⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-05 更新
A Cookbook for Community-driven Data Collection of Impaired Speech in LowResource Languages
Authors:Sumaya Ahmed Salihs, Isaac Wiafe, Jamal-Deen Abdulai, Elikem Doe Atsakpo, Gifty Ayoka, Richard Cave, Akon Obu Ekpezu, Catherine Holloway, Katrin Tomanek, Fiifi Baffoe Payin Winful
This study presents an approach for collecting speech samples to build Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) models for impaired speech, particularly, low-resource languages. It aims to democratize ASR technology and data collection by developing a “cookbook” of best practices and training for community-driven data collection and ASR model building. As a proof-of-concept, this study curated the first open-source dataset of impaired speech in Akan: a widely spoken indigenous language in Ghana. The study involved participants from diverse backgrounds with speech impairments. The resulting dataset, along with the cookbook and open-source tools, are publicly available to enable researchers and practitioners to create inclusive ASR technologies tailored to the unique needs of speech impaired individuals. In addition, this study presents the initial results of fine-tuning open-source ASR models to better recognize impaired speech in Akan.
本研究提出了一种收集语音样本的方法,用于构建针对受损语音(尤其是资源匮乏的语言)的自动语音识别(ASR)模型。本研究旨在通过开发社区驱动的数据收集和ASR模型构建的“最佳实践手册”和培训材料,使ASR技术和数据收集民主化。作为概念验证,本研究精心制作了加纳广泛使用的本土语言阿坎语的首个开源受损语音数据集。该研究涉及来自不同背景且存在言语障碍的参与者。所得数据集以及与手册和开源工具一起,可供研究人员和实践人员使用,以创建适合特定受损语音个体需求的包容性ASR技术。此外,本研究还展示了微调开源ASR模型以更好地识别阿坎语中的受损语音的初步结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This version has been reviewed and accepted for presentation at the InterSpeech 2025 conference to be held in Rotterdam from 17 to 21 August. 5 pages and 3 tables
Summary
本研究提出了一种收集语音样本的方法,用于构建针对受损语音,尤其是低资源语言的自动语音识别(ASR)模型。研究旨在通过开发最佳实践“手册”和培训材料,实现社区驱动的数据收集和ASR模型构建,从而普及ASR技术和数据采集。作为概念证明,本研究整理了首个开源的受损语音数据集——阿坎语:一种在加纳广泛使用的土著语言。研究涉及来自不同背景且存在语音缺陷的参与者。所得数据集以及手册和开源工具均公开可用,以便研究者和从业者根据语音障碍者的独特需求创建包容性的ASR技术。此外,本研究还展示了微调开源ASR模型以更好地识别受损的阿坎语的初步结果。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究提出了一种针对受损语音,特别是低资源语言的ASR模型的数据收集方法。
- 研究目标是普及ASR技术和数据采集,通过开发最佳实践手册和培训材料来实现。
- 作为概念证明,本研究创建了首个开源的阿坎语受损语音数据集。
- 数据集包括了来自不同背景且存在语音障碍的参与者。
- 数据集、手册和开源工具均公开可用,便于研究和开发适应语音障碍者需求的ASR技术。
- 研究展示了微调开源ASR模型以优化识别受损阿坎语的能力的初步成果。
- 此研究为构建更具包容性的ASR技术做出了贡献,特别关注语音障碍者的需求。
点此查看论文截图

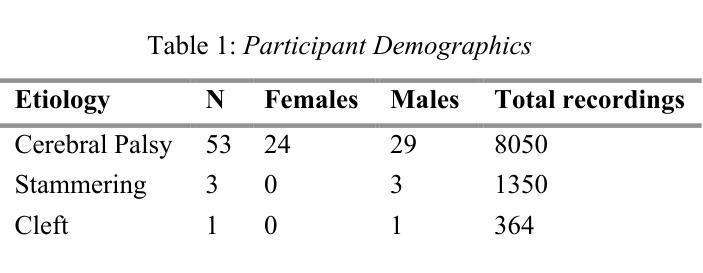
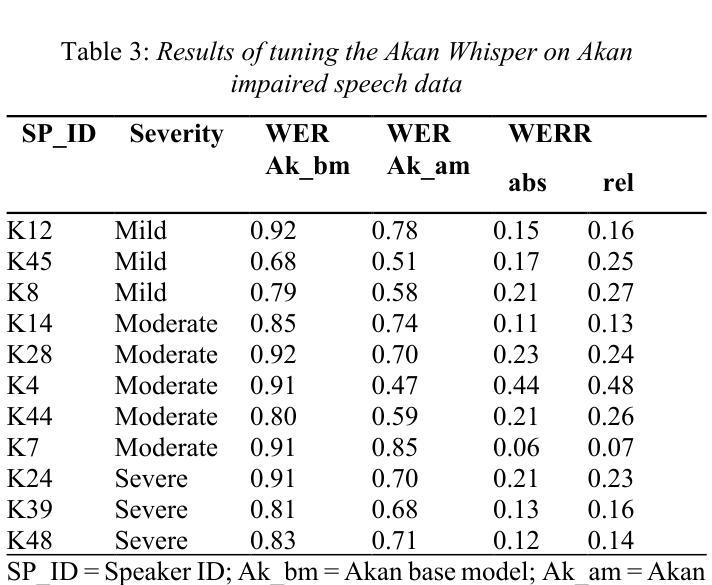
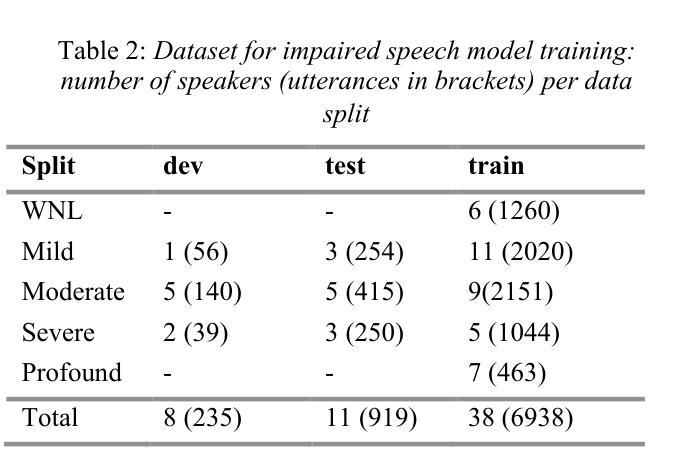
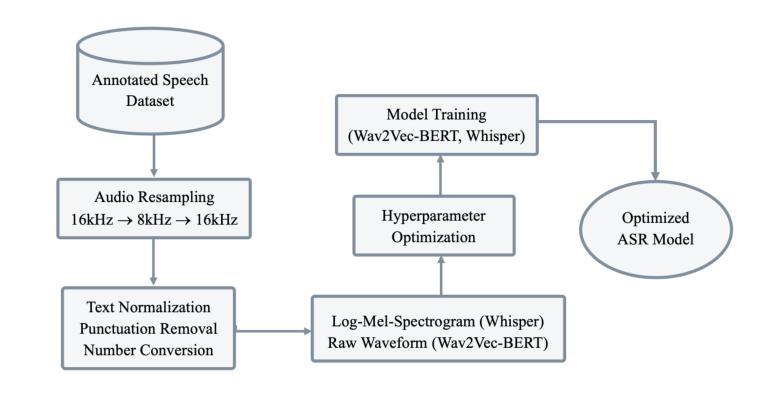
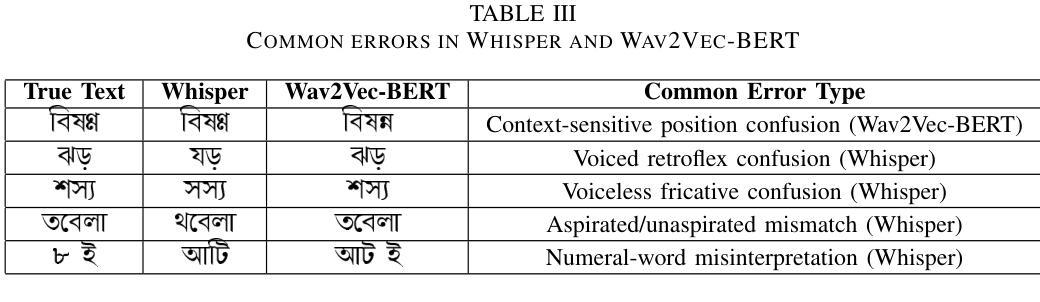
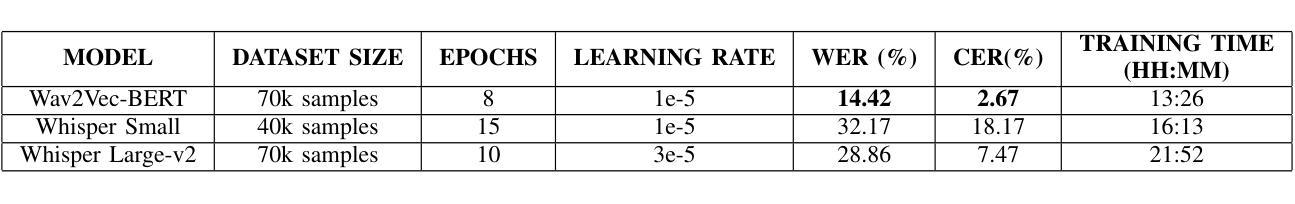
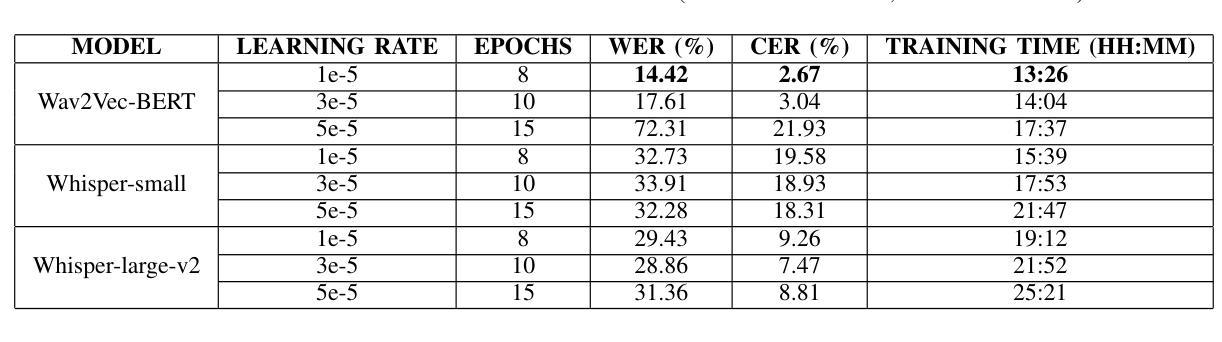
Adaptability of ASR Models on Low-Resource Language: A Comparative Study of Whisper and Wav2Vec-BERT on Bangla
Authors:Md Sazzadul Islam Ridoy, Sumi Akter, Md. Aminur Rahman
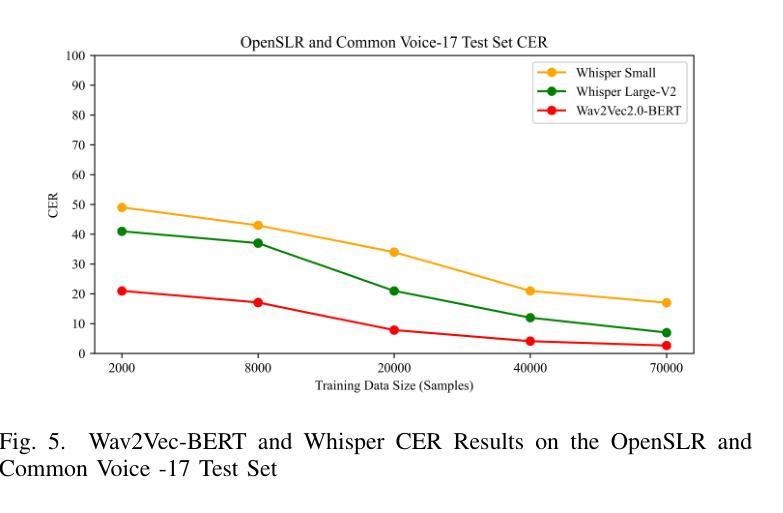
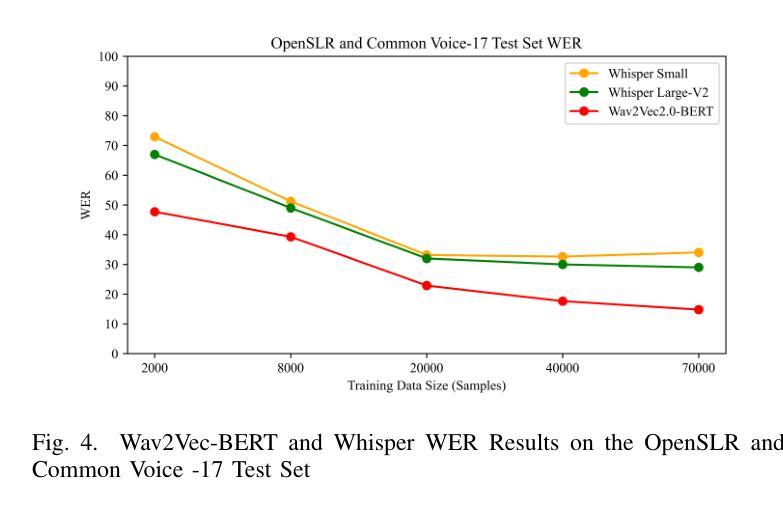
In recent years, neural models trained on large multilingual text and speech datasets have shown great potential for supporting low-resource languages. This study investigates the performances of two state-of-the-art Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) models, OpenAI’s Whisper (Small & Large-V2) and Facebook’s Wav2Vec-BERT on Bangla, a low-resource language. We have conducted experiments using two publicly available datasets: Mozilla Common Voice-17 and OpenSLR to evaluate model performances. Through systematic fine-tuning and hyperparameter optimization, including learning rate, epochs, and model checkpoint selection, we have compared the models based on Word Error Rate (WER), Character Error Rate (CER), Training Time, and Computational Efficiency. The Wav2Vec-BERT model outperformed Whisper across all key evaluation metrics, demonstrated superior performance while requiring fewer computational resources, and offered valuable insights to develop robust speech recognition systems in low-resource linguistic settings.
近年来,在大型多语言文本和语音数据集上训练的神经网络模型已显示出支持低资源语言的巨大潜力。本研究调查了两种最新自动语音识别(ASR)模型的性能,包括OpenAI的whisper(小型与大型-V2)和Facebook的Wav2Vec-BERT在低资源语言邦拉语上的表现。我们使用了两个公开可用的数据集Mozilla Common Voice-17和OpenSLR来评估模型性能。通过系统微调、超参数优化,包括学习率、周期和模型检查点选择,我们根据单词错误率(WER)、字符错误率(CER)、训练时间和计算效率比较了这些模型。Wav2Vec-BERT模型在各项关键评估指标上表现优于whisper,表现出优异的性能,同时需要较少的计算资源,为在低资源语言环境中开发稳健的语音识别系统提供了有价值的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
近年来,基于大型多语种文本和语音数据集的神经网络模型在低资源语言支持方面表现出巨大潜力。本研究采用最先进的自动语音识别(ASR)模型OpenAI的Whisper(小型和大型V2版本)和Facebook的Wav2Vec-BERT对低资源语言Bangla进行性能评估。通过实验评估,Wav2Vec-BERT模型在各项指标上优于Whisper,表现更优秀且计算资源需求更少,为在低资源语言环境中开发稳健的语音识别系统提供了有价值的见解。
Key Takeaways:
- 神经网络模型在低资源语言支持方面展现潜力。
- 评估了两种先进ASR模型:OpenAI的Whisper和Facebook的Wav2Vec-BERT在Bangla语言上的性能。
- 使用Mozilla Common Voice-17和OpenSLR两个公开数据集进行实验评估。
- 通过系统微调、超参数优化(包括学习率、周期和模型检查点选择)来比较模型性能。
- Wav2Vec-BERT模型在关键评估指标上优于Whisper。
- Wav2Vec-BERT模型表现更优秀且需要较少的计算资源。
点此查看论文截图

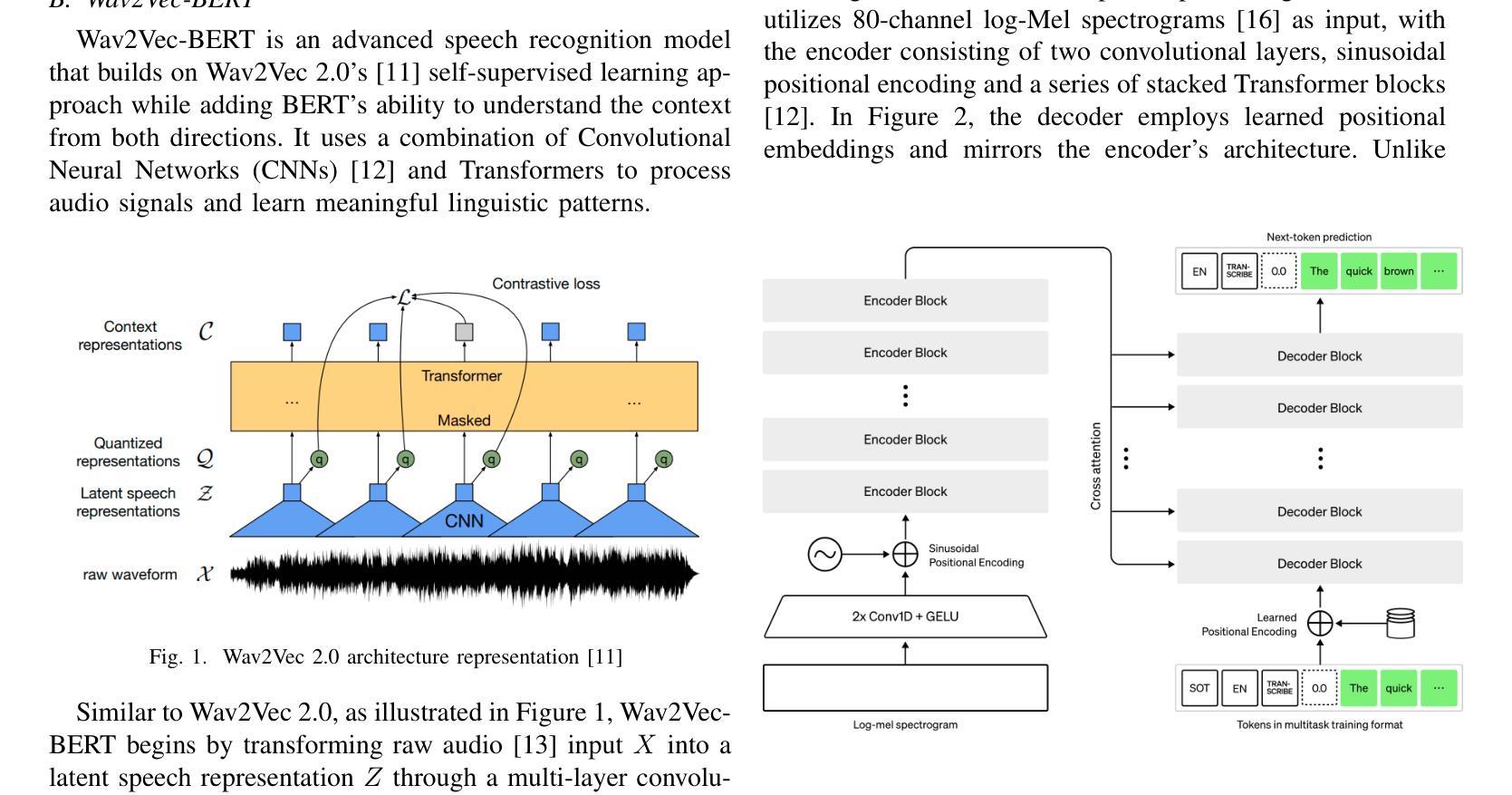
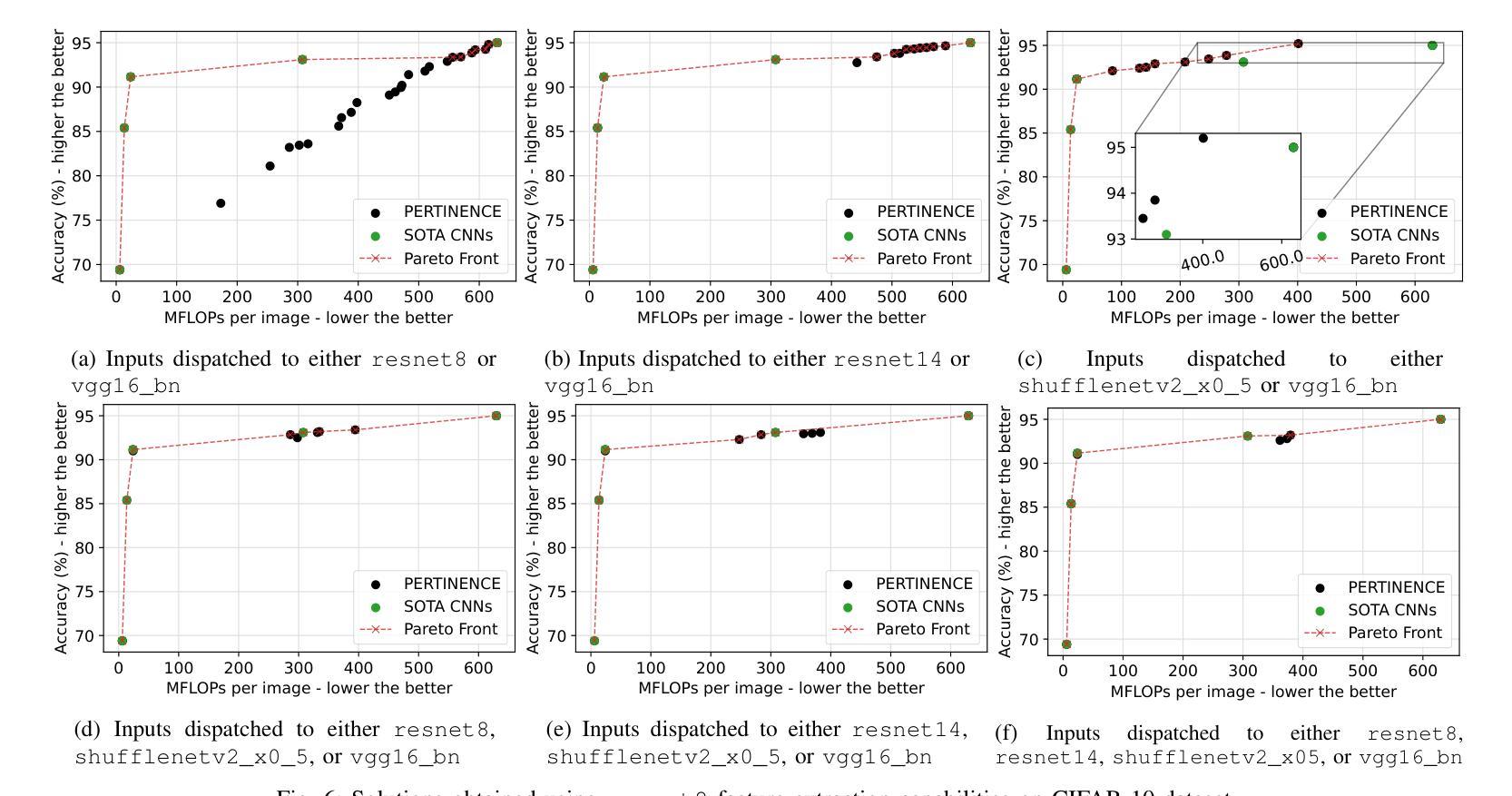
PERTINENCE: Input-based Opportunistic Neural Network Dynamic Execution
Authors:Omkar Shende, Gayathri Ananthanarayanan, Marcello Traiola
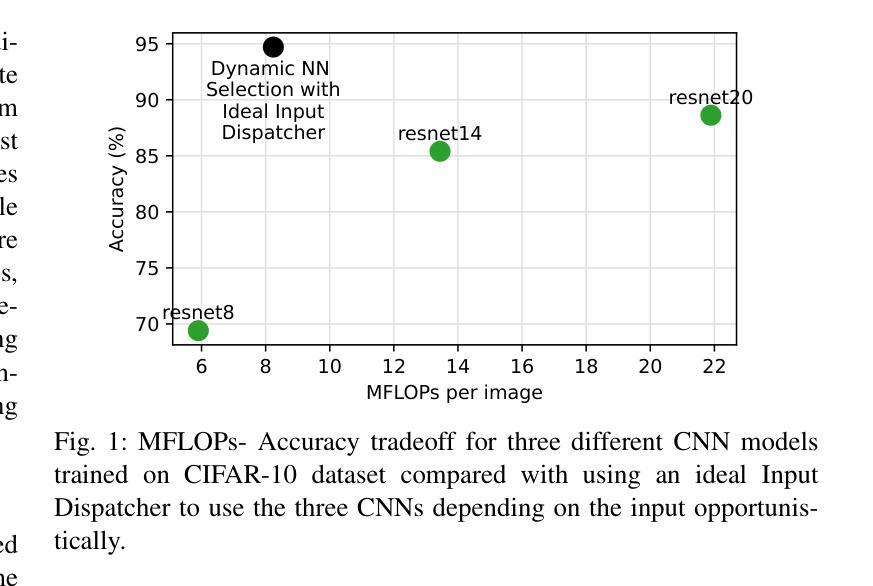
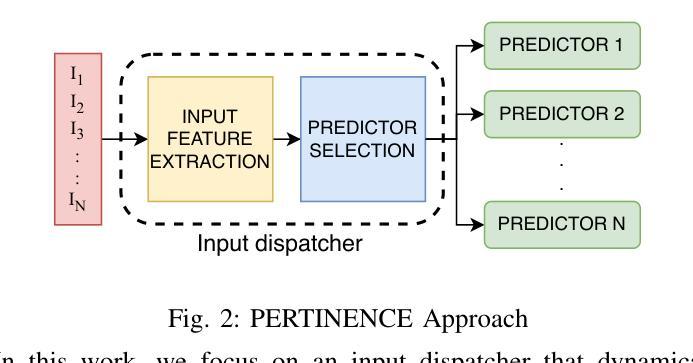
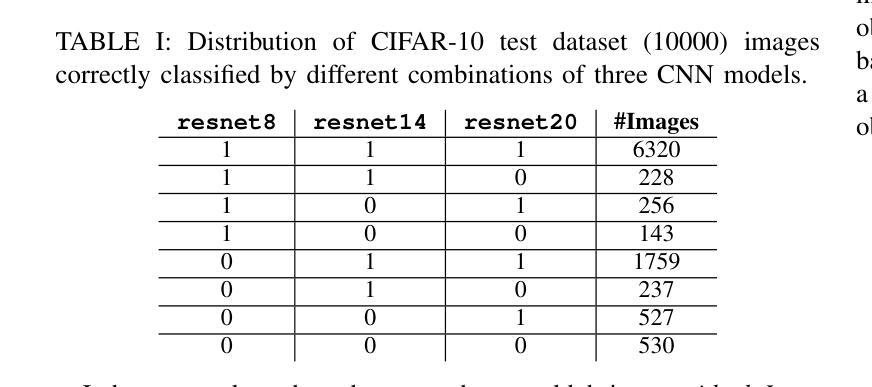
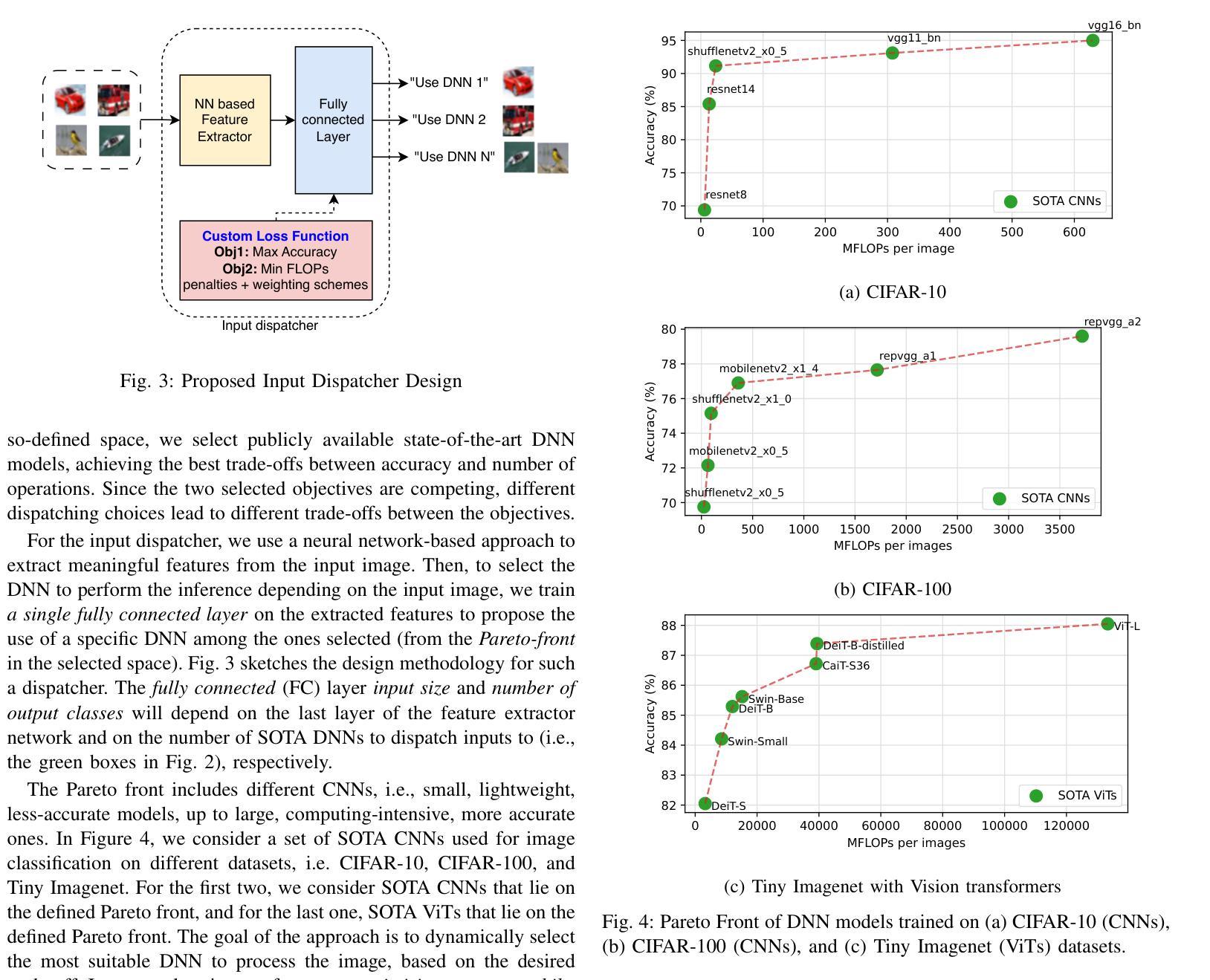
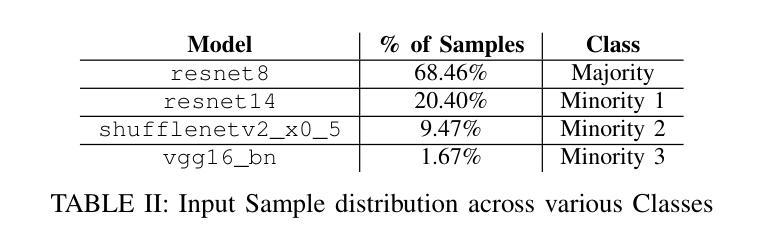
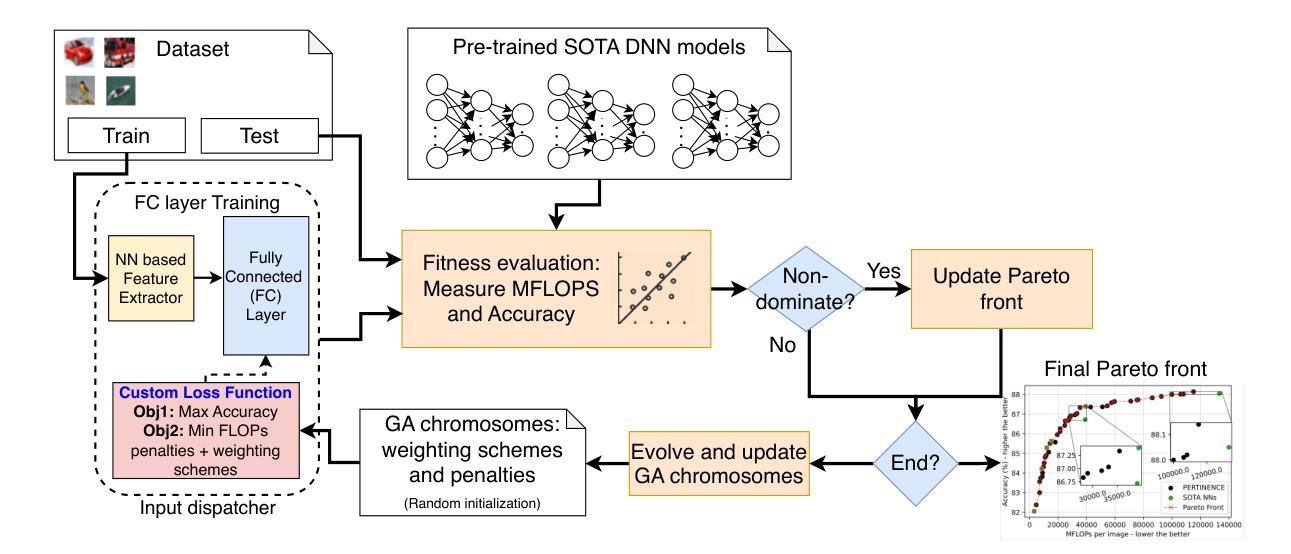
Deep neural networks (DNNs) have become ubiquitous thanks to their remarkable ability to model complex patterns across various domains such as computer vision, speech recognition, robotics, etc. While large DNN models are often more accurate than simpler, lightweight models, they are also resource- and energy-hungry. Hence, it is imperative to design methods to reduce reliance on such large models without significant degradation in output accuracy. The high computational cost of these models is often necessary only for a reduced set of challenging inputs, while lighter models can handle most simple ones. Thus, carefully combining properties of existing DNN models in a dynamic, input-based way opens opportunities to improve efficiency without impacting accuracy. In this work, we introduce PERTINENCE, a novel online method designed to analyze the complexity of input features and dynamically select the most suitable model from a pre-trained set to process a given input effectively. To achieve this, we employ a genetic algorithm to explore the training space of an ML-based input dispatcher, enabling convergence towards the Pareto front in the solution space that balances overall accuracy and computational efficiency. We showcase our approach on state-of-the-art Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) trained on the CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100, as well as Vision Transformers (ViTs) trained on TinyImageNet dataset. We report results showing PERTINENCE’s ability to provide alternative solutions to existing state-of-the-art models in terms of trade-offs between accuracy and number of operations. By opportunistically selecting among models trained for the same task, PERTINENCE achieves better or comparable accuracy with up to 36% fewer operations.
深度神经网络(DNNs)由于其跨多个领域(如计算机视觉、语音识别、机器人等)建立复杂模式的卓越能力而变得无处不在。虽然大型DNN模型通常比简单、轻量级的模型更准确,但它们也需要更多的资源和能源。因此,设计方法来减少对这样的大模型的依赖,同时不会显著降低输出精度,这是至关重要的。这些模型的高计算成本通常只是为了减少一些具有挑战性的输入而必需的,而较轻的模型可以处理大多数简单的输入。因此,以一种动态、基于输入的方式谨慎地结合现有DNN模型的属性,为提高效率提供了机会,而不会影响准确性。在这项工作中,我们引入了PERTINENCE,这是一种新的在线方法,旨在分析输入特征复杂性,并从预训练模型集中动态选择最适合的模型来处理给定输入。为实现这一目标,我们采用遗传算法来探索基于机器学习的输入调度器的训练空间,使解决方案在整体准确性和计算效率之间取得平衡。我们在CIFAR-10和CIFAR-100上训练的最新卷积神经网络(CNN)以及TinyImageNet数据集上训练的视觉转换器(ViT)上展示了我们的方法。报告结果显示,PERTINENCE能够在准确性和操作次数之间提供对现有最先进模型的替代解决方案。通过在有相同任务的模型中做出选择,PERTINENCE在具有高达36%更少操作的情况下实现了更好的或相当的准确性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
深度神经网络(DNN)在多个领域如计算机视觉、语音识别、机器人等中展现出强大的模式识别能力。虽然大型DNN模型通常比轻量级模型更准确,但它们消耗大量资源和能源。因此,设计方法来减少对大型模型的依赖,同时不显著降低输出准确性至关重要。本文介绍了一种名为PERTINENCE的新型在线方法,该方法旨在分析输入特征复杂性,并从预训练模型集中动态选择最适合的模型来处理给定输入。为实现这一目标,我们采用遗传算法来探索ML输入调度器的训练空间,以在解决方案空间中实现平衡总体准确度和计算效率的帕累托前沿。我们在CIFAR-10和CIFAR-100上训练的最新卷积神经网络(CNN)以及TinyImageNet数据集上训练的视觉转换器(ViT)上展示了我们的方法。结果表明,PERTINENCE能够在准确度与运算次数之间提供对现有最先进模型的替代解决方案。通过在相同任务训练的模型之间灵活选择,PERTINENCE实现了更好的或相当的准确性,同时减少了高达36%的运算次数。
关键见解
- 深度神经网络(DNN)在多个领域具有强大的模式识别能力,但大型模型资源消耗大。
- 提出了一种新型在线方法PERTINENCE,可根据输入特征复杂性动态选择最合适的模型。
- PERTINENCE采用遗传算法探索ML输入调度器的训练空间,实现帕累托最优,平衡准确度和计算效率。
- 在多个数据集上的实验表明,PERTINENCE提供了与现有最先进模型相当的准确性,同时显著减少了运算次数。
- PERTINENCE方法具有潜力在提高计算效率的同时不损失准确性。
- 通过灵活选择针对同一任务训练的模型,PERTINENCE实现了效率与性能的平衡。
点此查看论文截图

Learning from Random Subspace Exploration: Generalized Test-Time Augmentation with Self-supervised Distillation
Authors:Andrei Jelea, Ahmed Nabil Belbachir, Marius Leordeanu
We introduce Generalized Test-Time Augmentation (GTTA), a highly effective method for improving the performance of a trained model, which unlike other existing Test-Time Augmentation approaches from the literature is general enough to be used off-the-shelf for many vision and non-vision tasks, such as classification, regression, image segmentation and object detection. By applying a new general data transformation, that randomly perturbs multiple times the PCA subspace projection of a test input, GTTA forms robust ensembles at test time in which, due to sound statistical properties, the structural and systematic noises in the initial input data is filtered out and final estimator errors are reduced. Different from other existing methods, we also propose a final self-supervised learning stage in which the ensemble output, acting as an unsupervised teacher, is used to train the initial single student model, thus reducing significantly the test time computational cost, at no loss in accuracy. Our tests and comparisons to strong TTA approaches and SoTA models on various vision and non-vision well-known datasets and tasks, such as image classification and segmentation, speech recognition and house price prediction, validate the generality of the proposed GTTA. Furthermore, we also prove its effectiveness on the more specific real-world task of salmon segmentation and detection in low-visibility underwater videos, for which we introduce DeepSalmon, the largest dataset of its kind in the literature.
我们介绍了一种名为广义测试时间增强(GTTA)的有效方法,用于提高训练模型性能。与文献中的其他现有测试时间增强方法不同,GTTA具有足够的通用性,可以应用于许多视觉和非视觉任务,例如分类、回归、图像分割和对象检测。通过应用新的通用数据转换,多次随机扰动测试输入的PCA子空间投影,GTTA在测试时形成稳健的集合。由于具有良好的统计属性,初始输入数据中的结构和系统噪声被过滤掉,最终估计器误差减小。与其他现有方法不同,我们还提出了一个最终的自我监督学习阶段,其中集合输出作为无监督教师,用于训练初始单一学生模型,从而在不影响精度的情况下显著降低测试时间的计算成本。我们的测试和对各种视觉和非视觉知名数据集和任务上的强大TTA方法和最新模型的比较,如图像分类和分割、语音识别和房屋价格预测等,验证了所提出GTTA的通用性。此外,我们还证明了其在更具体的现实世界任务——低可见度水下视频中的鲑鱼分割和检测——的有效性,为此我们引入了DeepSalmon,这是文献中同类最大的数据集。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了广义测试时间增强(GTTA)方法,用于提高训练模型性能。与其他现有测试时间增强方法不同,GTTA具有足够的通用性,可广泛应用于许多视觉和非视觉任务,如分类、回归、图像分割和对象检测。它通过新的通用数据转换,随机扰动测试输入的PCA子空间投影,在测试时形成稳健的集合,过滤掉初始输入数据中的结构和系统性噪声,减少最终估计器误差。此外,还提出了一种最终的自监督学习阶段,利用集合输出作为无监督教师来训练初始单一学生模型,从而显著减少测试时间计算成本,同时不损失准确性。在多种视觉和非视觉的知名数据集和任务上的测试,验证了GTTA的通用性和有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了Generalized Test-Time Augmentation(GTTA)方法,适用于多种任务,如分类、回归、图像分割和对象检测。
- 通过新的通用数据转换,随机扰动测试输入的PCA子空间投影,形成稳健集合,减少估计器误差。
- 引入自监督学习阶段,利用集合输出作为无监督教师来训练学生模型,降低测试时间成本。
- GTTA方法具有广泛的适用性,可以在各种视觉和非视觉数据集上进行测试。
- 相比其他强TTA方法和最新模型,GTTA在多个任务上表现出优越的性能。
- 首次在文献中引入了DeepSalmon数据集,用于低可见度水下视频的鲑鱼分割和检测任务。
点此查看论文截图

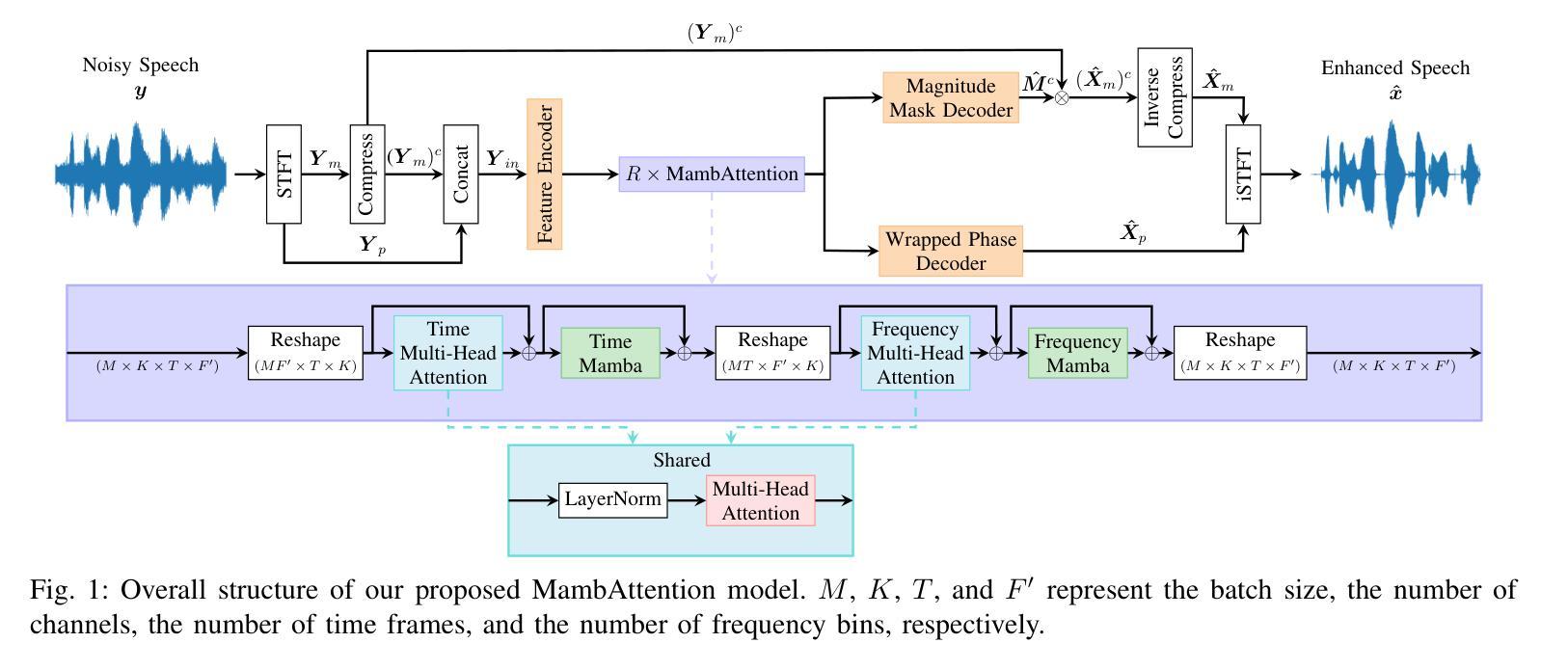
MambAttention: Mamba with Multi-Head Attention for Generalizable Single-Channel Speech Enhancement
Authors:Nikolai Lund Kühne, Jesper Jensen, Jan Østergaard, Zheng-Hua Tan
With the advent of new sequence models like Mamba and xLSTM, several studies have shown that these models match or outperform state-of-the-art models in single-channel speech enhancement, automatic speech recognition, and self-supervised audio representation learning. However, prior research has demonstrated that sequence models like LSTM and Mamba tend to overfit to the training set. To address this issue, previous works have shown that adding self-attention to LSTMs substantially improves generalization performance for single-channel speech enhancement. Nevertheless, neither the concept of hybrid Mamba and time-frequency attention models nor their generalization performance have been explored for speech enhancement. In this paper, we propose a novel hybrid architecture, MambAttention, which combines Mamba and shared time- and frequency-multi-head attention modules for generalizable single-channel speech enhancement. To train our model, we introduce VoiceBank+Demand Extended (VB-DemandEx), a dataset inspired by VoiceBank+Demand but with more challenging noise types and lower signal-to-noise ratios. Trained on VB-DemandEx, our proposed MambAttention model significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art LSTM-, xLSTM-, Mamba-, and Conformer-based systems of similar complexity across all reported metrics on two out-of-domain datasets: DNS 2020 and EARS-WHAM_v2, while matching their performance on the in-domain dataset VB-DemandEx. Ablation studies highlight the role of weight sharing between the time- and frequency-multi-head attention modules for generalization performance. Finally, we explore integrating the shared time- and frequency-multi-head attention modules with LSTM and xLSTM, which yields a notable performance improvement on the out-of-domain datasets. However, our MambAttention model remains superior on both out-of-domain datasets across all reported evaluation metrics.
随着Mamba和xLSTM等新序列模型的出现,多项研究表明这些模型在单通道语音增强、自动语音识别和自我监督音频表示学习方面达到了或超越了现有模型的性能。然而,先前的研究表明,像LSTM和Mamba这样的序列模型容易过度拟合训练集。为了解决这一问题,以前的研究表明,在LSTM中添加自注意力可以大大提高单通道语音增强的泛化性能。然而,关于混合Mamba和时间-频率注意力模型的概念及其泛化性能在语音增强方面的探索尚未出现。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型的混合架构MambAttention,它将Mamba和共享的时间与频率多头注意力模块相结合,用于通用的单通道语音增强。为了训练我们的模型,我们引入了VoiceBank+Demand Extended(VB-DemandEx)数据集,该数据集以VoiceBank+Demand为灵感,但具有更具挑战性的噪声类型和更低的信噪比。在VB-DemandEx上训练的MambAttention模型在两个域外数据集DNS 2020和EARS-WHAM_v2上所有报告的指标中都显著超越了现有复杂的基于LSTM、xLSTM、Mamba和Conformer的系统,同时在域内数据集VB-DemandEx上的性能与之相匹配。消融研究突出了时间与频率多头注意力模块权重共享在泛化性能中的作用。最后,我们探索了将共享的时间与频率多头注意力模块与LSTM和xLSTM集成,这在域外数据集上产生了显著的性能改进。然而,我们的MambAttention模型在两个域外数据集上的所有报告的评价指标上仍然表现最佳。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing for possible publication
Summary
本研究提出了一个名为MambAttention的混合架构,结合了Mamba和共享时间、频率多头注意力模块,用于通用的单通道语音增强。为训练模型,研究引入了更具挑战性的噪声类型和较低信噪比的VoiceBank+Demand扩展数据集。在跨域数据集DNS 2020和EARS-WHAM_v2上,MambAttention模型显著优于其他先进的LSTM、xLSTM、Mamba和Conformer模型,同时在领域内数据集VB-DemandEx上的性能相匹配。
Key Takeaways
- 新序列模型(如Mamba和xLSTM)在语音增强、语音识别和音频表示学习方面表现出与现有先进技术相当或更优的性能。
- LSTM和Mamba模型容易过度拟合训练集,添加自注意力机制可以改善其泛化性能。
- 引入了一种新型的混合架构MambAttention,结合了Mamba和共享时间、频率多头注意力模块,用于单通道语音增强。
- 引入了更具挑战性的VoiceBank+Demand扩展数据集(VB-DemandEx)用于模型训练。
- MambAttention模型在跨域数据集上显著优于其他先进模型。
- 权重共享在时间和频率多头注意力模块间对于模型的泛化性能起到关键作用。
点此查看论文截图

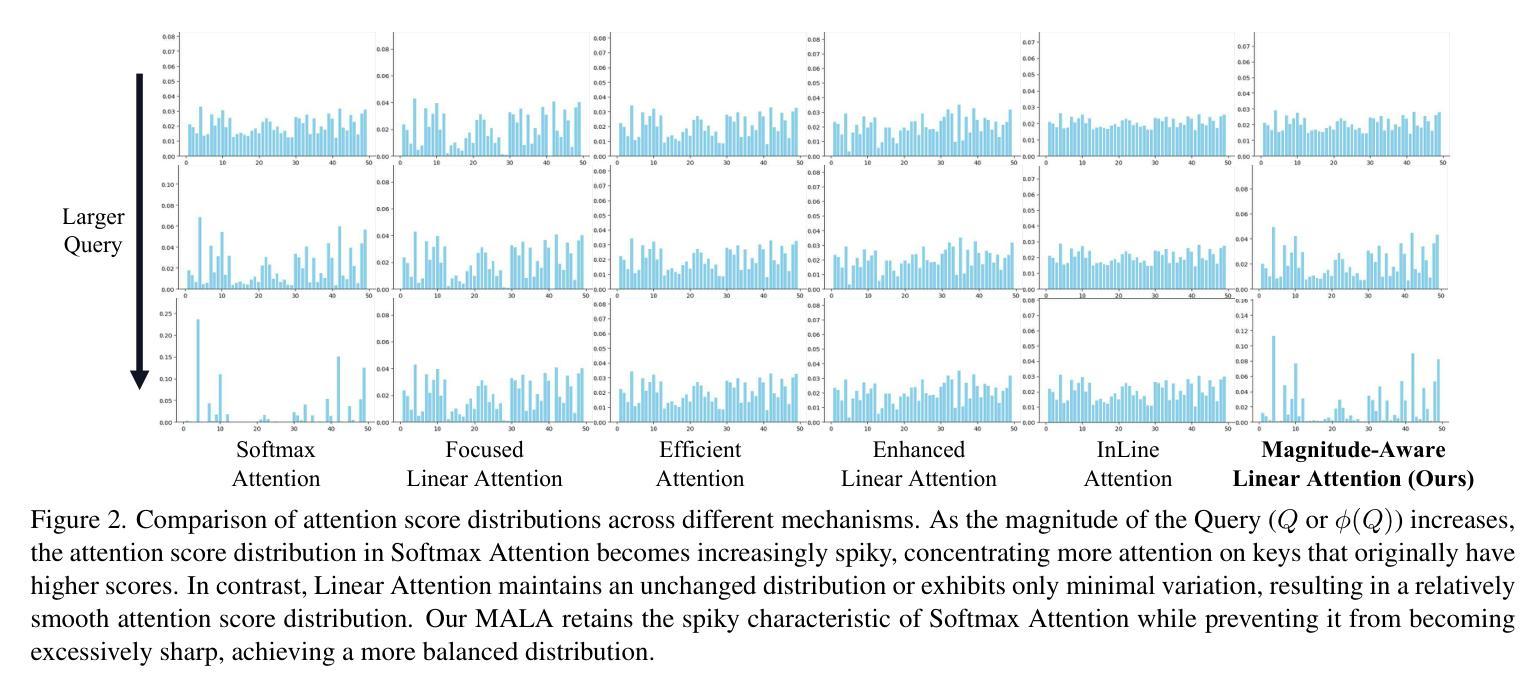
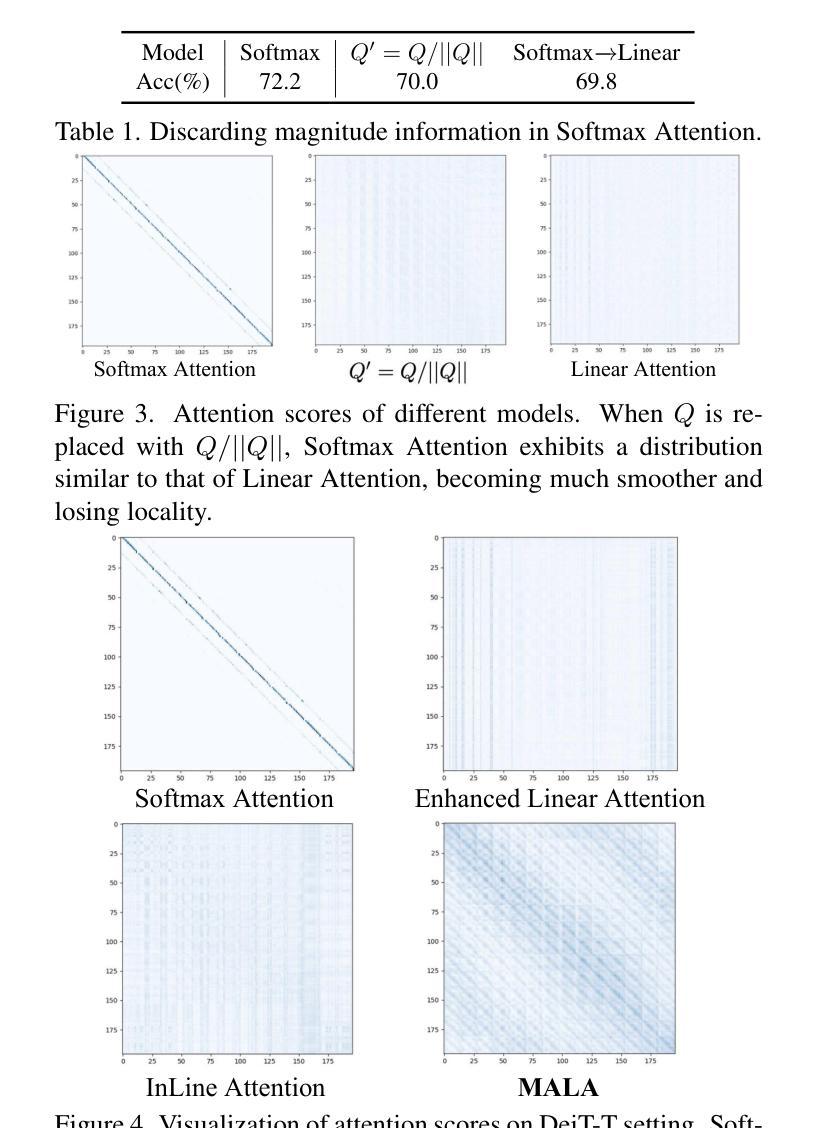
Rectifying Magnitude Neglect in Linear Attention
Authors:Qihang Fan, Huaibo Huang, Yuang Ai, ran He
As the core operator of Transformers, Softmax Attention exhibits excellent global modeling capabilities. However, its quadratic complexity limits its applicability to vision tasks. In contrast, Linear Attention shares a similar formulation with Softmax Attention while achieving linear complexity, enabling efficient global information modeling. Nevertheless, Linear Attention suffers from a significant performance degradation compared to standard Softmax Attention. In this paper, we analyze the underlying causes of this issue based on the formulation of Linear Attention. We find that, unlike Softmax Attention, Linear Attention entirely disregards the magnitude information of the Query. This prevents the attention score distribution from dynamically adapting as the Query scales. As a result, despite its structural similarity to Softmax Attention, Linear Attention exhibits a significantly different attention score distribution. Based on this observation, we propose Magnitude-Aware Linear Attention (MALA), which modifies the computation of Linear Attention to fully incorporate the Query’s magnitude. This adjustment allows MALA to generate an attention score distribution that closely resembles Softmax Attention while exhibiting a more well-balanced structure. We evaluate the effectiveness of MALA on multiple tasks, including image classification, object detection, instance segmentation, semantic segmentation, natural language processing, speech recognition, and image generation. Our MALA achieves strong results on all of these tasks. Code will be available at https://github.com/qhfan/MALA
作为Transformer的核心操作器,Softmax Attention展现出出色的全局建模能力。然而,其二次复杂度限制了其在视觉任务中的应用。相比之下,Linear Attention与Softmax Attention具有相似的公式,但实现了线性复杂度,能够实现有效的全局信息建模。然而,与标准的Softmax Attention相比,Linear Attention的性能显著下降。在本文中,我们基于Linear Attention的公式分析此问题的根本原因。我们发现,与Softmax Attention不同,Linear Attention完全忽略了Query的幅度信息。这阻止了注意力得分分布在Query规模扩大时动态适应。因此,尽管其与Softmax Attention结构相似,但Linear Attention的注意力得分分布却大不相同。基于此观察,我们提出了幅度感知Linear Attention(MALA),它修改了Linear Attention的计算以充分融入Query的幅度。这一调整使MALA能够生成与Softmax Attention相似的注意力得分分布,同时展现出更平衡的结构。我们在多个任务上评估了MALA的有效性,包括图像分类、目标检测、实例分割、语义分割、自然语言处理、语音识别和图像生成。我们的MALA在所有任务上都取得了强大的结果。代码将在https://github.com/qhfan/MALA找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV2025
Summary
本文探讨了Transformer中的核心操作,包括Softmax Attention和Linear Attention。Softmax Attention具有出色的全局建模能力,但其二次复杂性限制了其在视觉任务中的应用。Linear Attention与Softmax Attention具有相似的公式形式但具有线性复杂性,能够实现高效的全局信息建模。然而,Linear Attention相较于标准Softmax Attention存在性能下降的问题。本文分析了这一问题背后的原因,并提出了Magnitude-Aware Linear Attention(MALA)。MALA调整了Linear Attention的计算方式,充分融入了Query的幅度信息,生成了与Softmax Attention相似的注意力得分分布,并在多个任务上取得了良好效果。
Key Takeaways
- Softmax Attention具有优秀的全局建模能力,但其二次复杂性限制了其在视觉任务的应用。
- Linear Attention实现了高效的全局信息建模,但与Softmax Attention相比存在性能下降问题。
- Linear Attention性能下降的原因在于其忽视了Query的幅度信息,导致注意力得分分布无法动态适应Query的变化。
- MALA调整了Linear Attention的计算方式,融入了Query的幅度信息,生成了与Softmax Attention相似的注意力得分分布。
- MALA在多个任务上取得了良好效果,包括图像分类、目标检测、实例分割、语义分割、自然语言处理、语音识别和图像生成。
- MALA的代码将在https://github.com/qhfan/MALA上公开。
点此查看论文截图

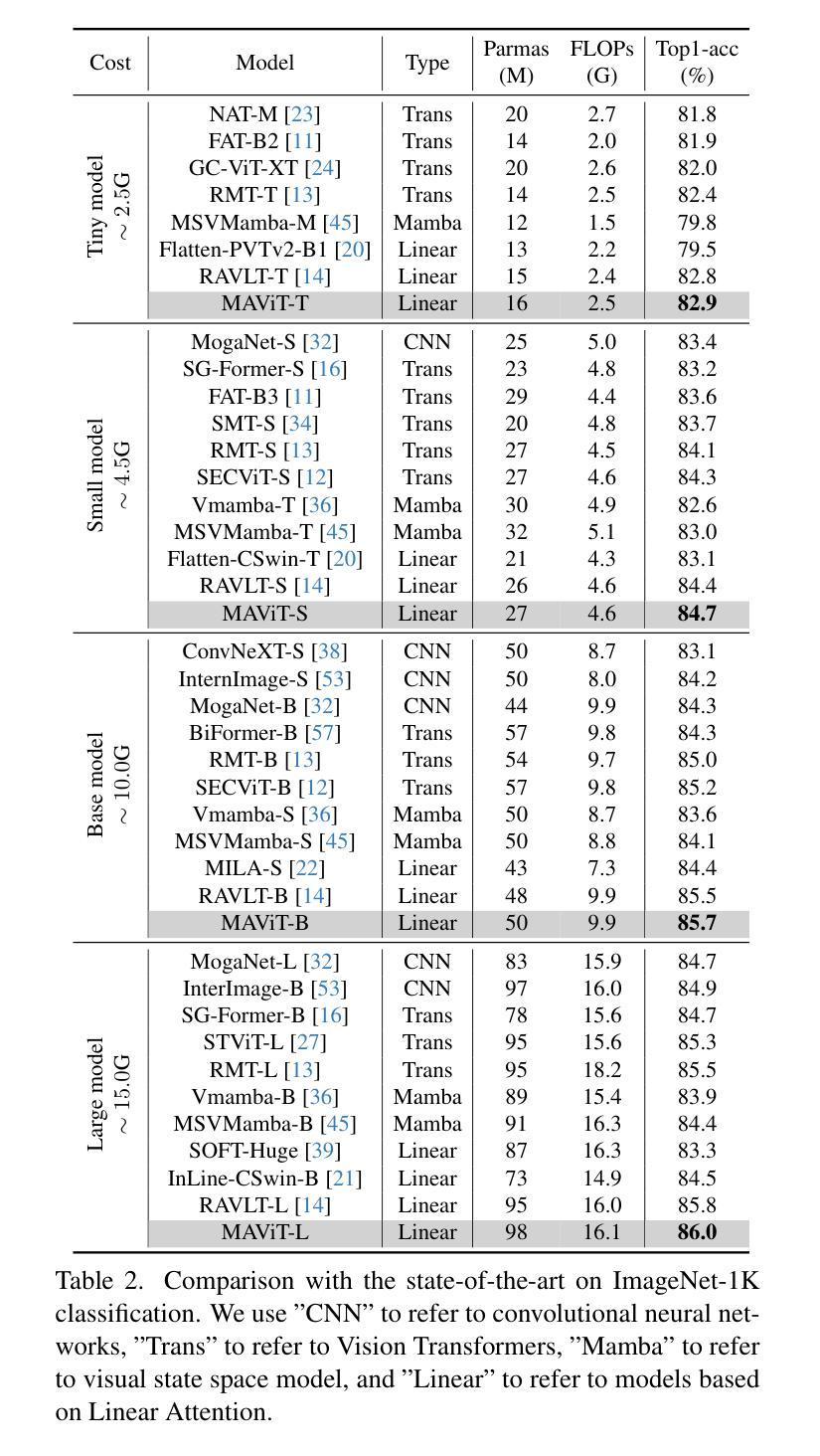
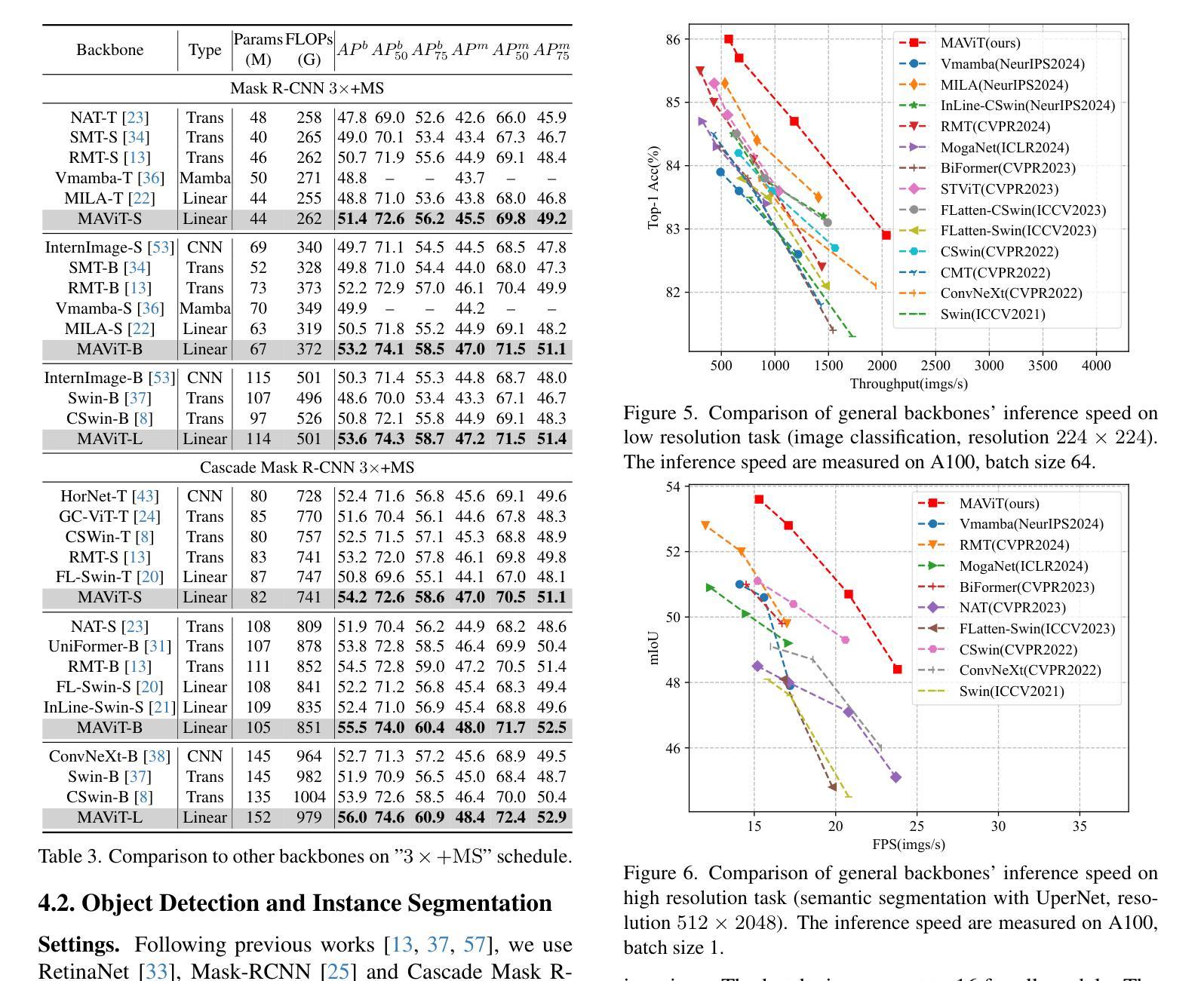
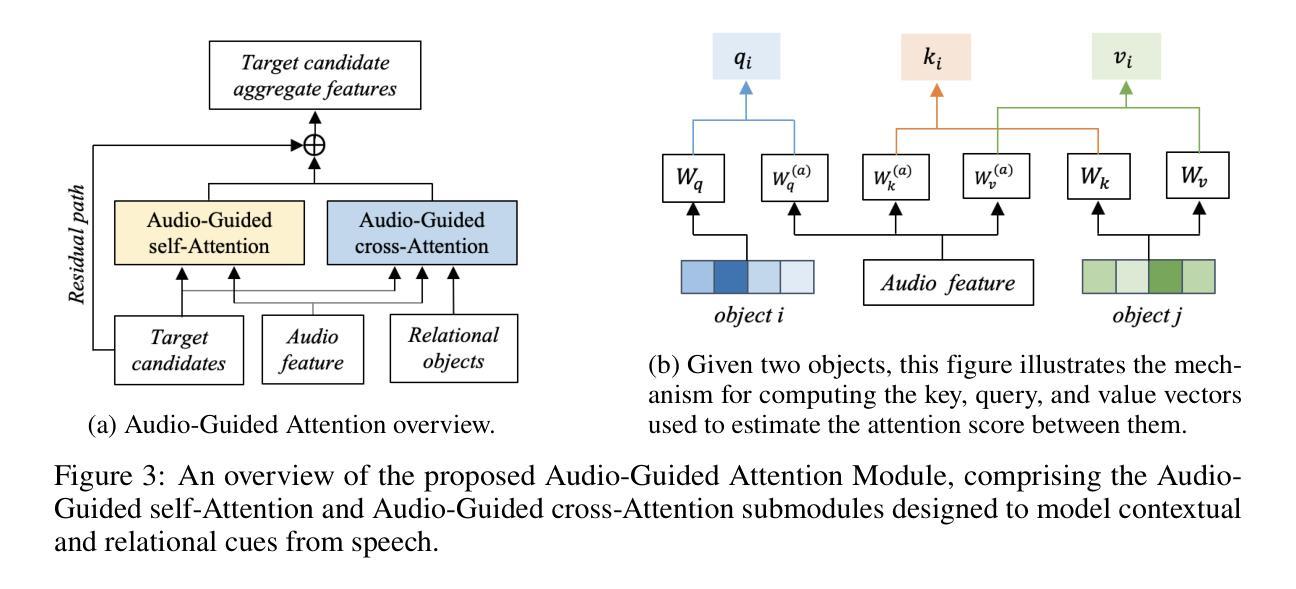
Audio-3DVG: Unified Audio - Point Cloud Fusion for 3D Visual Grounding
Authors:Duc Cao-Dinh, Khai Le-Duc, Anh Dao, Bach Phan Tat, Chris Ngo, Duy M. H. Nguyen, Nguyen X. Khanh, Thanh Nguyen-Tang
3D Visual Grounding (3DVG) involves localizing target objects in 3D point clouds based on natural language. While prior work has made strides using textual descriptions, leveraging spoken language-known as Audio-based 3D Visual Grounding-remains underexplored and challenging. Motivated by advances in automatic speech recognition (ASR) and speech representation learning, we propose Audio-3DVG, a simple yet effective framework that integrates audio and spatial information for enhanced grounding. Rather than treating speech as a monolithic input, we decompose the task into two complementary components. First, we introduce Object Mention Detection, a multi-label classification task that explicitly identifies which objects are referred to in the audio, enabling more structured audio-scene reasoning. Second, we propose an Audio-Guided Attention module that captures interactions between candidate objects and relational speech cues, improving target discrimination in cluttered scenes. To support benchmarking, we synthesize audio descriptions for standard 3DVG datasets, including ScanRefer, Sr3D, and Nr3D. Experimental results demonstrate that Audio-3DVG not only achieves new state-of-the-art performance in audio-based grounding, but also competes with text-based methods-highlighting the promise of integrating spoken language into 3D vision tasks.
3D视觉定位(3DVG)涉及在自然语言的指导下在3D点云中定位目标对象。虽然先前的工作在文本描述方面取得了进展,但利用口语的基于音频的3D视觉定位(Audio-based 3D Visual Grounding)仍然被忽视且具有挑战性。受自动语音识别(ASR)和语音表示学习的进步的推动,我们提出了Audio-3DVG,这是一个简单有效的框架,它集成了音频和空间信息以增强定位。我们并不将语音视为单一输入,而是将任务分解为两个互补的组成部分。首先,我们引入了对象提及检测,这是一个多标签分类任务,明确识别音频中提到的对象,从而实现更结构化的音频场景推理。其次,我们提出了Audio-Guided Attention模块,该模块捕获候选对象和关系语音线索之间的交互,提高了杂乱场景中目标物体的辨别能力。为了支持基准测试,我们对标准的3DVG数据集(包括ScanRefer、Sr3D和Nr3D)进行了音频描述合成。实验结果表明,Audio-3DVG不仅在基于音频的定位方面达到了新的最先进的性能水平,而且在基于文本的方法中也具有竞争力,这突显了将口语融入3D视觉任务的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Work in progress, 42 pages
摘要
Audio-3DVG是一个简单有效的框架,整合音频和空间信息,用于增强3D点云中目标对象的定位。该框架利用自动语音识别和语音表示学习技术,将语音分解为对象提及检测和语音引导注意力两个互补任务,提高了目标识别和场景推理能力。合成音频描述支持基准测试,实验结果证明Audio-3DVG在音频定位方面达到新的先进水平,并在与文本定位方法的竞争中展现出潜力。
要点掌握
- Audio-3DVG框架整合音频和空间信息,增强3D点云中目标对象的定位。
- 借助自动语音识别和语音表示学习技术,处理语音信息。
- 框架包含两个互补任务:对象提及检测和语音引导注意力。
- 对象提及检测是一个多标签分类任务,明确识别音频中提到的对象,使场景推理更加结构化。
- 语音引导注意力模块捕捉候选对象和关系语音线索之间的交互,提高杂乱场景中目标辨别能力。
- 为支持基准测试,合成音频描述用于标准3DVG数据集。
点此查看论文截图

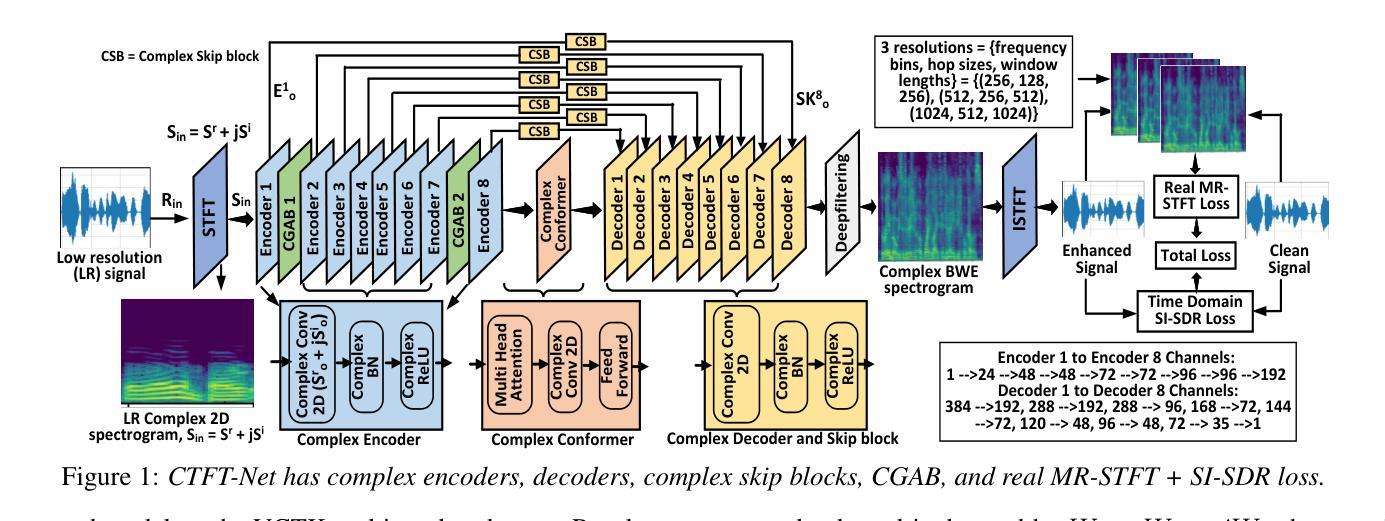
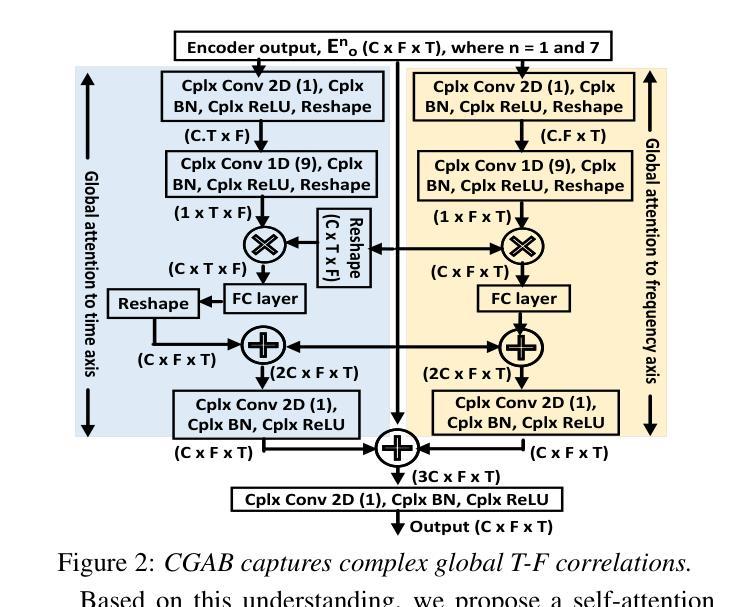
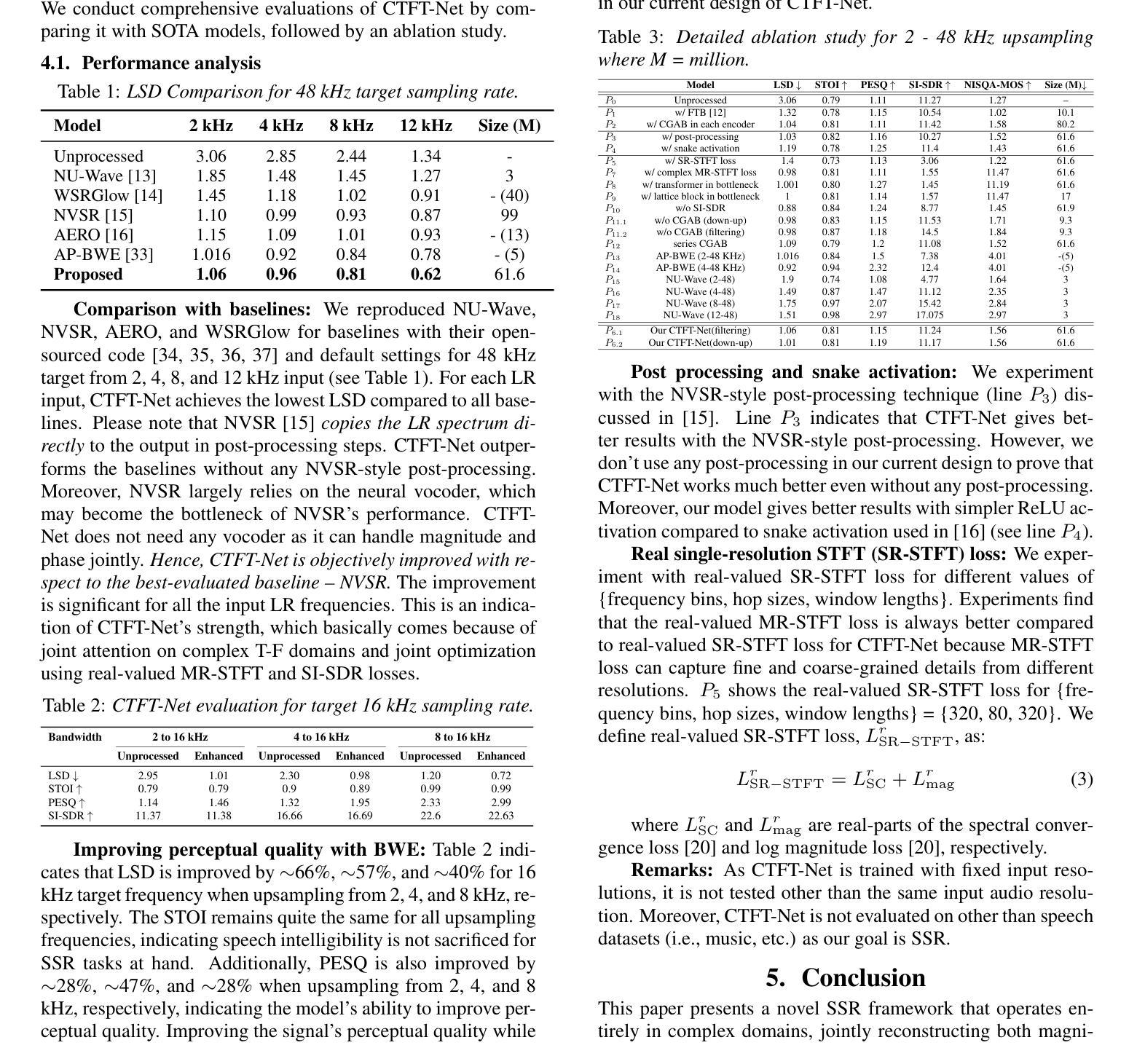
A High-Fidelity Speech Super Resolution Network using a Complex Global Attention Module with Spectro-Temporal Loss
Authors:Tarikul Islam Tamiti, Biraj Joshi, Rida Hasan, Rashedul Hasan, Taieba Athay, Nursad Mamun, Anomadarshi Barua
Speech super-resolution (SSR) enhances low-resolution speech by increasing the sampling rate. While most SSR methods focus on magnitude reconstruction, recent research highlights the importance of phase reconstruction for improved perceptual quality. Therefore, we introduce CTFT-Net, a Complex Time-Frequency Transformation Network that reconstructs both magnitude and phase in complex domains for improved SSR tasks. It incorporates a complex global attention block to model inter-phoneme and inter-frequency dependencies and a complex conformer to capture long-range and local features, improving frequency reconstruction and noise robustness. CTFT-Net employs time-domain and multi-resolution frequency-domain loss functions for better generalization. Experiments show CTFT-Net outperforms state-of-the-art models (NU-Wave, WSRGlow, NVSR, AERO) on the VCTK dataset, particularly for extreme upsampling (2 kHz to 48 kHz), reconstructing high frequencies effectively without noisy artifacts.
语音超分辨率(SSR)通过提高采样率来增强低分辨率语音。虽然大多数SSR方法主要集中在幅度重建上,但最近的研究强调了相位重建对提高感知质量的重要性。因此,我们引入了CTFT-Net,这是一种复杂的时间-频率转换网络,它在复杂域中重建幅度和相位,以改进SSR任务。它采用复杂的全局注意力块来建模音素间和频率间的依赖性,并采用复杂的转换器来捕获长程和局部特征,从而提高频率重建和抗噪性。CTFT-Net采用时域和多分辨率频域损失函数,以实现更好的泛化。实验表明,CTFT-Net在VCTK数据集上的表现优于最先进的模型(NU-Wave、WSRGlow、NVSR、AERO),特别是在极端上采样(2 kHz到48 kHz)情况下,能够有效地重建高频而无噪声伪影。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
语音超分辨率(SSR)通过提高采样率来提升低分辨率语音。当前大多数SSR方法主要关注幅度重建,但最新研究表明相位重建对于提高感知质量也很重要。因此,我们引入了CTFT-Net,这是一个在复杂域进行幅度和相位重建的复杂时频转换网络,以提高SSR任务的效果。它结合了复杂全局注意力块来建模音素间和频率间的依赖性,以及复杂变压器来捕捉长程和局部特征,提高了频率重建和噪声鲁棒性。CTFT-Net采用时域和多分辨率频域损失函数,以更好地推广。实验表明,CTFT-Net在VCTK数据集上优于其他最先进模型(NU-Wave、WSRGlow、NVSR、AERO),特别是在极端上采样(2 kHz至48 kHz)的情况下,能够有效地重建高频而没有噪声伪影。
Key Takeaways:
- 语音超分辨率(SSR)技术能通过提高采样率改善低分辨率语音。
- 目前的SSR方法多关注幅度重建,但相位重建对于提高语音感知质量也很重要。
- CTFT-Net是一个在复杂域进行幅度和相位重建的网络,旨在提高SSR效果。
- CTFT-Net结合了复杂全局注意力块和复杂变压器,以提高频率重建和噪声鲁棒性。
- CTFT-Net采用时域和多分辨率频域损失函数以实现更好的泛化能力。
- 实验表明CTFT-Net在VCTK数据集上的性能优于其他先进模型。
点此查看论文截图

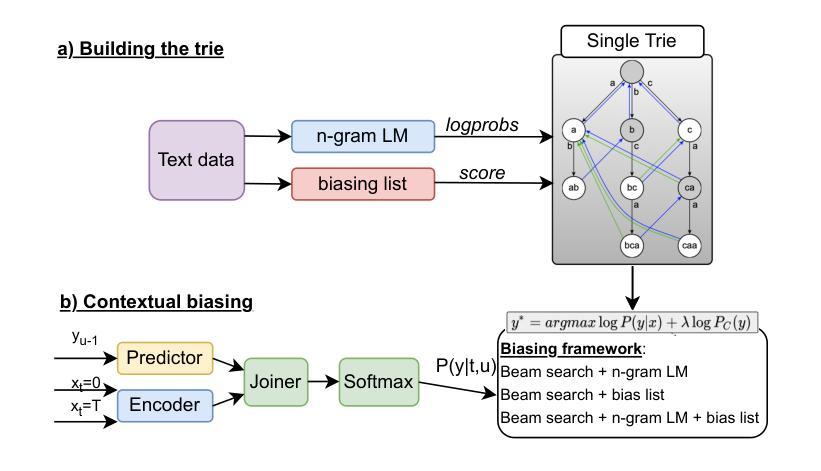
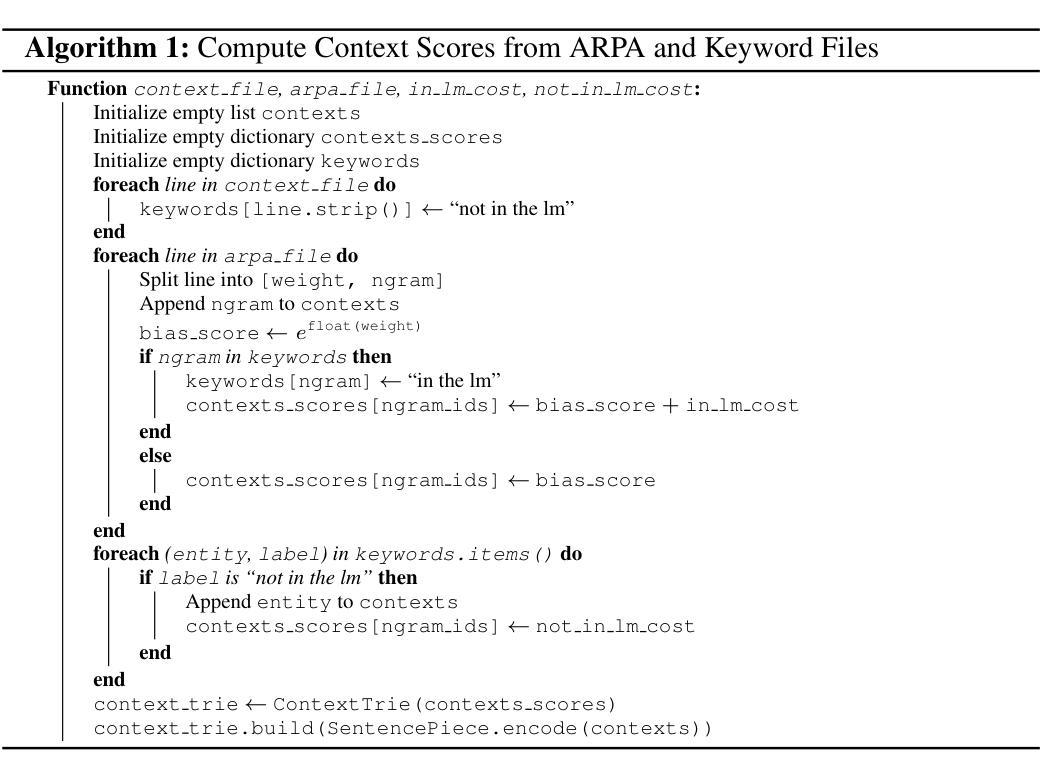
Unifying Global and Near-Context Biasing in a Single Trie Pass
Authors:Iuliia Thorbecke, Esaú Villatoro-Tello, Juan Zuluaga-Gomez, Shashi Kumar, Sergio Burdisso, Pradeep Rangappa, Andrés Carofilis, Srikanth Madikeri, Petr Motlicek, Karthik Pandia, Kadri Hacioğlu, Andreas Stolcke
Despite the success of end-to-end automatic speech recognition (ASR) models, challenges persist in recognizing rare, out-of-vocabulary words - including named entities (NE) - and in adapting to new domains using only text data. This work presents a practical approach to address these challenges through an unexplored combination of an NE bias list and a word-level n-gram language model (LM). This solution balances simplicity and effectiveness, improving entities’ recognition while maintaining or even enhancing overall ASR performance. We efficiently integrate this enriched biasing method into a transducer-based ASR system, enabling context adaptation with almost no computational overhead. We present our results on three datasets spanning four languages and compare them to state-of-the-art biasing strategies. We demonstrate that the proposed combination of keyword biasing and n-gram LM improves entity recognition by up to 32% relative and reduces overall WER by up to a 12% relative.
尽管端到端的自动语音识别(ASR)模型取得了成功,但在识别稀有、超出词汇表的单词(包括命名实体(NE))以及仅使用文本数据适应新领域方面仍存在挑战。本研究提出了一种通过NE偏置列表和词级n元语言模型(LM)的未探索组合来解决这些挑战的实际方法。此解决方案平衡了简单性和有效性,在保持或甚至提高总体ASR性能的同时,提高了实体的识别能力。我们有效地将这种丰富的偏向方法集成到基于转换器的ASR系统中,实现了上下文适应,几乎不需要计算开销。我们在三个跨越四种语言的数据集上展示我们的结果,并将它们与最新的偏向策略进行比较。我们证明了关键词偏向和n元LM的组合可以提高实体识别率,相对提高幅度高达32%,并将总体WER降低高达12%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to TSD2025
Summary
该文章介绍了一种针对自动语音识别(ASR)模型在识别稀有词和适应新领域方面的挑战的有效解决方案。通过结合命名实体(NE)偏列表和词级n-gram语言模型(LM),实现了简单有效的平衡,提高了实体识别能力,同时保持了整体ASR性能甚至有所提升。该方案被高效集成到基于转换器的ASR系统中,实现了上下文适应,几乎不增加计算开销。在跨越四种语言的三个数据集上的实验结果表明,关键词偏向与n-gram LM的组合提高了实体识别率达32%,并降低了整体字词错误率(WER)达12%。
Key Takeaways
- 文章中提出了一个解决自动语音识别(ASR)模型识别稀有词和适应新领域的新方法。
- 方法结合了命名实体(NE)偏列表和词级n-gram语言模型(LM),以实现简单性和有效性的平衡。
- 该方案可高效集成到基于转换器的ASR系统中,实现上下文适应,且几乎不增加计算开销。
- 实验结果表明,该方法提高了实体识别率,并降低了整体字词错误率(WER)。
- 与现有最先进的偏向策略相比,该方法在跨越四种语言的三个数据集上表现出更好的性能。
- 文章强调该方案在提高实体识别能力的同时,保持了或甚至提高了整体的ASR性能。
点此查看论文截图