⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-07 更新
MedDiff-FT: Data-Efficient Diffusion Model Fine-tuning with Structural Guidance for Controllable Medical Image Synthesis
Authors:Jianhao Xie, Ziang Zhang, Zhenyu Weng, Yuesheng Zhu, Guibo Luo
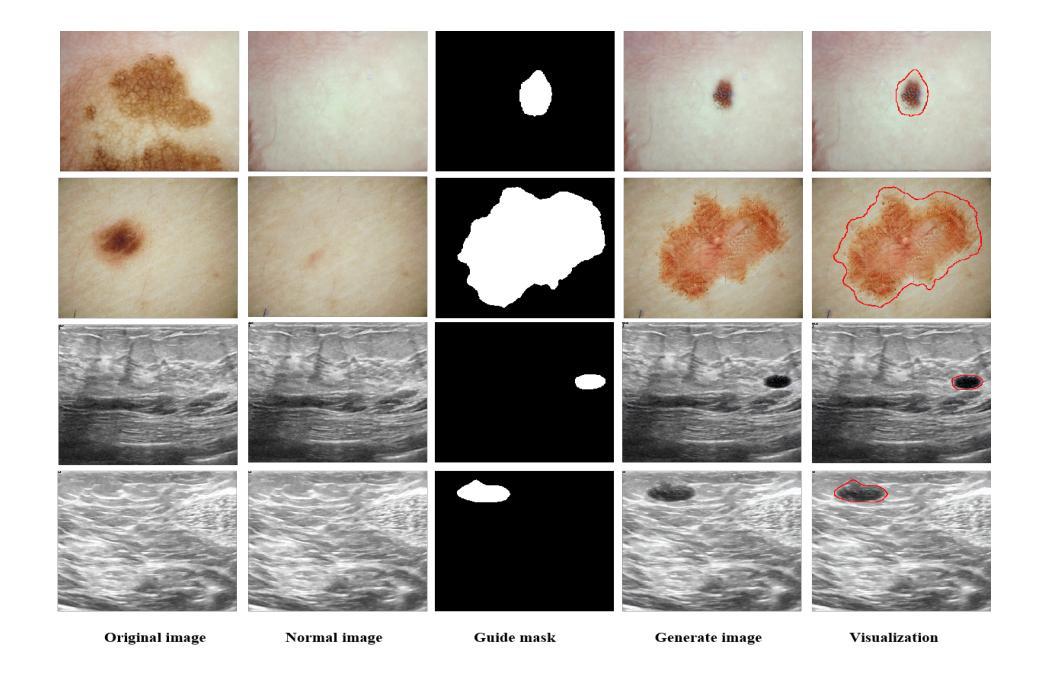
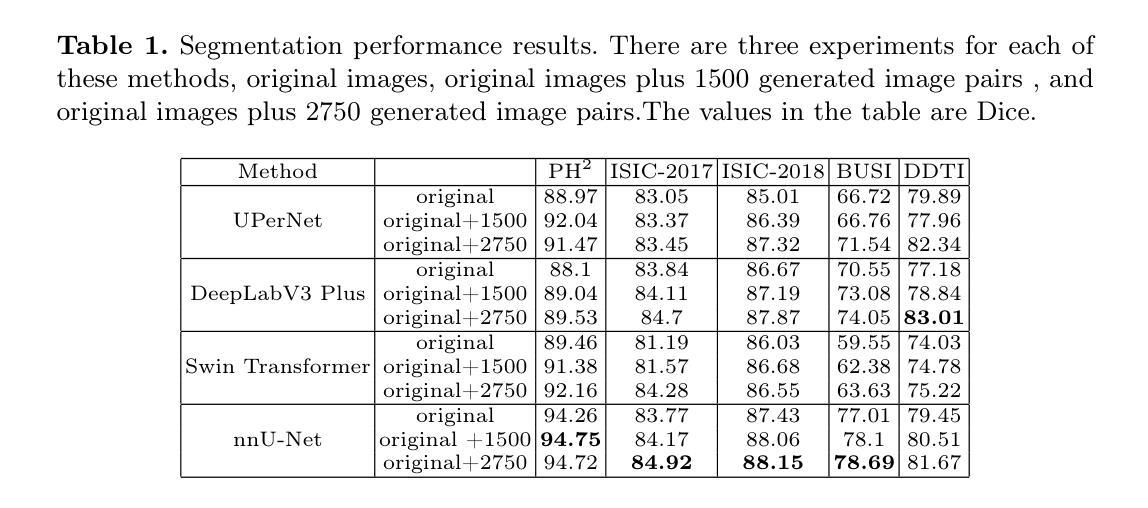
Recent advancements in deep learning for medical image segmentation are often limited by the scarcity of high-quality training data.While diffusion models provide a potential solution by generating synthetic images, their effectiveness in medical imaging remains constrained due to their reliance on large-scale medical datasets and the need for higher image quality. To address these challenges, we present MedDiff-FT, a controllable medical image generation method that fine-tunes a diffusion foundation model to produce medical images with structural dependency and domain specificity in a data-efficient manner. During inference, a dynamic adaptive guiding mask enforces spatial constraints to ensure anatomically coherent synthesis, while a lightweight stochastic mask generator enhances diversity through hierarchical randomness injection. Additionally, an automated quality assessment protocol filters suboptimal outputs using feature-space metrics, followed by mask corrosion to refine fidelity. Evaluated on five medical segmentation datasets,MedDiff-FT’s synthetic image-mask pairs improve SOTA method’s segmentation performance by an average of 1% in Dice score. The framework effectively balances generation quality, diversity, and computational efficiency, offering a practical solution for medical data augmentation. The code is available at https://github.com/JianhaoXie1/MedDiff-FT.
近期深度学习在医学图像分割方面的进展常常受到高质量训练数据稀缺的限制。虽然扩散模型通过生成合成图像提供了一种潜在的解决方案,但由于它们依赖于大规模医学数据集和对更高图像质量的需求,它们在医学成像中的有效性仍然受到限制。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了MedDiff-FT,这是一种可控的医学图像生成方法,它通过微调扩散基础模型以数据高效的方式产生具有结构依赖性和领域特异性的医学图像。在推理过程中,动态自适应引导掩膜施加空间约束以确保解剖结构连贯的合成,而轻量级随机掩膜生成器通过分层随机注入增强多样性。此外,自动质量评估协议使用特征空间度量过滤次优输出,随后通过掩膜腐蚀来提高保真度。在五个医学分割数据集上进行评估,MedDiff-FT的合成图像-掩膜对提高了最先进方法的分割性能,Dice得分平均提高1%。该框架有效地平衡了生成质量、多样性和计算效率,为医学数据增强提供了实用解决方案。代码可在https://github.com/JianhaoXie1/MedDiff-FT找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages,3 figures
Summary
本文介绍了针对医学图像分割领域深度学习算法训练数据不足的问题,提出了一种可控的医学图像生成方法MedDiff-FT。该方法通过微调扩散基础模型,以数据高效的方式生成具有结构依赖性和领域特异性的医学图像。通过动态自适应引导掩膜和轻量级随机掩膜生成器,确保合成图像的解剖结构一致性并增强多样性。同时,采用自动化质量评估协议过滤不佳输出,并通过掩膜腐蚀提高保真度。在五个医学分割数据集上的评估表明,MedDiff-FT生成的合成图像-掩膜对提高了最佳方法的分割性能,平均Dice得分提高1%。该方法在生成质量、多样性和计算效率之间取得了有效平衡,为医学数据增强提供了实用解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- MedDiff-FT是一种针对医学图像分割数据不足问题的可控医学图像生成方法。
- 通过微调扩散基础模型,MedDiff-FT能够生成具有结构依赖性和领域特异性的医学图像。
- 动态自适应引导掩膜和轻量级随机掩膜生成器用于确保合成图像的解剖结构一致性并增强多样性。
- 自动化质量评估协议用于过滤不佳的输出图像,并通过掩膜腐蚀提高图像的保真度。
- 在五个医学分割数据集上的评估显示,MedDiff-FT提高了分割性能,平均Dice得分提高1%。
- MedDiff-FT在生成质量、多样性和计算效率之间取得了平衡。
点此查看论文截图

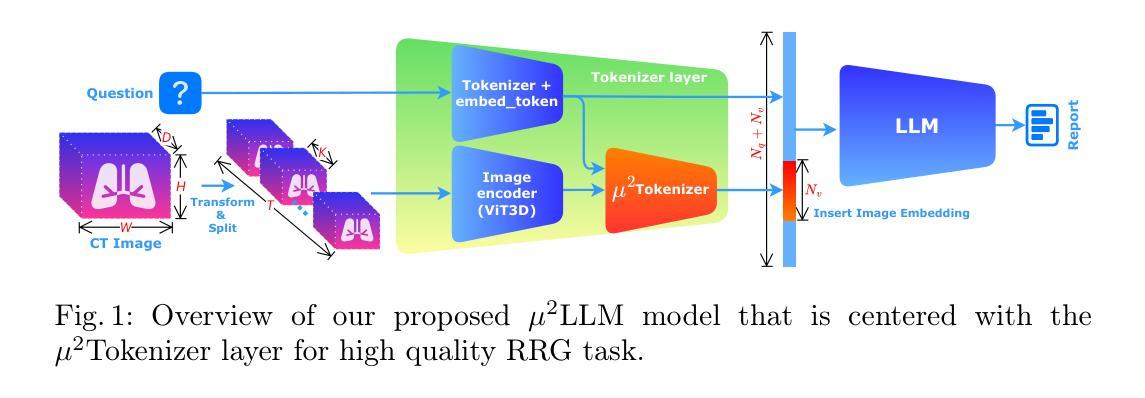
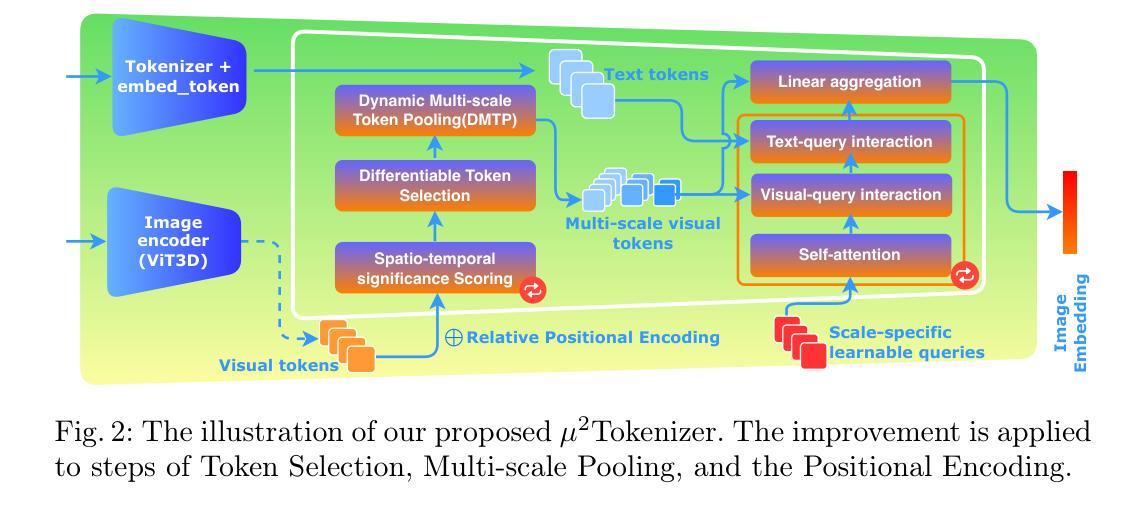
$μ^2$Tokenizer: Differentiable Multi-Scale Multi-Modal Tokenizer for Radiology Report Generation
Authors:Siyou Li, Pengyao Qin, Huanan Wu, Dong Nie, Arun J. Thirunavukarasu, Juntao Yu, Le Zhang
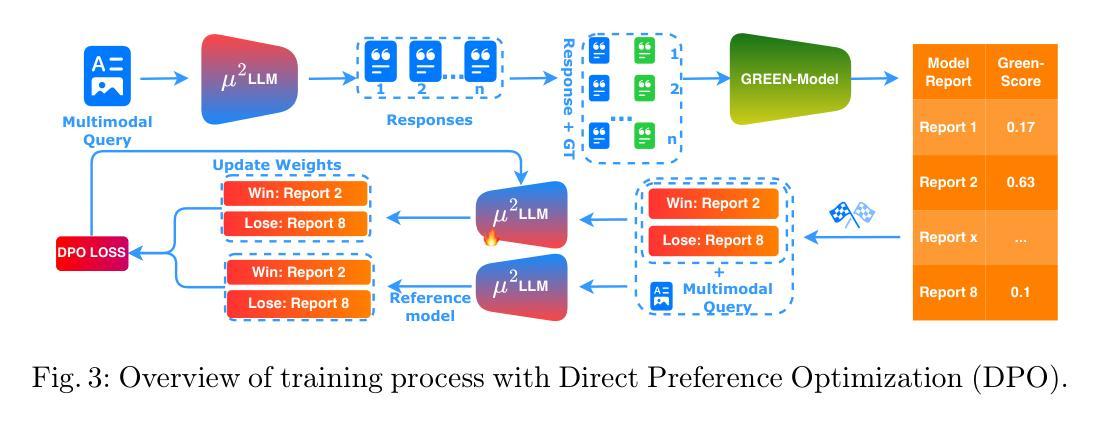
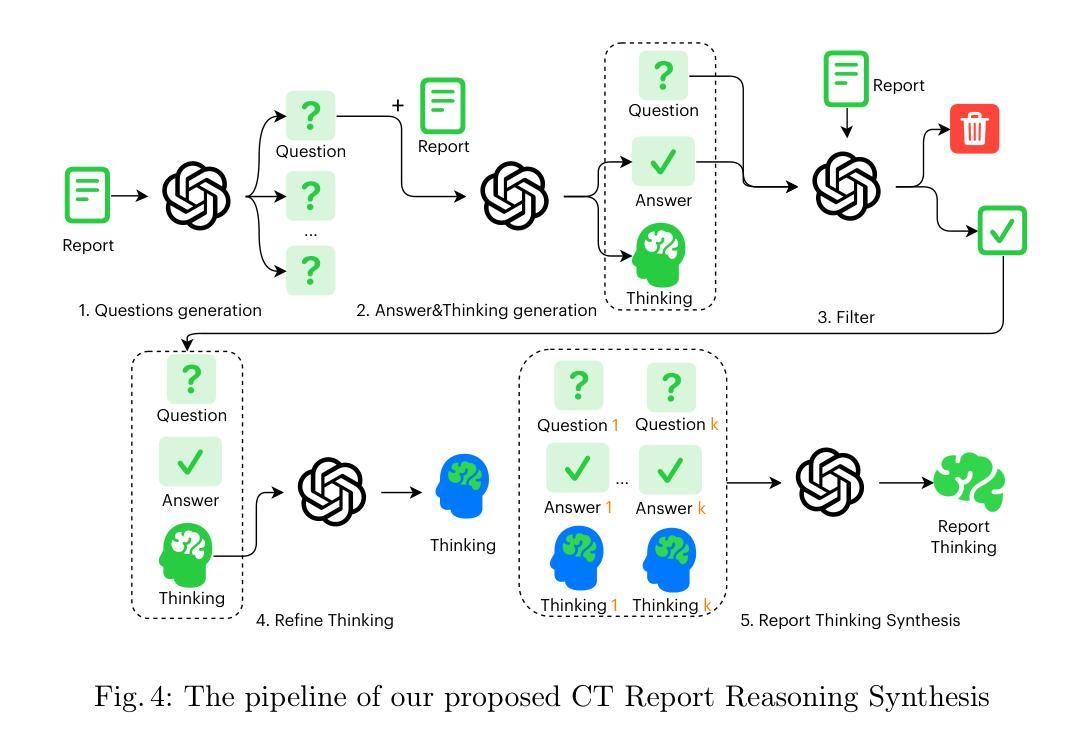
Automated radiology report generation (RRG) aims to produce detailed textual reports from clinical imaging, such as computed tomography (CT) scans, to improve the accuracy and efficiency of diagnosis and provision of management advice. RRG is complicated by two key challenges: (1) inherent complexity in extracting relevant information from imaging data under resource constraints, and (2) difficulty in objectively evaluating discrepancies between model-generated and expert-written reports. To address these challenges, we propose $\mu^2$LLM, a $\underline{\textbf{mu}}$ltiscale $\underline{\textbf{mu}}$ltimodal large language models for RRG tasks. The novel ${\mu}^2$Tokenizer, as an intermediate layer, integrates multi-modal features from the multiscale visual tokenizer and the text tokenizer, then enhances report generation quality through direct preference optimization (DPO), guided by GREEN-RedLlama. Experimental results on four large CT image-report medical datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms existing approaches, highlighting the potential of our fine-tuned $\mu^2$LLMs on limited data for RRG tasks. At the same time, for prompt engineering, we introduce a five-stage, LLM-driven pipeline that converts routine CT reports into paired visual-question-answer triples and citation-linked reasoning narratives, creating a scalable, high-quality supervisory corpus for explainable multimodal radiology LLM. All code, datasets, and models will be publicly available in our official repository. https://github.com/Siyou-Li/u2Tokenizer
自动化放射学报告生成(RRG)旨在从临床影像(如计算机断层扫描(CT))中产生详细的文本报告,以提高诊断和提供管理建议的准确性和效率。RRG面临两个主要挑战:一是在资源约束下从成像数据中提取相关信息所固有的复杂性;二是客观评估模型生成报告与专家编写报告之间的差异的难度。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了μ^2LLM,这是一个用于RRG任务的多尺度多模态大型语言模型。新型μ^2分词器作为中间层,集成了多尺度视觉分词器和文本分词器的多模态特征,然后通过直接偏好优化(DPO)提高报告生成质量,由GREEN-RedLlama指导。在四个大型CT图像报告医疗数据集上的实验结果表明,我们的方法优于现有方法,突显了我们在有限数据上微调μ^2LLM的潜力对于RRG任务。同时,对于提示工程,我们引入了五阶段LLM驱动流程,将常规CT报告转换为成对的视觉问答对和引文关联推理叙述,创建了一个可扩展的、高质量的解释性多模态放射学LLM监督语料库。所有代码、数据集和模型都将在我们的官方仓库中公开可用。[https://github.com/Siyou-Li/u2Tokenizer]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by MICCAI 2025
Summary
基于医学图像自动化生成报告的目标、面临的挑战以及μ²LLM模型的优势和特点。提出一种新型的多尺度多模态大型语言模型μ²LLM用于解决挑战,实现了高质量的报告生成,并展示了在四个大型CT图像报告数据集上的出色性能。同时介绍了其应用的提示工程管道和在线资源的共享计划。
Key Takeaways
- 自动化生成医学图像报告可提高诊断准确性和效率。
- μ²LLM模型解决了从医学图像数据中提取相关信息的复杂性和模型生成报告与专家书写报告之间的差异评估难题。
- 提出了一种新型的多尺度多模态大型语言模型μ²LLM用于报告生成任务。
- μ²Tokenizer作为中间层,集成了多模态特征,提高了报告生成质量。
- 通过实验验证,μ²LLM在四个大型CT图像报告数据集上的性能优于现有方法。
- 介绍了一种五阶段的提示工程管道,用于将常规CT报告转换为视觉问答对和引文链接推理叙述,为可解释的多模态放射学大型语言模型创建高质量监督语料库。
点此查看论文截图

PPFL-RDSN: Privacy-Preserving Federated Learning-based Residual Dense Spatial Networks for Encrypted Lossy Image Reconstruction
Authors:Peilin He, James Joshi
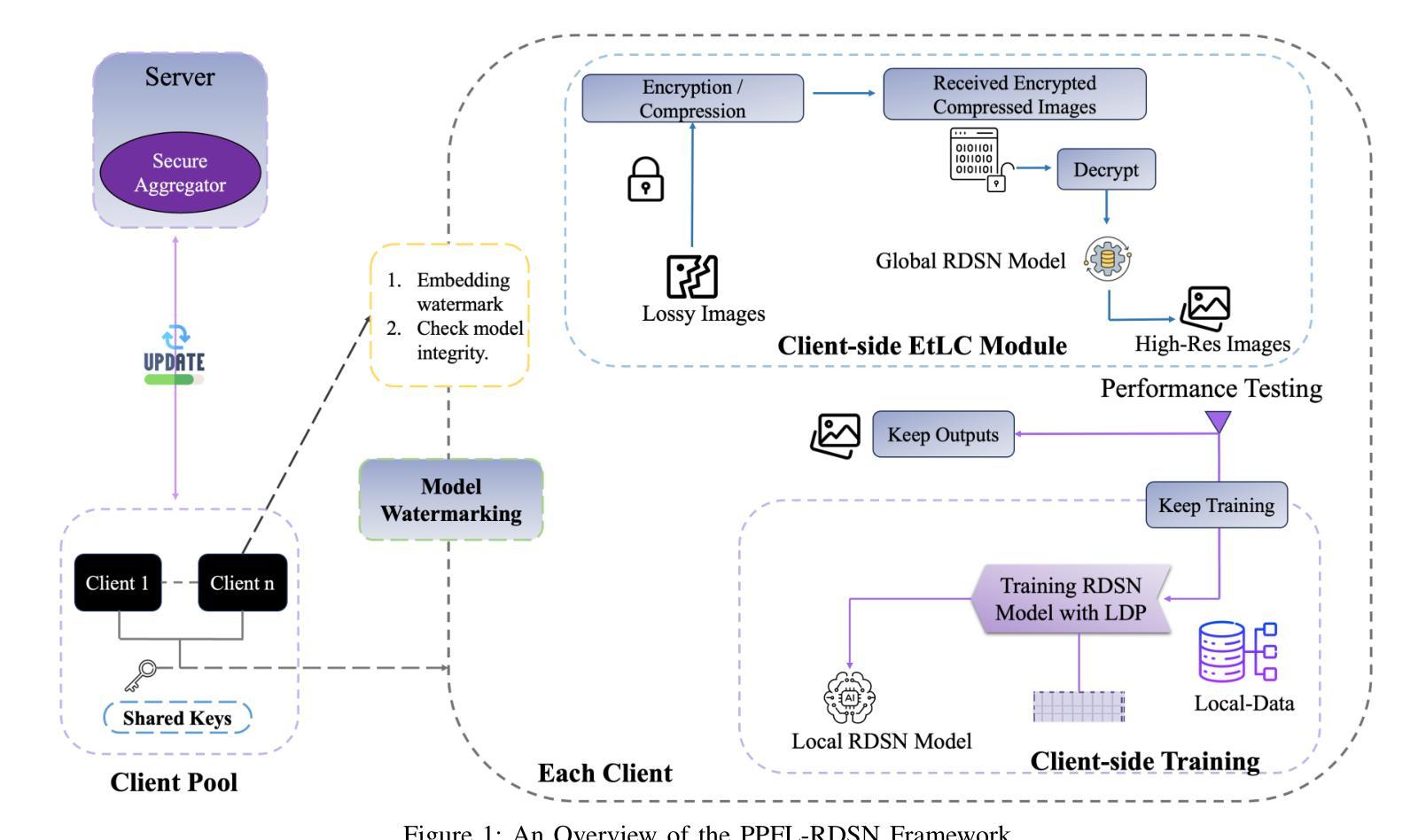
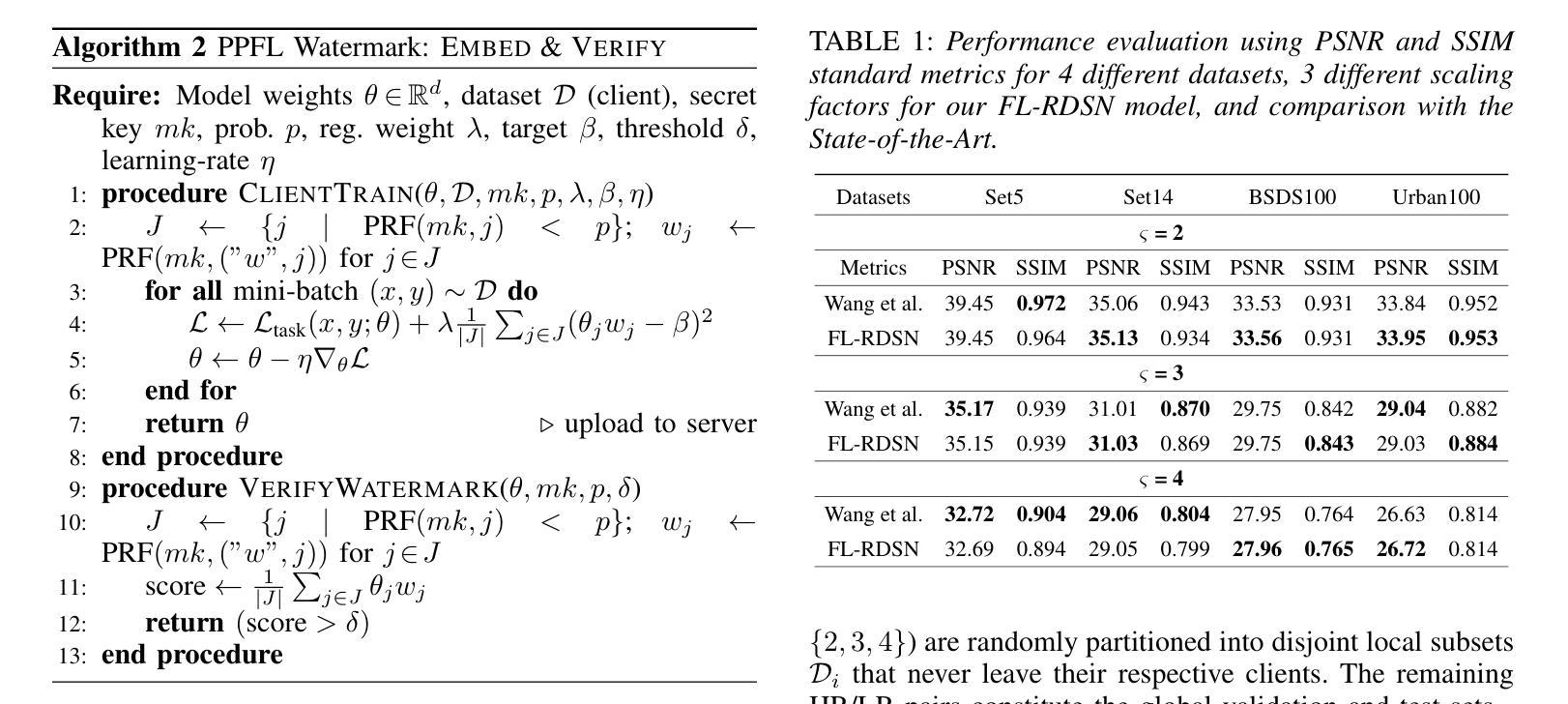
Reconstructing high-quality images from low-resolution inputs using Residual Dense Spatial Networks (RDSNs) is crucial yet challenging, particularly in collaborative scenarios where centralized training poses significant privacy risks, including data leakage and inference attacks, as well as high computational costs. We propose a novel Privacy-Preserving Federated Learning-based RDSN (PPFL-RDSN) framework specifically tailored for lossy image reconstruction. PPFL-RDSN integrates Federated Learning (FL), local differential privacy, and robust model watermarking techniques, ensuring data remains secure on local devices, safeguarding sensitive information, and maintaining model authenticity without revealing underlying data. Empirical evaluations show that PPFL-RDSN achieves comparable performance to the state-of-the-art centralized methods while reducing computational burdens, and effectively mitigates security and privacy vulnerabilities, making it a practical solution for secure and privacy-preserving collaborative computer vision applications.
利用残差密集空间网络(RDSNs)从低分辨率输入重建高质量图像是非常关键且具有挑战性的,特别是在协作场景中,集中训练带来了巨大的隐私风险,包括数据泄露和推理攻击,以及高昂的计算成本。我们提出了一种新型的基于隐私保护的联邦学习RDSN(PPFL-RDSN)框架,专门用于有损图像重建。PPFL-RDSN融合了联邦学习(FL)、本地差分隐私和稳健的模型水印技术,确保数据在本地设备上保持安全,保护敏感信息,并在不暴露底层数据的情况下保持模型的真实性。经验评估表明,PPFL-RDSN在达到最新集中方法相当性能的同时,减轻了计算负担,并有效缓解了安全和隐私漏洞,使其成为安全和隐私保护协作计算机视觉应用的实际解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper is under review; do not distribute
Summary
基于Residual Dense Spatial Networks(RDSNs)从低分辨率输入重建高质量图像至关重要且充满挑战,特别是在合作场景中,集中式训练存在数据泄露、推理攻击等隐私风险和较高的计算成本。我们提出了一种新型的隐私保护联邦学习驱动的RDSN(PPFL-RDSN)框架,专门针对有损图像重建设计。PPFL-RDSN结合了联邦学习(FL)、本地差分隐私和稳健的模型水印技术,确保数据在本地设备上保持安全,保护敏感信息,并在不暴露底层数据的情况下保持模型真实性。实证评估表明,PPFL-RDSN在实现与最新集中方法相当性能的同时,减轻了计算负担,有效缓解了安全和隐私漏洞,使其成为安全和隐私保护协同计算机视觉应用的实用解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- PPFL-RDSN框架结合了Residual Dense Spatial Networks(RDSNs)进行低分辨率图像重建。
- 在合作场景中,集中式训练存在数据泄露和推理攻击等隐私风险。
- PPFL-RDSN采用联邦学习(FL)以处理这些隐私问题。
- 本地差分隐私和模型水印技术被集成到PPFL-RDSN中,以增强数据安全性。
- PPFL-RDSN实现了与最新集中方法相当的性能。
- PPFL-RDSN能减轻计算负担,并有效缓解安全和隐私漏洞。
点此查看论文截图

Multimodal, Multi-Disease Medical Imaging Foundation Model (MerMED-FM)
Authors:Yang Zhou, Chrystie Wan Ning Quek, Jun Zhou, Yan Wang, Yang Bai, Yuhe Ke, Jie Yao, Laura Gutierrez, Zhen Ling Teo, Darren Shu Jeng Ting, Brian T. Soetikno, Christopher S. Nielsen, Tobias Elze, Zengxiang Li, Linh Le Dinh, Lionel Tim-Ee Cheng, Tran Nguyen Tuan Anh, Chee Leong Cheng, Tien Yin Wong, Nan Liu, Iain Beehuat Tan, Tony Kiat Hon Lim, Rick Siow Mong Goh, Yong Liu, Daniel Shu Wei Ting
Current artificial intelligence models for medical imaging are predominantly single modality and single disease. Attempts to create multimodal and multi-disease models have resulted in inconsistent clinical accuracy. Furthermore, training these models typically requires large, labour-intensive, well-labelled datasets. We developed MerMED-FM, a state-of-the-art multimodal, multi-specialty foundation model trained using self-supervised learning and a memory module. MerMED-FM was trained on 3.3 million medical images from over ten specialties and seven modalities, including computed tomography (CT), chest X-rays (CXR), ultrasound (US), pathology patches, color fundus photography (CFP), optical coherence tomography (OCT) and dermatology images. MerMED-FM was evaluated across multiple diseases and compared against existing foundational models. Strong performance was achieved across all modalities, with AUROCs of 0.988 (OCT); 0.982 (pathology); 0.951 (US); 0.943 (CT); 0.931 (skin); 0.894 (CFP); 0.858 (CXR). MerMED-FM has the potential to be a highly adaptable, versatile, cross-specialty foundation model that enables robust medical imaging interpretation across diverse medical disciplines.
当前用于医学成像的人工智能模型主要是单模态和单病种。尝试创建多模态和多病种模型的结果在临床准确性方面表现不一。此外,训练这些模型通常需要大量、劳动密集、标注良好的数据集。我们开发了MerMED-FM,这是一个最先进的、多模态、多专业的基础模型,采用自监督学习和内存模块进行训练。MerMED-FM在超过十个专业和七种模态的330万医学图像上进行训练,包括计算机断层扫描(CT)、胸部X射线(CXR)、超声波(US)、病理切片、彩色眼底摄影(CFP)、光学相干断层扫描(OCT)和皮肤科图像。MerMED-FM在多种疾病上进行了评估,并与现有的基础模型进行了比较。在所有模态下均取得了良好的性能,其中OCT的AUROC为0.988;病理学的AUROC为0.982;超声波的AUROC为0.951;CT的AUROC为0.943;皮肤病的AUROC为0.931;CFP的AUROC为0.894;CXR的AUROC为0.858。MerMED-FM具有巨大的潜力,可成为一个高度适应、通用、跨专业的基础模型,能够在不同的医学领域实现稳健的医学成像解读。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 42 pages, 3 composite figures, 4 tables
Summary
最新的医学成像人工智能模型MerMED-FM,集多模态、多专业于一身,采用自监督学习与记忆模块训练。模型在多种疾病与多种影像方式上表现优越,有望成为一个高度适应、通用性强、跨专业的医学成像基础模型。
Key Takeaways
- 当前医学成像人工智能模型主要为单模态和单疾病模型,创建多模态和多疾病模型的尝试导致临床准确性不一致。
- MerMED-FM是一个先进的多模态、多专业基础模型,经过自监督学习和记忆模块的训练。
- MerMED-FM在超过十个专业和七种模态的330万医学图像上进行训练,包括计算机断层扫描(CT)、胸部X射线(CXR)、超声(US)、病理贴片、彩色眼底摄影(CFP)、光学相干断层扫描(OCT)和皮肤科图像。
- MerMED-FM在多种疾病上的表现经过评估,并与现有基础模型进行比较,在所有模态中都表现出强大的性能。
- MerMED-FM的AUROC值在不同模态中表现优越,如在光学相干断层扫描(OCT)上为0.988,病理学上为0.982等。
- MerMED-FM具有成为高度适应、通用性强、跨专业的基础模型的潜力,能够实现对不同医学领域的稳健医学成像解读。
点此查看论文截图

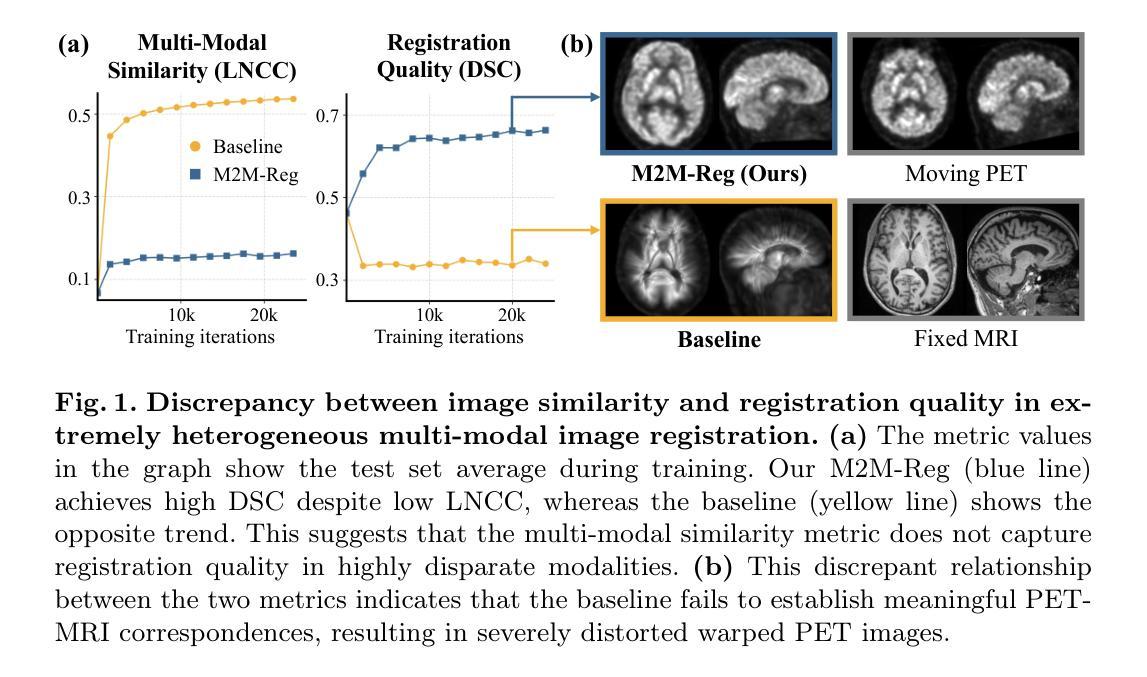
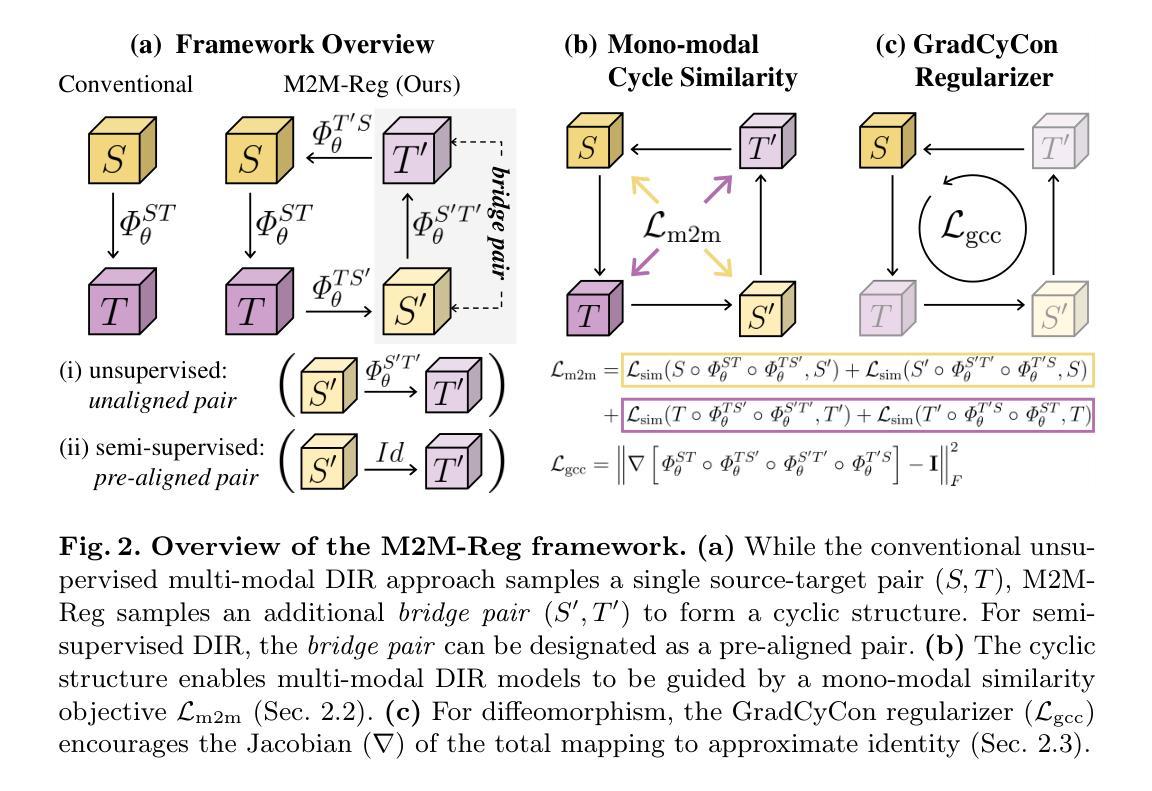
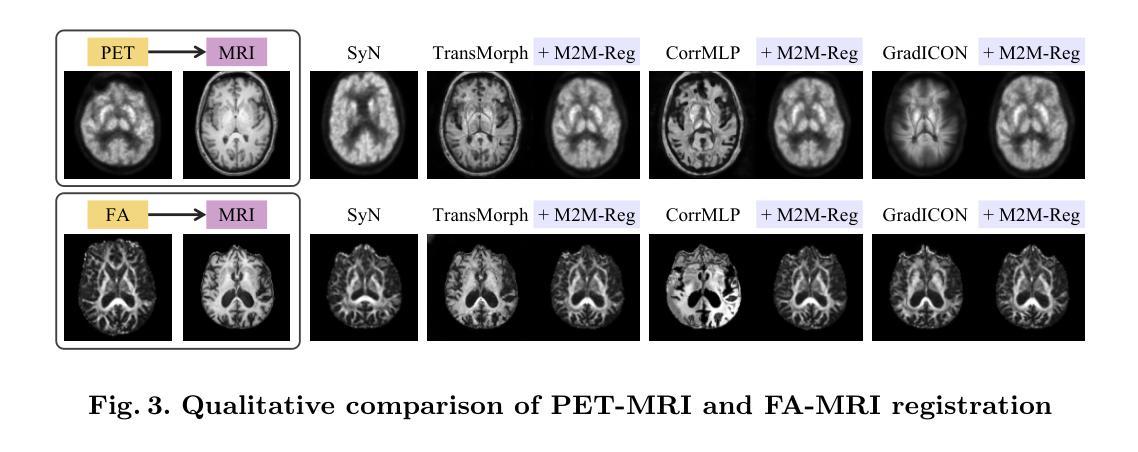
Mono-Modalizing Extremely Heterogeneous Multi-Modal Medical Image Registration
Authors:Kyobin Choo, Hyunkyung Han, Jinyeong Kim, Chanyong Yoon, Seong Jae Hwang
In clinical practice, imaging modalities with functional characteristics, such as positron emission tomography (PET) and fractional anisotropy (FA), are often aligned with a structural reference (e.g., MRI, CT) for accurate interpretation or group analysis, necessitating multi-modal deformable image registration (DIR). However, due to the extreme heterogeneity of these modalities compared to standard structural scans, conventional unsupervised DIR methods struggle to learn reliable spatial mappings and often distort images. We find that the similarity metrics guiding these models fail to capture alignment between highly disparate modalities. To address this, we propose M2M-Reg (Multi-to-Mono Registration), a novel framework that trains multi-modal DIR models using only mono-modal similarity while preserving the established architectural paradigm for seamless integration into existing models. We also introduce GradCyCon, a regularizer that leverages M2M-Reg’s cyclic training scheme to promote diffeomorphism. Furthermore, our framework naturally extends to a semi-supervised setting, integrating pre-aligned and unaligned pairs only, without requiring ground-truth transformations or segmentation masks. Experiments on the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) dataset demonstrate that M2M-Reg achieves up to 2x higher DSC than prior methods for PET-MRI and FA-MRI registration, highlighting its effectiveness in handling highly heterogeneous multi-modal DIR. Our code is available at https://github.com/MICV-yonsei/M2M-Reg.
在临床实践中,具有功能特征的成像方式,如正电子发射断层扫描(PET)和分数异性(FA),通常与结构参考(例如MRI、CT)对准,以进行准确的解释或群组分析,这需要多模式可变形图像配准(DIR)。然而,由于这些成像方式与标准结构扫描相比具有极大的异质性,传统无监督的DIR方法在学习可靠的空间映射时遇到困难,并且经常导致图像失真。我们发现,引导这些模型的相似度度量无法捕获高度不同模式之间的对齐。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了M2M-Reg(多对单注册),这是一个使用仅单模态相似度训练多模式DIR模型的新型框架,同时保留了无缝集成现有模型的既定架构范式。我们还介绍了GradCyCon,一种利用M2M-Reg的循环训练方案来促进微分同胚的正则化器。此外,我们的框架自然地扩展到半监督设置,仅整合预先对齐和未对齐的对,无需地面真实变换或分割掩膜。在阿尔茨海默病神经影像学倡议(ADNI)数据集上的实验表明,M2M-Reg在PET-MRI和FA-MRI配准方面的DSC得分高于先前方法高达2倍,突显其在处理高度异质多模式DIR方面的有效性。我们的代码可在https://github.com/MICV-yonsei/M2M-Reg找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 3 figures, 2 tables, Accepted at Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) 2025
Summary
针对医学图像中功能特性成像模式(如正电子发射断层扫描(PET)和分数各向异性(FA))与结构参考(如MRI、CT)的配准问题,M2M-Reg框架利用单模态相似性进行多模态可变形图像配准,提高了高度不同模态之间的对齐能力,降低图像失真。引入GradCyCon正则化器促进微分同胚。该框架可扩展到半监督设置,仅集成预对齐和非对齐对,无需地面真实变换或分割掩膜。在ADNI数据集上的实验显示,M2M-Reg的DSC得分较以前的方法高出两倍,证明其在处理高度异质的多模态可变形图像配准中的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像的功能特性成像模式(PET、FA等)与结构参考图像(MRI、CT)的配准在临床实践中非常重要。
- 由于成像模态的极端异质性,常规的无监督可变形图像配准(DIR)方法难以学习可靠的空间映射,并可能导致图像失真。
- M2M-Reg框架通过利用单模态相似性进行多模态DIR训练,解决了高度不同模态之间的配准问题。
- M2M-Reg框架引入的GradCyCon正则化器有助于促进微分同胚。
- 该框架可自然地扩展到半监督设置,能够集成预对齐和非对齐的图像对,无需额外的地面真实变换或分割掩膜。
- 在ADNI数据集上的实验表明,M2M-Reg在PET-MRI和FA-MRI配准方面的表现优于以前的方法,达到高达两倍的DSC得分。
点此查看论文截图

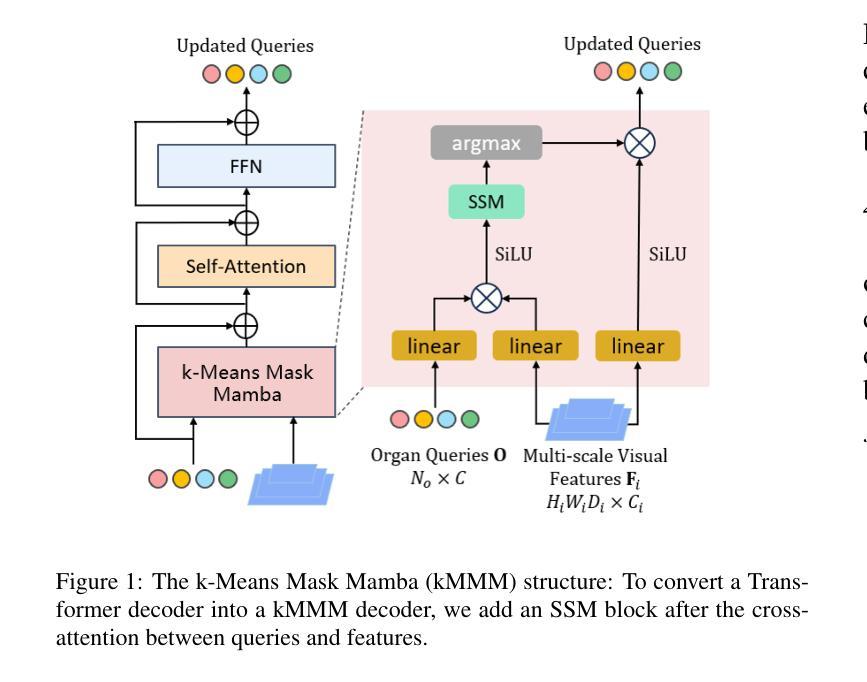
Unleashing Diffusion and State Space Models for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Rong Wu, Ziqi Chen, Liming Zhong, Heng Li, Hai Shu
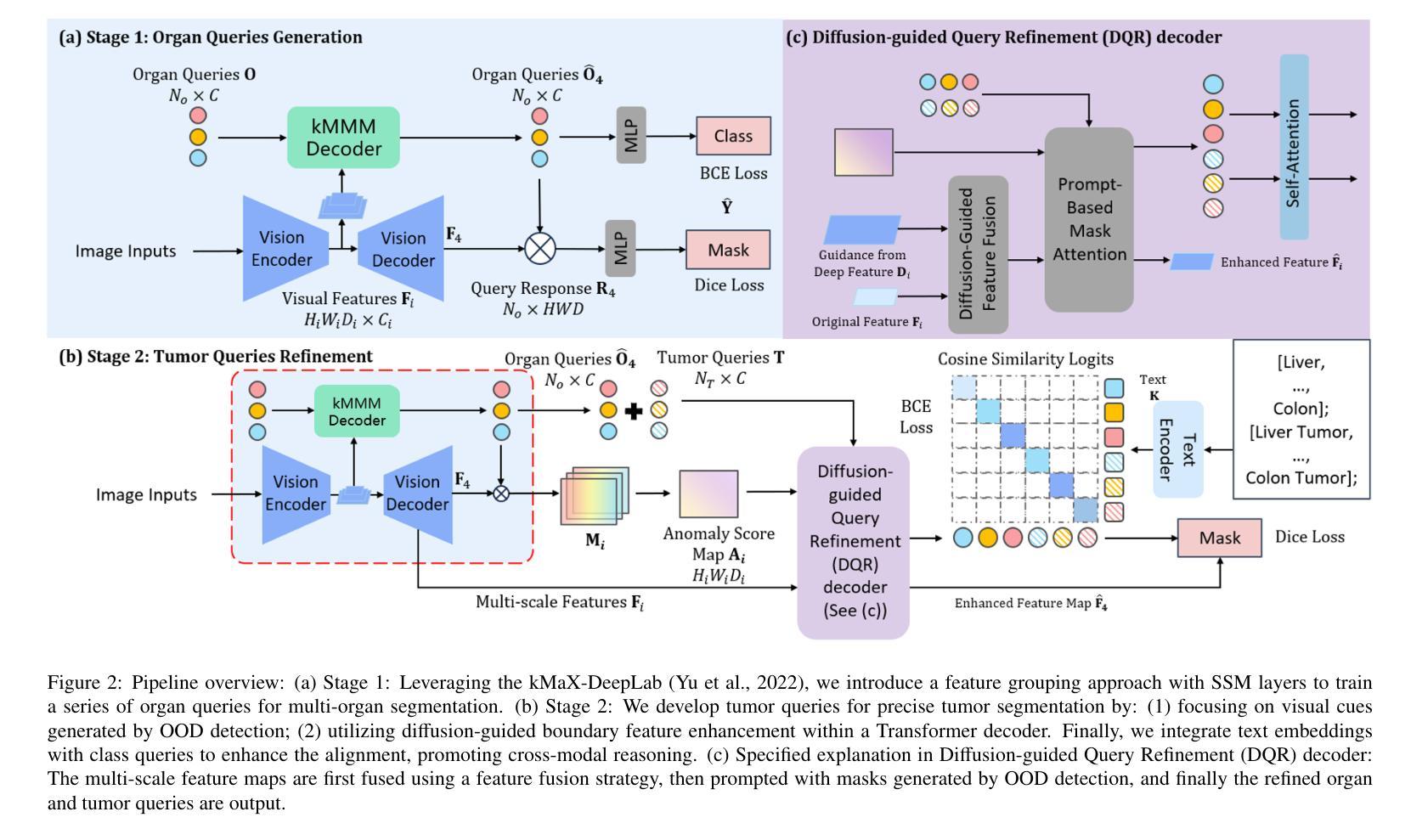
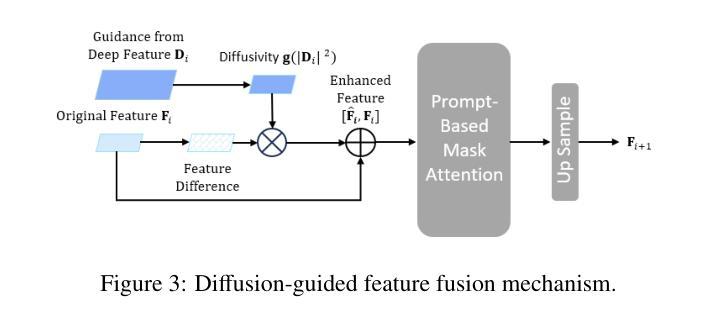
Existing segmentation models trained on a single medical imaging dataset often lack robustness when encountering unseen organs or tumors. Developing a robust model capable of identifying rare or novel tumor categories not present during training is crucial for advancing medical imaging applications. We propose DSM, a novel framework that leverages diffusion and state space models to segment unseen tumor categories beyond the training data. DSM utilizes two sets of object queries trained within modified attention decoders to enhance classification accuracy. Initially, the model learns organ queries using an object-aware feature grouping strategy to capture organ-level visual features. It then refines tumor queries by focusing on diffusion-based visual prompts, enabling precise segmentation of previously unseen tumors. Furthermore, we incorporate diffusion-guided feature fusion to improve semantic segmentation performance. By integrating CLIP text embeddings, DSM captures category-sensitive classes to improve linguistic transfer knowledge, thereby enhancing the model’s robustness across diverse scenarios and multi-label tasks. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superior performance of DSM in various tumor segmentation tasks. Code is available at https://github.com/Rows21/k-Means_Mask_Mamba.
现有仅在单一医学成像数据集上训练的分割模型,在遇到未见过的器官或肿瘤时,其稳健性常常不足。开发一种能够识别训练期间未出现的罕见或新型肿瘤类别的稳健模型,对于推动医学成像应用至关重要。我们提出了DSM,一个利用扩散状态和空间模型对训练数据以外的未见肿瘤类别进行分割的新型框架。DSM利用两组对象查询,在修改过的注意力解码器内进行训练,以提高分类准确度。起初,模型采用对象感知特征分组策略学习器官查询,以捕获器官层面的视觉特征。然后,它通过专注于基于扩散的视觉提示来优化肿瘤查询,从而实现先前未见肿瘤的精确分割。此外,我们融入了扩散引导特征融合,以改善语义分割性能。通过整合CLIP文本嵌入,DSM捕获类别敏感类,改善语言转移知识,从而增强模型在各种场景和多标签任务中的稳健性。大量实验表明,DSM在各种肿瘤分割任务中表现出卓越性能。代码可在https://github.com/Rows21/k-Means_Mask_Mamba获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种新型的医学图像分割框架DSM,该框架利用扩散和状态空间模型对训练数据以外的未知肿瘤类别进行分割。DSM通过两组对象查询提高分类精度,并首次使用对象感知特征分组策略学习器官查询,然后通过基于扩散的视觉提示细化肿瘤查询,实现对未见肿瘤的精确分割。此外,通过扩散引导的特征融合和CLIP文本嵌入的集成,DSM提高了语义分割性能,增强了模型在不同场景和多标签任务中的稳健性。实验证明,DSM在多种肿瘤分割任务中表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- DSM是一个新型的医学图像分割框架,能够处理训练数据以外的未知肿瘤类别。
- DSM利用扩散和状态空间模型,通过两组对象查询提高分类精度。
- DSM首次使用对象感知特征分组策略学习器官查询。
- 通过基于扩散的视觉提示,DSM能够精确分割未见肿瘤。
- DSM通过扩散引导的特征融合提高了语义分割性能。
- 结合CLIP文本嵌入,DSM增强了模型在不同场景和多标签任务中的稳健性。
点此查看论文截图

A Narrative Review on Large AI Models in Lung Cancer Screening, Diagnosis, and Treatment Planning
Authors:Jiachen Zhong, Yiting Wang, Di Zhu, Ziwei Wang
Lung cancer remains one of the most prevalent and fatal diseases worldwide, demanding accurate and timely diagnosis and treatment. Recent advancements in large AI models have significantly enhanced medical image understanding and clinical decision-making. This review systematically surveys the state-of-the-art in applying large AI models to lung cancer screening, diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment. We categorize existing models into modality-specific encoders, encoder-decoder frameworks, and joint encoder architectures, highlighting key examples such as CLIP, BLIP, Flamingo, BioViL-T, and GLoRIA. We further examine their performance in multimodal learning tasks using benchmark datasets like LIDC-IDRI, NLST, and MIMIC-CXR. Applications span pulmonary nodule detection, gene mutation prediction, multi-omics integration, and personalized treatment planning, with emerging evidence of clinical deployment and validation. Finally, we discuss current limitations in generalizability, interpretability, and regulatory compliance, proposing future directions for building scalable, explainable, and clinically integrated AI systems. Our review underscores the transformative potential of large AI models to personalize and optimize lung cancer care.
肺癌仍然是全球最常见和致命的疾病之一,需要准确及时的诊断和治疗。最近人工智能模型的大型进展已经显著提高了对医学图像的理解和临床决策。这篇综述系统地介绍了将大型人工智能模型应用于肺癌筛查、诊断、预后和治疗的最新进展。我们将现有模型分类为特定模态编码器、编码器-解码器框架和联合编码器架构,并重点介绍了CLIP、BLIP、Flamingo、BioViL-T和GLoRIA等关键示例。我们还进一步研究了它们在LIDC-IDRI、NLST和MIMIC-CXR等基准数据集上进行多模态学习任务的性能。应用包括肺结节检测、基因突变预测、多组学整合和个性化治疗计划,有临床部署和验证的初步证据。最后,我们讨论了目前在泛化性、解释性和合规性方面的局限性,并提出了构建可扩展、可解释和临床整合的人工智能系统的未来方向。我们的综述强调了大型人工智能模型在个性化优化肺癌治疗方面的巨大潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This request is based on the fact that one of the co-authors is a PhD student whose advisor has informed her that she was not authorized to publicly release this work without his prior approval. Unfortunately, this approval was not obtained, and as such, the submission was made without proper institutional and supervisory consent
总结
本文综述了大型人工智能模型在肺癌筛查、诊断、预后和治疗的最新应用进展,包括模态特定编码器、编码器-解码器框架和联合编码器架构。文章重点介绍了CLIP、BLIP、Flamingo、BioViL-T和GLoRIA等关键模型,并在LIDC-IDRI、NLST和MIMIC-CXR等基准数据集上评估了它们在多模态学习任务中的性能。大型人工智能模型在肺癌护理中的潜力在于个性化诊断和治疗计划的制定,但也存在通用性、可解释性和监管合规性的局限性。
关键见解
- 肺癌仍然是一个全球性的主要疾病,需要准确及时的诊断和治疗。
- 大型AI模型在医疗图像理解和临床决策制定方面的应用已经显著提高。
- 现有模型可分为模态特定编码器、编码器-解码器框架和联合编码器架构。
- 这些模型在肺癌筛查、诊断、预后和治疗方面展现出显著的应用潜力。
- 应用领域包括肺结节检测、基因突变预测、多组学整合和个性化治疗计划制定。
- 大型AI模型在临床部署和验证方面已有初步证据。
点此查看论文截图

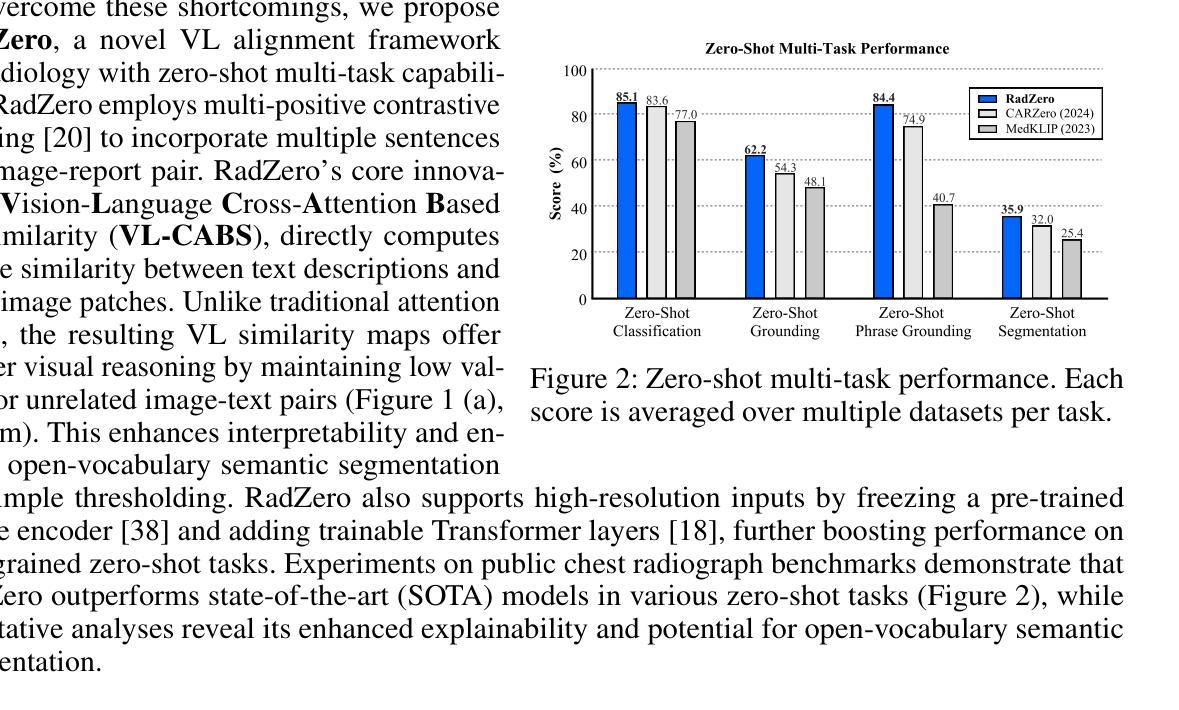
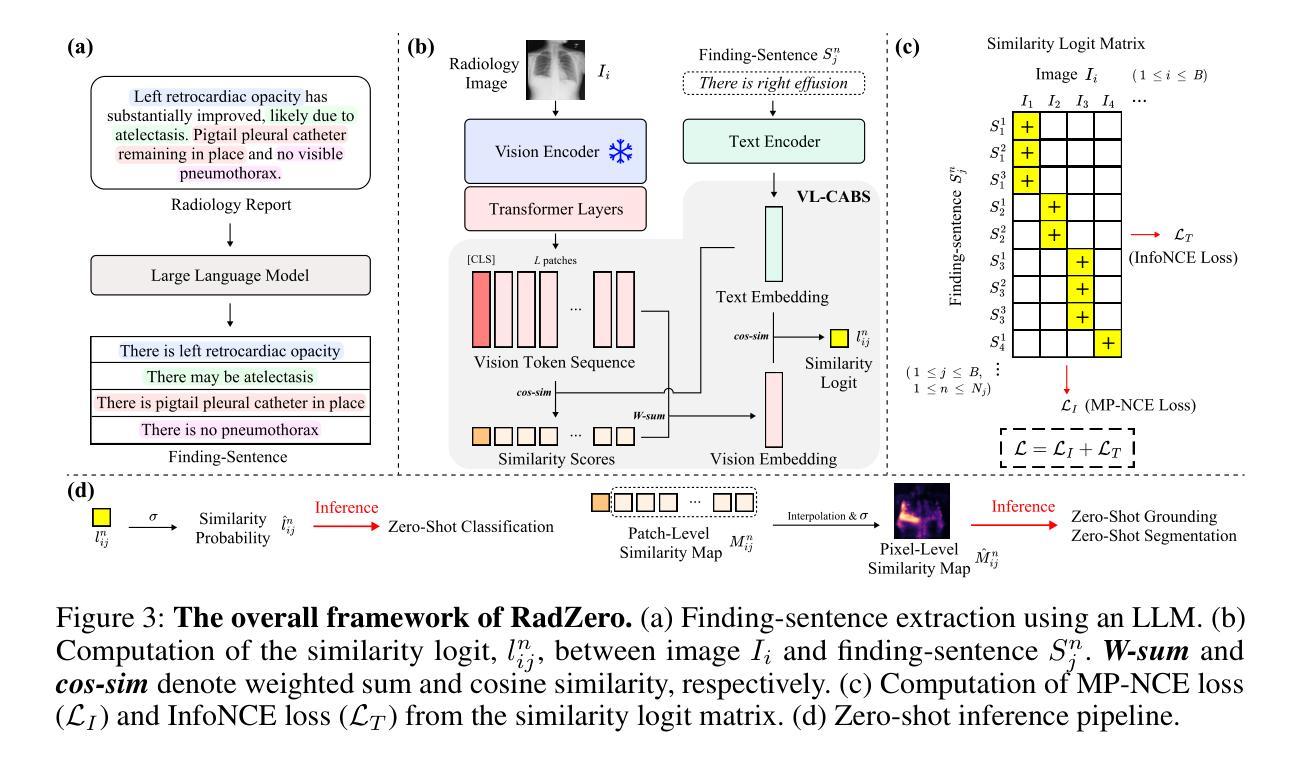
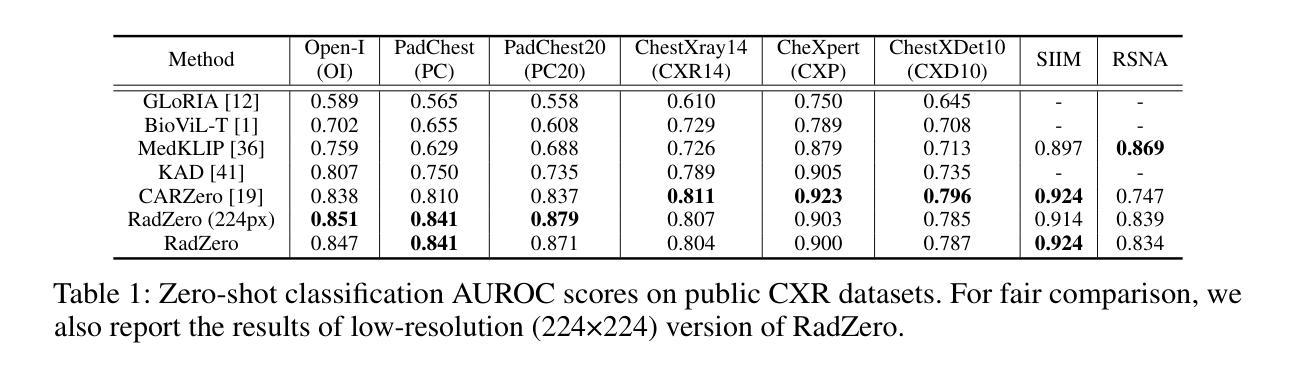
RadZero: Similarity-Based Cross-Attention for Explainable Vision-Language Alignment in Radiology with Zero-Shot Multi-Task Capability
Authors:Jonggwon Park, Soobum Kim, Byungmu Yoon, Kyoyun Choi
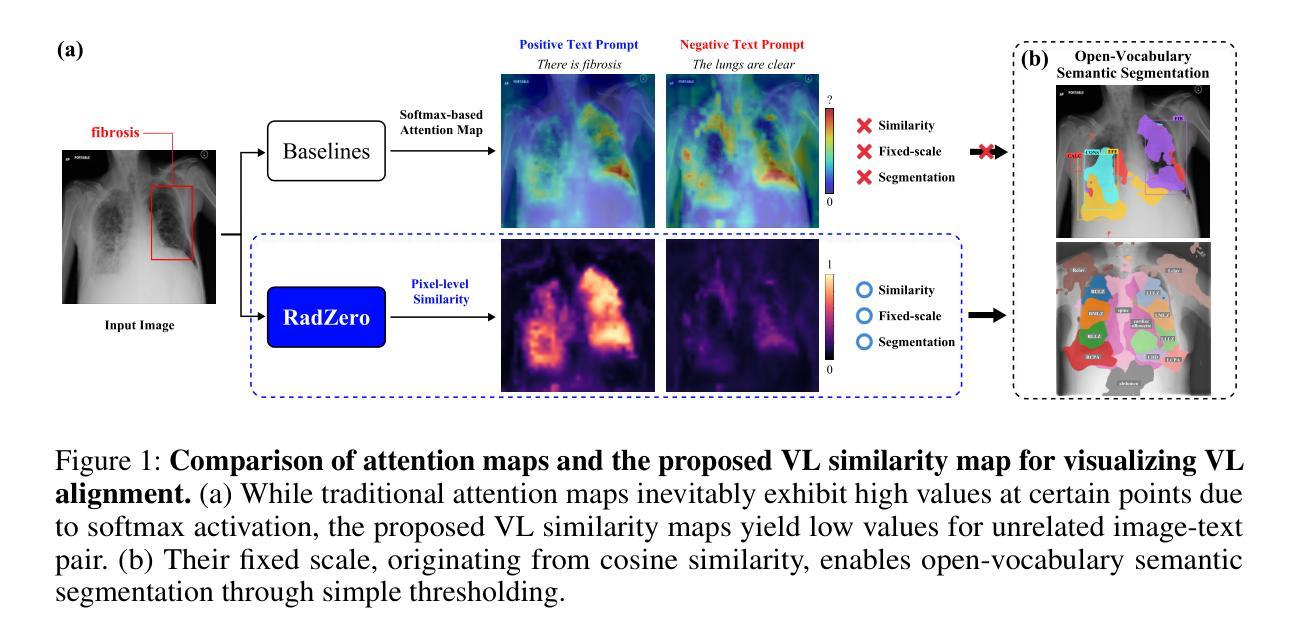
Recent advancements in multi-modal models have significantly improved vision-language (VL) alignment in radiology. However, existing approaches struggle to effectively utilize complex radiology reports for learning and offer limited interpretability through attention probability visualizations. To address these challenges, we introduce RadZero, a novel framework for VL alignment in radiology with zero-shot multi-task capability. A key component of our approach is VL-CABS (Vision-Language Cross-Attention Based on Similarity), which aligns text embeddings with local image features for interpretable, fine-grained VL reasoning. RadZero leverages large language models to extract concise semantic sentences from radiology reports and employs multi-positive contrastive training to effectively capture relationships between images and multiple relevant textual descriptions. It uses a pre-trained vision encoder with additional trainable Transformer layers, allowing efficient high-resolution image processing. By computing similarity between text embeddings and local image patch features, VL-CABS enables zero-shot inference with similarity probability for classification, and pixel-level VL similarity maps for grounding and segmentation. Experimental results on public chest radiograph benchmarks show that RadZero outperforms state-of-the-art methods in zero-shot classification, grounding, and segmentation. Furthermore, VL similarity map analysis highlights the potential of VL-CABS for improving explainability in VL alignment. Additionally, qualitative evaluation demonstrates RadZero’s capability for open-vocabulary semantic segmentation, further validating its effectiveness in medical imaging.
在医学影像学领域,多模态模型的最新进展极大地提高了视觉语言(VL)的对齐能力。然而,现有方法难以有效地利用复杂的放射学报告进行学习,并且通过注意力概率可视化提供的解释性有限。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了RadZero,这是一种具有零样本多任务能力的医学影像学视觉语言对齐新型框架。我们的方法的关键组件是VL-CABS(基于相似性的视觉语言交叉注意力),它将文本嵌入与局部图像特征对齐,以实现可解释、细粒度的视觉语言推理。RadZero利用大型语言模型从放射学报告中提取简洁语义句子,并采用多阳性对比训练有效地捕获图像与多个相关文本描述之间的关系。它使用预训练的视觉编码器以及额外的可训练Transformer层,以实现高效的高分辨率图像处理。通过计算文本嵌入和局部图像补丁特征之间的相似性,VL-CABS实现了零样本推理,具有相似性概率分类、像素级视觉语言相似性地图用于定位和分割。在公共胸部X光影像基准测试集上的实验结果表明,RadZero在零样本分类、定位和分割方面的性能超过了最先进的方法。此外,视觉语言相似性地图分析突出了VL-CABS在提高视觉语言对齐解释性方面的潜力。定性评估还证明了RadZero在开放词汇语义分割方面的能力,进一步验证了其在医学影像中的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了RadZero框架,该框架利用多模态模型提高了放射学中的视觉语言对齐效果。通过引入VL-CABS(基于相似性的视觉语言交叉注意力)和大型语言模型等技术,RadZero解决了现有方法面临的挑战,提高了报告的利用率和解释性。实验结果表明,RadZero在零样本分类、定位、分割等方面均优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- RadZero是一个用于放射学视觉语言对齐的新框架,具有零样本多任务能力。
- RadZero通过引入VL-CABS技术,实现了文本嵌入与局部图像特征的对齐,为可解释的精细视觉语言推理提供了基础。
- RadZero利用大型语言模型从放射学报告中提取简洁语义句子。
- 通过多阳性对比训练,RadZero能有效捕捉图像与多个相关文本描述之间的关系。
- RadZero使用预训练的视觉编码器,并添加可训练的Transformer层,以实现高效的高分辨率图像处理。
- RadZero的零样本推断能力通过计算文本嵌入和局部图像补丁特征之间的相似性来实现分类、定位与分割。
点此查看论文截图

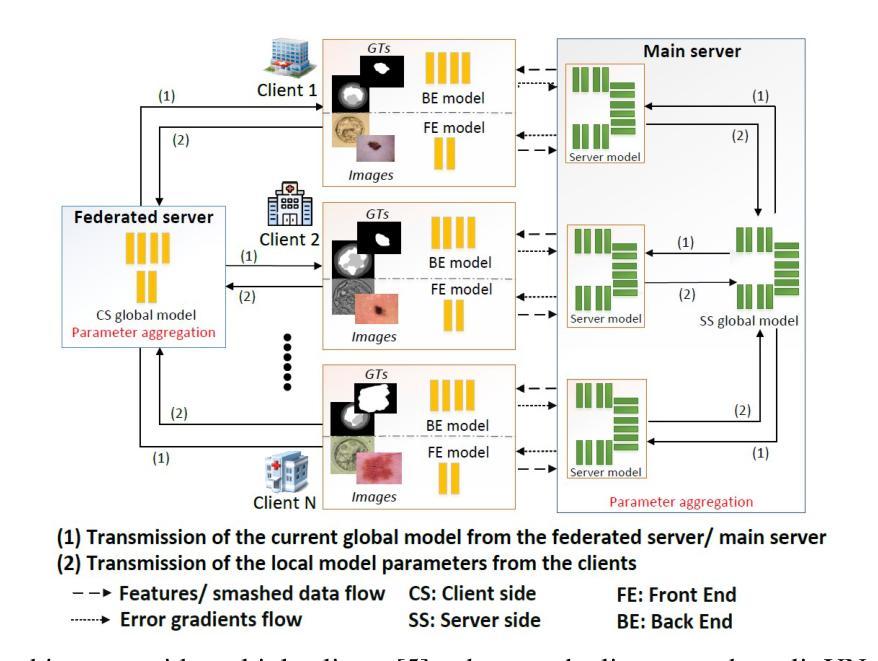
MedSegNet10: A Publicly Accessible Network Repository for Split Federated Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Chamani Shiranthika, Zahra Hafezi Kafshgari, Hadi Hadizadeh, Parvaneh Saeedi
Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL) have shown significant promise in healthcare, particularly in medical image segmentation, which is crucial for accurate disease diagnosis and treatment planning. Despite their potential, challenges such as data privacy concerns, limited annotated data, and inadequate training data persist. Decentralized learning approaches such as federated learning (FL), split learning (SL), and split federated learning (SplitFed/SFL) address these issues effectively. This paper introduces “MedSegNet10,” a publicly accessible repository designed for medical image segmentation using split-federated learning. MedSegNet10 provides a collection of pre-trained neural network architectures optimized for various medical image types, including microscopic images of human blastocysts, dermatoscopic images of skin lesions, and endoscopic images of lesions, polyps, and ulcers, with applications extending beyond these examples. By leveraging SplitFed’s benefits, MedSegNet10 allows collaborative training on privately stored, horizontally split data, ensuring privacy and integrity. This repository supports researchers, practitioners, trainees, and data scientists, aiming to advance medical image segmentation while maintaining patient data privacy. The repository is available at: https://vault.sfu.ca/index.php/s/ryhf6t12O0sobuX (password upon request to the authors).
机器学习(ML)和深度学习(DL)在医疗保健领域显示出巨大潜力,特别是在医学图像分割方面,这对于准确的疾病诊断和治疗计划至关重要。尽管存在潜力,但数据隐私担忧、缺乏注释数据和训练数据不足等挑战仍然存在。联邦学习(FL)、分割学习(SL)和分割联邦学习(SplitFed/SFL)等分布式学习方法有效地解决了这些问题。本文介绍了“MedSegNet10”,这是一个公开可访问的存储库,用于医学图像分割,采用分割联邦学习的方法。MedSegNet10提供了一系列针对各种医学图像类型进行优化的预训练神经网络架构,包括人类囊胚的显微镜图像、皮肤病变的皮肤科内镜图像、病变、息肉和溃疡的内窥镜图像等,应用范围不限于这些示例。通过利用SplitFed的优势,MedSegNet10可以在私密存储的水平分割数据上进行协作训练,确保隐私和完整性。该存储库支持研究人员、实践者、培训人员和数据分析师,旨在推动医学图像分割的发展,同时保持患者数据的隐私。该存储库位于:https://vault.sfu.ca/index.php/s/ryhf6t12O0sobuX(需向作者申请密码)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages, 14 figures
Summary
医学图像分割在疾病诊断和治疗计划中具有重要作用,机器学习(ML)和深度学习(DL)在该领域展现出巨大潜力。然而,数据隐私、标注数据有限和训练数据不足等问题仍然存在。本文介绍了MedSegNet10,一个采用分裂联合学习(SplitFed)的医学图像分割公开存储库。该存储库提供针对多种医学图像类型的预训练神经网络架构,包括人类囊胚显微镜图像、皮肤病变的皮肤科内镜图像以及病变、息肉和溃疡的内窥镜图像等。它旨在推进医学图像分割的研究,同时保持患者数据隐私。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割在疾病诊断和治疗计划中起重要作用。
- 机器学习和深度学习在医学图像分割领域具有显著潜力。
- 数据隐私、标注数据有限和训练数据不足是医学图像分割面临的挑战。
- 分裂联合学习(SplitFed)方法可以有效解决这些问题。
- MedSegNet10是一个采用SplitFed的医学图像分割公开存储库。
- MedSegNet10提供针对多种医学图像类型的预训练神经网络架构。
点此查看论文截图

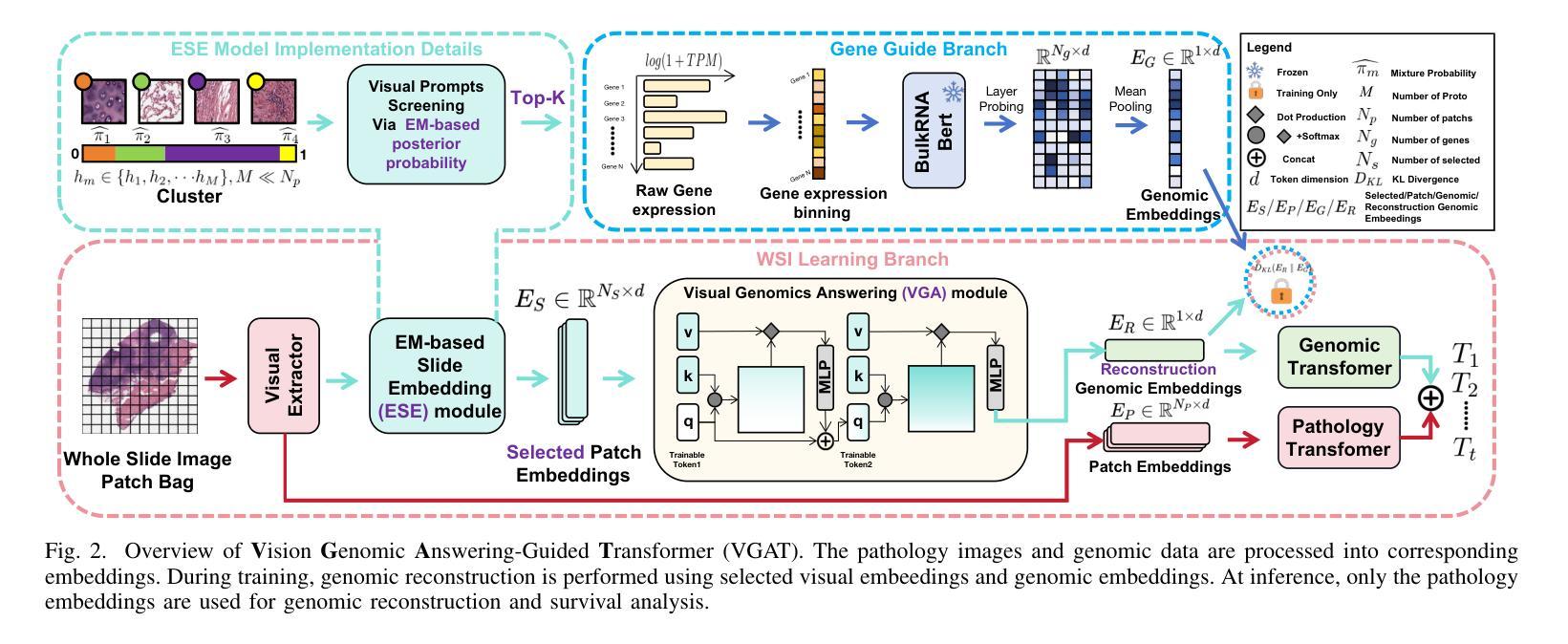
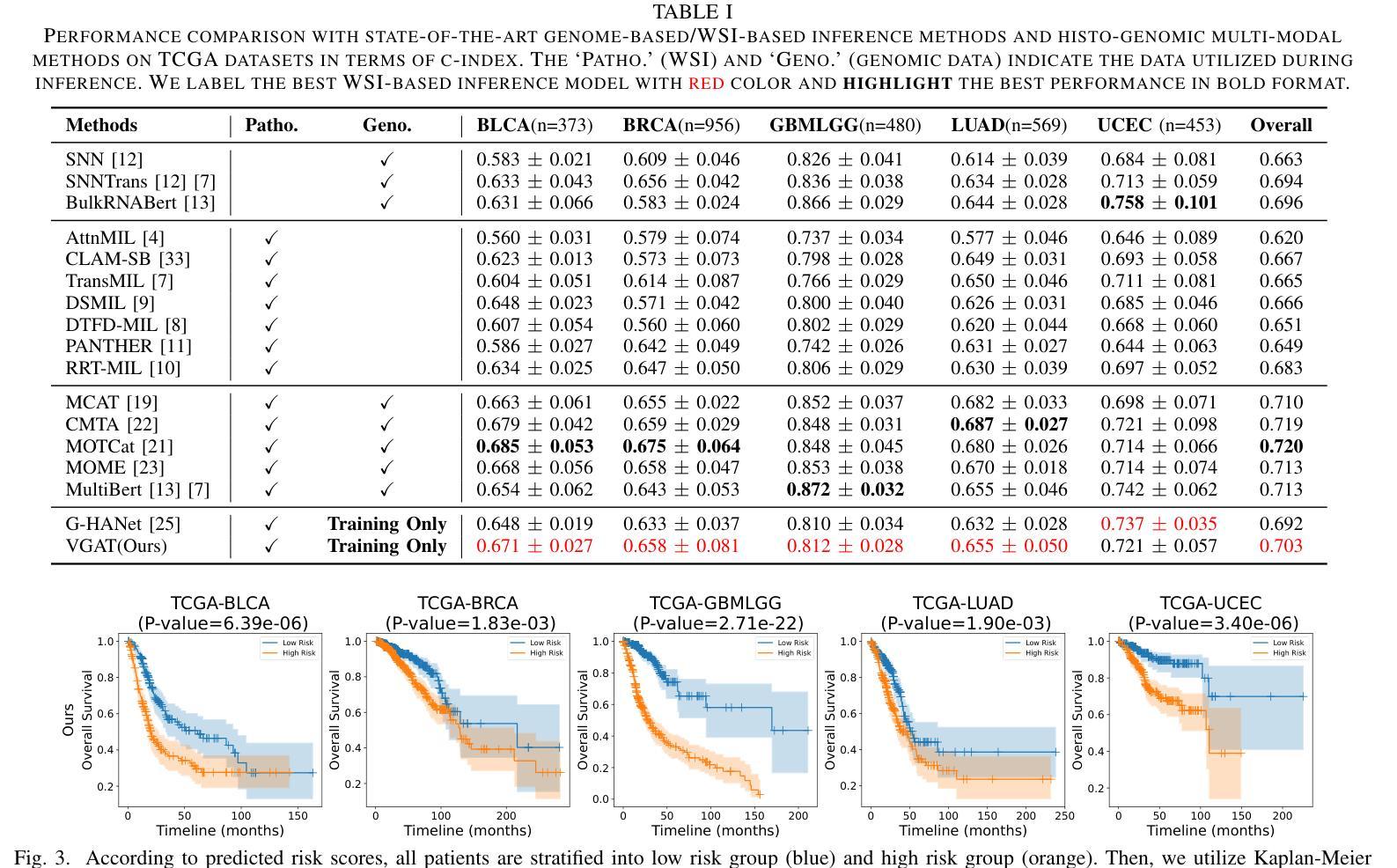
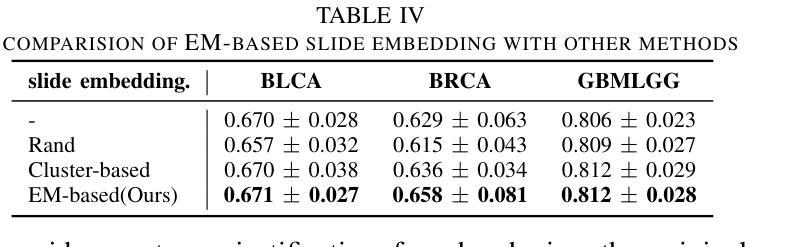
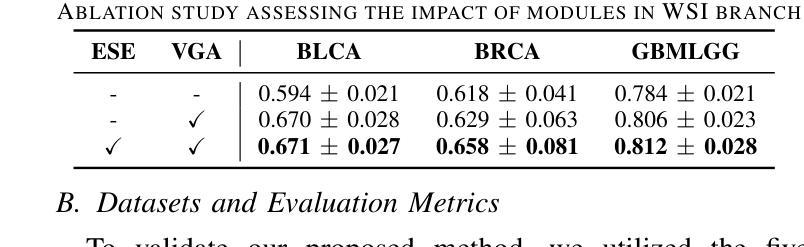
VGAT: A Cancer Survival Analysis Framework Transitioning from Generative Visual Question Answering to Genomic Reconstruction
Authors:Zizhi Chen, Minghao Han, Xukun Zhang, Shuwei Ma, Tao Liu, Xing Wei, Lihua Zhang
Multimodal learning combining pathology images and genomic sequences enhances cancer survival analysis but faces clinical implementation barriers due to limited access to genomic sequencing in under-resourced regions. To enable survival prediction using only whole-slide images (WSI), we propose the Visual-Genomic Answering-Guided Transformer (VGAT), a framework integrating Visual Question Answering (VQA) techniques for genomic modality reconstruction. By adapting VQA’s text feature extraction approach, we derive stable genomic representations that circumvent dimensionality challenges in raw genomic data. Simultaneously, a cluster-based visual prompt module selectively enhances discriminative WSI patches, addressing noise from unfiltered image regions. Evaluated across five TCGA datasets, VGAT outperforms existing WSI-only methods, demonstrating the viability of genomic-informed inference without sequencing. This approach bridges multimodal research and clinical feasibility in resource-constrained settings. The code link is https://github.com/CZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZ/VGAT.
将病理图像与基因组序列相结合的多模态学习能提高癌症生存分析能力,但由于资源匮乏地区基因组测序的有限访问性,其在临床实施中面临障碍。为了仅使用全幻灯片图像(Whole Slide Images, WSI)进行生存预测,我们提出了视觉基因组问答引导转换器(Visual-Genomic Answering-Guided Transformer,VGAT)框架,该框架融合了视觉问答(Visual Question Answering, VQA)技术,用于基因组模态重建。通过适应VQA的文本特征提取方法,我们得出了稳定的基因组表示,避免了原始基因组数据的维度挑战。同时,基于集群的视觉提示模块有选择地增强了判别性的WSI斑块,解决了未过滤图像区域的噪声问题。在五个TCGA数据集上进行的评估表明,VGAT在仅使用WSI的方法中表现突出,证明了在没有测序的情况下进行基因组信息推断的可行性。这种方法在多模态研究和资源受限环境中的临床可行性之间搭建了桥梁。代码链接是:代码链接地址。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICME2025
Summary
结合病理图像和基因组序列的多模态学习增强了癌症生存分析,但由于资源匮乏地区基因组测序的有限访问,面临临床实施障碍。为使用全幻灯片图像(WSI)进行生存预测,我们提出Visual-Genomic Answering-Guided Transformer(VGAT)框架,该框架整合视觉问答(VQA)技术用于基因组模态重建。通过适应VQA的文本特征提取方法,我们导出稳定的基因组表示,可避免原始基因组数据的维度挑战。同时,基于集群的视觉提示模块选择性地增强鉴别性的WSI斑块,解决未过滤图像区域的噪声问题。在五个TCGA数据集上的评估显示,VGAT在仅使用WSI的情况下表现出优于现有方法的效果,证明了无测序的基因组信息推断的可行性。该方法在资源受限环境中实现了多模态研究与临床可行性的结合。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态学习整合病理图像和基因组序列增强了癌症生存分析的效果。
- VGAT框架通过整合VQA技术用于基因组模态重建,克服了临床实施中的障碍。
- VGAT利用稳定的基因组表示来解决原始基因组数据的维度挑战。
- 基于集群的视觉提示模块增强了鉴别性的WSI斑块,降低了未过滤图像区域的噪声干扰。
- VGAT在多个数据集上的表现优于现有方法,证明了无测序的基因组信息推断的可行性。
- VGAT方法为资源受限环境中的临床实施提供了可能的多模态解决方案。
点此查看论文截图
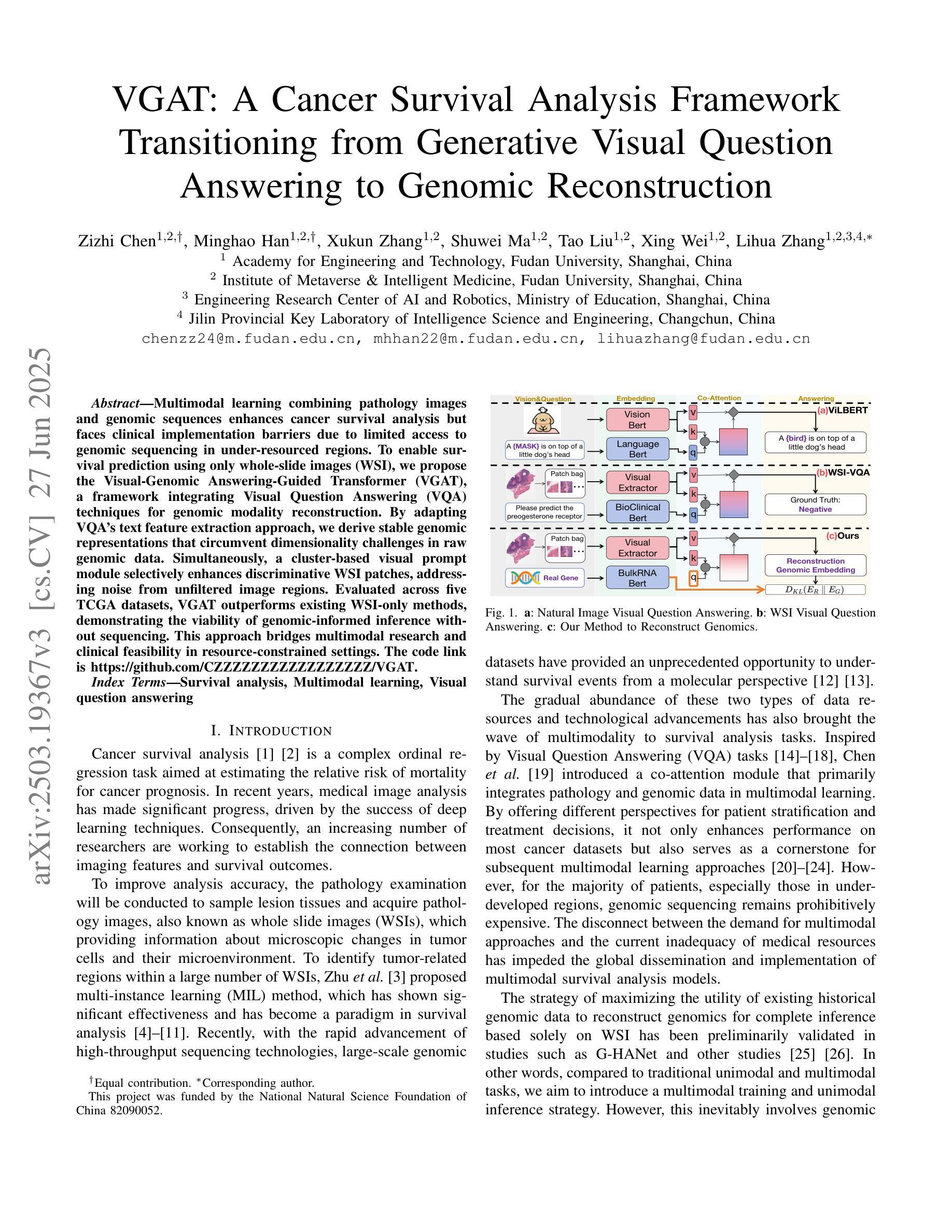
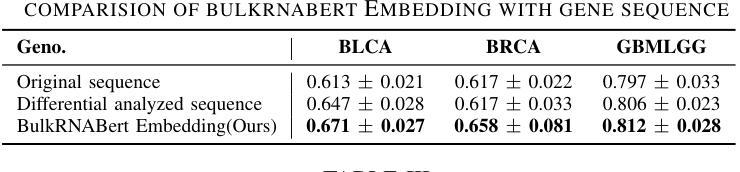
Efficient Self-Supervised Adaptation for Medical Image Analysis
Authors:Moein Sorkhei, Emir Konuk, Jingyu Guo, Chanjuan Meng, Christos Matsoukas, Kevin Smith
Self-supervised adaptation (SSA) improves foundation model transfer to medical domains but is computationally prohibitive. Although parameter efficient fine-tuning methods such as LoRA have been explored for supervised adaptation, their effectiveness for SSA remains unknown. In this work, we introduce efficient self-supervised adaptation (ESSA), a framework that applies parameter-efficient fine-tuning techniques to SSA with the aim of reducing computational cost and improving adaptation performance. Among the methods tested, Attention Projection Layer Adaptation (APLA) sets a new state-of-the-art, consistently surpassing full-parameter SSA and supervised fine-tuning across diverse medical tasks, while reducing GPU memory by up to 40.1% and increasing training throughput by 25.2%, all while maintaining inference efficiency.
自我监督适应(SSA)提高了基础模型在医学领域的迁移能力,但计算成本高昂。虽然LoRA等参数高效微调方法已被探索用于监督适应,但其在SSA中的有效性尚不清楚。在这项工作中,我们引入了高效自我监督适应(ESSA)框架,该框架将参数高效微调技术应用于SSA,旨在降低计算成本并提高适应性能。在测试的方法中,注意力投影层适应(APLA)表现卓越,持续超越全参数SSA和监督微调,在多种医学任务上表现出优异性能,同时降低GPU内存使用率高达40.1%,提高训练效率25.2%,同时保持推理效率。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
SSA(自监督适应)在基础模型向医学领域迁移时虽然能提高性能,但计算成本高昂。本研究引入了一种高效的自监督适应框架(ESSA),采用参数高效微调技术以降低计算成本并提高适应性能。其中,Attention Projection Layer Adaptation(APLA)方法表现卓越,相较于全参数SSA和监督微调在多种医学任务上表现更优秀,同时减少了GPU内存使用并提高了训练效率。
Key Takeaways
- SSA在提高基础模型在医学领域的迁移性能时面临计算成本问题。
- ESSA框架运用参数高效微调技术以解决SSA的计算成本问题。
- APLA方法在多种医学任务上表现优于全参数SSA和监督微调。
- APLA能减少GPU内存使用,提高训练效率。
- ESSA框架在维持推理效率的同时,提高了适应性能。
- 本研究为自监督适应提供了新的优化方向。
点此查看论文截图

RLCAD: Reinforcement Learning Training Gym for Revolution Involved CAD Command Sequence Generation
Authors:Xiaolong Yin, Xingyu Lu, Jiahang Shen, Jingzhe Ni, Hailong Li, Ruofeng Tong, Min Tang, Peng Du
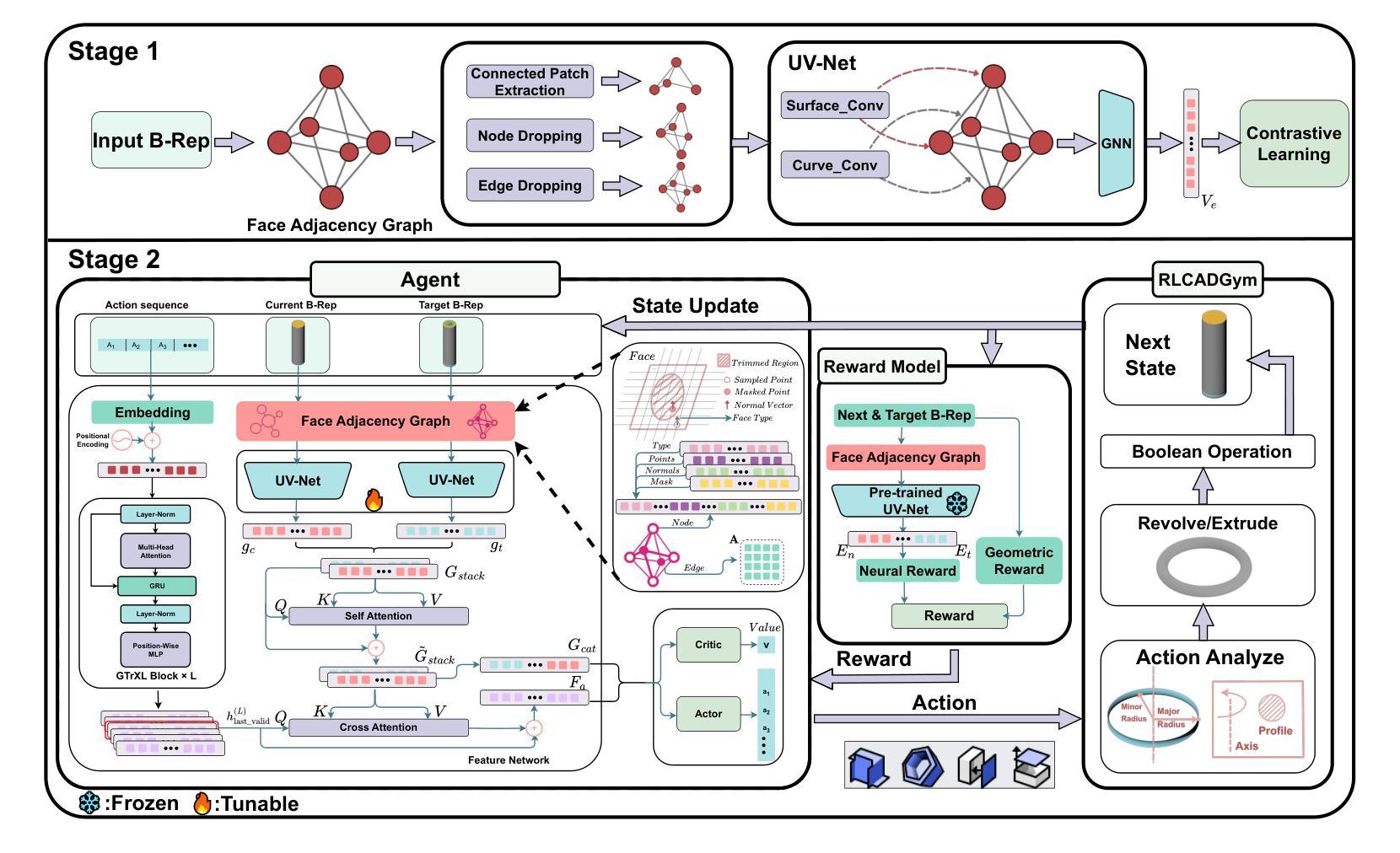
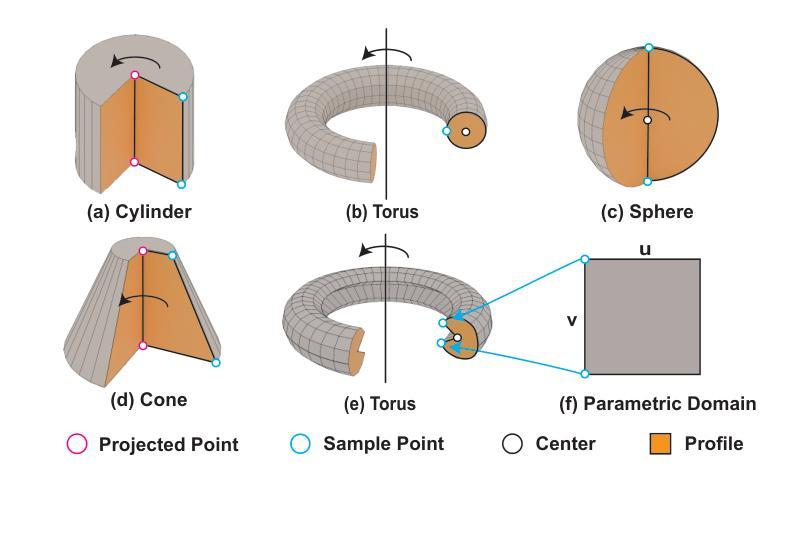
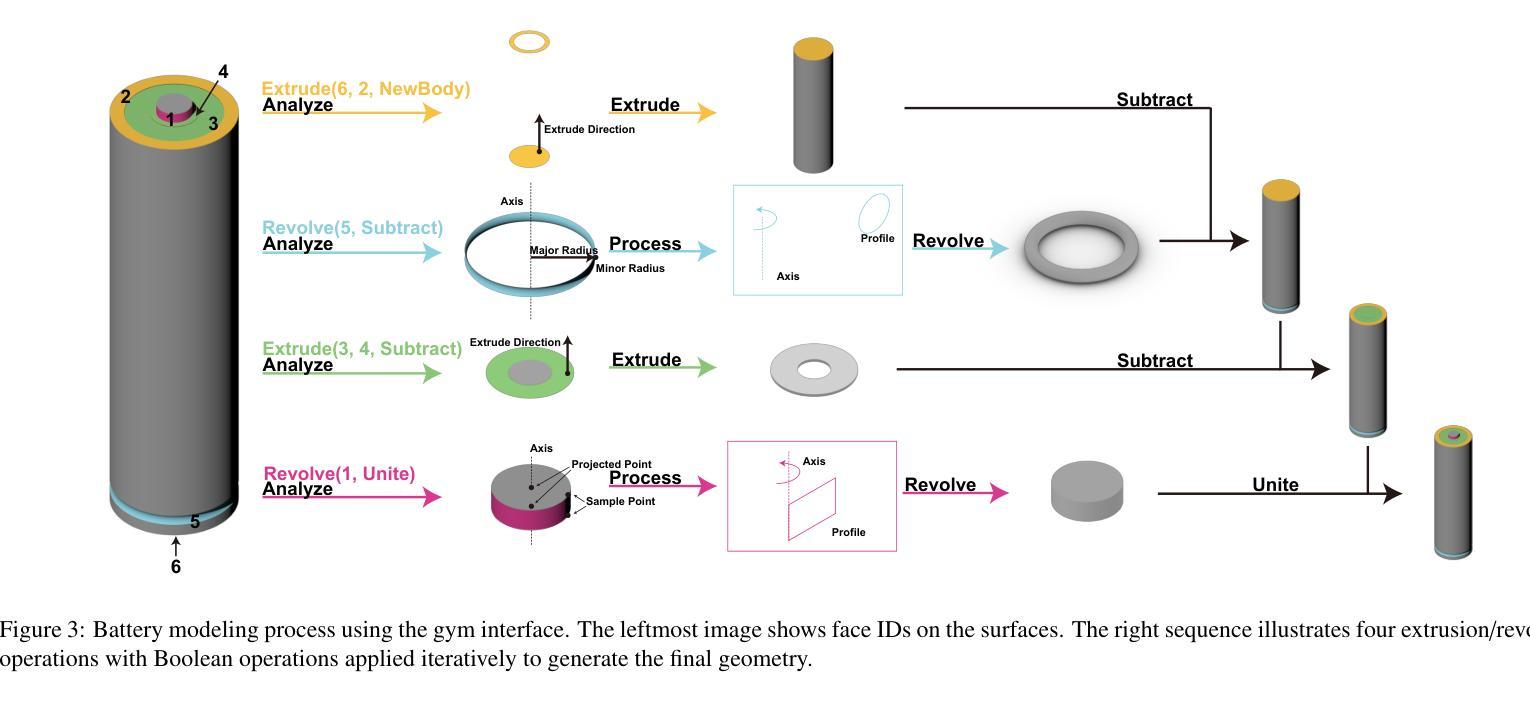
A CAD command sequence is a typical parametric design paradigm in 3D CAD systems where a model is constructed by overlaying 2D sketches with operations such as extrusion, revolution, and Boolean operations. Although there is growing academic interest in the automatic generation of command sequences, existing methods and datasets only support operations such as 2D sketching, extrusion,and Boolean operations. This limitation makes it challenging to represent more complex geometries. In this paper, we present a reinforcement learning (RL) training environment (gym) built on a CAD geometric engine. Given an input boundary representation (B-Rep) geometry, the policy network in the RL algorithm generates an action. This action, along with previously generated actions, is processed within the gym to produce the corresponding CAD geometry, which is then fed back into the policy network. The rewards, determined by the difference between the generated and target geometries within the gym, are used to update the RL network. Our method supports operations beyond sketches, Boolean, and extrusion, including revolution operations. With this training gym, we achieve state-of-the-art (SOTA) quality in generating command sequences from B-Rep geometries.
计算机辅助设计(CAD)命令序列是三维CAD系统中典型的参数化设计范例,其中模型是通过叠加二维草图并执行挤压、旋转和布尔运算等操作来构建的。尽管学术界对命令序列的自动生成越来越感兴趣,但现有方法和数据集仅支持二维草图、挤压和布尔运算等操作。这一局限性使得表示更复杂的几何形状具有挑战性。在本文中,我们提出了一个基于CAD几何引擎的强化学习(RL)训练环境(gym)。给定输入边界表示(B-Rep)几何体,RL算法中的策略网络会生成一个动作。该动作与先前生成的动作一起在gym中进行处理,以产生相应的CAD几何体,然后反馈到策略网络。奖励由gym内生成目标几何体之间的差异来确定,用于更新RL网络。我们的方法支持草图、布尔和挤压操作以外的操作,包括旋转操作。使用这个训练环境,我们在从B-Rep几何体生成命令序列方面达到了最新技术水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于强化学习(RL)的CAD几何引擎训练环境,能够生成命令序列以构建复杂的CAD模型。通过输入边界表示(B-Rep)几何体,策略网络生成动作,并通过处理这些动作生成相应的CAD几何体。奖励根据生成的CAD几何体与目标几何体之间的差异来确定,用于更新RL网络。此方法支持包括旋转操作在内的多种操作,实现了从B-Rep几何体生成命令序列的最优质量。
Key Takeaways
- 使用强化学习构建CAD训练环境,以生成命令序列。
- 输入为边界表示(B-Rep)几何体,输出为相应的CAD几何体。
- 策略网络在训练环境中生成动作,并通过处理这些动作生成CAD模型。
- 奖励基于生成的CAD模型与目标模型之间的差异确定,用于更新强化学习网络。
- 支持多种操作,包括旋转操作,这扩大了现有方法和数据集的支持范围。
- 该方法实现了从B-Rep几何体生成命令序列的最优质量。
点此查看论文截图

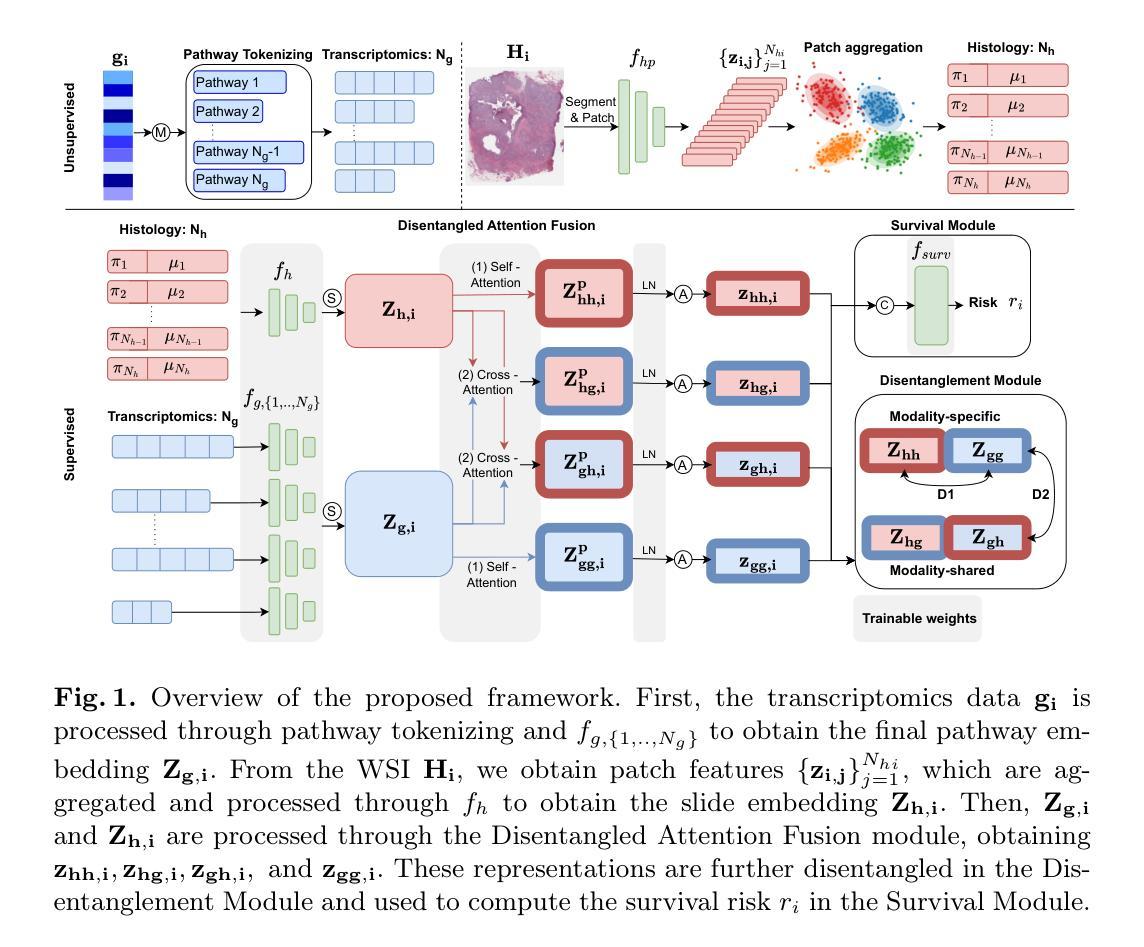
Disentangled and Interpretable Multimodal Attention Fusion for Cancer Survival Prediction
Authors:Aniek Eijpe, Soufyan Lakbir, Melis Erdal Cesur, Sara P. Oliveira, Sanne Abeln, Wilson Silva
To improve the prediction of cancer survival using whole-slide images and transcriptomics data, it is crucial to capture both modality-shared and modality-specific information. However, multimodal frameworks often entangle these representations, limiting interpretability and potentially suppressing discriminative features. To address this, we propose Disentangled and Interpretable Multimodal Attention Fusion (DIMAF), a multimodal framework that separates the intra- and inter-modal interactions within an attention-based fusion mechanism to learn distinct modality-specific and modality-shared representations. We introduce a loss based on Distance Correlation to promote disentanglement between these representations and integrate Shapley additive explanations to assess their relative contributions to survival prediction. We evaluate DIMAF on four public cancer survival datasets, achieving a relative average improvement of 1.85% in performance and 23.7% in disentanglement compared to current state-of-the-art multimodal models. Beyond improved performance, our interpretable framework enables a deeper exploration of the underlying interactions between and within modalities in cancer biology.
为了提高使用全幻灯片图像和转录组数据对癌症生存率的预测能力,捕获既适用于多种模式又适用于特定模式的信息至关重要。然而,多模式框架通常会将这些表示纠缠在一起,限制了可解释性并可能抑制辨别特征。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了“解缠且可解释的多模式注意力融合”(DIMAF)框架。这是一个多模式框架,它通过基于注意力的融合机制来分离模态内和模态间的交互作用,以学习独特的特定模态和共享模态的表示。我们引入了一种基于距离相关的损失来促进这些表示之间的解缠,并整合沙普利加法解释来评估它们对生存预测的相对贡献。我们在四个公共癌症生存数据集上评估了DIMAF,与当前最先进的多模式模型相比,性能平均提高了1.85%,解缠程度提高了23.7%。除了性能提升外,我们的可解释框架还使得我们能够更深入地探索癌症生物学中模式之间及其内部的潜在相互作用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 1 figure, 3 tables. Preprint submitted and accepted to MICCAI 2025. This preprint has not undergone peer review or any post-submission improvements or corrections
Summary
基于全滑图像和转录组学数据的癌症生存预测改进中,关键在于捕捉模态共享和模态特定的信息。为此,我们提出了一个可解释的多模态注意力融合框架(DIMAF),它通过注意力融合机制分离模态内和模态间的交互作用,学习不同的模态特定和模态共享表示。采用基于距离相关的损失来促进这些表示之间的解耦,并利用沙普利加法解释法评估其对生存预测的相对贡献。在四个公共癌症生存数据集上评估表明,与当前最先进的多模态模型相比,性能提高了平均1.85%,解耦程度提高了23.7%。除了提高性能外,我们的可解释框架还深入探索了癌症生物学中模态之间和模态内部的相互作用。
Key Takeaways
- 癌症生存预测改进的关键在于捕捉全滑图像和转录组学数据的模态共享与模态特定信息。
- 提出了一种名为DIMAF的多模态注意力融合框架,旨在解决现有框架在融合不同信息时存在的纠缠问题。
- DIMAF通过注意力机制分离模态内和模态间的交互作用,学习不同的模态特定和共享表示。
- 采用基于距离相关的损失函数来促进不同表示之间的解耦。
- 利用沙普利加法解释法评估不同信息对生存预测的相对贡献。
- 在四个公共癌症生存数据集上的评估显示,与现有模型相比,DIMAF在性能和解耦程度方面有所提升。
点此查看论文截图

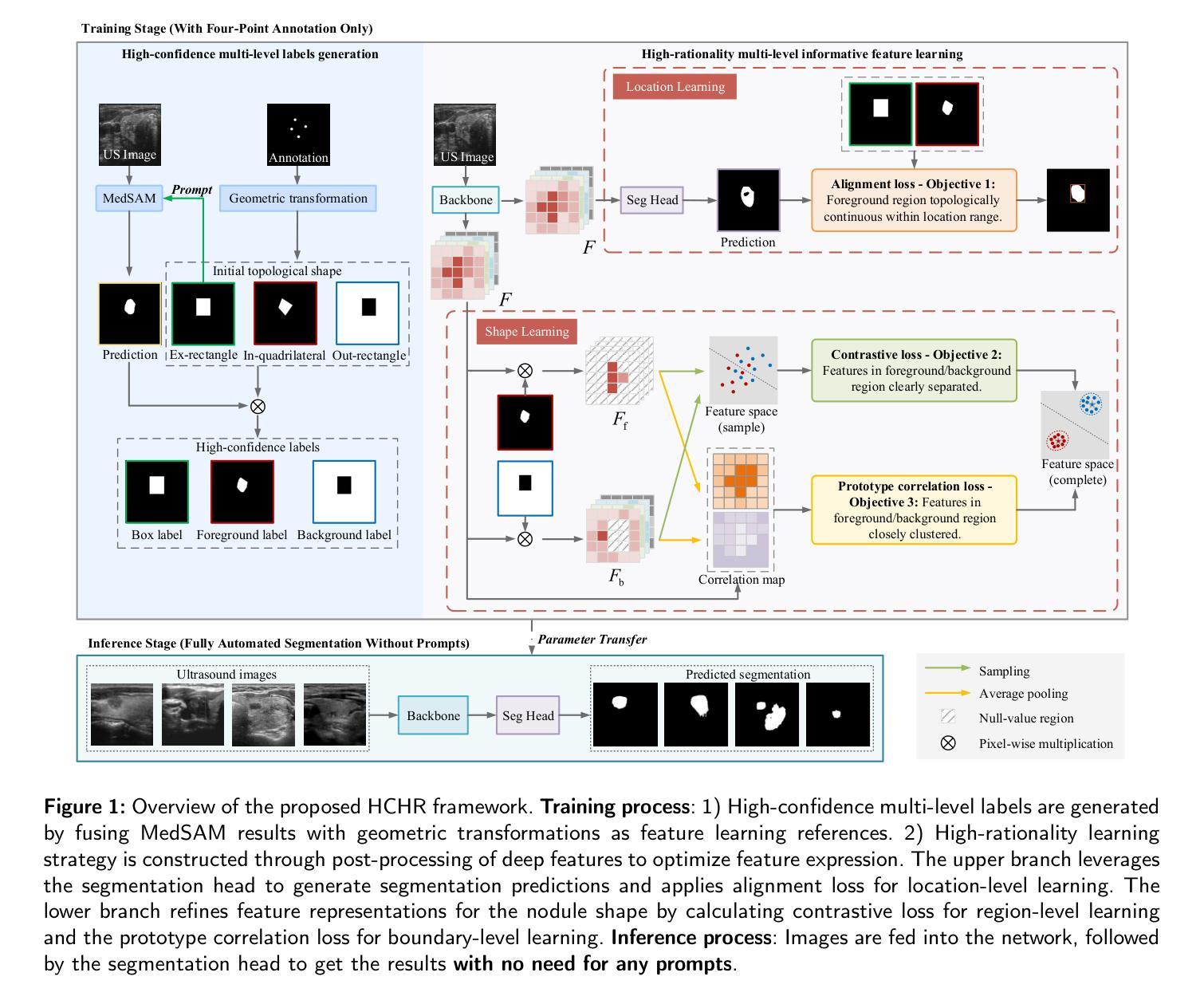
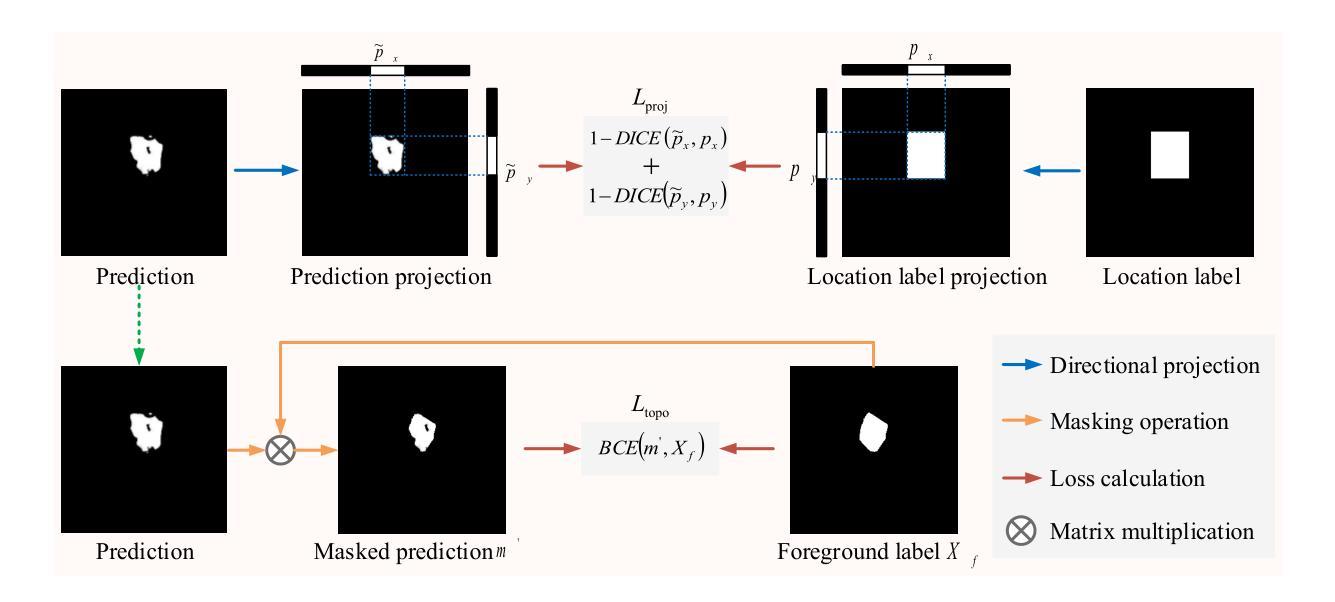
Weakly Supervised Segmentation Framework for Thyroid Nodule Based on High-confidence Labels and High-rationality Losses
Authors:Jianning Chi, Zelan Li, Geng Lin, MingYang Sun, Xiaosheng Yu
Weakly supervised segmentation methods can delineate thyroid nodules in ultrasound images efficiently using training data with coarse labels, but suffer from: 1) low-confidence pseudo-labels that follow topological priors, introducing significant label noise, and 2) low-rationality loss functions that rigidly compare segmentation with labels, ignoring discriminative information for nodules with diverse and complex shapes. To solve these issues, we clarify the objective and references for weakly supervised ultrasound image segmentation, presenting a framework with high-confidence pseudo-labels to represent topological and anatomical information and high-rationality losses to capture multi-level discriminative features. Specifically, we fuse geometric transformations of four-point annotations and MedSAM model results prompted by specific annotations to generate high-confidence box, foreground, and background labels. Our high-rationality learning strategy includes: 1) Alignment loss measuring spatial consistency between segmentation and box label, and topological continuity within the foreground label, guiding the network to perceive nodule location; 2) Contrastive loss pulling features from labeled foreground regions while pushing features from labeled foreground and background regions, guiding the network to learn nodule and background feature distribution; 3) Prototype correlation loss measuring consistency between correlation maps derived by comparing features with foreground and background prototypes, refining uncertain regions to accurate nodule edges. Experimental results show that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on the TN3K and DDTI datasets. The code is available at https://github.com/bluehenglee/MLI-MSC.
弱监督分割方法能够利用带有粗略标签的训练数据有效地在超声图像中描绘甲状腺结节,但存在以下问题:1)遵循拓扑先验的低置信度伪标签,引入了大量标签噪声;2)损失函数缺乏理性,生硬地将分割结果与标签进行比较,忽视了具有多样性和复杂形状的结节的判别信息。为了解决这些问题,我们明确了弱监督超声图像分割的目标和参考,提出了一个框架,利用高置信度伪标签来表示拓扑和解剖信息,以及高理性损失来捕捉多层次的判别特征。具体来说,我们通过融合四点注释的几何变换和MedSAM模型结果来生成高置信度的框、前景和背景标签。我们的高理性学习策略包括:1)对齐损失,测量分割与框标签之间的空间一致性,以及前景标签内的拓扑连续性,指导网络感知结节位置;2)对比损失,从标记的前景区域中提取特征,同时将标记的前景和背景区域中的特征推开,引导网络学习结节和背景特征分布;3)原型关联损失,测量通过比较特征与前景和背景原型得出的关联图之间的一致性,细化不确定区域以获取准确的结节边缘。实验结果表明,我们的方法在TN3K和DDTI数据集上达到了最新性能。代码可在https://github.com/bluehenglee/MLI-MSC上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 pages, 14 figures, 7 tables
Summary
本文解决弱监督超声图像分割中甲状腺结节的识别问题。通过使用高置信度的伪标签和高理性的损失函数,框架能够高效处理粗标签训练数据,并捕捉多级判别特征。通过融合几何变换和四点注释的MedSAM模型结果生成高置信度的标签,并设计了对齐损失、对比损失和原型关联损失,以指导网络感知结节位置、学习结节和背景特征分布,并优化不确定区域至准确的结节边缘。实验结果显示该方法在TN3K和DDTI数据集上达到领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- 弱监督分割方法利用粗标签数据在超声图像中有效勾勒甲状腺结节点。
- 现有方法存在低置信度伪标签引入的标签噪声问题以及刚性对比分割与标签的损失函数忽略结节复杂形状信息的问题。
- 提出使用高置信度伪标签代表拓扑和解剖信息,融合几何变换和特定注释生成高置信度标签。
- 设计高理性损失策略,包括对齐损失以指导网络感知结节位置,对比损失使网络学习结节和背景特征分布,以及原型关联损失以优化不确定区域至准确边缘。
- 方法在TN3K和DDTI数据集上表现优异。
- 提供实验代码链接。
点此查看论文截图

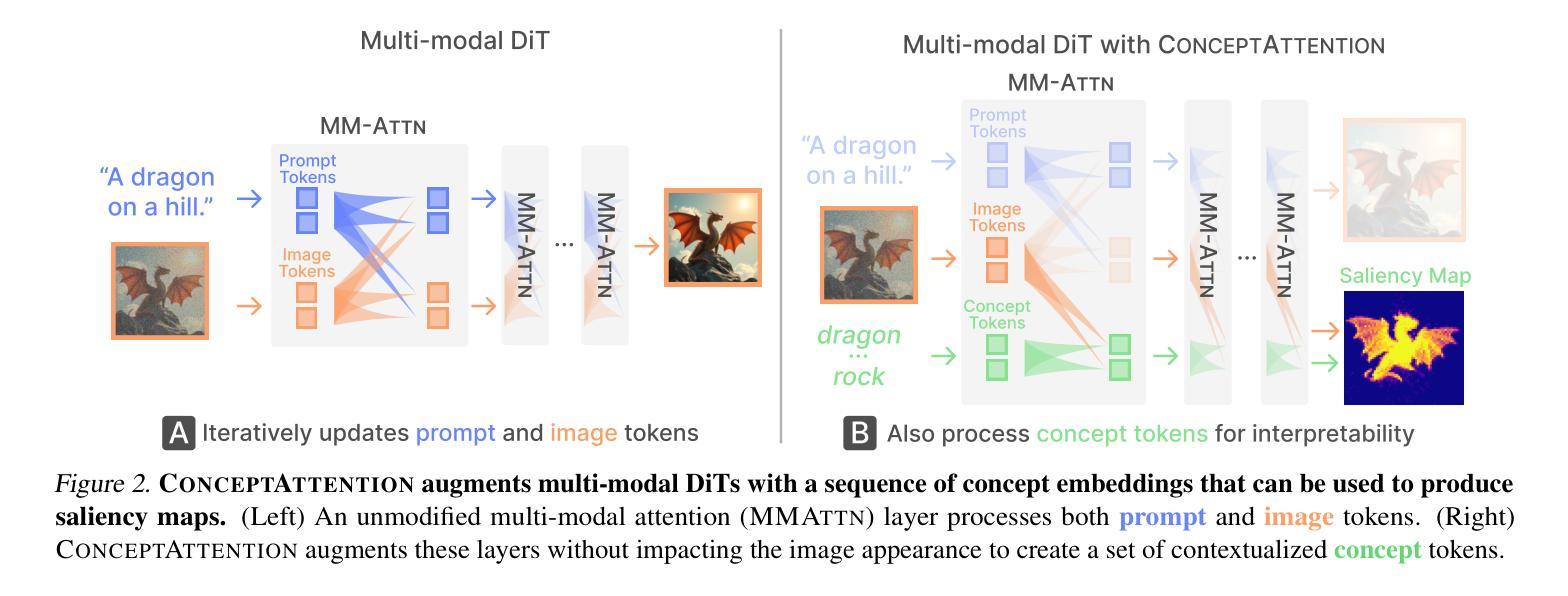
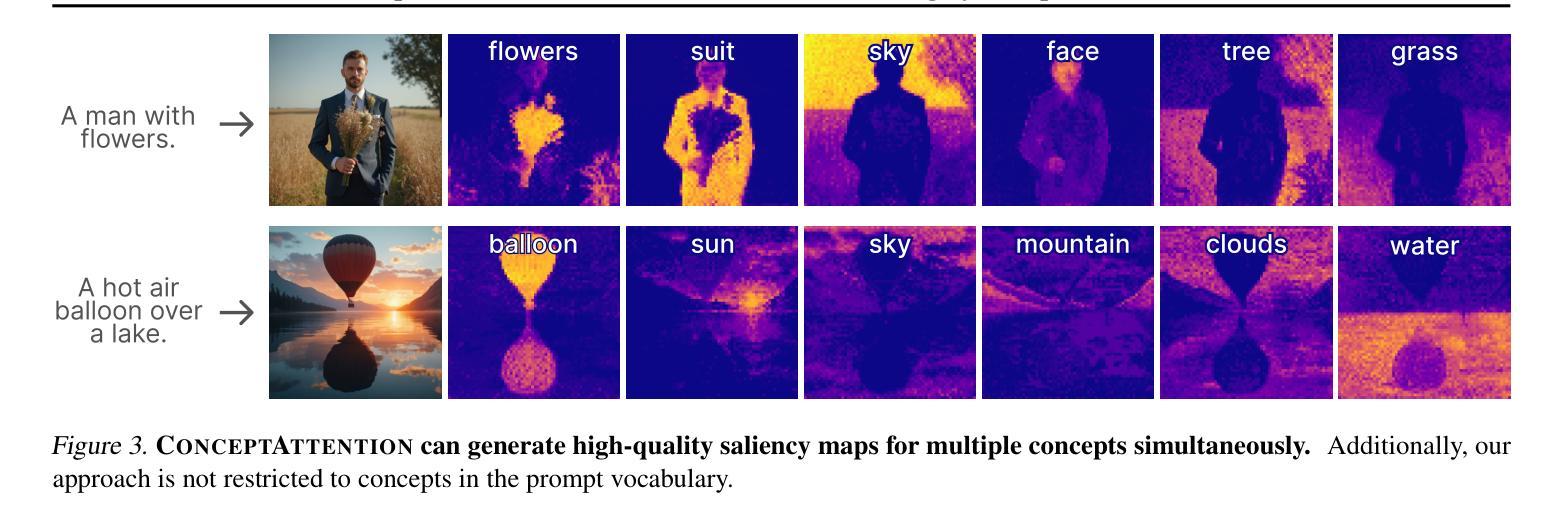
ConceptAttention: Diffusion Transformers Learn Highly Interpretable Features
Authors:Alec Helbling, Tuna Han Salih Meral, Ben Hoover, Pinar Yanardag, Duen Horng Chau
Do the rich representations of multi-modal diffusion transformers (DiTs) exhibit unique properties that enhance their interpretability? We introduce ConceptAttention, a novel method that leverages the expressive power of DiT attention layers to generate high-quality saliency maps that precisely locate textual concepts within images. Without requiring additional training, ConceptAttention repurposes the parameters of DiT attention layers to produce highly contextualized concept embeddings, contributing the major discovery that performing linear projections in the output space of DiT attention layers yields significantly sharper saliency maps compared to commonly used cross-attention maps. ConceptAttention even achieves state-of-the-art performance on zero-shot image segmentation benchmarks, outperforming 15 other zero-shot interpretability methods on the ImageNet-Segmentation dataset. ConceptAttention works for popular image models and even seamlessly generalizes to video generation. Our work contributes the first evidence that the representations of multi-modal DiTs are highly transferable to vision tasks like segmentation.
多模态扩散transformer(DiT)的丰富表示是否具有增强其可解释性的独特属性?我们引入了一种名为ConceptAttention的新方法,该方法利用DiT注意力层的表现力来生成高质量的显著性地图,精确地在图像中定位文本概念。ConceptAttention不需要额外的训练,它可以重新利用DiT注意力层的参数来生成高度上下文化的概念嵌入,并做出重大发现:在DiT注意力层的输出空间中进行线性投影会产生比常用的交叉注意力图更清晰的显著性地图。ConceptAttention甚至在零样本图像分割基准测试中实现了最先进的性能,在ImageNet-Segmentation数据集上超越了其他15种零样本可解释性方法。ConceptAttention适用于流行的图像模型,甚至可以无缝地推广到视频生成。我们的工作首次证明多模态DiT的表示高度适用于分割等视觉任务。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Oral Presentation at ICML 2025, Best Paper Award at CVPR Workshop on Visual Concepts
Summary
本文提出一种名为ConceptAttention的新方法,利用多模态扩散变压器(DiT)的表达能力强的注意力层生成高质量的显著性地图,精确定位图像中的文本概念。通过无需额外训练就能在DiT注意力层生成高度语境化的概念嵌入,主要发现对DiT注意力层的输出空间进行线性投影可以产生更清晰显著性地图。ConceptAttention在零样本图像分割基准测试中实现了最先进的性能,在ImageNet-Segmentation数据集上超越了其他15种零样本可解释性方法。ConceptAttention适用于流行的图像模型,并能够无缝推广到视频生成中。本文首次证明了多模态DiT的表征高度适用于分割等视觉任务。
Key Takeaways
- ConceptAttention利用DiT注意力层的丰富表示生成精确的定位文本概念的显著性地图。
- ConceptAttention通过无需额外训练就能使用DiT参数产生高度语境化的概念嵌入。
- 对DiT注意力层的输出空间进行线性投影可以产生更清晰的显著性地图。
- ConceptAttention在零样本图像分割方面表现优异,超越其他方法。
- ConceptAttention适用于多种图像模型,并可以推广到视频生成中。
- 多模态DiT的表征高度适用于分割等视觉任务。
点此查看论文截图

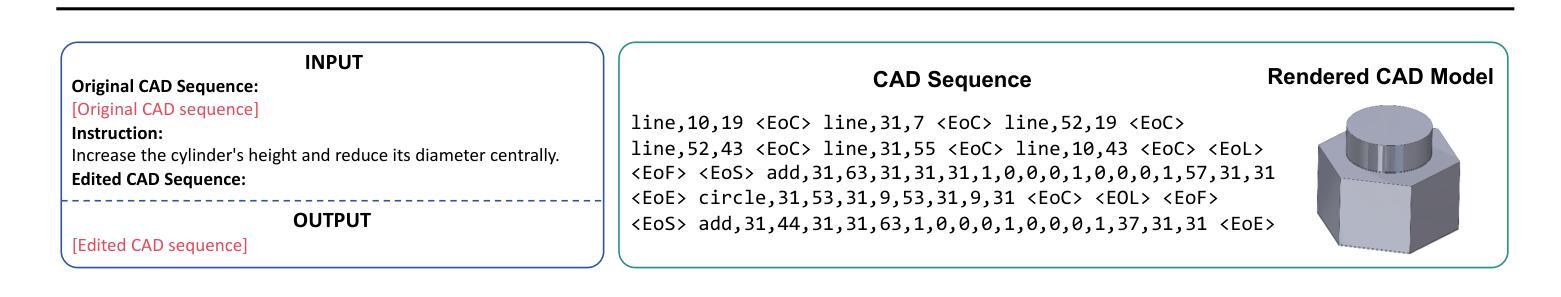
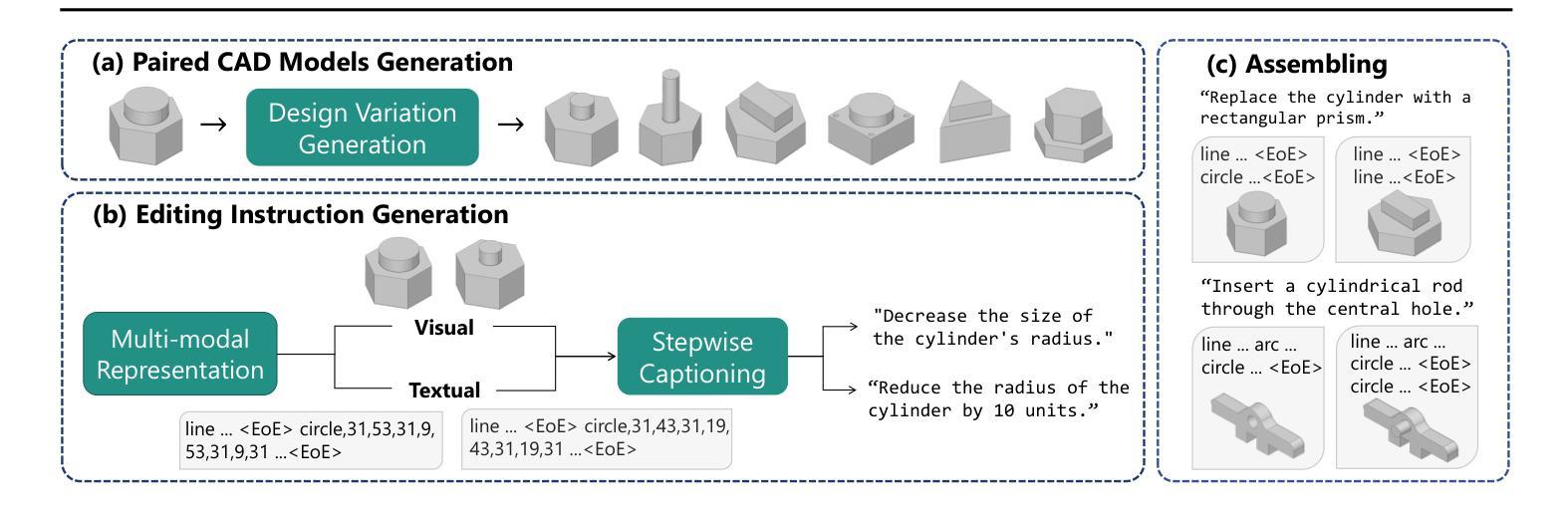
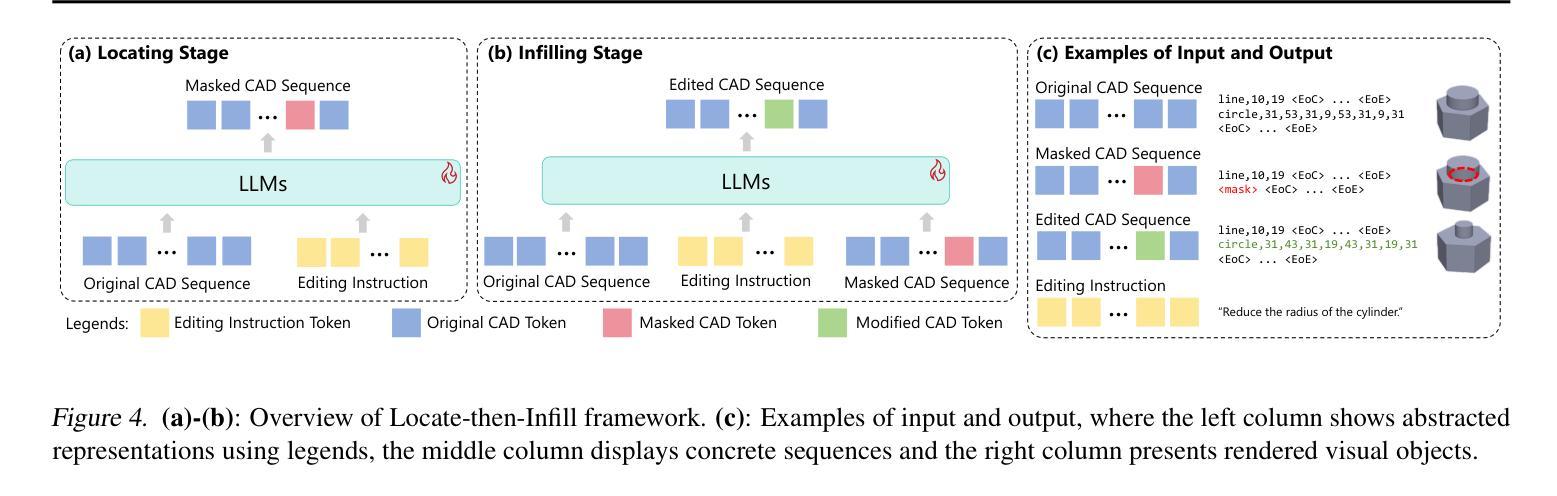
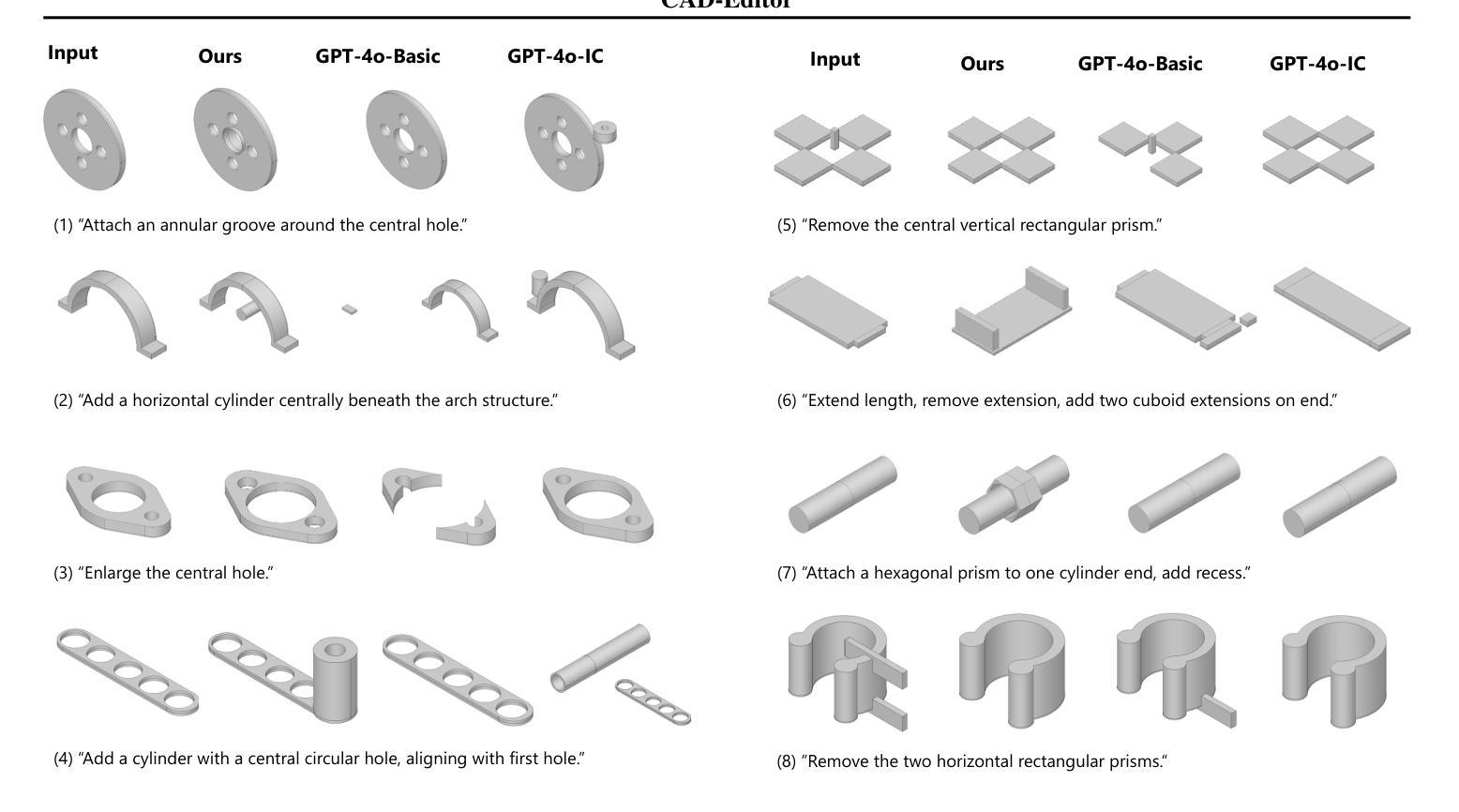
CAD-Editor: A Locate-then-Infill Framework with Automated Training Data Synthesis for Text-Based CAD Editing
Authors:Yu Yuan, Shizhao Sun, Qi Liu, Jiang Bian
Computer Aided Design (CAD) is indispensable across various industries. \emph{Text-based CAD editing}, which automates the modification of CAD models based on textual instructions, holds great potential but remains underexplored. Existing methods primarily focus on design variation generation or text-based CAD generation, either lacking support for text-based control or neglecting existing CAD models as constraints. We introduce \emph{CAD-Editor}, the first framework for text-based CAD editing. To address the challenge of demanding triplet data with accurate correspondence for training, we propose an automated data synthesis pipeline. This pipeline utilizes design variation models to generate pairs of original and edited CAD models and employs Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) to summarize their differences into editing instructions. To tackle the composite nature of text-based CAD editing, we propose a locate-then-infill framework that decomposes the task into two focused sub-tasks: locating regions requiring modification and infilling these regions with appropriate edits. Large Language Models (LLMs) serve as the backbone for both sub-tasks, leveraging their capabilities in natural language understanding and CAD knowledge. Experiments show that CAD-Editor achieves superior performance both quantitatively and qualitatively. The code is available at \url {https://github.com/microsoft/CAD-Editor}.
计算机辅助设计(CAD)在各行各业中都是不可或缺的。基于文本的CAD编辑能够自动根据文本指令修改CAD模型,这一技术潜力巨大,但尚未得到充分探索。现有方法主要集中在设计变体生成或基于文本的CAD生成上,它们要么不支持基于文本的控制,要么忽视了现有的CAD模型作为约束。我们引入了基于文本的CAD编辑首个框架——CAD-Editor。为解决训练所需的三元组数据对应不准确的问题,我们提出了自动化数据合成管道。该管道利用设计变体模型生成原始和编辑后的CAD模型对,并利用大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)将其差异总结为编辑指令。为解决基于文本的CAD编辑的复合性质,我们提出了先定位后填充框架,将任务分解为两个有针对性的子任务:定位需要修改的区域,并用适当的编辑填充这些区域。大型语言模型(LLMs)作为这两个子任务的后盾,利用其在自然语言理解和CAD知识方面的能力。实验表明,CAD-Editor在定量和定性方面都取得了卓越的性能。代码可在https://github.com/microsoft/CAD-Editor上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本基于计算机辅助设计(CAD)的编辑技术,介绍了文本基础上的CAD编辑的重要性和现有方法的不足。提出了CAD-Editor框架,通过自动化数据合成管道解决训练数据对应问题,并采用大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)进行编辑指令的总结。框架采用定位后填充的策略解决基于文本的CAD编辑的复合性质问题,并利用大型语言模型(LLMs)作为两个子任务的支柱。实验表明,CAD-Editor在定量和定性方面都取得了卓越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 文本基于计算机辅助设计(CAD)编辑的重要性及其现有方法的不足。
- 介绍CAD-Editor框架用于文本基础的CAD编辑。
- 自动化数据合成管道解决训练数据对应问题。
- 采用大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)总结编辑指令。
- CAD-Editor采用定位后填充策略解决基于文本的CAD编辑的复合性质问题。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)作为子任务的支柱,利用其自然语言理解和CAD知识。
- CAD-Editor在定量和定性方面都取得了卓越的实验性能。
点此查看论文截图


Semi-supervised Semantic Segmentation for Remote Sensing Images via Multi-scale Uncertainty Consistency and Cross-Teacher-Student Attention
Authors:Shanwen Wang, Xin Sun, Changrui Chen, Danfeng Hong, Jungong Han
Semi-supervised learning offers an appealing solution for remote sensing (RS) image segmentation to relieve the burden of labor-intensive pixel-level labeling. However, RS images pose unique challenges, including rich multi-scale features and high inter-class similarity. To address these problems, this paper proposes a novel semi-supervised Multi-Scale Uncertainty and Cross-Teacher-Student Attention (MUCA) model for RS image semantic segmentation tasks. Specifically, MUCA constrains the consistency among feature maps at different layers of the network by introducing a multi-scale uncertainty consistency regularization. It improves the multi-scale learning capability of semi-supervised algorithms on unlabeled data. Additionally, MUCA utilizes a Cross-Teacher-Student attention mechanism to guide the student network, guiding the student network to construct more discriminative feature representations through complementary features from the teacher network. This design effectively integrates weak and strong augmentations (WA and SA) to further boost segmentation performance. To verify the effectiveness of our model, we conduct extensive experiments on ISPRS-Potsdam and LoveDA datasets. The experimental results show the superiority of our method over state-of-the-art semi-supervised methods. Notably, our model excels in distinguishing highly similar objects, showcasing its potential for advancing semi-supervised RS image segmentation tasks.
半监督学习为遥感(RS)图像分割提供了一个吸引人的解决方案,减轻了劳动密集型的像素级标签的负担。然而,遥感图像带来了独特的挑战,包括丰富的多尺度特征和高的类间相似性。为了解决这些问题,本文提出了一种新型的半监督多尺度不确定性及交叉教师学生注意力(MUCA)模型,用于遥感图像语义分割任务。具体而言,MUCA通过引入多尺度不确定性一致性正则化,约束网络不同层特征图之间的一致性。它提高了半监督算法在未标记数据上的多尺度学习能力。此外,MUCA利用跨教师学生注意力机制来引导学生网络,通过教师网络的互补特征,引导学生网络构建更具区分性的特征表示。该设计有效地结合了弱增强和强增强(WA和SA),进一步提升了分割性能。为了验证我们模型的有效性,我们在ISPRS-Potsdam和LoveDA数据集上进行了大量实验。实验结果表明,我们的方法优于最新的半监督方法。值得注意的是,我们的模型在区分高度相似对象方面表现出色,展示了其在推进半监督遥感图像分割任务方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
半监督学习为解决遥感图像分割中劳动密集型的像素级标注负担提供了有吸引力的解决方案。本文提出一种新型半监督Multi-Scale Uncertainty and Cross-Teacher-Student Attention(MUCA)模型,用于遥感图像语义分割任务。MUCA通过引入多尺度不确定性一致性正则化,提高半监督算法在未标注数据上的多尺度学习能力。同时,MUCA利用跨教师学生注意力机制来引导学生网络构建更具区分性的特征表示。实验结果表明,该方法在ISPRS-Potsdam和LoveDA数据集上优于最新半监督方法,尤其在高相似度物体区分上表现突出。
Key Takeaways
- 半监督学习是解决遥感图像分割中劳动密集型像素级标注负担的有效方法。
- 本文提出一种新型的半监督MUCA模型,适用于遥感图像语义分割任务。
- MUCA模型通过引入多尺度不确定性一致性正则化,提高半监督算法在未标注数据上的多尺度学习能力。
- MUCA模型利用跨教师学生注意力机制,引导学生网络构建更具区分性的特征表示。
- MUCA模型结合了弱增强和强增强,进一步提升了分割性能。
- 在ISPRS-Potsdam和LoveDA数据集上的实验验证了MUCA模型的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

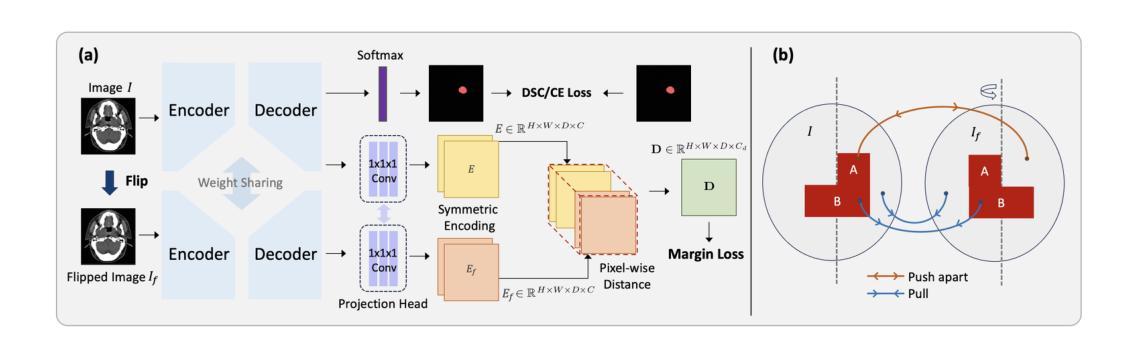
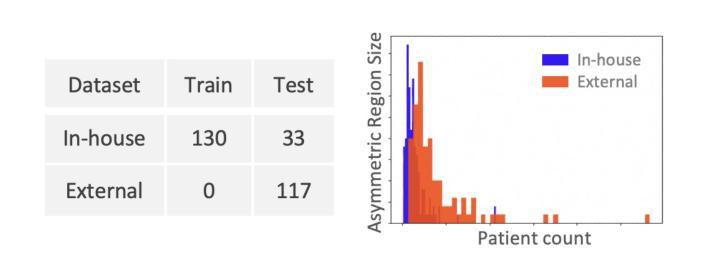
Leveraging Semantic Asymmetry for Precise Gross Tumor Volume Segmentation of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma in Planning CT
Authors:Zi Li, Ying Chen, Zeli Chen, Yanzhou Su, Tai Ma, Tony C. W. Mok, Yan-Jie Zhou, Yunhai Bai, Zhinlin Zheng, Le Lu, Yirui Wang, Jia Ge, Xianghua Ye, Senxiang Yan, Dakai Jin
In the radiation therapy of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), clinicians typically delineate the gross tumor volume (GTV) using non-contrast planning computed tomography to ensure accurate radiation dose delivery. However, the low contrast between tumors and adjacent normal tissues necessitates that radiation oncologists manually delineate the tumors, often relying on diagnostic MRI for guidance. % In this study, we propose a novel approach to directly segment NPC gross tumors on non-contrast planning CT images, circumventing potential registration errors when aligning MRI or MRI-derived tumor masks to planning CT. To address the low contrast issues between tumors and adjacent normal structures in planning CT, we introduce a 3D Semantic Asymmetry Tumor segmentation (SATs) method. Specifically, we posit that a healthy nasopharyngeal region is characteristically bilaterally symmetric, whereas the emergence of nasopharyngeal carcinoma disrupts this symmetry. Then, we propose a Siamese contrastive learning segmentation framework that minimizes the voxel-wise distance between original and flipped areas without tumor and encourages a larger distance between original and flipped areas with tumor. Thus, our approach enhances the sensitivity of features to semantic asymmetries. % Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed SATs achieves the leading NPC GTV segmentation performance in both internal and external testing, \emph{e.g.}, with at least 2% absolute Dice score improvement and 12% average distance error reduction when compared to other state-of-the-art methods in the external testing.
在鼻咽癌(NPC)的放射治疗过程中,临床医生通常使用非对比计划计算机断层扫描(CT)来精确描绘大体肿瘤体积(GTV),以确保准确的辐射剂量传递。然而,肿瘤与邻近正常组织之间的对比度较低,迫使放疗科医生手动描绘肿瘤,通常依赖诊断性磁共振成像(MRI)进行引导。在本研究中,我们提出了一种新的方法,可以直接在非对比计划CT图像上分割鼻咽癌的大体肿瘤,避免了将MRI或MRI衍生的肿瘤掩膜与规划CT进行配准时可能出现的潜在配准误差。为了解决规划CT中肿瘤与邻近正常结构之间对比度低的问题,我们引入了3D语义不对称肿瘤分割(SATs)方法。具体来说,我们认为健康的鼻咽区域具有典型的双侧对称性,而鼻咽癌的出现会破坏这种对称性。然后,我们提出了一种Siamese对比学习分割框架,该框架通过最小化原始和翻转区域的非肿瘤部位的体素间距离来训练模型,同时鼓励原始和带有肿瘤的翻转区域之间的距离最大化。因此,我们的方法提高了对语义不对称性的特征敏感性。大量实验表明,所提出的SATs在内部和外部测试中均实现了领先的NPC GTV分割性能,例如与外部测试中的其他最先进的方法相比,至少提高了2%的绝对Dice得分和降低了12%的平均距离误差。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本摘要针对鼻咽癌放射治疗的影像研究提出一种新的方法。此方法能直接在非对比度规划的计算机断层扫描图像中划分鼻咽癌肿瘤体积,从而避免MRI或MRI衍生的肿瘤掩膜与规划CT图像对齐时可能出现的注册误差。通过引入三维语义不对称肿瘤分割(SATs)方法来解决肿瘤与邻近正常结构之间对比度低的问题。实验证明,该方法在内部和外部测试中均实现了领先的鼻咽癌GTV分割性能。
Key Takeaways
- 鼻咽癌放射治疗通常使用非对比度规划计算机断层扫描来描绘肿瘤体积。
- 由于肿瘤与邻近正常组织之间的对比度低,通常需要放射肿瘤学家手动描绘肿瘤,并经常依赖诊断MRI进行引导。
- 本研究提出了一种直接对非对比度规划CT图像中的鼻咽癌肿瘤进行分割的新方法。
- 该方法引入三维语义不对称肿瘤分割(SATs)来解决肿瘤与邻近正常结构之间的对比度问题。
- SATs方法利用健康鼻咽区域的双侧对称性特征,而鼻咽癌的出现会破坏这种对称性。
- 研究采用Siamese对比学习分割框架,通过最小化原始和翻转区域的体素距离来增强特征对语义不对称的敏感性。
点此查看论文截图

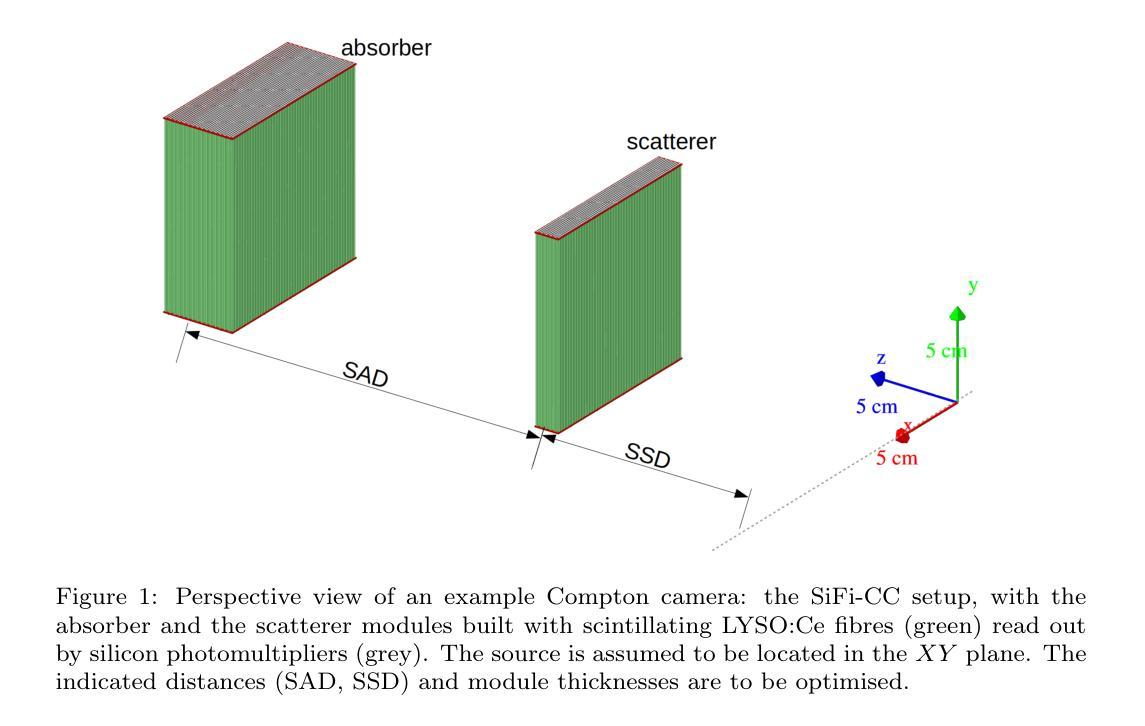
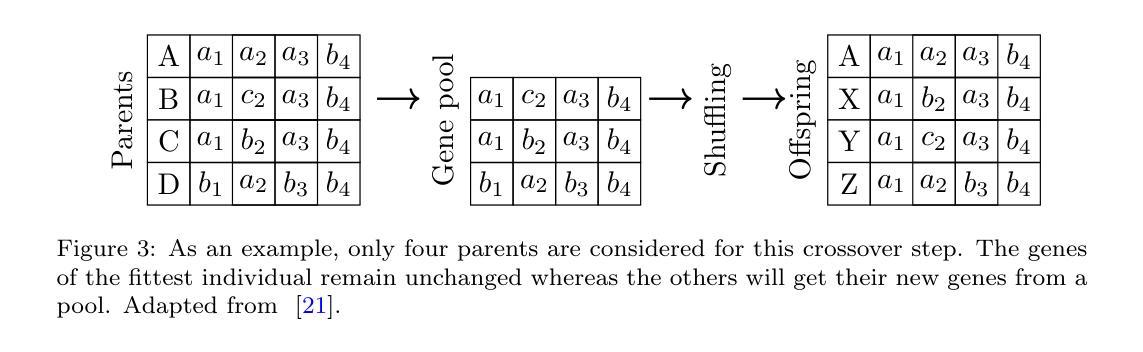
Genetic algorithm as a tool for detection setup optimisation: SiFi-CC case study
Authors:Jonas Kasper, Awal Awal, Ronja Hetzel, Magdalena Kołodziej, Katarzyna Rusiecka, Achim Stahl, Ming-Liang Wong, Aleksandra Wrońska
Objective: Proton therapy is a precision-focused cancer treatment where accurate proton beam range monitoring is critical to ensure effective dose delivery. This can be achieved by prompt gamma detection with a Compton camera like the SiFi-CC. This study aims to show the feasibility of optimising the geometry of SiFi-CC Compton camera for verification of dose distribution via prompt gamma detection using a genetic algorithm (GA). Approach: The SiFi-CC key geometric parameters for optimisation with the GA are the source-to-scatterer and scatterer-to-absorber distances, and the module thicknesses. The optimisation process was conducted with a software framework based on the Geant4 toolkit, which included detailed and realistic modelling of gamma interactions, detector response, and further steps such as event selection and image reconstruction. The performance of each individual configuration was evaluated using a fitness function incorporating factors related to gamma detection efficiency and image resolution. Results: The GA-optimised SiFi-CC configuration demonstrated the capability to detect a 5 mm proton beam range shift with a 2 mm resolution using 5e8 protons. The best-performing geometry, with 16 fibre layers in the scatterer, 36 layers in the absorber, source-to-scatterer distance 150 mm and scatterer-to-absorber distance 120 mm, has an imaging sensitivity of 5.58(1)e-5. Significance: This study demonstrates that the SiFi-CC setup, optimised through a GA, can reliably detect clinically relevant proton beam range shifts, improving real-time range verification accuracy in proton therapy. The presented implementation of a GA is a systematic and feasible way of searching for a SiFi-CC geometry that shows the best performance.
目标:质子疗法是一种精准癌症治疗方法,其中准确的质子束范围监测对于确保有效剂量传递至关重要。这可以通过使用SiFi-CC等康普顿相机进行即时伽马检测来实现。本研究旨在展示使用遗传算法(GA)优化SiFi-CC康普顿相机几何结构,通过即时伽马检测验证剂量分布的可行性。
方法:使用遗传算法进行优化的SiFi-CC关键几何参数包括源到散射器和散射器到吸收器的距离以及模块厚度。优化过程是在基于Geant4工具包的软件框架中进行的,其中包括伽马相互作用、探测器响应的详细和真实建模,以及事件选择和图像重建等进一步步骤。使用纳入与伽马检测效率和图像分辨率相关因素的适应度函数来评估每种配置的性能。
结果:经过遗传算法优化的SiFi-CC配置能够使用5e8个质子以2mm的分辨率检测出5mm的质子束范围偏移。表现最佳的几何结构具有散射器中的16层纤维、吸收器中的36层、源到散射器的距离为150mm以及散射器到吸收器的距离为120mm,其成像灵敏度为5.58(1)e-5。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 figures, 3 tables
摘要
本研究利用遗传算法(GA)优化SiFi-CC康普顿相机几何结构,通过即时伽马检测验证剂量分布。优化参数包括源散射器及散射器至吸收器的距离和模块厚度。经Geant4工具包进行详尽模拟,结果显示优化后的SiFi-CC可在使用5e8质子时检测到5毫米质子束范围偏移,分辨率达2毫米。最佳几何结构具有16层散射器和36层吸收器,源散射器距离为150毫米,散射器至吸收器距离为120毫米,成像灵敏度为5.58(1)e-5。该研究证实,通过遗传算法优化的SiFi-CC可准确检测临床相关的质子束范围偏移,提高质子疗法中的实时范围验证精度。
关键要点
- 本研究旨在利用遗传算法优化SiFi-CC康普顿相机的几何结构。
- 优化参数包括源至散射器、散射器至吸收器的距离以及模块厚度。
- 利用基于Geant4工具包的软件框架进行详细且现实的伽马相互作用、探测器响应等模拟。
- 遗传算法优化的SiFi-CC配置可检测到5毫米的质子束范围偏移,分辨率达到2毫米。
- 最佳表现的几何结构参数具体为:散射器有16层,吸收器有36层,源散射器距离为150毫米,散射器至吸收器距离为120毫米。
- 该研究验证了优化后的SiFi-CC在质子疗法中实时范围验证的准确性。
点此查看论文截图



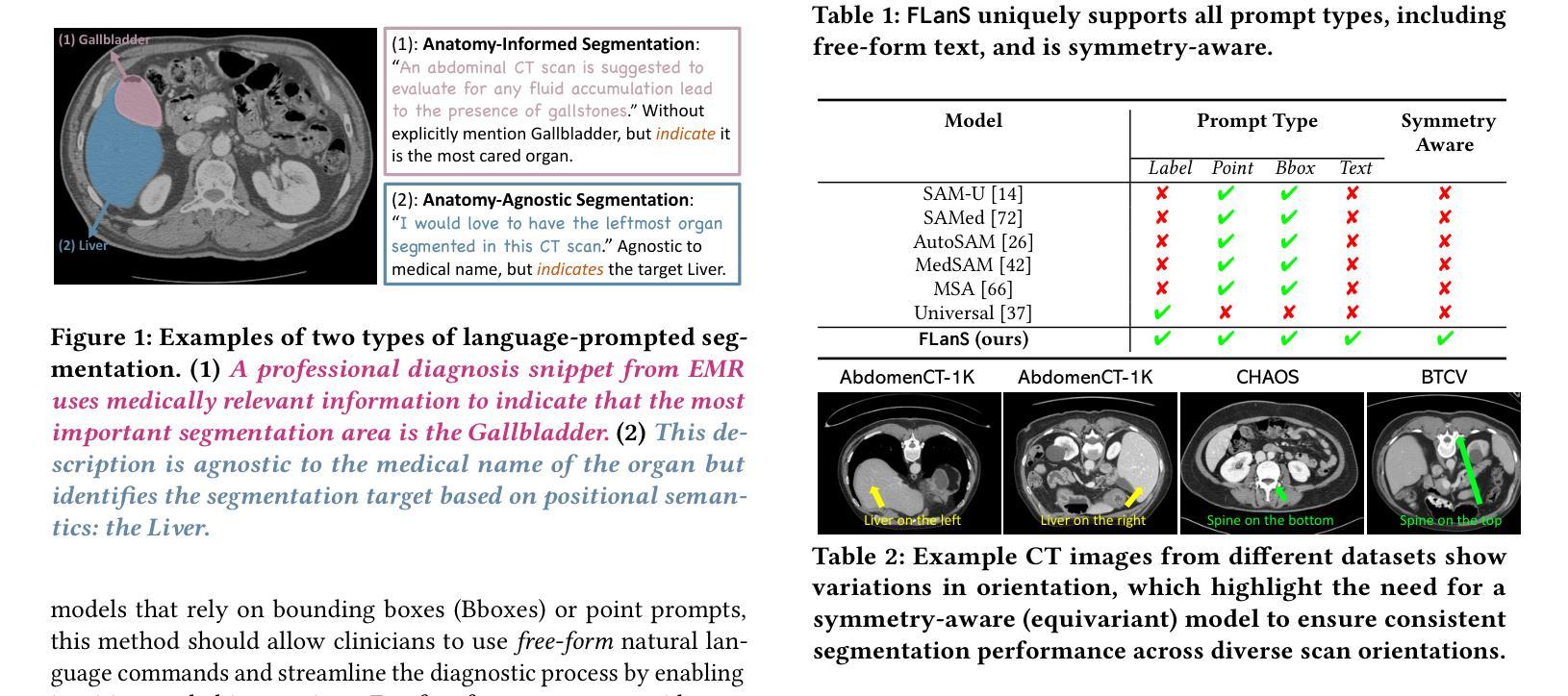
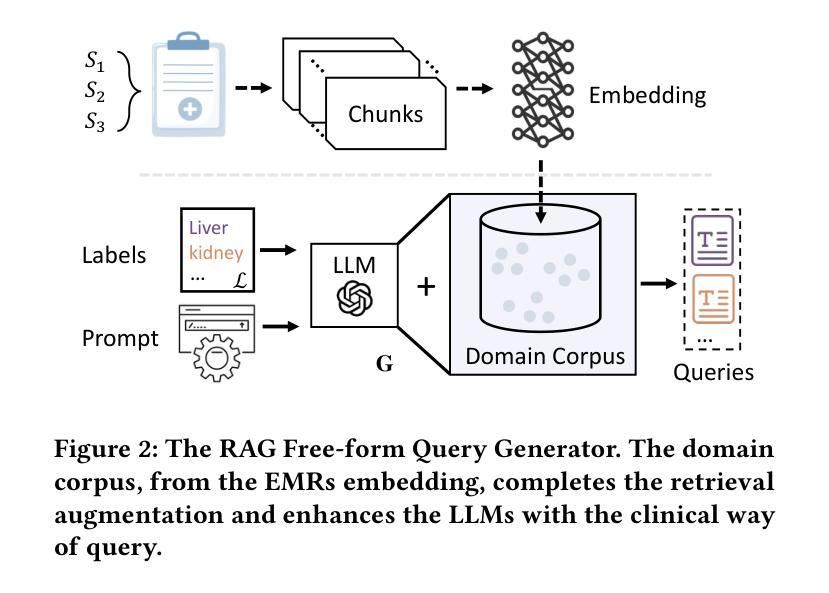
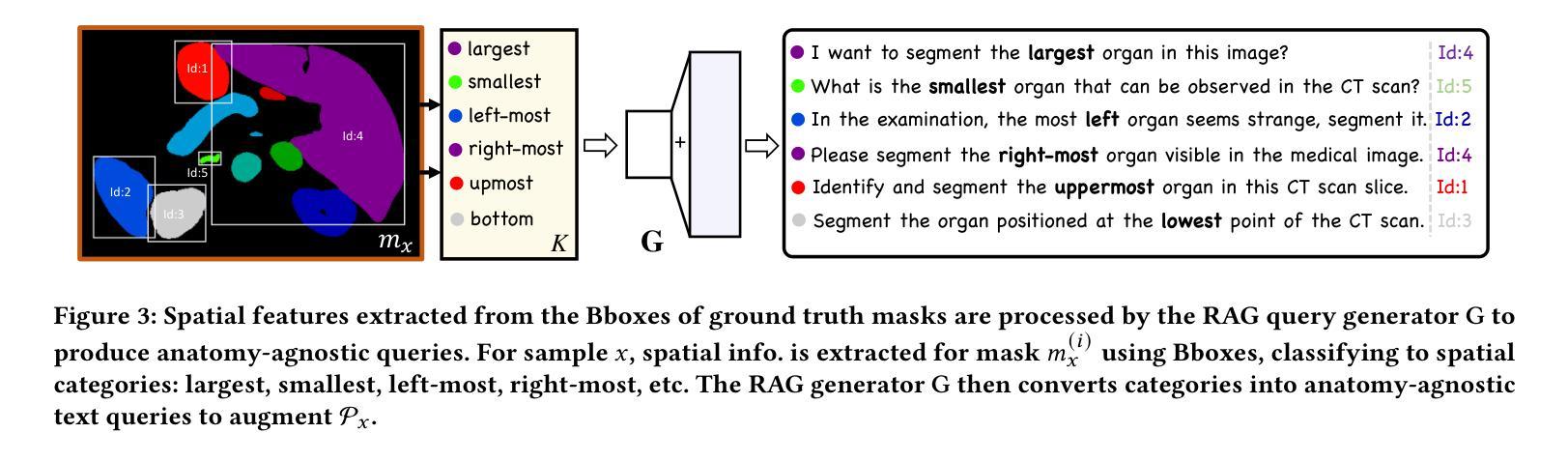
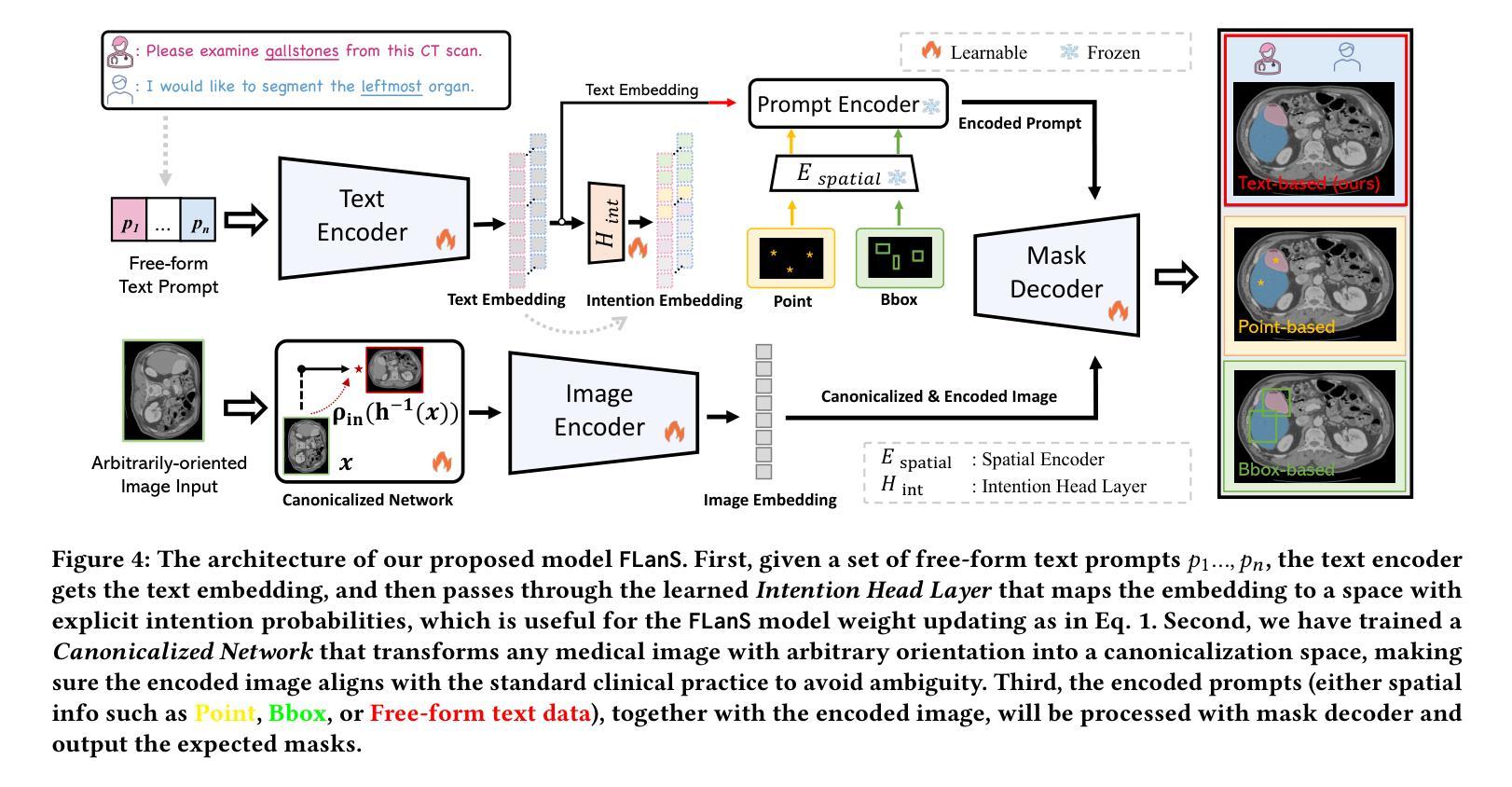
Segment as You Wish – Free-Form Language-Based Segmentation for Medical Images
Authors:Longchao Da, Rui Wang, Xiaojian Xu, Parminder Bhatia, Taha Kass-Hout, Hua Wei, Cao Xiao
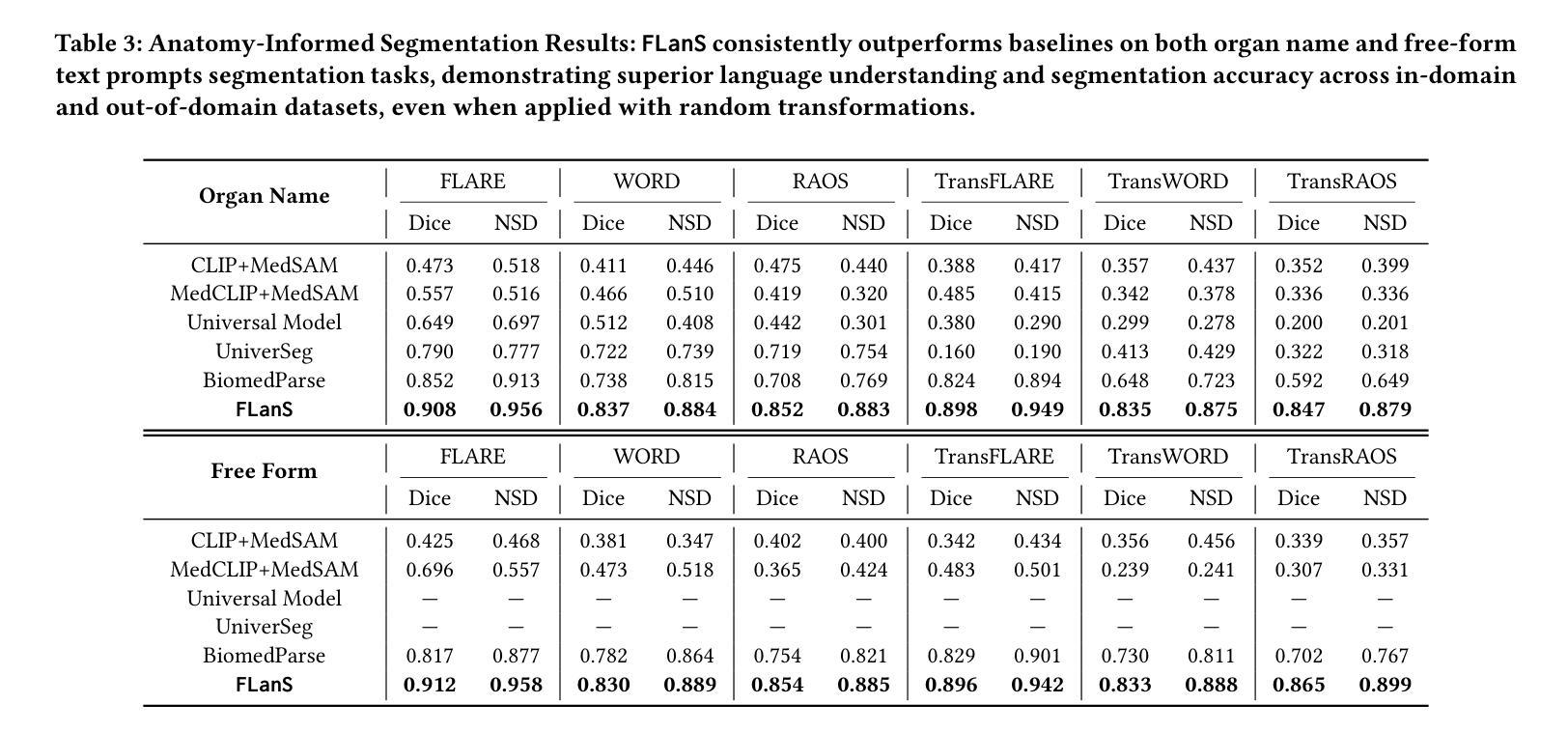
Medical imaging is crucial for diagnosing a patient’s health condition, and accurate segmentation of these images is essential for isolating regions of interest to ensure precise diagnosis and treatment planning. Existing methods primarily rely on bounding boxes or point-based prompts, while few have explored text-related prompts, despite clinicians often describing their observations and instructions in natural language. To address this gap, we first propose a RAG-based free-form text prompt generator, that leverages the domain corpus to generate diverse and realistic descriptions. Then, we introduce FLanS, a novel medical image segmentation model that handles various free-form text prompts, including professional anatomy-informed queries, anatomy-agnostic position-driven queries, and anatomy-agnostic size-driven queries. Additionally, our model also incorporates a symmetry-aware canonicalization module to ensure consistent, accurate segmentations across varying scan orientations and reduce confusion between the anatomical position of an organ and its appearance in the scan. FLanS is trained on a large-scale dataset of over 100k medical images from 7 public datasets. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate the model’s superior language understanding and segmentation precision, along with a deep comprehension of the relationship between them, outperforming SOTA baselines on both in-domain and out-of-domain datasets.
医学成像对于诊断患者的健康状况至关重要,而准确地对这些图像进行分割,对于隔离感兴趣区域以确保精确诊断和治疗计划制定至关重要。现有方法主要依赖于边界框或基于点的提示,尽管临床医生经常使用自然语言描述他们的观察和指示,但很少有方法探索文本相关的提示。为了弥补这一空白,我们首先提出了一种基于RAG的自由形式文本提示生成器,它利用领域语料库生成多样且现实的描述。然后,我们引入了FLanS,这是一种新的医学图像分割模型,能够处理各种自由形式的文本提示,包括专业解剖信息查询、解剖无关的位置驱动查询和解剖无关的大小驱动查询。此外,我们的模型还融入了一个对称感知规范化模块,以确保在不同扫描方向下实现一致、准确的分割,并减少器官解剖位置与其在扫描中出现的混淆。FLanS是在来自7个公共数据集的超过10万张医学图像的大规模数据集上进行训练的。综合实验证明了该模型出色的语言理解和分割精度,以及对两者关系的深入理解,在域内和域外数据集上都超越了最新技术基线。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 9 as main content. The paper was accepted to KDD2025
Summary
医学图像分割对于诊断患者健康状况至关重要。为实现更精确的分割,研究者提出了一种基于RAG的自由形式文本提示生成器,并结合FLanS新型医学图像分割模型,可处理多种自由形式文本提示,包括专业解剖学信息查询、非解剖学位置驱动查询和非解剖学尺寸驱动查询。该模型还配备了一个对称感知规范化模块,以确保在不同扫描方向上获得一致且精确的分割,并减少器官解剖位置与其在扫描中出现的混淆。FLanS在超过10万张医学图像的大规模数据集上进行训练,实验证明其在语言理解和分割精度方面的优越性,以及对两者关系的深刻理解,在域内和域外数据集上均优于现有技术基线。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割对于精确诊断患者健康状况至关重要。
- 现有方法主要依赖边界框或点基提示,较少探索文本相关提示。
- 研究者提出了一种基于RAG的自由形式文本提示生成器,以生成多样且现实的描述。
- 引入的FLanS模型能够处理各种自由形式文本提示,包括专业解剖学信息查询等。
- FLanS模型配备对称感知规范化模块,以确保一致的分割精度并减少解剖位置混淆。
- 模型在大规模数据集上进行训练,实验证明其语言理解和分割精度方面的优越性。
点此查看论文截图