⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-09 更新
CVFusion: Cross-View Fusion of 4D Radar and Camera for 3D Object Detection
Authors:Hanzhi Zhong, Zhiyu Xiang, Ruoyu Xu, Jingyun Fu, Peng Xu, Shaohong Wang, Zhihao Yang, Tianyu Pu, Eryun Liu
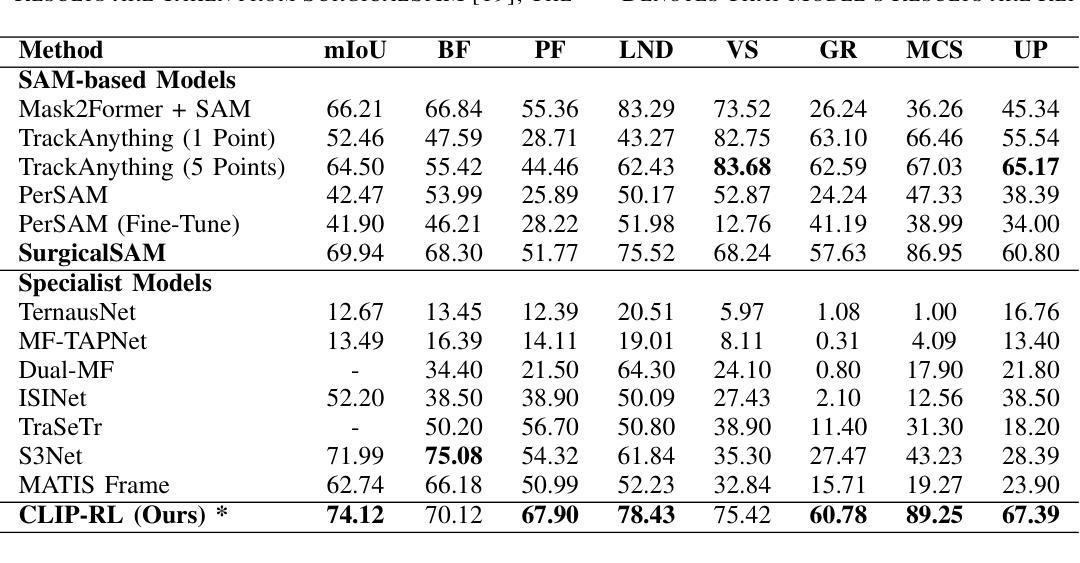
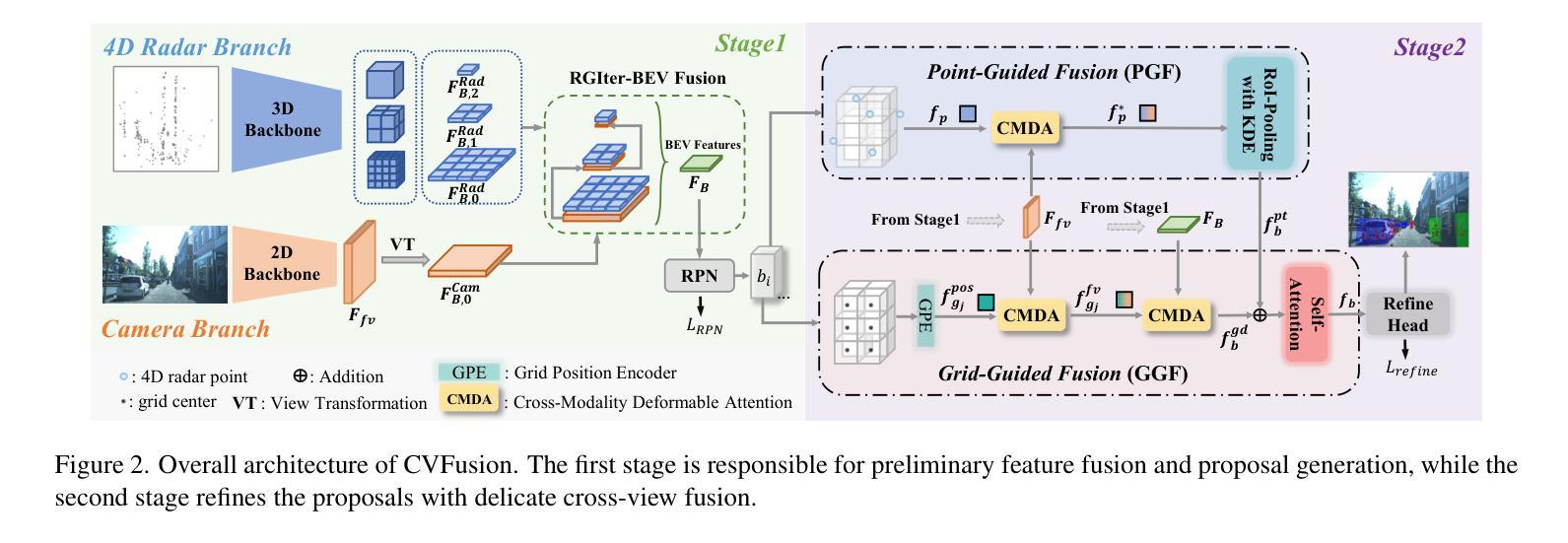
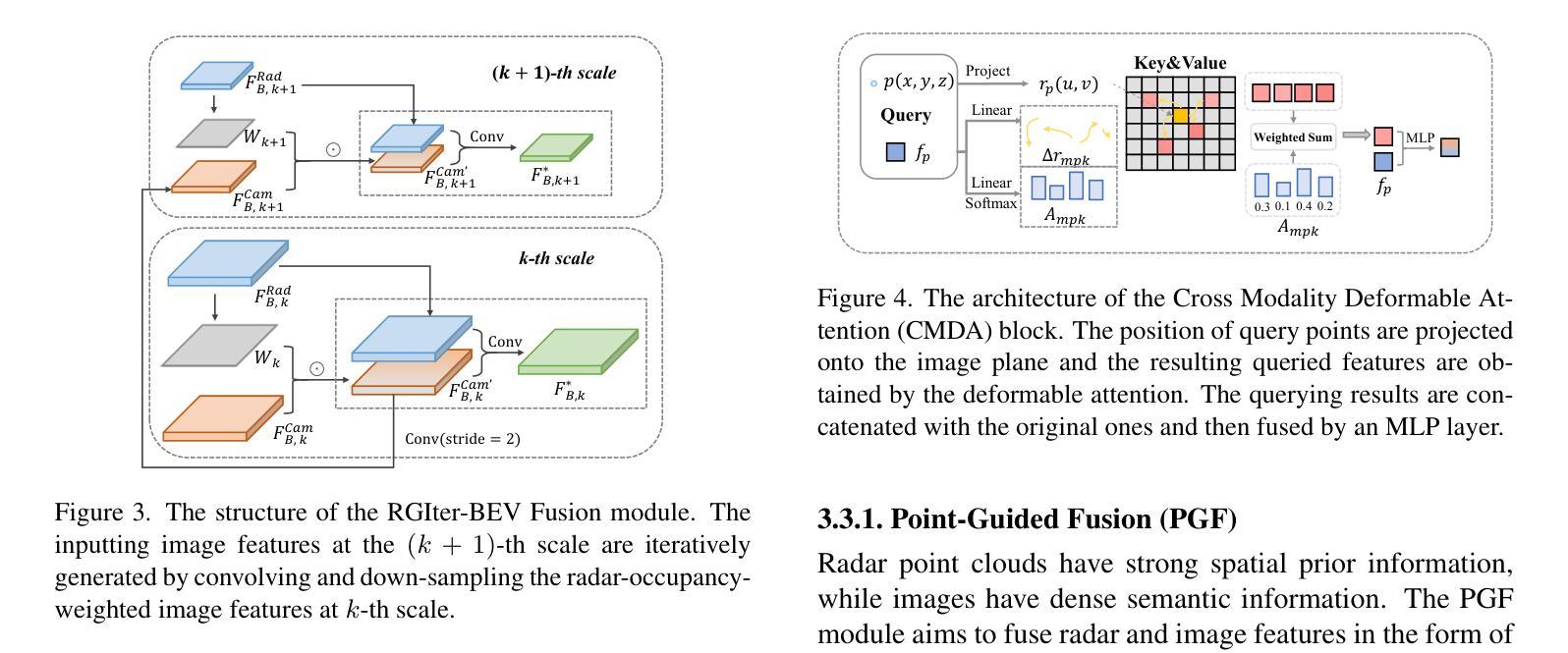
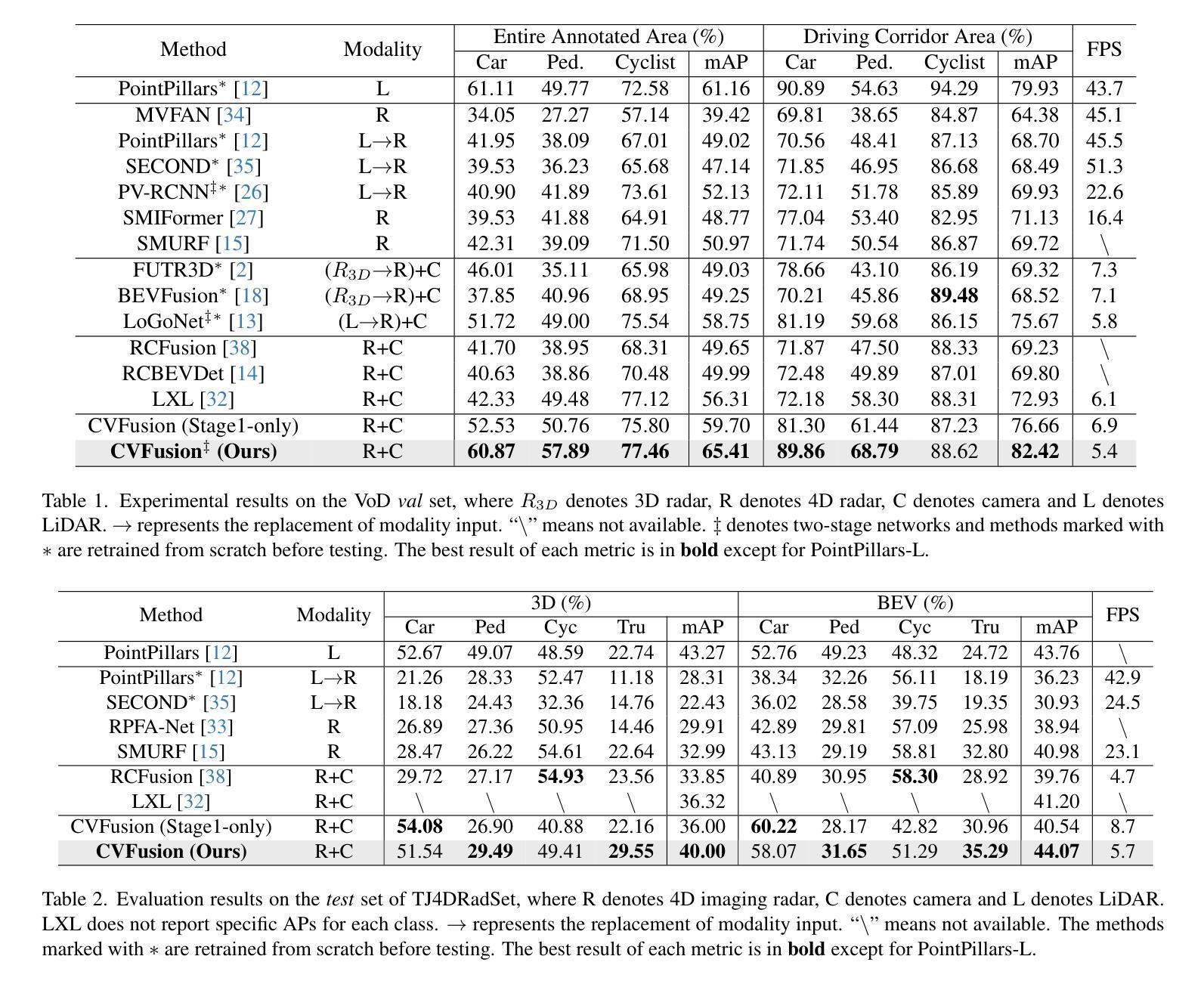
4D radar has received significant attention in autonomous driving thanks to its robustness under adverse weathers. Due to the sparse points and noisy measurements of the 4D radar, most of the research finish the 3D object detection task by integrating images from camera and perform modality fusion in BEV space. However, the potential of the radar and the fusion mechanism is still largely unexplored, hindering the performance improvement. In this study, we propose a cross-view two-stage fusion network called CVFusion. In the first stage, we design a radar guided iterative (RGIter) BEV fusion module to generate high-recall 3D proposal boxes. In the second stage, we aggregate features from multiple heterogeneous views including points, image, and BEV for each proposal. These comprehensive instance level features greatly help refine the proposals and generate high-quality predictions. Extensive experiments on public datasets show that our method outperforms the previous state-of-the-art methods by a large margin, with 9.10% and 3.68% mAP improvements on View-of-Delft (VoD) and TJ4DRadSet, respectively. Our code will be made publicly available.
4D雷达由于其恶劣天气下的稳健性而在自动驾驶领域备受关注。由于4D雷达的点数稀疏和测量噪声,大多数研究通过整合相机图像并在BEV空间进行模态融合来完成3D目标检测任务。然而,雷达的潜力和融合机制尚未得到充分探索,阻碍了性能的提升。在本研究中,我们提出了一种跨视图两阶段融合网络,名为CVFusion。在第一阶段,我们设计了雷达引导迭代(RGIter)BEV融合模块,以生成高召回率的3D候选框。在第二阶段,我们从多个异构视图(包括点、图像和BEV)为每个候选框聚合特征。这些全面的实例级特征有助于改进候选框并生成高质量预测。在公开数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法大幅超越了以前的最先进方法,在Delft视角(VoD)和TJ4DRadSet上的mAP分别提高了9.10%和3.68%。我们的代码将公开提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
这是一篇关于4D雷达在自动驾驶中应用的论文摘要。文章介绍了当前自主驾驶中对4D雷达的研究现状及其面临的主要挑战。研究提出了一种名为CVFusion的跨视角两阶段融合网络,旨在通过雷达引导迭代(RGIter)BEV融合模块生成高质量的三维提议框,并通过多视角特征聚合进一步提高预测精度。实验结果表明,该方法在公共数据集上的性能优于先前的方法,特别是在VoD和TJ4DRadSet数据集上的mAP指标有明显提升。
Key Takeaways
- 4D雷达在自动驾驶中受到广泛关注,因其恶劣天气下的稳健性。
- 研究提出了CVFusion网络,这是一种跨视角两阶段融合网络。
- 第一阶段设计了一个雷达引导迭代(RGIter)BEV融合模块,用于生成高质量的三维提议框。
- 第二阶段从不同视角(点、图像和BEV)聚合特征,以优化提议并生成高质量预测。
- 该方法在公共数据集上的性能显著优于先前的方法。
- 在VoD和TJ4DRadSet数据集上的mAP指标有明显提升。
点此查看论文截图

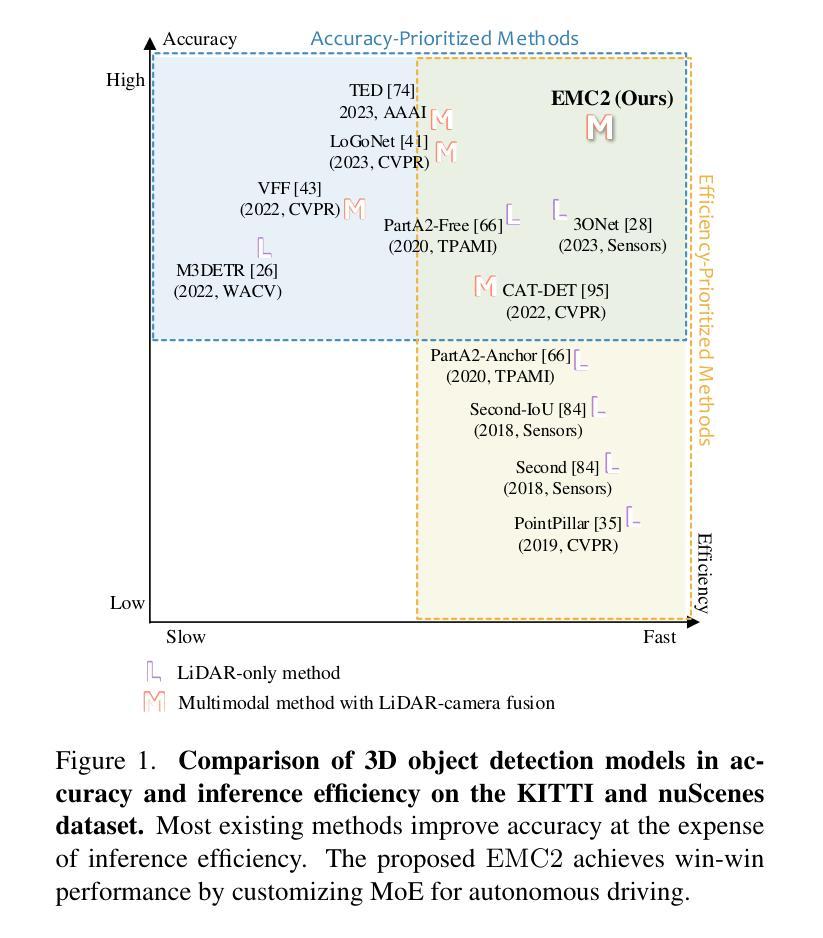
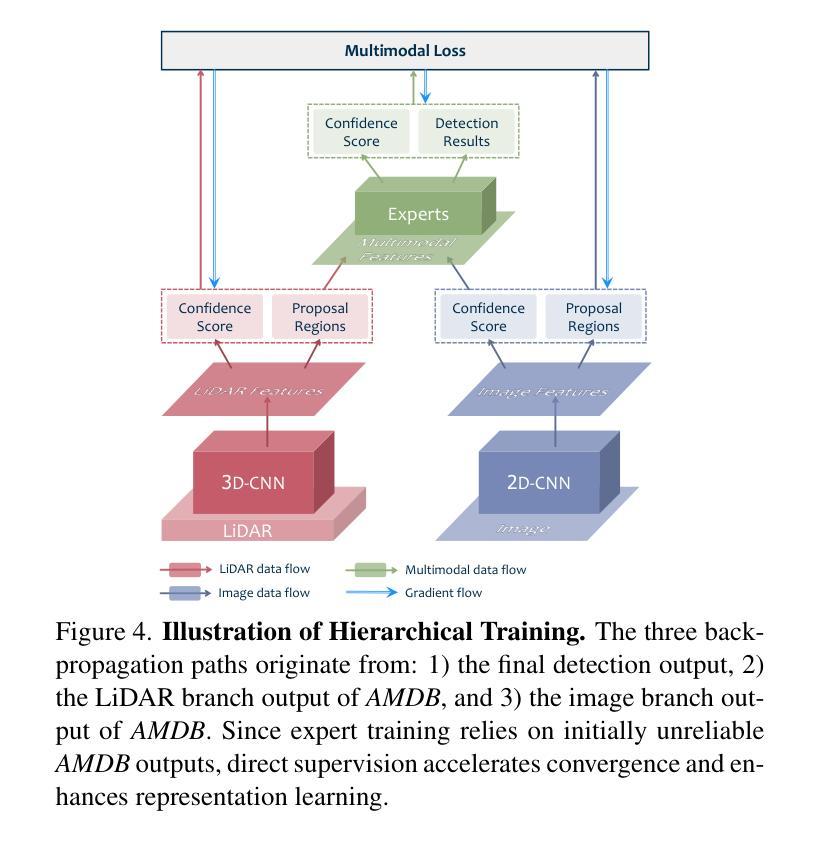
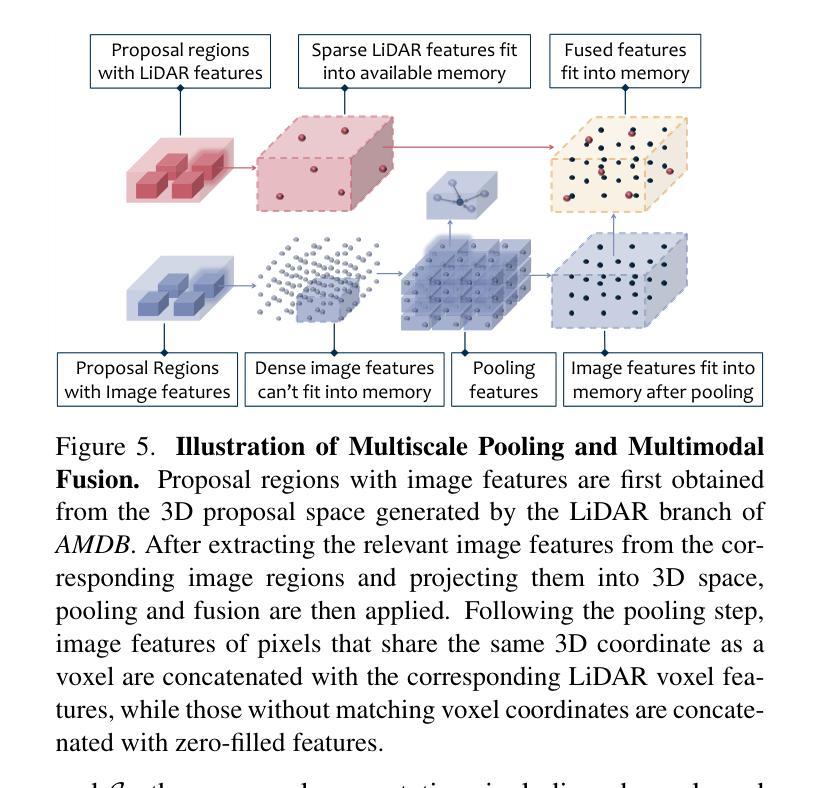
Towards Accurate and Efficient 3D Object Detection for Autonomous Driving: A Mixture of Experts Computing System on Edge
Authors:Linshen Liu, Boyan Su, Junyue Jiang, Guanlin Wu, Cong Guo, Ceyu Xu, Hao Frank Yang
This paper presents Edge-based Mixture of Experts (MoE) Collaborative Computing (EMC2), an optimal computing system designed for autonomous vehicles (AVs) that simultaneously achieves low-latency and high-accuracy 3D object detection. Unlike conventional approaches, EMC2 incorporates a scenario-aware MoE architecture specifically optimized for edge platforms. By effectively fusing LiDAR and camera data, the system leverages the complementary strengths of sparse 3D point clouds and dense 2D images to generate robust multimodal representations. To enable this, EMC2 employs an adaptive multimodal data bridge that performs multi-scale preprocessing on sensor inputs, followed by a scenario-aware routing mechanism that dynamically dispatches features to dedicated expert models based on object visibility and distance. In addition, EMC2 integrates joint hardware-software optimizations, including hardware resource utilization optimization and computational graph simplification, to ensure efficient and real-time inference on resource-constrained edge devices. Experiments on open-source benchmarks clearly show the EMC2 advancements as a end-to-end system. On the KITTI dataset, it achieves an average accuracy improvement of 3.58% and a 159.06% inference speedup compared to 15 baseline methods on Jetson platforms, with similar performance gains on the nuScenes dataset, highlighting its capability to advance reliable, real-time 3D object detection tasks for AVs.
本文提出了基于边缘计算的混合专家(MoE)协同计算(EMC2)系统。这是一种为自动驾驶车辆设计的最佳计算系统,能够同时实现低延迟和高精度的3D目标检测。不同于传统方法,EMC2采用了一种针对边缘平台的情景感知MoE架构。通过有效地融合激光雷达和相机数据,该系统利用稀疏的3D点云和密集的2D图像的互补优势,生成稳健的多模态表示。为此,EMC2采用自适应多模态数据桥,对传感器输入进行多尺度预处理,然后通过情景感知路由机制,根据目标可见性和距离动态将特征派发到专用专家模型。此外,EMC2集成了联合硬件软件优化,包括硬件资源利用优化和计算图简化,以确保在资源受限的边缘设备上实现高效实时推理。在公开基准测试上的实验清楚地表明了EMC2作为端到端系统的优势。在KITTI数据集上,与Jetson平台上的15种基准方法相比,它的平均精度提高了3.58%,推理速度提高了159.06%,在nuScenes数据集上也取得了类似的性能提升,这突显了其在推动自动驾驶车辆可靠实时3D目标检测任务方面的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICCV 2025
Summary
该论文提出了一种面向自动驾驶汽车的边缘计算系统——边缘基础混合专家协同计算系统(EMC2)。系统实现了低延迟高准确度的3D物体检测,结合了场景感知的混合专家架构和边缘平台优化技术。通过融合激光雷达和相机数据,系统利用稀疏的3D点云和密集的2D图像生成稳健的多模态表示。实验表明,与基准方法相比,在KITTI数据集上平均精度提高了3.58%,推理速度提高了159.06%,展示了其在自动驾驶车辆中的可靠实时3D物体检测能力。
Key Takeaways
以下是文本的主要观点摘要:
- EMC2是一个针对自动驾驶汽车的优化计算系统,实现了低延迟和高精度的3D物体检测。
- 系统结合了场景感知的混合专家架构和边缘平台优化技术。
- 通过融合激光雷达和相机数据,生成稳健的多模态表示。
- EMC2采用自适应多模态数据桥和场景感知路由机制,根据物体可见性和距离动态调度特征到专家模型。
- 系统集成了硬件和软件优化,包括硬件资源利用优化和计算图简化,确保在资源受限的边缘设备上实现高效实时推理。
点此查看论文截图


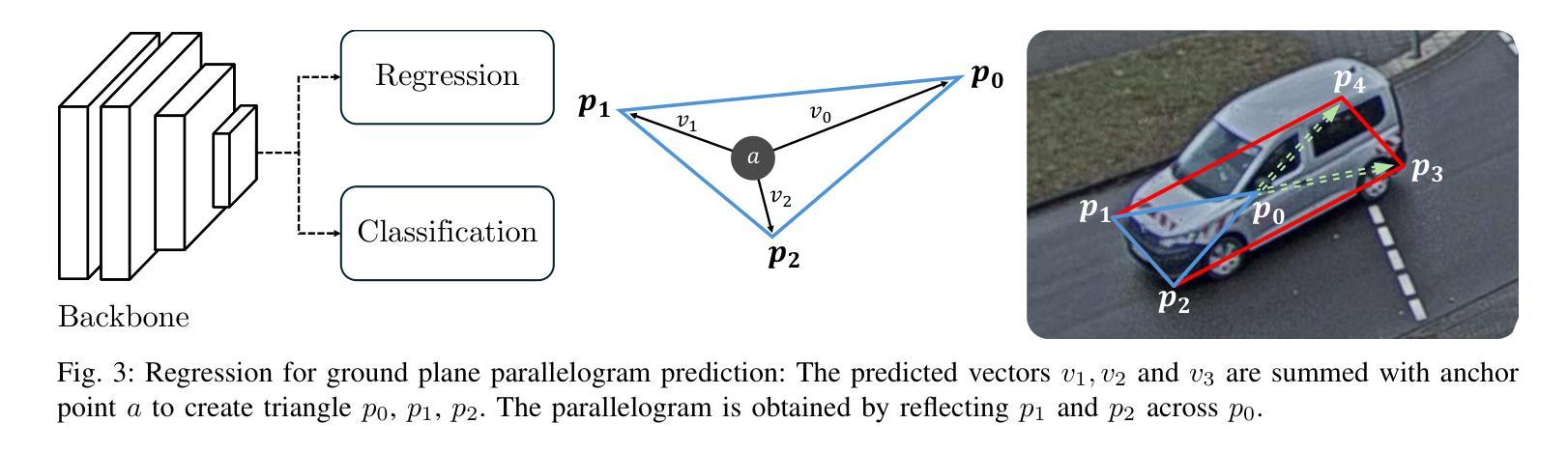
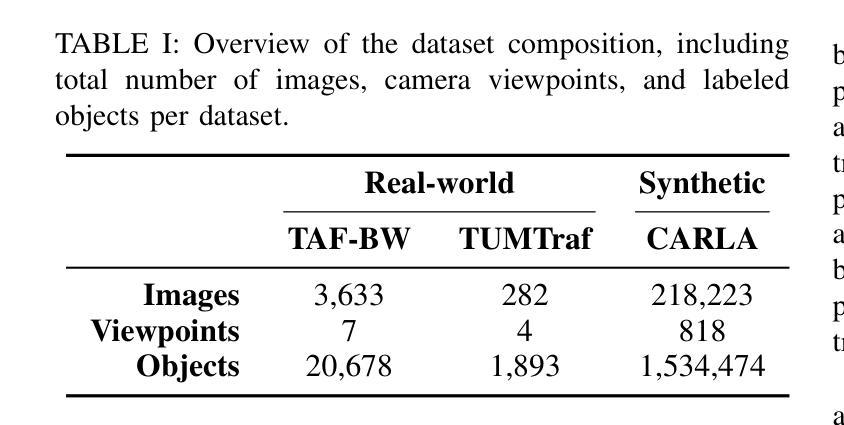
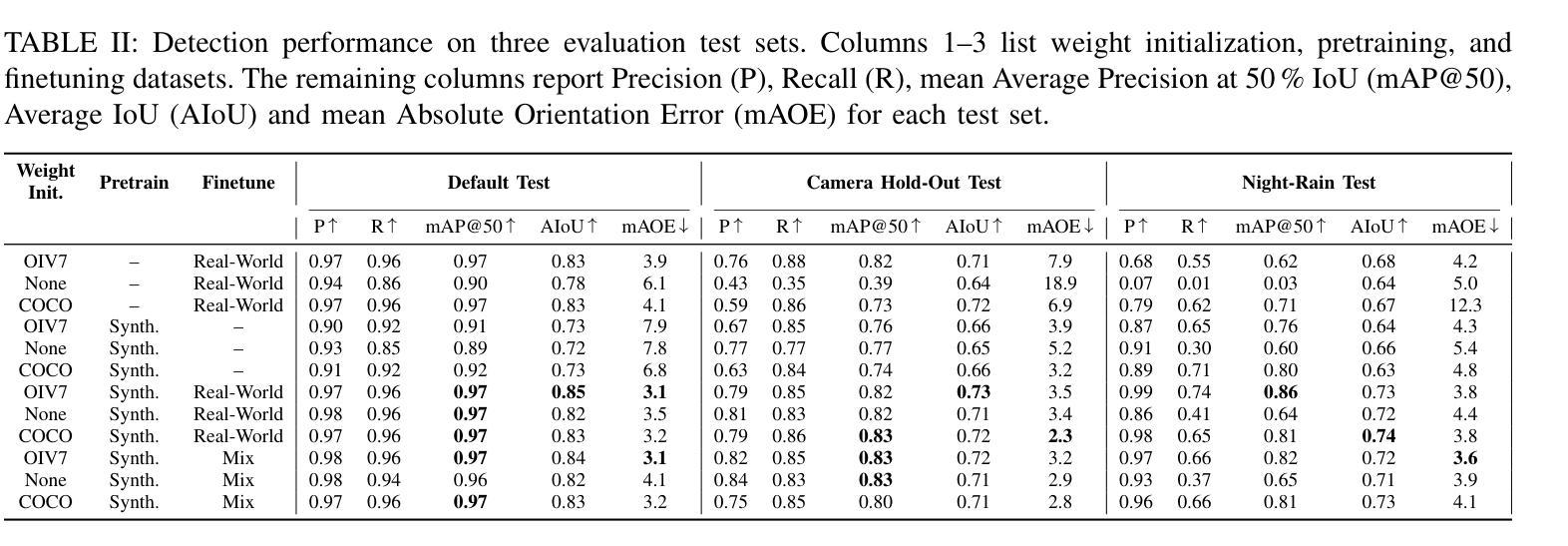
2.5D Object Detection for Intelligent Roadside Infrastructure
Authors:Nikolai Polley, Yacin Boualili, Ferdinand Mütsch, Maximilian Zipfl, Tobias Fleck, J. Marius Zöllner
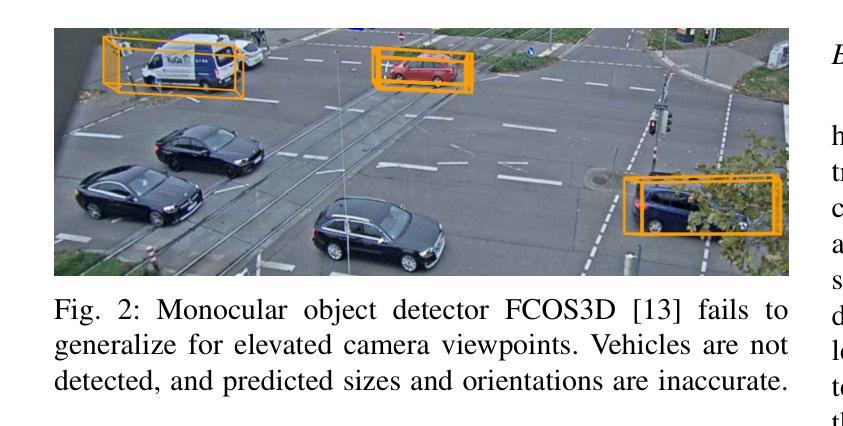
On-board sensors of autonomous vehicles can be obstructed, occluded, or limited by restricted fields of view, complicating downstream driving decisions. Intelligent roadside infrastructure perception systems, installed at elevated vantage points, can provide wide, unobstructed intersection coverage, supplying a complementary information stream to autonomous vehicles via vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication. However, conventional 3D object-detection algorithms struggle to generalize under the domain shift introduced by top-down perspectives and steep camera angles. We introduce a 2.5D object detection framework, tailored specifically for infrastructure roadside-mounted cameras. Unlike conventional 2D or 3D object detection, we employ a prediction approach to detect ground planes of vehicles as parallelograms in the image frame. The parallelogram preserves the planar position, size, and orientation of objects while omitting their height, which is unnecessary for most downstream applications. For training, a mix of real-world and synthetically generated scenes is leveraged. We evaluate generalizability on a held-out camera viewpoint and in adverse-weather scenarios absent from the training set. Our results show high detection accuracy, strong cross-viewpoint generalization, and robustness to diverse lighting and weather conditions. Model weights and inference code are provided at: https://gitlab.kit.edu/kit/aifb/ATKS/public/digit4taf/2.5d-object-detection
自动驾驶车辆的车载传感器可能会受到遮挡、视野受限或视角变化的影响,导致下游驾驶决策复杂化。安装在较高有利位置的智能路边基础设施感知系统可以提供宽阔、无遮挡的交叉路口覆盖范围,并通过车对万物(V2X)通信为自动驾驶车辆提供补充信息流。然而,传统的3D目标检测算法在由上而下的视角和陡峭的相机角度引起的领域变化下难以通用化。我们引入了一个专门针对基础设施路边安装的相机设计的2.5D目标检测框架。与传统的二维或三维目标检测不同,我们采用预测方法来检测图像帧中的车辆地面平面作为平行四边形。平行四边形保留了物体的平面位置、大小和方位,同时省略了高度信息,这在大多数下游应用中是不必要的。为了训练模型,我们结合了现实场景和合成场景。我们在未参与训练的相机视角和恶劣天气场景下评估了模型的通用性。我们的结果显示出较高的检测精度、较强的跨视角通用性以及适应不同光照和天气条件的稳健性。模型权重和推理代码可通过以下链接获取:https://gitlab.kit.edu/kit/aifb/ATKS/public/digit4taf/2.5d-object-detection
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at 2025 IEEE 28th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC)
Summary:
自主驾驶车辆的车载传感器可能受到遮挡、视野受限的影响,影响下游驾驶决策。为解决这一问题,研究者引入了智能路边感知系统,该系统可从高处监控交叉口并为自主车辆提供补充信息。然而,传统的三维物体检测算法难以应对由上而下的视角和陡峭相机角度带来的领域偏移。研究者提出一种适用于路边安装的2.5维物体检测框架,采用预测方法检测车辆的地面平面作为图像帧中的平行四边形。此框架在忽略不必要的高度信息的同时,保留了物体的平面位置、大小和方位。通过结合真实场景和合成场景进行训练,该框架具有良好的检测精度、跨视角的泛化能力以及适应各种照明和天气条件的稳健性。
Key Takeaways:
- 自主驾驶车辆的车载传感器可能受到遮挡或视野限制的影响。
- 智能路边基础设施感知系统可以提供广泛的、无遮挡的交叉口覆盖,为自主车辆提供补充信息。
- 传统三维物体检测算法难以适应由上而下的视角和陡峭相机角度带来的变化。
- 引入了一种2.5维物体检测框架,通过预测车辆地面平面为平行四边形进行检测。
- 该框架忽略物体高度信息,同时保留平面位置、大小和方位。
- 结合真实和合成场景进行训练,具有良好的检测精度和泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图



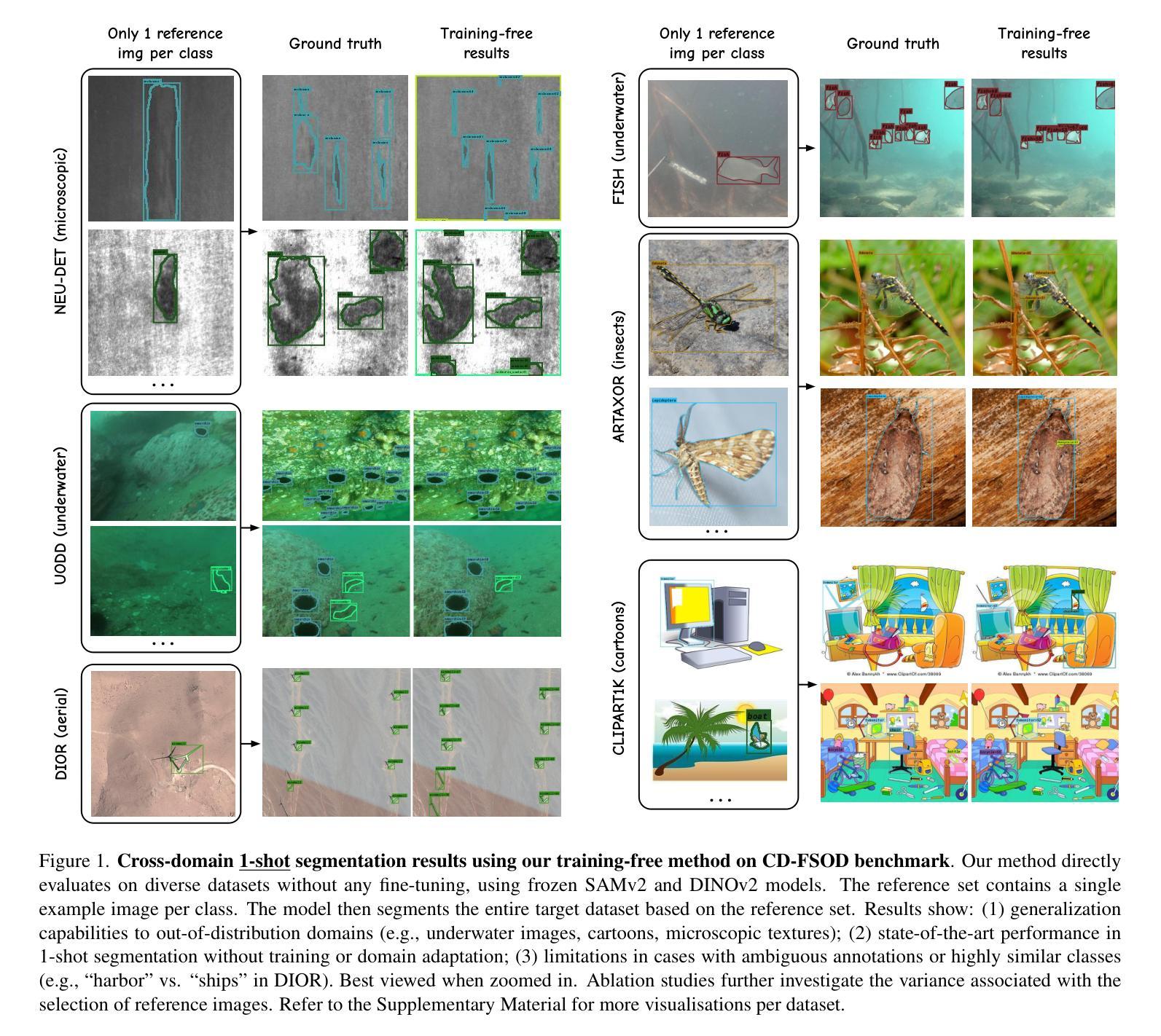
No time to train! Training-Free Reference-Based Instance Segmentation
Authors:Miguel Espinosa, Chenhongyi Yang, Linus Ericsson, Steven McDonagh, Elliot J. Crowley
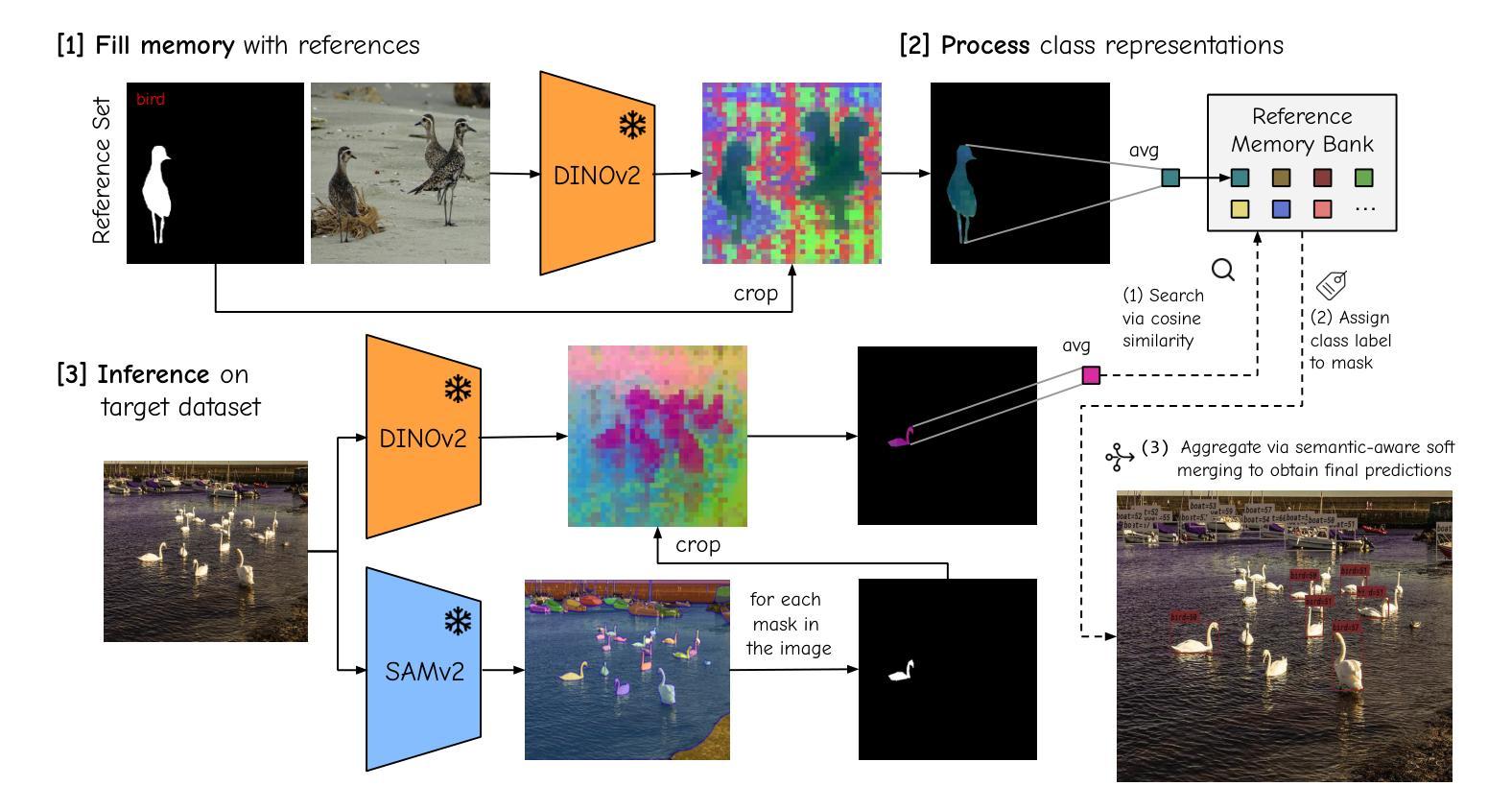
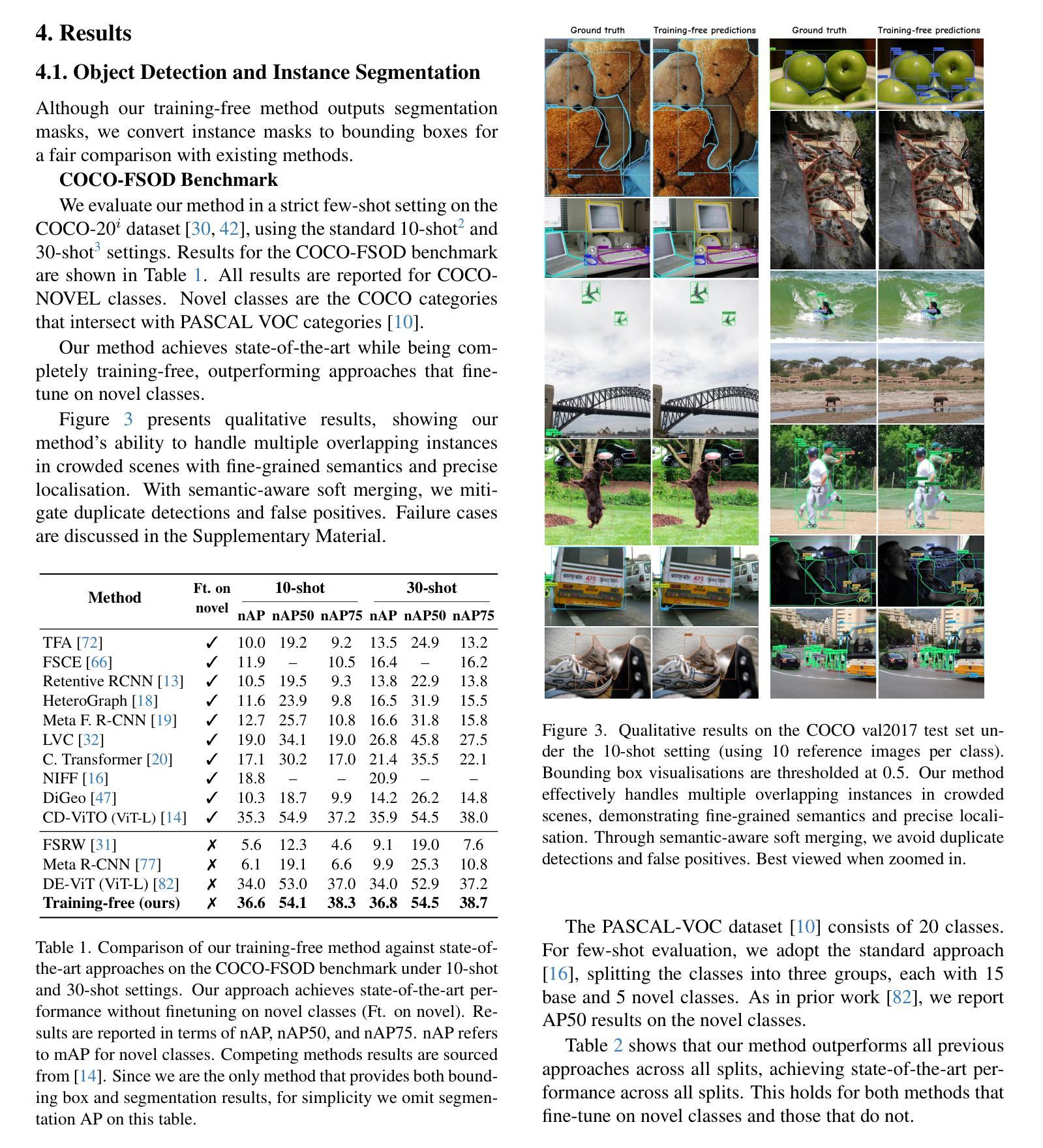
The performance of image segmentation models has historically been constrained by the high cost of collecting large-scale annotated data. The Segment Anything Model (SAM) alleviates this original problem through a promptable, semantics-agnostic, segmentation paradigm and yet still requires manual visual-prompts or complex domain-dependent prompt-generation rules to process a new image. Towards reducing this new burden, our work investigates the task of object segmentation when provided with, alternatively, only a small set of reference images. Our key insight is to leverage strong semantic priors, as learned by foundation models, to identify corresponding regions between a reference and a target image. We find that correspondences enable automatic generation of instance-level segmentation masks for downstream tasks and instantiate our ideas via a multi-stage, training-free method incorporating (1) memory bank construction; (2) representation aggregation and (3) semantic-aware feature matching. Our experiments show significant improvements on segmentation metrics, leading to state-of-the-art performance on COCO FSOD (36.8% nAP), PASCAL VOC Few-Shot (71.2% nAP50) and outperforming existing training-free approaches on the Cross-Domain FSOD benchmark (22.4% nAP).
历史上,图像分割模型的性能一直受到收集大规模标注数据的高成本的限制。Segment Anything Model(SAM)通过一种可提示的、与语义无关的分割范式缓解了这一原始问题,但仍然需要手动视觉提示或复杂的域相关提示生成规则来处理新图像。为了减轻这一新负担,我们的工作研究了在仅提供一小部分参考图像的情况下进行对象分割的任务。我们的关键见解是利用基础模型学到的强大语义先验知识,来识别参考图像和目标图像之间的相应区域。我们发现这种对应关系能够自动生成用于下游任务的实例级分割掩膜,并通过一个多阶段、无需训练的方法实现我们的想法,包括(1)构建内存银行;(2)表示聚合和(3)语义感知特征匹配。我们的实验显示在分割指标上取得了显著改进,并在COCO FSOD(36.8% nAP)、PASCAL VOC Few-Shot(71.2% nAP50)上达到了最先进的性能,并且在跨域FSOD基准测试上超越了现有的无训练方法(22.4% nAP)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint
Summary
图像分割模型的性能长期受到大规模标注数据收集成本高昂的制约。Segment Anything Model(SAM)通过可提示的、语义无关的分割范式缓解了这一问题,但仍需手动视觉提示或复杂的领域相关提示生成规则来处理新图像。为减轻这一新负担,我们的工作研究在仅提供少量参考图像的情况下进行目标分割的任务。我们的关键见解是利用基础模型学习的强语义先验知识,识别参考图像和目标图像之间的对应区域。我们发现这种对应关系能够自动生成用于下游任务的实例级分割掩膜,并通过一个包含(1)内存库构建、(2)表示聚合和(3)语义感知特征匹配的、无需训练的多阶段方法实现了我们的想法。实验表明,该方法在分割指标上取得了显著改进,并在COCO FSOD(36.8% nAP)、PASCAL VOC少数镜头(71.2% nAP50)上达到了最先进的性能,且在跨域FSOD基准测试上优于现有的无需训练的方法(22.4% nAP)。
Key Takeaways
- 图像分割模型长期受大规模标注数据制约。
- Segment Anything Model(SAM)引入可提示的分割范式,但仍需复杂提示操作。
- 研究在仅提供少量参考图像情况下的目标分割任务。
- 利用基础模型的强语义先验知识识别参考图像与目标图像间的对应区域。
- 对应关系能自动生成实例级分割掩膜,用于下游任务。
- 提出一个无需训练的多阶段方法,包括内存库构建、表示聚合和语义感知特征匹配。
点此查看论文截图

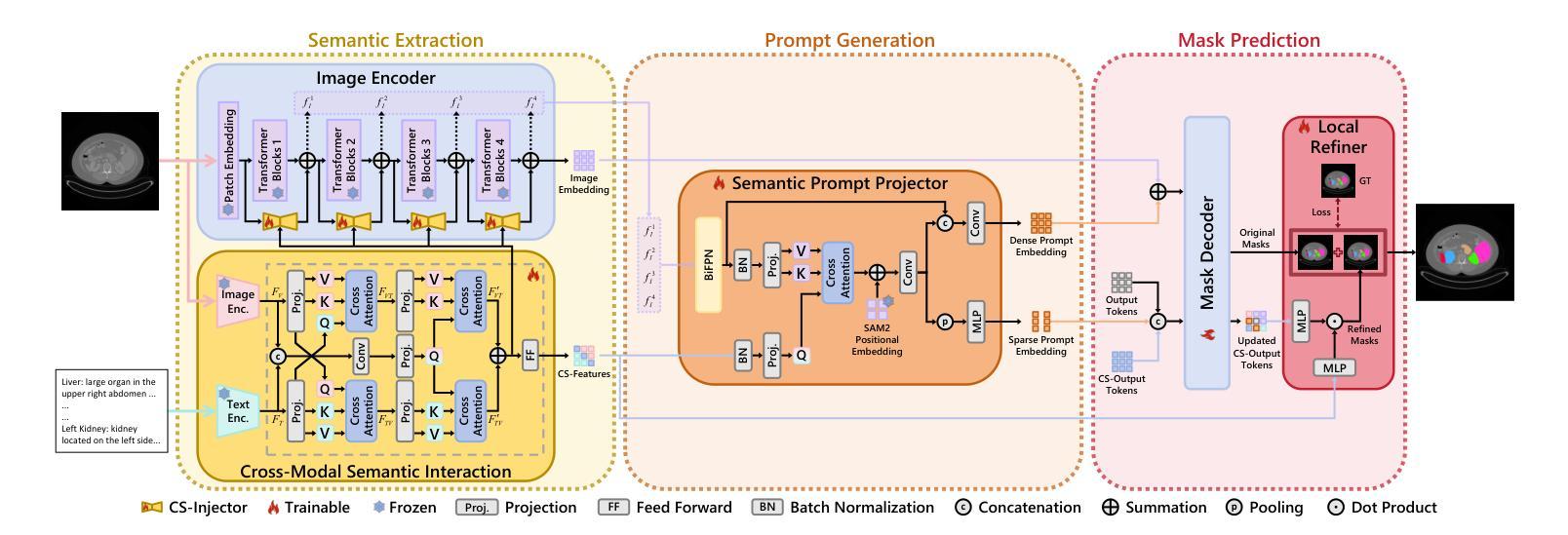
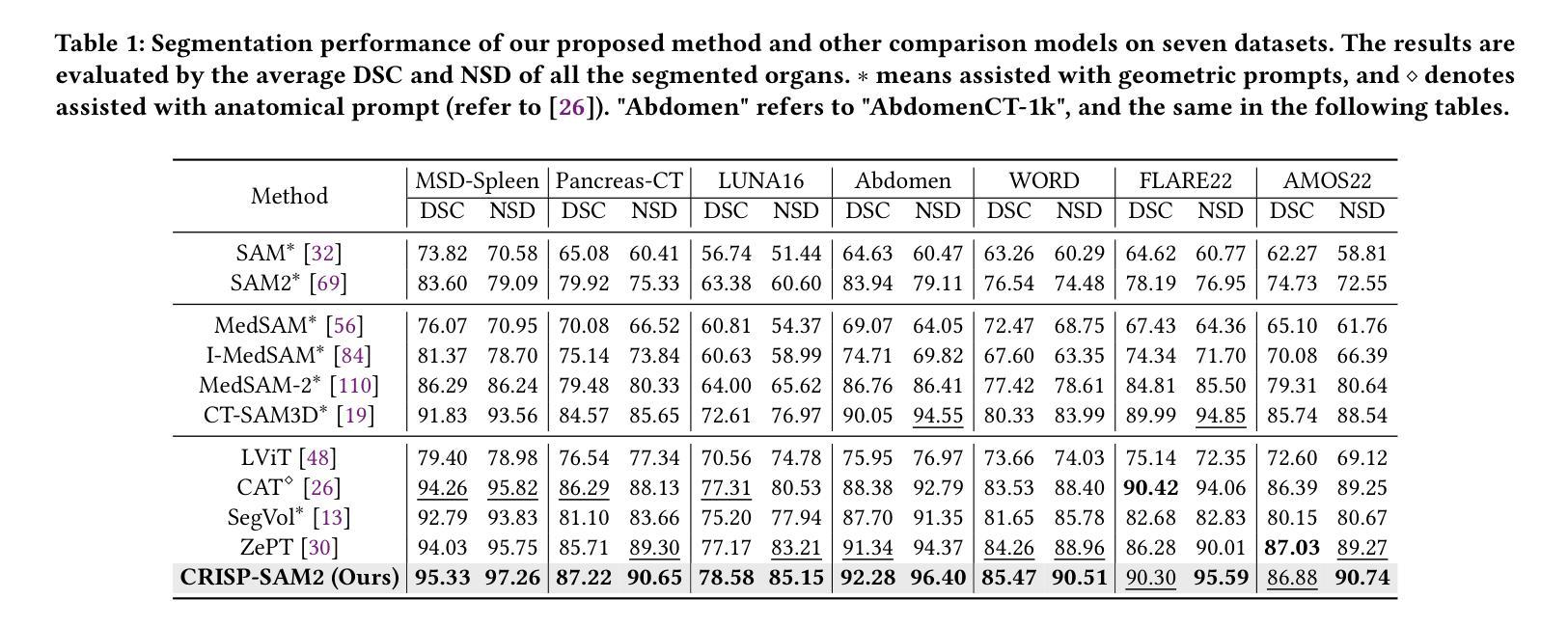
CRISP-SAM2: SAM2 with Cross-Modal Interaction and Semantic Prompting for Multi-Organ Segmentation
Authors:Xinlei Yu, Changmiao Wang, Hui Jin, Ahmed Elazab, Gangyong Jia, Xiang Wan, Changqing Zou, Ruiquan Ge
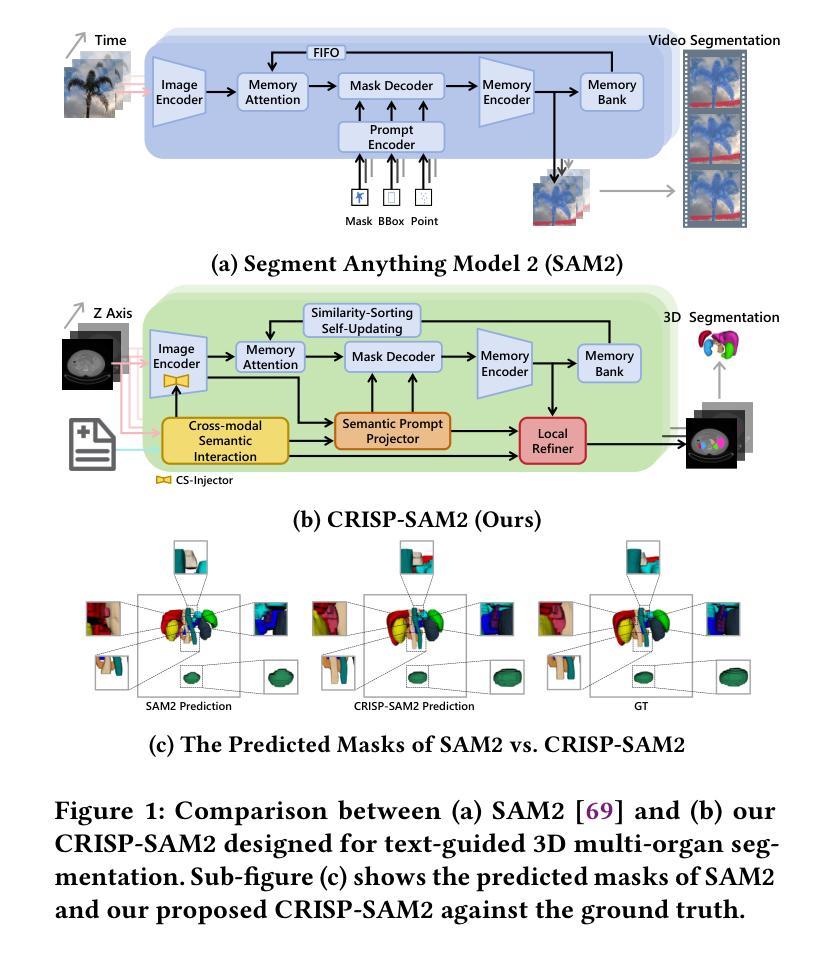
Multi-organ medical segmentation is a crucial component of medical image processing, essential for doctors to make accurate diagnoses and develop effective treatment plans. Despite significant progress in this field, current multi-organ segmentation models often suffer from inaccurate details, dependence on geometric prompts and loss of spatial information. Addressing these challenges, we introduce a novel model named CRISP-SAM2 with CRoss-modal Interaction and Semantic Prompting based on SAM2. This model represents a promising approach to multi-organ medical segmentation guided by textual descriptions of organs. Our method begins by converting visual and textual inputs into cross-modal contextualized semantics using a progressive cross-attention interaction mechanism. These semantics are then injected into the image encoder to enhance the detailed understanding of visual information. To eliminate reliance on geometric prompts, we use a semantic prompting strategy, replacing the original prompt encoder to sharpen the perception of challenging targets. In addition, a similarity-sorting self-updating strategy for memory and a mask-refining process is applied to further adapt to medical imaging and enhance localized details. Comparative experiments conducted on seven public datasets indicate that CRISP-SAM2 outperforms existing models. Extensive analysis also demonstrates the effectiveness of our method, thereby confirming its superior performance, especially in addressing the limitations mentioned earlier. Our code is available at: https://github.com/YU-deep/CRISP_SAM2.git.
医学多器官分割是医学图像处理的重要组成部分,对于医生进行准确的诊断和制定有效的治疗方案至关重要。尽管该领域取得了重大进展,但现有的多器官分割模型往往存在细节不准确、依赖几何提示以及空间信息丢失等问题。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了一种名为CRISP-SAM2的新模型,该模型基于SAM2具有跨模态交互和语义提示。该模型是一种很有前途的方法,可以通过器官的文本描述来进行多器官医学分割。我们的方法首先通过渐进的交叉注意力交互机制将视觉和文本输入转换为跨模态上下文语义。然后,这些语义被注入图像编码器,以增强对视觉信息的详细理解。为了减少对几何提示的依赖,我们采用了一种语义提示策略,以替代原始提示编码器,提高了对具有挑战性的目标的感知能力。此外,还采用了相似度排序的自更新策略对内存进行更新和掩膜细化过程,进一步适应医学影像并增强局部细节。在七个公共数据集上进行的对比实验表明,CRISP-SAM2优于现有模型。广泛的分析也证明了我们的方法的有效性,从而证实了其卓越性能,特别是在解决上述提到的局限性方面。我们的代码可在:https://github.com/YU-deep/CRISP_SAM2.git获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted By ACMMM25
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为CRISP-SAM2的多器官医学分割模型,该模型通过跨模态交互和语义提示技术解决了当前模型在细节准确性、几何提示依赖性和空间信息损失等方面的问题。CRISP-SAM2模型通过将视觉和文本输入转换为跨模态上下文语义,并注入图像编码器以增强对视觉信息的详细理解。此外,采用语义提示策略消除对几何提示的依赖,并采用相似度排序自更新策略和掩膜细化过程进一步适应医学成像并增强局部细节。在七个公共数据集上的对比实验表明,CRISP-SAM2模型优于现有模型。
Key Takeaways
- 多器官医学分割是医疗图像处理中的关键部分,对于医生的准确诊断和治疗计划制定至关重要。
- 当前的多器官分割模型存在细节不准确、依赖几何提示和损失空间信息等问题。
- 引入的CRISP-SAM2模型通过跨模态交互和语义提示技术解决上述问题。
- CRISP-SAM2将视觉和文本输入转换为跨模态上下文语义,提高视觉信息的理解。
- 语义提示策略消除对几何提示的依赖,并采用相似度排序自更新策略和掩膜细化过程来提高模型的性能。
- 在七个公共数据集上的对比实验证明CRISP-SAM2模型优于现有模型。
点此查看论文截图
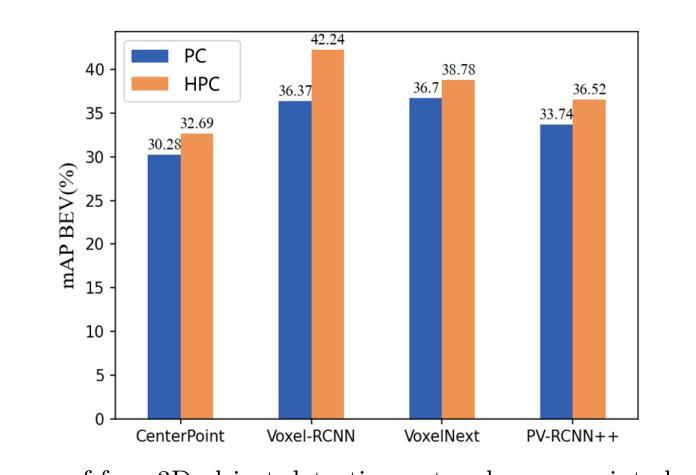
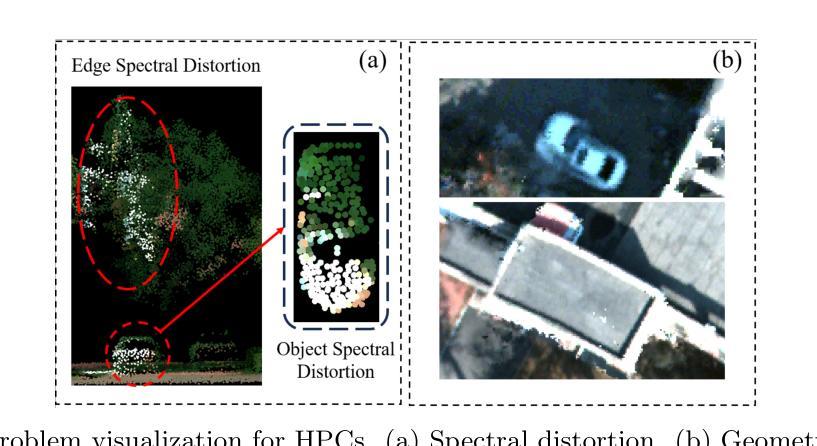
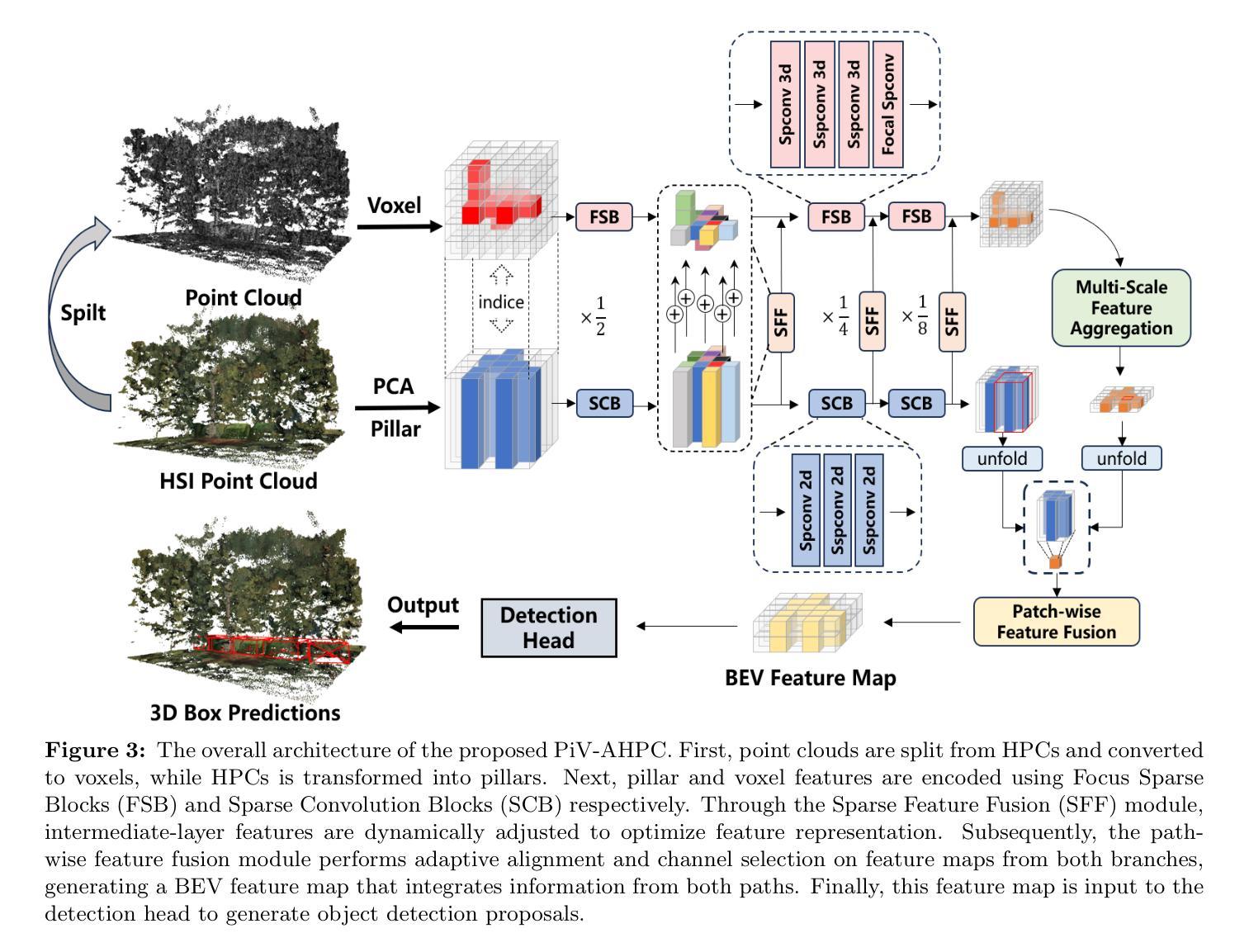
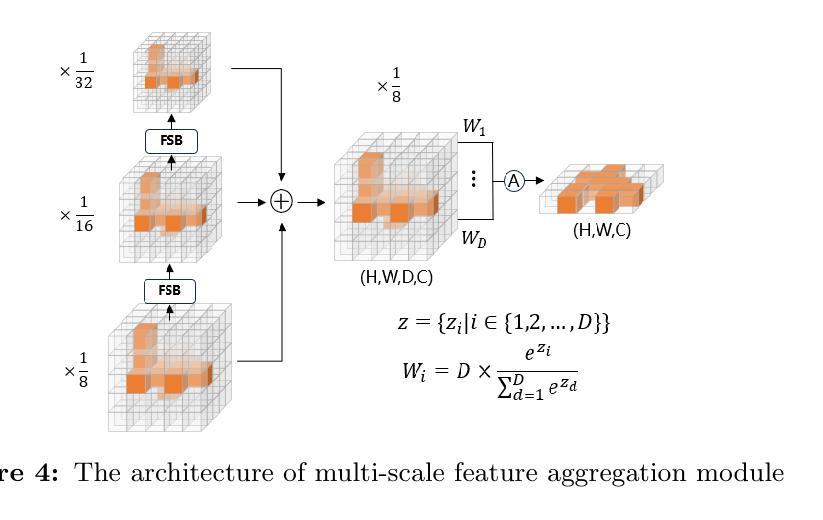
Pillar-Voxel Fusion Network for 3D Object Detection in Airborne Hyperspectral Point Clouds
Authors:Yanze Jiang, Yanfeng Gu, Xian Li
Hyperspectral point clouds (HPCs) can simultaneously characterize 3D spatial and spectral information of ground objects, offering excellent 3D perception and target recognition capabilities. Current approaches for generating HPCs often involve fusion techniques with hyperspectral images and LiDAR point clouds, which inevitably lead to geometric-spectral distortions due to fusion errors and obstacle occlusions. These adverse effects limit their performance in downstream fine-grained tasks across multiple scenarios, particularly in airborne applications. To address these issues, we propose PiV-AHPC, a 3D object detection network for airborne HPCs. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first attempt at this HPCs task. Specifically, we first develop a pillar-voxel dual-branch encoder, where the former captures spectral and vertical structural features from HPCs to overcome spectral distortion, while the latter emphasizes extracting accurate 3D spatial features from point clouds. A multi-level feature fusion mechanism is devised to enhance information interaction between the two branches, achieving neighborhood feature alignment and channel-adaptive selection, thereby organically integrating heterogeneous features and mitigating geometric distortion. Extensive experiments on two airborne HPCs datasets demonstrate that PiV-AHPC possesses state-of-the-art detection performance and high generalization capability.
高光谱点云(HPC)可以同时表征地面物体的3D空间和光谱信息,提供出色的3D感知和目标识别能力。目前生成HPC的方法通常涉及高光谱图像和激光雷达点云的融合技术,由于融合误差和障碍物遮挡,不可避免地会导致几何光谱失真。这些不利影响在多场景下的下游精细任务中限制了其性能,特别是在空中应用方面。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了PiV-AHPC,这是一个用于空中HPC的3D对象检测网络。据我们所知,这是HPC任务上的首次尝试。具体来说,我们首先开发了一个柱体-体素双分支编码器,前者从HPC中提取光谱和垂直结构特征以克服光谱失真,而后者则侧重于从点云中提取准确的3D空间特征。设计了一种多层次特征融合机制,以增强两个分支之间的信息交互,实现邻域特征对齐和通道自适应选择,从而有机地融合异质特征并减轻几何失真。在两个空中HPC数据集上的大量实验表明,PiV-AHPC具有最先进的检测性能和高泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
超光谱点云(HPCs)能同时描述地面物体的三维空间与光谱信息,具备出色的三维感知和目标识别能力。当前生成HPCs的方法大多采用与超光谱图像和激光雷达点云的融合技术,但由于融合误差和遮挡问题,不可避免地会出现几何光谱失真。这些问题在多场景下游精细任务中,特别是在空中应用中的性能表现尤为突出。为解决这些问题,我们首次提出PiV-AHPC——一种用于空中HPCs的三维目标检测网络。该网络通过构建支柱体素双分支编码器,克服光谱失真并提取准确的3D空间特征,同时设计多层次特征融合机制,强化信息交互,实现邻域特征对齐和通道自适应选择,从而有机融合异构图特征并减轻几何失真。在两组空中HPCs数据集上的实验表明,PiV-AHPC具备一流检测性能和高泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 超光谱点云(HPCs)融合了三维空间和光谱信息,为地面物体提供了卓越的三维感知和目标识别功能。
- 当前HPC生成方法主要基于融合技术,但存在几何光谱失真问题。
- PiV-AHPC网络首次尝试解决空中HPCs的三维目标检测问题。
- PiV-AHPC采用支柱体素双分支编码器,分别处理光谱和垂直结构特征以及准确的3D空间特征。
- 多层次特征融合机制强化了信息交互,实现了特征对齐和通道自适应选择。
- 实验证明,PiV-AHPC在检测性能和泛化能力上均达到一流水平。
点此查看论文截图

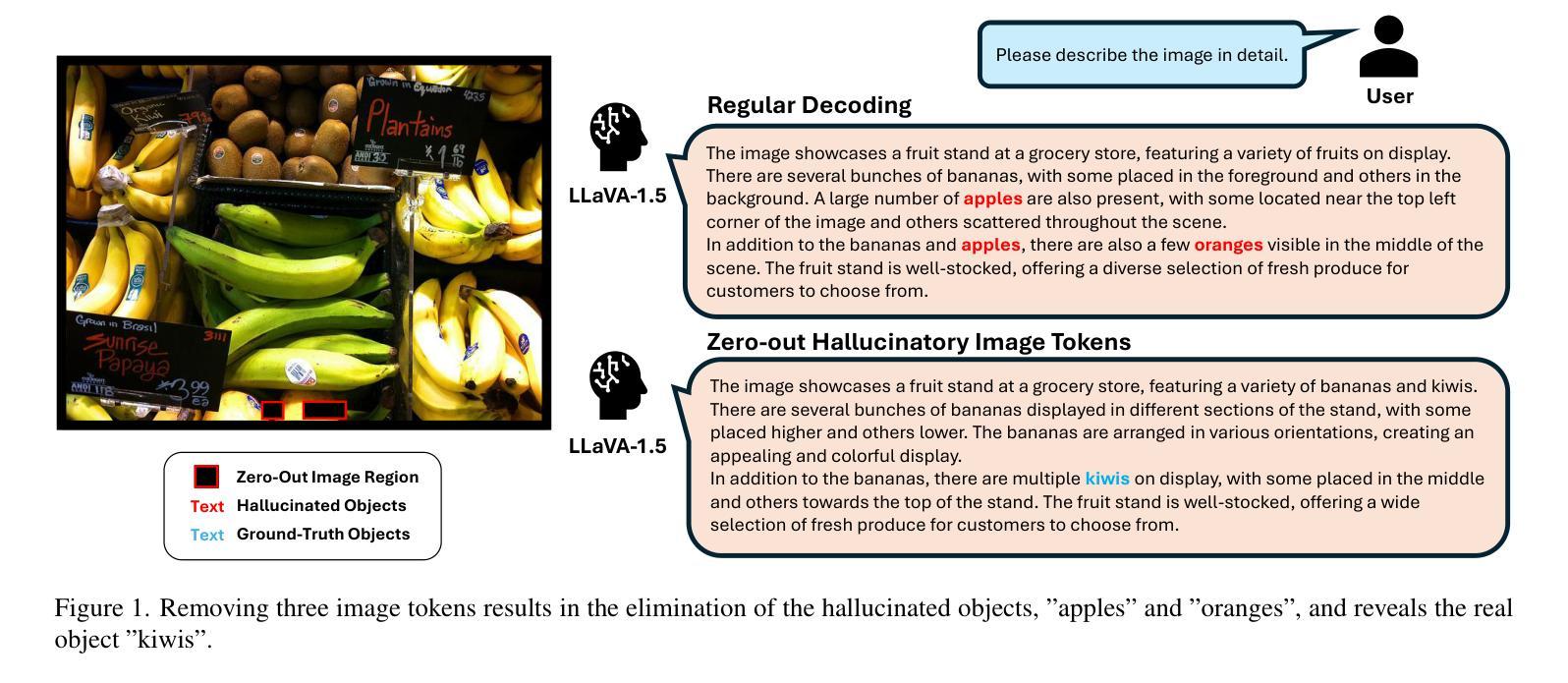
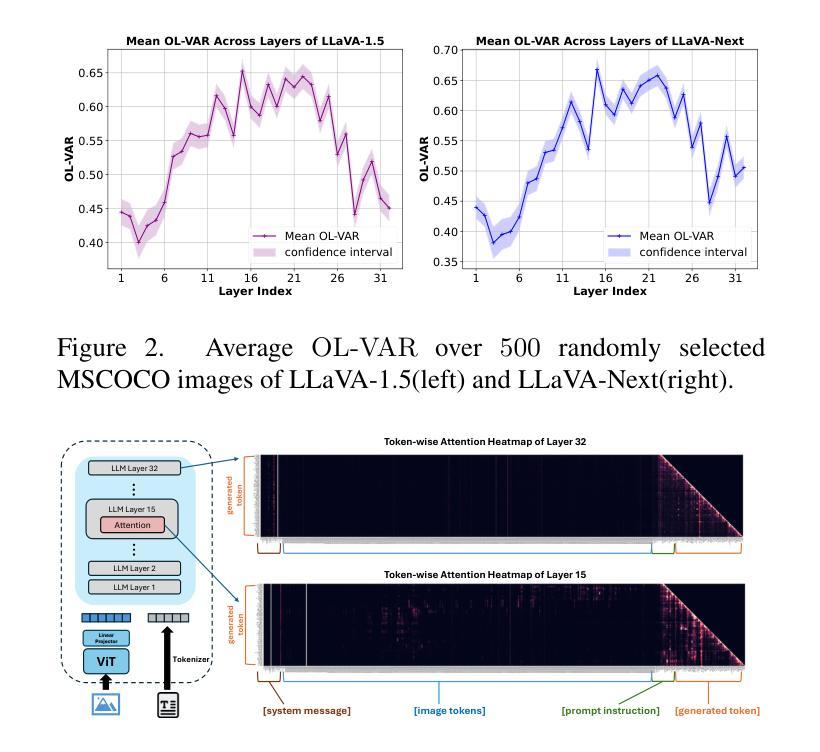
Hallucinatory Image Tokens: A Training-free EAZY Approach on Detecting and Mitigating Object Hallucinations in LVLMs
Authors:Liwei Che, Tony Qingze Liu, Jing Jia, Weiyi Qin, Ruixiang Tang, Vladimir Pavlovic
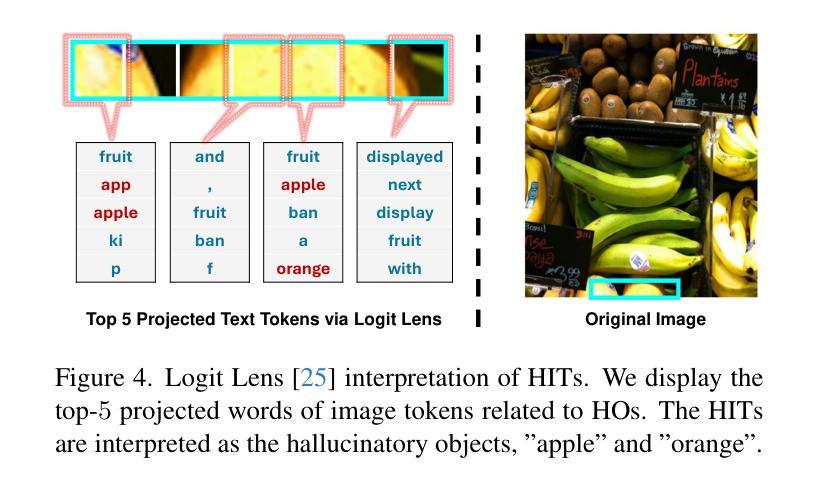
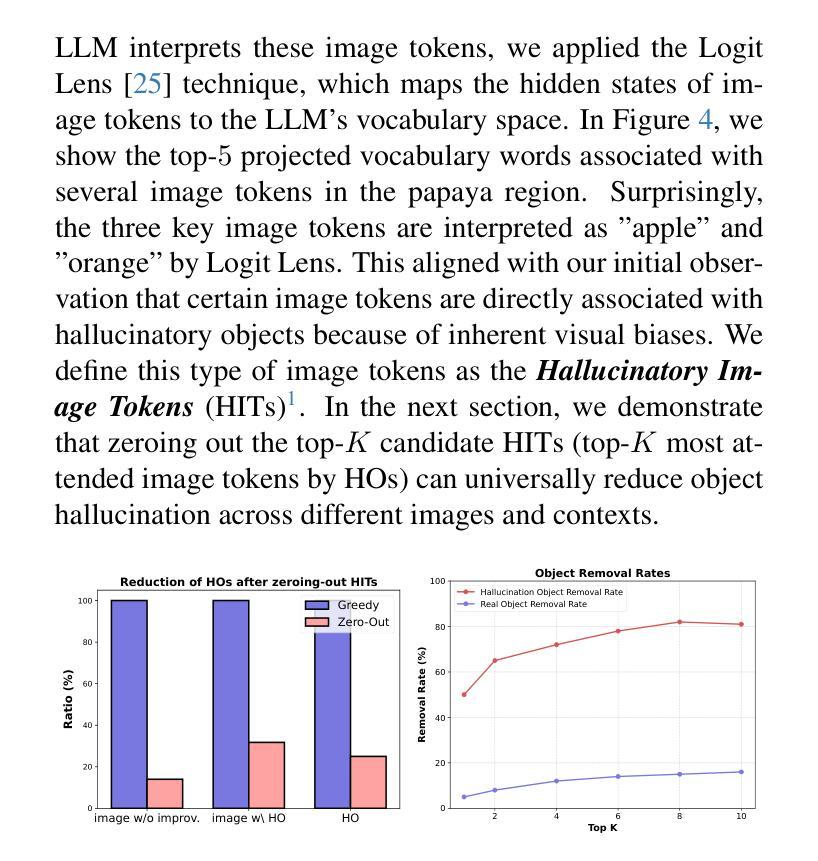
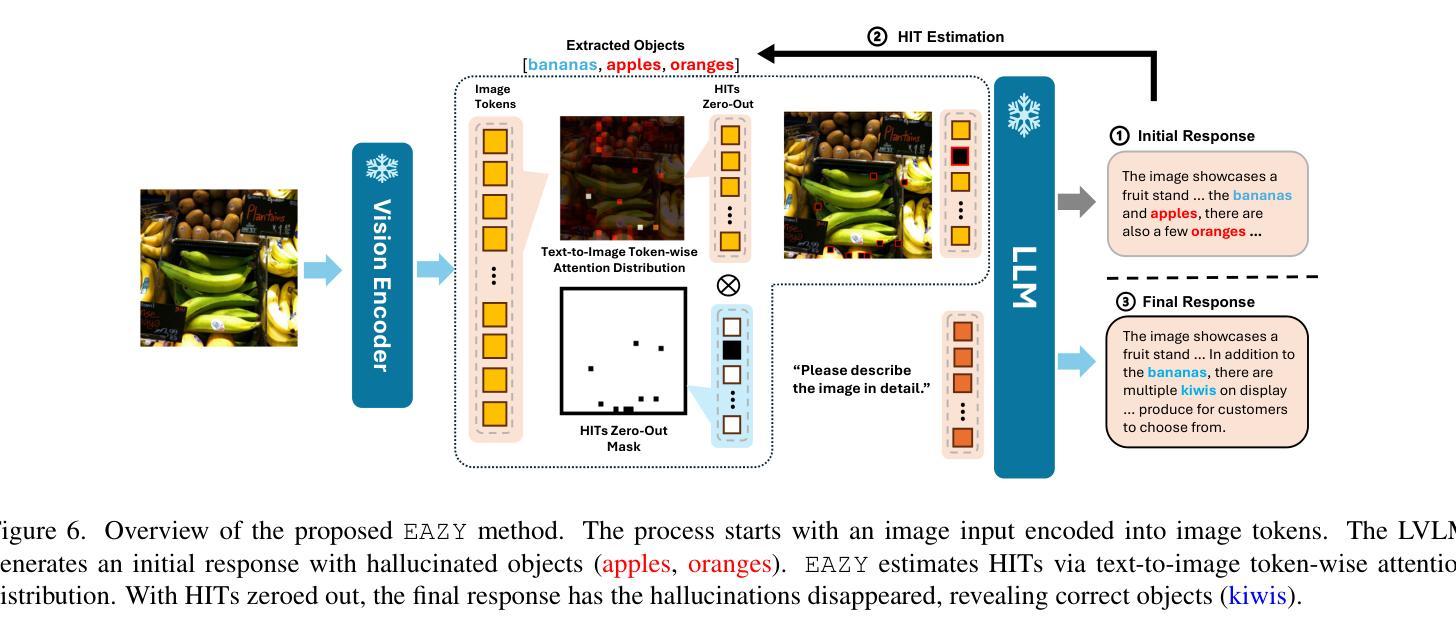
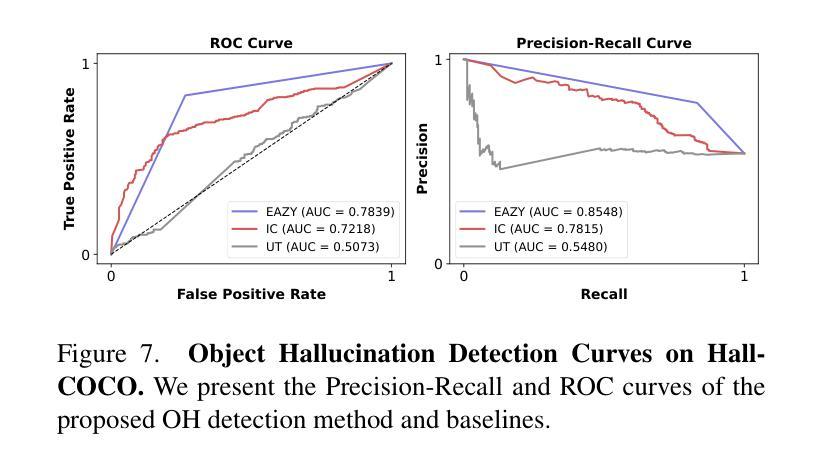
Despite their remarkable potential, Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) still face challenges with object hallucination, a problem where their generated outputs mistakenly incorporate objects that do not actually exist. Although most works focus on addressing this issue within the language-model backbone, our work shifts the focus to the image input source, investigating how specific image tokens contribute to hallucinations. Our analysis reveals a striking finding: a small subset of image tokens with high attention scores are the primary drivers of object hallucination. By removing these hallucinatory image tokens (only 1.5% of all image tokens), the issue can be effectively mitigated. This finding holds consistently across different models and datasets. Building on this insight, we introduce EAZY, a novel, training-free method that automatically identifies and Eliminates hAllucinations by Zeroing out hallucinatorY image tokens. We utilize EAZY for unsupervised object hallucination detection, achieving 15% improvement compared to previous methods. Additionally, EAZY demonstrates remarkable effectiveness in mitigating hallucinations while preserving model utility and seamlessly adapting to various LVLM architectures.
尽管大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)具有显著潜力,但它们仍面临对象幻觉的挑战,这是一个生成输出中误包含实际不存在的对象的问题。虽然大多数工作都集中在解决语言模型主干中的问题,但我们的工作将重点转向图像输入源,研究特定的图像标记是如何导致幻觉的。我们的分析揭示了一个惊人的发现:具有高注意力分数的少量图像标记是对象幻觉的主要驱动力。通过移除这些产生幻觉的图像标记(仅占所有图像标记的1.5%),可以有效地减轻问题。这一发现在不同的模型和数据集上始终适用。在此基础上,我们引入了无需训练的EAZY方法,该方法能够自动识别和消除通过清零幻觉标记的图像来消除幻觉标记(Zeroing out hallucinatorY)。我们利用EAZY进行无监督对象幻觉检测,与之前的方法相比取得了15%的改进。此外,EAZY在缓解幻觉的同时保持模型效用,并能无缝适应各种LVLM架构。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICCV2025
Summary:大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)虽潜力巨大,但仍面临对象幻觉问题,即其生成输出会错误地融入实际不存在的对象。现有研究大多关注语言模型的内部结构来解决这个问题,但本研究转向图像输入源,探讨特定的图像令牌如何导致幻觉。研究发现:具有较高注意力分数的一小部分图像令牌是对象幻觉的主要驱动力。移除这些幻觉图像令牌(仅占所有图像令牌的1.5%),可以有效地缓解这一问题。本研究还引入了一种名为EAZY的新方法,该方法无需训练即可自动识别并消除幻觉,通过对产生幻觉的图像令牌进行清零操作,实现了无监督对象幻觉检测的显著改善,提高了15%。同时,EAZY在保持模型实用性的同时,轻松适应各种LVLM架构。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)存在对象幻觉问题,即生成输出会错误地融入实际不存在的对象。
- 研究发现,具有较高注意力分数的少部分图像令牌是对象幻觉的主要驱动力。
- 通过移除这些幻觉图像令牌,可以有效地缓解对象幻觉问题。
- 引入了一种新的方法EAZY,无需训练即可自动识别并消除幻觉。
- EAZY通过对产生幻觉的图像令牌进行清零操作,实现了无监督对象幻觉检测的显著改善。
- EAZY相较于之前的方法有15%的改进。
点此查看论文截图

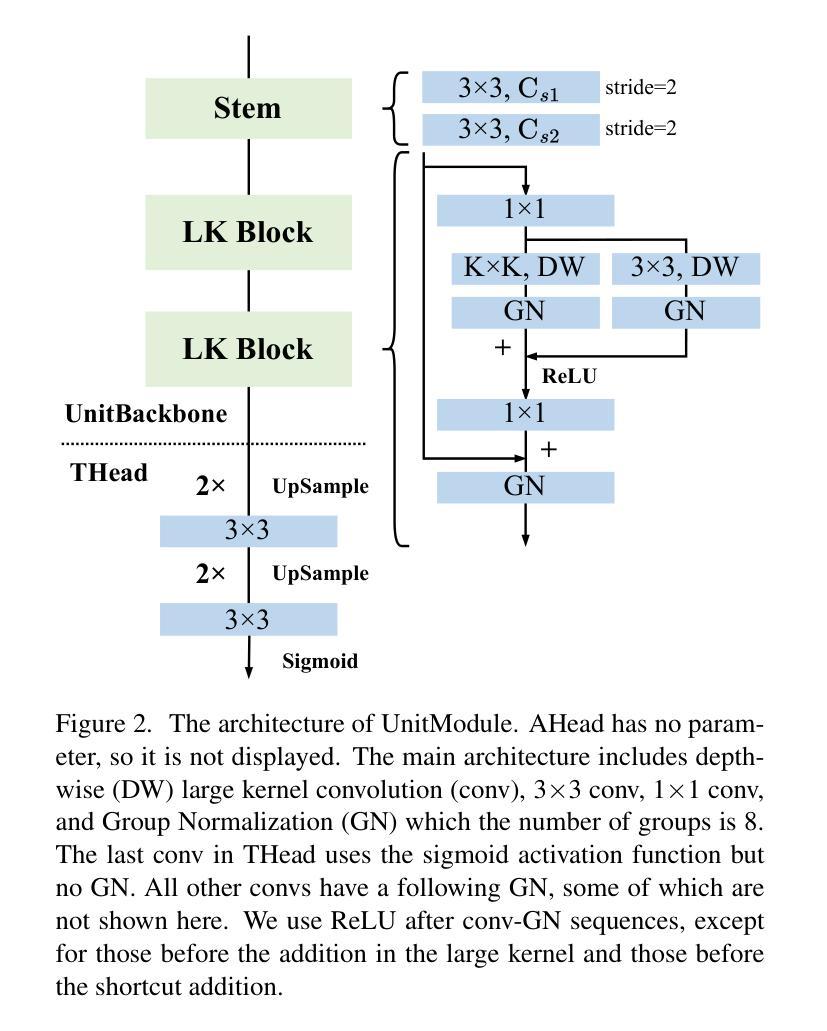
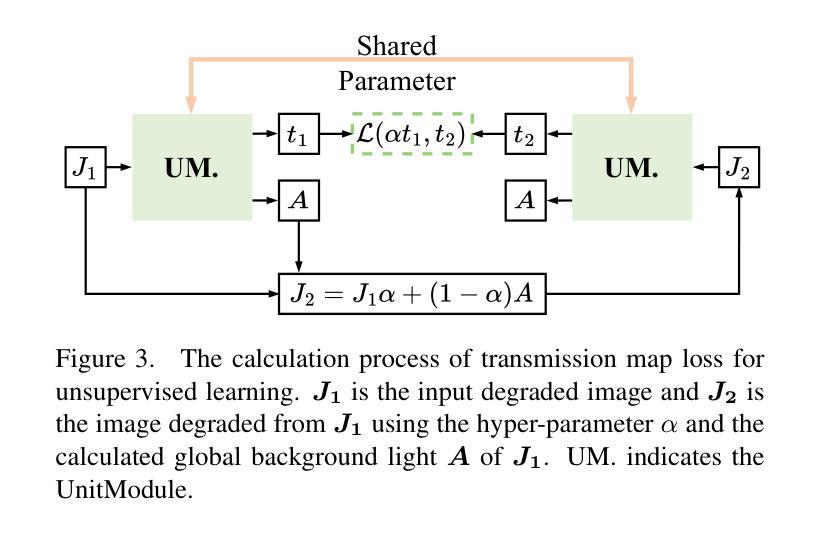
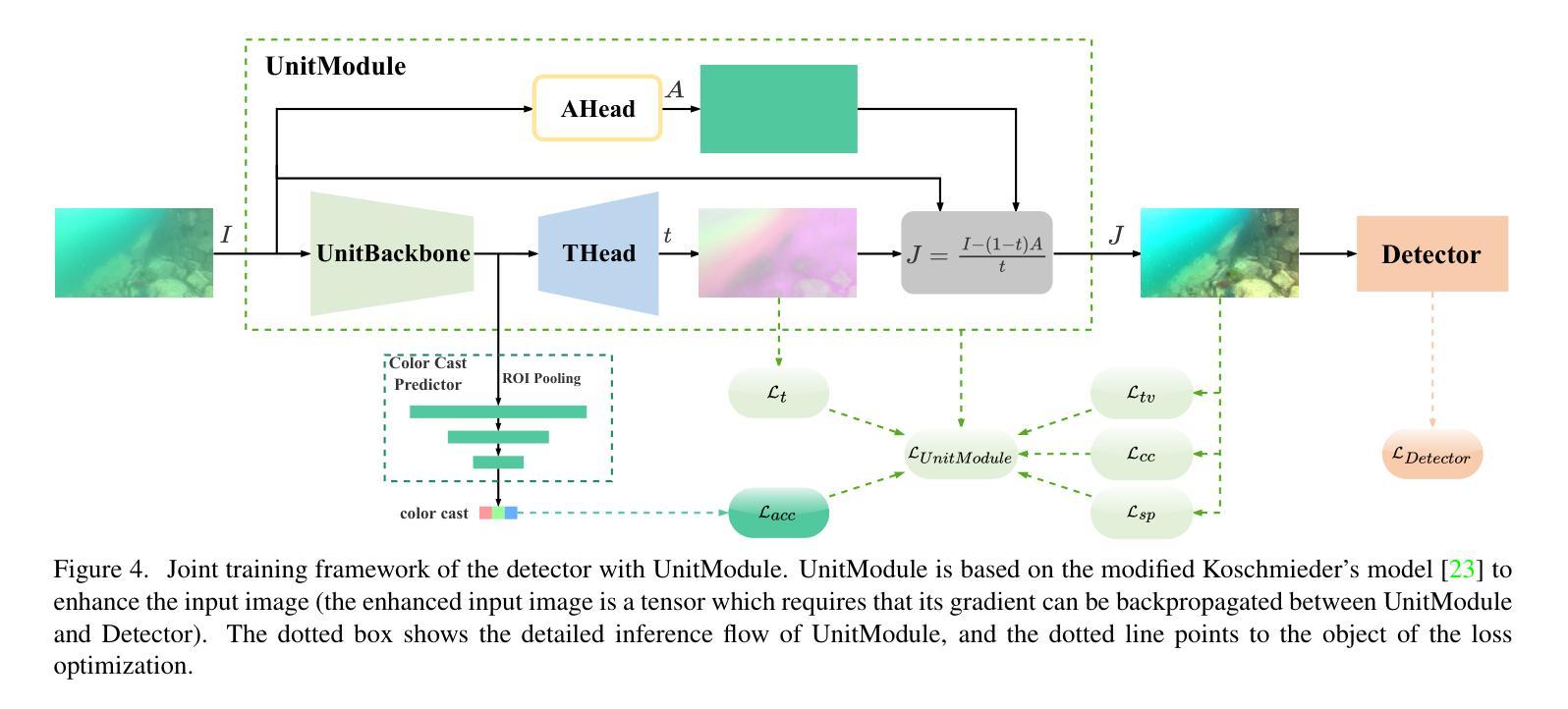
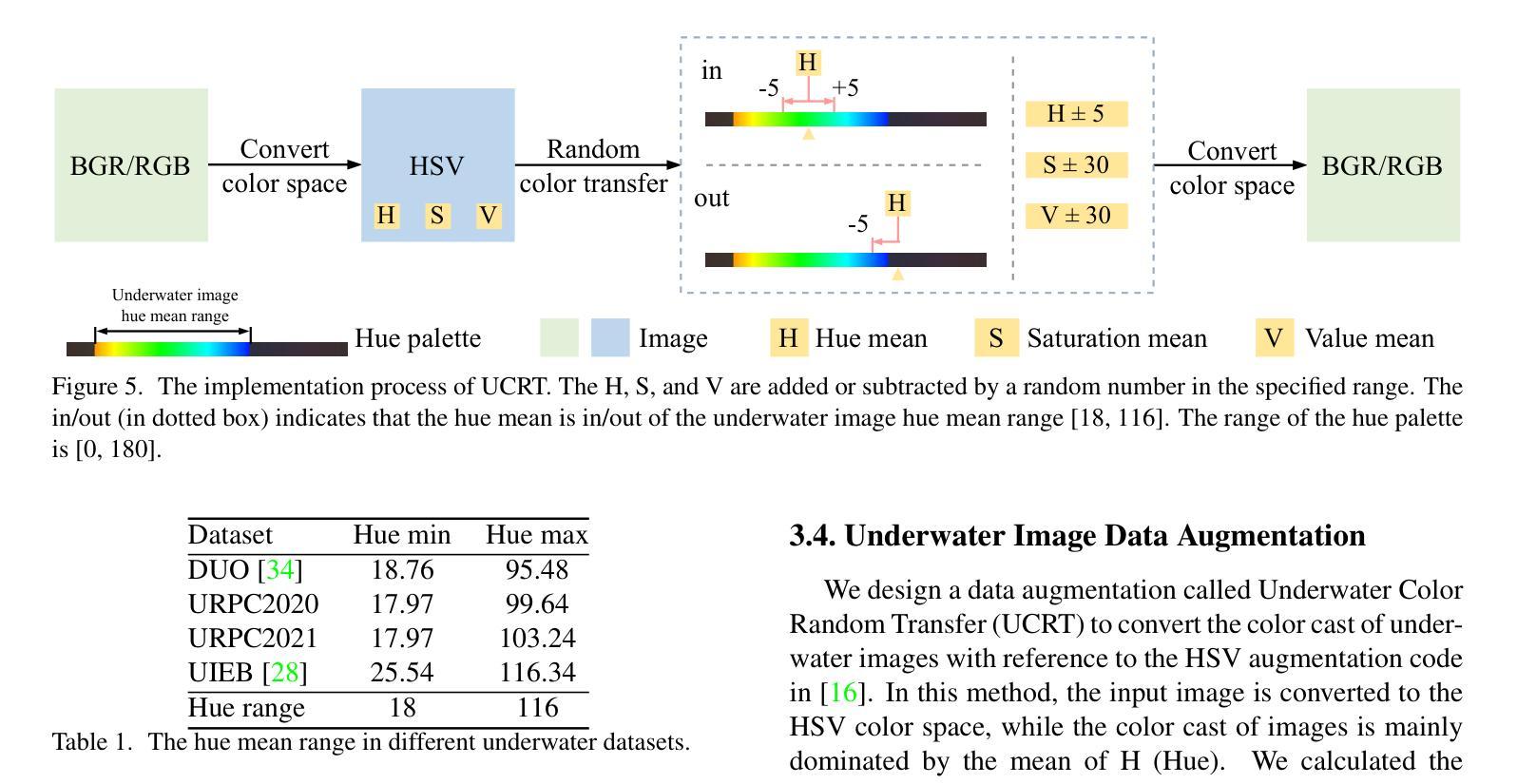
UnitModule: A Lightweight Joint Image Enhancement Module for Underwater Object Detection
Authors:Zhuoyan Liu, Bo Wang, Ye Li, Jiaxian He, Yunfeng Li
Underwater object detection faces the problem of underwater image degradation, which affects the performance of the detector. Underwater object detection methods based on noise reduction and image enhancement usually do not provide images preferred by the detector or require additional datasets. In this paper, we propose a plug-and-play \textbf{U}nderwater joi\textbf{n}t \textbf{i}mage enhancemen\textbf{t} \textbf{Module} (UnitModule) that provides the input image preferred by the detector. We design an unsupervised learning loss for the joint training of UnitModule with the detector without additional datasets to improve the interaction between UnitModule and the detector. Furthermore, a color cast predictor with the assisting color cast loss and a data augmentation called Underwater Color Random Transfer (UCRT) are designed to improve the performance of UnitModule on underwater images with different color casts. Extensive experiments are conducted on DUO for different object detection models, where UnitModule achieves the highest performance improvement of 2.6 AP for YOLOv5-S and gains the improvement of 3.3 AP on the brand-new test set ((\text{URPC}_{test})). And UnitModule significantly improves the performance of all object detection models we test, especially for models with a small number of parameters. In addition, UnitModule with a small number of parameters of 31K has little effect on the inference speed of the original object detection model. Our quantitative and visual analysis also demonstrates the effectiveness of UnitModule in enhancing the input image and improving the perception ability of the detector for object features. The code is available at https://github.com/LEFTeyex/UnitModule.
水下目标检测面临着水下图像退化的问题,这一问题会影响检测器的性能。基于噪声减少和图像增强的水下目标检测方法通常不提供检测器所偏好的图像,或者需要额外的数据集。在本文中,我们提出了一种即插即用的水下联合图像增强模块(UnitModule),该模块可提供检测器所偏好的输入图像。我们为UnitModule与检测器的联合训练设计了一种无监督学习损失,而无需额外数据集,以提高UnitModule与检测器之间的交互。此外,还设计了带有辅助色彩投射损失的色彩投射预测器,以及一种名为水下色彩随机转换(UCRT)的数据增强方法,以提高UnitModule在不同色彩投射的水下图像上的性能。在DUO数据集上对不同的目标检测模型进行了大量实验,UnitModule在YOLOv5-S上实现了最高的性能提升2.6 AP,并在全新测试集URPCtest上实现了3.3 AP的提升。UnitModule显著提高了我们所测试的所有目标检测模型的性能,尤其是对于参数数量较少的模型。此外,UnitModule参数数量较少,仅有31K个参数,对原始目标检测模型的推理速度几乎没有影响。我们的定量和视觉分析还证明了UnitModule在增强输入图像和提高检测器对目标特征的感知能力方面的有效性。代码可在https://github.com/LEFTeyex/UnitModule找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 10 figures, 13 tables, accepted by PR
Summary
水下目标检测面临图像退化问题,影响检测性能。本文提出了一种即插即用型的水下联合图像增强模块(UnitModule),为检测器提供首选的输入图像。该模块设计了一种无监督学习损失,可与检测器进行联合训练,无需额外数据集即可改善模块与检测器之间的交互。此外,还设计了色彩投射预测器和数据增强方法,以提高UnitModule在不同色彩投射水下图像上的性能。实验表明,UnitModule对多种目标检测模型都有显著的性能提升,特别是在参数较少的模型上。该模块参数较少,对原始目标检测模型的推理速度影响较小。
Key Takeaways
- 水下目标检测面临图像退化问题。
- 提出了一种即插即用型的水下联合图像增强模块(UnitModule),为检测器提供优化的输入图像。
- UnitModule通过无监督学习损失与检测器联合训练,无需额外数据集。
- 色彩投射预测器和数据增强方法用于提高UnitModule在不同水下图像上的性能。
- UnitModule对多种目标检测模型有显著性能提升,尤其适用于参数较少的模型。
- UnitModule参数较少,对原始目标检测模型的推理速度影响较小。
点此查看论文截图