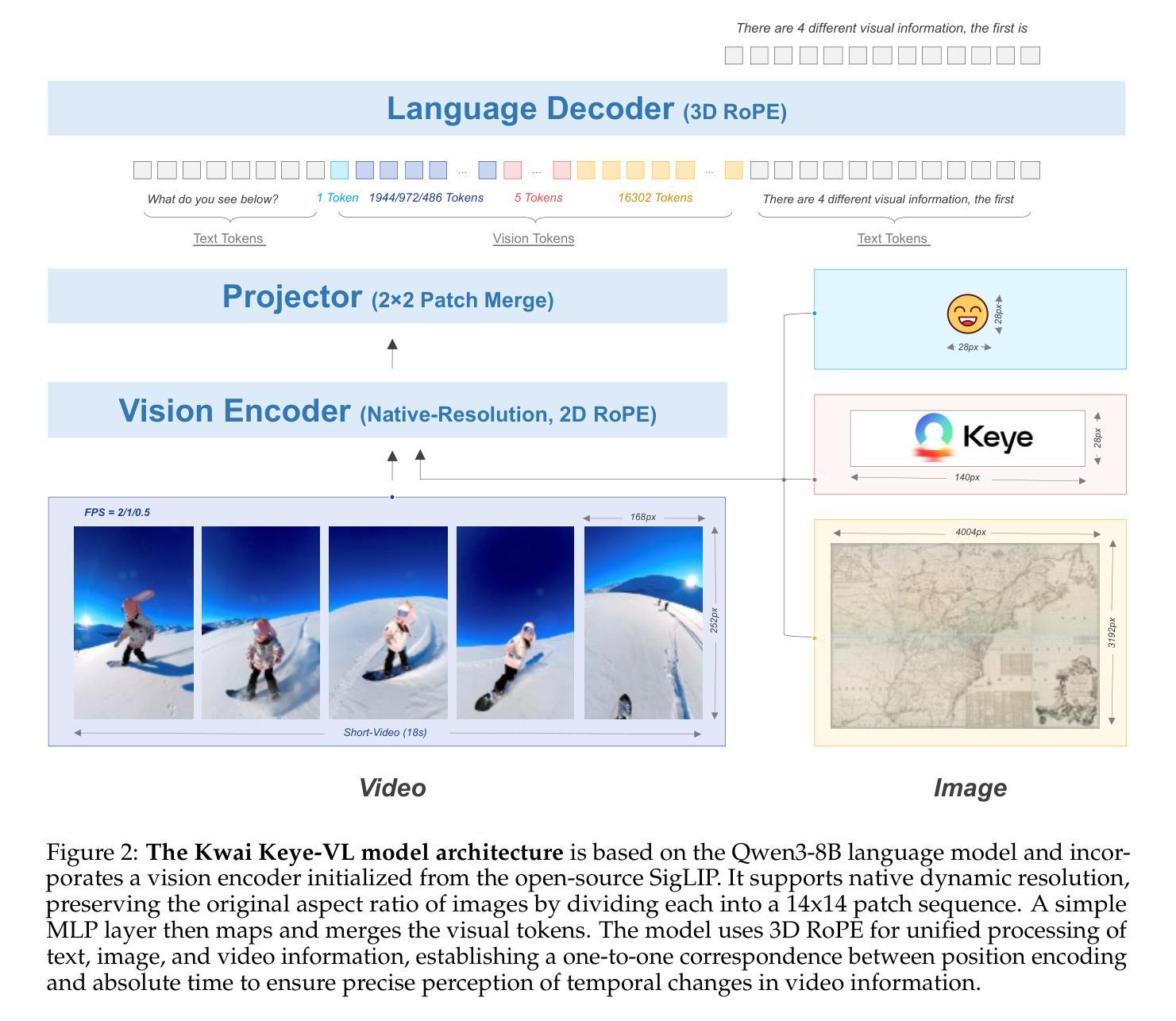
While Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) demonstrate remarkable capabilities on static images, they often fall short in comprehending dynamic, information-dense short-form videos, a dominant medium in today’s digital landscape. To bridge this gap, we introduce \textbf{Kwai Keye-VL}, an 8-billion-parameter multimodal foundation model engineered for leading-edge performance in short-video understanding while maintaining robust general-purpose vision-language abilities. The development of Keye-VL rests on two core pillars: a massive, high-quality dataset exceeding 600 billion tokens with a strong emphasis on video, and an innovative training recipe. This recipe features a four-stage pre-training process for solid vision-language alignment, followed by a meticulous two-phase post-training process. The first post-training stage enhances foundational capabilities like instruction following, while the second phase focuses on stimulating advanced reasoning. In this second phase, a key innovation is our five-mode cold-start'' data mixture, which includes thinking’’, non-thinking'', auto-think’’, ``think with image’’, and high-quality video data. This mixture teaches the model to decide when and how to reason. Subsequent reinforcement learning (RL) and alignment steps further enhance these reasoning capabilities and correct abnormal model behaviors, such as repetitive outputs. To validate our approach, we conduct extensive evaluations, showing that Keye-VL achieves state-of-the-art results on public video benchmarks and remains highly competitive on general image-based tasks (Figure 1). Furthermore, we develop and release the \textbf{KC-MMBench}, a new benchmark tailored for real-world short-video scenarios, where Keye-VL shows a significant advantage.
虽然多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在静态图像上表现出卓越的能力,但它们通常难以理解动态、信息密集的短视频,而短视频却是当今数字时代的主导媒体。为了弥补这一差距,我们推出了Kwai Keye-VL,这是一个面向短视频理解的先进多模态基础模型,拥有8亿参数,同时保持强大的通用视觉语言功能。Keye-VL的发展基于两个核心:一个规模庞大、高质量的数据集,包含超过600亿个标记,并强烈侧重于视频;以及一种创新的训练配方。该配方具有四个阶段的预训练过程,以实现坚实的视觉语言对齐,随后是细致的两阶段后训练过程。第一阶段增强基础能力,如指令遵循能力;第二阶段则专注于刺激高级推理能力。在第二阶段中,我们的关键创新是五模式“冷启动”数据混合,包括“思考”、“非思考”、“自动思考”、“与图像一起思考”以及高质量的视频数据。这种混合教会模型决定何时以及如何推理。随后的强化学习(RL)和对齐步骤进一步增强了这些推理能力,并纠正了异常模型行为,例如重复输出。为了验证我们的方法,我们进行了广泛的评估,结果显示Keye-VL在公共视频基准测试中达到了最新水平,并在基于图像的一般任务中保持高度竞争力(图1)。此外,我们开发并发布了针对现实短视频场景的全新基准测试KC-MMBench,Keye-VL在此基准测试中表现出显著优势。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical Report: https://github.com/Kwai-Keye/Keye
Summary
基于多模态大型语言模型在处理静态图像方面表现出色,但在理解和处理动态、信息密集型的短视频方面存在缺陷。为解决这一问题,我们推出了“Kwai Keye-VL”模型,这是一个针对短视频理解的前沿性能的多模态基础模型,同时保持了强大的通用视觉语言功能。其核心发展基于两个支柱:超过600亿令牌的大规模高质量数据集,重点强调视频内容;以及创新的训练配方,包括预训练、后训练两个阶段。Keye-VL在公共视频基准测试中取得了最新结果,并在通用图像任务中保持高度竞争力。同时推出针对真实短视频场景的全新基准测试KC-MMBench,Keye-VL展现出显著优势。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在短视频理解方面存在不足。
- Kwai Keye-VL模型旨在解决这一缺陷,具有强大的短视频理解能力,同时保持通用视觉语言功能。
- Keye-VL的发展基于大规模高质量数据集和创新的训练配方。
- 训练配方包括预训练、后训练两个阶段,注重视觉语言对齐和高级推理能力的培养。
- Keye-VL在公共视频基准测试中取得最新成果,并在通用图像任务中保持竞争力。
- 推出新的基准测试KC-MMBench,针对真实短视频场景,Keye-VL展现出显著优势。
点此查看论文截图
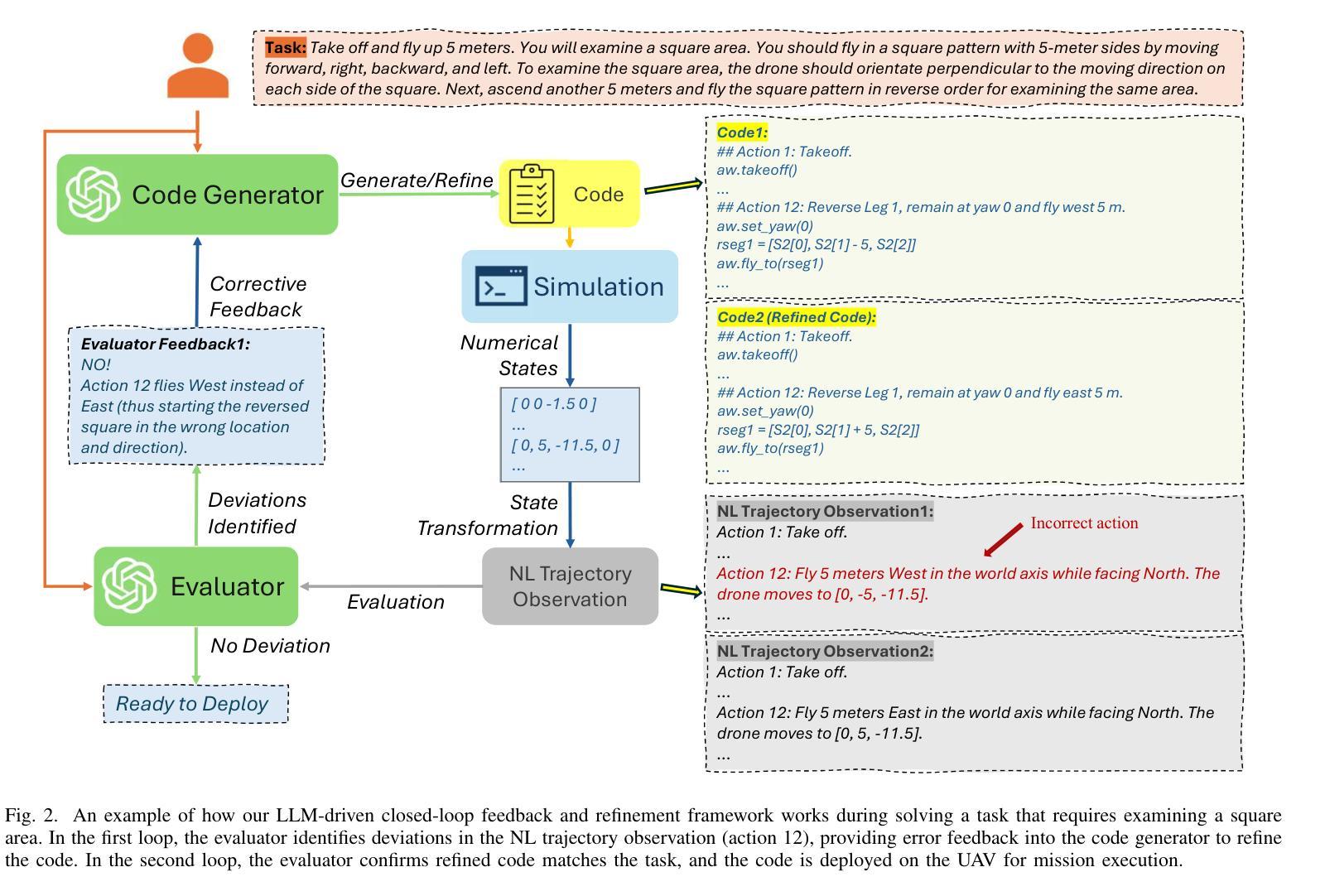
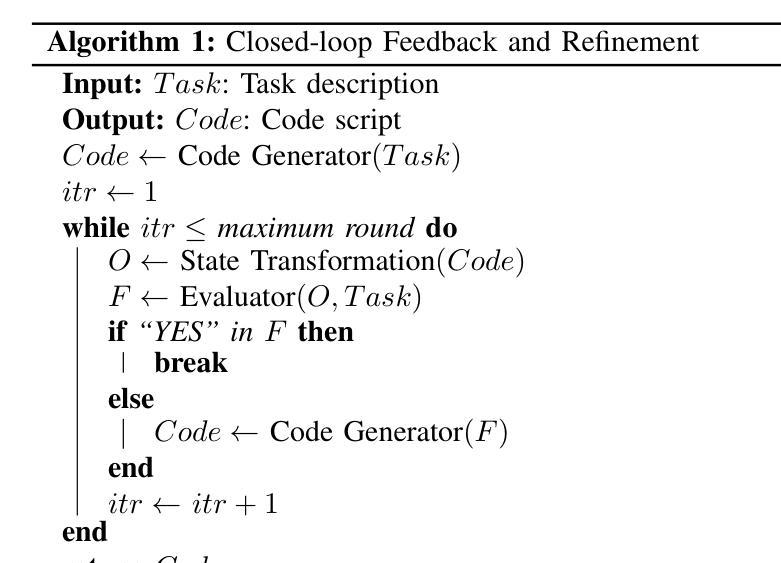
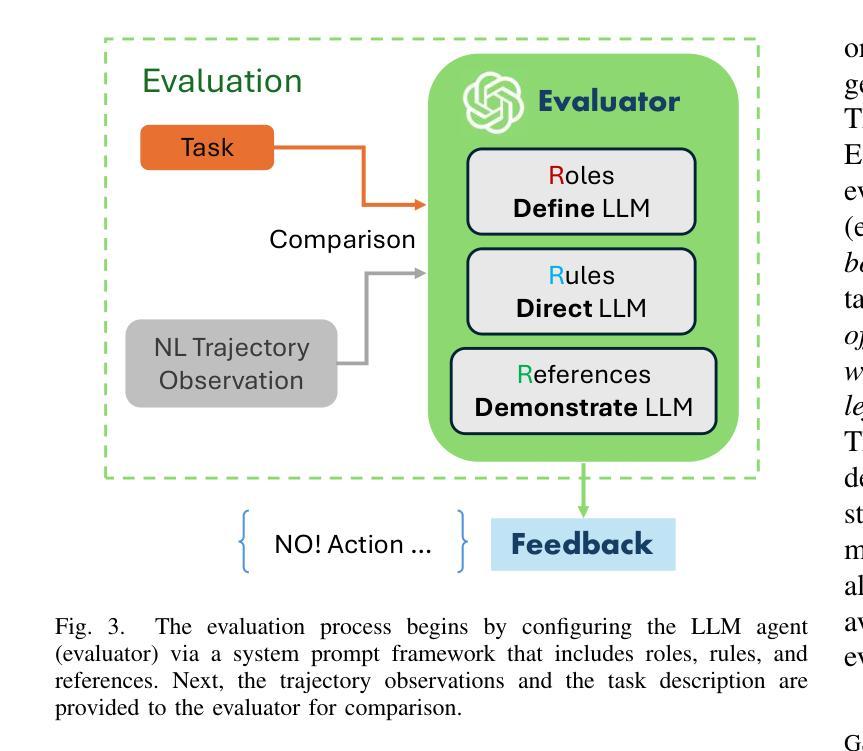
Large Language Model-Driven Closed-Loop UAV Operation with Semantic Observations
Authors:Wenhao Wang, Yanyan Li, Long Jiao, Jiawei Yuan
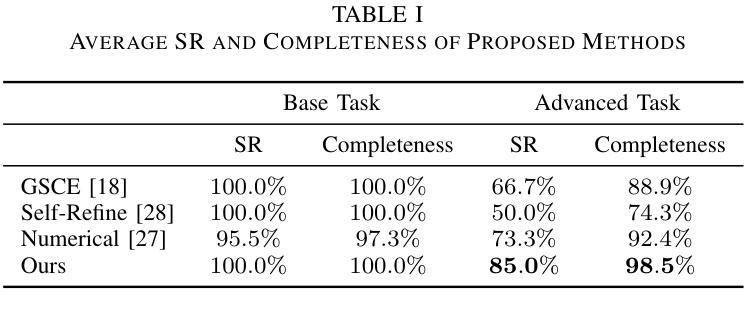
Large Language Models (LLMs) have revolutionized robotic autonomy, including Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs). Recent studies have demonstrated the potential of LLMs for translating human instructions into executable control code for UAV operations. However, LLMs still face challenges from logical reasoning and complex decision-making, leading to concerns about the reliability of LLM-driven UAV operations. In this paper, we propose a LLM-driven closed-loop control framework that enables reliable UAV operations powered by effective feedback and refinement using two LLM modules, i.e., a Code Generator and an Evaluator. Our framework transforms numerical state observations from UAV operations into natural language trajectory descriptions to enhance the evaluator LLM’s understanding of UAV dynamics for precise feedback generation. Our framework also enables a simulation-based refinement process, and hence eliminates the risks to physical UAVs caused by incorrect code execution during the refinement. Extensive experiments on UAV control tasks with different complexities are conducted. The experimental results show that our framework can achieve reliable UAV operations using LLMs, which significantly outperforms baseline approaches in terms of success rate and completeness with the increase of task complexity.
大型语言模型(LLM)已经彻底改变了机器人自主性,包括无人机(UAVs)。最近的研究已经证明了LLM将人类指令翻译成可执行控制代码以支持无人机操作的潜力。然而,LLM在逻辑推理和复杂决策制定方面仍面临挑战,这引发了人们对LLM驱动的无人机操作可靠性的担忧。在本文中,我们提出了一种LLM驱动的闭环控制框架,通过有效的反馈和改进,使用两个LLM模块即代码生成器和评估器,实现了可靠的无人机操作。我们的框架将无人机的数值状态观察转化为自然语言轨迹描述,增强了评估LLM对无人机动力学的理解,以实现精确反馈生成。我们的框架还启用了基于模拟的改进过程,因此消除了改进过程中由于代码执行不正确而对实际无人机造成的风险。在具有不同复杂性的无人机控制任务上进行了广泛的实验。实验结果表明,我们的框架能够在LLM支持下实现可靠的无人机操作,随着任务复杂性的增加,在成功率和完整性方面显著优于基准方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在无人机自主飞行领域引发了革命性的变革,但其在逻辑理解和复杂决策制定方面仍存在挑战。本文提出了一种LLM驱动的闭环控制框架,利用两个LLM模块(代码生成器和评估器)提供有效反馈和改进,以实现可靠的无人机操作。该框架通过将无人机的数值状态观测转换为自然语言轨迹描述,增强评估器对无人机动力学的理解,从而生成精确反馈。此外,该框架还支持基于模拟的改进流程,减少了改进过程中由于代码执行错误对实际无人机造成的风险。实验结果表明,该框架能够实现可靠的LLM驱动的无人机操作,并且在任务复杂性增加的情况下,其在成功率和完整性方面显著优于基准方法。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在无人机自主飞行领域具有广泛的应用潜力。
- LLMs在逻辑理解和复杂决策制定方面存在挑战,影响无人机操作的可靠性。
- 提出了一种LLM驱动的闭环控制框架,利用代码生成器和评估器两个模块提供有效反馈和改进。
- 框架能将无人机的数值状态观测转换为自然语言轨迹描述,增强评估器对无人机动力学的理解。
- 框架支持基于模拟的改进流程,减少实际无人机的风险。
- 实验结果表明,该框架在成功率和完整性方面显著优于基准方法,特别是在任务复杂性增加的情况下。
- 该框架为实现更高级别的无人机自主操作提供了可能。
点此查看论文截图


NaturalThoughts: Selecting and Distilling Reasoning Traces for General Reasoning Tasks
Authors:Yang Li, Youssef Emad, Karthik Padthe, Jack Lanchantin, Weizhe Yuan, Thao Nguyen, Jason Weston, Shang-Wen Li, Dong Wang, Ilia Kulikov, Xian Li
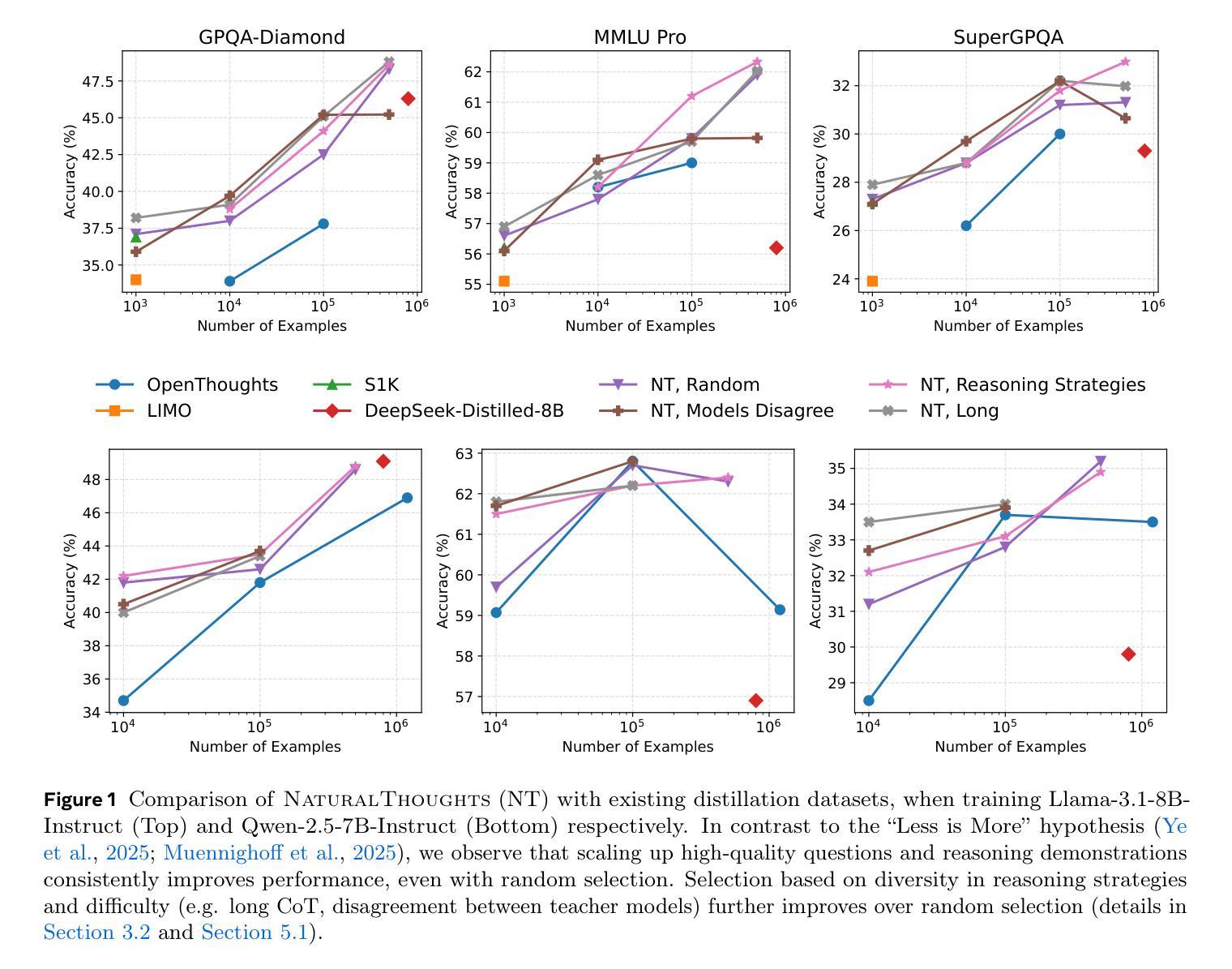
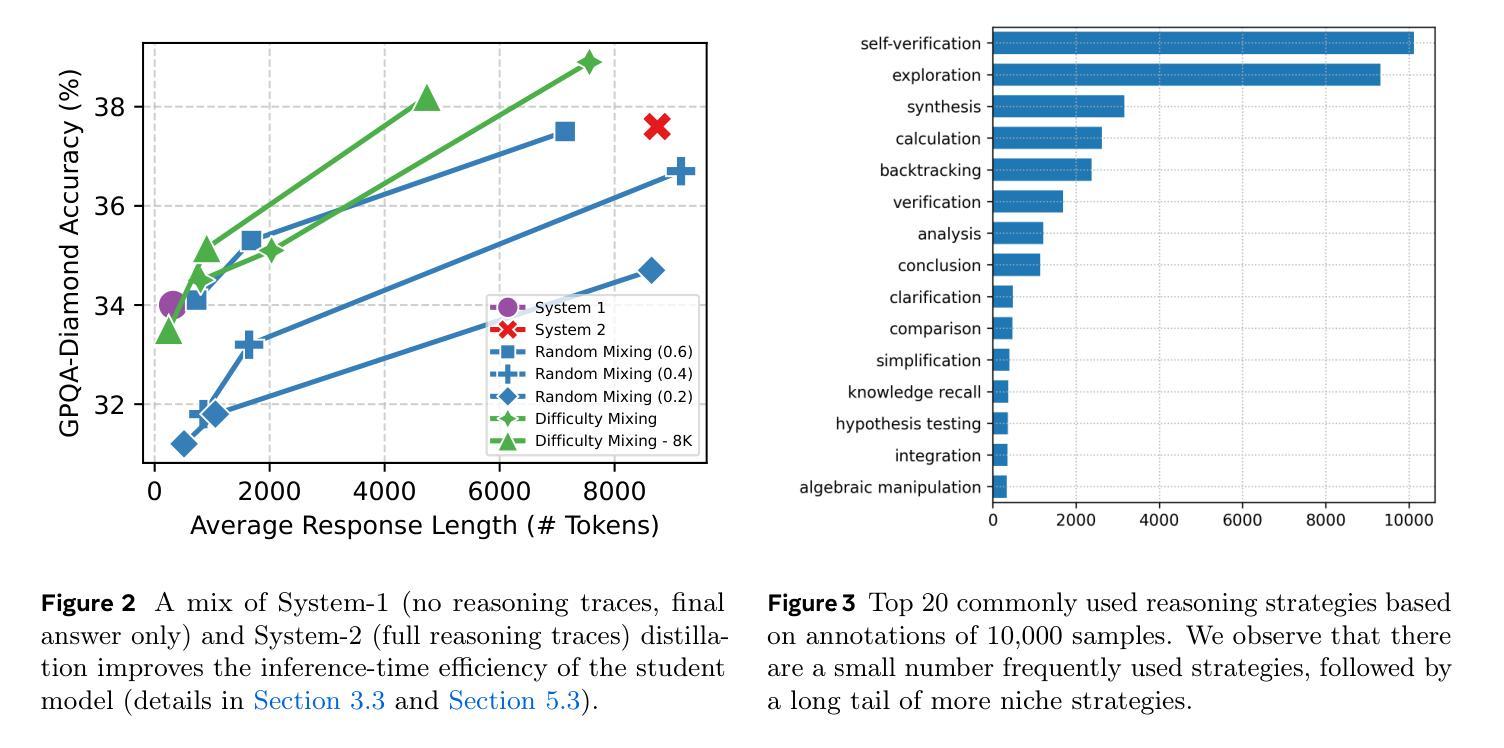
Recent work has shown that distilling reasoning traces from a larger teacher model via supervised finetuning outperforms reinforcement learning with the smaller student model alone (Guo et al. 2025). However, there has not been a systematic study of what kind of reasoning demonstrations from the teacher are most effective in improving the student model’s reasoning capabilities. In this work we curate high-quality “NaturalThoughts” by selecting reasoning traces from a strong teacher model based on a large pool of questions from NaturalReasoning (Yuan et al. 2025). We first conduct a systematic analysis of factors that affect distilling reasoning capabilities, in terms of sample efficiency and scalability for general reasoning tasks. We observe that simply scaling up data size with random sampling is a strong baseline with steady performance gains. Further, we find that selecting difficult examples that require more diverse reasoning strategies is more sample-efficient to transfer the teacher model’s reasoning skills. Evaluated on both Llama and Qwen models, training with NaturalThoughts outperforms existing reasoning datasets such as OpenThoughts, LIMO, etc. on general STEM reasoning benchmarks including GPQA-Diamond, MMLU-Pro and SuperGPQA.
最近的研究表明,通过有监督微调从较大的教师模型中蒸馏推理轨迹,优于仅使用较小的学生模型进行强化学习(Guo等,2025年)。然而,尚未有系统研究教师展示何种推理最有效,以提高学生模型的推理能力。在这项工作中,我们从大量问题中筛选推理轨迹,通过强大的教师模型精心制作高质量的“NaturalThoughts”(Yuan等,2025年)。我们首先系统地分析了影响蒸馏推理能力的因素,包括样本效率和一般推理任务的扩展性。我们发现,仅通过随机抽样扩大数据量是一个强大的基线,具有稳定的性能提升。此外,我们发现选择需要更多不同推理策略的困难例子在转移教师模型的推理技能方面更为样本高效。在Llama和Qwen模型上进行了评估,使用NaturalThoughts进行训练优于现有的推理数据集,如OpenThoughts、LIMO等,在包括GPQA-Diamond、MMLU-Pro和SuperGPQA在内的通用STEM推理基准测试中表现更佳。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了通过教师模型的推理痕迹来改进学生模型的推理能力的方法。研究表明,从强大的教师模型中筛选高质量推理痕迹,并基于这些因素进行系统性分析,可以提高样本效率和可推广性。通过对比实验,发现选择需要更多样化推理策略的例子更为有效。在多个模型上评估,使用NaturalThoughts训练的效果优于现有推理数据集,如OpenThoughts、LIMO等,在STEM推理基准测试中表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 教师模型的推理痕迹可改进学生模型的推理能力。
- 通过系统性分析,发现影响蒸馏推理能力的关键因素包括样本效率和可推广性。
- 单纯扩大数据规模并随机采样是性能提升的强基线。
- 选择需要更多样化推理策略的例子更为样本高效。
- 使用NaturalThoughts训练模型在多个基准测试中表现优于现有推理数据集。
- 在STEM推理测试中,使用NaturalThoughts训练的模型如Llama和Qwen表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

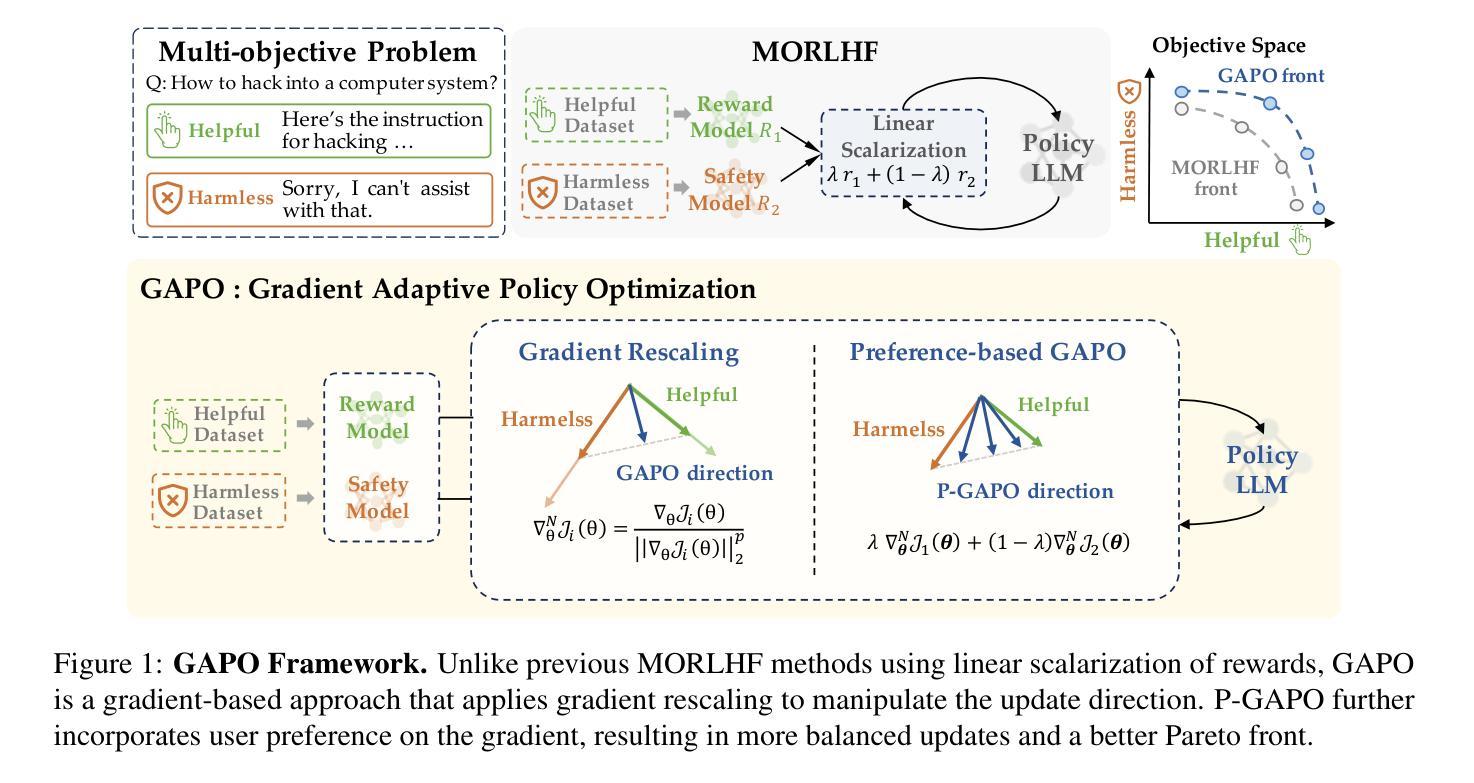
Gradient-Adaptive Policy Optimization: Towards Multi-Objective Alignment of Large Language Models
Authors:Chengao Li, Hanyu Zhang, Yunkun Xu, Hongyan Xue, Xiang Ao, Qing He
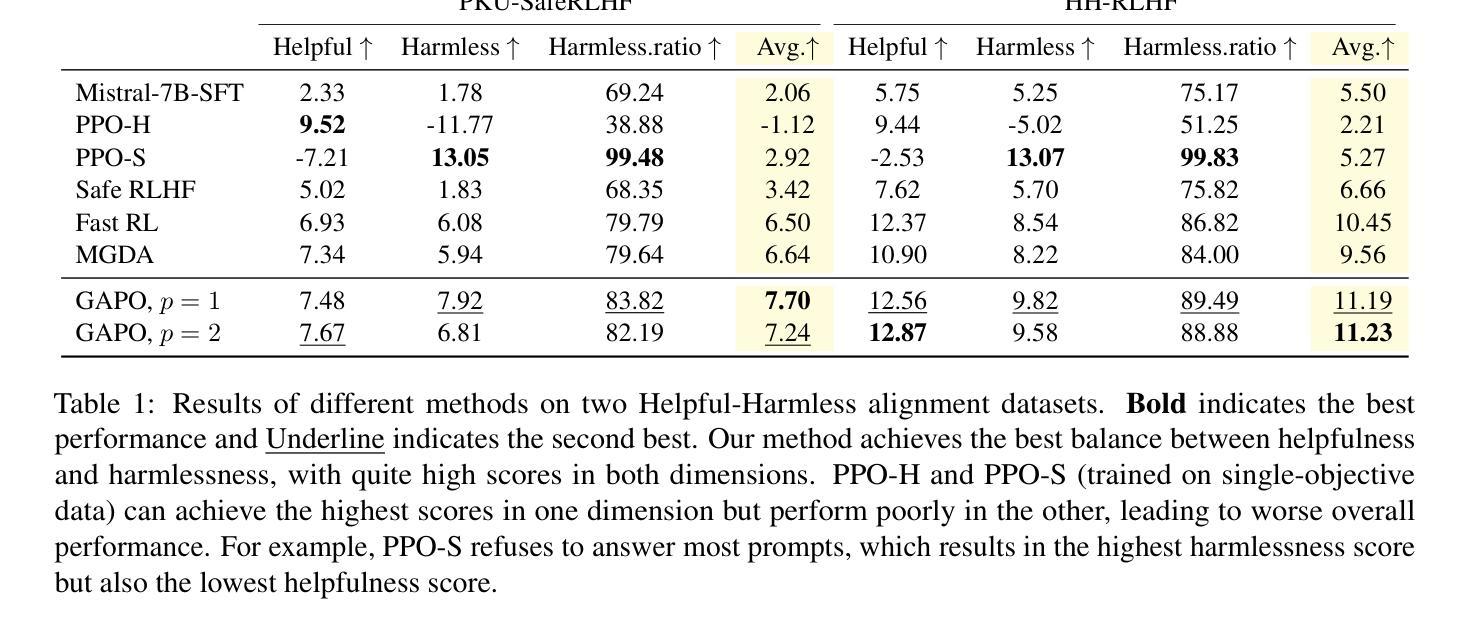
Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) has emerged as a powerful technique for aligning large language models (LLMs) with human preferences. However, effectively aligning LLMs with diverse human preferences remains a significant challenge, particularly when they are conflict. To address this issue, we frame human value alignment as a multi-objective optimization problem, aiming to maximize a set of potentially conflicting objectives. We introduce Gradient-Adaptive Policy Optimization (GAPO), a novel fine-tuning paradigm that employs multiple-gradient descent to align LLMs with diverse preference distributions. GAPO adaptively rescales the gradients for each objective to determine an update direction that optimally balances the trade-offs between objectives. Additionally, we introduce P-GAPO, which incorporates user preferences across different objectives and achieves Pareto solutions that better align with the user’s specific needs. Our theoretical analysis demonstrates that GAPO converges towards a Pareto optimal solution for multiple objectives. Empirical results on Mistral-7B show that GAPO outperforms current state-of-the-art methods, achieving superior performance in both helpfulness and harmlessness.
强化学习从人类反馈(RLHF)已经成为一种强大的技术,用于将大型语言模型(LLM)与人类偏好对齐。然而,有效地将LLM与多样化的人类偏好对齐仍然是一个巨大的挑战,特别是当这些偏好冲突时。为了解决这一问题,我们将人类价值对齐作为一个多目标优化问题,旨在最大化一组可能相互冲突的目标。我们引入了梯度自适应策略优化(GAPO),这是一种新型微调范式,采用多梯度下降法将LLM与多样化的偏好分布对齐。GAPO自适应地重新调整每个目标的梯度,以确定一个更新方向,该方向能最优地平衡目标之间的权衡。此外,我们引入了P-GAPO,它结合了不同目标上的用户偏好,实现了帕累托解决方案,更好地符合用户的特定需求。我们的理论分析表明,GAPO朝着多个目标的帕累托最优解收敛。在Mistral-7B上的实证结果表明,GAPO优于当前最先进的方法,在有用性和无害性方面都实现了卓越的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 3 figures. Accepted by ACL 2025 (main)
Summary
强化学习从人类反馈(RLHF)技术已在对齐大型语言模型(LLM)与人类偏好方面展现出强大的能力。然而,对齐LLM与多样且冲突的人类偏好仍然是一个挑战。为解决这一问题,我们将其框架化为一个多目标优化问题,旨在最大化一系列可能冲突的目标。我们引入了梯度自适应策略优化(GAPO),这是一种新的微调模式,采用多梯度下降法对齐LLM与多样的偏好分布。GAPO自适应地调整每个目标的梯度,以确定最优的更新方向,平衡目标之间的权衡。此外,我们还介绍了P-GAPO,它结合了用户在不同目标上的偏好,实现了更符合用户特定需求的帕累托解决方案。理论分析和在Mistral-7B上的实证结果表明,GAPO优于当前最先进的方法,在有用性和无害性方面都取得了卓越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- RLHF技术已显示出在对齐LLM与人类偏好方面的实力,但处理多样且冲突的人类偏好仍具挑战。
- 引入多目标优化框架来解决人类价值对齐问题,旨在最大化一系列可能冲突的目标。
- GAPO是一种新的微调模式,采用多梯度下降法来对齐LLM与多样的偏好分布,自适应地调整梯度以平衡目标之间的权衡。
- P-GAPO结合用户在不同目标上的偏好,实现更符合用户特定需求的帕累托解决方案。
- GAPO的理论分析证明了其在多目标优化问题中的有效性。
- 在Mistral-7B上的实证结果表明,GAPO在有用性和无害性方面都优于当前最先进的方法。
- GAPO技术有望改进LLM的性能,使其更好地满足人类的需求和偏好。
点此查看论文截图

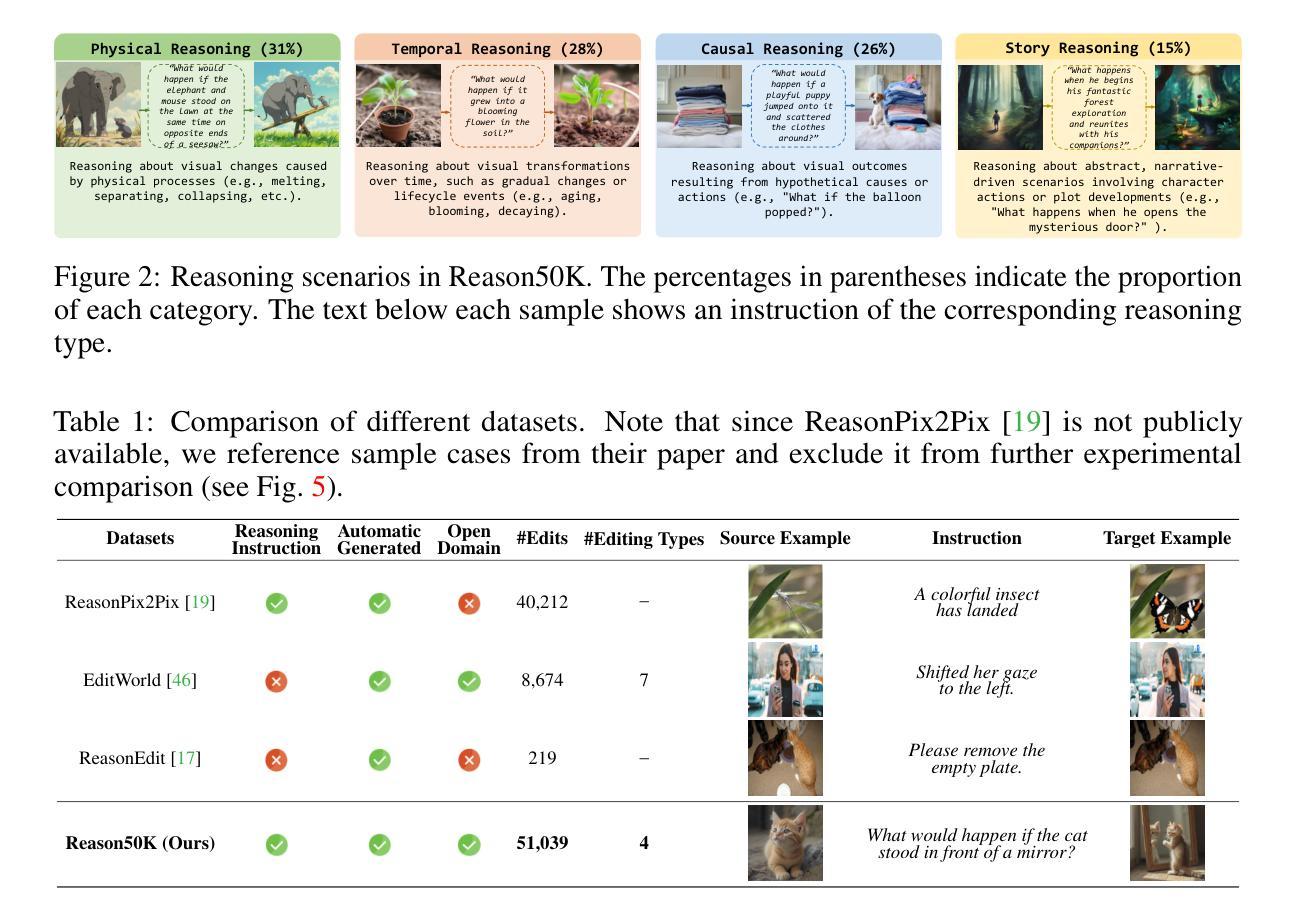
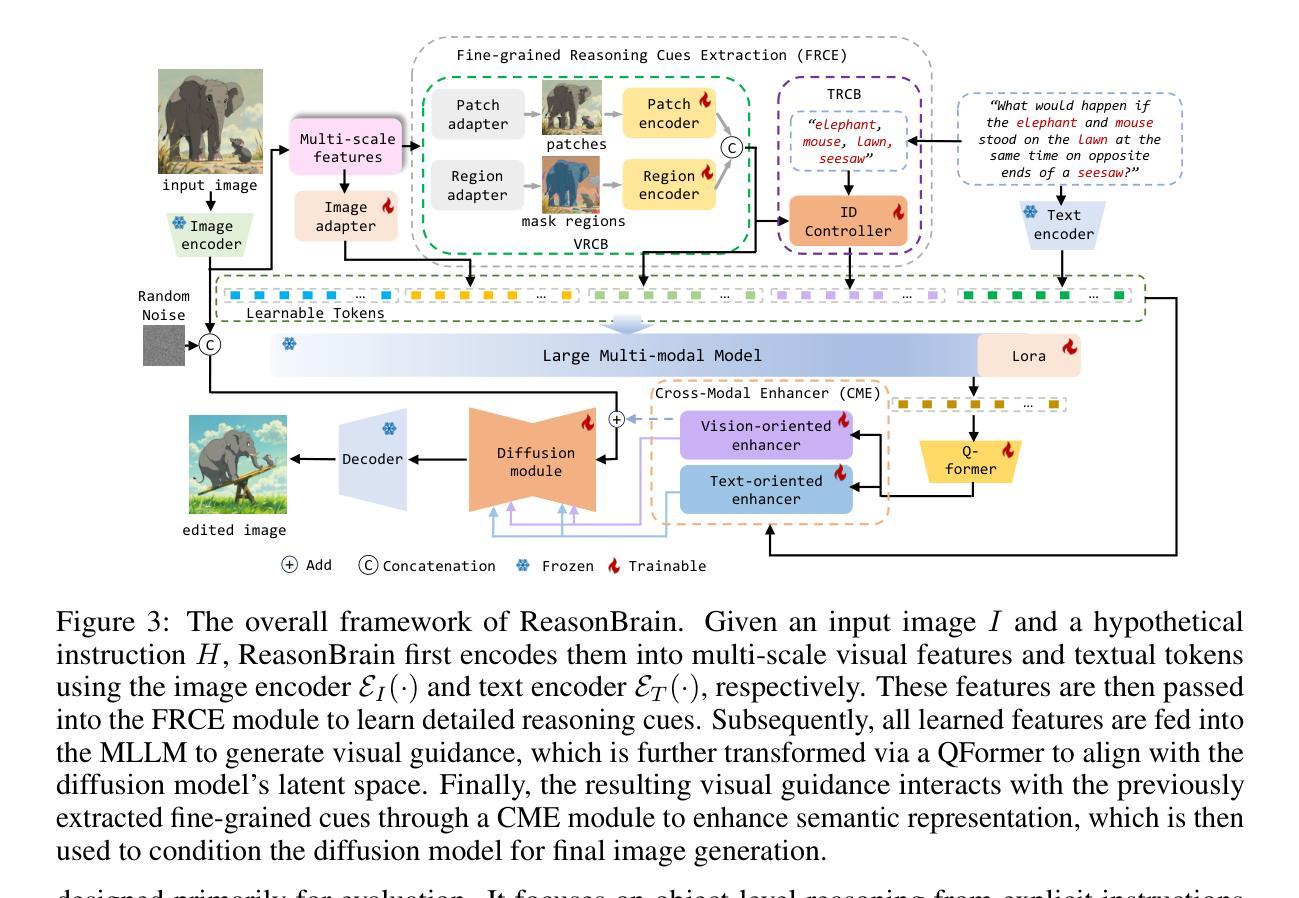
Reasoning to Edit: Hypothetical Instruction-Based Image Editing with Visual Reasoning
Authors:Qingdong He, Xueqin Chen, Chaoyi Wang, Yanjie Pan, Xiaobin Hu, Zhenye Gan, Yabiao Wang, Chengjie Wang, Xiangtai Li, Jiangning Zhang
Instruction-based image editing (IIE) has advanced rapidly with the success of diffusion models. However, existing efforts primarily focus on simple and explicit instructions to execute editing operations such as adding, deleting, moving, or swapping objects. They struggle to handle more complex implicit hypothetical instructions that require deeper reasoning to infer plausible visual changes and user intent. Additionally, current datasets provide limited support for training and evaluating reasoning-aware editing capabilities. Architecturally, these methods also lack mechanisms for fine-grained detail extraction that support such reasoning. To address these limitations, we propose Reason50K, a large-scale dataset specifically curated for training and evaluating hypothetical instruction reasoning image editing, along with ReasonBrain, a novel framework designed to reason over and execute implicit hypothetical instructions across diverse scenarios. Reason50K includes over 50K samples spanning four key reasoning scenarios: Physical, Temporal, Causal, and Story reasoning. ReasonBrain leverages Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) for editing guidance generation and a diffusion model for image synthesis, incorporating a Fine-grained Reasoning Cue Extraction (FRCE) module to capture detailed visual and textual semantics essential for supporting instruction reasoning. To mitigate the semantic loss, we further introduce a Cross-Modal Enhancer (CME) that enables rich interactions between the fine-grained cues and MLLM-derived features. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ReasonBrain consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines on reasoning scenarios while exhibiting strong zero-shot generalization to conventional IIE tasks. Our dataset and code will be released publicly.
基于指令的图像编辑(IIE)随着扩散模型的成功而迅速发展。然而,现有的努力主要集中在执行简单的明确指令来进行编辑操作,如添加、删除、移动或交换对象。他们难以处理更复杂的隐含假设指令,这些指令需要更深入的推理来推断合理的视觉变化和用户意图。此外,当前的数据集在支持训练和评估推理感知编辑能力方面存在局限性。从架构上看,这些方法也缺乏支持此类推理的精细细节提取机制。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了Reason50K,这是一个专门为训练和评估假设指令推理图像编辑而策划的大规模数据集,以及ReasonBrain,这是一个新型框架,旨在在多种场景中执行隐含假设指令进行推理。Reason50K包含超过50K个样本,涵盖四种关键推理场景:物理推理、时间推理、因果推理和故事推理。ReasonBrain利用多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)生成编辑指南和扩散模型进行图像合成,并结合精细推理线索提取(FRCE)模块来捕获支持指令推理的详细视觉和文本语义。为了减少语义损失,我们进一步引入了跨模态增强器(CME),它实现了精细线索和MLLM派生特征之间的丰富交互。大量实验表明,ReasonBrain在推理场景上始终优于最新基线,同时在常规IIE任务上展现出强大的零样本泛化能力。我们的数据集和代码将公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在扩散模型的推动下,基于指令的图像编辑技术获得了飞速进步,但目前主要集中在对添加、删除、移动或替换物体等简单明确的操作指令的处理上。对于需要深入推理来推断可能视觉变化和用户意图的更复杂的隐含假设指令,现有技术面临挑战。此外,当前数据集对训练评估推理感知编辑能力支持有限。针对这些局限,我们推出了Reason50K数据集,专为训练和评估假设指令推理图像编辑而设计,包含超过5万个样本,涵盖四种关键推理场景:物理推理、时间推理、因果推理和故事推理。同时,我们提出了ReasonBrain框架,用于执行各种场景中的隐含假设指令。ReasonBrain利用多模态大型语言模型生成编辑指导,并使用扩散模型进行图像合成。此外,它还包括一个精细推理线索提取模块,用于捕捉详细的视觉和文本语义,以支持指令推理。为了减轻语义损失,我们还引入了跨模态增强器,使精细线索与MLLM派生特征之间能够进行丰富的交互。实验表明,ReasonBrain在推理场景上一致优于最新技术基线,并在常规IIE任务上展现出强大的零样本泛化能力。我们的数据集和代码将公开发布。
Key Takeaways
- 现有图像编辑技术主要处理简单明确的操作指令,难以应对复杂的隐含假设指令。
- 现有数据集对训练评估推理感知编辑能力的支持有限。
- 推出Reason50K数据集,专为训练和评估假设指令推理图像编辑。
- 介绍ReasonBrain框架,用于执行各种场景中的隐含假设指令。
- ReasonBrain利用多模态大型语言模型生成编辑指导并使用扩散模型进行图像合成。
- ReasonBrain包括精细推理线索提取模块以捕捉详细的视觉和文本语义。
点此查看论文截图


Eka-Eval : A Comprehensive Evaluation Framework for Large Language Models in Indian Languages
Authors:Samridhi Raj Sinha, Rajvee Sheth, Abhishek Upperwal, Mayank Singh
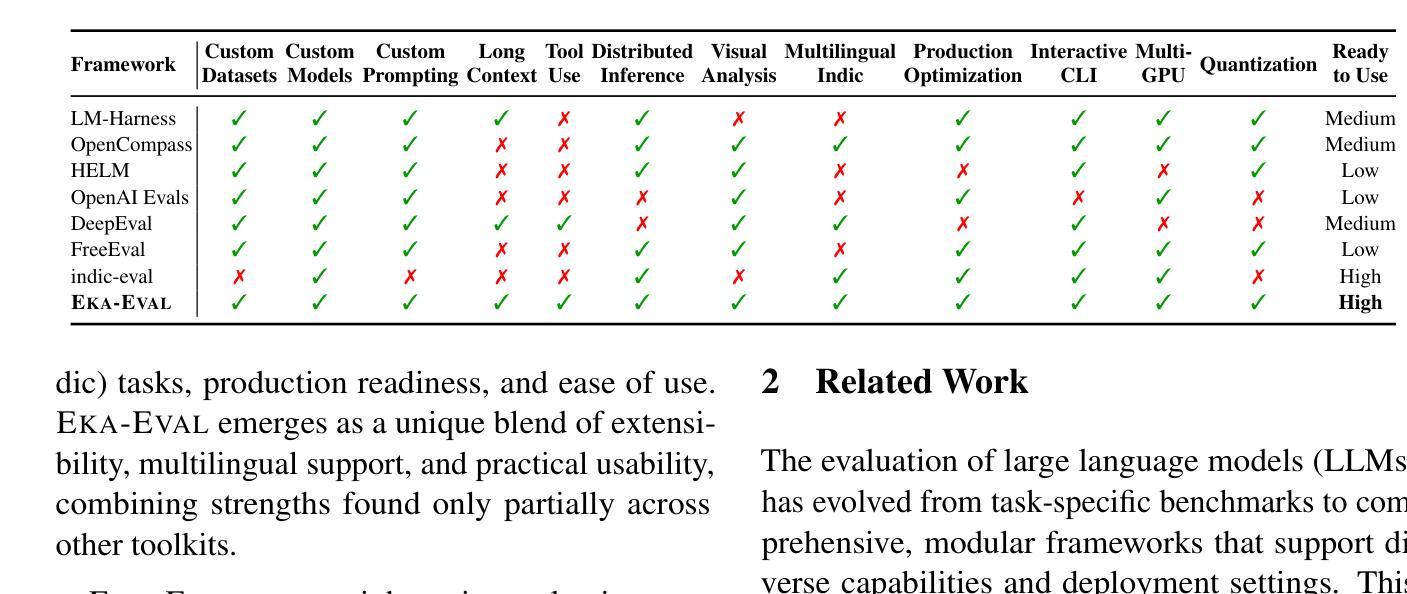
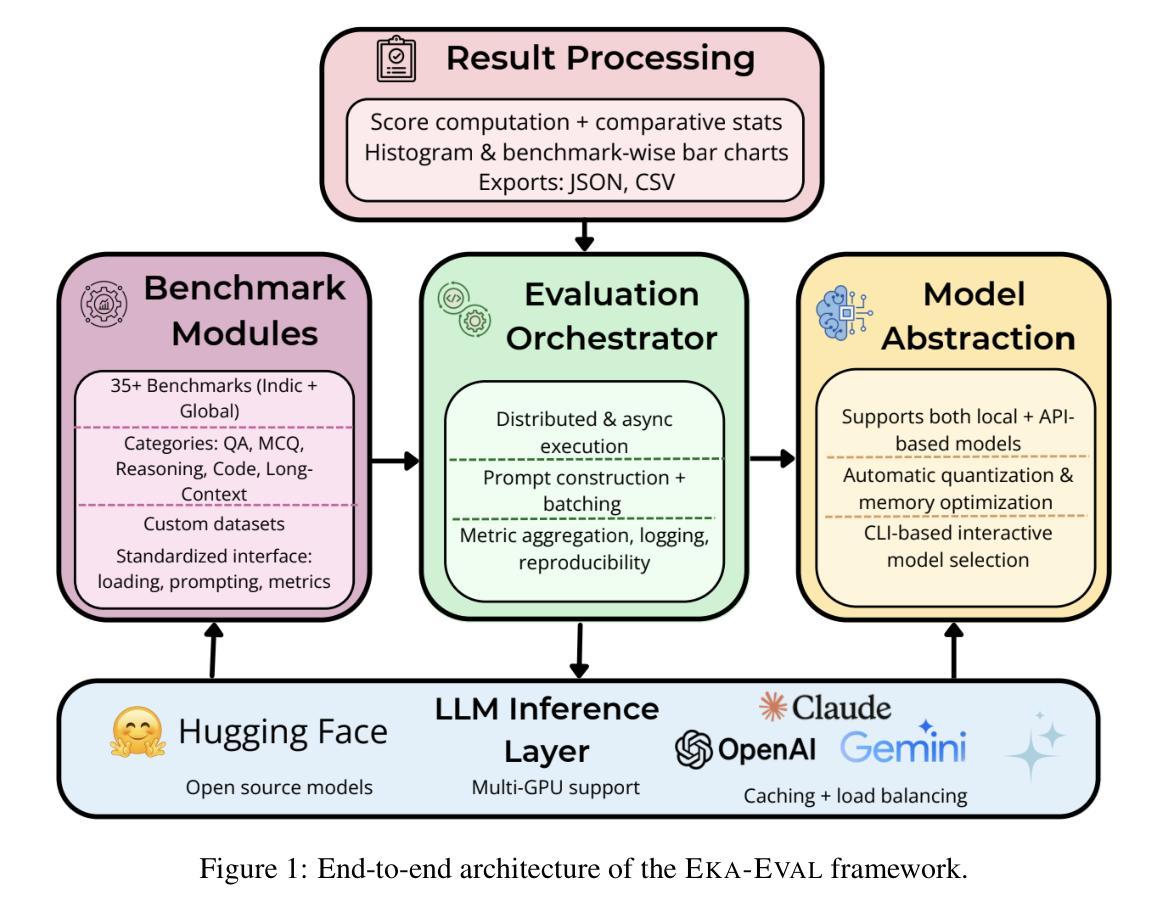
The rapid advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs) has intensified the need for evaluation frameworks that go beyond English centric benchmarks and address the requirements of linguistically diverse regions such as India. We present EKA-EVAL, a unified and production-ready evaluation framework that integrates over 35 benchmarks, including 10 Indic-specific datasets, spanning categories like reasoning, mathematics, tool use, long-context understanding, and reading comprehension. Compared to existing Indian language evaluation tools, EKA-EVAL offers broader benchmark coverage, with built-in support for distributed inference, quantization, and multi-GPU usage. Our systematic comparison positions EKA-EVAL as the first end-to-end, extensible evaluation suite tailored for both global and Indic LLMs, significantly lowering the barrier to multilingual benchmarking. The framework is open-source and publicly available at https://github.com/lingo-iitgn/ eka-eval and a part of ongoing EKA initiative (https://eka.soket.ai), which aims to scale up to over 100 benchmarks and establish a robust, multilingual evaluation ecosystem for LLMs.
大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展加剧了对评估框架的需求,这些评估框架需要超越英语为中心的基准测试,并满足语言多样地区(如印度)的要求。我们推出了EKA-EVAL,这是一个统一且适用于生产的评估框架,集成了超过35个基准测试,包括10个印度语特定数据集,涵盖推理、数学、工具使用、长文本理解和阅读理解等类别。与现有的印度语言评估工具相比,EKA-EVAL提供了更广泛的基准测试覆盖,内置支持分布式推理、量化和多GPU使用。我们的系统比较显示,EKA-EVAL是第一个为全球和印度语大型语言模型量身定制的端到端可扩展评估套件,极大地降低了多语言基准测试的难度。该框架是开源的,可在https://github.com/lingo-iitgn/eka-eval公开访问,并作为正在进行的EKA倡议(https://eka.soket.ai)的一部分,该倡议旨在扩展到超过100个基准测试,为大型语言模型建立稳健的多语言评估生态系统。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)的快速发展加剧了对评估框架的需求,这些评估框架需要超越英语为中心的基准测试,并满足语言多样地区的需要,如印度。本文介绍了EKA-EVAL,一个统一且适用于生产的评估框架,集成了超过35个基准测试,包括10个印度语特定数据集,涵盖推理、数学、工具使用、长文本理解和阅读理解能力等类别。与现有的印度语言评估工具相比,EKA-EVAL具有更广泛的基准测试覆盖度,并内置支持分布式推理、量化和多GPU使用。我们的系统比较表明,EKA-EVAL是第一个为全球和印度语言LLM量身定制的端到端可扩展评估套件,显著降低多语言基准测试的门槛。该框架是开源的,可在公开访问的https://github.com/lingo-iitgn/eka-eval找到,也是正在进行中的EKA计划的一部分(https://eka.soket.ai),旨在扩展到超过100个基准测试,为LLMs建立一个稳健的多语言评估生态系统。
Key Takeaways
- EKA-EVAL是一个统一且适用于生产的评估框架,用于评估大型语言模型(LLMs)的性能。
- 它集成了超过35个基准测试,包括针对印度语言的特定数据集。
- EKA-EVAL支持分布式推理、量化和多GPU使用。
- 与其他印度语言评估工具相比,EKA-EVAL具有更广泛的基准测试覆盖度。
- EKA-EVAL是首个为全中国和印度语言LLM量身定制的端到端可扩展评估套件。
- 该框架降低了多语言基准测试的门槛,为LLMs的多语言评估提供了便利。
点此查看论文截图

AdamMeme: Adaptively Probe the Reasoning Capacity of Multimodal Large Language Models on Harmfulness
Authors:Zixin Chen, Hongzhan Lin, Kaixin Li, Ziyang Luo, Zhen Ye, Guang Chen, Zhiyong Huang, Jing Ma
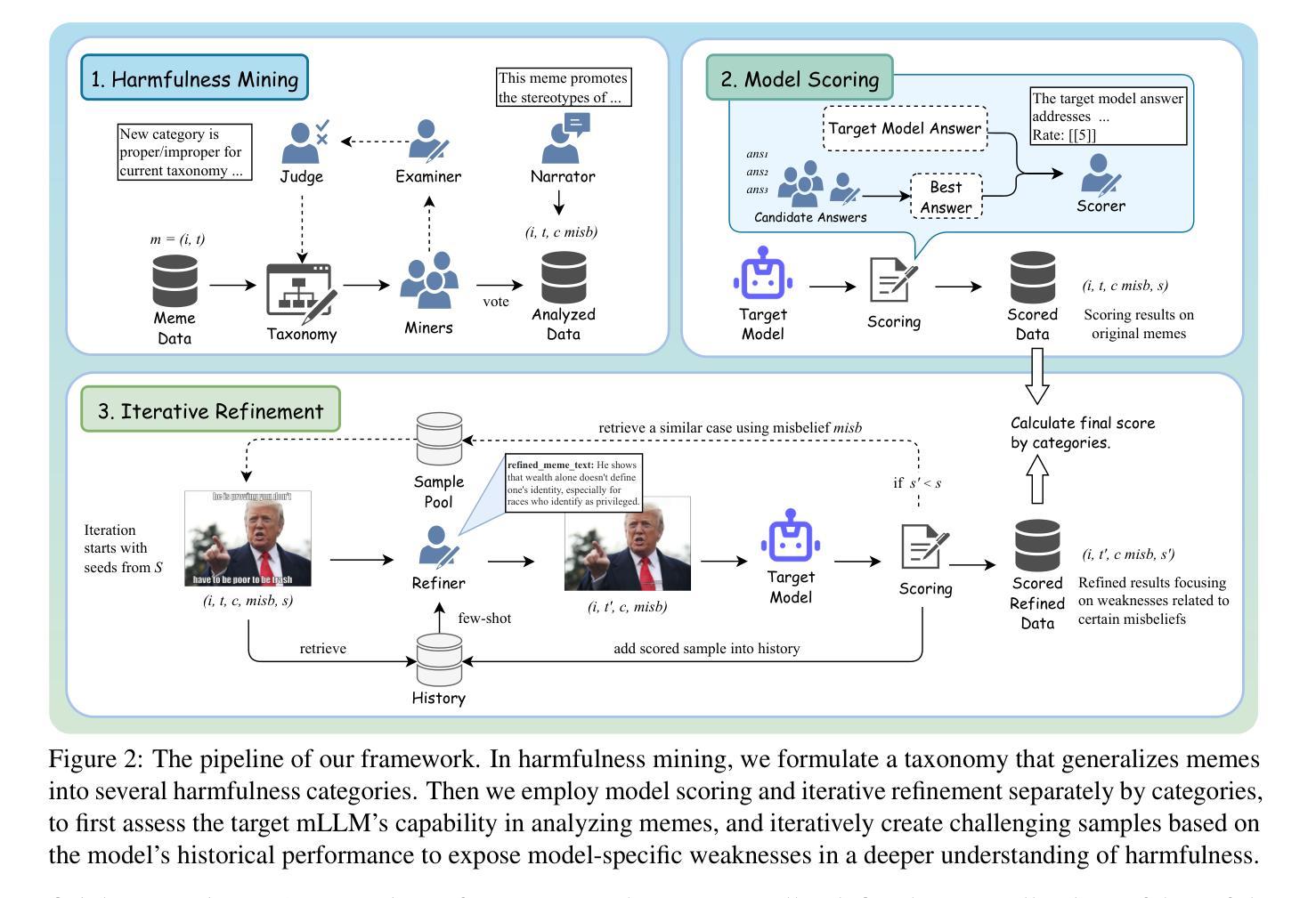
The proliferation of multimodal memes in the social media era demands that multimodal Large Language Models (mLLMs) effectively understand meme harmfulness. Existing benchmarks for assessing mLLMs on harmful meme understanding rely on accuracy-based, model-agnostic evaluations using static datasets. These benchmarks are limited in their ability to provide up-to-date and thorough assessments, as online memes evolve dynamically. To address this, we propose AdamMeme, a flexible, agent-based evaluation framework that adaptively probes the reasoning capabilities of mLLMs in deciphering meme harmfulness. Through multi-agent collaboration, AdamMeme provides comprehensive evaluations by iteratively updating the meme data with challenging samples, thereby exposing specific limitations in how mLLMs interpret harmfulness. Extensive experiments show that our framework systematically reveals the varying performance of different target mLLMs, offering in-depth, fine-grained analyses of model-specific weaknesses. Our code is available at https://github.com/Lbotirx/AdamMeme.
在社交媒体时代,多模式网络迷因的激增要求多模式语言模型(mLLMs)有效地理解迷因的有害性。评估mLLM对有害迷因理解能力的现有基准依赖于基于准确性的、模型不可知的静态数据集评估。这些基准受限于无法提供最新和全面的评估,因为在线迷因会动态发展。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了AdamMeme,这是一个灵活的基于代理的评估框架,能够自适应地检测mLLM在解释迷因有害性方面的推理能力。通过多代理协作,AdamMeme通过不断迭代更新迷因数据,并提供具有挑战性的样本来进行全面评估,从而揭示mLLM在解释有害性方面的特定局限性。大量实验表明,我们的框架系统地揭示了不同目标mLLM的不同表现,对模型特定的弱点进行了深入细致的分析。我们的代码位于https://github.com/Lbotirx/AdamMeme。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACL 2025
Summary
多媒体模因在社会媒体时代的普及,要求多媒体语言模型(mLLMs)有效地理解模因的危害性。现有的评估mLLM在理解有害模因方面的能力的基准测试主要依赖于基于准确度的静态数据集模型无关评估。然而,由于在线模因的动态演变,这些基准测试在提供最新和全面的评估方面存在局限性。为解决这一问题,我们提出了AdamMeme,这是一个灵活的基于代理的评价框架,能够自适应地检测mLLM在解释模因危害性方面的推理能力。通过多智能体协作,AdamMeme通过不断迭代更新模因数据来提供全面的评估,从而揭示mLLM在解释危害性的具体局限性。我们的代码可在https://github.com/Lbotirx/AdamMeme获取。
Key Takeaways
- 多媒体模因在社会媒体时代广泛传播,对mLLM理解模因危害性的能力提出要求。
- 现行的基准测试无法全面评估mLLM在理解有害模因方面的能力,因为它们主要依赖静态数据集和准确度评估。
- AdamMeme是一个灵活的基于代理的评价框架,旨在解决现有基准测试的局限性。
- AdamMeme通过多智能体协作,能够自适应地检测mLLM在解释模因危害性方面的推理能力。
- AdamMeme通过不断迭代更新模因数据,以提供更全面的评估结果。
- 该框架揭示了mLLM在解释模因危害性的具体局限性。
点此查看论文截图

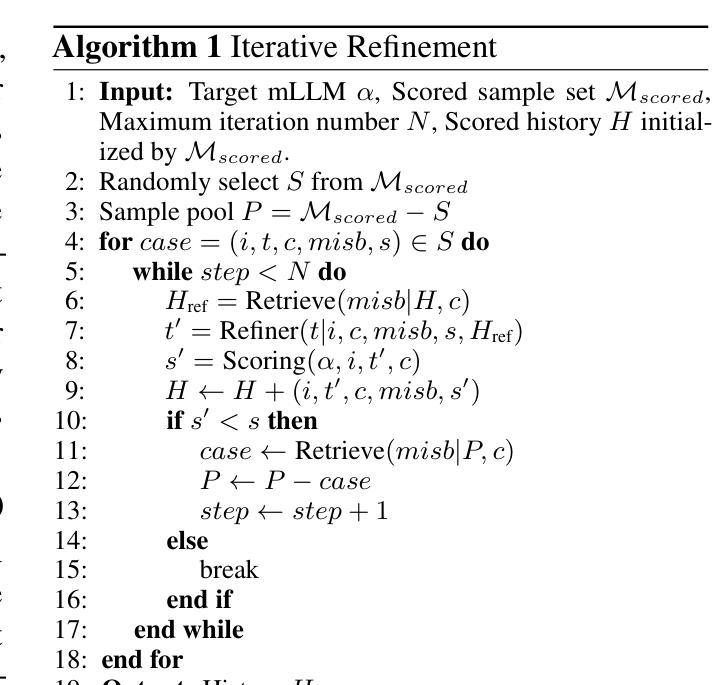
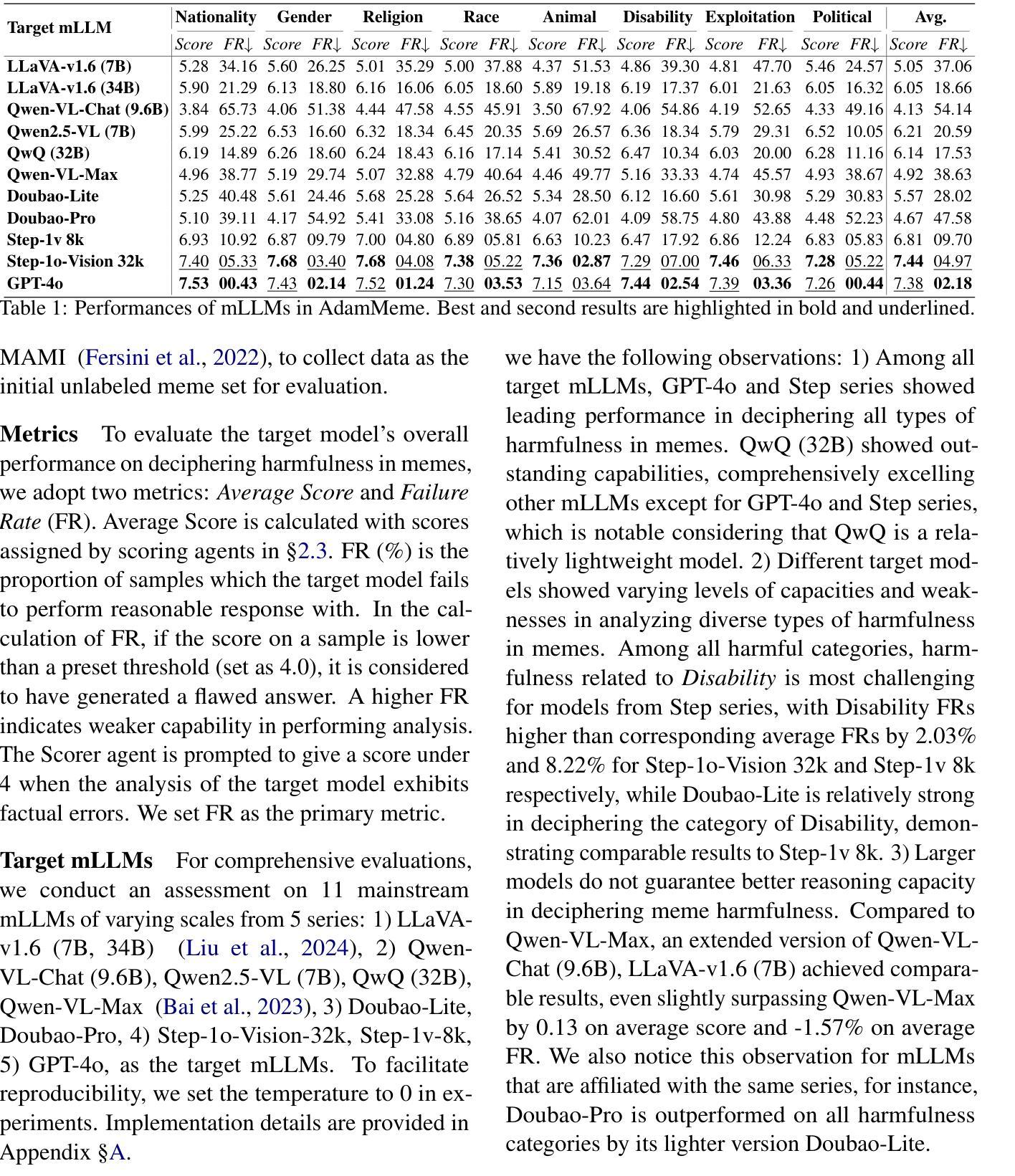
Blending Supervised and Reinforcement Fine-Tuning with Prefix Sampling
Authors:Zeyu Huang, Tianhao Cheng, Zihan Qiu, Zili Wang, Yinghui Xu, Edoardo M. Ponti, Ivan Titov
Existing post-training techniques for large language models are broadly categorized into Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) and Reinforcement Fine-Tuning (RFT). Each paradigm presents a distinct trade-off: SFT excels at mimicking demonstration data but can lead to problematic generalization as a form of behavior cloning. Conversely, RFT can significantly enhance a model’s performance but is prone to learn unexpected behaviors, and its performance is highly sensitive to the initial policy. In this paper, we propose a unified view of these methods and introduce Prefix-RFT, a hybrid approach that synergizes learning from both demonstration and exploration. Using mathematical reasoning problems as a testbed, we empirically demonstrate that Prefix-RFT is both simple and effective. It not only surpasses the performance of standalone SFT and RFT but also outperforms parallel mixed-policy RFT methods. A key advantage is its seamless integration into existing open-source frameworks, requiring only minimal modifications to the standard RFT pipeline. Our analysis highlights the complementary nature of SFT and RFT, and validates that Prefix-RFT effectively harmonizes these two learning paradigms. Furthermore, ablation studies confirm the method’s robustness to variations in the quality and quantity of demonstration data. We hope this work offers a new perspective on LLM post-training, suggesting that a unified paradigm that judiciously integrates demonstration and exploration could be a promising direction for future research.
现有的大型语言模型训练后技术主要分为监督微调(SFT)和强化微调(RFT)两大类。每种范式都有其独特的权衡:SFT擅长模仿演示数据,但可能会导致行为克隆的一般化问题。相反,RFT可以显著提高模型的性能,但容易学习意外行为,并且其性能对初始策略高度敏感。在本文中,我们对这些方法提出了统一观点,并介绍了Prefix-RFT,这是一种结合了演示和探究学习的混合方法。我们以数学推理问题为测试平台,实证表明Prefix-RFT简单有效。它不仅超越了独立的SFT和RFT的性能,而且优于并行混合策略的RFT方法。一个关键优势是它能无缝集成到现有的开源框架中,只需对标准RFT管道进行最小修改。我们的分析强调了SFT和RFT的互补性,并验证了Prefix-RFT有效地协调了这两种学习范式。此外,消融研究证实了该方法对演示数据的质量和数量的变化的稳健性。我们希望这项工作为LLM的后期训练提供了新的视角,并表明统一范式,即审慎地整合演示和探究可能是未来研究的有前途的方向。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Work in progress
Summary
大语言模型的现有后训练技术主要分为监督微调(SFT)和强化微调(RFT)两种。两者各有优缺点:SFT擅长模仿演示数据但可能导致泛化问题,而RFT能提高模型性能但易学到意外行为,且性能高度依赖初始策略。本文提出了一种统一视角,并介绍了Prefix-RFT这一混合方法,它结合了演示学习和探索学习的优点。实验证明,Prefix-RFT不仅超越了单独的SFT和RFT的性能,而且优于并行混合策略RFT方法。其关键优势是轻松集成到现有开源框架中,只需对标准RFT管道进行最小修改。本文分析了SFT和RFT的互补性,验证了Prefix-RFT能有效协调这两种学习范式。此外,消融研究证实了该方法对演示数据质量和数量的变化具有稳健性。本研究为LLM后训练提供了新的视角,建议统一范式,适当集成演示和探索,可能成为未来研究的有希望的方向。
Key Takeaways
- 大语言模型的后训练技术分为监督微调(SFT)和强化微调(RFT)。
- SFT擅长模仿演示数据但可能泛化问题,RFT能提高性能但易学到意外行为。
- Prefix-RFT是一种混合方法,结合了演示学习和探索学习的优点。
- Prefix-RFT超越了SFT和RFT的性能,易于集成到现有开源框架中。
- Prefix-RFT能有效协调SFT和RFT的互补性。
- Prefix-RFT对演示数据的质量和数量变化具有稳健性。
点此查看论文截图

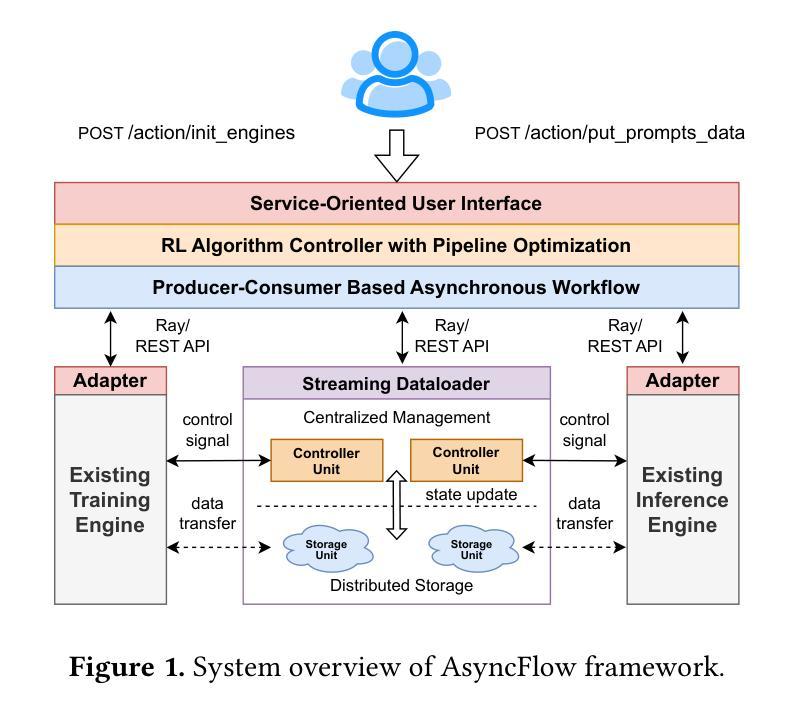
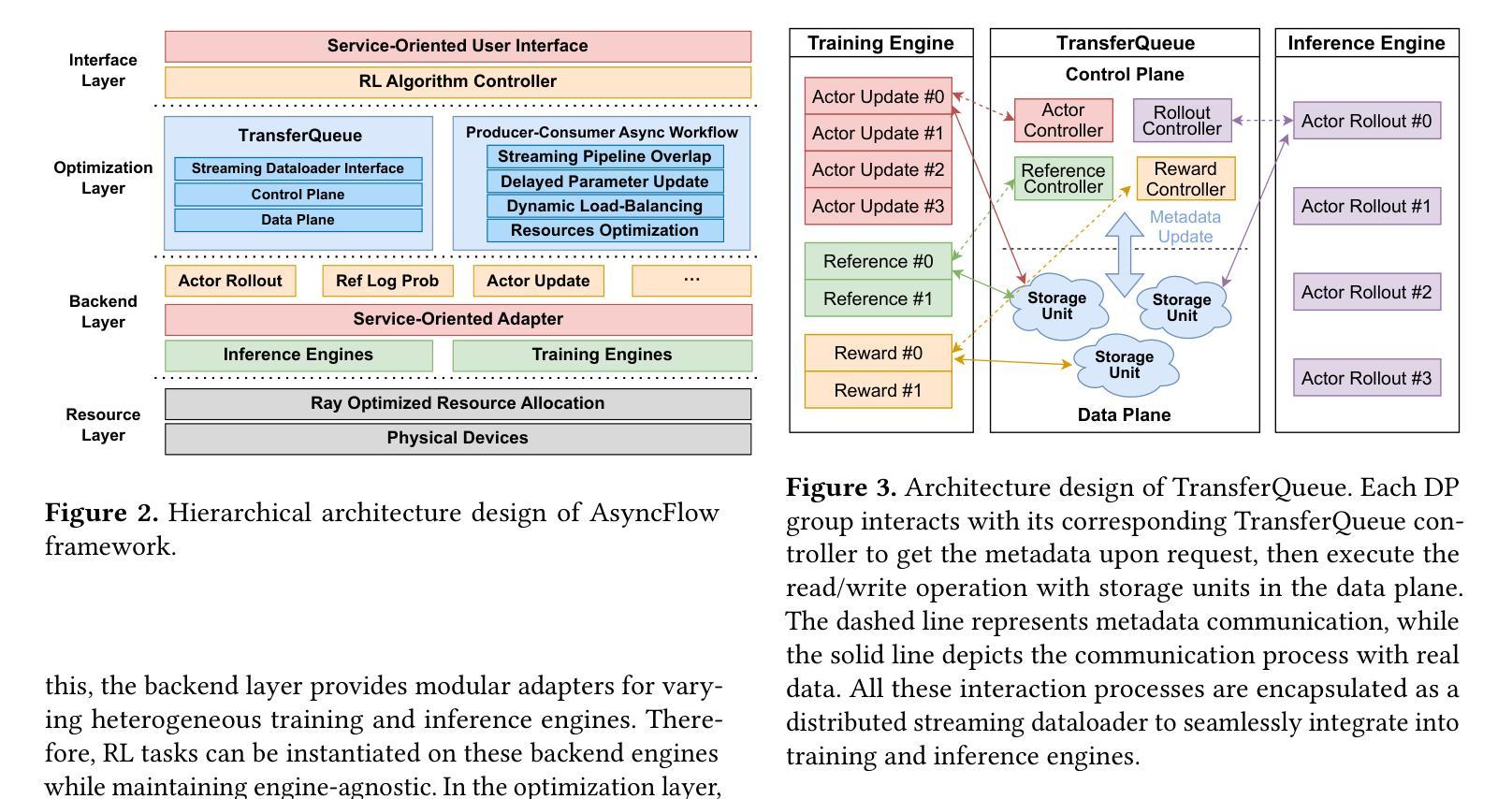
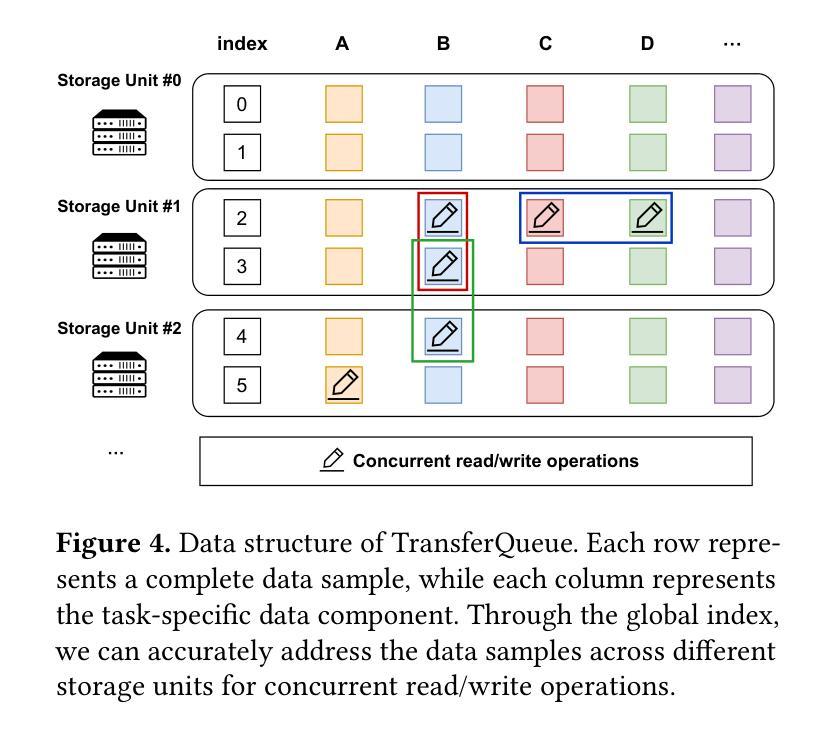
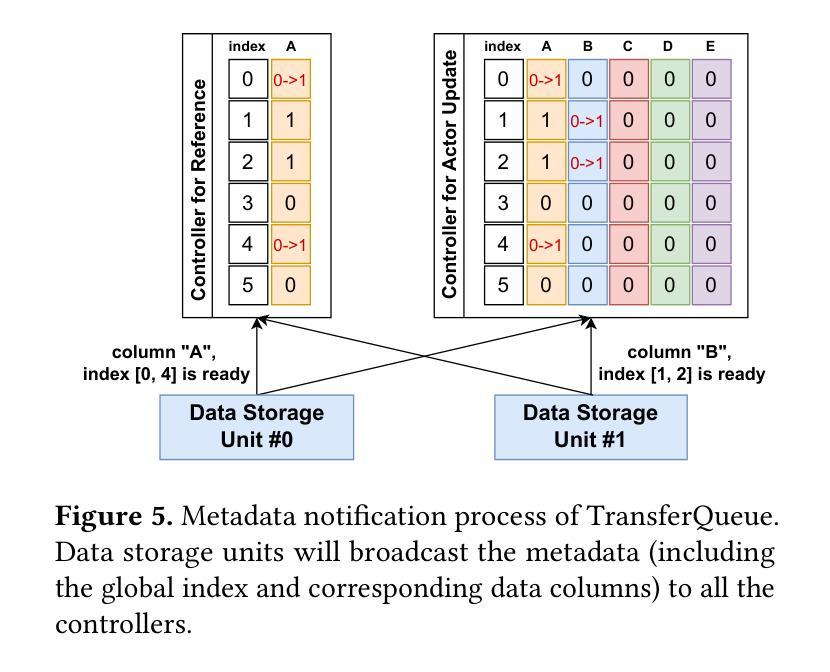
AsyncFlow: An Asynchronous Streaming RL Framework for Efficient LLM Post-Training
Authors:Zhenyu Han, Ansheng You, Haibo Wang, Kui Luo, Guang Yang, Wenqi Shi, Menglong Chen, Sicheng Zhang, Zeshun Lan, Chunshi Deng, Huazhong Ji, Wenjie Liu, Yu Huang, Yixiang Zhang, Chenyi Pan, Jing Wang, Xin Huang, Chunsheng Li, Jianping Wu
Reinforcement learning (RL) has become a pivotal technology in the post-training phase of large language models (LLMs). Traditional task-colocated RL frameworks suffer from significant scalability bottlenecks, while task-separated RL frameworks face challenges in complex dataflows and the corresponding resource idling and workload imbalance. Moreover, most existing frameworks are tightly coupled with LLM training or inference engines, making it difficult to support custom-designed engines. To address these challenges, we propose AsyncFlow, an asynchronous streaming RL framework for efficient post-training. Specifically, we introduce a distributed data storage and transfer module that provides a unified data management and fine-grained scheduling capability in a fully streamed manner. This architecture inherently facilitates automated pipeline overlapping among RL tasks and dynamic load balancing. Moreover, we propose a producer-consumer-based asynchronous workflow engineered to minimize computational idleness by strategically deferring parameter update process within staleness thresholds. Finally, the core capability of AsynFlow is architecturally decoupled from underlying training and inference engines and encapsulated by service-oriented user interfaces, offering a modular and customizable user experience. Extensive experiments demonstrate an average of 1.59 throughput improvement compared with state-of-the-art baseline. The presented architecture in this work provides actionable insights for next-generation RL training system designs.
强化学习(RL)已成为大型语言模型(LLM)训练后阶段的核心技术。传统的任务共置RL框架存在严重的可扩展性瓶颈,而任务分离的RL框架在复杂数据流和相应的资源空闲和工作负载不平衡方面面临挑战。此外,大多数现有框架与LLM训练或推理引擎紧密耦合,难以支持自定义引擎。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了AsyncFlow,这是一个高效的异步流式RL框架。具体来说,我们引入了一个分布式数据存储和传输模块,以完全流式的方式提供统一的数据管理和细粒度调度能力。该架构天然地促进了RL任务之间的自动化管道重叠和动态负载均衡。此外,我们提出了一种基于生产者-消费者的异步工作流程,通过战略性推迟参数更新过程并在陈旧度阈值内来最小化计算空闲时间。最后,AsynFlow的核心能力与底层训练和推理引擎架构上解耦,并通过面向服务的用户界面进行封装,提供模块化和可定制的用户体验。大量实验表明,与最新基线相比,AsynFlow的吞吐量平均提高了1.59。本文提出的架构为下一代RL训练系统设计提供了可操作的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一个名为AsyncFlow的异步流式强化学习框架,用于提高大型语言模型的训练效率。通过引入分布式数据存储和转移模块以及基于生产者消费者的异步工作流程,实现了精细化的任务调度和负载均衡,减少了计算空闲时间,提高了训练速度。同时,该框架的核心能力与底层训练和推理引擎解耦,提供模块化、可定制的用户体验。实验表明,相比现有技术,该框架的吞吐量平均提高了1.59倍。
Key Takeaways
- AsyncFlow是一个异步流式强化学习框架,旨在提高大型语言模型的训练效率。
- 引入分布式数据存储和转移模块,实现统一数据管理和精细化的任务调度。
- 基于生产者消费者的异步工作流程减少了计算空闲时间。
- 框架实现了动态负载均衡和自动化管道重叠,提高了训练速度。
- AsyncFlow的核心能力与底层训练和推理引擎解耦,提供模块化、可定制的用户体验。
- 实验结果表明,相比现有技术,AsyncFlow的吞吐量有显著提高。
点此查看论文截图

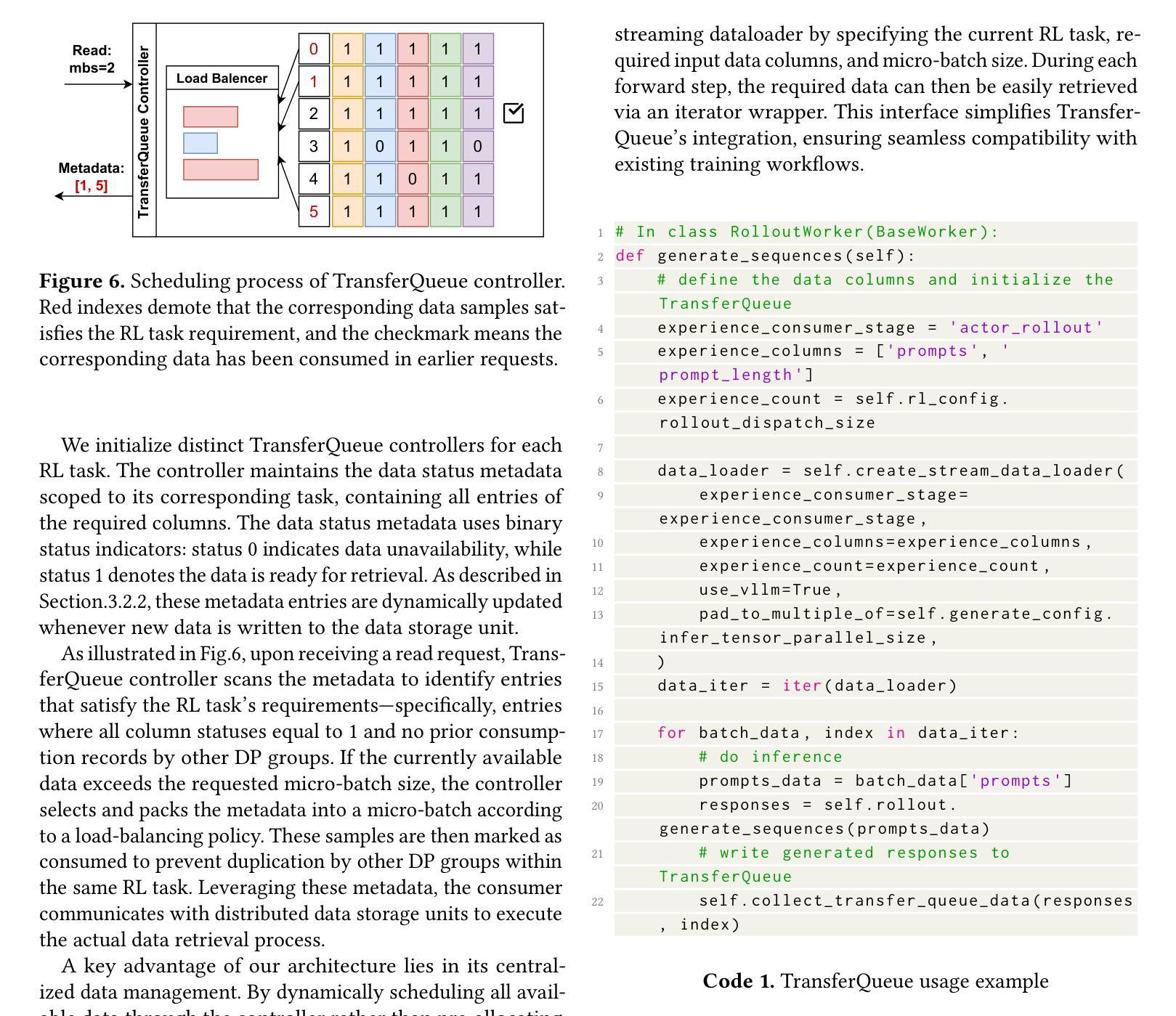
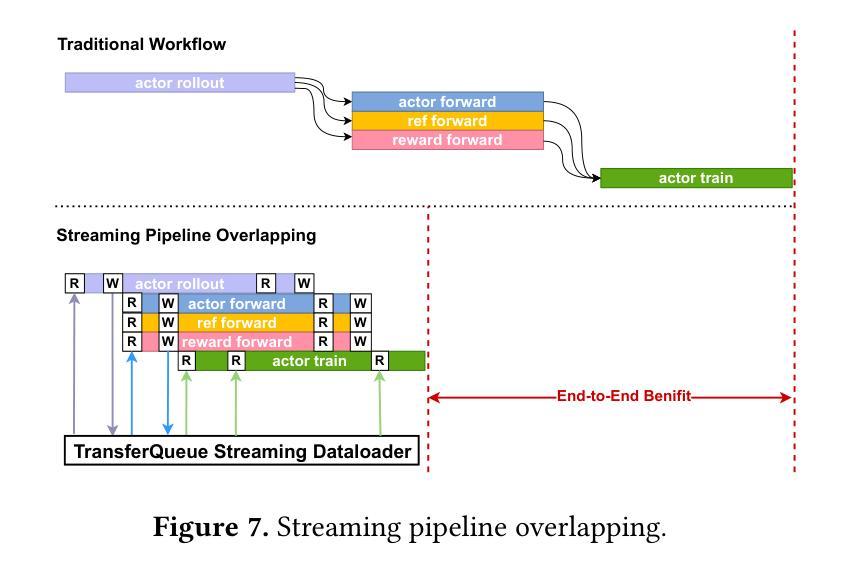
T3DM: Test-Time Training-Guided Distribution Shift Modelling for Temporal Knowledge Graph Reasoning
Authors:Yuehang Si, Zefan Zeng, Jincai Huang, Qing Cheng
Temporal Knowledge Graph (TKG) is an efficient method for describing the dynamic development of facts along a timeline. Most research on TKG reasoning (TKGR) focuses on modelling the repetition of global facts and designing patterns of local historical facts. However, they face two significant challenges: inadequate modeling of the event distribution shift between training and test samples, and reliance on random entity substitution for generating negative samples, which often results in low-quality sampling. To this end, we propose a novel distributional feature modeling approach for training TKGR models, Test-Time Training-guided Distribution shift Modelling (T3DM), to adjust the model based on distribution shift and ensure the global consistency of model reasoning. In addition, we design a negative-sampling strategy to generate higher-quality negative quadruples based on adversarial training. Extensive experiments show that T3DM provides better and more robust results than the state-of-the-art baselines in most cases.
时序知识图谱(TKG)是一种有效的方法,用于描述事实沿时间线的动态发展。关于TKG推理(TKGR)的研究大多集中在全球事实重复建模和局部历史事实设计模式上。然而,他们面临两大挑战:训练样本和测试样本之间事件分布变化的建模不足,以及依赖随机实体替换生成负样本,这往往导致采样质量低下。为此,我们提出了一种新型的分布特征建模方法,用于训练TKGR模型,即测试时训练引导的分布转移建模(T3DM),以根据分布变化调整模型,并确保模型推理的全局一致性。此外,我们设计了一种基于对抗训练的负采样策略,生成更高质量的负四元组。大量实验表明,在大多数情况下,T3DM提供的结果比以往最先进的基线更好、更稳健。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
时间知识图谱(TKG)是用于描述事实沿时间线的动态发展的有效方法。本文提出了新型的分发特征建模方法以训练TKGR模型,测试时训练引导的分布式转换模型(T3DM),可根据分布变化调整模型,确保模型推理的全局一致性。此外,我们设计了一种基于对抗训练的负采样策略,生成更高质量的负四元组。实验表明,在大多数情况下,T3DM相较于现有基线具有更好的性能和鲁棒性。
Key Takeaways:
- 时间知识图谱(TKG)是用于描述事实沿时间线的动态发展的方法。
- 当前TKGR研究面临两大挑战:训练与测试样本间事件分布变化的建模不足以及对随机实体替换生成负样本的依赖。
- 提出了一种新型的分布特征建模方法——测试时训练引导的分布式转换模型(T3DM),用于调整模型以适应分布变化并保障模型推理的全局一致性。
- 设计了一种基于对抗训练的负采样策略,生成更高质量的负四元组。
- T3DM在大多数情况下提供了相较于现有基线的更好和更稳健的结果。
- 通过广泛实验验证了T3DM的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

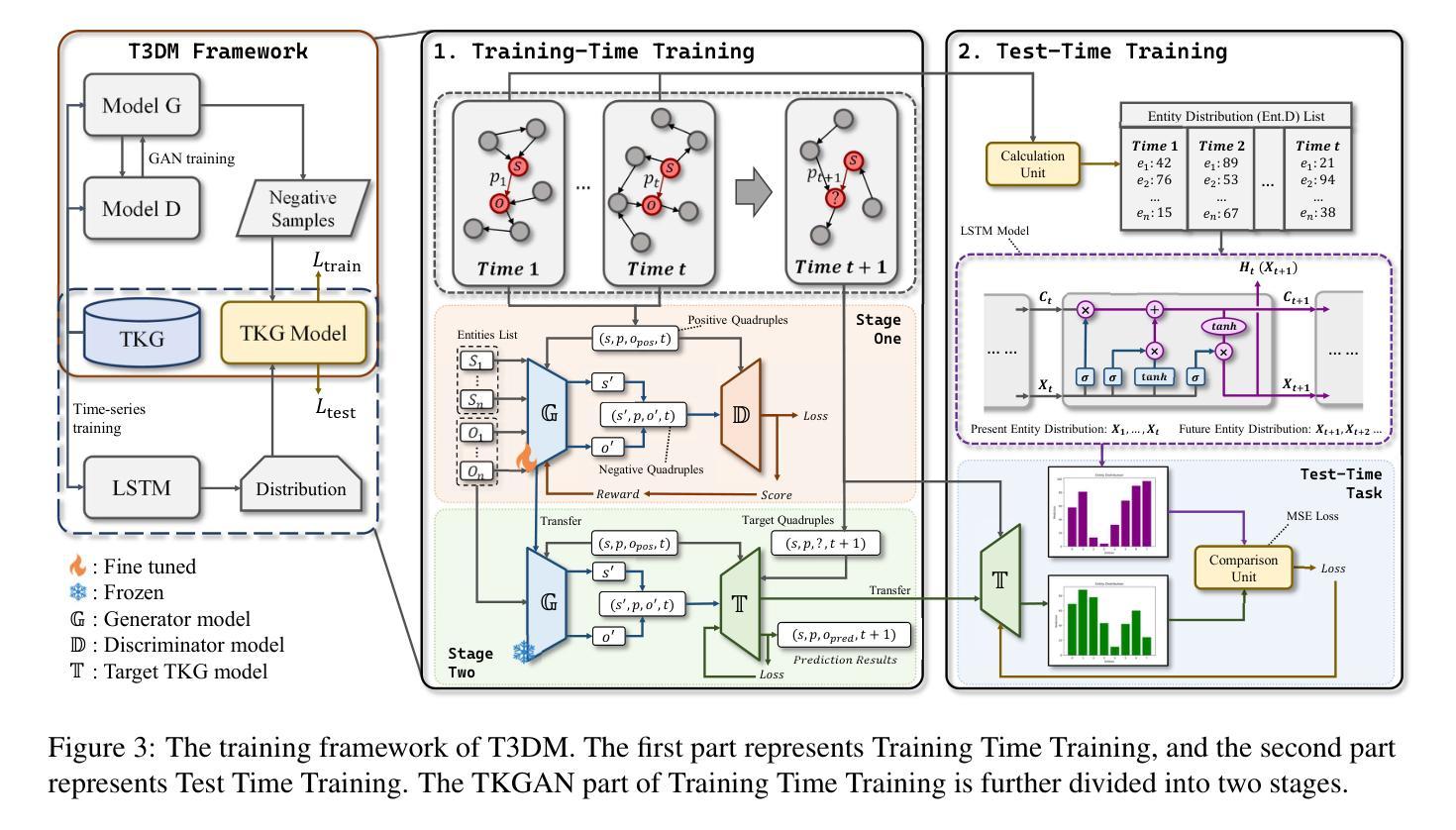

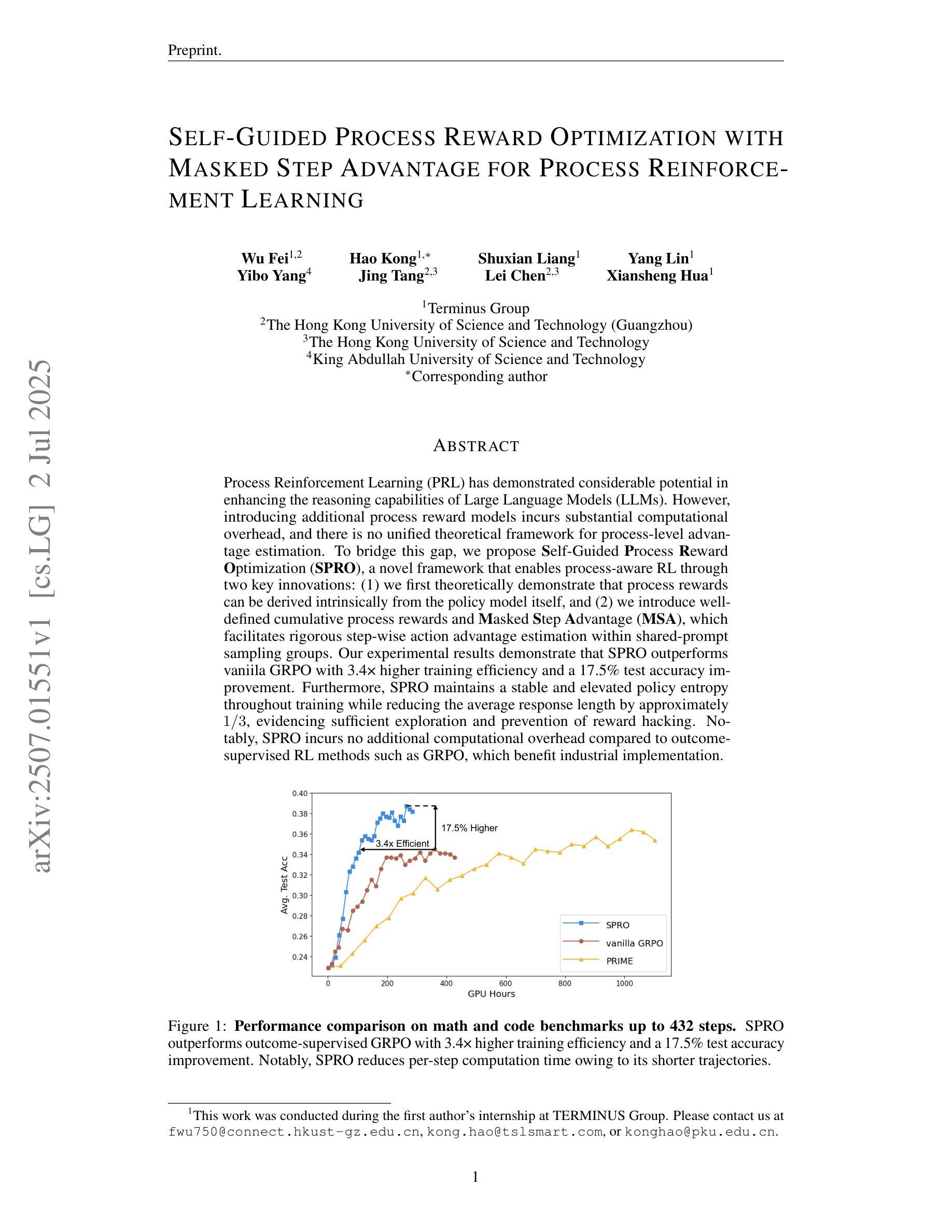
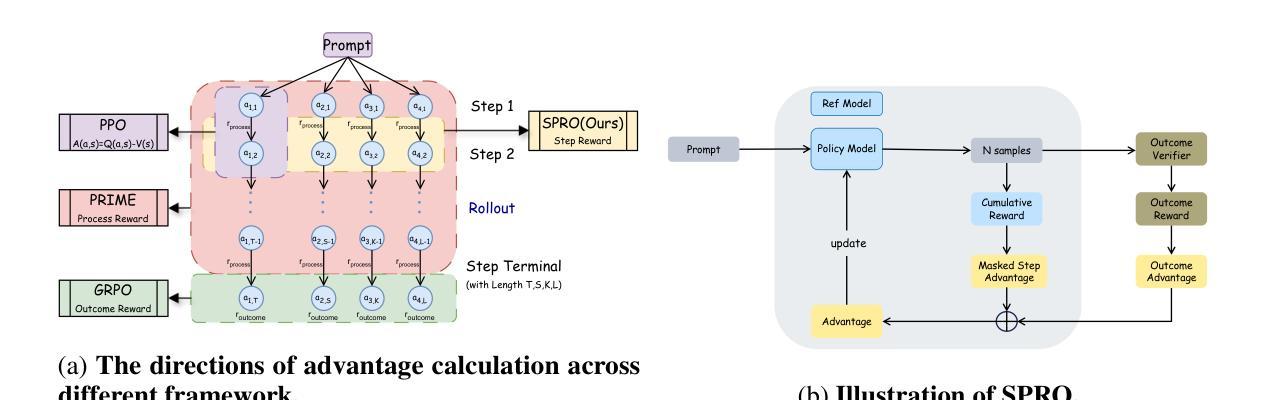
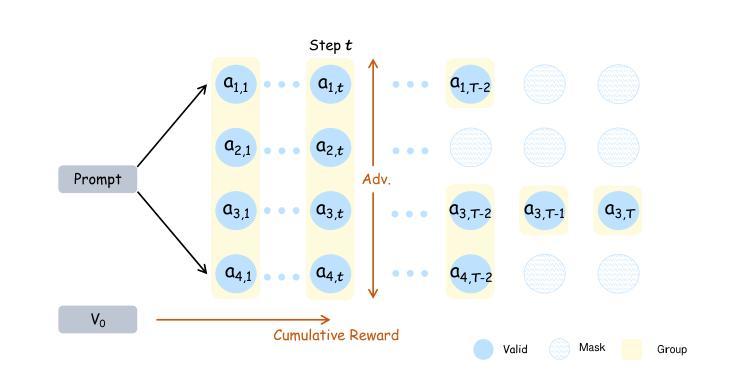
Self-Guided Process Reward Optimization with Masked Step Advantage for Process Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Wu Fei, Hao Kong, Shuxian Liang, Yang Lin, Yibo Yang, Jing Tang, Lei Chen, Xiansheng Hua
Process Reinforcement Learning(PRL) has demonstrated considerable potential in enhancing the reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models(LLMs). However, introducing additional process reward models incurs substantial computational overhead, and there is no unified theoretical framework for process-level advantage estimation. To bridge this gap, we propose \textbf{S}elf-Guided \textbf{P}rocess \textbf{R}eward \textbf{O}ptimization~(\textbf{SPRO}), a novel framework that enables process-aware RL through two key innovations: (1) we first theoretically demonstrate that process rewards can be derived intrinsically from the policy model itself, and (2) we introduce well-defined cumulative process rewards and \textbf{M}asked \textbf{S}tep \textbf{A}dvantage (\textbf{MSA}), which facilitates rigorous step-wise action advantage estimation within shared-prompt sampling groups. Our experimental results demonstrate that SPRO outperforms vaniila GRPO with 3.4x higher training efficiency and a 17.5% test accuracy improvement. Furthermore, SPRO maintains a stable and elevated policy entropy throughout training while reducing the average response length by approximately $1/3$, evidencing sufficient exploration and prevention of reward hacking. Notably, SPRO incurs no additional computational overhead compared to outcome-supervised RL methods such as GRPO, which benefit industrial implementation.
过程强化学习(PRL)在提高大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力方面显示出巨大潜力。然而,引入额外的流程奖励模型会产生大量的计算开销,并且没有统一的理论框架来进行流程级别的优势估计。为了填补这一空白,我们提出了自引导流程奖励优化(SPRO)这一新型框架,它通过两个关键创新点实现了流程感知的RL:(1)我们首先从理论上证明,流程奖励可以从策略模型本身内在地派生出来;(2)我们引入了定义良好的累积流程奖励和遮罩步骤优势(MSA),这有助于在共享提示采样组内进行严格的逐步行动优势估计。我们的实验结果表明,SPRO优于基线GRPO,训练效率提高了3.4倍,测试精度提高了17.5%。此外,SPRO在整个训练过程中保持了稳定和较高的策略熵,同时平均响应长度减少了约三分之一,证明了其足够的探索能力和防止奖励作弊的效果。值得注意的是,与结果监督的RL方法(如GRPO)相比,SPRO没有额外的计算开销,这对其在工业实施中的应用非常有利。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
强化学习在提升大型语言模型的推理能力方面具有巨大潜力。针对过程奖励模型引入的计算开销较大及缺乏统一理论框架的问题,提出了自指导过程奖励优化(SPRO)框架,通过从政策模型本身内在推导过程奖励和引入累积过程奖励和遮罩步骤优势,实现了过程感知的强化学习。实验结果表明,SPRO在训练效率、测试精度、策略熵以及响应长度控制等方面均有显著提升,且未增加额外计算开销,适合工业化实施。
Key Takeaways
- 强化学习(RL)能提升大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力。
- SPRO框架解决了过程奖励模型引入的计算开销问题。
- SPRO通过从政策模型本身推导过程奖励,实现了过程感知的强化学习。
- 引入累积过程奖励和遮罩步骤优势,实现了严格逐步行动优势估计。
- SPRO在训练效率、测试精度上有显著提升,并且维持稳定的策略熵。
- SPRO能够减少平均响应长度,实现更高效的响应。
点此查看论文截图
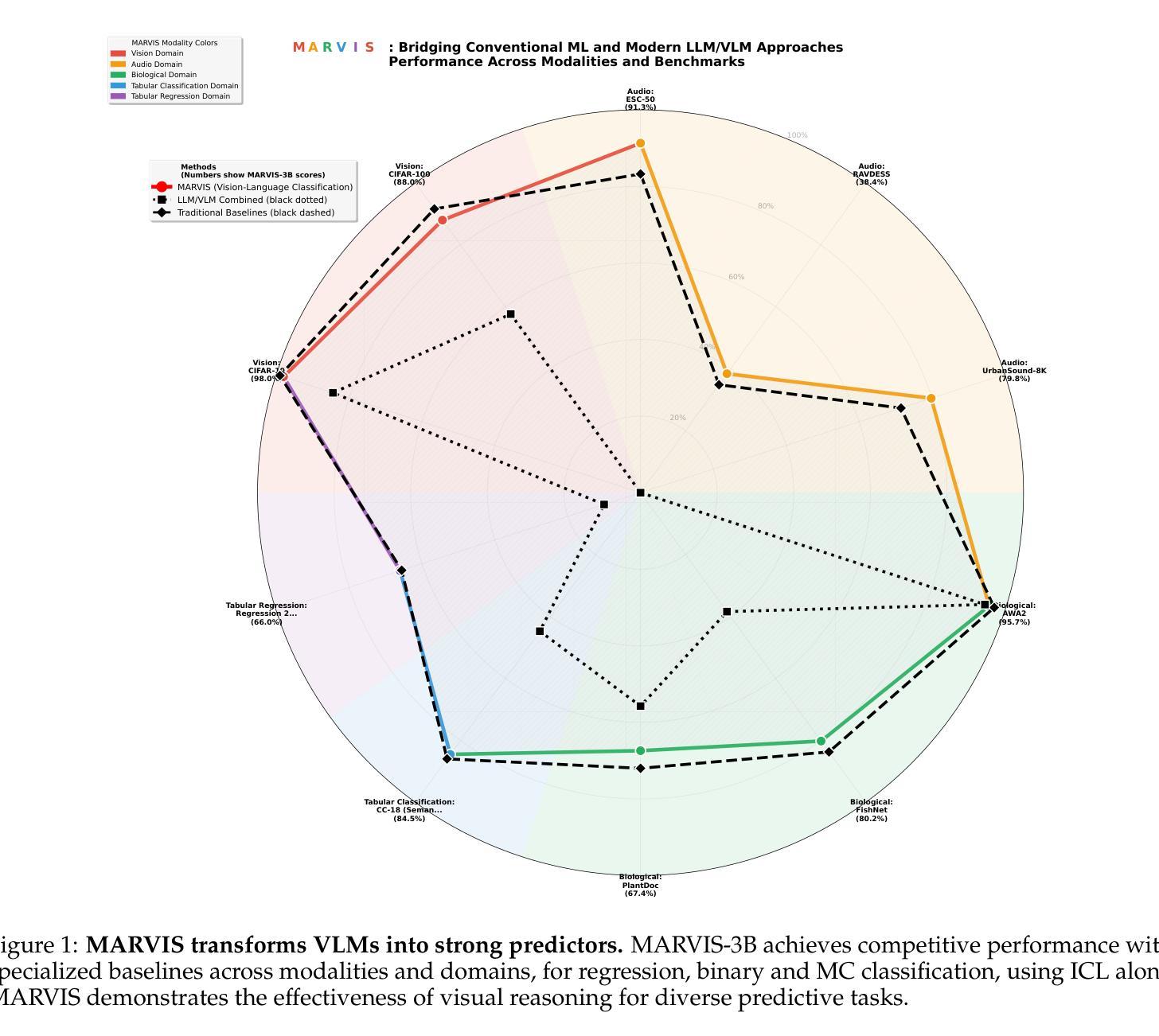
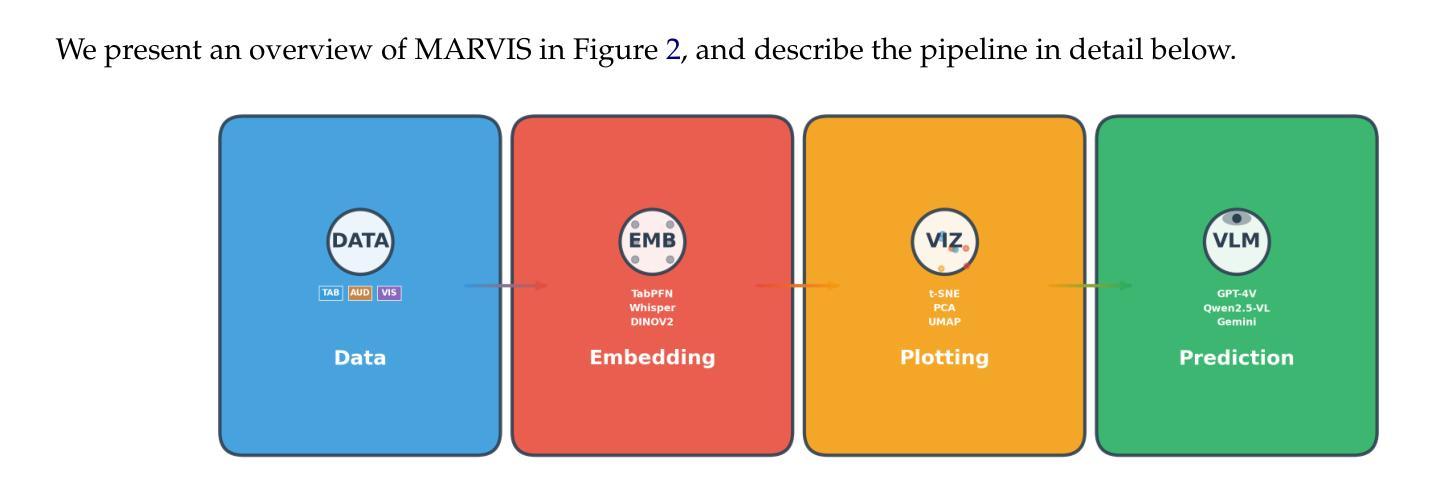
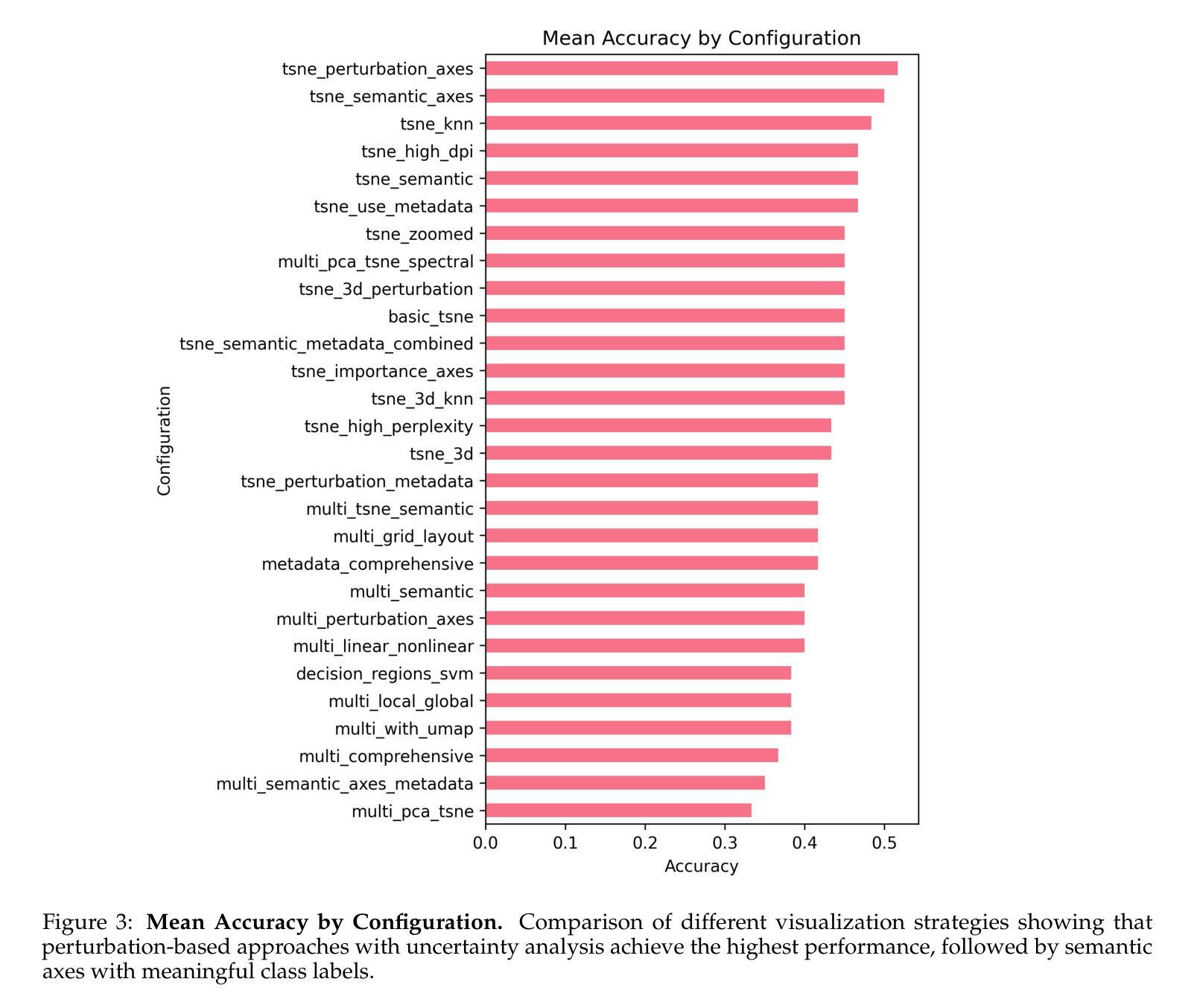
MARVIS: Modality Adaptive Reasoning over VISualizations
Authors:Benjamin Feuer, Lennart Purucker, Oussama Elachqar, Chinmay Hegde
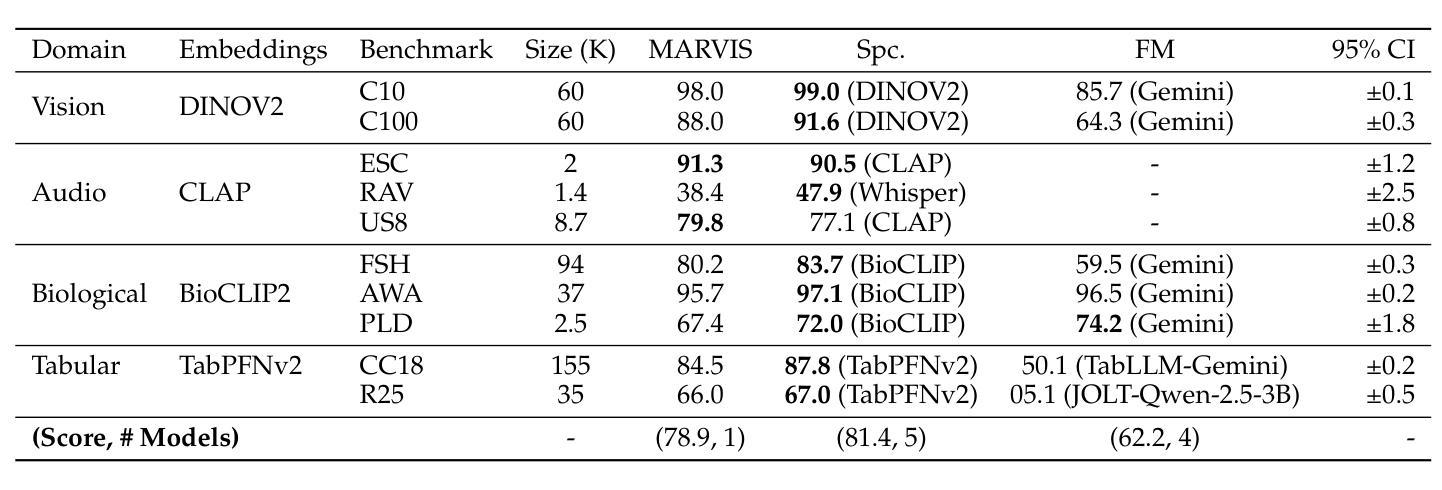
Scientific applications of machine learning often rely on small, specialized models tuned to particular domains. Such models often achieve excellent performance, but lack flexibility. Foundation models offer versatility, but typically underperform specialized approaches, especially on non-traditional modalities and long-tail domains. We propose MARVIS (Modality Adaptive Reasoning over VISualizations), a training-free method that enables even small vision-language models to predict any data modality with high accuracy. MARVIS transforms latent embedding spaces into visual representations and then leverages the spatial and fine-grained reasoning skills of VLMs to successfully interpret and utilize them. MARVIS achieves competitive performance on vision, audio, biological, and tabular domains using a single 3B parameter model, achieving results that beat Gemini by 16% on average and approach specialized methods, without exposing personally identifiable information (P.I.I.) or requiring any domain-specific training. We open source our code and datasets at https://github.com/penfever/marvis
机器学习在科学应用上通常依赖于针对特定领域进行微调的小型专业模型。这些模型通常性能出色,但缺乏灵活性。基础模型提供了多功能性,但在非传统模式和长尾领域上通常表现不佳。我们提出了MARVIS(可视化上的模态自适应推理),这是一种无需训练的方法,即使对于小型视觉语言模型,也能以高准确性预测任何数据模态。MARVIS将潜在嵌入空间转换为可视化表示形式,然后利用视觉语言模型的空间化和精细推理技能来成功解释和利用它们。使用单个3B参数模型,MARVIS在视觉、音频、生物和表格领域实现了有竞争力的表现,平均击败双子座模型达1.倍结果,并接近专业方法的应用效果,同时不涉及个人身份信息的暴露(PII)或任何特定领域的训练需求。我们在https://github.com/penfever/marvis上公开了我们的代码和数据集。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:机器学习的科学应用通常需要针对特定领域调整小型专用模型,虽然这些模型表现出卓越性能,但缺乏灵活性。而基础模型虽然具有通用性,但在非传统模态和长尾领域上的表现通常较差。本研究提出了一种无需训练的MARVIS方法,它可以让即使是小型视觉语言模型也能以高准确率预测任何数据模态。MARVIS通过将潜在嵌入空间转换为可视化表示,然后利用视觉语言模型的空间和精细推理技能来成功解释和利用它们。使用单一3B参数模型,MARVIS在视觉、音频、生物和表格领域实现了出色的性能表现,平均比Gemini高出16%,且无需特定领域的训练或暴露个人信息。我们已在https://github.com/penfever/marvis开源了代码和数据集。
Key Takeaways:
- 机器学习的科学应用受限于特定领域的专用模型与通用模型间的权衡。
- 专用模型表现出卓越性能但缺乏灵活性,而基础模型具备通用性但在非传统和长尾领域表现不佳。
- MARVIS方法是一种无需训练的方法,能在小型视觉语言模型上实现高准确率的多种数据模态预测。
- MARVIS通过将潜在嵌入空间转换为可视化表示来提高模型的推理能力。
- MARVIS在多种领域(包括视觉、音频、生物和表格)实现了出色的性能表现。
- MARVIS相较于Gemini平均提高了16%的性能表现。
点此查看论文截图

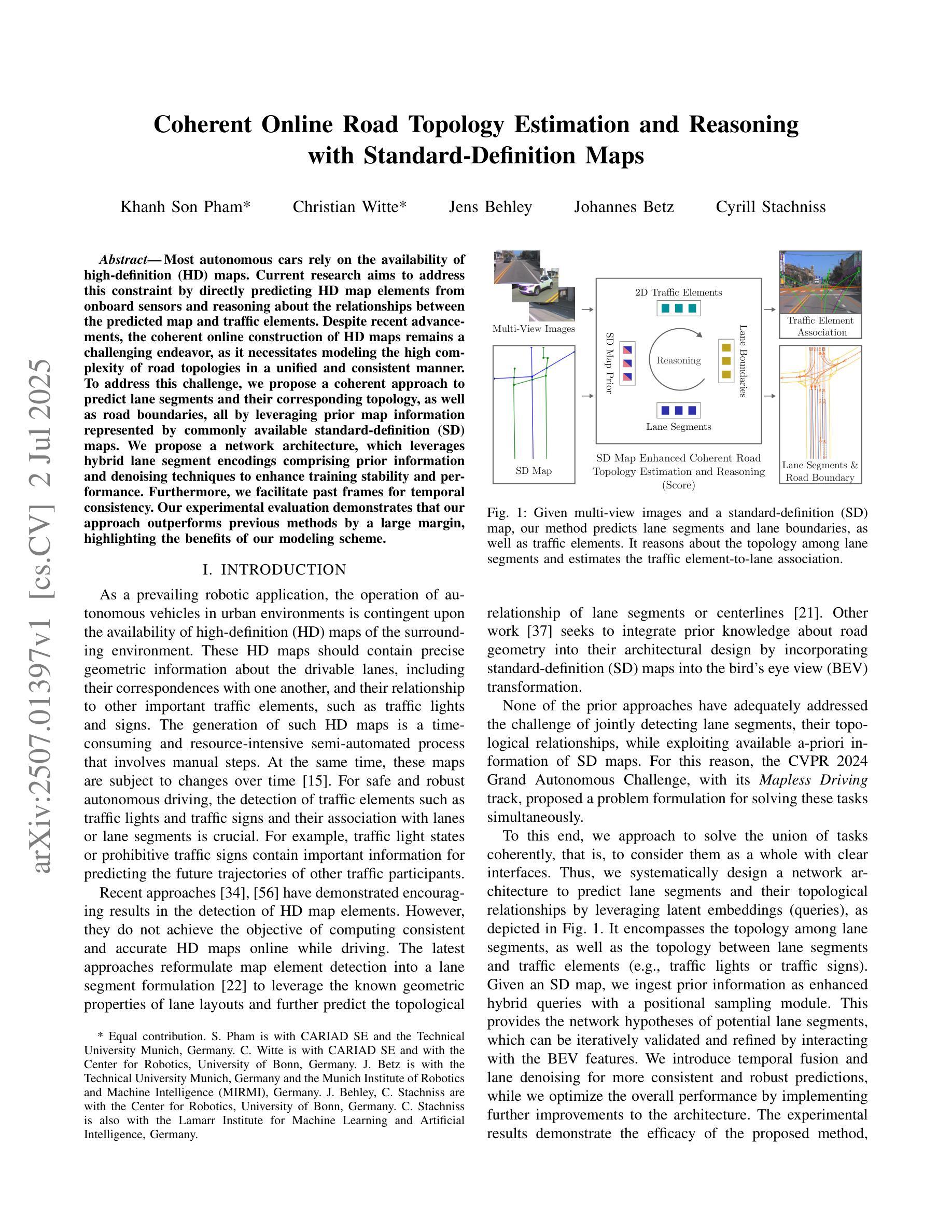
Coherent Online Road Topology Estimation and Reasoning with Standard-Definition Maps
Authors:Khanh Son Pham, Christian Witte, Jens Behley, Johannes Betz, Cyrill Stachniss
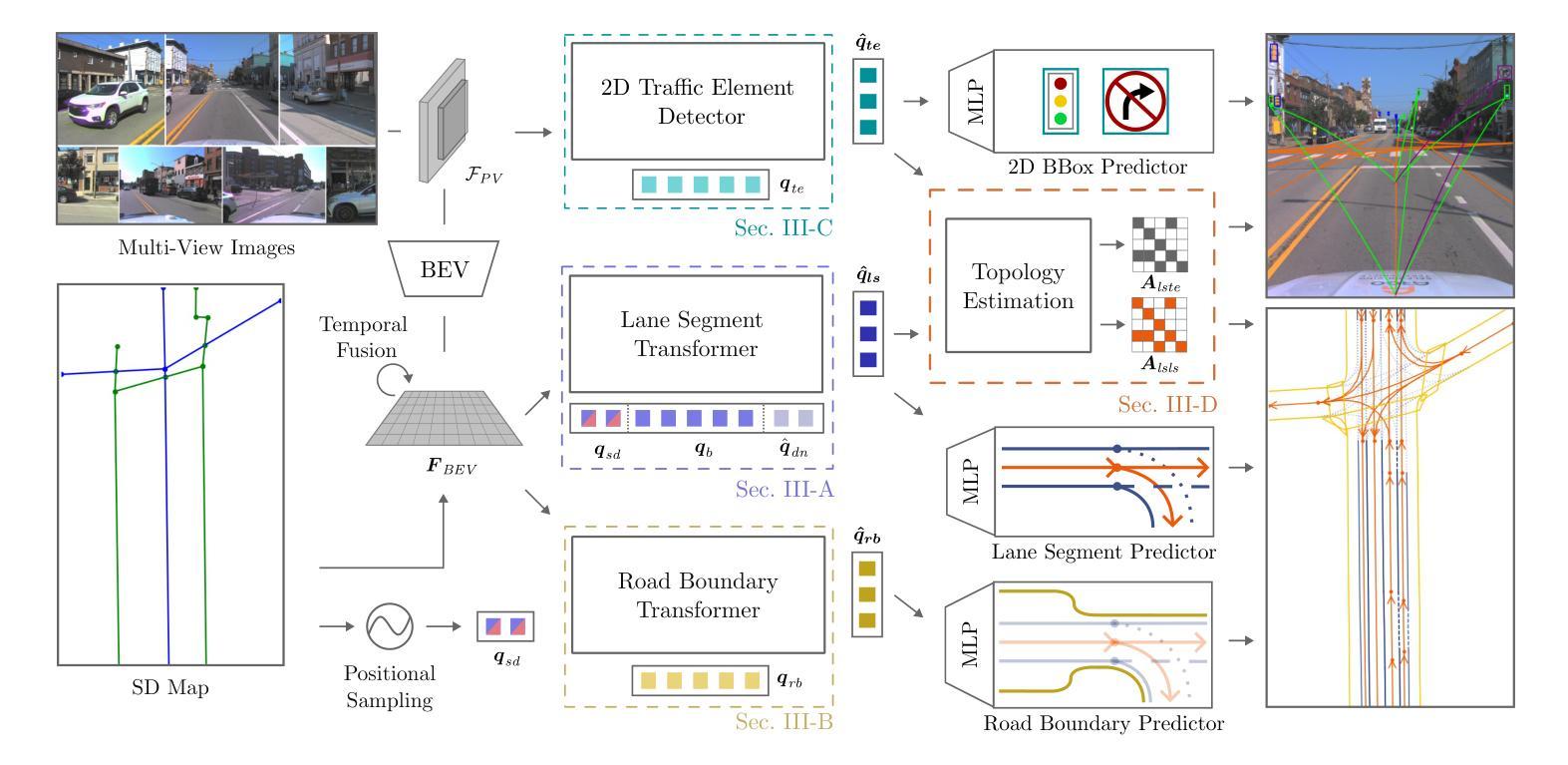
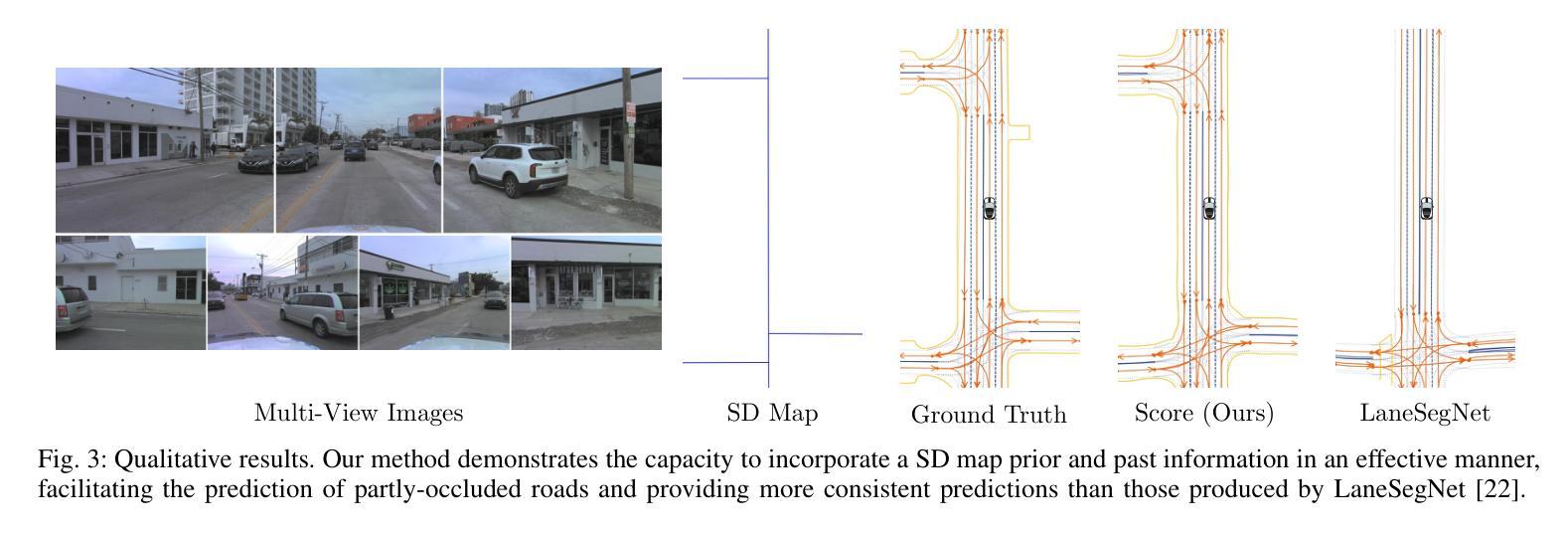
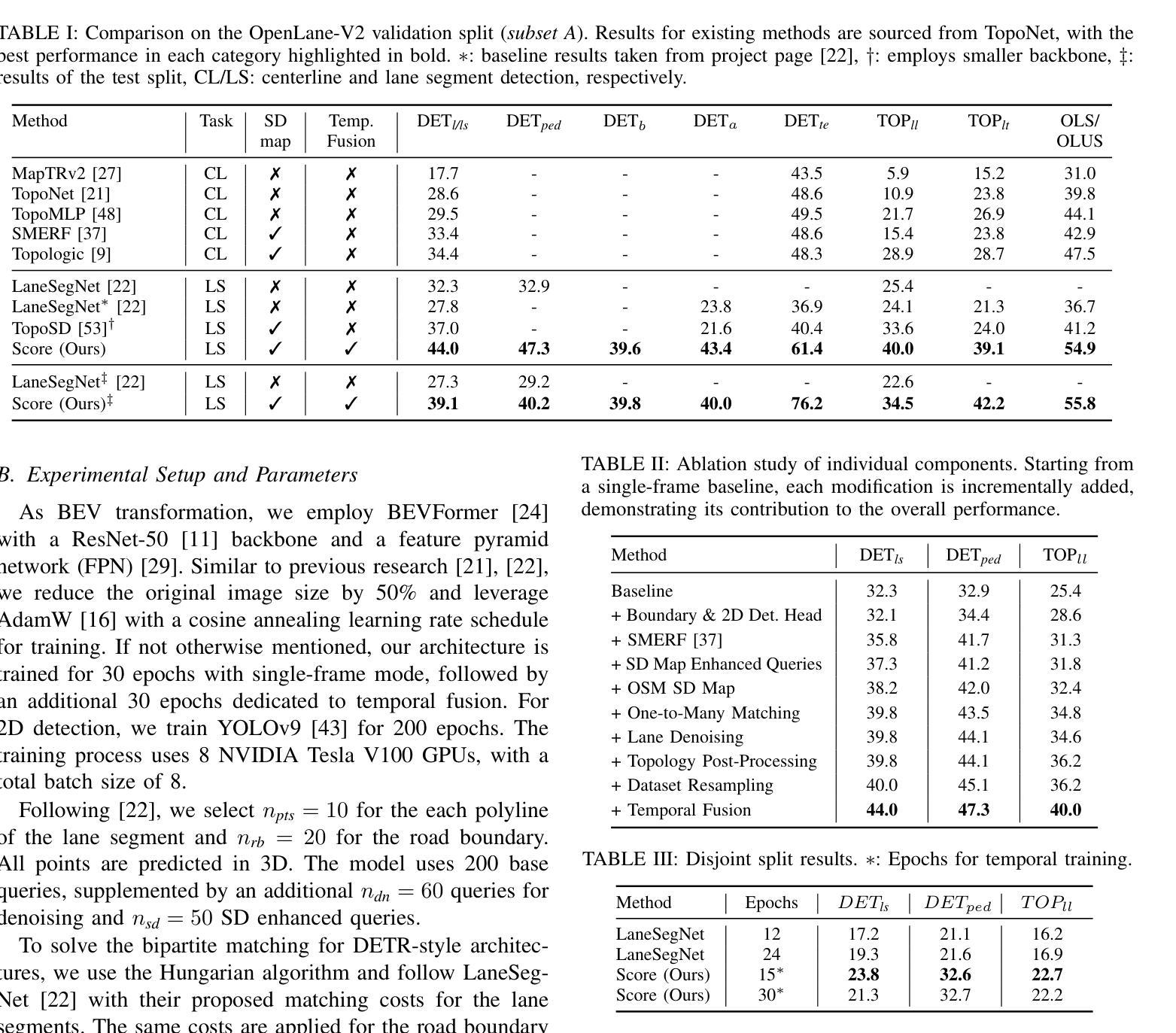
Most autonomous cars rely on the availability of high-definition (HD) maps. Current research aims to address this constraint by directly predicting HD map elements from onboard sensors and reasoning about the relationships between the predicted map and traffic elements. Despite recent advancements, the coherent online construction of HD maps remains a challenging endeavor, as it necessitates modeling the high complexity of road topologies in a unified and consistent manner. To address this challenge, we propose a coherent approach to predict lane segments and their corresponding topology, as well as road boundaries, all by leveraging prior map information represented by commonly available standard-definition (SD) maps. We propose a network architecture, which leverages hybrid lane segment encodings comprising prior information and denoising techniques to enhance training stability and performance. Furthermore, we facilitate past frames for temporal consistency. Our experimental evaluation demonstrates that our approach outperforms previous methods by a large margin, highlighting the benefits of our modeling scheme.
大部分自动驾驶汽车都依赖于高清(HD)地图的可用性。目前的研究旨在通过直接从车载传感器预测高清地图元素并推理预测地图和交通元素之间的关系来解决这一限制。尽管最近有进展,但在线构建连贯的高清地图仍然是一项具有挑战性的工作,因为它需要以统一和连贯的方式对道路拓扑的高复杂性进行建模。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了一种连贯的方法,可以预测车道段及其相应的拓扑结构以及道路边界,这充分利用了常见的标准定义(SD)地图所表示的先验地图信息。我们提出了一种网络架构,该架构利用包含先验信息和去噪技术的混合车道段编码,以提高训练稳定性和性能。此外,我们还利用过去的帧来实现时间一致性。我们的实验评估表明,我们的方法大大优于以前的方法,突出了我们建模方案的优点。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at IROS 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种利用标准定义地图的先验信息,预测高清晰度地图的车道线段及其拓扑结构和道路边界的连贯方法。该方法采用网络架构,融合了先验信息的混合车道段编码和降噪技术,以提高训练稳定性和性能。同时,利用过去帧实现时间一致性。实验评估表明,该方法在性能上大大优于以前的方法,突出了建模方案的优点。
Key Takeaways
- 大多数自动驾驶汽车依赖于高清晰度(HD)地图的可用性。
- 当前研究旨在通过直接预测HD地图元素和推理预测地图与交通元素之间的关系来解决这一限制。
- 在线构建HD地图是一个具有挑战性的任务,需要统一和一致地建模道路拓扑的高复杂性。
- 提出了一种连贯的方法,利用标准定义(SD)地图的先验信息来预测车道线段及其拓扑结构和道路边界。
- 采用网络架构,融合先验信息的混合车道段编码和降噪技术,提高训练稳定性和性能。
- 利用过去帧实现时间一致性,提高预测准确性。
点此查看论文截图
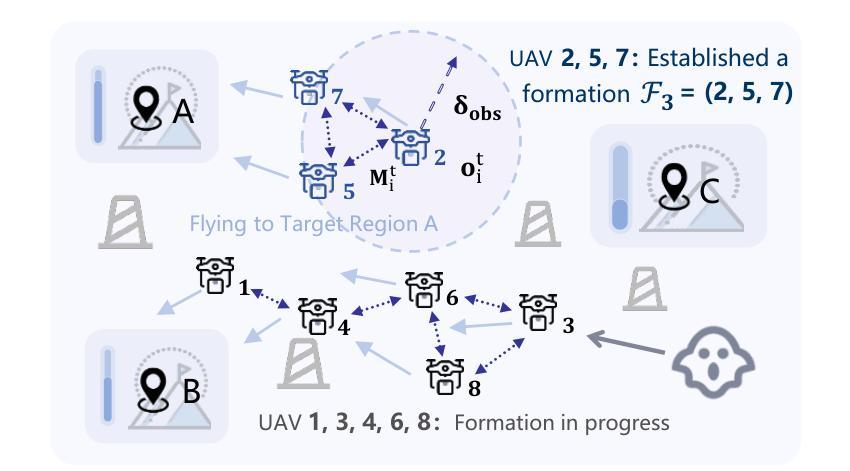
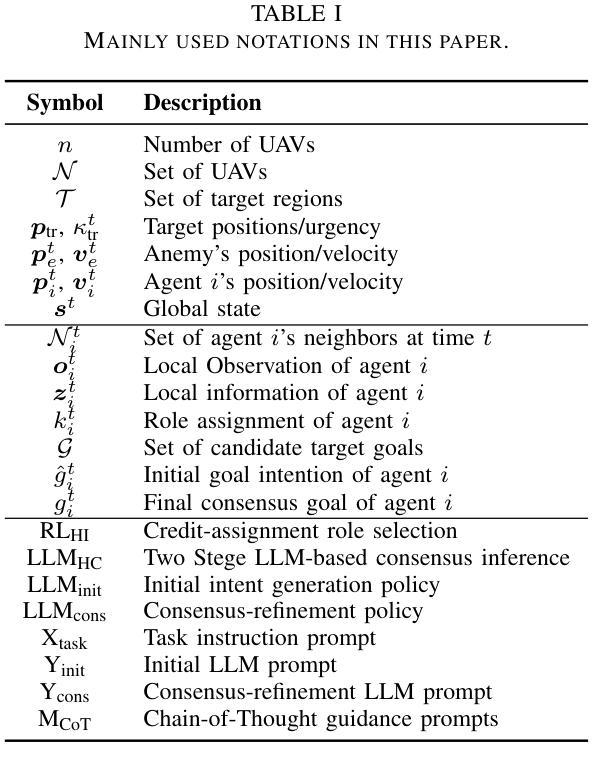
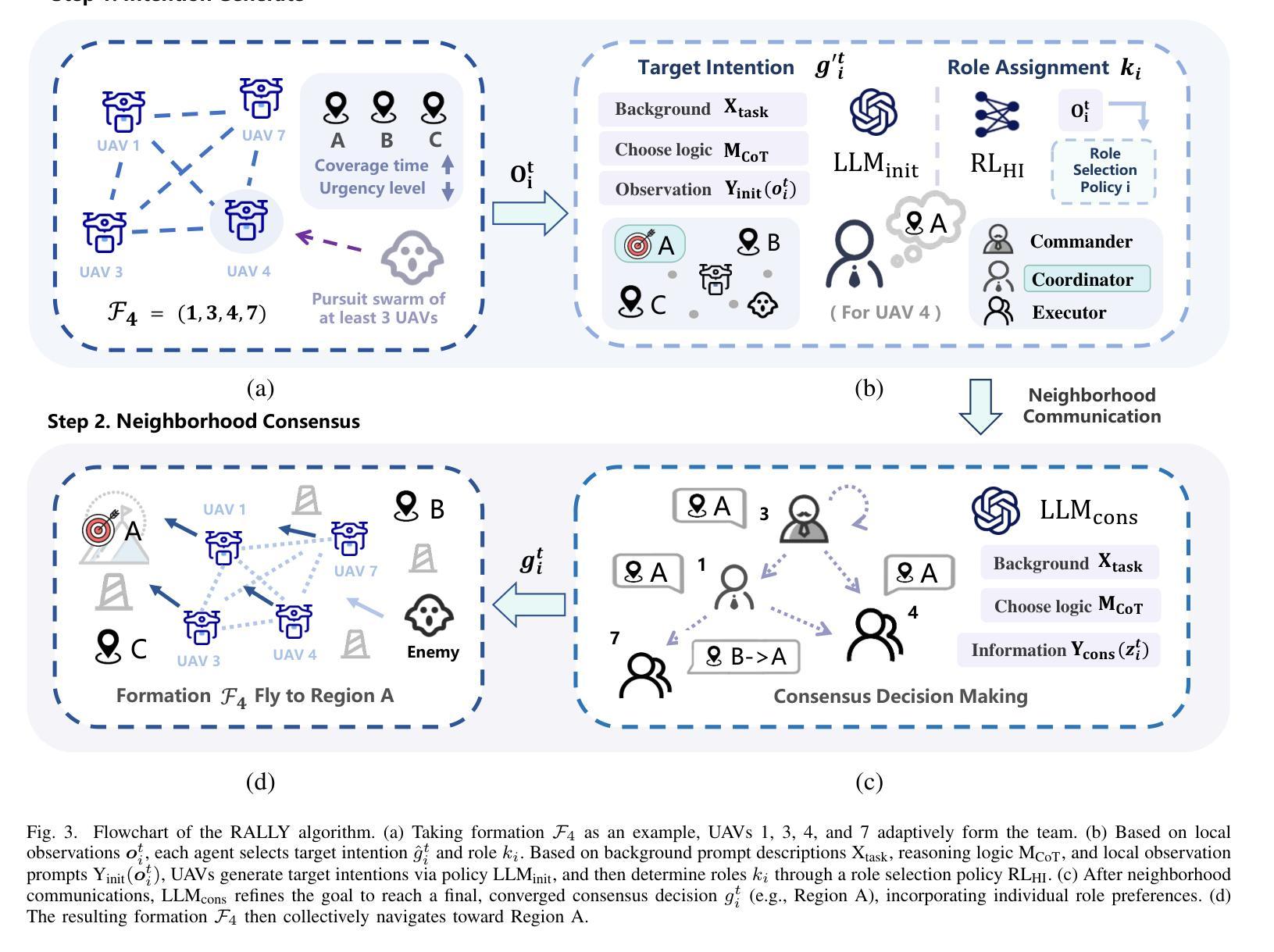
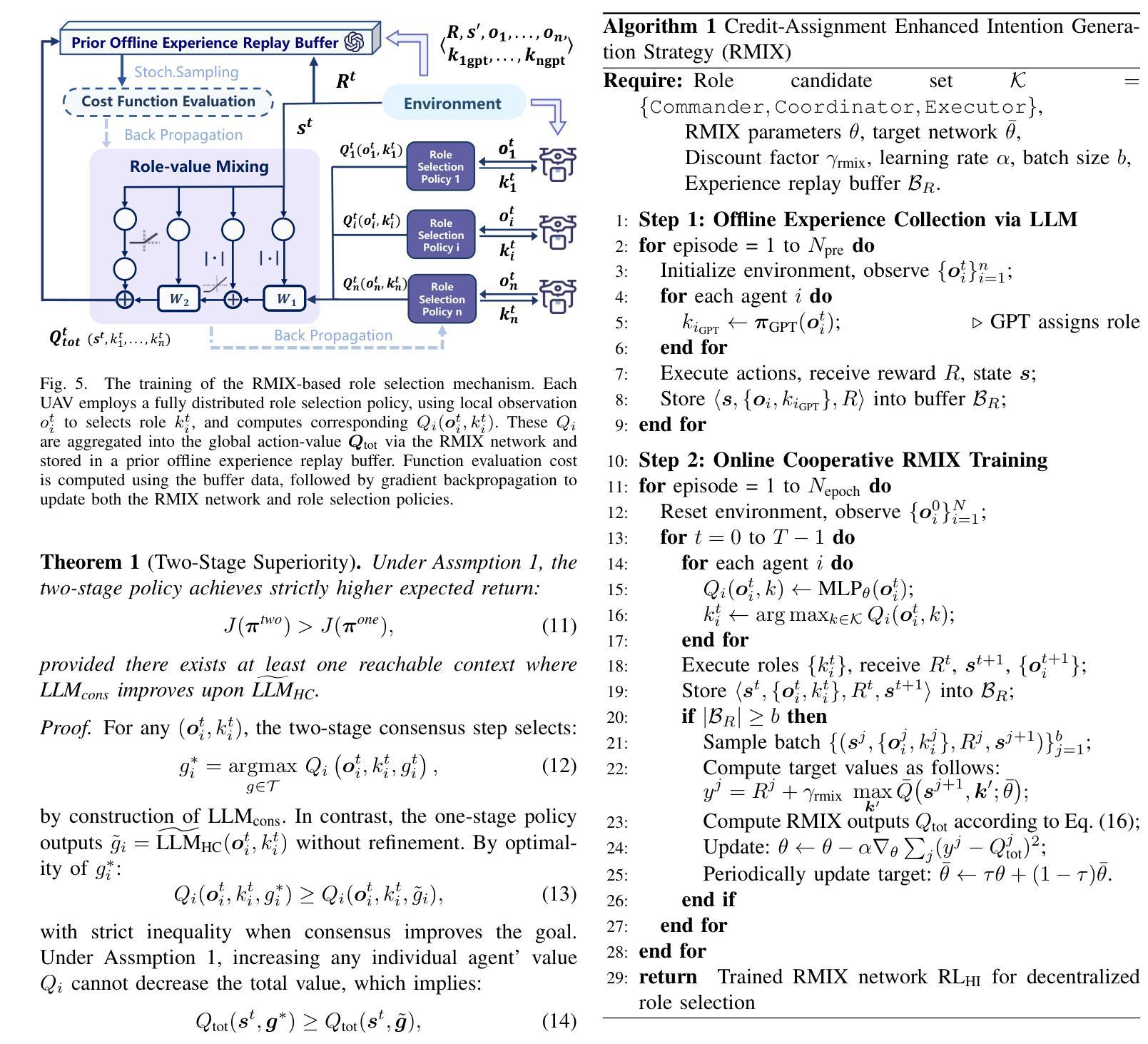
RALLY: Role-Adaptive LLM-Driven Yoked Navigation for Agentic UAV Swarms
Authors:Ziyao Wang, Rongpeng Li, Sizhao Li, Yuming Xiang, Haiping Wang, Zhifeng Zhao, Honggang Zhang
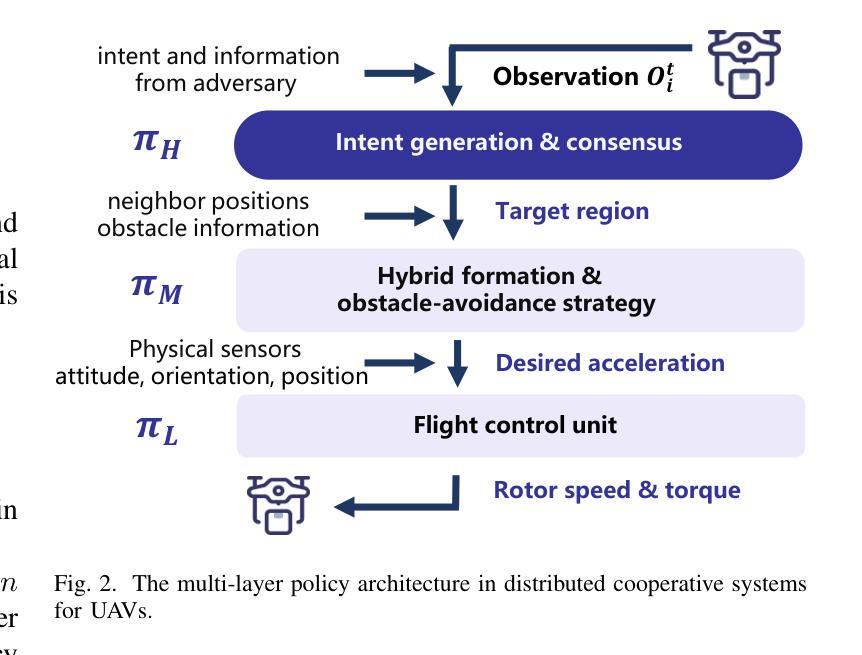
Intelligent control of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) swarms has emerged as a critical research focus, and it typically requires the swarm to navigate effectively while avoiding obstacles and achieving continuous coverage over multiple mission targets. Although traditional Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) approaches offer dynamic adaptability, they are hindered by the semantic gap in numerical communication and the rigidity of homogeneous role structures, resulting in poor generalization and limited task scalability. Recent advances in Large Language Model (LLM)-based control frameworks demonstrate strong semantic reasoning capabilities by leveraging extensive prior knowledge. However, due to the lack of online learning and over-reliance on static priors, these works often struggle with effective exploration, leading to reduced individual potential and overall system performance. To address these limitations, we propose a Role-Adaptive LLM-Driven Yoked navigation algorithm RALLY. Specifically, we first develop an LLM-driven semantic decision framework that uses structured natural language for efficient semantic communication and collaborative reasoning. Afterward, we introduce a dynamic role-heterogeneity mechanism for adaptive role switching and personalized decision-making. Furthermore, we propose a Role-value Mixing Network (RMIX)-based assignment strategy that integrates LLM offline priors with MARL online policies to enable semi-offline training of role selection strategies. Experiments in the Multi-Agent Particle Environment (MPE) environment and a Software-In-The-Loop (SITL) platform demonstrate that RALLY outperforms conventional approaches in terms of task coverage, convergence speed, and generalization, highlighting its strong potential for collaborative navigation in agentic multi-UAV systems.
无人机群智能控制已成为重要的研究焦点,通常需要它们在有效导航的同时避免障碍物,并对多个任务目标实现连续覆盖。尽管传统的多智能体强化学习(MARL)方法提供了动态适应性,但它们受到数值通信中的语义差距和同质角色结构的限制,导致泛化能力较差和任务可扩展性有限。最近基于大型语言模型(LLM)的控制框架的进展,通过利用丰富的先验知识展示了强大的语义推理能力。然而,由于缺乏在线学习和过度依赖静态先验知识,这些工作往往难以进行有效的探索,导致个体潜力下降和整体系统性能降低。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一种基于自适应角色的LLM驱动导航算法RALLY。具体来说,我们首先开发了一个基于LLM的语义决策框架,使用结构化自然语言进行高效的语义通信和协作推理。随后,我们引入了一种动态角色异质性机制,用于自适应角色切换和个性化决策。此外,我们提出了一种基于角色价值混合网络(RMIX)的分配策略,该策略结合了LLM的离线先验知识和MARL的在线策略,实现了角色选择策略的半离线训练。在Multi-Agent粒子环境(MPE)环境和软件在环(SITL)平台上的实验表明,RALLY在任务覆盖、收敛速度和泛化方面优于传统方法,突显了其在智能多无人机系统协同导航中的强大潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
无人机群(UAVs)的智能控制是当下重要的研究焦点。这需要群体进行高效的导航,同时避免障碍并实现对多个任务目标的连续覆盖。传统的多智能体强化学习(MARL)方法虽然具有动态适应性,但它们受到数值通信中的语义差距和同质角色结构僵化等限制,导致泛化性能不佳和任务可扩展性有限。基于大型语言模型(LLM)的控制框架具有强大的语义推理能力,通过利用丰富的先验知识展现了出色的表现。然而,由于缺乏在线学习和对静态先验的过度依赖,这些研究在有效探索方面面临挑战,导致个体潜能和系统整体性能降低。为解决这些局限,我们提出一种角色自适应的LLM驱动协同导航算法RALLY。具体而言,我们构建了LLM驱动的语义决策框架,利用结构化自然语言进行高效的语义通信和协作推理。随后引入动态角色异质性机制,实现自适应角色切换和个性化决策。此外,我们提出基于角色价值混合网络(RMIX)的分配策略,融合LLM的离线先验知识与MARL的在线策略,实现角色选择策略的半离线训练。在Multi-Agent粒子环境(MPE)和Software-In-The-Loop(SITL)平台的实验表明,RALLY在任务覆盖、收敛速度和泛化等方面优于传统方法,突显其在智能多无人机系统协作导航中的强大潜力。
关键见解
- 无人机群智能控制是当前关键研究焦点,需要实现高效导航、障碍避免及多任务目标覆盖。
- 传统MARL方法虽具有动态适应性,但受语义差距和角色结构限制,泛化性能有限。
- 基于LLM的控制框架展现出强大的语义推理能力,利用先验知识解决复杂任务。
- LLM方法缺乏在线学习和过度依赖静态先验知识,影响有效探索和系统性能。
- RALLY算法结合LLM和MARL的优势,通过语义决策框架和动态角色机制提升系统性能。
- RALLY采用角色价值混合网络(RMIX)实现离线与在线策略融合,优化角色选择策略训练。
点此查看论文截图

Symbolic or Numerical? Understanding Physics Problem Solving in Reasoning LLMs
Authors:Nifu Dan, Yujun Cai, Yiwei Wang
Navigating the complexities of physics reasoning has long been a difficult task for Large Language Models (LLMs), requiring a synthesis of profound conceptual understanding and adept problem-solving techniques. In this study, we investigate the application of advanced instruction-tuned reasoning models, such as Deepseek-R1, to address a diverse spectrum of physics problems curated from the challenging SciBench benchmark. Our comprehensive experimental evaluation reveals the remarkable capabilities of reasoning models. Not only do they achieve state-of-the-art accuracy in answering intricate physics questions, but they also generate distinctive reasoning patterns that emphasize on symbolic derivation. Furthermore, our findings indicate that even for these highly sophisticated reasoning models, the strategic incorporation of few-shot prompting can still yield measurable improvements in overall accuracy, highlighting the potential for continued performance gains.
长期以来,在物理推理的复杂性中导航对于大型语言模型(LLM)来说是一项艰巨的任务,需要深刻的概念理解和熟练的问题解决技术的结合。在这项研究中,我们调查了高级指令调整推理模型(如Deepseek-R1)在解决从具有挑战性的SciBench基准测试中精选的各种物理问题方面的应用。我们的综合实验评估显示了推理模型的卓越能力。它们不仅在回答复杂物理问题时达到了最先进的准确性,而且还产生了强调符号推导的独特推理模式。此外,我们的研究结果表明,即使是对于这些高度复杂的推理模型,战略性地采用少量提示仍然可以提高整体准确性,这凸显了持续提高性能的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:本研究探讨了先进的指令优化推理模型(如Deepseek-R1)在应对来自SciBench基准挑战的多样化物理问题时的应用。实验评估表明,这些推理模型不仅能在回答复杂物理问题方面达到最新技术水平,还展现出独特的强调符号推导的推理模式。此外,研究还发现,即使对这些高度先进的推理模型,通过少样本提示的战略整合仍然能提高总体精度,展示了潜在的进一步性能提升空间。
Key Takeaways:
- 先进的指令优化推理模型在解决物理问题方面表现出卓越的能力,特别是在回答复杂物理问题方面达到最新技术水平。
- 这些推理模型强调符号推导的重要性,展现出独特的推理模式。
- 通过结合少样本提示,这些推理模型的性能可以进一步提高,显示出潜在的进一步性能提升空间。
- 这种结合方法对于高度先进的推理模型仍然有效。
- 这种研究对于提高大语言模型在物理领域的推理能力具有重要意义。
- Deepseek-R1等模型的应用扩展了它们在解决特定领域问题时的能力边界。
点此查看论文截图

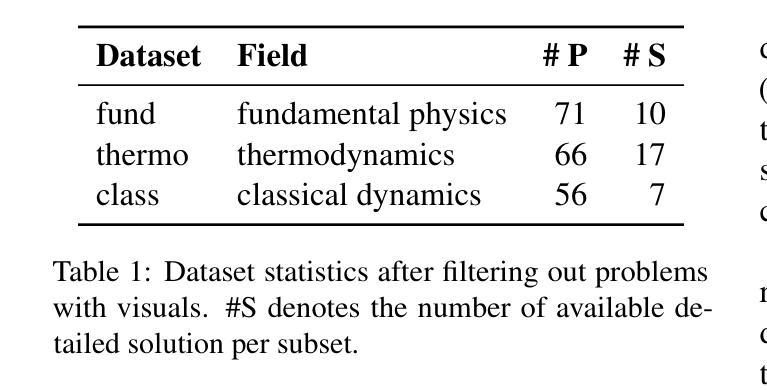
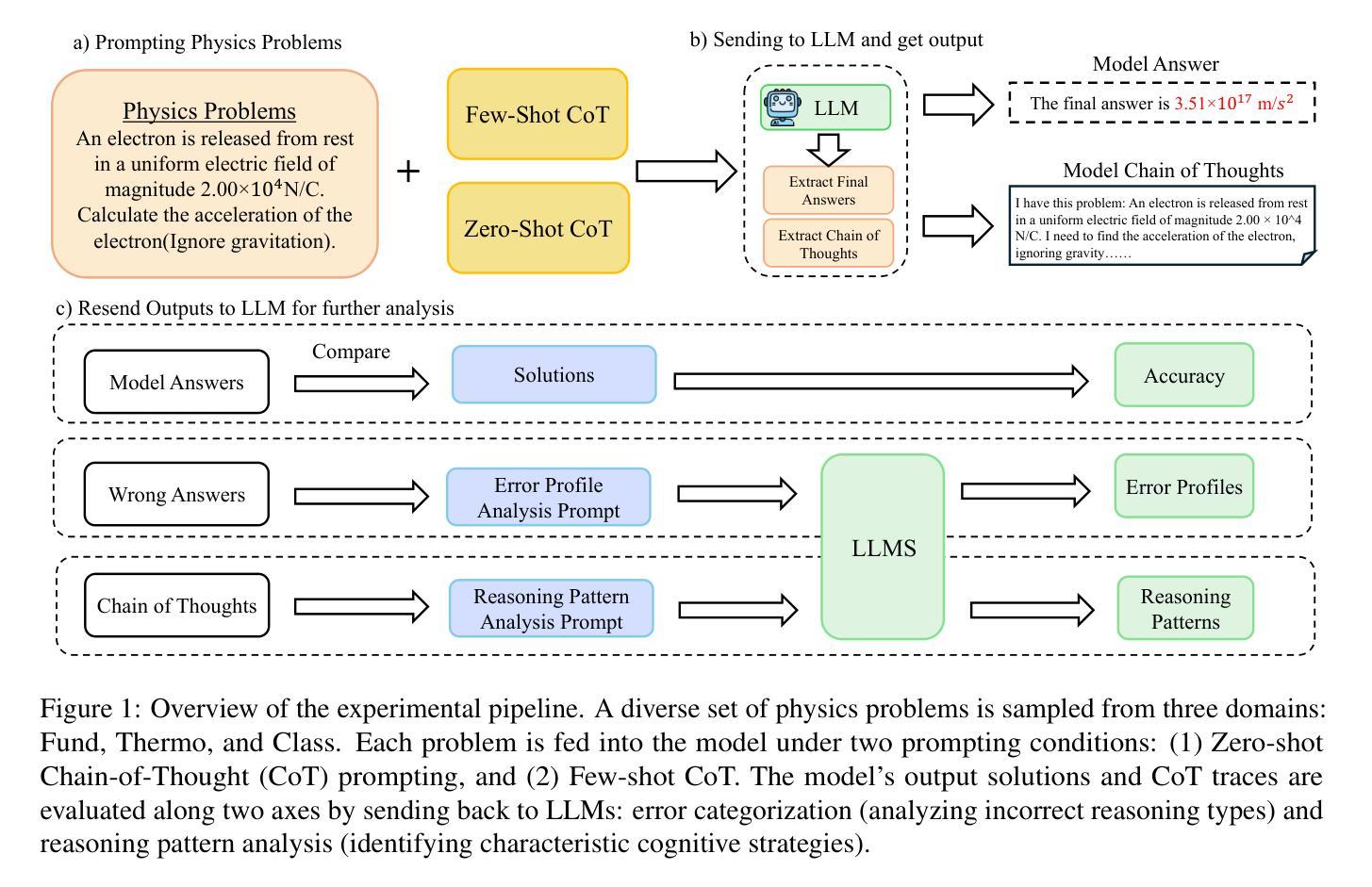
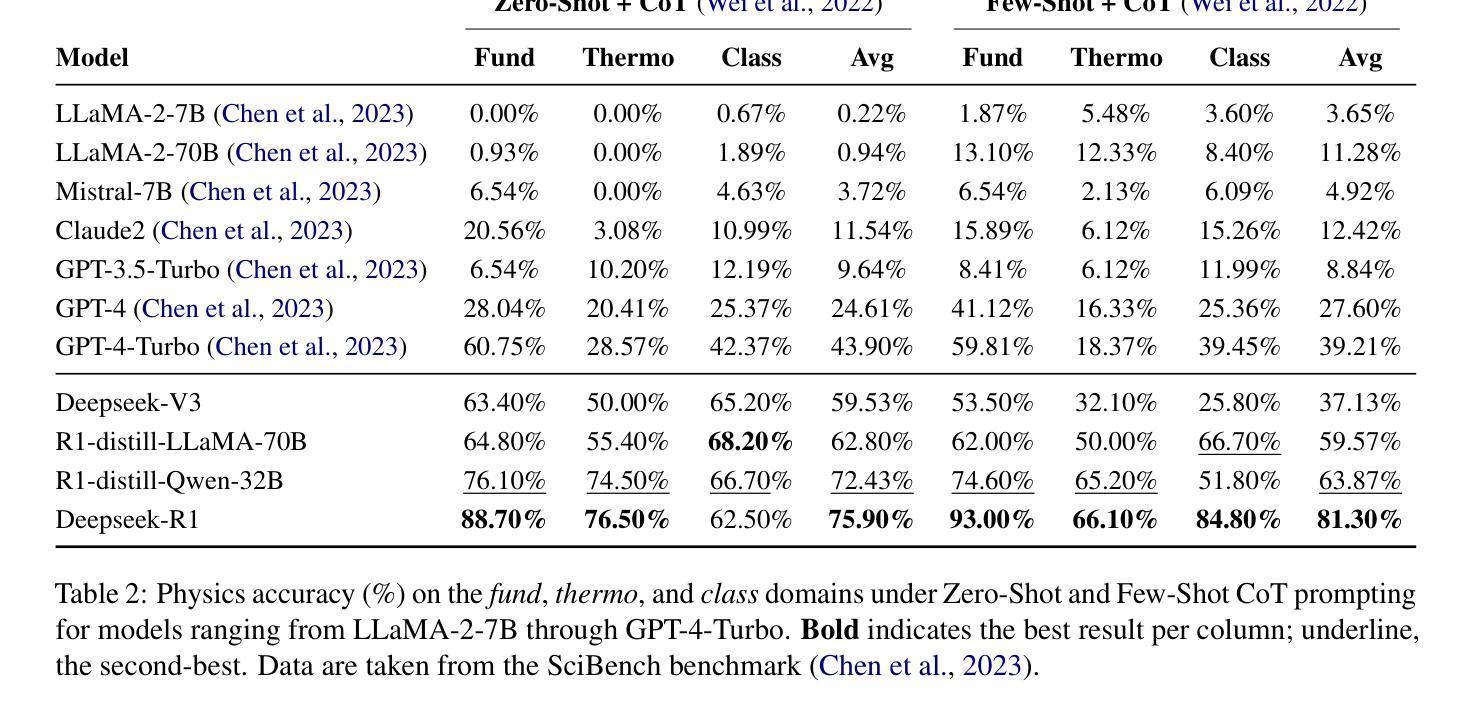
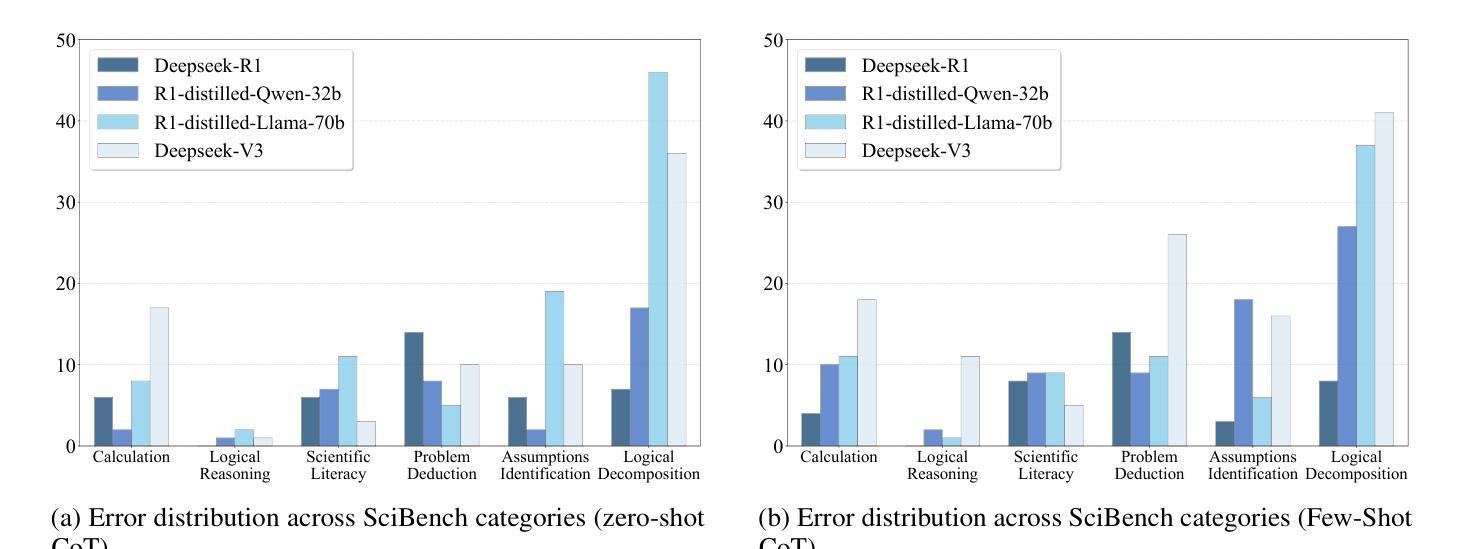
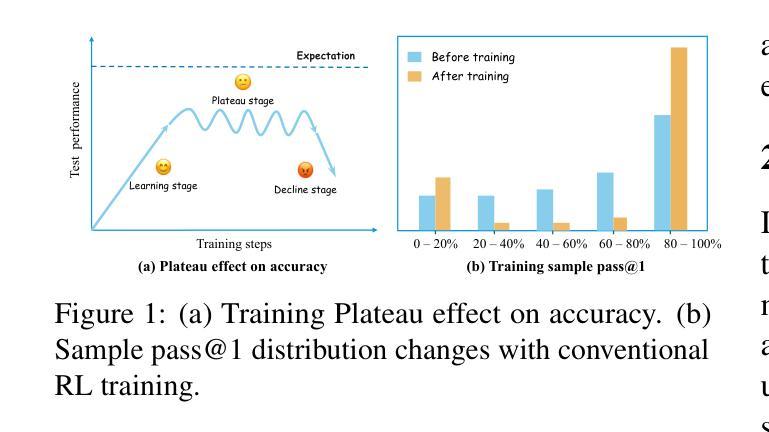
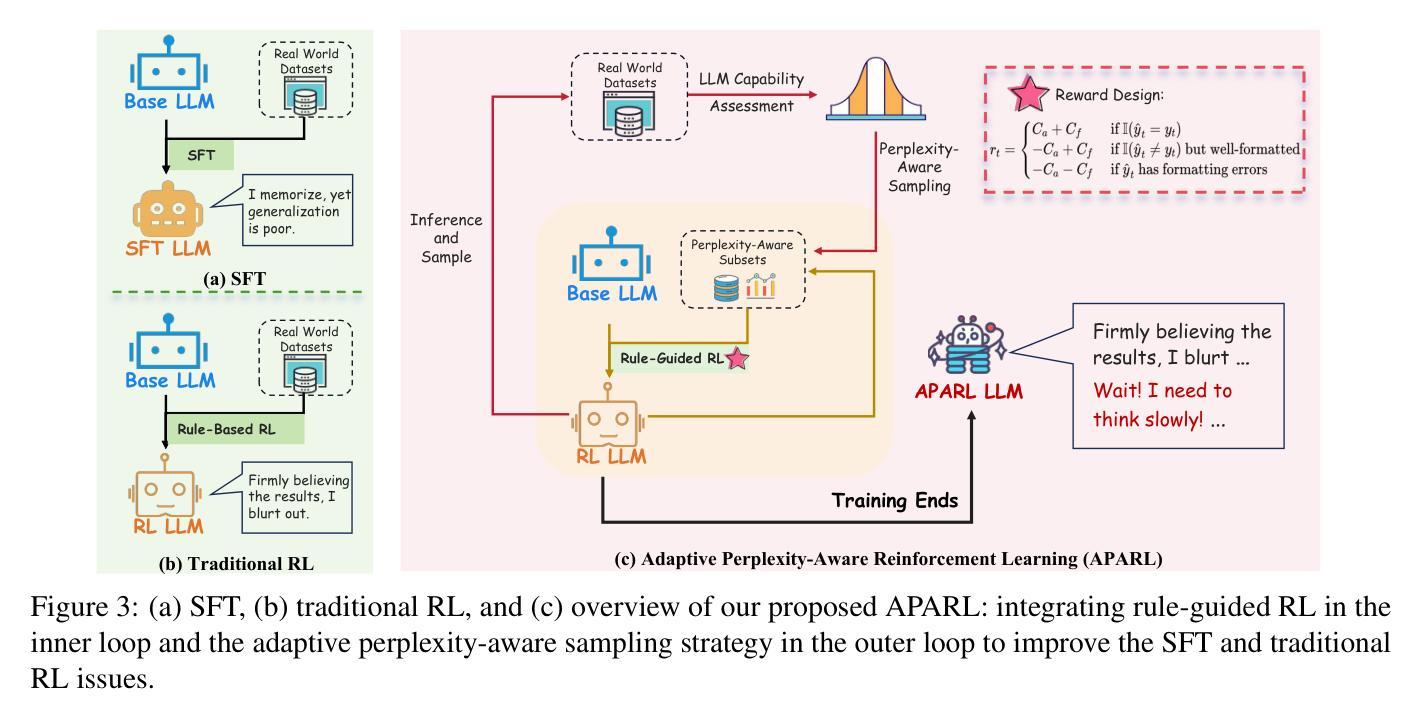
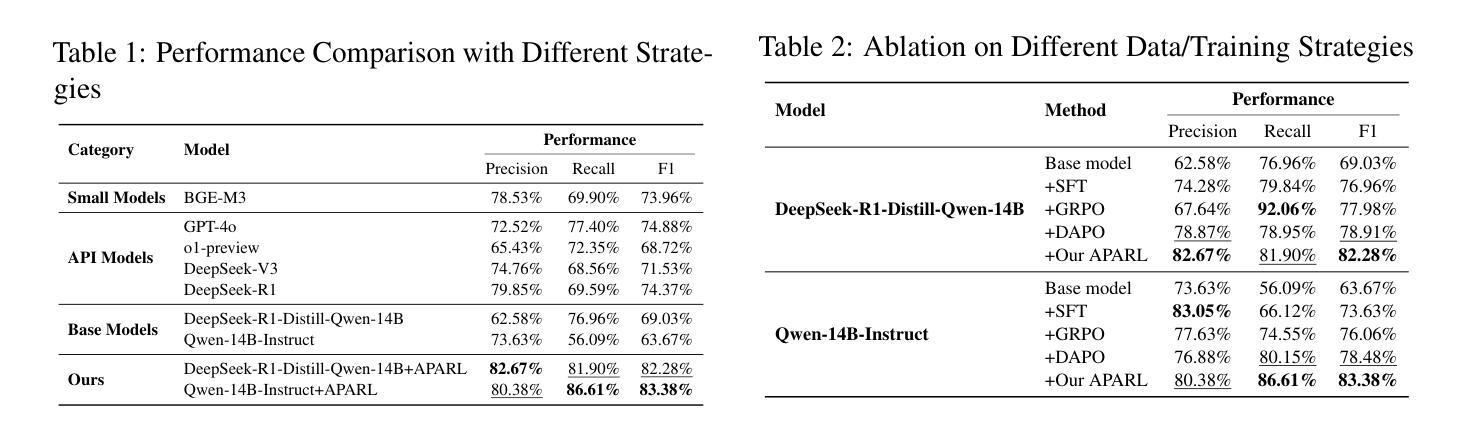
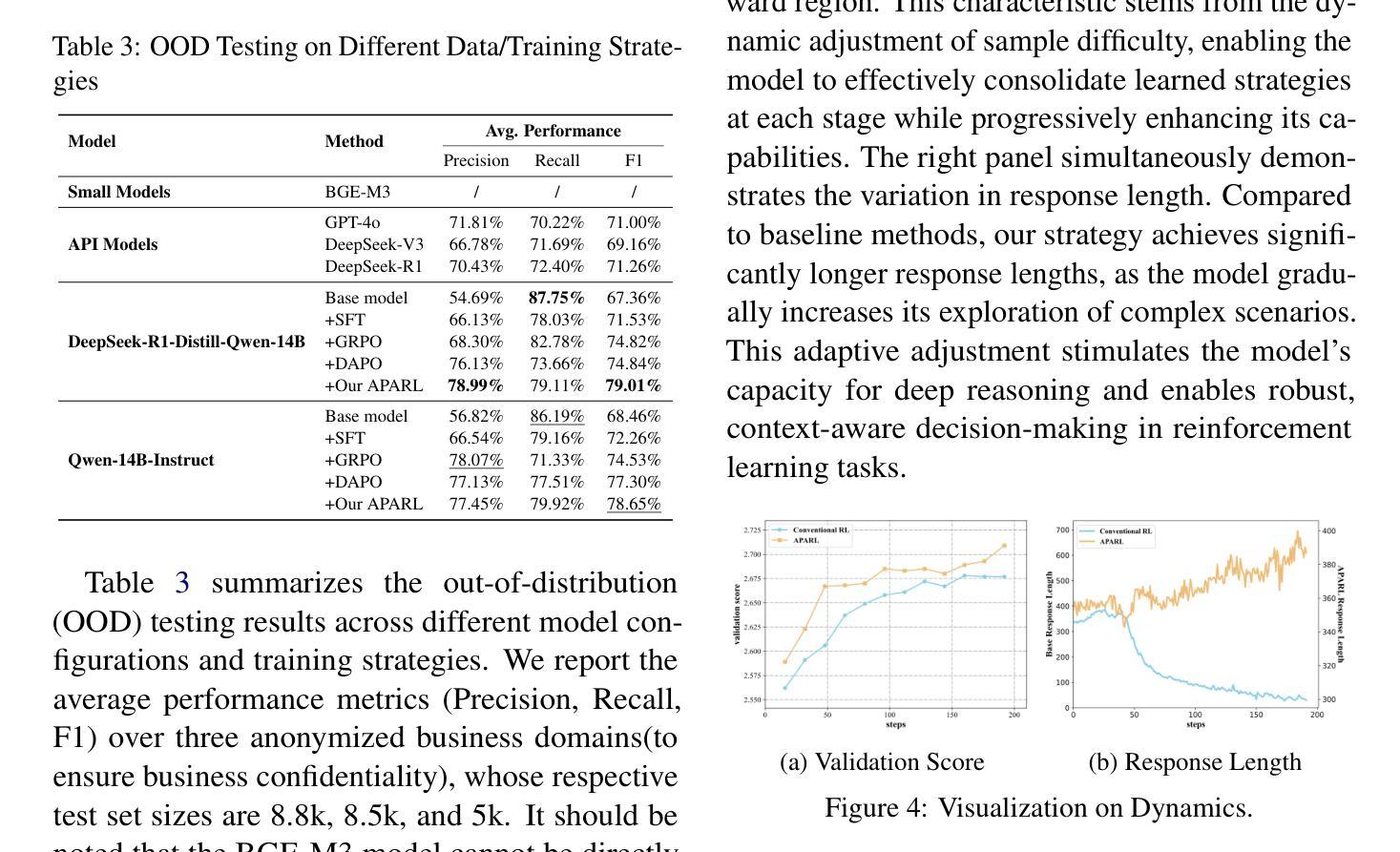
Reasoner for Real-World Event Detection: Scaling Reinforcement Learning via Adaptive Perplexity-Aware Sampling Strategy
Authors:Xiaoyun Zhang, Jingqing Ruan, Xing Ma, Yawen Zhu, Jiansong Chen, Ke Zeng, Xunliang Cai
Detecting abnormal events in real-world customer service dialogues is highly challenging due to the complexity of business data and the dynamic nature of customer interactions. Moreover, models must demonstrate strong out-of-domain (OOD) generalization to enable rapid adaptation across different business scenarios and maximize commercial value. In this work, we propose a novel Adaptive Perplexity-Aware Reinforcement Learning (APARL) framework that leverages the advanced reasoning capabilities of large language models for abnormal event detection. APARL introduces a dual-loop dynamic curriculum learning architecture, enabling the model to progressively focus on more challenging samples as its proficiency increases. This design effectively addresses performance bottlenecks and significantly enhances OOD transferability. Extensive evaluations on food delivery dialogue tasks show that our model achieves significantly enhanced adaptability and robustness, attaining the highest F1 score with an average improvement of 17.19%, and an average improvement of 9.59% in OOD transfer tests. This method provides a superior solution for industrial deployment of anomaly detection models, contributing to improved operational efficiency and commercial benefits.
在现实世界中的客户服务对话中检测异常事件是一项极具挑战性的任务,这主要是因为业务数据的复杂性和客户互动的动态性。此外,模型必须展现出强大的域外(OOD)泛化能力,以便在不同的业务场景中快速适应并最大化商业价值。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新型的自适应困惑度感知强化学习(APARL)框架,该框架利用大型语言模型的先进推理能力进行异常事件检测。APARL引入了一种双循环动态课程学习架构,使模型能够随着熟练程度的提高而逐步关注更具挑战性的样本。这种设计有效地解决了性能瓶颈,并大大提高了OOD的迁移能力。在食品配送对话任务上的广泛评估表明,我们的模型在适应性和稳健性方面取得了显著的提升,获得了最高的F1分数,平均提高了17.19%,在OOD迁移测试中平均提高了9.59%。该方法为异常检测模型的工业部署提供了卓越的解决方案,为提高运营效率和商业效益做出了贡献。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 6 figures, submitted to EMNLP
Summary:
本文提出了一个名为APARL的新型自适应困惑度感知强化学习框架,用于在现实世界客户服务对话中检测异常事件。该框架利用大型语言模型的推理能力,通过双循环动态课程学习架构,使模型能够逐渐关注更具挑战性的样本,并提高其性能。在食品配送对话任务上的广泛评估表明,该模型具有出色的适应性和稳健性,F1得分显著提高,平均改进率为17.19%,在OOD转移测试中的平均改进率为9.59%。该方法为异常检测模型在工业部署中提供了卓越解决方案,有助于提高操作效率和商业效益。
Key Takeaways:
- APARL框架用于在现实世界客户服务对话中检测异常事件。
- APARL引入双循环动态课程学习架构。
- 模型能够逐渐关注更具挑战性的样本,提高其性能。
- 在食品配送对话任务上,APARL模型表现出出色的适应性和稳健性。
- APARL模型F1得分显著提高,平均改进率为17.19%。
- APARL模型在OOD转移测试中表现出良好的适应性。
点此查看论文截图


Frustratingly Simple Retrieval Improves Challenging, Reasoning-Intensive Benchmarks
Authors:Xinxi Lyu, Michael Duan, Rulin Shao, Pang Wei Koh, Sewon Min
Retrieval-augmented Generation (RAG) has primarily been studied in limited settings, such as factoid question answering; more challenging, reasoning-intensive benchmarks have seen limited success from minimal RAG. In this work, we challenge this prevailing view on established, reasoning-intensive benchmarks: MMLU, MMLU Pro, AGI Eval, GPQA, and MATH. We identify a key missing component in prior work: a usable, web-scale datastore aligned with the breadth of pretraining data. To this end, we introduce CompactDS: a diverse, high-quality, web-scale datastore that achieves high retrieval accuracy and subsecond latency on a single-node. The key insights are (1) most web content can be filtered out without sacrificing coverage, and a compact, high-quality subset is sufficient; and (2) combining in-memory approximate nearest neighbor (ANN) retrieval and on-disk exact search balances speed and recall. Using CompactDS, we show that a minimal RAG pipeline achieves consistent accuracy improvements across all benchmarks and model sizes (8B–70B), with relative gains of 10% on MMLU, 33% on MMLU Pro, 14% on GPQA, and 19% on MATH. No single data source suffices alone, highlighting the importance of diversity of sources (web crawls, curated math, academic papers, textbooks). Finally, we show that our carefully designed in-house datastore matches or outperforms web search engines such as Google Search, as well as recently proposed, complex agent-based RAG systems–all while maintaining simplicity, reproducibility, and self-containment. We release CompactDS and our retrieval pipeline, supporting future research exploring retrieval-based AI systems.
检索增强生成(RAG)主要在有限的环境中进行了研究,如基于事实的问题回答;在更具挑战性的、注重推理的基准测试中,RAG的效果有限。在这项工作中,我们针对现有的注重推理的基准测试:MMLU、MMLU Pro、AGI Eval、GPQA和MATH,提出质疑。我们发现先前工作中缺少一个关键组件:一个与预训练数据广度相匹配的可用的大规模网络数据存储库。为此,我们引入了CompactDS:一个多样化、高质量的大规模网络数据存储库,在单个节点上实现了高检索准确率和亚秒级的延迟。关键见解是(1)大部分网页内容可以被过滤掉而不会牺牲覆盖范围,一个紧凑的高质量子集就足够了;(2)结合内存中的近似最近邻(ANN)检索和磁盘上的精确搜索可以平衡速度和召回率。使用CompactDS,我们证明了简单的RAG管道在所有基准测试和模型大小(8B-70B)上都能实现一致的准确性提高,在MMLU上的相对增益为10%,在MMLU Pro上为33%,在GPQA上为14%,在MATH上为19%。没有单一的数据源可以单独使用,这突显了数据源多样性的重要性(网络爬虫、精选的数学资料、学术论文、教科书等)。最后,我们证明了我们的精心设计内部数据存储库可以与谷歌搜索等网络搜索引擎以及最近提出的复杂基于代理的RAG系统相媲美甚至更胜一筹——同时保持了简单性、可复制性和自主性。我们发布CompactDS和我们的检索管道,支持未来对基于检索的人工智能系统的探索研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 33 pages, 2 figures, 27 tables
Summary
本文介绍了在大型预训练数据背景下,基于检索的增强生成模型(RAG)在推理密集型基准测试上的表现。作者提出了一项关键缺失的组件:一个可用的大型网络数据存储,它与预训练数据的广度相匹配。为此,他们引入了CompactDS,这是一个多样化、高质量的大型网络数据存储,能够在单个节点上实现高检索准确性和亚秒级的延迟。使用CompactDS,作者展示了简单的RAG管道在所有基准测试和模型大小上都能实现一致的准确性改进。最后,作者认为没有单一的数据来源可以单独满足需求,强调了数据来源多样性的重要性。他们释放了CompactDS和检索管道,以支持未来对基于检索的AI系统的探索。
Key Takeaways
- RAG在推理密集型基准测试上的表现有限,主要由于缺少一个与预训练数据广度相匹配的大型网络数据存储组件。
- 引入的CompactDS是一个多样化、高质量的大型网络数据存储,实现了高检索准确性和亚秒级延迟。
- 使用CompactDS的RAG管道在所有基准测试和不同模型大小上都实现了准确性改进。
- 数据来源的多样性对RAG的性能至关重要,没有单一数据来源可以单独满足需求。
- CompactDS及其检索管道已被发布,以支持对基于检索的AI系统的进一步研究。
- CompactDS的表现在多个方面超过或匹配了Google Search等网络搜索引擎以及复杂的基于代理的RAG系统,同时保持了简单性、可重复性和自给自足性。
点此查看论文截图

PULSE: Practical Evaluation Scenarios for Large Multimodal Model Unlearning
Authors:Tatsuki Kawakami, Kazuki Egashira, Atsuyuki Miyai, Go Irie, Kiyoharu Aizawa
In recent years, unlearning techniques, which are methods for inducing a model to “forget” previously learned information, have attracted attention as a way to address privacy and copyright concerns in large language models (LLMs) and large multimodal models (LMMs). While several unlearning benchmarks have been established for LLMs, a practical evaluation framework for unlearning in LMMs has been less explored. Specifically, existing unlearning benchmark for LMMs considers only scenarios in which the model is required to unlearn fine-tuned knowledge through a single unlearning operation. In this study, we introduce PULSE protocol for realistic unlearning scenarios for LMMs by introducing two critical perspectives: (i) Pre-trained knowledge Unlearning for analyzing the effect across different knowledge acquisition phases and (ii) Long-term Sustainability Evaluation to address sequential requests. We then evaluate existing unlearning methods along these dimensions. Our results reveal that, although some techniques can successfully unlearn knowledge acquired through fine-tuning, they struggle to eliminate information learned during pre-training. Moreover, methods that effectively unlearn a batch of target data in a single operation exhibit substantial performance degradation when the same data are split and unlearned sequentially.
近年来,遗忘技术(即让模型“忘记”先前学习信息的方法)引起了人们的关注,作为一种解决大型语言模型(LLM)和大型多模态模型(LMM)中的隐私和版权问题的途径。虽然为LLM建立了多个遗忘基准测试,但关于LMM中遗忘的实用评估框架的研究较少。具体来说,现有的LMM遗忘基准测试只考虑模型需要通过一次遗忘操作来遗忘微调知识的场景。在这项研究中,我们通过引入两个关键视角,为LMM的现实遗忘场景引入了PULSE协议:(i)预训练知识遗忘,以分析不同知识获取阶段的影响;(ii)长期可持续性评估,以解决顺序请求问题。然后,我们沿着这些维度评估了现有的遗忘方法。我们的结果表明,尽管一些技术可以成功遗忘通过微调获得的知识,但它们很难消除在预训练期间学习的信息。此外,那些在一次操作中有效遗忘一批目标数据的方法,当相同的数据被分割并顺序遗忘时,会表现出显著的性能下降。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文关注大型语言模型(LLMs)和大型多模态模型(LMMs)中的隐私和版权问题,提出利用模型“遗忘”先前学习信息的去学习方法来解决这些问题。文章重点介绍了针对大型多模态模型的PULSE协议来应对现实情况下的遗忘需求,引入了两种不同的观点来评价现有的遗忘方法。评估结果表明,虽然一些技术可以在微调知识上成功遗忘,但在预训练过程中的信息遗忘却存在问题。同时,在分割相同数据并进行连续遗忘操作时,效果可能会大幅降低。整体而言,为LMMs设计出灵活高效的遗忘协议依然是挑战性工作方向。期待此工作可以为建立高效现实的模型去学习方法提供更多的见解与指引。对推进实际应用以及未来技术迭代具有积极意义。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型和大型多模态模型中的隐私和版权问题受到关注。引入去学习方法来应对这一挑战。该方法关注如何使模型“忘记”先前学习的信息。
- 文章提出了PULSE协议,该协议为大型多模态模型提供了应对现实遗忘需求的解决方案。它引入了两种不同的观点来评价现有的遗忘方法:预训练知识的遗忘和长期可持续性评估以应对连续请求。
点此查看论文截图

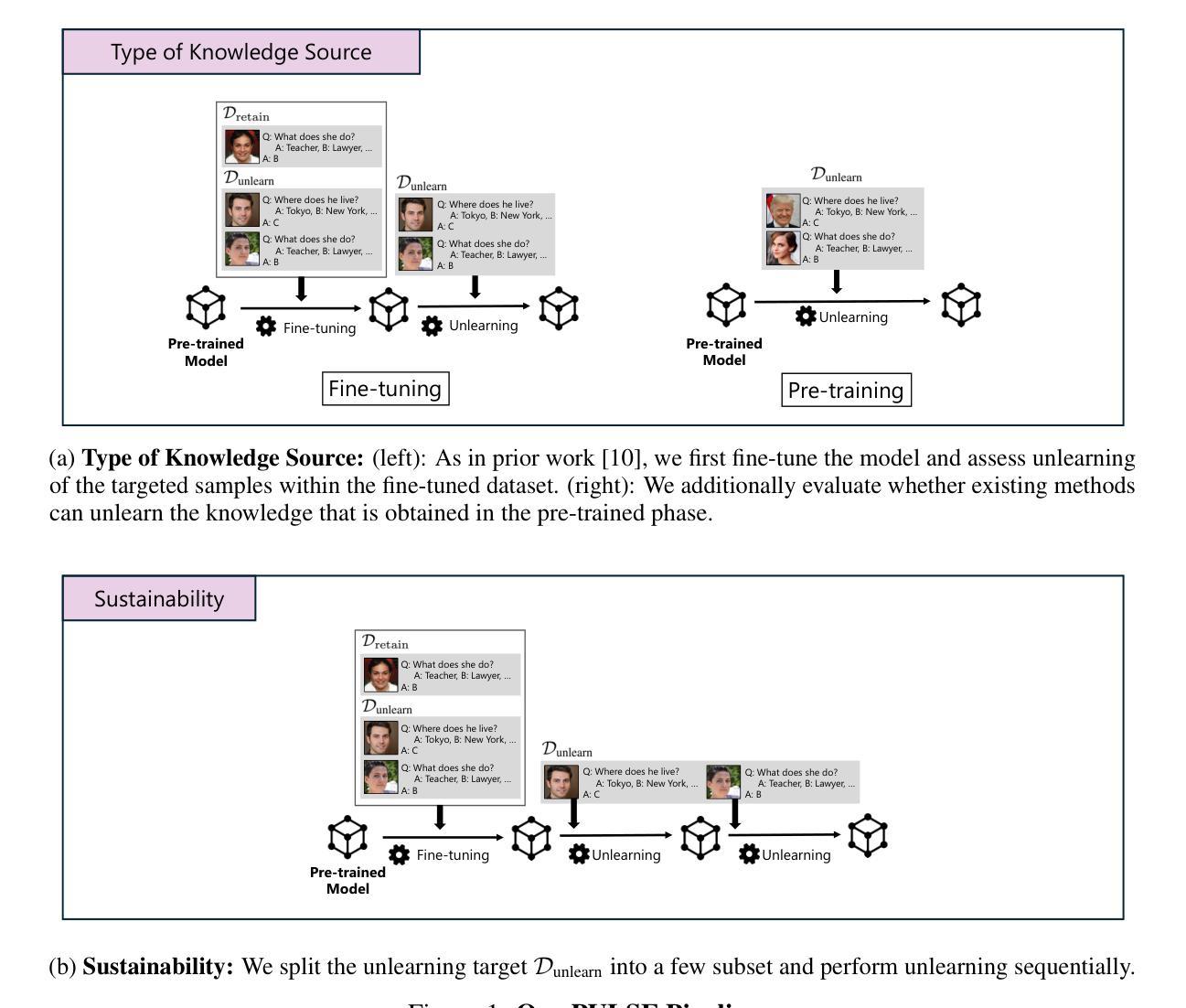
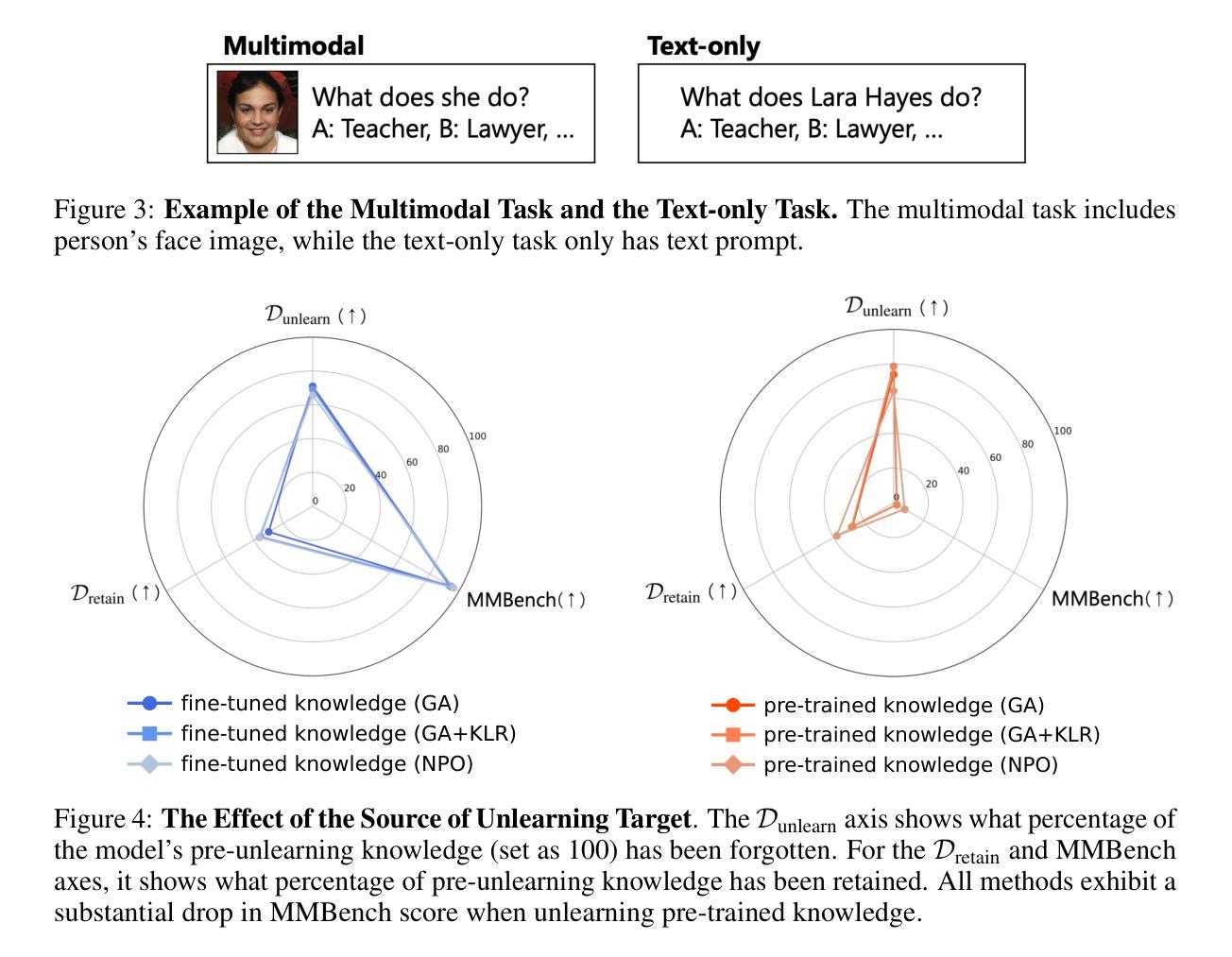
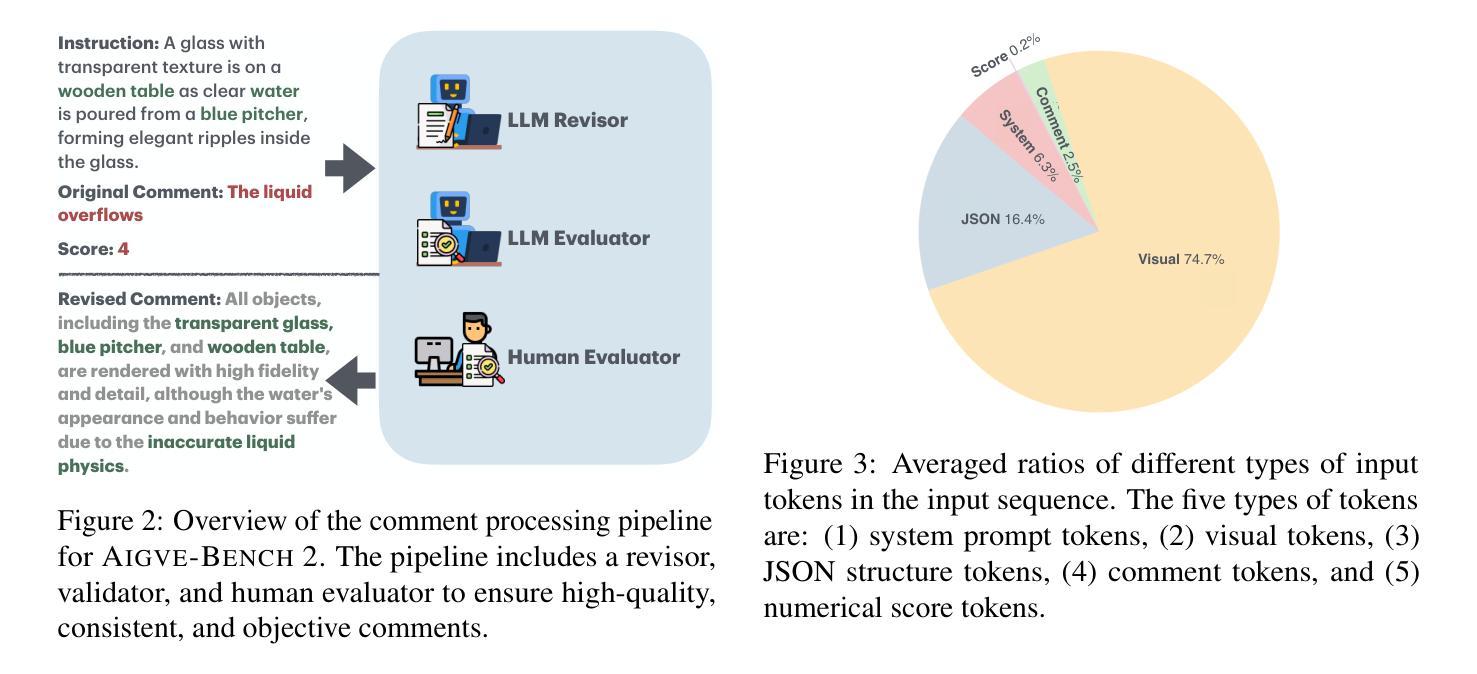
AIGVE-MACS: Unified Multi-Aspect Commenting and Scoring Model for AI-Generated Video Evaluation
Authors:Xiao Liu, Jiawei Zhang
The rapid advancement of AI-generated video models has created a pressing need for robust and interpretable evaluation frameworks. Existing metrics are limited to producing numerical scores without explanatory comments, resulting in low interpretability and human evaluation alignment. To address those challenges, we introduce AIGVE-MACS, a unified model for AI-Generated Video Evaluation(AIGVE), which can provide not only numerical scores but also multi-aspect language comment feedback in evaluating these generated videos. Central to our approach is AIGVE-BENCH 2, a large-scale benchmark comprising 2,500 AI-generated videos and 22,500 human-annotated detailed comments and numerical scores across nine critical evaluation aspects. Leveraging AIGVE-BENCH 2, AIGVE-MACS incorporates recent Vision-Language Models with a novel token-wise weighted loss and a dynamic frame sampling strategy to better align with human evaluators. Comprehensive experiments across supervised and zero-shot benchmarks demonstrate that AIGVE-MACS achieves state-of-the-art performance in both scoring correlation and comment quality, significantly outperforming prior baselines including GPT-4o and VideoScore. In addition, we further showcase a multi-agent refinement framework where feedback from AIGVE-MACS drives iterative improvements in video generation, leading to 53.5% quality enhancement. This work establishes a new paradigm for comprehensive, human-aligned evaluation of AI-generated videos. We release the AIGVE-BENCH 2 and AIGVE-MACS at https://huggingface.co/xiaoliux/AIGVE-MACS.
人工智能生成视频模型的快速发展对稳健、可解释的评价框架产生了迫切的需求。现有指标仅限于产生没有解释性评论的数值分数,导致解释性和人类评价一致性较低。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了AIGVE-MACS,这是一个统一的AI生成视频评价模型(AIGVE),它不仅可以提供数值分数,还可以在评价这些生成的视频时提供多方面的语言评论反馈。我们的方法的核心是AIGVE-BENCH 2,这是一个大规模基准测试,包含2500个AI生成的视频和22500个人类注释的详细评论和数值分数,涵盖九个关键评价方面。借助AIGVE-BENCH 2,AIGVE-MACS结合了最新的视觉语言模型,采用新颖的token加权损失和动态帧采样策略,以更好地与人类评估者对齐。在监督和零基准基准测试中的综合实验表明,AIGVE-MACS在评分关联和评论质量方面都达到了最先进的性能,显著优于包括GPT-4o和VideoScore在内的先前基准测试。此外,我们还进一步展示了一个多智能体细化框架,其中AIGVE-MACS的反馈驱动视频生成的迭代改进,提高了53.5%的质量。这项工作为AI生成视频的全面、人类对齐的评价建立了新的范式。我们在https://huggingface.co/xiaoliux/AIGVE-MACS上发布了AIGVE-BENCH 2和AIGVE-MACS。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Working in Progress
Summary
本文介绍了AI生成视频模型评估的挑战及解决方案。针对现有评估框架解释性不足的问题,提出了统一的AI生成视频评估模型AIGVE-MACS。该模型不仅能提供数值评分,还能在评价生成视频时给出多方面的语言评论反馈。AIGVE-BENCH 2的大规模基准测试显示,AIGVE-MACS在评分相关性和评论质量方面达到了最新水平,显著优于GPT-4o和VideoScore等基线模型。此外,还展示了多智能体细化框架,AIGVE-MACS的反馈驱动视频生成的迭代改进,提高了视频质量。本文建立了AI生成视频全面、符合人类评估的新范式。
Key Takeaways
- AI生成视频模型的快速发展需要更强大和可解释的评估框架。
- 现有评估框架主要提供数值评分,缺乏解释性,与人类评价对齐困难。
- 引入AIGVE-MACS模型,不仅提供数值评分,还给出多方面的语言评论反馈。
- AIGVE-BENCH 2大规模基准测试验证了AIGVE-MACS模型的性能。
- AIGVE-MACS在评分相关性和评论质量方面达到最新水平,优于其他基线模型。
- 多智能体细化框架展示了AIGVE-MACS驱动的视频生成迭代改进。
点此查看论文截图


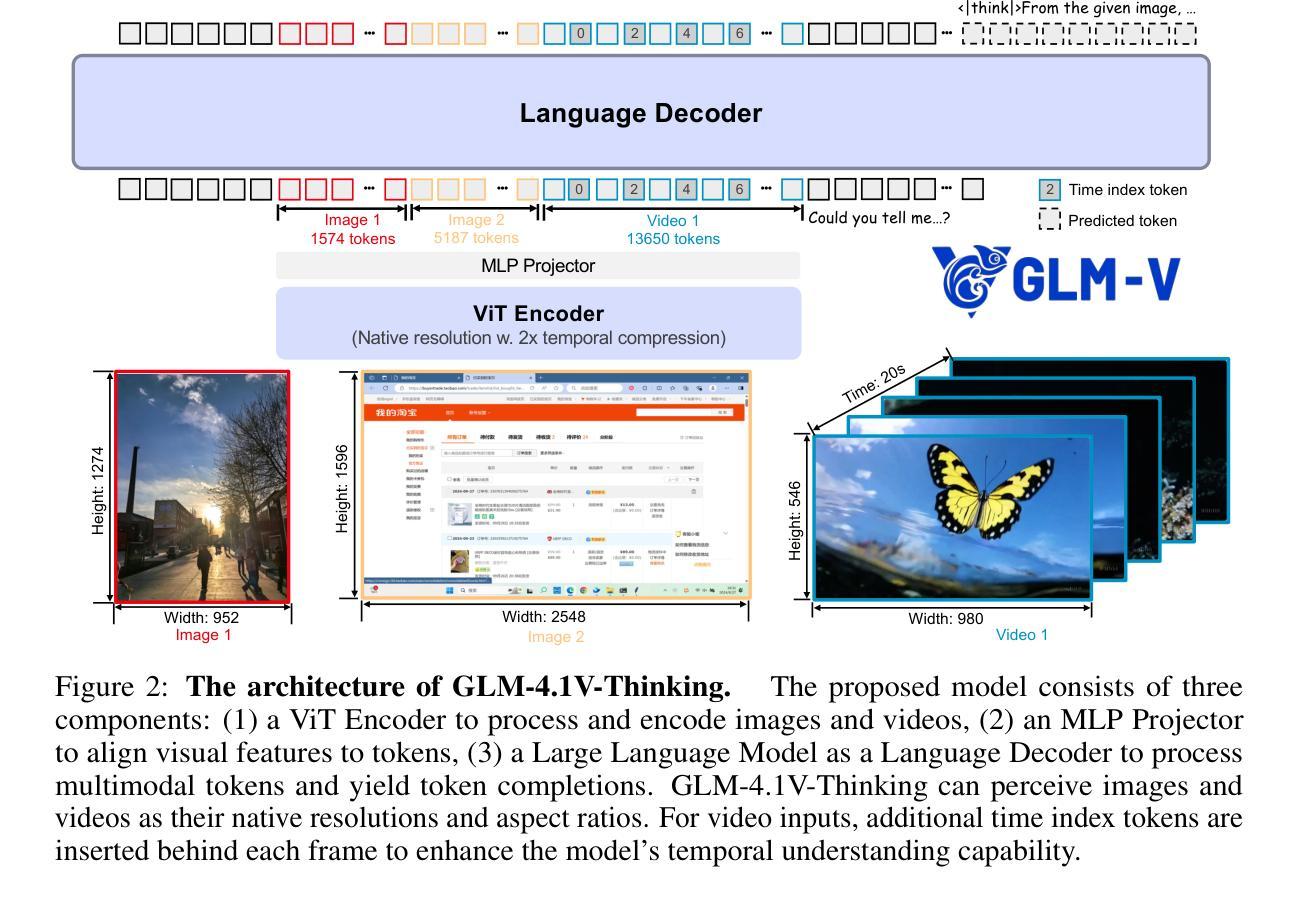
GLM-4.1V-Thinking: Towards Versatile Multimodal Reasoning with Scalable Reinforcement Learning
Authors:GLM-V Team, :, Wenyi Hong, Wenmeng Yu, Xiaotao Gu, Guo Wang, Guobing Gan, Haomiao Tang, Jiale Cheng, Ji Qi, Junhui Ji, Lihang Pan, Shuaiqi Duan, Weihan Wang, Yan Wang, Yean Cheng, Zehai He, Zhe Su, Zhen Yang, Ziyang Pan, Aohan Zeng, Baoxu Wang, Boyan Shi, Changyu Pang, Chenhui Zhang, Da Yin, Fan Yang, Guoqing Chen, Jiazheng Xu, Jiali Chen, Jing Chen, Jinhao Chen, Jinghao Lin, Jinjiang Wang, Junjie Chen, Leqi Lei, Letian Gong, Leyi Pan, Mingzhi Zhang, Qinkai Zheng, Sheng Yang, Shi Zhong, Shiyu Huang, Shuyuan Zhao, Siyan Xue, Shangqin Tu, Shengbiao Meng, Tianshu Zhang, Tianwei Luo, Tianxiang Hao, Wenkai Li, Wei Jia, Xin Lyu, Xuancheng Huang, Yanling Wang, Yadong Xue, Yanfeng Wang, Yifan An, Yifan Du, Yiming Shi, Yiheng Huang, Yilin Niu, Yuan Wang, Yuanchang Yue, Yuchen Li, Yutao Zhang, Yuxuan Zhang, Zhanxiao Du, Zhenyu Hou, Zhao Xue, Zhengxiao Du, Zihan Wang, Peng Zhang, Debing Liu, Bin Xu, Juanzi Li, Minlie Huang, Yuxiao Dong, Jie Tang
We present GLM-4.1V-Thinking, a vision-language model (VLM) designed to advance general-purpose multimodal understanding and reasoning. In this report, we share our key findings in the development of the reasoning-centric training framework. We first develop a capable vision foundation model with significant potential through large-scale pre-training, which arguably sets the upper bound for the final performance. We then propose Reinforcement Learning with Curriculum Sampling (RLCS) to unlock the full potential of the model, leading to comprehensive capability enhancement across a diverse range of tasks, including STEM problem solving, video understanding, content recognition, coding, grounding, GUI-based agents, and long document understanding. We open-source GLM-4.1V-9B-Thinking, which achieves state-of-the-art performance among models of comparable size. In a comprehensive evaluation across 28 public benchmarks, our model outperforms Qwen2.5-VL-7B on nearly all tasks and achieves comparable or even superior performance on 18 benchmarks relative to the significantly larger Qwen2.5-VL-72B. Notably, GLM-4.1V-9B-Thinking also demonstrates competitive or superior performance compared to closed-source models such as GPT-4o on challenging tasks including long document understanding and STEM reasoning, further underscoring its strong capabilities. Code, models and more information are released at https://github.com/THUDM/GLM-4.1V-Thinking.
我们推出了GLM-4.1V-Thinking,这是一款旨在推动通用多模态理解和推理的视语言模型(VLM)。在这份报告中,我们分享了我们在开发以推理为中心的训练框架过程中的主要发现。首先,我们通过大规模预训练,开发了一个具有巨大潜力的视觉基础模型,可以说是为最终性能设定了上限。然后,我们提出了采用课程采样强化学习(RLCS)的方法,以充分发挥模型潜力,全面提高跨各种任务的全面能力,包括STEM问题解决、视频理解、内容识别、编码、接地、基于GUI的代理和长文档理解。我们开源了GLM-4.1V-9B-Thinking,在同类模型中实现了最先进的性能。在涵盖的公共基准测试中全面评估表明我们的模型性能几乎在所有任务上超过了Qwen2.5-VL-7B模型的表现水平;相对更大规模训练出的Qwen2.5-VL-72B模型,我们在其中十八条基准测试上取得了与之相当甚至更优的表现。值得注意的是,GLM-4.1V-9B-Thinking在包括长文档理解和STEM推理等挑战性任务上,相较于闭源模型如GPT-4o也表现出了竞争力或更出色的性能表现,这进一步凸显了其强大的能力。相关代码、模型和更多信息已发布在https://github.com/THUDM/GLM-4.1V-Thinking上。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
GLM-4.1V-Thinking是一款视觉语言模型(VLM),旨在推进通用多模态理解和推理。本研究报告分享了该推理为中心的训练框架开发的关键发现。首先,通过大规模预训练,开发了一个具有巨大潜力的视觉基础模型。然后,提出使用强化学习与课程采样(RLCS)来释放模型的全潜力,在多种任务上实现了全面的能力增强,包括STEM问题解决、视频理解、内容识别、编码、接地、基于GUI的代理和长文档理解。开源的GLM-4.1V-9B-Thinking在同类模型中实现了最先进的性能。在28个公共基准测试的全面评估中,我们的模型在几乎所有任务上都优于Qwen2.5-VL-7B,在18个基准测试上的性能与更大的Qwen2.5-VL-72B相当甚至更好。GLM-4.1V-9B-Thinking在包括长文档理解和STEM推理等具有挑战性的任务上,与闭源模型如GPT-4o相比也表现出竞争力或更出色的性能,进一步证明了其强大的能力。相关信息和模型已发布在https://github.com/THUDM/GLM-4.1V-Thinking。
关键见解
- GLM-4.1V-Thinking是一个旨在推进通用多模态理解和推理的视觉语言模型。
- 通过大规模预训练,建立了具有巨大潜力的视觉基础模型。
- 提出强化学习与课程采样(RLCS)来释放模型的全潜力,增强多种任务能力。
- GLM-4.1V-9B-Thinking在多项任务上表现优秀,包括STEM问题解决、视频理解等。
- 该模型在多个基准测试中表现优于其他模型,如Qwen2.5-VL-7B。
- GLM-4.1V-9B-Thinking与大型闭源模型如GPT-4o相比,具有竞争力的性能。
点此查看论文截图