⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-05 更新
LocalDyGS: Multi-view Global Dynamic Scene Modeling via Adaptive Local Implicit Feature Decoupling
Authors:Jiahao Wu, Rui Peng, Jianbo Jiao, Jiayu Yang, Luyang Tang, Kaiqiang Xiong, Jie Liang, Jinbo Yan, Runling Liu, Ronggang Wang
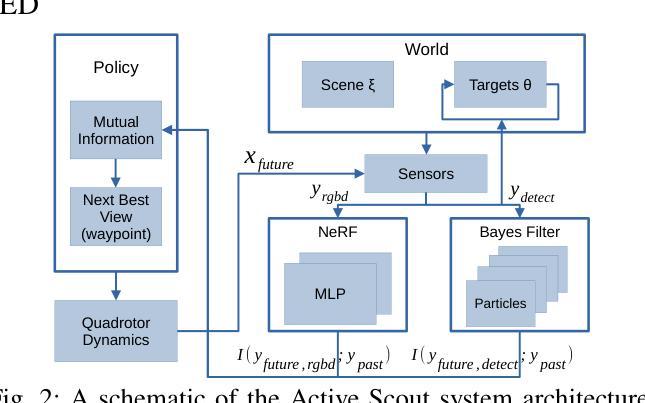
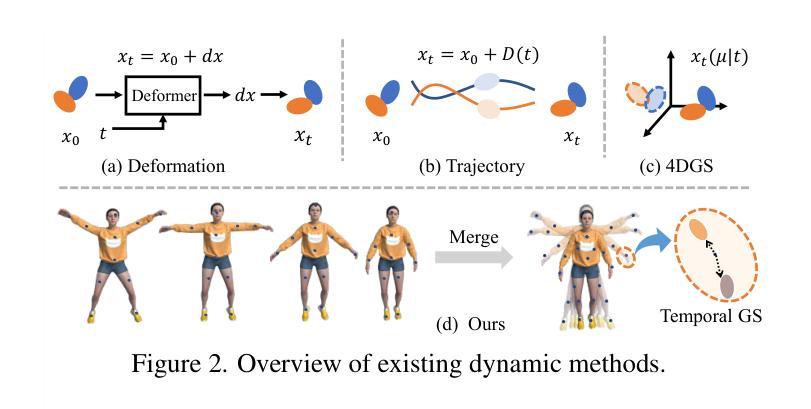
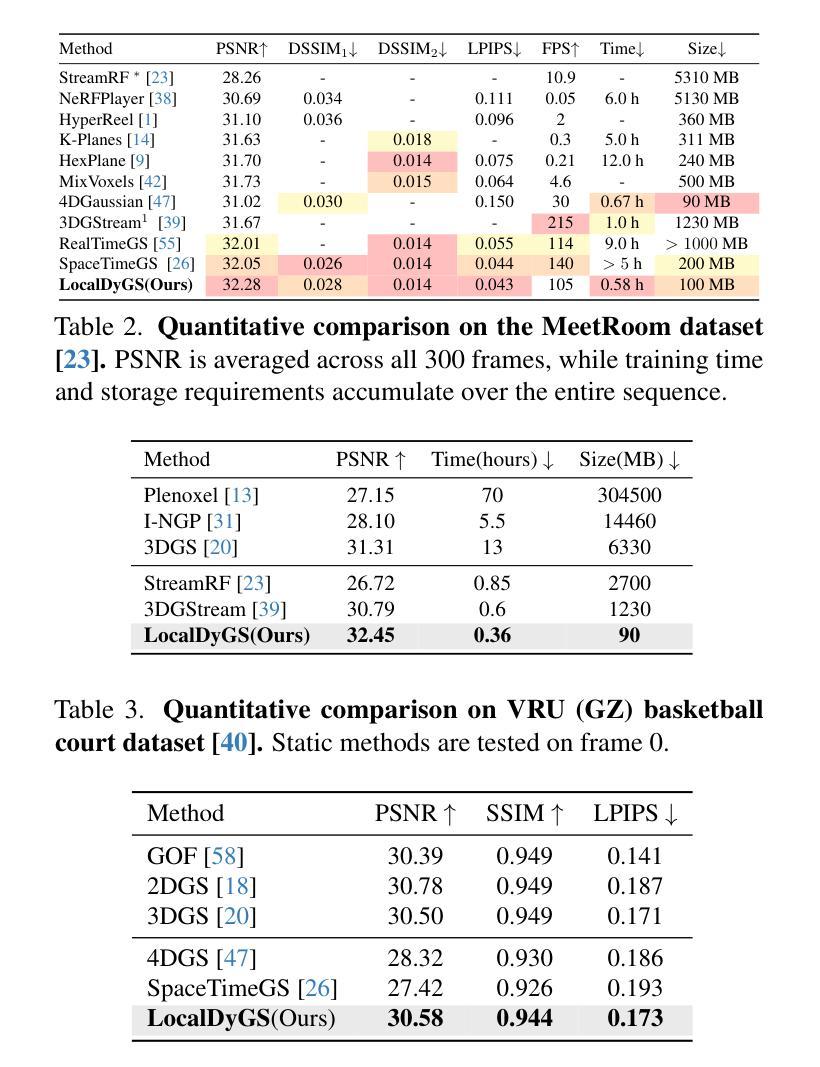
Due to the complex and highly dynamic motions in the real world, synthesizing dynamic videos from multi-view inputs for arbitrary viewpoints is challenging. Previous works based on neural radiance field or 3D Gaussian splatting are limited to modeling fine-scale motion, greatly restricting their application. In this paper, we introduce LocalDyGS, which consists of two parts to adapt our method to both large-scale and fine-scale motion scenes: 1) We decompose a complex dynamic scene into streamlined local spaces defined by seeds, enabling global modeling by capturing motion within each local space. 2) We decouple static and dynamic features for local space motion modeling. A static feature shared across time steps captures static information, while a dynamic residual field provides time-specific features. These are combined and decoded to generate Temporal Gaussians, modeling motion within each local space. As a result, we propose a novel dynamic scene reconstruction framework to model highly dynamic real-world scenes more realistically. Our method not only demonstrates competitive performance on various fine-scale datasets compared to state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods, but also represents the first attempt to model larger and more complex highly dynamic scenes. Project page: https://wujh2001.github.io/LocalDyGS/.
由于现实世界中存在复杂且高度动态的运动,从多视角输入合成任意视角的动态视频是一项挑战。之前基于神经辐射场或3D高斯涂抹的工作仅限于对精细动作的建模,极大地限制了其应用。在本文中,我们介绍了LocalDyGS,它由两部分组成,使我们的方法能够适应大规模和精细动作的场景:1)我们将复杂的动态场景分解为由种子定义的流线型局部空间,通过捕捉每个局部空间内的运动来实现全局建模。2)我们将静态和动态特征解耦,以进行局部空间运动建模。跨时间步长共享的静态特征捕捉静态信息,而动态残差场则提供特定时间的特征。这些特征被结合并解码以生成时间高斯,对每个局部空间内的运动进行建模。因此,我们提出了一种新的动态场景重建框架,以更真实的方式对高度动态的现实世界场景进行建模。我们的方法不仅在各种精细数据集上表现出与最新技术相竞争的性能,而且还首次尝试对更大、更复杂的高度动态场景进行建模。项目页面:https://wujh2001.github.io/LocalDyGS/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025
Summary
本文提出了LocalDyGS方法,用于从多视角输入中合成动态视频,并能任意改变视角。针对复杂且高度动态的运动场景,该方法通过分解场景为局部空间并捕捉每个局部空间内的运动,实现了全局建模,同时解决了对精细运动场景的建模限制。该方法包含两部分:一是以种子定义流线型局部空间,二是将静态和动态特征解耦以进行局部空间运动建模。静态特征用于捕捉场景静态信息,而动态残差场提供时间相关特征。最后通过组合这两部分生成模拟真实场景动态的临时高斯模型。相较于其他方法,LocalDyGS不仅在精细数据集上表现出竞争性能,更首次尝试处理更大且更复杂的高度动态场景。详情可见项目页面。
Key Takeaways
- LocalDyGS方法解决了从多视角输入合成动态视频并任意改变视角的难题。
- 该方法通过将复杂动态场景分解为局部空间进行全局建模。
- 通过解耦静态和动态特征进行局部空间运动建模。
- 使用静态特征捕捉场景静态信息,并用动态残差场模拟时间相关特征。
- 结合静态和动态特征生成临时高斯模型,以模拟真实场景的动态特性。
- LocalDyGS在精细数据集上表现出优秀的性能,且首次尝试处理更大、更复杂的高度动态场景。
点此查看论文截图


Improving GANs by leveraging the quantum noise from real hardware
Authors:Hongni Jin, Kenneth M. Merz Jr
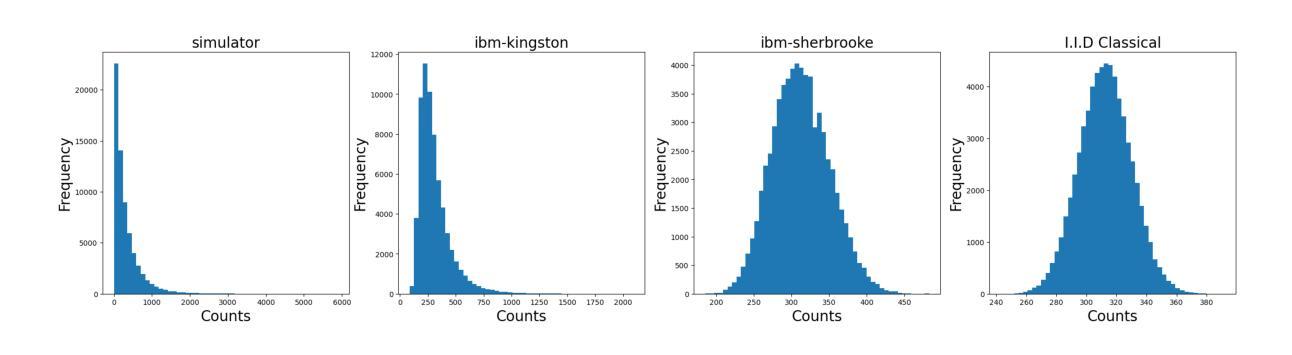
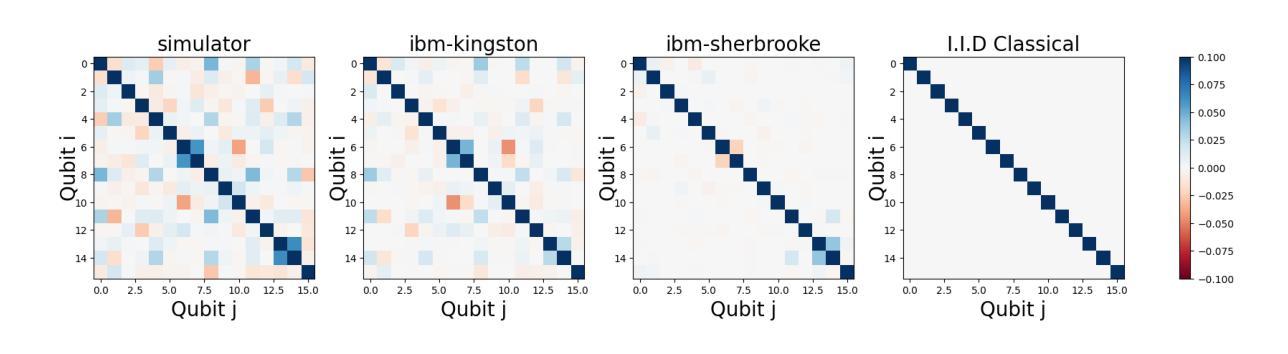
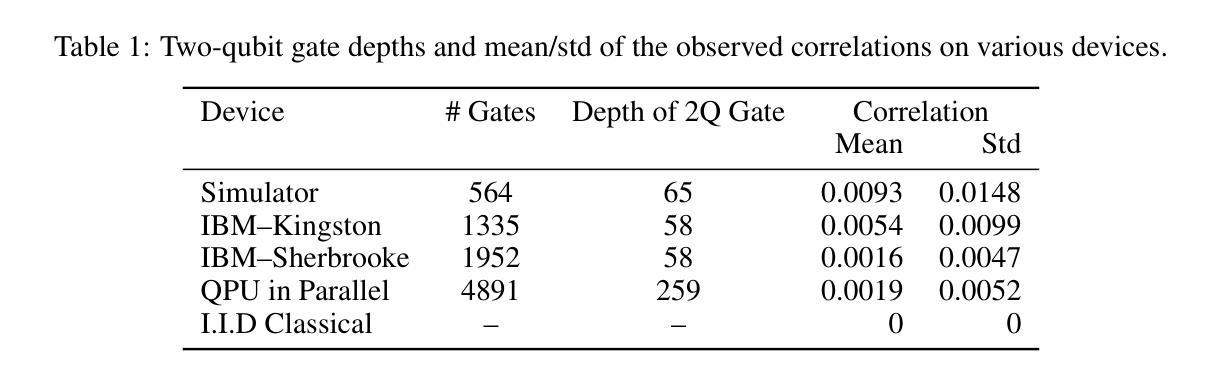
We propose a novel approach to generative adversarial networks (GANs) in which the standard i.i.d. Gaussian latent prior is replaced or hybridized with a quantum-correlated prior derived from measurements of a 16-qubit entangling circuit. Each latent sample is generated by grouping repeated shots per qubit into a binary fraction, applying the inverse Gaussian CDF to obtain a 16-dimensional Gaussian vector whose joint copula reflects genuine quantum entanglement, and then projecting into the high-dimensional space via a fixed random matrix. By pre-sampling tens of millions of bitstrings, either from a noiseless simulator or from IBM hardware, we build large pools of independent but internally quantum-correlated latents. We integrate this prior into three representative architectures (WGAN, SNGAN, BigGAN) on CIFAR-10, making no changes to the neural network structure or training hyperparameters. The hybrid latent representations incorporating hardware-derived noise consistently lower the FID relative to both the classical baseline and the simulator variant, especially when the quantum component constitutes a substantial fraction of the prior. In addition, we execute on the QPU in parallel to not only save computing time but also further decrease the FID up to 17% in BigGAN. These results indicate that intrinsic quantum randomness and device-specific imperfections can provide a structured inductive bias that enhances GAN performance. Our work demonstrates a practical pipeline for leveraging noisy quantum hardware to enrich deep-generative modeling, opening a new interface between quantum information and machine learning. All code and data are available at https://github.com/Neon8988/GAN_QN.git.
我们提出了一种新的生成对抗网络(GAN)方法,该方法将标准的独立同分布(i.i.d.)高斯潜在先验替换或混合为来源于一个由量子纠缠电路测量得到的量子相关先验。每个潜在样本是通过将每个量子比特的重复测量组合成二进制分数来生成的,然后应用逆高斯累积分布函数来得到反映真实量子纠缠关系的多维高斯向量,并通过固定的随机矩阵投影到高维空间中。通过从无噪声模拟器或IBM硬件进行数以万计的位串预采样,我们建立了大量独立但内部量子相关的潜在样本池。我们将这种先验知识应用于CIFAR-10数据集上的三种代表性架构(WGAN、SNGAN、BigGAN),并未对神经网络结构或训练超参数进行任何更改。融入硬件衍生噪声的混合潜在表示形式相对于经典基准和模拟器变体始终降低了FID得分,特别是在量子成分构成先验很大一部分时更是如此。此外,我们在量子处理器上并行执行,不仅节省了计算时间,而且在BigGAN中将FID进一步降低了高达17%。这些结果表明,内在量子随机性和设备特定的缺陷可以提供一种结构化的归纳偏置,从而提高GAN的性能。我们的工作展示了一个利用噪声量子硬件丰富深度生成建模的实际流程,为量子信息和机器学习之间打开了新的接口。所有代码和数据都可在https://github.com/Neon8988/GAN_QN.git获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该研究提出了一种新颖的方法,将量子相关先验引入生成对抗网络(GANs)。该方法利用量子纠缠电路的测量结果,构建量子相关先验,替换或混合标准独立同分布的高斯潜在先验。研究者在CIFAR-10数据集上对三种具有代表性的架构进行了实践,证明新方法与经典方法和模拟器版本相比,降低了Frechet Inception Distance (FID)。此外,研究在量子脉冲单元(QPU)上执行并行操作,以节省计算时间并进一步提高FID。此研究展示了利用噪声量子硬件丰富深度生成建模的实用管道,为量子信息和机器学习之间开辟了新的接口。
Key Takeaways
- 研究提出了一种新颖的GAN方法,将量子相关先验引入GANs中。
- 利用量子纠缠电路测量结果构建量子相关先验。
- 对三种具有代表性的架构进行了实践,在CIFAR-10数据集上降低FID。
- 使用预采样大量独立但内部具有量子关联潜伏的方法构建潜伏期池。
- 在量子脉冲单元上执行并行操作以提高效率并进一步提高FID。
- 研究展示了利用噪声量子硬件丰富深度生成建模的实用管道。
点此查看论文截图

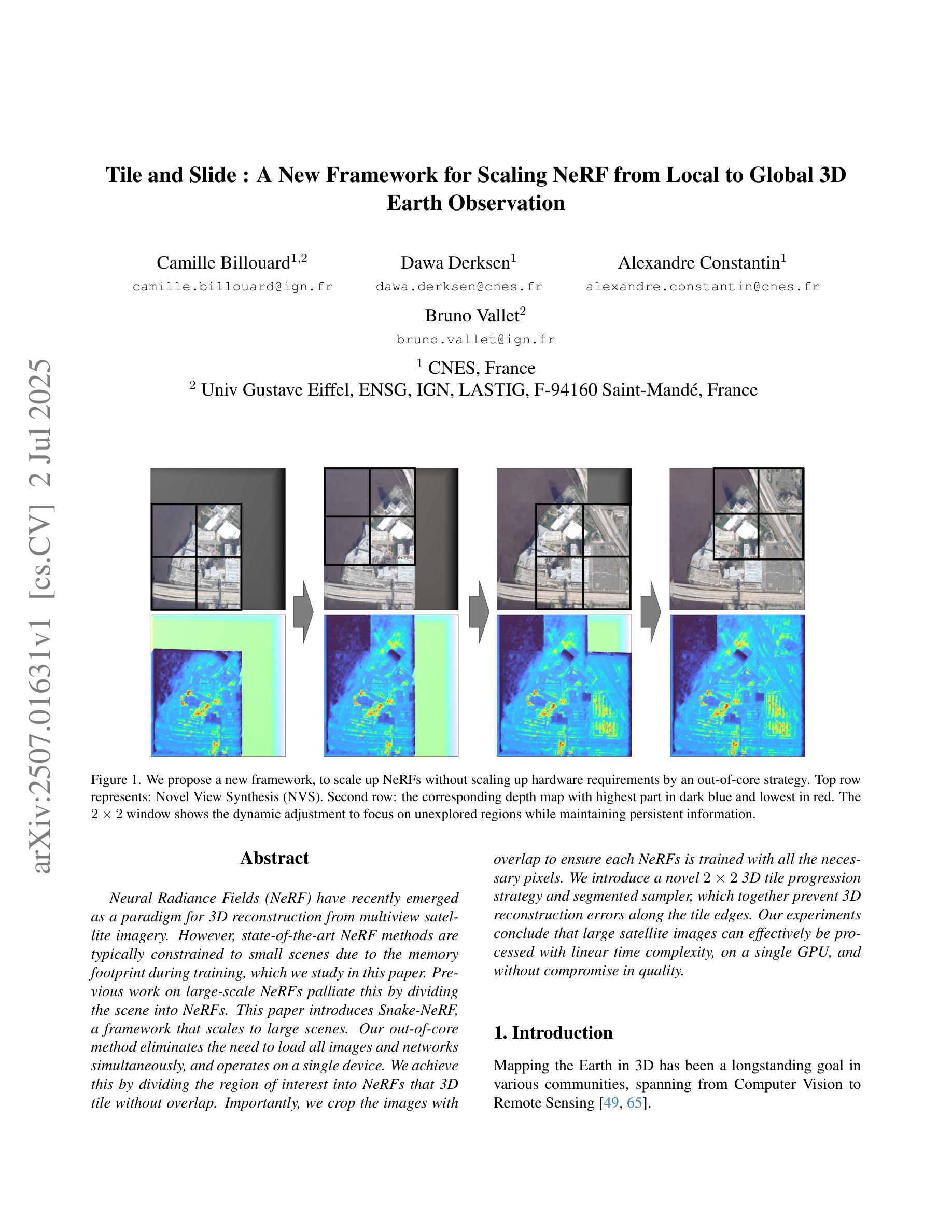
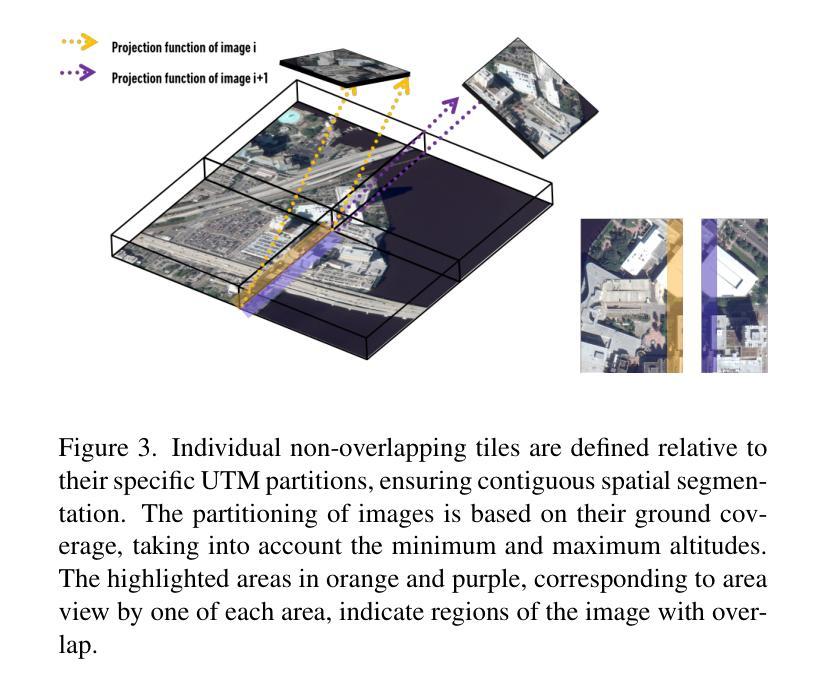
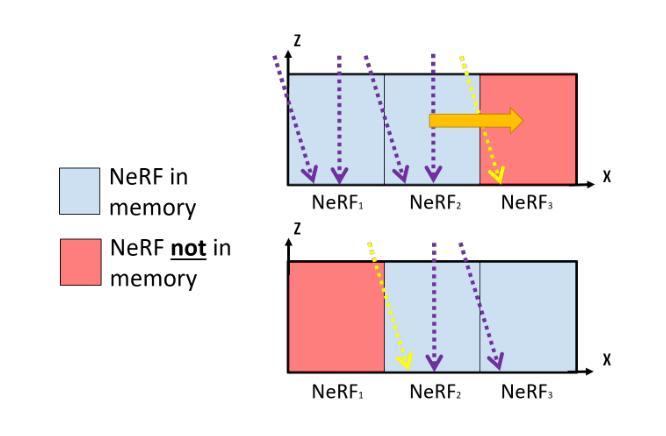
Tile and Slide : A New Framework for Scaling NeRF from Local to Global 3D Earth Observation
Authors:Camille Billouard, Dawa Derksen, Alexandre Constantin, Bruno Vallet
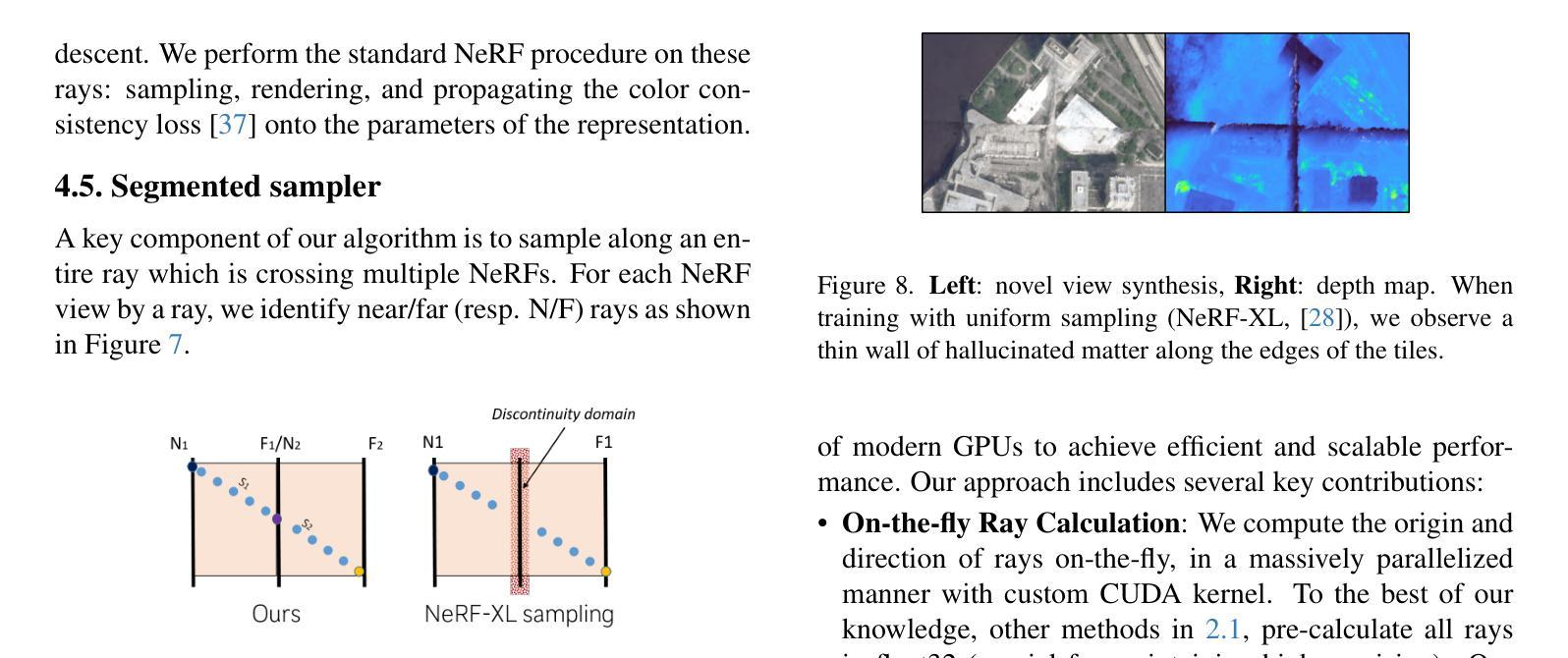
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have recently emerged as a paradigm for 3D reconstruction from multiview satellite imagery. However, state-of-the-art NeRF methods are typically constrained to small scenes due to the memory footprint during training, which we study in this paper. Previous work on large-scale NeRFs palliate this by dividing the scene into NeRFs. This paper introduces Snake-NeRF, a framework that scales to large scenes. Our out-of-core method eliminates the need to load all images and networks simultaneously, and operates on a single device. We achieve this by dividing the region of interest into NeRFs that 3D tile without overlap. Importantly, we crop the images with overlap to ensure each NeRFs is trained with all the necessary pixels. We introduce a novel $2\times 2$ 3D tile progression strategy and segmented sampler, which together prevent 3D reconstruction errors along the tile edges. Our experiments conclude that large satellite images can effectively be processed with linear time complexity, on a single GPU, and without compromise in quality.
神经辐射场(NeRF)最近已经发展成为一种从多角度卫星图像进行三维重建的范例。然而,最先进的NeRF方法通常受限于小场景,因为训练过程中的内存占用较大,本文对此进行了研究。之前关于大规模NeRF的工作通过将场景划分为NeRF来缓解这一问题。本文介绍了Snake-NeRF框架,该框架可以扩展到大规模场景。我们的外部核心方法消除了需要同时加载所有图像和网络的需求,并在单个设备上运行。我们通过将感兴趣区域划分为没有重叠的NeRF来实现这一点,这些NeRF以三维形式平铺场景。重要的是,我们裁剪了重叠的图像,以确保每个NeRF都能使用所有必要的像素进行训练。我们引入了一种新颖的$2\times 2$三维平铺进展策略和分段采样器,这两者相结合,防止了平铺边缘处的三维重建错误。我们的实验得出结论,可以在单个GPU上以线性时间复杂度有效地处理大型卫星图像,而不会牺牲质量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICCV 2025 Workshop 3D-VAST (From street to space: 3D Vision Across Altitudes). Version before camera ready. Our code will be made public after the conference
摘要
NeRF技术已逐渐成为从多视角卫星图像进行3D重建的一种范例。但当前最先进的NeRF方法通常受限于训练时的内存占用,无法应用于大场景。本文提出了Snake-NeRF框架,该框架可以扩展到大场景。通过一种称为“出核”的方法,Snake-NeRF无需同时加载所有图像和网络,可在单个设备上运行。通过将感兴趣区域划分为无重叠的NeRF进行3D平铺来实现这一点。为了确保每个NeRF都能训练到所有必要的像素,我们采用了一种新颖的裁剪图像重叠的策略。我们还引入了一种新颖的$2\times 2$的3D平铺进展策略和分段采样器,它们共同防止了瓷砖边缘的3D重建错误。实验表明,使用单GPU处理大型卫星图像可实现线性时间复杂度,且不会降低质量。
要点摘要
- NeRF技术已成为从多视角卫星图像进行3D重建的重要方法,但受限于内存占用无法应用于大场景。
- Snake-NeRF框架通过“出核”方法解决此问题,可在单个设备上运行,无需同时加载所有图像和网络。
- Snake-NeRF通过将感兴趣区域划分为无重叠的NeRF进行3D平铺来实现扩展到大场景。
- 采用裁剪图像重叠的策略确保每个NeRF都能训练到所有必要的像素。
- 引入新颖的$2\times 2$的3D平铺进展策略和分段采样器,防止瓷砖边缘的3D重建错误。
- 实验证明,使用单GPU处理大型卫星图像的时间复杂度为线性,且不会降低质量。
- Snake-NeRF为处理大场景卫星图像的3D重建提供了新的可能性。
点此查看论文截图

PlantSegNeRF: A few-shot, cross-dataset method for plant 3D instance point cloud reconstruction via joint-channel NeRF with multi-view image instance matching
Authors:Xin Yang, Ruiming Du, Hanyang Huang, Jiayang Xie, Pengyao Xie, Leisen Fang, Ziyue Guo, Nanjun Jiang, Yu Jiang, Haiyan Cen
Organ segmentation of plant point clouds is a prerequisite for the high-resolution and accurate extraction of organ-level phenotypic traits. Although the fast development of deep learning has boosted much research on segmentation of plant point clouds, the existing techniques for organ segmentation still face limitations in resolution, segmentation accuracy, and generalizability across various plant species. In this study, we proposed a novel approach called plant segmentation neural radiance fields (PlantSegNeRF), aiming to directly generate high-precision instance point clouds from multi-view RGB image sequences for a wide range of plant species. PlantSegNeRF performed 2D instance segmentation on the multi-view images to generate instance masks for each organ with a corresponding ID. The multi-view instance IDs corresponding to the same plant organ were then matched and refined using a specially designed instance matching module. The instance NeRF was developed to render an implicit scene, containing color, density, semantic and instance information. The implicit scene was ultimately converted into high-precision plant instance point clouds based on the volume density. The results proved that in semantic segmentation of point clouds, PlantSegNeRF outperformed the commonly used methods, demonstrating an average improvement of 16.1%, 18.3%, 17.8%, and 24.2% in precision, recall, F1-score, and IoU compared to the second-best results on structurally complex datasets. More importantly, PlantSegNeRF exhibited significant advantages in plant point cloud instance segmentation tasks. Across all plant datasets, it achieved average improvements of 11.7%, 38.2%, 32.2% and 25.3% in mPrec, mRec, mCov, mWCov, respectively. This study extends the organ-level plant phenotyping and provides a high-throughput way to supply high-quality 3D data for the development of large-scale models in plant science.
植物点云器官分割是高分辨率和准确提取器官水平表型特征的前提。尽管深度学习的快速发展推动了植物点云分割的研究,但现有的器官分割技术在分辨率、分割精度和跨物种泛化能力方面仍存在局限性。本研究提出了一种名为PlantSegNeRF的新方法,旨在直接从多视角RGB图像序列生成高精度实例点云,适用于广泛的植物物种。PlantSegNeRF对多视角图像进行2D实例分割,为每个器官生成具有相应ID的实例掩膜。然后,使用专门设计的实例匹配模块对对应于同一植物器官的多视角实例ID进行匹配和细化。开发了实例NeRF来呈现包含颜色、密度、语义和实例信息的隐式场景。最终,基于体积密度将隐式场景转换为高精度植物实例点云。结果证明,在点云语义分割中,PlantSegNeRF优于常用方法,在结构复杂的数据集上,精度、召回率、F1分数和IoU平均提高了16.1%、18.3%、17.8%和24.2%。更重要的是,PlantSegNeRF在植物点云实例分割任务中表现出显著优势。在所有植物数据集上,mPrec、mRec、mCov和mWCov平均提高了11.7%、38.2%、32.2%和25.3%。该研究扩展了植物表型学的器官水平研究,并为植物科学大规模模型开发提供了一种高通量、高质量3D数据供应方式。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一个名为PlantSegNeRF的新方法,用于直接生成高精确度的植物器官实例点云。该方法通过对多视角RGB图像序列进行二维实例分割,生成每个器官的实例掩模和对应ID。然后,使用专门设计的实例匹配模块匹配和细化同一植物器官的跨视角实例ID。进一步开发实例NeRF技术,渲染包含颜色、密度、语义和实例信息的隐场景,最终根据体积密度转换为高精度植物实例点云。在点云语义分割方面,PlantSegNeRF相较于常用方法表现出卓越性能,平均提升精度、召回率、F1分数和IoU分别为16.1%、18.3%、17.8%和24.2%。在植物点云实例分割任务中,PlantSegNeRF展现出显著优势,在所有植物数据集上平均提升mPrec、mRec、mCov和mWCov分别为11.7%、38.2%、32.2%和25.3%。该研究扩展了植物表型组学的器官层面应用,为植物科学的大规模模型开发提供高质量3D数据的高通量方式。
Key Takeaways
- PlantSegNeRF是一种用于植物点云实例分割的新方法,可直接生成高精确度植物器官实例点云。
- 该方法通过多视角RGB图像序列进行二维实例分割,并生成实例掩模和对应ID。
- PlantSegNeRF使用实例NeRF技术渲染包含多种信息的隐场景,并转换为点云。
- 在语义分割方面,PlantSegNeRF较常规方法有所提升,特别是在复杂结构数据集上。
- 在植物点云实例分割任务中,PlantSegNeRF展现出显著优势,适用于多种植物数据集。
- 该研究扩展了植物表型组学的应用,尤其是在器官层面。
点此查看论文截图

DeGauss: Dynamic-Static Decomposition with Gaussian Splatting for Distractor-free 3D Reconstruction
Authors:Rui Wang, Quentin Lohmeyer, Mirko Meboldt, Siyu Tang
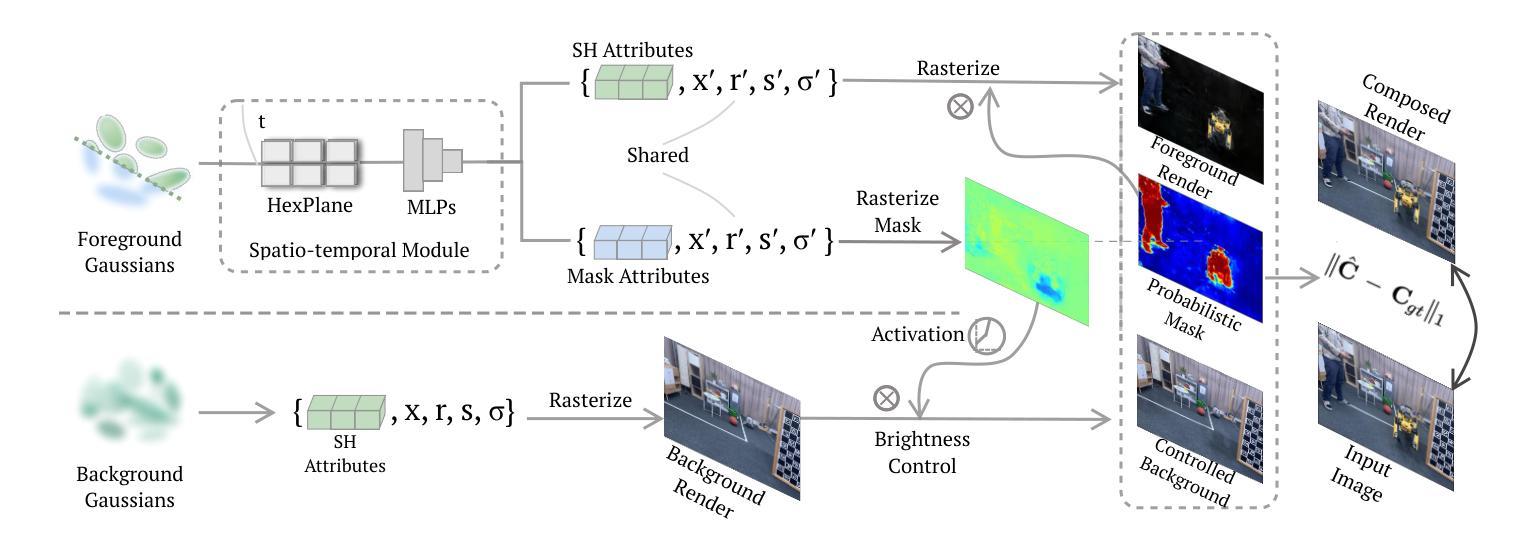
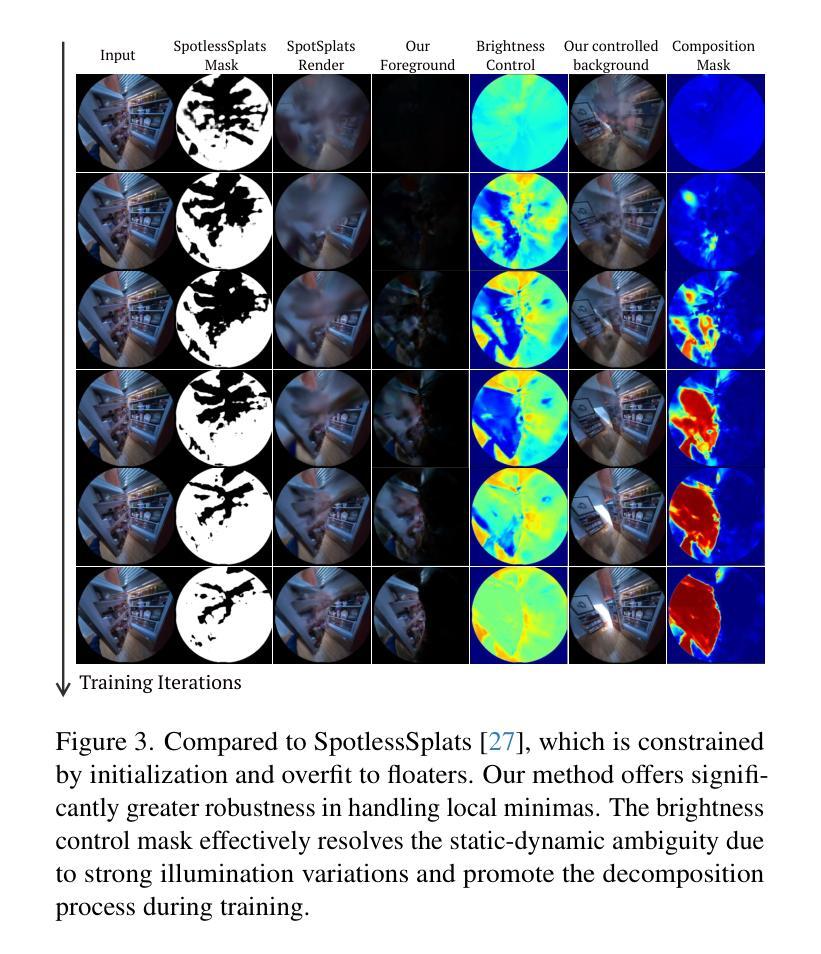
Reconstructing clean, distractor-free 3D scenes from real-world captures remains a significant challenge, particularly in highly dynamic and cluttered settings such as egocentric videos. To tackle this problem, we introduce DeGauss, a simple and robust self-supervised framework for dynamic scene reconstruction based on a decoupled dynamic-static Gaussian Splatting design. DeGauss models dynamic elements with foreground Gaussians and static content with background Gaussians, using a probabilistic mask to coordinate their composition and enable independent yet complementary optimization. DeGauss generalizes robustly across a wide range of real-world scenarios, from casual image collections to long, dynamic egocentric videos, without relying on complex heuristics or extensive supervision. Experiments on benchmarks including NeRF-on-the-go, ADT, AEA, Hot3D, and EPIC-Fields demonstrate that DeGauss consistently outperforms existing methods, establishing a strong baseline for generalizable, distractor-free 3D reconstructionin highly dynamic, interaction-rich environments. Project page: https://batfacewayne.github.io/DeGauss.io/
从真实世界的捕捉中重建干净、无干扰物的3D场景仍然是一个巨大的挑战,特别是在高度动态和杂乱的环境中,如第一人称视频。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了DeGauss,这是一个简单而稳健的自监督动态场景重建框架,基于解耦的动态静态高斯喷涂设计。DeGauss使用前景高斯对动态元素进行建模,使用背景高斯对静态内容进行建模,并使用概率掩膜来协调它们的组合,以实现独立但互补的优化。DeGauss在多种真实场景中都表现得非常稳健,从随意的图像集合到长的动态第一人称视频,无需依赖复杂的启发式方法或广泛的监督。在包括NeRF-on-the-go、ADT、AEA、Hot3D和EPIC-Fields等多个基准测试上的实验表明,DeGauss始终优于现有方法,为高度动态、交互丰富的环境中的通用、无干扰物3D重建建立了强大的基线。项目页面:https://batfacewayne.github.io/DeGauss.io/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025
Summary
本文介绍了DeGauss,一种基于动态静态高斯涂抹技术的简单而稳健的自监督动态场景重建框架。它通过前景高斯模型模拟动态元素,背景高斯模型模拟静态内容,并利用概率掩膜进行协调组合,实现独立但互补的优化。DeGauss在不同真实场景,从日常图像集到长动态第一人称视频中都表现稳健,无需依赖复杂的启发式方法或大量监督。实验结果表明,DeGauss在包括NeRF-on-the-go、ADT、AEA、Hot3D和EPIC-Fields等多个基准测试上均表现优异,为高度动态、交互丰富的环境中的无干扰物3D重建建立了强有力的基线。
Key Takeaways
- DeGauss是一个用于动态场景重建的自监督框架,适用于第一人称视频等动态和杂乱的环境。
- 它采用动态静态高斯涂抹设计,通过前景和背景高斯模型分别模拟动态和静态元素。
- DeGauss使用概率掩膜来协调动态和静态元素的组合,实现独立且互补的优化。
- 框架具有广泛的适用性,可以在不同真实场景中表现稳健,包括日常图像集和长动态视频。
- 无需依赖复杂的启发式方法或大量监督,框架具有良好的可推广性。
- 实验结果表明,DeGauss在多个基准测试上表现优异,具有领先的性能。
点此查看论文截图


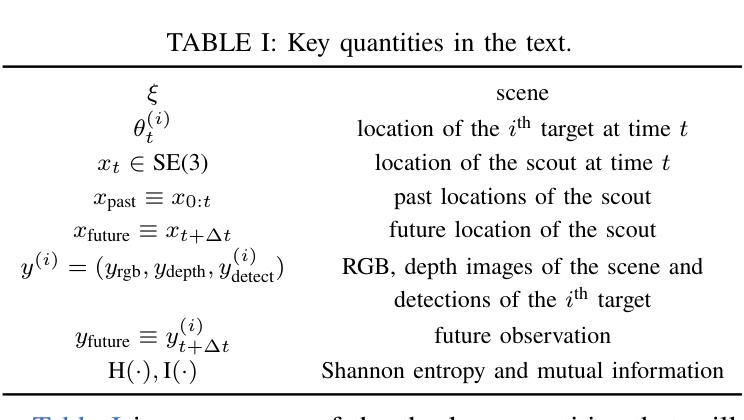
Active Scout: Multi-Target Tracking Using Neural Radiance Fields in Dense Urban Environments
Authors:Christopher D. Hsu, Pratik Chaudhari
We study pursuit-evasion games in highly occluded urban environments, e.g. tall buildings in a city, where a scout (quadrotor) tracks multiple dynamic targets on the ground. We show that we can build a neural radiance field (NeRF) representation of the city – online – using RGB and depth images from different vantage points. This representation is used to calculate the information gain to both explore unknown parts of the city and track the targets – thereby giving a completely first-principles approach to actively tracking dynamic targets. We demonstrate, using a custom-built simulator using Open Street Maps data of Philadelphia and New York City, that we can explore and locate 20 stationary targets within 300 steps. This is slower than a greedy baseline, which does not use active perception. But for dynamic targets that actively hide behind occlusions, we show that our approach maintains, at worst, a tracking error of 200m; the greedy baseline can have a tracking error as large as 600m. We observe a number of interesting properties in the scout’s policies, e.g., it switches its attention to track a different target periodically, as the quality of the NeRF representation improves over time, the scout also becomes better in terms of target tracking. Code is available at https://github.com/grasp-lyrl/ActiveScout.
我们研究在高度遮挡的城市环境中的追踪与躲避游戏,例如在城市中的高层建筑中,侦察无人机(四旋翼飞行器)追踪地面上的多个动态目标。我们展示了可以在线构建城市神经辐射场(NeRF)表示的能力,这通过使用从不同视角获得的RGB和深度图像实现。这种表示用于计算探索城市未知部分和追踪目标的信息增益,从而为积极追踪动态目标提供了完全基于第一性原则的方法。我们使用基于费城和纽约市Open Street Maps数据的自定义模拟器进行演示,证明我们可以在300步内探索和定位20个静止目标。这慢于贪婪基线,后者不使用主动感知。但对于主动在遮挡物后隐藏的动态目标,我们展示我们的方法在最坏情况下保持200米的跟踪误差;而贪婪基线的跟踪误差可能高达600米。我们观察到侦察无人机策略的一些有趣属性,例如,随着NeRF表示的质量随时间提高,它会定期将注意力转向追踪不同的目标,并且侦察无人机的目标追踪能力也变得越来越强。相关代码可在https://github.com/grasp-lyrl/ActiveScout找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 10 figures, 2 tables, IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) 2024
Summary
该研究利用神经网络辐射场(NeRF)技术,在城市等高度遮挡环境中进行目标追踪。通过在线构建城市NeRF表示,结合RGB和深度图像,实现对多个动态目标的探索与追踪。研究采用自定义模拟器,利用费城和纽约市的开放街道地图数据,可探索和定位静止目标。对于动态目标,该研究的方法能在最差情况下保持200米的追踪误差,优于贪婪基线算法的600米误差。随着NeRF表示的质量提高,侦察机的目标追踪能力也得到提升。相关代码已公开。
Key Takeaways
- 研究利用NeRF技术在城市等高遮挡环境中进行目标追踪。
- 通过在线构建城市NeRF表示,结合RGB和深度图像,实现对多个动态目标的探索与追踪。
- 采用自定义模拟器,可探索和定位静止目标。
- 对于动态目标,该方法能在最差情况下保持较低的追踪误差。
- 随着NeRF表示的质量提高,侦察机的目标追踪能力有所提升。
- 该研究提供了基于第一性原则的主动目标追踪方法。
点此查看论文截图