⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-08 更新
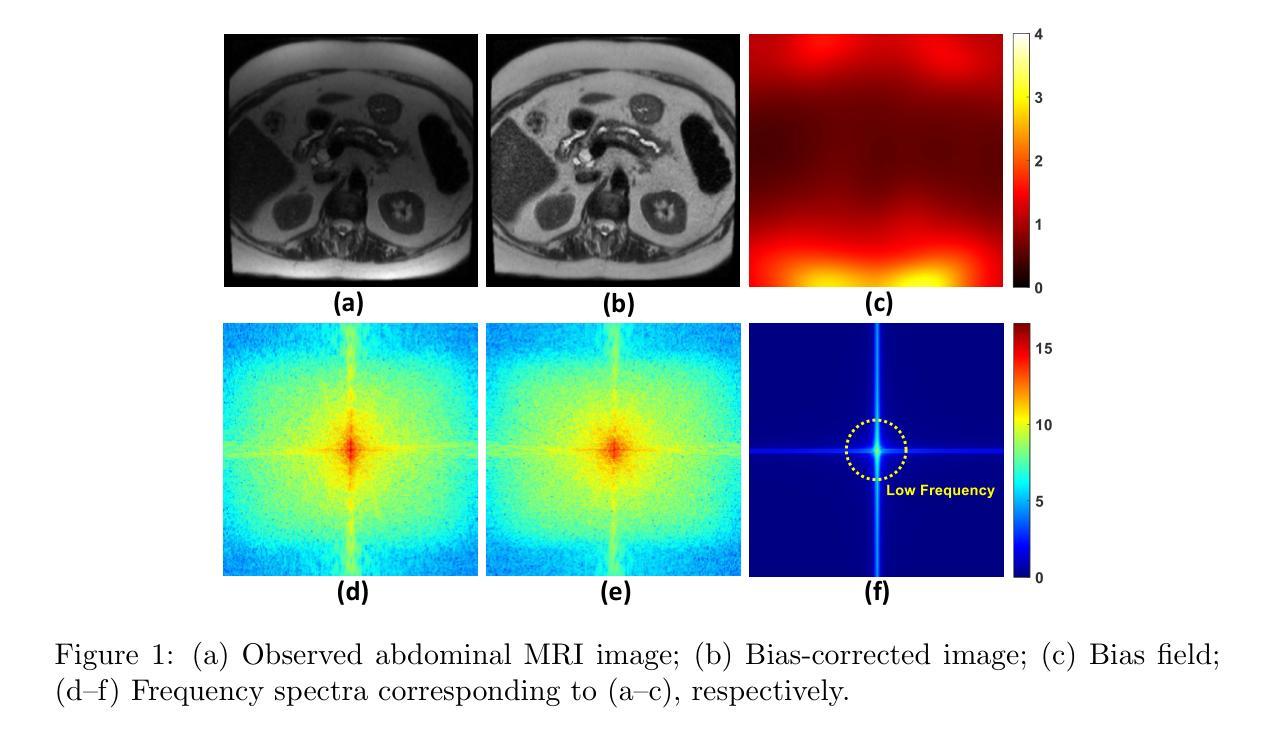
VHU-Net: Variational Hadamard U-Net for Body MRI Bias Field Correction
Authors:Xin Zhu, Ahmet Enis Cetin, Gorkem Durak, Batuhan Gundogdu, Ziliang Hong, Hongyi Pan, Ertugrul Aktas, Elif Keles, Hatice Savas, Aytekin Oto, Hiten Patel, Adam B. Murphy, Ashley Ross, Frank Miller, Baris Turkbey, Ulas Bagci
Bias field artifacts in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans introduce spatially smooth intensity inhomogeneities that degrade image quality and hinder downstream analysis. To address this challenge, we propose a novel variational Hadamard U-Net (VHU-Net) for effective body MRI bias field correction. The encoder comprises multiple convolutional Hadamard transform blocks (ConvHTBlocks), each integrating convolutional layers with a Hadamard transform (HT) layer. Specifically, the HT layer performs channel-wise frequency decomposition to isolate low-frequency components, while a subsequent scaling layer and semi-soft thresholding mechanism suppress redundant high-frequency noise. To compensate for the HT layer’s inability to model inter-channel dependencies, the decoder incorporates an inverse HT-reconstructed transformer block, enabling global, frequency-aware attention for the recovery of spatially consistent bias fields. The stacked decoder ConvHTBlocks further enhance the capacity to reconstruct the underlying ground-truth bias field. Building on the principles of variational inference, we formulate a new evidence lower bound (ELBO) as the training objective, promoting sparsity in the latent space while ensuring accurate bias field estimation. Comprehensive experiments on abdominal and prostate MRI datasets demonstrate the superiority of VHU-Net over existing state-of-the-art methods in terms of intensity uniformity, signal fidelity, and tissue contrast. Moreover, the corrected images yield substantial downstream improvements in segmentation accuracy. Our framework offers computational efficiency, interpretability, and robust performance across multi-center datasets, making it suitable for clinical deployment.
磁共振成像(MRI)扫描中的偏置场伪影引入了空间平滑强度不均匀性,降低了图像质量,阻碍了下游分析。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一种新型的变分哈达玛U形网络(VHU-Net),用于有效的体MRI偏置场校正。编码器由多个卷积哈达玛变换块(ConvHTBlocks)组成,每个块都结合了卷积层和哈达玛变换(HT)层。具体来说,HT层执行通道频率分解,以隔离低频分量,而随后的缩放层和半软阈值机制抑制冗余的高频噪声。为了弥补HT层无法建模通道间依赖性的不足,解码器采用了一个逆HT重建的变换块,能够实现全局频率感知注意力以恢复空间一致的偏置场。堆叠的解码器ConvHT块进一步增强了重建潜在真实偏置场的能力。基于变分推理的原理,我们将新的证据下限(ELBO)作为训练目标,以促进潜在空间的稀疏性,同时确保准确的偏置场估计。在腹部和前列腺MRI数据集上的综合实验表明,VHU-Net在强度均匀性、信号保真度和组织对比度方面优于现有最先进的方法。此外,校正后的图像在分割精度上产生了显著的下游改进。我们的框架具有计算效率高、可解释性强、多中心数据集性能稳健等优点,适合临床部署。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对磁共振成像(MRI)扫描中的偏置场伪影问题,提出一种新型的变分Hadamard U-Net(VHU-Net)进行有效的体MRI偏置场校正。该网络通过结合卷积层和Hadamard变换层,实现了对低频频谱的分解以及对冗余高频噪声的抑制。利用逆HT重建的解码器块实现全局频率感知注意力,恢复空间一致的偏置场。通过变分推断原理制定新的证据下限(ELBO)作为训练目标,在潜在空间中促进稀疏性并确保准确的偏置场估计。在腹部和前列腺MRI数据集上的实验表明,VHU-Net在强度均匀性、信号保真度和组织对比度方面优于现有先进技术。校正后的图像在分割精度上有显著提高,且该框架具有计算效率高、可解释性强和多中心数据集表现稳健等优点,适合临床部署。
Key Takeaways
- 磁共振成像(MRI)中的偏置场伪影会引入空间平滑强度不均匀性,影响图像质量和后续分析。
- 提出一种新型的变分Hadamard U-Net(VHU-Net)进行MRI偏置场校正。
- VHU-Net结合卷积层和Hadamard变换层,有效分解低频频谱并抑制冗余高频噪声。
- 逆HT重建的解码器块实现全局频率感知注意力,有助于恢复空间一致的偏置场。
- 通过变分推断原理制定新的证据下限(ELBO)作为训练目标,确保准确估计偏置场。
- 在腹部和前列腺MRI数据集上的实验表明,VHU-Net在多个评估指标上优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

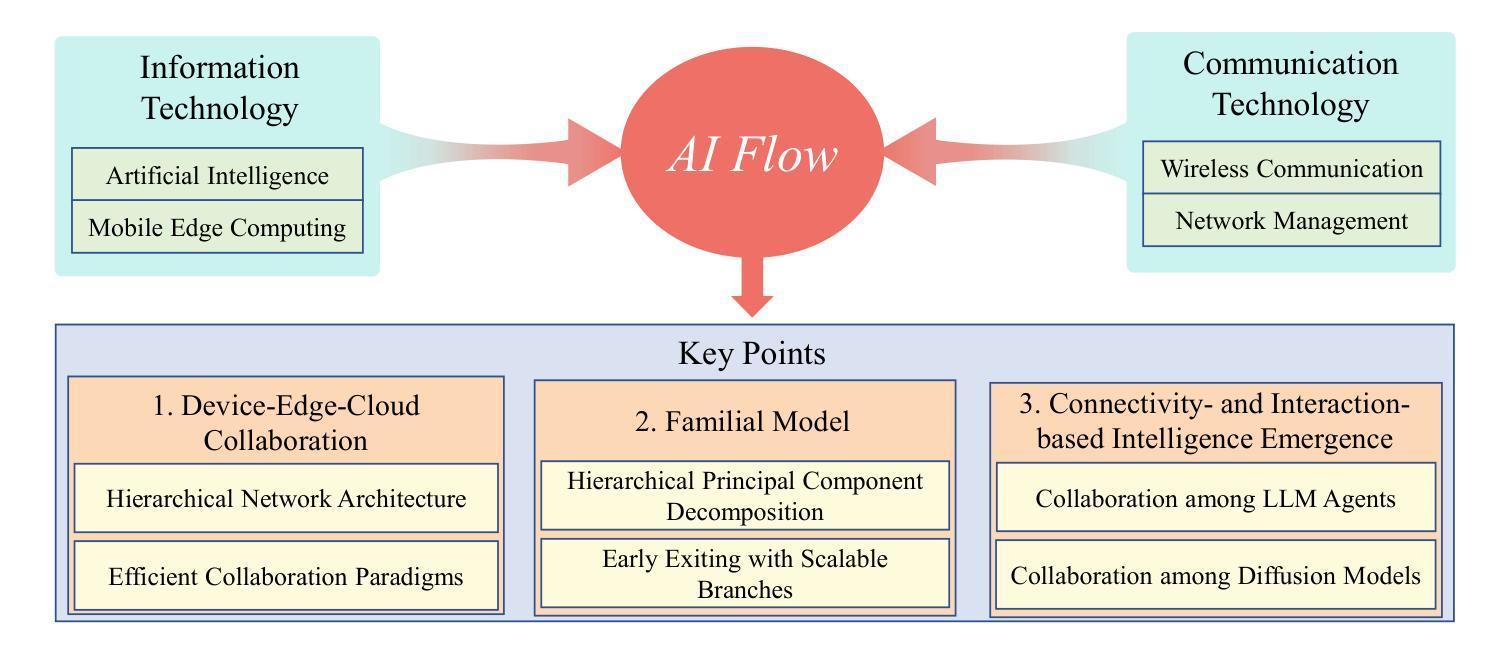
AI Flow: Perspectives, Scenarios, and Approaches
Authors:Hongjun An, Wenhan Hu, Sida Huang, Siqi Huang, Ruanjun Li, Yuanzhi Liang, Jiawei Shao, Yiliang Song, Zihan Wang, Cheng Yuan, Chi Zhang, Hongyuan Zhang, Wenhao Zhuang, Xuelong Li
Pioneered by the foundational information theory by Claude Shannon and the visionary framework of machine intelligence by Alan Turing, the convergent evolution of information and communication technologies (IT/CT) has created an unbroken wave of connectivity and computation. This synergy has sparked a technological revolution, now reaching its peak with large artificial intelligence (AI) models that are reshaping industries and redefining human-machine collaboration. However, the realization of ubiquitous intelligence faces considerable challenges due to substantial resource consumption in large models and high communication bandwidth demands. To address these challenges, AI Flow has been introduced as a multidisciplinary framework that integrates cutting-edge IT and CT advancements, with a particular emphasis on the following three key points. First, device-edge-cloud framework serves as the foundation, which integrates end devices, edge servers, and cloud clusters to optimize scalability and efficiency for low-latency model inference. Second, we introduce the concept of familial models, which refers to a series of different-sized models with aligned hidden features, enabling effective collaboration and the flexibility to adapt to varying resource constraints and dynamic scenarios. Third, connectivity- and interaction-based intelligence emergence is a novel paradigm of AI Flow. By leveraging communication networks to enhance connectivity, the collaboration among AI models across heterogeneous nodes achieves emergent intelligence that surpasses the capability of any single model. The innovations of AI Flow provide enhanced intelligence, timely responsiveness, and ubiquitous accessibility to AI services, paving the way for the tighter fusion of AI techniques and communication systems.
在信息理论先驱克劳德·香农和人工智能先驱艾伦·图灵开创性理论框架下,信息和通信技术的融合(IT/CT)不断演化,推动了连接和计算的不间断浪潮。这种协同作用引发了一场技术革命,现在随着大型人工智能模型的崛起达到顶峰,正在重塑产业并重新定义人机协作。然而,实现无处不在的智能面临着巨大的挑战,因为大型模型需要大量的资源消耗和高通信带宽需求。为了解决这些挑战,引入了AI Flow这一跨学科框架,整合了前沿的IT和CT技术,特别是以下三个关键点。首先,设备边缘云框架是核心基础,它将终端设备、边缘服务器和云集群整合在一起,优化可扩展性,提高低延迟模型推理的效率。其次,我们引入了家族模型的概念,这是指具有对齐隐藏特征的一系列不同大小的模型,能够实现有效的协作和适应不同的资源约束和动态场景。第三,基于连接和交互的智能涌现是AI Flow的新范式。通过利用通信网络增强连接性,不同节点上的人工智能模型之间的协作实现了涌现智能,超越了任何单一模型的能力。AI Flow的创新提供了增强的智能、及时响应和无处不在的人工智能服务访问能力,为人工智能技术和通信系统之间的紧密融合铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Authors are with Institute of Artificial Intelligence (TeleAI), China Telecom, China. Author names are listed alphabetically by surname. This work was conducted at TeleAI, facilitated by Dr. Jiawei Shao (e-mail: shaojw2@chinatelecom.cn) under the leadership of Prof. Xuelong Li. The corresponding author is Prof. Xuelong Li (e-mail: xuelong li@ieee.org), the CTO and Chief Scientist of China Telecom
Summary
信息论创始人克劳德·香农与人工智能先驱艾伦·图灵开创性的理论为信息与通信技术(IT/CT)的融合演变奠定了基础。这一协同进化创造了连接和计算的持续浪潮,引发了一场技术革命。如今,大型人工智能模型正重塑产业并重新定义人机协作。然而,实现普遍智能面临着巨大的挑战,如大型模型的高资源消耗和通信带宽的高需求。为解决这些挑战,AI Flow作为一个跨学科框架应运而生,集成了最前沿的IT和CT技术,重点包括:设备边缘云框架、家族模型的概念以及基于连接和交互的智力涌现新模式。这些创新为增强智能、及时响应和无处不在的AI服务访问提供了条件,为人工智能技术和通信系统的紧密融合铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways
- 信息与通信技术融合演变基于香农的信息论和图灵的人工智能框架。
- 大型人工智能模型正重塑产业并重新定义人机协作,但实现普遍智能面临挑战。
- AI Flow框架集成IT和CT技术,以应对资源消耗和通信带宽的挑战。
- 设备边缘云框架是AI Flow的基础,整合终端、边缘服务器和云集群,优化可扩展性和效率。
- 家族模型概念包含不同大小的模型,具有对齐的隐藏特征,适应资源约束和动态场景。
- 基于连接和交互的智力涌现是AI Flow的新型模式,通过通信网络增强连接,实现模型间协作涌现智能。
点此查看论文截图


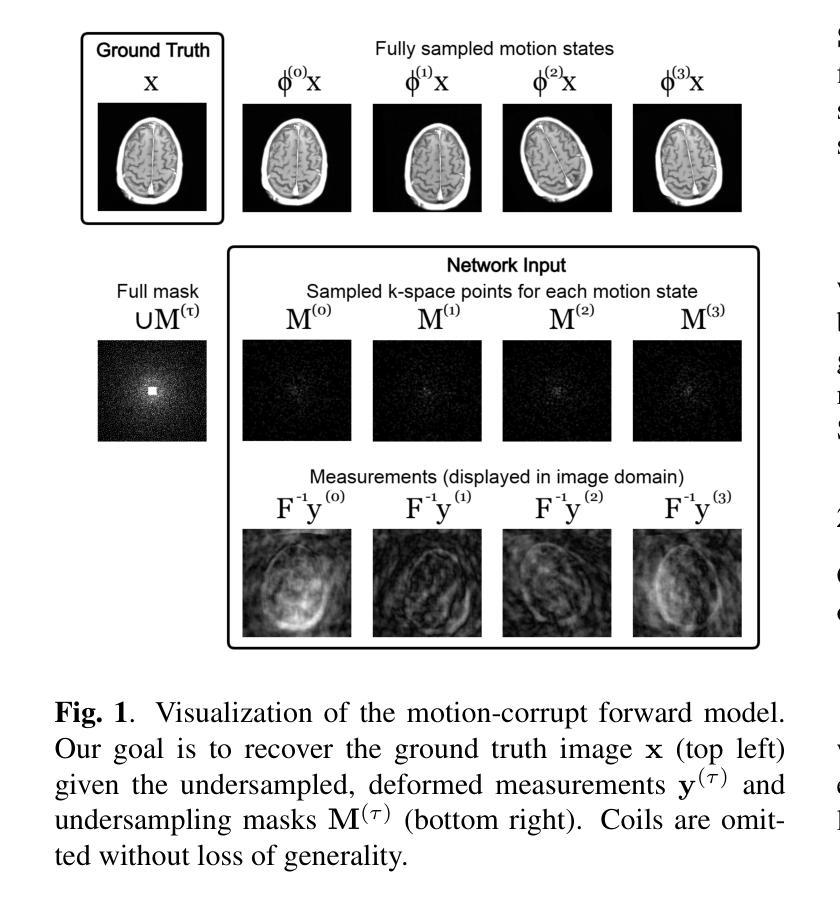
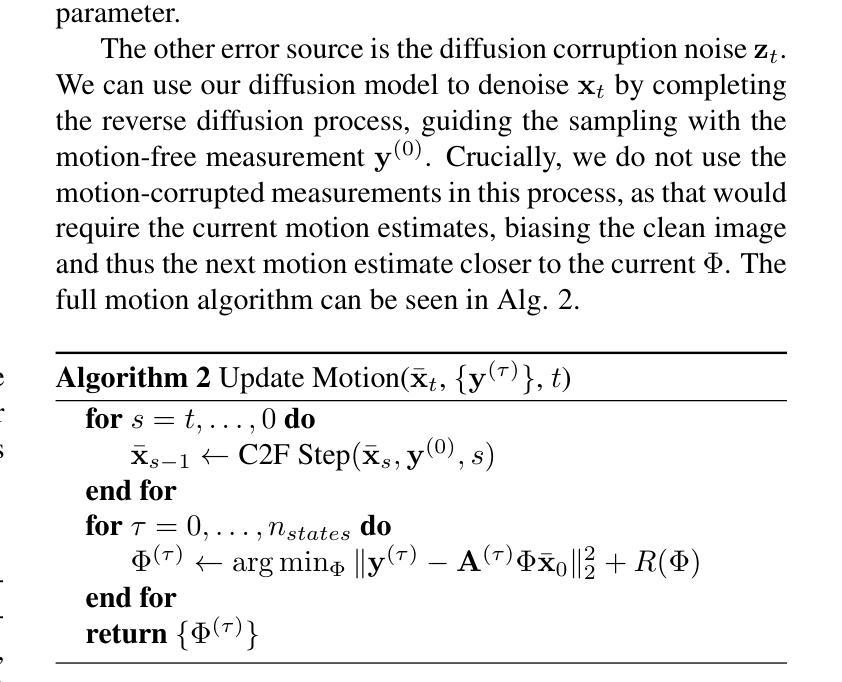
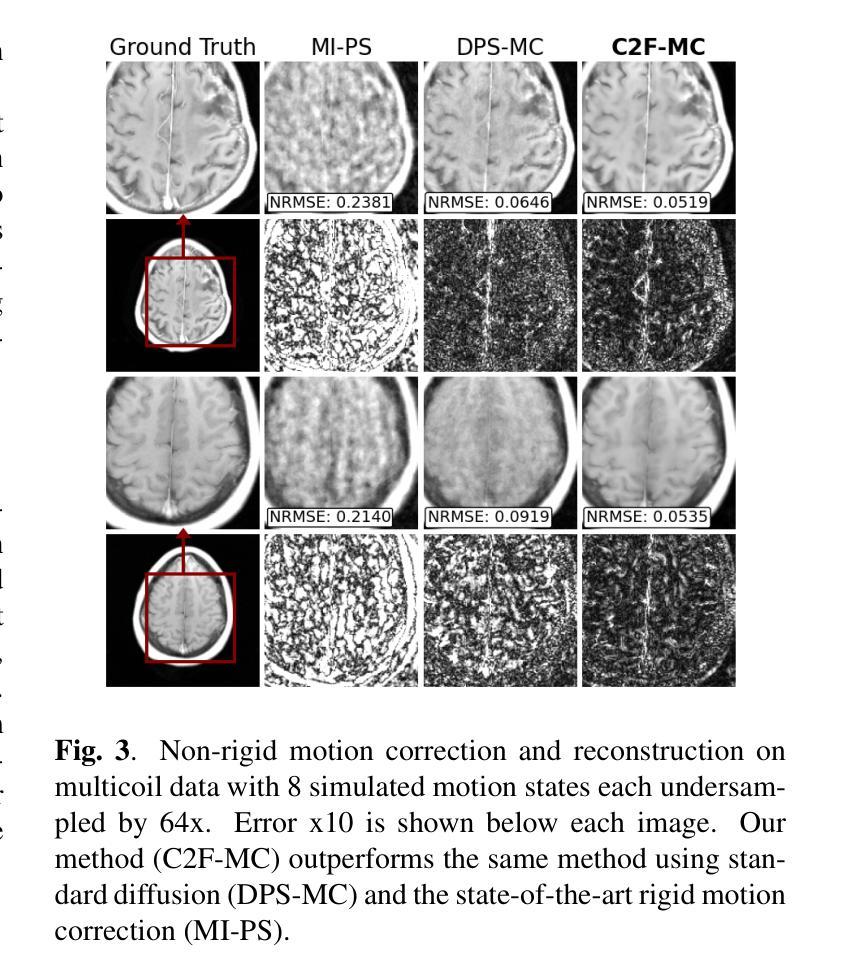
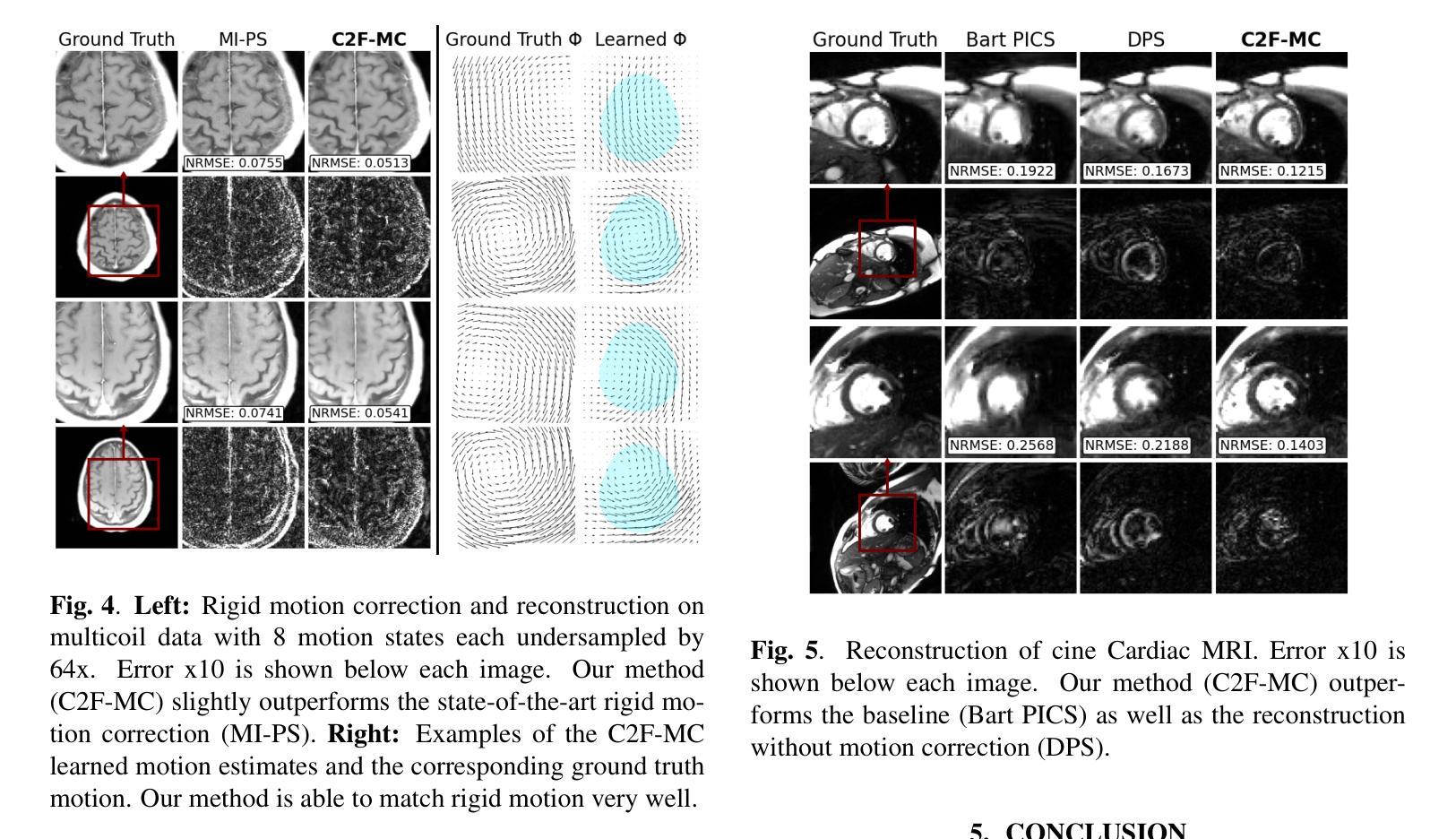
Non-rigid Motion Correction for MRI Reconstruction via Coarse-To-Fine Diffusion Models
Authors:Frederic Wang, Jonathan I. Tamir
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is highly susceptible to motion artifacts due to the extended acquisition times required for k-space sampling. These artifacts can compromise diagnostic utility, particularly for dynamic imaging. We propose a novel alternating minimization framework that leverages a bespoke diffusion model to jointly reconstruct and correct non-rigid motion-corrupted k-space data. The diffusion model uses a coarse-to-fine denoising strategy to capture large overall motion and reconstruct the lower frequencies of the image first, providing a better inductive bias for motion estimation than that of standard diffusion models. We demonstrate the performance of our approach on both real-world cine cardiac MRI datasets and complex simulated rigid and non-rigid deformations, even when each motion state is undersampled by a factor of 64x. Additionally, our method is agnostic to sampling patterns, anatomical variations, and MRI scanning protocols, as long as some low frequency components are sampled during each motion state.
磁共振成像(MRI)由于k空间采样所需的长时间采集而易受到运动伪影的影响。这些伪影可能损害诊断的效用,特别是在动态成像中。我们提出了一种新型的交替最小化框架,它利用专门的扩散模型来联合重建和纠正非刚性运动受损的k空间数据。该扩散模型采用由粗到细的降噪策略,首先捕获整体大运动并重建图像的低频部分,为运动估计提供了比标准扩散模型更好的归纳偏置。我们在现实世界的电影心脏MRI数据集和复杂的模拟刚性和非刚性变形上展示了我们的方法性能,即使在每种运动状态按64倍欠采样的情况下也是如此。此外,我们的方法对于采样模式、解剖差异和MRI扫描协议持开放性态度,只要在每个运动状态下采样一些低频成分即可。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICIP 2025
Summary
本文提出一种基于交替最小化框架和专用扩散模型的非刚性运动腐蚀k空间数据联合重建和校正方法。该扩散模型采用由粗到细的降噪策略,先捕捉整体大运动并重建图像的低频部分,为运动估计提供更好的归纳偏置。该方法在真实电影心脏MRI数据集和复杂的模拟刚性和非刚性变形上表现出良好的性能,即使在每个运动状态欠采样64倍的情况下也是如此。此方法对于采样模式、解剖变异和MRI扫描协议具有通用性,只要在每个运动状态下采样一些低频成分即可。
Key Takeaways
- MRI对运动伪影高度敏感,由于k空间采样的扩展采集时间,运动伪影会影响诊断效用,特别是在动态成像中。
- 提出了一种新颖的交替最小化框架,结合了专用的扩散模型来联合重建和校正非刚性运动腐蚀的k空间数据。
- 扩散模型采用由粗到细的降噪策略,首先重建图像的低频部分,为运动估计提供更好的基础。
- 方法在真实电影心脏MRI数据集和模拟的刚性和非刚性变形上进行了演示,性能良好。
- 即使在严重的欠采样情况下(每个运动状态欠采样64倍),该方法仍然有效。
- 该方法对采样模式、解剖变异和MRI扫描协议具有通用性。
点此查看论文截图


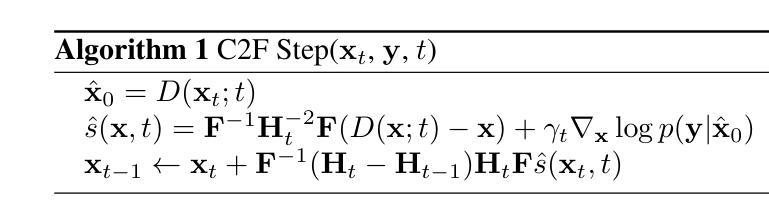
XGeM: A Multi-Prompt Foundation Model for Multimodal Medical Data Generation
Authors:Daniele Molino, Francesco Di Feola, Eliodoro Faiella, Deborah Fazzini, Domiziana Santucci, Linlin Shen, Valerio Guarrasi, Paolo Soda
The adoption of Artificial Intelligence in medical imaging holds great promise, yet it remains hindered by challenges such as data scarcity, privacy concerns, and the need for robust multimodal integration. While recent advances in generative modeling have enabled high-quality synthetic data generation, existing approaches are often limited to unimodal, unidirectional synthesis and therefore lack the ability to jointly synthesize multiple modalities while preserving clinical consistency. To address this challenge, we introduce XGeM, a 6.77-billion-parameter multimodal generative model designed to support flexible, any-to-any synthesis between medical data modalities. XGeM constructs a shared latent space via contrastive learning and introduces a novel Multi-Prompt Training strategy, enabling conditioning on arbitrary subsets of input modalities. This design allows the model to adapt to heterogeneous clinical inputs and generate multiple outputs jointly, preserving both semantic and structural coherence. We extensively validate XGeM: first we benchmark it against five competitors on the MIMIC-CXR dataset, a state-of-the-art dataset for multi-view Chest X-ray and radiological report generation. Secondly, we perform a Visual Turing Test with expert radiologists to assess the realism and clinical relevance of the generated data, ensuring alignment with real-world scenarios. Finally, we show how XGeM can support key medical data challenges such as anonymization, class imbalance, and data scarcity, underscoring its utility as a foundation model for medical data synthesis. Project page is at https://cosbidev.github.io/XGeM/.
将人工智能应用于医学成像领域具有巨大的潜力,但仍面临着数据稀缺、隐私担忧以及需要稳健的多模式集成等挑战。虽然最近生成建模技术的进步已实现了高质量合成数据的生成,但现有方法通常仅限于单模式、单向的合成,因此缺乏同时合成多种模式并保持临床一致性的能力。为了解决这一挑战,我们引入了XGeM,这是一个拥有67.7亿参数的多模式生成模型,旨在支持医学数据模式之间的灵活、任意到任意的合成。XGeM通过对比学习构建了一个共享潜在空间,并引入了一种新颖的多提示训练策略,能够实现以输入模式的任意子集为条件。这种设计使模型能够适应多样化的临床输入,并联合生成多个输出,同时保持语义和结构的一致性。我们对XGeM进行了广泛验证:首先,我们在MIMIC-CXR数据集上与五种竞争对手进行了基准测试,这是一个用于多视图胸部X射线和放射学报告生成的最先进数据集。其次,我们与专家放射科医生进行了一场视觉图灵测试,以评估生成数据的现实主义和临床相关性,确保其与真实世界场景的一致性。最后,我们展示了XGeM如何支持医学数据的关键挑战,如匿名化、类别不平衡和数据稀缺,强调其在医学数据合成基础模型中的实用性。项目页面为:[https://cosbidev.github.io/XGeM/] 。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
人工智能在医学成像领域具有巨大潜力,但仍面临数据稀缺、隐私顾虑和多模态融合等挑战。近期生成建模的进步推动了高质量合成数据的生成,但现有方法大多局限于单模态、单向合成,无法在多模态间进行联合合成并保持临床一致性。为解决此问题,我们推出XGeM,一个6.77亿参数的多模态生成模型,支持医学数据模态间的灵活任意合成。XGeM通过对比学习构建共享潜在空间,并引入全新多提示训练策略,可基于任意输入模态子集进行条件设置。此设计使模型能适应异质临床输入,联合生成多个输出,同时保持语义和结构的一致性。我们全面验证了XGeM的性能:首先在MIMIC-CXR数据集上与五种竞品进行基准测试,该数据集用于多视角胸部X光与放射报告生成,处于业界领先地位;其次,我们进行视觉图灵测试,邀请专家放射医师评估生成数据的真实性和临床相关性,确保与真实场景对齐;最后,我们展示了XGeM如何支持医学数据的关键挑战,如匿名化、类别不平衡和数据稀缺问题,凸显其作为医学数据合成基础模型的实用性。项目页面地址为链接。
Key Takeaways
- 人工智能在医学成像中面临数据稀缺、隐私顾虑和多模态融合的挑战。
- 现有生成建模方法大多局限于单模态数据合成,缺乏多模态间的联合合成能力。
- XGeM是一个多模态生成模型,支持医学数据模态间的任意合成,构建共享潜在空间并引入多提示训练策略。
- XGeM可以在异质临床输入条件下工作,联合生成多个输出并保持临床一致性。
- XGeM在MIMIC-CXR数据集上进行了基准测试,并与多种竞品对比表现出优势。
- 通过视觉图灵测试,XGeM生成的数据具有真实性和临床相关性。
- XGeM有助于解决医学数据的关键挑战,如匿名化、类别不平衡和数据稀缺问题。
点此查看论文截图

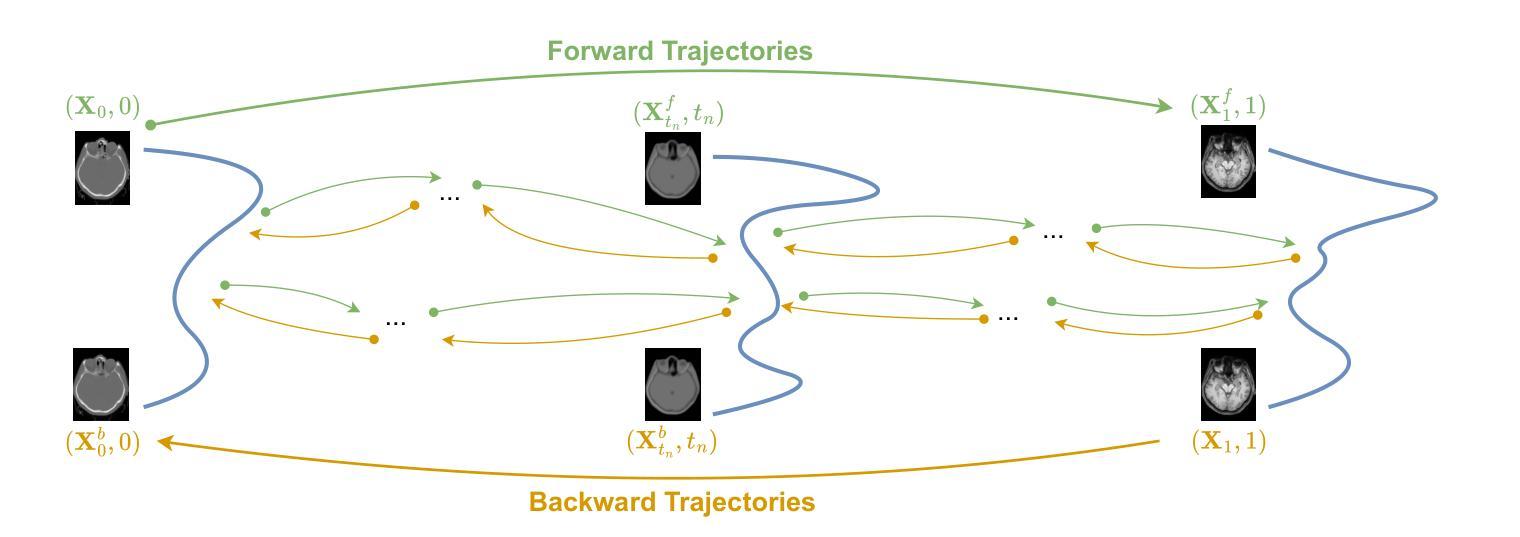
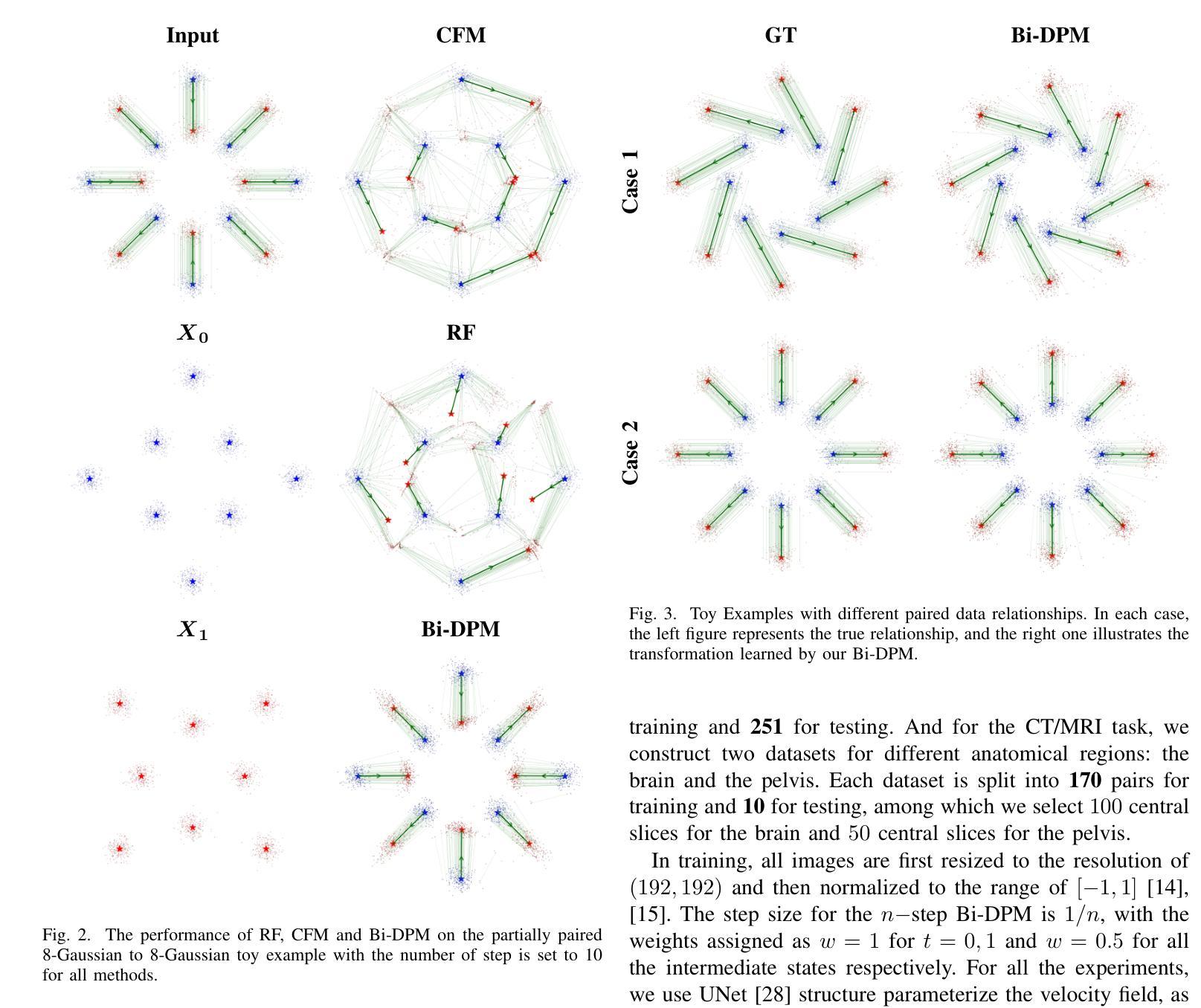
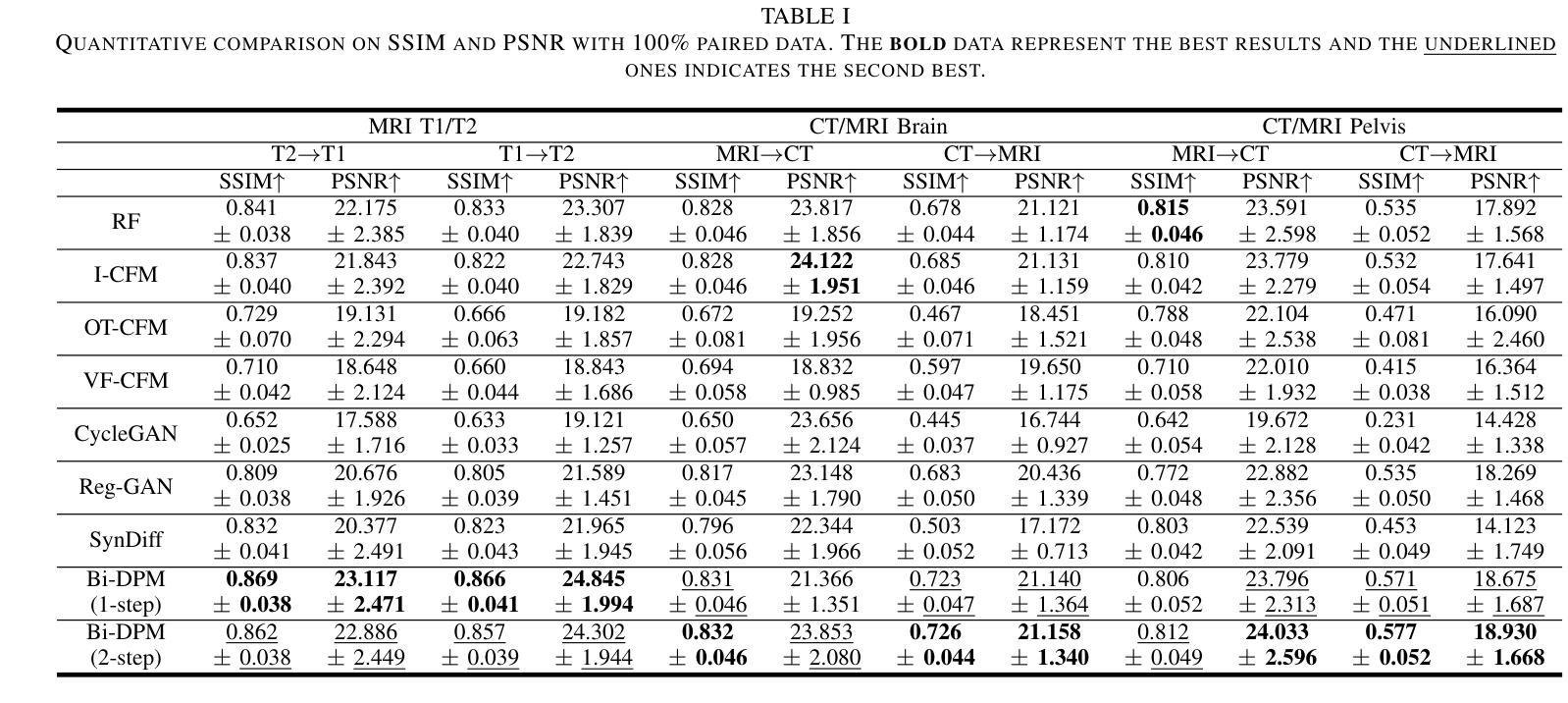
Bi-modality medical images synthesis by a bi-directional discrete process matching method
Authors:Zhe Xiong, Qiaoqiao Ding, Xiaoqun Zhang
Recently, medical image synthesis gains more and more popularity, along with the rapid development of generative models. Medical image synthesis aims to generate an unacquired image modality, often from other observed data modalities. Synthesized images can be used for clinical diagnostic assistance, data augmentation for model training and validation or image quality improving. In the meanwhile, the flow-based models are among the successful generative models for the ability of generating realistic and high-quality synthetic images. However, most flow-based models require to calculate flow ordinary different equation (ODE) evolution steps in synthesis process, for which the performances are significantly limited by heavy computation time due to a large number of time iterations. In this paper, we propose a novel flow-based model, namely bi-directional Discrete Process Matching (Bi-DPM) to accomplish the bi-modality image synthesis tasks. Different to other flow matching based models, we propose to utilize both forward and backward ODE flows and enhance the consistency on the intermediate images over a few discrete time steps, resulting in a synthesis process maintaining high-quality generations for both modalities under the guidance of paired data. Our experiments on three datasets of MRI T1/T2 and CT/MRI demonstrate that Bi-DPM outperforms other state-of-the-art flow-based methods for bi-modality image synthesis, delivering higher image quality with accurate anatomical regions.
随着生成模型的快速发展,医学图像合成越来越受到欢迎。医学图像合成的目标是从其他已观察到的数据模态生成未获得的图像模态。合成的图像可用于临床诊断辅助、模型训练和验证的数据增强或图像质量改进。与此同时,基于流的模型是生成现实和高质量合成图像的成功的生成模型之一。然而,大多数基于流的模型需要在合成过程中计算流普通微分方程(ODE)的演化步骤,由于大量时间迭代,其性能受到计算时间长的限制。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型的基于流的模型,即双向离散过程匹配(Bi-DPM),以完成双向图像合成任务。与其他基于流匹配的模型不同,我们提出利用正向和反向ODE流,并增强几个离散时间步骤中中间图像的一致性,从而在保证配对数据引导的情况下,使两种模态的合成过程保持高质量生成。我们在MRI T1/T2和CT/MRI的三个数据集上的实验表明,Bi-DPM在双向图像合成方面优于其他最先进的基于流的方法,能够生成具有准确解剖区域的高质量图像。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种新型双向离散过程匹配(Bi-DPM)流程模型,用于完成双模态图像合成任务。该模型利用正向和反向ODE流,提高中间图像在几个离散时间步骤上的一致性,在配对数据的指导下,保持两种模态的高质量生成。实验表明,Bi-DPM在双模态图像合成上优于其他先进流程模型,提供准确解剖区域的更高质量图像。
Key Takeaways
- 医疗图像合成随着生成模型的快速发展而越来越受欢迎。
- 医疗图像合成的目标是从其他观察到的数据模态生成未获得的图像模态。
- 合成图像可用于临床诊断辅助、模型训练和验证的数据增强以及图像质量改进。
- 流模型在生成真实高质量的合成图像方面表现出成功。
- 大多数流程模型需要在合成过程中计算流常微分方程(ODE)进化步骤,但由于大量时间迭代,性能受到计算时间长的限制。
- 本文提出了一种新型双向离散过程匹配(Bi-DPM)流程模型,该模型利用正向和反向ODE流,提高中间图像一致性,并在配对数据的指导下保持高质量生成。
点此查看论文截图

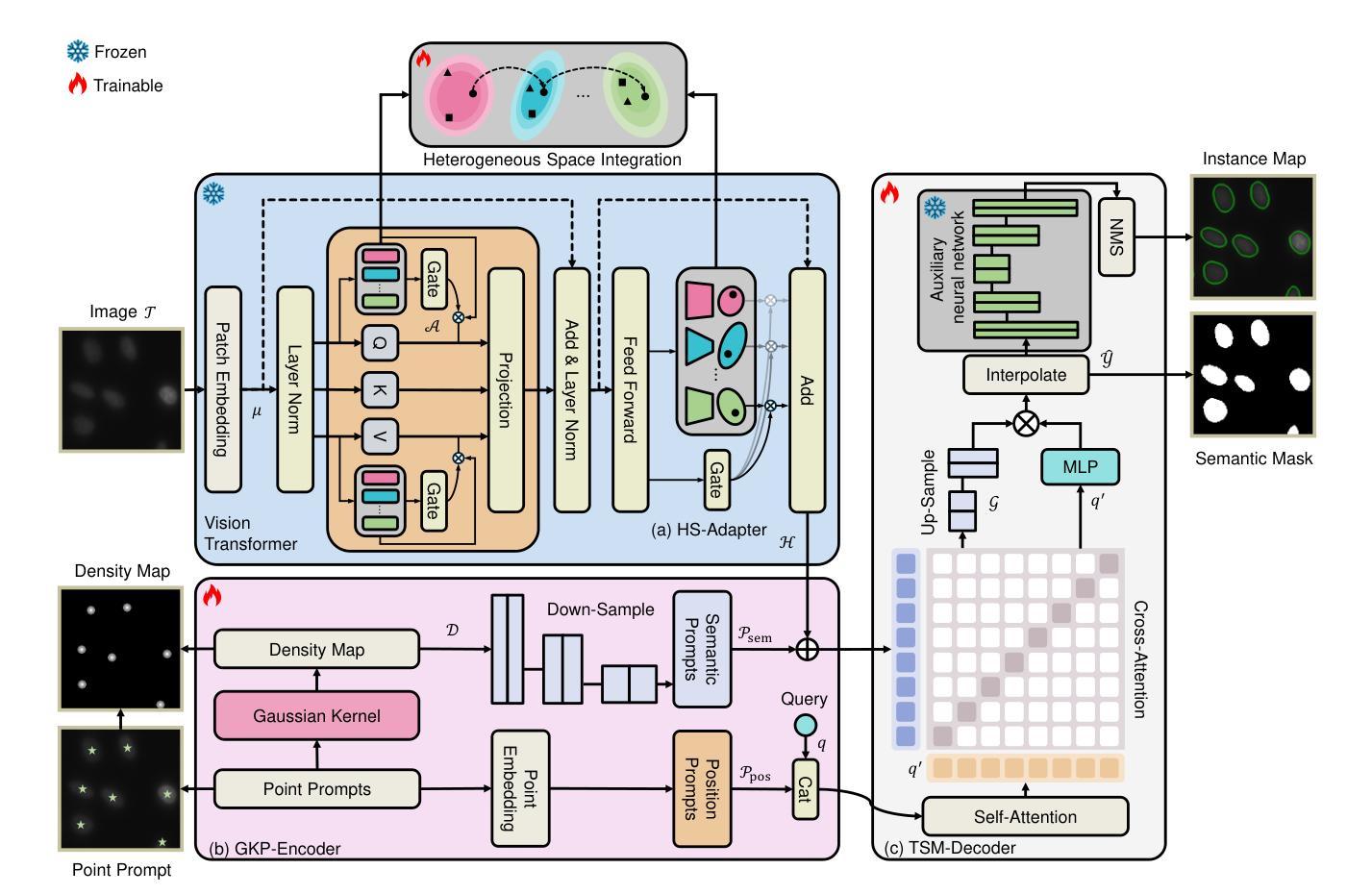
NuSegDG: Integration of Heterogeneous Space and Gaussian Kernel for Domain-Generalized Nuclei Segmentation
Authors:Zhenye Lou, Qing Xu, Zekun Jiang, Xiangjian He, Zhen Chen, Yi Wang, Chenxin Li, Maggie M. He, Wenting Duan
Domain-generalized nuclei segmentation refers to the generalizability of models to unseen domains based on knowledge learned from source domains and is challenged by various image conditions, cell types, and stain strategies. Recently, the Segment Anything Model (SAM) has made great success in universal image segmentation by interactive prompt modes (e.g., point and box). Despite its strengths, the original SAM presents limited adaptation to medical images. Moreover, SAM requires providing manual bounding box prompts for each object to produce satisfactory segmentation masks, so it is laborious in nuclei segmentation scenarios. To address these limitations, we propose a domain-generalizable framework for nuclei image segmentation, abbreviated to NuSegDG. Specifically, we first devise a Heterogeneous Space Adapter (HS-Adapter) to learn multi-dimensional feature representations of different nuclei domains by injecting a small number of trainable parameters into the image encoder of SAM. To alleviate the labor-intensive requirement of manual prompts, we introduce a Gaussian-Kernel Prompt Encoder (GKP-Encoder) to generate density maps driven by a single point, which guides segmentation predictions by mixing position prompts and semantic prompts. Furthermore, we present a Two-Stage Mask Decoder (TSM-Decoder) to effectively convert semantic masks to instance maps without the manual demand for morphological shape refinement. Based on our experimental evaluations, the proposed NuSegDG demonstrates state-of-the-art performance in nuclei instance segmentation, exhibiting superior domain generalization capabilities. The source code is available at https://github.com/xq141839/NuSegDG.
领域泛化核分割(Domain-Generalized Nuclei Segmentation)指的是模型在未见领域中的泛化能力,基于从源领域学到的知识,它面临着各种图像条件、细胞类型和染色策略的挑战。最近,通过交互式提示模式(如点和框),Segment Anything Model(SAM)在通用图像分割方面取得了巨大成功。尽管其强大,但原始SAM对医学图像的适应性有限。此外,SAM需要为每个对象提供手动边界框提示以产生令人满意的分割掩码,因此在细胞核分割场景中很繁琐。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一个用于细胞核图像分割的领域泛化框架,简称为NuSegDG。具体来说,我们首先设计了一个Heterogeneous Space Adapter(HS-Adapter),通过向SAM的图像编码器注入少量可训练参数,学习不同核领域的多维特征表示。为了减轻繁琐的手动提示要求,我们引入了Gaussian-Kernel Prompt Encoder(GKP-Encoder)来生成由单点驱动的概率密度图,通过混合位置提示和语义提示来指导分割预测。此外,我们提出了一种Two-Stage Mask Decoder(TSM-Decoder),能够有效地将语义掩码转换为实例图,无需对形态进行手动细化。我们的实验评估表明,所提出的NuSegDG在细胞核实例分割方面达到了最新性能水平,表现出卓越领域泛化能力。源代码可在https://github.com/xq141839/NuSegDG 获得。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
领域泛化细胞核分割指的是模型在未见领域中的泛化能力,基于从源领域学到的知识。面临各种图像条件、细胞类型和染色策略的挑战。最近,Segment Anything Model(SAM)在通用图像分割中通过交互式提示模式(如点和框)取得了巨大成功。然而,原始SAM在医学图像上的适应性有限。此外,SAM需要为每个对象提供手动边界框提示以产生满意的分割掩膜,因此在细胞核分割场景中很繁琐。针对这些局限性,我们提出了一个用于细胞核图像分割的领域泛化框架,简称为NuSegDG。具体而言,我们设计了一个Heterogeneous Space Adapter(HS-Adapter)来学习不同细胞核领域的多维特征表示,方法是通过在SAM的图像编码器中注入少量可训练参数。为了减轻对手动提示的劳动强度要求,我们引入了Gaussian-Kernel Prompt Encoder(GKP-Encoder)来生成由单点驱动的概率密度图,通过混合位置提示和语义提示来指导分割预测。此外,我们还提出了一个Two-Stage Mask Decoder(TSM-Decoder),可以有效地将语义掩膜转换为实例图,无需进行形态学形状精修的手动需求。我们的实验评估表明,所提出的NuSegDG在细胞核实例分割方面表现出卓越的性能和领域泛化能力。
关键见解
- 领域泛化细胞核分割是医学图像分析的一个重要挑战,涉及模型在不同条件下的适应性。
- Segment Anything Model(SAM)在通用图像分割中取得了成功,但在医学图像中的适应性有限。
- 提出的NuSegDG框架通过引入Heterogeneous Space Adapter(HS-Adapter)增强了模型对细胞核领域的适应性。
- Gaussian-Kernel Prompt Encoder(GKP-Encoder)减轻了手动提示的需求,能够自动生成密度图进行分割预测。
- Two-Stage Mask Decoder(TSM-Decoder)有效将语义掩膜转换为实例图,减少了形态学形状精修的需要。
- NuSegDG框架在细胞核实例分割方面表现出卓越的性能和领域泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

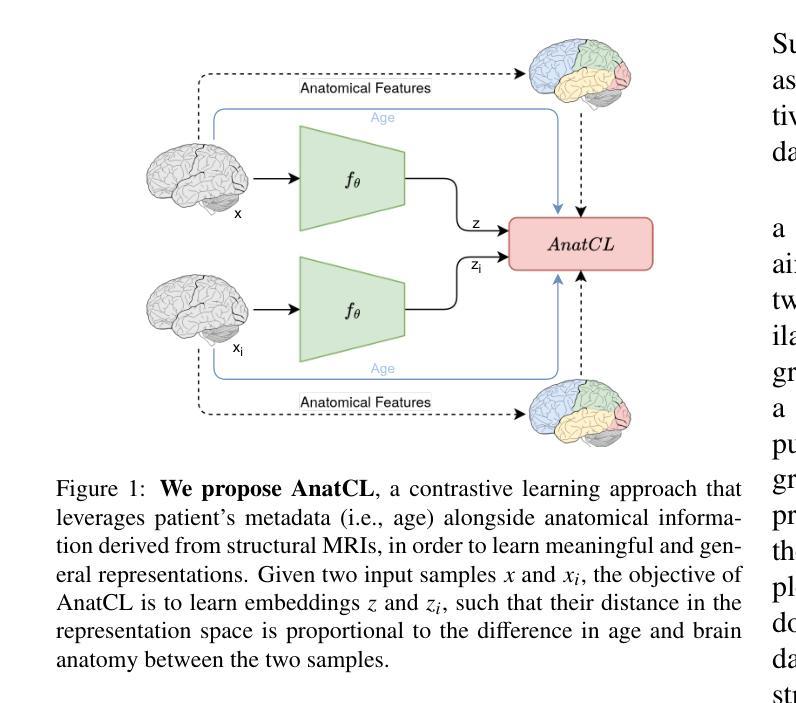
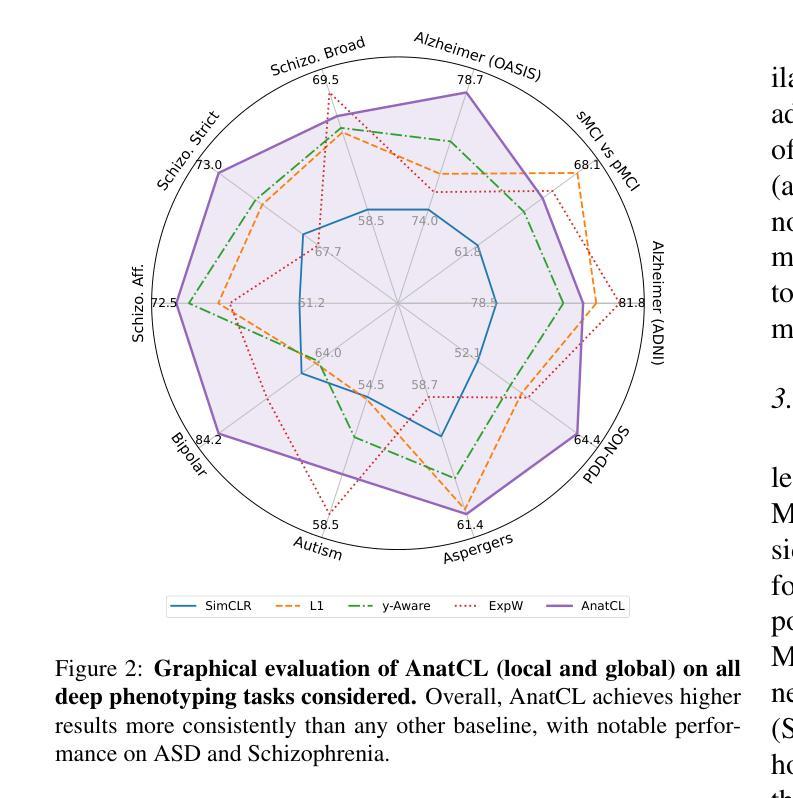
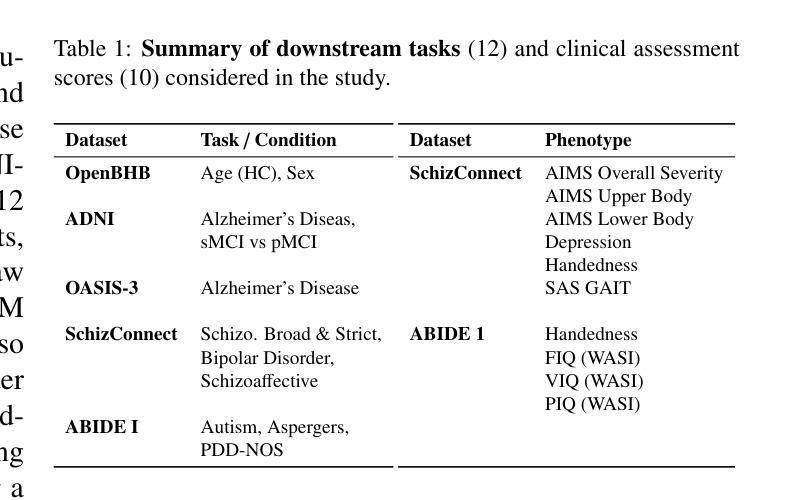
Anatomical Foundation Models for Brain MRIs
Authors:Carlo Alberto Barbano, Matteo Brunello, Benoit Dufumier, Marco Grangetto
Deep Learning (DL) in neuroimaging has become increasingly relevant for detecting neurological conditions and neurodegenerative disorders. One of the most predominant biomarkers in neuroimaging is represented by brain age, which has been shown to be a good indicator for different conditions, such as Alzheimer’s Disease. Using brain age for weakly supervised pre-training of DL models in transfer learning settings has also recently shown promising results, especially when dealing with data scarcity of different conditions. On the other hand, anatomical information of brain MRIs (e.g. cortical thickness) can provide important information for learning good representations that can be transferred to many downstream tasks. In this work, we propose AnatCL, an anatomical foundation model for brain MRIs that i.) leverages anatomical information in a weakly contrastive learning approach, and ii.) achieves state-of-the-art performances across many different downstream tasks. To validate our approach we consider 12 different downstream tasks for the diagnosis of different conditions such as Alzheimer’s Disease, autism spectrum disorder, and schizophrenia. Furthermore, we also target the prediction of 10 different clinical assessment scores using structural MRI data. Our findings show that incorporating anatomical information during pre-training leads to more robust and generalizable representations. Pre-trained models can be found at: https://github.com/EIDOSLAB/AnatCL.
深度学习(DL)在神经成像中对于检测神经系统疾病和神经退行性疾病变得越来越重要。神经成像中最主要的生物标志物之一就是脑年龄,它已被证明是不同疾病(如阿尔茨海默病)的良好指标。在迁移学习环境中,使用脑年龄对深度学习模型进行弱监督预训练也显示出有前途的结果,尤其是在处理不同疾病的稀缺数据时。另一方面,大脑MRI的解剖学信息(例如皮层厚度)可以为学习良好的表示提供重要信息,这些表示可以转移到许多下游任务。在这项工作中,我们提出了AnatCL,这是一个用于大脑MRI的解剖学基础模型,它一)以弱对比学习的方式利用解剖学信息,二)在许多不同的下游任务上实现了最先进的性能。为了验证我们的方法,我们考虑了12个不同的下游任务,用于诊断不同的疾病,如阿尔茨海默病、自闭症谱系障碍和精神分裂症。此外,我们还致力于使用结构MRI数据预测10种不同的临床评估分数。我们的研究结果表明,在预训练过程中融入解剖学信息会导致更稳健和可推广的表示。预训练模型可以在以下网址找到:https://github.com/EIDOSLAB/AnatCL。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Updated version; added ablation study
Summary
深度学习在神经影像中的应用对于检测神经性疾病和神经退行性疾病越来越重要。脑年龄是神经影像中最重要的生物标志物之一,可用于预测多种疾病,如阿尔茨海默症。利用脑年龄对深度学习模型进行弱监督预训练,在数据稀缺的情况下展现出良好的应用前景。另一方面,脑部MRI的结构信息(如皮层厚度)可以为学习良好表示提供重要信息,这些表示可应用于许多下游任务。本工作提出AnatCL模型,通过弱对比学习利用结构信息,并在多种下游任务上达到最新水平。该模型对阿尔茨海默症、自闭症谱系障碍和精神分裂症等疾病的诊断以及基于结构MRI数据的临床评分预测等12项下游任务进行了验证。研究发现,在预训练阶段融入结构信息有助于形成更稳健和通用的表示。预训练模型可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/EIDOSLAB/AnatCL。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在神经影像中的应用在检测神经性疾病和神经退行性疾病方面的重要性。
- 脑年龄作为神经影像中的关键生物标志物,对预测不同疾病有良好表现。
- 利用脑年龄对深度学习模型进行弱监督预训练在数据稀缺情况下显示出良好的应用前景。
- 脑部MRI的结构信息(如皮层厚度)为学习良好表示提供重要信息,适用于多种下游任务。
- AnatCL模型通过弱对比学习利用结构信息,并在多种下游任务上达到最新性能水平。
- AnatCL模型在多种疾病的诊断和临床评分预测等任务进行了验证。
点此查看论文截图

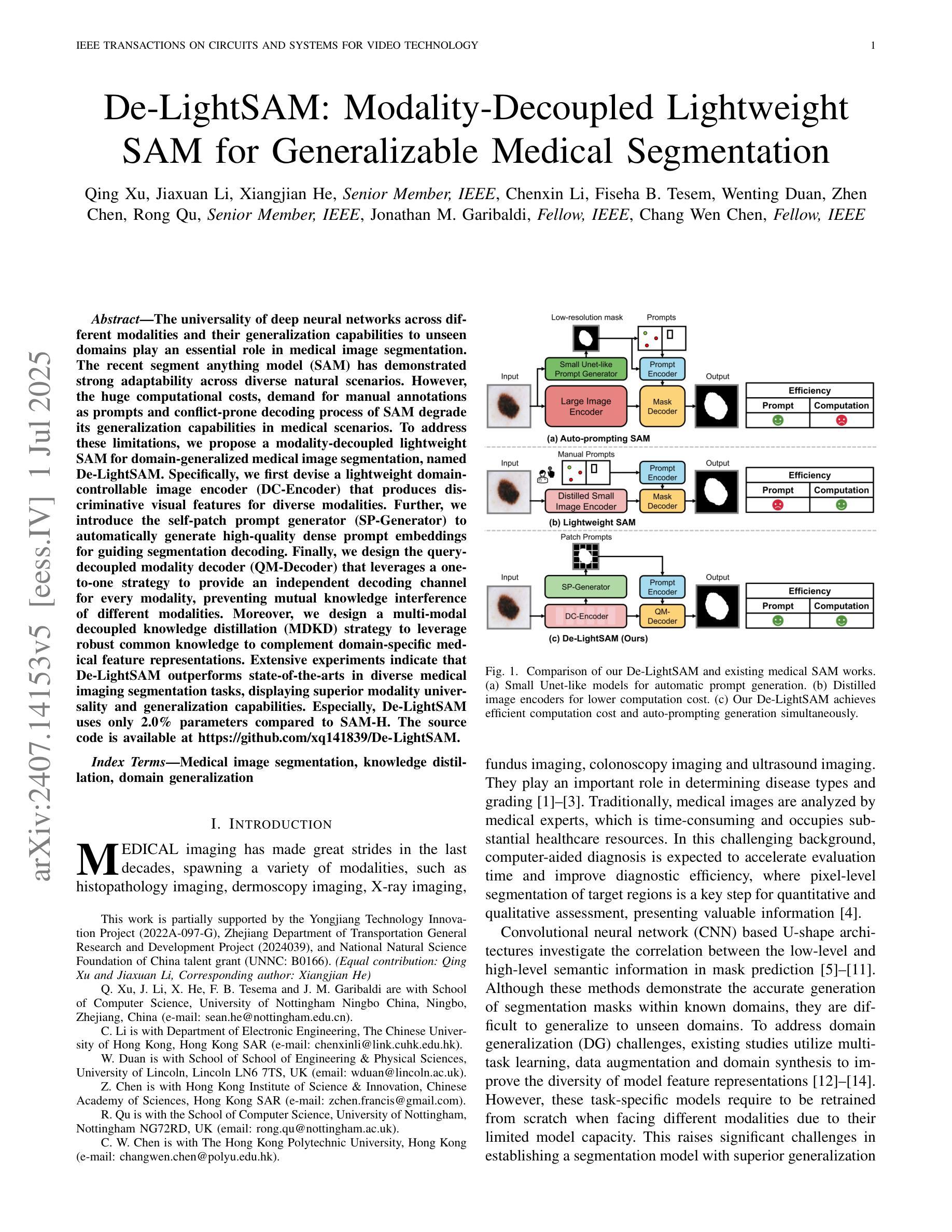
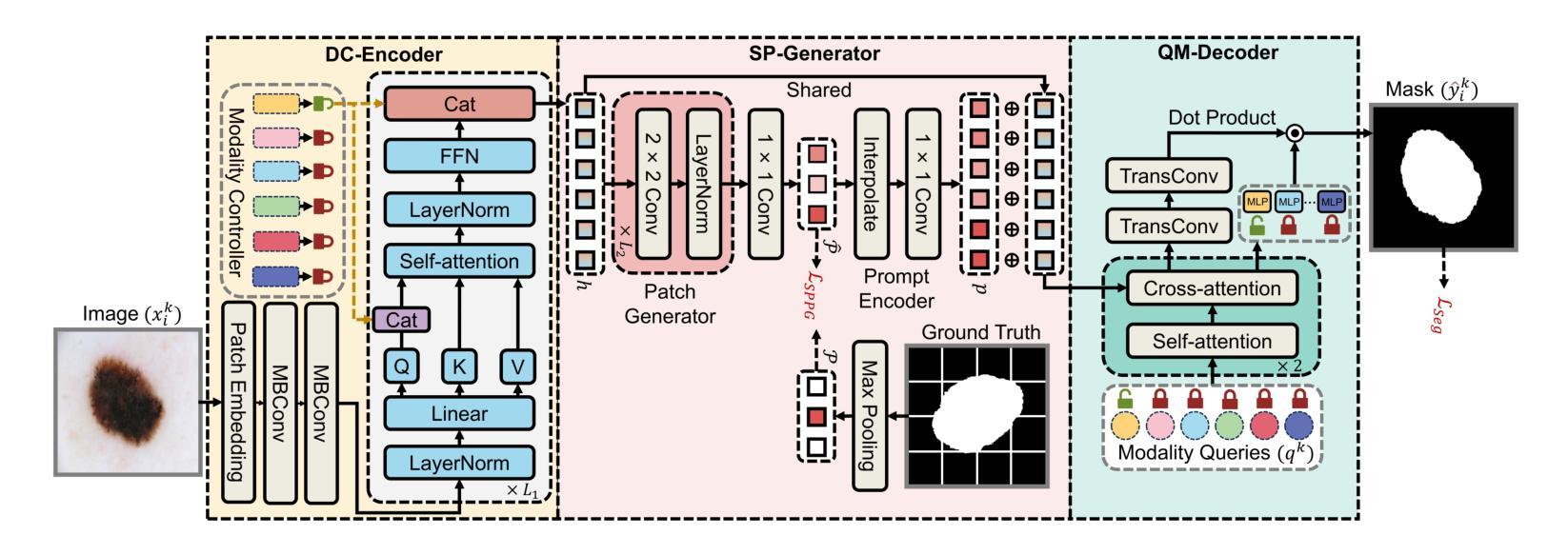
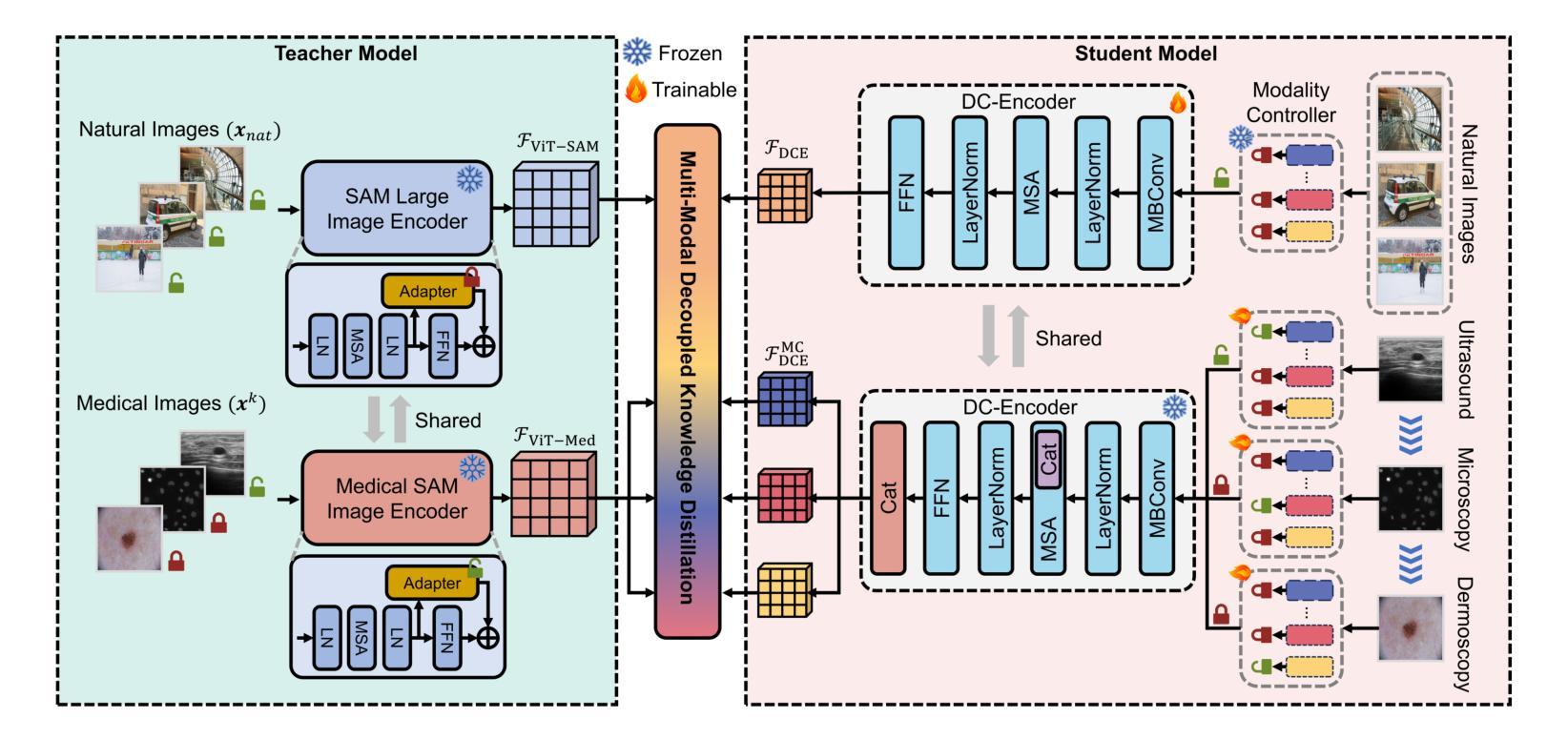
De-LightSAM: Modality-Decoupled Lightweight SAM for Generalizable Medical Segmentation
Authors:Qing Xu, Jiaxuan Li, Xiangjian He, Chenxin Li, Fiseha B. Tesem, Wenting Duan, Zhen Chen, Rong Qu, Jonathan M. Garibaldi, Chang Wen Chen
The universality of deep neural networks across different modalities and their generalization capabilities to unseen domains play an essential role in medical image segmentation. The recent segment anything model (SAM) has demonstrated strong adaptability across diverse natural scenarios. However, the huge computational costs, demand for manual annotations as prompts and conflict-prone decoding process of SAM degrade its generalization capabilities in medical scenarios. To address these limitations, we propose a modality-decoupled lightweight SAM for domain-generalized medical image segmentation, named De-LightSAM. Specifically, we first devise a lightweight domain-controllable image encoder (DC-Encoder) that produces discriminative visual features for diverse modalities. Further, we introduce the self-patch prompt generator (SP-Generator) to automatically generate high-quality dense prompt embeddings for guiding segmentation decoding. Finally, we design the query-decoupled modality decoder (QM-Decoder) that leverages a one-to-one strategy to provide an independent decoding channel for every modality, preventing mutual knowledge interference of different modalities. Moreover, we design a multi-modal decoupled knowledge distillation (MDKD) strategy to leverage robust common knowledge to complement domain-specific medical feature representations. Extensive experiments indicate that De-LightSAM outperforms state-of-the-arts in diverse medical imaging segmentation tasks, displaying superior modality universality and generalization capabilities. Especially, De-LightSAM uses only 2.0% parameters compared to SAM-H. The source code is available at https://github.com/xq141839/De-LightSAM.
深度神经网络在不同模态之间的通用性以及它们对未见领域的泛化能力在医学图像分割中扮演着至关重要的角色。最近的“任何事物分割模型”(SAM)已在多种自然场景中表现出了强大的适应性。然而,SAM的巨大计算成本、对手动注释的提示需求以及易冲突解码过程,使其在医学场景中泛化能力受限。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了一种用于领域泛化医学图像分割的模态解耦轻量化SAM,名为De-LightSAM。具体来说,我们首先设计了一种轻量级域可控图像编码器(DC-Encoder),用于生成不同模态的判别性视觉特征。此外,我们引入了自修补提示生成器(SP-Generator),用于自动生成高质量密集提示嵌入,以指导分割解码。最后,我们设计了查询解耦模态解码器(QM-Decoder),它采用一对一策略,为每种模态提供独立的解码通道,防止不同模态之间的知识相互干扰。此外,我们设计了一种多模态解耦知识蒸馏(MDKD)策略,利用稳健的通用知识来补充领域特定的医学特征表示。大量实验表明,在多种医学成像分割任务中,De-LightSAM的性能优于其他最新技术,显示出卓越的模态通用性和泛化能力。值得一提的是,相较于SAM-H,De-LightSAM仅使用其2.0%的参数。源代码可在https://github.com/xq141839/De-LightSAM获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under Review
Summary
本文介绍了针对医学图像分割的深度学习模型De-LightSAM。该模型解决了SAM模型在医学场景中的计算成本高、需要手动标注提示和易冲突解码等问题。De-LightSAM通过设计轻量级域可控图像编码器、自补丁提示生成器和查询解耦模态解码器,提高了模型的跨模态通用性和计算效率。此外,还设计了多模态解耦知识蒸馏策略,以利用稳健的通用知识来补充特定领域的医学特征表示。实验表明,De-LightSAM在多种医学图像分割任务上优于其他模型,具有出色的跨模态通用性和泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- De-LightSAM解决了SAM模型在医学图像分割中的计算成本高、需要手动标注提示和易冲突解码的问题。
- De-LightSAM通过设计轻量级域可控图像编码器(DC-Encoder)提高模型的跨模态通用性。
- 自补丁提示生成器(SP-Generator)能够自动产生高质量密集提示嵌入,引导分割解码。
- 查询解耦模态解码器(QM-Decoder)采用一对一策略,为每种模态提供独立解码通道,防止不同模态之间的知识干扰。
- 多模态解耦知识蒸馏(MDKD)策略利用稳健的通用知识来补充特定领域的医学特征表示。
- De-LightSAM在多种医学图像分割任务上表现出优异的性能,优于其他模型。
- De-LightSAM的参数使用量仅为SAM-H的2.0%,更加轻量级。
点此查看论文截图
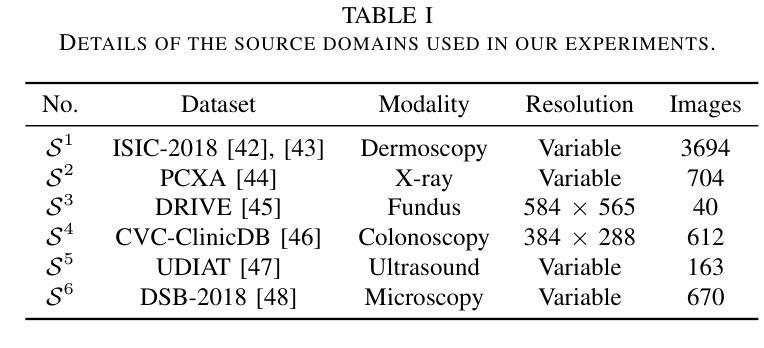
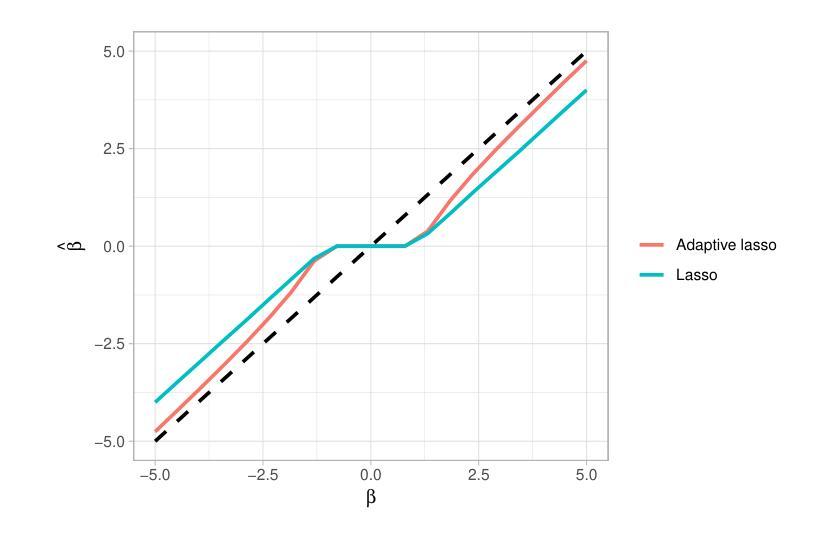
Comparing Lasso and Adaptive Lasso in High-Dimensional Data: A Genetic Survival Analysis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Authors:Pilar González-Barquero, Rosa E. Lillo, Álvaro Méndez-Civieta
In high-dimensional survival analysis, effective variable selection is crucial for both model interpretation and predictive performance. This paper investigates Cox regression with lasso and adaptive lasso penalties in genomic datasets where covariates far outnumber observations. We propose and evaluate four weight calculation strategies for adaptive lasso specifically designed for high-dimensional settings: ridge regression, principal component analysis (PCA), univariate Cox regression, and random survival forest (RSF) based weights. To address the inherent variability in high dimensional model selection, we develop a robust procedure that evaluates performance across multiple data partitions and selects variables based on a novel importance index. Extensive simulation studies demonstrate that adaptive lasso with ridge and PCA weights significantly outperforms standard lasso in variable selection accuracy while maintaining similar or better predictive performance across various correlation structures, censoring proportions (0-80%), and dimensionality settings. These improvements are particularly pronounced in highly-censored scenarios, making our approach valuable for real-world genetic studies with limited observed events. We apply our methodology to triple-negative breast cancer data with 234 patients, over 19500 variables and 82% censoring, identifying key genetic and clinical prognostic factors. Our findings demonstrate that adaptive lasso with appropriate weight calculation provides more stable and interpretable models for high-dimensional survival analysis.
在高维生存分析中,有效的变量选择对于模型解释和预测性能都至关重要。本文研究了在基因组数据集中使用lasso和自适应lasso惩罚的Cox回归,其中协变量远远超过观测值。我们针对高维环境专门提出了四种自适应lasso权重计算策略,并对其进行了评估:岭回归、主成分分析(PCA)、单变量Cox回归和基于随机生存森林(RSF)的权重。为了解决高维模型选择中的固有变化性,我们开发了一种稳健的程序,该程序可以在多个数据分区中评估性能,并根据新的重要性指数选择变量。大量的模拟研究表明,使用岭和PCA权重的自适应lasso在变量选择准确性上显著优于标准lasso,同时在各种关联结构、审查比例(0-80%)和高维设置下保持相似或更好的预测性能。这些改进在高度审查的场景中尤为突出,使我们的方法对于具有有限观察事件的真实世界遗传研究具有价值。我们将该方法应用于234例三阴性乳腺癌数据,超过19500个变量和82%的审查,以确定关键的遗传和临床预后因素。我们的研究结果表明,使用适当权重计算的自适应lasso为高维生存分析提供了更稳定和可解释的模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages, 3 figures, 6 tables
Summary
本文探讨了高维生存分析中,使用岭回归、主成分分析、单变量Cox回归和随机生存森林权重计算策略的自适应Lasso方法在基因组数据集上的变量选择效果。研究结果表明,自适应Lasso方法能够有效选择重要变量,在预测性能和模型解释性上表现优于标准Lasso方法。在高度截断的情况下表现尤为出色,适合应用于真实世界的遗传研究。研究最后通过三重阴性乳腺癌数据集验证了方法的实用性和有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 高维生存分析中,有效的变量选择对于模型解释和预测性能至关重要。
- 自适应Lasso方法结合了Cox回归与惩罚项,特别适用于高维数据集。
- 提出了四种针对自适应Lasso的重量计算策略,包括岭回归、主成分分析、单变量Cox回归和随机生存森林。
- 自适应Lasso方法在多数据分区上的表现稳健,通过新型重要性指数选择变量。
- 模拟研究表明,自适应Lasso在变量选择准确性上显著优于标准Lasso,并且在各种相关性结构、截断比例和维度设置上维持相似的预测性能或有所提升。
- 在高度截断的场景下,自适应Lasso的改进尤为显著,这对真实世界的遗传研究具有实用价值。
点此查看论文截图

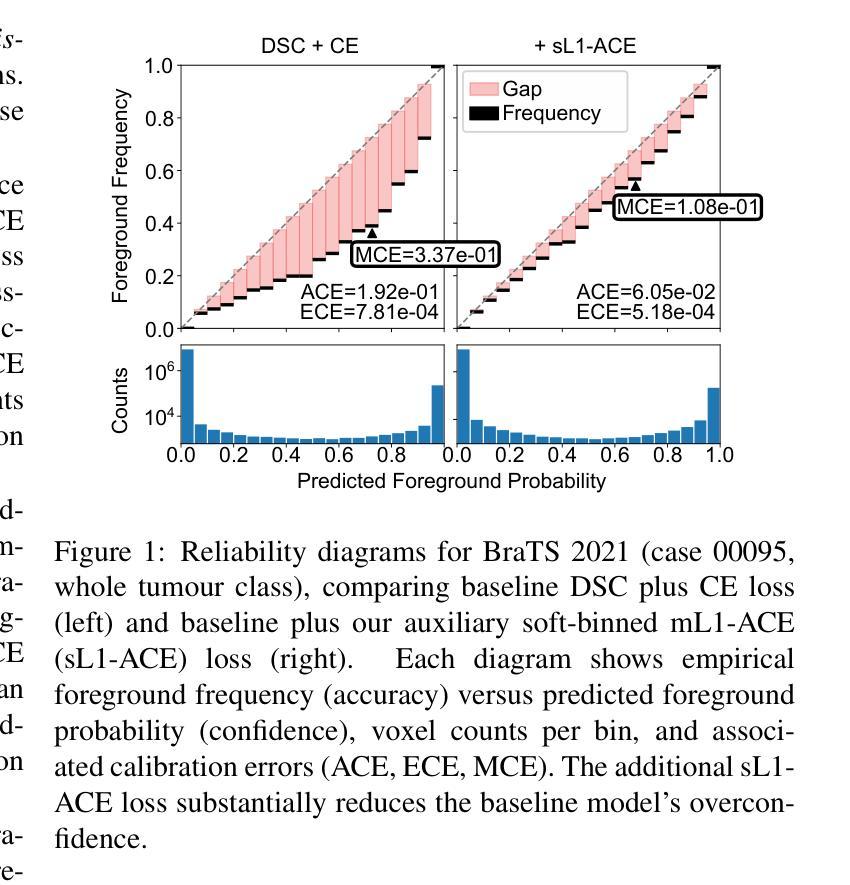
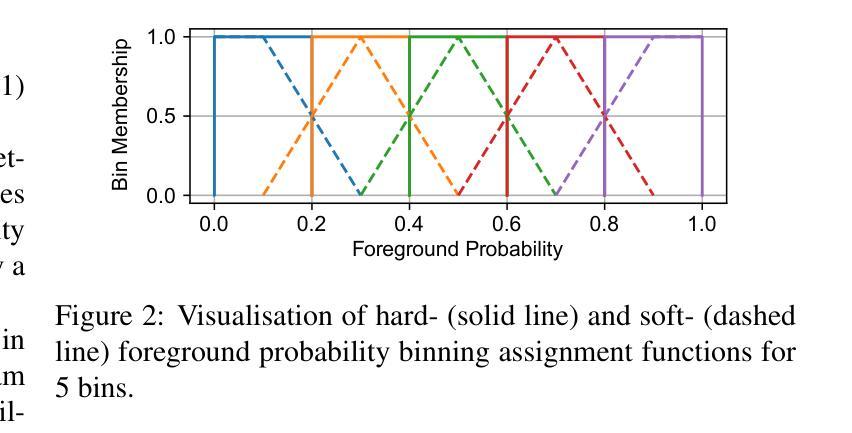
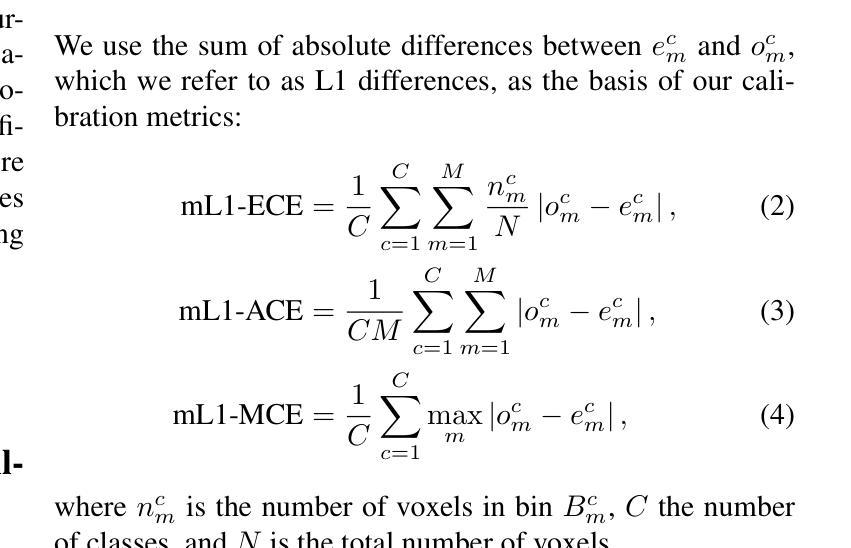
Average Calibration Error: A Differentiable Loss for Improved Reliability in Image Segmentation
Authors:Theodore Barfoot, Luis Garcia-Peraza-Herrera, Ben Glocker, Tom Vercauteren
Deep neural networks for medical image segmentation often produce overconfident results misaligned with empirical observations. Such miscalibration, challenges their clinical translation. We propose to use marginal L1 average calibration error (mL1-ACE) as a novel auxiliary loss function to improve pixel-wise calibration without compromising segmentation quality. We show that this loss, despite using hard binning, is directly differentiable, bypassing the need for approximate but differentiable surrogate or soft binning approaches. Our work also introduces the concept of dataset reliability histograms which generalises standard reliability diagrams for refined visual assessment of calibration in semantic segmentation aggregated at the dataset level. Using mL1-ACE, we reduce average and maximum calibration error by 45% and 55% respectively, maintaining a Dice score of 87% on the BraTS 2021 dataset. We share our code here: https://github.com/cai4cai/ACE-DLIRIS
针对医学图像分割的深度学习网络常常产生过于自信的结果,这些结果与实证观察不符。这种误校准对其临床翻译构成了挑战。我们建议使用边际L1平均校准误差(mL1-ACE)作为一种新的辅助损失函数,以提高像素级的校准,同时不损害分割质量。我们表明,尽管使用了硬分箱,但这种损失是直接可微分的,从而绕过了需要使用近似但可微分的替代或软分箱方法的需求。我们的工作还引入了数据集可靠性直方图的概念,它推广了标准可靠性图,用于对数据集级别的语义分割校准进行精细的视觉评估。使用mL1-ACE,我们将平均和最大校准误差分别降低了45%和55%,同时在BraTS 2021数据集上保持了87%的Dice得分。我们的代码分享在这里:https://github.com/cai4cai/ACE-DLIRIS
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对医学图像分割中深度神经网络产生的过度自信结果问题,提出使用边际L1平均校准误差(mL1-ACE)作为新型辅助损失函数,改善像素级校准而不影响分割质量。引入数据集可靠性直方图,便于精细可视化评估语义分割的校准情况。
Key Takeaways
- 深度神经网络在医学图像分割中常产生过度自信的结果,与实际情况不符。
- 引入边际L1平均校准误差(mL1-ACE)作为新的辅助损失函数,改善像素级校准。
- mL1-ACE损失函数使用硬分箱,但具备直接可微性,无需近似但可微的替代或软分箱方法。
- 引入数据集可靠性直方图,用于精细可视化评估语义分割的校准情况,便于在数据集层面进行校准评估。
- 使用mL1-ACE,平均校准误差和最大校准误差分别降低了45%和55%。
- 在BraTS 2021数据集上,维持87%的Dice得分。
- 研究成果已共享于:https://github.com/cai4cai/ACE-DLIRIS
点此查看论文截图

Improving Robustness and Reliability in Medical Image Classification with Latent-Guided Diffusion and Nested-Ensembles
Authors:Xing Shen, Hengguan Huang, Brennan Nichyporuk, Tal Arbel
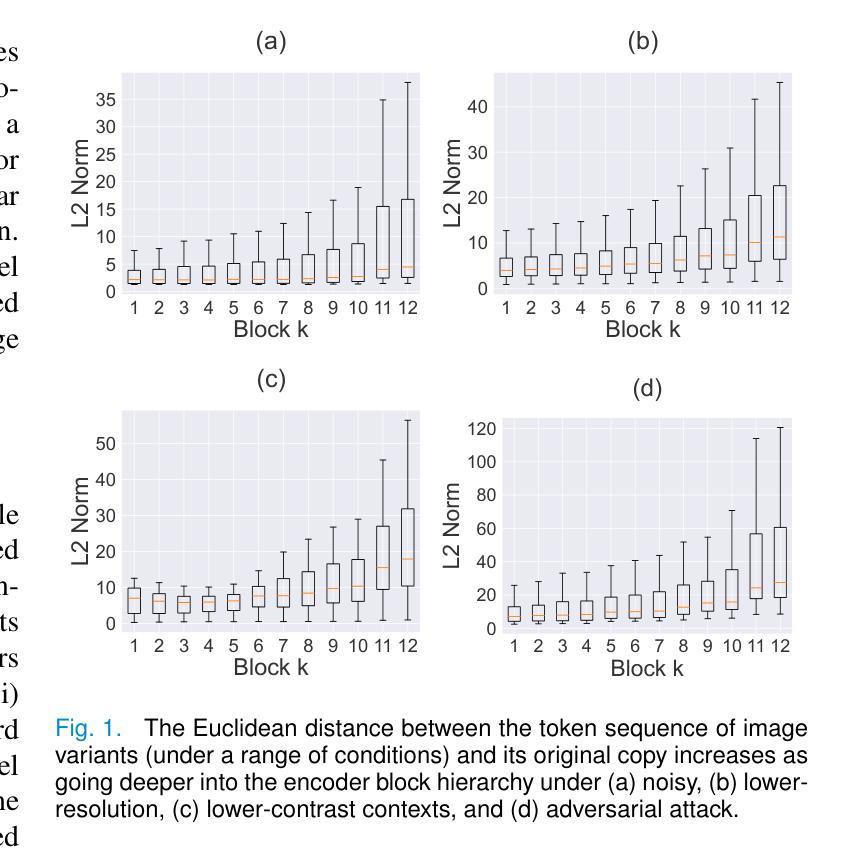
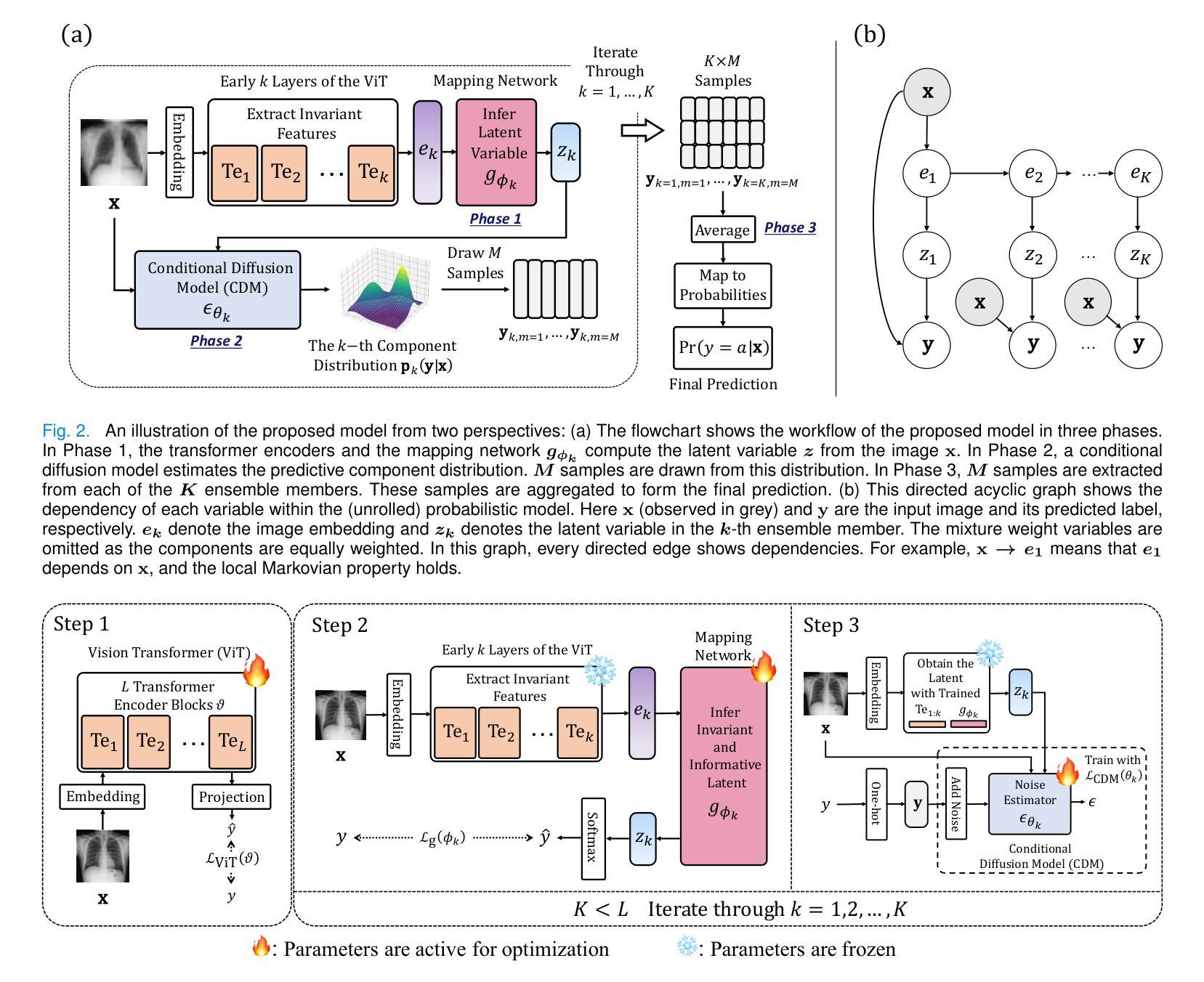
Once deployed, medical image analysis methods are often faced with unexpected image corruptions and noise perturbations. These unknown covariate shifts present significant challenges to deep learning based methods trained on “clean” images. This often results in unreliable predictions and poorly calibrated confidence, hence hindering clinical applicability. While recent methods have been developed to address specific issues such as confidence calibration or adversarial robustness, no single framework effectively tackles all these challenges simultaneously. To bridge this gap, we propose LaDiNE, a novel ensemble learning method combining the robustness of Vision Transformers with diffusion-based generative models for improved reliability in medical image classification. Specifically, transformer encoder blocks are used as hierarchical feature extractors that learn invariant features from images for each ensemble member, resulting in features that are robust to input perturbations. In addition, diffusion models are used as flexible density estimators to estimate member densities conditioned on the invariant features, leading to improved modeling of complex data distributions while retaining properly calibrated confidence. Extensive experiments on tuberculosis chest X-rays and melanoma skin cancer datasets demonstrate that LaDiNE achieves superior performance compared to a wide range of state-of-the-art methods by simultaneously improving prediction accuracy and confidence calibration under unseen noise, adversarial perturbations, and resolution degradation.
部署医疗图像分析方法后,它们经常面临意外的图像损坏和噪声干扰。这些未知的协变量变化给基于“干净”图像训练的深度学习方法带来了巨大的挑战。这通常会导致预测结果不可靠和置信度校准不佳,从而阻碍了其在临床上的适用性。虽然最近已经开发了一些方法来解决信心校准或对抗稳健性等问题,但没有单一框架能有效地同时解决所有这些挑战。为了填补这一空白,我们提出了LaDiNE,这是一种新型集成学习方法,将视觉变压器的稳健性与基于扩散的生成模型的可靠性相结合,以提高医疗图像分类的可靠性。具体来说,我们使用变压器编码器块作为分层特征提取器,从每个集成成员学习图像的恒定特征,从而产生对输入扰动具有鲁棒性的特征。此外,扩散模型被用作灵活的密度估计器,根据恒定特征估计成员密度,从而在保留适当校准的置信度的同时,实现对复杂数据分布的改进建模。在肺结核胸部X射线和黑色素瘤皮肤癌数据集上的大量实验表明,LaDiNE通过同时提高预测精度和置信度校准,在未见的噪声、对抗性扰动和分辨率下降的情况下,实现了与一系列最先进的方法相比的卓越性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2025
Summary
医学图像分析方法在实际应用中常遭遇图像损坏和噪声干扰等挑战。针对此问题,我们提出一种新型集成学习方法LaDiNE,结合Vision Transformer和扩散生成模型的稳健性,提高医学图像分类的可靠性。实验证明,LaDiNE在不同噪声、对抗性干扰和分辨率下降的情况下,预测准确率和置信度校准均优于其他先进方法。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分析方法面临未知协变量偏移的挑战,影响深度学习的预测可靠性和临床适用性。
- LaDiNE是一种新型集成学习方法,结合Vision Transformer和扩散生成模型的优点。
- LaDiNE通过变压器编码器块提取图像的不变特征,增强对输入扰动的稳健性。
- 扩散模型作为灵活的密度估计器,估计成员密度并基于不变特征进行条件建模。
- LaDiNE能提高预测准确性和置信度校准,在未见噪声、对抗性干扰和分辨率降低的情况下表现优异。
- 实验在肺结核胸部X射线和黑色素瘤皮肤癌数据集上验证了LaDiNE的优越性。
点此查看论文截图