⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-09 更新
Physics-Guided Dual Implicit Neural Representations for Source Separation
Authors:Yuan Ni, Zhantao Chen, Alexander N. Petsch, Edmund Xu, Cheng Peng, Alexander I. Kolesnikov, Sugata Chowdhury, Arun Bansil, Jana B. Thayer, Joshua J. Turner
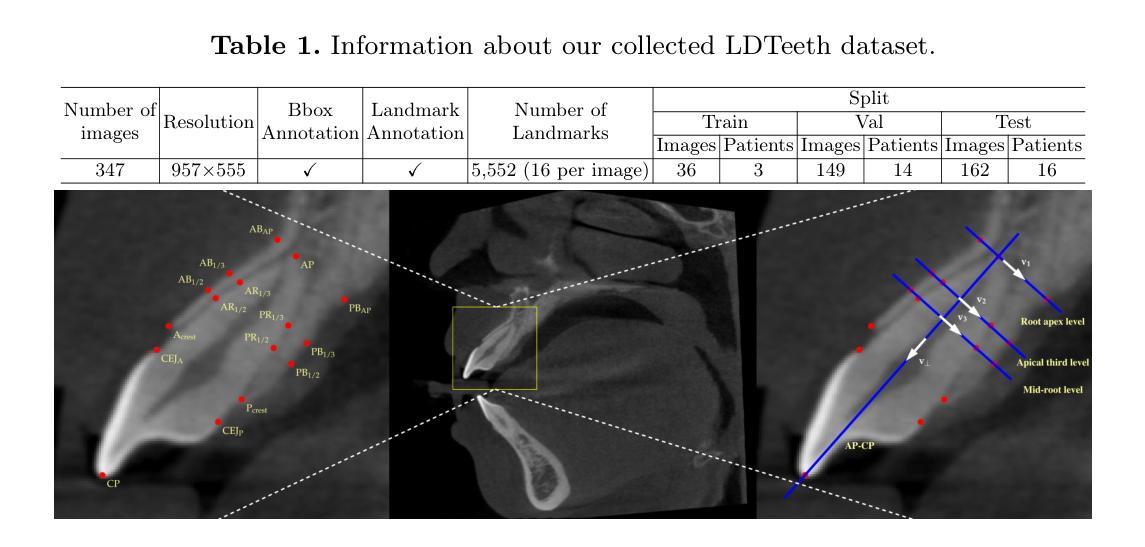
Significant challenges exist in efficient data analysis of most advanced experimental and observational techniques because the collected signals often include unwanted contributions–such as background and signal distortions–that can obscure the physically relevant information of interest. To address this, we have developed a self-supervised machine-learning approach for source separation using a dual implicit neural representation framework that jointly trains two neural networks: one for approximating distortions of the physical signal of interest and the other for learning the effective background contribution. Our method learns directly from the raw data by minimizing a reconstruction-based loss function without requiring labeled data or pre-defined dictionaries. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework by considering a challenging case study involving large-scale simulated as well as experimental momentum-energy-dependent inelastic neutron scattering data in a four-dimensional parameter space, characterized by heterogeneous background contributions and unknown distortions to the target signal. The method is found to successfully separate physically meaningful signals from a complex or structured background even when the signal characteristics vary across all four dimensions of the parameter space. An analytical approach that informs the choice of the regularization parameter is presented. Our method offers a versatile framework for addressing source separation problems across diverse domains, ranging from superimposed signals in astronomical measurements to structural features in biomedical image reconstructions.
在大多数先进的实验和观测技术的有效数据分析方面存在重大挑战,因为收集的信号通常包括不需要的贡献,例如背景和信号失真,这可能会掩盖与物理相关的感兴趣的信息。为了解决这个问题,我们开发了一种基于双隐神经表示框架的自监督机器学习方法进行源分离,该框架联合训练两个神经网络:一个用于近似感兴趣的物理信号的失真,另一个用于学习有效的背景贡献。我们的方法直接从原始数据中学习,通过最小化基于重建的损失函数,无需标记的数据或预先定义的词典。我们通过考虑涉及大规模模拟以及实验动量能量依赖的非弹性中子散射数据的具有挑战性的案例研究来展示我们框架的有效性,该数据在由异质背景贡献和未知目标信号失真表征的四维参数空间中。该方法即使在信号特征在参数空间的所有四个维度上都发生变化时,也能成功地从复杂或结构化背景中分离出物理上有意义的信号。给出了一个分析方法来指导正则化参数的选择。我们的方法为解决不同领域的源分离问题提供了一个通用的框架,范围从天文测量中的叠加信号到生物医学图像重建中的结构特征。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种利用双隐神经网络表示框架的自监督机器学习方法进行源分离。该方法通过直接最小化基于重建的损失函数来从原始数据中学习,无需标记数据或预定义词典。实验结果表明,该方法在处理大型模拟和实验动量能量依赖弹性中子散射数据时,即使在四维参数空间中信号特性发生变化时,也能成功分离出物理意义明显的信号。此外,本文还提出了一种分析正则化参数选择的分析方法,并指出该方法可广泛应用于不同领域中的源分离问题。
Key Takeaways
- 源分离是处理实验和观测数据的重要挑战,因为收集的信号通常包含背景和不想要的失真。
- 提出了一种基于双隐神经网络表示框架的自监督机器学习方法进行源分离。
- 方法直接从原始数据中学习,通过最小化重建损失函数进行优化,无需标记数据或预定义词典。
- 方法在处理大型模拟和实验动量能量依赖弹性中子散射数据时表现出良好的效果。
- 即使在四维参数空间中信号特性变化时,也能成功分离物理意义明显的信号。
- 提供了一种分析正则化参数选择的方法。
点此查看论文截图

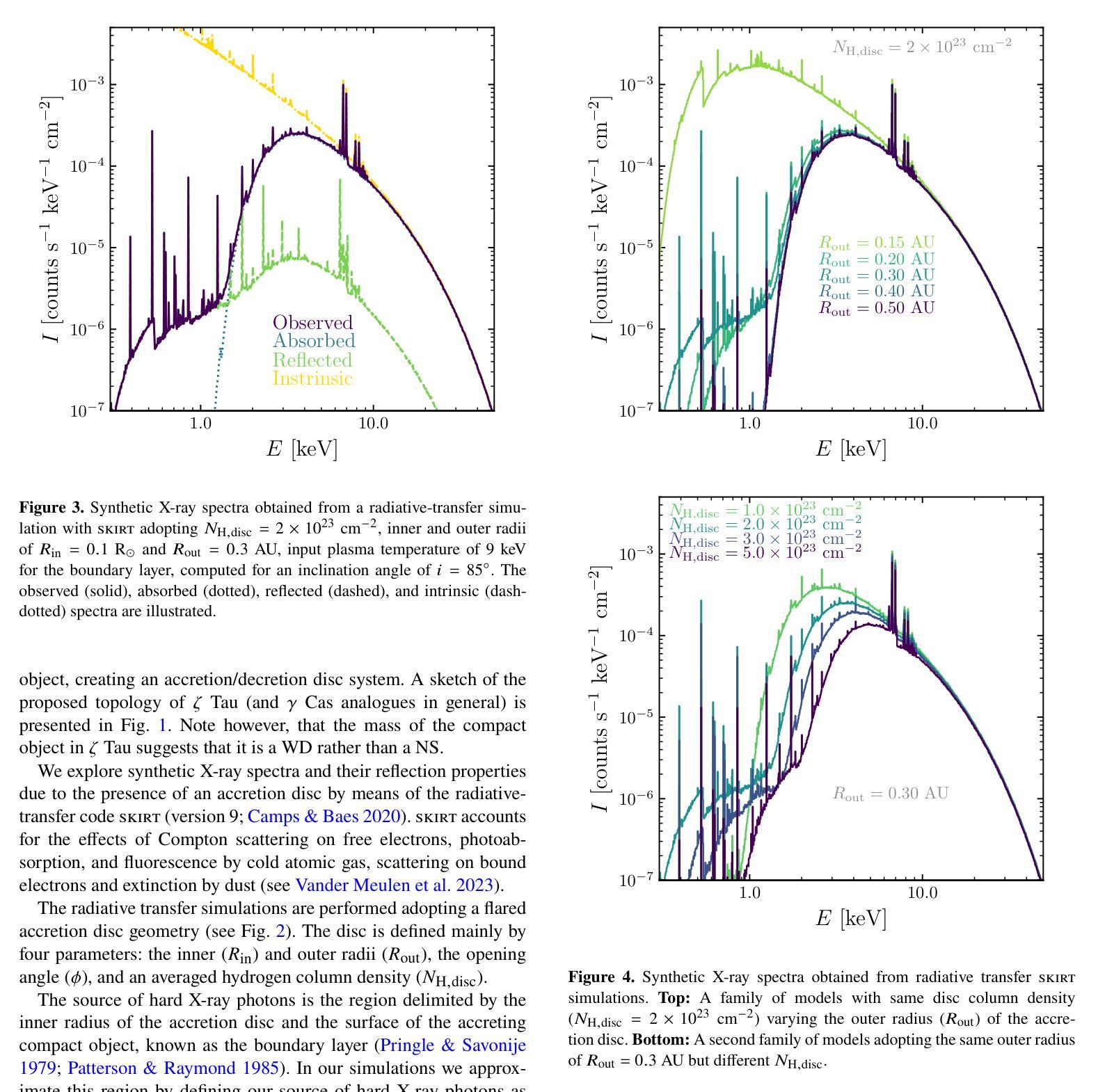
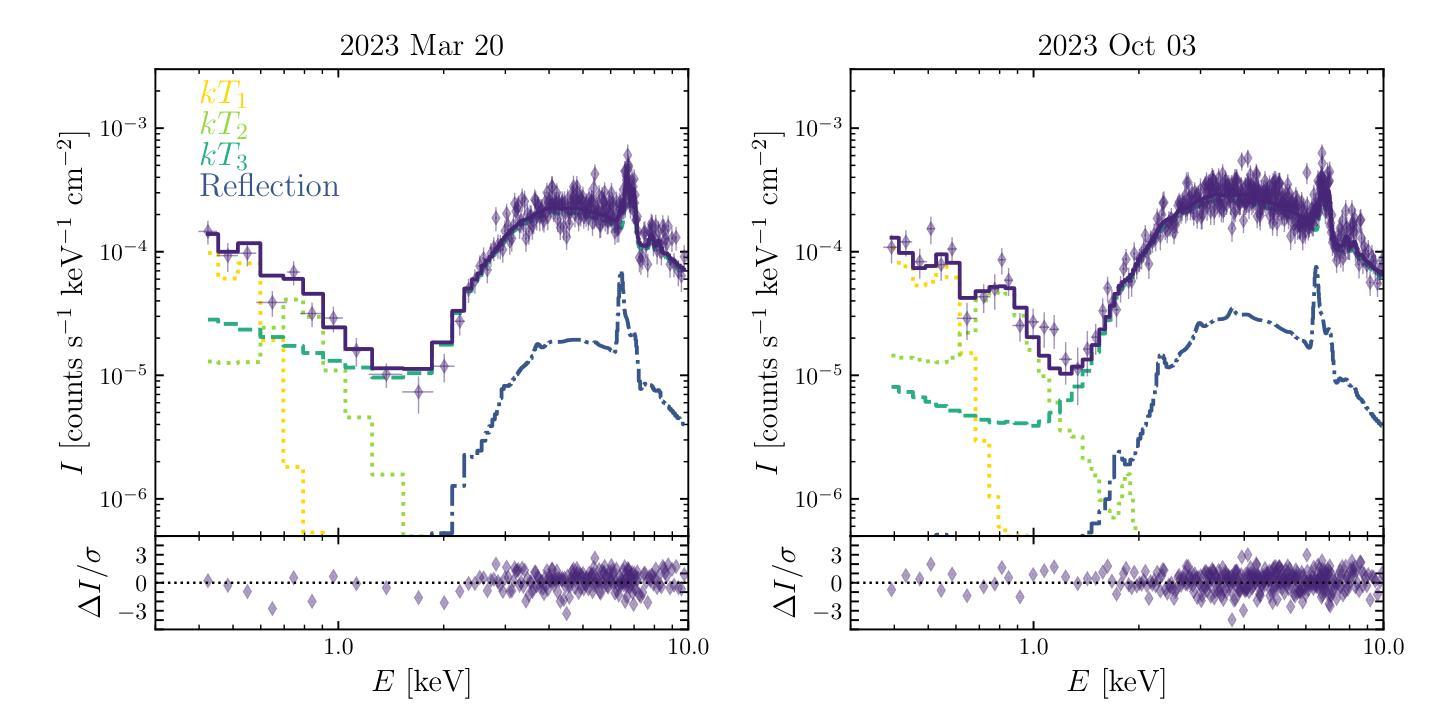
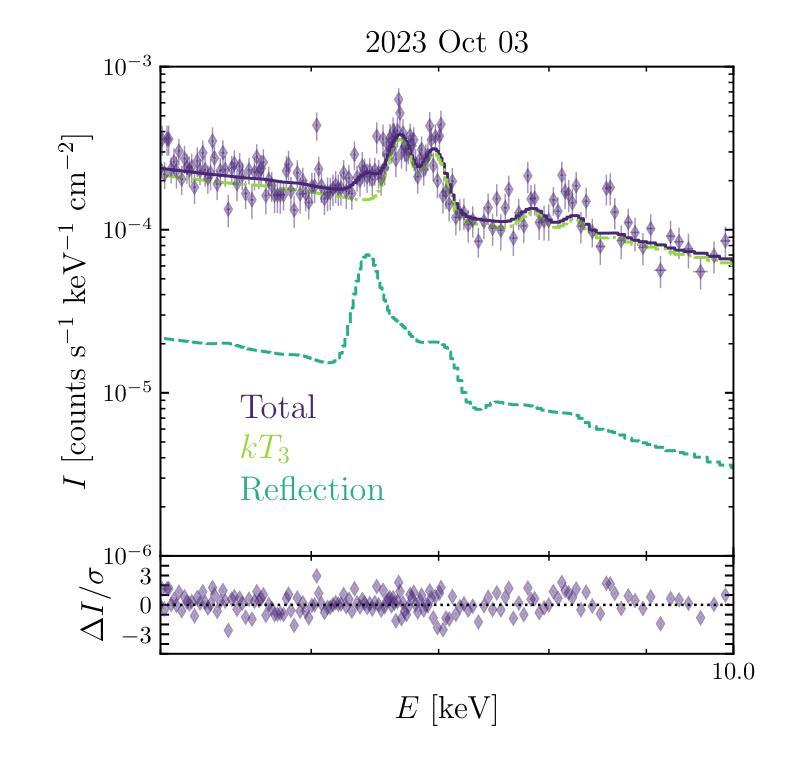
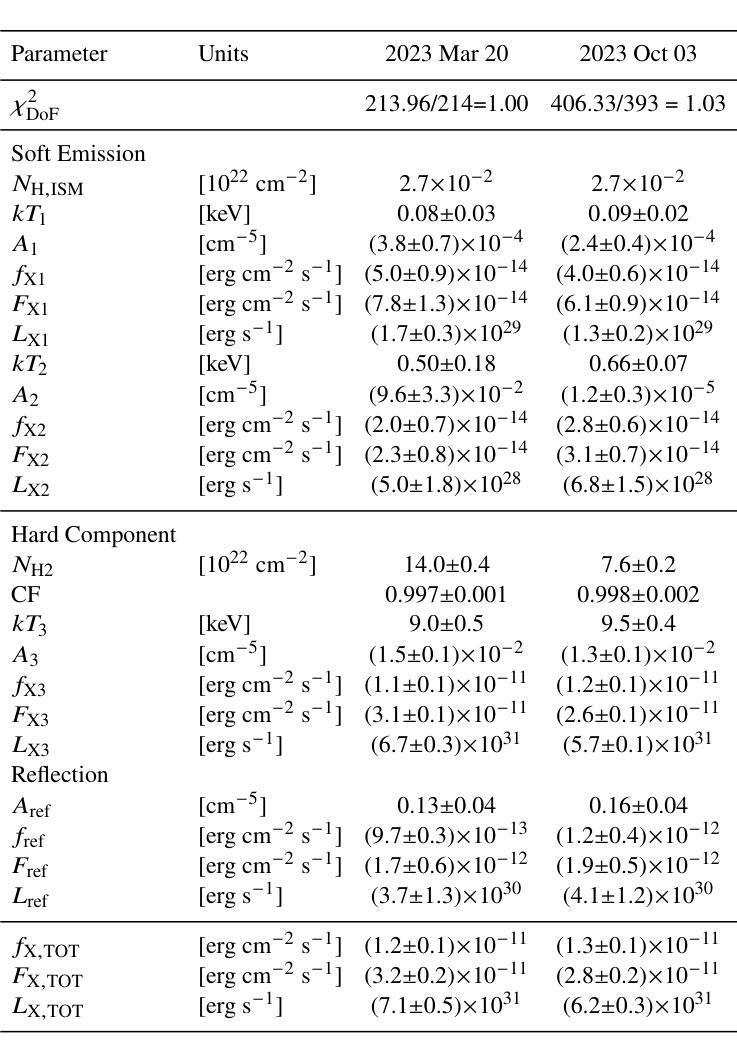
Tiānguān ($ζ$ Tau) as a binary system consisting of a Be-star and an accreting White Dwarf: opening a gate to understanding enigmatic $γ$ Cas analogues
Authors:Jesús A. Toalá, Lidia M. Oskinova, Diego A. Vasquez-Torres
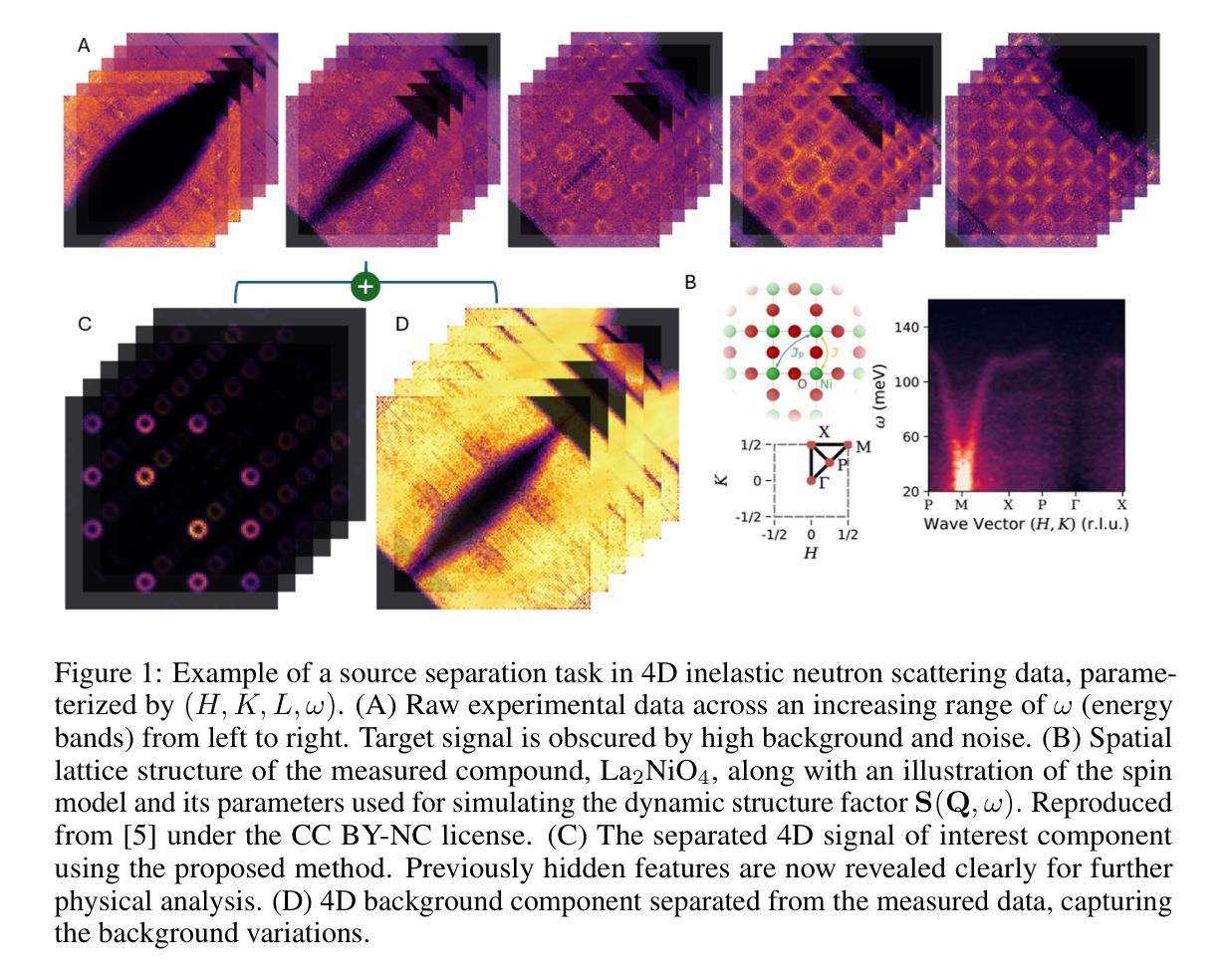
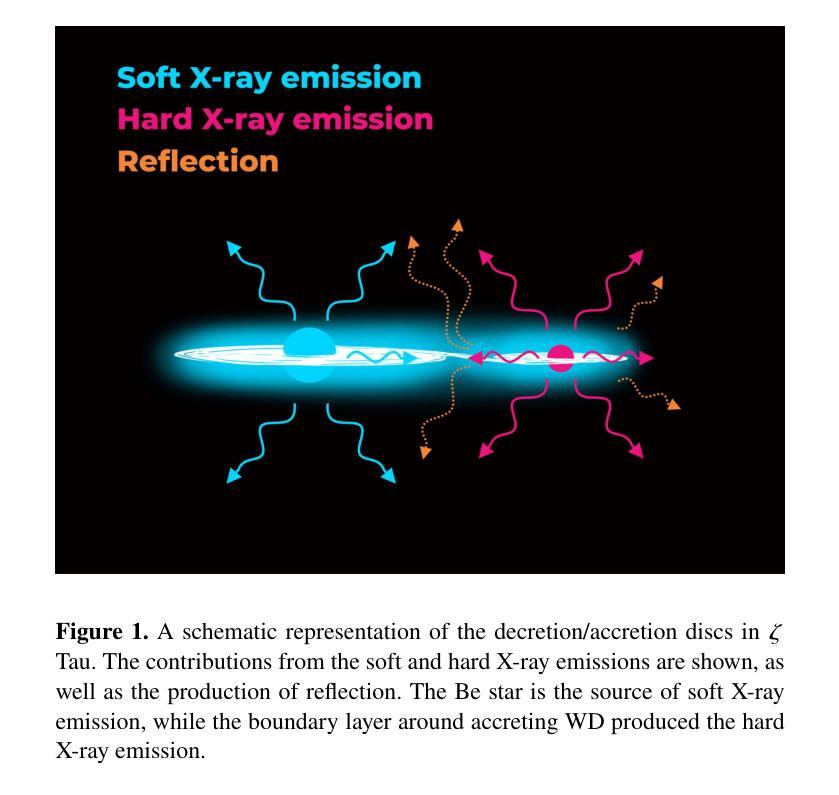
The analogues of $\gamma$ Cassiopea are binary early type Be stars which are X-ray bright and have hard thermal X-ray spectra. The nature of low-mass companions in these stars and mechanisms of their X-ray emission remain enigmatic. Among the proposed ideas is the presence of an accretion disc around a white dwarf (WD) companion to the Be star donor. We use modern radiative transfer models accounting for reflection physics in order to calculate the synthetic spectra of such systems, and assume that the hottest plasma is thermal and is located in the accretion disc boundary layer. The models are then used to analyse the archival X-ray observations of the $\gamma$ Cas analogue $\zeta$ Tau (a.k.a. Ti={a}ngu={a}n) which were obtained by the XMM-Newton telescope. Comparisons with X-ray-emitting symbiotic systems, particularly $\delta$- and $\beta/\delta$-type systems, support the idea that the hard X-ray emission in $\zeta$ Tau is best explained by a WD accreting wind material of the Be star. The plasma temperature and luminosity of the boundary layer associated with the accretion disc are used to estimate a mass accretion rate of $\dot{M}_\mathrm{acc} \approx 4\times 10^{-10}$ M$_\odot$ yr$^{-1}$, implying a nova recurrence time above 10$^{5}$ yr. Our analysis advances the understanding the production of hard X-ray emission in $\gamma$ Cas analogues, further supporting the idea of accreting WDs as companions of Be-stars in these systems.
γ仙后座的类似物是早期类型的Be双星,它们X射线亮度高且具有硬热X射线光谱。这些恒星中的低质量伴星以及它们的X射线发射机制仍然是个谜。其中提出的想法之一是存在围绕Be星供体的白矮星(WD)伴星的一个吸积盘。我们使用考虑反射物理的现代辐射传递模型来计算这种系统的合成光谱,并假设最热的等离子体是热态并且位于吸积盘边界层中。然后,这些模型被用来分析由XMM-牛顿望远镜获得的γ仙后座类似物ζ金牛星(也称为Tiānguān)的档案X射线观测结果。与X射线发射的共生系统(特别是δ型和β/δ型系统)的比较支持这一观点,即ζ金牛星的硬X射线发射最好用白矮星吸收风物质来解释。与吸积盘相关的边界层的等离子体温度和光度被用来估计质量吸积率$\dot{M}_\mathrm{acc} \approx 4\times 10^{-10}$ M⊙yr^-1,这意味着新星再现时间超过10^5年。我们的分析推进了对γ仙后座类似物产生硬X射线发射的理解,进一步支持了在这些系统中吸收白矮星作为Be星的伴星的想法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 6 figures, 1 table; Submitted to MNRAS (comments are welcome)
Summary
γ型仙后座类似星体的X射线发射机制和低质量伴侣星的性质仍然神秘。研究团队采用辐射传输模型计算这类系统的合成光谱,并假设最热的等离子体位于吸积盘边界层,呈热态。通过对τ型仙女的XMM-牛顿望远镜存档X射线观测数据的分析,以及与发射X射线的共生系统的比较,支持了WD吸积Be星风物质产生硬X射线发射的观点。
Key Takeaways
- γ型仙后座类似星体是X射线明亮的早期型Be双星,具有硬热X射线光谱特征。
- 这些星体的低质量伴侣星和X射线发射机制仍然不清楚。
- 辐射传输模型被用来计算这类星体的合成光谱,并假设最热的等离子体位于吸积盘边界层。
- 对ζ Tau(即天苑)的XMM-牛顿望远镜存档X射线观测数据的分析支持了WD吸积Be星风物质产生硬X射线发射的观点。
- 等离子体温度和边界层光度被用来估计吸积盘的质量吸积率约为4×10^-10 M⊕ yr^-1。
- 这暗示了新星复发的周期超过10^5年。
点此查看论文截图

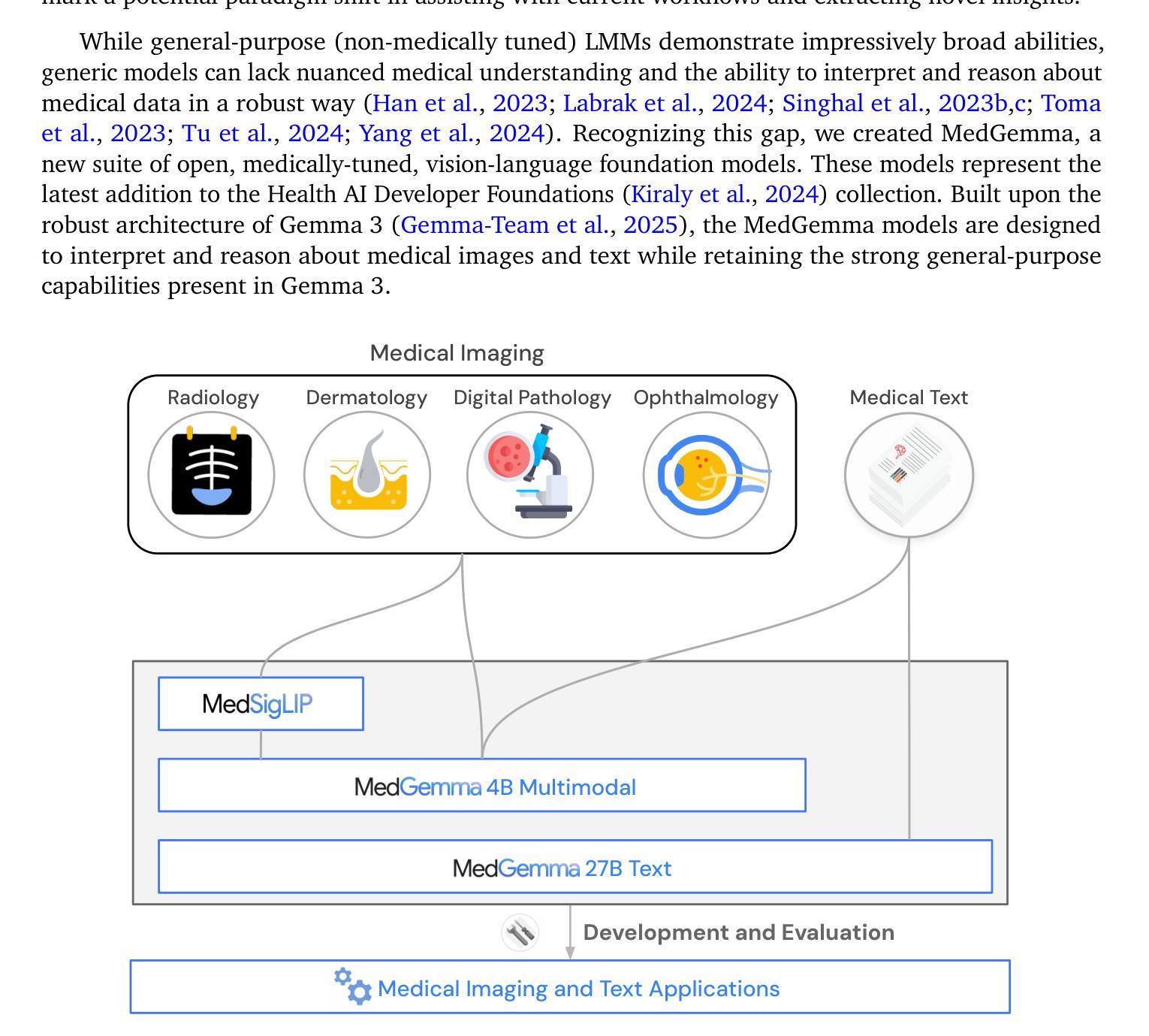
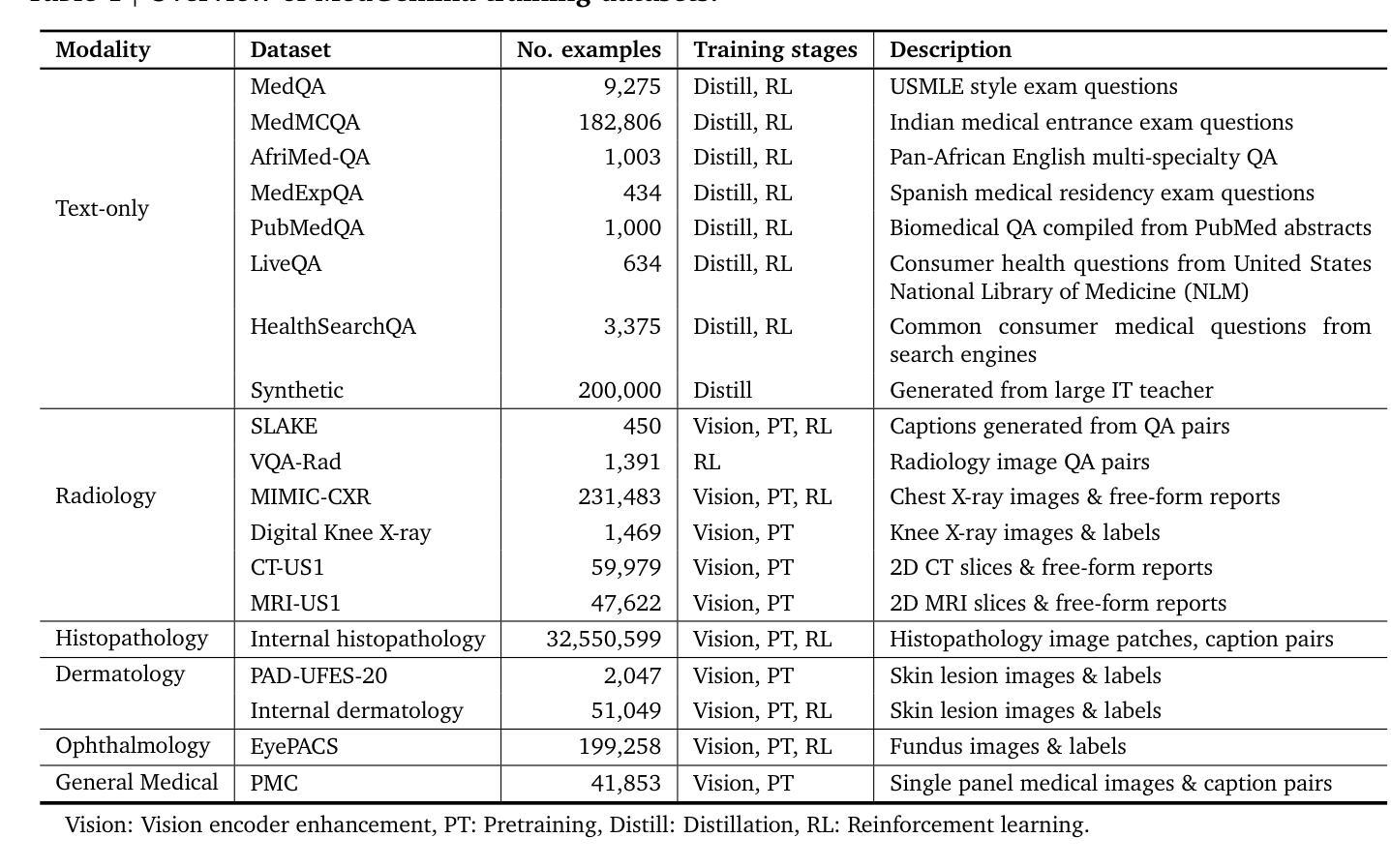
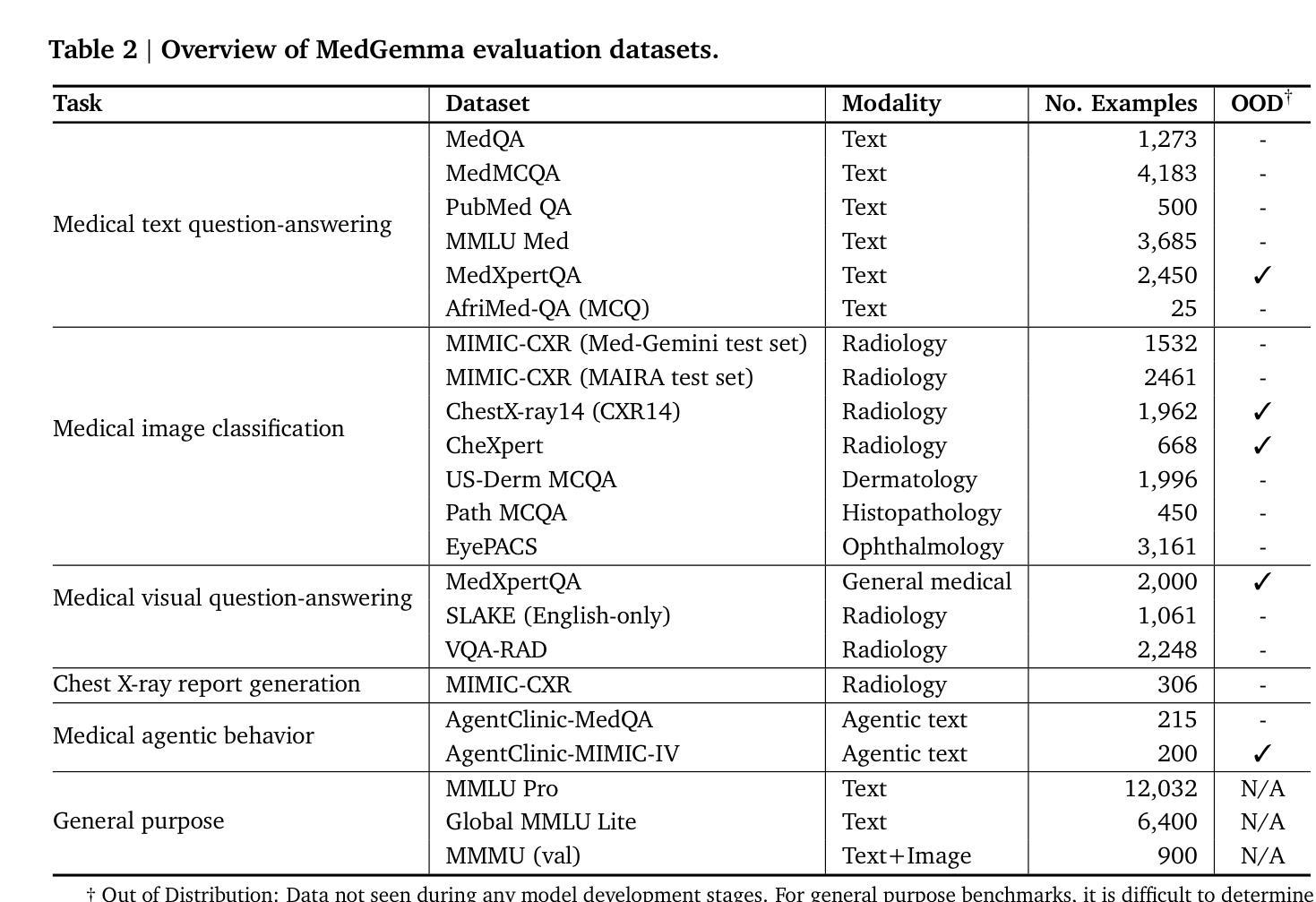
MedGemma Technical Report
Authors:Andrew Sellergren, Sahar Kazemzadeh, Tiam Jaroensri, Atilla Kiraly, Madeleine Traverse, Timo Kohlberger, Shawn Xu, Fayaz Jamil, Cían Hughes, Charles Lau, Justin Chen, Fereshteh Mahvar, Liron Yatziv, Tiffany Chen, Bram Sterling, Stefanie Anna Baby, Susanna Maria Baby, Jeremy Lai, Samuel Schmidgall, Lu Yang, Kejia Chen, Per Bjornsson, Shashir Reddy, Ryan Brush, Kenneth Philbrick, Howard Hu, Howard Yang, Richa Tiwari, Sunny Jansen, Preeti Singh, Yun Liu, Shekoofeh Azizi, Aishwarya Kamath, Johan Ferret, Shreya Pathak, Nino Vieillard, Ramona Merhej, Sarah Perrin, Tatiana Matejovicova, Alexandre Ramé, Morgane Riviere, Louis Rouillard, Thomas Mesnard, Geoffrey Cideron, Jean-bastien Grill, Sabela Ramos, Edouard Yvinec, Michelle Casbon, Elena Buchatskaya, Jean-Baptiste Alayrac, Dmitry, Lepikhin, Vlad Feinberg, Sebastian Borgeaud, Alek Andreev, Cassidy Hardin, Robert Dadashi, Léonard Hussenot, Armand Joulin, Olivier Bachem, Yossi Matias, Katherine Chou, Avinatan Hassidim, Kavi Goel, Clement Farabet, Joelle Barral, Tris Warkentin, Jonathon Shlens, David Fleet, Victor Cotruta, Omar Sanseviero, Gus Martins, Phoebe Kirk, Anand Rao, Shravya Shetty, David F. Steiner, Can Kirmizibayrak, Rory Pilgrim, Daniel Golden, Lin Yang
Artificial intelligence (AI) has significant potential in healthcare applications, but its training and deployment faces challenges due to healthcare’s diverse data, complex tasks, and the need to preserve privacy. Foundation models that perform well on medical tasks and require less task-specific tuning data are critical to accelerate the development of healthcare AI applications. We introduce MedGemma, a collection of medical vision-language foundation models based on Gemma 3 4B and 27B. MedGemma demonstrates advanced medical understanding and reasoning on images and text, significantly exceeding the performance of similar-sized generative models and approaching the performance of task-specific models, while maintaining the general capabilities of the Gemma 3 base models. For out-of-distribution tasks, MedGemma achieves 2.6-10% improvement on medical multimodal question answering, 15.5-18.1% improvement on chest X-ray finding classification, and 10.8% improvement on agentic evaluations compared to the base models. Fine-tuning MedGemma further improves performance in subdomains, reducing errors in electronic health record information retrieval by 50% and reaching comparable performance to existing specialized state-of-the-art methods for pneumothorax classification and histopathology patch classification. We additionally introduce MedSigLIP, a medically-tuned vision encoder derived from SigLIP. MedSigLIP powers the visual understanding capabilities of MedGemma and as an encoder achieves comparable or better performance than specialized medical image encoders. Taken together, the MedGemma collection provides a strong foundation of medical image and text capabilities, with potential to significantly accelerate medical research and development of downstream applications. The MedGemma collection, including tutorials and model weights, can be found at https://goo.gle/medgemma.
人工智能(AI)在医疗应用方面拥有巨大的潜力,但由于医疗数据的多样性、任务的复杂性以及需要保护隐私,其在训练和部署方面面临挑战。能够在医疗任务上表现良好且需要较少任务特定调整数据的基础模型,对于加速医疗AI应用的开发至关重要。我们引入了MedGemma,这是一系列基于Gemma 3 4B和27B的医疗视觉语言基础模型的集合。MedGemma展示了先进的医疗理解和推理能力,在图像和文本上超越了类似大小的生成模型的性能,并接近任务特定模型的性能,同时保持了Gemma 3基础模型的通用能力。对于离分布任务,MedGemma在医疗多模式问答上实现了2.6-10%的改进,在胸部X射线检查结果分类上实现了15.5-18.1%的改进,在智能评估上实现了10.8%的改进,相较于基础模型有所提升。进一步微调MedGemma可以在子域中提高性能,将电子病历信息检索中的错误减少50%,并达到气胸分类和组织学斑块分类的现有最新专业方法的可比性能。此外,我们还引入了MedSigLIP,这是一个经过医学调整的视觉编码器,源于SigLIP。MedSigLIP为MedGemma的视觉理解能力提供支持,作为编码器,其性能与专用医疗图像编码器相当或更好。总体而言,MedGemma系列提供了强大的医疗图像和文本能力基础,具有加速医疗研究和下游应用开发的巨大潜力。MedGemma系列,包括教程和模型权重,可以在https://goo.gle/medgemma找到。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
AI在医疗保健应用方面具有巨大潜力,但其训练和部署面临多样化数据、复杂任务和隐私保护等方面的挑战。我们引入MedGemma,这是一款基于Gemma 3 4B和27B的医疗视觉语言基础模型集合。MedGemma在图像和文本上展现出高级医疗理解和推理能力,其性能显著优于类似大小的生成模型,并接近任务特定模型的性能,同时保持Gemma 3基础模型的通用能力。对于离群任务,MedGemma在医疗多模式问答、胸部X射线发现分类和智能体评估等方面相比基础模型有所改善。微调MedGemma可进一步提高子域的性能,减少电子健康记录信息检索中的错误,并达到气胸分类和组织学斑块分类的现有专业最先进方法的性能。此外,我们还引入了MedSigLIP,这是一个经过医学调整的视觉编码器。作为编码器,MedSigLIP在MedGemma的视觉理解能力方面具有强大作用,其性能可与专业医疗图像编码器相当或更好。总的来说,MedGemma集合为医疗图像和文本功能提供了坚实的基础,具有加速医学研究并推动下游应用开发潜力。可以在goo.gle/medgemma找到MedGemma集合(包括教程和模型权重)。
关键见解
- AI在医疗保健应用中有巨大潜力,但面临数据多样性和隐私保护等挑战。
- MedGemma是一个基于医疗视觉语言的基础模型集合,展现出高级医疗理解和推理能力。
- MedGemma相较于类似大小的生成模型有更好的性能表现,并在某些任务上接近任务特定模型。
- MedGemma在处理离群任务时表现出优异的性能改进。
- 通过微调MedGemma可进一步提高性能,特别是在特定子域中。
- MedSigLIP是一个经过医学调整的视觉编码器,为MedGemma的视觉理解能力提供了强大支持。
点此查看论文截图

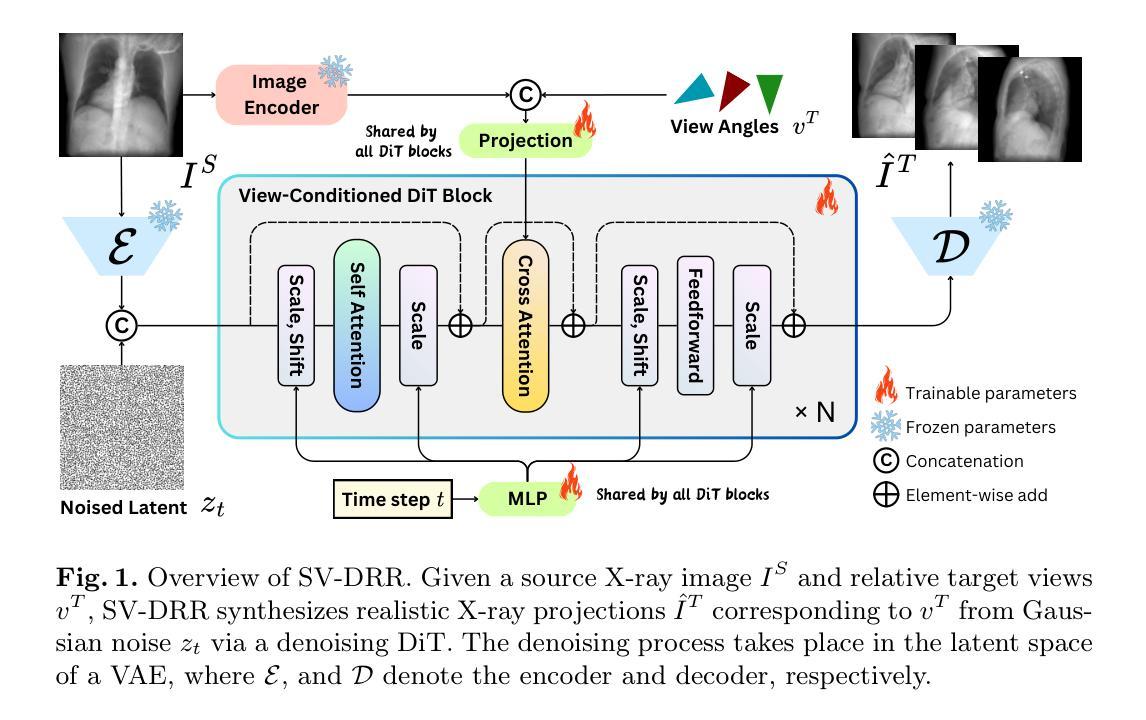
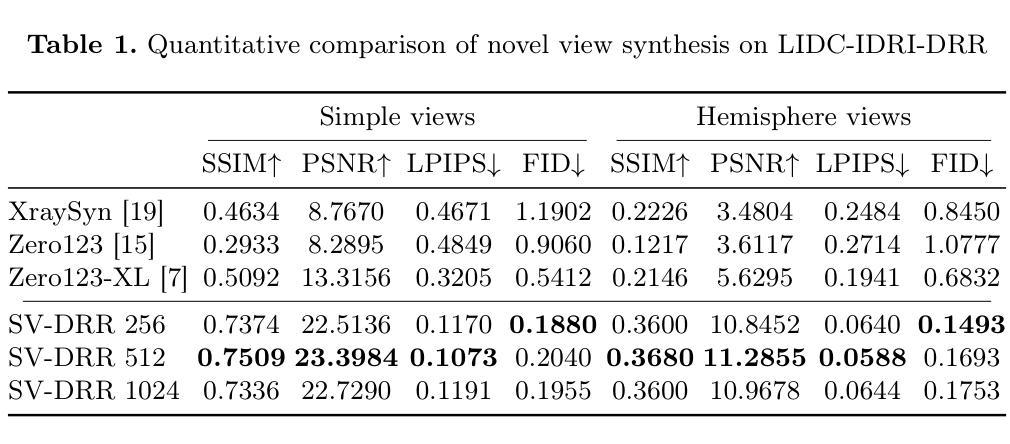
SV-DRR: High-Fidelity Novel View X-Ray Synthesis Using Diffusion Model
Authors:Chun Xie, Yuichi Yoshii, Itaru Kitahara
X-ray imaging is a rapid and cost-effective tool for visualizing internal human anatomy. While multi-view X-ray imaging provides complementary information that enhances diagnosis, intervention, and education, acquiring images from multiple angles increases radiation exposure and complicates clinical workflows. To address these challenges, we propose a novel view-conditioned diffusion model for synthesizing multi-view X-ray images from a single view. Unlike prior methods, which are limited in angular range, resolution, and image quality, our approach leverages the Diffusion Transformer to preserve fine details and employs a weak-to-strong training strategy for stable high-resolution image generation. Experimental results demonstrate that our method generates higher-resolution outputs with improved control over viewing angles. This capability has significant implications not only for clinical applications but also for medical education and data extension, enabling the creation of diverse, high-quality datasets for training and analysis. Our code is available at GitHub.
X射线成像是一种快速且成本效益高的工具,用于可视化人体内部结构。虽然多视角X射线成像提供了补充信息,增强了诊断、干预和教育,但从多个角度获取图像增加了辐射暴露并使得临床工作流程复杂化。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种基于扩散模型的新型视角合成方法,可以从单一视角合成多视角X射线图像。不同于先前在角度范围、分辨率和图像质量方面有限的方法,我们的方法利用扩散变压器来保留细节,并采用由弱到强的训练策略来进行稳定的高分辨率图像生成。实验结果表明,我们的方法生成了更高分辨率的输出,并增强了对比控制视角的能力。这项能力不仅在临床应用方面有着重大意义,也在医疗教育和数据扩展方面有着巨大潜力,能够创建多样且高质量的数据集用于训练和数据分析。我们的代码可在GitHub上获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by MICCAI2025
Summary
本文提出一种基于扩散模型的新型多视角X射线图像合成方法,可从单一视角合成多视角X射线图像。该方法利用扩散变压器保存细节,采用由弱至强的训练策略实现稳定的高分辨率图像生成。实验结果表明,该方法生成的高分辨率图像具有更好的视角控制力,对临床应用、医学教育和数据扩展具有重要意义。
Key Takeaways
- X射线成像是一种快速、经济的内部人体结构可视化工具。
- 多视角X射线成像能够提供互补信息,增强诊断、干预和教育的效果。
- 现有方法在多视角X射线图像合成方面存在角度范围、分辨率和图像质量的局限。
- 本文提出了一种基于扩散模型的新型合成方法,利用扩散变压器保存细节并实现高分辨率图像生成。
- 该方法采用由弱至强的训练策略,实现了稳定的高分辨率图像生成和对视角的良好控制。
- 实验结果表明,该方法生成的高分辨率图像具有更好的视角控制力,在多个领域具有潜在应用,如临床应用、医学教育和数据扩展等。
点此查看论文截图

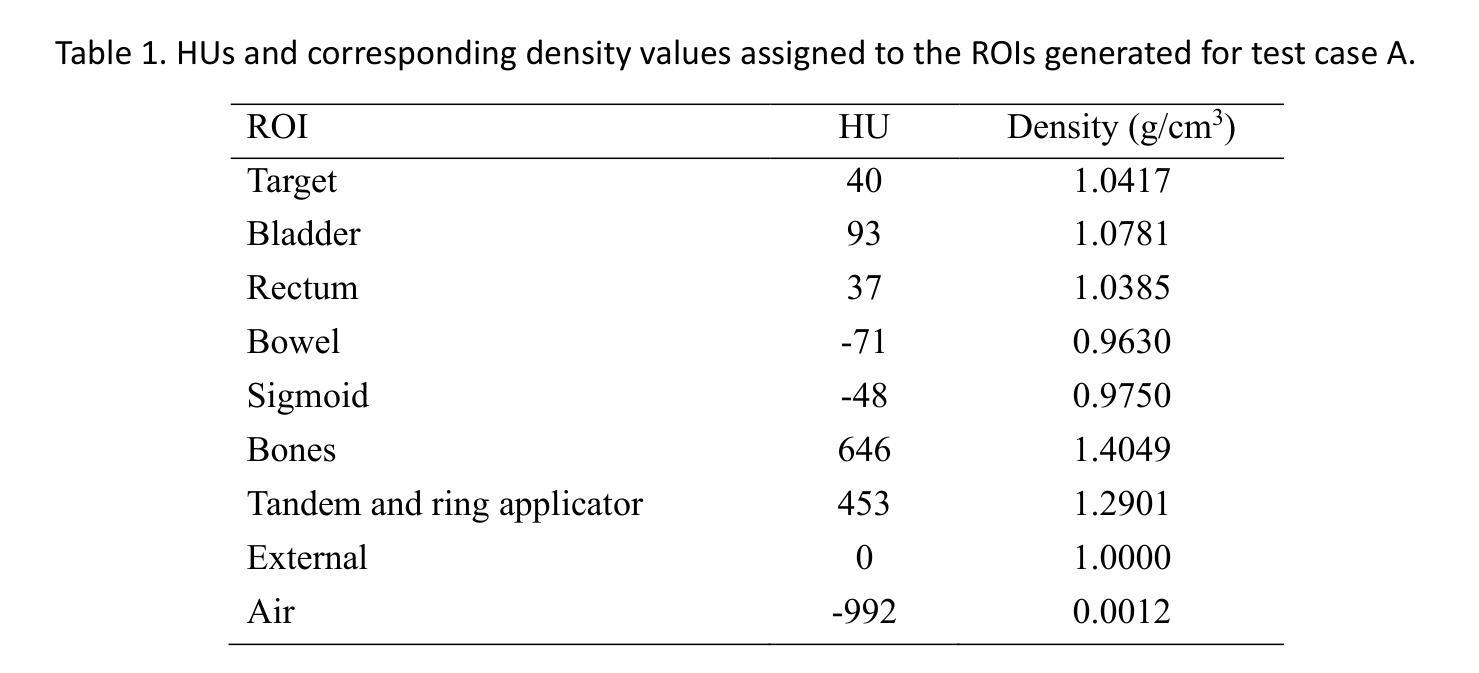
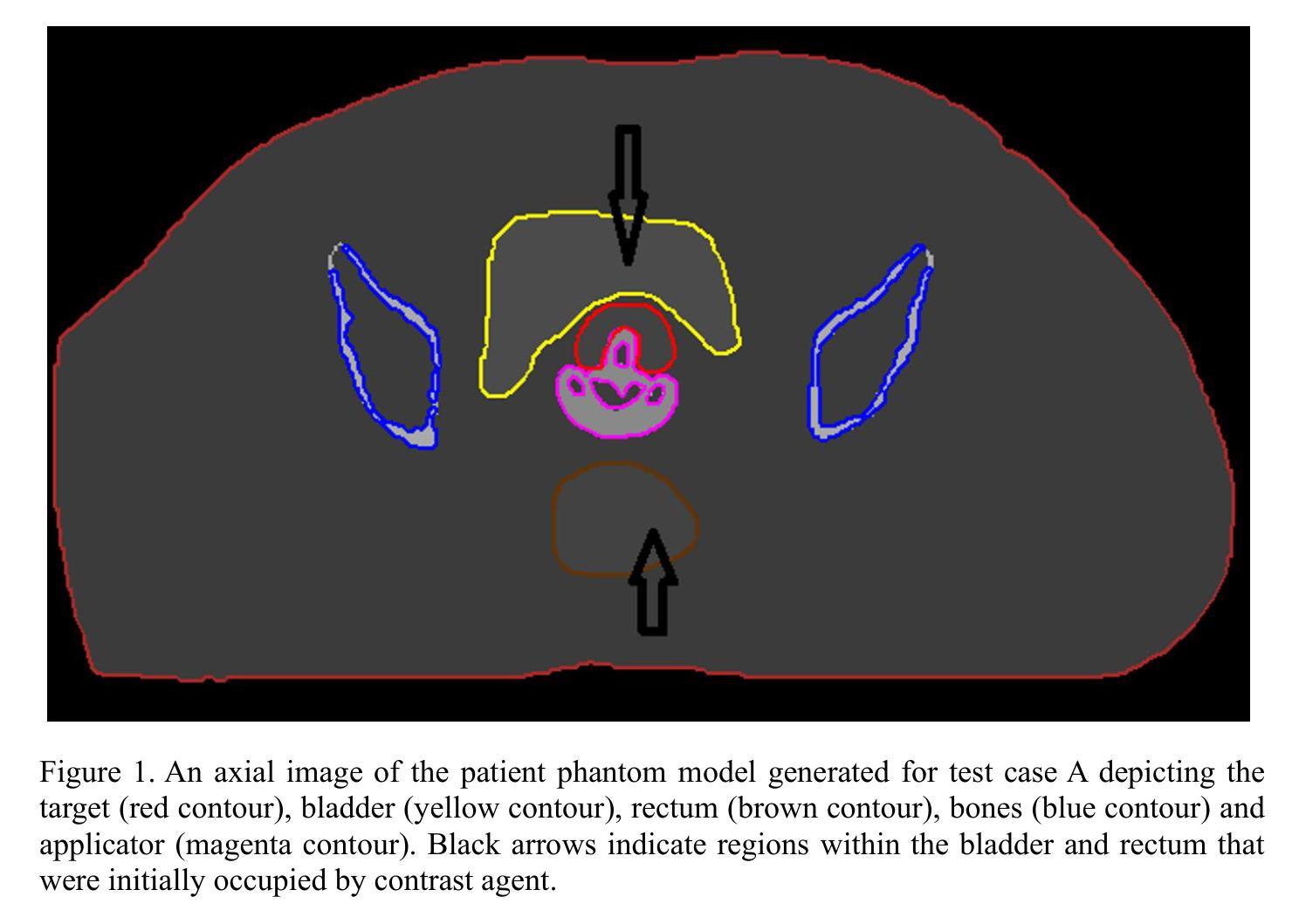
Clinical test cases for model-based dose calculation algorithm commissioning, QA and benchmarking, for 192Ir HDR brachytherapy of gynecologic cancers
Authors:V. Peppa, M. Robitaille, F. Akbari, S. A. Enger, R. M. Thomson, F. Mourtada, G. P. Fonseca
Purpose: To develop clinically relevant test cases for commissioning Model-Based Dose Calculation Algorithms (MBDCAs) for 192Ir High Dose Rate (HDR) gynecologic brachytherapy following the workflow proposed by the TG-186 report and the WGDCAB report 372. Acquisition and Validation Methods: Two cervical cancer intracavitary HDR brachytherapy patient models were created, using either uniformly structured regions or realistic segmentation. The computed tomography (CT) images of the models were converted to DICOM CT images via MATLAB and imported into two Treatment Planning Systems (TPSs) with MBDCA capability. The clinical segmentation was expanded to include additional organs at risk. The actual clinical treatment plan was generally maintained, with the source replaced by a generic 192Ir HDR source. Dose to medium in medium calculations were performed using the MBDCA option of each TPS, and three different Monte Carlo (MC) simulation codes. MC results agreed within statistical uncertainty, while comparisons between MBDCA and MC dose distributions highlighted both strengths and limitations of the studied MBDCAs, suggesting potential approaches to overcome the challenges. Data Format and Usage Notes: The datasets for the developed cases are available online at http://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.15720996. The DICOM files include the treatment plan for each case, TPS, and the corresponding reference MC dose data. The package also contains a TPS- and case-specific user guide for commissioning the MBDCAs, and files needed to replicate the MC simulations. Potential Applications: The provided datasets and proposed methodology offer a commissioning framework for TPSs using MBDCAs, and serve as a benchmark for brachytherapy researchers using MC methods. They also facilitate intercomparisons of MBDCA performance and provide a quality assurance resource for evaluating future TPS software updates.
目的:根据TG-186报告和WGDCAB报告372提出的工作流程,为基于模型的剂量计算算法(MBDCAs)开发适用于临床的测试用例,这些算法用于192Ir高剂量率(HDR)妇科腔内近距离放射治疗。
获取和验证方法:创建了两个宫颈癌HDR腔内近距离放射治疗患者模型,这些模型采用均匀结构化区域或现实分割。将模型计算机断层扫描(CT)图像通过MATLAB转换为DICOM CT图像,并导入两个具备MBDCA功能的放射治疗计划系统(TPS)。临床分割被扩展以包括额外的风险器官。实际的临床治疗计划基本保持不变,源被替换为通用的192Ir HDR源。使用每个TPS的MBDCA选项和三种不同的蒙特卡洛(MC)模拟代码,对介质中的剂量进行剂量计算。MC结果符合统计不确定性,而MBDCA和MC剂量分布的比较突出了所研究MBDCA的优势和局限性,这暗示了克服这些挑战的可能方法。
数据格式和使用注意事项:所开发案例的数据集可通过http://doi.org/在线获取。DICOM文件包含每个案例的治疗计划、TPS和相应的参考MC剂量数据。该软件包还包含针对TPS和案例特定的用户指南,用于调试MBDCAs,以及复制MC模拟所需的文件。潜在应用:所提供的数据集和提出的方法为使用MBDCAs的TPS提供了一个调试框架,并为使用MC方法的近距离放射治疗研究者提供了一个基准。它们还促进了MBDCA性能的相互比较,并为评估未来的TPS软件更新提供了一个质量保证资源。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To be published in Medical Physics
Summary
本文介绍了基于模型剂量计算算法(MBDCA)的192Ir高剂量率(HDR)妇科腔内近距离治疗的测试案例开发。通过创建两个宫颈癌HDR腔内近距离治疗患者模型,对MBDCA进行了验证和评估。通过蒙特卡洛(MC)模拟与MBDCA的比较,揭示了MBDCA的优势和局限性,并提出了克服挑战的方法。提供的数据集和方法为TPS系统提供了委托框架,并为近距离治疗研究者提供了基准测试资源。
Key Takeaways
- 利用MBDCAs对HDR妇科腔内近距离治疗进行建模测试案例开发。
- 创建了两个宫颈癌HDR腔内近距离治疗患者模型进行验证。
- 通过MATLAB将CT图像转换为DICOM CT图像,并导入具有MBDCA功能的两个治疗计划系统(TPS)。
- 临床分割扩展到包括额外的风险器官在内。
- 使用MBDCA选项和三种不同的蒙特卡洛模拟代码进行剂量计算。
- MC结果与MBDCA之间的比较揭示了MBDCA的优势和局限性。
点此查看论文截图

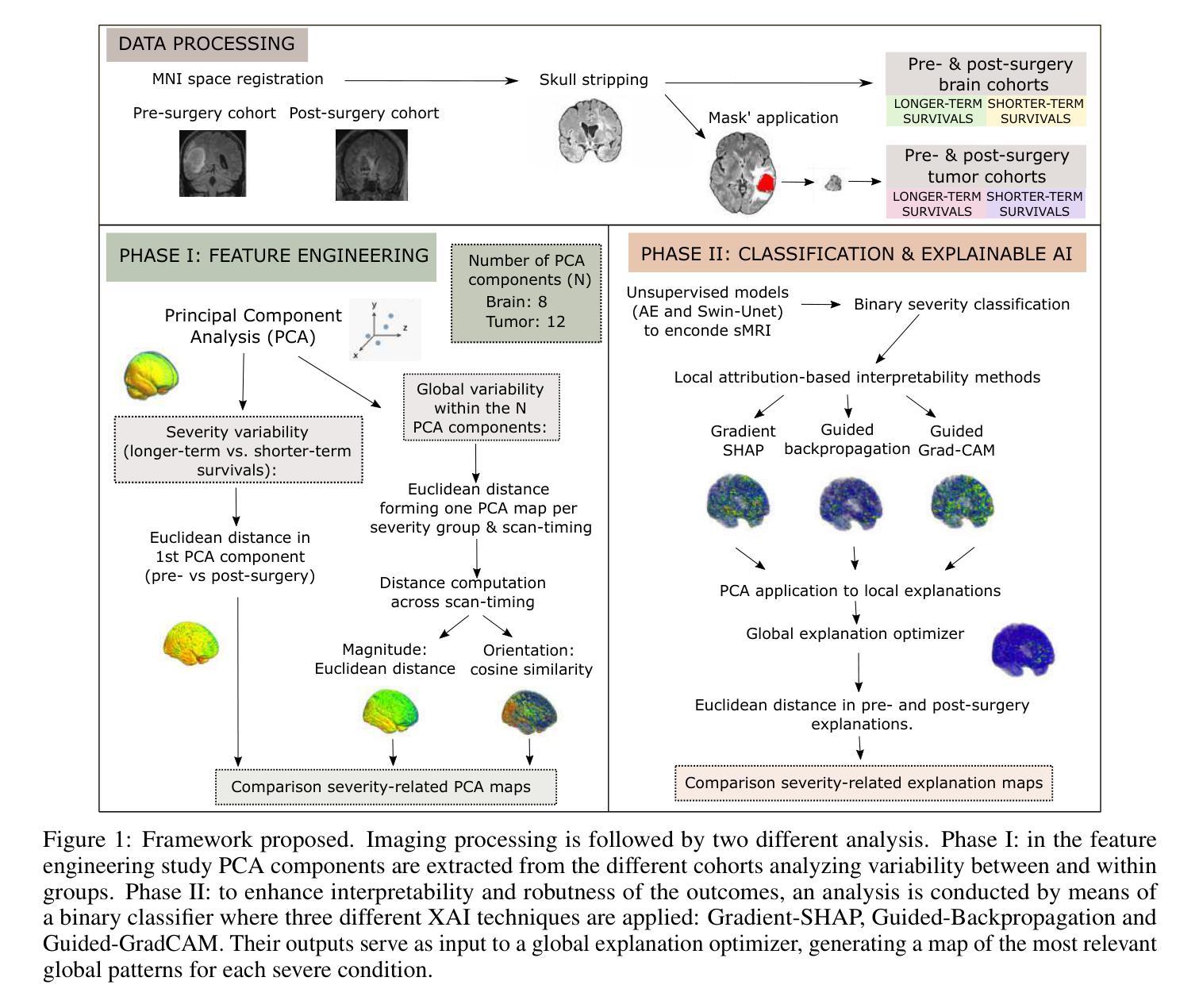
Uncovering Neuroimaging Biomarkers of Brain Tumor Surgery with AI-Driven Methods
Authors:Carmen Jimenez-Mesa, Yizhou Wan, Guilio Sansone, Francisco J. Martinez-Murcia, Javier Ramirez, Pietro Lio, Juan M. Gorriz, Stephen J. Price, John Suckling, Michail Mamalakis
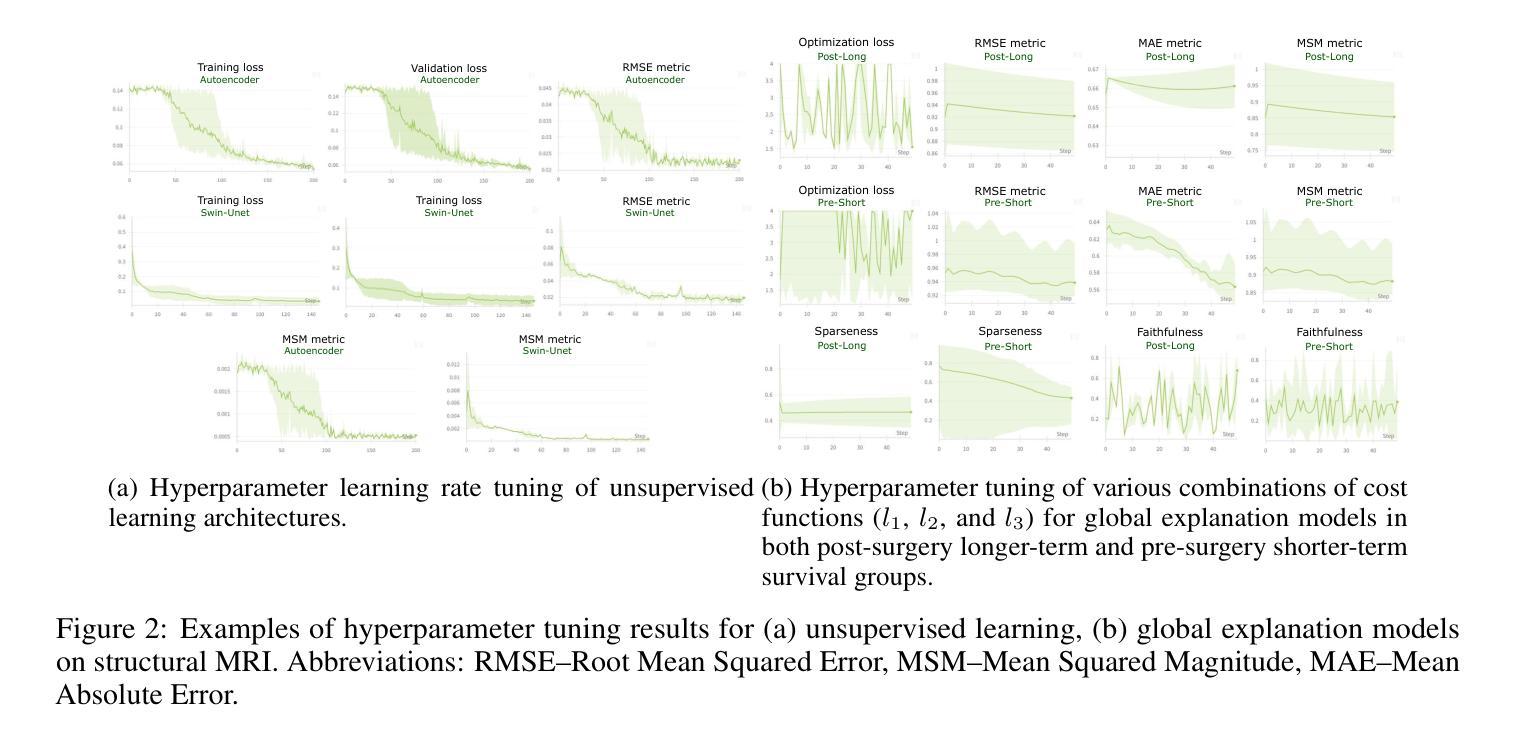
Brain tumor resection is a complex procedure with significant implications for patient survival and quality of life. Predictions of patient outcomes provide clinicians and patients the opportunity to select the most suitable onco-functional balance. In this study, global features derived from structural magnetic resonance imaging in a clinical dataset of 49 pre- and post-surgery patients identified potential biomarkers associated with survival outcomes. We propose a framework that integrates Explainable AI (XAI) with neuroimaging-based feature engineering for survival assessment, offering guidance for surgical decision-making. In this study, we introduce a global explanation optimizer that refines survival-related feature attribution in deep learning models, enhancing interpretability and reliability. Our findings suggest that survival is influenced by alterations in regions associated with cognitive and sensory functions, indicating the importance of preserving areas involved in decision-making and emotional regulation during surgery to improve outcomes. The global explanation optimizer improves both fidelity and comprehensibility of explanations compared to state-of-the-art XAI methods. It effectively identifies survival-related variability, underscoring its relevance in precision medicine for brain tumor treatment.
脑肿瘤切除是一种对患者生存和生活质量有重大影响的复杂手术。预测患者预后为临床医生和患者提供了选择最适当肿瘤功能平衡的机会。本研究从临床数据集中收集了来自结构磁共振成像的全身特征,这些数据集包含49名手术前后的患者,并识别了与生存结果相关的潜在生物标志物。我们提出了一种将可解释的AI(XAI)与基于神经成像的特征工程相结合的框架,用于生存评估,为手术决策提供了指导。在本研究中,我们引入了一种全局解释优化器,对深度学习模型中的生存相关特征属性进行精炼,提高了可解释性和可靠性。我们的研究结果表明,生存受到与认知和感觉功能相关区域的改变的影响,这表明在手术过程中保留参与决策和情绪调节的区域对于改善结果至关重要。与最新的XAI方法相比,全局解释优化器提高了解释的保真度和易懂性。它有效地识别了与生存相关的变异性,强调了其在脑肿瘤治疗的精准医学中的相关性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了脑肿瘤切除手术对患者生存和生活质量的影响,并提出了一种结合可解释人工智能(XAI)和神经成像特征工程的生存评估框架,为手术决策提供支持。研究发现,生存与认知和情感功能区域的改变有关,全局解释优化器能提高深度学习模型的解释性和可靠性,有效识别与生存相关的变量。
Key Takeaways
- 脑肿瘤切除手术对患者的生存和生活质量有重要影响。
- 结合可解释人工智能(XAI)和神经成像特征工程可评估患者生存情况。
- 生存与认知和情感功能区域的改变有关。
- 全局解释优化器提高了深度学习模型的解释性和可靠性。
- 该优化器能有效识别与生存相关的变量。
- 全局解释优化器在精确医学领域,特别是在脑肿瘤治疗中有重要应用。
点此查看论文截图

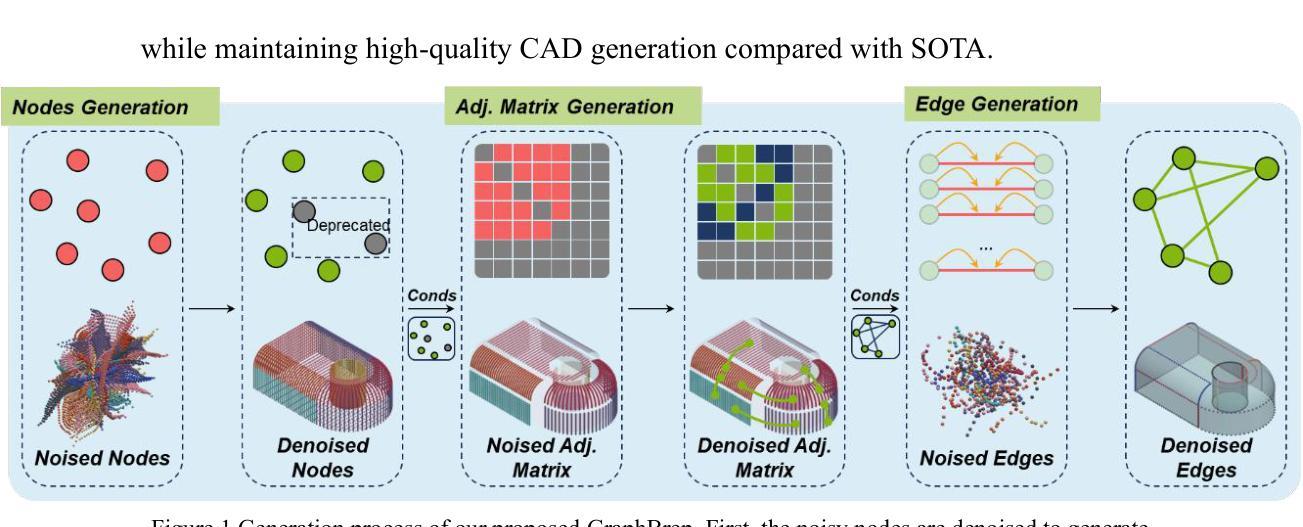
GraphBrep: Learning B-Rep in Graph Structure for Efficient CAD Generation
Authors:Weilin Lai, Tie Xu, Hu Wang
Direct B-Rep generation is increasingly important in CAD workflows, eliminating costly modeling sequence data and supporting complex features. A key challenge is modeling joint distribution of the misaligned geometry and topology. Existing methods tend to implicitly embed topology into the geometric features of edges. Although this integration ensures feature alignment, it also causes edge geometry to carry more redundant structural information compared to the original B-Rep, leading to significantly higher computational cost. To reduce redundancy, we propose GraphBrep, a B-Rep generation model that explicitly represents and learns compact topology. Following the original structure of B-Rep, we construct an undirected weighted graph to represent surface topology. A graph diffusion model is employed to learn topology conditioned on surface features, serving as the basis for determining connectivity between primitive surfaces. The explicit representation ensures a compact data structure, effectively reducing computational cost during both training and inference. Experiments on two large-scale unconditional datasets and one category-conditional dataset demonstrate the proposed method significantly reduces training and inference times (up to 31.3% and 56.3% for given datasets, respectively) while maintaining high-quality CAD generation compared with SOTA.
直接B-Rep生成在CAD工作流程中越来越重要,它消除了昂贵的建模序列数据并支持复杂特征。一个关键挑战是对错位几何和拓扑进行联合分布建模。现有方法倾向于将拓扑隐式嵌入到边缘的几何特征中。虽然这种集成确保了特征对齐,但也导致边缘几何携带了比原始B-Rep更多的冗余结构信息,从而产生了更高的计算成本。为了减少冗余,我们提出了GraphBrep,这是一种显式表示并学习紧凑拓扑的B-Rep生成模型。遵循B-Rep的原始结构,我们构建了一个无向加权图来表示表面拓扑。采用图扩散模型来学习基于表面特征的拓扑,作为确定原始表面之间连接性的基础。显式表示确保了一个紧凑的数据结构,有效地减少了训练和推理过程中的计算成本。在两个大规模无条件数据集和一个类别条件数据集上的实验表明,所提出的方法显著减少了训练和推理时间(对于给定数据集分别最多减少31.3%和56.3%),同时保持与最新技术相当的高质量CAD生成。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
直接B-Rep生成在CAD工作流程中日益重要,能够消除昂贵的建模序列数据并支持复杂特征。现有方法倾向于将拓扑隐含地嵌入边缘的几何特征中,导致边缘几何携带了与原始B-Rep相比更多的冗余结构信息,从而增加了计算成本。为解决此问题,本文提出了GraphBrep模型,它显式表示并学习紧凑拓扑。我们按照B-Rep的原始结构构建了一个无向加权图来表示表面拓扑,并使用图扩散模型来学习基于表面特征的拓扑,作为确定基本表面之间连接性的基础。显式表示确保了紧凑的数据结构,在训练和推理期间有效降低了计算成本。实验表明,该方法在大型无条件数据集和类别条件数据集上的训练时间和推理时间分别减少了最多达31.3%和56.3%,同时保持了高质量的CAD生成效果。
Key Takeaways
- 直接B-Rep生成在CAD流程中的重要性在于消除昂贵的建模序列数据并支持复杂特征。
- 现有方法将拓扑隐含嵌入边缘几何特征中,导致边缘几何携带冗余结构信息。
- GraphBrep模型被提出以显式表示并学习紧凑拓扑,通过构建无向加权图表示表面拓扑。
- 图扩散模型用于学习基于表面特征的拓扑,作为确定基本表面之间连接性的基础。
- 显式表示确保紧凑的数据结构,有效降低训练和推理期间的计算成本。
- 实验结果显示,GraphBrep模型在大型数据集上显著减少了训练时间和推理时间。
点此查看论文截图

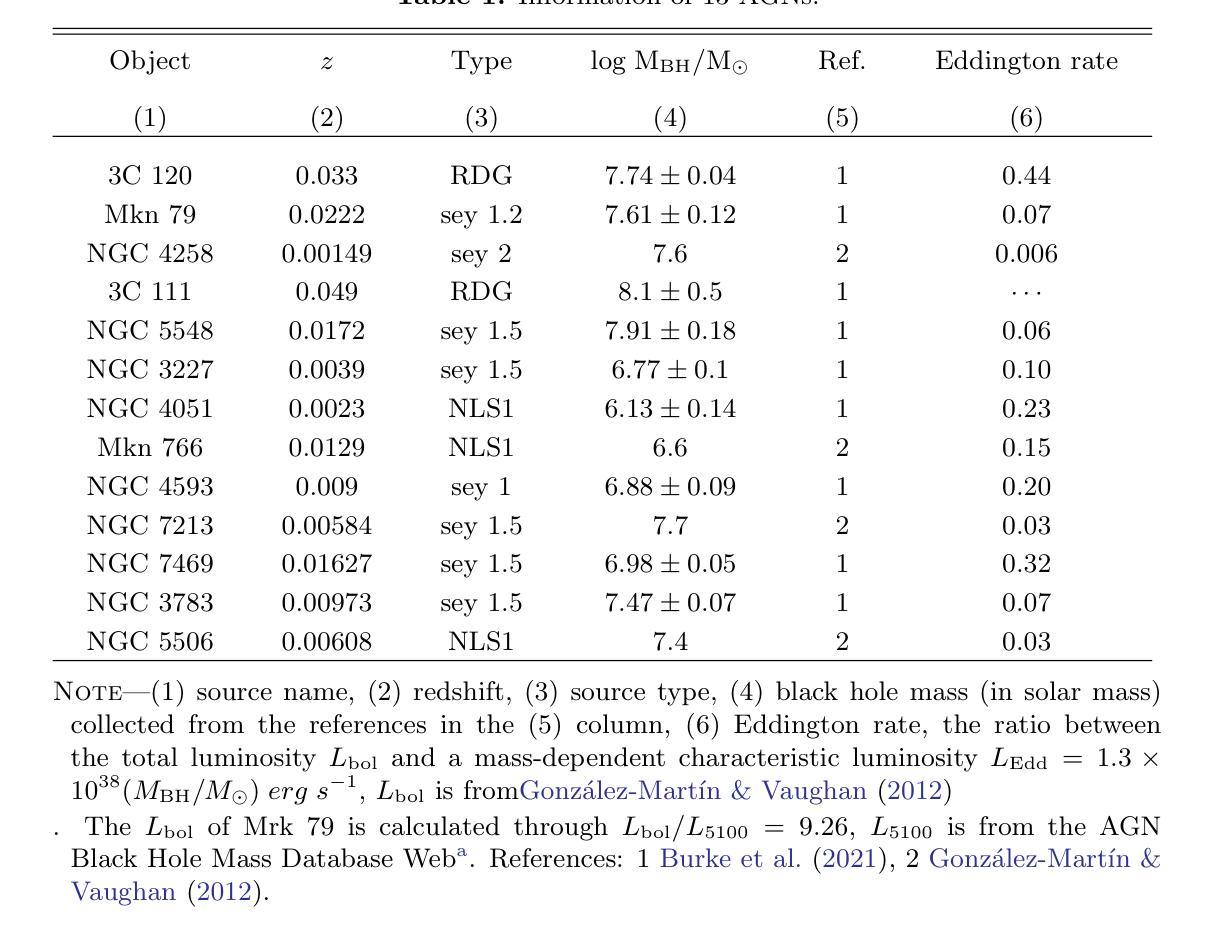
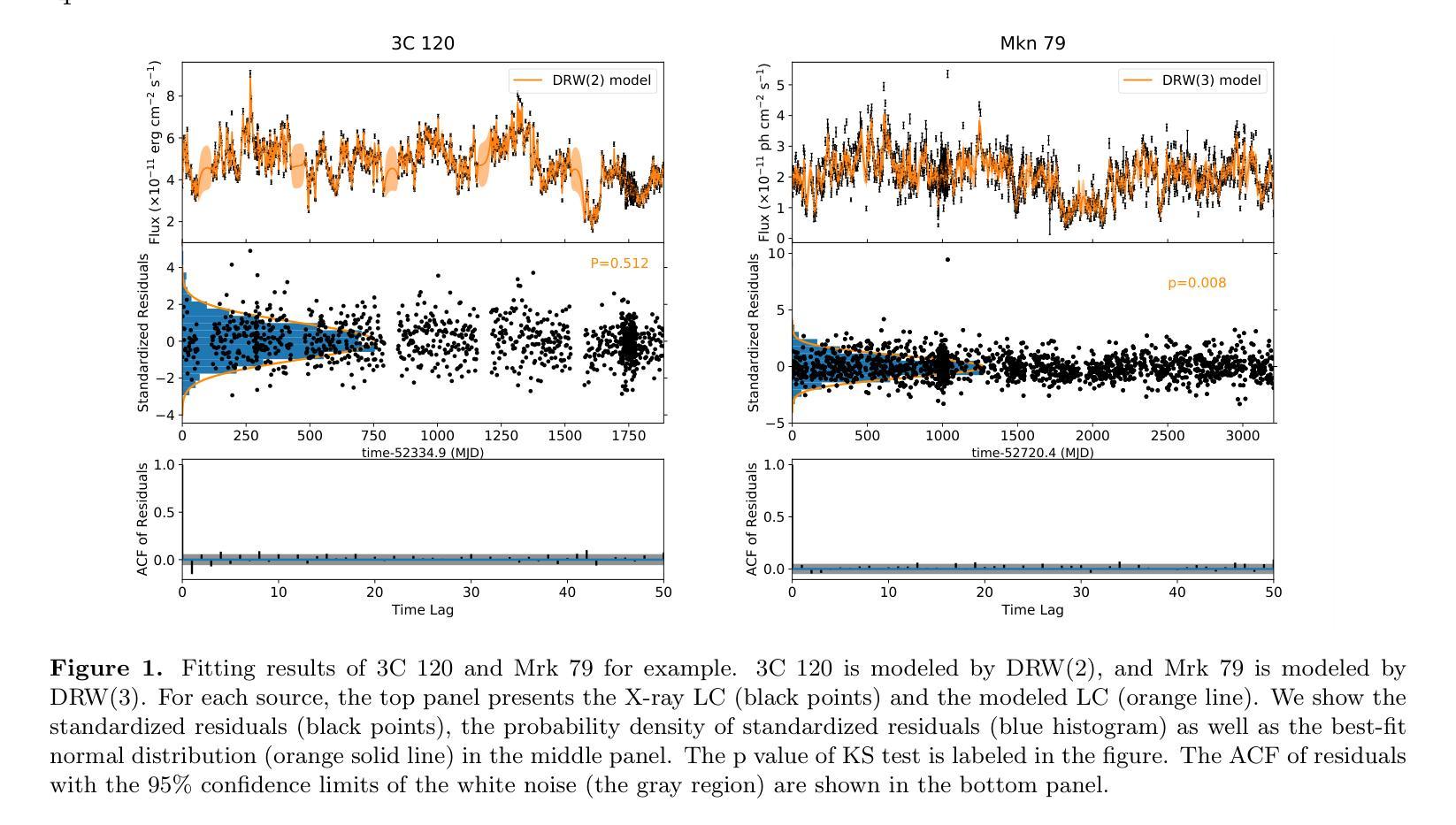
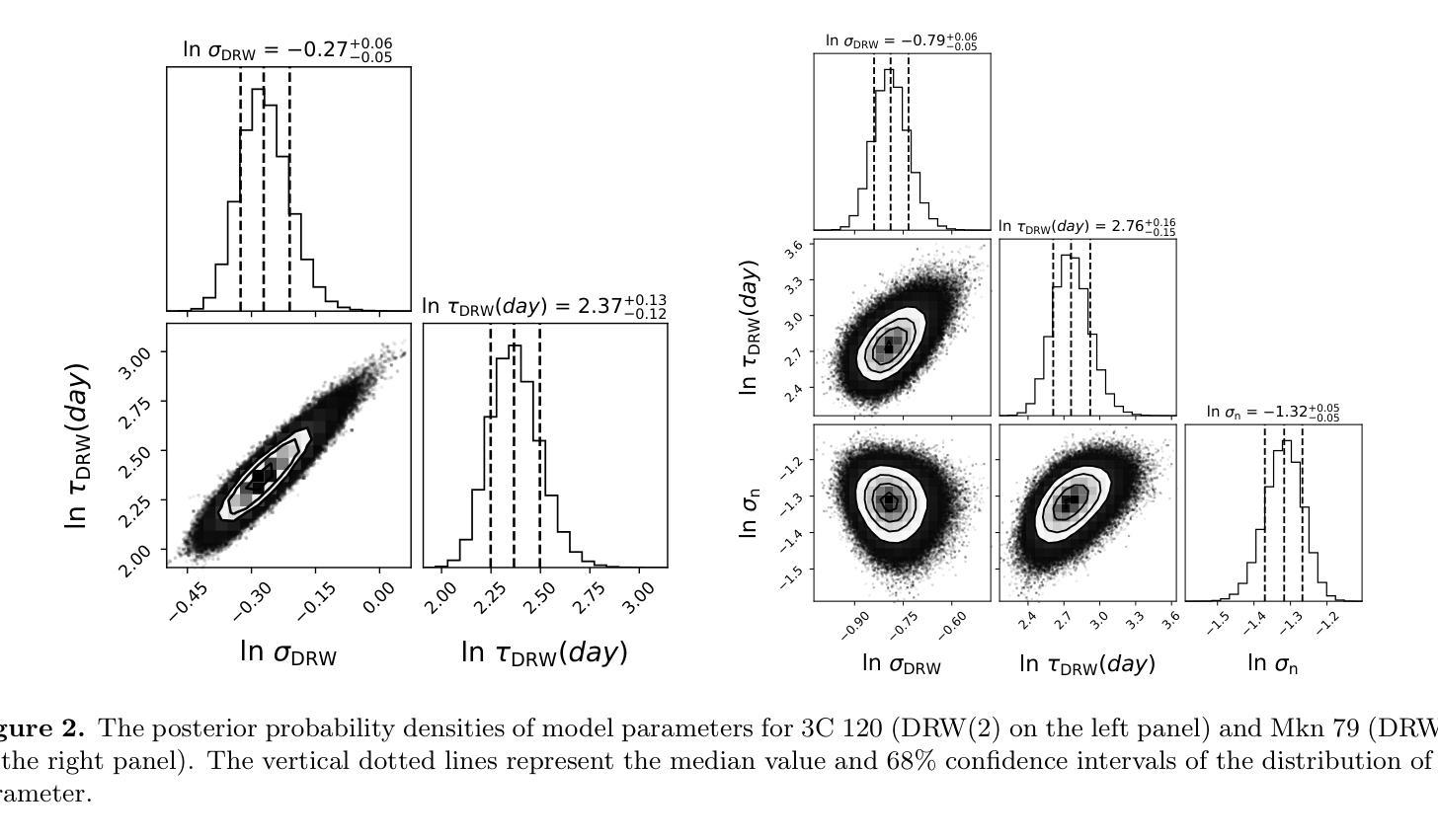
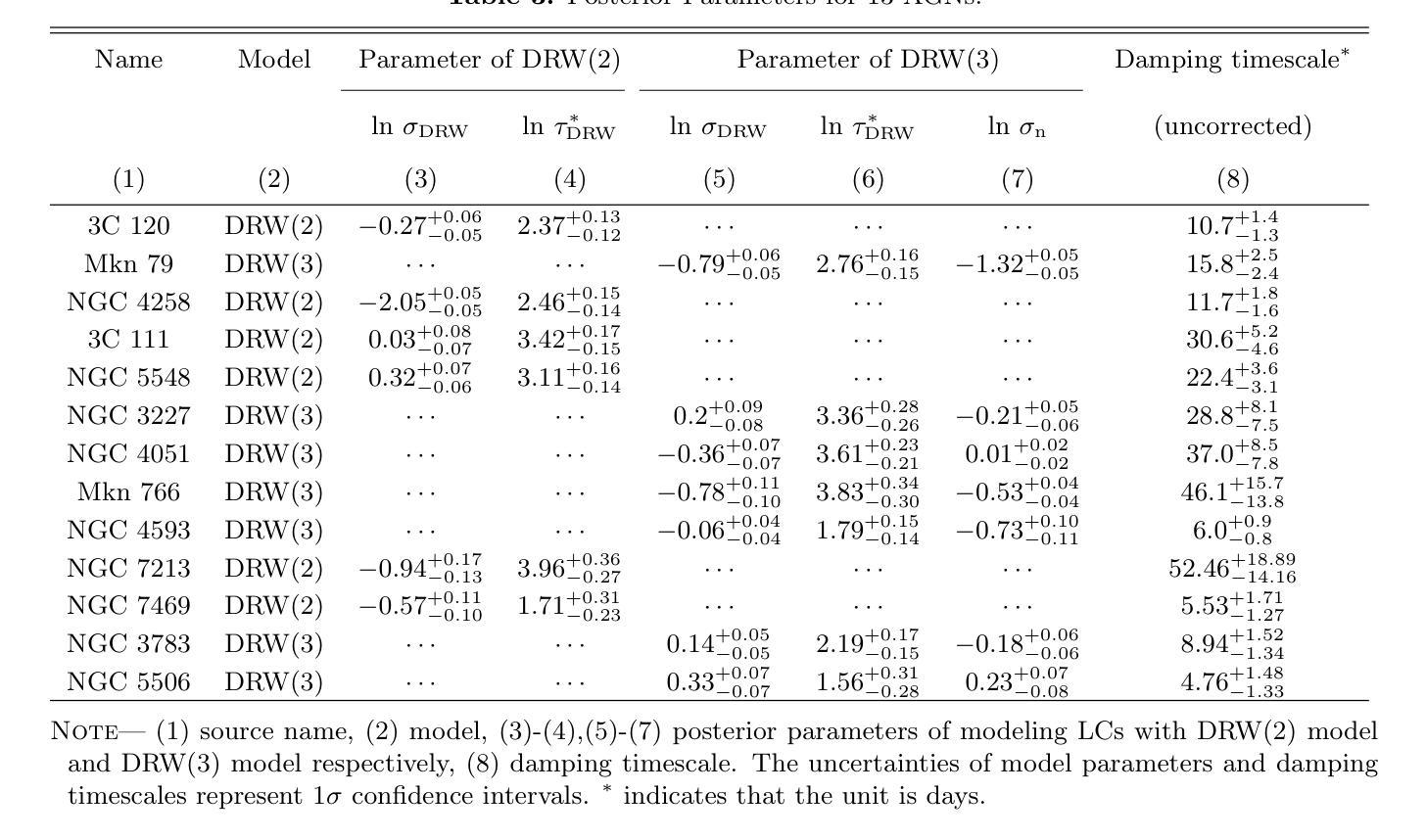
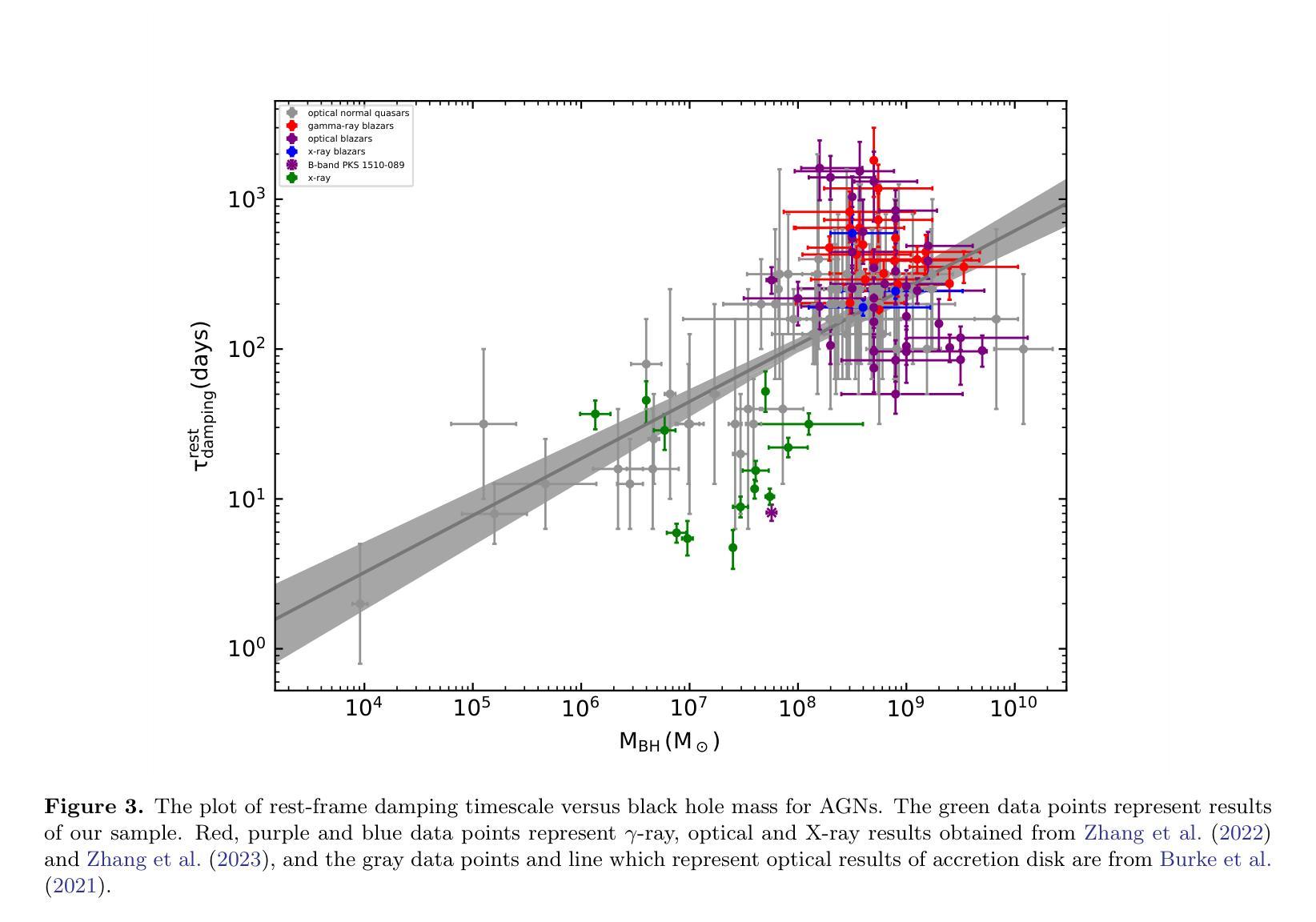
Gaussian Process Modeling Coronal X-ray Variability of Active Galactic Nuclei
Authors:Haiyun Zhang, Dahai Yan, Li Zhang, Niansheng Tang
The corona is an integral component of active galactic nuclei (AGNs) which can produce the X-ray emission. However, many of its physical properties and the mechanisms powering this emission remain a mystery. In this work, we study the coronal X-ray variabilities of 13 AGNs by Gaussian Process. 2-10 keV light curves of 13 AGNs can be successfully described by the damped-random walk (DRW) model. The extracted coronal X-ray timescales range from 3 to 50 days. In the plot of variability timescale versus black hole mass, the coronal X-ray timescales of four sources occupy almost the same region as the optical timescales of the accretion disk, with the latter matching the predicted thermal instability timescale of the disk. In contrast, the X-ray timescales of the remaining sources exhibit a systematic offset toward lower values. We propose that the coronal X-ray variability may be driven by internal processes within the corona itself (such as thermal conduction). On the other hand, it may also be triggered by local thermal instabilities occurring in different regions (close to the central black hole) of the accretion disk, which propagate to the corona via disk-corona coupling.
星冕是活动星系核(AGNs)的重要组成部分,能够产生X射线发射。然而,关于其许多物理性质和驱动这种发射的机制仍然是个谜。在这项工作中,我们使用高斯过程研究了13个活动星系核的X射线可变性。这13个活动星系核的2-10 keV光变曲线可以通过阻尼随机游走(DRW)模型成功描述。提取的星冕X射线时间尺度范围为3至50天。在时间尺度与黑洞质量的图中,四个源的星冕X射线时间尺度几乎占据与吸积盘光学时间尺度相同的区域,后者与预期的盘热不稳定时间尺度相匹配。相比之下,其余源的X射线时间尺度表现出向较低值的有规律偏移。我们提出,星冕X射线可变性可能是由星冕内部过程本身所驱动的(如热传导)。另一方面,它也可能是由吸积盘不同区域(靠近中心黑洞)发生的局部热不稳定所触发,通过盘冕耦合传播到星冕。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 5 figures, accepted for publication in ApJ
Summary
此文本研究了活跃星系核(AGNs)的X射线发射及其物理特性。通过对13个AGNs的X射线变化性进行高斯过程研究,发现其时间尺度在3至50天之间。部分源的时间尺度与吸积盘的光学时间尺度相似,可能受到热传导等内部过程的影响;而其他源的时间尺度则较低,可能是由吸积盘不同区域的局部热不稳定引起的。
Key Takeaways
- 活跃星系核(AGNs)的X射线发射中,corona起到了关键作用。
- 通过高斯过程研究了13个AGNs的X射线变化性。
- 成功使用阻尼随机游走(DRW)模型描述这些AGNs的X射线光变曲线。
- 提取的coronal X射线时间尺度在3至50天之间。
- 部分源的时间尺度与吸积盘的光学时间尺度相似,可能与内部过程(如热传导)有关。
- 其他源的时间尺度较低,可能是由吸积盘不同区域的局部热不稳定引起的。
点此查看论文截图

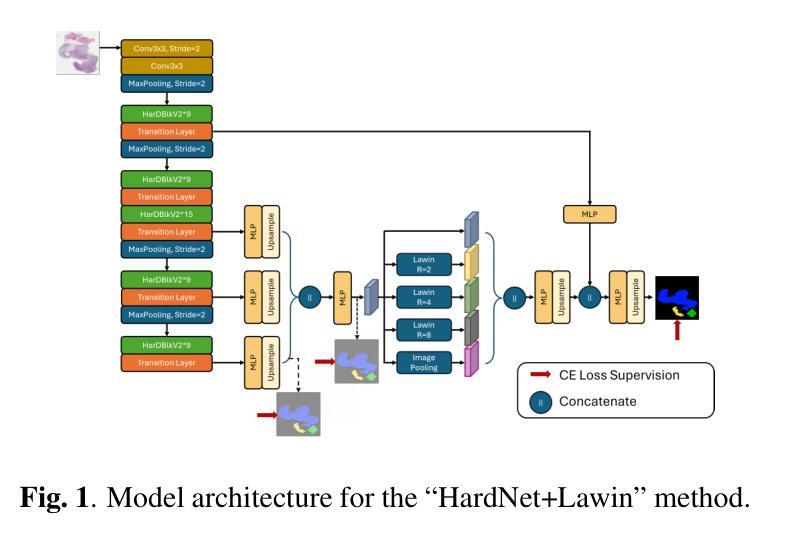
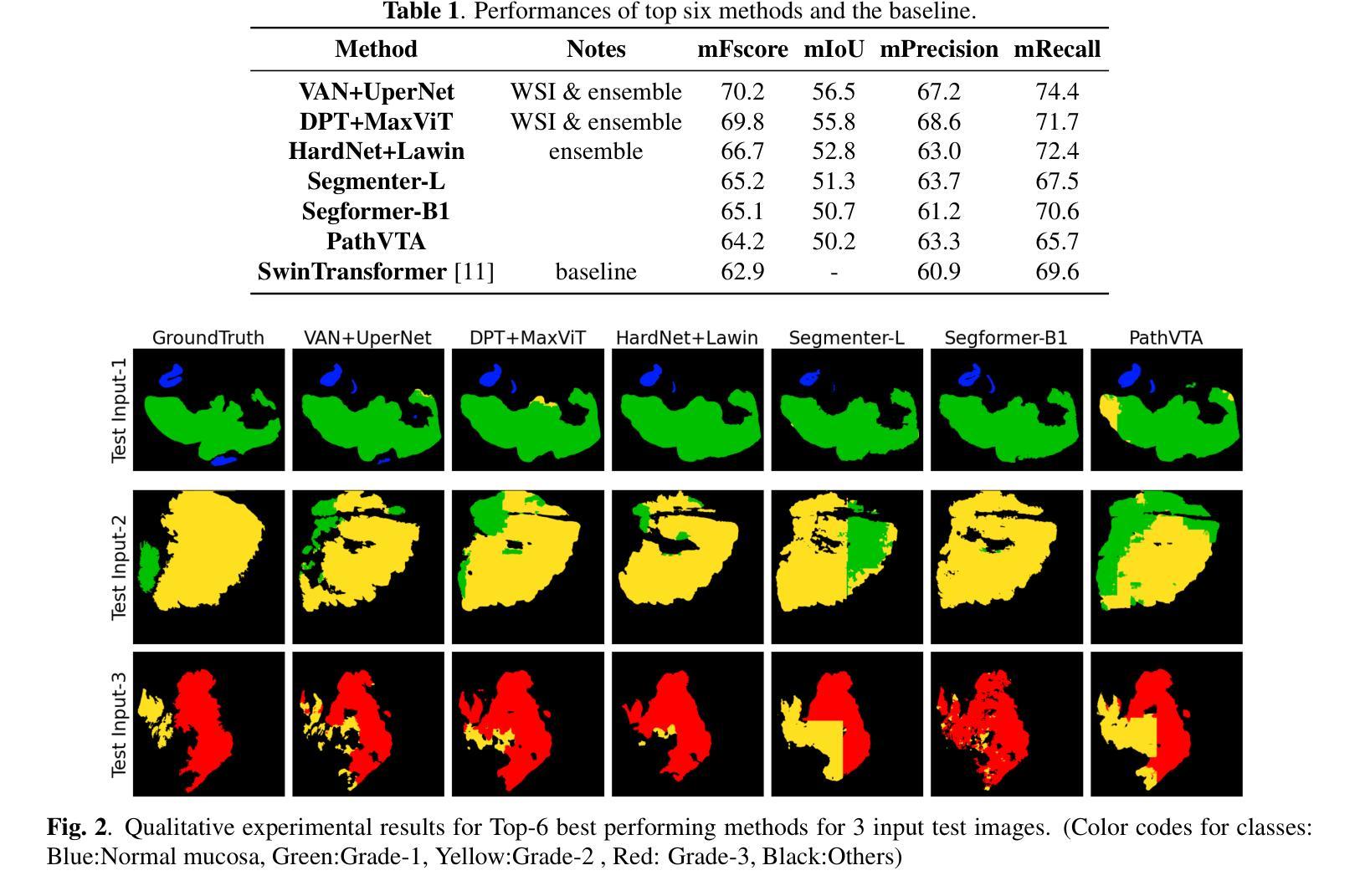
Colorectal Cancer Tumor Grade Segmentation in Digital Histopathology Images: From Giga to Mini Challenge
Authors:Alper Bahcekapili, Duygu Arslan, Umut Ozdemir, Berkay Ozkirli, Emre Akbas, Ahmet Acar, Gozde B. Akar, Bingdou He, Shuoyu Xu, Umit Mert Caglar, Alptekin Temizel, Guillaume Picaud, Marc Chaumont, Gérard Subsol, Luc Téot, Fahad Alsharekh, Shahad Alghannam, Hexiang Mao, Wenhua Zhang
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most diagnosed cancer and the second leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. Accurate histopathological grading of CRC is essential for prognosis and treatment planning but remains a subjective process prone to observer variability and limited by global shortages of trained pathologists. To promote automated and standardized solutions, we organized the ICIP Grand Challenge on Colorectal Cancer Tumor Grading and Segmentation using the publicly available METU CCTGS dataset. The dataset comprises 103 whole-slide images with expert pixel-level annotations for five tissue classes. Participants submitted segmentation masks via Codalab, evaluated using metrics such as macro F-score and mIoU. Among 39 participating teams, six outperformed the Swin Transformer baseline (62.92 F-score). This paper presents an overview of the challenge, dataset, and the top-performing methods
结直肠癌(CRC)是全球诊断率第三高的癌症,也是导致癌症相关死亡的第二大主要原因。CRC的准确组织病理学分级对预后和治疗计划至关重要,但仍是一个主观过程,容易受观察者变异性的影响,并受到全球训练有素病理学家短缺的限制。为了推广自动化和标准化的解决方案,我们使用了公开可用的METU CCTGS数据集,组织了国际图像剖析大奖赛的结直肠癌肿瘤分级和分割挑战赛。该数据集包含103张全幻灯片图像,包含五种组织的专家像素级注释。参赛者通过Codalab提交分割掩膜,使用宏观F分数和mIoU等度量指标进行评估。在3e个参赛团队中,有六个团队的表现超过了Swin Transformer基线(F分数为62.92)。本文介绍了挑战赛、数据集和表现最好的方法概况。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted Grand Challenge Paper ICIP 2025
Summary
本文介绍了结直肠癌(CRC)的全球性诊断与治疗现状,强调准确组织病理学分级对预后和治疗计划的重要性。针对当前存在的观察者主观差异和病理医师全球短缺的问题,介绍了通过举办ICIP Grand Challenge促进的自动化和标准化解决方案。文章还介绍了使用的公开可用的METU CCTGS数据集和评价指标,如宏F分数和mIoU等。在参与挑战的39支队伍中,有六支队伍超越了Swin Transformer基线模型(F分数为62.92)。
Key Takeaways
- 结直肠癌是全球诊断率第三、致死率第二的癌症。
- 准确的组织病理学分级对结直肠癌的预后和治疗计划至关重要。
- 当前组织病理学分级存在观察者主观差异和病理医师全球短缺的问题。
- 为促进自动化和标准化的解决方案,举办了ICIP Grand Challenge。
- 公开的METU CCTGS数据集包含专家像素级标注的五种组织类别的信息,用于训练和评估模型。
- 采用宏F分数和mIoU等评价指标来衡量模型性能。
点此查看论文截图

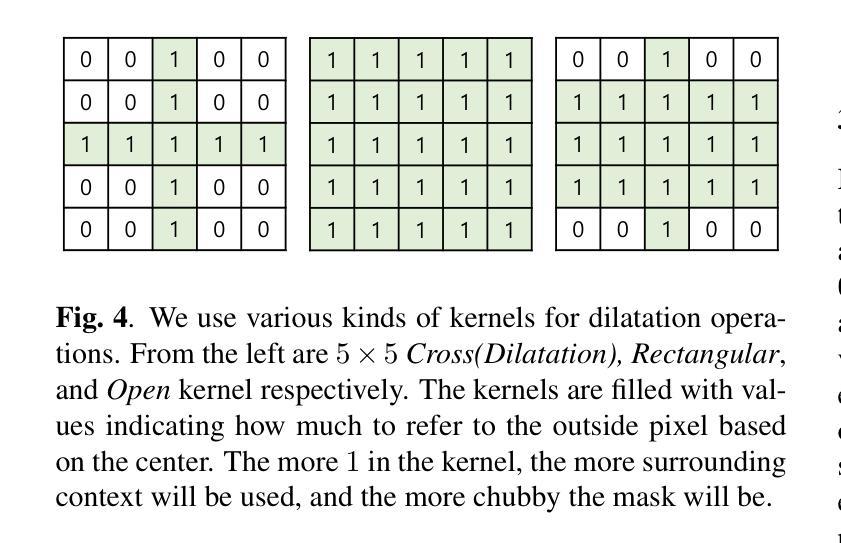
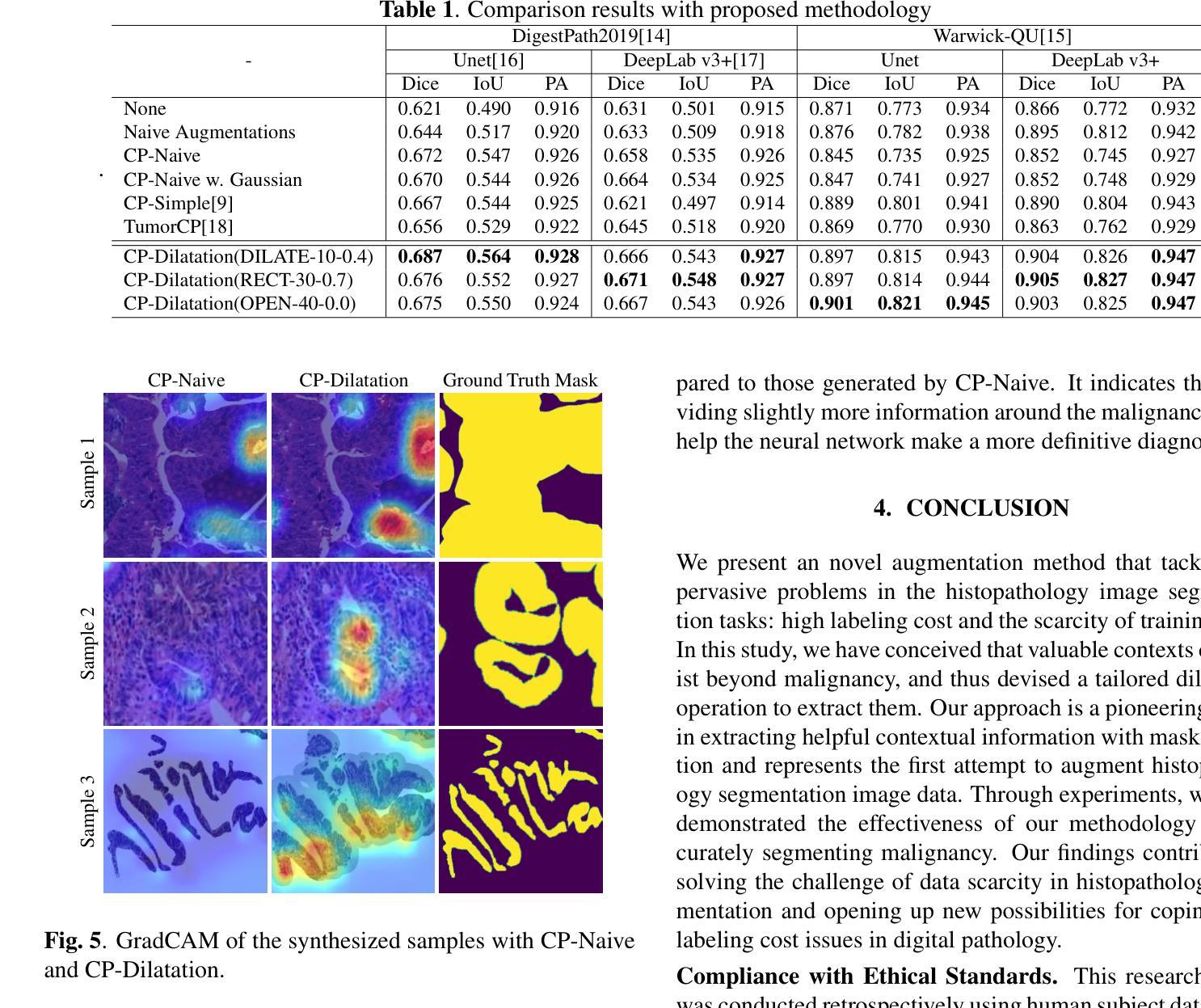
CP-Dilatation: A Copy-and-Paste Augmentation Method for Preserving the Boundary Context Information of Histopathology Images
Authors:Sungrae Hong, Sol Lee, Mun Yong Yi
Medical AI diagnosis including histopathology segmentation has derived benefits from the recent development of deep learning technology. However, deep learning itself requires a large amount of training data and the medical image segmentation masking, in particular, requires an extremely high cost due to the shortage of medical specialists. To mitigate this issue, we propose a new data augmentation method built upon the conventional Copy and Paste (CP) augmentation technique, called CP-Dilatation, and apply it to histopathology image segmentation. To the well-known traditional CP technique, the proposed method adds a dilation operation that can preserve the boundary context information of the malignancy, which is important in histopathological image diagnosis, as the boundary between the malignancy and its margin is mostly unclear and a significant context exists in the margin. In our experiments using histopathology benchmark datasets, the proposed method was found superior to the other state-of-the-art baselines chosen for comparison.
医学人工智能诊断,包括病理分割,受益于最近深度学习技术的发展。然而,深度学习本身需要大量的训练数据,尤其是医学图像分割掩膜,由于医学专家短缺,其成本极高。为了缓解这一问题,我们提出了一种基于传统复制粘贴(CP)增强技术的新数据增强方法,称为CP-膨胀法,并将其应用于病理图像分割。与传统众所周知的CP技术相比,该方法增加了一个膨胀操作,可以保留恶性肿瘤的边界上下文信息,这在病理图像诊断中非常重要,因为恶性肿瘤与其边缘之间的边界大多不清楚,边缘中存在重要的上下文。在使用病理基准数据集进行的实验中,该方法被证明优于其他选定的最新基线方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 5 figures
Summary
医学人工智能诊断中的组织病理学分割受益于深度学习技术的发展。然而,深度学习需要大量训练数据,医学图像分割尤其需要大量标注数据,因医学专家短缺导致成本极高。为解决此问题,我们提出一种基于传统复制粘贴(CP)增强技术的新数据增强方法——CP-Dilation,并应用于组织病理学图像分割。相较于传统CP技术,新方法添加膨胀操作,可保留恶性边界上下文信息。在组织病理学基准数据集的实验中,新方法优于其他对比的基线模型。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在医学人工智能诊断和组织病理学分割中发挥了重要作用。
- 医学图像分割需要大量的标注数据,因医学专家短缺导致成本高昂。
- 提出了一种新的数据增强方法CP-Dilation,基于传统的复制粘贴(CP)增强技术。
- CP-Dilation方法通过添加膨胀操作,能够保留恶性边界的上下文信息。
- 恶性边界的识别对于组织病理学图像诊断非常重要。
- 在组织病理学基准数据集的实验中,CP-Dilation方法优于其他先进基线模型。
点此查看论文截图


HiLa: Hierarchical Vision-Language Collaboration for Cancer Survival Prediction
Authors:Jiaqi Cui, Lu Wen, Yuchen Fei, Bo Liu, Luping Zhou, Dinggang Shen, Yan Wang
Survival prediction using whole-slide images (WSIs) is crucial in cancer re-search. Despite notable success, existing approaches are limited by their reliance on sparse slide-level labels, which hinders the learning of discriminative repre-sentations from gigapixel WSIs. Recently, vision language (VL) models, which incorporate additional language supervision, have emerged as a promising solu-tion. However, VL-based survival prediction remains largely unexplored due to two key challenges. First, current methods often rely on only one simple lan-guage prompt and basic cosine similarity, which fails to learn fine-grained associ-ations between multi-faceted linguistic information and visual features within WSI, resulting in inadequate vision-language alignment. Second, these methods primarily exploit patch-level information, overlooking the intrinsic hierarchy of WSIs and their interactions, causing ineffective modeling of hierarchical interac-tions. To tackle these problems, we propose a novel Hierarchical vision-Language collaboration (HiLa) framework for improved survival prediction. Specifically, HiLa employs pretrained feature extractors to generate hierarchical visual features from WSIs at both patch and region levels. At each level, a series of language prompts describing various survival-related attributes are constructed and aligned with visual features via Optimal Prompt Learning (OPL). This ap-proach enables the comprehensive learning of discriminative visual features cor-responding to different survival-related attributes from prompts, thereby improv-ing vision-language alignment. Furthermore, we introduce two modules, i.e., Cross-Level Propagation (CLP) and Mutual Contrastive Learning (MCL) to maximize hierarchical cooperation by promoting interactions and consistency be-tween patch and region levels. Experiments on three TCGA datasets demonstrate our SOTA performance.
在癌症研究中,利用全切片图像(WSI)进行生存预测至关重要。尽管已有一些成功的方法,但它们依赖于稀疏的切片级标签,这阻碍了从gigapixel WSI中学习判别表示。最近,结合额外语言监督的视听语言(VL)模型的出现为解决这一问题提供了有前景的解决方案。然而,基于VL的生存预测仍然因两大挑战而未被充分探索。首先,当前的方法通常只依赖一个简单的语言提示和基本余弦相似性,这无法学习WSI内部多面语言信息与视觉特征之间的精细关联,导致视觉语言对齐不足。其次,这些方法主要利用补丁级别的信息,忽略了WSI的内在层次及其交互作用,导致层次交互建模无效。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种新型的分层视听语言协作(HiLa)框架,用于改进生存预测。具体来说,HiLa使用预训练的特征提取器生成来自WSI的层次化视觉特征,这些特征在补丁和区域层面都有涉及。在每个层面上,构建一系列描述各种生存相关属性的语言提示,并通过最佳提示学习(OPL)与视觉特征进行对齐。这种方法能够从提示中全面学习对应于不同生存相关属性的判别性视觉特征,从而提高视听语言对齐的效果。此外,我们引入了跨级传播(CLP)和相互对比学习(MCL)两个模块,通过促进补丁和区域级别之间的交互和一致性来最大限度地实现层次协作。在三个TCGA数据集上的实验证明了我们的SOTA性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by MICCAI2025
Summary
基于全幻灯片图像(WSIs)的生存预测在癌症研究中至关重要。现有方法受限于稀疏的幻灯片级标签,无法从吉像素WSIs中学习判别表示。最近,结合附加语言监督的视听语言(VL)模型的出现为解决这一问题提供了希望。然而,基于VL的生存预测仍存在两大挑战。为解决这些问题,我们提出了新颖的分层视听协作(HiLa)框架,以改进生存预测。HiLa使用预训练的特征提取器生成WSIs的分层视觉特征,并通过最佳提示学习(OPL)与描述各种生存相关属性的语言提示进行对齐。此外,还引入了跨级传播(CLP)和相互对比学习(MCL)两个模块,以通过促进补丁和区域级别之间的交互和一致性来最大化分层合作。在三个TCGA数据集上的实验证明了其卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 生存预测在癌症研究中非常重要,全幻灯片图像(WSIs)是核心数据。
- 现有方法受限于稀疏的标签,无法有效学习判别特征。
- 视听语言(VL)模型为解决问题提供了新方向,但面临两大挑战。
- 提出的HiLa框架利用预训练特征提取器生成分层视觉特征,并与语言提示进行精细对齐。
- HiLa框架通过最佳提示学习(OPL)提高视听语言对齐的精准度。
- 引入跨级传播(CLP)和相互对比学习(MCL)模块以最大化分层合作。
- 在三个TCGA数据集上的实验证明了HiLa框架的卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图

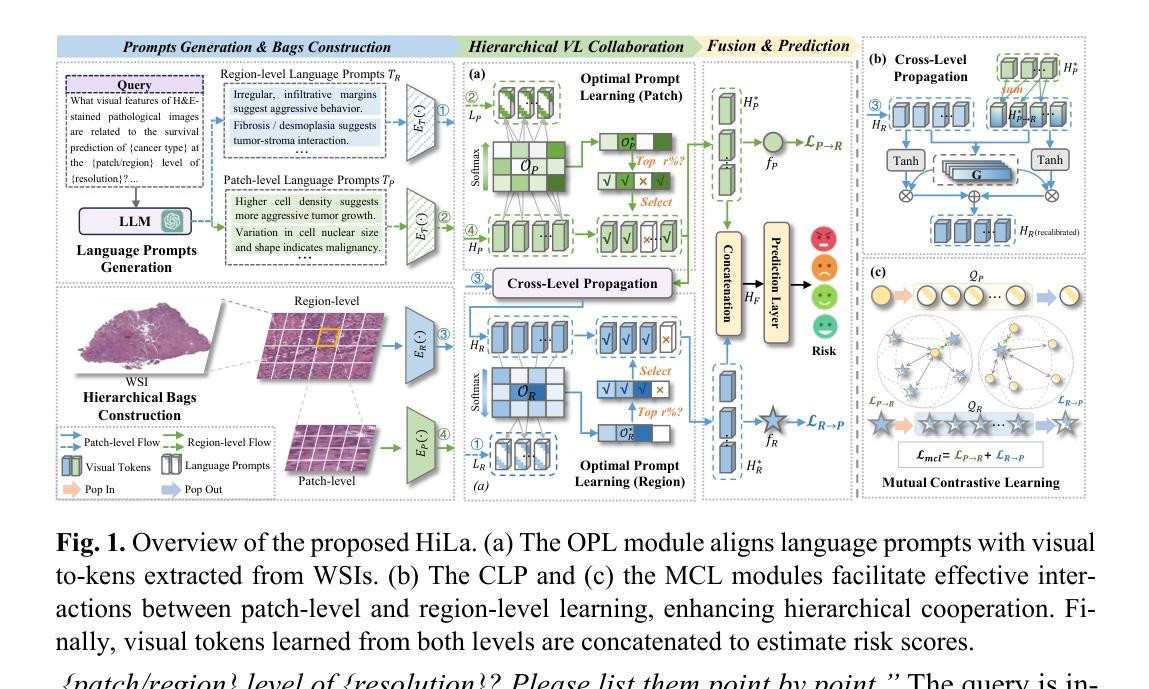
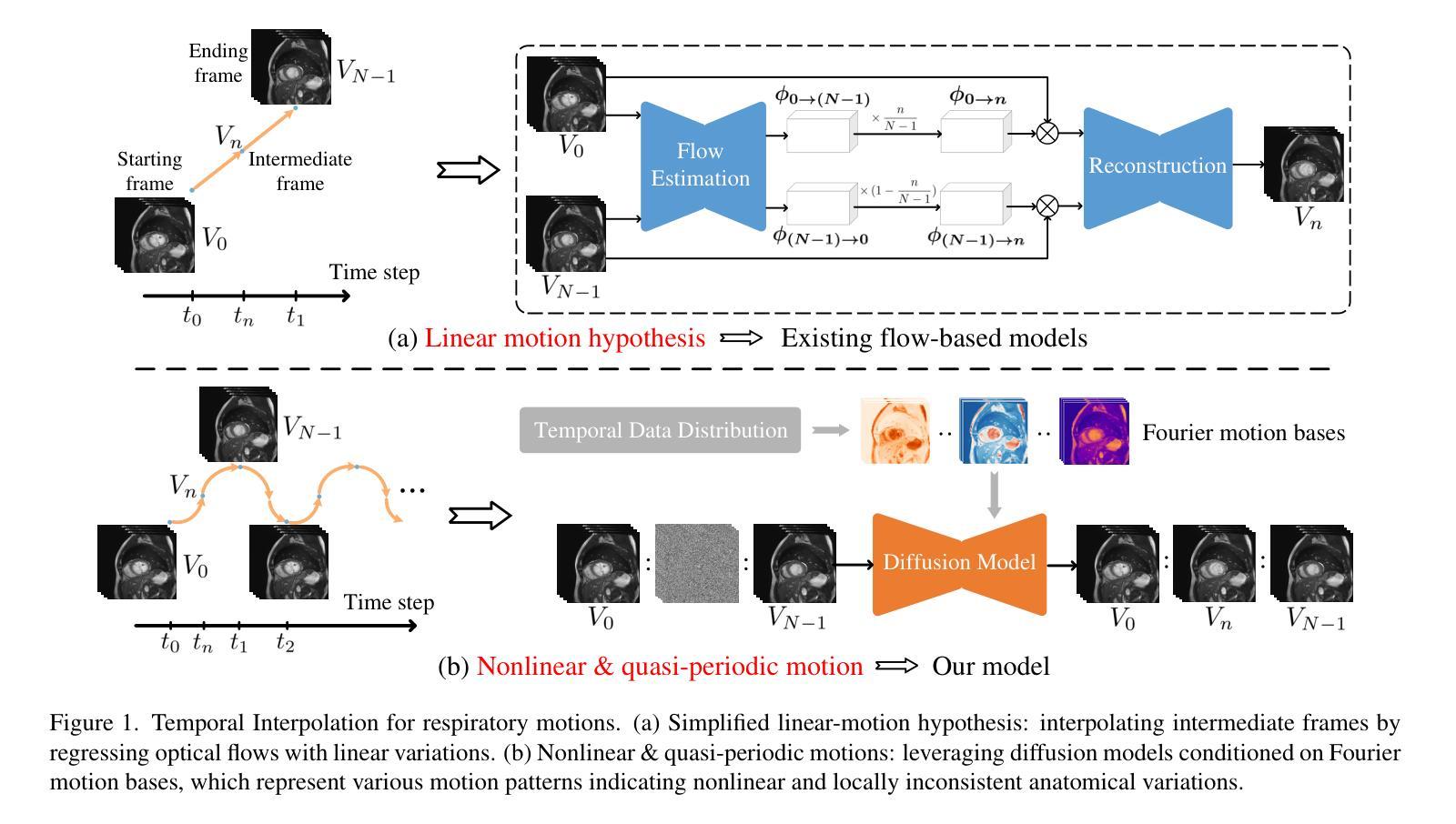
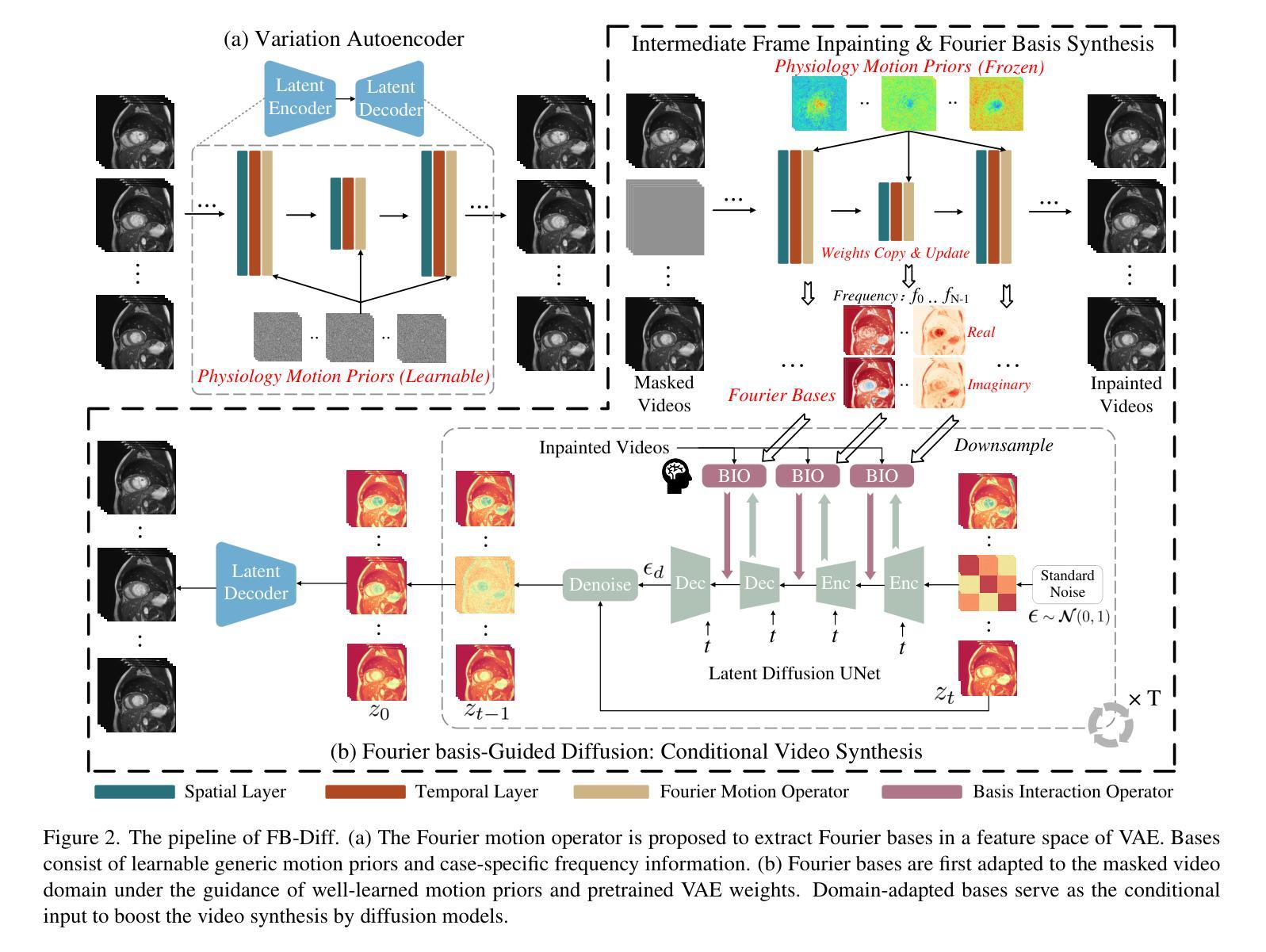
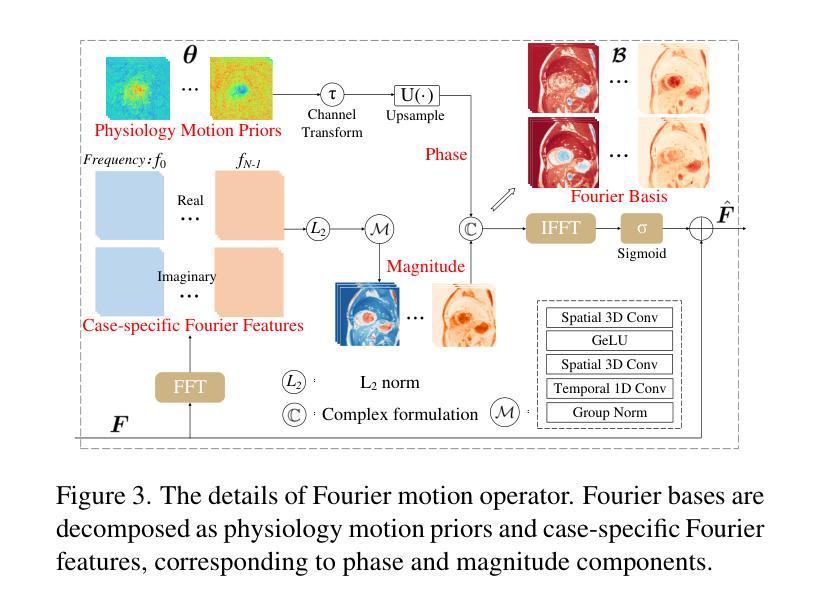
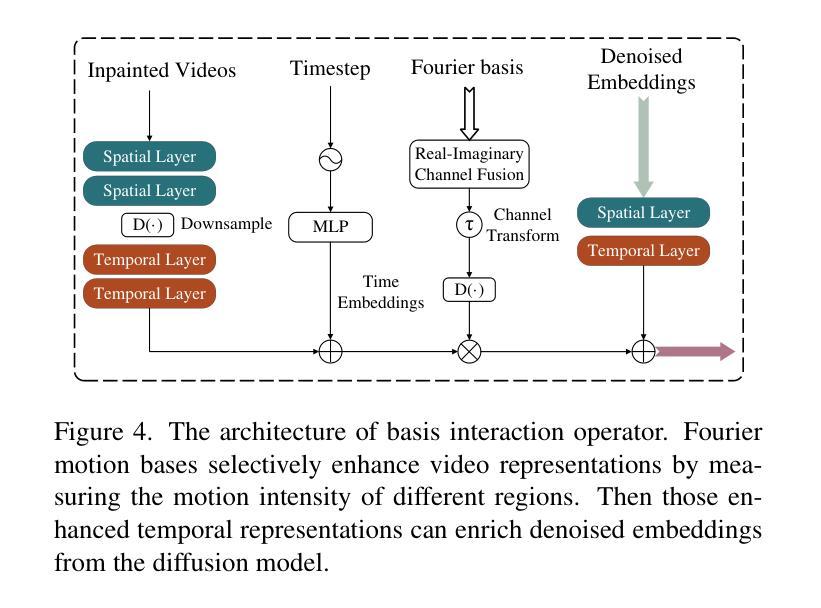
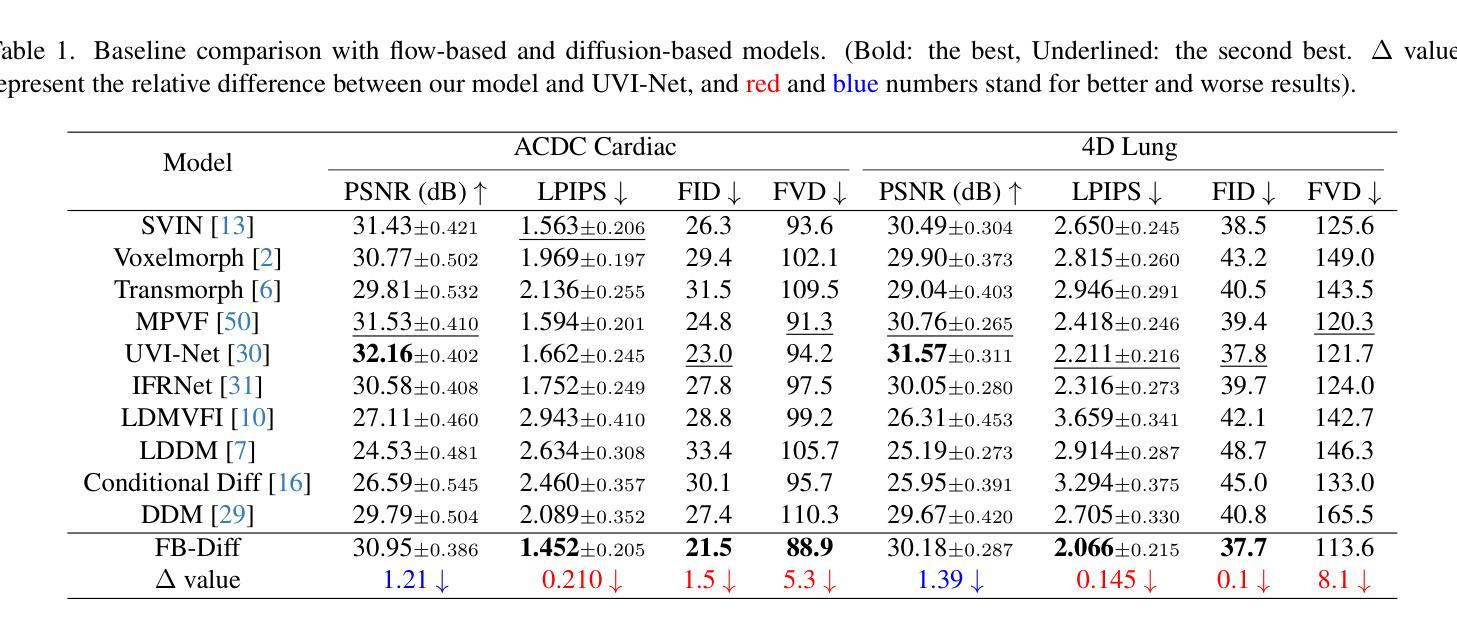
FB-Diff: Fourier Basis-guided Diffusion for Temporal Interpolation of 4D Medical Imaging
Authors:Xin You, Runze Yang, Chuyan Zhang, Zhongliang Jiang, Jie Yang, Nassir Navab
The temporal interpolation task for 4D medical imaging, plays a crucial role in clinical practice of respiratory motion modeling. Following the simplified linear-motion hypothesis, existing approaches adopt optical flow-based models to interpolate intermediate frames. However, realistic respiratory motions should be nonlinear and quasi-periodic with specific frequencies. Intuited by this property, we resolve the temporal interpolation task from the frequency perspective, and propose a Fourier basis-guided Diffusion model, termed FB-Diff. Specifically, due to the regular motion discipline of respiration, physiological motion priors are introduced to describe general characteristics of temporal data distributions. Then a Fourier motion operator is elaborately devised to extract Fourier bases by incorporating physiological motion priors and case-specific spectral information in the feature space of Variational Autoencoder. Well-learned Fourier bases can better simulate respiratory motions with motion patterns of specific frequencies. Conditioned on starting and ending frames, the diffusion model further leverages well-learned Fourier bases via the basis interaction operator, which promotes the temporal interpolation task in a generative manner. Extensive results demonstrate that FB-Diff achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) perceptual performance with better temporal consistency while maintaining promising reconstruction metrics. Codes are available.
在4D医学成像的时间插值任务中,对于呼吸运动建模的临床实践起到了关键作用。遵循简化的线性运动假设,现有方法采用基于光流模型进行中间帧插值。然而,现实的呼吸运动应该是非线性、准周期性的,并具有特定的频率。基于这一特性,我们从频率角度解决时间插值问题,并提出了一种傅里叶基础引导的扩散模型,称为FB-Diff。具体而言,由于呼吸的常规运动规律,我们引入生理运动先验来描述时间数据分布的一般特征。然后精心设计了傅里叶运动算子,通过结合生理运动先验和案例特定的光谱信息,在变分自动编码器的特征空间中提取傅里叶基础。学习良好的傅里叶基础能更好地模拟具有特定频率的运动模式。基于起始帧和结束帧的条件,扩散模型进一步利用学习良好的傅里叶基础,通过基础交互算子,以生成方式促进时间插值任务。大量结果表明,FB-Diff达到了最先进的感知性能,具有更好的时间一致性,同时保持了有希望的重建指标。相关代码已公开。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种针对四维医学成像的临时插帧任务的方法。该方法采用傅里叶基础引导扩散模型(FB-Diff),从频率角度解决临时插帧问题。该方法引入生理运动先验来描述临时数据分布的一般特征,通过精细设计的傅里叶运动算符提取傅里叶基础,再结合扩散模型和基础交互算符,以生成方式促进临时插帧任务。实验结果表明,FB-Diff在感知性能和重建指标上均达到最佳水平。
Key Takeaways
- 医学成像中的临时插帧任务对于呼吸运动建模的临床实践至关重要。
- 现有方法主要采用基于光学流的模型进行中间帧插值,但真实呼吸运动应是非线性、准周期性的。
- 本文从频率角度解决临时插帧问题,提出一种傅里叶基础引导的扩散模型(FB-Diff)。
- 引入生理运动先验来描述临时数据分布的一般特征。
- 通过傅里叶运动算符结合生理运动先验和特定频谱信息,提取傅里叶基础。
- FB-Diff通过基础交互算符,在给定起始和结束帧的条件下,利用学习良好的傅里叶基础促进临时插帧任务的生成。
点此查看论文截图

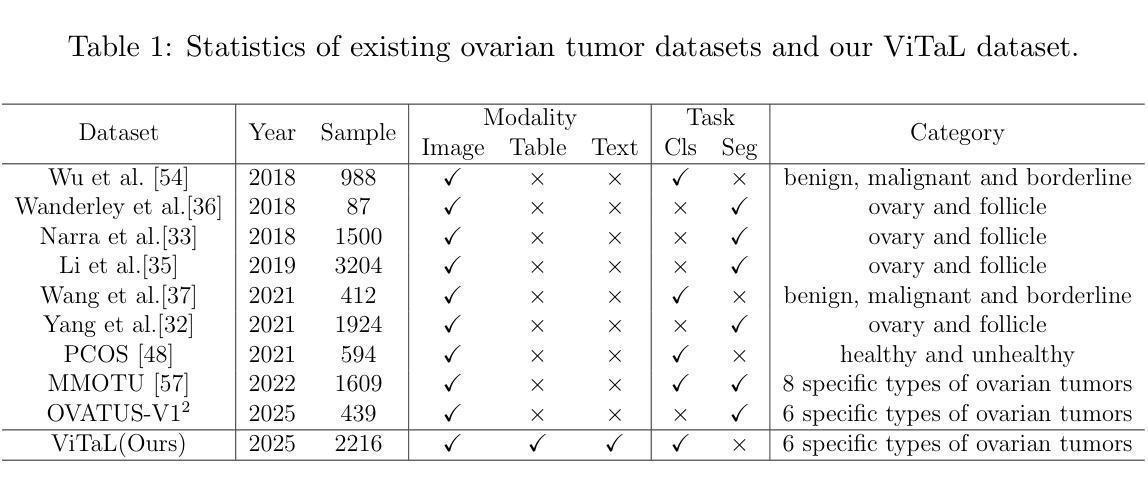
ViTaL: A Multimodality Dataset and Benchmark for Multi-pathological Ovarian Tumor Recognition
Authors:You Zhou, Lijiang Chen, Guangxia Cui, Wenpei Bai, Yu Guo, Shuchang Lyu, Guangliang Cheng, Qi Zhao
Ovarian tumor, as a common gynecological disease, can rapidly deteriorate into serious health crises when undetected early, thus posing significant threats to the health of women. Deep neural networks have the potential to identify ovarian tumors, thereby reducing mortality rates, but limited public datasets hinder its progress. To address this gap, we introduce a vital ovarian tumor pathological recognition dataset called \textbf{ViTaL} that contains \textbf{V}isual, \textbf{T}abular and \textbf{L}inguistic modality data of 496 patients across six pathological categories. The ViTaL dataset comprises three subsets corresponding to different patient data modalities: visual data from 2216 two-dimensional ultrasound images, tabular data from medical examinations of 496 patients, and linguistic data from ultrasound reports of 496 patients. It is insufficient to merely distinguish between benign and malignant ovarian tumors in clinical practice. To enable multi-pathology classification of ovarian tumor, we propose a ViTaL-Net based on the Triplet Hierarchical Offset Attention Mechanism (THOAM) to minimize the loss incurred during feature fusion of multi-modal data. This mechanism could effectively enhance the relevance and complementarity between information from different modalities. ViTaL-Net serves as a benchmark for the task of multi-pathology, multi-modality classification of ovarian tumors. In our comprehensive experiments, the proposed method exhibited satisfactory performance, achieving accuracies exceeding 90% on the two most common pathological types of ovarian tumor and an overall performance of 85%. Our dataset and code are available at https://github.com/GGbond-study/vitalnet.
卵巢肿瘤是一种常见的妇科疾病,如果早期未被发现,会迅速恶化成严重的健康危机,从而对女性的健康构成重大威胁。深度神经网络有潜力识别卵巢肿瘤,从而降低死亡率,但有限的公开数据集阻碍了其进展。为了弥补这一空白,我们引入了一个重要的卵巢肿瘤病理识别数据集,名为“ViTaL”,它包含了496名患者跨越六个病理类别的视觉、表格和语言模式数据。ViTaL数据集由三个子集组成,对应于不同的患者数据模式:来自2216张二维超声图像的视觉数据、来自496名患者的医学检查表格数据以及来自4 9 6名患者的超声报告语言数据。在临床上,仅仅区分良性和恶性卵巢肿瘤是不够的。为了实现卵巢肿瘤的多病理分类,我们提出了一种基于三元层次偏移注意机制(THOAM)的ViTaL-Net,以最小化多模式数据特征融合过程中的损失。该机制可以有效地增强不同模式信息之间的相关性和互补性。ViTaL-Net可作为卵巢肿瘤多病理、多模式分类任务的标准。我们的综合实验表明,该方法表现良好,在两种最常见的卵巢肿瘤病理类型上的准确率超过90%,总体性能达到85%。我们的数据集和代码可在https://github.com/GGbond-study/vitalnet上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了卵巢肿瘤作为一种常见的妇科疾病,早期发现对其治疗至关重要。为解决当前深度学习在卵巢肿瘤识别方面的数据缺口问题,研究团队推出了一个包含视觉、表格和语言学数据的多模式卵巢肿瘤病理识别数据集——ViTaL数据集。此外,还提出了一种基于Triplet Hierarchical Offset Attention Mechanism(THOAM)的ViTaL-Net模型,用于多模式数据的特征融合,提高不同信息之间的相关性和互补性,实现对卵巢肿瘤的多病理分类。实验表明,该方法在两种最常见的卵巢肿瘤病理类型上的准确率超过90%,总体性能达到85%。数据集和代码已公开分享。
Key Takeaways
- 卵巢肿瘤是常见的妇科疾病,早期发现对治疗至关重要。
- 缺乏公共数据集限制了深度学习在卵巢肿瘤识别方面的进展。
- 推出了一个包含视觉、表格和语言学数据的多模式卵巢肿瘤病理识别数据集——ViTaL数据集。
- ViTaL数据集包含三种不同类型的患者数据:来自2216张二维超声图像的视觉数据、来自496名患者的医学检查表格数据以及来自相同患者的超声报告语言学数据。
- 提出了基于Triplet Hierarchical Offset Attention Mechanism(THOAM)的ViTaL-Net模型,用于多模式数据的特征融合和多病理分类。
- ViTaL-Net模型在两种最常见的卵巢肿瘤病理类型上的准确率超过90%,总体性能达到85%。
点此查看论文截图

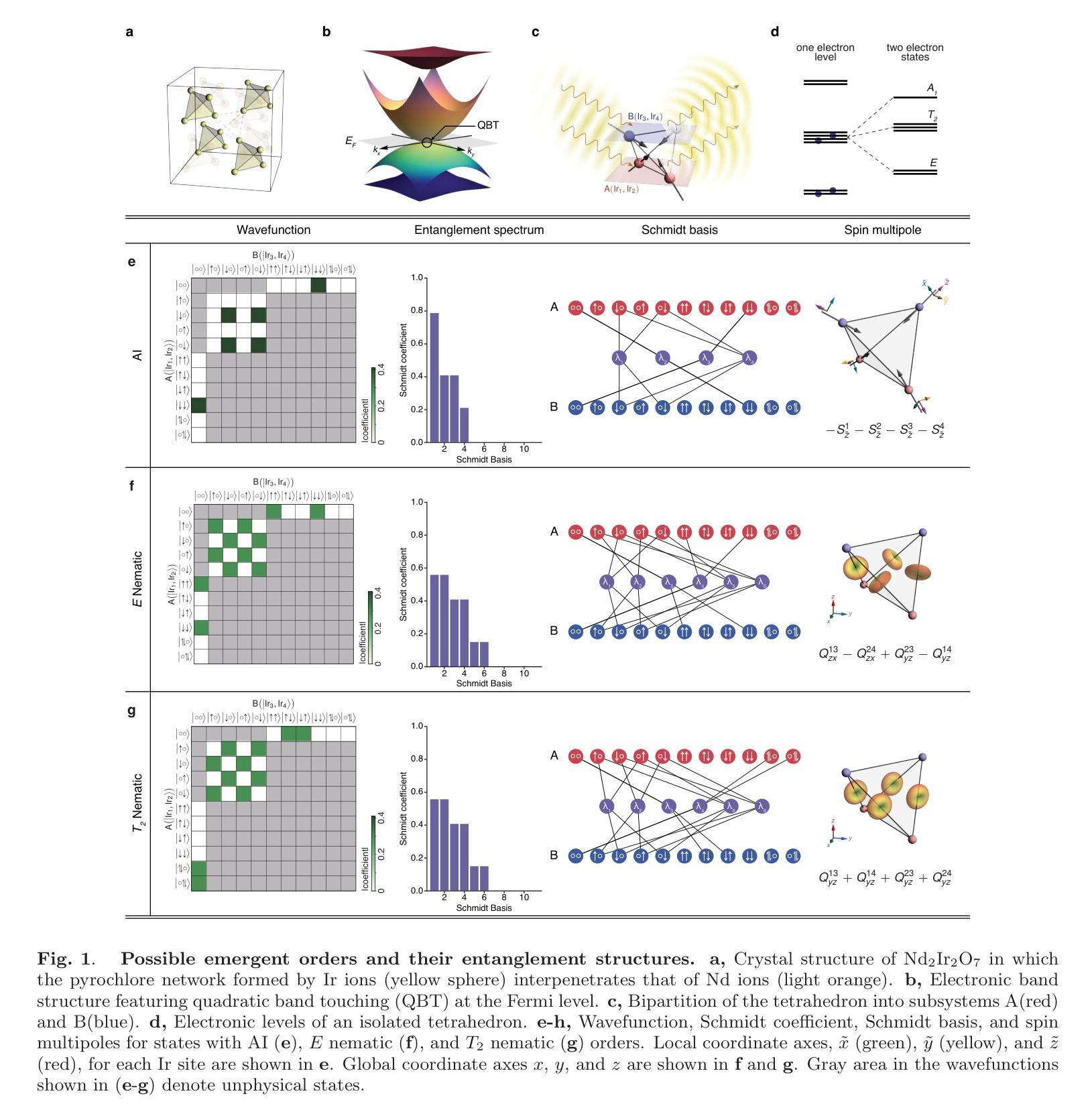
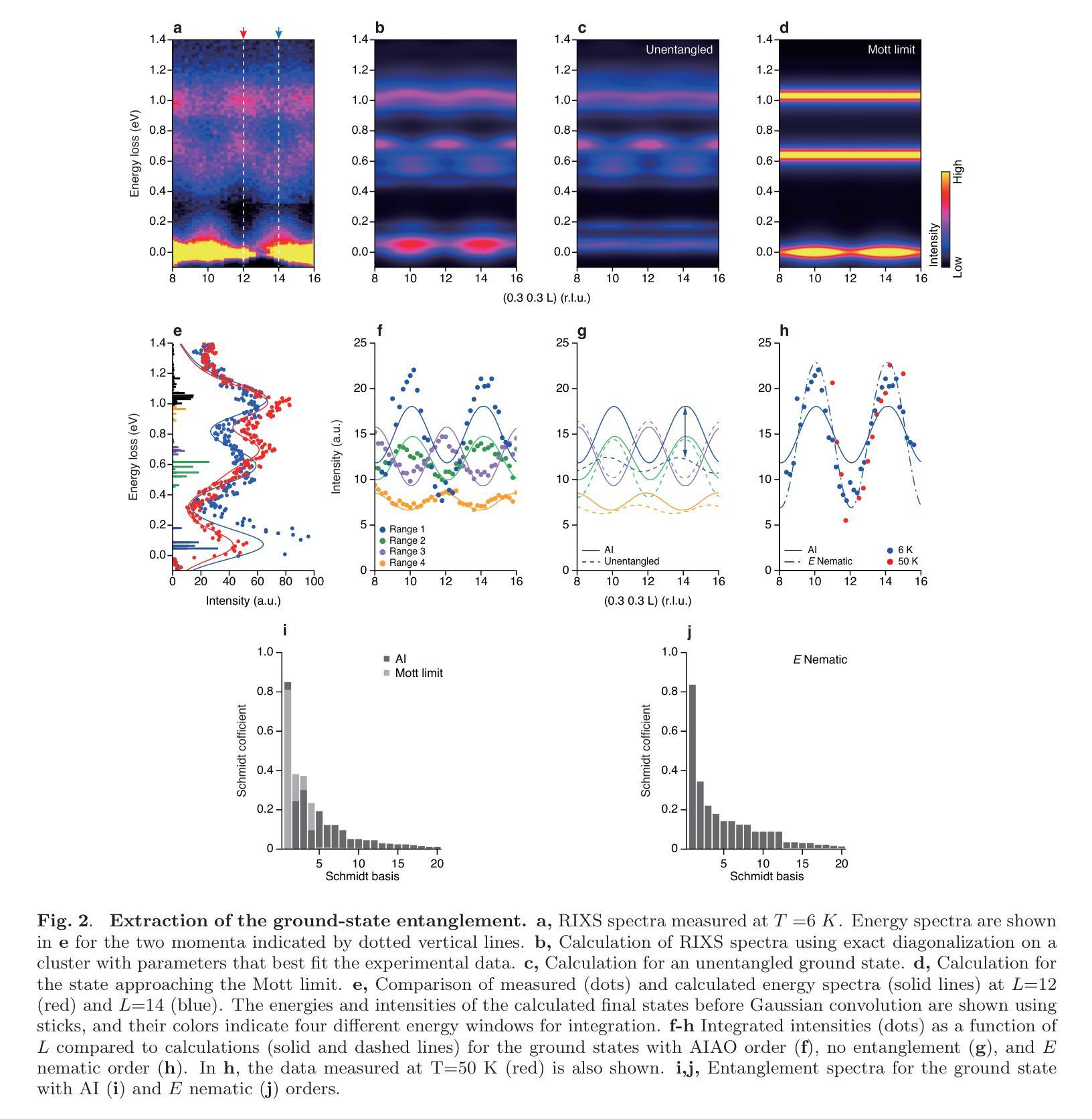
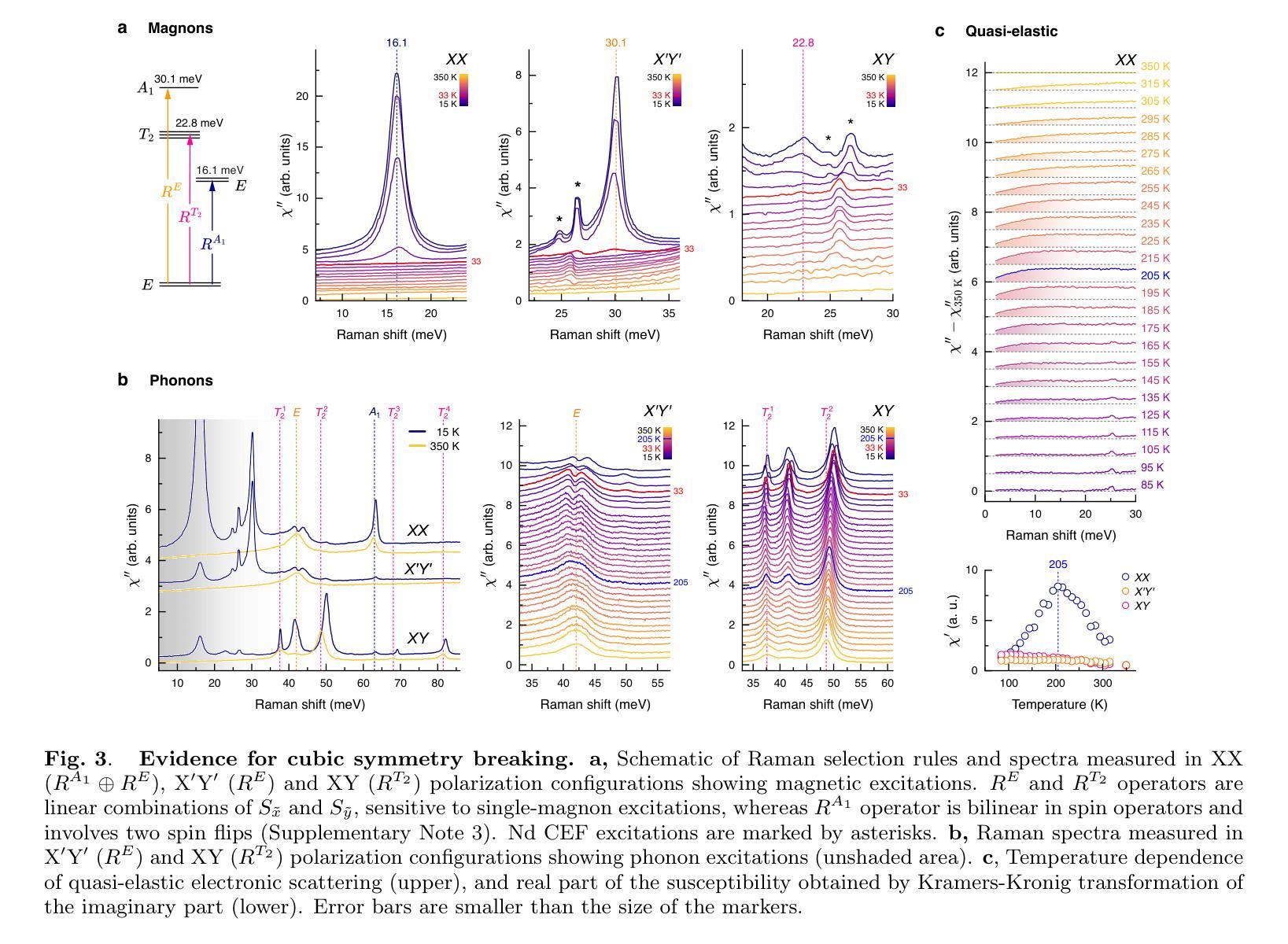
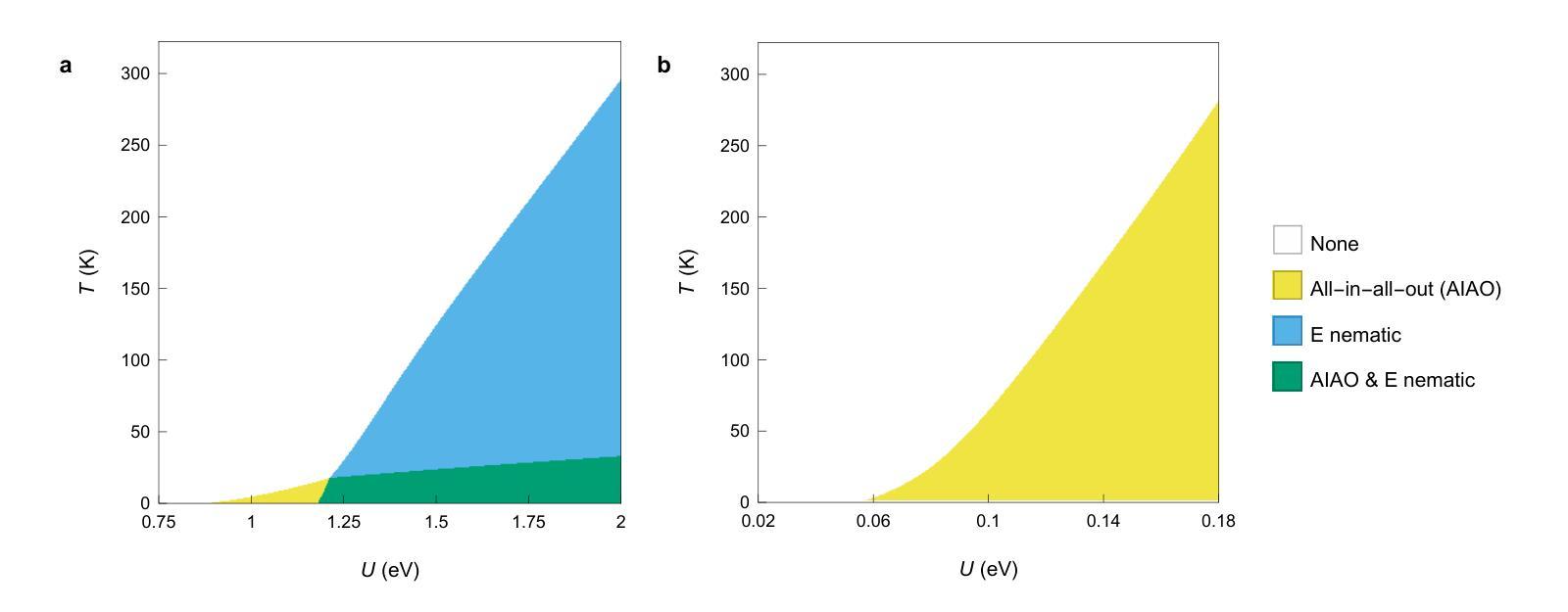
Intertwined Orders in a Quantum-Entangled Metal
Authors:Junyoung Kwon, Jaehwon Kim, Gwansuk Oh, Seyoung Jin, Kwangrae Kim, Hoon Kim, Seunghyeok Ha, Hyun-Woo J. Kim, GiBaik Sim, Bjorn Wehinger, Gaston Garbarino, Nour Maraytta, Michael Merz, Matthieu Le Tacon, Christoph J. Sahle, Alessandro Longo, Jungho Kim, Ara Go, Gil Young Cho, Beom Hyun Kim, B. J. Kim
Entanglement underpins quantum information processing and computing, yet its experimental quantification in complex, many-body condensed matter systems remains a considerable challenge. Here, we reveal a highly entangled electronic phase proximate to a quantum metal-insulator transition, identified by resonant inelastic x-ray scattering interferometry. This approach reveals that entanglement across atomic sites generates characteristic interference patterns, which our model accurately reproduces, enabling extraction of a full entanglement spectrum and resolution of the underlying quantum states. Our analysis of the pyrochlore iridate Nd2Ir2O7 demonstrates that the system undergoes pronounced quantum fluctuations in its spin, orbital and charge degrees of freedom, even in the presence of a long-range ‘all-in-all-out’ antiferromagnetic order. Importantly, the observed entanglement signatures facilitate the coexistence of multiple exotic symmetry-breaking orders. Complementary investigations using Raman spectroscopy corroborate the presence of these hidden orders and their emergent excitations. In particular, we observe a two-magnon-bound state below the lowest single-magnon excitation energy, which, together with split phonon modes, provides strong evidence for cubic symmetry-breaking orders of magnetic origin juxtaposed with the all-in-all-out order. Our work thus establishes a direct link between quantum entanglement and emergent unconventional orders, opening new avenues for investigating quantum materials.
纠缠是量子信息处理与计算的基础,但在复杂的、多体凝聚态系统中对其进行实验量化仍然是一个巨大的挑战。在这里,我们通过共振非弹性X射线散射干涉仪揭示了一种高度纠缠的电子相,它位于量子金属绝缘体转变附近。这种方法揭示了原子位点之间的纠缠会产生特征干涉图案,我们的模型准确地再现了这些图案,能够提取完整的纠缠谱并解决潜在的量子态。我们对烧绿矿含铱酸盐Nd2Ir2O7的分析表明,即使在远程的“全进全出”反铁磁序存在的情况下,该系统在自旋、轨道和电荷自由度上也经历了明显的量子波动。重要的是,观察到的纠缠特征促进了多种奇异的对称破缺序的共存。使用拉曼光谱法进行的补充调查证实了这些隐藏订单及其新兴兴奋剂的存在。特别是,我们观察到低于最低单磁激发能量的两磁子束缚态,以及与分裂的声子模式相结合,这为与“全进全出”顺序相邻的磁起源的立方对称破缺顺序提供了强有力的证据。因此,我们的工作建立了量子纠缠与新兴非传统顺序之间的直接联系,为调查量子材料开辟了新途径。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
量子纠缠是量子信息处理与计算的基础,但在复杂的、多体凝聚态系统中对其进行实验量化仍然是一个巨大的挑战。本文通过共振非弹性X射线散射干涉测量法揭示了一种高度纠缠的电子相位,它位于量子金属-绝缘体转变附近。该研究通过原子位点的纠缠产生特征干涉模式,我们的模型准确再现了这些模式,从而提取了完整的纠缠谱并解决了一些基本的量子状态。我们对锆酸盐的研究表明,该系统在旋转、轨道和电荷自由度方面经历了明显的量子波动,即使在长程的“全进全出”反铁磁排序中也是如此。观察到的重要纠缠特征使得多个异种对称性破缺共存成为可能。拉曼光谱法验证隐藏着的量子排序的存在以及其新兴激发的存在。观察到低于最低单磁激发能量的两磁子束缚态以及分裂的声子模式,这为磁起源的立方对称性破缺排序提供了强有力的证据。我们的研究在量子纠缠和新兴的非传统排序之间建立了直接联系,为调查量子材料开辟了新途径。
Key Takeaways
- 实验揭示了高度纠缠的电子相位在量子金属-绝缘体转变附近的特征。
- 通过共振非弹性X射线散射干涉测量法,观察到了原子位点的纠缠产生的特征干涉模式。
- 准确的模型复现了这些干涉模式,从而能够提取完整的纠缠谱。
- 在锆酸盐的研究中,发现了系统在旋转、轨道和电荷自由度方面的量子波动。
- 观察到的重要纠缠特征支持了多个异种对称性破缺的共存可能性。
- 拉曼光谱法验证了隐藏的量子排序的存在及其新兴激发。
点此查看论文截图

An Explainable Transformer Model for Alzheimer’s Disease Detection Using Retinal Imaging
Authors:Saeed Jamshidiha, Alireza Rezaee, Farshid Hajati, Mojtaba Golzan, Raymond Chiong
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disorder that affects millions worldwide. In the absence of effective treatment options, early diagnosis is crucial for initiating management strategies to delay disease onset and slow down its progression. In this study, we propose Retformer, a novel transformer-based architecture for detecting AD using retinal imaging modalities, leveraging the power of transformers and explainable artificial intelligence. The Retformer model is trained on datasets of different modalities of retinal images from patients with AD and age-matched healthy controls, enabling it to learn complex patterns and relationships between image features and disease diagnosis. To provide insights into the decision-making process of our model, we employ the Gradient-weighted Class Activation Mapping algorithm to visualize the feature importance maps, highlighting the regions of the retinal images that contribute most significantly to the classification outcome. These findings are compared to existing clinical studies on detecting AD using retinal biomarkers, allowing us to identify the most important features for AD detection in each imaging modality. The Retformer model outperforms a variety of benchmark algorithms across different performance metrics by margins of up to 11.
阿尔茨海默病(AD)是一种影响全球数百万人的神经退行性疾病。由于没有有效的治疗选择,早期诊断对于启动管理策略以延迟疾病发作和减缓其进展至关重要。在这项研究中,我们提出了Retformer,这是一种基于变压器的新型架构,利用变压器和可解释人工智能的力量,通过视网膜成像模式检测AD。Retformer模型接受来自AD患者和年龄相匹配的健康对照者的不同模式的视网膜图像数据集进行训练,使其能够学习图像特征与疾病诊断之间的复杂模式和关系。为了深入了解模型的决策过程,我们采用带梯度的类激活映射算法来可视化特征重要性图,突出显示对分类结果贡献最大的视网膜图像区域。这些发现与现有的关于使用视网膜生物标志物检测AD的临床研究进行比较,使我们能够在每种成像模式中识别出对AD检测最重要的特征。Retformer模型在各种性能指标上均优于各种基准算法,优势幅度高达11%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages, 8 figures
Summary
本研究提出了一种基于视网膜成像的阿尔茨海默病(AD)检测新方法——Retformer。该方法利用Transformer和可解释人工智能技术的优势,通过多模态视网膜图像数据集进行训练,学习图像特征与疾病诊断之间的复杂模式和关系。采用梯度加权类激活映射算法可视化特征重要性图,以揭示模型决策过程中的关键区域。Retformer模型在多个性能指标上优于现有算法,准确率提升幅度最高达11%。
Key Takeaways
- Retformer是一种基于Transformer的架构,用于通过视网膜成像检测阿尔茨海默病。
- 该模型利用多模态视网膜图像数据集进行训练,学习图像特征与疾病诊断之间的复杂模式。
- 采用梯度加权类激活映射算法揭示模型决策过程中的关键区域。
- Retformer模型在多个性能指标上表现出优异的性能,优于现有算法。
- 该研究通过与现有临床研究比较,确定了不同成像模式下检测阿尔茨海默病的关键特征。
- 视网膜成像可能为阿尔茨海默病的早期检测和疾病管理策略提供有效工具。
- 该方法的应用有助于延迟阿尔茨海默病的发病并减缓其进展。
点此查看论文截图

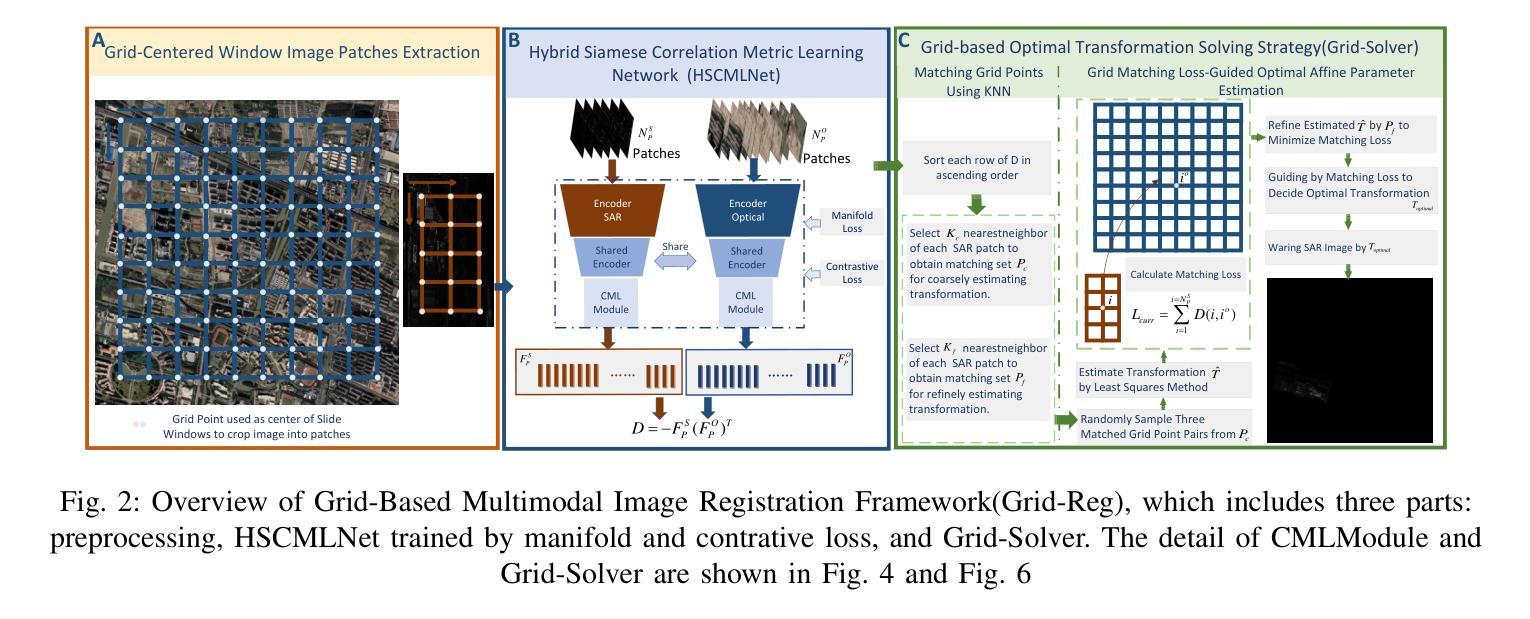
Grid-Reg: Grid-Based SAR and Optical Image Registration Across Platforms
Authors:Xiaochen Wei, Weiwei Guo, Zenghui Zhang, Wenxian Yu
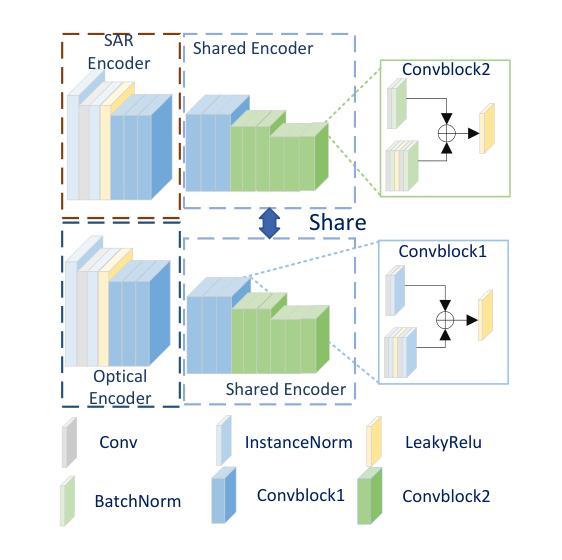
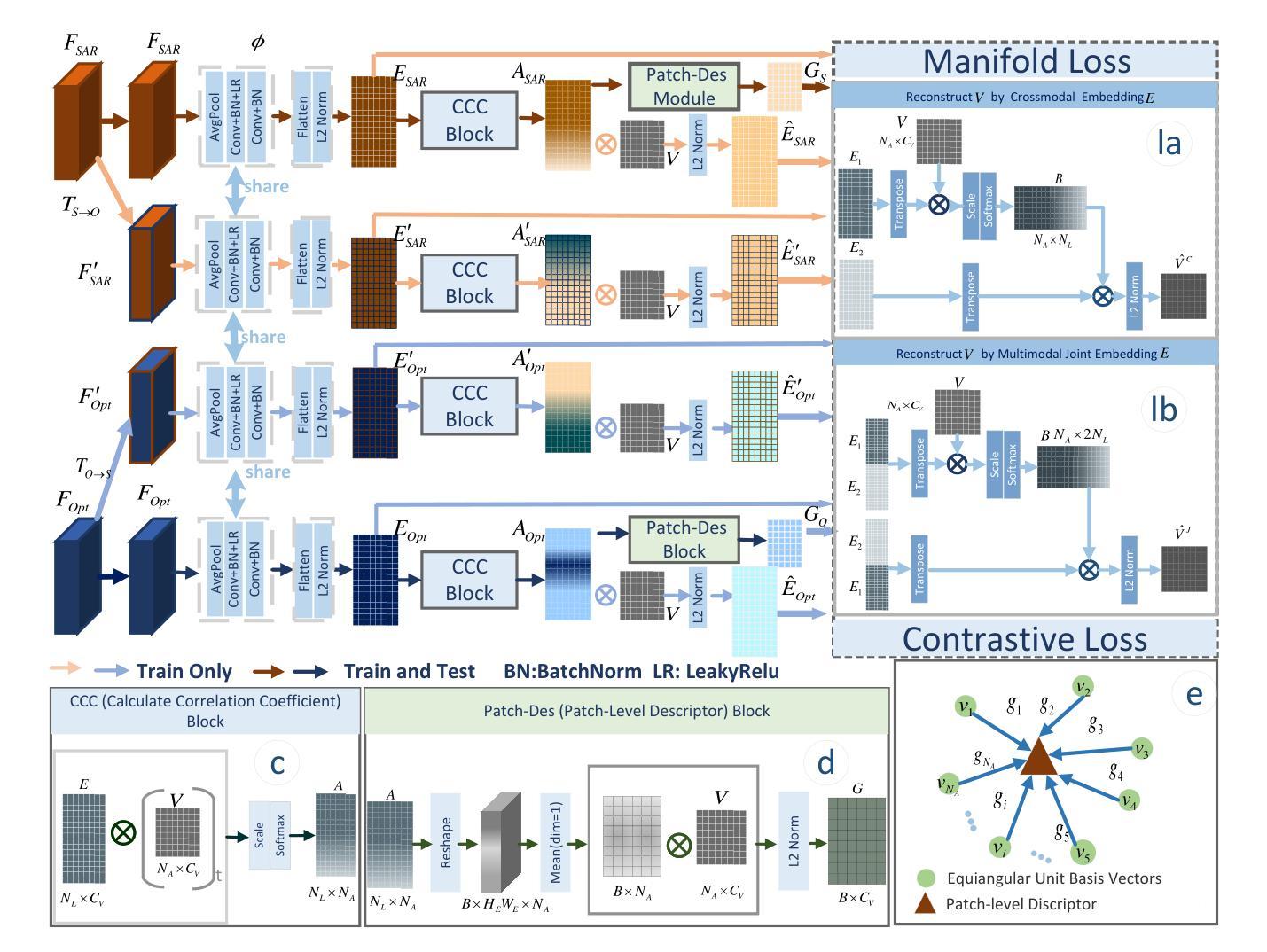
Registering airborne SAR with spaceborne optical images is crucial for SAR image interpretation and geo-localization. It is challenging for this cross-platform heterogeneous image registration due to significant geometric and radiation differences, which current methods fail to handle. To tackle these challenges, we propose a novel grid-based multimodal registration framework (Grid-Reg) across airborne and space-born platforms, including a new domain-robust descriptor extraction network, Hybrid Siamese Correlation Metric Learning Network (HSCMLNet) and a grid-based solver (Grid-solver) for transformation parameters estimation. Our Grid-Reg is based on detector-free and global matching loss rather than accurate keypoint correspondences. These accurate correspondences are inherently difficult in heterogeneous images with large geometric deformation. By Grid-Solver, our Grid-Reg estimates transformation parameters by optimizing robust global matching loss-based patch correspondences of whole images in a coarse-to-fine strategy. To robustly calculate the similarity between patches, specifically that have noise and change objects, we propose HSCMLNet, including a hybrid Siamese module to extract high-level features of multimodal images and a correlation learning module (CMLModule) based equiangular unit basis vectors (EUBVs). Moreover, we propose a manifold loss EUBVsLoss to constrain the normalized correlation between local embeddings of patches and EUBVs. Furthermore, we curate a new challenging benchmark dataset of SAR-to-optical registration using real-world UAV MiniSAR data and optical images from Google Earth. We extensively analyze factors affecting registration accuracy and compare our method with state-of-the-art techniques on this dataset, showing superior performance.
将空中SAR图像与太空光学图像进行配准对于SAR图像解读和地理定位至关重要。由于显著的几何和辐射差异,这种跨平台异质图像配准面临挑战,而现有方法无法处理这些差异。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种基于网格的多模式配准框架(Grid-Reg),适用于空中和太空平台,包括新的域稳健描述符提取网络、混合西姆斯相关度量学习网络(HSCMLNet)和基于网格的求解器(Grid-solver)来估计变换参数。我们的Grid-Reg基于检测器自由和全局匹配损失,而不是准确的关键点对应关系。在具有大几何变形的异质图像中,这些准确的对应关系本质上是困难的。通过Grid-Solver,我们的Grid-Reg采用由粗到细的策略,通过优化基于全局匹配损失的图像补丁对应关系来估计变换参数。为了稳健地计算补丁之间的相似性,特别是那些具有噪声和变化目标的补丁,我们提出了HSCMLNet,包括一个混合西姆斯模块来提取多模式图像的高级特征和一个基于等角单位基向量(EUBVs)的相关学习模块(CMLModule)。此外,我们提出了一种流形损失EUBVsLoss来约束补丁局部嵌入与EUBVs之间的归一化相关性。此外,我们使用来自Google Earth的真实无人机MiniSAR数据和光学图像,创建了一个新的具有挑战性的SAR到光学配准基准数据集。我们全面分析了影响配准精度的因素,并在该数据集上与最先进的技术进行了比较,显示了优越的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
针对空中SAR图像与太空光学图像的注册问题,存在显著几何和辐射差异,当前方法难以处理。为此,我们提出一种基于网格的多模态注册框架(Grid-Reg),包括Hybrid Siamese Correlation Metric Learning Network(HSCMLNet)和基于网格的求解器(Grid-solver)。Grid-Reg基于无检测器和全局匹配损失,无需准确的关键点对应关系。通过Grid-solver,我们的Grid-Reg采用粗到细的策略,通过优化基于全局匹配损失的图像补丁对应关系来估计转换参数。为计算噪声和变化对象之间的补丁相似性,我们提出HSCMLNet,包括提取多模态图像高级特征的混合Siamese模块和基于等角单位基向量(EUBVs)的相关性学习模块(CMLModule)。此外,我们引入流形损失EUBVsLoss来约束补丁局部嵌入与EUBVs之间的归一化相关性。我们创建了一个新的具有挑战性的SAR到光学注册基准数据集,并在该数据集上分析了影响注册精度的因素,与最新技术相比,展现了优越的性能。
关键见解
- 空中SAR图像与太空光学图像之间的注册对于SAR图像解读和地理定位至关重要。
- 当前方法难以处理跨平台和异质图像之间的显著差异。
- 提出了一种基于网格的多模态注册框架(Grid-Reg),用于处理空中和太空平台之间的异质图像。
- Grid-Reg利用无检测器和全局匹配损失,避免了在具有大几何变形的异质图像中寻找准确对应点的困难。
- 引入了Hybrid Siamese Correlation Metric Learning Network (HSCMLNet) 来计算补丁之间的相似性,特别是处理含噪声和变化对象的补丁。
- 提出了一种新的流形损失EUBVsLoss,用于约束局部嵌入与等角单位基向量(EUBVs)之间的归一化相关性。
点此查看论文截图

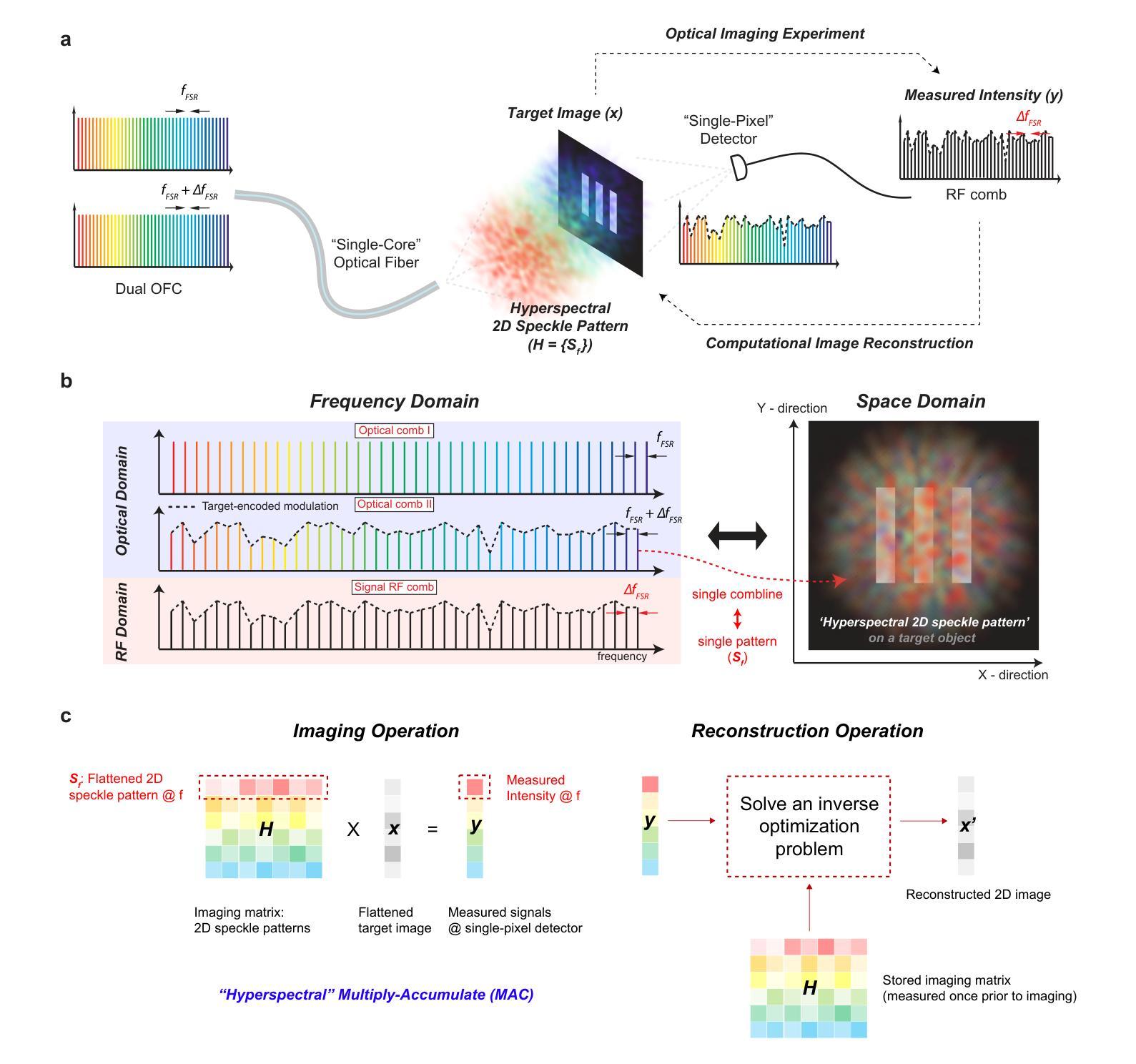
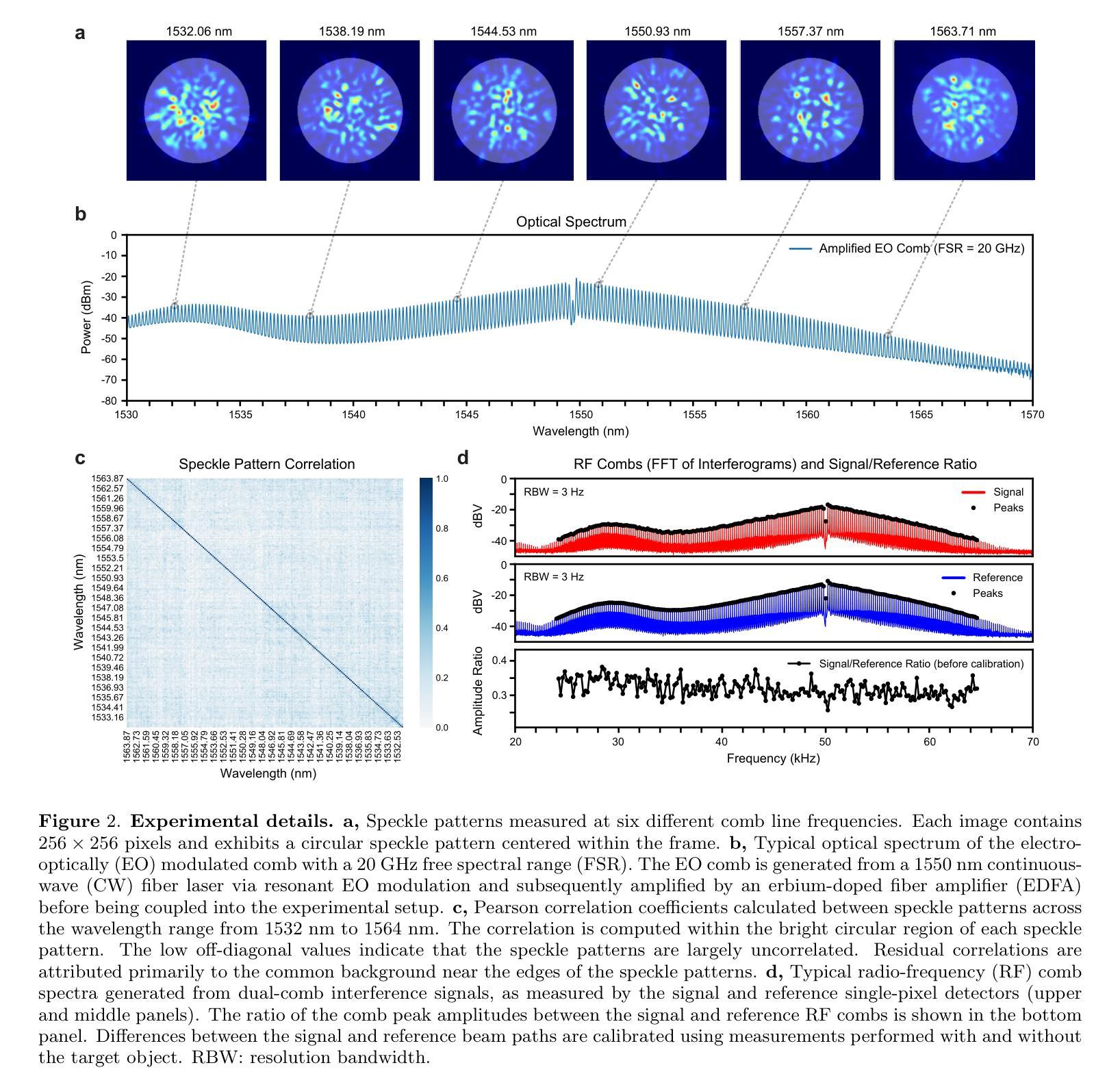
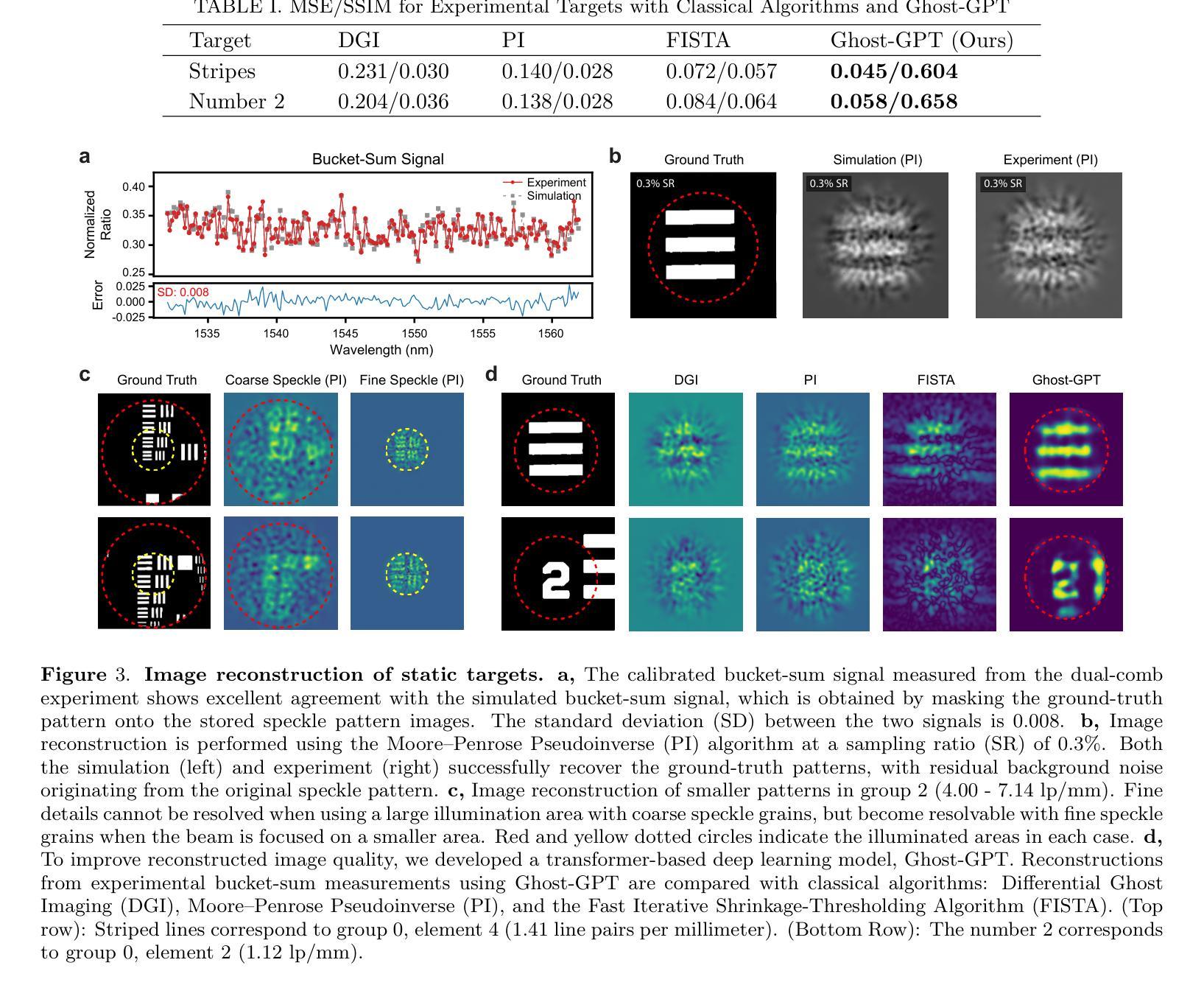
Hyperspectral Dual-Comb Compressive Imaging for Minimally-Invasive Video-Rate Endomicroscopy
Authors:Myoung-Gyun Suh, David Dang, Maodong Gao, Yucheng Jin, Byoung Jun Park, Beyonce Hu, Wilton J. M. Kort-Kamp, Ho Wai, Lee
Endoscopic imaging is essential for real-time visualization of internal organs, yet conventional systems remain bulky, complex, and expensive due to their reliance on large, multi-element optical components. This limits their accessibility to delicate or constrained anatomical regions. Achieving real-time, high-resolution endomicroscopy using compact, low-cost hardware at the hundred-micron scale remains an unsolved challenge. Optical fibers offer a promising route toward miniaturization by providing sub-millimeter-scale imaging channels; however, existing fiber-based methods typically rely on raster scanning or multicore bundles, which limit the resolution and imaging speed. In this work, we overcome these limitations by integrating dual-comb interferometry with compressive ghost imaging and advanced computational reconstruction. Our technique, hyperspectral dual-comb compressive imaging, utilizes optical frequency combs to generate wavelength-multiplexed speckle patterns that are delivered through a single-core fiber and detected by a single-pixel photodetector. This parallel speckle illumination and detection enable snapshot compression and acquisition of image information using zero-dimensional hardware, completely eliminating the need for both spatial and spectral scanning. To decode these highly compressed signals, we develop a transformer-based deep learning model capable of rapid, high-fidelity image reconstruction at extremely low sampling ratios. This approach significantly outperforms classical ghost imaging methods in both speed and accuracy, achieving video-rate imaging with a dramatically simplified optical front-end. Our results represent a major advance toward minimally invasive, cost-effective endomicroscopy and provide a generalizable platform for optical sensing in applications where hardware constraints are critical.
内窥镜成像对于内部器官的实时可视化至关重要,然而,传统系统由于其依赖于大型多元光学组件,仍然庞大、复杂和昂贵。这限制了其在精细或受限的解剖区域的可达性。在紧凑、低成本硬件的百微米尺度上实现实时高分辨率的内窥镜检查仍然是一个未解决的挑战。光纤通过提供亚毫米级的成像通道,为实现小型化提供了有前景的途径;然而,现有的光纤方法通常依赖于栅格扫描或多芯捆扎,这限制了分辨率和成像速度。在这项工作中,我们通过将双梳干涉仪与压缩鬼成像和先进的计算重建相结合,克服了这些局限性。我们的技术——超光谱双梳压缩成像,利用光学频率梳产生波长多路复用的斑点模式,这些模式通过单芯光纤传输并由单像素光电探测器检测。这种并行斑点照明和检测实现了图像的即时压缩和获取,使用零维硬件获取图像信息,完全消除了对空间和光谱扫描的需求。为了解码这些高度压缩的信号,我们开发了一种基于变压器的深度学习模型,能够以极低的采样率快速进行高保真度的图像重建。这种方法在速度和准确性方面都大大优于传统的鬼成像方法,实现了视频速率的成像,大大简化了光学前端。我们的研究结果代表了实现微创、经济的内窥镜检查的重大进步,并为硬件约束关键的应用中的光学传感提供了一个可推广的平台。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于双频梳干涉与压缩鬼成像技术的高光谱成像新方法,通过单芯光纤传输波长多路复用散斑图案,实现无需空间与光谱扫描的实时高保真图像重建,为微创、经济的内窥镜检查提供了重大进展。
Key Takeaways
- 内窥成像在医学领域具有重要性,但传统系统存在体积大、复杂、昂贵等问题。
- 实现实时、高分辨率的端微内窥镜在微米尺度上仍面临挑战。
- 光纤为实现微型化提供有前途的路线,但现有方法受限于分辨率和成像速度。
- 本文通过集成双频梳干涉与压缩鬼成像技术,克服这些限制。
- 采用光学频率梳生成波长多路复用散斑图案,通过单芯光纤传输并实现单像素探测器检测。
- 此方法实现了无需空间与光谱扫描的实时高保真图像重建。
点此查看论文截图

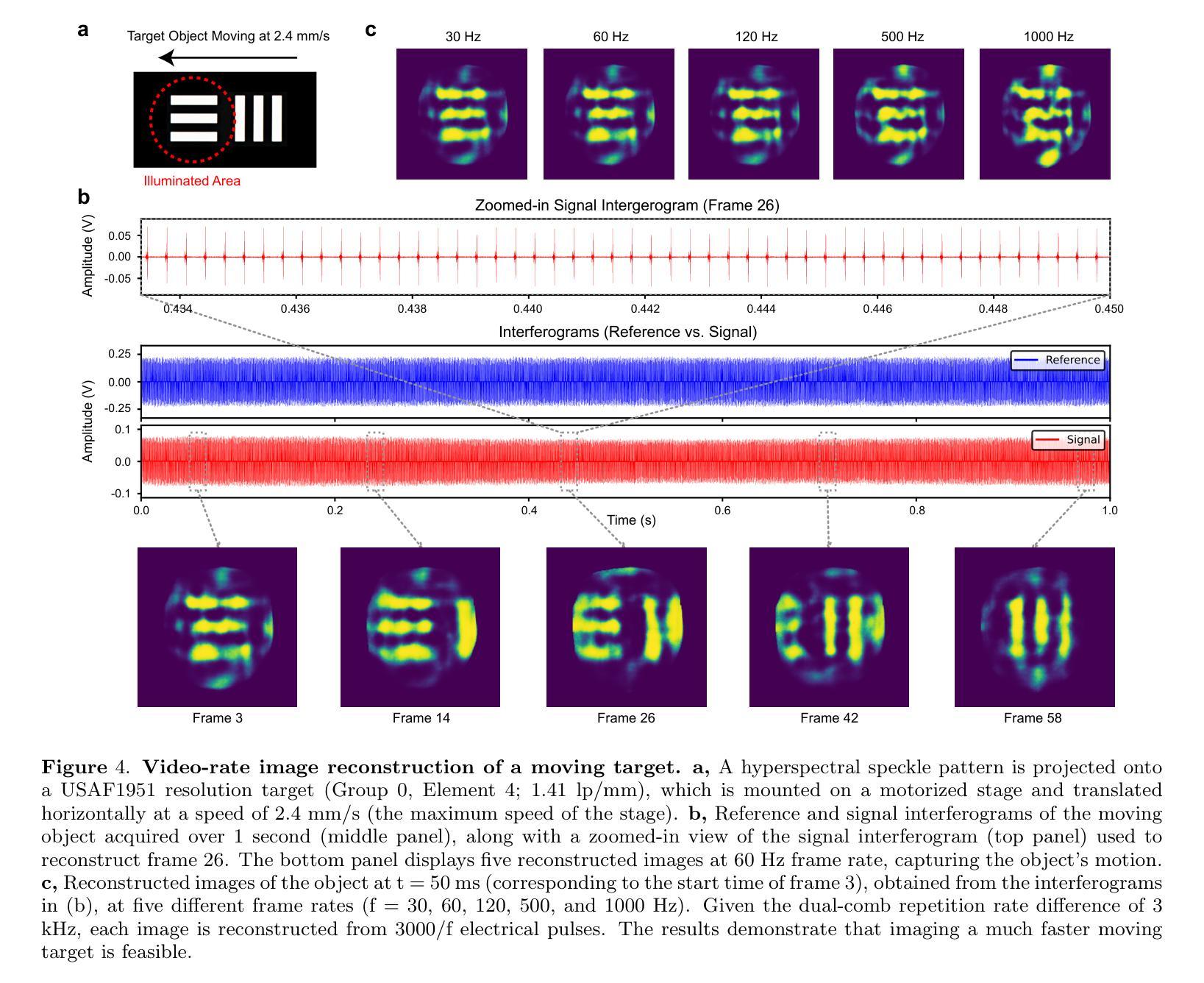
Bridging Vision and Language: Optimal Transport-Driven Radiology Report Generation via LLMs
Authors:Haifeng Zhao, Yufei Zhang, Leilei Ma, Shuo Xu, Dengdi Sun
Radiology report generation represents a significant application within medical AI, and has achieved impressive results. Concurrently, large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable performance across various domains. However, empirical validation indicates that general LLMs tend to focus more on linguistic fluency rather than clinical effectiveness, and lack the ability to effectively capture the relationship between X-ray images and their corresponding texts, thus resulting in poor clinical practicability. To address these challenges, we propose Optimal Transport-Driven Radiology Report Generation (OTDRG), a novel framework that leverages Optimal Transport (OT) to align image features with disease labels extracted from reports, effectively bridging the cross-modal gap. The core component of OTDRG is Alignment & Fine-Tuning, where OT utilizes results from the encoding of label features and image visual features to minimize cross-modal distances, then integrating image and text features for LLMs fine-tuning. Additionally, we design a novel disease prediction module to predict disease labels contained in X-ray images during validation and testing. Evaluated on the MIMIC-CXR and IU X-Ray datasets, OTDRG achieves state-of-the-art performance in both natural language generation (NLG) and clinical efficacy (CE) metrics, delivering reports that are not only linguistically coherent but also clinically accurate.
医学影像报告生成在医学人工智能领域具有重大应用,并已取得了令人印象深刻的效果。同时,大型语言模型(LLMs)在各种领域都表现出了卓越的性能。然而,经验验证表明,通用LLMs更侧重于语言流畅性而非临床有效性,缺乏有效捕捉X光图像与其对应文本之间关系的能力,从而导致临床实用性较差。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了基于最优传输驱动的医学影像报告生成(OTDRG)新型框架,该框架利用最优传输(OT)对齐图像特征与从报告中提取的疾病标签,有效弥合了跨模态差距。OTDRG的核心组件是对齐与微调,其中OT利用标签特征和图像视觉特征的编码结果来最小化跨模态距离,然后整合图像和文本特征进行LLMs微调。此外,我们还设计了一个新型疾病预测模块,在验证和测试阶段预测X光图像中包含的疾病标签。在MIMIC-CXR和IU X光数据集上评估,OTDRG在自然语言生成(NLG)和临床有效性(CE)指标上均达到了最新技术水平,生成的报告不仅语言连贯,而且临床准确。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出Optimal Transport-Driven Radiology Report Generation(OTDRG)框架,利用Optimal Transport(OT)技术对齐图像特征与从报告中提取的疾病标签,有效缩小跨模态差距,从而提高医学图像报告的生成质量和临床实用性。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像报告生成是医学AI的重要应用之一,但现有的大型语言模型在临床医学应用中表现欠佳,需要更有效的方式来实现跨模态信息对齐。
- OTDRG框架利用Optimal Transport技术对齐图像特征和疾病标签,缩小跨模态差距。
- OTDRG的核心组件是Alignment & Fine-Tuning,通过利用标签特征和图像视觉特征的编码结果来最小化跨模态距离,然后整合图像和文本特征进行大型语言模型的微调。
- 设计了新型疾病预测模块,能在验证和测试阶段预测X光图像中的疾病标签。
- 在MIMIC-CXR和IU X-Ray数据集上评估,OTDRG在自然语言生成和临床有效性方面都达到最佳性能。
- OTDRG生成的报告不仅语言连贯,而且临床准确度高。
点此查看论文截图

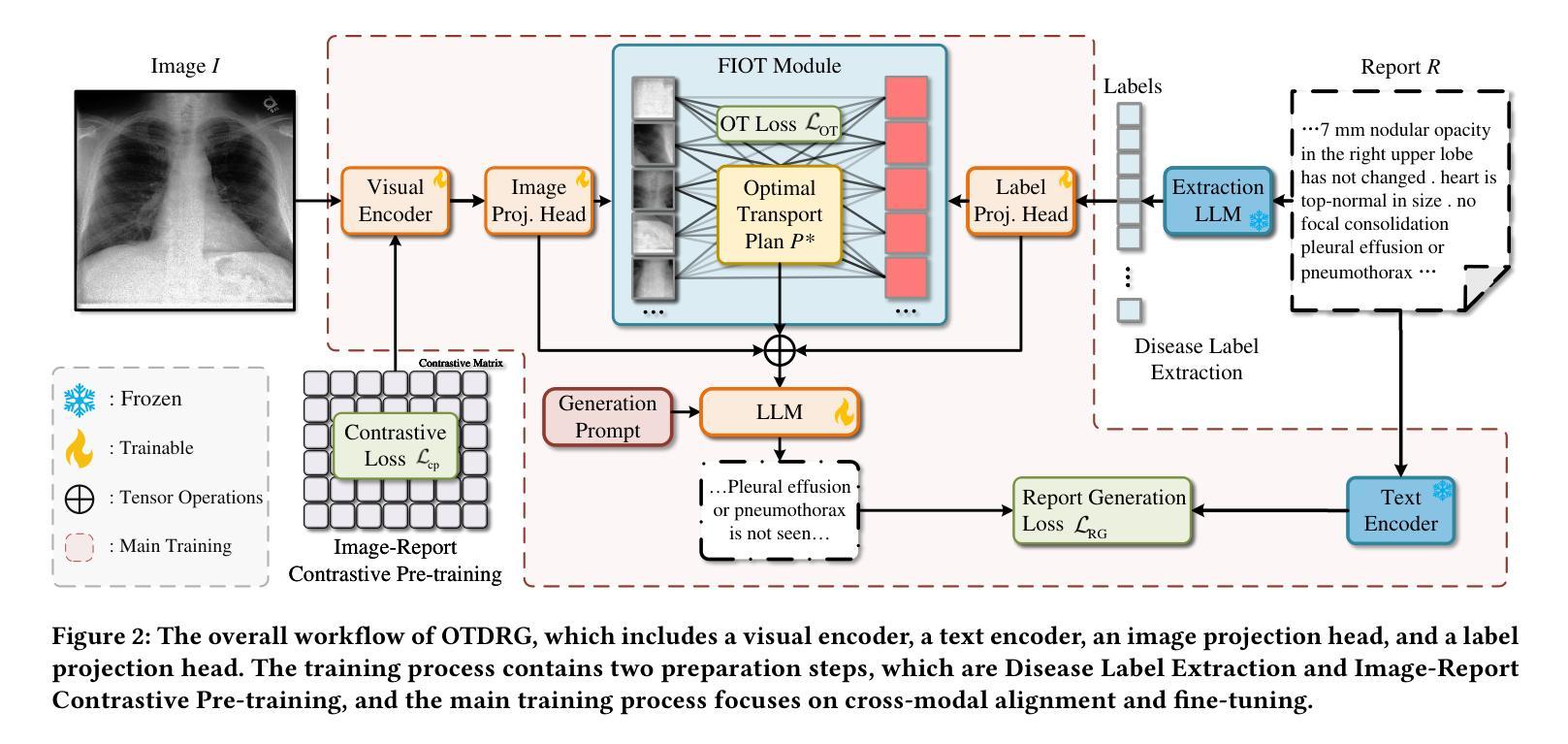
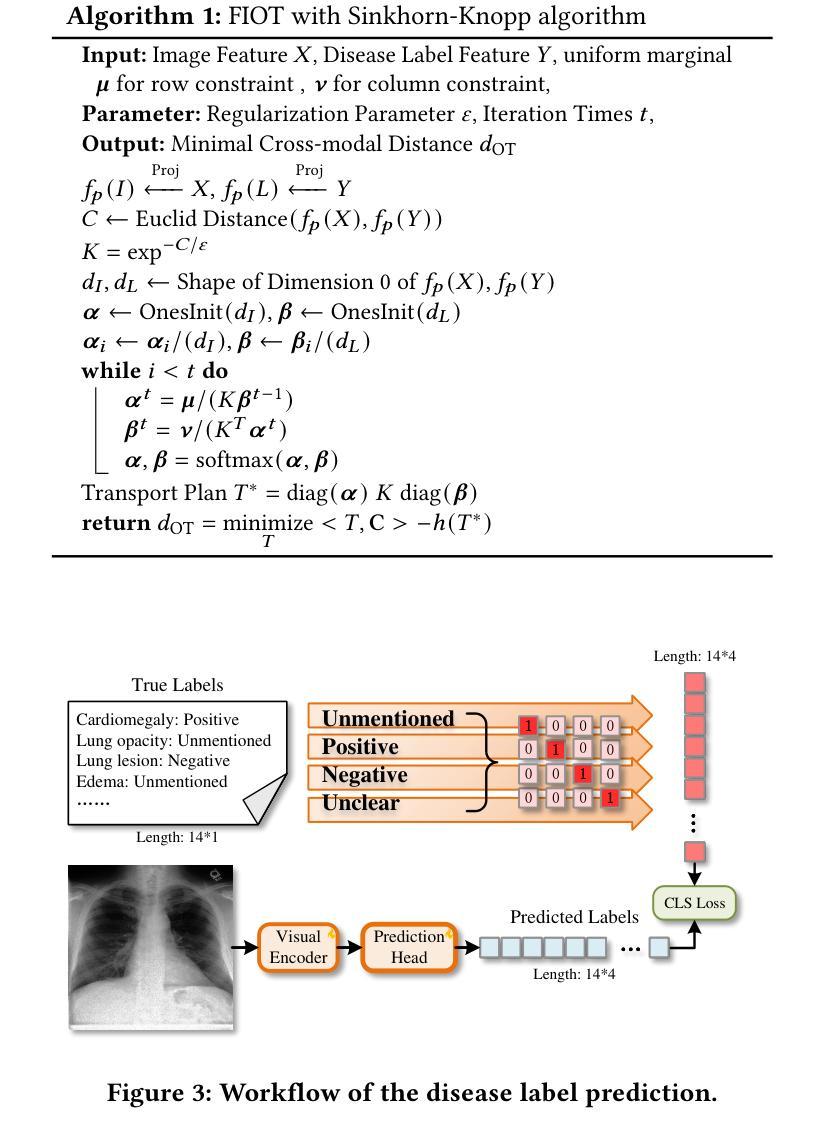

ChestGPT: Integrating Large Language Models and Vision Transformers for Disease Detection and Localization in Chest X-Rays
Authors:Shehroz S. Khan, Petar Przulj, Ahmed Ashraf, Ali Abedi
The global demand for radiologists is increasing rapidly due to a growing reliance on medical imaging services, while the supply of radiologists is not keeping pace. Advances in computer vision and image processing technologies present significant potential to address this gap by enhancing radiologists’ capabilities and improving diagnostic accuracy. Large language models (LLMs), particularly generative pre-trained transformers (GPTs), have become the primary approach for understanding and generating textual data. In parallel, vision transformers (ViTs) have proven effective at converting visual data into a format that LLMs can process efficiently. In this paper, we present ChestGPT, a deep-learning framework that integrates the EVA ViT with the Llama 2 LLM to classify diseases and localize regions of interest in chest X-ray images. The ViT converts X-ray images into tokens, which are then fed, together with engineered prompts, into the LLM, enabling joint classification and localization of diseases. This approach incorporates transfer learning techniques to enhance both explainability and performance. The proposed method achieved strong global disease classification performance on the VinDr-CXR dataset, with an F1 score of 0.76, and successfully localized pathologies by generating bounding boxes around the regions of interest. We also outline several task-specific prompts, in addition to general-purpose prompts, for scenarios radiologists might encounter. Overall, this framework offers an assistive tool that can lighten radiologists’ workload by providing preliminary findings and regions of interest to facilitate their diagnostic process.
随着对医学成像服务日益增长的依赖,全球对放射科医生的需求迅速增加,而放射科医生的供应却跟不上这一需求。计算机视觉和图像处理技术的进步为解决这一差距提供了巨大潜力,通过增强放射科医生的能力和提高诊断准确性。大型语言模型(LLMs)尤其是预训练生成变压器(GPTs)已成为理解和生成文本数据的主要方法。同时,视觉变压器(ViTs)已证明其在将视觉数据转换为LLMs可以高效处理格式方面的有效性。在本文中,我们提出了ChestGPT,这是一个深度学习框架,它将EVA ViT与Llama 2 LLM集成在一起,用于对胸部X射线图像中的疾病进行分类并定位感兴趣区域。ViT将X射线图像转换为令牌,然后连同工程提示一起输入到LLM中,从而实现疾病的联合分类和定位。这种方法结合了迁移学习技术,以提高解释性和性能。所提出的方法在VinDr-CXR数据集上实现了强大的全球疾病分类性能,F1分数为0.76,并通过围绕感兴趣区域生成边界框成功定位了病理。我们还概述了除通用提示外,针对放射科医生可能遇到的各种情景的特定任务提示。总的来说,该框架提供了一个辅助工具,通过提供初步发现和感兴趣区域来减轻放射科医生的工作量,促进他们的诊断过程。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 5 figures, 4 tables
Summary
医学影像学需求激增与放射科医生资源不足之间矛盾日益凸显,计算机视觉和图像处理技术的进展为解决这一矛盾带来机遇。本文介绍了ChestGPT,一个深度学习框架,它通过集成EVA ViT和Llama 2 LLM,对胸片X射线图像进行疾病分类和感兴趣区域定位。该框架利用转换学习技术提高解释性和性能,在VinDr-CXR数据集上取得了较高的全球疾病分类性能(F1分数为0.76),并能成功定位病理区域。此框架为放射科医生提供初步诊断结果和感兴趣区域提示,可减轻其工作量。
Key Takeaways
- 全球对放射科医生的需求迅速增长,但供应不足。
- 计算机视觉和图像处理技术有助于解决这一矛盾。
- ChestGPT是一个深度学习框架,结合了EVA ViT和Llama 2 LLM,用于X射线图像的疾病分类和区域定位。
- 该框架使用转换学习技术以提高解释性和性能。
- 在VinDr-CXR数据集上取得了较高的疾病分类性能(F1分数为0.76)。
- 该框架能成功定位病理区域,生成围绕感兴趣区域的边界框。
点此查看论文截图

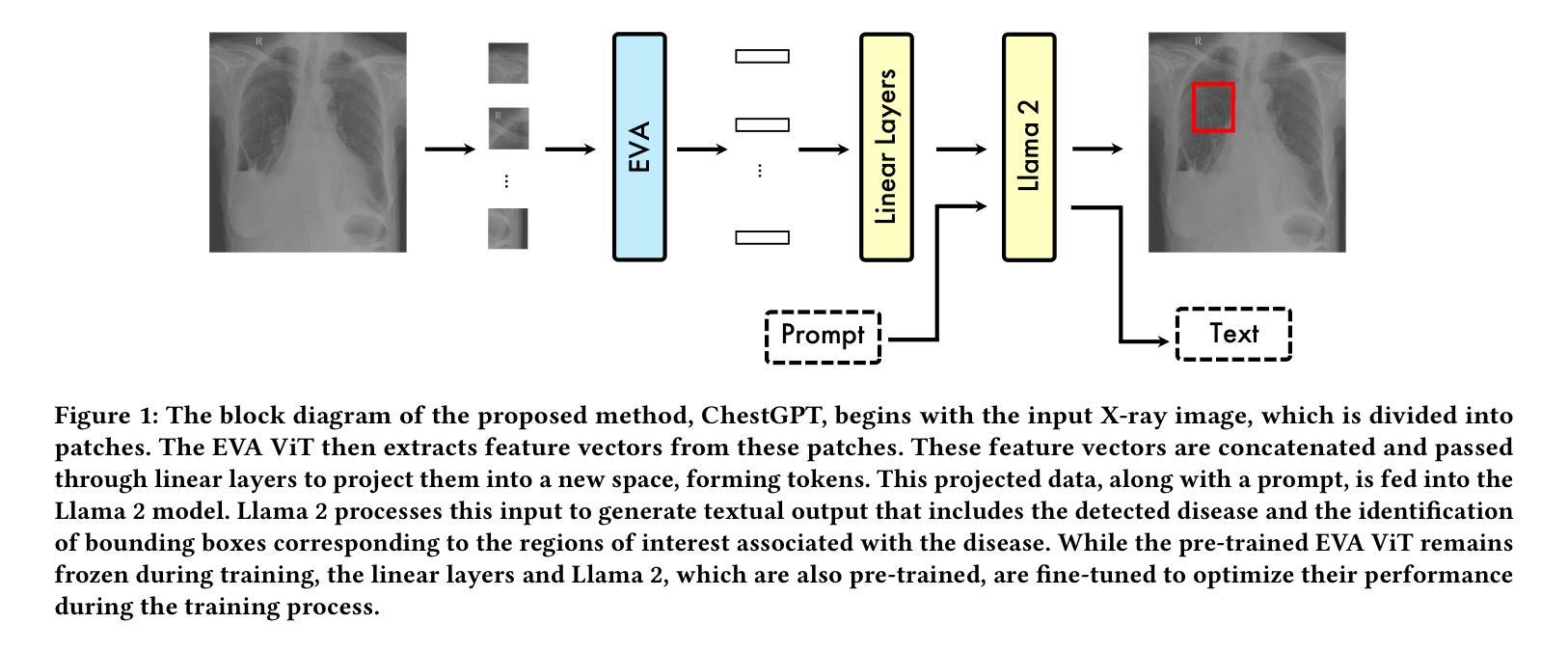
SAMed-2: Selective Memory Enhanced Medical Segment Anything Model
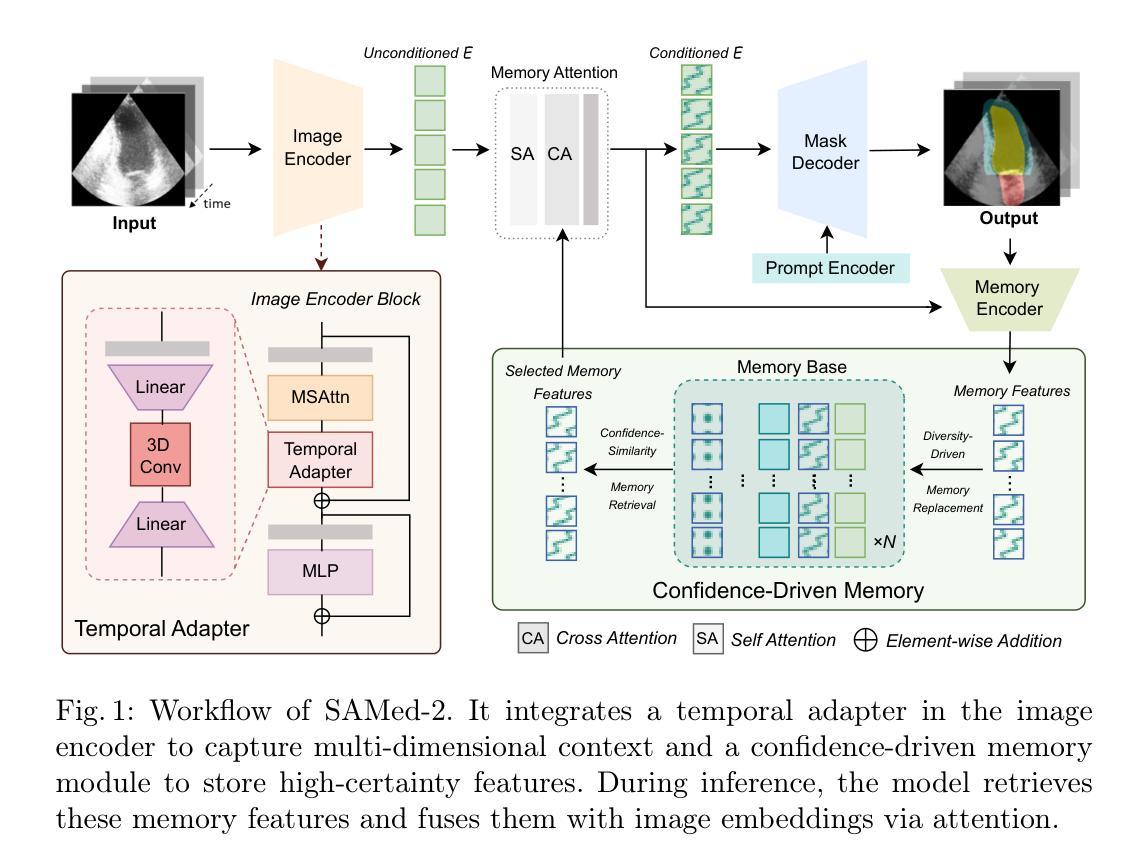
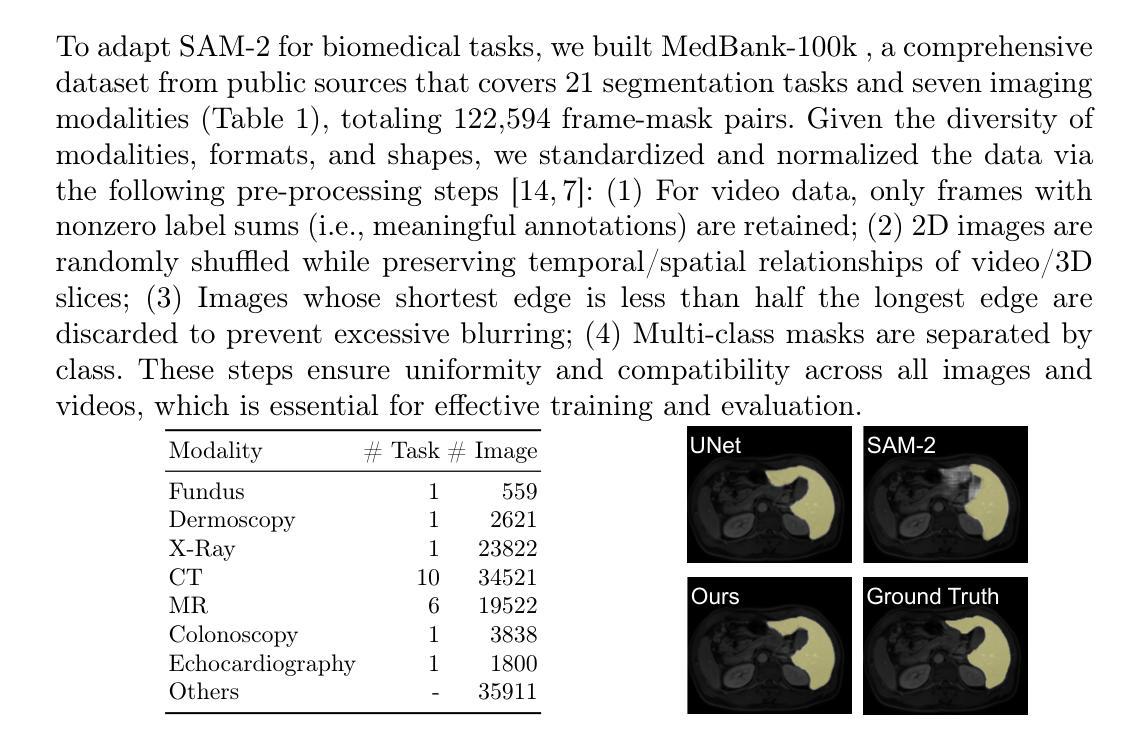
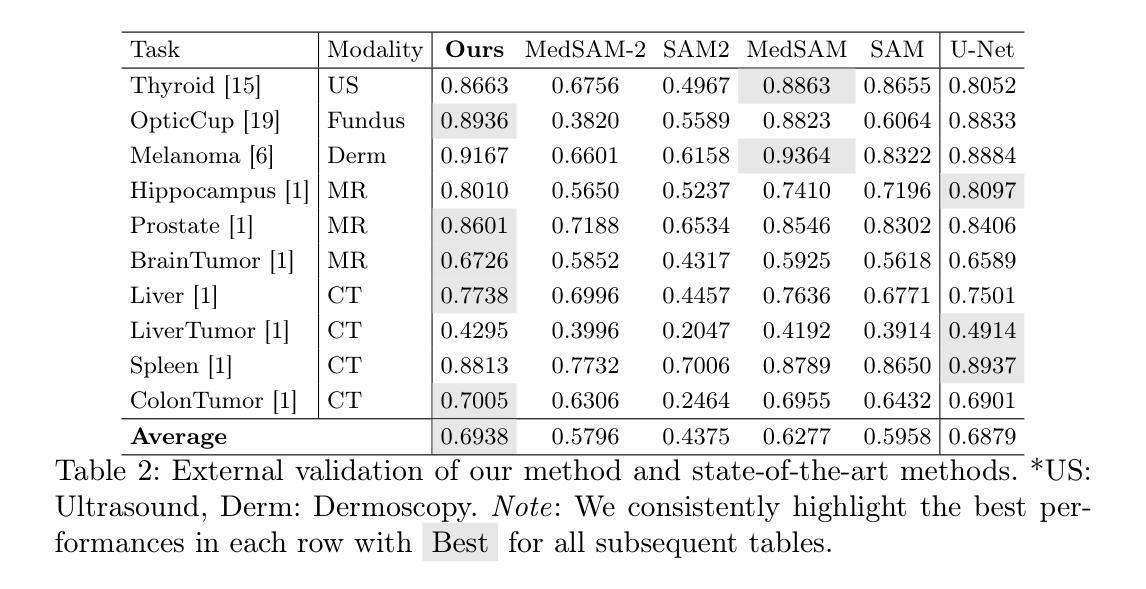
Authors:Zhiling Yan, Sifan Song, Dingjie Song, Yiwei Li, Rong Zhou, Weixiang Sun, Zhennong Chen, Sekeun Kim, Hui Ren, Tianming Liu, Quanzheng Li, Xiang Li, Lifang He, Lichao Sun
Recent “segment anything” efforts show promise by learning from large-scale data, but adapting such models directly to medical images remains challenging due to the complexity of medical data, noisy annotations, and continual learning requirements across diverse modalities and anatomical structures. In this work, we propose SAMed-2, a new foundation model for medical image segmentation built upon the SAM-2 architecture. Specifically, we introduce a temporal adapter into the image encoder to capture image correlations and a confidence-driven memory mechanism to store high-certainty features for later retrieval. This memory-based strategy counters the pervasive noise in large-scale medical datasets and mitigates catastrophic forgetting when encountering new tasks or modalities. To train and evaluate SAMed-2, we curate MedBank-100k, a comprehensive dataset spanning seven imaging modalities and 21 medical segmentation tasks. Our experiments on both internal benchmarks and 10 external datasets demonstrate superior performance over state-of-the-art baselines in multi-task scenarios. The code is available at: https://github.com/ZhilingYan/Medical-SAM-Bench.
最近的“分割任何事物”的努力通过从大规模数据中学习显示出潜力,但直接将此类模型应用于医学图像仍然存在挑战,这主要是由于医学数据的复杂性、标注的噪声以及跨不同模态和解剖结构进行持续学习的要求。在这项工作中,我们提出了SAMed-2,这是一个基于SAM-2架构的新医学图像分割基础模型。具体来说,我们在图像编码器中加入了一个时间适配器来捕捉图像相关性,并引入了一种基于信心的内存机制来存储高确定性特征以供以后检索。这种基于内存的策略对抗了大规模医学数据集中普遍存在的噪声,并减轻了遇到新任务或模态时的灾难性遗忘。为了训练和评估SAMed-2,我们整理了MedBank-100k数据集,这是一个涵盖七种成像模态和21个医学分割任务的综合数据集。我们在内部基准测试和10个外部数据集上的实验表明,在多任务场景中,它的性能优于最新基准测试。代码可用在:https://github.com/ZhilingYan/Medical-SAM-Bench。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by MICCAI 2025
Summary
基于SAM-2架构,针对医学图像分割任务,提出了SAMed-2基础模型。该模型引入了时间适配器捕捉图像关联,并采用了信心驱动的记忆机制来存储高确定性特征以供后续检索。此记忆策略有助于应对大规模医学数据集中的普遍噪声,并在遇到新任务或模态时减轻灾难性遗忘。为训练和评估SAMed-2,我们创建了包含七种成像模态和21项医学分割任务的MedBank-100k综合数据集。实验表明,该模型在多任务场景下的性能优于现有先进技术。
Key Takeaways
- SAMed-2模型是基于SAM-2架构构建的,用于医学图像分割。
- 引入了时间适配器来捕捉医学图像中的关联。
- 采用信心驱动的记忆机制来应对医学数据集中普遍存在的噪声问题。
- 该记忆机制有助于减轻在遇到新任务或模态时的灾难性遗忘问题。
- MedBank-100k数据集用于训练和评估SAMed-2模型,包含七种成像模态和21项医学分割任务。
- 实验结果表明,SAMed-2模型在多任务场景下的性能优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图