⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-04 更新
evMLP: An Efficient Event-Driven MLP Architecture for Vision
Authors:Zhentan Zheng
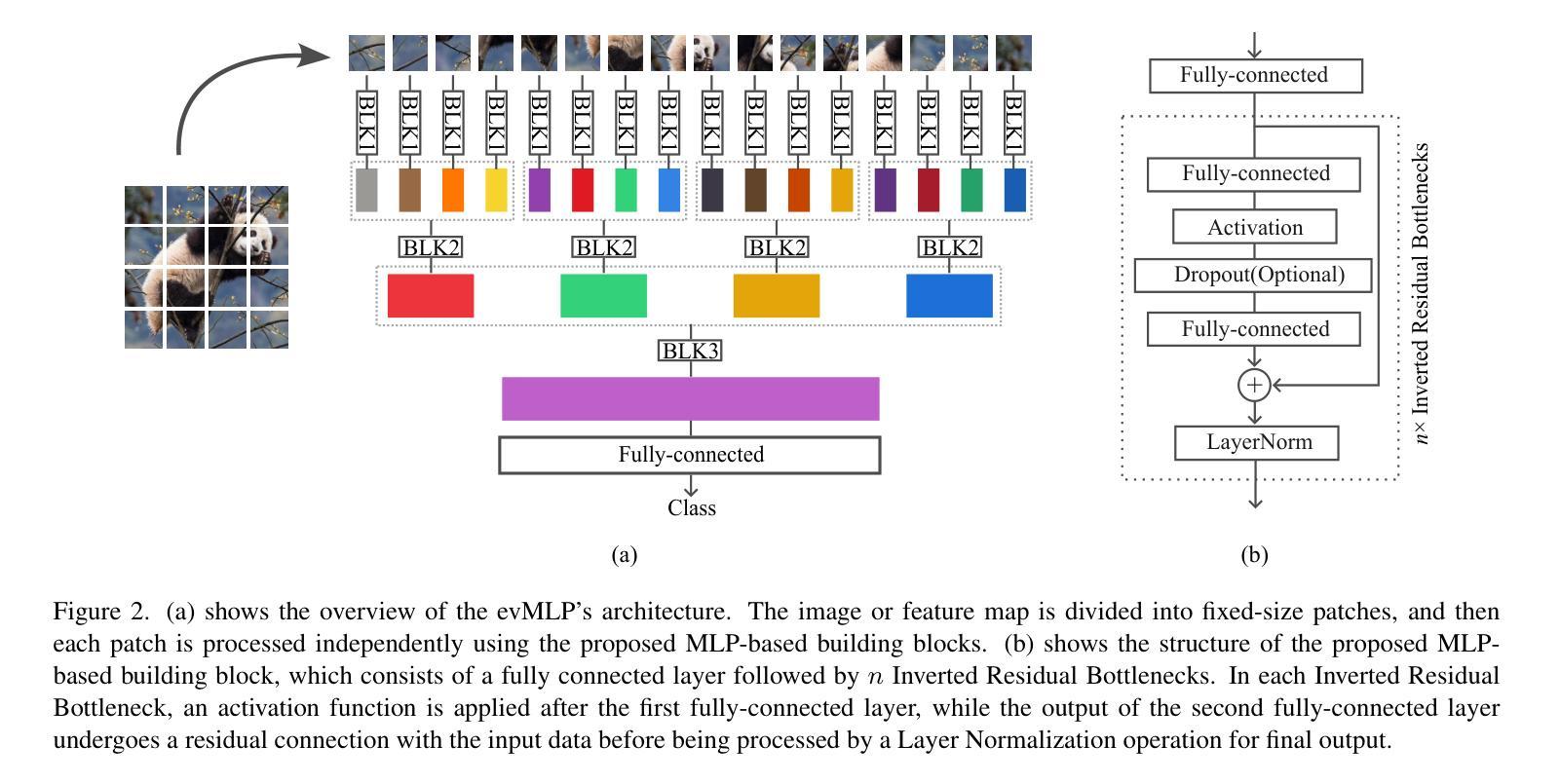
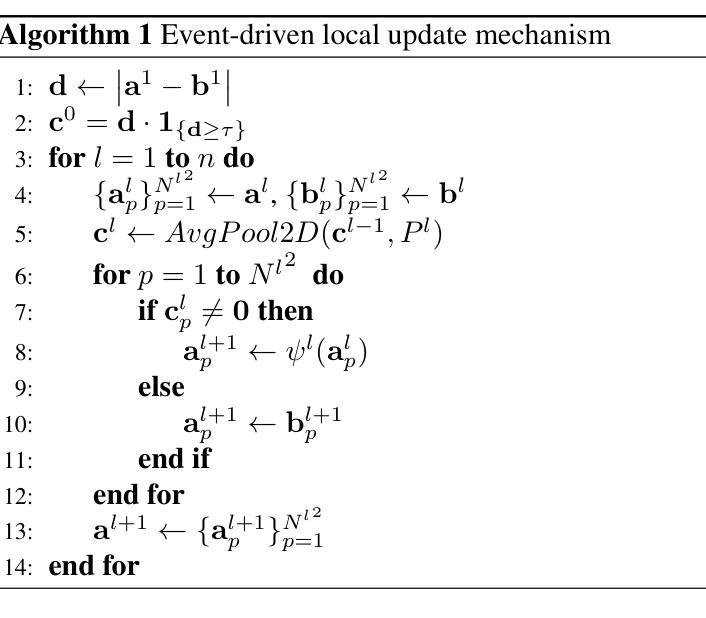
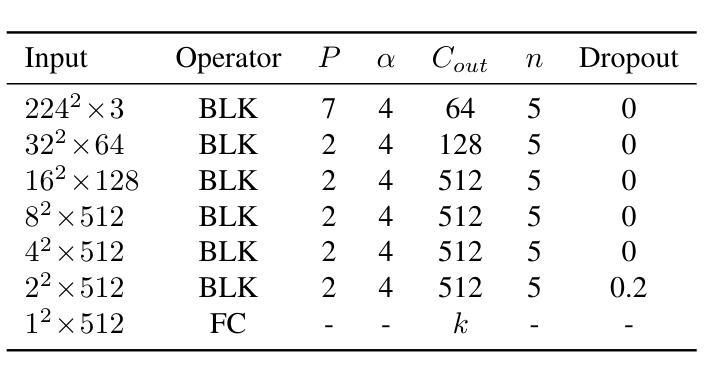
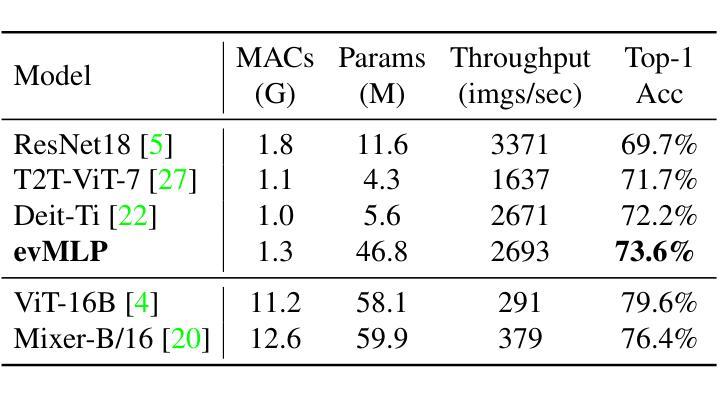
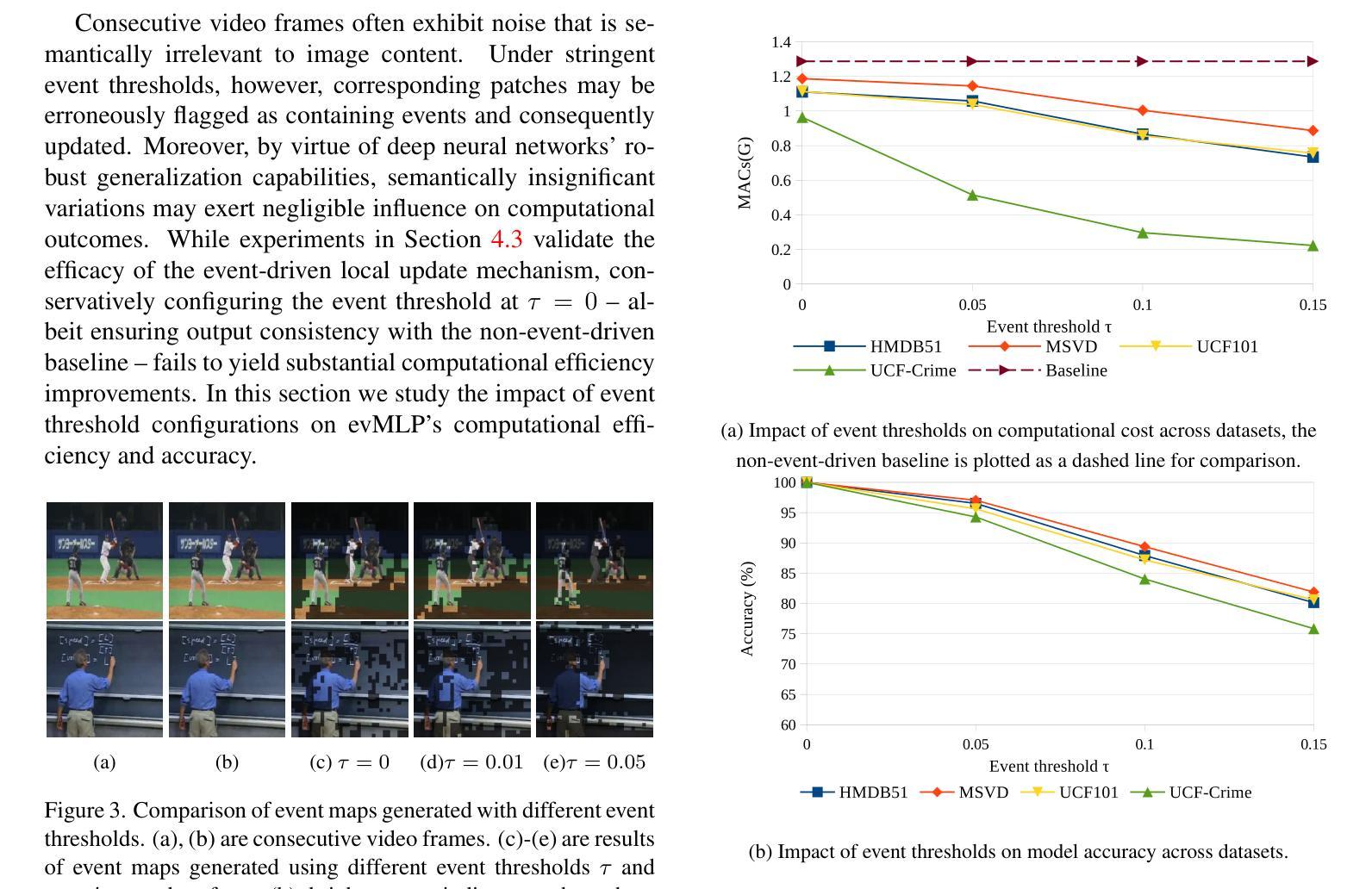
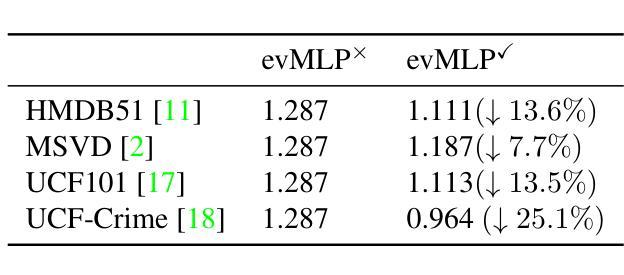
Deep neural networks have achieved remarkable results in computer vision tasks. In the early days, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) were the mainstream architecture. In recent years, Vision Transformers (ViTs) have become increasingly popular. In addition, exploring applications of multi-layer perceptrons (MLPs) has provided new perspectives for research into vision model architectures. In this paper, we present evMLP accompanied by a simple event-driven local update mechanism. The proposed evMLP can independently process patches on images or feature maps via MLPs. We define changes between consecutive frames as “events”. Under the event-driven local update mechanism, evMLP selectively processes patches where events occur. For sequential image data (e.g., video processing), this approach improves computational performance by avoiding redundant computations. Through ImageNet image classification experiments, evMLP attains accuracy competitive with state-of-the-art models. More significantly, experimental results on multiple video datasets demonstrate that evMLP reduces computational cost via its event-driven local update mechanism while maintaining output consistency with its non-event-driven baseline. The code and trained models are available at https://github.com/i-evi/evMLP.
深度神经网络在计算机视觉任务中取得了显著成果。在早期,卷积神经网络(CNNs)是主流架构。近年来,视觉转换器(ViTs)越来越受欢迎。此外,多层感知器(MLPs)的应用研究为视觉模型架构的研究提供了新的视角。在本文中,我们提出了带有简单事件驱动局部更新机制的evMLP。所提出的evMLP可以通过MLP独立处理图像或特征图上的补丁。我们将连续帧之间的变化定义为“事件”。在事件驱动的局部更新机制下,evMLP会选择性地处理发生事件的地方。对于序列图像数据(例如视频处理),这种方法通过避免冗余计算来提高计算性能。通过ImageNet图像分类实验,evMLP的准确率达到了前沿模型的竞争水平。更重要的是,多个视频数据集的实验结果表明,evMLP通过其事件驱动的局部更新机制降低了计算成本,同时保持了与非事件驱动基准模型的输出一致性。代码和训练好的模型可在https://github.com/i-evi/evMLP找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了evMLP模型,该模型结合了多层感知器(MLPs)和事件驱动局部更新机制。evMLP能独立处理图像或特征图上的块,对连续帧之间的变化定义为“事件”,并仅选择事件发生的块进行处理。这种方法提高了计算性能,尤其是在处理序列图像数据(如视频处理)时。实验结果表明,evMLP在维持输出一致性的同时,通过事件驱动局部更新机制降低了计算成本。
Key Takeaways
- evMLP结合了多层感知器(MLPs)和事件驱动局部更新机制,提供了一种新的视觉模型架构。
- evMLP能独立处理图像或特征图上的块。
- 事件被定义为连续帧之间的变化,evMLP仅选择事件发生的块进行处理。
- 这种处理方法提高了计算性能,尤其在处理序列图像数据时。
- 实验结果显示,evMLP在ImageNet图像分类任务中具有与最新模型竞争的准确性。
- 在多个视频数据集上的实验结果表明,evMLP通过事件驱动局部更新机制降低了计算成本。
点此查看论文截图

Are Vision Transformer Representations Semantically Meaningful? A Case Study in Medical Imaging
Authors:Montasir Shams, Chashi Mahiul Islam, Shaeke Salman, Phat Tran, Xiuwen Liu
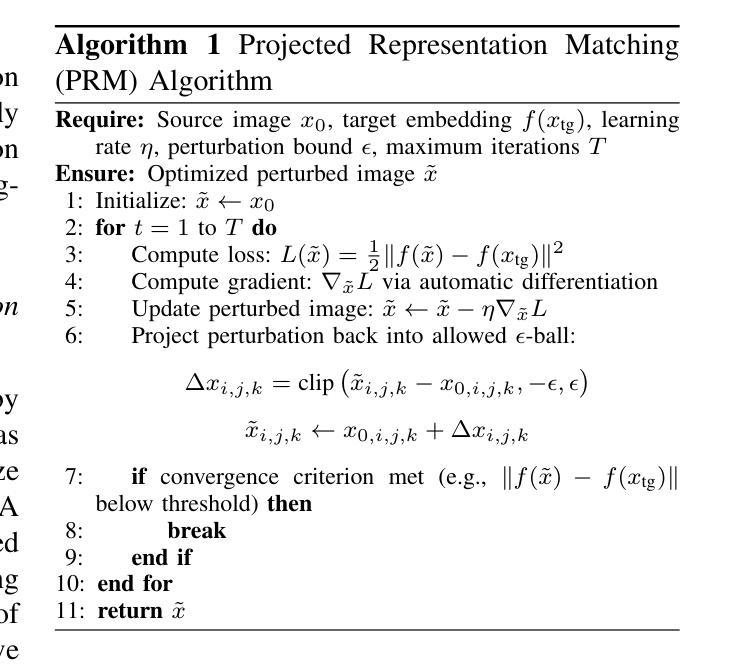
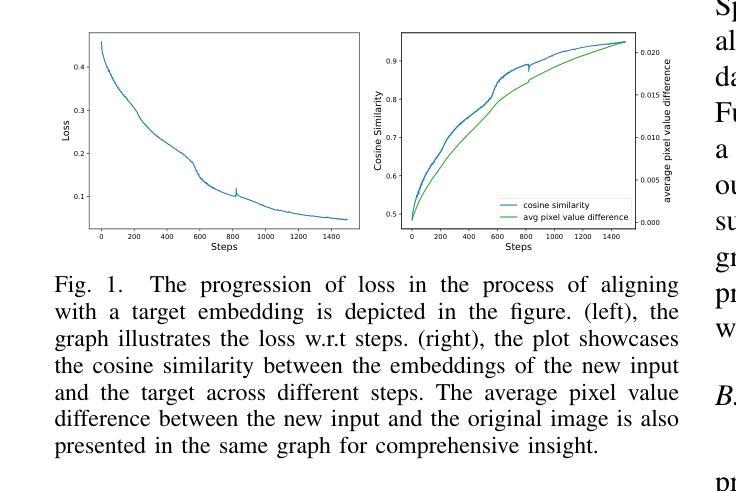
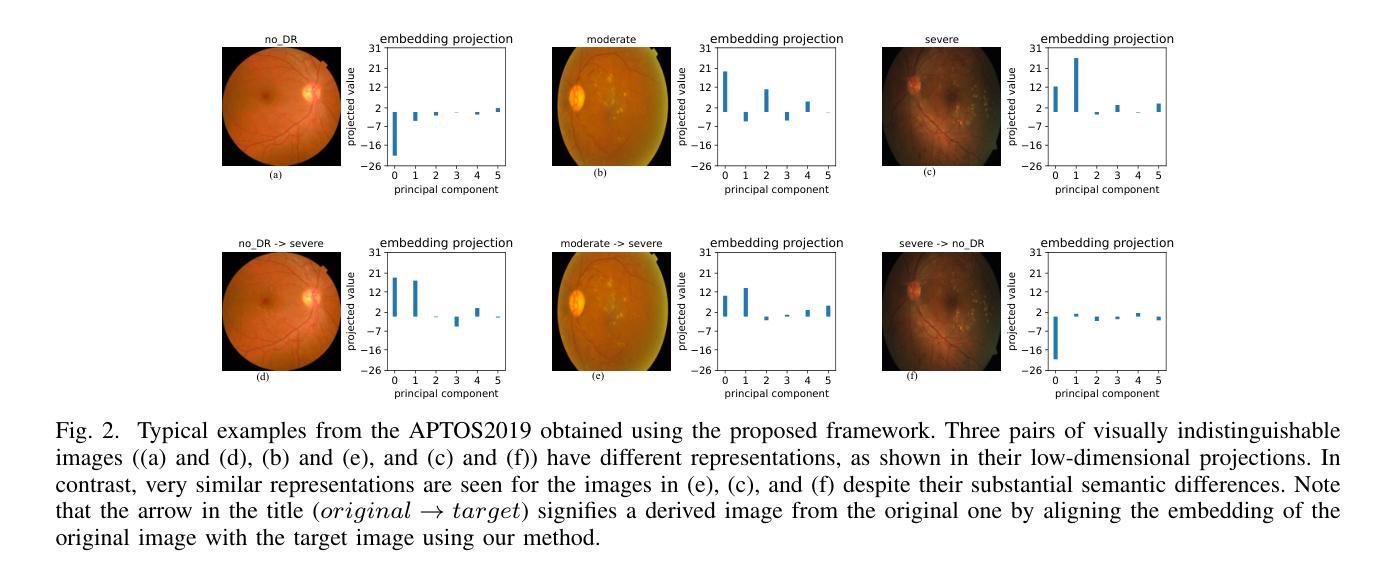
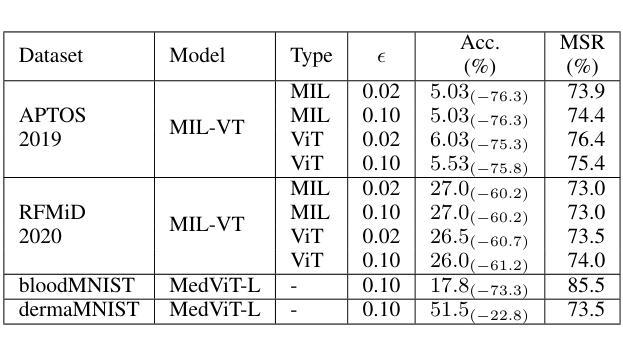
Vision transformers (ViTs) have rapidly gained prominence in medical imaging tasks such as disease classification, segmentation, and detection due to their superior accuracy compared to conventional deep learning models. However, due to their size and complex interactions via the self-attention mechanism, they are not well understood. In particular, it is unclear whether the representations produced by such models are semantically meaningful. In this paper, using a projected gradient-based algorithm, we show that their representations are not semantically meaningful and they are inherently vulnerable to small changes. Images with imperceptible differences can have very different representations; on the other hand, images that should belong to different semantic classes can have nearly identical representations. Such vulnerability can lead to unreliable classification results; for example, unnoticeable changes cause the classification accuracy to be reduced by over 60%. %. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to systematically demonstrate this fundamental lack of semantic meaningfulness in ViT representations for medical image classification, revealing a critical challenge for their deployment in safety-critical systems.
视觉转换器(ViTs)在医学成像任务(如疾病分类、分割和检测)中迅速崭露头角,与传统深度学习模型相比,它们具有更高的准确性。然而,由于其规模和通过自注意力机制产生的复杂交互,人们对其理解尚不充分。尤其不清楚的是,此类模型产生的表示是否具有语义意义。在本文中,我们使用基于投影的梯度算法,证明它们的表示并不具有语义意义,并且本质上是脆弱的,容易受微小变化的影响。具有几乎无法察觉差异的图像可能会有截然不同的表示;另一方面,本应属于不同语义类别的图像可能会有几乎相同的表示。这种脆弱性可能导致分类结果不可靠;例如,难以察觉的变化导致分类准确率降低超过60%。据我们所知,这是首次系统地证明在医学图像分类中ViT表示缺乏基本语义意义的工作,揭示了其在安全关键系统中部署的关键挑战。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages
Summary
本文指出,尽管Vision Transformers(ViTs)在医疗图像分类、分割和检测等任务中表现出较高的准确性,但其表示缺乏语义意义,容易受到微小变化的影响。使用基于梯度下降算法的研究表明,微小差异的图像可以有截然不同的表示,而本应属于不同语义类的图像却可能有几乎相同的表示。这种脆弱性导致分类结果不可靠,微小变化可能导致分类准确率下降超过60%。这一发现揭示了ViT在医疗图像分类中的关键挑战,对于其在安全关键系统的部署构成重大挑战。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformers(ViTs)在医疗成像任务中表现优异,但存在缺乏语义意义的问题。
- ViTs容易受到微小变化的影响,微小差异可能导致截然不同的表示。
- 本应属于不同语义类的图像可能具有几乎相同的表示。
- 这种缺乏语义意义的表示会导致分类结果不可靠。
- 微小变化可能导致ViTs的分类准确率下降超过60%。
- 这是首次系统地证明ViT在医疗图像分类中表示缺乏语义意义的工作。
点此查看论文截图

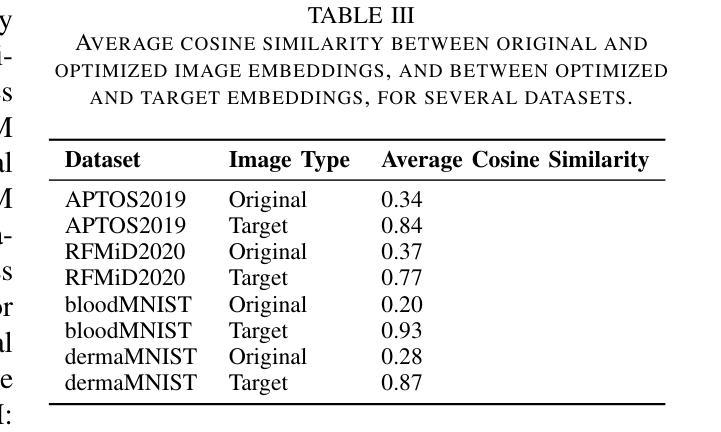
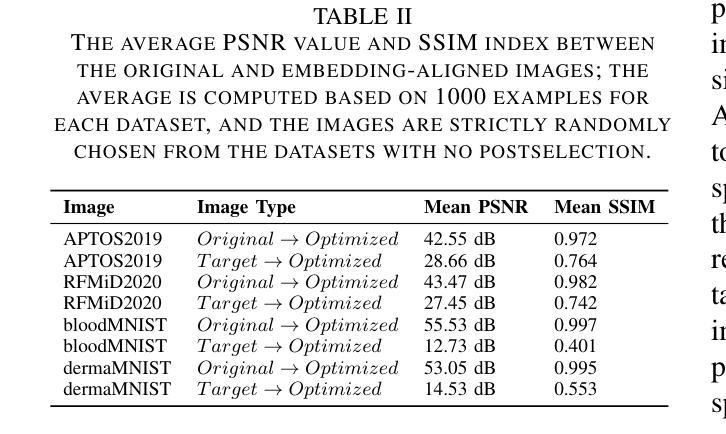
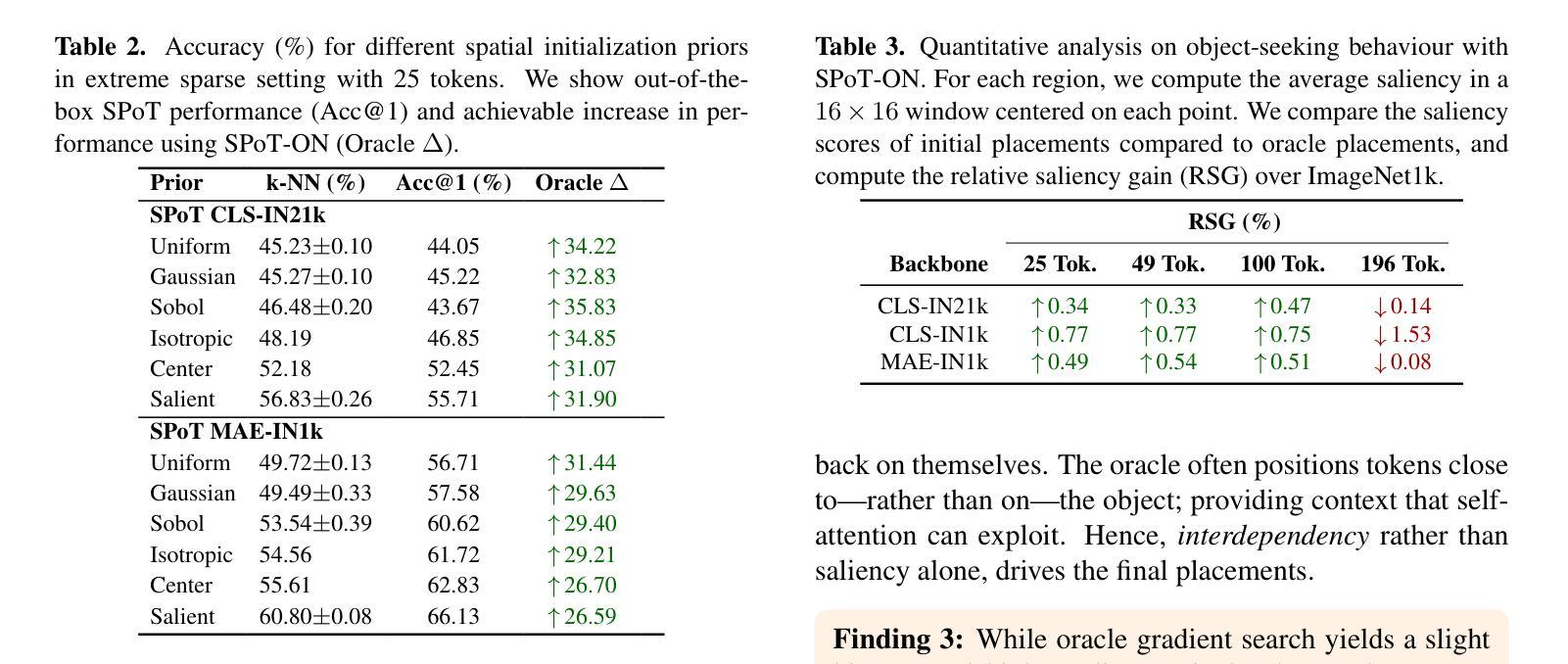
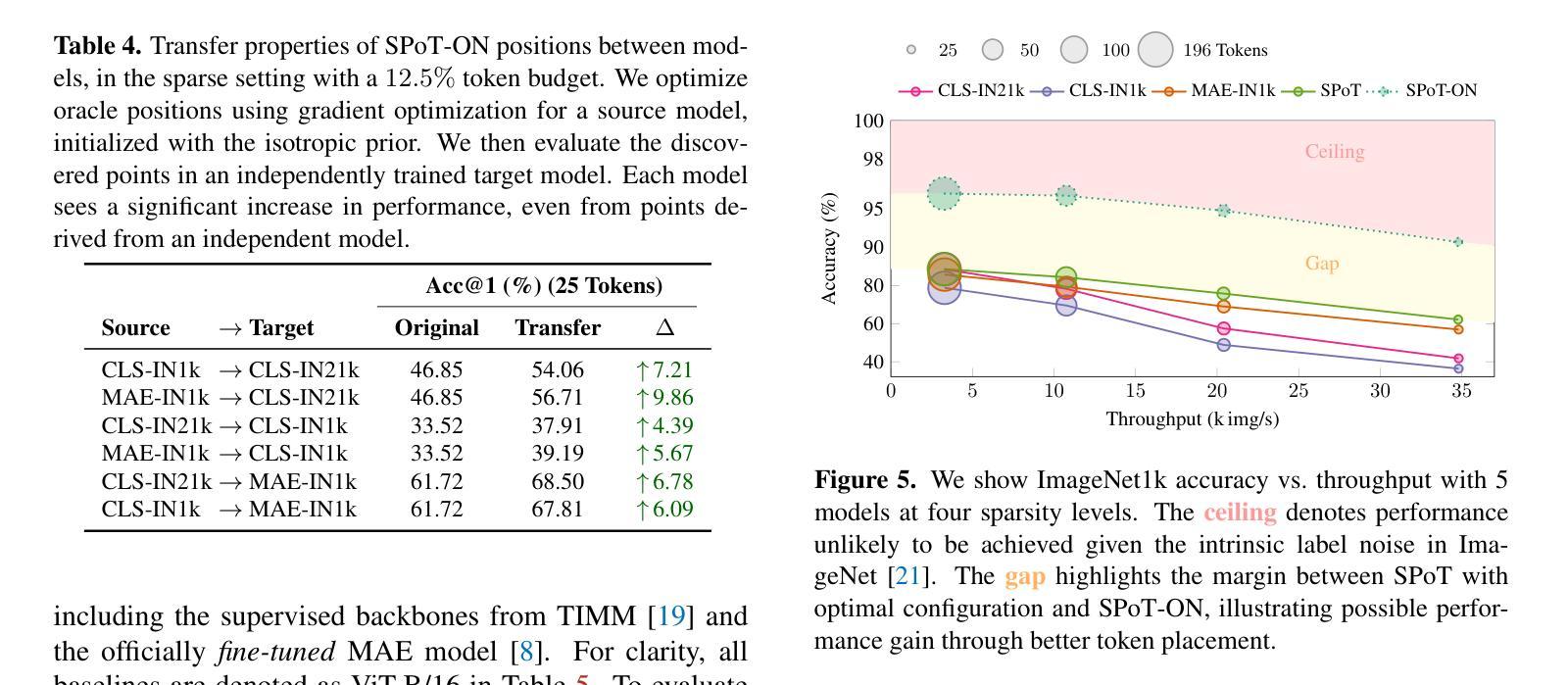
SPoT: Subpixel Placement of Tokens in Vision Transformers
Authors:Martine Hjelkrem-Tan, Marius Aasan, Gabriel Y. Arteaga, Adín Ramírez Rivera
Vision Transformers naturally accommodate sparsity, yet standard tokenization methods confine features to discrete patch grids. This constraint prevents models from fully exploiting sparse regimes, forcing awkward compromises. We propose Subpixel Placement of Tokens (SPoT), a novel tokenization strategy that positions tokens continuously within images, effectively sidestepping grid-based limitations. With our proposed oracle-guided search, we uncover substantial performance gains achievable with ideal subpixel token positioning, drastically reducing the number of tokens necessary for accurate predictions during inference. SPoT provides a new direction for flexible, efficient, and interpretable ViT architectures, redefining sparsity as a strategic advantage rather than an imposed limitation.
视觉Transformer自然地适应了稀疏性,但标准的令牌化方法将特征限制在离散补丁网格中。这一约束阻止了模型充分利用稀疏状态,迫使模型做出妥协。我们提出了Subpixel Token放置(SPoT)这种新型令牌化策略,能够在图像中连续放置令牌,有效地避免了基于网格的限制。通过我们提出的以oracle引导搜索,我们发现理想的子像素令牌放置可以实现显著的性能提升,极大地减少了推理过程中进行准确预测所需的令牌数量。SPoT为灵活、高效和可解释的ViT架构提供了新的方向,将稀疏性重新定义为战略优势而不是强制限制。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To appear in Workshop on Efficient Computing under Limited Resources: Visual Computing (ICCV 2025). Code available at https://github.com/dsb-ifi/SPoT
Summary
视觉转换器自然地适应稀疏性,但标准的令牌化方法将特征限制在离散补丁网格中。这种约束阻止了模型充分利用稀疏状态,迫使模型做出妥协。我们提出了Subpixel Placement of Tokens(SPoT)这一新的令牌化策略,该策略能够在图像中连续放置令牌,有效地避免了基于网格的限制。通过提出的oracle引导搜索,我们发现理想的子像素令牌位置可实现显著的性能提升,在推理过程中大大降低了准确预测所需的令牌数量。SPoT为灵活、高效、可解释的ViT架构提供了新的方向,重新定义稀疏性为战略优势而非强制限制。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉转换器具有适应稀疏性的自然特性。
- 传统的令牌化方法限制特征在离散补丁网格中,阻碍了模型性能的提升。
- SPoT策略能够在图像中连续放置令牌,突破基于网格的限制。
- 通过oracle引导搜索,发现理想子像素令牌位置能显著提高模型性能。
- SPoT策略降低了推理过程中准确预测所需的令牌数量,提升了模型的效率。
- SPoT为视觉变压器架构的发展提供了新的方向。
点此查看论文截图


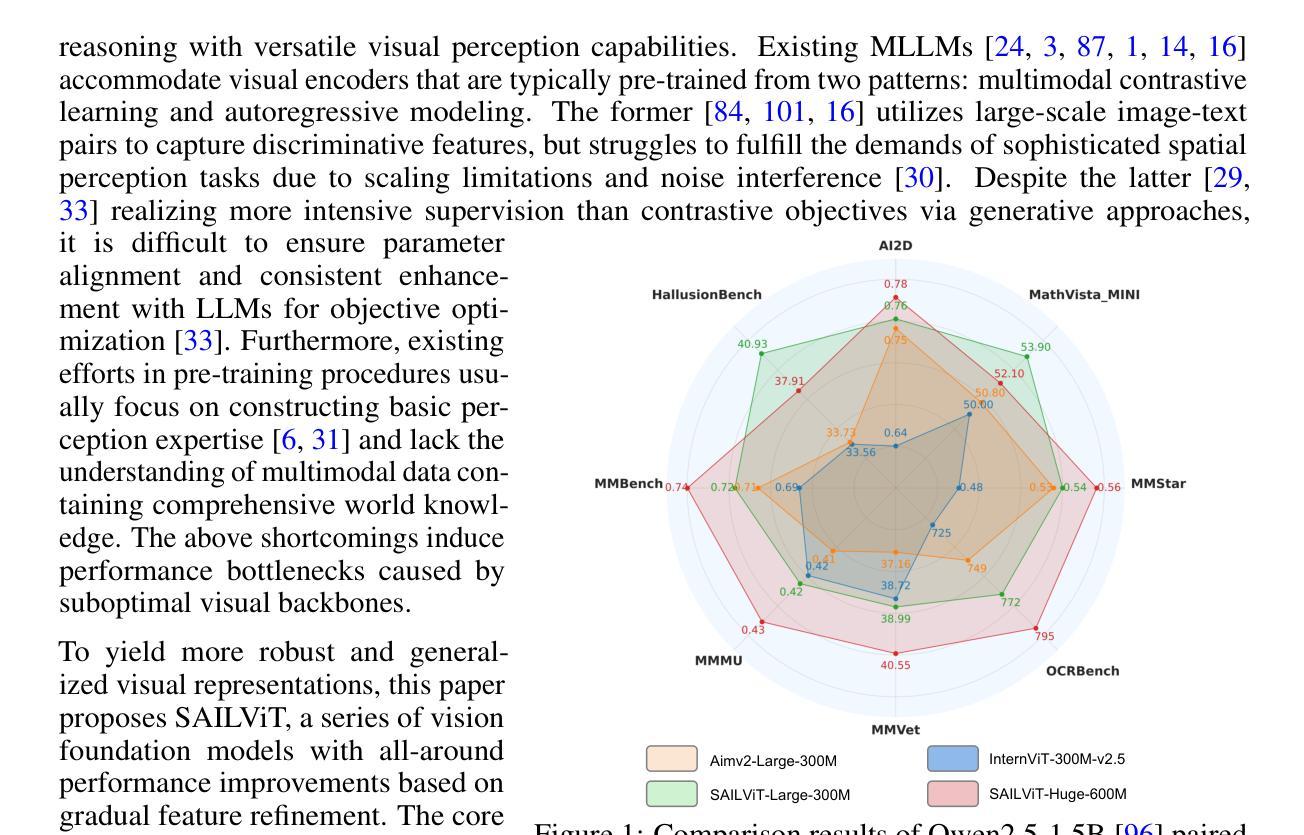
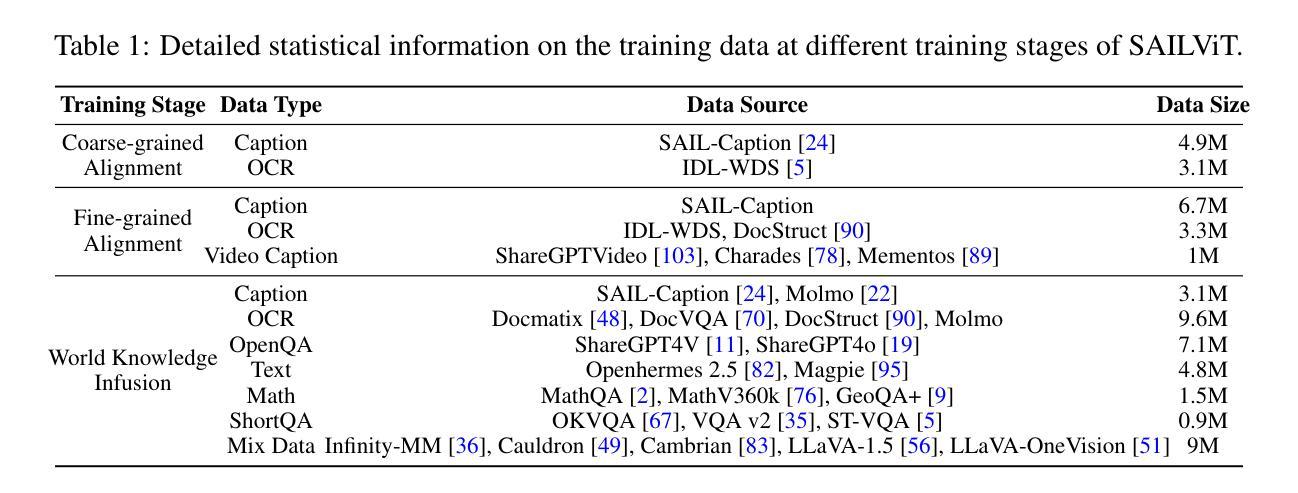
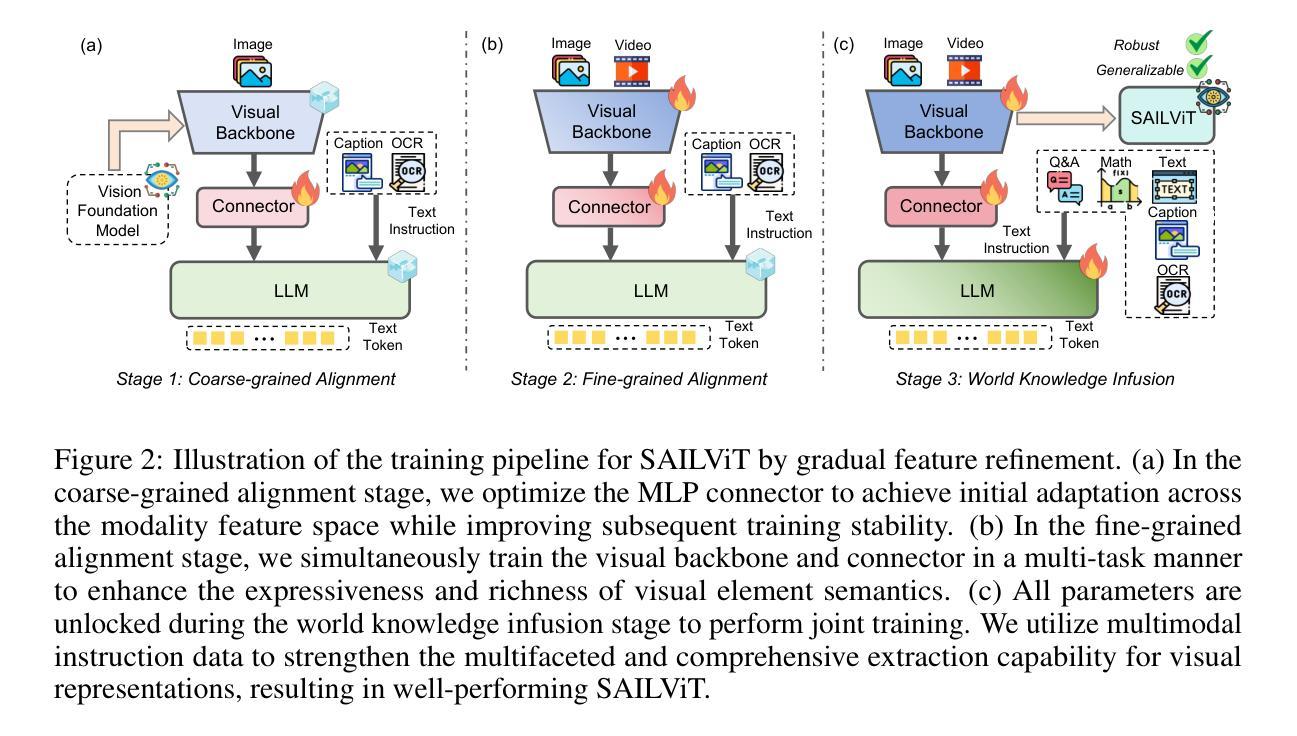
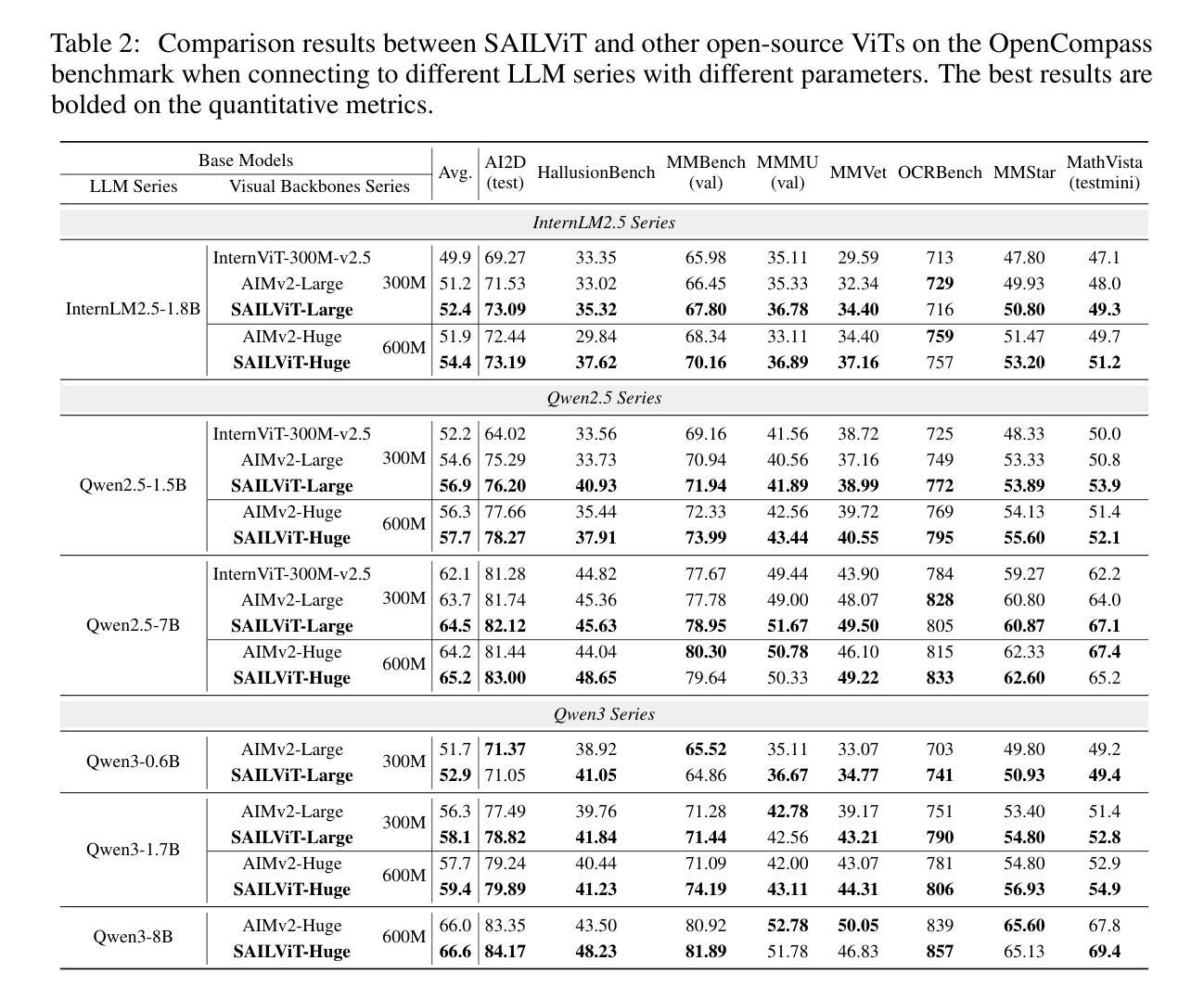
SAILViT: Towards Robust and Generalizable Visual Backbones for MLLMs via Gradual Feature Refinement
Authors:Weijie Yin, Dingkang Yang, Hongyuan Dong, Zijian Kang, Jiacong Wang, Xiao Liang, Chao Feng, Jiao Ran
Vision Transformers (ViTs) are essential as foundation backbones in establishing the visual comprehension capabilities of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). Although most ViTs achieve impressive performance through image-text pair-based contrastive learning or self-supervised mechanisms, they struggle to engage in connector-based co-training directly with LLMs due to potential parameter initialization conflicts and modality semantic gaps. To address the above challenges, this paper proposes SAILViT, a gradual feature learning-enhanced ViT for facilitating MLLMs to break through performance bottlenecks in complex multimodal interactions. SAILViT achieves coarse-to-fine-grained feature alignment and world knowledge infusion with gradual feature refinement, which better serves target training demands. We perform thorough empirical analyses to confirm the powerful robustness and generalizability of SAILViT across different dimensions, including parameter sizes, model architectures, training strategies, and data scales. Equipped with SAILViT, existing MLLMs show significant and consistent performance improvements on the OpenCompass benchmark across extensive downstream tasks. SAILViT series models are released at https://huggingface.co/BytedanceDouyinContent.
视觉Transformer(ViT)作为基础骨干在多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)的视觉理解能力构建中起到了关键作用。虽然大多数ViT通过基于图像文本对比的对比学习或自监督机制取得了令人印象深刻的性能,但由于潜在的参数初始化冲突和模态语义鸿沟,它们在直接与LLM进行基于连接器的协同训练方面遇到了困难。针对上述挑战,本文提出了SAILViT,这是一种用于促进MLLM在复杂多模态交互中突破性能瓶颈的逐步特征学习增强型ViT。SAILViT通过逐步特征细化实现粗到细粒度的特征对齐和世界知识注入,更好地服务于目标训练需求。我们进行了彻底的实证分析,以验证SAILViT在不同维度,包括参数大小、模型架构、训练策略和数据规模上的强大稳健性和通用性。配备SAILViT的现有MLLM在OpenCompass基准测试上表现出显著且一致的性能改进。SAILViT系列模型已发布在https://huggingface.co/BytedanceDouyinContent上。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF We release SAILViT, a series of versatile vision foundation models
Summary
ViTs作为多模态大语言模型(MLLMs)的视觉理解基础骨架至关重要。尽管大多数ViTs通过图像文本对对比学习或自监督机制取得了令人印象深刻的性能,但它们与LLMs的直接连接器共训练面临着潜在的参数初始化冲突和模态语义鸿沟的挑战。为解决上述问题,本文提出了SAILViT,这是一种具有渐进特征学习能力的ViT,有助于MLLMs在复杂的多模态交互中突破性能瓶颈。SAILViT通过渐进特征细化实现粗到细粒度的特征对齐和世界知识注入,更好地服务于目标训练需求。通过彻底的实证分析,我们证实了SAILViT在不同维度上的强大稳健性和泛化能力,包括参数大小、模型架构、训练策略和数据规模。配备SAILViT的现有MLLMs在OpenCompass基准测试上的下游任务中显示出显著且一致的性能改进。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformers (ViTs) 扮演多模态大语言模型(MLLMs)视觉理解基础骨架的关键角色。
- ViTs虽然能通过图像文本对比学习或自监督机制取得良好性能,但在与LLMs直接连接器共训练时面临参数初始化冲突和模态语义鸿沟的挑战。
- SAILViT是一种改进的ViT模型,通过渐进特征学习能力,有助于MLLMs在复杂多模态交互中突破性能瓶颈。
- SAILViT实现粗到细粒度的特征对齐和世界知识注入。
- 实证分析表明,SAILViT在参数大小、模型架构、训练策略和数据规模等多个维度上具有强大的稳健性和泛化能力。
- 配备SAILViT的MLLMs在OpenCompass基准测试上的性能得到显著改善。
点此查看论文截图

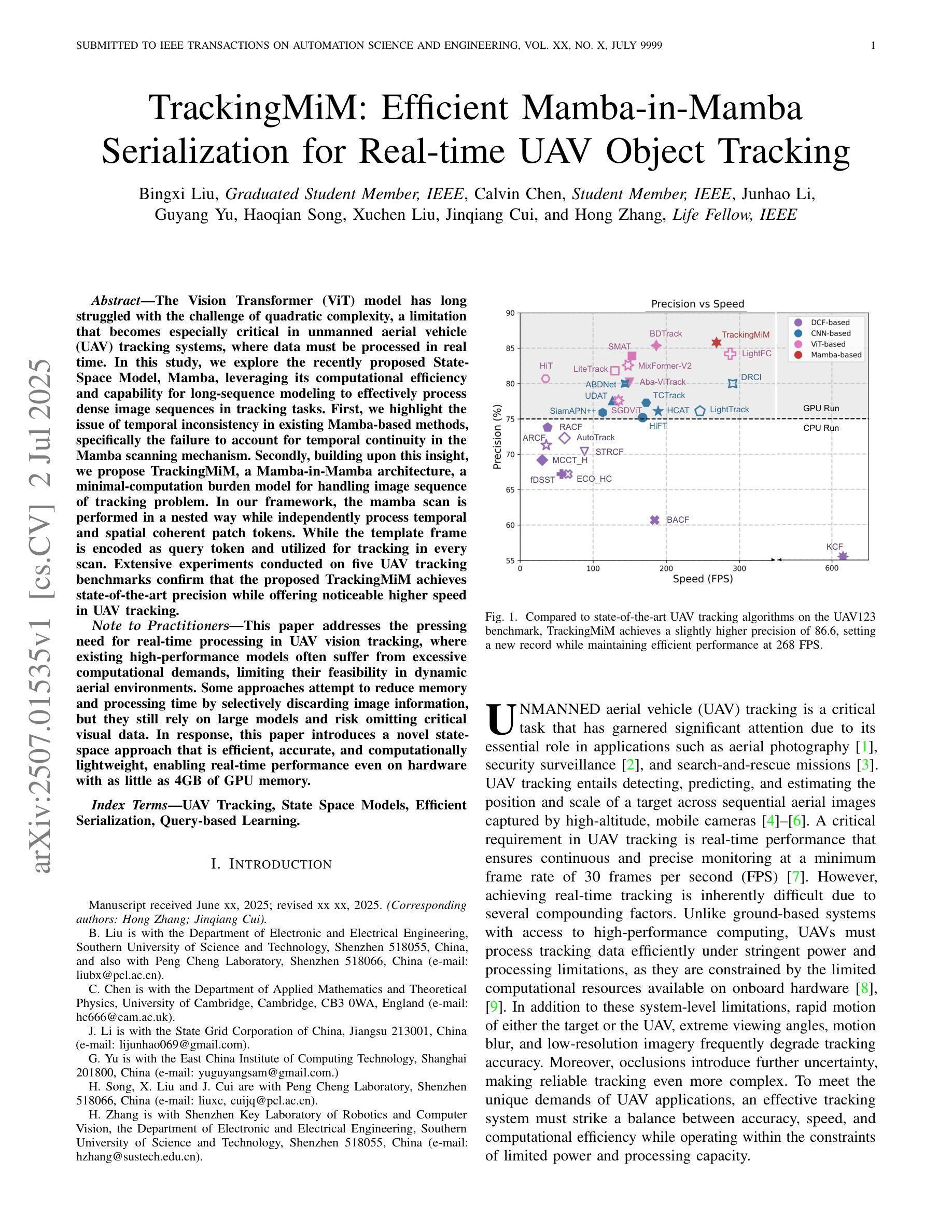
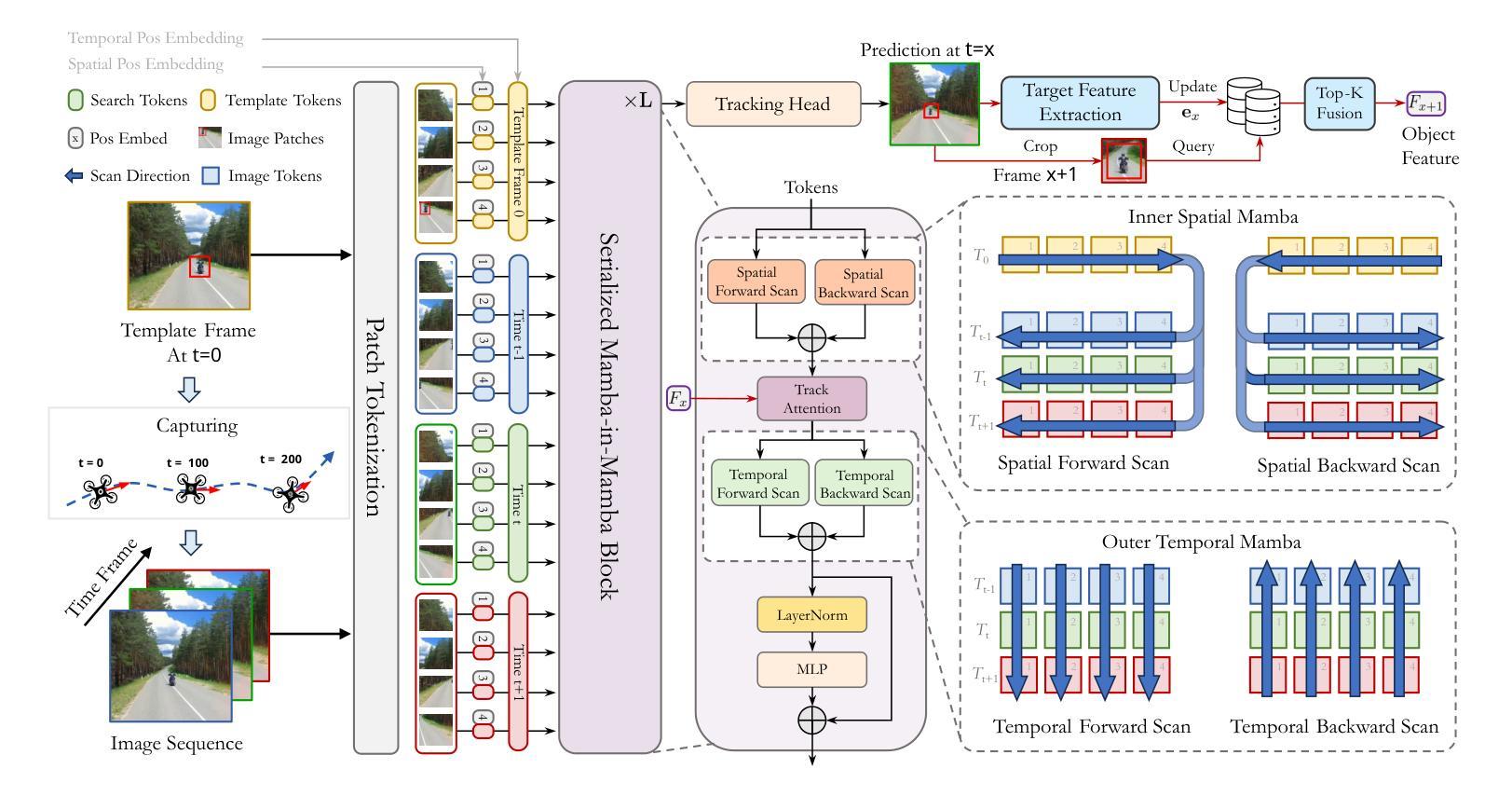
TrackingMiM: Efficient Mamba-in-Mamba Serialization for Real-time UAV Object Tracking
Authors:Bingxi Liu, Calvin Chen, Junhao Li, Guyang Yu, Haoqian Song, Xuchen Liu, Jinqiang Cui, Hong Zhang
The Vision Transformer (ViT) model has long struggled with the challenge of quadratic complexity, a limitation that becomes especially critical in unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) tracking systems, where data must be processed in real time. In this study, we explore the recently proposed State-Space Model, Mamba, leveraging its computational efficiency and capability for long-sequence modeling to effectively process dense image sequences in tracking tasks. First, we highlight the issue of temporal inconsistency in existing Mamba-based methods, specifically the failure to account for temporal continuity in the Mamba scanning mechanism. Secondly, building upon this insight,we propose TrackingMiM, a Mamba-in-Mamba architecture, a minimal-computation burden model for handling image sequence of tracking problem. In our framework, the mamba scan is performed in a nested way while independently process temporal and spatial coherent patch tokens. While the template frame is encoded as query token and utilized for tracking in every scan. Extensive experiments conducted on five UAV tracking benchmarks confirm that the proposed TrackingMiM achieves state-of-the-art precision while offering noticeable higher speed in UAV tracking.
Vision Transformer(ViT)模型长期以来一直面临着二次复杂度的挑战,这一限制在无人飞行器(UAV)跟踪系统中尤为关键,因为数据必须实时处理。在这项研究中,我们探索了最近提出的State-Space Model,即Mamba模型,利用其计算效率和长序列建模能力,有效处理跟踪任务中的密集图像序列。首先,我们强调了现有Mamba方法中存在的时间不一致性问题,特别是Mamba扫描机制未能考虑到时间的连续性。其次,基于这一见解,我们提出了TrackingMiM,这是一个Mamba-in-Mamba架构,是一个用于处理跟踪问题图像序列的最小计算负担模型。在我们的框架中,mamba扫描以嵌套的方式进行,同时独立处理时间和空间连贯的补丁令牌。同时,模板帧被编码为查询令牌,并在每次扫描中用于跟踪。在五个UAV跟踪基准测试上进行的广泛实验证实,所提出的TrackingMiM达到了最先进的精度,同时在UAV跟踪中提供了明显的更高速度。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages
Summary
该文章介绍了针对Vision Transformer模型在处理无人机追踪系统中的二次复杂度问题进行研究的结果。文章探讨了最近提出的State-Space模型Mamba在解决该问题方面的潜力,并指出了现有Mamba方法存在的时序不一致性问题。在此基础上,文章提出了一种基于Mamba的TrackingMiM架构,该架构以最小的计算负担处理跟踪问题的图像序列。实验证明,TrackingMiM在五个无人机追踪基准测试中达到了最先进的精度,同时在无人机追踪中提供了更高的速度。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformer模型在无人机追踪系统中面临二次复杂度挑战。
- State-Space模型Mamba在处理实时数据处理方面具有计算效率和长期序列建模能力。
- 现有Mamba方法存在时序不一致性问题,未能充分考虑时序连续性。
- TrackingMiM架构被提出,它是一种基于Mamba的嵌套扫描方式处理跟踪问题的图像序列的模型。
- TrackingMiM能同时处理时序和空间连贯的补丁令牌,并将模板帧编码为查询令牌,用于每次扫描中的跟踪。
- TrackingMiM在五个无人机追踪基准测试中实现了最先进的精度。
点此查看论文截图
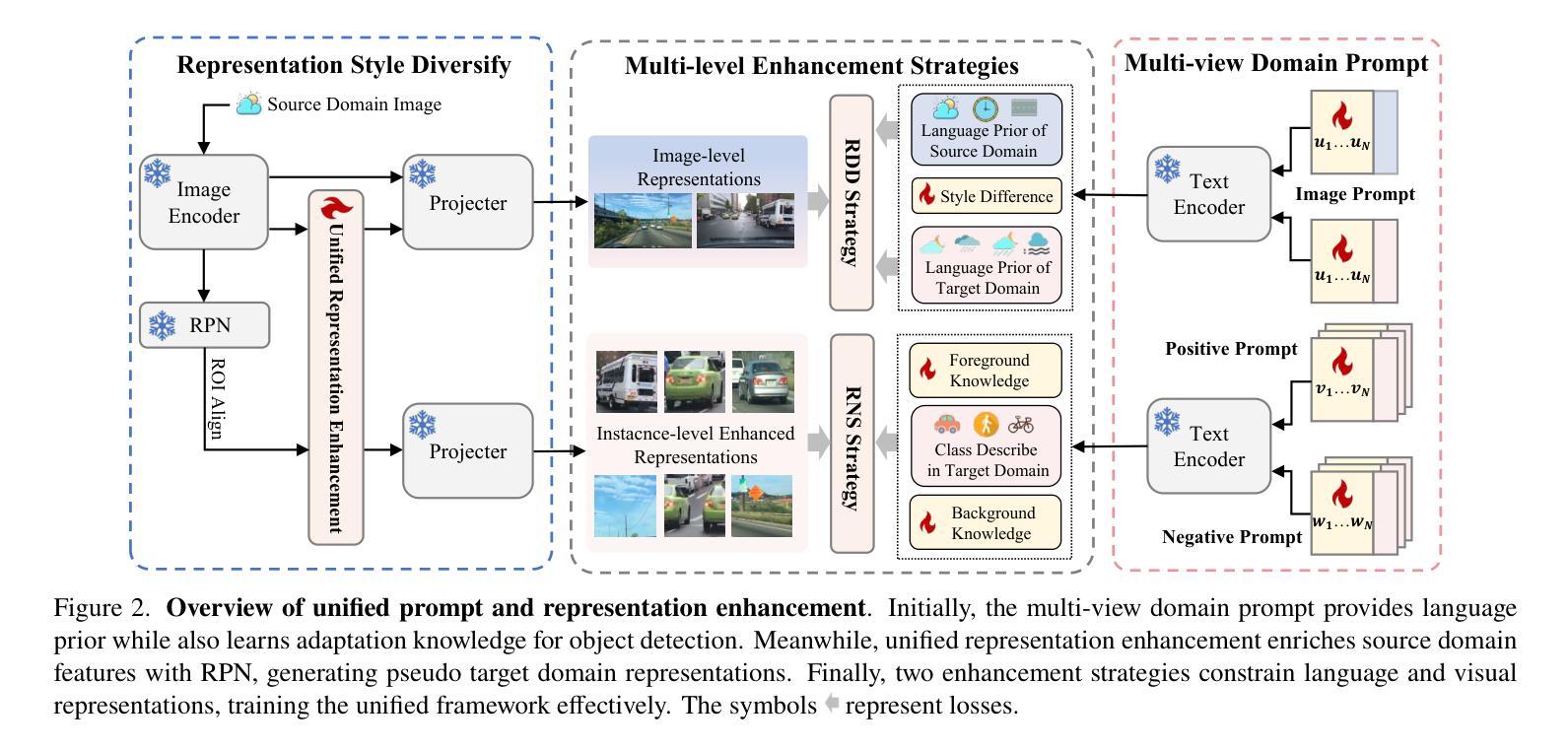
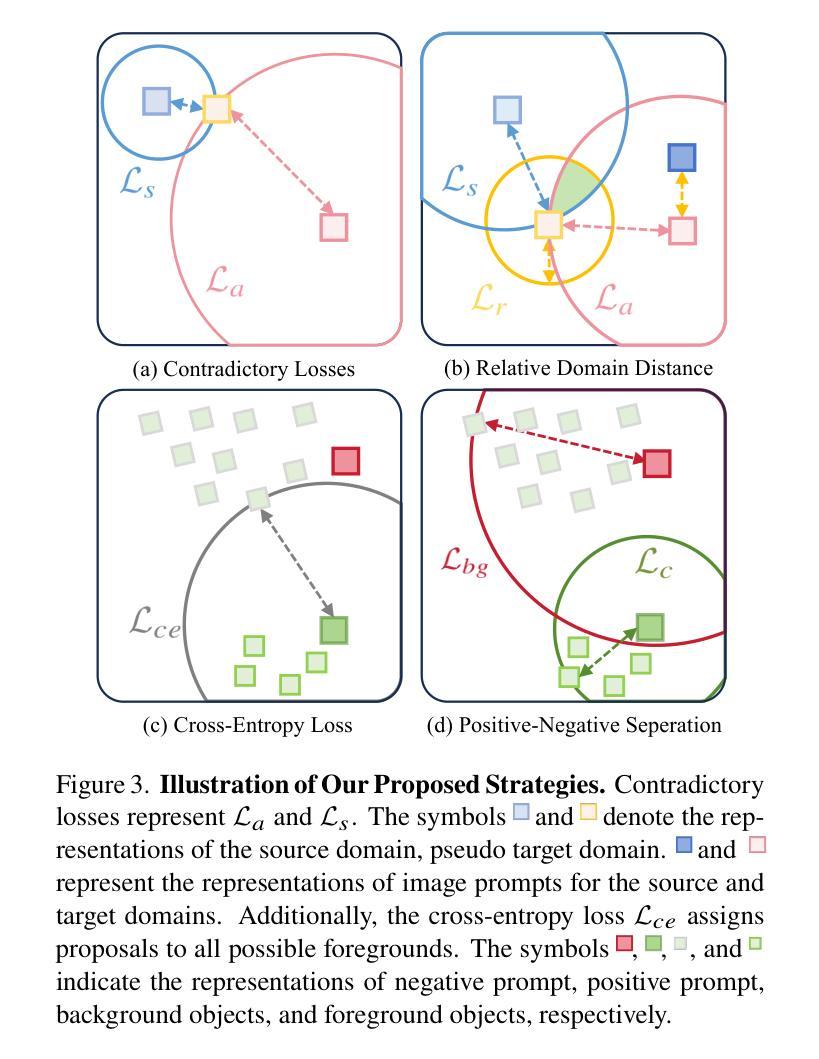
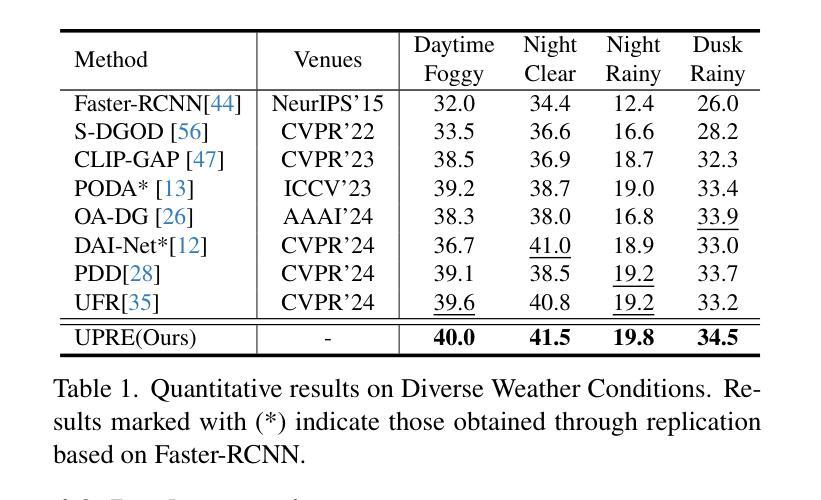
UPRE: Zero-Shot Domain Adaptation for Object Detection via Unified Prompt and Representation Enhancement
Authors:Xiao Zhang, Fei Wei, Yong Wang, Wenda Zhao, Feiyi Li, Xiangxiang Chu
Zero-shot domain adaptation (ZSDA) presents substantial challenges due to the lack of images in the target domain. Previous approaches leverage Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to tackle this challenge, exploiting their zero-shot learning capabilities. However, these methods primarily address domain distribution shifts and overlook the misalignment between the detection task and VLMs, which rely on manually crafted prompts. To overcome these limitations, we propose the unified prompt and representation enhancement (UPRE) framework, which jointly optimizes both textual prompts and visual representations. Specifically, our approach introduces a multi-view domain prompt that combines linguistic domain priors with detection-specific knowledge, and a visual representation enhancement module that produces domain style variations. Furthermore, we introduce multi-level enhancement strategies, including relative domain distance and positive-negative separation, which align multi-modal representations at the image level and capture diverse visual representations at the instance level, respectively. Extensive experiments conducted on nine benchmark datasets demonstrate the superior performance of our framework in ZSDA detection scenarios. Code is available at https://github.com/AMAP-ML/UPRE.
零样本域自适应(ZSDA)由于目标域缺乏图像而面临巨大挑战。之前的方法利用视觉语言模型(VLM)来应对这一挑战,发挥它们的零样本学习能力。然而,这些方法主要解决域分布转移问题,而忽略了检测任务与VLM之间的不匹配,VLM依赖于手工制作的提示。为了克服这些限制,我们提出了统一提示和表示增强(UPRE)框架,该框架联合优化了文本提示和视觉表示。具体而言,我们的方法引入了一种多视图域提示,将语言域先验知识与检测特定知识相结合,以及一个视觉表示增强模块,用于生成域风格变化。此外,我们引入了多层次增强策略,包括相对域距离和正负分离,分别在图像级别对齐多模式表示,在实例级别捕获多样化的视觉表示。在九个基准数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,我们的框架在ZSDA检测场景中具有卓越的性能。代码可在https://github.com/AMAP-ML/UPRE找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV2025
Summary
本文提出一种名为UPRE的统一提示和表示增强框架,用于解决零镜头域适应(ZSDA)检测中的挑战。该框架联合优化文本提示和视觉表示,通过引入多视角域提示和视觉表示增强模块,并结合相对域距离和多级增强策略,提高了ZSDA检测场景的性能。
Key Takeaways
- UPRE框架解决了零镜头域适应(ZSDA)检测中的挑战,通过联合优化文本提示和视觉表示。
- 引入多视角域提示,结合语言域先验和检测特定知识。
- 视觉表示增强模块用于生成具有域风格变化的表示。
- 采用相对域距离和正负分离的多级增强策略,分别对齐图像级别的多模式表示和捕获实例级别的多样视觉表示。
- 在九个基准数据集上进行的广泛实验证明了UPRE框架在ZSDA检测场景中的优越性。
- 代码已公开,便于研究者和开发者使用。
点此查看论文截图

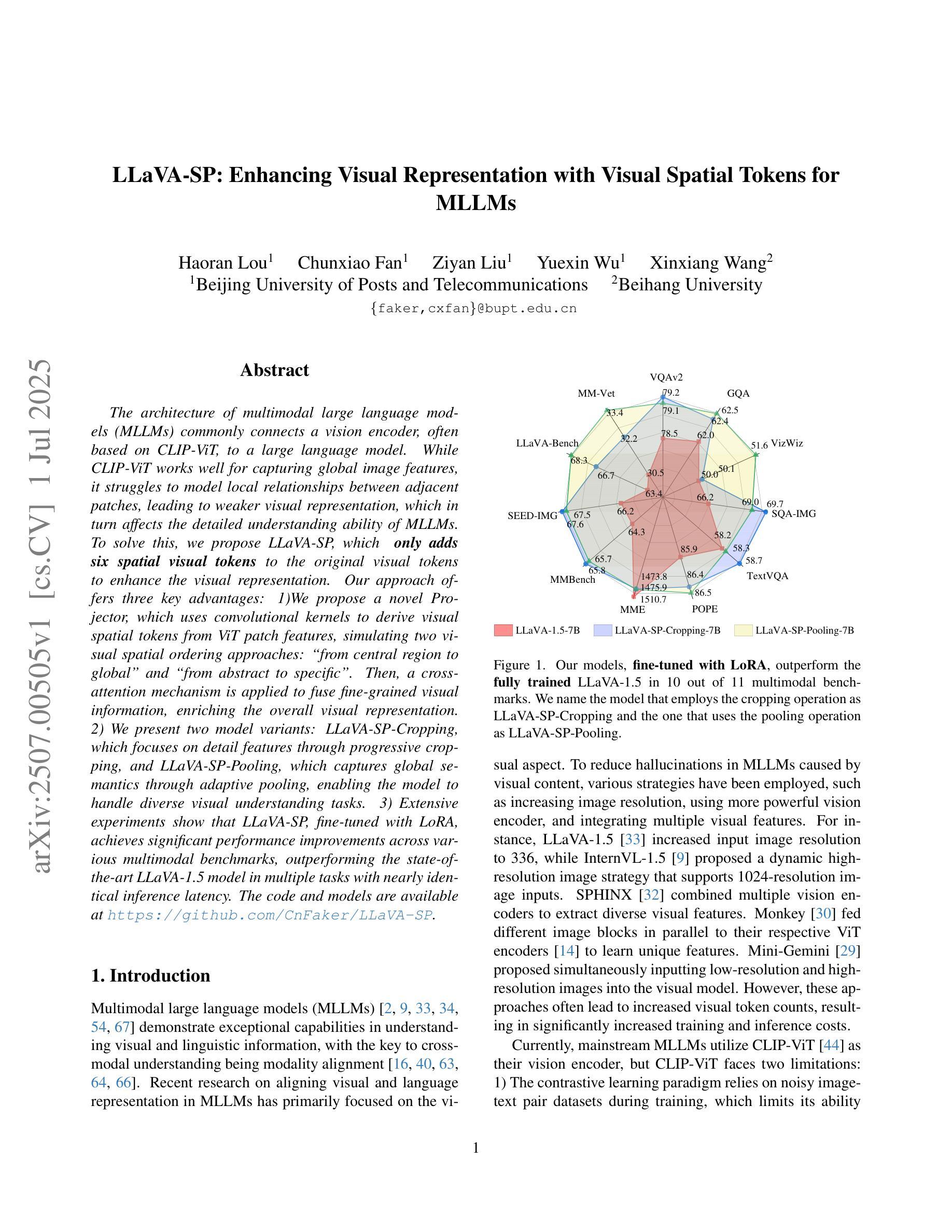
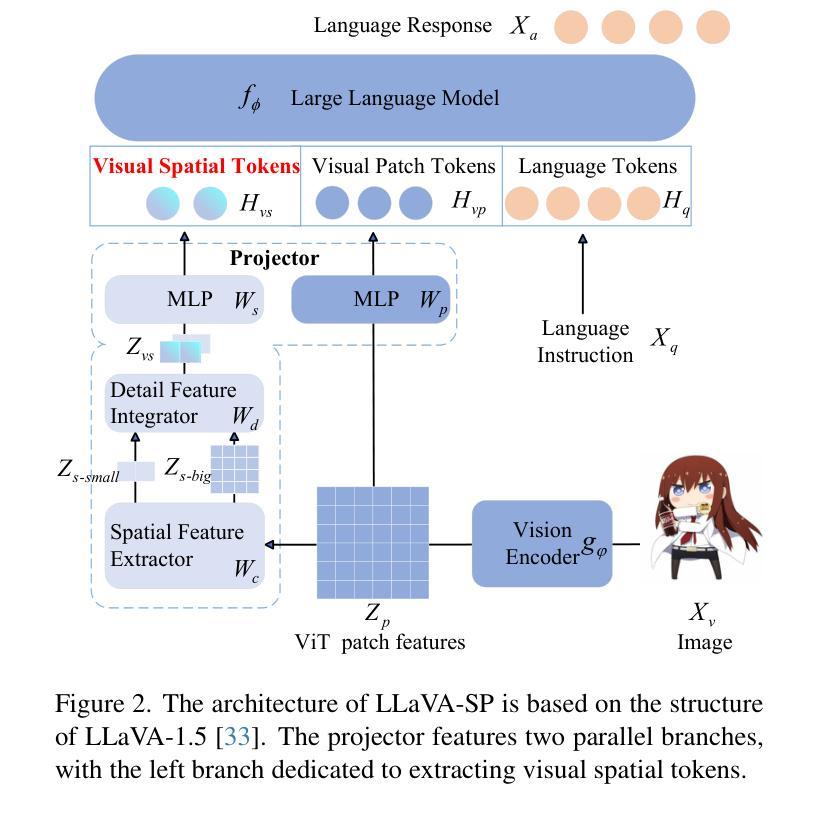
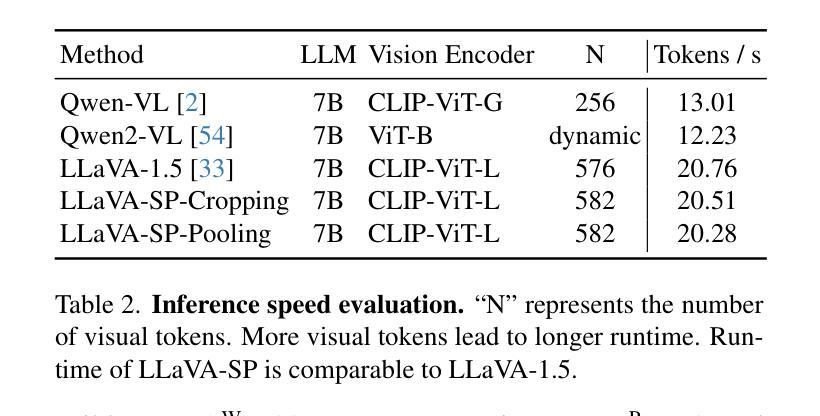
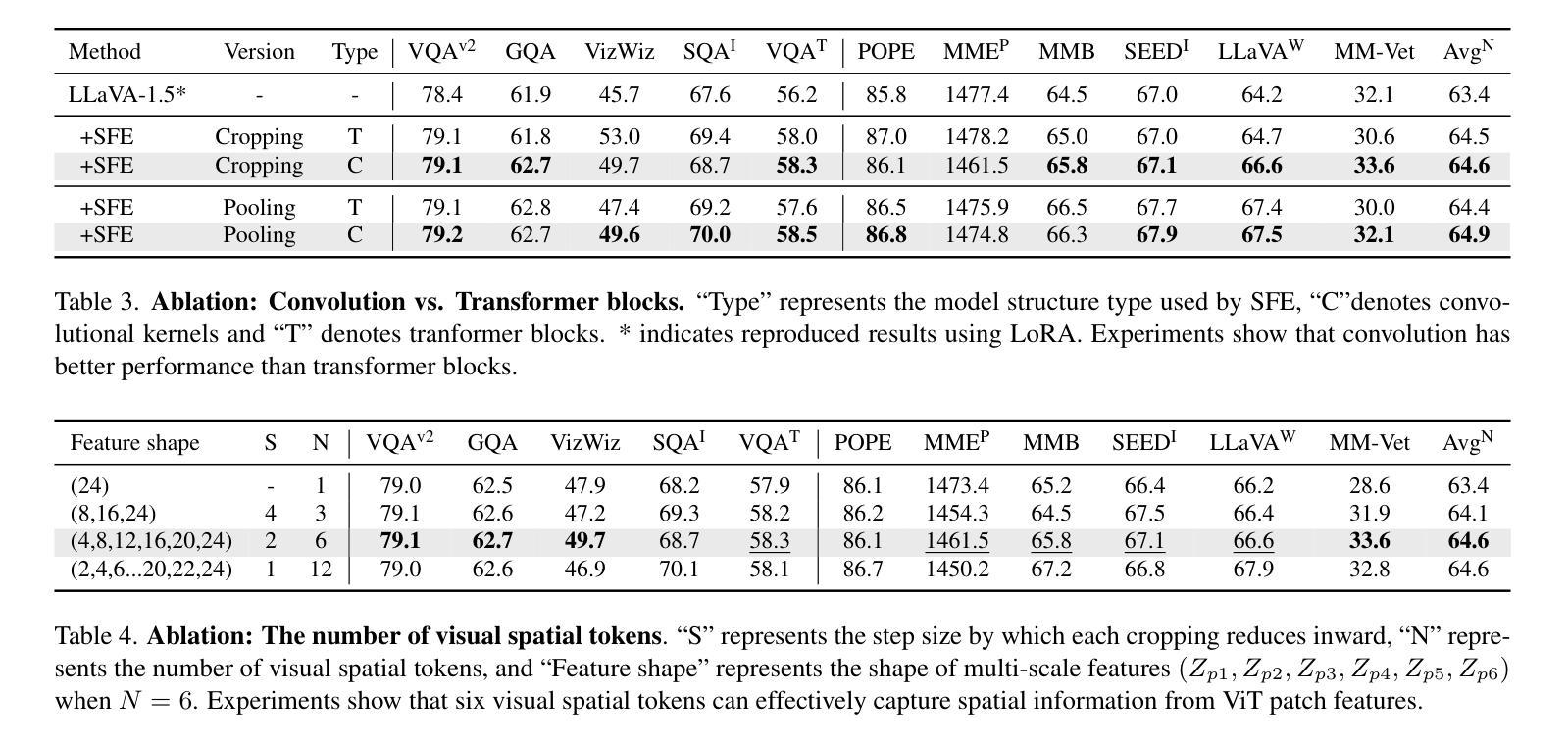
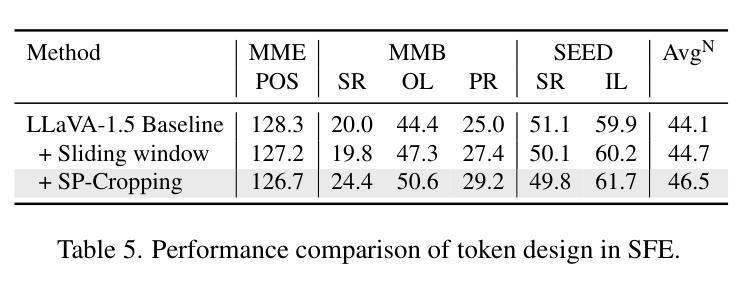
LLaVA-SP: Enhancing Visual Representation with Visual Spatial Tokens for MLLMs
Authors:Haoran Lou, Chunxiao Fan, Ziyan Liu, Yuexin Wu, Xinxiang Wang
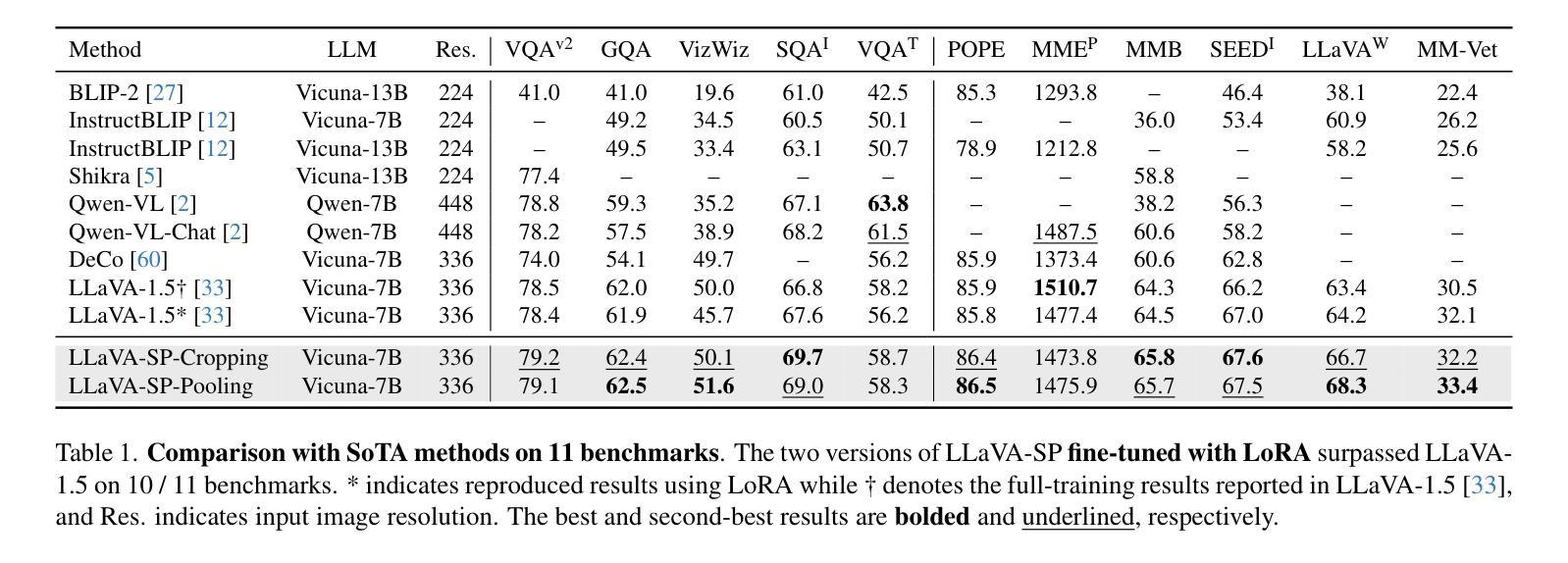
The architecture of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) commonly connects a vision encoder, often based on CLIP-ViT, to a large language model. While CLIP-ViT works well for capturing global image features, it struggles to model local relationships between adjacent patches, leading to weaker visual representation, which in turn affects the detailed understanding ability of MLLMs. To solve this, we propose LLaVA-SP, which \textbf{ only adds six spatial visual tokens} to the original visual tokens to enhance the visual representation. Our approach offers three key advantages: 1)We propose a novel Projector, which uses convolutional kernels to derive visual spatial tokens from ViT patch features, simulating two visual spatial ordering approaches: from central region to global" and from abstract to specific”. Then, a cross-attention mechanism is applied to fuse fine-grained visual information, enriching the overall visual representation. 2) We present two model variants: LLaVA-SP-Cropping, which focuses on detail features through progressive cropping, and LLaVA-SP-Pooling, which captures global semantics through adaptive pooling, enabling the model to handle diverse visual understanding tasks. 3) Extensive experiments show that LLaVA-SP, fine-tuned with LoRA, achieves significant performance improvements across various multimodal benchmarks, outperforming the state-of-the-art LLaVA-1.5 model in multiple tasks with nearly identical inference latency. The code and models are available at \href{https://github.com/CnFaker/LLaVA-SP}{\texttt{https://github.com/CnFaker/LLaVA-SP}}.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的架构通常将基于CLIP-ViT的视觉编码器连接到大型语言模型。虽然CLIP-ViT在捕捉全局图像特征方面表现良好,但在对相邻补丁之间的局部关系进行建模时遇到困难,导致视觉表示较弱,进而影响了MLLM的详细理解能力。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了LLaVA-SP,它通过在原始视觉标记中添加六个空间视觉标记来增强视觉表示。我们的方法提供了三个关键优势:
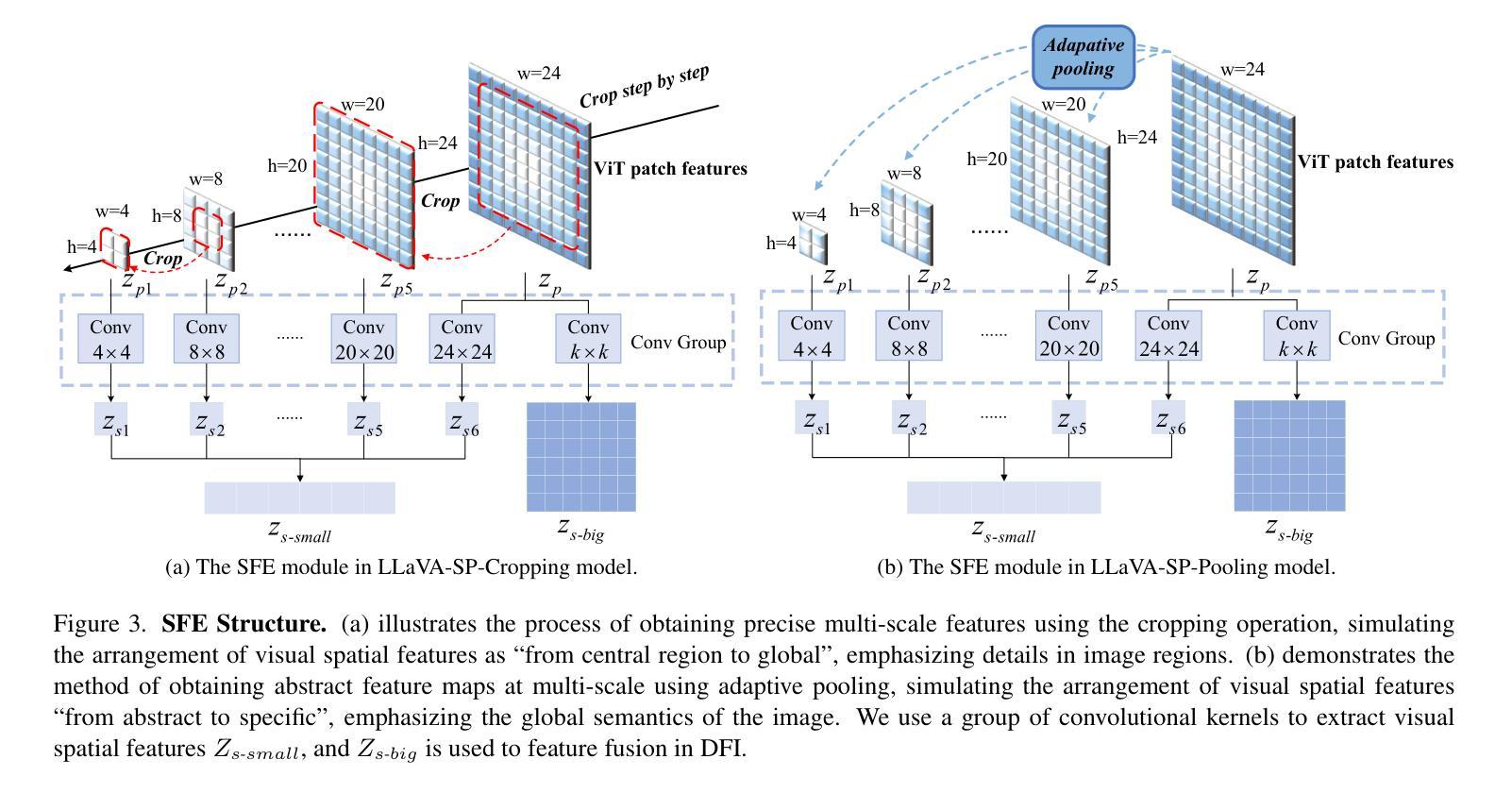
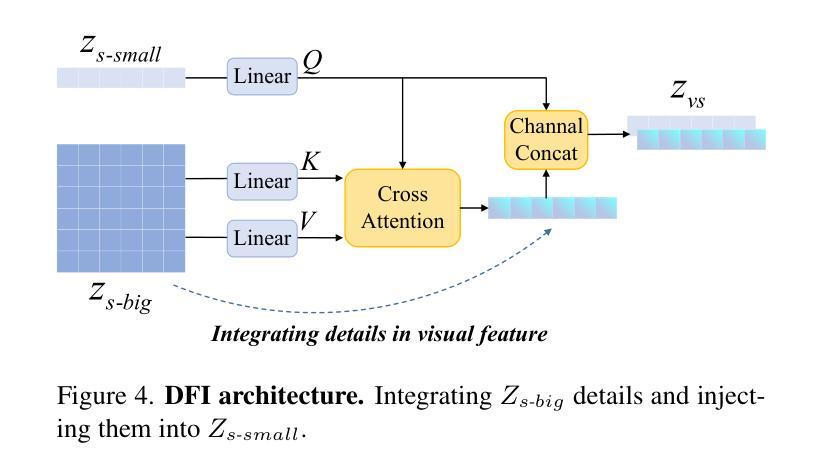
1)我们提出了一种新型投影仪,该投影仪使用卷积核从ViT补丁特征中推导出视觉空间标记,模拟两种视觉空间排序方法:“从中心区域到全局”和“从抽象到具体”。然后应用交叉注意力机制融合精细的视觉信息,丰富整体的视觉表示。
2)我们推出了两款模型变体:LLaVA-SP-Cropping,通过渐进裁剪关注细节特征;以及LLaVA-SP-Pooling,通过自适应池化捕捉全局语义,使模型能够处理各种视觉理解任务。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV
Summary
该文本介绍了一种名为LLaVA-SP的多模态大型语言模型架构改进方案。针对CLIP-ViT在捕捉局部图像关系方面的不足,LLaVA-SP仅添加六个空间视觉令牌来增强视觉表示。该方法通过卷积核生成空间视觉令牌,模拟两种视觉空间排序方法,并通过跨注意力机制融合精细视觉信息,丰富了整体视觉表示。该方法还提供了两种模型变体,并在多种多模态基准测试中实现了显著的性能提升。LLaVA-SP与LoRA微调后,在多任务中优于当前先进的LLaVA-1.5模型,且推理延迟几乎相同。
Key Takeaways
- LLaVA-SP针对CLIP-ViT在捕捉局部图像关系方面的不足提出了解决方案。
- LLaVA-SP通过添加六个空间视觉令牌增强视觉表示。
- 使用卷积核生成空间视觉令牌,模拟两种视觉空间排序方法。
- 跨注意力机制用于融合精细视觉信息,丰富整体视觉表示。
- LLaVA-SP提供两种模型变体,以适应不同的视觉理解任务。
- 广泛实验表明,LLaVA-SP在多模态基准测试中实现了显著性能提升。
- LLaVA-SP与LoRA微调后,在多任务中优于LLaVA-1.5模型,且推理延迟低。
点此查看论文截图
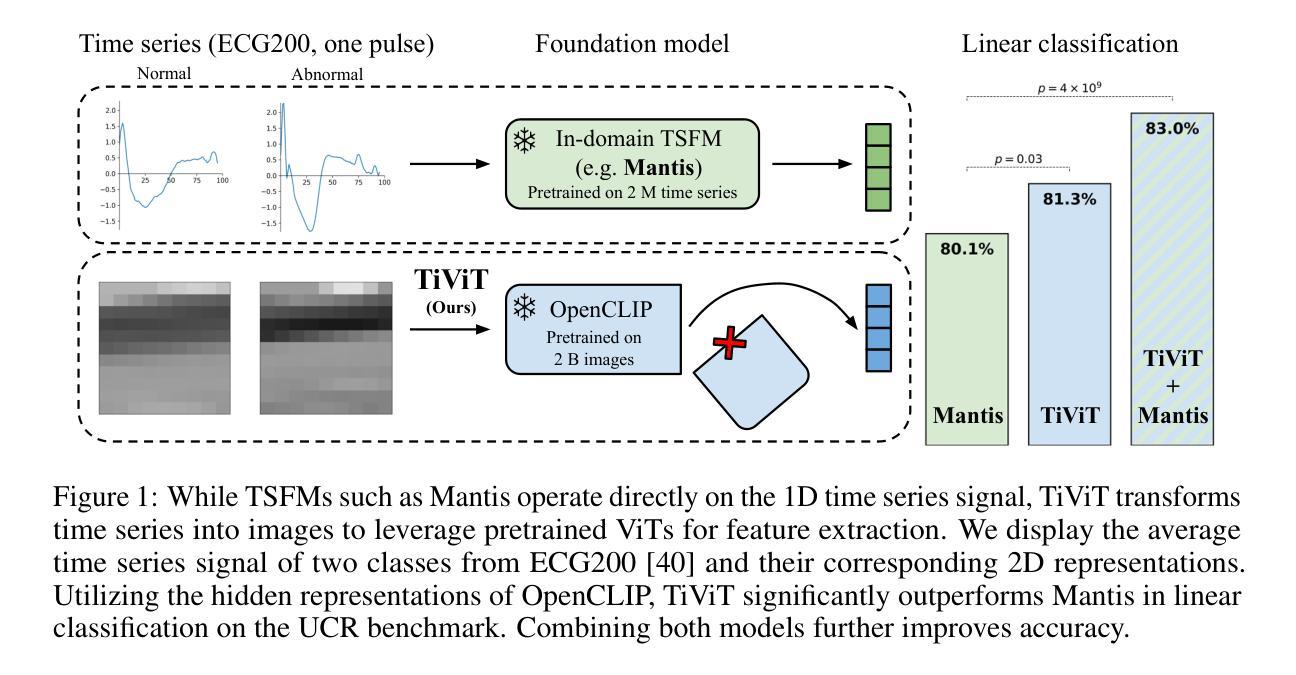
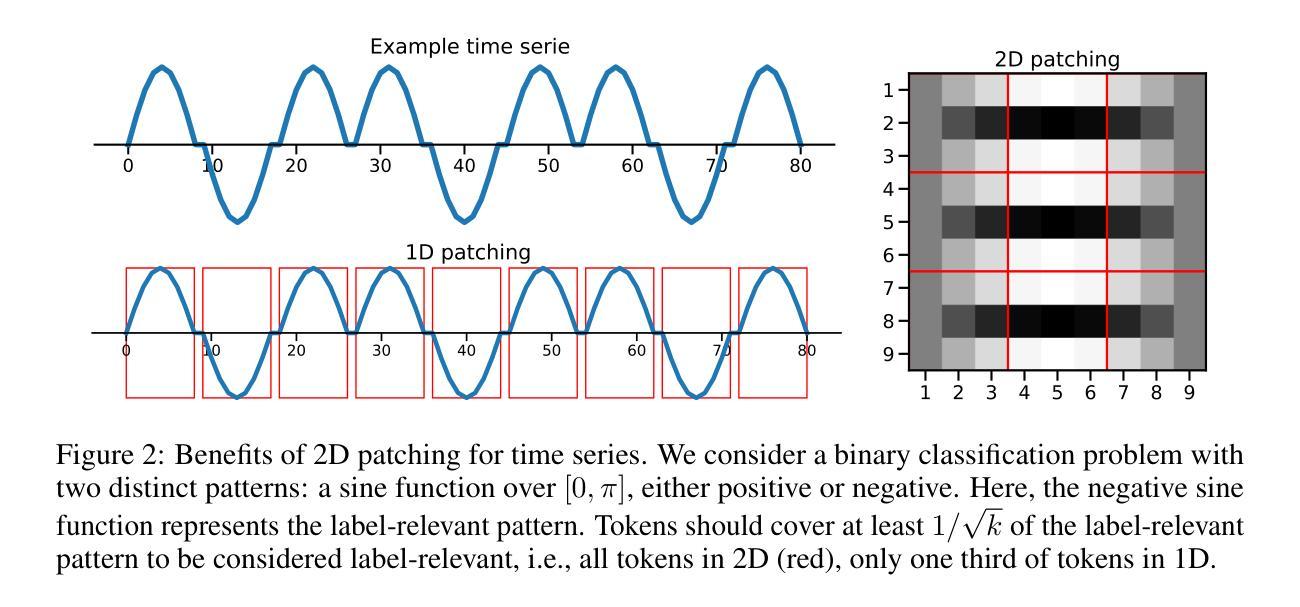
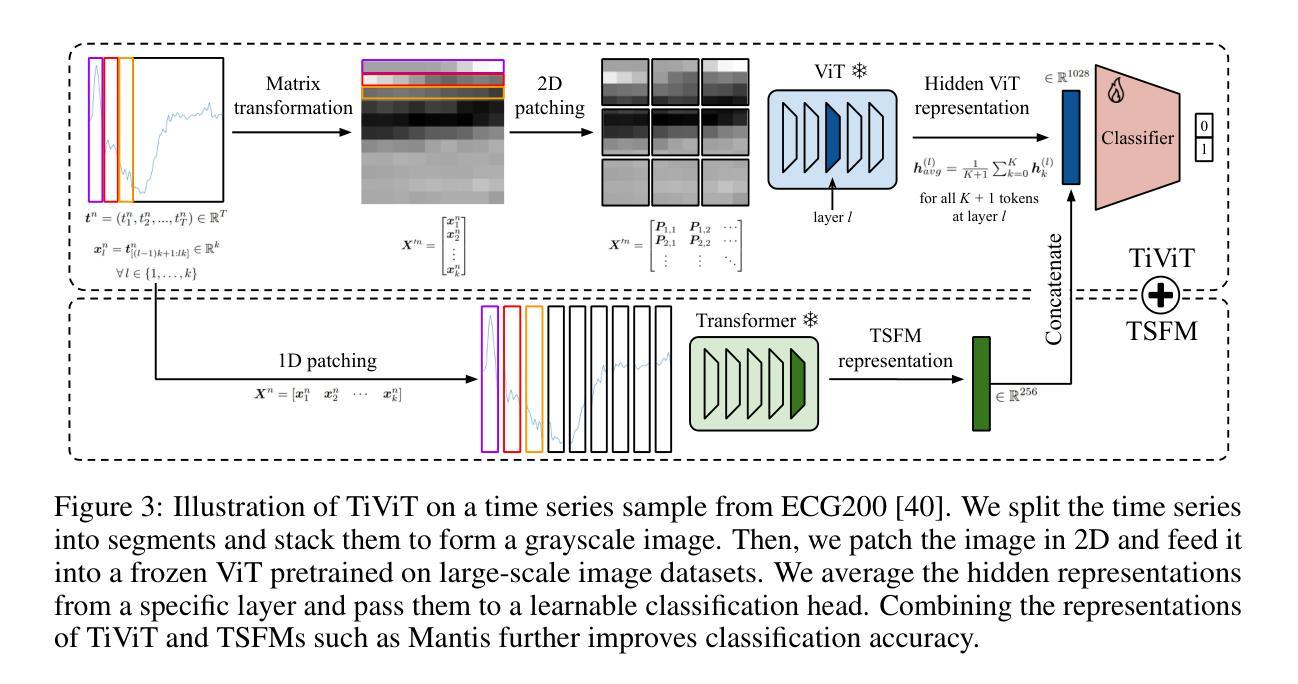
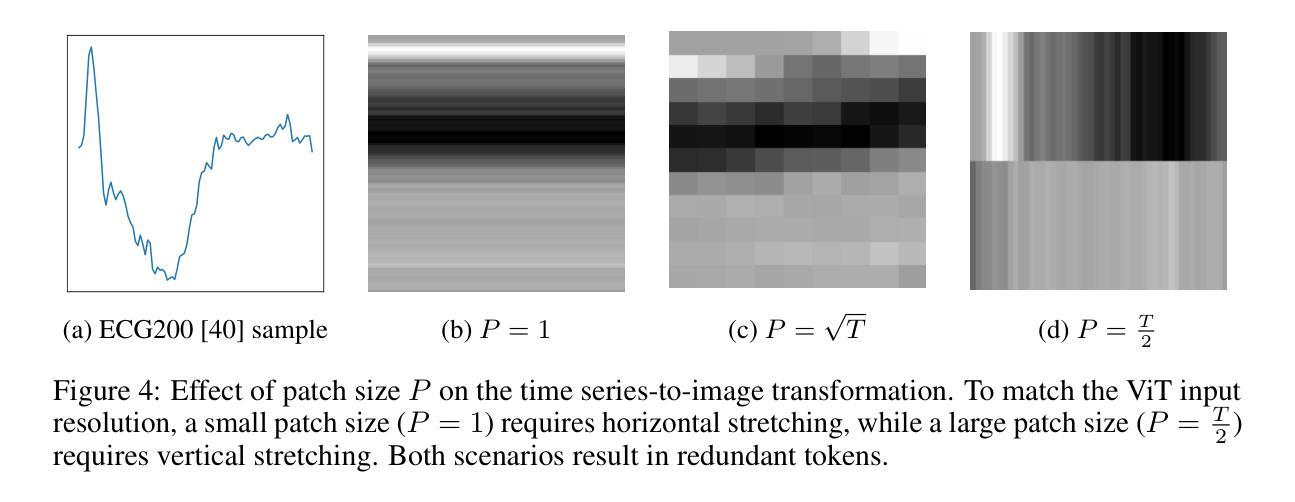
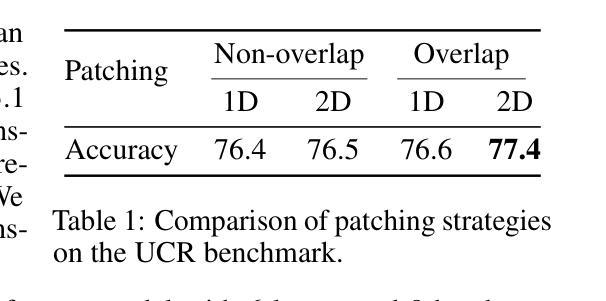
Time Series Representations for Classification Lie Hidden in Pretrained Vision Transformers
Authors:Simon Roschmann, Quentin Bouniot, Vasilii Feofanov, Ievgen Redko, Zeynep Akata
Time series classification is a fundamental task in healthcare and industry, yet the development of time series foundation models (TSFMs) remains limited by the scarcity of publicly available time series datasets. In this work, we propose Time Vision Transformer (TiViT), a framework that converts time series into images to leverage the representational power of frozen Vision Transformers (ViTs) pretrained on large-scale image datasets. First, we theoretically motivate our approach by analyzing the 2D patching of ViTs for time series, showing that it can increase the number of label-relevant tokens and reduce the sample complexity. Second, we empirically demonstrate that TiViT achieves state-of-the-art performance on standard time series classification benchmarks by utilizing the hidden representations of large OpenCLIP models. We explore the structure of TiViT representations and find that intermediate layers with high intrinsic dimension are the most effective for time series classification. Finally, we assess the alignment between TiViT and TSFM representation spaces and identify a strong complementarity, with further performance gains achieved by combining their features. Our findings reveal a new direction for reusing vision representations in a non-visual domain. Code is available at https://github.com/ExplainableML/TiViT.
时间序列分类是医疗和工业领域的一项基础任务,然而,由于公开可用时间序列数据集的稀缺,时间序列基础模型(TSFMs)的发展受到限制。在这项工作中,我们提出了时间视觉转换器(TiViT),这是一个将时间序列转换为图像以利用在大型图像数据集上预训练的冻结视觉转换器(ViT)的表示能力的框架。首先,我们通过分析用于时间序列的ViT的2D补丁从理论上证明了我们的方法,表明它可以增加标签相关令牌的数量并降低样本复杂性。其次,我们通过实证证明,TiViT利用大型OpenCLIP模型的隐藏表示,在标准时间序列分类基准测试上实现了最先进的性能。我们探索了TiViT表示的结构,发现具有高内在维度的中间层对时间序列分类最为有效。最后,我们评估了TiViT和TSFM表示空间之间的对齐情况,并发现了强烈的互补性,通过结合它们的特征实现了进一步的性能提升。我们的研究为在非视觉领域重新使用视觉表示提供了新的方向。代码可在https://github.com/ExplainableML/TiViT找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint
Summary
本文提出了Time Vision Transformer(TiViT)框架,将时间序列转化为图像,利用在大型图像数据集上预训练的冻结Vision Transformer(ViT)的表示能力。理论分析表明,ViT的2D贴片处理可以提高标签相关令牌的数目并降低样本复杂性。在标准时间序列分类基准测试上,TiViT利用大型OpenCLIP模型的隐藏表示取得了最先进的性能。研究发现,具有高中维数的中间层对于时间序列分类最为有效。最后,评估了TiViT与TSFMs的代表性空间对齐情况,发现它们具有很强的互补性,通过结合其特征可以实现进一步的性能提升。这为在非视觉领域重新利用视觉表示提供了新的方向。
Key Takeaways
- Time Vision Transformer (TiViT) 框架能将时间序列转化为图像,利用Vision Transformer(ViT)在大型图像数据集上的预训练表示能力。
- 理论分析显示ViT的2D贴片处理能提高标签相关令牌的数目并降低样本复杂性。
- 在标准时间序列分类基准测试中,TiViT取得了最先进的性能。
- 研究发现,TiViT的中间层对于时间序列分类最为有效,这些层具有高中维数。
- TiViT与TSFMs的代表性空间具有强互补性,结合其特征可进一步提高性能。
- 此研究为在非视觉领域重新利用视觉表示提供了新的方向。
点此查看论文截图

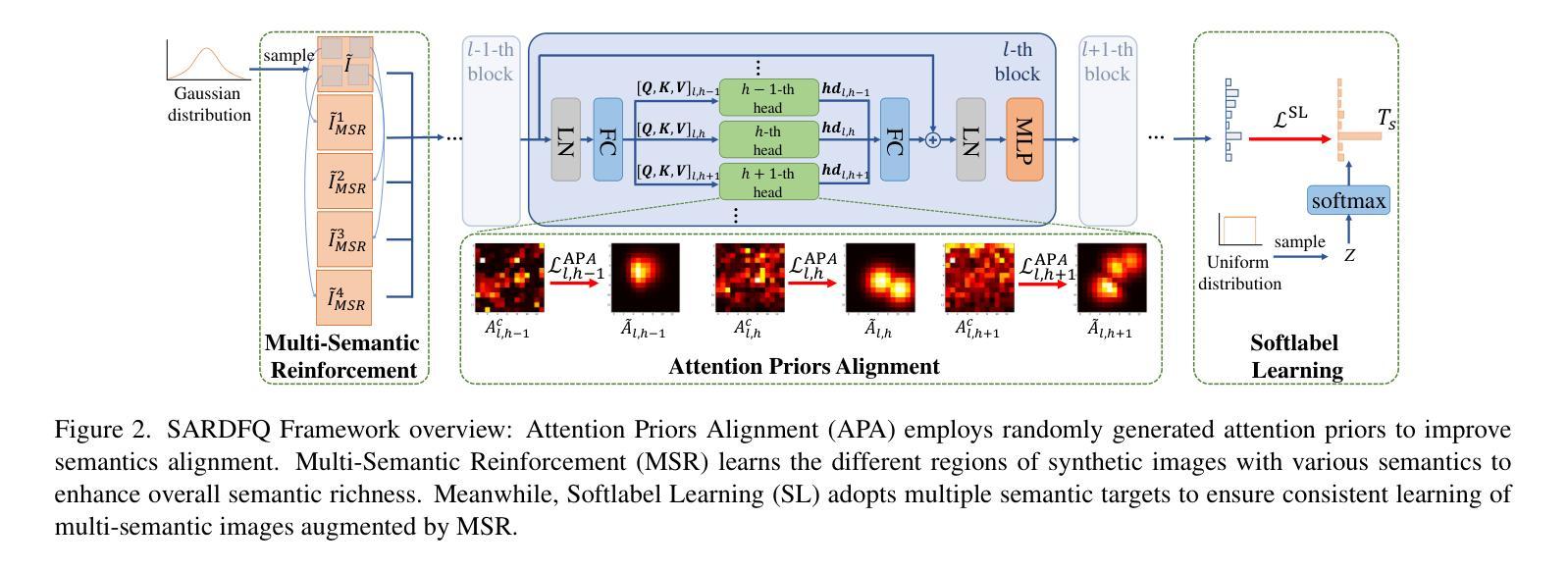
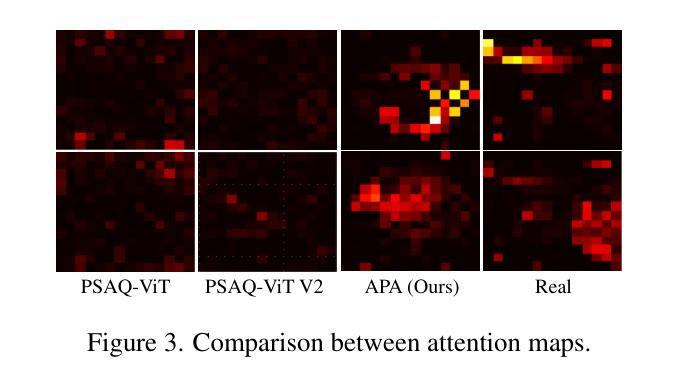
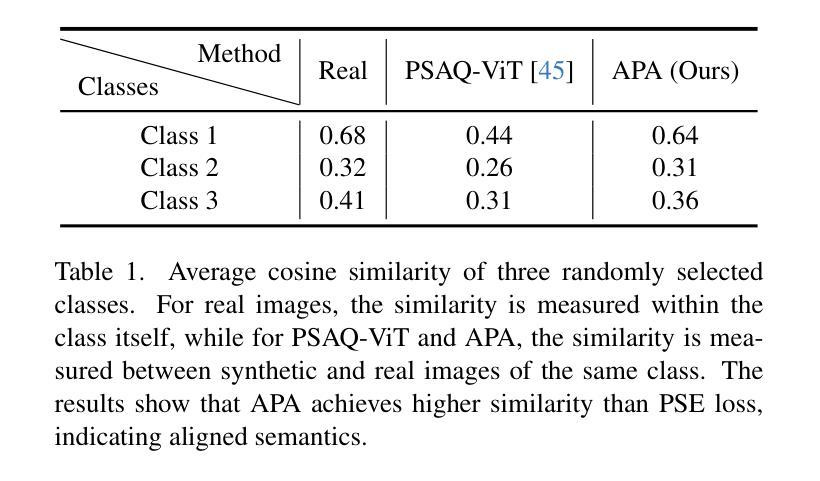
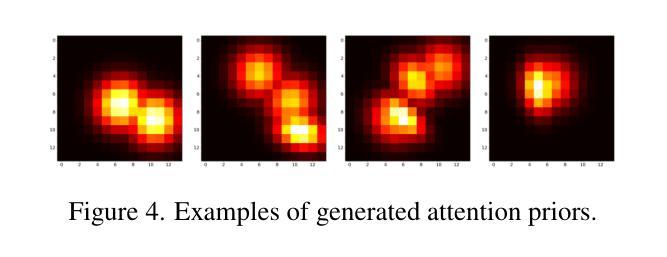
Semantic Alignment and Reinforcement for Data-Free Quantization of Vision Transformers
Authors:Yunshan Zhong, Yuyao Zhou, Yuxin Zhang, Wanchen Sui, Shen Li, Yong Li, Fei Chao, Rongrong Ji
Data-free quantization (DFQ) enables model quantization without accessing real data, addressing concerns regarding data security and privacy. With the growing adoption of Vision Transformers (ViTs), DFQ for ViTs has garnered significant attention. However, existing DFQ methods exhibit two limitations: (1) semantic distortion, where the semantics of synthetic images deviate substantially from those of real images, and (2) semantic inadequacy, where synthetic images contain extensive regions with limited content and oversimplified textures, leading to suboptimal quantization performance. To address these limitations, we propose SARDFQ, a novel Semantics Alignment and Reinforcement Data-Free Quantization method for ViTs. To address semantic distortion, SARDFQ incorporates Attention Priors Alignment (APA), which optimizes synthetic images to follow randomly generated structure attention priors. To mitigate semantic inadequacy, SARDFQ introduces Multi-Semantic Reinforcement (MSR), leveraging localized patch optimization to enhance semantic richness across synthetic images. Furthermore, SARDFQ employs Soft-Label Learning (SL), wherein multiple semantic targets are adapted to facilitate the learning of multi-semantic images augmented by MSR. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of SARDFQ, significantly surpassing existing methods. For example, SARDFQ improves top-1 accuracy on ImageNet by 15.52% for W4A4 ViT-B. The code is at https://github.com/zysxmu/SARDFQ.
无数据量化(DFQ)能够在无需访问真实数据的情况下实现模型量化,解决了数据安全和隐私的担忧。随着视觉转换器(ViTs)的广泛应用,ViTs的无数据量化(DFQ)已引起广泛关注。然而,现有的DFQ方法存在两个局限性:(1)语义失真,即合成图像的语义与真实图像的语义存在较大偏差;(2)语义不足,合成图像包含大量内容有限、纹理过于简单的区域,导致量化性能不佳。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了SARDFQ,一种用于视觉转换器的新型语义对齐和强化无数据量化方法。为了解决语义失真问题,SARDFQ结合了注意力先验对齐(APA),优化合成图像以遵循随机生成的结构注意力先验。为了缓解语义不足的问题,SARDFQ引入了多语义强化(MSR),利用局部补丁优化来增强合成图像中的语义丰富性。此外,SARDFQ采用软标签学习(SL),适应多个语义目标,以促进由MSR增强的多语义图像的学习。大量实验证明了SARDFQ的有效性,显著超越了现有方法。例如,SARDFQ在ImageNet上的top-1准确率提高了15.52%,适用于W4A4 ViT-B。代码地址为:https://github.com/zysxmu/SARDFQ。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV2025
Summary
数据无关量化(DFQ)可在不接触真实数据的情况下实现模型量化,关注数据安全和隐私保护。针对视觉变压器(ViTs)的DFQ存在语义失真和语义不足的问题。为此,提出一种新型的语义对齐和强化数据无关量化方法SARDFQ。通过优化合成图像遵循随机生成的结构注意力先验来解决语义失真问题。此外,SARDFQ引入了多语义强化(MSR)来减轻语义不足的问题,通过局部补丁优化增强合成图像的语义丰富性。采用软标签学习(SL),适应多个语义目标,促进由MSR增强的多语义图像的学习。实验证明SARDFQ效果显著,显著优于现有方法,例如W4A4 ViT-B在ImageNet上的top-1准确率提高15.52%。详情可访问相关代码库。
Key Takeaways
- 数据无关量化(DFQ)允许在不接触真实数据的情况下进行模型量化,注重数据安全和隐私。
- 针对ViTs的现有DFQ方法存在语义失真和语义不足的问题。
- SARDFQ是一种新型的针对ViTs的DFQ方法,通过Attention Priors Alignment (APA)解决语义失真问题。
- SARDFQ引入Multi-Semantic Reinforcement (MSR)来增强合成图像的语义丰富性,解决语义不足的问题。
- SARDFQ采用Soft-Label Learning (SL),适应多个语义目标,促进多语义图像的学习。
- 实验证明SARDFQ在性能上显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

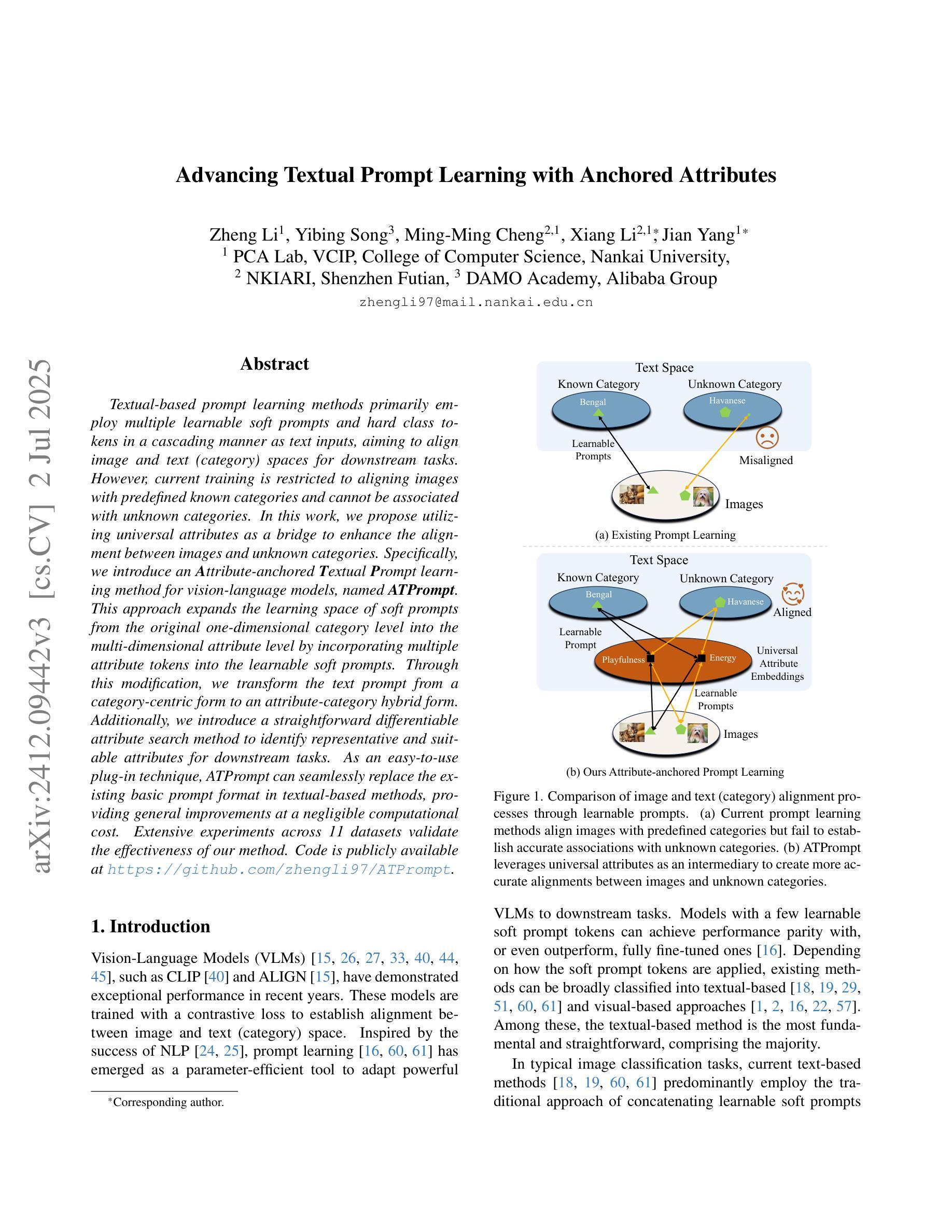
Advancing Textual Prompt Learning with Anchored Attributes
Authors:Zheng Li, Yibing Song, Ming-Ming Cheng, Xiang Li, Jian Yang
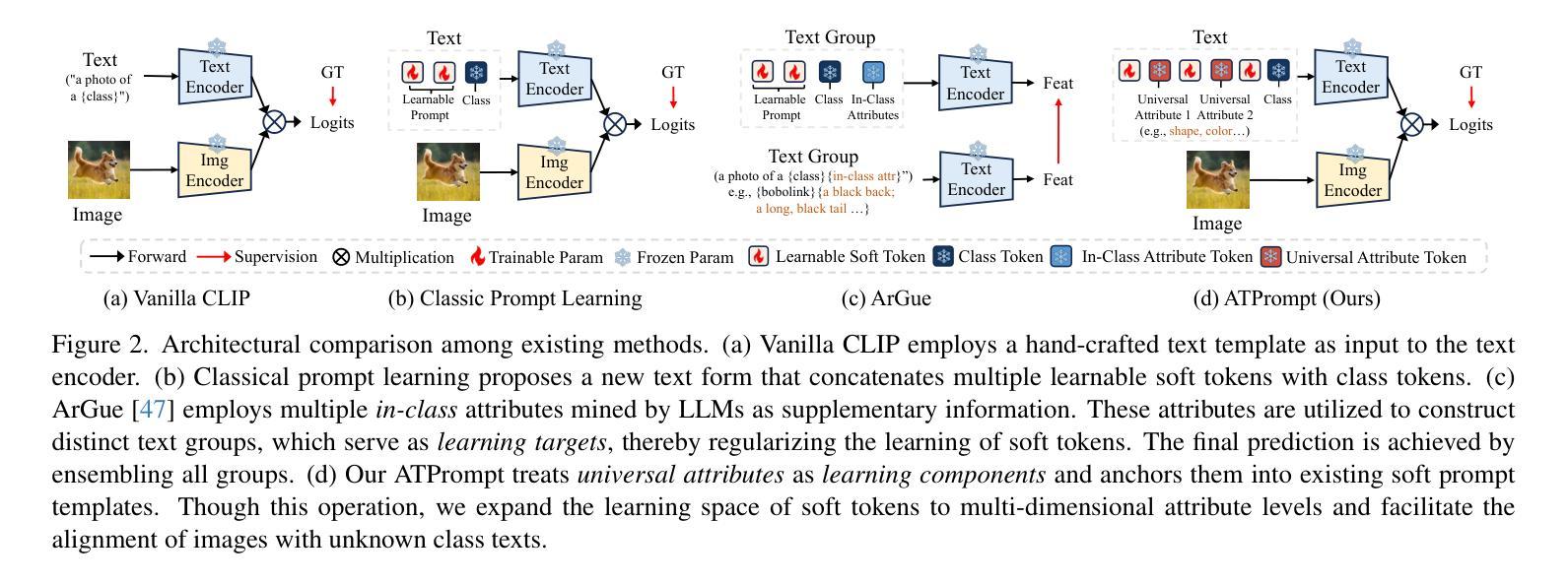
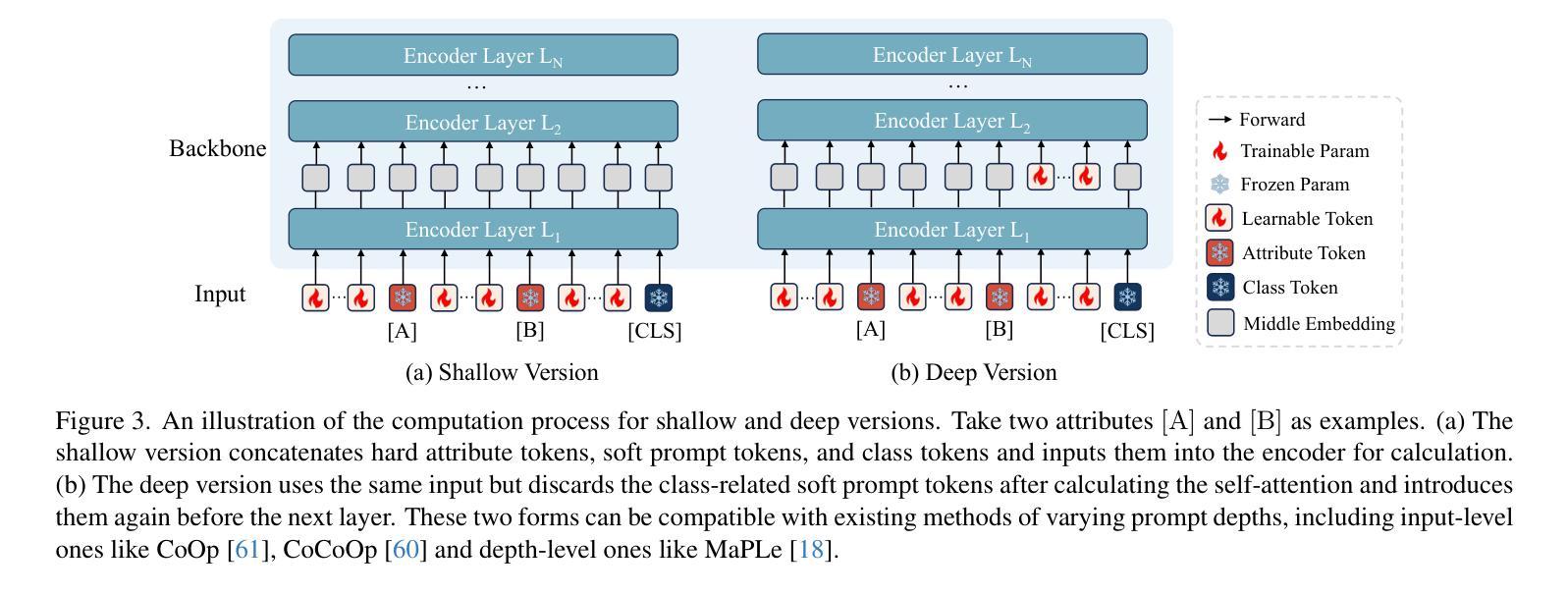
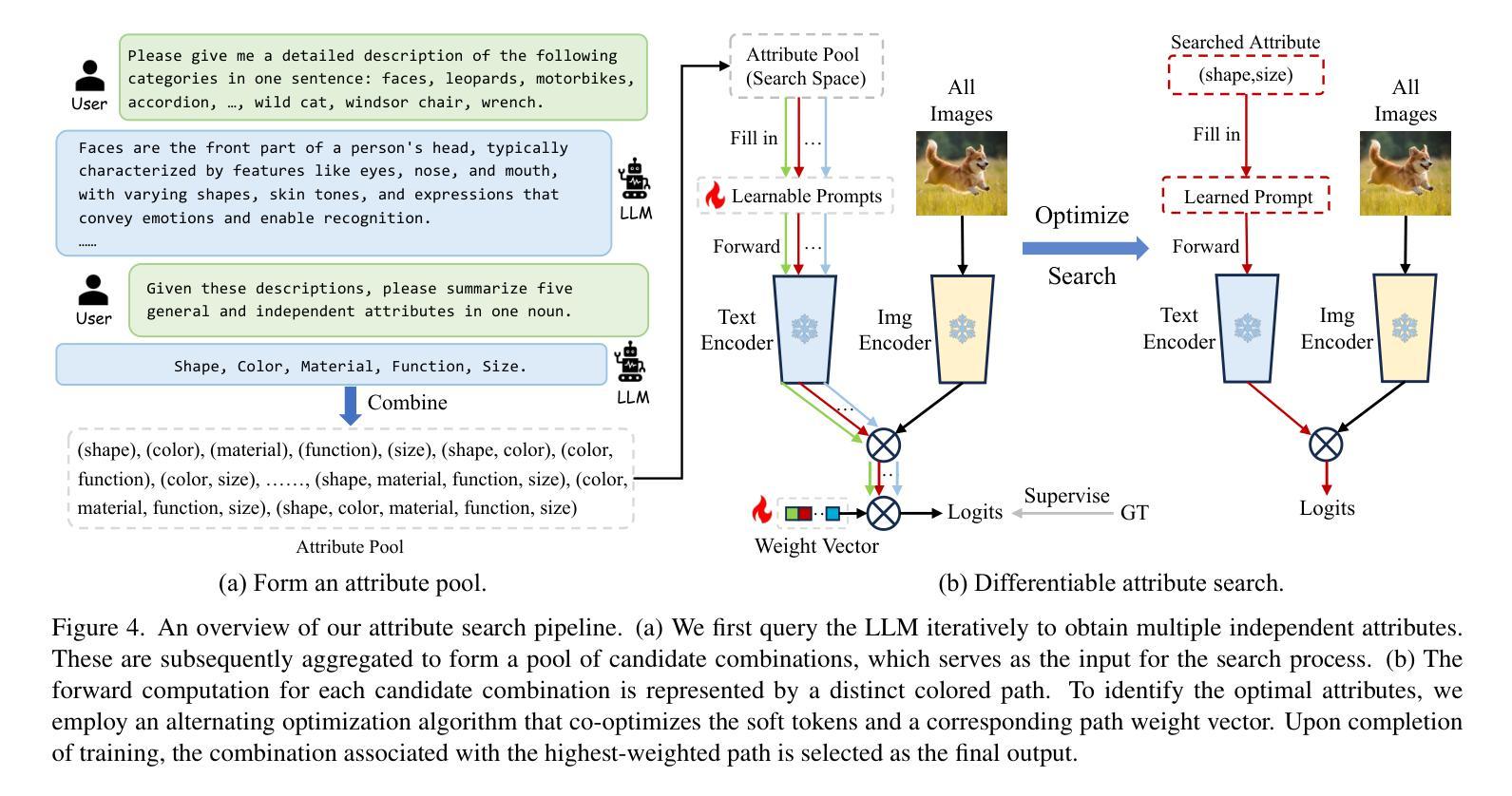
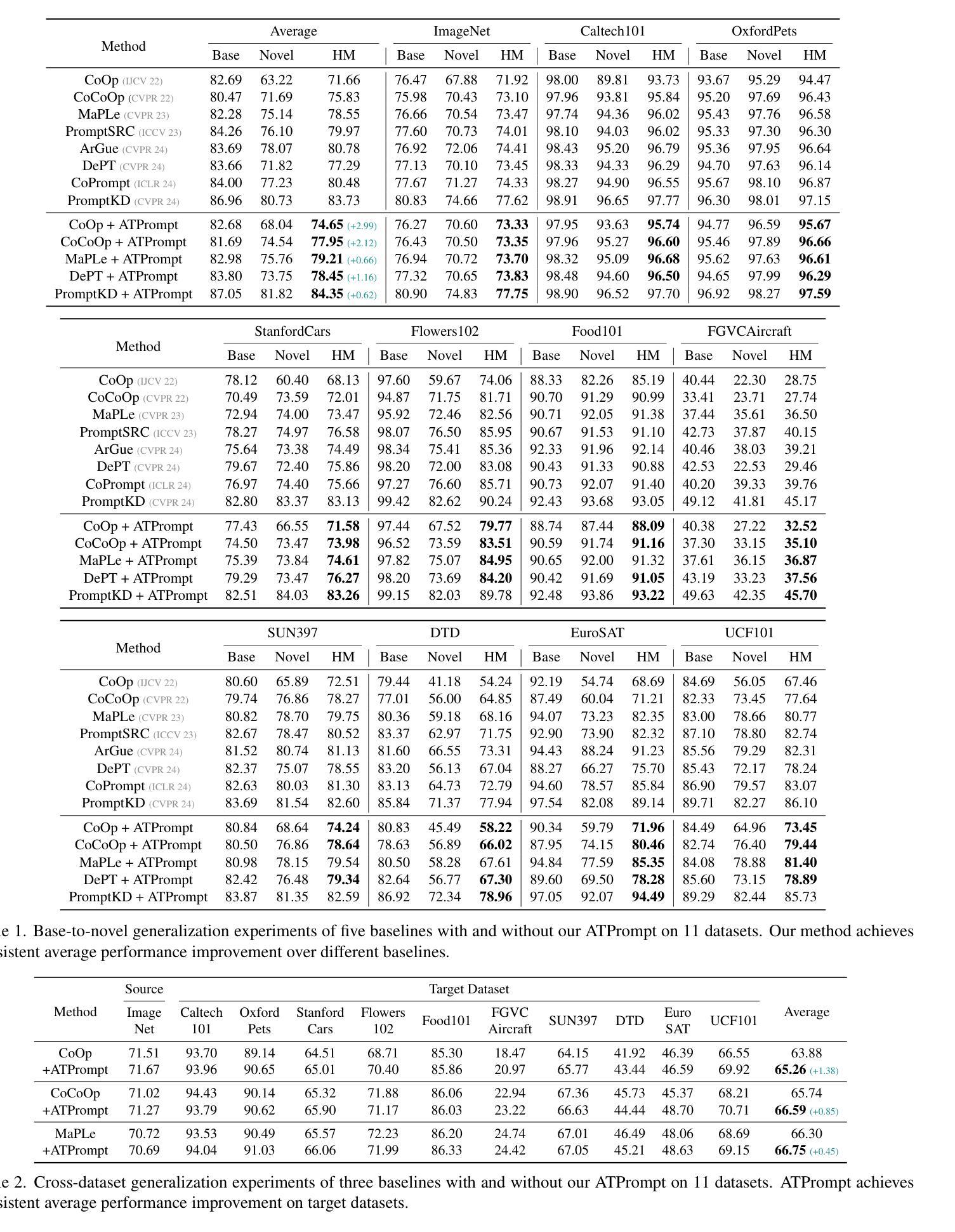
Textual-based prompt learning methods primarily employ multiple learnable soft prompts and hard class tokens in a cascading manner as text inputs, aiming to align image and text (category) spaces for downstream tasks. However, current training is restricted to aligning images with predefined known categories and cannot be associated with unknown categories. In this work, we propose utilizing universal attributes as a bridge to enhance the alignment between images and unknown categories. Specifically, we introduce an Attribute-anchored Textual Prompt learning method for vision-language models, named ATPrompt. This approach expands the learning space of soft prompts from the original one-dimensional category level into the multi-dimensional attribute level by incorporating multiple attribute tokens into the learnable soft prompts. Through this modification, we transform the text prompt from a category-centric form to an attribute-category hybrid form. Additionally, we introduce a straightforward differentiable attribute search method to identify representative and suitable attributes for downstream tasks. As an easy-to-use plug-in technique, ATPrompt can seamlessly replace the existing basic prompt format in textual-based methods, providing general improvements at a negligible computational cost. Extensive experiments across 11 datasets validate the effectiveness of our method. Code is publicly available at https://github.com/zhengli97/ATPrompt.
基于文本的提示学习方法主要使用多个可学习的软提示和硬类别令牌以级联方式作为文本输入,旨在对齐图像和文本(类别)空间以进行下游任务。然而,当前训练仅限于对齐图像与预定义的已知类别,无法与未知类别相关联。在本文中,我们提出利用通用属性作为桥梁,增强图像与未知类别之间的对齐。具体来说,我们为视觉语言模型引入了一种名为ATPrompt的属性锚定文本提示学习方法。该方法通过将多个属性令牌融入可学习的软提示中,将软提示的学习空间从原始的一维类别层面扩展到多维属性层面。通过这一改进,我们将文本提示从以类别为中心的形式转变为属性-类别混合形式。此外,我们还引入了一种简单的可区分属性搜索方法,用于识别下游任务的代表性和合适属性。作为一种易于使用的插件技术,ATPrompt可以无缝替换基于文本方法中的基本提示格式,以微小的计算成本提供一般的改进。在11个数据集上的大量实验验证了我们的方法的有效性。代码公开在https://github.com/zhengli97/ATPrompt。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025. Code: https://github.com/zhengli97/ATPrompt. Project Page: https://zhengli97.github.io/ATPrompt/
Summary
在文本基于提示的学习方法基础上,提出一种利用通用属性作为桥梁,增强图像与未知类别之间对齐的方法。引入属性锚定的文本提示学习方法,通过结合多个属性标记,将软提示的学习空间从原始的一维类别层面扩展到多维属性层面。此外,还介绍了一种简单的可微属性搜索方法,用于确定下游任务的代表性属性。作为一种易于使用的插件技术,ATPrompt可以无缝地替换现有文本提示方法中的基本格式,以微小的计算成本提供一般性的改进。
Key Takeaways
- 文本基于提示的学习方法主要通过级联多个可学习的软提示和硬类别标记作为文本输入,旨在实现对下游任务中的图像和文本(类别)空间的对齐。
- 当前训练限制在于只能对齐已知类别的图像,无法关联未知类别。
- 提出利用通用属性作为桥梁,增强图像与未知类别之间的对齐。
- 引入属性锚定的文本提示学习方法(ATPrompt),将软提示的学习空间扩展到多维属性层面。
- ATPrompt将文本提示从以类别为中心的形式转变为属性-类别混合形式。
- ATPrompt提供了一种简单的可微属性搜索方法,用于确定适合下游任务的代表性属性。
点此查看论文截图
Semantic Equitable Clustering: A Simple and Effective Strategy for Clustering Vision Tokens
Authors:Qihang Fan, Huaibo Huang, Mingrui Chen, Ran He
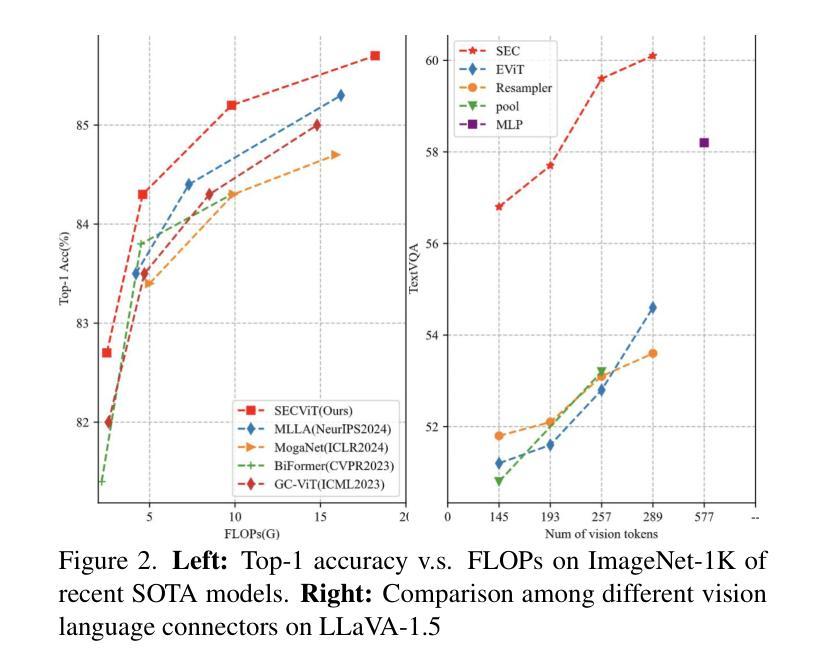
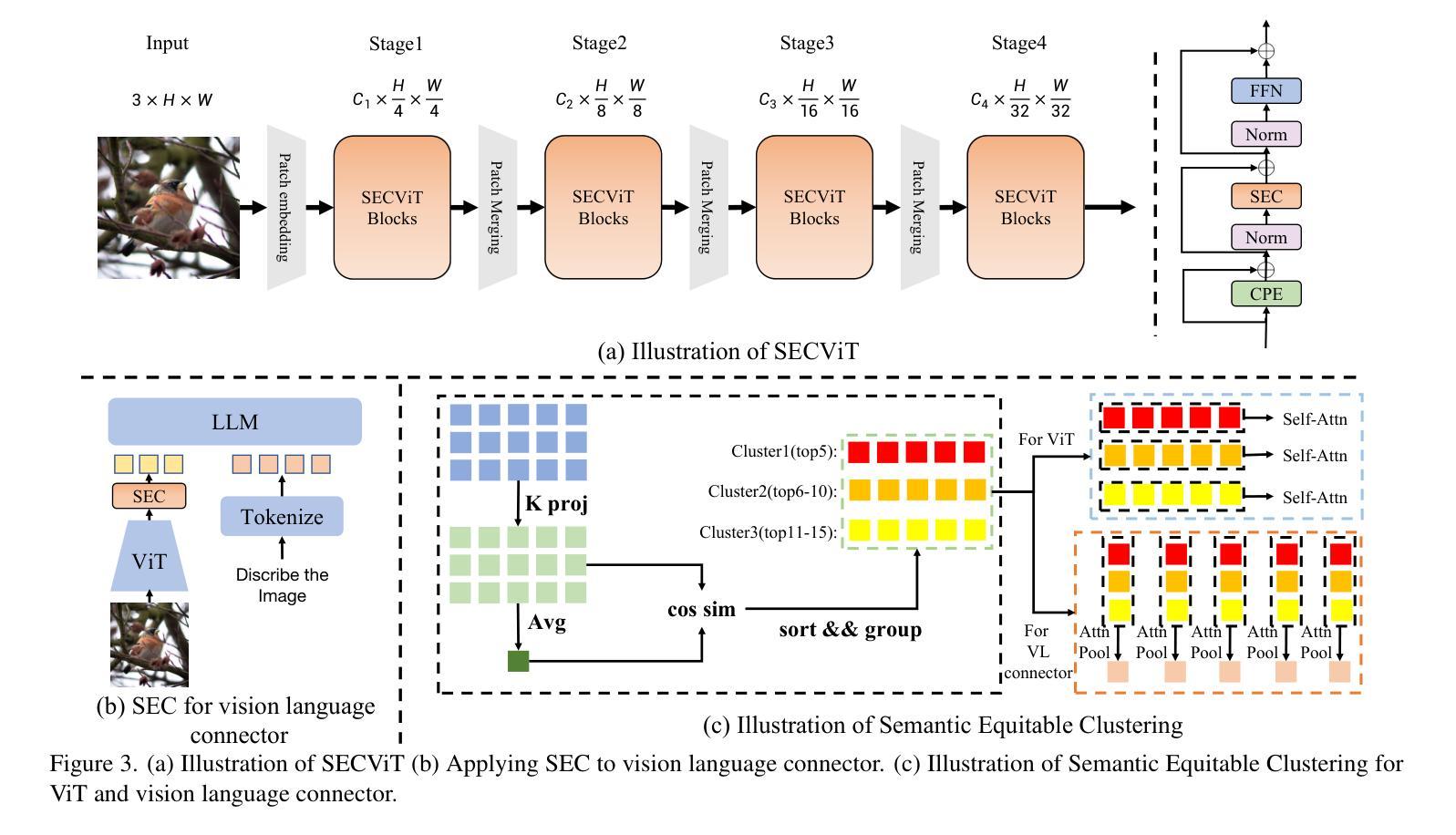
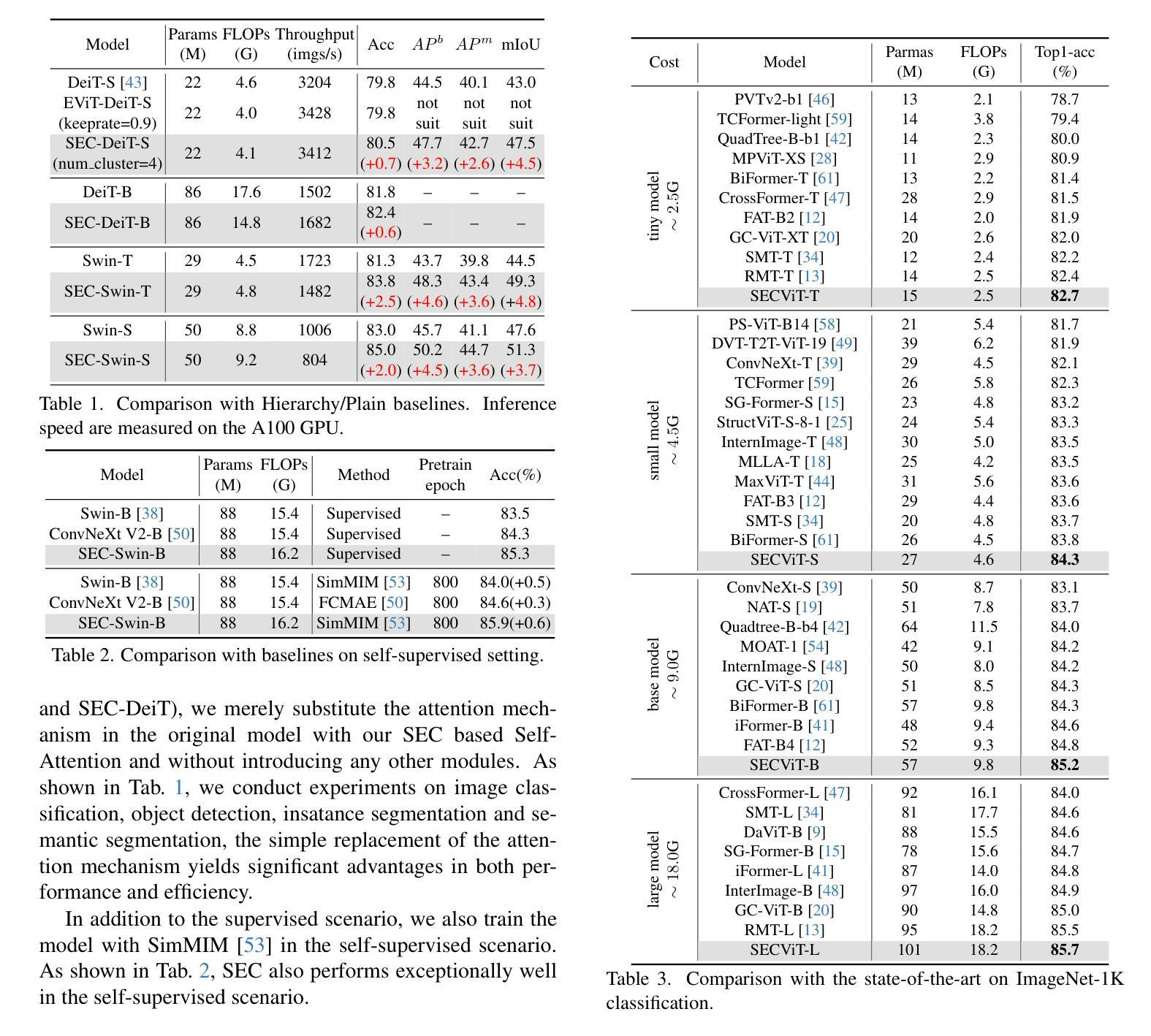
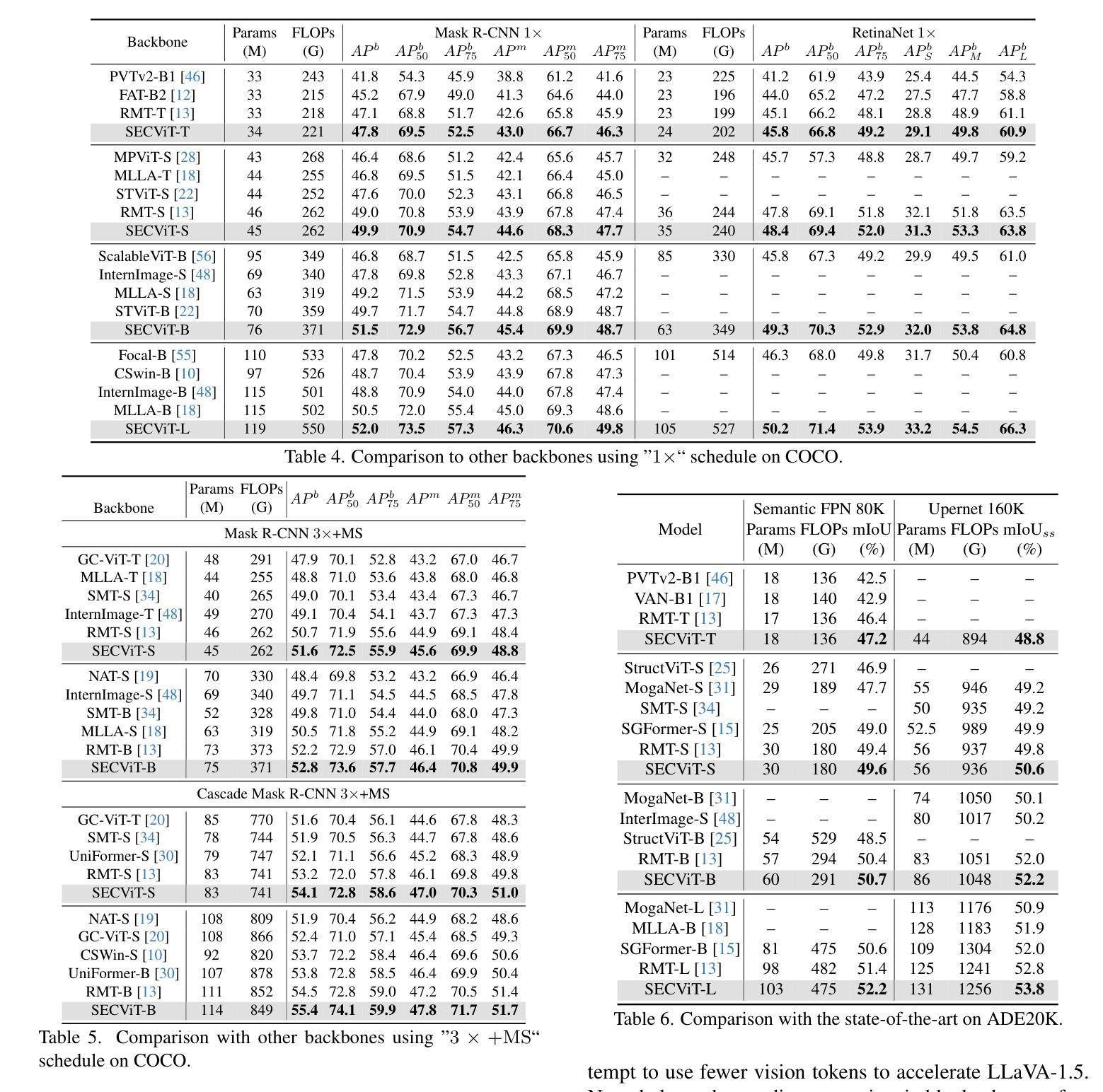
The Vision Transformer (ViT) has gained prominence for its superior relational modeling prowess. However, its global attention mechanism’s quadratic complexity poses substantial computational burdens. A common remedy spatially groups tokens for self-attention, reducing computational requirements. Nonetheless, this strategy neglects semantic information in tokens, possibly scattering semantically-linked tokens across distinct groups, thus compromising the efficacy of self-attention intended for modeling inter-token dependencies. Motivated by these insights, we introduce a fast and balanced clustering method, named Semantic Equitable Clustering (SEC). SEC clusters tokens based on their global semantic relevance in an efficient, straightforward manner. In contrast to traditional clustering methods requiring multiple iterations, our method achieves token clustering in a single pass. Additionally, SEC regulates the number of tokens per cluster, ensuring a balanced distribution for effective parallel processing on current computational platforms without necessitating further optimization. Capitalizing on SEC, we propose a versatile vision backbone, SECViT. Comprehensive experiments in image classification, object detection, instance segmentation, and semantic segmentation validate the effectiveness of SECViT. Moreover, SEC can be conveniently and swiftly applied to multimodal large language models (MLLM), such as LLaVA, to serve as a vision language connector, effectively accelerating the model’s efficiency while maintaining unchanged or better performance.
Vision Transformer(ViT)因其出色的关系建模能力而备受瞩目。然而,其全局注意力机制的二次复杂性带来了巨大的计算负担。一种常见的补救方法是空间分组令牌进行自注意力,以降低计算要求。然而,这种策略忽略了令牌中的语义信息,可能将语义上相关联的令牌分散到不同的组,从而损害自注意力在建模令牌间依赖关系时的有效性。
基于这些见解,我们引入了一种快速且均衡的聚类方法,称为语义均衡聚类(SEC)。SEC以高效、简单的方式,基于令牌的全局语义相关性对令牌进行聚类。与传统的需要多次迭代的聚类方法不同,我们的方法可以在单次传递中实现令牌聚类。此外,SEC还调节每个集群中的令牌数量,确保在当前计算平台上进行有效的并行处理,而无需进一步优化。
利用SEC,我们提出了一种通用的视觉主干网SECViT。在图像分类、目标检测、实例分割和语义分割方面的综合实验验证了SECViT的有效性。此外,SEC还可以轻松快速地应用于多模态大型语言模型(MLLM),如LLaVA,作为视觉语言连接器,在保持性能不变或更好的情况下有效提高模型的效率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV2025
Summary
本文介绍了Vision Transformer(ViT)在关系建模方面的优势,但其全局注意力机制的二次复杂性带来了较大的计算负担。为解决这一问题,提出了一种快速均衡聚类方法——Semantic Equitable Clustering(SEC)。SEC基于全局语义相关性对令牌进行聚类,实现了高效直接的聚类方式。相较于传统聚类方法的多迭代过程,SEC实现了单遍聚类。此外,SEC调控每个集群的令牌数量,确保了在现有计算平台上的有效并行处理。基于SEC,提出了一种通用的视觉主干SECViT。在图像分类、目标检测、实例分割和语义分割等方面的实验验证了SECViT的有效性。此外,SEC可轻松快速地应用于多模态大型语言模型(MLLM),如LLaVA,作为视觉语言连接器,在保持性能不变或更好的情况下,有效提高模型的效率。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformer (ViT) 展现出卓越的关系建模能力,但其全局注意力机制的二次复杂性带来计算负担。
- 现有的空间分组令牌策略忽略了令牌间的语义信息,可能影响建模效果。
- 引入了一种快速均衡聚类方法——Semantic Equitable Clustering (SEC),基于全局语义相关性进行高效直接的聚类。
- SEC实现了单遍聚类过程,并调控每个集群的令牌数量,便于在现有计算平台上的并行处理。
- 基于SEC提出了SECViT模型,用于提高图像分类、目标检测等任务的性能。
- SEC可以方便地应用于多模态大型语言模型(MLLM),作为视觉语言连接器以提高模型效率并保持性能。
点此查看论文截图