⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-05 更新
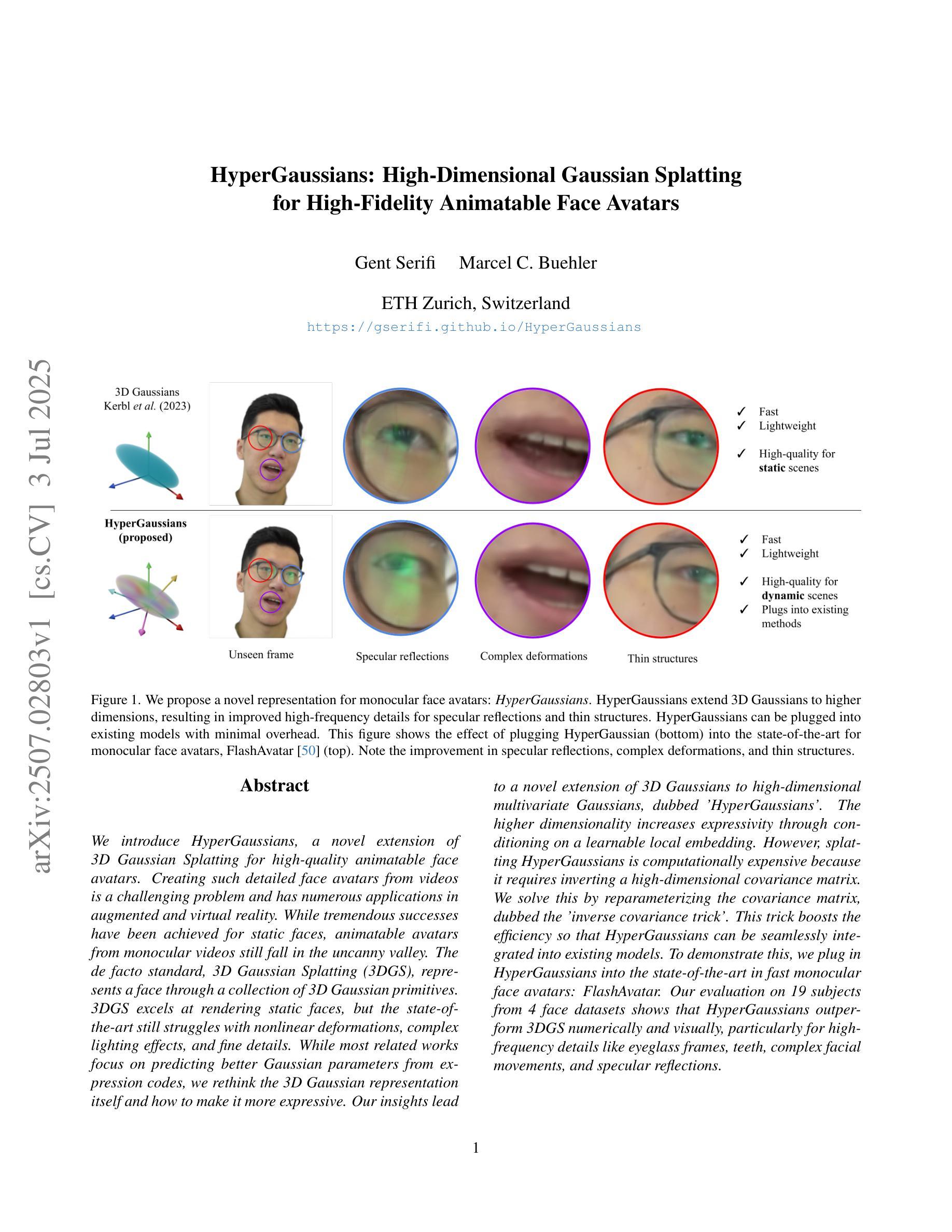
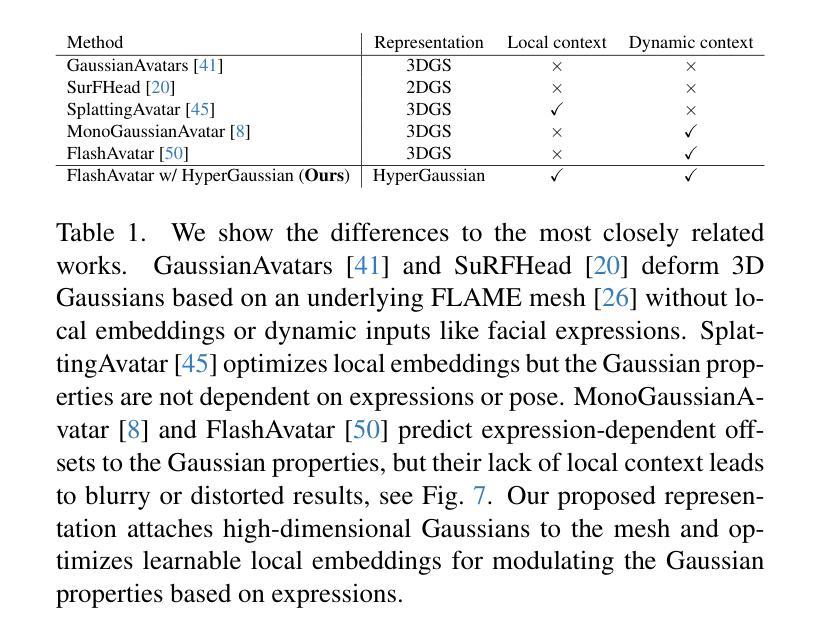
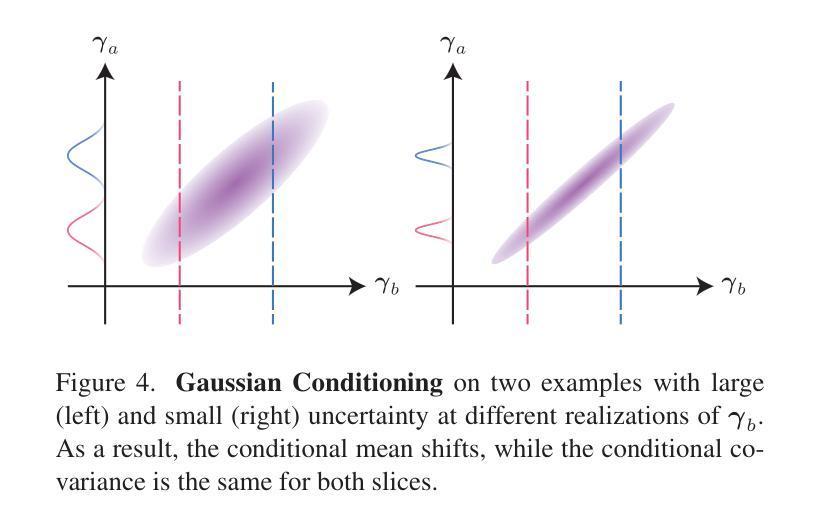
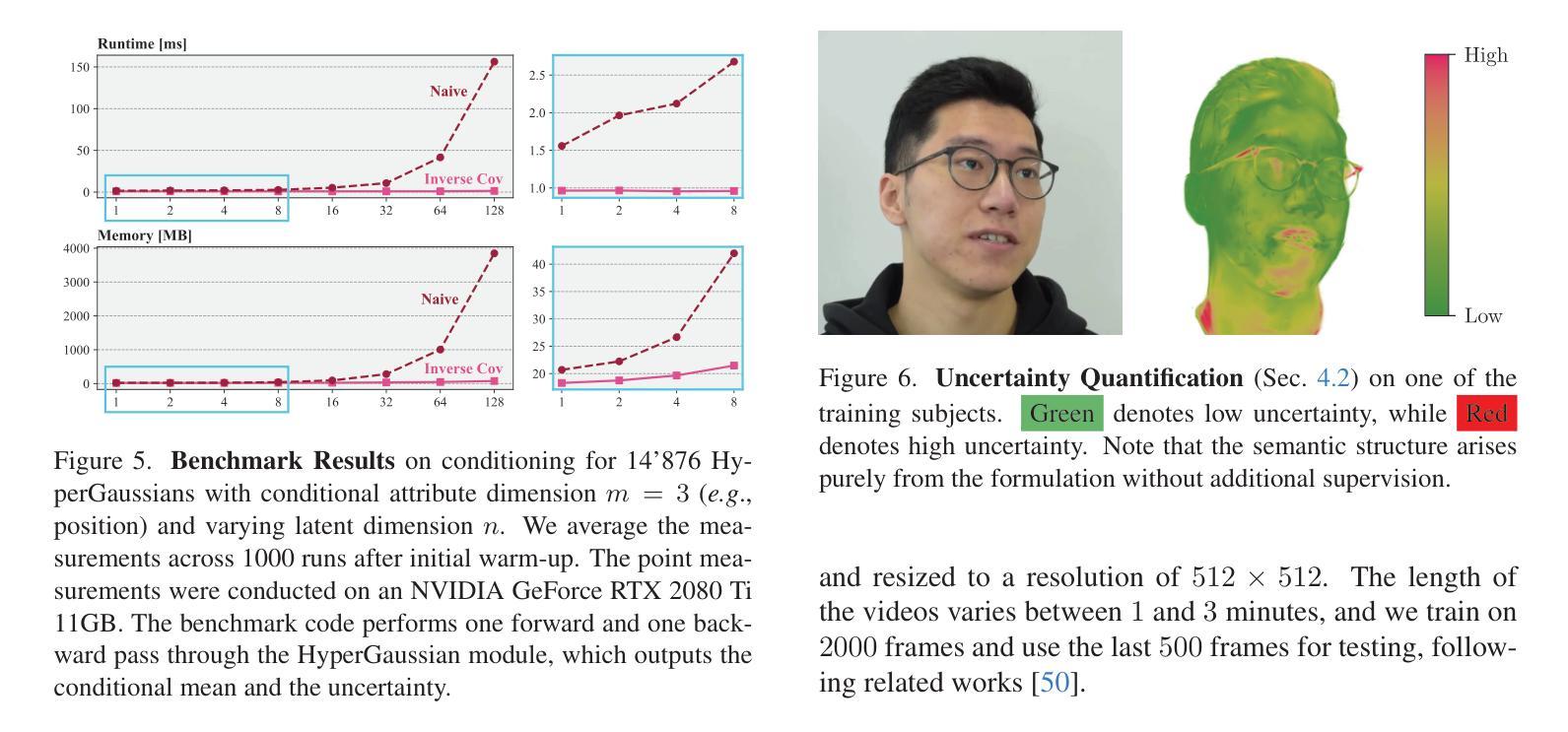
HyperGaussians: High-Dimensional Gaussian Splatting for High-Fidelity Animatable Face Avatars
Authors:Gent Serifi, Marcel C. Bühler
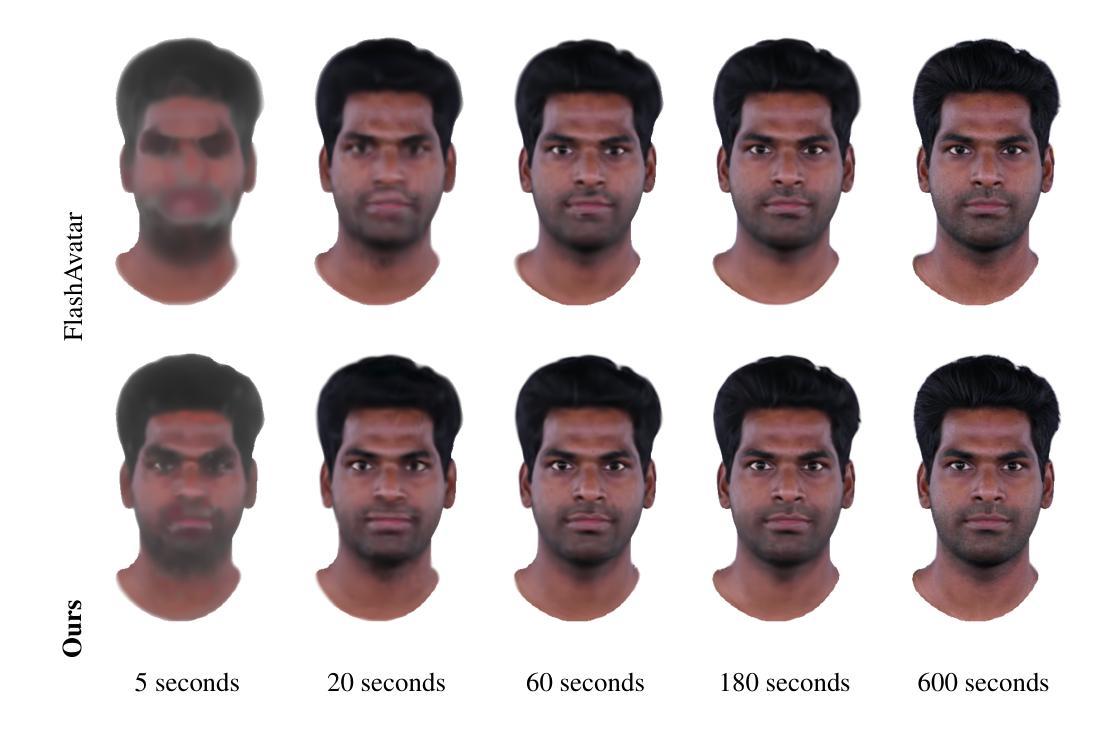
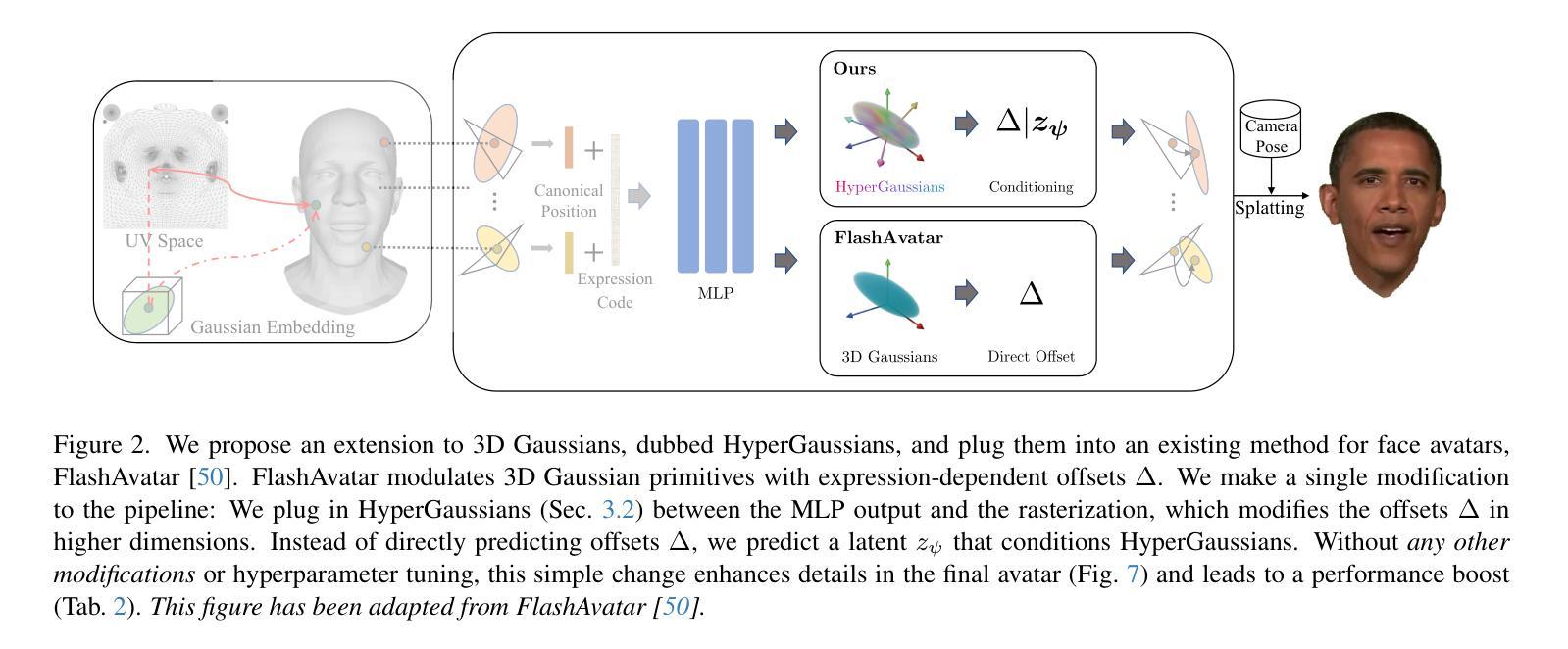
We introduce HyperGaussians, a novel extension of 3D Gaussian Splatting for high-quality animatable face avatars. Creating such detailed face avatars from videos is a challenging problem and has numerous applications in augmented and virtual reality. While tremendous successes have been achieved for static faces, animatable avatars from monocular videos still fall in the uncanny valley. The de facto standard, 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), represents a face through a collection of 3D Gaussian primitives. 3DGS excels at rendering static faces, but the state-of-the-art still struggles with nonlinear deformations, complex lighting effects, and fine details. While most related works focus on predicting better Gaussian parameters from expression codes, we rethink the 3D Gaussian representation itself and how to make it more expressive. Our insights lead to a novel extension of 3D Gaussians to high-dimensional multivariate Gaussians, dubbed ‘HyperGaussians’. The higher dimensionality increases expressivity through conditioning on a learnable local embedding. However, splatting HyperGaussians is computationally expensive because it requires inverting a high-dimensional covariance matrix. We solve this by reparameterizing the covariance matrix, dubbed the ‘inverse covariance trick’. This trick boosts the efficiency so that HyperGaussians can be seamlessly integrated into existing models. To demonstrate this, we plug in HyperGaussians into the state-of-the-art in fast monocular face avatars: FlashAvatar. Our evaluation on 19 subjects from 4 face datasets shows that HyperGaussians outperform 3DGS numerically and visually, particularly for high-frequency details like eyeglass frames, teeth, complex facial movements, and specular reflections.
我们介绍了HyperGaussians,这是3D高斯贴图的一种新型扩展,用于创建高质量的可动画面部化身。从视频中创建如此详细的面部化身是一个具有挑战性的问题,并且在增强和虚拟现实中有许多应用。虽然静态面孔已经取得了巨大的成功,但从单目视频中创建的可动画化身仍然处于不真实与真实之间的境地。现行标准3D高斯贴图(3DGS)通过一组3D高斯原始数据表示面部。3DGS在呈现静态面孔方面非常出色,但最新技术仍然难以处理非线性变形、复杂的灯光效果和精细细节。大多数相关作品都专注于从表情代码中预测更好的高斯参数,而我们重新思考了3D高斯表示本身以及如何使其更具表现力。我们的见解导致将3D高斯扩展到了高维多元高斯,称为“HyperGaussians”。更高的维度通过以可学习局部嵌入为条件来增加表现力。然而,绘制HyperGaussians的计算成本很高,因为它需要反转高维协方差矩阵。我们通过重新参数化协方差矩阵解决了这个问题,称为“逆协方差技巧”。这种技巧提高了效率,使得HyperGaussians可以无缝地集成到现有模型中。为了证明这一点,我们将HyperGaussians插入到现有快速单目面部化身技术的最新成果中:FlashAvatar。我们对来自四个面部数据集的19个主题进行的评估表明,HyperGaussians在数值和视觉上均优于3DGS,尤其是在眼镜框、牙齿、复杂面部运动和镜面反射等高频细节方面。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://gserifi.github.io/HyperGaussians
摘要
本文介绍了HyperGaussians,这是一种基于三维高斯混色的新型扩展技术,用于创建高质量的可动画面部化身。该技术对于从视频创建详细的面部化身具有挑战性,但在增强和虚拟现实等领域具有广泛应用。尽管静态面部渲染已经取得了巨大成功,但从单目视频中创建的可动画化身仍然在“尴尬之谷”阶段。本文提出的HyperGaussians通过引入高维多元高斯分布,扩展了三维高斯表示法,提高了其表现力。同时,为解决混色HyperGaussians所需的高维协方差矩阵计算成本较高的问题,采用协方差矩阵重新参数化的方法(“逆协方差技巧”),提高了计算效率,使HyperGaussians能够无缝集成到现有模型中。将HyperGaussians应用于当前先进的快速单目面部化身技术FlashAvatar中,对四个面部数据集的19名主体的评估显示,HyperGaussians在数值和视觉上均优于三维高斯混色技术,特别是在眼镜框、牙齿、复杂面部动作和镜面反射等高频细节方面表现更出色。
关键见解
- 介绍了一种新型技术HyperGaussians,该技术扩展了三维高斯混色技术以创建更详细的可动画面部化身。
- HyperGaussians通过引入高维多元高斯分布提高了表现力。
- 提出了一种解决HyperGaussians混色计算成本高的方法——“逆协方差技巧”,提高了计算效率。
- 将HyperGaussians集成到现有模型(如FlashAvatar)中,以改进面部化身的质量。
- HyperGaussians在复杂面部动作和高频细节(如眼镜框和牙齿)的渲染上表现优异。
- 对多个数据集进行的评估表明,HyperGaussians在数值和视觉上均优于现有技术(如三维高斯混色)。
点此查看论文截图

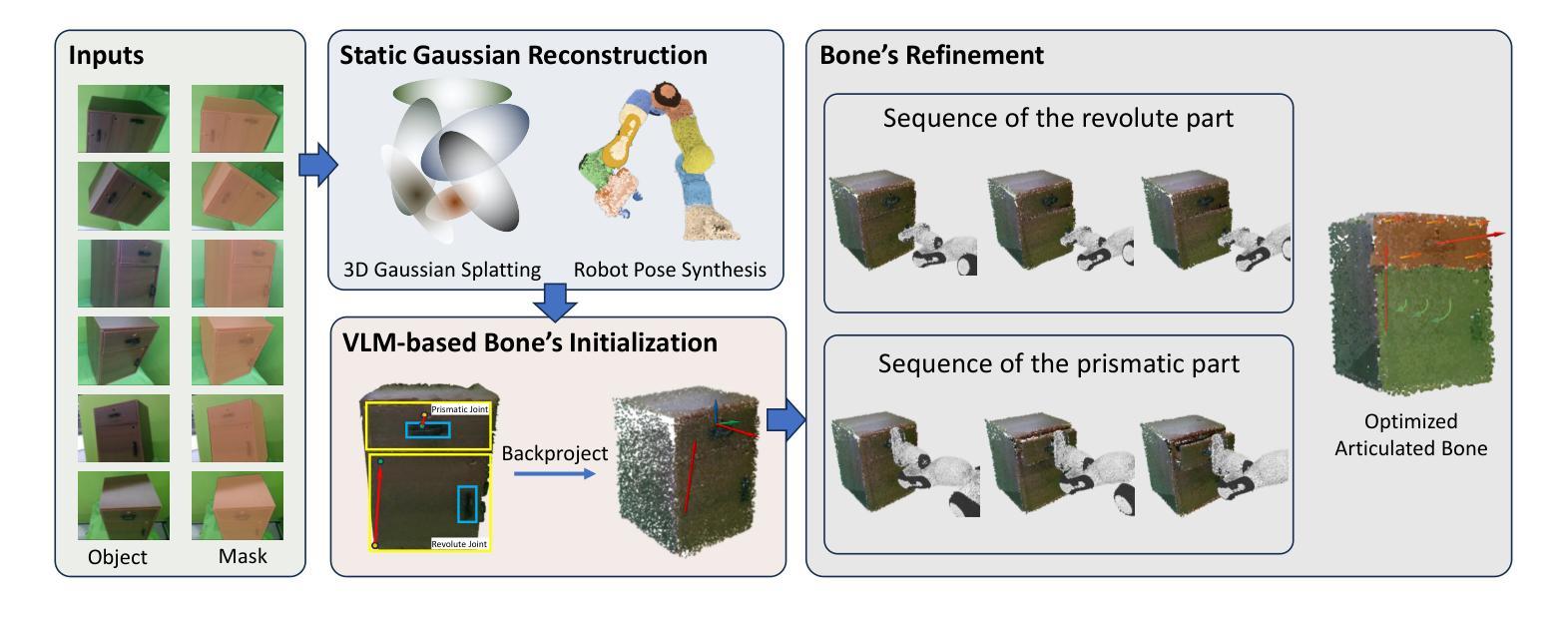
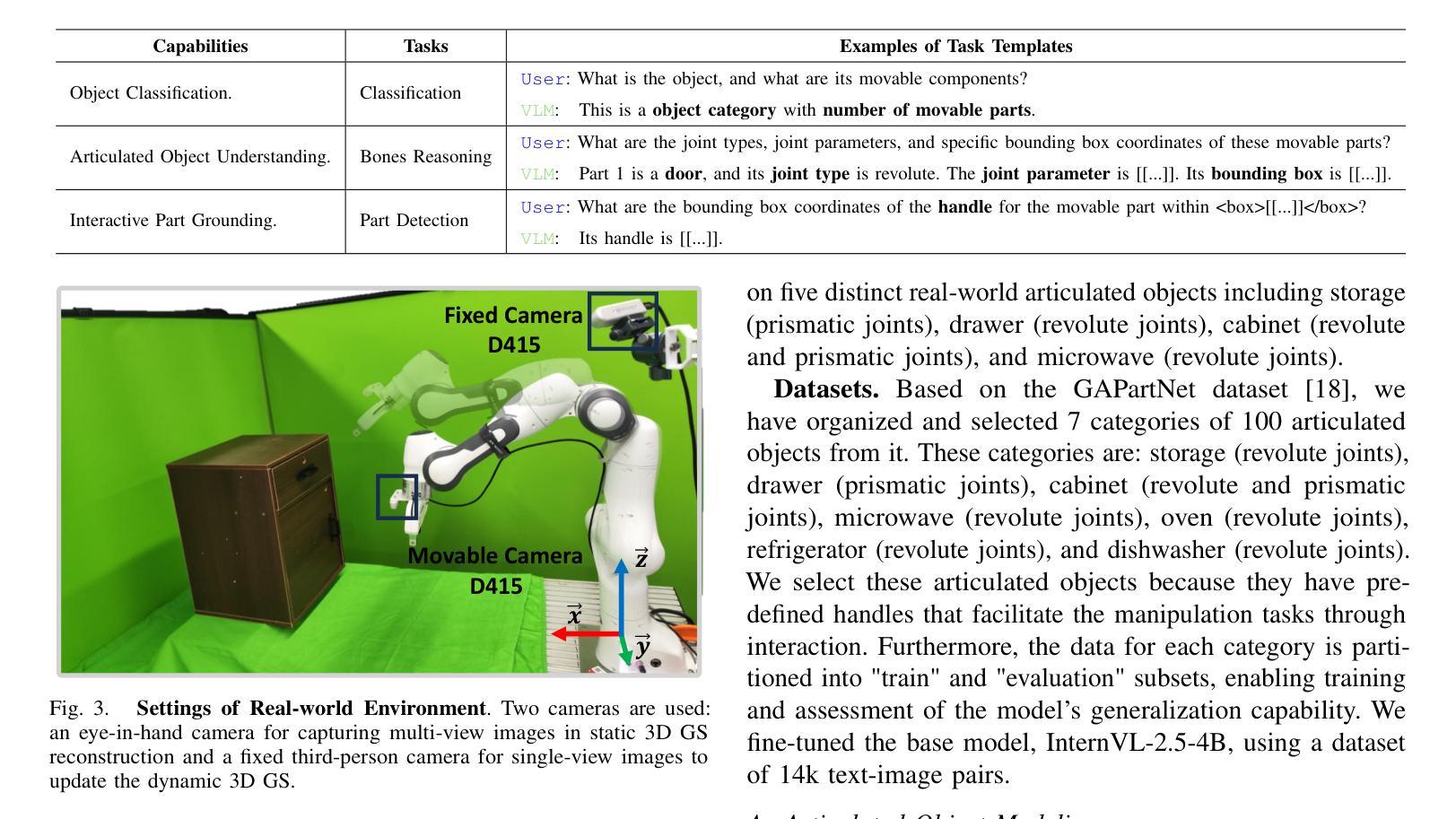
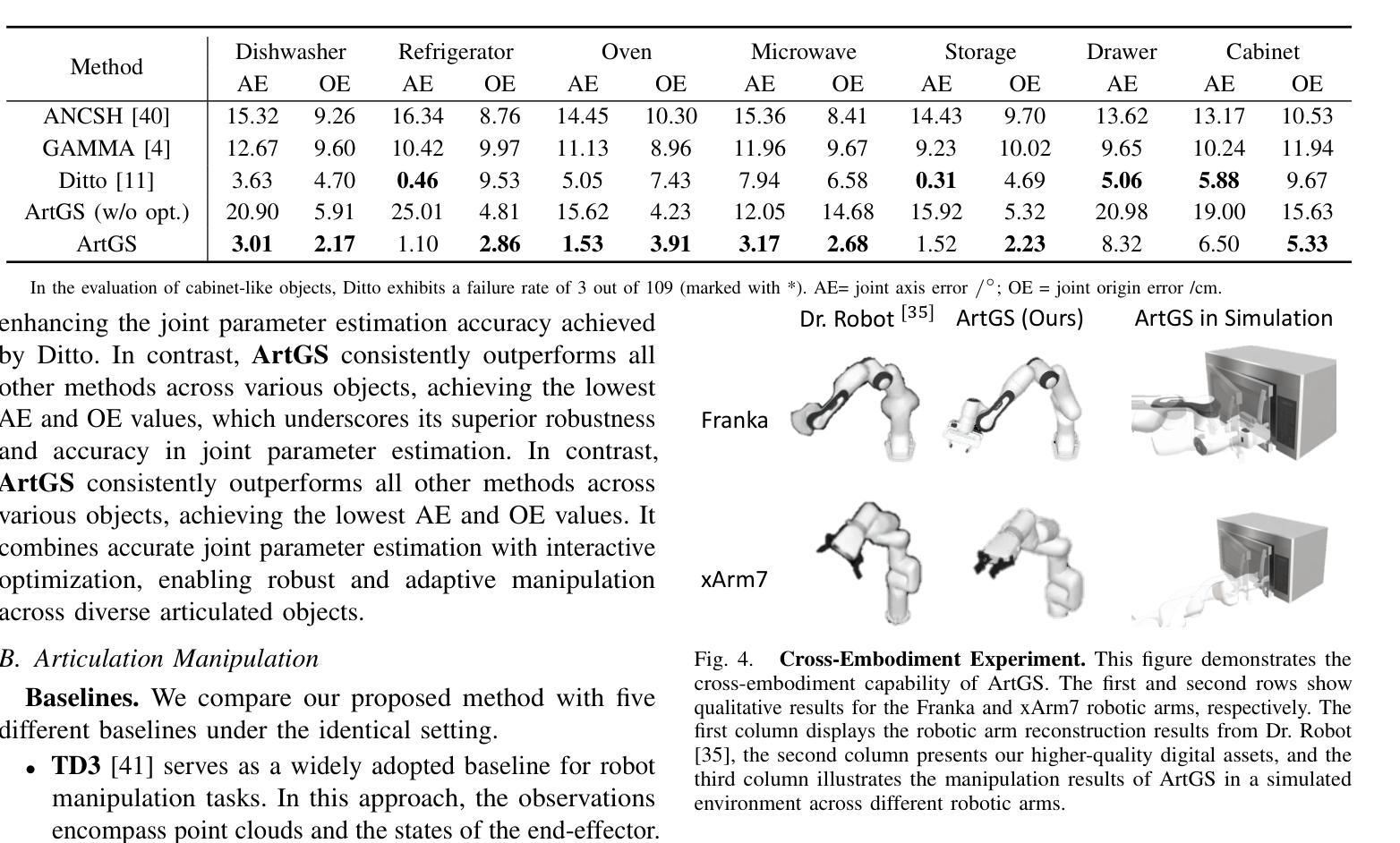
ArtGS:3D Gaussian Splatting for Interactive Visual-Physical Modeling and Manipulation of Articulated Objects
Authors:Qiaojun Yu, Xibin Yuan, Yu jiang, Junting Chen, Dongzhe Zheng, Ce Hao, Yang You, Yixing Chen, Yao Mu, Liu Liu, Cewu Lu
Articulated object manipulation remains a critical challenge in robotics due to the complex kinematic constraints and the limited physical reasoning of existing methods. In this work, we introduce ArtGS, a novel framework that extends 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) by integrating visual-physical modeling for articulated object understanding and interaction. ArtGS begins with multi-view RGB-D reconstruction, followed by reasoning with a vision-language model (VLM) to extract semantic and structural information, particularly the articulated bones. Through dynamic, differentiable 3DGS-based rendering, ArtGS optimizes the parameters of the articulated bones, ensuring physically consistent motion constraints and enhancing the manipulation policy. By leveraging dynamic Gaussian splatting, cross-embodiment adaptability, and closed-loop optimization, ArtGS establishes a new framework for efficient, scalable, and generalizable articulated object modeling and manipulation. Experiments conducted in both simulation and real-world environments demonstrate that ArtGS significantly outperforms previous methods in joint estimation accuracy and manipulation success rates across a variety of articulated objects. Additional images and videos are available on the project website: https://sites.google.com/view/artgs/home
关节式对象操作仍然是机器人技术中的一项关键挑战,因为存在复杂的运动学约束和现有方法的物理推理有限。在这项工作中,我们引入了ArtGS,这是一个通过整合视觉物理建模来扩展三维高斯贴片技术(3DGS)的新型框架,用于关节式对象的理解和交互。ArtGS始于多视角RGB-D重建,随后利用视觉语言模型(VLM)进行推理,以提取语义和结构信息,特别是关节骨骼。通过基于动态、可区分3DGS的渲染,ArtGS优化了关节骨骼的参数,确保物理一致的动态约束,并增强了操作策略。通过利用动态高斯贴片技术、跨体态适应性和闭环优化,ArtGS建立了一个高效、可扩展和通用的关节式对象建模和操作的新框架。在模拟和真实环境中所进行的实验表明,ArtGS在关节估计准确性和操作成功率方面大大优于以前的方法,适用于各种关节式对象。更多图片和视频可在项目网站查看:https://sites.google.com/view/artgs/home
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IROS 2025
Summary
本文提出了一个名为ArtGS的新框架,通过集成视觉物理建模来实现关节可动对象的操控和交互,使用视觉-语言模型提取语义和结构信息,并利用动态可微分的3DGS渲染技术优化关节参数,确保物理一致性运动约束,提高了操控策略。在模拟和真实环境中进行的实验表明,ArtGS在关节估计准确性和操控成功率方面显著优于先前的方法。
Key Takeaways
- ArtGS是一个基于视觉物理建模的框架,用于关节可动对象的操控和交互。
- 利用多视角RGB-D重建进行初步对象理解。
- 通过结合视觉语言模型(VLM)提取语义和结构信息,特别是关节骨信息。
- 使用动态、可微分的3DGS渲染技术进行关节参数优化。
- 引入动态高斯蒙版、跨嵌入适应性和闭环优化机制提升框架效率。
- ArtGS在关节估计准确性和操控成功率上超越先前方法。
点此查看论文截图


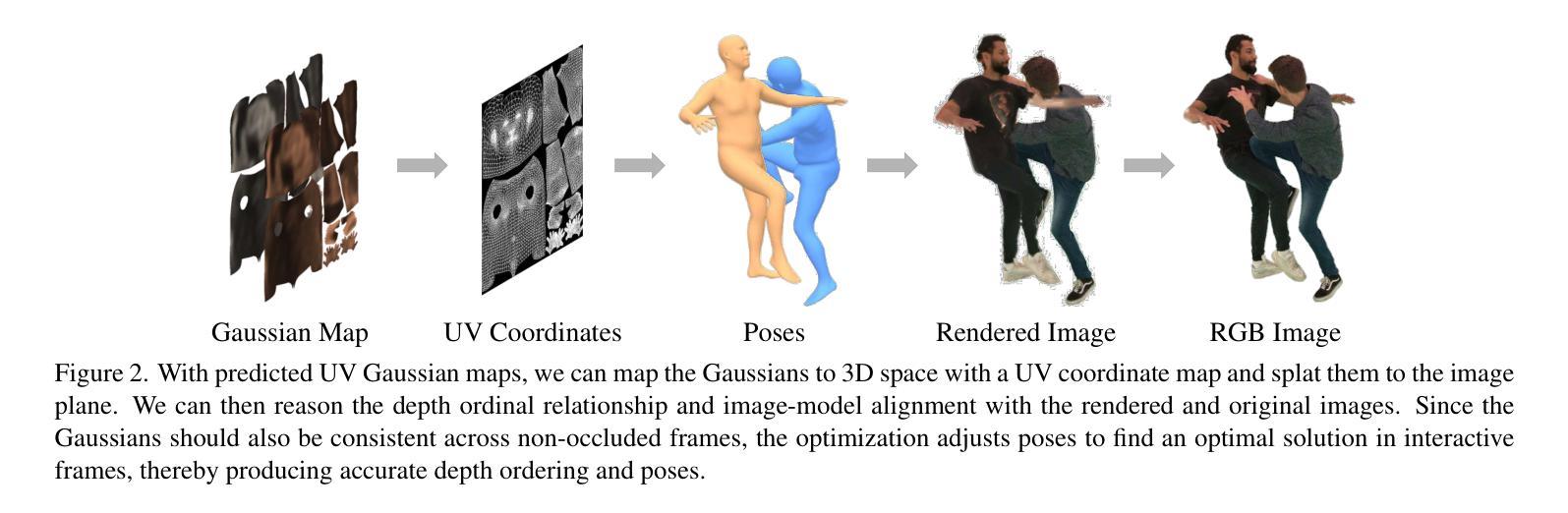
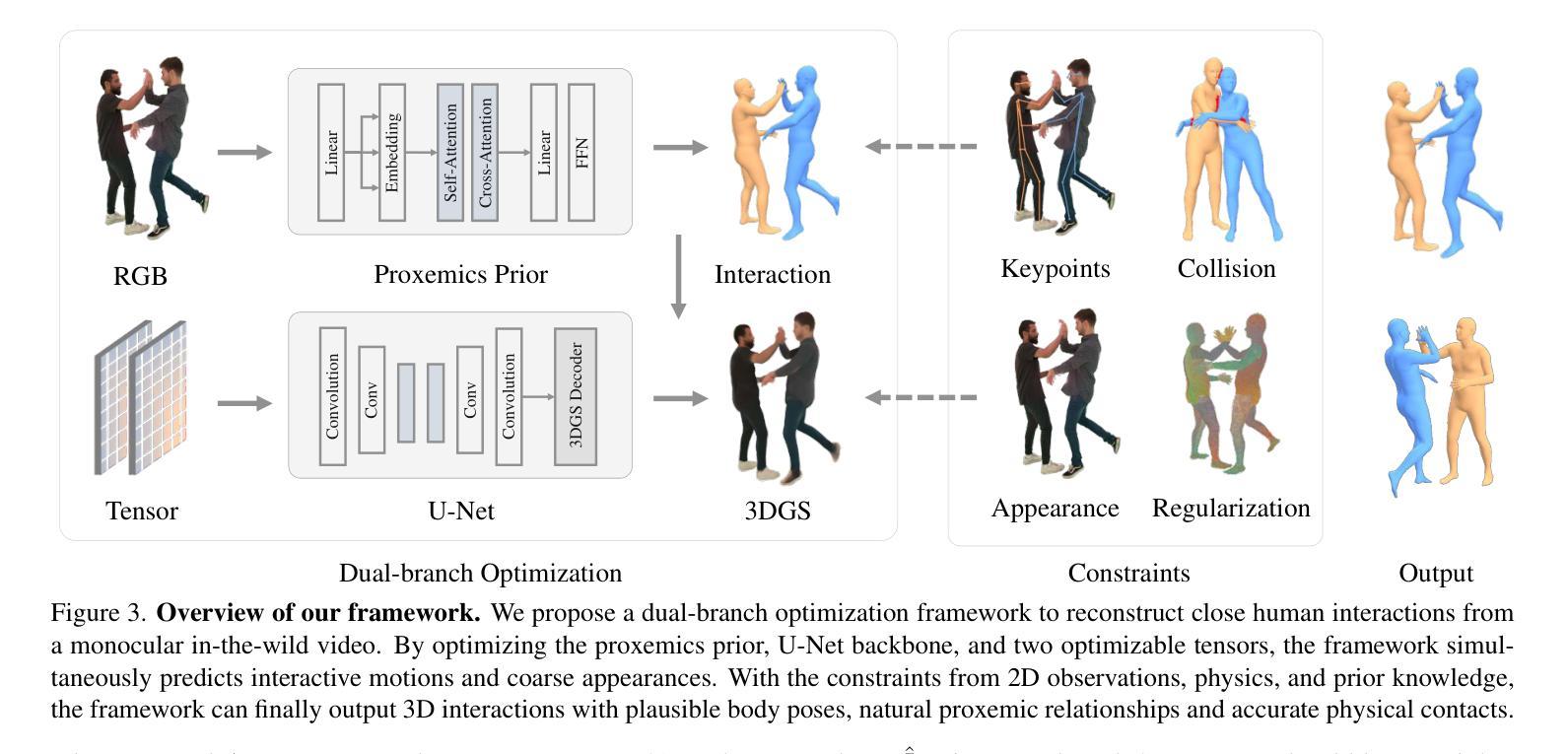
Reconstructing Close Human Interaction with Appearance and Proxemics Reasoning
Authors:Buzhen Huang, Chen Li, Chongyang Xu, Dongyue Lu, Jinnan Chen, Yangang Wang, Gim Hee Lee
Due to visual ambiguities and inter-person occlusions, existing human pose estimation methods cannot recover plausible close interactions from in-the-wild videos. Even state-of-the-art large foundation models~(\eg, SAM) cannot accurately distinguish human semantics in such challenging scenarios. In this work, we find that human appearance can provide a straightforward cue to address these obstacles. Based on this observation, we propose a dual-branch optimization framework to reconstruct accurate interactive motions with plausible body contacts constrained by human appearances, social proxemics, and physical laws. Specifically, we first train a diffusion model to learn the human proxemic behavior and pose prior knowledge. The trained network and two optimizable tensors are then incorporated into a dual-branch optimization framework to reconstruct human motions and appearances. Several constraints based on 3D Gaussians, 2D keypoints, and mesh penetrations are also designed to assist the optimization. With the proxemics prior and diverse constraints, our method is capable of estimating accurate interactions from in-the-wild videos captured in complex environments. We further build a dataset with pseudo ground-truth interaction annotations, which may promote future research on pose estimation and human behavior understanding. Experimental results on several benchmarks demonstrate that our method outperforms existing approaches. The code and data are available at https://www.buzhenhuang.com/works/CloseApp.html.
由于视觉模糊和人与人之间的相互遮挡,现有的人体姿态估计方法无法从野生视频中恢复出合理的紧密交互。即使是最先进的大型基础模型(例如SAM)也无法在这种具有挑战性的场景中准确区分人体语义。在这项工作中,我们发现人的外观可以提供一种直接的线索来解决这些障碍。基于这一观察,我们提出了一种双分支优化框架,通过人体外观、社交空间学(proxemics)和物理定律的约束来重建准确的交互动作和合理的身体接触。具体来说,我们首先对扩散模型进行训练,学习人类的空间行为学和姿态先验知识。然后将训练好的网络和两个可优化的张量纳入双分支优化框架中,以重建人体动作和外观。还设计了基于3D高斯分布、2D关键点以及网格穿透的多种约束来帮助优化。凭借空间学先验知识和多样化的约束条件,我们的方法能够从复杂环境中捕获的野生视频中估计出准确的人体交互动作。我们还建立了一个带有伪地面真实交互注释的数据集,这可能有助于推动未来在姿态估计和人类行为理解方面的研究。在几个基准测试上的实验结果证明,我们的方法优于现有方法。代码和数据集可在https://www.buzhenhuang.com/works/CloseApp.html找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文针对人类姿态估计在复杂环境中的难点进行了深入研究,发现人类外观是突破这一问题的关键线索。因此提出一个基于人体外观、社交距离和人类行为约束的双分支优化框架来准确重建人类运动。结合扩散模型进行学习和训练网络,在模拟不同复杂环境下的场景,可以有效地估计人类交互动作。该研究还建立了一个包含伪真实交互注释的数据集,促进了姿态估计和人类行为理解的研究。实验结果表明,该方法优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 现有的人类姿态估计方法在处理复杂环境中的紧密交互时存在困难。
- 人类外观信息是解决这一问题的关键线索。
- 提出了一种基于人体外观、社交距离和人类行为约束的双分支优化框架来重建准确的人类运动。
- 利用扩散模型学习人类行为模式和姿态先验知识。
- 通过多种约束(如3D高斯分布、2D关键点、网格穿透等)辅助优化过程。
- 建立了一个包含伪真实交互注释的数据集,有助于推动姿态估计和人类行为理解的研究。
点此查看论文截图

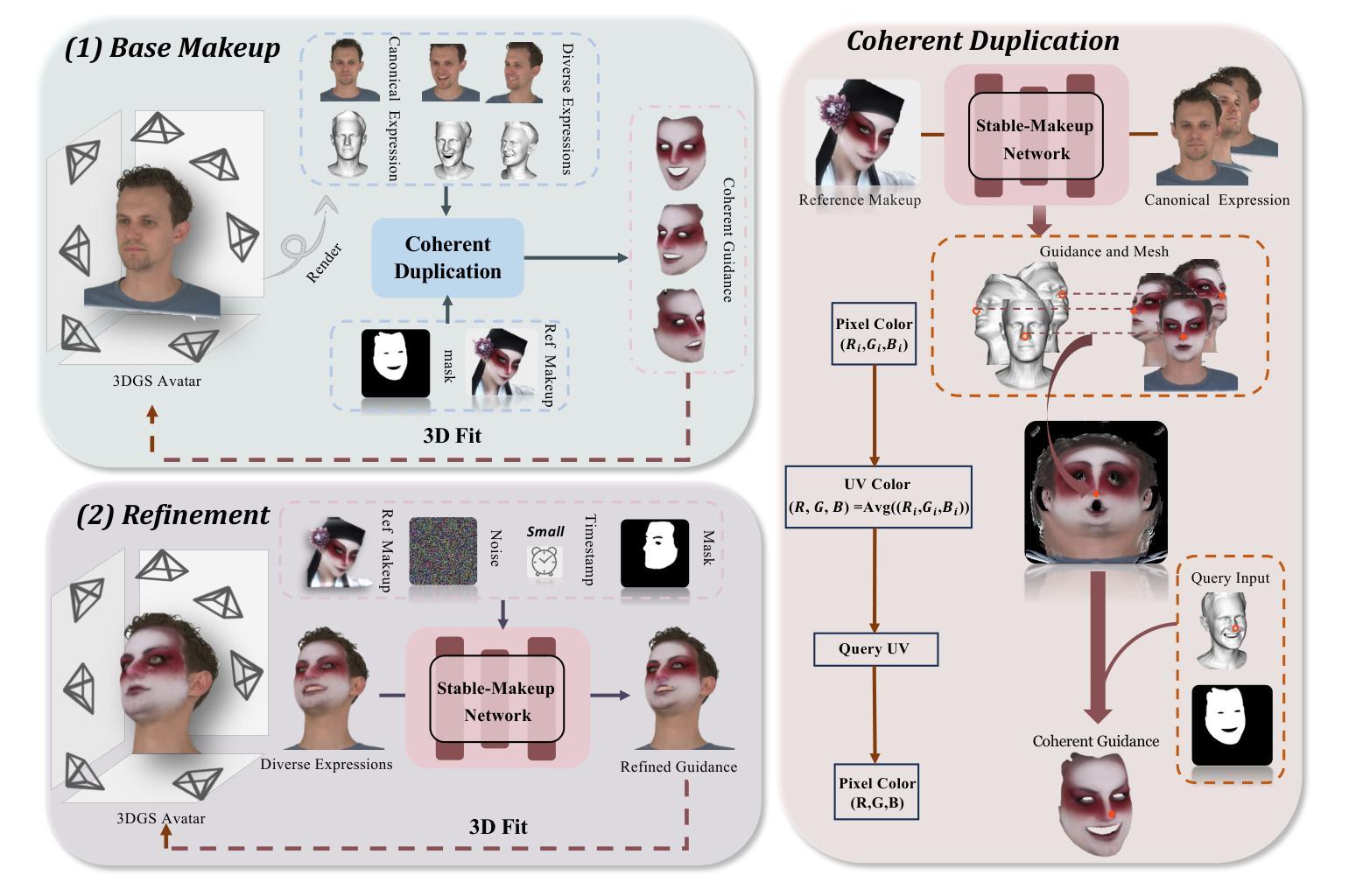
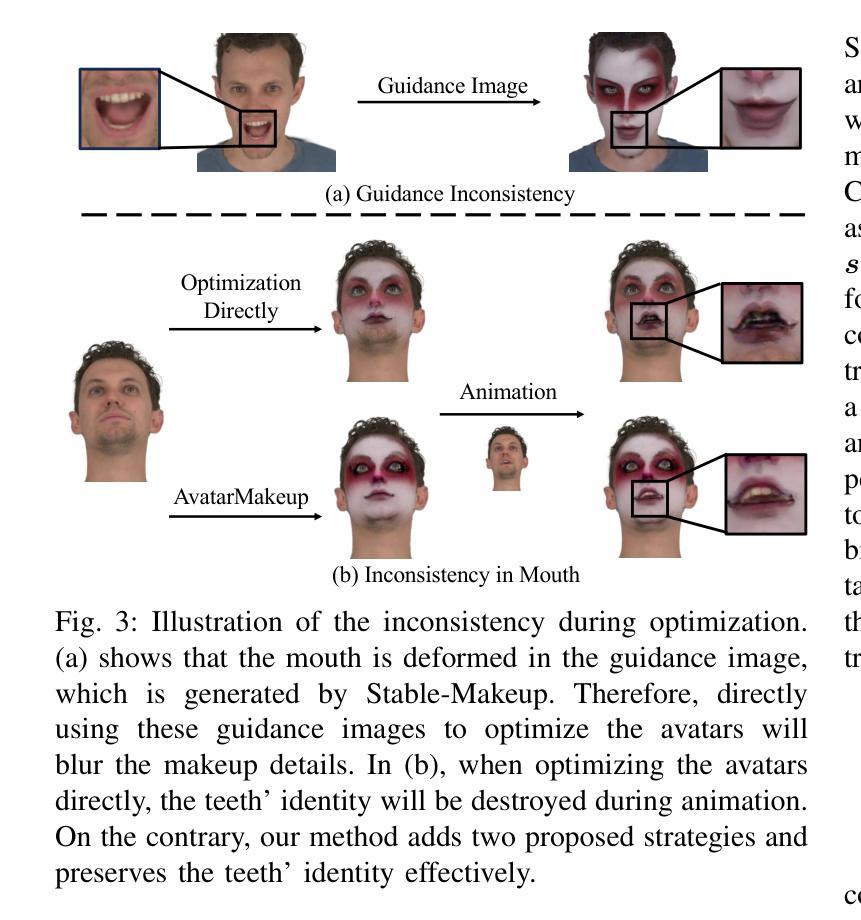
AvatarMakeup: Realistic Makeup Transfer for 3D Animatable Head Avatars
Authors:Yiming Zhong, Xiaolin Zhang, Ligang Liu, Yao Zhao, Yunchao Wei
Similar to facial beautification in real life, 3D virtual avatars require personalized customization to enhance their visual appeal, yet this area remains insufficiently explored. Although current 3D Gaussian editing methods can be adapted for facial makeup purposes, these methods fail to meet the fundamental requirements for achieving realistic makeup effects: 1) ensuring a consistent appearance during drivable expressions, 2) preserving the identity throughout the makeup process, and 3) enabling precise control over fine details. To address these, we propose a specialized 3D makeup method named AvatarMakeup, leveraging a pretrained diffusion model to transfer makeup patterns from a single reference photo of any individual. We adopt a coarse-to-fine idea to first maintain the consistent appearance and identity, and then to refine the details. In particular, the diffusion model is employed to generate makeup images as supervision. Due to the uncertainties in diffusion process, the generated images are inconsistent across different viewpoints and expressions. Therefore, we propose a Coherent Duplication method to coarsely apply makeup to the target while ensuring consistency across dynamic and multiview effects. Coherent Duplication optimizes a global UV map by recoding the averaged facial attributes among the generated makeup images. By querying the global UV map, it easily synthesizes coherent makeup guidance from arbitrary views and expressions to optimize the target avatar. Given the coarse makeup avatar, we further enhance the makeup by incorporating a Refinement Module into the diffusion model to achieve high makeup quality. Experiments demonstrate that AvatarMakeup achieves state-of-the-art makeup transfer quality and consistency throughout animation.
类似于现实生活中的面部美容,3D虚拟角色需要个性化定制以增强其视觉吸引力,但这个领域仍然没有得到足够的探索。尽管当前的3D高斯编辑方法可以适应面部化妆的目的,但这些方法未能满足实现真实化妆效果的基本需求:1)在可驱动的表情中确保一致的外观,2)在化妆过程中保留身份特征,以及3)对细节进行精确控制。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种专门的3D化妆方法,名为AvatarMakeup,它利用预训练的扩散模型从任何个人的单张参考照片中转移化妆模式。我们采用由粗到细的理念,首先保持外观和身份的一致性,然后细化细节。特别是,利用扩散模型生成化妆图像作为监督。由于扩散过程中的不确定性,生成的图像在不同的视角和表情上存在差异。因此,我们提出了一种连贯复制方法,将化妆粗略地应用到目标上,同时确保动态和多视角效果的一致性。连贯复制通过重新编码生成化妆图像之间的平均面部属性来优化全局UV映射。通过查询全局UV映射,它很容易合成来自任意视角和表情的连贯化妆指导,以优化目标角色。给定粗略的化妆角色,我们进一步通过将细化模块融入到扩散模型中,以提高化妆品质量。实验表明,AvatarMakeup在动画过程中实现了先进的化妆转移质量和一致性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种名为AvatarMakeup的3D虚拟角色化妆方法,该方法利用预训练的扩散模型从单一参考照片转移妆容。采用由粗到细的策略,先保持外观和身份的连续性,再细化细节。使用扩散模型生成妆容图像作为监督,并提出Coherent Duplication方法确保动态和多视角下的妆容一致性。通过优化全局UV映射,合成任意视角和表情下的连贯妆容指导。进一步通过引入细化模块提升妆容质量。实验表明,AvatarMakeup在化妆转移质量和动画一致性方面达到领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- 3D虚拟角色需要个性化定制以增强其视觉吸引力,但当前方法无法满足真实妆容效果的要求。
- 提出了AvatarMakeup方法,利用预训练的扩散模型从单一参考照片转移妆容。
- 采用由粗到细的策略,先保证外观和身份的连续性,再细化细节。
- 使用扩散模型生成妆容图像作为监督,但存在不确定性问题。
- 提出Coherent Duplication方法,优化全局UV映射,确保动态和多视角下的妆容一致性。
- 引入细化模块提升妆容质量。
点此查看论文截图



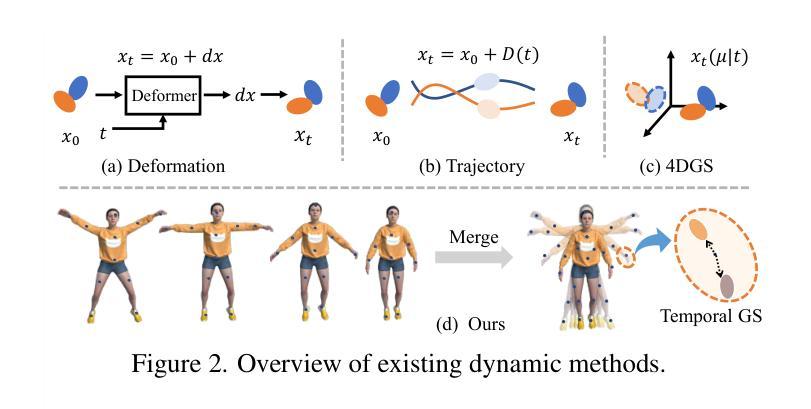
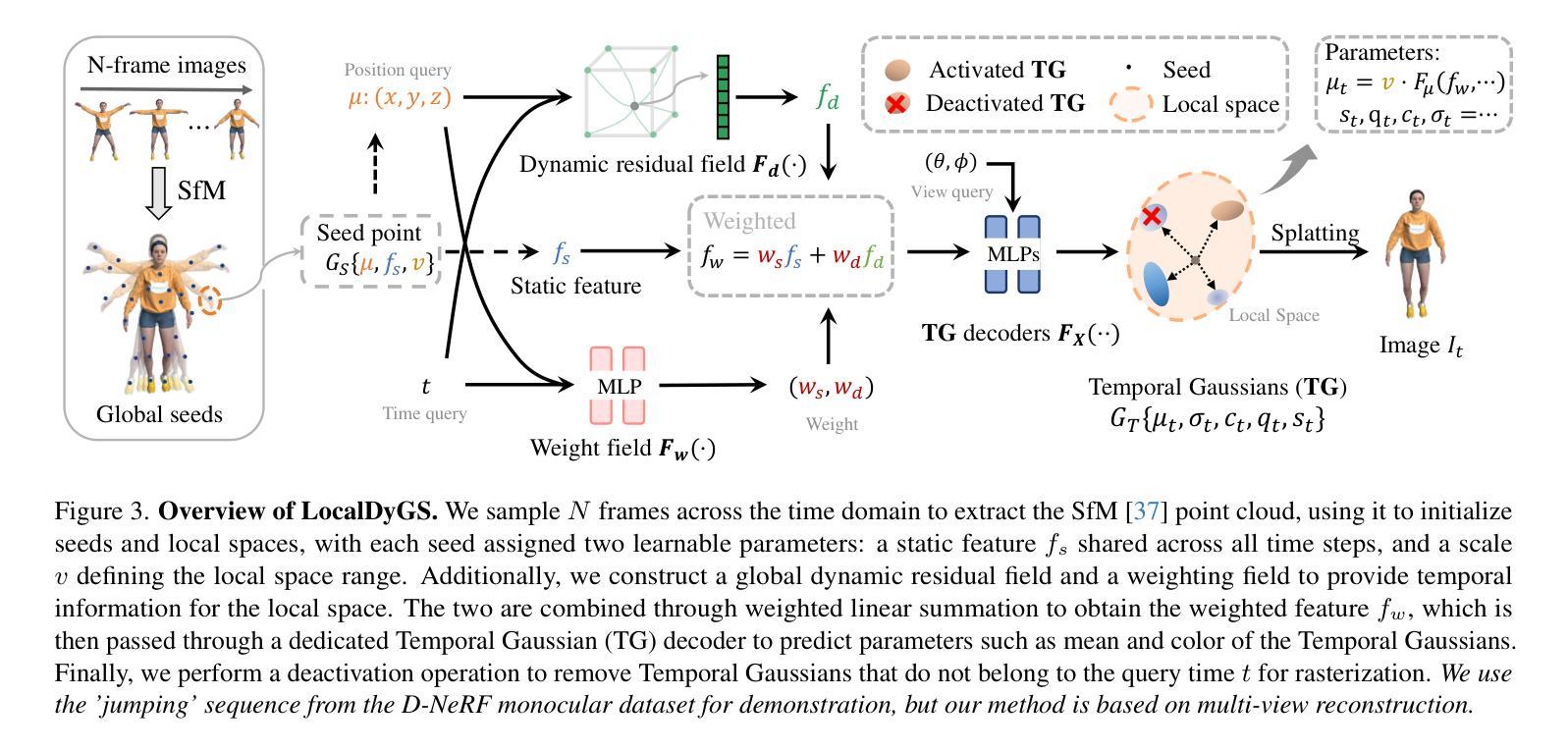
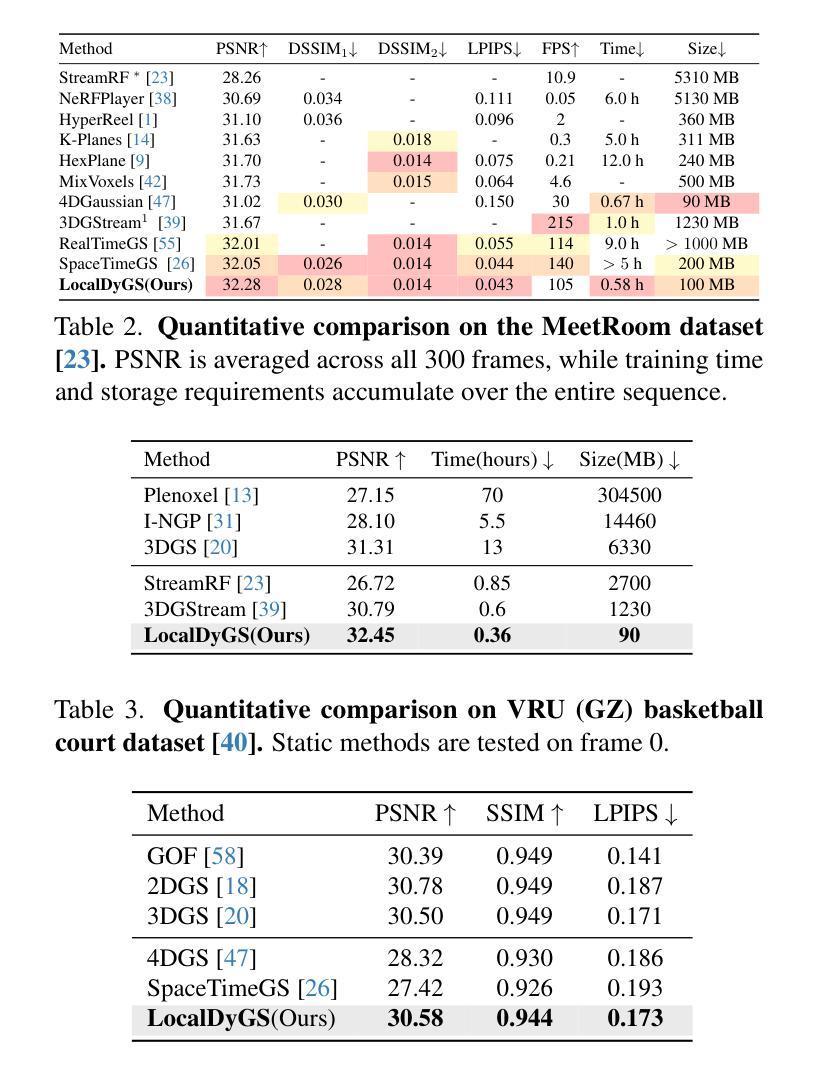
LocalDyGS: Multi-view Global Dynamic Scene Modeling via Adaptive Local Implicit Feature Decoupling
Authors:Jiahao Wu, Rui Peng, Jianbo Jiao, Jiayu Yang, Luyang Tang, Kaiqiang Xiong, Jie Liang, Jinbo Yan, Runling Liu, Ronggang Wang
Due to the complex and highly dynamic motions in the real world, synthesizing dynamic videos from multi-view inputs for arbitrary viewpoints is challenging. Previous works based on neural radiance field or 3D Gaussian splatting are limited to modeling fine-scale motion, greatly restricting their application. In this paper, we introduce LocalDyGS, which consists of two parts to adapt our method to both large-scale and fine-scale motion scenes: 1) We decompose a complex dynamic scene into streamlined local spaces defined by seeds, enabling global modeling by capturing motion within each local space. 2) We decouple static and dynamic features for local space motion modeling. A static feature shared across time steps captures static information, while a dynamic residual field provides time-specific features. These are combined and decoded to generate Temporal Gaussians, modeling motion within each local space. As a result, we propose a novel dynamic scene reconstruction framework to model highly dynamic real-world scenes more realistically. Our method not only demonstrates competitive performance on various fine-scale datasets compared to state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods, but also represents the first attempt to model larger and more complex highly dynamic scenes. Project page: https://wujh2001.github.io/LocalDyGS/.
由于现实世界中复杂且高度动态的动态,从多视角输入合成任意视角的动态视频是一项挑战。之前基于神经辐射场或3D高斯贴图的工作仅限于对精细动作的建模,极大地限制了其应用。在本文中,我们介绍了LocalDyGS,它由两部分组成,使我们的方法能够适应大规模和精细动作的场景:1)我们将复杂的动态场景分解为由种子定义的流线型局部空间,通过捕捉每个局部空间内的运动来进行全局建模。2)我们将静态和动态特征解耦,用于局部空间运动建模。一个跨时间步共享的静态特征捕捉静态信息,而一个动态残差场提供特定时间的特征。这些特征相结合并解码,生成时序高斯,模拟每个局部空间内的运动。因此,我们提出了一种新的动态场景重建框架,以更真实的方式对高度动态的现实世界场景进行建模。我们的方法不仅在各种精细数据集上展现出与最新技术相竞争的性能,而且还首次尝试对更大、更复杂的动态场景进行建模。项目页面:https://wujh2001.github.io/LocalDyGS/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025
Summary
本文提出一种名为LocalDyGS的新方法,用于合成动态视频。该方法通过分解复杂动态场景、解构静态与动态特征,建立局部空间运动模型,以应对真实世界中复杂且高度动态的运动。此框架不仅在精细尺度数据集上表现卓越,更是首次尝试模拟更大、更复杂的场景运动。详情请参见项目网页。
Key Takeaways
- LocalDyGS方法能处理真实世界中的复杂且高度动态的运动场景。
- 方法通过分解复杂动态场景到局部空间进行建模,以应对大规模运动场景。
- 静态和动态特征被解耦,以便更准确地捕捉局部空间的运动特性。
- 通过结合静态特征和动态残差场,生成时间高斯模型,以模拟局部空间的运动。
- LocalDyGS不仅在精细尺度数据集上的性能具有竞争力,而且能够模拟更大、更复杂的场景运动。
- 项目网页提供了更多关于LocalDyGS方法的详细信息。
点此查看论文截图


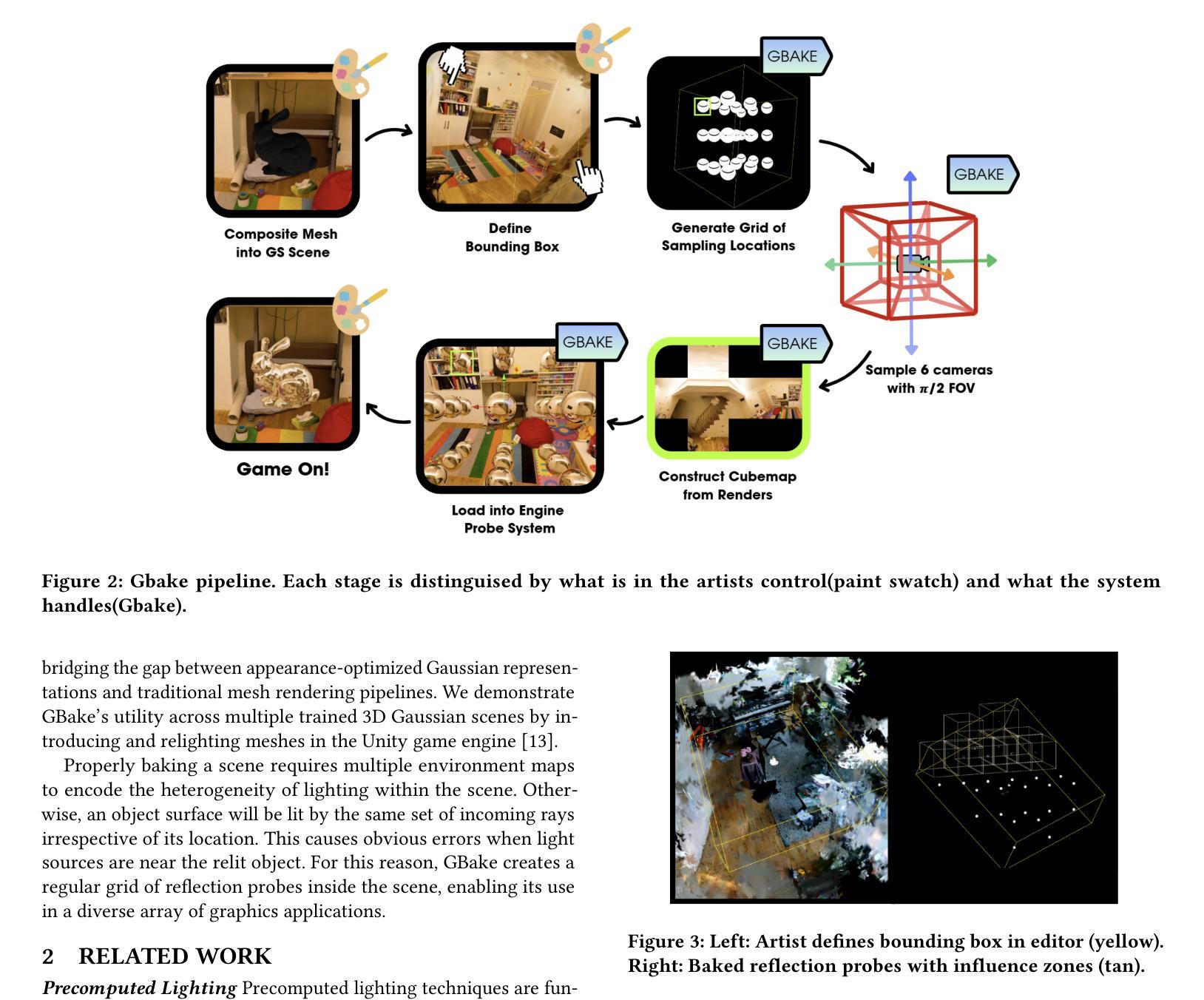
Gbake: Baking 3D Gaussian Splats into Reflection Probes
Authors:Stephen Pasch, Joel K. Salzman, Changxi Zheng
The growing popularity of 3D Gaussian Splatting has created the need to integrate traditional computer graphics techniques and assets in splatted environments. Since 3D Gaussian primitives encode lighting and geometry jointly as appearance, meshes are relit improperly when inserted directly in a mixture of 3D Gaussians and thus appear noticeably out of place. We introduce GBake, a specialized tool for baking reflection probes from Gaussian-splatted scenes that enables realistic reflection mapping of traditional 3D meshes in the Unity game engine.
随着三维高斯混合技术的日益普及,需要在混合环境中集成传统的计算机图形技术和资源。由于三维高斯基本体将光照和几何结构共同编码为外观,因此当直接插入混合的三维高斯中时,网格会重新照明不当,从而显得格格不入。我们引入了GBake,这是一个用于从高斯混合场景中烘焙反射探针的专用工具,它能够在Unity游戏引擎中实现传统三维网格的真实反射映射。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF SIGGRAPH 2025 Posters
Summary
随着三维高斯混合技术的普及,需要将传统计算机图形技术资产融入混合环境。由于高斯原始数据同时编码光照和几何外观,直接插入混合高斯中的网格会重新照明不当,导致突兀感。为此,我们引入了GBake工具,它能从高斯混合场景中烘焙反射探针,实现在Unity游戏引擎中传统三维网格的真实反射映射。
Key Takeaways
- 三维高斯混合技术的普及带来了对传统计算机图形技术资产整合的需求。
- 3D Gaussian primitives联合编码光照和几何外观,导致直接插入混合高斯环境中的网格照明出现问题。
- 高斯环境下的网格需要重新照明以避免突兀感。
- GBake工具是为了解决在Unity游戏引擎中传统三维网格在高斯混合场景中的真实反射映射问题而开发的。
- GBake工具能从高斯混合场景中烘焙反射探针。
- 通过使用GBake工具,可以实现在Unity游戏引擎中更真实的渲染效果。
点此查看论文截图




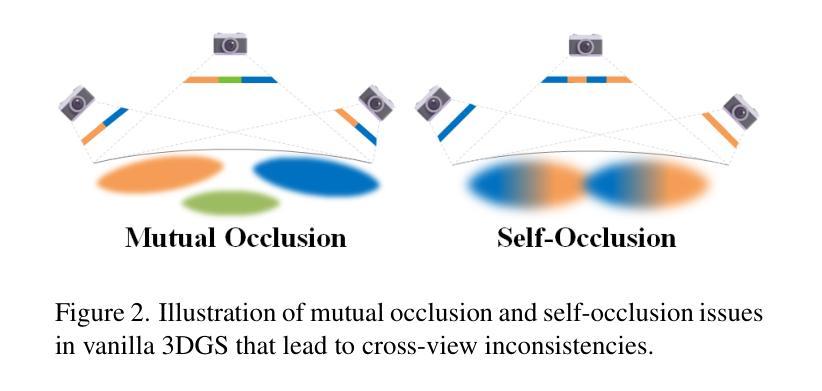
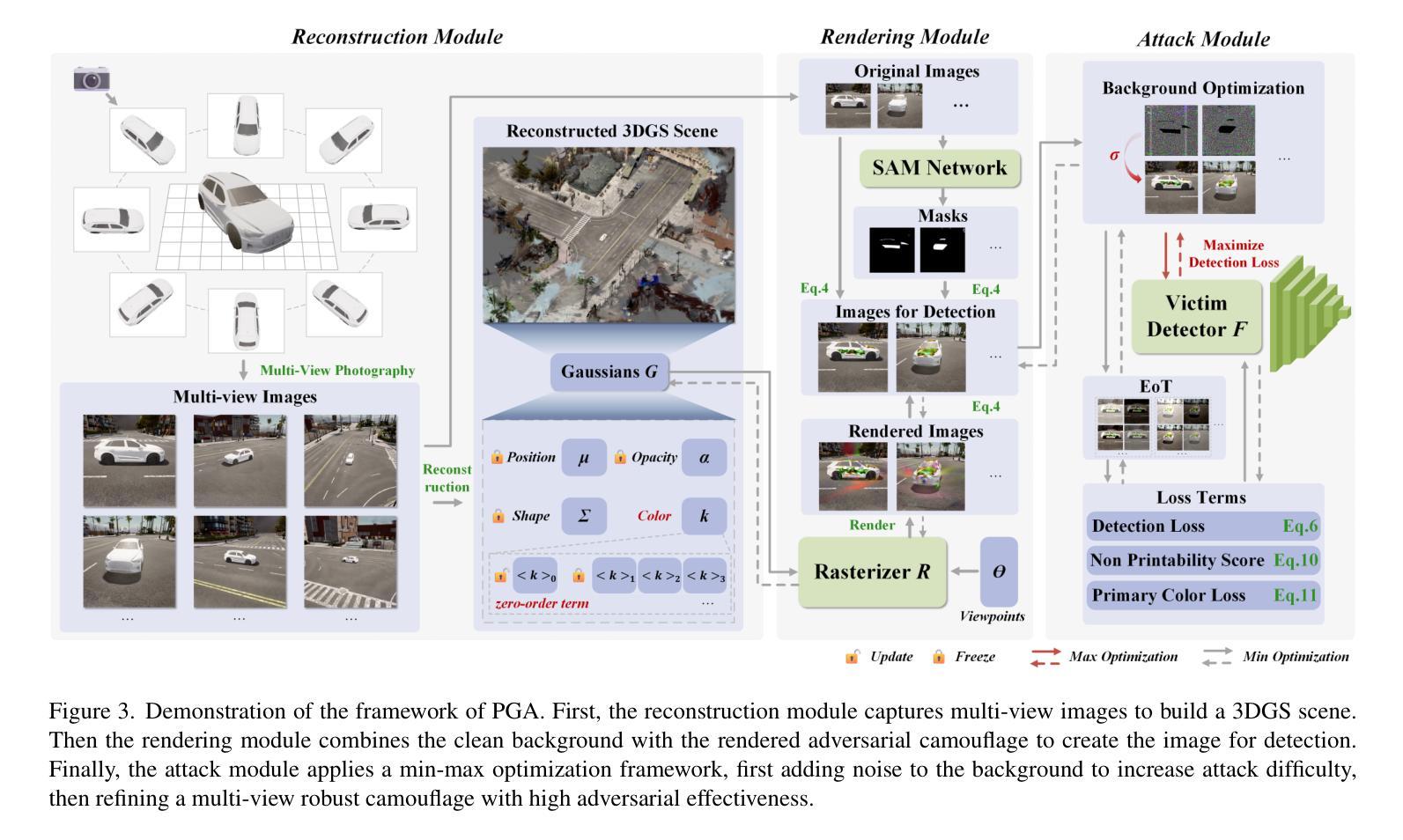
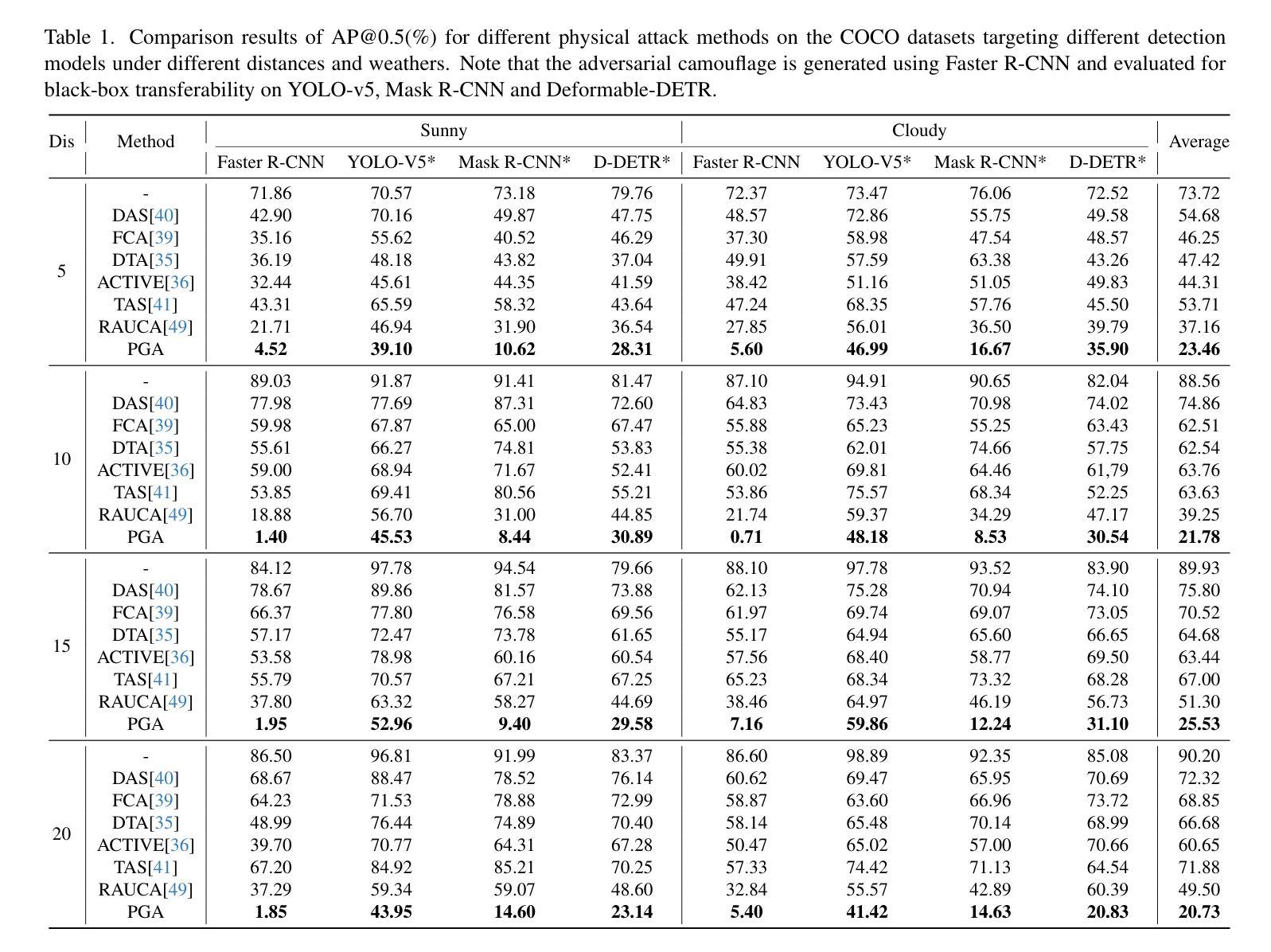
3D Gaussian Splatting Driven Multi-View Robust Physical Adversarial Camouflage Generation
Authors:Tianrui Lou, Xiaojun Jia, Siyuan Liang, Jiawei Liang, Ming Zhang, Yanjun Xiao, Xiaochun Cao
Physical adversarial attack methods expose the vulnerabilities of deep neural networks and pose a significant threat to safety-critical scenarios such as autonomous driving. Camouflage-based physical attack is a more promising approach compared to the patch-based attack, offering stronger adversarial effectiveness in complex physical environments. However, most prior work relies on mesh priors of the target object and virtual environments constructed by simulators, which are time-consuming to obtain and inevitably differ from the real world. Moreover, due to the limitations of the backgrounds in training images, previous methods often fail to produce multi-view robust adversarial camouflage and tend to fall into sub-optimal solutions. Due to these reasons, prior work lacks adversarial effectiveness and robustness across diverse viewpoints and physical environments. We propose a physical attack framework based on 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), named PGA, which provides rapid and precise reconstruction with few images, along with photo-realistic rendering capabilities. Our framework further enhances cross-view robustness and adversarial effectiveness by preventing mutual and self-occlusion among Gaussians and employing a min-max optimization approach that adjusts the imaging background of each viewpoint, helping the algorithm filter out non-robust adversarial features. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness and superiority of PGA. Our code is available at:https://github.com/TRLou/PGA.
物理对抗攻击方法揭示了深度神经网络的脆弱性,并对自动驾驶等安全关键场景构成了重大威胁。与基于补丁的攻击相比,基于伪装攻击的物攻击方法是一种更有前途的方法,在复杂的物理环境中具有更强的对抗效果。然而,大多数早期的研究依赖于目标物体的网格先验和模拟器构建的虚拟环境,这些都需要耗费大量时间且不可避免地与真实世界存在差异。此外,由于训练图像背景的限制,之前的方法往往无法生成多视角稳健的对抗伪装,并倾向于陷入次优解。由于这些原因,早期的研究在跨越不同视角和物理环境方面的对抗效果和稳健性方面存在不足。我们提出了一种基于三维高斯拼贴(3DGS)的物理攻击框架,名为PGA。该框架具有快速精确重建少量图像的能力以及逼真的渲染能力。我们的框架通过防止高斯之间的相互和自遮挡并采用最小最大优化方法调整每个视角的成像背景,进一步提高了跨视角的稳健性和对抗效果,帮助算法过滤掉非稳健的对抗特征。大量实验验证了PGA的有效性和优越性。我们的代码可在:https://github.com/TRLou/PGA访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025
Summary
基于物理的攻击方法揭示了深度神经网络的安全漏洞,特别是在自动驾驶等安全关键场景中构成了重大威胁。相比于基于补丁的攻击方法,伪装攻击是一种更有前景的方法,能够在复杂的物理环境中实现更强的对抗性效果。然而,大多数先前的研究依赖于目标物体的网格先验和由模拟器构建的虚拟环境,这些环境耗时且不可避免地与真实世界存在差异。此外,由于训练图像背景的限制,先前的方法往往难以生成多视角的鲁棒对抗伪装,并容易陷入次优解决方案。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了基于三维高斯拼贴(3DGS)的物理攻击框架——PGA。该框架具有快速精确重建和逼真的渲染能力。通过防止高斯之间的互相遮挡和自我遮挡以及采用调整每个视点成像背景的minmax优化方法,该框架增强了跨视角的鲁棒性和对抗性效果,使算法能够过滤掉非鲁棒的对抗特征。实验证明PGA的有效性优于其他方法。我们的代码可通过链接访问:[链接地址]。
Key Takeaways
- 物理对抗攻击方法揭示了深度神经网络的安全漏洞,特别是在自动驾驶等安全关键场景中。
- 伪装攻击是一种在复杂物理环境中实现更强对抗性效果的有前景的方法。
- 大多数先前研究依赖于虚拟环境,这些环境与真实世界存在差异。
- 训练图像背景的限制导致先前方法难以生成多视角的鲁棒对抗伪装。
- 提出的基于三维高斯拼贴(3DGS)的物理攻击框架PGA具有快速精确重建和逼真的渲染能力。
- PGA通过防止高斯之间的互相遮挡和自我遮挡以及采用minmax优化方法增强了跨视角的鲁棒性和对抗性效果。
点此查看论文截图

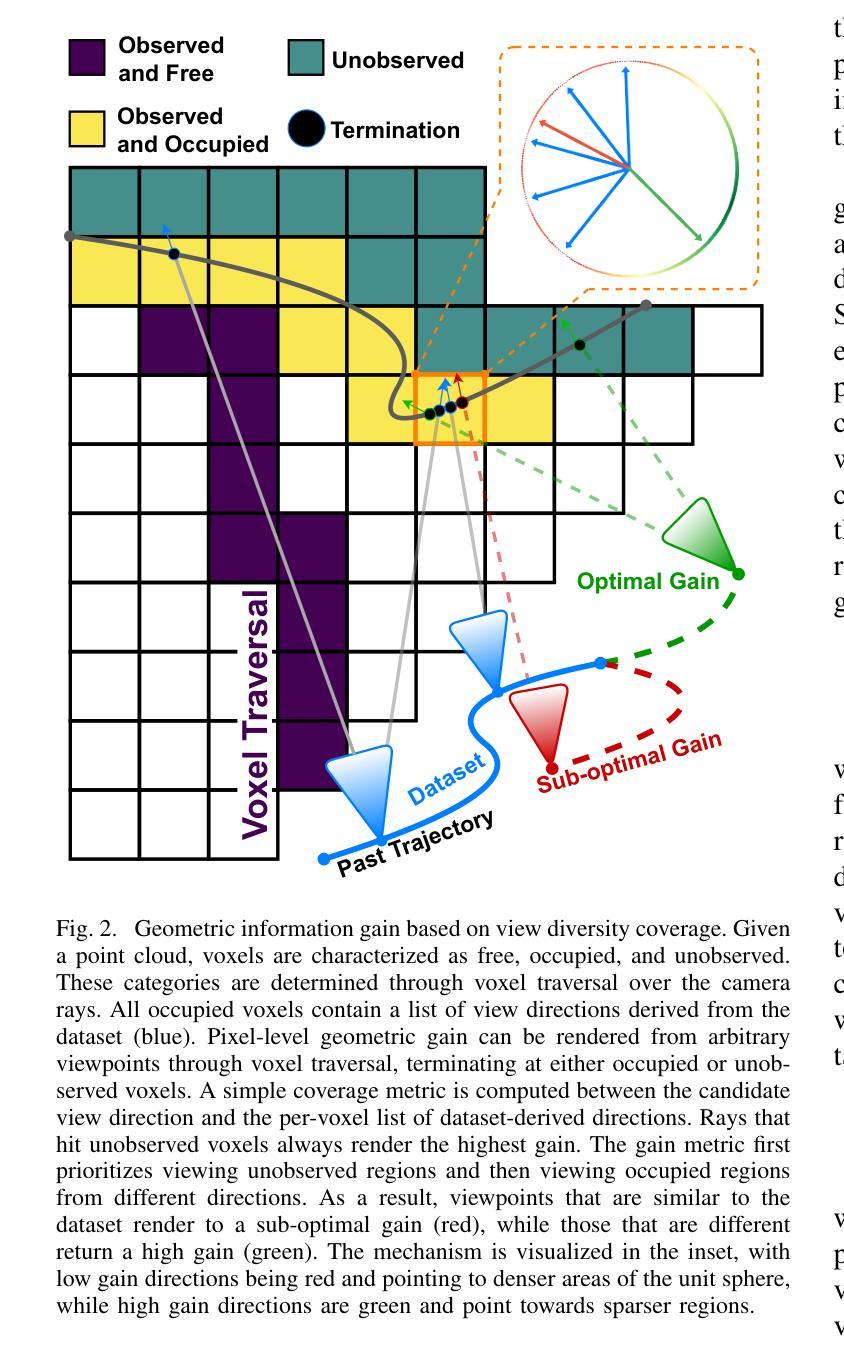
VISTA: Open-Vocabulary, Task-Relevant Robot Exploration with Online Semantic Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Keiko Nagami, Timothy Chen, Javier Yu, Ola Shorinwa, Maximilian Adang, Carlyn Dougherty, Eric Cristofalo, Mac Schwager
We present VISTA (Viewpoint-based Image selection with Semantic Task Awareness), an active exploration method for robots to plan informative trajectories that improve 3D map quality in areas most relevant for task completion. Given an open-vocabulary search instruction (e.g., “find a person”), VISTA enables a robot to explore its environment to search for the object of interest, while simultaneously building a real-time semantic 3D Gaussian Splatting reconstruction of the scene. The robot navigates its environment by planning receding-horizon trajectories that prioritize semantic similarity to the query and exploration of unseen regions of the environment. To evaluate trajectories, VISTA introduces a novel, efficient viewpoint-semantic coverage metric that quantifies both the geometric view diversity and task relevance in the 3D scene. On static datasets, our coverage metric outperforms state-of-the-art baselines, FisherRF and Bayes’ Rays, in computation speed and reconstruction quality. In quadrotor hardware experiments, VISTA achieves 6x higher success rates in challenging maps, compared to baseline methods, while matching baseline performance in less challenging maps. Lastly, we show that VISTA is platform-agnostic by deploying it on a quadrotor drone and a Spot quadruped robot. Open-source code will be released upon acceptance of the paper.
我们提出VISTA(基于视点图像选择并具有语义任务感知能力),这是一种机器人主动探索方法,用于规划能够改善任务完成相关区域的三维地图质量的轨迹。给定开放词汇搜索指令(例如,“寻找一个人”),VISTA允许机器人在探索环境以寻找感兴趣对象的同时,实时构建场景的语义三维高斯喷溅重建。机器人通过规划具有优先语义相似性和探索未知区域的未来地平线轨迹来导航环境。为了评估轨迹,VISTA引入了一种新的高效视点语义覆盖度量标准,该标准可以量化三维场景中的几何视图多样性和任务相关性。在静态数据集上,我们的覆盖度量标准在计算速度和重建质量方面优于最新基线FisherRF和贝叶斯射线。在四旋翼硬件实验中,与基线方法相比,VISTA在具有挑战性的地图上实现了高达六倍的成功率提升,同时在不太具有挑战性的地图上保持基线性能。最后,我们通过将其部署在四旋翼无人机和Spot四足机器人上证明了VISTA具有平台中立性。论文被接受后将发布开源代码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 4 figures
Summary
本文提出了一个名为VISTA的机器人主动探索方法,用于规划信息轨迹以提高3D地图质量,重点关注与任务完成相关的区域。VISTA可处理开放式词汇搜索指令,使机器人在探索环境寻找目标对象的同时,实时构建场景的语义3D高斯混合重建模型。通过规划不断接近地平线的轨迹,机器人能够优先考虑到查询的语义相似性和对未观测区域的探索。VISTA引入了一种新的、高效的视点语义覆盖度量标准,以量化三维场景中的几何视图多样性和任务相关性。在静态数据集上,其覆盖度量在计算速度和重建质量上优于最新基线FisherRF和Bayes射线。在无人机的硬件实验中,与基线方法相比,VISTA在具有挑战性的地图上成功率提高了六倍,同时在不太具有挑战性的地图上保持了基线性能。此外,我们还展示了VISTA的平台无关性,可以在无人机和Spot四足机器人上部署。
Key Takeaways
- VISTA是一种机器人主动探索方法,用于规划信息轨迹以提高3D地图质量。
- VISTA可处理开放式词汇搜索指令,结合语义探索和实时3D重建。
- 机器人通过规划不断接近地平线的轨迹来平衡查询的语义相似性和对未观测区域的探索。
- VISTA引入了一种新的视点语义覆盖度量标准,以量化三维场景中的几何视图多样性和任务相关性。
- 在静态数据集上,VISTA的覆盖度量在计算速度和重建质量方面优于其他方法。
- 在硬件实验中,VISTA在挑战性地图上表现出更高的成功率,同时在不太具有挑战性的地图上保持了基线性能。
点此查看论文截图


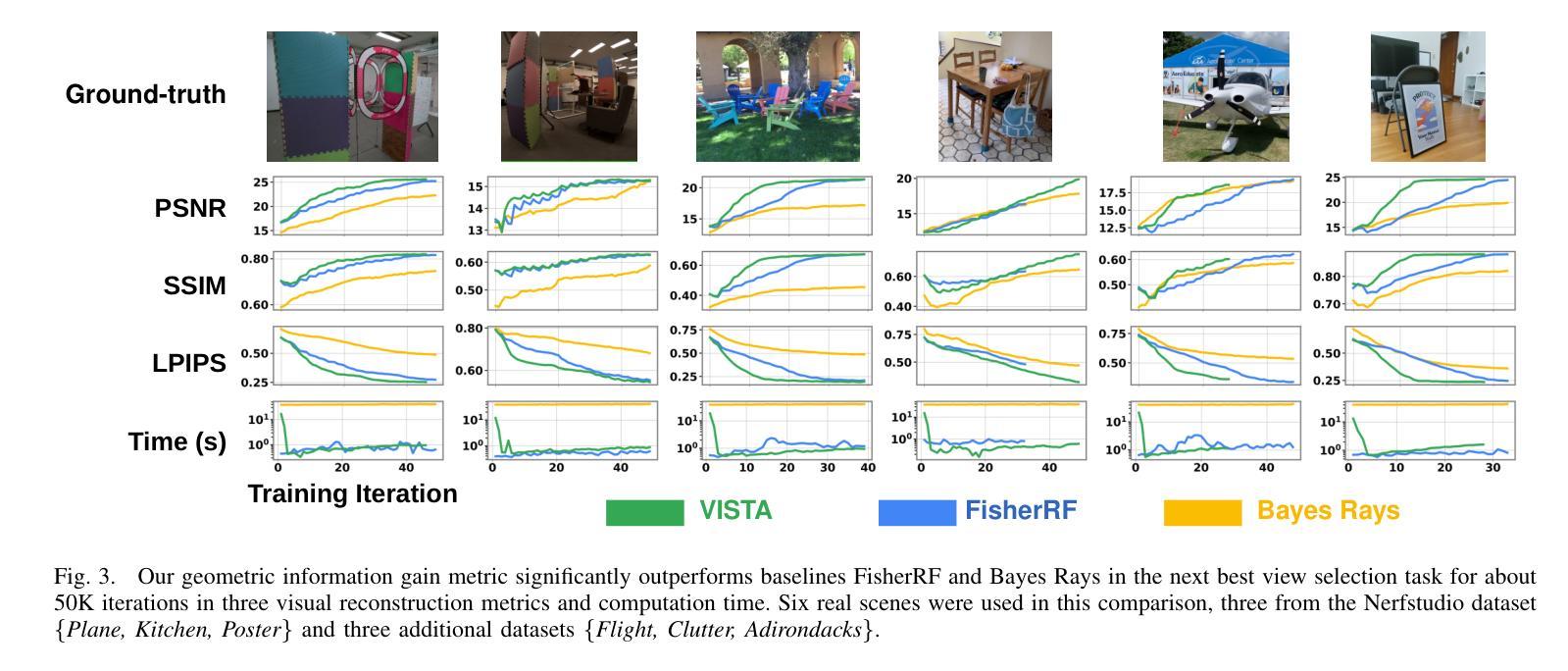
Masks make discriminative models great again!
Authors:Tianshi Cao, Marie-Julie Rakotosaona, Ben Poole, Federico Tombari, Michael Niemeyer
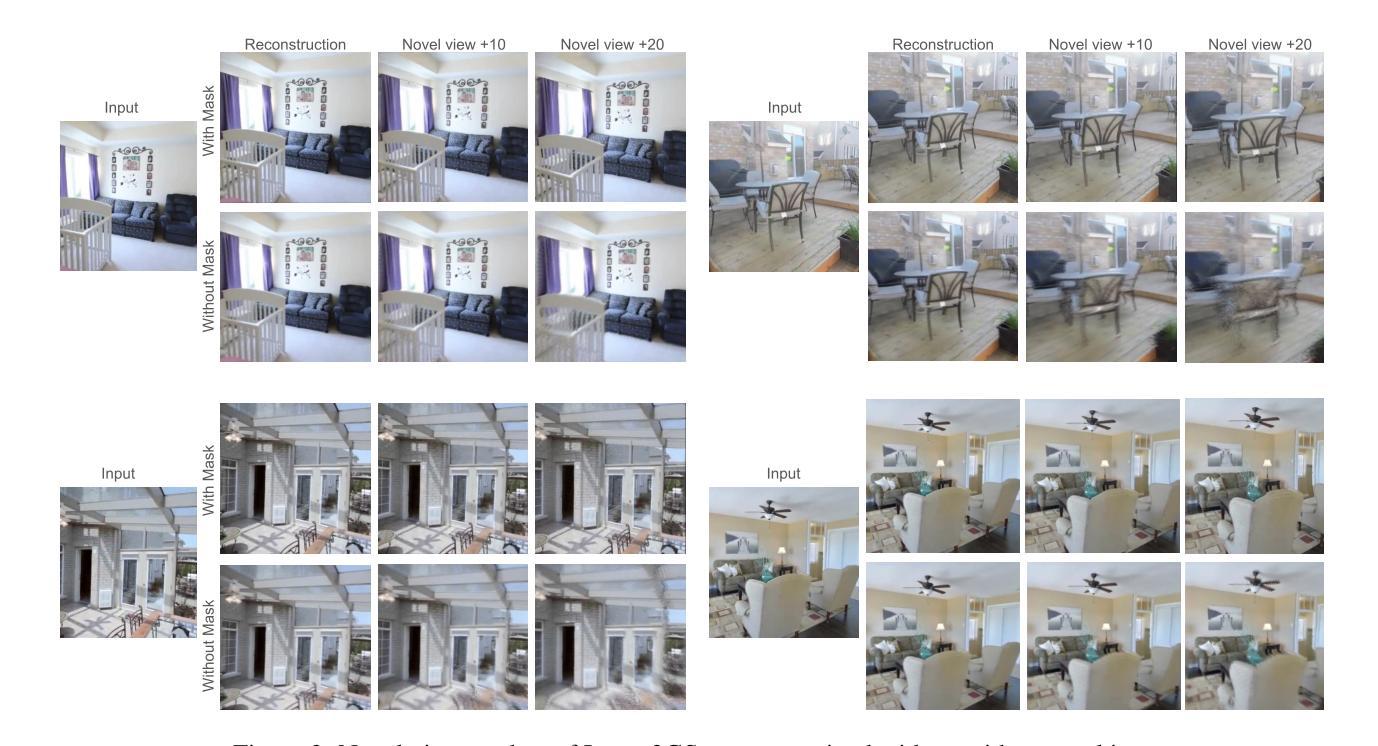
We present Image2GS, a novel approach that addresses the challenging problem of reconstructing photorealistic 3D scenes from a single image by focusing specifically on the image-to-3D lifting component of the reconstruction process. By decoupling the lifting problem (converting an image to a 3D model representing what is visible) from the completion problem (hallucinating content not present in the input), we create a more deterministic task suitable for discriminative models. Our method employs visibility masks derived from optimized 3D Gaussian splats to exclude areas not visible from the source view during training. This masked training strategy significantly improves reconstruction quality in visible regions compared to strong baselines. Notably, despite being trained only on masked regions, Image2GS remains competitive with state-of-the-art discriminative models trained on full target images when evaluated on complete scenes. Our findings highlight the fundamental struggle discriminative models face when fitting unseen regions and demonstrate the advantages of addressing image-to-3D lifting as a distinct problem with specialized techniques.
我们提出了Image2GS这一新方法,专注于解决从单一图像重建写实风格的3D场景这一难题。我们的方法重点研究重建过程中的图像到3D转换环节。通过解除提升问题(将图像转换为表示可见内容的3D模型)与补全问题(凭空想象输入中不存在的部分)之间的耦合关系,我们创造了一个更确定性的任务,更适合判别模型来处理。我们的方法使用由优化后的3D高斯展布派生的可见性掩码,在训练过程中排除源视角不可见的区域。与强大的基线相比,这种掩码训练策略在可见区域的重建质量方面显著提高。值得注意的是,尽管仅在掩码区域上进行训练,但当在完整场景上评估时,Image2GS仍与在完整目标图像上训练的最新判别模型竞争。我们的研究突出了判别模型在面对未知区域拟合时的基本挑战,并展示了将图像到3D转换作为一个具有专门技术的问题来解决的优点。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
图像重建中的单幅图像到三维场景的转换问题,可以通过采用专门的图像到三维提升技术来解决。本文提出一种名为Image2GS的新方法,通过将提升问题和完成问题分离,实现了从图像到三维模型的转换。采用基于优化的三维高斯掩模进行训练,显著提高可见区域的重建质量。Image2GS方法表现出独特的优势,在解决特定问题时展现了较高的性能。
Key Takeaways
- Image2GS专注于从单幅图像重建三维场景的提升问题,分离了提升问题和完成问题。
- 使用优化的三维高斯掩模在训练过程中排除源视图不可见区域,从而提高可见区域的重建质量。
- Image2GS在训练时仅针对掩模区域进行训练,但在完整场景评估时仍与全目标图像训练的最新判别模型竞争。
- 该方法强调了判别模型在拟合未见区域时的基本挑战,并展示了采用专门技术的图像到三维提升问题的优势。
点此查看论文截图



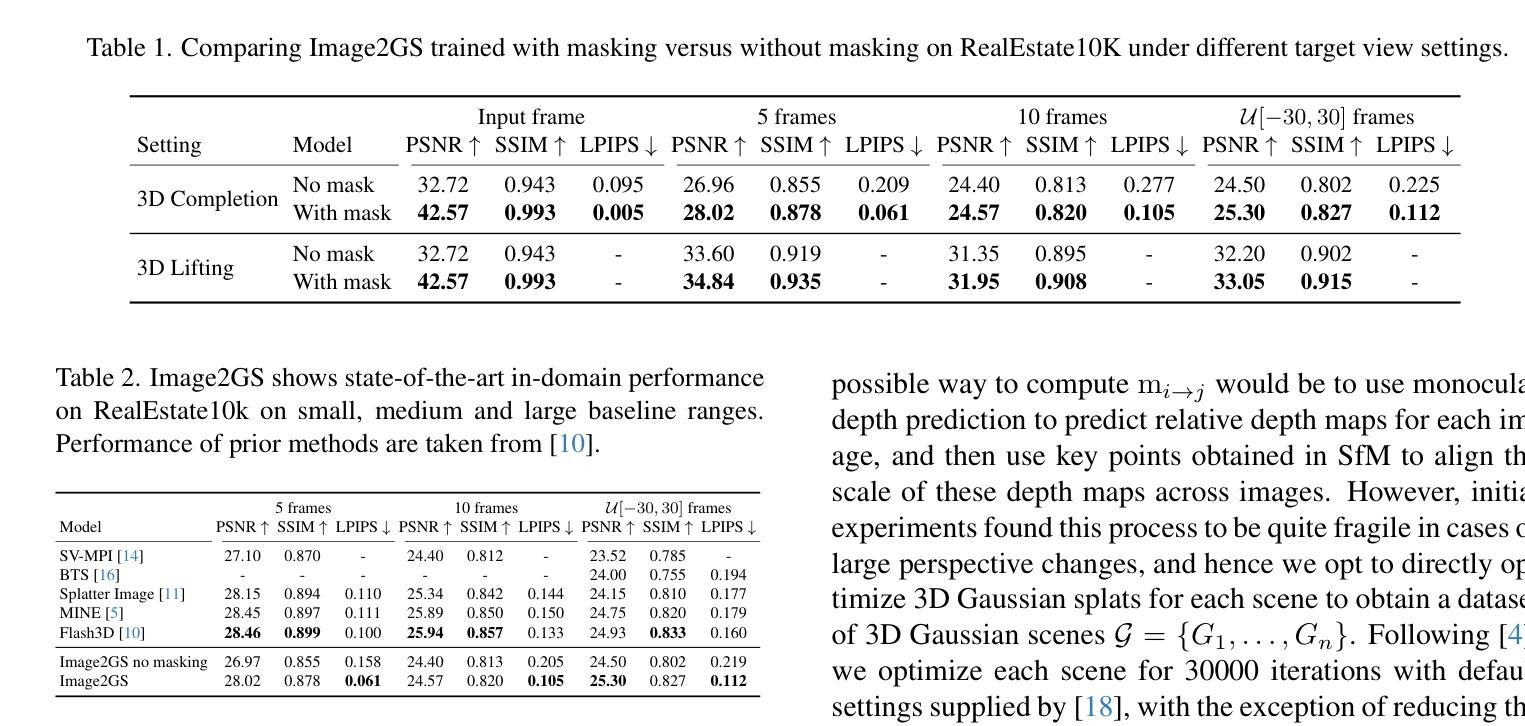
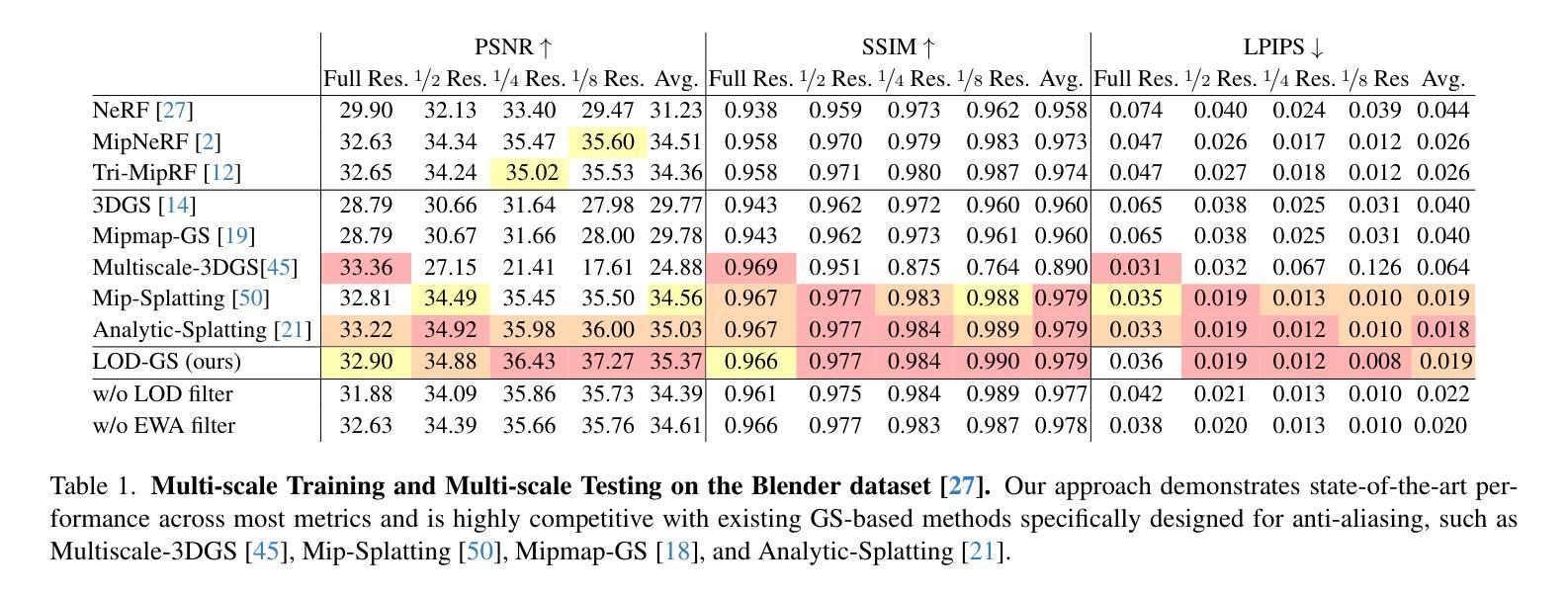
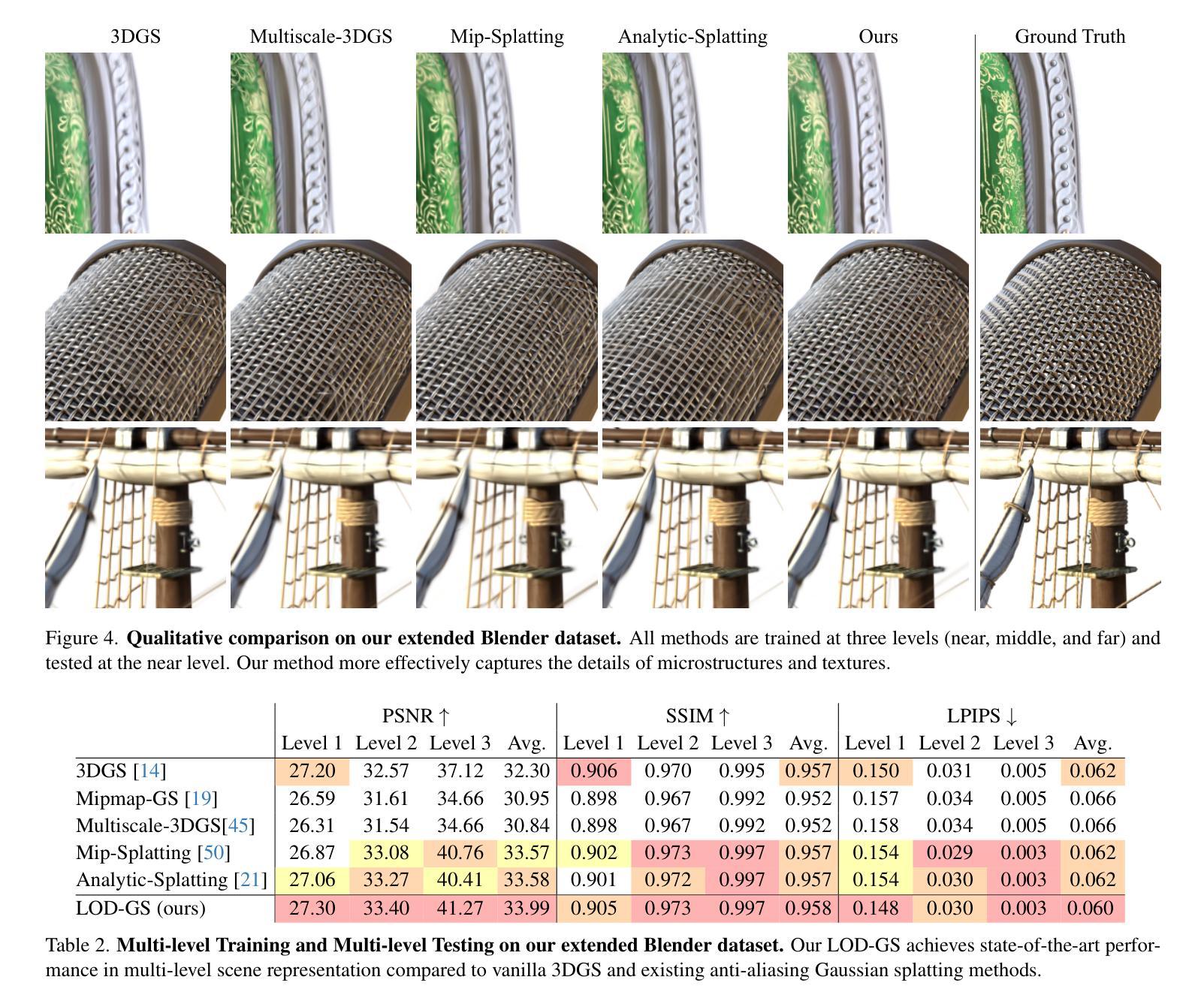
LOD-GS: Level-of-Detail-Sensitive 3D Gaussian Splatting for Detail Conserved Anti-Aliasing
Authors:Zhenya Yang, Bingchen Gong, Kai Chen, Qi Dou
Despite the advancements in quality and efficiency achieved by 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) in 3D scene rendering, aliasing artifacts remain a persistent challenge. Existing approaches primarily rely on low-pass filtering to mitigate aliasing. However, these methods are not sensitive to the sampling rate, often resulting in under-filtering and over-smoothing renderings. To address this limitation, we propose LOD-GS, a Level-of-Detail-sensitive filtering framework for Gaussian Splatting, which dynamically predicts the optimal filtering strength for each 3D Gaussian primitive. Specifically, we introduce a set of basis functions to each Gaussian, which take the sampling rate as input to model appearance variations, enabling sampling-rate-sensitive filtering. These basis function parameters are jointly optimized with the 3D Gaussian in an end-to-end manner. The sampling rate is influenced by both focal length and camera distance. However, existing methods and datasets rely solely on down-sampling to simulate focal length changes for anti-aliasing evaluation, overlooking the impact of camera distance. To enable a more comprehensive assessment, we introduce a new synthetic dataset featuring objects rendered at varying camera distances. Extensive experiments on both public datasets and our newly collected dataset demonstrate that our method achieves SOTA rendering quality while effectively eliminating aliasing. The code and dataset have been open-sourced.
尽管三维高斯拼贴(3DGS)在三维场景渲染中取得了质量和效率的提升,但混叠伪影仍然是一个持续存在的挑战。现有方法主要依赖低通滤波来减轻混叠。然而,这些方法对采样率不够敏感,通常会导致滤波不足和过度平滑的渲染结果。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了LOD-GS,这是一个用于高斯拼贴的细节层次敏感滤波框架,能够动态预测每个三维高斯基元的最佳滤波强度。具体来说,我们为每个高斯引入了一组基函数,以采样率作为输入来模拟外观变化,从而实现采样率敏感滤波。这些基函数的参数与三维高斯以端到端的方式进行联合优化。采样率受到焦距和相机距离的影响。然而,现有方法和数据集仅通过下采样来模拟焦距变化以进行抗混叠评估,忽略了相机距离的影响。为了进行更全面的评估,我们引入了一个新的合成数据集,该数据集包含在不同相机距离下呈现的对象。在公共数据集和我们新收集的数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法达到了先进的渲染质量,同时有效地消除了混叠。相关代码和数据集已开源。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对3D场景渲染中的抗锯齿问题,提出了一种基于Level-of-Detail(LOD)敏感性的高斯Splatting(LOD-GS)滤波框架。该框架通过动态预测每个3D高斯基元的最佳滤波强度来解决现有方法的局限性。同时引入了一套基础函数,用于对采样率进行建模,实现采样率敏感滤波。通过优化基础函数参数和3D高斯参数,达到先进的渲染质量,有效消除锯齿效应。此外,本文还引入了一个新的合成数据集,用于全面评估不同相机距离下的抗锯齿效果。代码和数据集已开源。
Key Takeaways
- 现有的基于低通滤波的抗锯齿方法因缺乏采样率的敏感性,可能导致过滤不足和过度平滑的渲染结果。
- LOD-GS滤波框架通过动态预测每个3D高斯基元的最佳滤波强度来解决这一问题。
- LOD-GS引入了基础函数来建模采样率的变化,包括相机焦距和距离的影响。
- 仅依赖降采样模拟焦距变化的现有方法和数据集无法全面评估抗锯齿效果,忽视了相机距离的影响。为此引入了新的合成数据集用于全面评估性能。实验表明LOD-GS可有效消除锯齿并达到领先的渲染质量。数据和代码已经开源以供研究使用。
点此查看论文截图

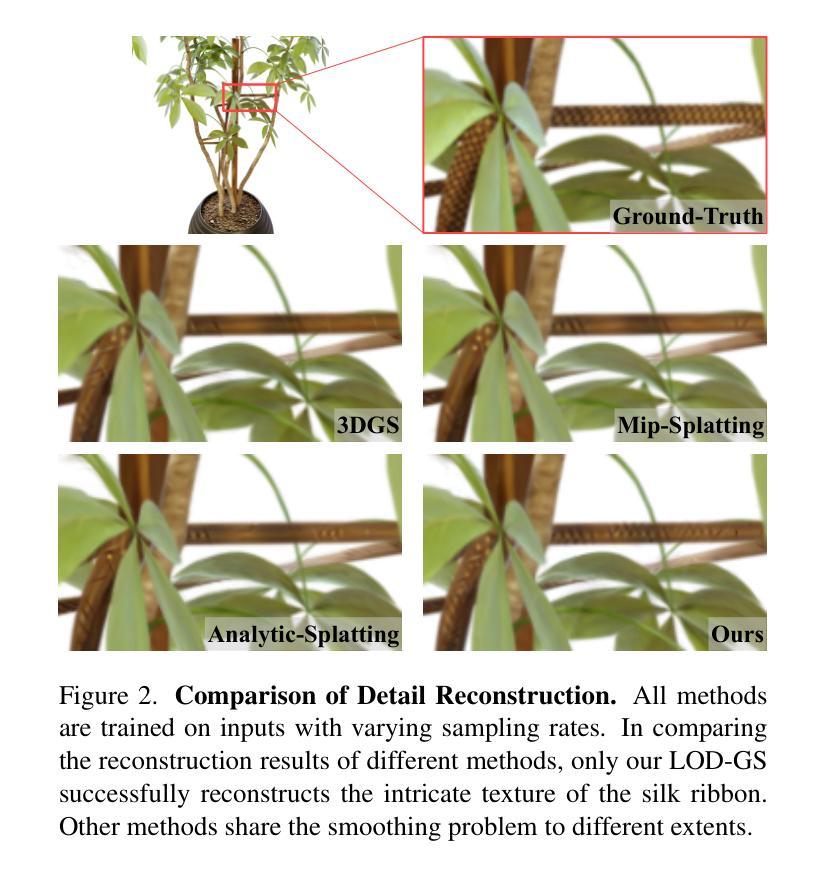
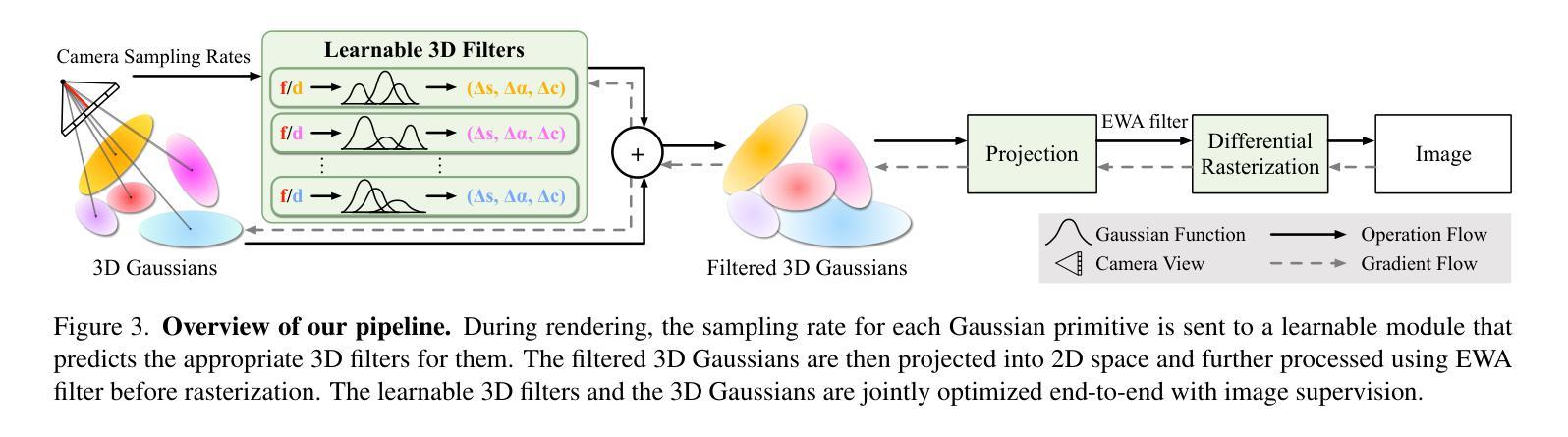
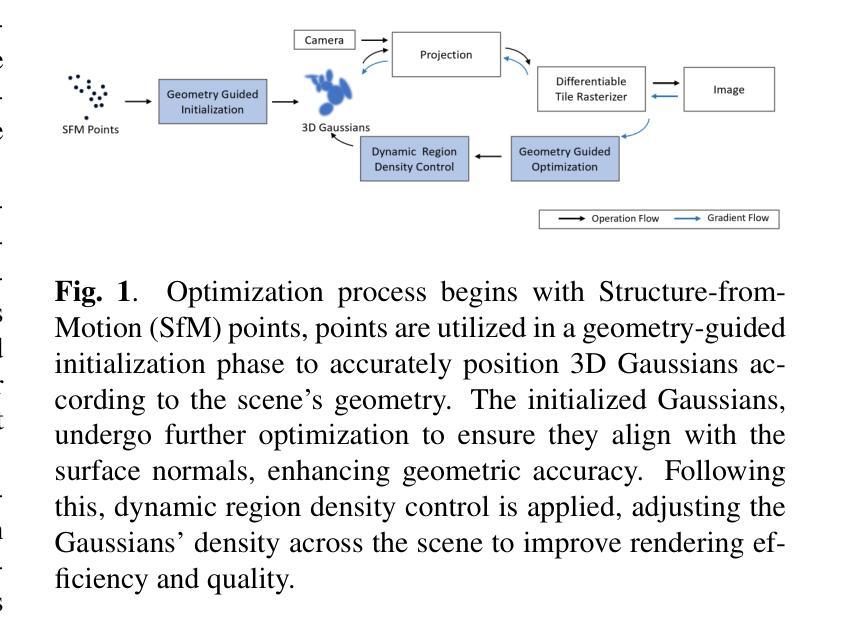
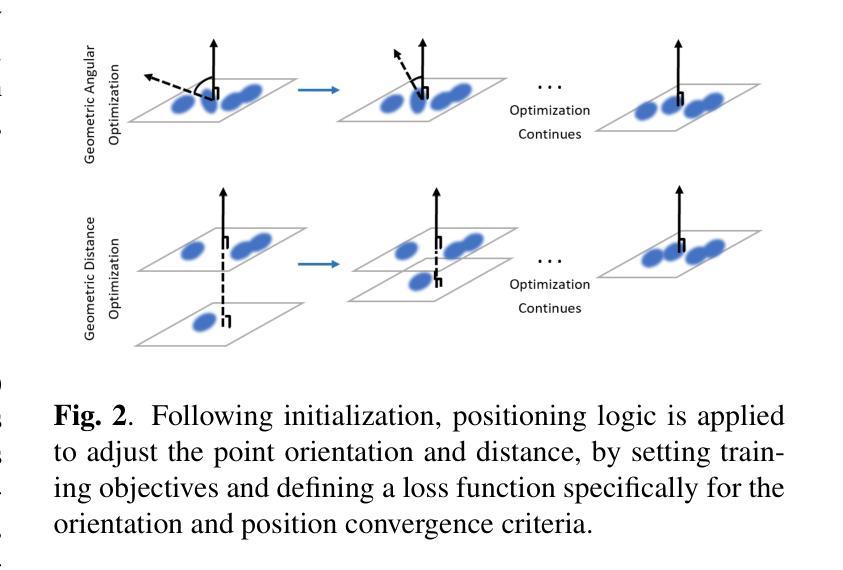
GDGS: 3D Gaussian Splatting Via Geometry-Guided Initialization And Dynamic Density Control
Authors:Xingjun Wang, Lianlei Shan
We propose a method to enhance 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS)~\cite{Kerbl2023}, addressing challenges in initialization, optimization, and density control. Gaussian Splatting is an alternative for rendering realistic images while supporting real-time performance, and it has gained popularity due to its explicit 3D Gaussian representation. However, 3DGS heavily depends on accurate initialization and faces difficulties in optimizing unstructured Gaussian distributions into ordered surfaces, with limited adaptive density control mechanism proposed so far. Our first key contribution is a geometry-guided initialization to predict Gaussian parameters, ensuring precise placement and faster convergence. We then introduce a surface-aligned optimization strategy to refine Gaussian placement, improving geometric accuracy and aligning with the surface normals of the scene. Finally, we present a dynamic adaptive density control mechanism that adjusts Gaussian density based on regional complexity, for visual fidelity. These innovations enable our method to achieve high-fidelity real-time rendering and significant improvements in visual quality, even in complex scenes. Our method demonstrates comparable or superior results to state-of-the-art methods, rendering high-fidelity images in real time.
我们提出了一种改进3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)的方法\cite{Kerbl2023},以解决初始化、优化和密度控制方面的挑战。高斯拼贴是一种用于呈现真实图像的技术,支持实时性能,由于其明确的3D高斯表示而广受欢迎。然而,3DGS严重依赖于准确的初始化,并且在将无序的高斯分布优化为有序的曲面时面临困难,目前提出的自适应密度控制机制有限。我们的第一项关键贡献是通过几何引导初始化来预测高斯参数,确保精确放置和更快的收敛速度。然后,我们引入了一种与曲面对齐的优化策略,以细化高斯放置,提高几何精度并与场景的表面法线对齐。最后,我们提出了一种动态自适应密度控制机制,根据区域复杂性调整高斯密度,以提高视觉保真度。这些创新使我们的方法能够实现高保真实时渲染和视觉质量的显着提高,即使在复杂的场景中也是如此。我们的方法与最新技术相比,呈现出相当或更好的结果,能够实时呈现高保真图像。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
增强3D高斯绘制(3DGS)方法,解决初始化、优化和密度控制方面的挑战。该方法通过几何引导初始化预测高斯参数,确保精确放置和更快收敛;引入表面对齐优化策略,提高几何精度和场景表面法线对齐;提出动态自适应密度控制机制,根据区域复杂性调整高斯密度,以提高视觉保真度。这些创新使该方法实现高保真实时渲染,在复杂场景中显著提高视觉质量,与最新方法相比具有相当或更优的结果。
Key Takeaways
- 提出增强3D高斯绘制(3DGS)方法,解决初始化、优化和密度控制的挑战。
- 通过几何引导初始化预测高斯参数,确保精确放置和更快收敛。
- 引入表面对齐优化策略,提高几何精度和场景表面法线对齐。
- 提出动态自适应密度控制机制,根据区域复杂性调整高斯密度。
- 实现高保真实时渲染,显著提高视觉质量。
- 方法在复杂场景中表现良好。
- 与最新方法相比,具有相当或更优的结果。
点此查看论文截图

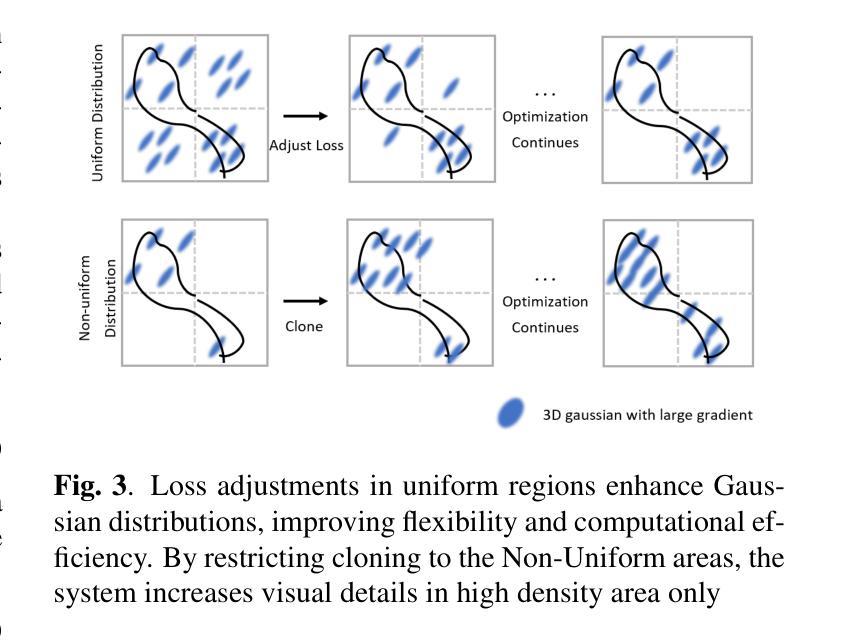

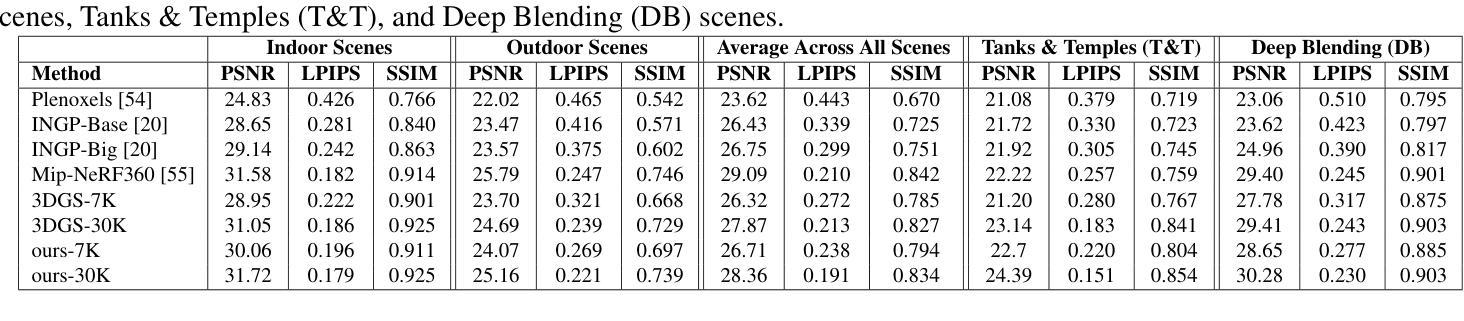
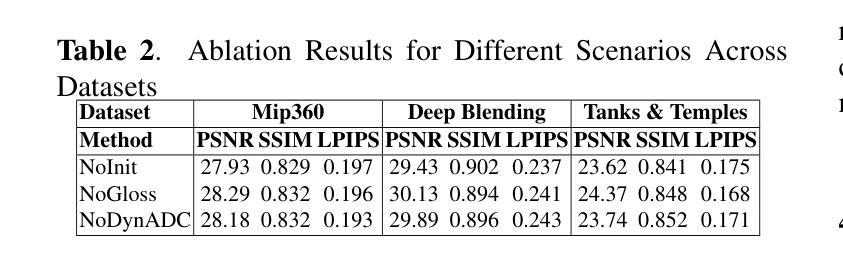
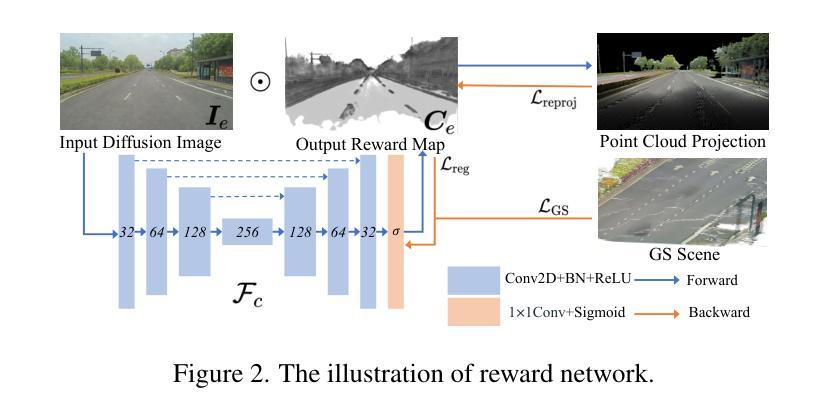
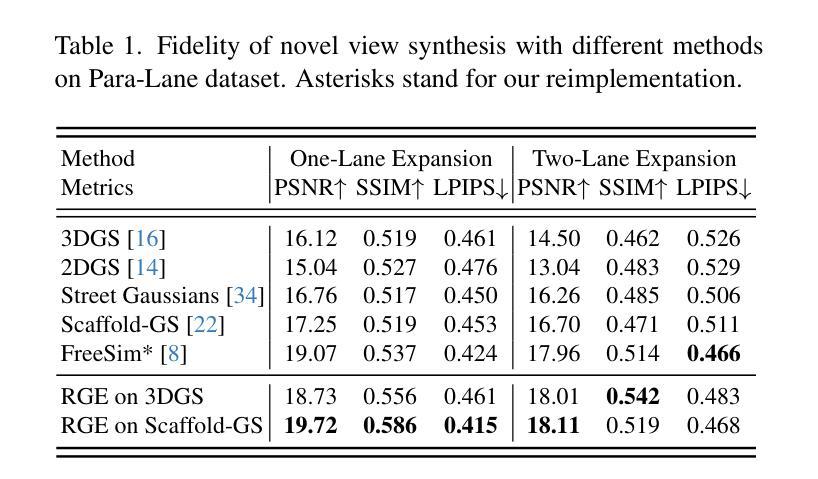
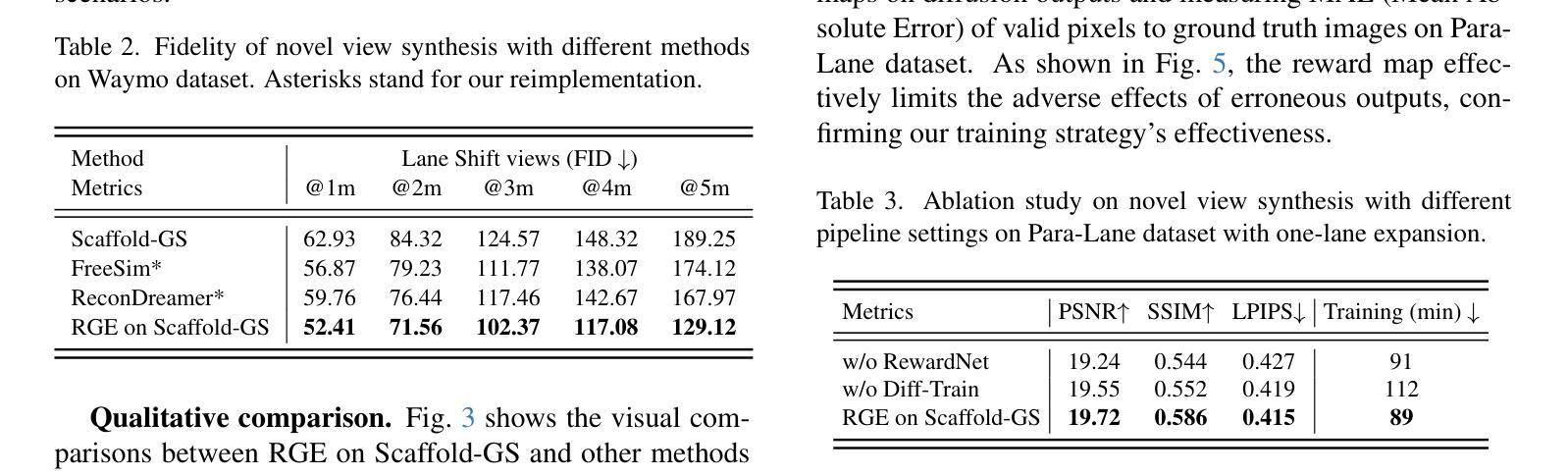
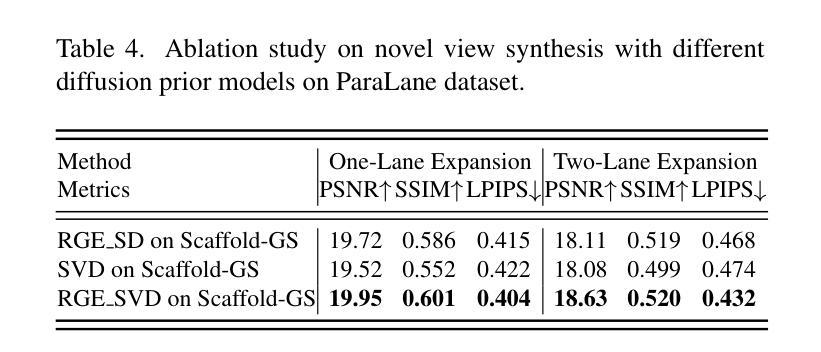
RGE-GS: Reward-Guided Expansive Driving Scene Reconstruction via Diffusion Priors
Authors:Sicong Du, Jiarun Liu, Qifeng Chen, Hao-Xiang Chen, Tai-Jiang Mu, Sheng Yang
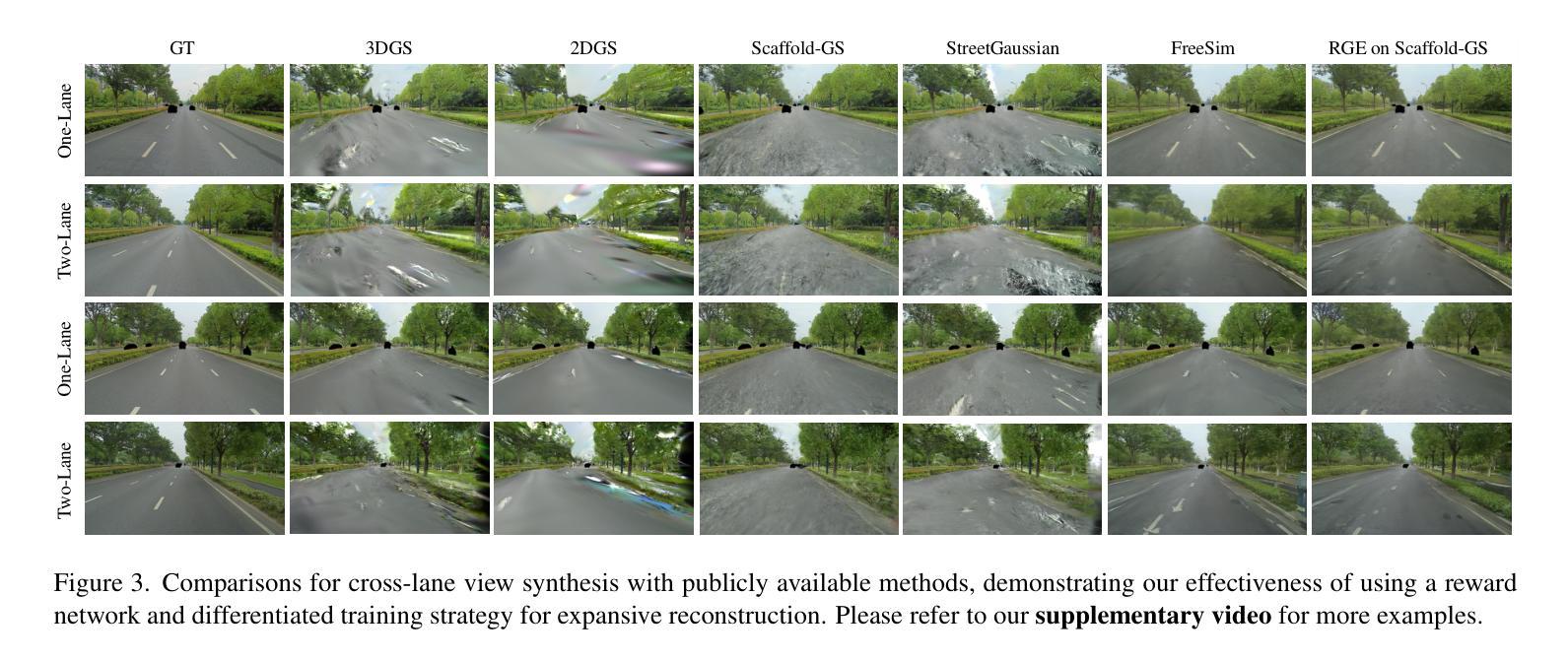
A single-pass driving clip frequently results in incomplete scanning of the road structure, making reconstructed scene expanding a critical requirement for sensor simulators to effectively regress driving actions. Although contemporary 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) techniques achieve remarkable reconstruction quality, their direct extension through the integration of diffusion priors often introduces cumulative physical inconsistencies and compromises training efficiency. To address these limitations, we present RGE-GS, a novel expansive reconstruction framework that synergizes diffusion-based generation with reward-guided Gaussian integration. The RGE-GS framework incorporates two key innovations: First, we propose a reward network that learns to identify and prioritize consistently generated patterns prior to reconstruction phases, thereby enabling selective retention of diffusion outputs for spatial stability. Second, during the reconstruction process, we devise a differentiated training strategy that automatically adjust Gaussian optimization progress according to scene converge metrics, which achieving better convergence than baseline methods. Extensive evaluations of publicly available datasets demonstrate that RGE-GS achieves state-of-the-art performance in reconstruction quality. Our source-code will be made publicly available at https://github.com/CN-ADLab/RGE-GS.
单通道驾驶视频剪辑经常导致对道路结构的不完全扫描,这使得重建场景成为传感器模拟器有效回归驾驶动作的关键要求。尽管当前的3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)技术实现了令人印象深刻的重建质量,但其通过集成扩散先验值的直接扩展常常会引入累积的物理不一致性并影响训练效率。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了RGE-GS,这是一种新型扩展重建框架,它协同基于扩散的生成与奖励引导的高斯积分。RGE-GS框架包含两个关键创新点:首先,我们提出了一种奖励网络,该网络在重建阶段之前学习识别和优先生成一致的模式,从而能够有选择地保留扩散输出以实现空间稳定性。其次,在重建过程中,我们制定了一种差异化的训练策略,该策略可根据场景收敛指标自动调整高斯优化进度,从而实现比基线方法更好的收敛效果。对公开可用数据集的广泛评估表明,RGE-GS在重建质量方面达到了最新技术水平。我们的源代码将在https://github.com/CN-ADLab/RGE-GS上公开。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于单通道驾驶片段常常导致道路结构扫描不完整的问题,研究者提出一种新型重建框架RGE-GS,该框架结合了扩散生成与奖励引导的高斯积分技术。其主要创新点包括奖励网络的引入和差异化训练策略的设计。奖励网络能够识别并优先保留重建阶段的一致性生成模式,从而实现扩散输出的选择性保留,提高空间稳定性;差异化训练策略则根据场景收敛指标自动调整高斯优化进程,以实现更高的收敛效果。RGE-GS框架在公开数据集上的评估结果展现出其重建质量优于现有方法。相关源代码将在GitHub上公开。
Key Takeaways
- 单通道驾驶片段导致道路结构扫描不完整的问题。
- RGE-GS是一种新型重建框架,结合了扩散生成与奖励引导的高斯积分技术。
- 奖励网络能够识别并优先保留一致性生成模式,提高空间稳定性。
- 差异化训练策略能够根据场景收敛指标自动调整高斯优化进程。
- RGE-GS框架在公开数据集上的重建质量优于现有方法。
- 该研究的源代码将在GitHub上公开,便于他人参考和使用。
点此查看论文截图

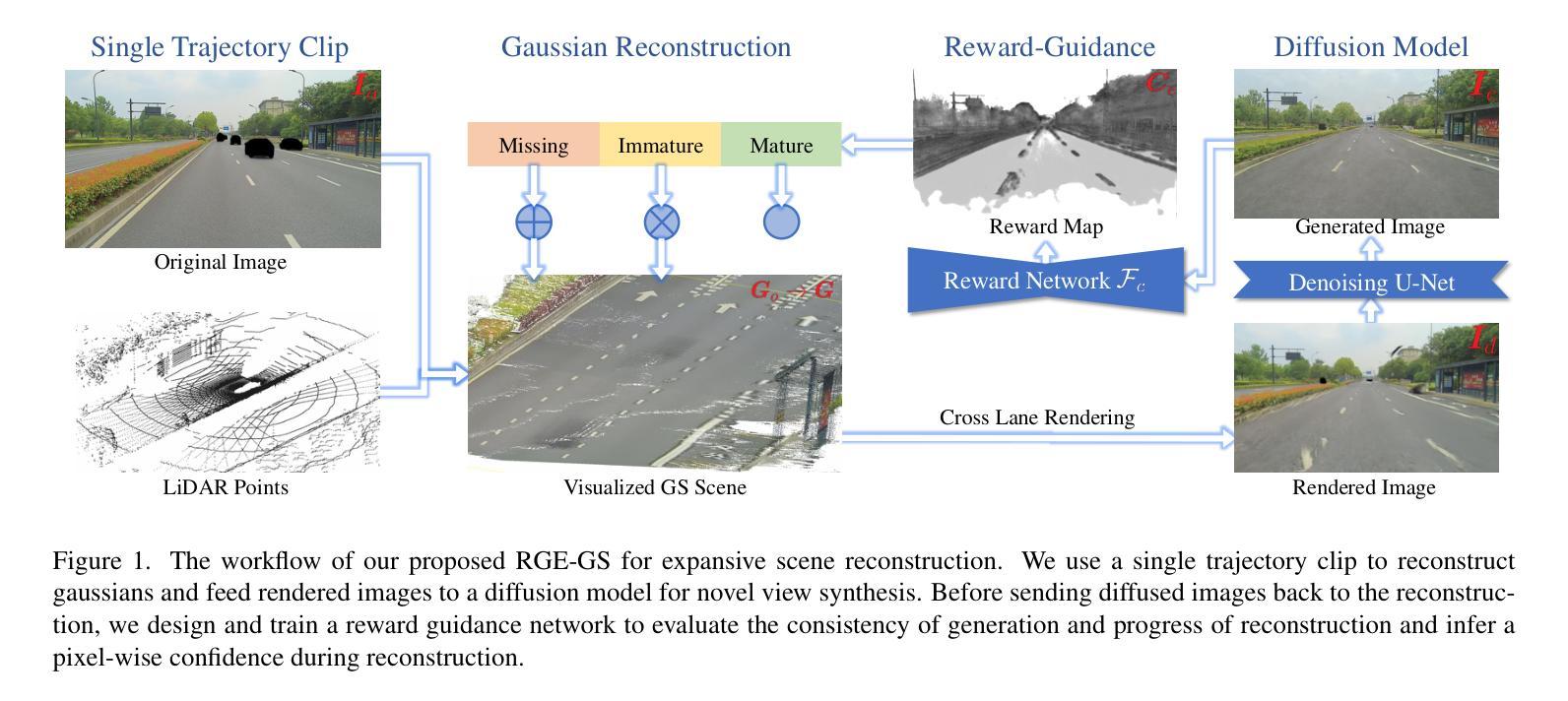

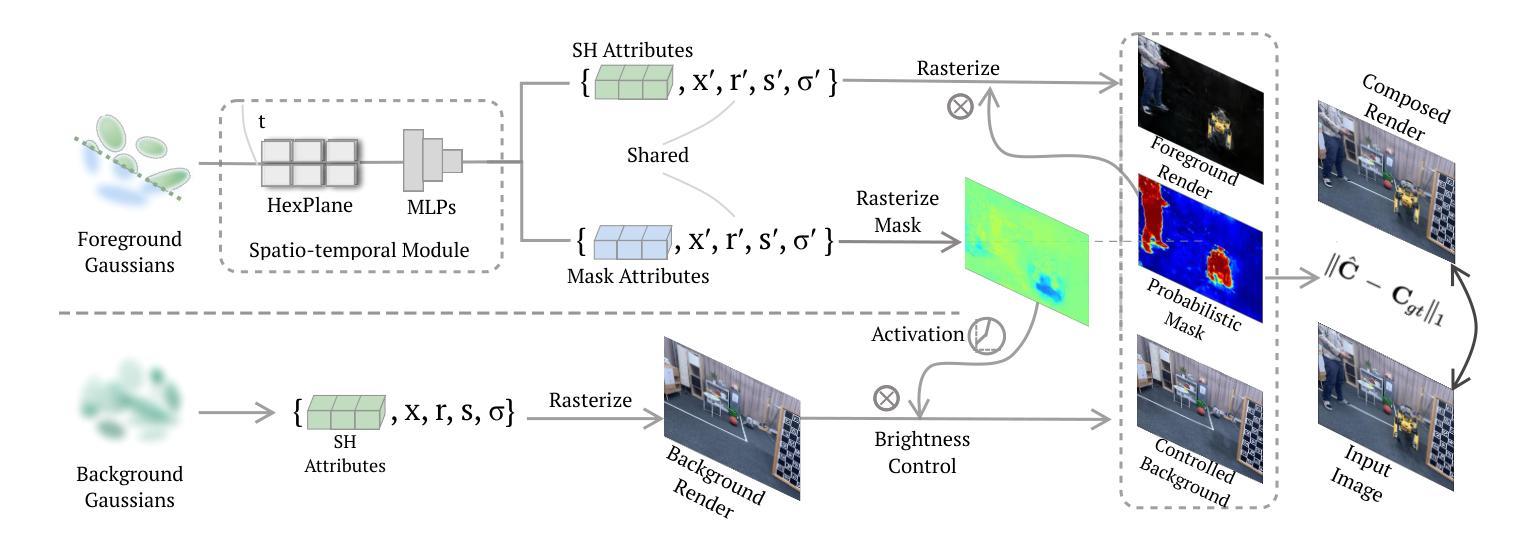
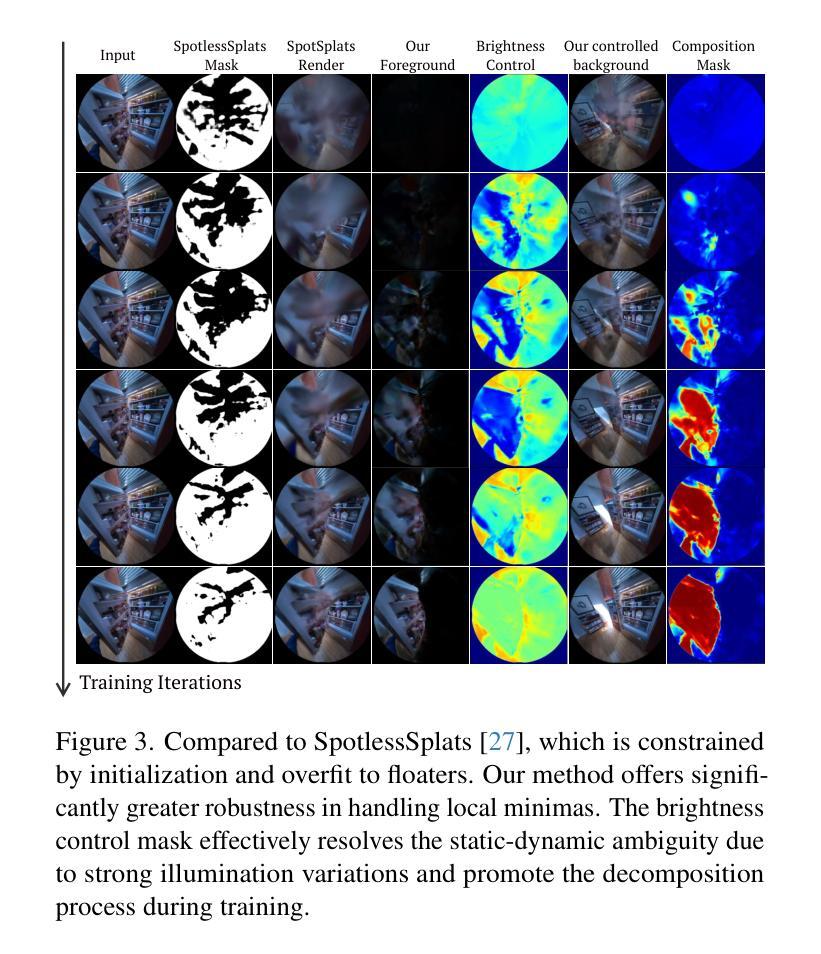
DeGauss: Dynamic-Static Decomposition with Gaussian Splatting for Distractor-free 3D Reconstruction
Authors:Rui Wang, Quentin Lohmeyer, Mirko Meboldt, Siyu Tang
Reconstructing clean, distractor-free 3D scenes from real-world captures remains a significant challenge, particularly in highly dynamic and cluttered settings such as egocentric videos. To tackle this problem, we introduce DeGauss, a simple and robust self-supervised framework for dynamic scene reconstruction based on a decoupled dynamic-static Gaussian Splatting design. DeGauss models dynamic elements with foreground Gaussians and static content with background Gaussians, using a probabilistic mask to coordinate their composition and enable independent yet complementary optimization. DeGauss generalizes robustly across a wide range of real-world scenarios, from casual image collections to long, dynamic egocentric videos, without relying on complex heuristics or extensive supervision. Experiments on benchmarks including NeRF-on-the-go, ADT, AEA, Hot3D, and EPIC-Fields demonstrate that DeGauss consistently outperforms existing methods, establishing a strong baseline for generalizable, distractor-free 3D reconstructionin highly dynamic, interaction-rich environments. Project page: https://batfacewayne.github.io/DeGauss.io/
从现实世界捕捉中重建干净、无干扰物的3D场景仍然是一个重大挑战,特别是在高度动态和杂乱的环境中,如第一人称视频。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了DeGauss,这是一个简单而稳健的基于解耦动态静态高斯涂布设计的动态场景重建自监督框架。DeGauss使用前景高斯对动态元素进行建模,使用背景高斯对静态内容进行建模,并使用概率掩膜来协调它们的组合,实现独立但互补的优化。DeGauss在多种真实场景中具有稳健的泛化能力,从随意的图像集合到冗长、动态的第一人称视频,无需依赖复杂的启发式方法或广泛的监督。在包括NeRF-on-the-go、ADT、AEA、Hot3D和EPIC-Fields等基准测试上的实验表明,DeGauss始终优于现有方法,为在高度动态、交互丰富的环境中的通用无干扰物3D重建建立了强大的基准线。项目页面:https://batfacewayne.github.io/DeGauss.io/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为DeGauss的简洁、稳健的自监督动态场景重建框架,用于从真实世界捕捉中重建无干扰物的3D场景。该框架基于动态静态高斯斑点设计的解耦设计,使用概率掩膜协调动态元素和静态内容的组合,使它们能够独立但互补地进行优化。DeGauss能够广泛应用于各种真实场景,从随机图像集合到长的动态第一人称视频,且无需依赖复杂的启发式方法或广泛的监督。在多个基准测试上的实验结果表明,DeGauss在高度动态、交互丰富的环境中,在无干扰物的3D重建方面始终优于现有方法,为通用化的3D重建建立了强大的基线。
Key Takeaways
- DeGauss是一个自监督的动态场景重建框架,能够处理真实世界捕捉的无干扰物3D场景重建。
- 框架采用动态静态高斯斑点设计的解耦设计,分别建模动态元素和静态内容。
- 使用概率掩膜协调动态和静态内容的组合,实现独立且互补的优化。
- DeGauss适用于多种真实场景,从随机图像集合到长动态第一人称视频。
- 该框架无需复杂的启发式方法或广泛的监督即可实现良好的性能。
- 在多个基准测试上,DeGauss的表现优于现有方法,尤其在高度动态、交互丰富的环境中的表现更为出色。
点此查看论文截图


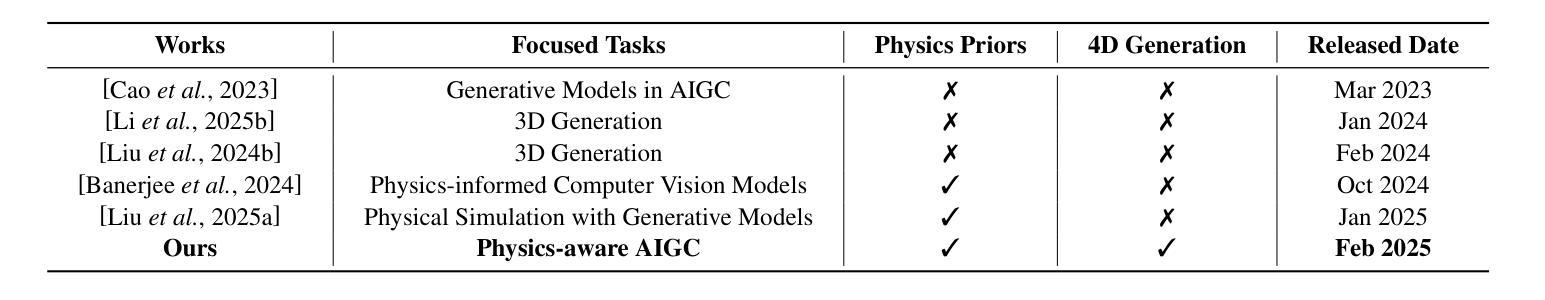
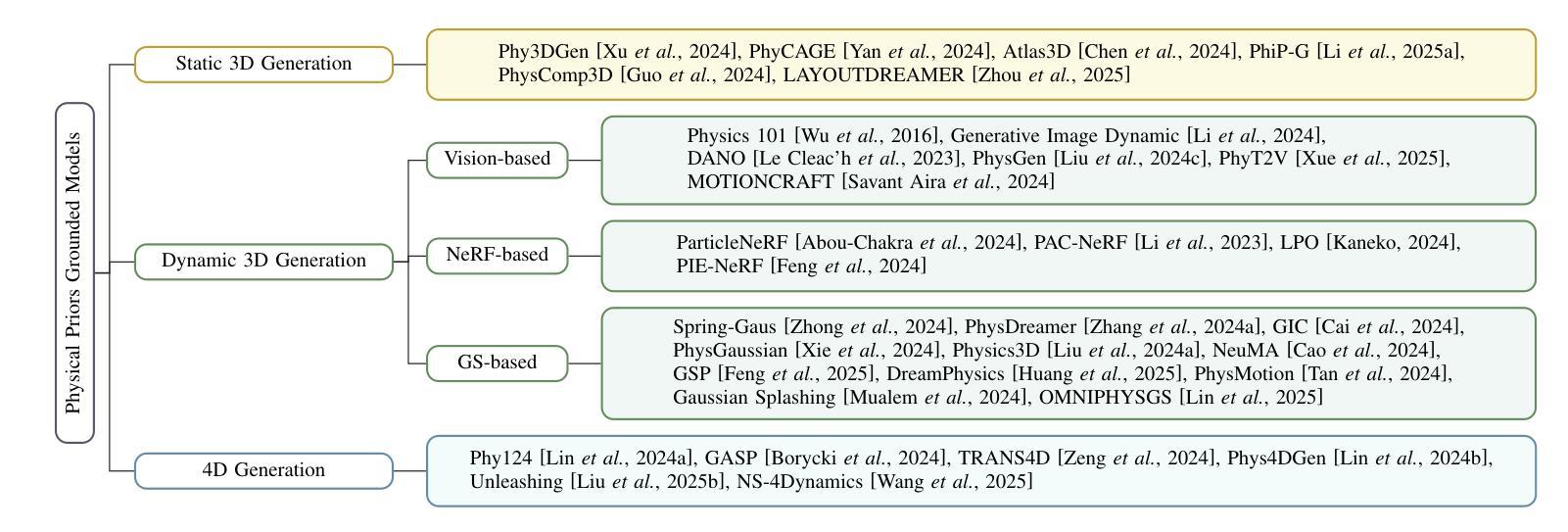
Grounding Creativity in Physics: A Brief Survey of Physical Priors in AIGC
Authors:Siwei Meng, Yawei Luo, Ping Liu
Recent advancements in AI-generated content have significantly improved the realism of 3D and 4D generation. However, most existing methods prioritize appearance consistency while neglecting underlying physical principles, leading to artifacts such as unrealistic deformations, unstable dynamics, and implausible objects interactions. Incorporating physics priors into generative models has become a crucial research direction to enhance structural integrity and motion realism. This survey provides a review of physics-aware generative methods, systematically analyzing how physical constraints are integrated into 3D and 4D generation. First, we examine recent works in incorporating physical priors into static and dynamic 3D generation, categorizing methods based on representation types, including vision-based, NeRF-based, and Gaussian Splatting-based approaches. Second, we explore emerging techniques in 4D generation, focusing on methods that model temporal dynamics with physical simulations. Finally, we conduct a comparative analysis of major methods, highlighting their strengths, limitations, and suitability for different materials and motion dynamics. By presenting an in-depth analysis of physics-grounded AIGC, this survey aims to bridge the gap between generative models and physical realism, providing insights that inspire future research in physically consistent content generation.
近期人工智能生成内容的进展极大地提高了3D和4D生成的逼真度。然而,大多数现有方法优先考虑外观的一致性,却忽略了基本的物理原理,导致出现不真实的变形、不稳定的动态以及不合理的物体交互等伪影。将物理先验知识融入生成模型已成为增强结构完整性和运动逼真度的重要研究方向。本文综述了物理感知的生成方法,系统分析了如何将物理约束融入3D和4D生成。首先,我们研究了将物理先验知识融入静态和动态3D生成的最新工作,按表示类型对方法进行分类,包括基于视觉的、基于NeRF的和基于高斯拼贴的方法。其次,我们探索了4D生成的新兴技术,重点关注使用物理模拟对时间动态进行建模的方法。最后,我们对主要方法进行了比较分析,突出了它们各自的优势、局限性和在不同材料和运动动力学方面的适用性。通过对基于物理原理的人工智能生成内容的深入分析,本文旨在弥合生成模型和物理逼真之间的鸿沟,提供能激发未来在物理一致性内容生成方面研究的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IJCAI 2025 Survey Track
Summary
近期人工智能生成内容的技术进步已显著提高3D和4D生成的逼真度。然而,现有方法多注重外观一致性,忽视底层物理原理,导致生成内容出现不真实变形、动态不稳定、物体交互不合理等问题。融入物理先验知识到生成模型已成为增强结构完整性和运动逼真度的关键研究方向。本文综述了物理感知生成方法,系统分析如何将物理约束融入3D和4D生成。首先,我们研究了将物理先验知识融入静态和动态3D生成的最新工作,按表现形式分类,包括基于视觉、NeRF和Gaussian Splatting的方法。其次,我们探讨了4D生成的新兴技术,重点关注通过物理模拟对时间动态进行建模的方法。最后,我们对主要方法进行了对比分析,突出其优势、局限性和在不同材料和运动动力学方面的适用性。本文旨在填补生成模型与物理现实主义之间的鸿沟,为物理一致的内容生成提供洞察,激发未来研究灵感。
Key Takeaways
- AI生成的3D和4D内容在逼真度上有了显著提升,但存在不真实变形、动态不稳定等问题。
- 融入物理先验知识到生成模型是增强结构完整性和运动逼真度的关键。
- 静态和动态3D生成的最新工作按表现形式分类,包括基于视觉、NeRF和Gaussian Splatting的方法。
- 4D生成技术正关注通过物理模拟对时间动态进行建模的方法。
- 物理感知生成方法在不同材料和运动动力学方面有不同的适用性和局限性。
- 本文旨在填补生成模型与物理现实主义之间的鸿沟。
点此查看论文截图

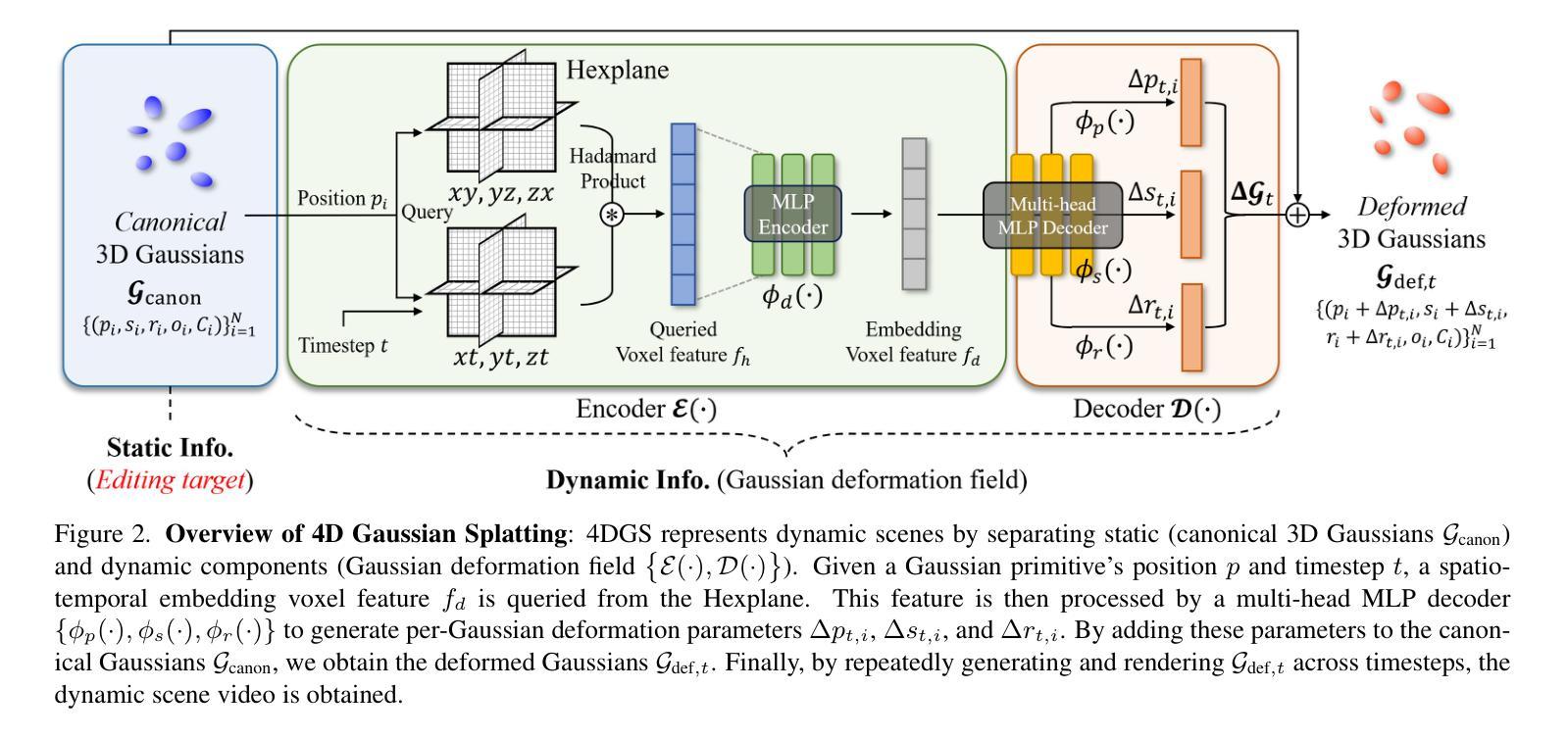
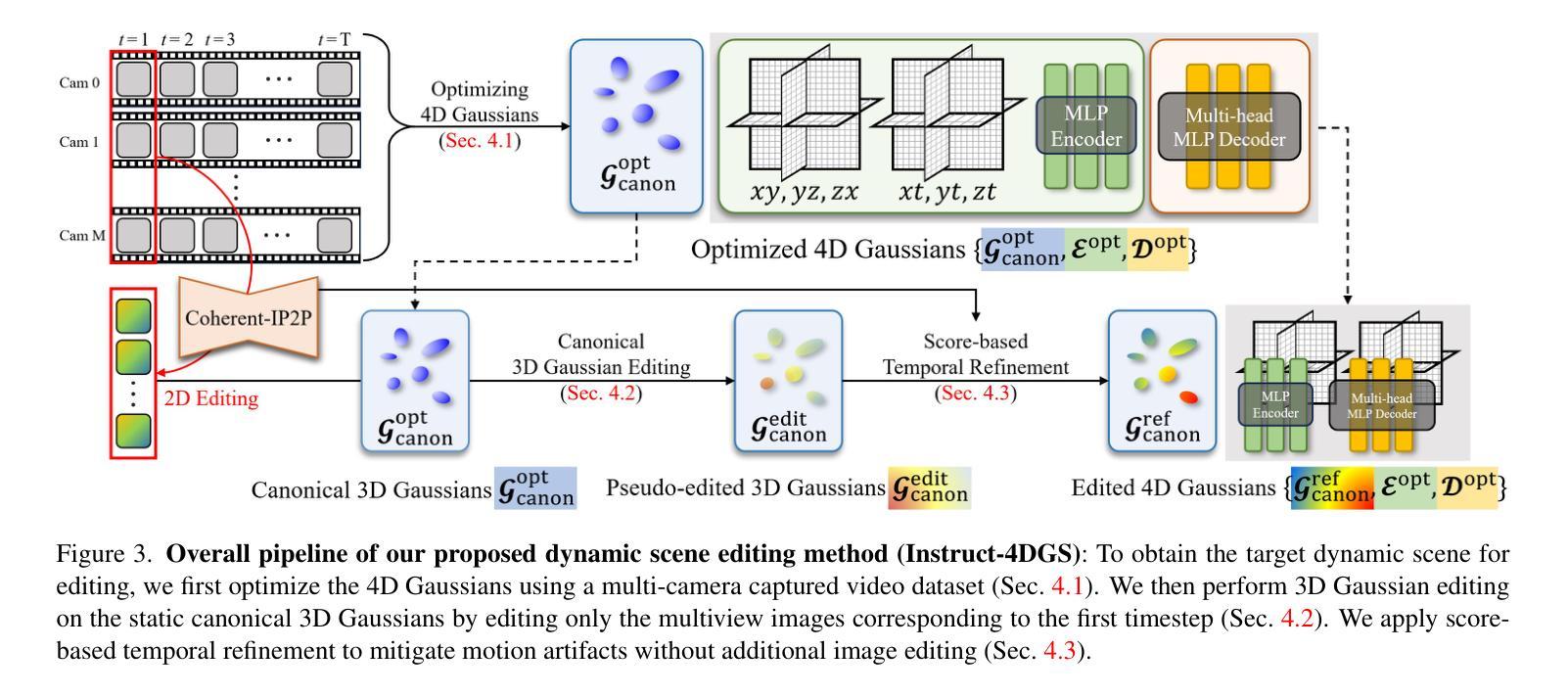
Instruct-4DGS: Efficient Dynamic Scene Editing via 4D Gaussian-based Static-Dynamic Separation
Authors:Joohyun Kwon, Hanbyel Cho, Junmo Kim
Recent 4D dynamic scene editing methods require editing thousands of 2D images used for dynamic scene synthesis and updating the entire scene with additional training loops, resulting in several hours of processing to edit a single dynamic scene. Therefore, these methods are not scalable with respect to the temporal dimension of the dynamic scene (i.e., the number of timesteps). In this work, we propose Instruct-4DGS, an efficient dynamic scene editing method that is more scalable in terms of temporal dimension. To achieve computational efficiency, we leverage a 4D Gaussian representation that models a 4D dynamic scene by combining static 3D Gaussians with a Hexplane-based deformation field, which captures dynamic information. We then perform editing solely on the static 3D Gaussians, which is the minimal but sufficient component required for visual editing. To resolve the misalignment between the edited 3D Gaussians and the deformation field, which may arise from the editing process, we introduce a refinement stage using a score distillation mechanism. Extensive editing results demonstrate that Instruct-4DGS is efficient, reducing editing time by more than half compared to existing methods while achieving high-quality edits that better follow user instructions. Code and results: https://hanbyelcho.info/instruct-4dgs/
最近的4D动态场景编辑方法需要对用于动态场景合成的数千张2D图像进行编辑,并通过额外的训练循环更新整个场景,导致编辑单个动态场景需要数小时的处理时间。因此,这些方法在动态场景的时空维度上(即时序数量)并不具备可扩展性。在这项工作中,我们提出了Instruct-4DGS,一种高效的动态场景编辑方法,在时空维度上更具可扩展性。为了实现计算效率,我们采用了一种4D高斯表示法,通过结合静态3D高斯和基于Hexplane的变形场来模拟一个4D动态场景,其中变形场捕捉动态信息。然后,我们仅在静态的3D高斯上进行编辑,这是视觉编辑所需的最小但足够的组件。为了解决编辑后的3D高斯和变形场之间可能出现的错位问题,我们引入了一个使用评分蒸馏机制的优化阶段。大量的编辑结果表明,Instruct-4DGS是高效的,与现有方法相比,编辑时间减少了超过一半,同时实现了高质量的编辑,更好地遵循了用户的指令。相关代码和结果可通过https://hanbyelcho.info/instruct-4dgs/查看。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025. The first two authors contributed equally
Summary
基于当前四维动态场景编辑方法需要处理数千张二维图像用于动态场景合成,并且需要额外的训练循环来更新整个场景,编辑单个动态场景需要数小时的处理时间。因此,这些方法在动态场景的时空维度上并不具备可扩展性。本研究提出了一种高效的四维动态场景编辑方法——Instruct-4DGS,该方法在时空维度上更具可扩展性。为提升计算效率,本研究采用四维高斯表示法,结合静态三维高斯与基于六平面的变形场来模拟四维动态场景。编辑过程仅针对静态三维高斯进行,这是视觉编辑所需的最小且充分的组件。为解决编辑过程中可能出现的编辑后的三维高斯与变形场之间的不匹配问题,引入了一种基于分数蒸馏的细化阶段。大量的编辑结果证明,Instruct-4DGS方法高效,与现有方法相比,编辑时间减少了一半以上,同时实现了高质量的编辑,更好地遵循了用户的指令。
Key Takeaways
- 当前四维动态场景编辑方法存在处理时间长、不便于编辑大量动态场景的问题。
- Instruct-4DGS方法被提出,以提高四维动态场景编辑的效率与时空维度的可扩展性。
- Instruct-4DGS采用四维高斯表示法,结合静态三维高斯与基于六平面的变形场来模拟和编辑四维动态场景。
- 编辑过程主要针对静态三维高斯进行,这是视觉编辑的最小且充分组件。
- 为解决编辑后可能出现的三维高斯与变形场不匹配问题,引入了基于分数蒸馏的细化阶段。
- Instruct-4DGS方法大大减少了编辑时间,与现有方法相比效率提高一倍以上。
- Instruct-4DGS实现了高质量的编辑,更好地遵循了用户的指令。
点此查看论文截图


GLS: Geometry-aware 3D Language Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Jiaxiong Qiu, Liu Liu, Xinjie Wang, Tianwei Lin, Wei Sui, Zhizhong Su
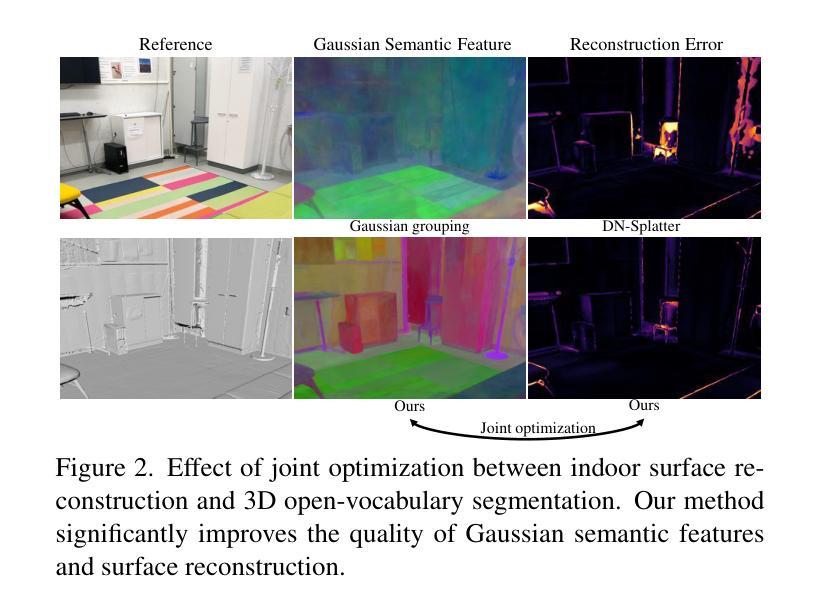
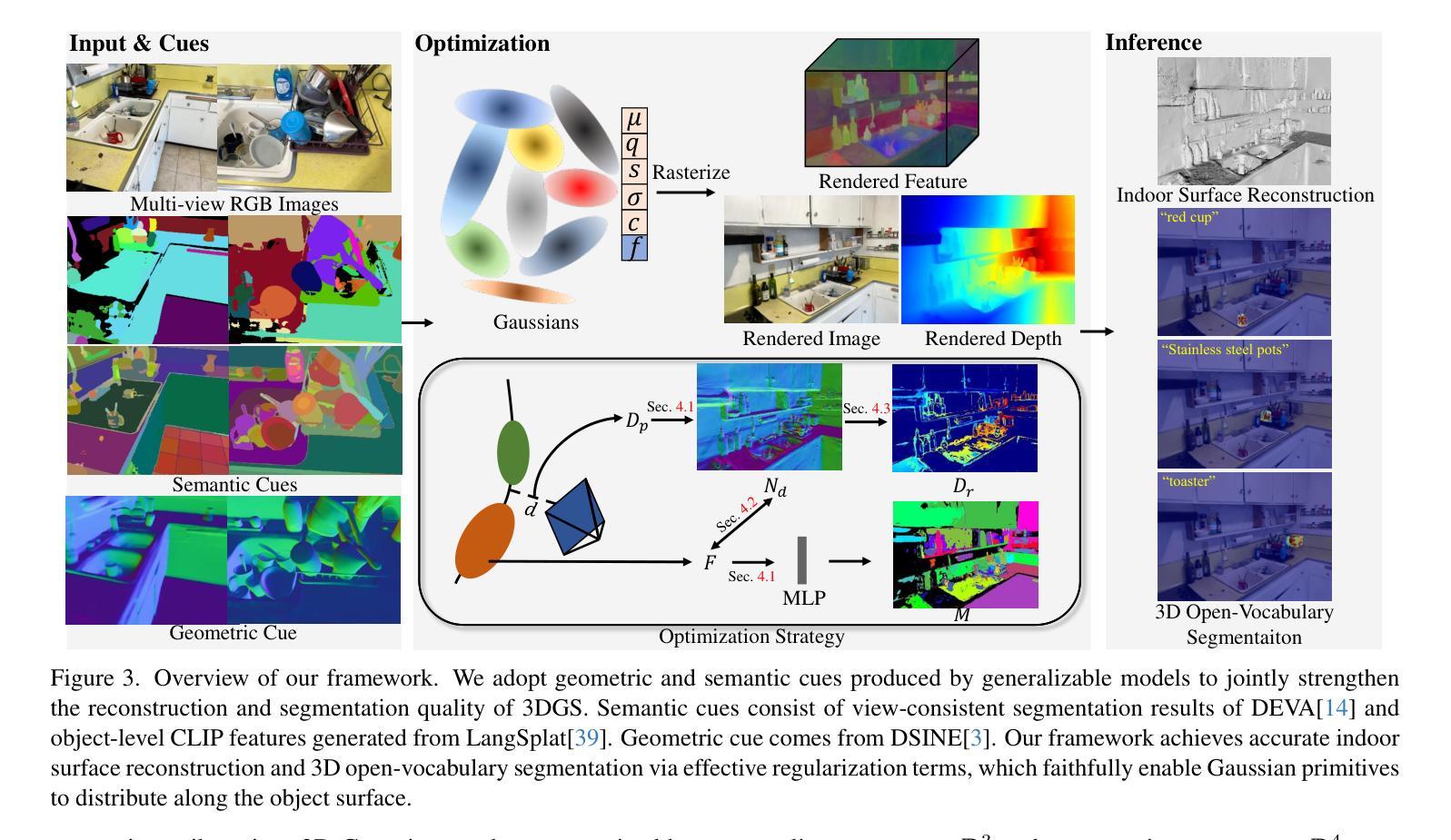
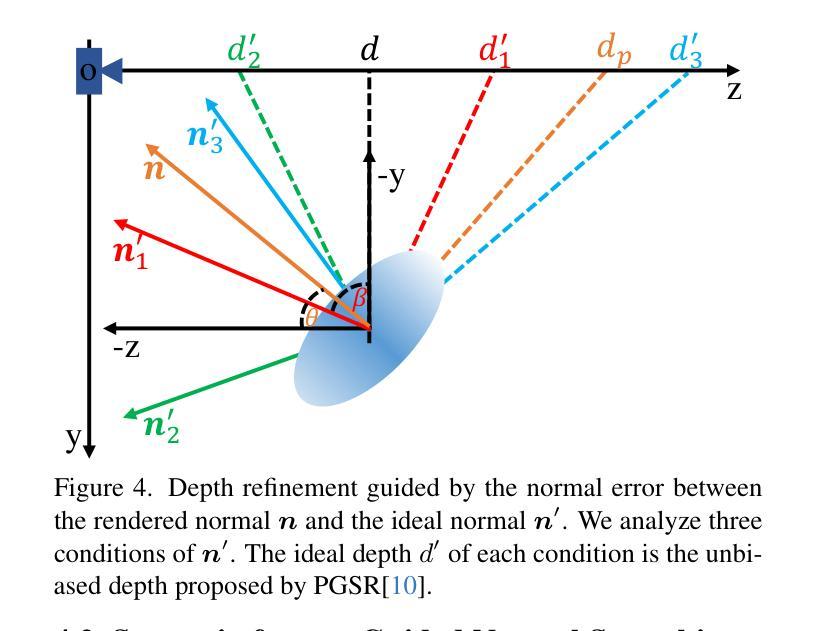
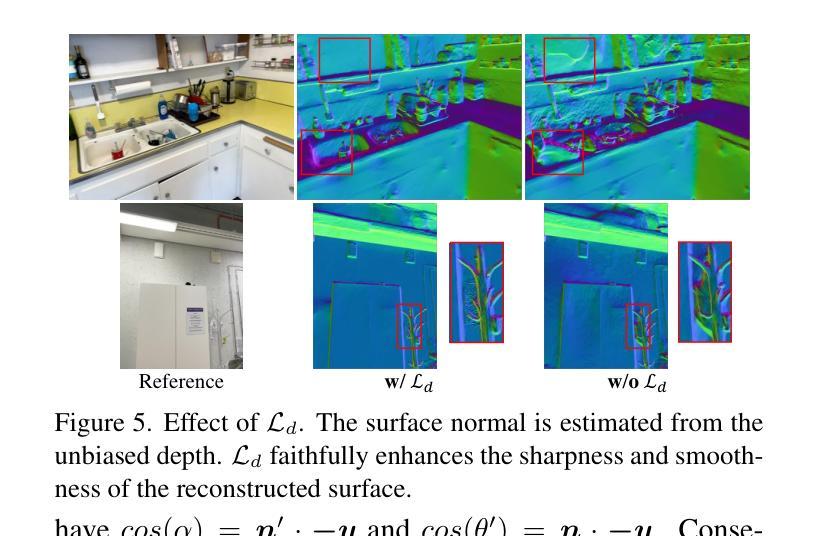
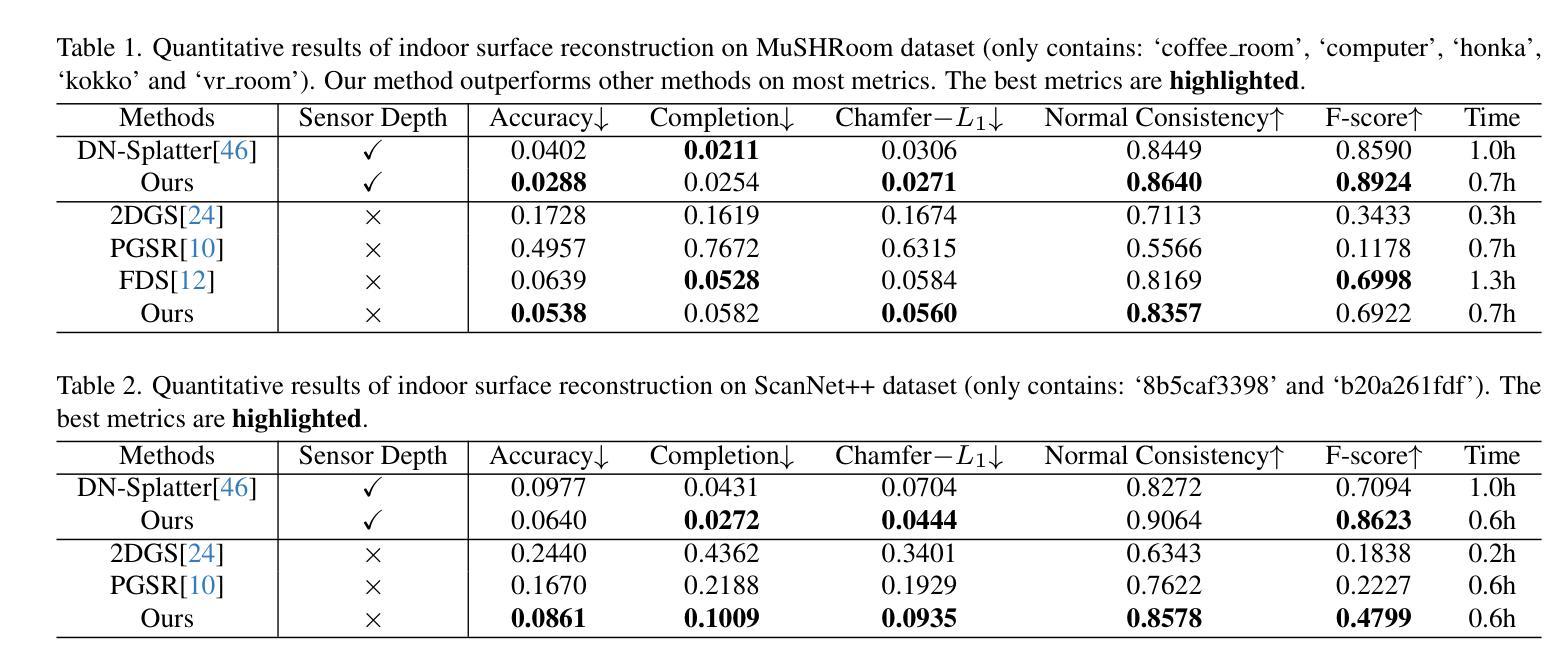
Recently, 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has achieved impressive performance on indoor surface reconstruction and 3D open-vocabulary segmentation. This paper presents GLS, a unified framework of 3D surface reconstruction and open-vocabulary segmentation based on 3DGS. GLS extends two fields by improving their sharpness and smoothness. For indoor surface reconstruction, we introduce surface normal prior as a geometric cue to guide the rendered normal, and use the normal error to optimize the rendered depth. For 3D open-vocabulary segmentation, we employ 2D CLIP features to guide instance features and enhance the surface smoothness, then utilize DEVA masks to maintain their view consistency. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of jointly optimizing surface reconstruction and 3D open-vocabulary segmentation, where GLS surpasses state-of-the-art approaches of each task on MuSHRoom, ScanNet++ and LERF-OVS datasets. Project webpage: https://jiaxiongq.github.io/GLS_ProjectPage.
最近,3D高斯贴图(3DGS)在室内表面重建和3D开放词汇分割方面取得了令人印象深刻的性能。本文提出了基于3DGS的GLS,这是一个统一的3D表面重建和开放词汇分割框架。GLS通过提高锐度和平滑度来扩展这两个领域。对于室内表面重建,我们引入表面法线先验作为几何线索来引导渲染法线,并使用法线误差来优化渲染深度。对于3D开放词汇分割,我们采用2D CLIP特征来引导实例特征并增强表面平滑度,然后使用DEVA遮罩来保持视图一致性。大量实验表明,联合优化表面重建和3D开放词汇分割是有效的,其中GLS在MuSHRoom、ScanNet++和LERF-OVS数据集上超越了每个任务的最先进方法。项目网页:https://jiaxiongq.github.io/GLS_ProjectPage。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical Report
Summary
基于三维高斯拼贴技术(3DGS),本文提出了GLS统一框架,用于室内表面重建和三维开放词汇分割。在室内表面重建方面,引入法线先验作为几何线索来指导渲染法线,并利用法线误差优化渲染深度。在三维开放词汇分割方面,采用二维CLIP特征引导实例特征并增强表面平滑度,利用DEVA掩膜保持视图一致性。通过联合优化表面重建和三维开放词汇分割,GLS在MuSHRoom、ScanNet++和LERF-OVS数据集上的性能超越了各任务的最先进方法。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了基于三维高斯拼贴技术(3DGS)的GLS统一框架,用于室内表面重建和三维开放词汇分割。
- 在室内表面重建中,引入法线先验作为几何线索指导渲染法线,并通过法线误差优化渲染深度。
- 采用二维CLIP特征引导实例特征,增强表面平滑度,并利用DEVA掩膜保持视图一致性。
- 通过联合优化表面重建和三维开放词汇分割任务,GLS在多个数据集上的性能超越现有方法。
- GLS框架提高了两个领域的清晰度与平滑度。
点此查看论文截图