⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-05 更新
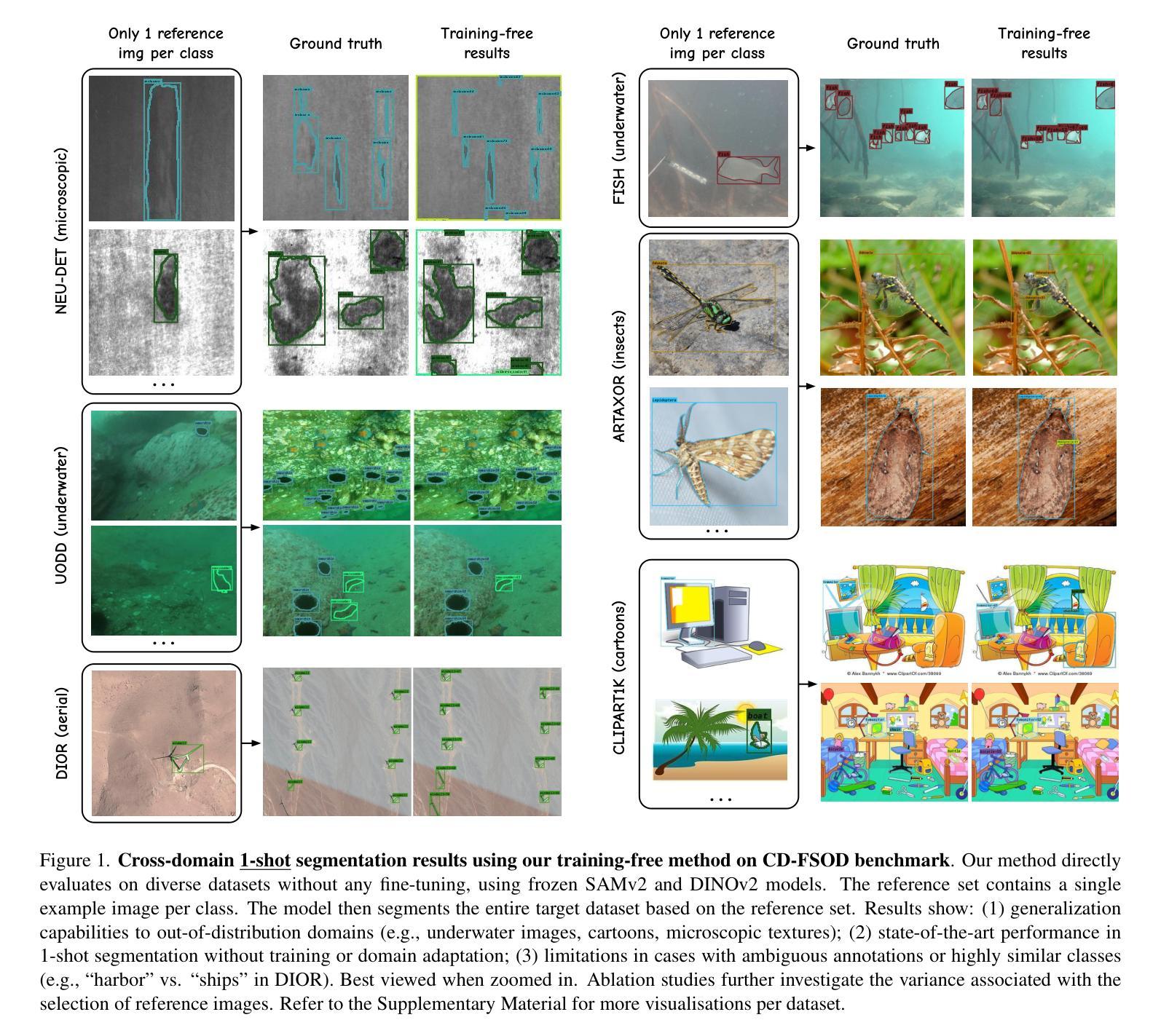
No time to train! Training-Free Reference-Based Instance Segmentation
Authors:Miguel Espinosa, Chenhongyi Yang, Linus Ericsson, Steven McDonagh, Elliot J. Crowley
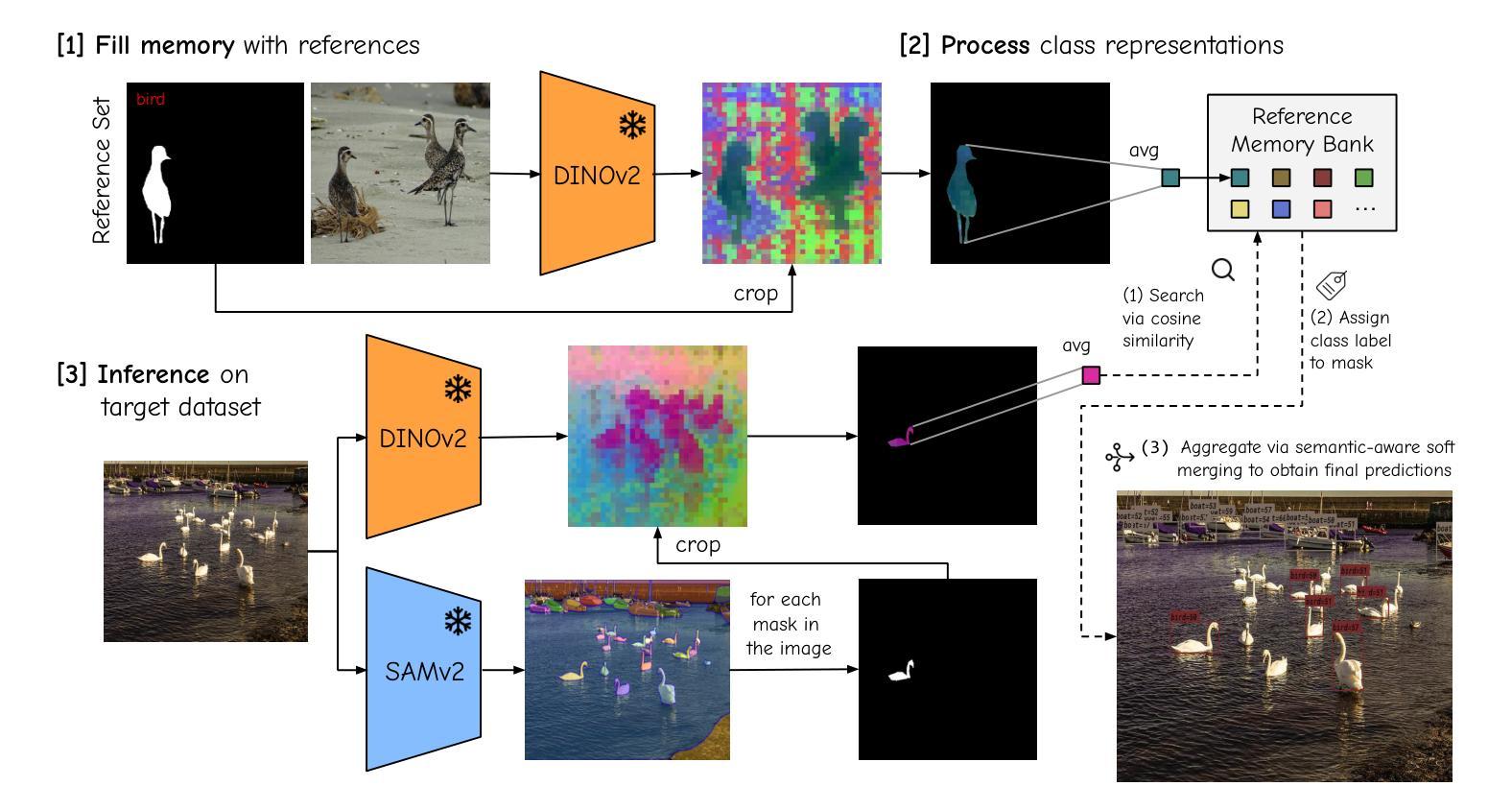
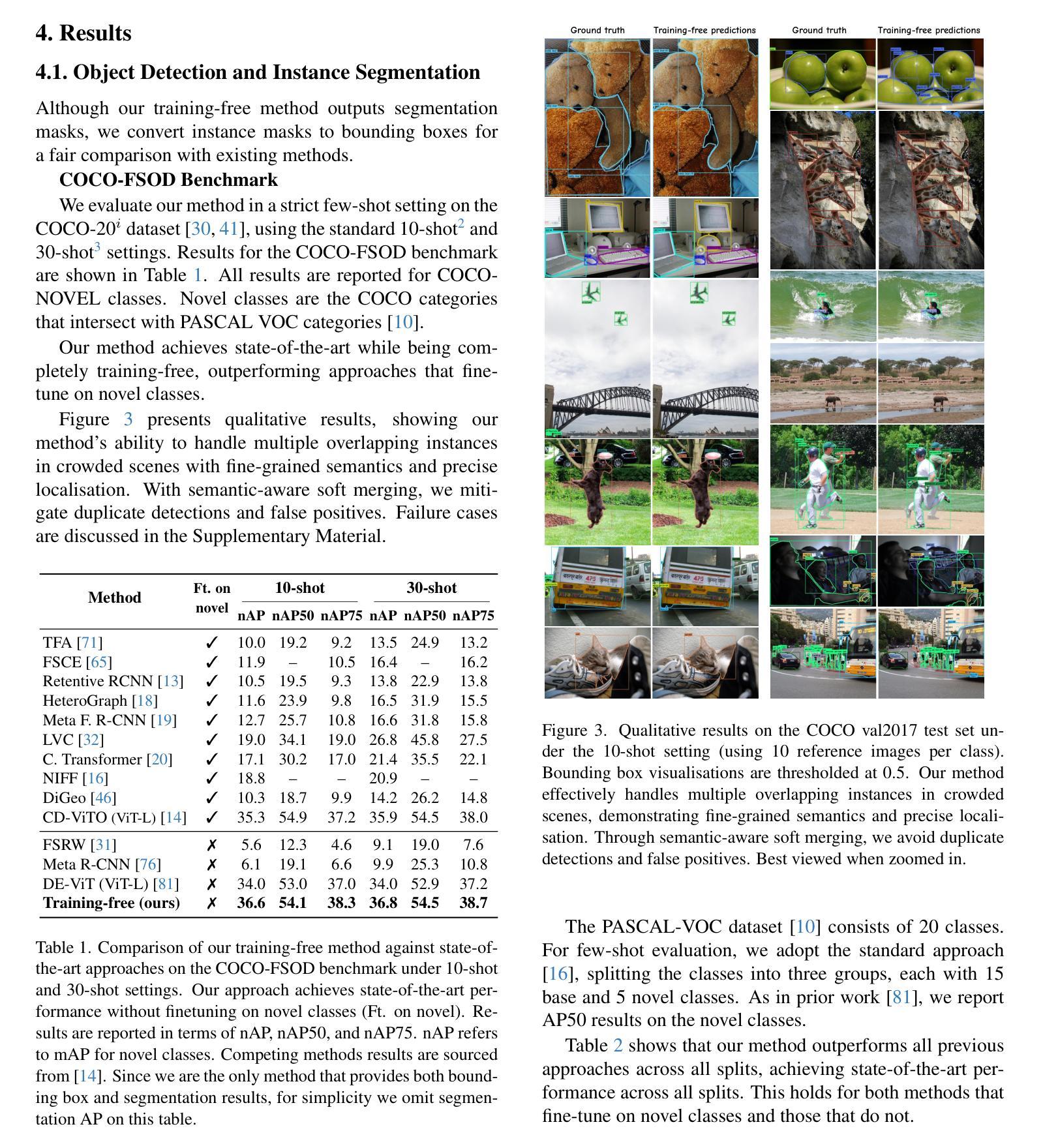
The performance of image segmentation models has historically been constrained by the high cost of collecting large-scale annotated data. The Segment Anything Model (SAM) alleviates this original problem through a promptable, semantics-agnostic, segmentation paradigm and yet still requires manual visual-prompts or complex domain-dependent prompt-generation rules to process a new image. Towards reducing this new burden, our work investigates the task of object segmentation when provided with, alternatively, only a small set of reference images. Our key insight is to leverage strong semantic priors, as learned by foundation models, to identify corresponding regions between a reference and a target image. We find that correspondences enable automatic generation of instance-level segmentation masks for downstream tasks and instantiate our ideas via a multi-stage, training-free method incorporating (1) memory bank construction; (2) representation aggregation and (3) semantic-aware feature matching. Our experiments show significant improvements on segmentation metrics, leading to state-of-the-art performance on COCO FSOD (36.8% nAP), PASCAL VOC Few-Shot (71.2% nAP50) and outperforming existing training-free approaches on the Cross-Domain FSOD benchmark (22.4% nAP).
历史上,图像分割模型的性能一直受到大规模标注数据收集成本高昂的制约。Segment Anything Model(SAM)通过一种可提示、语义无关的分段范式缓解了这一原始问题,但处理新图像时仍需要手动视觉提示或复杂的域相关提示生成规则。为了减轻这一新负担,我们的工作研究了在仅提供一小部分参考图像的情况下进行对象分割的任务。我们的关键见解是利用基础模型学到的强大语义先验知识,来识别参考图像和目标图像之间的相应区域。我们发现这种对应关系能够自动生成用于下游任务的实例级分割掩膜,并通过一个多阶段、无需训练的方法实现我们的想法,包括(1)构建内存银行;(2)表示聚合和(3)语义感知特征匹配。我们的实验显示,在分割指标上取得了显著改进,并在COCO FSOD上达到了最先进的性能(36.8% nAP),PASCAL VOC Few-Shot(71.2% nAP50),并在跨域FSOD基准测试上超越了现有的无训练方法(22.4% nAP)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint
Summary
一种名为Segment Anything Model(SAM)的图像分割模型通过提示驱动的分割范式解决了大规模标注数据收集成本高昂的问题。本研究进一步探索了仅使用少量参考图像进行物体分割任务的可能性。研究的关键在于利用基础模型学习的强语义先验知识,在参考图像和目标图像之间识别对应区域。通过构建记忆库、表示聚合和语义感知特征匹配的多阶段、无训练方法,实现了实例级分割掩膜的自动生成,显著提高了分割指标,并在COCO FSOD、PASCAL VOC Few-Shot和Cross-Domain FSOD基准测试中实现了卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- Segment Anything Model (SAM) 解决了大规模标注数据收集成本高昂的问题。
- 研究采用少量参考图像进行物体分割的新方法。
- 利用基础模型学习的强语义先验知识,识别参考图像与目标图像之间的对应区域。
- 通过多阶段、无训练方法实现实例级分割掩膜的自动生成。
- 方法包括记忆库构建、表示聚合和语义感知特征匹配。
- 在COCO FSOD、PASCAL VOC Few-Shot等基准测试中实现了显著改进和卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图

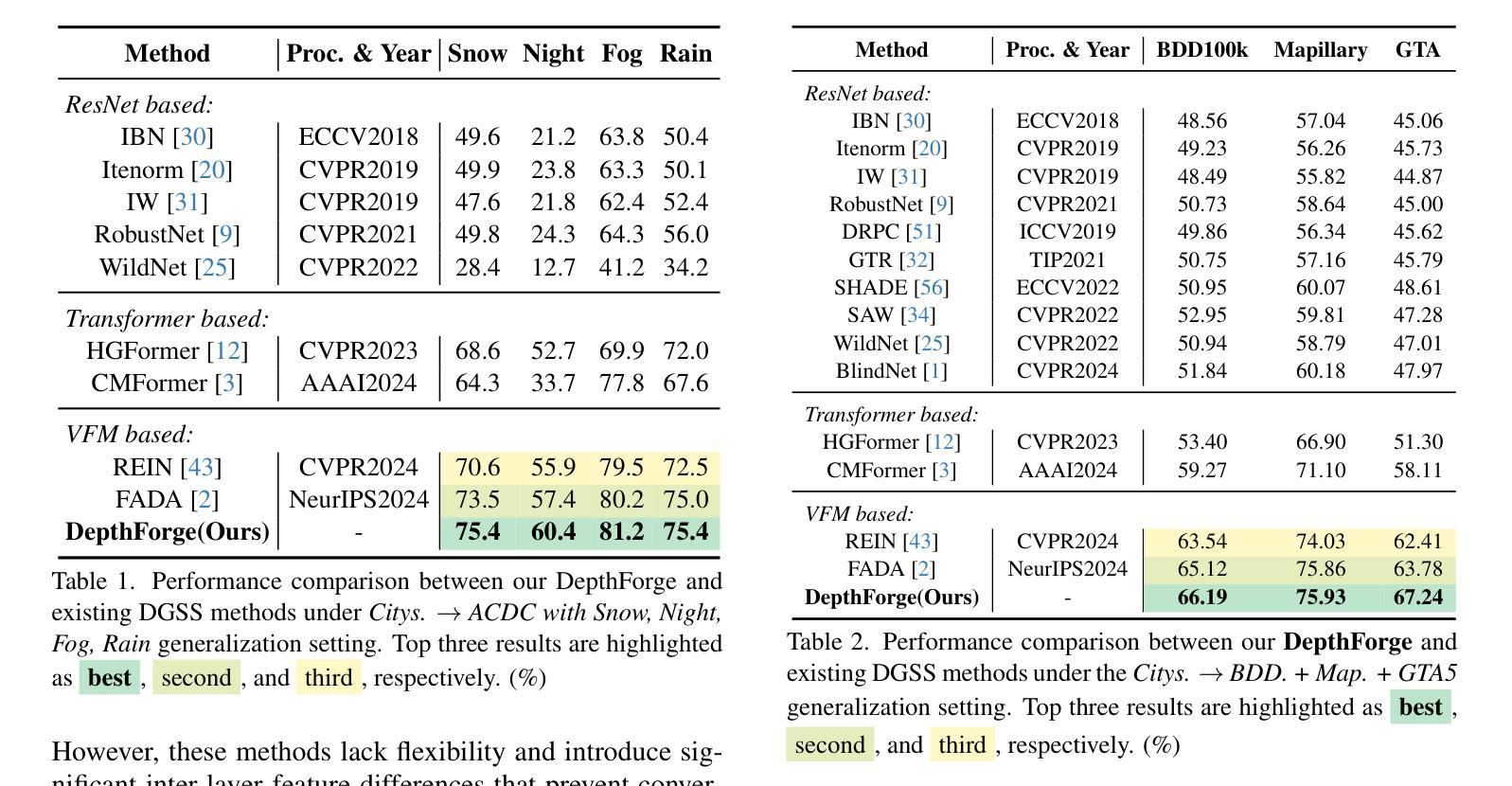
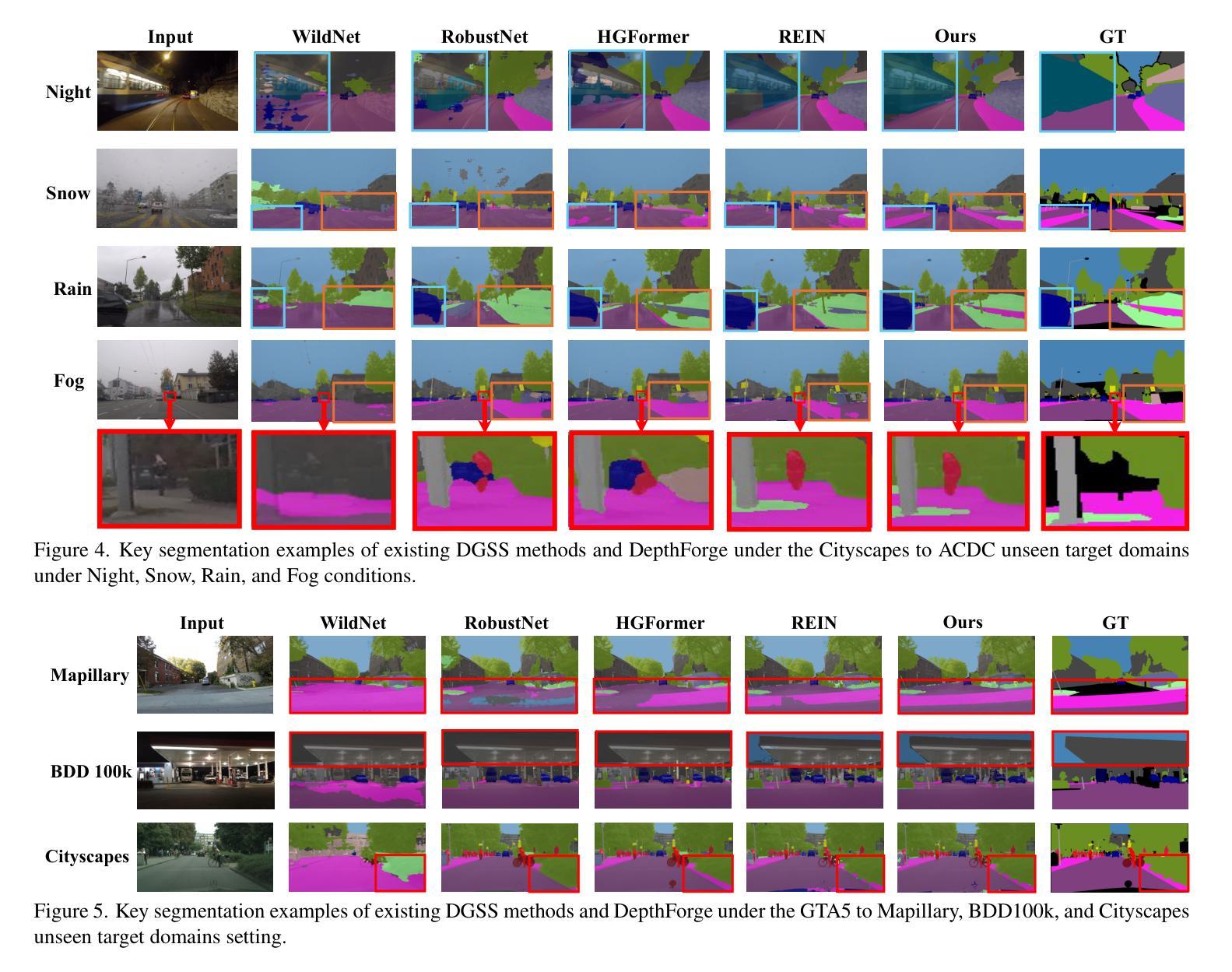
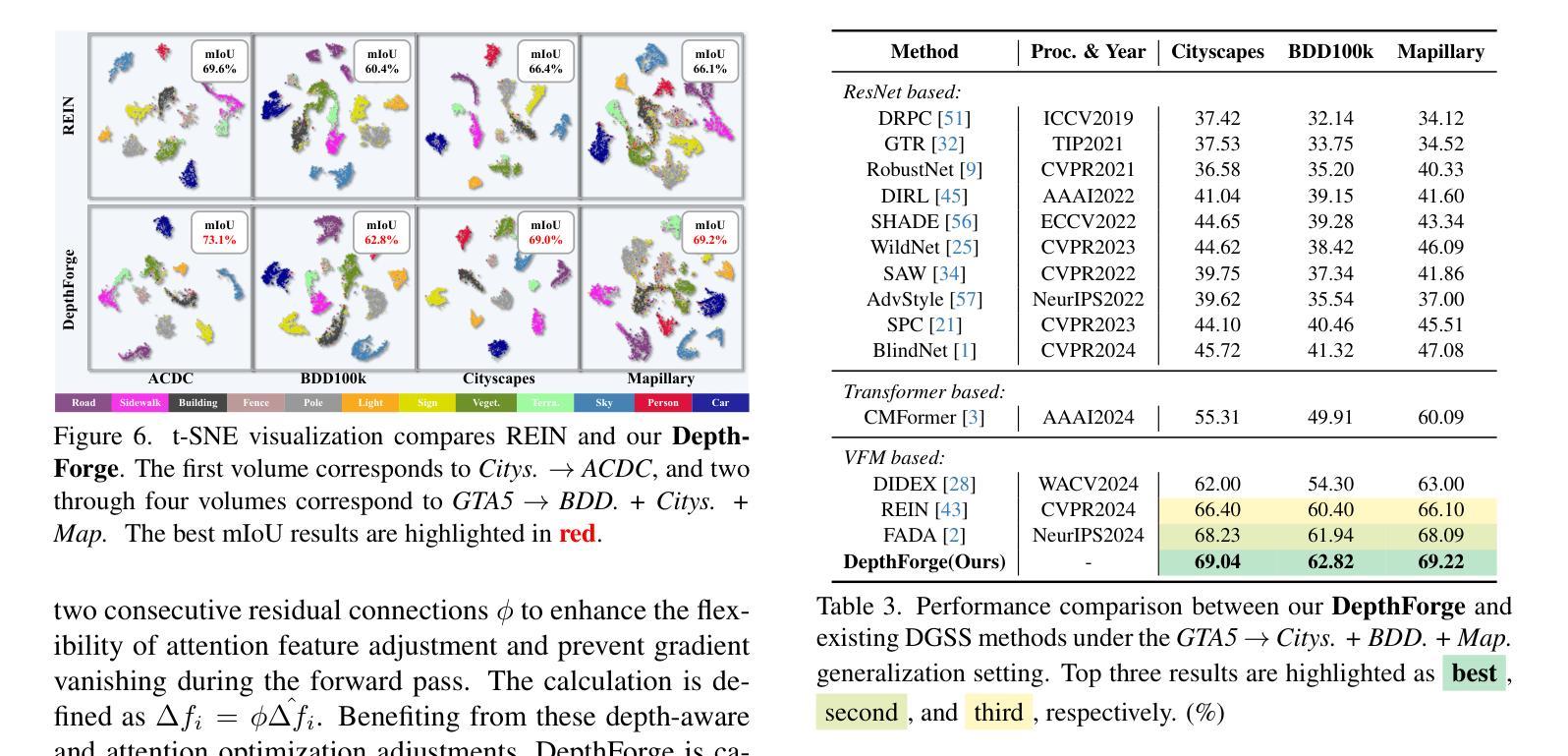
Stronger, Steadier & Superior: Geometric Consistency in Depth VFM Forges Domain Generalized Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Siyu Chen, Ting Han, Changshe Zhang, Xin Luo, Meiliu Wu, Guorong Cai, Jinhe Su
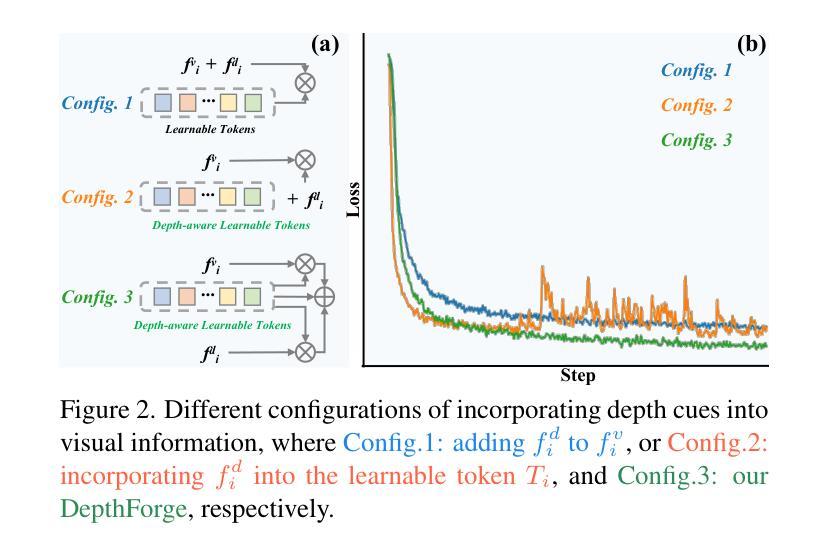
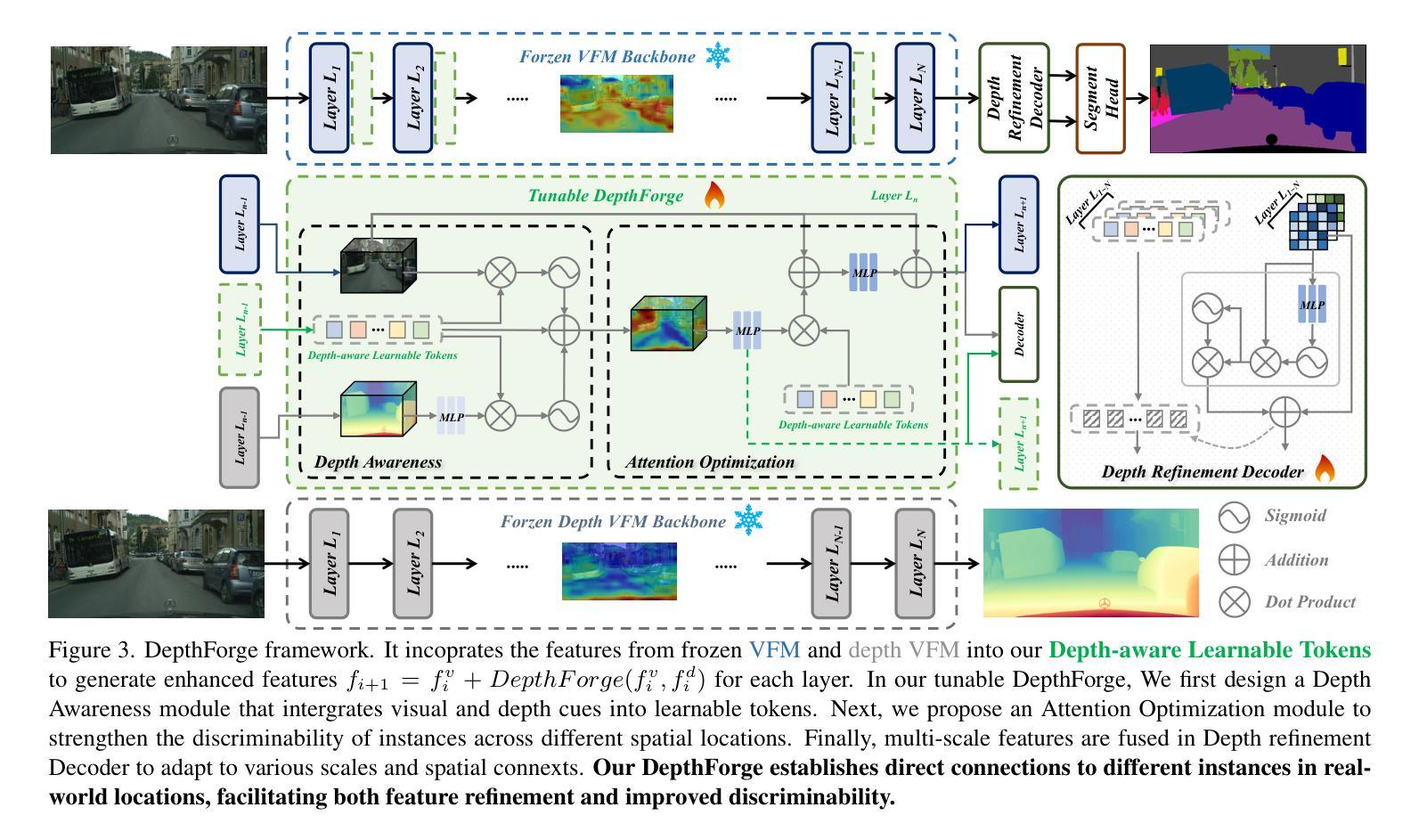
Vision Foundation Models (VFMs) have delivered remarkable performance in Domain Generalized Semantic Segmentation (DGSS). However, recent methods often overlook the fact that visual cues are susceptible, whereas the underlying geometry remains stable, rendering depth information more robust. In this paper, we investigate the potential of integrating depth information with features from VFMs, to improve the geometric consistency within an image and boost the generalization performance of VFMs. We propose a novel fine-tuning DGSS framework, named DepthForge, which integrates the visual cues from frozen DINOv2 or EVA02 and depth cues from frozen Depth Anything V2. In each layer of the VFMs, we incorporate depth-aware learnable tokens to continuously decouple domain-invariant visual and spatial information, thereby enhancing depth awareness and attention of the VFMs. Finally, we develop a depth refinement decoder and integrate it into the model architecture to adaptively refine multi-layer VFM features and depth-aware learnable tokens. Extensive experiments are conducted based on various DGSS settings and five different datsets as unseen target domains. The qualitative and quantitative results demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms alternative approaches with stronger performance, steadier visual-spatial attention, and superior generalization ability. In particular, DepthForge exhibits outstanding performance under extreme conditions (e.g., night and snow). Code is available at https://github.com/anonymouse-xzrptkvyqc/DepthForge.
视觉基础模型(VFMs)在领域通用语义分割(DGSS)方面取得了显著的成绩。然而,最近的方法往往忽略了这样一个事实,即视觉线索是易变的,而基础几何则是稳定的,这使得深度信息更加稳健。在本文中,我们探讨了将深度信息与VFMs的特征相结合,以提高图像内的几何一致性并提升VFMs的泛化性能。我们提出了一种新型的微调DGSS框架,名为DepthForge,它结合了来自冻结的DINOv2或EVA02的视觉线索和来自冻结的Depth Anything V2的深度线索。在VFMs的每一层中,我们引入了深度感知的可学习令牌,以连续地解耦领域不变的视觉和空间信息,从而提高VFMs的深度感知和注意力。最后,我们开发了一个深度细化解码器并将其集成到模型架构中,以自适应地细化多层VFM特征和深度感知的可学习令牌。基于不同的DGSS设置和五个不同的数据集作为未见过的目标领域进行了广泛实验。定性和定量结果表明,我们的方法在性能上显著优于其他方法,具有更强的性能、更稳定的视觉-空间注意力和更好的泛化能力。特别是,DepthForge在极端条件下(例如夜晚和雪地)表现出卓越的性能。代码可在https://github.com/anonymouse-xzrptkvyqc/DepthForge找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025
Summary
本文探讨了将深度信息融入视觉基础模型(VFMs)以提升领域广义语义分割(DGSS)性能的方法。文章提出一个名为DepthForge的新型微调DGSS框架,结合来自冻结的DINOv2或EVA02的视觉线索和来自冻结的Depth Anything V2的深度线索。该框架在每一层VFM中融入深度感知的可学习令牌,以持续分离领域不变视觉和空间信息,增强VFM的深度感知和注意力。通过深度细化解码器自适应地优化多层VFM特征和深度感知可学习令牌,实验结果显示DepthForge在多种DGSS设置和五个不同数据集上表现出卓越性能,尤其在极端条件下(如夜晚和雪地)。
Key Takeaways
- VFM在DGSS中表现出卓越性能,但忽略视觉线索易受干扰而基础几何保持稳定的现实。
- 提出了DepthForge框架,结合了视觉线索和深度线索,以增强几何一致性并提升VFM的泛化性能。
- DepthForge通过融入深度感知的可学习令牌,在每一层VFM中分离领域不变视觉和空间信息。
- 深度细化解码器自适应地优化多层VFM特征和深度感知可学习令牌。
- 实验结果显示DepthForge在多种DGSS设置和多个数据集上显著优于其他方法,特别是在极端条件下。
点此查看论文截图

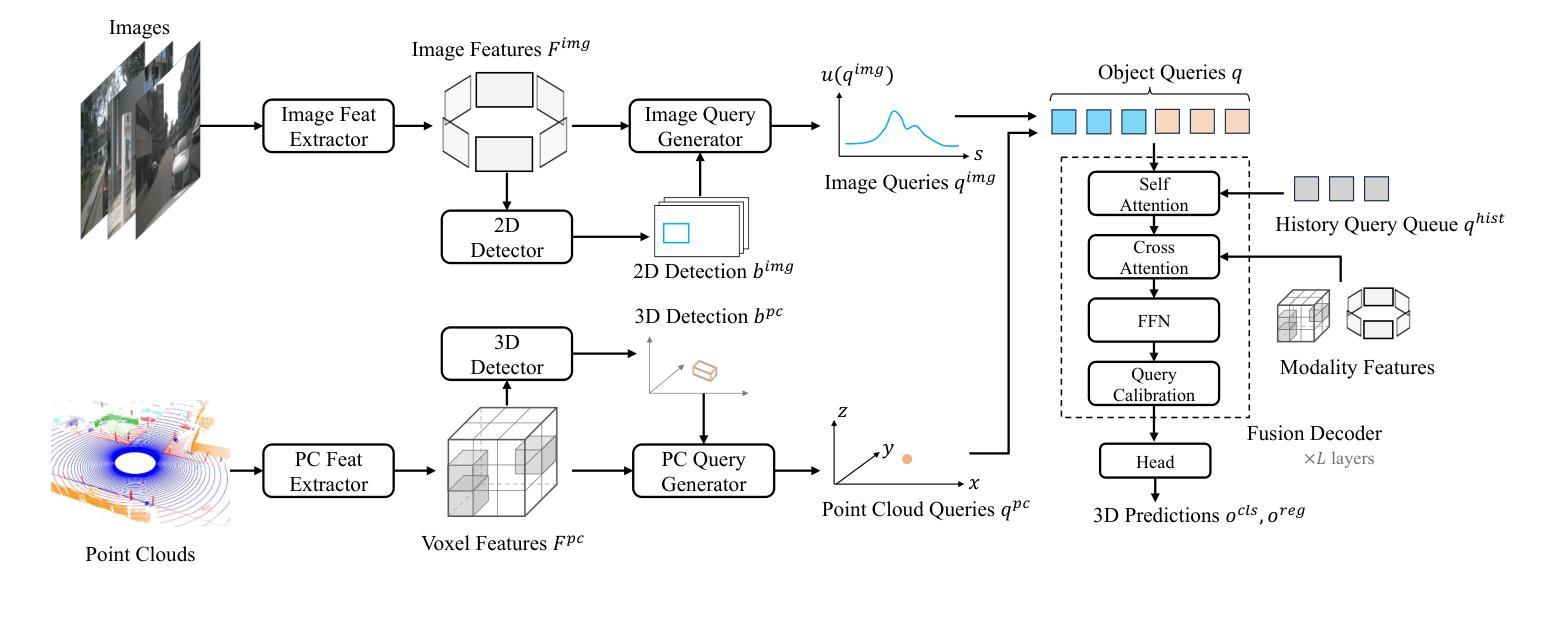
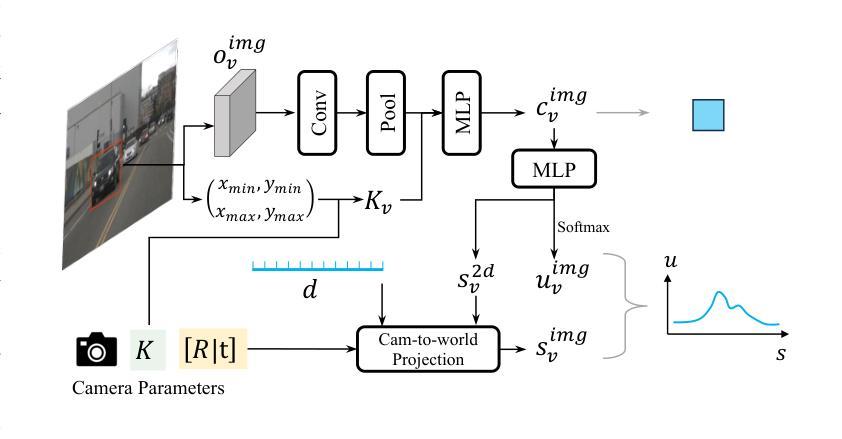
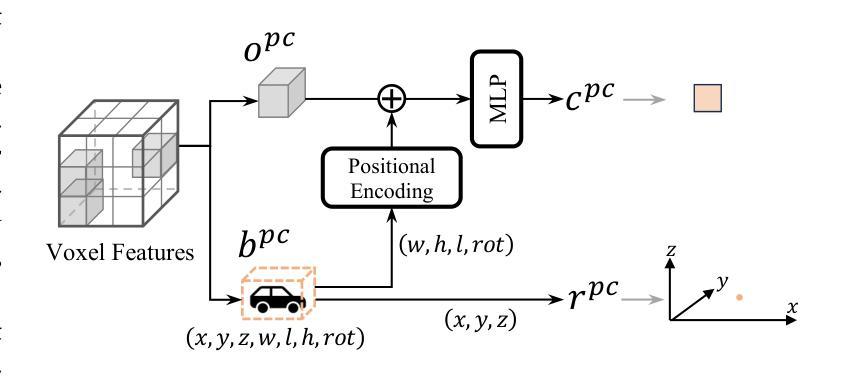
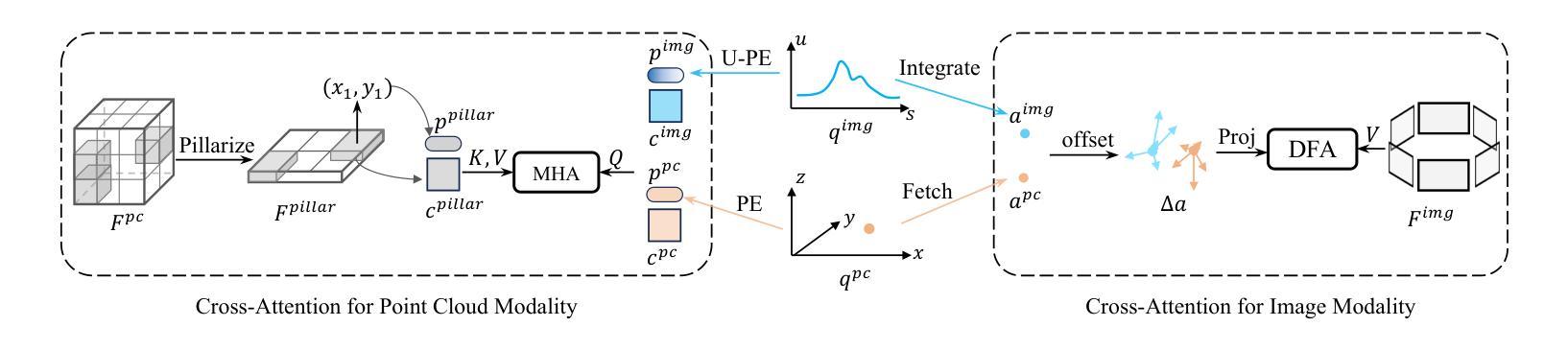
MV2DFusion: Leveraging Modality-Specific Object Semantics for Multi-Modal 3D Detection
Authors:Zitian Wang, Zehao Huang, Yulu Gao, Naiyan Wang, Si Liu
The rise of autonomous vehicles has significantly increased the demand for robust 3D object detection systems. While cameras and LiDAR sensors each offer unique advantages–cameras provide rich texture information and LiDAR offers precise 3D spatial data–relying on a single modality often leads to performance limitations. This paper introduces MV2DFusion, a multi-modal detection framework that integrates the strengths of both worlds through an advanced query-based fusion mechanism. By introducing an image query generator to align with image-specific attributes and a point cloud query generator, MV2DFusion effectively combines modality-specific object semantics without biasing toward one single modality. Then the sparse fusion process can be accomplished based on the valuable object semantics, ensuring efficient and accurate object detection across various scenarios. Our framework’s flexibility allows it to integrate with any image and point cloud-based detectors, showcasing its adaptability and potential for future advancements. Extensive evaluations on the nuScenes and Argoverse2 datasets demonstrate that MV2DFusion achieves state-of-the-art performance, particularly excelling in long-range detection scenarios.
自动驾驶汽车的兴起对鲁棒的3D物体检测系统提出了巨大的需求。虽然摄像机和激光雷达传感器各有独特的优势——摄像机提供丰富的纹理信息,激光雷达提供精确的3D空间数据——但仅依赖单一模态往往会导致性能局限。本文介绍了MV2DFusion,这是一个多模态检测框架,它通过先进的查询融合机制整合了两种技术的优势。通过引入图像查询生成器和点云查询生成器,MV2DFusion有效地结合了特定模态的对象语义,而不会偏向于任何一种单一模态。然后,基于有价值的对象语义完成稀疏融合过程,确保在各种场景中进行高效且准确的物体检测。我们的框架灵活性高,可以与任何基于图像和点云的检测器进行集成,展示了其适应性和未来进步的潜力。在nuScenes和Argoverse2数据集上的广泛评估表明,MV2DFusion达到了最先进的性能,特别是在远程检测场景中表现尤为出色。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着自动驾驶车辆的兴起,对可靠的3D物体检测系统需求大增。本论文提出了MV2DFusion,这是一种多模态检测框架,结合了摄像头和激光雷达传感器的优势,通过先进的查询融合机制来实现图像和点云数据的融合。该框架能够高效准确地检测各种场景中的物体,尤其擅长远距离检测场景。其灵活性允许与任何图像和点云检测器集成,展示了其适应未来技术发展的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 自主车辆崛起带动了对高性能3D物体检测系统的需求。
- MV2DFusion是一个多模态检测框架,结合了摄像头和激光雷达传感器的优势。
- 通过查询融合机制实现了图像和点云数据的融合。
- 该框架能高效准确地在各种场景中检测物体。
- MV2DFusion尤其擅长远距离检测场景。
- 框架具有灵活性,能与任何图像和点云检测器集成。
点此查看论文截图