⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-06 更新
Application of the microscopic optical potential of chiral effective field theory in astrophysical neutron-capture reactions
Authors:Bing Wang, Dong Bai, Yi Xu
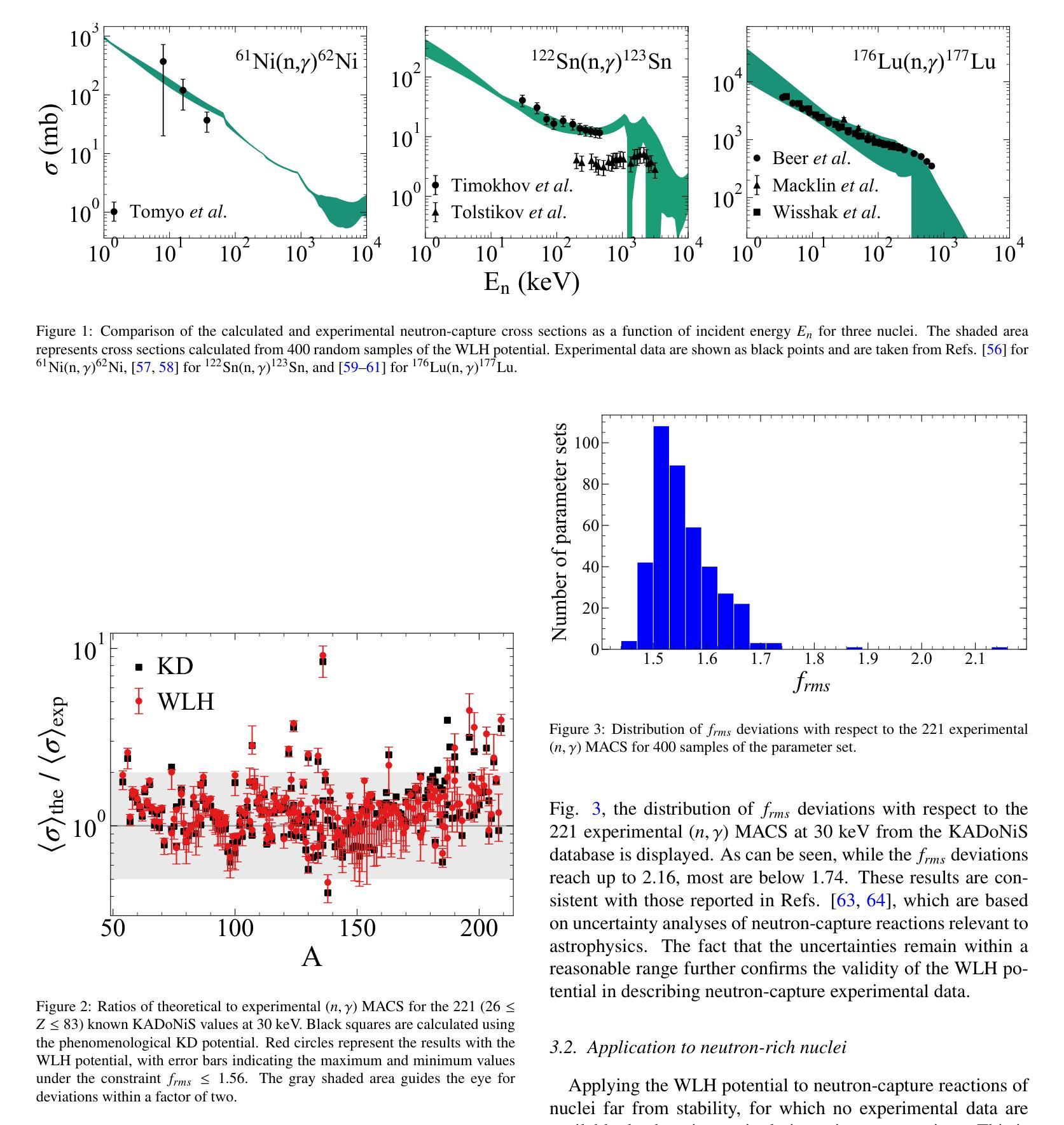
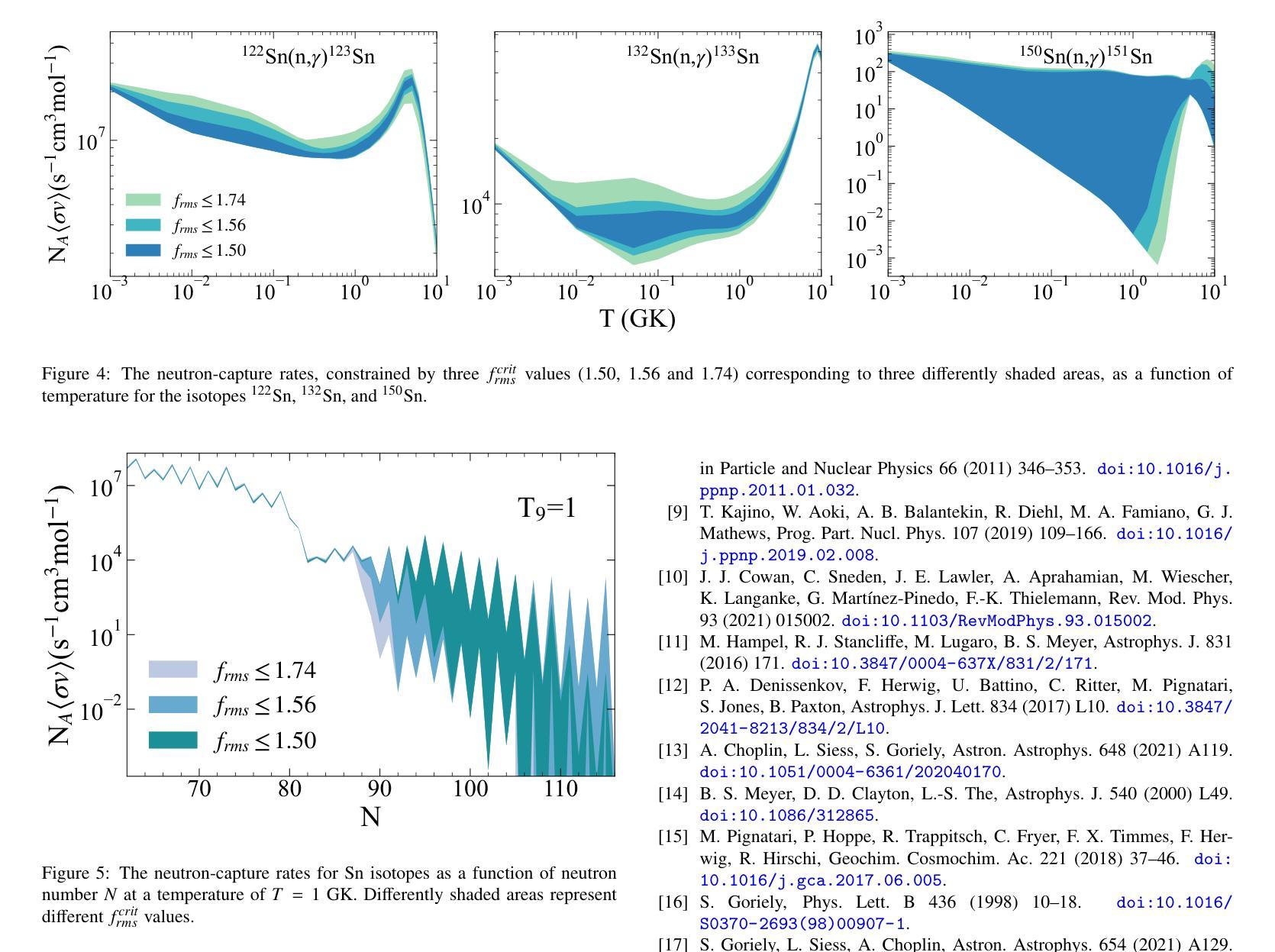
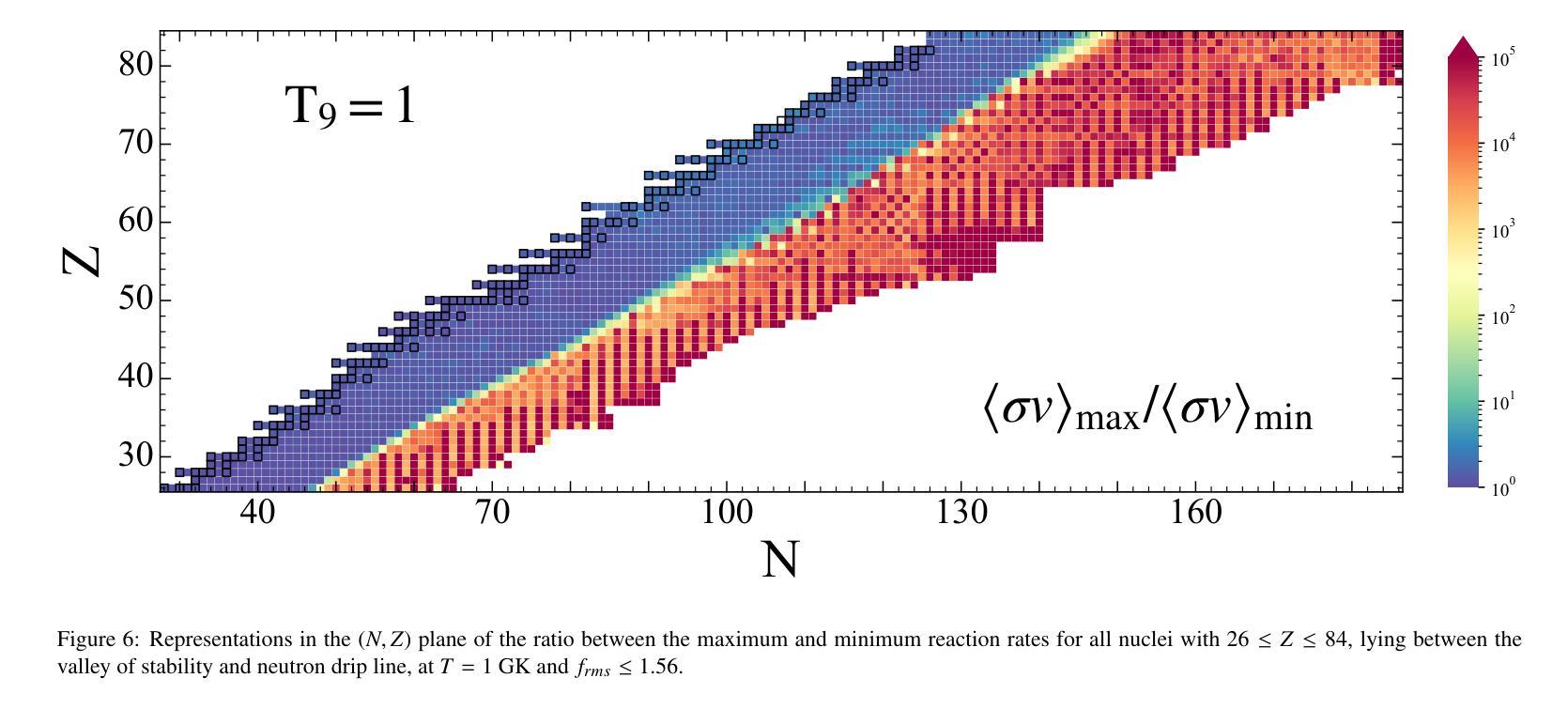
The microscopic global nucleon-nucleus optical potential proposed by Whitehead, Lim, and Holt (WLH) is a state-of-the-art potential developed within the framework of many-body perturbation theory using realistic nuclear interactions from chiral effective field theory. Given its potentially greater predictive power for reactions involving exotic isotopes, we apply it to the calculations of astrophysical neutron-capture reactions for the first time, which are particularly important to the nucleosynthesis of elements heavier than iron. It is found that this potential provides a good description of experimental known neutron-capture cross sections and Maxwellian-averaged cross sections. For unstable neutron-rich nuclei, we comprehensively calculate the neutron-capture reaction rates for all nuclei with $26\leq Z\leq84$, located between the valley of stability and the neutron drip line, using the backward-forward Monte Carlo method with the $f_{rms}$ deviation as the $\chi^2$ estimator. The results reveal a noticeable separation in the uncertainty of rates around an isospin asymmetry of 0.28 under the constraint $f_{rms} \leq 1.56$. This highlights the critical role of isospin dependence in optical potentials and suggests that future developments of the WLH potential may pay special attention to the isospin dependence.
Whitehead、Lim和Holt提出的微观全局核子-核光学势是一种前沿势,它基于多体扰动理论框架开发,并使用手性有效场理论中的现实核相互作用。由于它对涉及奇异同位素的反应具有更大的预测能力,我们首次将其应用于天文中子捕获反应的计算,这对重于铁的元素的核合成特别重要。研究发现,该势对已知的中子捕获截面和麦克斯韦平均截面提供了很好的描述。对于不稳定的中子富核,我们全面计算了位于稳定谷和中子滴线之间的所有原子核($26\leq Z\leq84$)的中子捕获反应速率,采用逆向正向蒙特卡洛方法,以$f_{rms}$偏差作为$\chi^2$估算器。结果表明,在isospin不对称性为0.28的情况下,不确定性有明显的分离,且在$f_{rms} \leq 1.56$的约束下。这突出了光学势中的同位旋依赖性的关键作用,并暗示未来对WLH势的发展可能需要特别注意同位旋依赖性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了Whitehead、Lim和Holt提出的微观全球核子-核光学势,该势是在多体扰动理论的框架内,使用来自手性有效场理论的现实核相互作用而发展的。文章首次将其应用于计算对天体物理学中的中子捕获反应,这对重于铁的元素的核合成特别重要。该势很好地描述了已知的中子捕获截面和麦克斯韦平均截面。对于不稳定的中子富核,文章计算了位于稳定谷和中子滴线之间的所有$26\leq Z\leq84$核的中子捕获反应速率,结果显示在总质子数约为质量数的四分之一时不确定性显著分离。这突显了光学势中同位素依赖性的关键作用,建议未来对WLH势的发展应特别注意同位素依赖性。
Key Takeaways
- Whitehead、Lim和Holt提出了基于多体扰动理论和手性有效场理论的微观全球核子-核光学势。
- 该势首次被应用于计算天体物理学中的中子捕获反应,这对重元素核合成研究至关重要。
- 该势能很好地描述已知的中子捕获截面和麦克斯韦平均截面。
- 对于不稳定的中子富核,文章计算了特定范围内的中子捕获反应速率。
- 在总质子数约为质量数的四分之一时,反应速率的不确定性显著分离。
- 这突显了光学势中同位素依赖性的关键作用。
点此查看论文截图

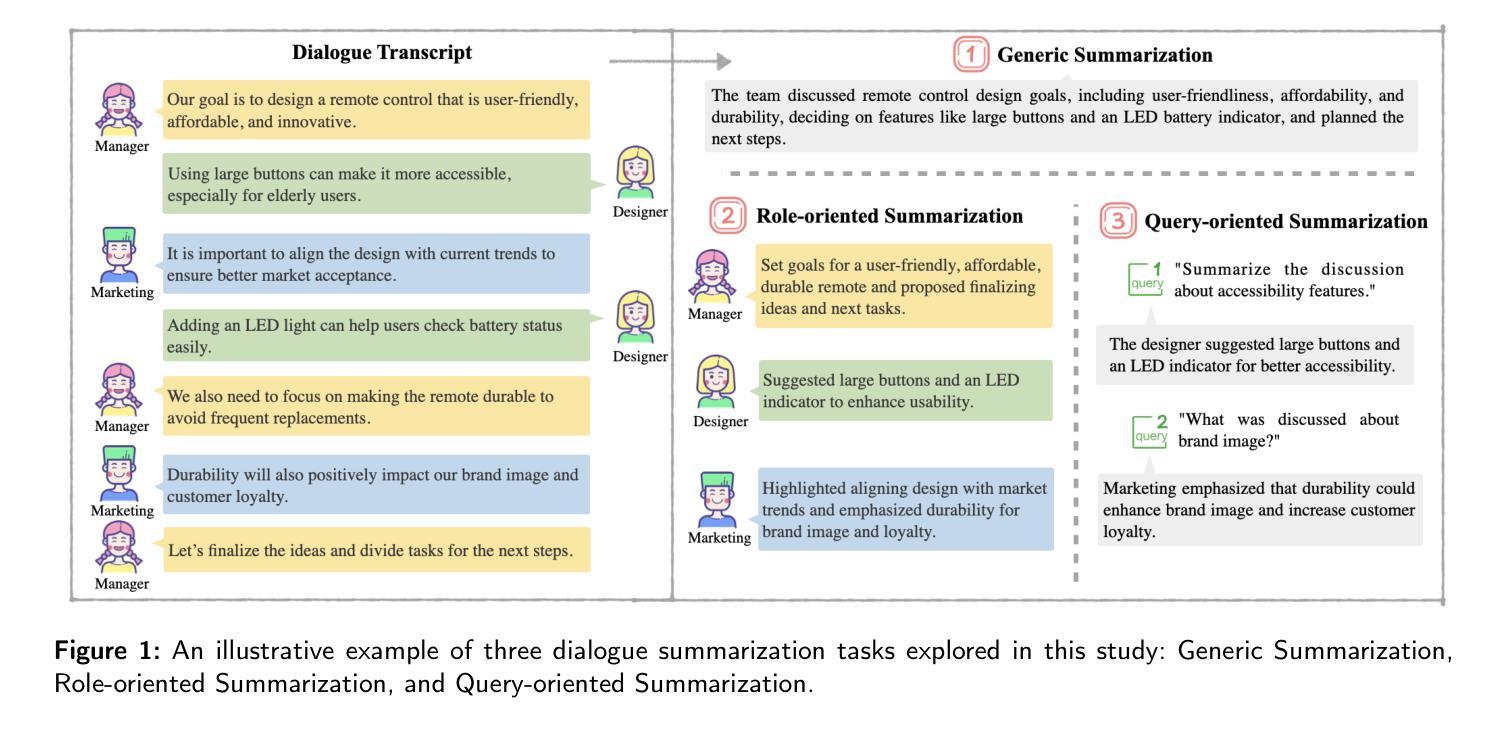
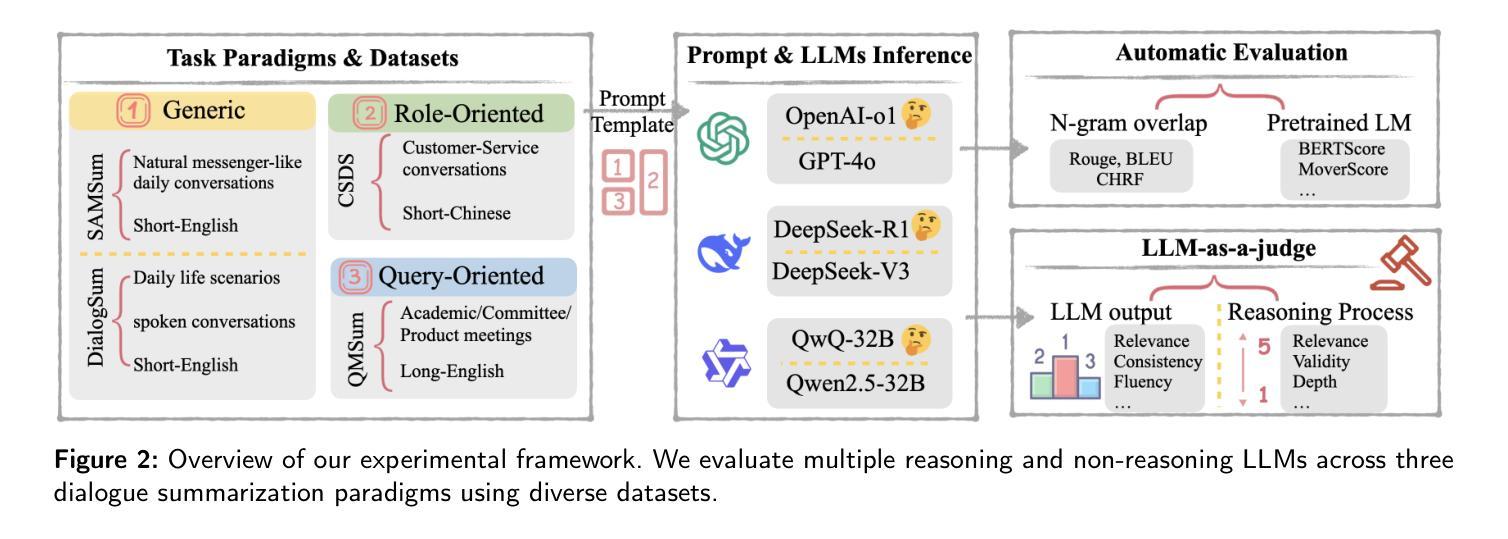
Reasoning or Not? A Comprehensive Evaluation of Reasoning LLMs for Dialogue Summarization
Authors:Keyan Jin, Yapeng Wang, Leonel Santos, Tao Fang, Xu Yang, Sio Kei Im, Hugo Gonçalo Oliveira
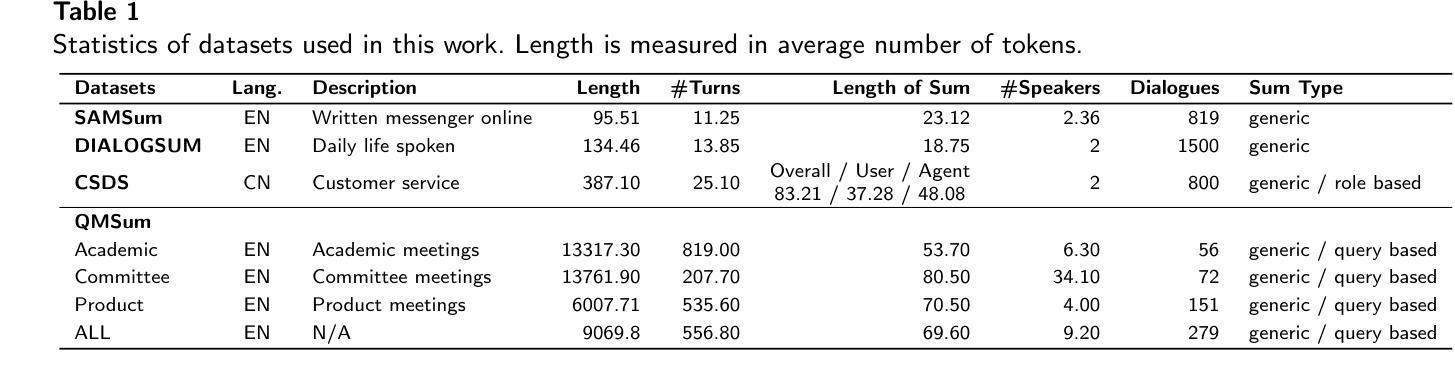
Dialogue summarization is a challenging task with significant practical value in customer service, meeting analysis, and conversational AI. Although large language models (LLMs) have achieved substantial progress in summarization tasks, the performance of step-by-step reasoning architectures-specifically Long Chain-of-Thought (CoT) implementations such as OpenAI-o1 and DeepSeek-R1-remains unexplored for dialogue scenarios requiring concurrent abstraction and conciseness. In this work, we present the first comprehensive and systematic evaluation of state-of-the-art reasoning LLMs and non-reasoning LLMs across three major paradigms-generic, role-oriented, and query-oriented dialogue summarization. Our study spans diverse languages, domains, and summary lengths, leveraging strong benchmarks (SAMSum, DialogSum, CSDS, and QMSum) and advanced evaluation protocols that include both LLM-based automatic metrics and human-inspired criteria. Contrary to trends in other reasoning-intensive tasks, our findings show that explicit stepwise reasoning does not consistently improve dialogue summarization quality. Instead, reasoning LLMs are often prone to verbosity, factual inconsistencies, and less concise summaries compared to their non-reasoning counterparts. Through scenario-specific analyses and detailed case studies, we further identify when and why explicit reasoning may fail to benefit-or even hinder-summarization in complex dialogue contexts. Our work provides new insights into the limitations of current reasoning LLMs and highlights the need for targeted modeling and evaluation strategies for real-world dialogue summarization.
对话摘要是一项具有客户服务、会议分析和会话人工智能等实际应用价值的挑战任务。尽管大型语言模型(LLM)在摘要任务方面取得了重大进展,但在需要并发抽象和简洁性的对话场景中,分步推理架构(特别是长链思维(CoT)实施,如OpenAI-o1和DeepSeek-R1)的表现仍未被探索。在这项工作中,我们对最先进的推理LLM和非推理LLM进行了首次全面系统的评估,涵盖了三种主要的范式:通用、面向角色和面向查询的对话摘要。我们的研究涵盖了多种语言、领域和摘要长度,利用强大的基准测试(SAMSum、DialogSum、CSDS和QMSum)和先进的评估协议,包括基于LLM的自动指标和人类启发标准。与其他需要逻辑推理的密集型任务趋势相反,我们的研究发现,明确的逐步推理并不能持续提高对话摘要的质量。相反,与没有推理功能的LLM相比,具有推理功能的LLM往往容易出现冗余、事实不一致和摘要不够简洁的问题。通过特定场景分析和详细的案例研究,我们还进一步确定了何时以及为什么明确的推理可能在复杂的对话环境中无法带来好处,甚至可能产生阻碍。我们的工作提供了对当前推理LLM局限性的新见解,并强调了针对现实世界对话摘要进行有针对性的建模和评估策略的需求。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文全面评估了先进的大型语言模型(LLM)在对话摘要任务中的性能,特别探讨了基于长链思维(CoT)的推理模型在对话场景中的表现。研究发现在对话摘要任务中,明确的步骤推理并不总能提升摘要质量。相反,推理LLM易产生冗长、事实错误和不够简洁的摘要。本研究揭示了当前推理LLM的局限性,并强调了为真实世界对话摘要任务进行针对性建模和评估的必要性。
Key Takeaways
- 对话摘要是一个具有实践价值的挑战任务,在客户服务、会议分析和对话式AI中有广泛应用。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)已在摘要任务中取得显著进展,但针对对话场景的推理架构,如长链思维(CoT),尚未得到充分探索。
- 推理LLM在对话摘要任务中并不总是能提高性能,有时会产生冗长、事实错误和不简洁的摘要。
- 现有的LLM在复杂对话上下文中的摘要任务中存在局限性。
- 研究发现了针对不同对话摘要任务的针对性建模和评估策略的必要性。
- 场景特定的分析和详细案例研究揭示了何时以及为何明确的推理可能无法对复杂的对话上下文中的摘要任务产生积极影响,甚至产生阻碍。
点此查看论文截图

Efficient Out-of-Scope Detection in Dialogue Systems via Uncertainty-Driven LLM Routing
Authors:Álvaro Zaera, Diana Nicoleta Popa, Ivan Sekulic, Paolo Rosso
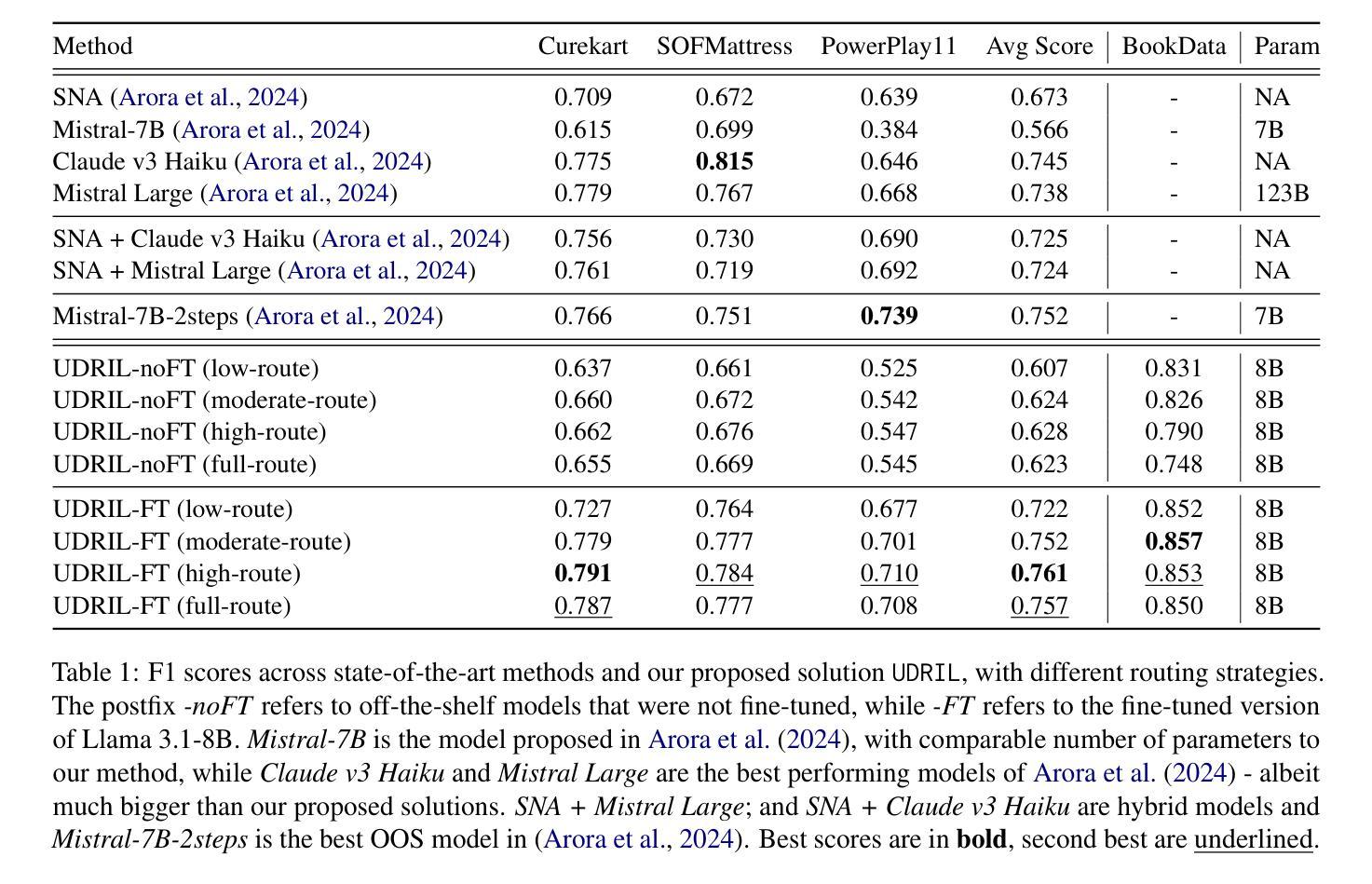
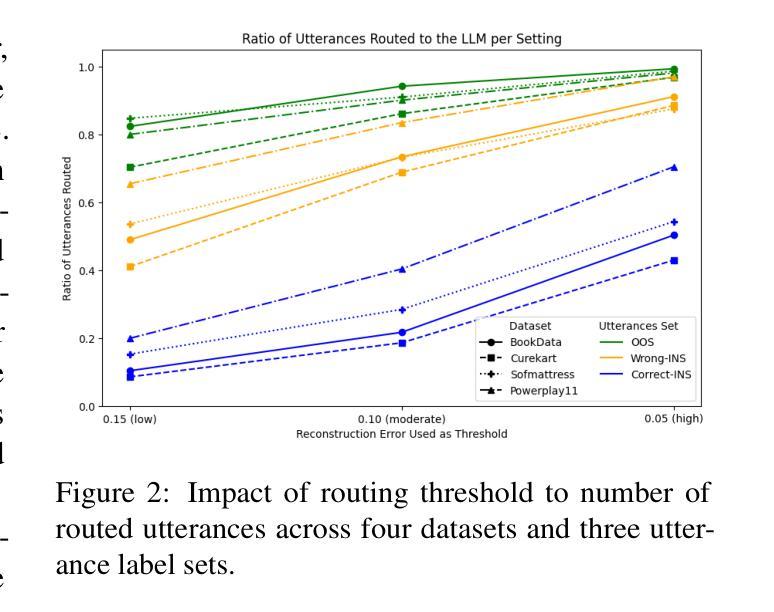
Out-of-scope (OOS) intent detection is a critical challenge in task-oriented dialogue systems (TODS), as it ensures robustness to unseen and ambiguous queries. In this work, we propose a novel but simple modular framework that combines uncertainty modeling with fine-tuned large language models (LLMs) for efficient and accurate OOS detection. The first step applies uncertainty estimation to the output of an in-scope intent detection classifier, which is currently deployed in a real-world TODS handling tens of thousands of user interactions daily. The second step then leverages an emerging LLM-based approach, where a fine-tuned LLM is triggered to make a final decision on instances with high uncertainty. Unlike prior approaches, our method effectively balances computational efficiency and performance, combining traditional approaches with LLMs and yielding state-of-the-art results on key OOS detection benchmarks, including real-world OOS data acquired from a deployed TODS.
面向任务的对话系统(TODS)中的意图识别是技术层面一大挑战,需要处理看不见和复杂的查询问题,以保障系统的稳健性。在此工作中,我们提出一个全新的简单模块化框架,它结合了不确定性建模与经过精细训练的大型语言模型(LLM),以提高意外情况识别(OOS)的有效性和准确性。第一步是向当前已经在处理数万个用户每日互动的实时TODS系统中部署的面向意图检测分类器的输出应用不确定性估计。第二步利用新兴的大型语言模型,对于具有较大不确定性的案例触发精细训练的大型语言模型做出最终决策。不同于传统方法,我们的方法能够有效平衡计算效率和性能表现,通过将传统方法和大型语言模型结合并应用现实应用获得最优表现成果。这包括对实时大型TODS获得的现实世界意外情况数据的测试。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种结合不确定性建模和微调大型语言模型(LLM)的新型模块化框架,用于任务导向对话系统(TODS)中的超出范围(OOS)意图检测。该方法首先估计在范围意图检测分类器输出上的不确定性,然后在具有不确定性的实例上触发微调LLM进行最终决策。该方法结合了传统方法和LLM的优势,实现了计算效率和性能之间的平衡,并在关键的OOS检测基准测试中取得了最先进的成果。
Key Takeaways
- OOS意图检测是任务导向对话系统(TODS)的关键挑战,需要确保对未见和模糊查询的鲁棒性。
- 提出了一种新型模块化框架,结合了不确定性建模和微调大型语言模型(LLM)进行OOS检测。
- 该方法首先应用不确定性估计到现有的在范围意图检测分类器上。
- 利用新兴的大型语言模型(LLM)进行最终决策,特别是在具有不确定性的实例上。
- 方法结合了传统方法和LLM的优势,实现了计算效率和性能之间的平衡。
- 在关键的OOS检测基准测试上取得了最先进的成果。
点此查看论文截图

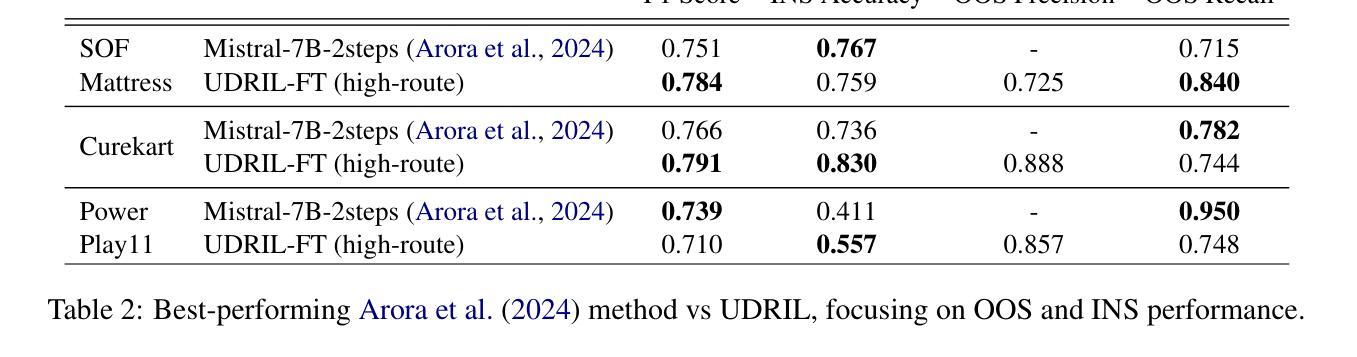
Physics-informed Ground Reaction Dynamics from Human Motion Capture
Authors:Cuong Le, Huy-Phuong Le, Duc Le, Minh-Thien Duong, Van-Binh Nguyen, My-Ha Le
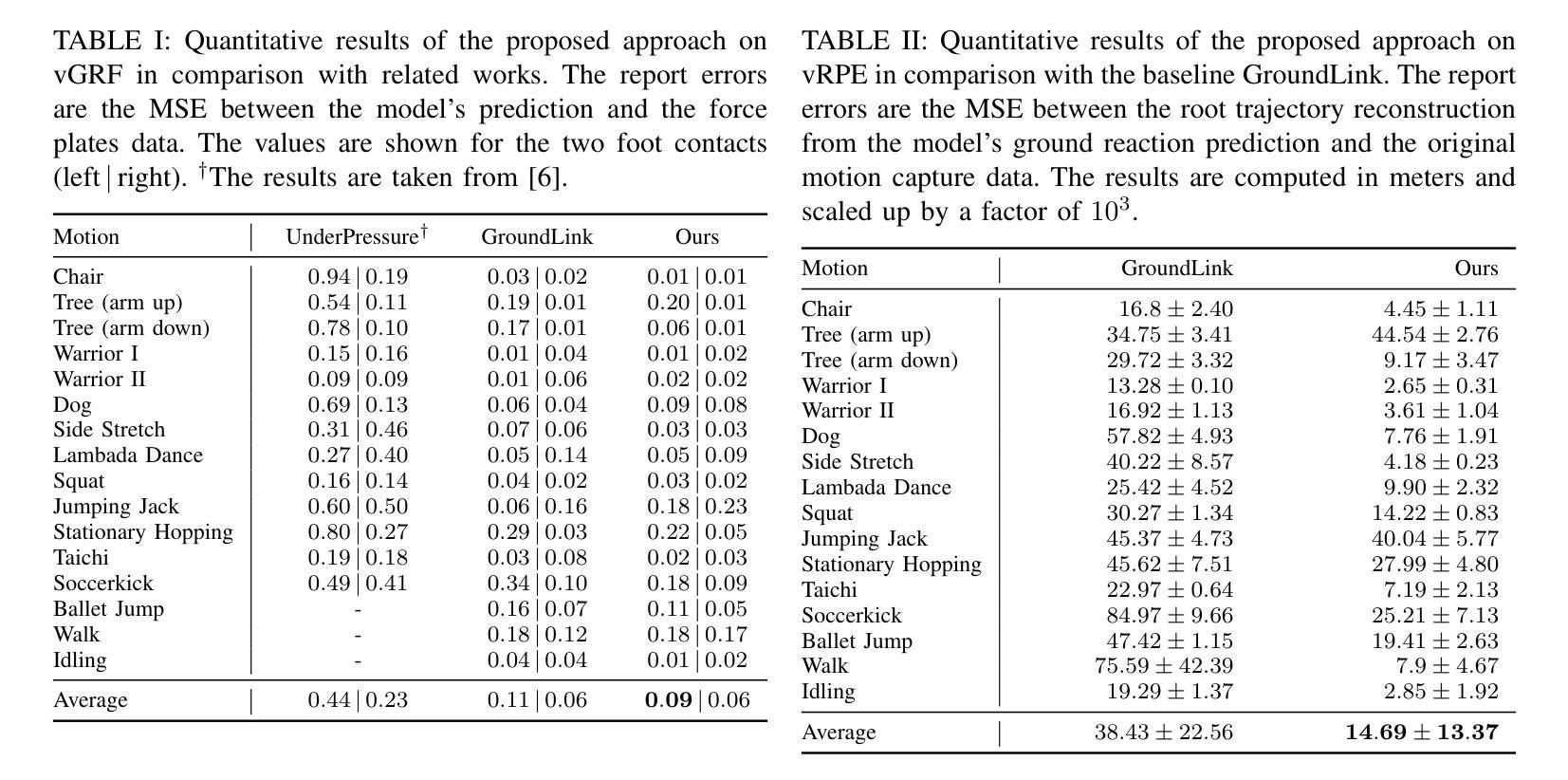
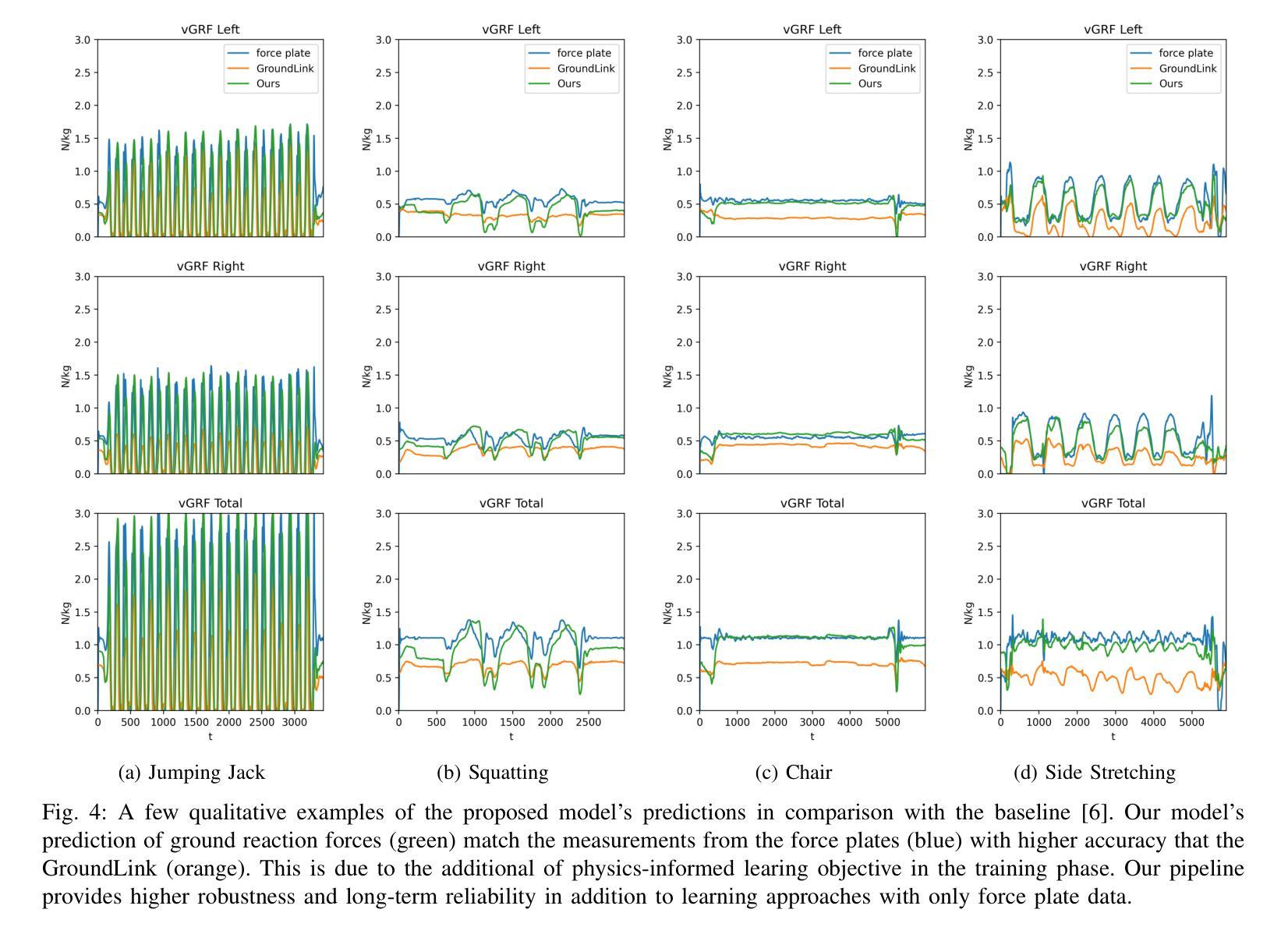
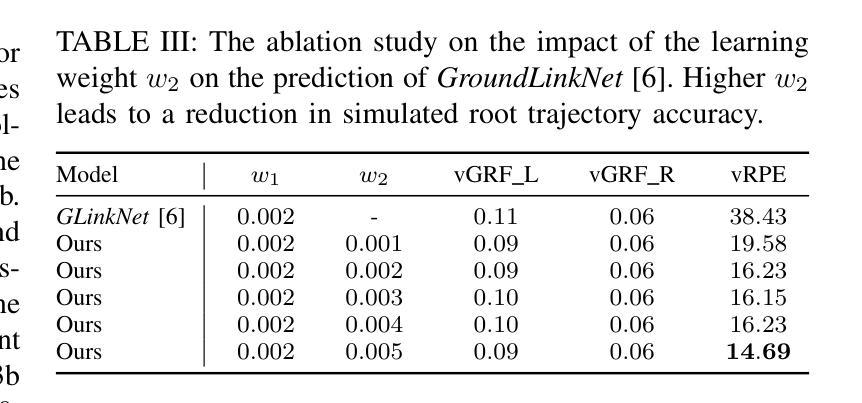
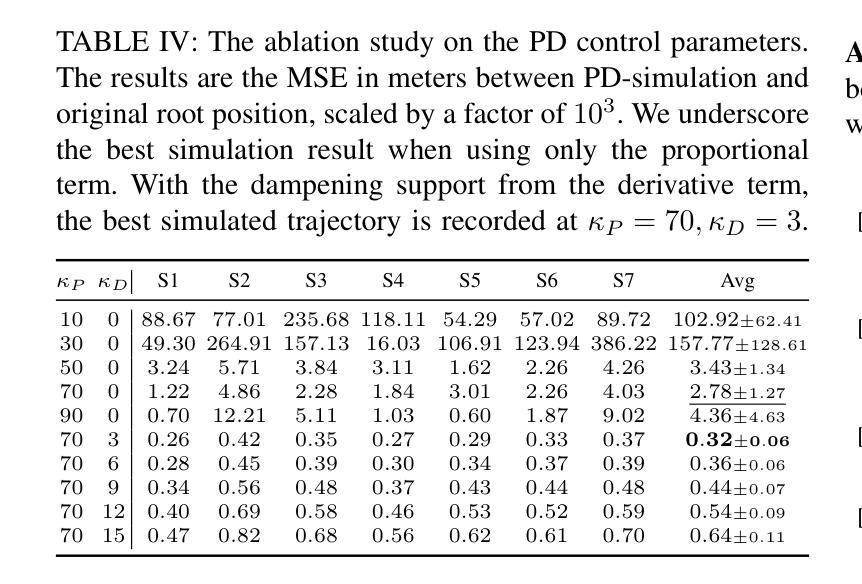
Body dynamics are crucial information for the analysis of human motions in important research fields, ranging from biomechanics, sports science to computer vision and graphics. Modern approaches collect the body dynamics, external reactive force specifically, via force plates, synchronizing with human motion capture data, and learn to estimate the dynamics from a black-box deep learning model. Being specialized devices, force plates can only be installed in laboratory setups, imposing a significant limitation on the learning of human dynamics. To this end, we propose a novel method for estimating human ground reaction dynamics directly from the more reliable motion capture data with physics laws and computational simulation as constrains. We introduce a highly accurate and robust method for computing ground reaction forces from motion capture data using Euler’s integration scheme and PD algorithm. The physics-based reactive forces are used to inform the learning model about the physics-informed motion dynamics thus improving the estimation accuracy. The proposed approach was tested on the GroundLink dataset, outperforming the baseline model on: 1) the ground reaction force estimation accuracy compared to the force plates measurement; and 2) our simulated root trajectory precision. The implementation code is available at https://github.com/cuongle1206/Phys-GRD
人体动力学是分析人体运动的重要信息,在生物力学、运动科学、计算机视觉和图形学等重要研究领域都发挥着关键作用。现代的方法通过力板收集人体动力学,特别是外部反应力,并与人体运动捕获数据进行同步,学习从黑箱深度学习模型中估计动力学。由于力板是专业设备,只能在实验室环境中安装,因此对学习人体动力学造成了重大限制。为此,我们提出了一种新方法,可以直接从更可靠的运动捕获数据中估计人体地面反应动力学,以物理定律和计算模拟作为约束。我们引入了一种使用欧拉积分方案和PD算法从运动捕获数据中计算地面反应力的高精度且稳健的方法。基于物理的反应力用于向学习模型提供关于物理信息的运动动力学,从而提高估计精度。所提出的方法在GroundLink数据集上进行了测试,与基线模型相比在以下方面表现出优越性:1)地面反应力的估计精度与力板测量结果的比较;2)我们的模拟根轨迹精度。实现代码可在https://github.com/cuongle1206/Phys-GRD中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 4 figures, 4 tables, HSI 2025
摘要
本文提出一种新型方法,利用运动捕捉数据直接估计人体地面反应动力学,采用物理定律和计算模拟作为约束,无需使用专门的力板设备。通过欧拉积分方案和PD算法,从运动捕捉数据中计算地面反应力,提高学习模型的物理信息运动动力学估算精度。该方法在GroundLink数据集上进行测试,相较于基准模型,在地面反应力估算精度和模拟根轨迹精度方面表现更优。
要点掌握
- 人体动力学研究的重要性:在生物力学、运动科学、计算机视觉和图形学等领域中,人体动力学分析具有重要意义。
- 现代方法通过力板收集人体动力学信息,并与运动捕捉数据同步,通过深度学习模型进行估算。
- 力板的局限性:只能安装在实验室环境,限制了人体动力学的学习。
- 新方法介绍:提出一种从运动捕捉数据估计地面反应动力的新方法,使用物理定律和计算模拟作为约束。
- 采用欧拉积分方案和PD算法计算地面反应力,提高学习模型的物理信息运动动力学估算精度。
- 测试与性能:在GroundLink数据集上测试,结果显示新方法在地面反应力估算精度和模拟根轨迹精度方面优于基准模型。
点此查看论文截图
Who Should I Listen To? Adaptive Collaboration in Personalized Federated Learning
Authors:Amr Abourayya, Jens Kleesiek, Bharat Rao, Michael Kamp
Data heterogeneity is a central challenge in federated learning, and personalized federated learning (PFL) aims to address it by tailoring models to each client’s distribution. Yet many PFL methods fail to outperform local or centralized baselines, suggesting a mismatch between the collaboration they enforce and the structure of the data. We propose an approach based on adaptive collaboration, where clients decide adaptively not only how much to rely on others, but also whom to trust at the level of individual examples. We instantiate this principle in FEDMOSAIC, a federated co-training method in which clients exchange predictions over a shared unlabeled dataset. This enables fine-grained trust decisions that are difficult to achieve with parameter sharing alone. Each client adjusts its loss weighting based on the agreement between private and public data, and contributes to global pseudo-labels in proportion to its estimated per-example confidence. Empirically, FEDMOSAIC improves upon state-of-the-art PFL methods across diverse non-IID settings, and we provide convergence guarantees under standard assumptions. Our results demonstrate the potential of data-aware collaboration for robust and effective personalization.
数据异构性是联邦学习中的核心挑战,个性化联邦学习(PFL)旨在通过为每个客户端的分布定制模型来解决这一问题。然而,许多PFL方法未能超越本地或集中基准测试的成绩,这表明它们所强制的协作与数据结构之间存在不匹配。我们提出了一种基于自适应协作的方法,客户端不仅自适应地决定依赖他人的程度,而且在单个示例的层面上决定信任谁。我们将这一原则实例化在FEDMOSAIC中,这是一种联邦协同训练方法,客户端在共享的无标签数据集上交换预测。这使得通过单纯的参数共享难以实现精细的信任决策。每个客户端根据私有数据和公共数据之间的协议调整其损失权重,并根据其估计的每个示例的置信度按比例对全局伪标签做出贡献。经验上,FEDMOSAIC在多种非独立同分布环境中都优于最新的PFL方法,并在标准假设下提供了收敛保证。我们的结果展示了数据感知协作在稳健和有效的个性化方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了数据异构性在联邦学习中的核心挑战,以及个性化联邦学习(PFL)如何通过针对每个客户端的分布定制模型来应对这一挑战。然而,许多PFL方法未能超越本地或集中式基准测试,这表明它们所施行的协作与数据结构之间存在不匹配。本文提出了一种基于自适应协作的方法,其中客户端会自适应地决定不仅要多依赖他人,而且还要在个别示例层面上信任谁。我们以FEDMOSAIC为例,这是一种联邦协同训练方法,客户端在共享的无标签数据集上交换预测。这种方法实现了精细的信任决策,仅凭参数共享难以实现这一点。每个客户端都会根据私有和公共数据之间的协议调整其损失权重,并根据其估算的每个示例的置信度按比例对全局伪标签做出贡献。经验表明,FEDMOSAIC在多种非IID环境中都优于最新的PFL方法,并在标准假设下提供了收敛保证。我们的结果展示了数据感知协作对于稳健和有效的个性化潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 数据异构性是联邦学习中的核心挑战,个性化联邦学习(PFL)致力于通过定制模型来应对此挑战。
- 现有PFL方法未能显著超越本地或集中式基准测试,表明协作方式与数据结构之间存在不匹配。
- 提出一种基于自适应协作的方法,客户端可以自适应地决定依赖程度和信任对象。
- FEDMOSAIC是一种联邦协同训练方法,通过交换预测来实现精细的信任决策。
- 客户端根据私有和公共数据之间的协议调整损失权重,并根据置信度对全局伪标签做出贡献。
- FEDMOSAIC在多种非IID环境中表现优于其他PFL方法。
点此查看论文截图


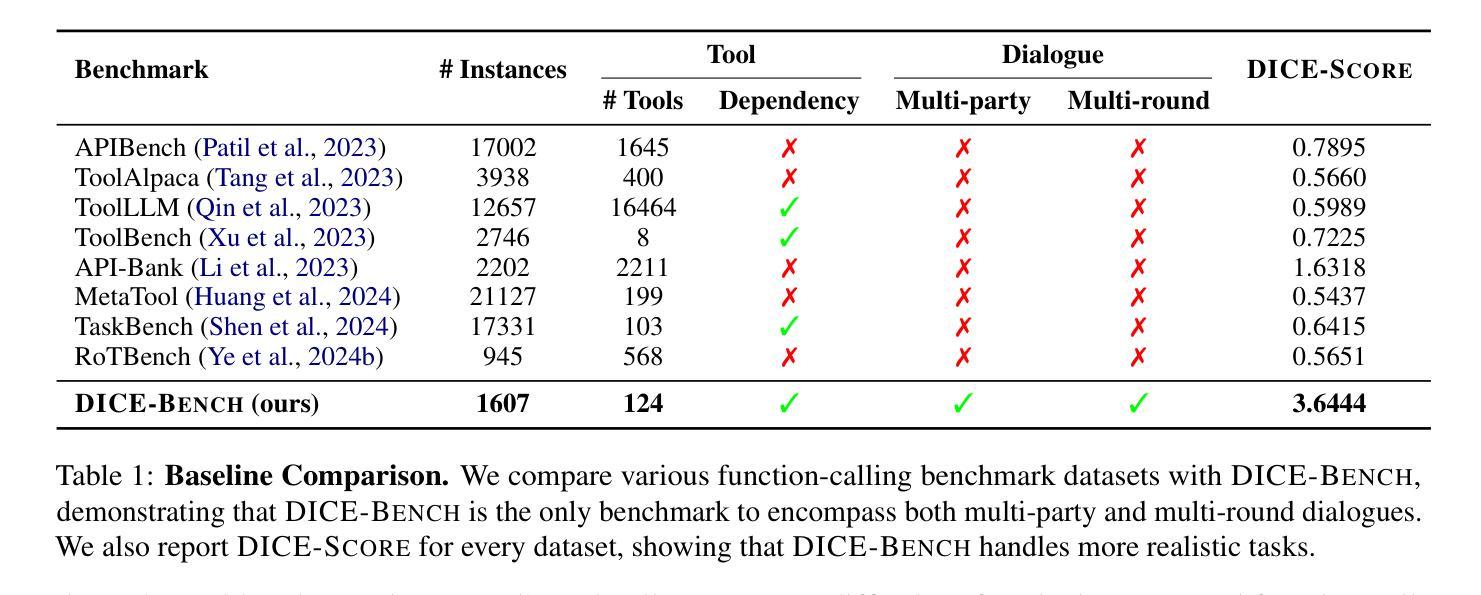
DICE-BENCH: Evaluating the Tool-Use Capabilities of Large Language Models in Multi-Round, Multi-Party Dialogues
Authors:Kyochul Jang, Donghyeon Lee, Kyusik Kim, Dongseok Heo, Taewhoo Lee, Woojeong Kim, Bongwon Suh
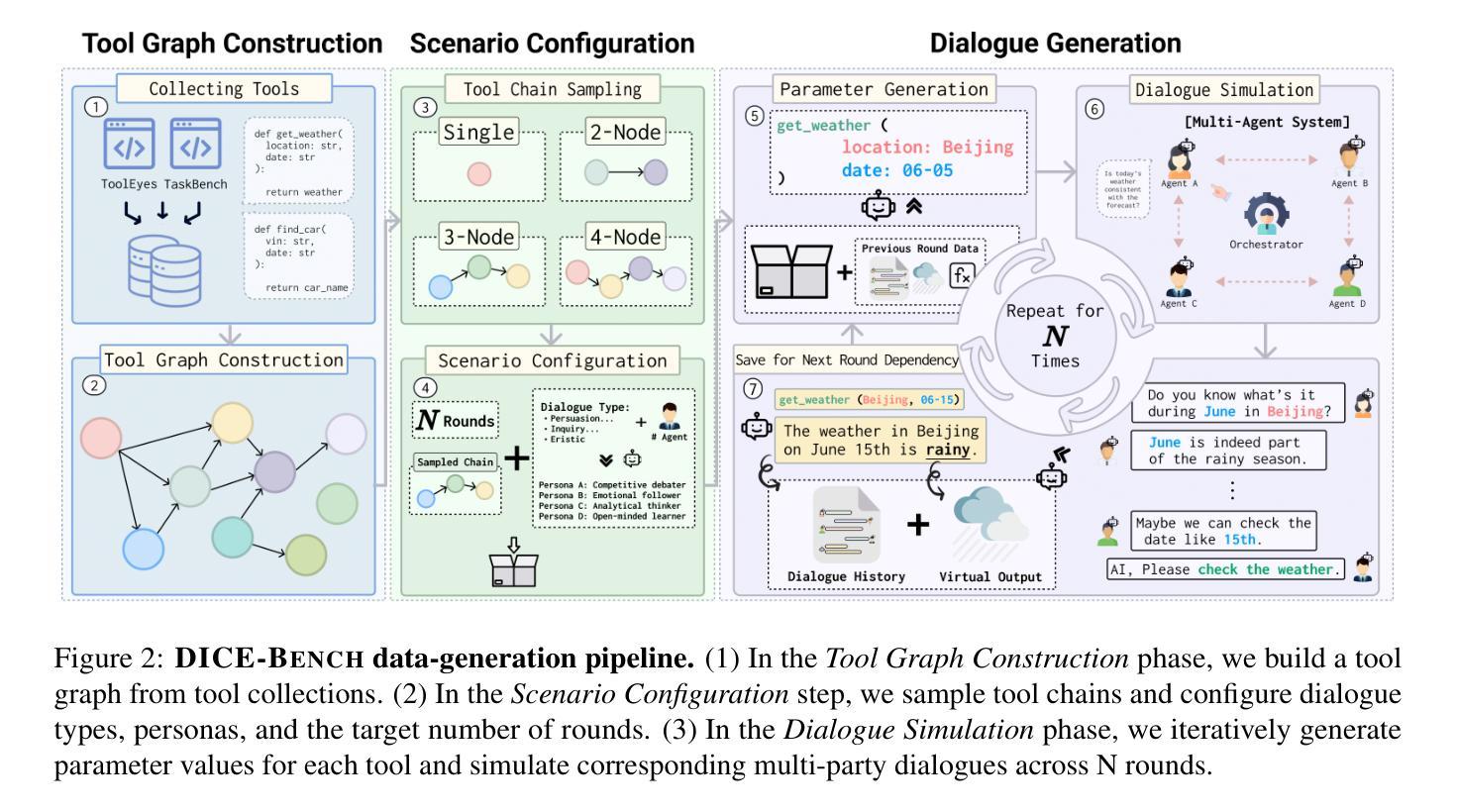
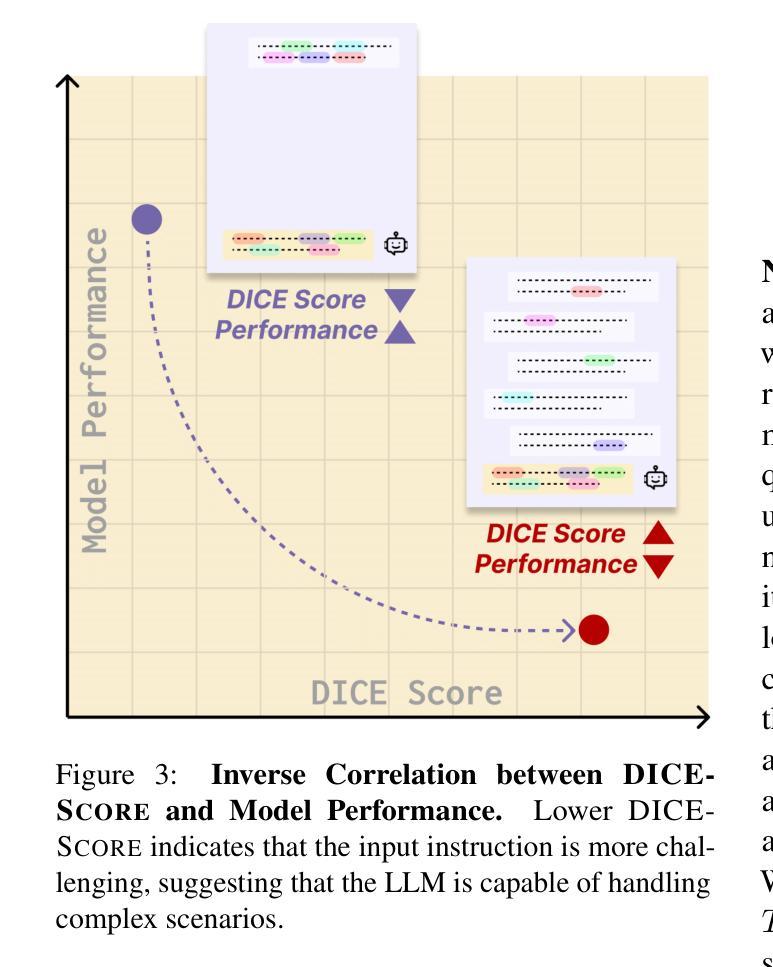
Existing function-calling benchmarks focus on single-turn interactions. However, they overlook the complexity of real-world scenarios. To quantify how existing benchmarks address practical applications, we introduce DICE-SCORE, a metric that evaluates the dispersion of tool-related information such as function name and parameter values throughout the dialogue. Analyzing existing benchmarks through DICE-SCORE reveals notably low scores, highlighting the need for more realistic scenarios. To address this gap, we present DICE-BENCH, a framework that constructs practical function-calling datasets by synthesizing conversations through a tool graph that maintains dependencies across rounds and a multi-agent system with distinct personas to enhance dialogue naturalness. The final dataset comprises 1,607 high-DICE-SCORE instances. Our experiments on 19 LLMs with DICE-BENCH show that significant advances are still required before such models can be deployed effectively in real-world settings. Our code and data are all publicly available: https://snuhcc.github.io/DICE-Bench/.
现有的函数调用基准测试主要关注单轮交互,但忽略了真实世界的复杂性。为了量化现有基准测试在解决实际问题方面的表现,我们引入了DICE-SCORE这一度量标准,它评估工具相关信息(如函数名和参数值)在对话中的分散程度。通过对现有基准测试进行DICE-SCORE分析,我们发现得分普遍较低,这凸显了更需要现实场景的需求。为了解决这一差距,我们提出了DICE-BENCH框架,该框架通过工具图合成对话来构建实用的函数调用数据集,该工具图可以保持跨轮的依赖关系,并包含一个具有不同角色的多智能体系统,以增强对话的自然性。最终的数据集包含1607个高DICE-SCORE实例。我们在DICE-BENCH上对19个大型语言模型进行的实验表明,在将这些模型有效部署到现实世界环境之前,仍需要大量的进步。我们的代码和数据都是公开可用的:https://snuhcc.github.io/DICE-Bench/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, ACL 2025 Vienna
Summary
该文介绍了现有函数调用基准测试主要关注单轮交互,但忽略了真实世界的复杂性。为此,提出了DICE-SCORE评估指标,用于评估工具相关信息在对话中的分散程度。对现有基准测试的DICE-SCORE分析显示得分较低,突显了需要更现实的场景。为解决这一差距,提出了DICE-BENCH框架,通过工具图和多智能体系统构建实际函数调用数据集,以增强对话的自然性。实验表明,在DICE-BENCH上仍需要进一步改进大型语言模型才能在现实世界中有效部署。
Key Takeaways
- 现有函数调用基准测试主要关注单轮交互,忽略了真实世界的复杂性。
- DICE-SCORE评估指标用于评估工具相关信息在对话中的分散程度。
- 对现有基准测试的DICE-SCORE分析显示得分较低。
- DICE-BENCH框架旨在解决现有基准测试与现实需求之间的差距。
- DICE-BENCH通过工具图和多智能体系统构建实际函数调用数据集。
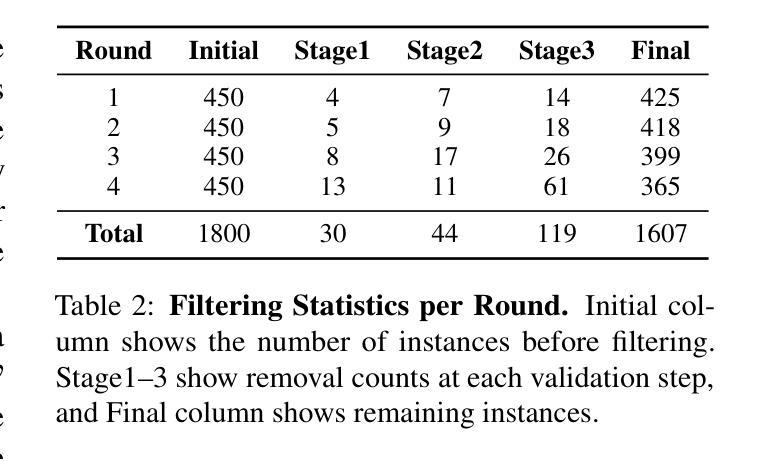
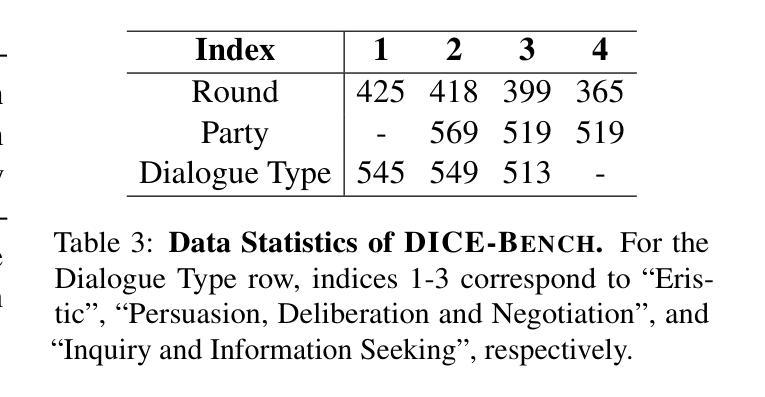
- DICE-BENCH数据集包含1,607个高DICE-SCORE实例。
点此查看论文截图