⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-06 更新
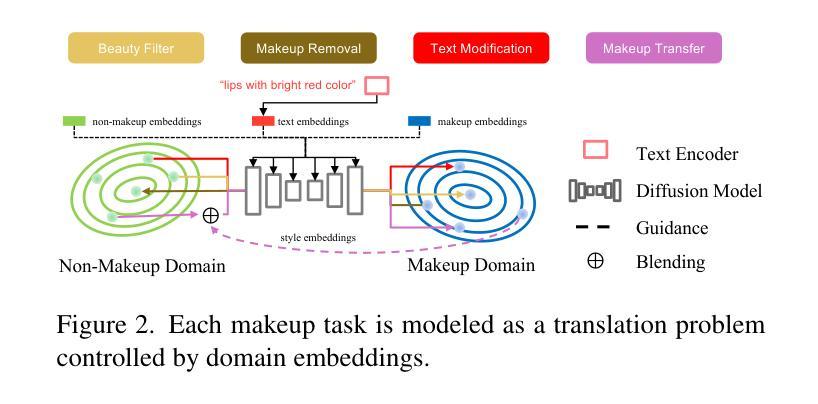
MAD: Makeup All-in-One with Cross-Domain Diffusion Model
Authors:Bo-Kai Ruan, Hong-Han Shuai
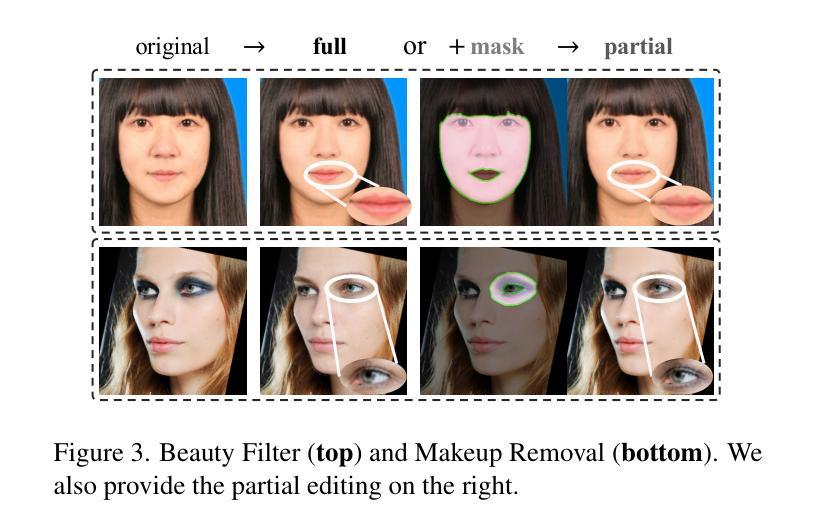
Existing makeup techniques often require designing multiple models to handle different inputs and align features across domains for different makeup tasks, e.g., beauty filter, makeup transfer, and makeup removal, leading to increased complexity. Another limitation is the absence of text-guided makeup try-on, which is more user-friendly without needing reference images. In this study, we make the first attempt to use a single model for various makeup tasks. Specifically, we formulate different makeup tasks as cross-domain translations and leverage a cross-domain diffusion model to accomplish all tasks. Unlike existing methods that rely on separate encoder-decoder configurations or cycle-based mechanisms, we propose using different domain embeddings to facilitate domain control. This allows for seamless domain switching by merely changing embeddings with a single model, thereby reducing the reliance on additional modules for different tasks. Moreover, to support precise text-to-makeup applications, we introduce the MT-Text dataset by extending the MT dataset with textual annotations, advancing the practicality of makeup technologies.
现有的化妆技术通常需要设计多个模型来处理不同的输入,并在不同的化妆任务(如美颜滤镜、化妆迁移和化妆移除)之间跨域对齐特征,这增加了复杂性。另一个局限性在于缺乏文本引导的化妆试戴功能,该功能在用户无需参考图像的情况下更为友好。在本研究中,我们首次尝试使用单一模型进行各种化妆任务。具体来说,我们将不同的化妆任务制定为跨域翻译,并利用跨域扩散模型来完成所有任务。与现有方法不同,这些方法依赖于单独的编码器-解码器配置或基于循环的机制,我们建议使用不同的域嵌入来促进域控制。这允许通过简单地更改嵌入来使用单个模型进行无缝域切换,从而减少对不同任务模块的依赖。此外,为了支持精确的文本到化妆应用程序,我们通过扩展MT数据集并添加文本注释来引入MT-Text数据集,从而提高了化妆技术的实用性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPRW2025
Summary
本文提出使用单一模型完成多种化妆任务的研究。通过跨域扩散模型实现不同化妆任务,如美容滤镜、化妆迁移和化妆移除等。采用不同域嵌入实现域控制,支持精确文本指导的化妆应用,并扩展MT数据集,创建MT-Text数据集以推动化妆技术的实用性。
Key Takeaways
- 使用单一模型处理多种化妆任务,简化设计复杂性。
- 采用跨域扩散模型实现不同化妆任务,如美容滤镜和化妆迁移等。
- 利用不同域嵌入实现域控制,方便在不同领域间无缝切换。
- 通过改变嵌入方式,仅使用一个模型即可完成各种任务,减少对额外模块的依赖。
- 为了支持精确的文本指导的化妆应用,扩展MT数据集创建MT-Text数据集。
- 通过文本注释提高数据集的实用性。
点此查看论文截图



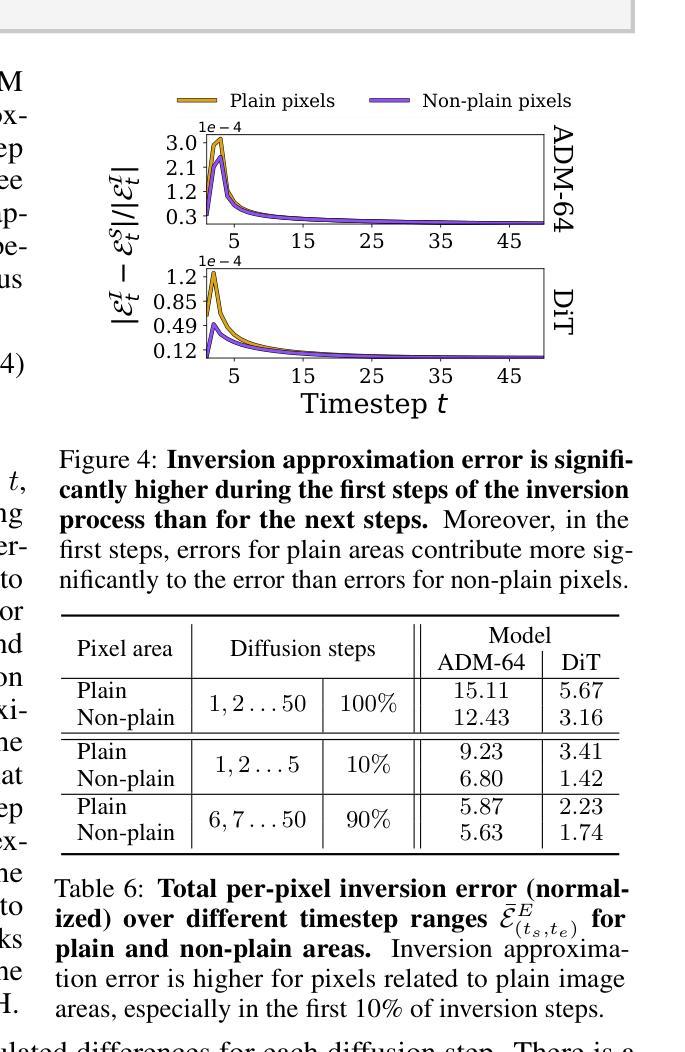
There and Back Again: On the relation between Noise and Image Inversions in Diffusion Models
Authors:Łukasz Staniszewski, Łukasz Kuciński, Kamil Deja
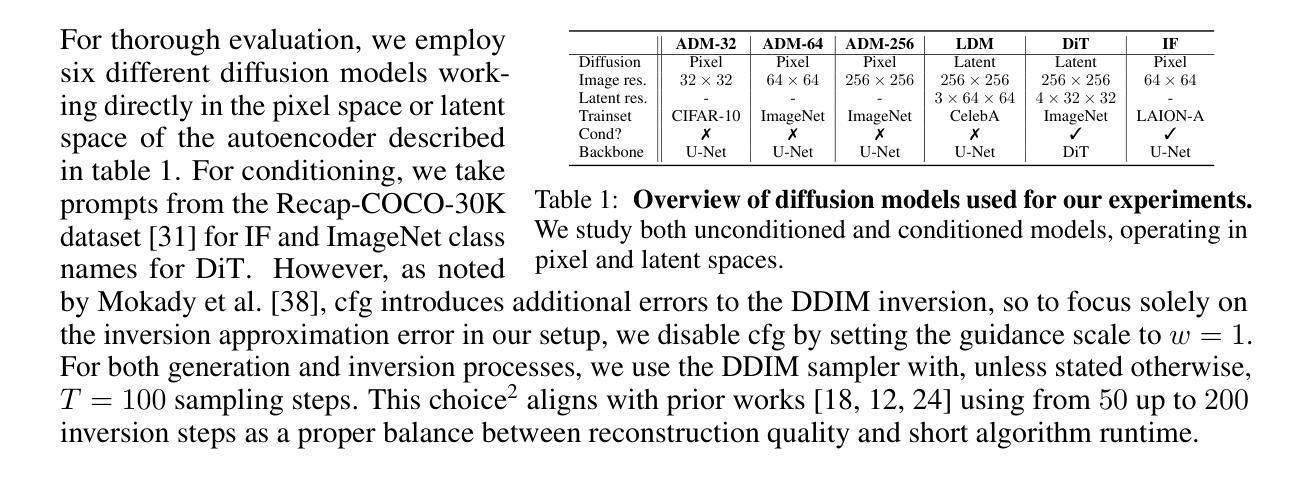
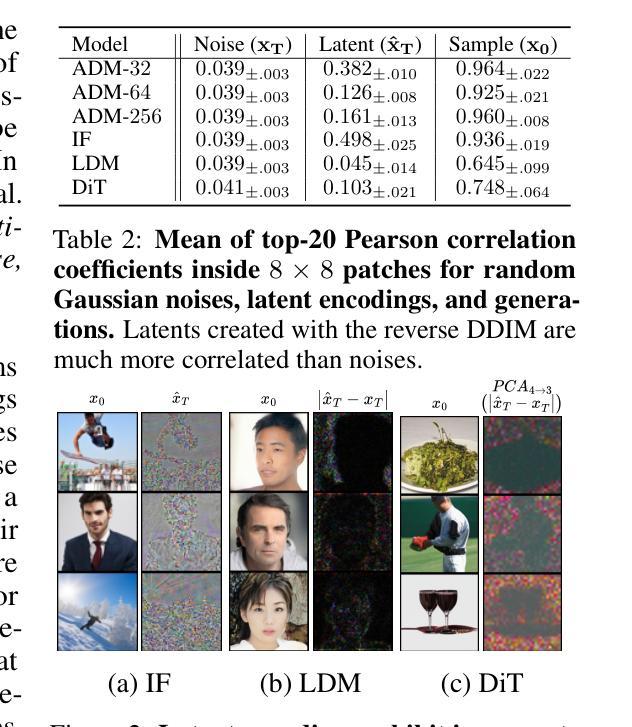
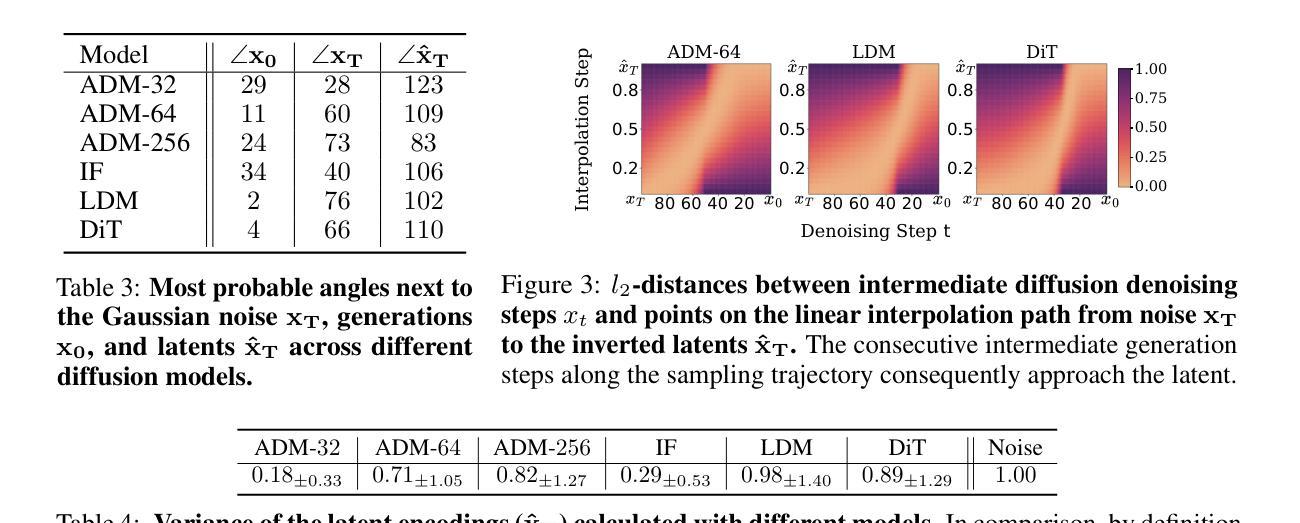
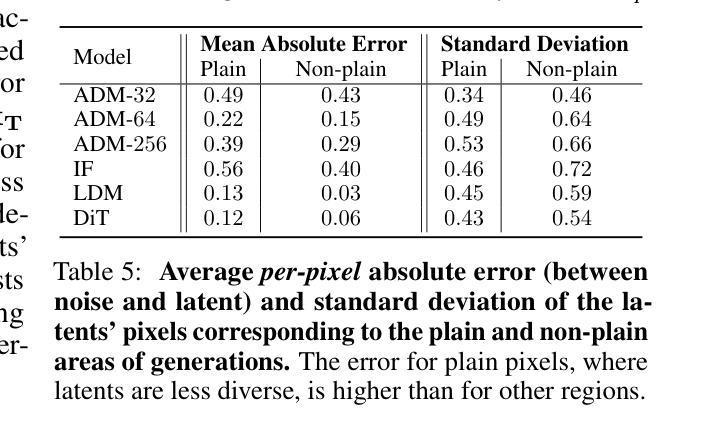
Diffusion Models achieve state-of-the-art performance in generating new samples but lack a low-dimensional latent space that encodes the data into meaningful features. Inversion-based methods address this by reversing the denoising trajectory, mapping each image back to its approximated starting noise. In this work, we thoroughly analyze this procedure and focus on the relation between the initial Gaussian noise, the generated samples, and their corresponding latent encodings obtained through the DDIM inversion. First, we show that latents exhibit structural patterns in the form of less diverse noise predicted for smooth image regions. As a consequence of this divergence, we present that the space of image inversions is notably less manipulative than the original Gaussian noise. Next, we explain the origin of the phenomenon, demonstrating that, during the first inversion steps, the noise prediction error is much more significant for the plain areas than for the rest of the image. As a surprisingly simple solution, we propose to replace the first DDIM Inversion steps with a forward diffusion process, which successfully decorrelates latent encodings, leading to higher quality editions and interpolations. The code is available at https://github.com/luk-st/taba.
扩散模型在生成新样本方面达到了最先进的性能,但缺乏一个低维潜在空间,无法将数据编码为有意义的特征。基于反转的方法通过反转去噪轨迹来解决这个问题,将每张图像映射回其近似初始噪声。在这项工作中,我们彻底分析了这一过程,并重点关注初始高斯噪声、生成样本以及通过DDIM反转获得的相应潜在编码之间的关系。首先,我们展示潜在值在平滑图像区域的预测噪声中表现出结构模式,形式为较少的多样性。由于这种分歧,我们提出图像反转的空间明显比原始高斯噪声更不容易操控。接下来,我们解释了这种现象的起源,证明在第一次反转步骤中,对于平坦区域,噪声预测误差比图像其余部分更为显著。作为一个出人意料的简单解决方案,我们提出用正向扩散过程替换最初的DDIM反转步骤,这成功地解耦了潜在编码,导致更高的编辑和插值质量。代码可在https://github.com/luk-st/taba找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint
Summary
本文探讨了Diffusion Models在生成新样本时的最新性能表现,并针对其缺乏低维潜在空间的问题进行了分析。研究中,研究者们采用基于反演的方法,通过将图像反演回其近似初始噪声来解决这一问题。研究重点是初始高斯噪声、生成样本以及通过DDIM反演获得的相应潜在编码之间的关系。研究结果显示,潜在空间展现出结构化模式,平滑图像区域的噪声预测较少。反演空间相较于原始高斯噪声的操控性显著降低。此外,研究还解释了该现象的起因,并发现最初的反演步骤中的噪声预测误差在平坦区域上比其他区域更为显著。为解决这一问题,研究者们提出了一个简单的方法,即用正向扩散过程替换最初的DDIM反演步骤,成功地去除了潜在编码的相关性,提高了编辑和插值的质量。相关代码已上传至GitHub仓库“taba”。
Key Takeaways
- Diffusion Models虽能生成先进样本,但不具备将数据编码为有意义的特征的低维潜在空间。
- 基于反演的方法通过将图像反演回其近似初始噪声来解决此问题。
- 潜在空间展现出结构化模式,平滑图像区域的噪声预测较少。
- 反演空间相较于原始高斯噪声的操控性显著降低。
- 最初的反演步骤中的噪声预测误差在平坦区域上更为显著。
- 用正向扩散过程替换最初的DDIM反演步骤可以提高编辑和插值的质量。
点此查看论文截图