⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-05 更新
No time to train! Training-Free Reference-Based Instance Segmentation
Authors:Miguel Espinosa, Chenhongyi Yang, Linus Ericsson, Steven McDonagh, Elliot J. Crowley
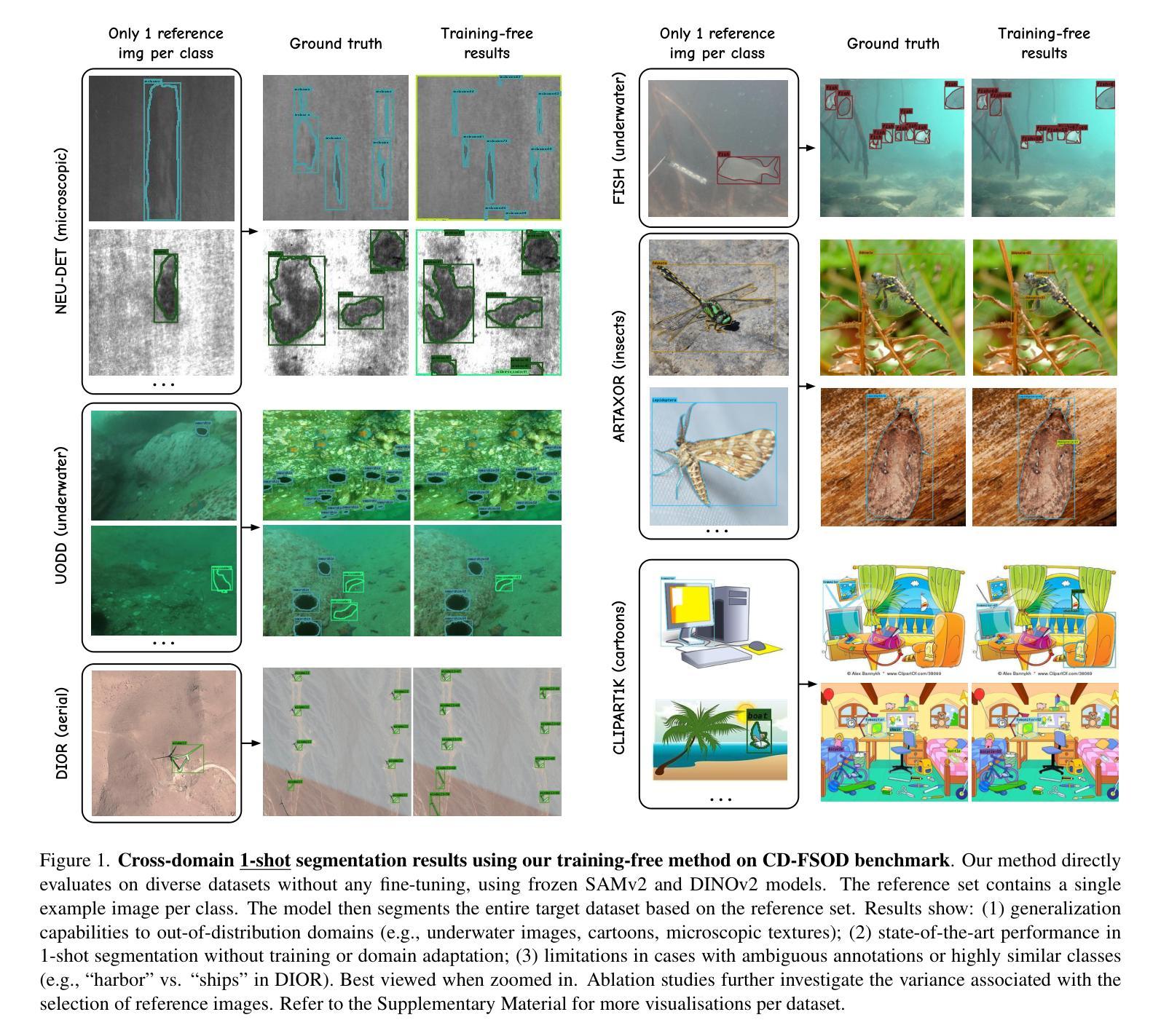
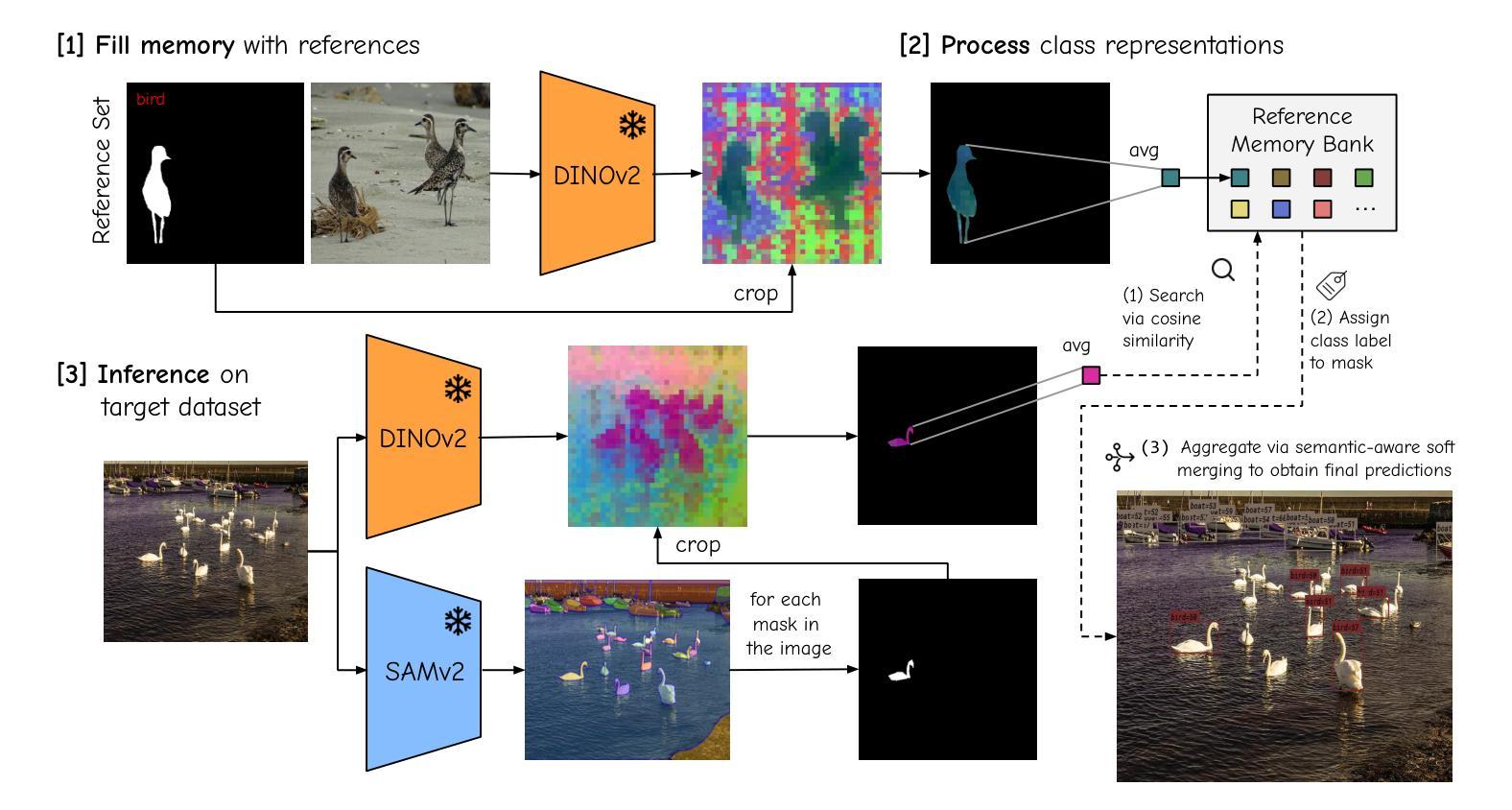
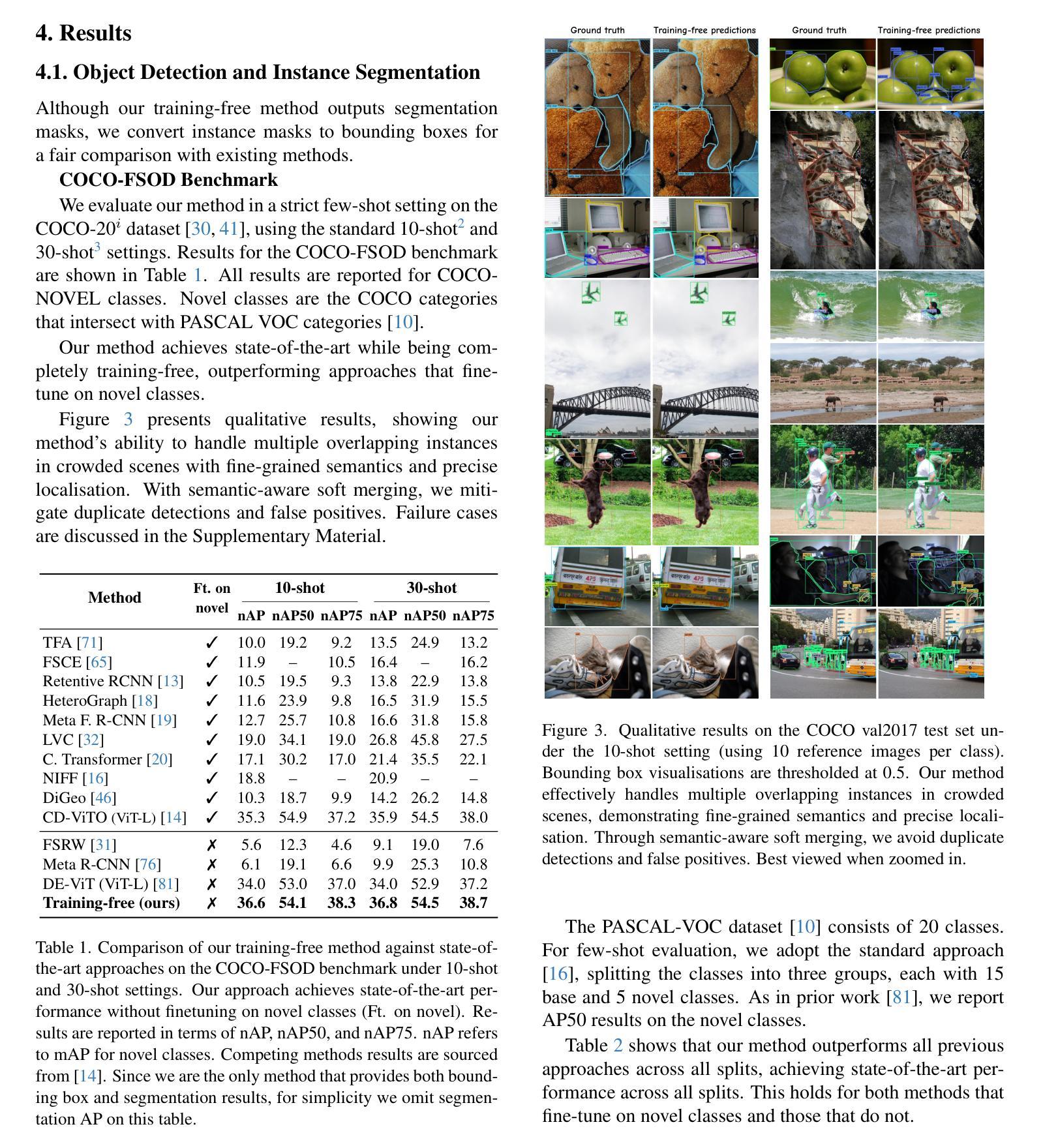
The performance of image segmentation models has historically been constrained by the high cost of collecting large-scale annotated data. The Segment Anything Model (SAM) alleviates this original problem through a promptable, semantics-agnostic, segmentation paradigm and yet still requires manual visual-prompts or complex domain-dependent prompt-generation rules to process a new image. Towards reducing this new burden, our work investigates the task of object segmentation when provided with, alternatively, only a small set of reference images. Our key insight is to leverage strong semantic priors, as learned by foundation models, to identify corresponding regions between a reference and a target image. We find that correspondences enable automatic generation of instance-level segmentation masks for downstream tasks and instantiate our ideas via a multi-stage, training-free method incorporating (1) memory bank construction; (2) representation aggregation and (3) semantic-aware feature matching. Our experiments show significant improvements on segmentation metrics, leading to state-of-the-art performance on COCO FSOD (36.8% nAP), PASCAL VOC Few-Shot (71.2% nAP50) and outperforming existing training-free approaches on the Cross-Domain FSOD benchmark (22.4% nAP).
历史上,图像分割模型的性能一直受到收集大规模标注数据的高成本的限制。Segment Anything Model(SAM)通过可提示的、与语义无关的分割范式缓解了这一原始问题,但仍然存在需要手动视觉提示或复杂的域相关提示生成规则来处理新图像的问题。为了减轻这一新负担,我们的工作研究了在仅提供一小组参考图像的情况下进行目标分割的任务。我们的关键见解是利用基础模型学到的强大语义先验知识,来识别参考图像和目标图像之间的对应区域。我们发现这种对应关系能够自动生成用于下游任务的实例级分割掩码,并通过一个多阶段、无需训练的方法实现我们的想法,该方法包括(1)构建内存银行;(2)表示聚合和(3)语义感知特征匹配。我们的实验显示,在分割指标上取得了显著改进,达到了COCO FSOD(nAP 36.8%)、PASCAL VOC少镜头(nAP50 71.2%)的先进水平,并在跨域FSOD基准测试上超越了现有的无需训练的方法(nAP 22.4%)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint
Summary
本文提出一种基于少量参考图像进行物体分割的方法。通过利用强大的语义先验知识,结合基础模型学习到的特征,实现在目标图像与参考图像间对应区域的自动识别和实例级分割掩模的生成。实验结果在COCO FSOD等数据集上表现出显著的改进,并达到了业界领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- Segment Anything Model (SAM) 解决了大规模标注数据收集成本高昂的问题,但仍需手动视觉提示或复杂的领域相关提示生成规则来处理新图像。
- 研究提出了一种基于少量参考图像进行物体分割的新方法。
- 利用强大的语义先验知识,结合基础模型,在目标图像和参考图像之间识别对应区域。
- 通过自动生成实例级分割掩模,促进下游任务的应用。
- 实现了多阶段、无需训练的方法,包括建立内存库、表示聚合和语义感知特征匹配。
- 在COCO FSOD、PASCAL VOC Few-Shot等数据集上的实验结果显著,表现出优越性。
点此查看论文截图

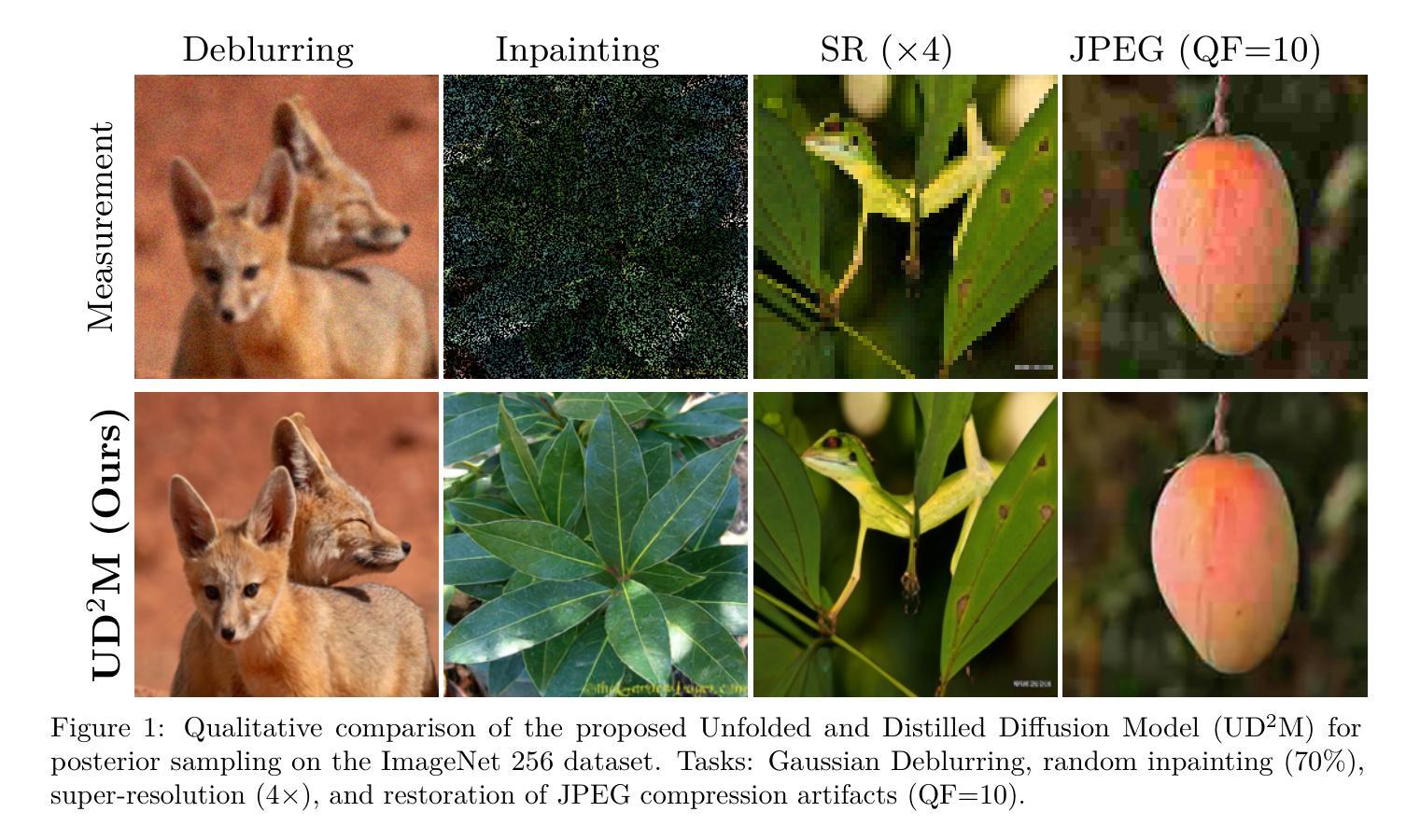
Learning few-step posterior samplers by unfolding and distillation of diffusion models
Authors:Charlesquin Kemajou Mbakam, Jonathan Spence, Marcelo Pereyra
Diffusion models (DMs) have emerged as powerful image priors in Bayesian computational imaging. Two primary strategies have been proposed for leveraging DMs in this context: Plug-and-Play methods, which are zero-shot and highly flexible but rely on approximations; and specialized conditional DMs, which achieve higher accuracy and faster inference for specific tasks through supervised training. In this work, we introduce a novel framework that integrates deep unfolding and model distillation to transform a DM image prior into a few-step conditional model for posterior sampling. A central innovation of our approach is the unfolding of a Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) algorithm - specifically, the recently proposed LATINO Langevin sampler (Spagnoletti et al., 2025) - representing the first known instance of deep unfolding applied to a Monte Carlo sampling scheme. We demonstrate our proposed unfolded and distilled samplers through extensive experiments and comparisons with the state of the art, where they achieve excellent accuracy and computational efficiency, while retaining the flexibility to adapt to variations in the forward model at inference time.
扩散模型(DMs)在贝叶斯计算成像中已作为强大的图像先验项出现。在此上下文中,已经提出了两种主要策略来利用DMs:即插即用方法,它们是零射击且高度灵活但依赖于近似值;以及通过监督训练针对特定任务实现更高精度和更快推理的专用条件DMs。在这项工作中,我们引入了一个新型框架,该框架集成了深度展开和模型蒸馏,将DM图像先验项转化为用于后采样的一步式条件模型。我们的方法的一个核心创新之处在于展开马尔可夫链蒙特卡洛(MCMC)算法——特别是最近提出的LATINO Langevin采样器(Spagnoletti等人,2025)——这代表了已知第一个用于蒙特卡洛采样方案的深度展开实例。我们通过大量实验以及与最新技术的比较来证明我们提出的展开和蒸馏采样器具有出色的准确性和计算效率,同时在推理时间保持适应正向模型变化的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 28 pages, 16 figures, 10 tables
摘要
扩散模型(DMs)在贝叶斯计算成像中作为图像先验具有强大的能力。本研究介绍了一种结合深度展开和模型蒸馏的新框架,将扩散模型图像先验转化为用于后采样分析的几步条件模型。核心创新在于马尔可夫链蒙特卡罗算法的展开,特别是最近提出的LATINO Langevin采样器,代表了深度展开首次应用于蒙特卡罗采样方案。实验证明,与现有技术相比,所提出的展开和蒸馏采样器具有出色的准确性和计算效率,同时保留了适应前向模型变化的能力。
关键见解
- 扩散模型(DMs)作为贝叶斯计算成像中的图像先验具有强大的能力。
- 引入了一种结合深度展开和模型蒸馏的新框架,用于转化扩散模型图像先验为条件模型进行后采样分析。
- 展开马尔可夫链蒙特卡罗算法在研究中占据核心地位,特别是应用了LATINO Langevin采样器。
- 此框架是深度展开首次应用于蒙特卡罗采样方案的实例。
- 与现有技术相比,所提出的采样器具有出色的准确性和计算效率。
- 提出的框架能够在推理时适应前向模型的变异。
- 该研究为贝叶斯计算成像中的扩散模型应用提供了新的视角和方法论支持。
点此查看论文截图

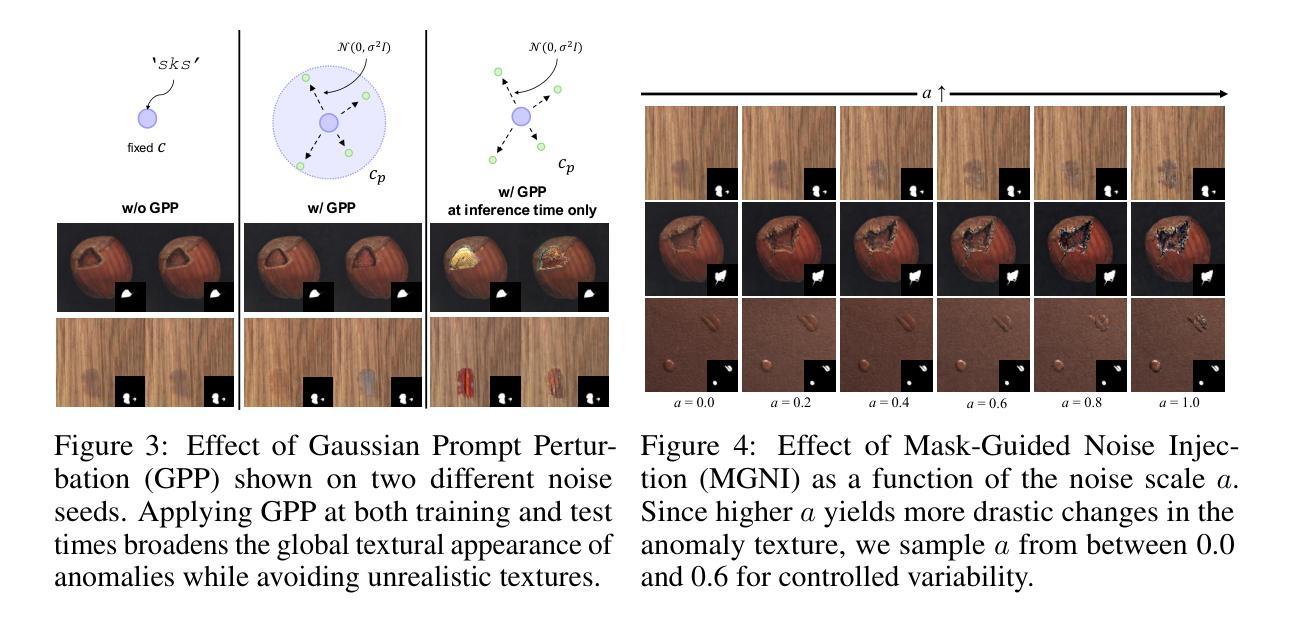
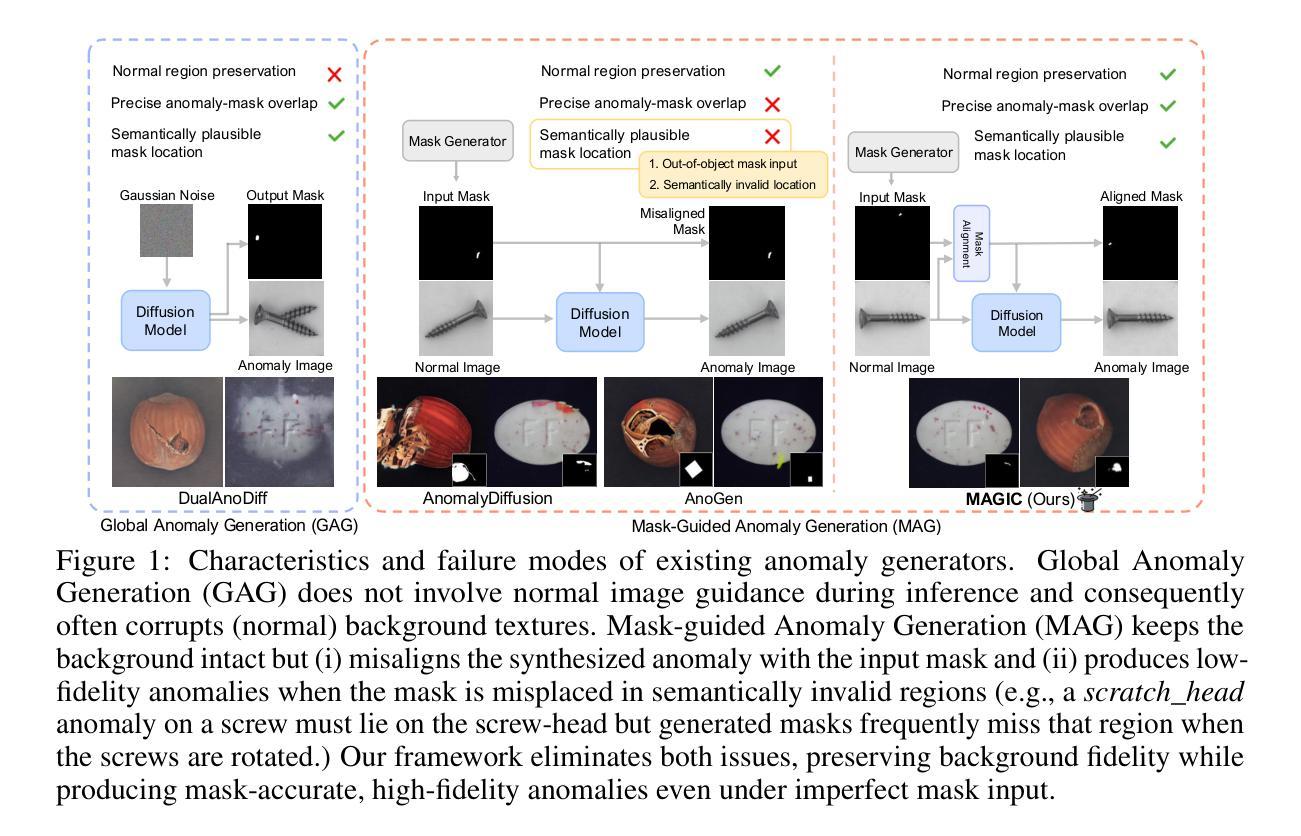
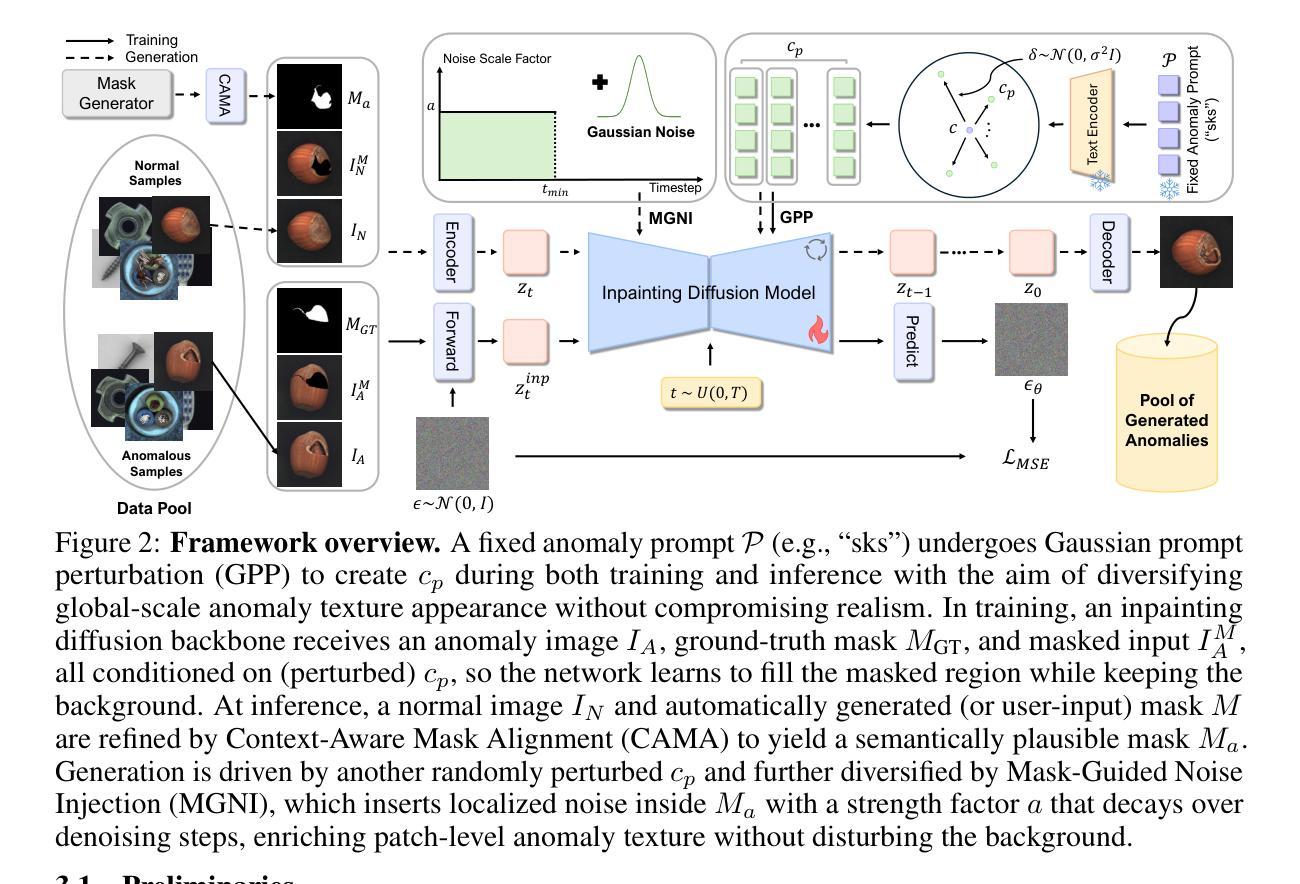
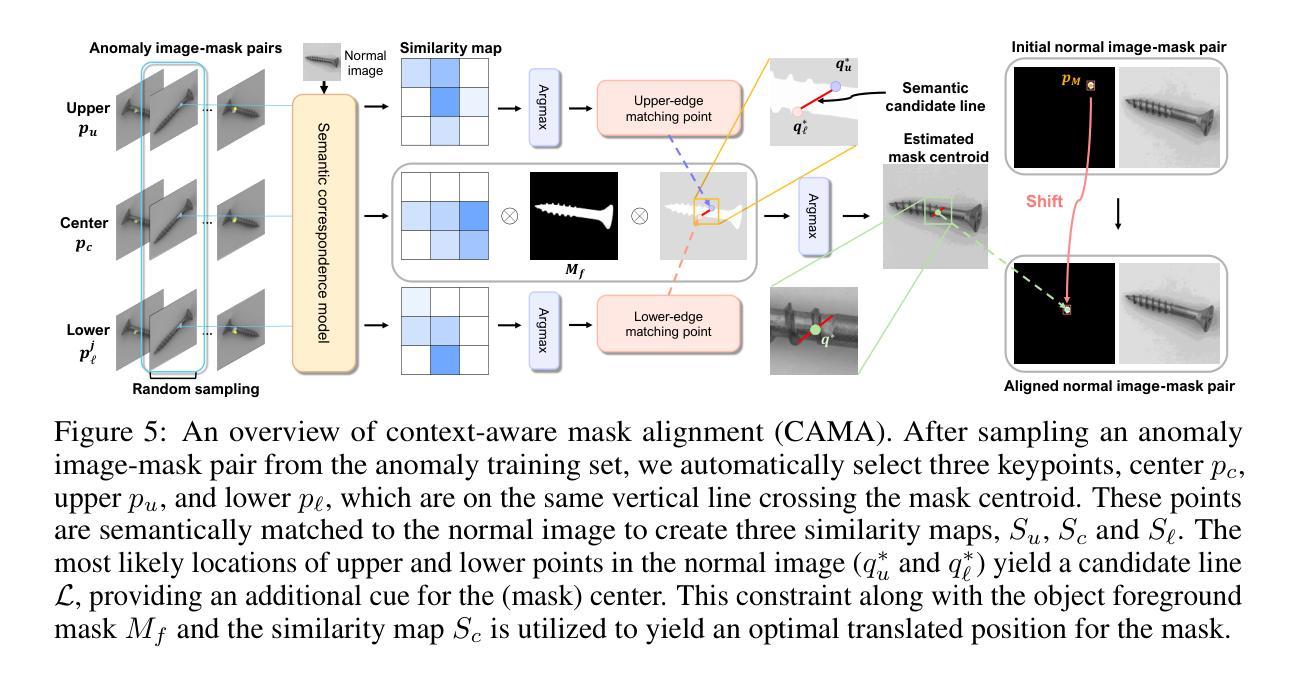
MAGIC: Mask-Guided Diffusion Inpainting with Multi-Level Perturbations and Context-Aware Alignment for Few-Shot Anomaly Generation
Authors:JaeHyuck Choi, MinJun Kim, JeHyeong Hong
Few-shot anomaly generation is emerging as a practical solution for augmenting the scarce anomaly data in industrial quality control settings. An ideal generator would meet three demands at once, namely (i) keep the normal background intact, (ii) inpaint anomalous regions to tightly overlap with the corresponding anomaly masks, and (iii) generate anomalous regions in a semantically valid location, while still producing realistic, diverse appearances from only a handful of real examples. Existing diffusion-based methods usually satisfy at most two of these requirements: global anomaly generators corrupt the background, whereas mask-guided ones often falter when the mask is imprecise or misplaced. We propose MAGIC–Mask-guided inpainting with multi-level perturbations and Context-aware alignment–to resolve all three issues. At its core, MAGIC fine-tunes a Stable Diffusion inpainting backbone that preserves normal regions and ensures strict adherence of the synthesized anomaly to the supplied mask, directly addressing background corruption and misalignment. To offset the diversity loss that fine-tuning can cause, MAGIC adds two complementary perturbation strategies: (i) Gaussian prompt-level perturbation applied during fine-tuning and inference that broadens the global appearance of anomalies while avoiding low-fidelity textual appearances, and (ii) mask-guided spatial noise injection that enriches local texture variations. Additionally, the context-aware mask alignment module forms semantic correspondences and relocates masks so that every anomaly remains plausibly contained within the host object, eliminating out-of-boundary artifacts. Under a consistent identical evaluation protocol on the MVTec-AD dataset, MAGIC outperforms previous state-of-the-arts in downstream anomaly tasks.
少数镜头异常生成(Few-shot anomaly generation)作为一种实用解决方案,正逐渐崭露头角,用于在工业质量控制环境中扩充稀缺的异常数据。理想的生成器需要同时满足三个要求,即(i)保持正常背景不变,(ii)将异常区域填充以紧密覆盖对应的异常掩膜,(iii)在语义有效的位置生成异常区域,同时仅使用少量真实示例即可产生真实且多样化的外观。现有的基于扩散的方法最多只能满足其中两个要求:全局异常生成器会破坏背景,而掩膜引导的方法在掩膜不精确或错位时往往会遇到困难。我们提出了MAGIC方法——一种带有多级扰动和上下文感知对齐的掩膜引导填充法来解决这三个问题。MAGIC的核心是微调Stable Diffusion填充骨干网,以保留正常区域并确保合成异常严格遵循提供的掩膜,直接解决了背景破坏和对齐不精确的问题。为了弥补微调可能导致的多样性损失,MAGIC增加了两种互补的扰动策略:(i)在微调期间和推理期间应用高斯提示级扰动,以扩大异常的总体外观,同时避免低保真度的文本外观;(ii)掩膜引导的空间噪声注入丰富了局部纹理变化。此外,上下文感知的掩膜对齐模块形成了语义对应关系并重新定位了掩膜,使每个异常都合理地包含在主体对象中,消除了边界外的伪影。在MVTec-AD数据集上采用一致相同的评估协议,MAGIC在下游异常任务中的表现超过了以前的最先进方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 6 figures
Summary
本文提出了一种名为MAGIC的少数样本异常生成方法,用于工业质量控制设置中异常数据的增强。该方法通过微调Stable Diffusion模型作为核心,解决背景破坏和不匹配问题,同时通过两种互补的扰动策略增强异常多样性,且上下文感知的掩膜对齐模块使异常区域语义上更合理。在MVTec-AD数据集上的评估表明,MAGIC在下游异常任务中表现优于先前技术。
Key Takeaways
- 少数样本异常生成是解决工业质量控制中异常数据稀缺问题的实用方法。
- 理想的生成器需满足三个需求:保持正常背景、精确覆盖异常区域以及生成语义合理的异常地点。
- 现有扩散方法通常最多满足两个要求,全球异常生成器会破坏背景,而掩膜引导的生成器在掩膜不精确或错位时经常失效。
- MAGIC方法通过微调Stable Diffusion模型解决背景破坏和不匹配问题。
- MAGIC通过两种互补的扰动策略增强异常多样性:高斯提示级别扰动和掩膜引导的空间噪声注入。
- 上下文感知的掩膜对齐模块使异常区域语义上更合理,避免了边界外的伪影。
点此查看论文截图


ViRefSAM: Visual Reference-Guided Segment Anything Model for Remote Sensing Segmentation
Authors:Hanbo Bi, Yulong Xu, Ya Li, Yongqiang Mao, Boyuan Tong, Chongyang Li, Chunbo Lang, Wenhui Diao, Hongqi Wang, Yingchao Feng, Xian Sun
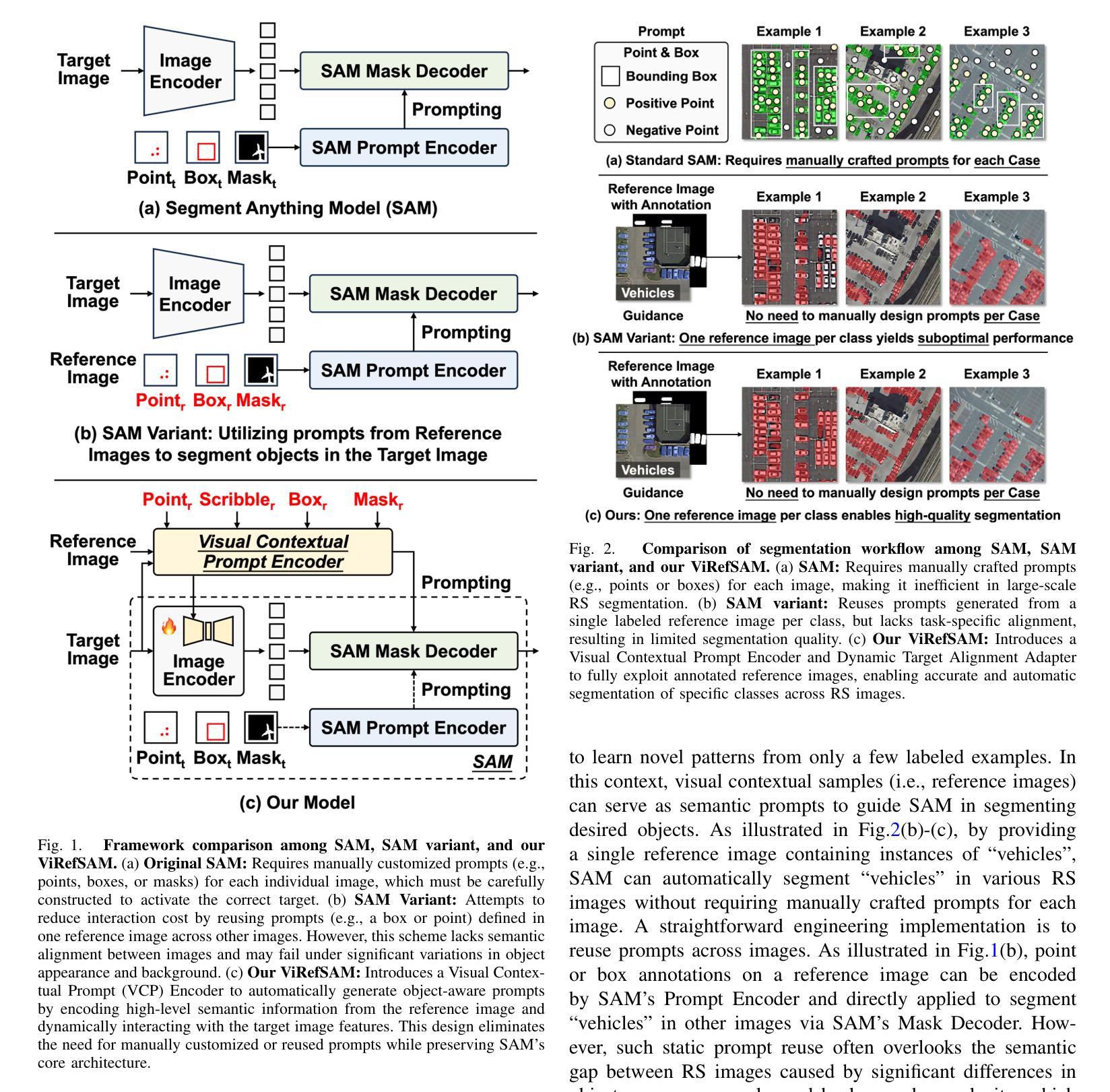
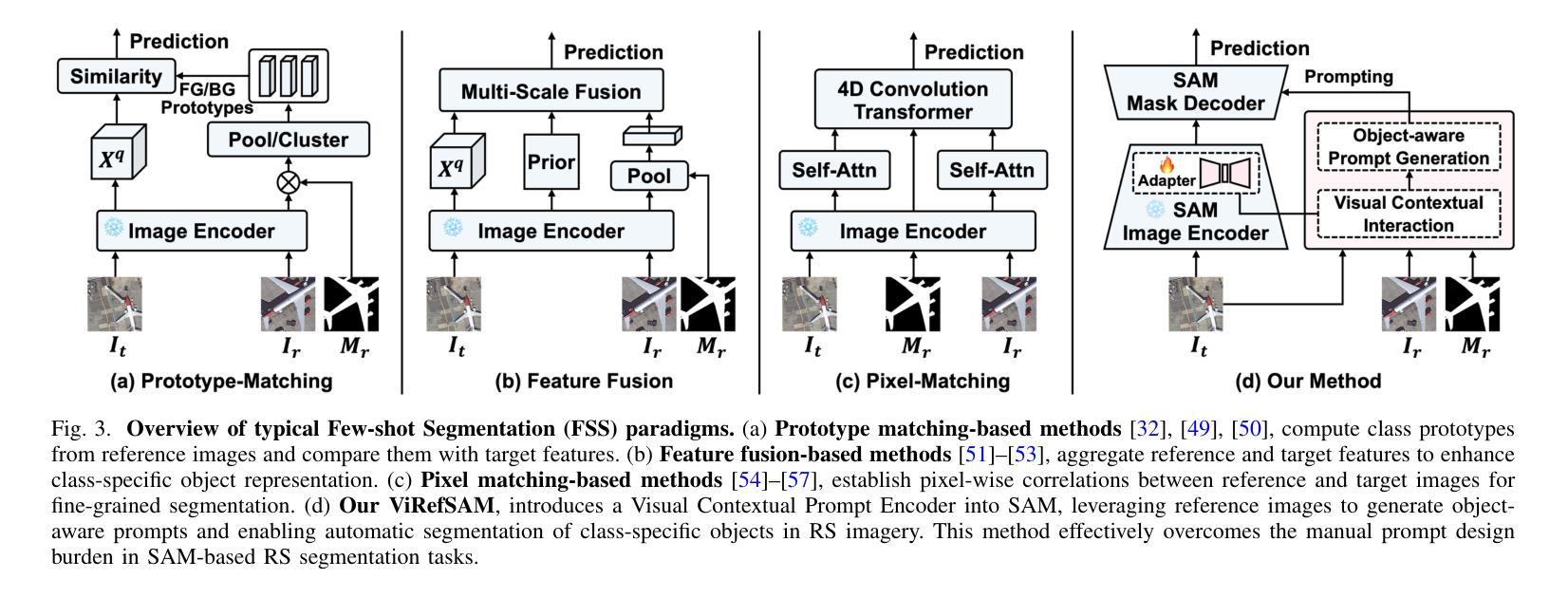
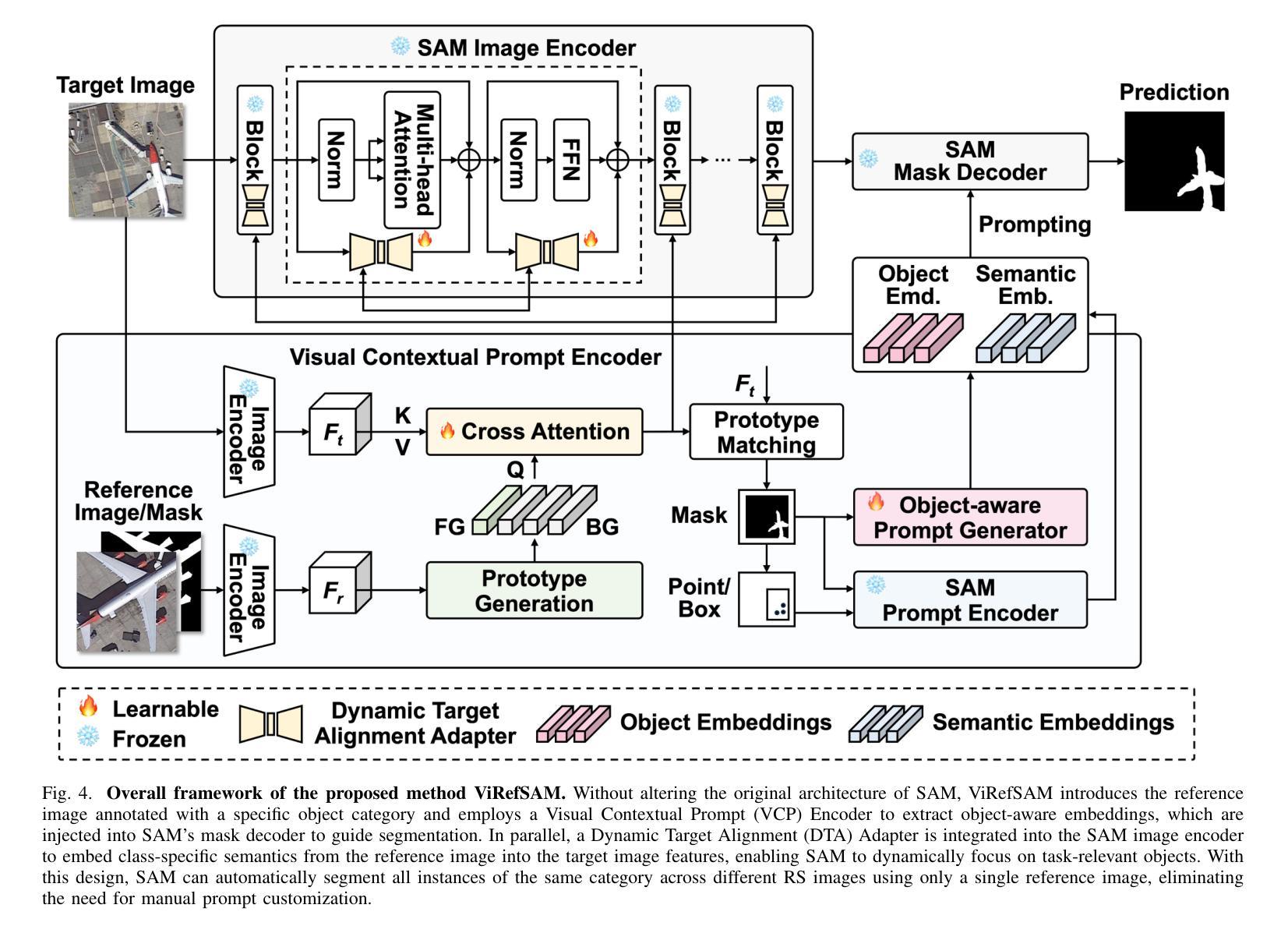
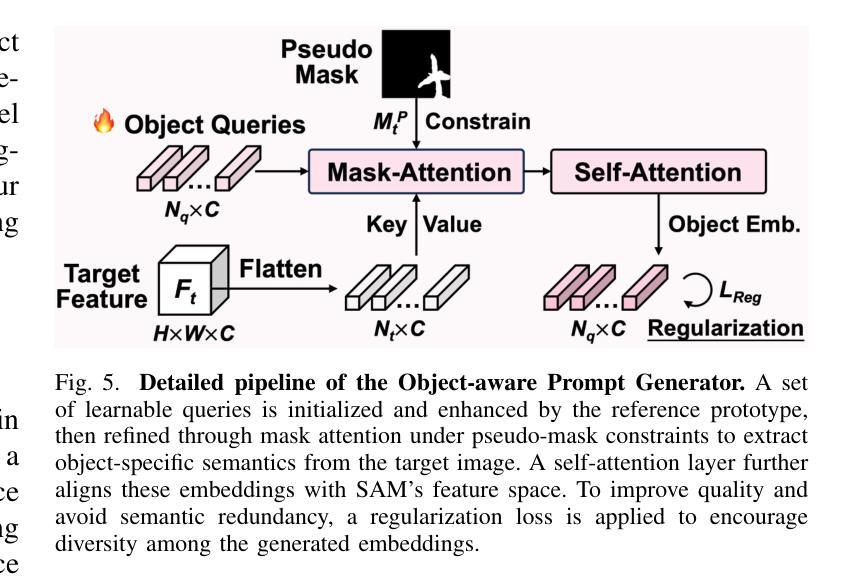
The Segment Anything Model (SAM), with its prompt-driven paradigm, exhibits strong generalization in generic segmentation tasks. However, applying SAM to remote sensing (RS) images still faces two major challenges. First, manually constructing precise prompts for each image (e.g., points or boxes) is labor-intensive and inefficient, especially in RS scenarios with dense small objects or spatially fragmented distributions. Second, SAM lacks domain adaptability, as it is pre-trained primarily on natural images and struggles to capture RS-specific semantics and spatial characteristics, especially when segmenting novel or unseen classes. To address these issues, inspired by few-shot learning, we propose ViRefSAM, a novel framework that guides SAM utilizing only a few annotated reference images that contain class-specific objects. Without requiring manual prompts, ViRefSAM enables automatic segmentation of class-consistent objects across RS images. Specifically, ViRefSAM introduces two key components while keeping SAM’s original architecture intact: (1) a Visual Contextual Prompt Encoder that extracts class-specific semantic clues from reference images and generates object-aware prompts via contextual interaction with target images; and (2) a Dynamic Target Alignment Adapter, integrated into SAM’s image encoder, which mitigates the domain gap by injecting class-specific semantics into target image features, enabling SAM to dynamically focus on task-relevant regions. Extensive experiments on three few-shot segmentation benchmarks, including iSAID-5$^i$, LoveDA-2$^i$, and COCO-20$^i$, demonstrate that ViRefSAM enables accurate and automatic segmentation of unseen classes by leveraging only a few reference images and consistently outperforms existing few-shot segmentation methods across diverse datasets.
Segment Anything Model(SAM)以其基于提示的范式在通用分割任务中展现出强大的泛化能力。然而,将SAM应用于遥感(RS)图像仍然面临两大挑战。首先,手动为每张图像构建精确提示(例如点或框)是劳动密集型的,且效率低下,特别是在具有密集小目标或空间碎片分布的遥感场景中。其次,SAM缺乏领域适应性,因为它主要是在自然图像上进行预训练的,在捕获遥感特定的语义和空间特征方面存在困难,尤其是在分割新颖或未见类别时。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该论文介绍了Segment Anything Model(SAM)在处理遥感图像时面临的挑战,并提出了ViRefSAM框架来解决这些问题。ViRefSAM利用少量标注的参考图像,通过视觉上下文提示编码器和动态目标对齐适配器两个关键组件,实现了对遥感图像中类一致性对象的自动分割。这一框架在多个数据集上的实验结果表明,它能够在仅使用少量参考图像的情况下实现对未见类的准确自动分割,并一致优于现有的少样本分割方法。
Key Takeaways
- Segment Anything Model (SAM)面临在遥感图像分割中的两大挑战:手动构建精确提示的劳动密集型和低效性,以及缺乏针对遥感图像特定语义和空间特性的域适应性。
- ViRefSAM框架通过利用少量标注的参考图像来解决这些问题,这些参考图像包含特定类别的对象。
- ViRefSAM框架包含两个关键组件:视觉上下文提示编码器和动态目标对齐适配器。
- 视觉上下文提示编码器从参考图像中提取特定类别的语义线索,并通过与目标图像的上下文交互生成对象感知提示。
- 动态目标对齐适配器被集成到SAM的图像编码器中,通过注入特定类别的语义信息来缩小域差距,使SAM能够动态关注任务相关区域。
- 在多个数据集上的实验结果表明,ViRefSAM能够利用少量参考图像实现对未见类的准确自动分割。
点此查看论文截图

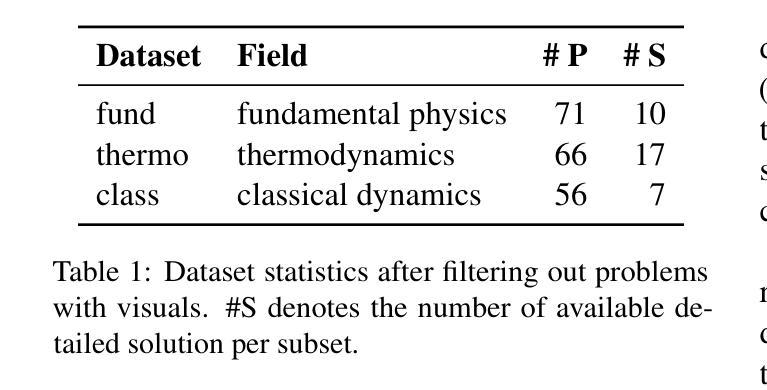
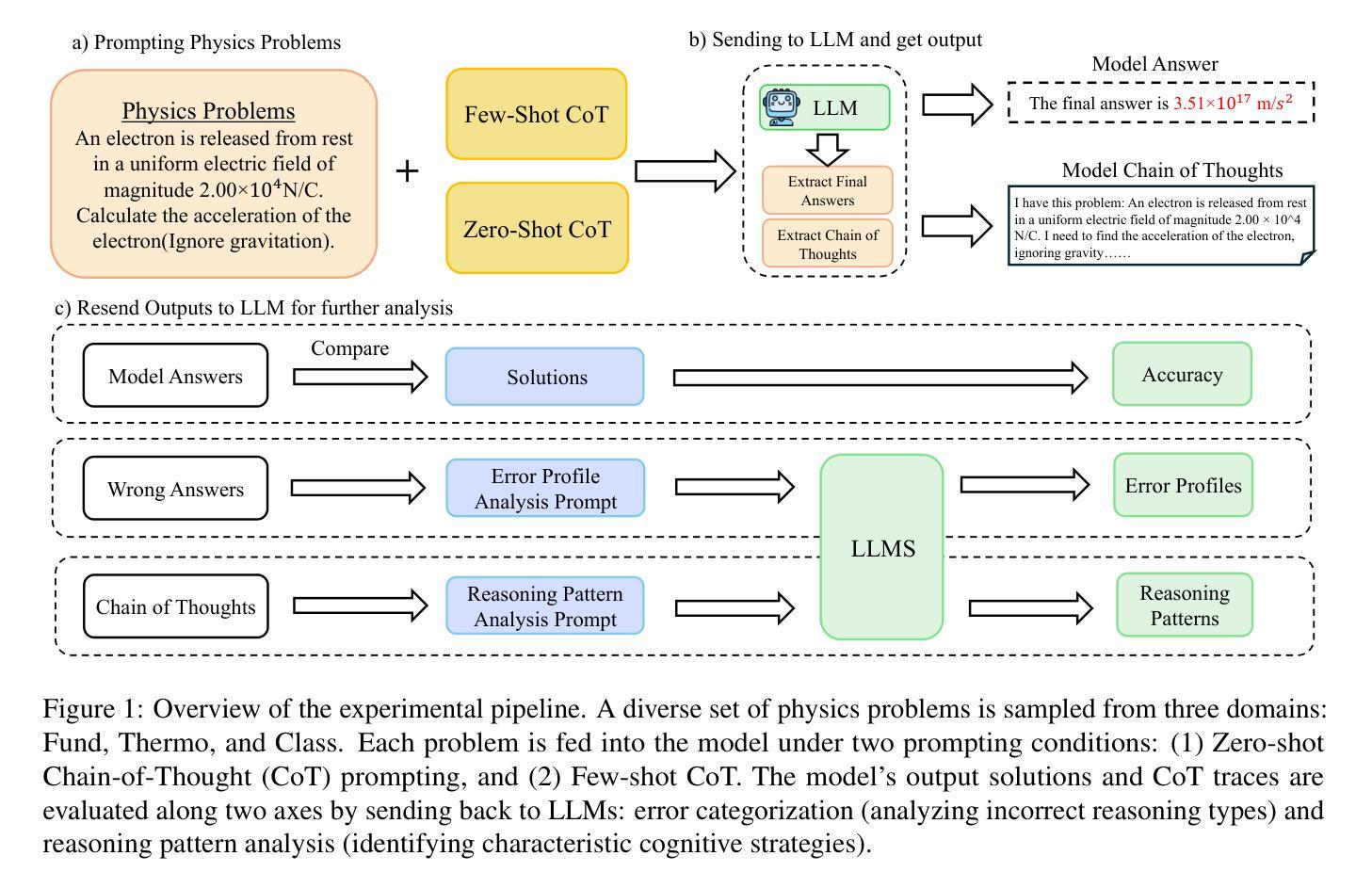
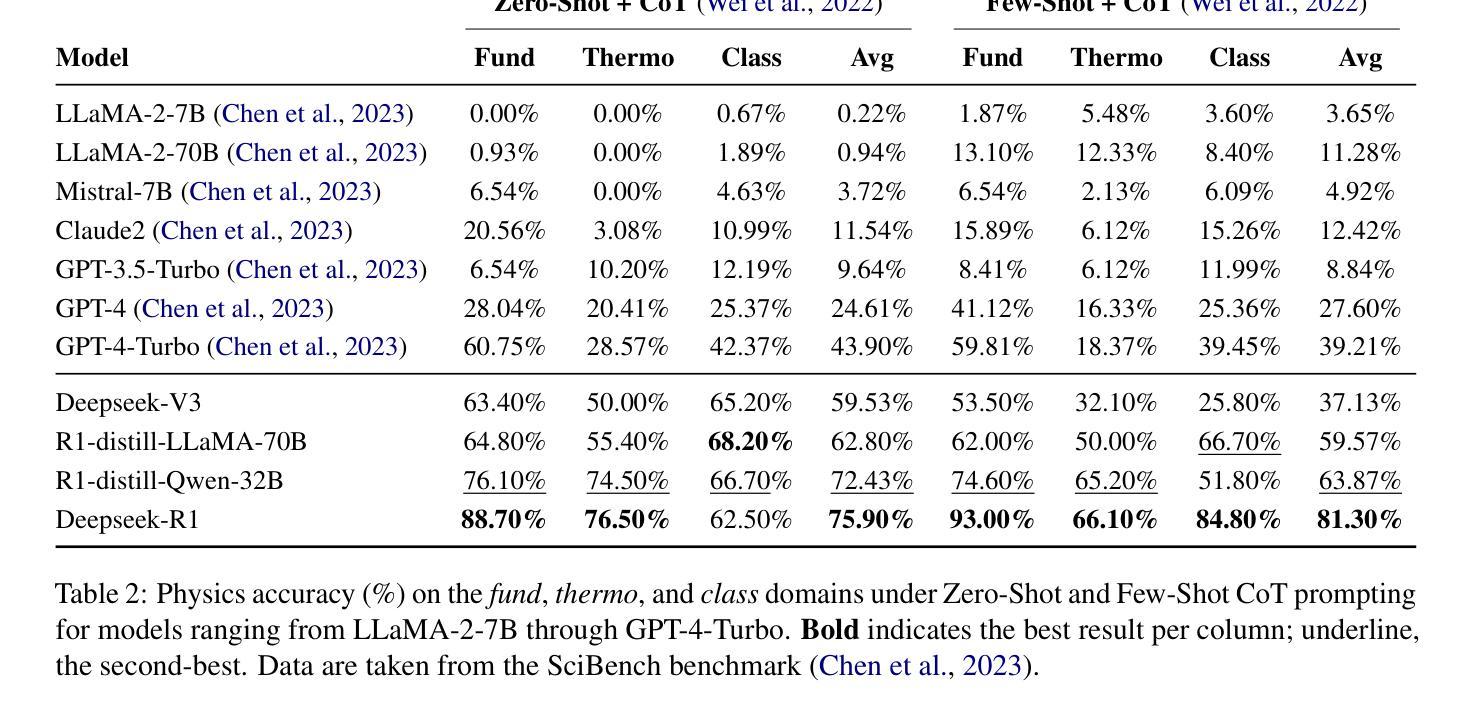
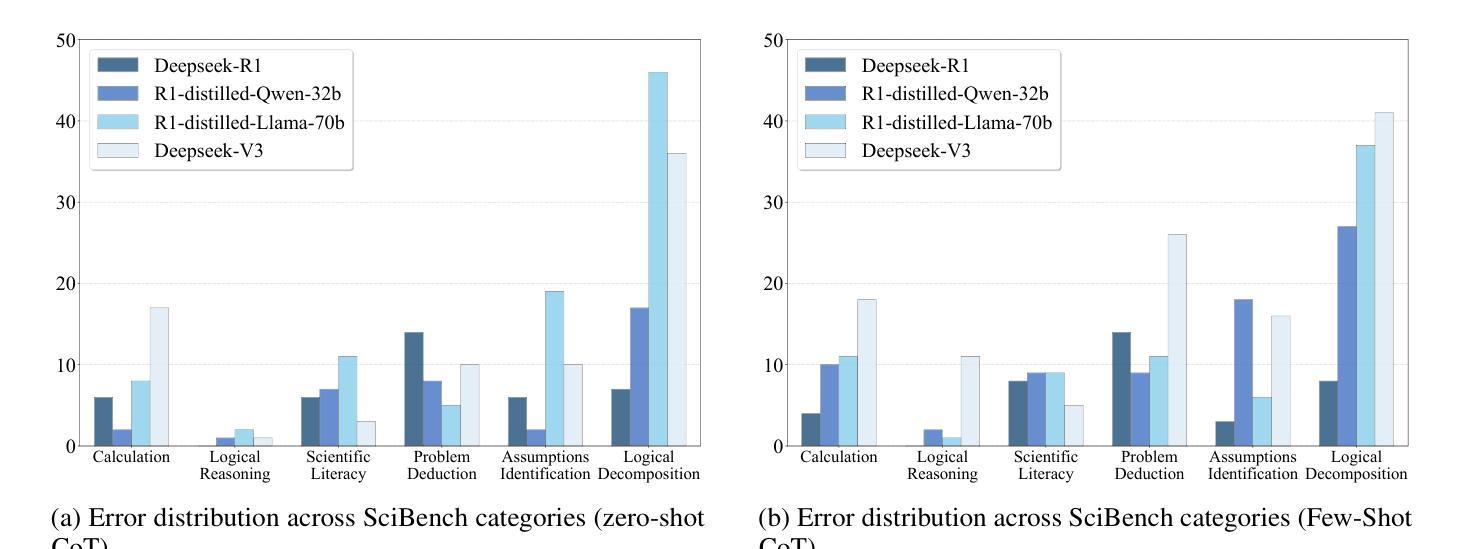
Symbolic or Numerical? Understanding Physics Problem Solving in Reasoning LLMs
Authors:Nifu Dan, Yujun Cai, Yiwei Wang
Navigating the complexities of physics reasoning has long been a difficult task for Large Language Models (LLMs), requiring a synthesis of profound conceptual understanding and adept problem-solving techniques. In this study, we investigate the application of advanced instruction-tuned reasoning models, such as Deepseek-R1, to address a diverse spectrum of physics problems curated from the challenging SciBench benchmark. Our comprehensive experimental evaluation reveals the remarkable capabilities of reasoning models. Not only do they achieve state-of-the-art accuracy in answering intricate physics questions, but they also generate distinctive reasoning patterns that emphasize on symbolic derivation. Furthermore, our findings indicate that even for these highly sophisticated reasoning models, the strategic incorporation of few-shot prompting can still yield measurable improvements in overall accuracy, highlighting the potential for continued performance gains.
长期以来,对于大型语言模型(LLM)来说,应对复杂的物理推理是一项艰巨的任务,它要求有深刻的概念理解和熟练的问题解决技巧的综合应用。在这项研究中,我们研究了先进指令调优推理模型(如Deepseek-R1)在应对从具有挑战性的SciBench基准测试中精选出的各种物理问题时的应用。我们的综合实验评估展示了推理模型的卓越能力。这些模型不仅在回答复杂物理问题时达到了最先进的准确性,而且产生了强调符号推导的独特推理模式。此外,我们的研究还发现,即使是对于这些高度复杂的推理模型,通过战略性地融入少量提示(few-shot prompting),仍然可以提高总体准确性,这突显了未来性能提升的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究探讨了先进的指令调优推理模型(如Deepseek-R1)在解决一系列来自SciBench基准测试的物理问题时的应用。实验表明,这些模型不仅在回答复杂物理问题方面达到了最新技术水平,还展现出独特的强调符号推导的推理模式。此外,研究还发现,即使是这些高度复杂的推理模型,通过战略性地引入少量提示,仍可实现总体准确性的显著提高,显示出潜在的性能提升空间。
Key Takeaways
- 先进的指令调优推理模型在解决物理问题方面表现出卓越的能力。
- 这些模型能够通过符号推导来强调独特的推理模式。
- 在高度复杂的推理模型中,通过引入少量提示,可以显著提高总体准确性。
- 这些模型在回答复杂物理问题时达到了最新技术水平。
- 研究表明,持续的性能提升具有潜在可能性。
- Deepseek-R1等模型在物理问题解答方面具有广泛应用前景。
点此查看论文截图

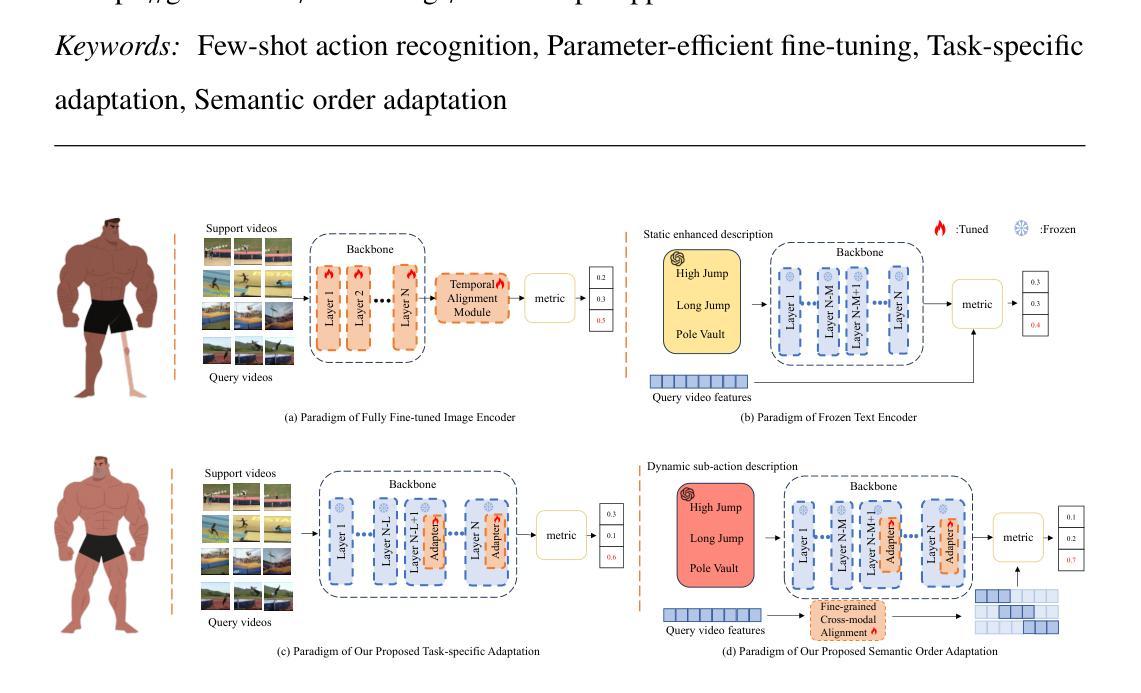
Task-Adapter++: Task-specific Adaptation with Order-aware Alignment for Few-shot Action Recognition
Authors:Congqi Cao, Peiheng Han, Yueran zhang, Yating Yu, Qinyi Lv, Lingtong Min, Yanning zhang
Large-scale pre-trained models have achieved remarkable success in language and image tasks, leading an increasing number of studies to explore the application of pre-trained image models, such as CLIP, in the domain of few-shot action recognition (FSAR). However, current methods generally suffer from several problems: 1) Direct fine-tuning often undermines the generalization capability of the pre-trained model; 2) The exploration of task-specific information is insufficient in the visual tasks; 3) The semantic order information is typically overlooked during text modeling; 4) Existing cross-modal alignment techniques ignore the temporal coupling of multimodal information. To address these, we propose Task-Adapter++, a parameter-efficient dual adaptation method for both image and text encoders. Specifically, to make full use of the variations across different few-shot learning tasks, we design a task-specific adaptation for the image encoder so that the most discriminative information can be well noticed during feature extraction. Furthermore, we leverage large language models (LLMs) to generate detailed sequential sub-action descriptions for each action class, and introduce semantic order adapters into the text encoder to effectively model the sequential relationships between these sub-actions. Finally, we develop an innovative fine-grained cross-modal alignment strategy that actively maps visual features to reside in the same temporal stage as semantic descriptions. Extensive experiments fully demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed method, which achieves state-of-the-art performance on 5 benchmarks consistently. The code is open-sourced at https://github.com/Jaulin-Bage/Task-Adapter-pp.
大规模预训练模型在语言和图像任务中取得了显著的成功,引发越来越多的研究探索预训练图像模型,如CLIP,在少样本动作识别(FSAR)领域的应用。然而,当前的方法普遍存在以下问题:1)直接微调往往会削弱预训练模型的泛化能力;2)视觉任务中特定任务信息的探索不足;3)文本建模时通常忽略了语义顺序信息;4)现有的跨模态对齐技术忽略了多模态信息的时序耦合。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了Task-Adapter++,这是一种参数高效的图像和文本编码器的双重适应方法。具体来说,为了充分利用不同少样本学习任务之间的差异,我们为图像编码器设计了特定任务的适应方法,以便在特征提取过程中充分注意到最具区分性的信息。此外,我们利用大型语言模型(LLM)为每个动作类别生成详细的序列子动作描述,并在文本编码器中引入语义顺序适配器,以有效地建模这些子动作之间的序列关系。最后,我们开发了一种创新的精细跨模态对齐策略,该策略能够主动将视觉特征映射到与语义描述相同的时序阶段。大量的实验充分证明了所提方法的有效性和优越性,该方法在5个基准测试上均达到了最新性能水平。代码已开源在https://github.com/Jaulin-Bage/Task-Adapter-pp。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF extended work of Task-Adapter
Summary
大规模预训练模型在语言和图像任务中取得了显著的成功,引发了对预训练图像模型如CLIP在少镜头动作识别(FSAR)领域应用的探索。针对现有方法存在的问题,如直接微调影响模型泛化能力、视觉任务中特定信息探索不足、文本建模时忽略语义顺序信息以及跨模态对齐技术忽略多模态信息的时序耦合等,我们提出了Task-Adapter++,一种参数高效的图像和文本编码器的双重适应方法。该方法通过设计任务特定适应的图像编码器,利用大型语言模型生成每个动作类的详细序列子动作描述,并在文本编码器中引入语义顺序适配器,有效建模这些子动作之间的序列关系。此外,我们开发了一种创新的精细跨模态对齐策略,积极将视觉特征映射到与语义描述相同的时序阶段。该方法在五个基准测试上均达到了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 大规模预训练模型在语言和图像任务中表现出色,推动了少镜头动作识别(FSAR)领域的研究。
- 当前方法存在直接微调影响模型泛化能力、视觉任务中特定信息探索不足等问题。
- Task-Adapter++是一种参数高效的图像和文本编码器的双重适应方法,旨在解决这些问题。
- 该方法利用大型语言模型生成每个动作类的详细序列子动作描述。
- Task-Adapter++引入了语义顺序适配器,以有效建模子动作之间的序列关系。
- 开发了一种创新的精细跨模态对齐策略,实现视觉特征和语义描述的积极映射。
- 该方法在五个基准测试上均达到了最先进的性能,并公开了代码。
点此查看论文截图

Optimal strategies to perform multilingual analysis of social content for a novel dataset in the tourism domain
Authors:Maxime Masson, Rodrigo Agerri, Christian Sallaberry, Marie-Noelle Bessagnet, Annig Le Parc Lacayrelle, Philippe Roose
The rising influence of social media platforms in various domains, including tourism, has highlighted the growing need for efficient and automated Natural Language Processing (NLP) strategies to take advantage of this valuable resource. However, the transformation of multilingual, unstructured, and informal texts into structured knowledge still poses significant challenges, most notably the never-ending requirement for manually annotated data to train deep learning classifiers. In this work, we study different NLP techniques to establish the best ones to obtain competitive performances while keeping the need for training annotated data to a minimum. To do so, we built the first publicly available multilingual dataset (French, English, and Spanish) for the tourism domain, composed of tourism-related tweets. The dataset includes multilayered, manually revised annotations for Named Entity Recognition (NER) for Locations and Fine-grained Thematic Concepts Extraction mapped to the Thesaurus of Tourism and Leisure Activities of the World Tourism Organization, as well as for Sentiment Analysis at the tweet level. Extensive experimentation comparing various few-shot and fine-tuning techniques with modern language models demonstrate that modern few-shot techniques allow us to obtain competitive results for all three tasks with very little annotation data: 5 tweets per label (15 in total) for Sentiment Analysis, 30 tweets for Named Entity Recognition of Locations and 1K tweets annotated with fine-grained thematic concepts, a highly fine-grained sequence labeling task based on an inventory of 315 classes. We believe that our results, grounded in a novel dataset, pave the way for applying NLP to new domain-specific applications, reducing the need for manual annotations and circumventing the complexities of rule-based, ad-hoc solutions.
随着社交媒体平台在包括旅游在内的各个领域影响力的不断提升,高效且自动化的自然语言处理(NLP)策略的需求也日益增长,以便充分利用这一宝贵资源。然而,将多语言、非结构化和非正式文本转化为结构化知识仍然面临重大挑战,其中最显著的是对用于训练深度学习分类器的手动注释数据的无止境需求。在这项工作中,我们研究了不同的NLP技术,以找出表现最佳的方案,同时尽量减少对训练注释数据的依赖。为此,我们构建了首个面向旅游领域的公开可用多语言数据集(包括法语、英语和西班牙语),数据集由旅游相关的推文组成。该数据集包含针对地点命名实体识别(NER)的分层手动修订注释,以及精细主题概念提取映射到世界旅游组织休闲活动词典的注释,还有推文级别的情感分析注释。通过广泛实验比较各种少样本和微调技术与现代语言模型,结果表明现代少样本技术只需很少量的注释数据即可在所有三项任务中获得具有竞争力的结果:情感分析仅需每标签5条推文(总计1s条),地点命名实体识别需要30条推文,而基于精细概念集的序列标注任务则需要精细粒度注释的1K条推文(共包含315个类别)。我们相信,基于新数据集的结果为将NLP应用于新的特定领域应用铺平了道路,减少了对手动注释的需求,避免了基于规则的临时解决方案的复杂性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了社交媒体平台在旅游等领域的影响日益突出背景下,如何利用高效的自然语言处理(NLP)策略实现旅游领域的多语种数据的有效利用。为了解决如何从多元、非结构化及非正式文本中提炼结构化知识的问题,研究建立了一个涵盖旅游相关的多元数据集,通过对比不同的NLP技术发现现代少数学习技巧只需极少的人工标注数据即可实现优秀的表现。本研究为将NLP应用于新的领域特定应用提供了可能,减少了人工标注的需求,避免了基于规则和临时解决方案的复杂性。
Key Takeaways
- 社会媒体平台对旅游等领域的影响力增长,凸显了需要有效的自然语言处理策略。
- 当前从多语种、非结构化及非正式文本中转化结构知识是一大挑战。
- 研究建立了首个针对旅游领域的多语种数据集,包含地点命名实体识别、精细主题概念提取和情绪分析。
- 利用现代少数学习技巧在极少人工标注数据下取得出色的表现。如情感分析仅需要五个标注数据点,地点命名实体识别需要三十个标注数据点,精细主题概念提取则需要一千个标注数据点。
点此查看论文截图