⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-09 更新
SegmentDreamer: Towards High-fidelity Text-to-3D Synthesis with Segmented Consistency Trajectory Distillation
Authors:Jiahao Zhu, Zixuan Chen, Guangcong Wang, Xiaohua Xie, Yi Zhou
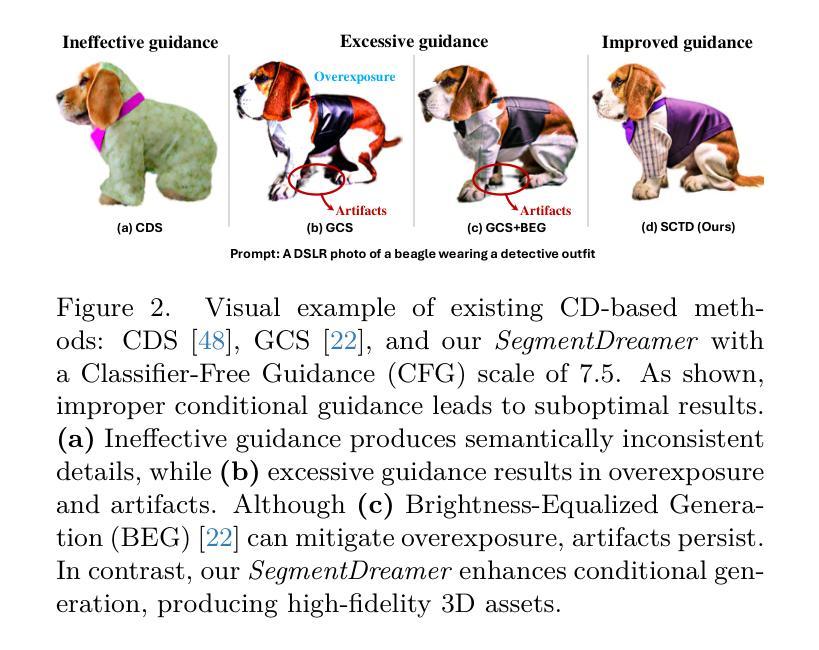
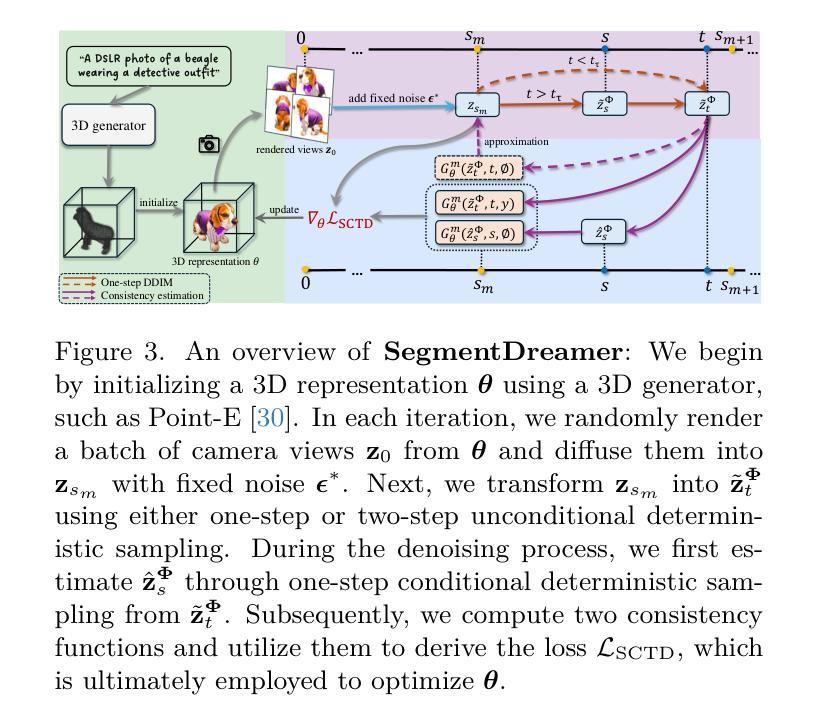
Recent advancements in text-to-3D generation improve the visual quality of Score Distillation Sampling (SDS) and its variants by directly connecting Consistency Distillation (CD) to score distillation. However, due to the imbalance between self-consistency and cross-consistency, these CD-based methods inherently suffer from improper conditional guidance, leading to sub-optimal generation results. To address this issue, we present SegmentDreamer, a novel framework designed to fully unleash the potential of consistency models for high-fidelity text-to-3D generation. Specifically, we reformulate SDS through the proposed Segmented Consistency Trajectory Distillation (SCTD), effectively mitigating the imbalance issues by explicitly defining the relationship between self- and cross-consistency. Moreover, SCTD partitions the Probability Flow Ordinary Differential Equation (PF-ODE) trajectory into multiple sub-trajectories and ensures consistency within each segment, which can theoretically provide a significantly tighter upper bound on distillation error. Additionally, we propose a distillation pipeline for a more swift and stable generation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our SegmentDreamer outperforms state-of-the-art methods in visual quality, enabling high-fidelity 3D asset creation through 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS).
近期文本到3D生成的进展通过直接将一致性蒸馏(CD)与分数蒸馏相联系,提高了分数蒸馏采样(SDS)及其变体的视觉质量。然而,由于自一致性(self-consistency)和跨一致性(cross-consistency)之间的不平衡,这些基于CD的方法本质上存在不当的条件指导,导致生成结果不理想。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了SegmentDreamer,这是一个旨在充分发挥一致性模型在高质量文本到3D生成中的潜力而设计的新型框架。具体来说,我们通过提出的分段一致性轨迹蒸馏(SCTD)重新定义了SDS,通过明确界定自一致性和跨一致性之间的关系,有效地缓解了不平衡问题。此外,SCTD将概率流常微分方程(PF-ODE)轨迹划分为多个子轨迹,确保每个分段内的一致性,这在理论上可以为蒸馏误差提供更紧密的上限。我们还提出了一种蒸馏管道,以实现更快更稳定的生成过程。大量实验表明,我们的SegmentDreamer在视觉质量上超过了最先进的方法,通过三维高斯拼贴(3DGS)实现了高保真度的三维资产创建。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025, project page: https://zjhjojo.github.io/
Summary
本文介绍了SegmentDreamer框架,该框架通过引入分段一致性轨迹蒸馏(SCTD)来改进文本到3D生成的视觉质量。SCTD解决了现有方法中自一致性(self-consistency)与跨一致性(cross-consistency)之间的不平衡问题,并通过明确两者的关系以及将概率流常微分方程(PF-ODE)轨迹分割成多个子轨迹来确保每个分段的一致性,从而提高了蒸馏效率并降低了蒸馏误差。此外,还提出了一种蒸馏管道,以提高生成过程的效率和稳定性。实验表明,SegmentDreamer在视觉质量方面优于现有方法,并能够通过3D高斯拼接(3DGS)实现高保真度的3D资产创建。
Key Takeaways
- SegmentDreamer框架通过引入分段一致性轨迹蒸馏(SCTD)来改进文本到3D生成的视觉质量。
- SCTD解决了自一致性(self-consistency)与跨一致性(cross-consistency)之间的不平衡问题。
- SCTD明确了自一致性与跨一致性的关系,并通过分割概率流常微分方程轨迹来提高蒸馏效率。
- 分段一致性确保每个子轨迹内的一致性,降低了蒸馏误差。
- 提出的蒸馏管道提高了生成过程的效率和稳定性。
- SegmentDreamer在视觉质量方面优于现有方法。
- 通过3D高斯拼接(3DGS)可实现高保真度的3D资产创建。
点此查看论文截图

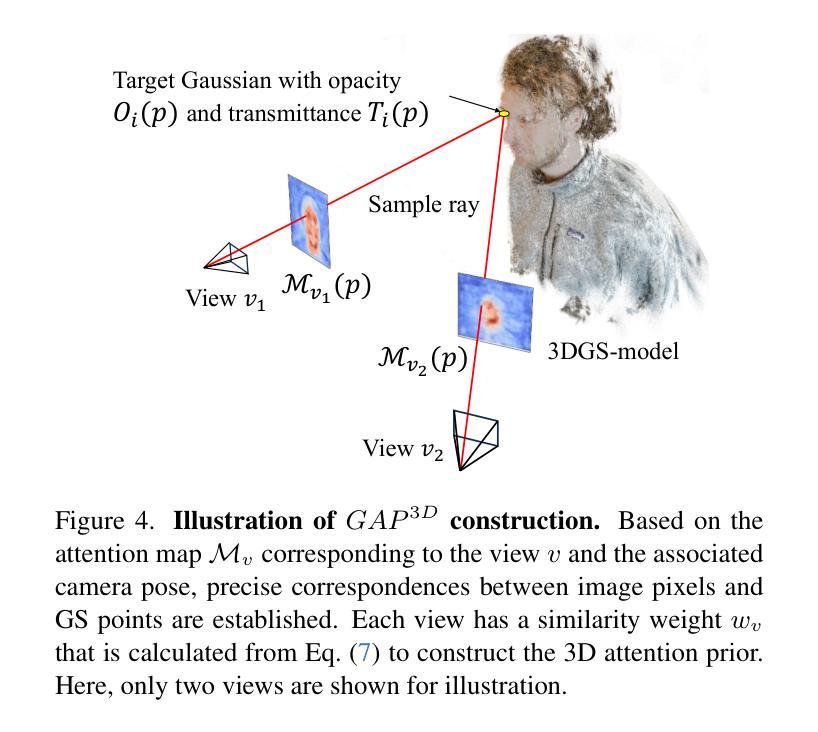
InterGSEdit: Interactive 3D Gaussian Splatting Editing with 3D Geometry-Consistent Attention Prior
Authors:Minghao Wen, Shengjie Wu, Kangkan Wang, Dong Liang
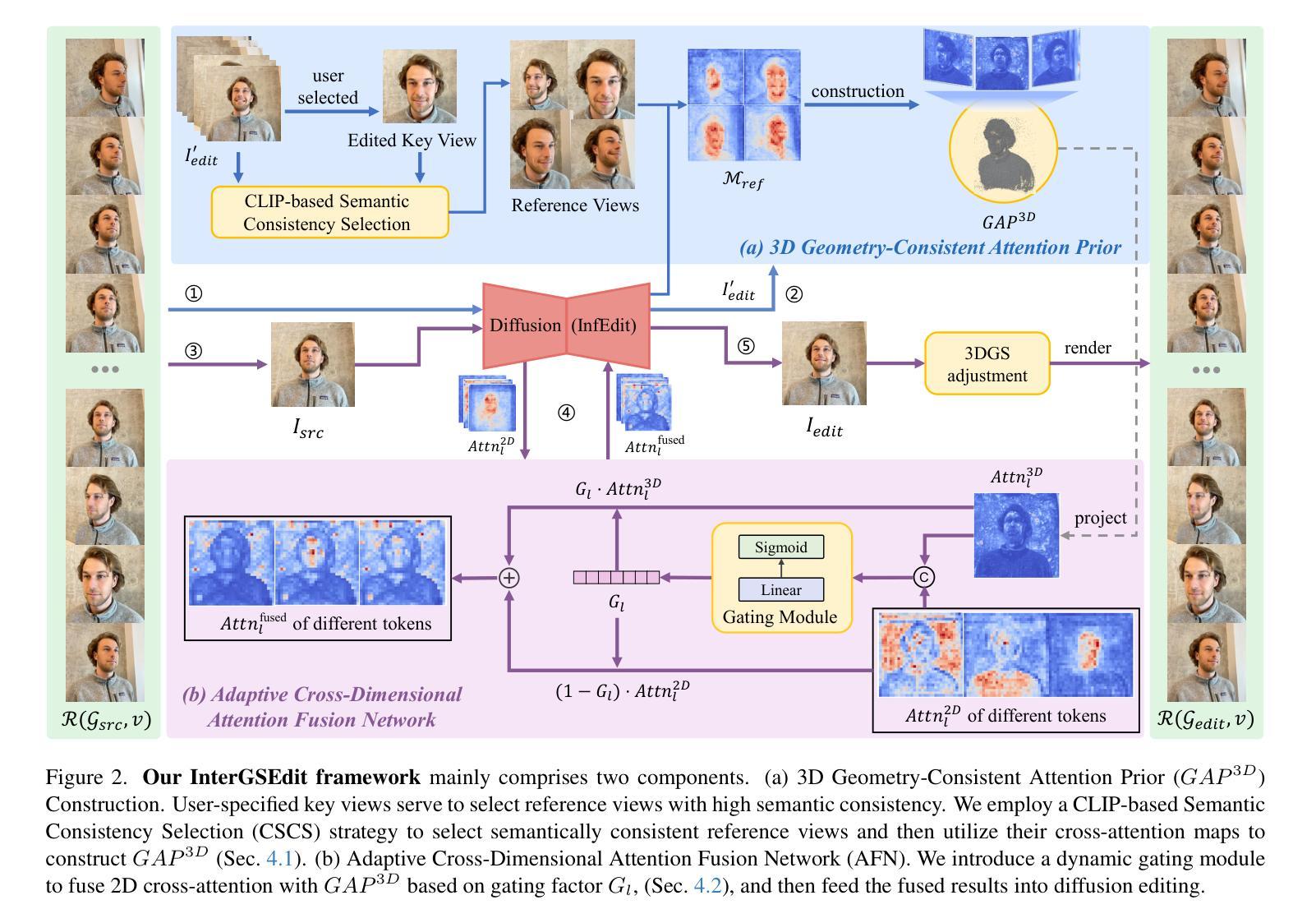
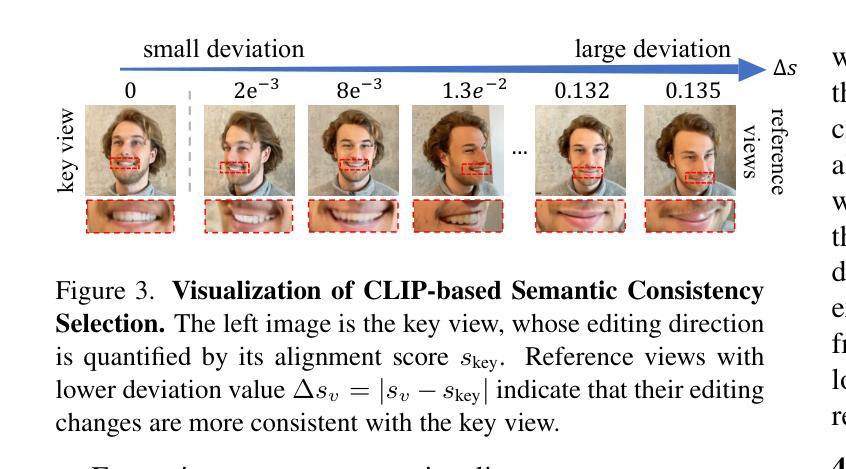
3D Gaussian Splatting based 3D editing has demonstrated impressive performance in recent years. However, the multi-view editing often exhibits significant local inconsistency, especially in areas of non-rigid deformation, which lead to local artifacts, texture blurring, or semantic variations in edited 3D scenes. We also found that the existing editing methods, which rely entirely on text prompts make the editing process a “one-shot deal”, making it difficult for users to control the editing degree flexibly. In response to these challenges, we present InterGSEdit, a novel framework for high-quality 3DGS editing via interactively selecting key views with users’ preferences. We propose a CLIP-based Semantic Consistency Selection (CSCS) strategy to adaptively screen a group of semantically consistent reference views for each user-selected key view. Then, the cross-attention maps derived from the reference views are used in a weighted Gaussian Splatting unprojection to construct the 3D Geometry-Consistent Attention Prior ($GAP^{3D}$). We project $GAP^{3D}$ to obtain 3D-constrained attention, which are fused with 2D cross-attention via Attention Fusion Network (AFN). AFN employs an adaptive attention strategy that prioritizes 3D-constrained attention for geometric consistency during early inference, and gradually prioritizes 2D cross-attention maps in diffusion for fine-grained features during the later inference. Extensive experiments demonstrate that InterGSEdit achieves state-of-the-art performance, delivering consistent, high-fidelity 3DGS editing with improved user experience.
基于3D高斯融合技术的3D编辑在近年来表现出了令人印象深刻的性能。然而,多视图编辑经常表现出显著的局部不一致性,特别是在非刚性变形区域,这导致编辑的3D场景中出现局部伪影、纹理模糊或语义变化。我们还发现,现有的编辑方法完全依赖于文本提示,使编辑过程成为“一次性交易”,使用户难以灵活地控制编辑程度。针对这些挑战,我们提出了InterGSEdit,这是一个通过交互式选择用户偏好关键视图进行高质量3DGS编辑的新型框架。我们提出了一种基于CLIP的语义一致性选择(CSCS)策略,该策略可自适应地筛选与用户选择的关键视图语义一致的参考视图组。然后,从参考视图派生的跨注意力图用于加权高斯融合反投影,以构建3D几何一致性注意力先验($GAP^{3D}$)。我们将$GAP^{3D}$投影以获得3D约束注意力,其通过注意力融合网络(AFN)与2D跨注意力融合。AFN采用自适应注意力策略,在早期推理中优先3D约束注意力以实现几何一致性,并在后期推理中逐渐优先使用扩散中的2D跨注意力图以获取精细特征。大量实验表明,InterGSEdit达到了业界最佳性能,实现了具有一致性和高保真度的3DGS编辑,并改善了用户体验。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
基于三维高斯喷绘的3D编辑技术在近年来表现出令人印象深刻的效果。然而,多视角编辑经常会在非刚性变形区域展现出显著的局部不一致性,导致编辑后的三维场景出现局部伪影、纹理模糊或语义变化等问题。现有编辑方法完全依赖于文本提示,使得编辑过程成为一次性的交易,难以让用户灵活地控制编辑程度。针对这些挑战,我们提出了InterGSEdit,一种基于用户偏好交互式选择关键视图的高质量三维几何结构(3DGS)编辑框架。我们提出了一种基于CLIP的语义一致性选择(CSCS)策略,自适应筛选用户选择的每个关键视图的一组语义一致参考视图。然后,从参考视图派生的跨注意力图用于加权高斯喷绘反投影,以构建三维几何一致性注意力先验($GAP^{3D}$)。我们将$GAP^{3D}$投影以获得三维约束注意力,并将其与二维跨注意力通过注意力融合网络(AFN)融合。AFN采用自适应注意力策略,在推理早期优先三维约束注意力以实现几何一致性,并在后期推理中逐渐优先二维跨注意力图以获取精细特征。大量实验表明,InterGSEdit达到了最先进的性能,实现了具有一致性和高保真度的3DGS编辑,并改善了用户体验。
关键见解
- InterGSEdit框架被提出,用于高质量的三维几何结构(3DGS)编辑,通过用户交互选择关键视图以增强编辑质量。
- 引入CLIP基础的语义一致性选择(CSCS)策略,自适应筛选语义一致参考视图。
- 利用跨注意力图结合加权高斯喷绘反投影,构建三维几何一致性注意力先验($GAP^{3D}$)。
- 通过投影$GAP^{3D}$获取三维约束注意力,并与二维跨注意力融合。
- 注意力融合网络(AFN)采用自适应注意力策略,在推理过程中实现几何一致性与精细特征的平衡。
- InterGSEdit达到了最先进的性能,在保持几何一致性的同时实现了高保真度的3DGS编辑。
点此查看论文截图


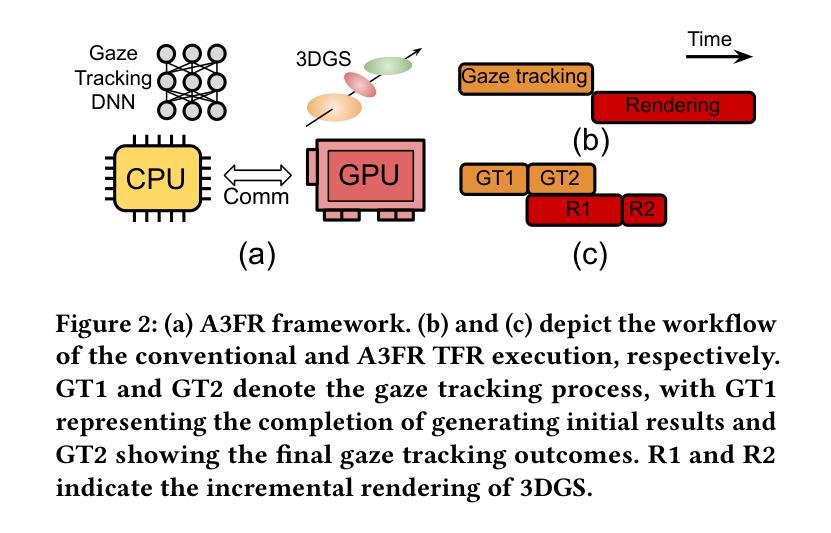
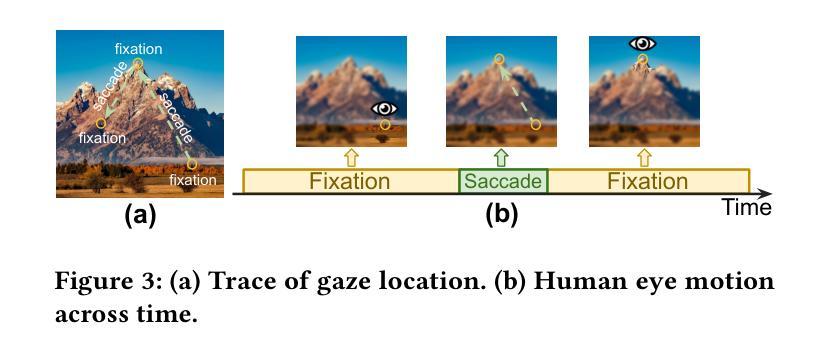
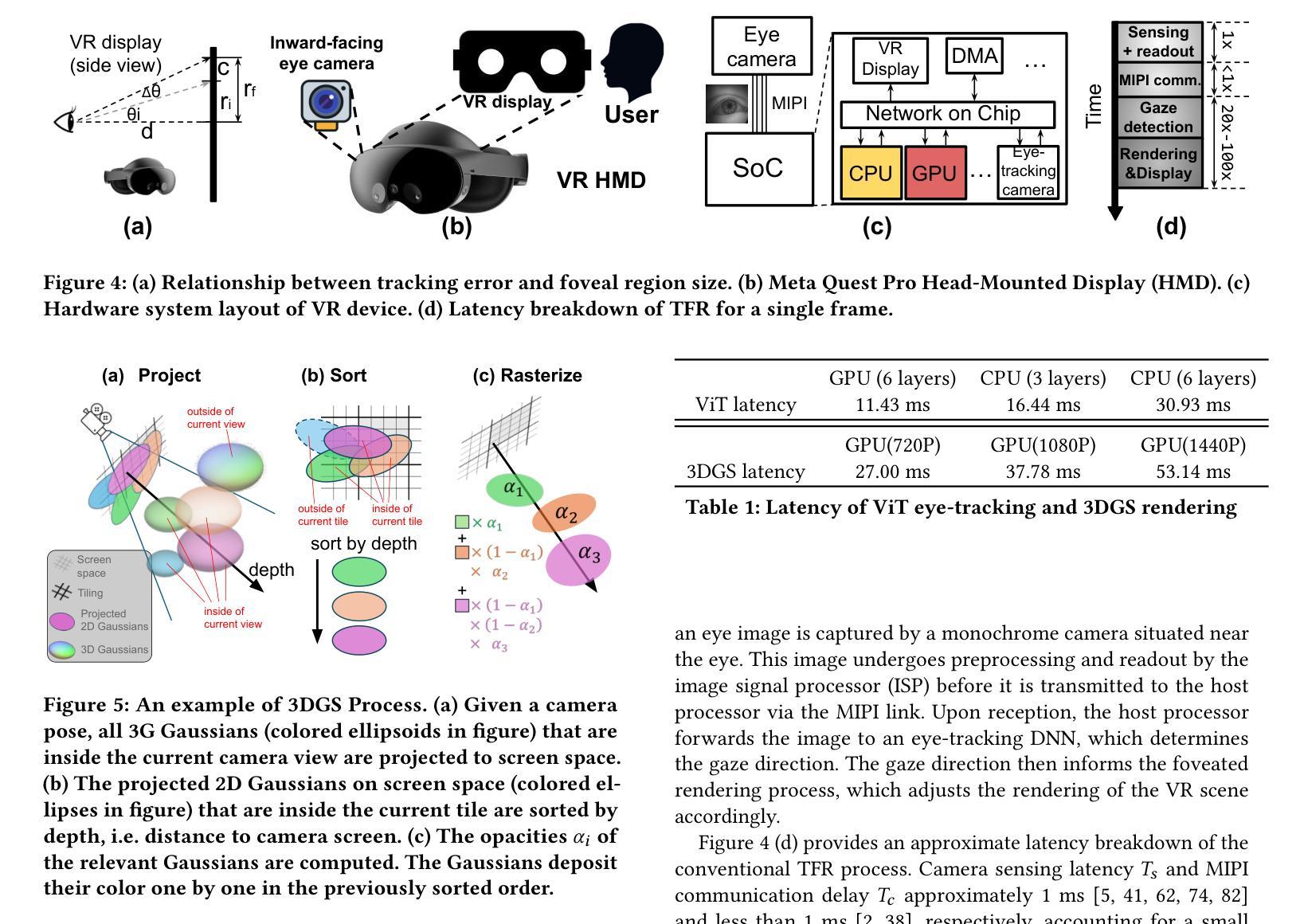
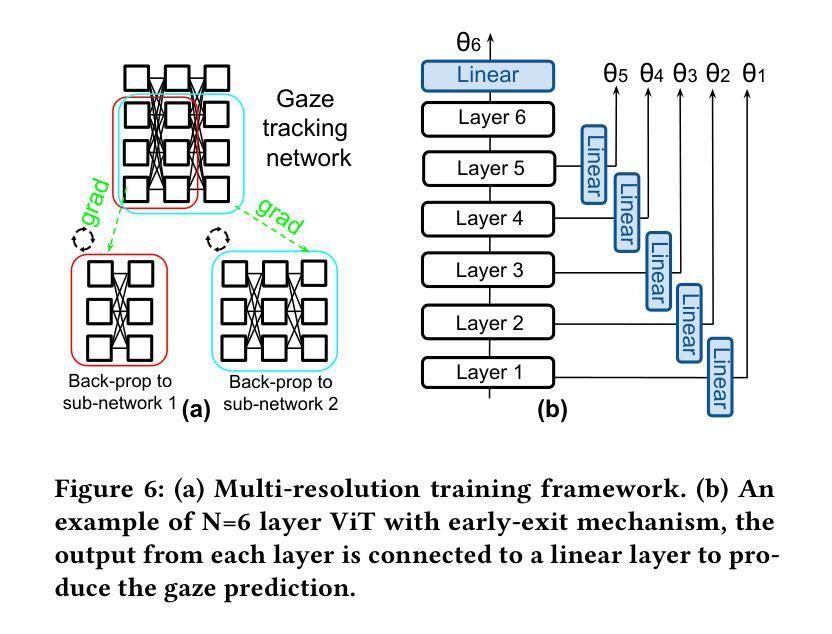
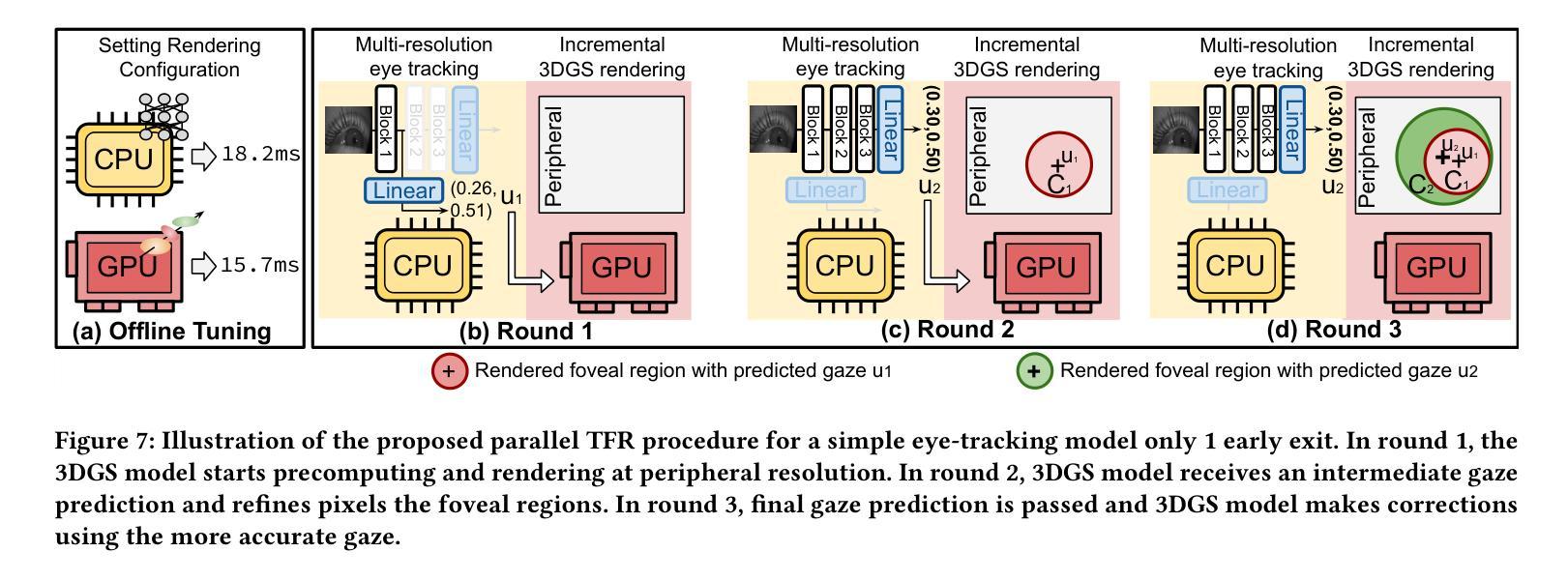
A3FR: Agile 3D Gaussian Splatting with Incremental Gaze Tracked Foveated Rendering in Virtual Reality
Authors:Shuo Xin, Haiyu Wang, Sai Qian Zhang
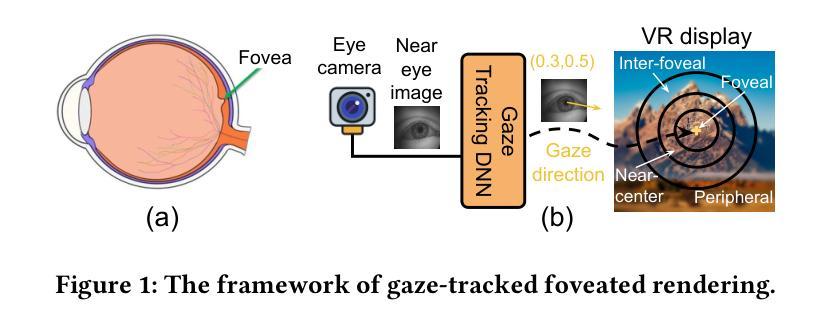
Virtual reality (VR) significantly transforms immersive digital interfaces, greatly enhancing education, professional practices, and entertainment by increasing user engagement and opening up new possibilities in various industries. Among its numerous applications, image rendering is crucial. Nevertheless, rendering methodologies like 3D Gaussian Splatting impose high computational demands, driven predominantly by user expectations for superior visual quality. This results in notable processing delays for real-time image rendering, which greatly affects the user experience. Additionally, VR devices such as head-mounted displays (HMDs) are intricately linked to human visual behavior, leveraging knowledge from perception and cognition to improve user experience. These insights have spurred the development of foveated rendering, a technique that dynamically adjusts rendering resolution based on the user’s gaze direction. The resultant solution, known as gaze-tracked foveated rendering, significantly reduces the computational burden of the rendering process. Although gaze-tracked foveated rendering can reduce rendering costs, the computational overhead of the gaze tracking process itself can sometimes outweigh the rendering savings, leading to increased processing latency. To address this issue, we propose an efficient rendering framework called~\textit{A3FR}, designed to minimize the latency of gaze-tracked foveated rendering via the parallelization of gaze tracking and foveated rendering processes. For the rendering algorithm, we utilize 3D Gaussian Splatting, a state-of-the-art neural rendering technique. Evaluation results demonstrate that A3FR can reduce end-to-end rendering latency by up to $2\times$ while maintaining visual quality.
虚拟现实(VR)极大地改变了沉浸式数字界面,通过增强用户参与度和开拓各种行业的新可能性,从而极大地推动了教育、专业实践和娱乐业的发展。在其众多应用中,图像渲染至关重要。然而,像3D高斯喷射(3D Gaussian Splatting)这样的渲染方法带来了很高的计算需求,这主要受到用户对优质视觉效果的期待驱动。这导致实时图像渲染出现明显的处理延迟,极大地影响了用户体验。此外,VR设备(如头戴式显示器(HMD))与人类视觉行为紧密相连,它们利用感知和认知的知识来改善用户体验。这些见解催生了一种名为凝视点渲染的技术,该技术根据用户的注视方向动态调整渲染分辨率。由此产生的解决方案,即眼动追踪凝视点渲染,显著减少了渲染过程的计算负担。尽管眼动追踪凝视点渲染可以降低渲染成本,但眼动追踪过程本身的计算开销有时会超过渲染节省的成本,导致处理延迟增加。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种高效的渲染框架,名为“A3FR”,旨在通过并行化眼动追踪和凝视点渲染过程来最小化眼动追踪凝视点渲染的延迟。对于渲染算法,我们采用最先进的神经渲染技术——3D高斯喷射。评估结果表明,A3FR可以将端到端的渲染延迟减少两倍,同时保持视觉质量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACM International Conference on Supercomputing 2025
Summary
虚拟现实(VR)通过提高用户参与度并开拓各行业新可能,极大改变了沉浸式数字接口,推进教育、职业实践和娱乐的发展。但3D高斯泼斑等渲染方法因用户追求优质视觉体验而计算需求巨大,造成实时图像渲染处理延迟,影响用户体验。结合人类视觉行为和感知认知的见解,出现基于用户注视点动态调整渲染分辨率的注视点渲染技术。为降低注视点渲染的计算负担,我们提出了高效的渲染框架A3FR,通过并行处理注视跟踪和焦点渲染过程,最小化注视点渲染的延迟。采用先进的3D高斯泼斑渲染算法,评估结果显示A3FR可在保持视觉质量的同时,将端到端渲染延迟降低高达两倍。
Key Takeaways
- 虚拟现实(VR)通过提高用户参与度和拓宽行业新应用,极大改变了沉浸式数字接口。
- 3D Gaussian Splatting等渲染方法计算量大,造成实时图像渲染处理延迟。
- 用户视觉行为结合感知认知见解,引领注视点渲染技术的发展。
- 注视点渲染技术动态调整渲染分辨率,降低计算负担。
- 提出的A3FR渲染框架通过并行处理注视跟踪和焦点渲染,最小化延迟。
- A3FR采用3D Gaussian Splatting渲染算法,能有效降低渲染延迟。
点此查看论文截图

Gaussian-LIC2: LiDAR-Inertial-Camera Gaussian Splatting SLAM
Authors:Xiaolei Lang, Jiajun Lv, Kai Tang, Laijian Li, Jianxin Huang, Lina Liu, Yong Liu, Xingxing Zuo
This paper proposes an innovative LiDAR-Inertial-Camera SLAM system with 3D Gaussian Splatting, which is the first to jointly consider visual quality, geometric accuracy, and real-time performance. It robustly and accurately estimates poses while building a photo-realistic 3D Gaussian map in real time that enables high-quality novel view RGB and depth rendering. To effectively address under-reconstruction in regions not covered by the LiDAR, we employ a lightweight zero-shot depth model that synergistically combines RGB appearance cues with sparse LiDAR measurements to generate dense depth maps. The depth completion enables reliable Gaussian initialization in LiDAR-blind areas, significantly improving system applicability for sparse LiDAR sensors. To enhance geometric accuracy, we use sparse but precise LiDAR depths to supervise Gaussian map optimization and accelerate it with carefully designed CUDA-accelerated strategies. Furthermore, we explore how the incrementally reconstructed Gaussian map can improve the robustness of odometry. By tightly incorporating photometric constraints from the Gaussian map into the continuous-time factor graph optimization, we demonstrate improved pose estimation under LiDAR degradation scenarios. We also showcase downstream applications via extending our elaborate system, including video frame interpolation and fast 3D mesh extraction. To support rigorous evaluation, we construct a dedicated LiDAR-Inertial-Camera dataset featuring ground-truth poses, depth maps, and extrapolated trajectories for assessing out-of-sequence novel view synthesis. Extensive experiments on both public and self-collected datasets demonstrate the superiority and versatility of our system across LiDAR sensors with varying sampling densities. Both the dataset and code will be made publicly available on project page https://xingxingzuo.github.io/gaussian_lic2.
本文提出了一种创新的LiDAR-Inertial-Camera SLAM系统,该系统采用3D高斯扩展技术,是首个同时考虑视觉质量、几何精度和实时性能的系统。它能够在构建逼真的3D高斯地图的同时,实现精确的姿态估计,从而实现高质量的新型视图RGB和深度渲染。为了解决激光雷达未覆盖区域的重建不足问题,我们采用了一种轻量级的零深度模型,该模型将RGB外观线索与稀疏的激光雷达测量值相结合,生成密集的深度地图。深度完成使激光雷达盲区的高斯初始化更为可靠,极大地提高了系统对稀疏激光雷达传感器的适用性。为提高几何精度,我们使用稀疏但精确的激光雷达深度值来监督高斯地图优化,并通过精心设计的CUDA加速策略来加速优化过程。此外,我们还探讨了逐步重建的高斯地图如何增强里程计的稳健性。通过将高斯地图的光度约束紧密地融入连续时间因子图优化中,我们在激光雷达退化场景下展示了改进的姿态估计。我们还通过扩展我们精细的系统来展示下游应用,包括视频帧插值和快速3D网格提取。为支持严格的评估,我们构建了一个专用的LiDAR-Inertial-Camera数据集,该数据集具有用于评估不按顺序排列的新型视图合成的真实姿态、深度图和轨迹。在公共和自我收集的数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的系统在具有不同采样密度的激光雷达传感器上具有卓越性和通用性。数据集和代码均将在项目页面上进行公开,网址为:https://xingxingzuo.github.io/gaussian_lic2。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种创新的LiDAR-Inertial-Camera SLAM系统,结合3D高斯拼贴技术,首创性地同时考虑视觉质量、几何精度和实时性能。该系统能稳健准确地估计姿态,同时实时构建逼真的3D高斯地图,实现高质量的新视角RGB和深度渲染。通过轻量级零深度模型有效解决了LiDAR未覆盖区域的重建问题,该模型融合RGB外观线索和稀疏LiDAR测量数据生成密集深度图。深度补全技术在LiDAR盲区实现可靠的Gaussian初始化,显著提高系统对稀疏LiDAR传感器的适用性。利用精确的LiDAR深度数据优化Gaussian地图,加速CUDA加速策略下的优化过程。此外,探讨了增量重建的Gaussian地图如何提高里程计的稳健性。通过将Gaussian地图的光度约束融入连续时间因子图优化,提高了LiDAR退化场景下的姿态估计精度。该系统还扩展至视频帧插值和快速3D网格提取等下游应用。为严格评估,建立了专用的LiDAR-Inertial-Camera数据集,包含真实姿态、深度图和轨迹,以评估新颖视图合成的性能。在公开和自我收集的数据集上的实验证明了该系统在不同密度的LiDAR传感器上的优越性和通用性。
Key Takeaways
- 创新的LiDAR-Inertial-Camera SLAM系统结合了3D高斯拼贴技术。
- 系统能实时构建逼真的3D高斯地图并实现高质量的新视角RGB和深度渲染。
- 采用轻量级零深度模型解决LiDAR未覆盖区域的重建问题。
- 深度补全技术提高系统对稀疏LiDAR传感器的适用性。
- 利用精确的LiDAR深度数据优化Gaussian地图,并加速优化过程。
- Gaussian地图的引入提高了姿态估计的稳健性,尤其在LiDAR退化场景下。
点此查看论文截图

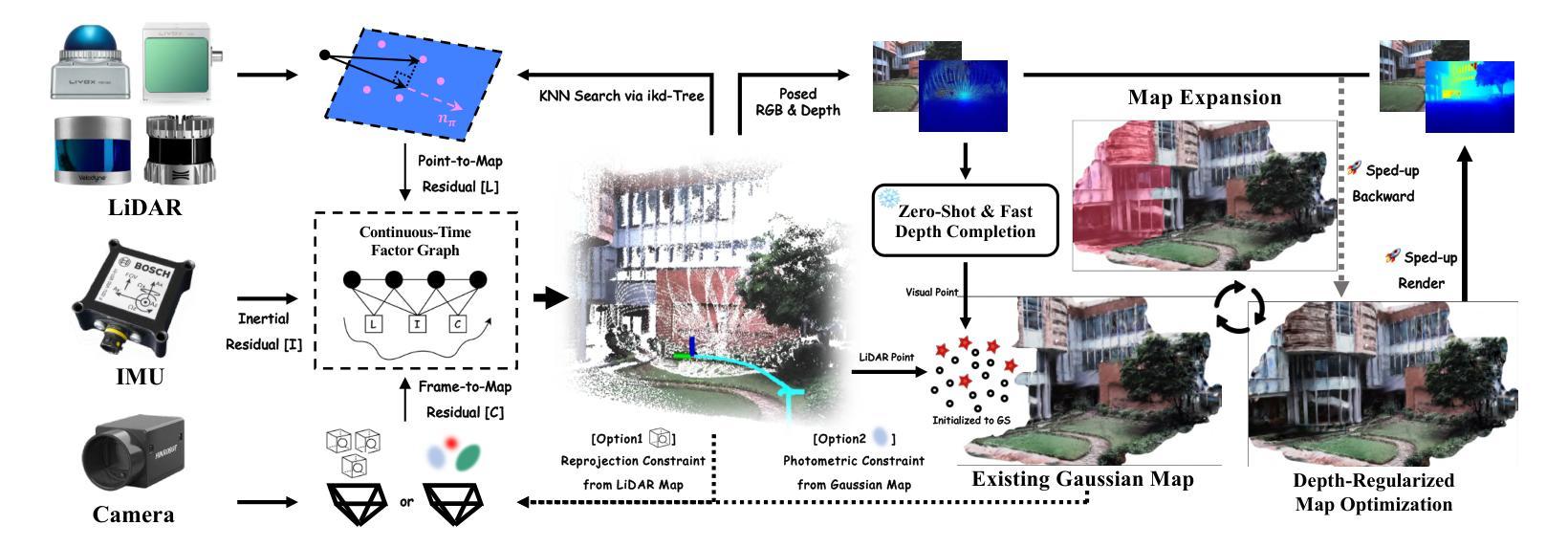
ArmGS: Composite Gaussian Appearance Refinement for Modeling Dynamic Urban Environments
Authors:Guile Wu, Dongfeng Bai, Bingbing Liu
This work focuses on modeling dynamic urban environments for autonomous driving simulation. Contemporary data-driven methods using neural radiance fields have achieved photorealistic driving scene modeling, but they suffer from low rendering efficacy. Recently, some approaches have explored 3D Gaussian splatting for modeling dynamic urban scenes, enabling high-fidelity reconstruction and real-time rendering. However, these approaches often neglect to model fine-grained variations between frames and camera viewpoints, leading to suboptimal results. In this work, we propose a new approach named ArmGS that exploits composite driving Gaussian splatting with multi-granularity appearance refinement for autonomous driving scene modeling. The core idea of our approach is devising a multi-level appearance modeling scheme to optimize a set of transformation parameters for composite Gaussian refinement from multiple granularities, ranging from local Gaussian level to global image level and dynamic actor level. This not only models global scene appearance variations between frames and camera viewpoints, but also models local fine-grained changes of background and objects. Extensive experiments on multiple challenging autonomous driving datasets, namely, Waymo, KITTI, NOTR and VKITTI2, demonstrate the superiority of our approach over the state-of-the-art methods.
本文重点关注为自动驾驶仿真建模动态城市环境。虽然当前使用神经网络辐射场的数据驱动方法已经实现了摄影真实的驾驶场景建模,但它们的渲染效率较低。最近,一些方法探索了使用3D高斯喷涂技术为动态城市场景建模,实现了高保真重建和实时渲染。然而,这些方法往往忽略了帧之间和摄像机视点之间的细微变化建模,导致结果不理想。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种名为ArmGS的新方法,该方法利用复合驾驶高斯喷涂和多粒度外观细化技术为自动驾驶场景建模。我们的方法的核心思想是设计一种多层次外观建模方案,以优化从多个粒度(从局部高斯级别到全局图像级别和动态参与者级别)的复合高斯细化的转换参数。这不仅模拟了帧之间和摄像机视点之间的全局场景外观变化,还模拟了背景和对象的局部细微变化。在多个具有挑战性的自动驾驶数据集(即Waymo、KITTI、NOTR和VKITTI2)上的大量实验表明,我们的方法优于最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical report
Summary
本文提出了一种名为ArmGS的新方法,利用复合驾驶高斯喷涂(Gaussian splatting)与多粒度外观细化技术,为自动驾驶场景建模。该方法优化了多级别变换参数,用于精细模拟场景中的全局与局部变化,从而在多个挑战性的自动驾驶数据集上展现出优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 当前自主驾驶模拟中的动态城市环境建模主要利用数据驱动方法和神经网络辐射场技术,但渲染效率较低。
- 近期一些方法开始探索使用3D高斯喷涂技术建模动态城市场景,能够实现高保真重建和实时渲染。
- 当前方法忽略了帧间和摄像头视角的细微变化,导致结果不尽人意。
- 本文提出的ArmGS方法结合了复合驾驶高斯喷涂与多粒度外观细化技术,旨在优化全局和局部场景的精细建模。
- ArmGS方法通过优化多级别变换参数,实现了从局部高斯级别到全局图像级别以及动态演员级别的精细建模。
- 该方法在多个挑战性的自动驾驶数据集上进行了广泛实验验证,并展示了其相较于现有方法的优越性。
点此查看论文截图

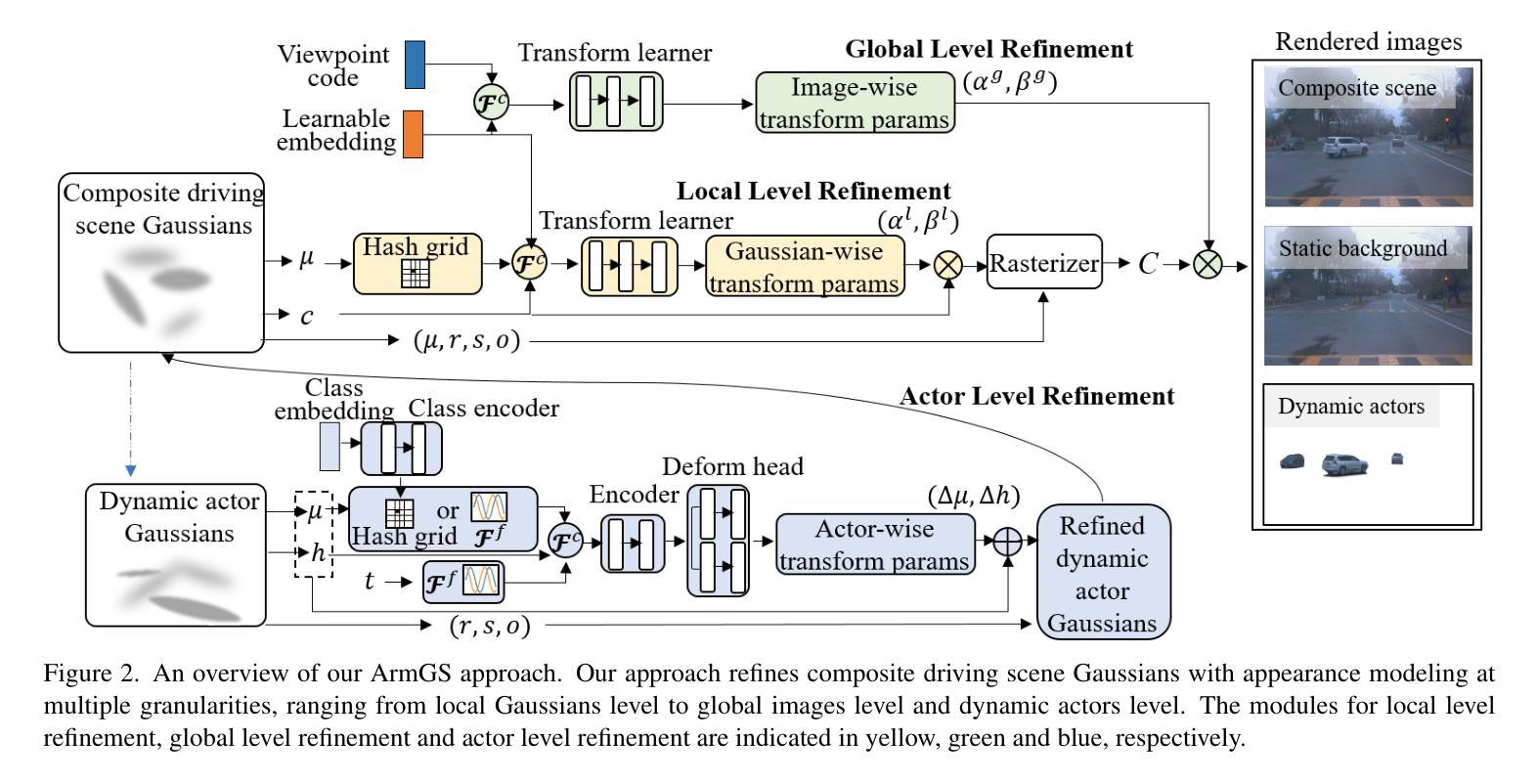

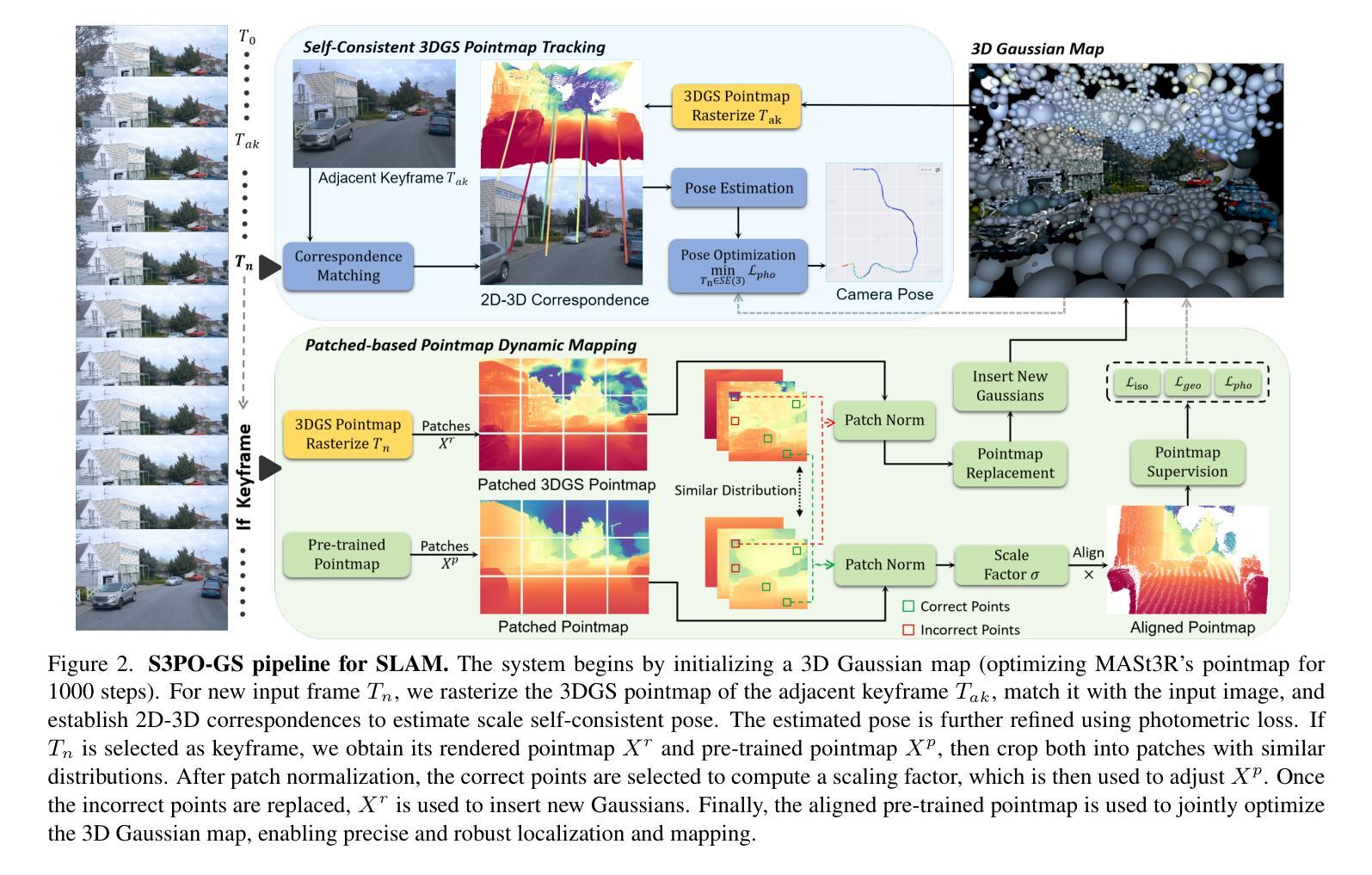
Outdoor Monocular SLAM with Global Scale-Consistent 3D Gaussian Pointmaps
Authors:Chong Cheng, Sicheng Yu, Zijian Wang, Yifan Zhou, Hao Wang
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has become a popular solution in SLAM due to its high-fidelity and real-time novel view synthesis performance. However, some previous 3DGS SLAM methods employ a differentiable rendering pipeline for tracking, \textbf{lack geometric priors} in outdoor scenes. Other approaches introduce separate tracking modules, but they accumulate errors with significant camera movement, leading to \textbf{scale drift}. To address these challenges, we propose a robust RGB-only outdoor 3DGS SLAM method: S3PO-GS. Technically, we establish a self-consistent tracking module anchored in the 3DGS pointmap, which avoids cumulative scale drift and achieves more precise and robust tracking with fewer iterations. Additionally, we design a patch-based pointmap dynamic mapping module, which introduces geometric priors while avoiding scale ambiguity. This significantly enhances tracking accuracy and the quality of scene reconstruction, making it particularly suitable for complex outdoor environments. Our experiments on the Waymo, KITTI, and DL3DV datasets demonstrate that S3PO-GS achieves state-of-the-art results in novel view synthesis and outperforms other 3DGS SLAM methods in tracking accuracy. Project page: https://3dagentworld.github.io/S3PO-GS/.
3D高斯融合(3DGS)因其高保真和实时新颖视图合成性能而在SLAM中成为一种流行的解决方案。然而,一些先前的3DGS SLAM方法采用可微渲染管线进行跟踪,缺乏户外场景的几何先验。其他方法引入了单独的跟踪模块,但它们在大范围的相机移动时会产生累积误差,导致尺度漂移。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种鲁棒的仅RGB户外3DGS SLAM方法:S3PO-GS。技术上,我们建立了一个基于3DGS点图的自洽跟踪模块,避免了累积的尺度漂移,并以更少的迭代次数实现了更精确和鲁棒性的跟踪。此外,我们设计了一个基于补丁的点图动态映射模块,它引入了几何先验信息,同时避免了尺度模糊性。这显著提高了跟踪精度和场景重建质量,使其特别适合复杂的户外环境。我们在Waymo、KITTI和DL3DV数据集上的实验表明,S3PO-GS在新视角合成方面达到了最先进的水平,并在跟踪精度上优于其他3DGS SLAM方法。项目页面:https://3dagentworld.github.io/S3PO-GS/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV2025
Summary
本文介绍了基于RGB的户外三维高斯融合SLAM方法(S3PO-GS)。它使用了一种新颖的跟踪模块来克服之前方法在户外场景中由于缺乏几何先验而导致的跟踪问题,并引入了动态映射模块来避免尺度漂移,从而提高跟踪精度和场景重建质量。实验证明,S3PO-GS在新型视图合成和跟踪精度方面均达到了领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS因其高保真度和实时新视图合成性能而在SLAM中受到关注。
- 以往的某些方法在户外场景中使用可微分渲染管道进行跟踪,但缺乏几何先验信息。
- 一些方法引入了独立的跟踪模块,但相机运动幅度较大时会导致误差累积,引发尺度漂移问题。
- S3PO-GS建立了一个基于三维高斯点图的自洽跟踪模块,避免累积尺度漂移并实现了更准确和稳健的跟踪。
- 通过基于补丁的点图动态映射模块引入几何先验,避免了尺度歧义性,增强了跟踪精度和场景重建质量。
点此查看论文截图

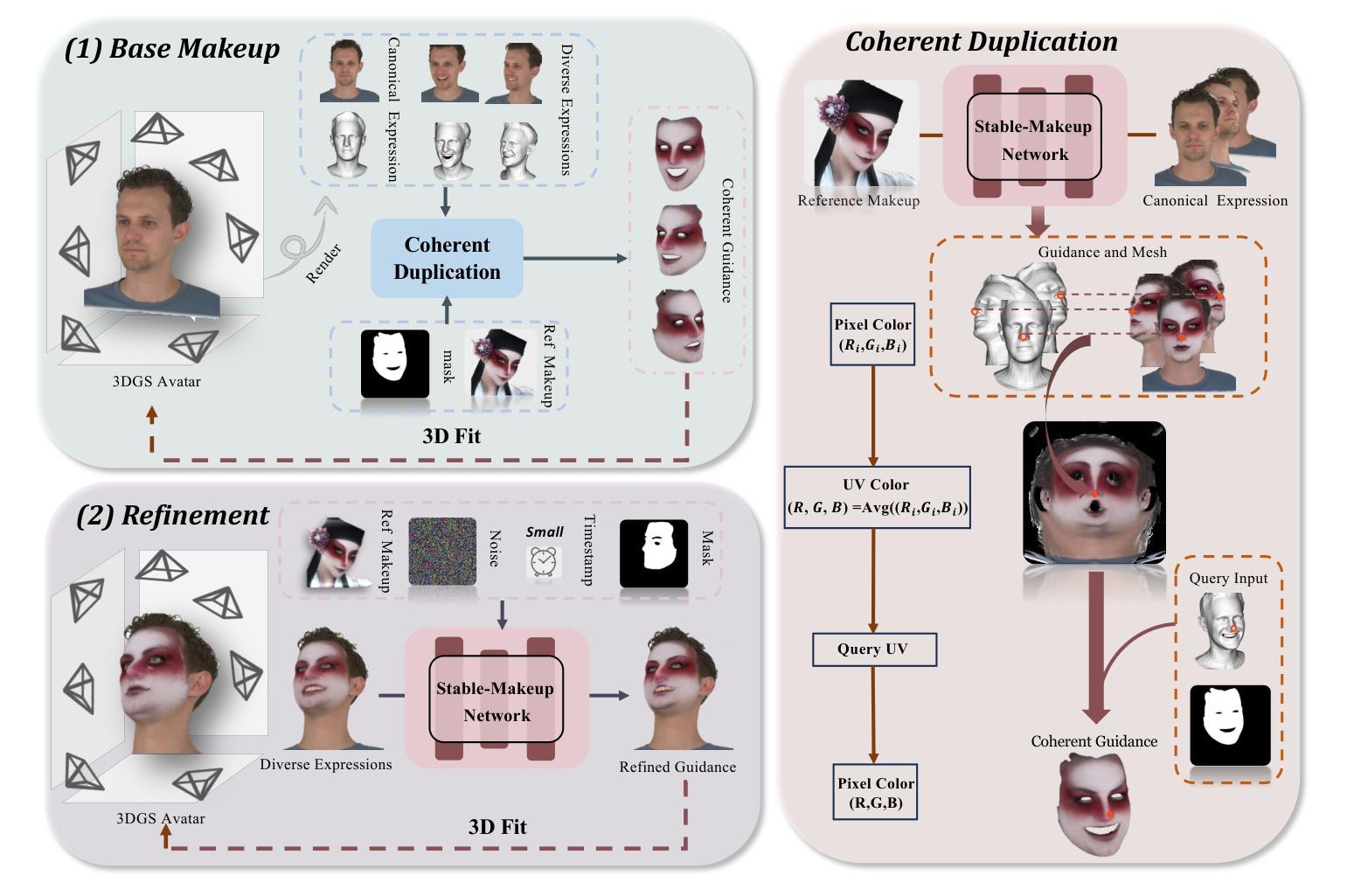
AvatarMakeup: Realistic Makeup Transfer for 3D Animatable Head Avatars
Authors:Yiming Zhong, Xiaolin Zhang, Ligang Liu, Yao Zhao, Yunchao Wei
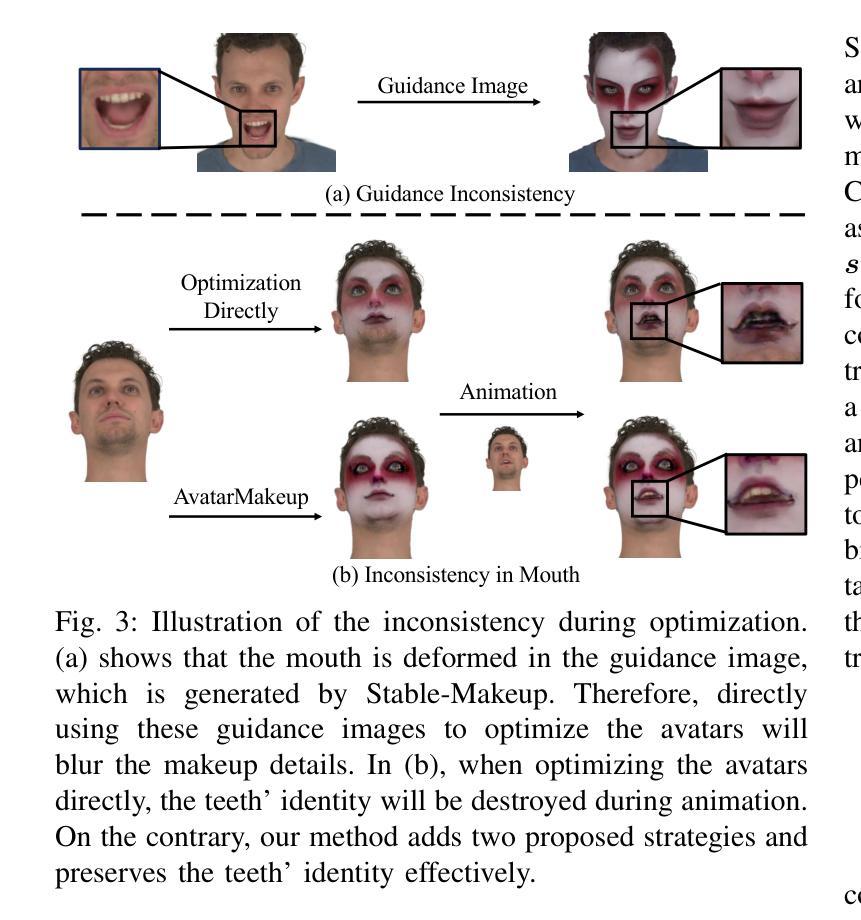
Similar to facial beautification in real life, 3D virtual avatars require personalized customization to enhance their visual appeal, yet this area remains insufficiently explored. Although current 3D Gaussian editing methods can be adapted for facial makeup purposes, these methods fail to meet the fundamental requirements for achieving realistic makeup effects: 1) ensuring a consistent appearance during drivable expressions, 2) preserving the identity throughout the makeup process, and 3) enabling precise control over fine details. To address these, we propose a specialized 3D makeup method named AvatarMakeup, leveraging a pretrained diffusion model to transfer makeup patterns from a single reference photo of any individual. We adopt a coarse-to-fine idea to first maintain the consistent appearance and identity, and then to refine the details. In particular, the diffusion model is employed to generate makeup images as supervision. Due to the uncertainties in diffusion process, the generated images are inconsistent across different viewpoints and expressions. Therefore, we propose a Coherent Duplication method to coarsely apply makeup to the target while ensuring consistency across dynamic and multiview effects. Coherent Duplication optimizes a global UV map by recoding the averaged facial attributes among the generated makeup images. By querying the global UV map, it easily synthesizes coherent makeup guidance from arbitrary views and expressions to optimize the target avatar. Given the coarse makeup avatar, we further enhance the makeup by incorporating a Refinement Module into the diffusion model to achieve high makeup quality. Experiments demonstrate that AvatarMakeup achieves state-of-the-art makeup transfer quality and consistency throughout animation.
类似于现实生活中的面部美容,3D虚拟角色需要个性化定制以增强其视觉吸引力,但这个领域仍然没有得到足够的探索。尽管当前的3D高斯编辑方法可以适应面部化妆的目的,但这些方法未能满足实现真实化妆效果的基本需求:1)在可驱动的表情中确保一致的外观,2)在化妆过程中保持身份识别,以及3)对细节进行精确控制。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种专门的3D化妆方法,名为AvatarMakeup,它利用预训练的扩散模型从任何个人的单张参考照片中转移化妆模式。我们采用由粗到细的理念,首先保持外观和身份的的一致性,然后细化细节。特别是,利用扩散模型生成化妆图像作为监督。由于扩散过程中的不确定性,生成的图像在不同的视角和表情下存在不一致性。因此,我们提出了一种协同复制方法,将化妆粗略地应用到目标上,同时确保动态和多视角效果的一致性。协同复制通过重新编码生成化妆图像之间的平均面部属性来优化全局UV地图。通过查询全局UV地图,它很容易合成来自任意视角和表情的连贯化妆指导,以优化目标角色。对于粗略的化妆角色,我们进一步通过将其纳入扩散模型中增强化妆效果,从而实现高质量的化妆效果。实验表明,AvatarMakeup在动画过程中实现了最先进的化妆转移质量和一致性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种名为AvatarMakeup的3D虚拟角色化妆方法,该方法利用预训练的扩散模型从单一参考照片转移妆容。为解决现有3D高斯编辑方法在虚拟角色化妆方面存在的不足,如保持动态表情和视角变化时妆容的一致性、保持身份识别以及在精细控制细节方面的需求,本文采用从粗到精的策略,首先确保妆容的一致性和身份识别,再精细处理细节。利用扩散模型生成妆容图像作为监督,并提出Coherent Duplication方法,确保动态和多元视角下的妆容一致性。最后,通过引入细化模块进一步提高妆容质量。
Key Takeaways
- 3D虚拟角色需要个性化化妆以增强视觉吸引力,但此领域尚未得到充分探索。
- 当前3D高斯编辑方法在虚拟角色化妆方面存在缺陷,无法满足真实妆容效果的要求。
- AvatarMakeup方法利用预训练的扩散模型从单一参考照片转移妆容,解决上述问题。
- 采用从粗到精的策略,先保证妆容的一致性和身份识别,再精细处理细节。
- 利用扩散模型生成妆容图像作为监督,并提出Coherent Duplication方法确保动态和多元视角下的妆容一致性。
- 通过引入细化模块进一步提高妆容质量。
点此查看论文截图



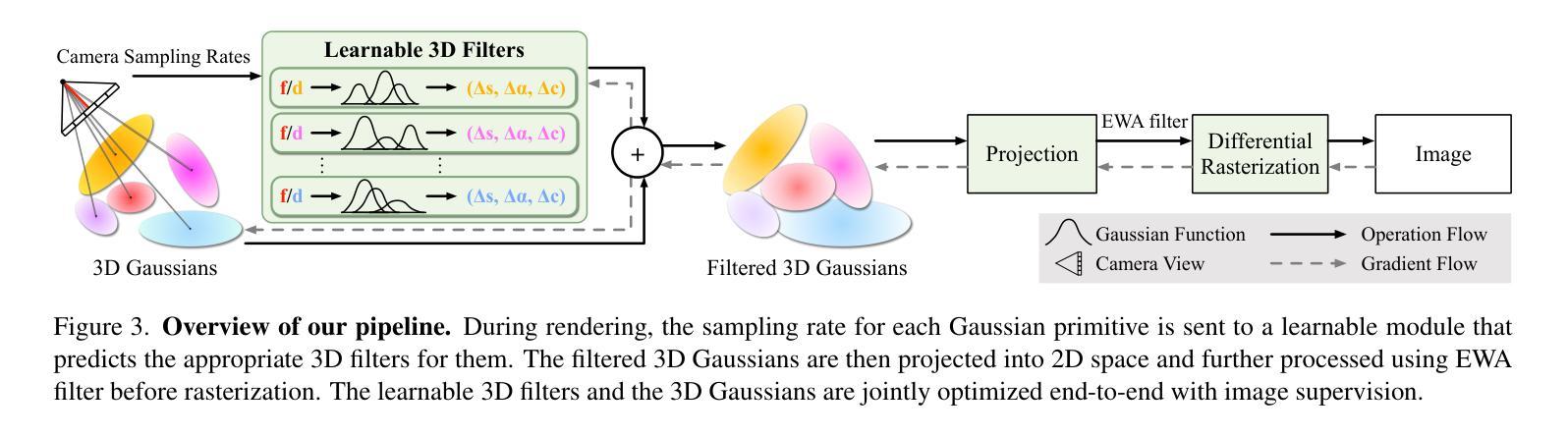
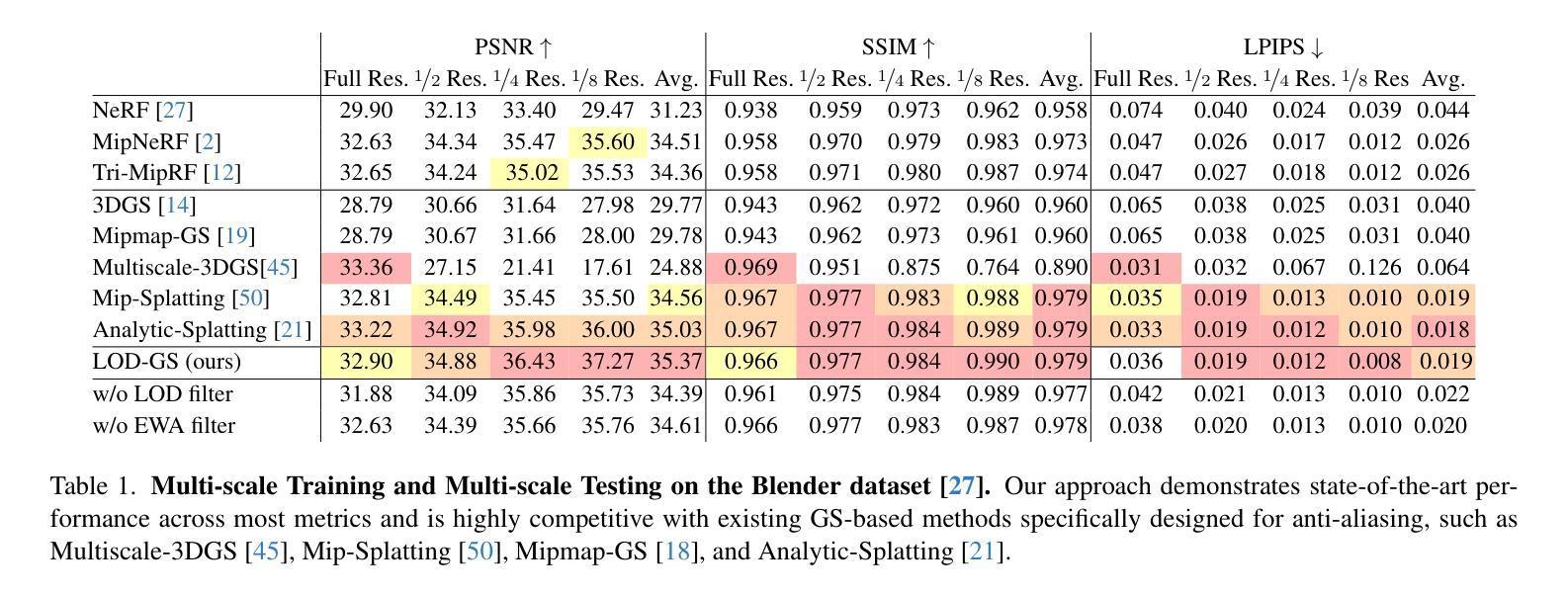
LOD-GS: Level-of-Detail-Sensitive 3D Gaussian Splatting for Detail Conserved Anti-Aliasing
Authors:Zhenya Yang, Bingchen Gong, Kai Chen
Despite the advancements in quality and efficiency achieved by 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) in 3D scene rendering, aliasing artifacts remain a persistent challenge. Existing approaches primarily rely on low-pass filtering to mitigate aliasing. However, these methods are not sensitive to the sampling rate, often resulting in under-filtering and over-smoothing renderings. To address this limitation, we propose LOD-GS, a Level-of-Detail-sensitive filtering framework for Gaussian Splatting, which dynamically predicts the optimal filtering strength for each 3D Gaussian primitive. Specifically, we introduce a set of basis functions to each Gaussian, which take the sampling rate as input to model appearance variations, enabling sampling-rate-sensitive filtering. These basis function parameters are jointly optimized with the 3D Gaussian in an end-to-end manner. The sampling rate is influenced by both focal length and camera distance. However, existing methods and datasets rely solely on down-sampling to simulate focal length changes for anti-aliasing evaluation, overlooking the impact of camera distance. To enable a more comprehensive assessment, we introduce a new synthetic dataset featuring objects rendered at varying camera distances. Extensive experiments on both public datasets and our newly collected dataset demonstrate that our method achieves SOTA rendering quality while effectively eliminating aliasing. The code and dataset have been open-sourced.
尽管3D高斯模糊贴图技术(3DGS)在3D场景渲染中取得了质量和效率的提升,但混叠伪影仍然是一个持续存在的挑战。现有的方法主要依赖低通滤波来减轻混叠现象。然而,这些方法对采样率并不敏感,往往导致滤波不足和过度平滑的渲染结果。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了LOD-GS,这是一个面向细节层次的滤波框架,用于高斯模糊贴图技术,它能动态预测每个3D高斯原始图形的最佳滤波强度。具体来说,我们对每个高斯引入了一组基函数,以采样率为输入来模拟外观变化,从而实现采样率敏感滤波。这些基函数的参数与3D高斯以端到端的方式进行联合优化。采样率受到焦距和相机距离的影响。然而,现有方法和数据集仅依赖下采样来模拟焦距变化以进行抗混叠评估,忽略了相机距离的影响。为了进行更全面的评估,我们引入了一个新的合成数据集,该数据集以不同相机距离呈现的对象进行渲染。在公共数据集和我们新收集的数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法达到了最先进的渲染质量,同时有效地消除了混叠。代码和数据集已经开源。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
3DGS在渲染场景中出现的混淆问题一直是研究者关注的难题。目前多采用低通滤波方式抑制混淆,但由于对不同采样率缺乏敏感性,容易出现过滤不足或过度平滑的问题。本研究提出了LOD-GS,一个基于细节层次的滤波框架,为高斯拼贴技术动态预测最佳滤波强度。研究引入了基于采样率的基函数,优化采样率敏感滤波,并通过实验证明该方法能有效消除混淆,达到最佳渲染效果。此外,研究还建立了一个全新的合成数据集,用于全面评估不同距离下的抗混淆效果。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS在场景渲染中的混淆问题仍是一大挑战。现有解决方案多依赖于低通滤波来缓解此问题。然而这些方法未对不同采样率敏感,容易导致过滤不足或过度平滑的渲染结果。
- 为解决这一问题,本研究提出了LOD-GS框架,它能够为高斯拼贴技术中的每个三维高斯原始数据动态预测最佳的滤波强度。
- LOD-GS引入了基于采样率的基函数,这些函数以采样率为输入来模拟外观变化,从而进行采样率敏感滤波。这些基函数的参数与三维高斯数据以端到端的方式进行联合优化。
点此查看论文截图


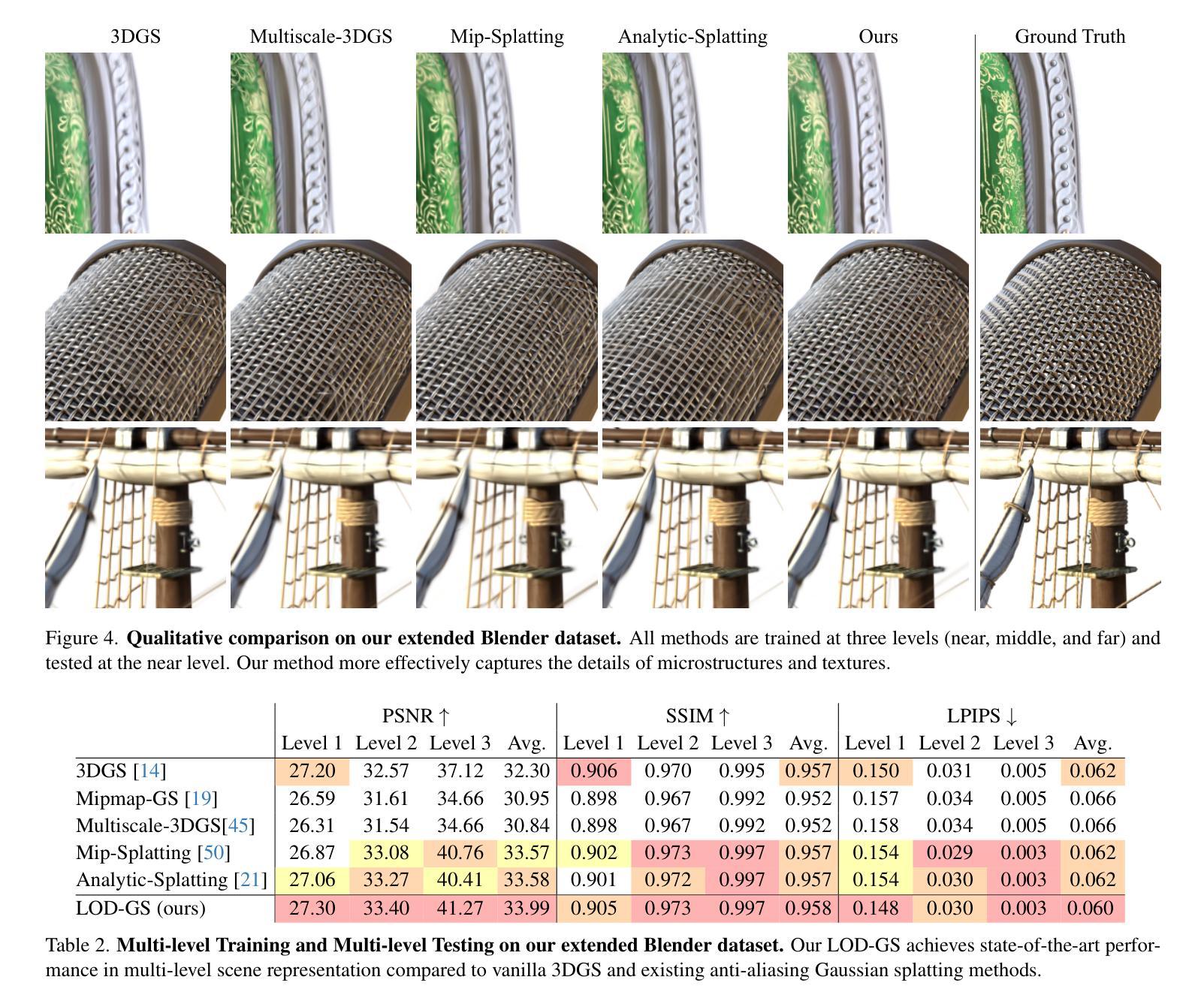
EndoFlow-SLAM: Real-Time Endoscopic SLAM with Flow-Constrained Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Taoyu Wu, Yiyi Miao, Zhuoxiao Li, Haocheng Zhao, Kang Dang, Jionglong Su, Limin Yu, Haoang Li
Efficient three-dimensional reconstruction and real-time visualization are critical in surgical scenarios such as endoscopy. In recent years, 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has demonstrated remarkable performance in efficient 3D reconstruction and rendering. Most 3DGS-based Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) methods only rely on the appearance constraints for optimizing both 3DGS and camera poses. However, in endoscopic scenarios, the challenges include photometric inconsistencies caused by non-Lambertian surfaces and dynamic motion from breathing affects the performance of SLAM systems. To address these issues, we additionally introduce optical flow loss as a geometric constraint, which effectively constrains both the 3D structure of the scene and the camera motion. Furthermore, we propose a depth regularisation strategy to mitigate the problem of photometric inconsistencies and ensure the validity of 3DGS depth rendering in endoscopic scenes. In addition, to improve scene representation in the SLAM system, we improve the 3DGS refinement strategy by focusing on viewpoints corresponding to Keyframes with suboptimal rendering quality frames, achieving better rendering results. Extensive experiments on the C3VD static dataset and the StereoMIS dynamic dataset demonstrate that our method outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in novel view synthesis and pose estimation, exhibiting high performance in both static and dynamic surgical scenes.
在内窥镜等手术场景中,高效的三维重建和实时可视化至关重要。近年来,三维高斯扩展(3DGS)在高效的三维重建和渲染方面表现出卓越的性能。大多数基于3DGS的同时定位与地图构建(SLAM)方法仅依赖外观约束来优化3DGS和相机姿态。然而,在内窥镜场景中,非朗伯表面引起的光度不一致性和呼吸引起的动态运动影响了SLAM系统的性能。为了解决这些问题,我们额外引入了光流损失作为几何约束,有效地约束了场景的三维结构和相机运动。此外,我们提出了一种深度正则化策略,以缓解光度不一致性的问题,并确保在内窥镜场景中3DGS深度渲染的有效性。另外,为了改进SLAM系统中的场景表示,我们改进了3DGS细化策略,重点关注与关键帧对应且渲染质量较差的视点,实现更好的渲染结果。在C3VD静态数据集和StereoMIS动态数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法在新型视图合成和姿态估计方面优于现有最先进的算法,在静态和动态手术场景中均表现出高性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been accepted at MICCAI2025
Summary
本文介绍了在手术场景(如内窥镜)中,三维重建和实时可视化技术的重要性。文章指出,近年来三维高斯描画(3DGS)在高效的三维重建和渲染方面表现出卓越性能。针对内窥镜场景中遇到的挑战,如光度不一致性和动态运动造成的同步定位和地图构建(SLAM)系统性能下降问题,引入了光学流损失作为几何约束,并提出深度正则化策略来缓解光度不一致性问题。此外,通过改进3DGS优化策略,提高场景在SLAM系统中的表示效果。实验证明,该方法在新型视图合成和姿态估计方面表现优于现有先进技术,适用于静态和动态手术场景。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS在高效三维重建和渲染方面具有卓越性能。
- 内窥镜场景中面临光度不一致性和动态运动挑战。
- 引入光学流损失作为几何约束,有效约束场景的三维结构和相机运动。
- 提出深度正则化策略,确保3DGS深度渲染在内窥镜场景中的有效性。
- 通过改进3DGS优化策略,提高SLAM系统中场景的表现。
- 方法在新型视图合成和姿态估计方面表现优异。
点此查看论文截图


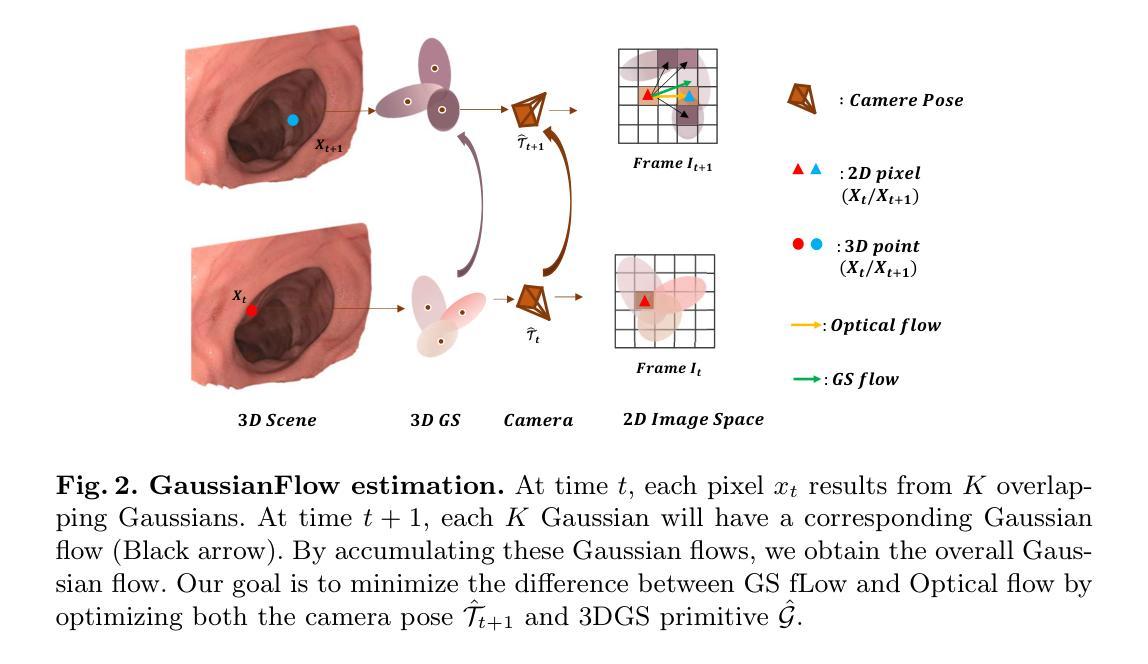
GaussRender: Learning 3D Occupancy with Gaussian Rendering
Authors:Loïck Chambon, Eloi Zablocki, Alexandre Boulch, Mickaël Chen, Matthieu Cord
Understanding the 3D geometry and semantics of driving scenes is critical for safe autonomous driving. Recent advances in 3D occupancy prediction have improved scene representation but often suffer from visual inconsistencies, leading to floating artifacts and poor surface localization. Existing voxel-wise losses (e.g., cross-entropy) fail to enforce visible geometric coherence. In this paper, we propose GaussRender, a module that improves 3D occupancy learning by enforcing projective consistency. Our key idea is to project both predicted and ground-truth 3D occupancy into 2D camera views, where we apply supervision. Our method penalizes 3D configurations that produce inconsistent 2D projections, thereby enforcing a more coherent 3D structure. To achieve this efficiently, we leverage differentiable rendering with Gaussian splatting. GaussRender seamlessly integrates with existing architectures while maintaining efficiency and requiring no inference-time modifications. Extensive evaluations on multiple benchmarks (SurroundOcc-nuScenes, Occ3D-nuScenes, SSCBench-KITTI360) demonstrate that GaussRender significantly improves geometric fidelity across various 3D occupancy models (TPVFormer, SurroundOcc, Symphonies), achieving state-of-the-art results, particularly on surface-sensitive metrics such as RayIoU. The code is open-sourced at https://github.com/valeoai/GaussRender.
理解驾驶场景的3D几何和语义对于安全自动驾驶至关重要。最近3D占用预测方面的进展改善了场景表示,但经常遭受视觉不一致的困扰,导致浮动伪影和表面定位不佳。现有的体素级损失(例如,交叉熵)无法强制实施可见的几何一致性。在本文中,我们提出了GaussRender,这是一个通过实施投影一致性改进3D占用学习的模块。我们的核心思想是将预测的和真实的3D占用投影到2D相机视图中,并在那里应用监督。我们的方法惩罚产生不一致2D投影的3D配置,从而强制实施更连贯的3D结构。为了实现高效性,我们利用可微分渲染和高斯平铺技术。GaussRender可以无缝地集成到现有架构中,同时保持效率,并且不需要进行推理时间修改。在多个基准测试(SurroundOcc-nuScenes、Occ3D-nuScenes、SSCBench-KITTI360)上的广泛评估表明,GaussRender显著提高了各种3D占用模型的几何保真度(TPVFormer、SurroundOcc、Symphonies),实现了最新结果,特别是在对表面敏感的指标(例如RayIoU)上。代码已公开在https://github.com/valeoai/GaussRender。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025
摘要
针对自动驾驶中的三维场景理解,本文提出GaussRender模块,通过投影一致性改善三维占据学习。将预测的和真实的三维占据信息投影到二维相机视角,应用监督学习,惩罚产生不一致二维投影的三维配置,从而强制更连贯的三维结构。利用可微分渲染和高斯涂斑技术实现高效方法。GaussRender可无缝集成现有架构,维持效率且无需推理时间修改。在多个基准测试上评估,证明GaussRender能显著提高各种三维占据模型的几何保真度,达到先进水平,尤其在于表面敏感指标如RayIoU。代码已开源。
关键见解
- 理解和模拟驾驶场景的三维几何和语义对安全自动驾驶至关重要。
- 最近的3D占用预测进展改善了场景表示,但存在视觉不一致性问题,导致浮动伪影和表面定位不佳。
- 现有的体素损失(如交叉熵)未能强制实施几何一致性。
- 本文提出GaussRender模块,通过投影一致性改进3D occupancy学习。
- GaussRender将预测的和真实的三维占据信息投影到二维相机视角,并在此应用监督,从而强制实施更连贯的三维结构。
- 方法利用可微分渲染和高斯涂斑技术实现高效,可无缝集成到现有架构中,同时保持效率,且无需在推理时间进行修改。
点此查看论文截图

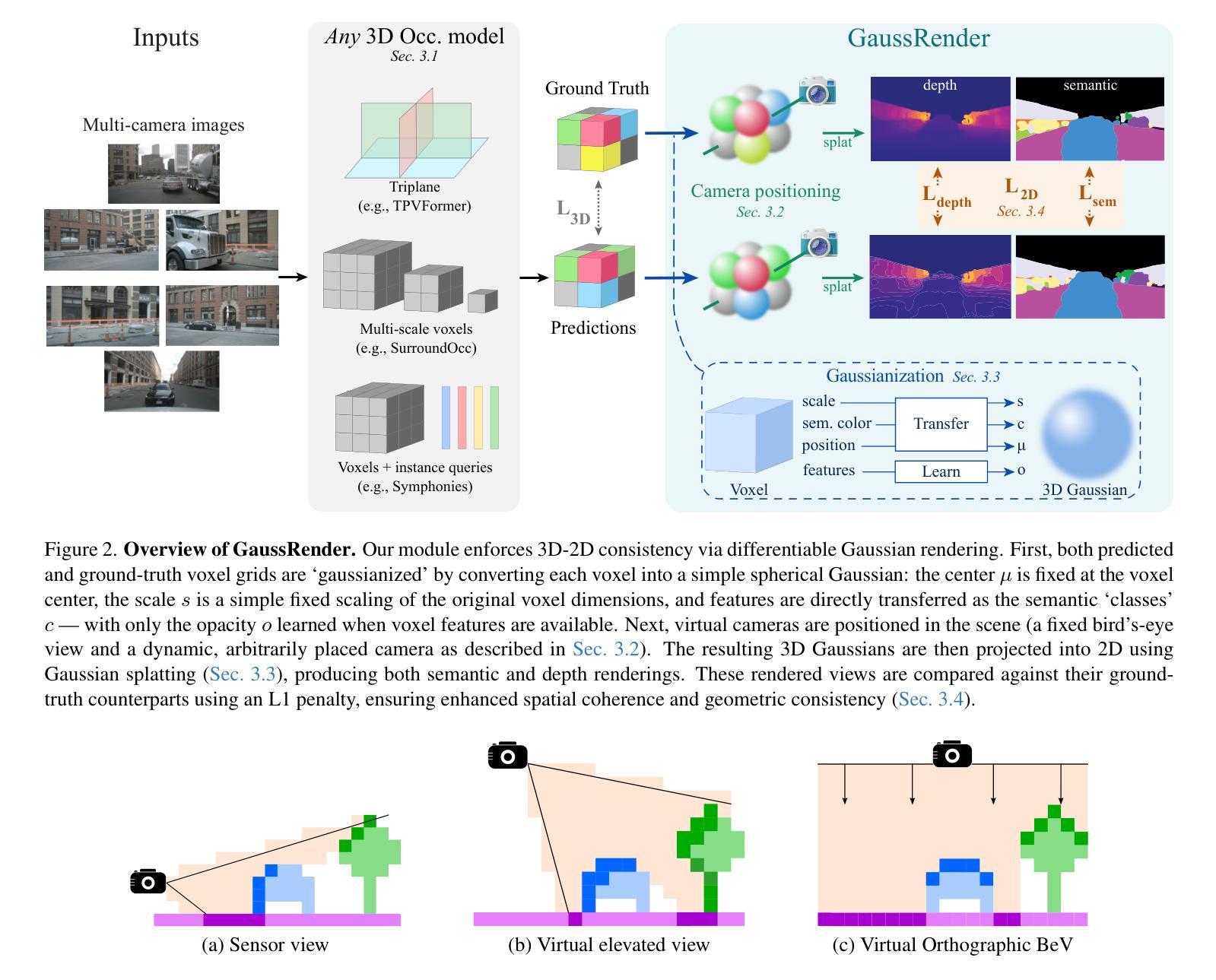

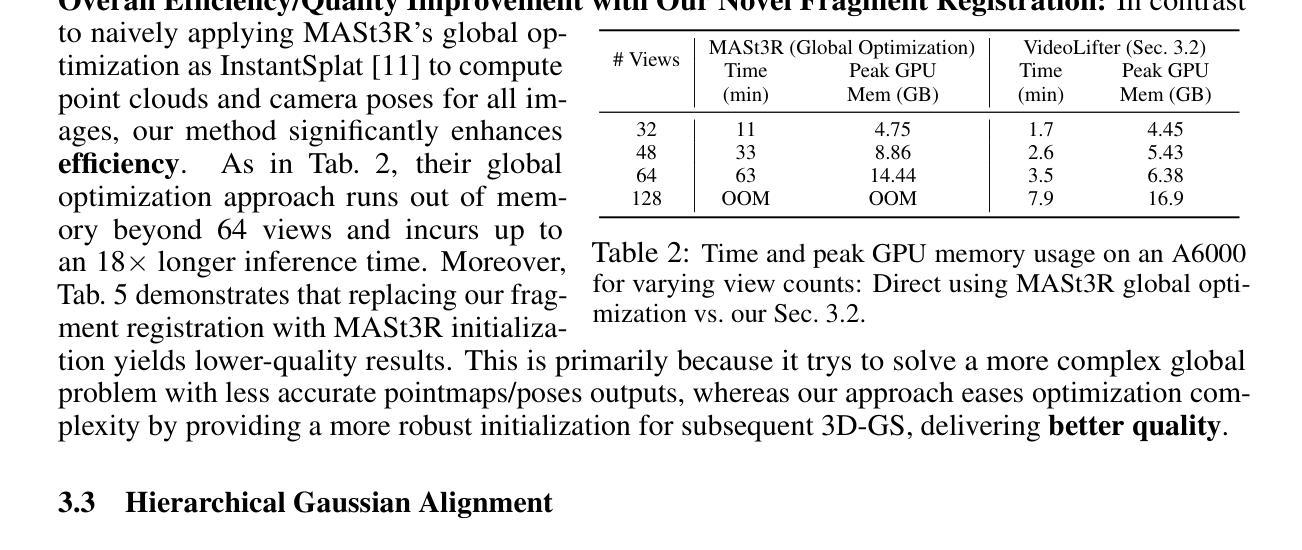
VideoLifter: Lifting Videos to 3D with Fast Hierarchical Stereo Alignment
Authors:Wenyan Cong, Hanqing Zhu, Kevin Wang, Jiahui Lei, Colton Stearns, Yuanhao Cai, Leonidas Guibas, Zhangyang Wang, Zhiwen Fan
Efficiently reconstructing 3D scenes from monocular video remains a core challenge in computer vision, vital for applications in virtual reality, robotics, and scene understanding. Recently, frame-by-frame progressive reconstruction without camera poses is commonly adopted, incurring high computational overhead and compounding errors when scaling to longer videos. To overcome these issues, we introduce VideoLifter, a novel video-to-3D pipeline that leverages a local-to-global strategy on a fragment basis, achieving both extreme efficiency and SOTA quality. Locally, VideoLifter leverages learnable 3D priors to register fragments, extracting essential information for subsequent 3D Gaussian initialization with enforced inter-fragment consistency and optimized efficiency. Globally, it employs a tree-based hierarchical merging method with key frame guidance for inter-fragment alignment, pairwise merging with Gaussian point pruning, and subsequent joint optimization to ensure global consistency while efficiently mitigating cumulative errors. This approach significantly accelerates the reconstruction process, reducing training time by over 82% while holding better visual quality than current SOTA methods.
从单目视频中高效重建3D场景仍然是计算机视觉领域的一个核心挑战,对于虚拟现实、机器人技术和场景理解等应用至关重要。近期,采用无需相机姿态的逐帧渐进重建方法被广泛采用,这在处理较长视频时会导致较高的计算开销和累积误差。为了克服这些问题,我们引入了VideoLifter,这是一种新型的视频到3D的流水线,它采用基于片段的局部到全局策略,实现了极高的效率和最先进的技术质量。在局部上,VideoLifter利用可学习的3D先验知识对片段进行注册,提取关键信息为后续3D高斯初始化提供基础,并加强片段间的一致性以及优化效率。在全局上,它采用基于树的层次合并方法,借助关键帧指导进行片段间对齐、高斯点修剪的配对合并以及随后的联合优化,确保全局一致性,同时有效地减轻了累积误差。这种方法显著加速了重建过程,训练时间减少了超过82%,同时保持了比当前最先进技术更高的视觉质量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF project page: https://videolifter.github.io
Summary
本文介绍了VideoLifter这一新型视频转3D管道技术,该技术采用局部到全局的策略,在片段基础上实现极高的效率和先进的质量。局部上,VideoLifter利用可学习的3D先验知识来注册片段,为后续3D高斯初始化提取必要信息并强制片段间的一致性及优化效率。全局上,它采用基于树结构的层次合并方法,带有关键帧引导、配对合并和高斯点修剪等策略,确保全局一致性并有效减少累积误差。这种方法大大加快了重建过程,减少了超过82%的训练时间,同时提供比当前先进技术更好的视觉效果。
Key Takeaways
以下是关于文中介绍的关键点的要点:
- VideoLifter技术实现了从视频到3D场景的快速高效重建,用于虚拟现实、机器人和场景理解等应用。
- 传统的帧逐帧重建方式因计算量大和误差累积问题而受到挑战。
- VideoLifter采用局部到全局的策略,通过片段处理实现高效和高质。
- 在局部层面,利用可学习的3D先验知识注册片段,为后续初始化提供必要信息,并强化片段间的一致性和优化效率。
- 在全局层面,采用基于树的层次合并方法,确保全局一致性并减少累积误差。
- VideoLifter通过关键帧引导、配对合并和高斯点修剪等技术提高了重建的质量和效率。
点此查看论文截图


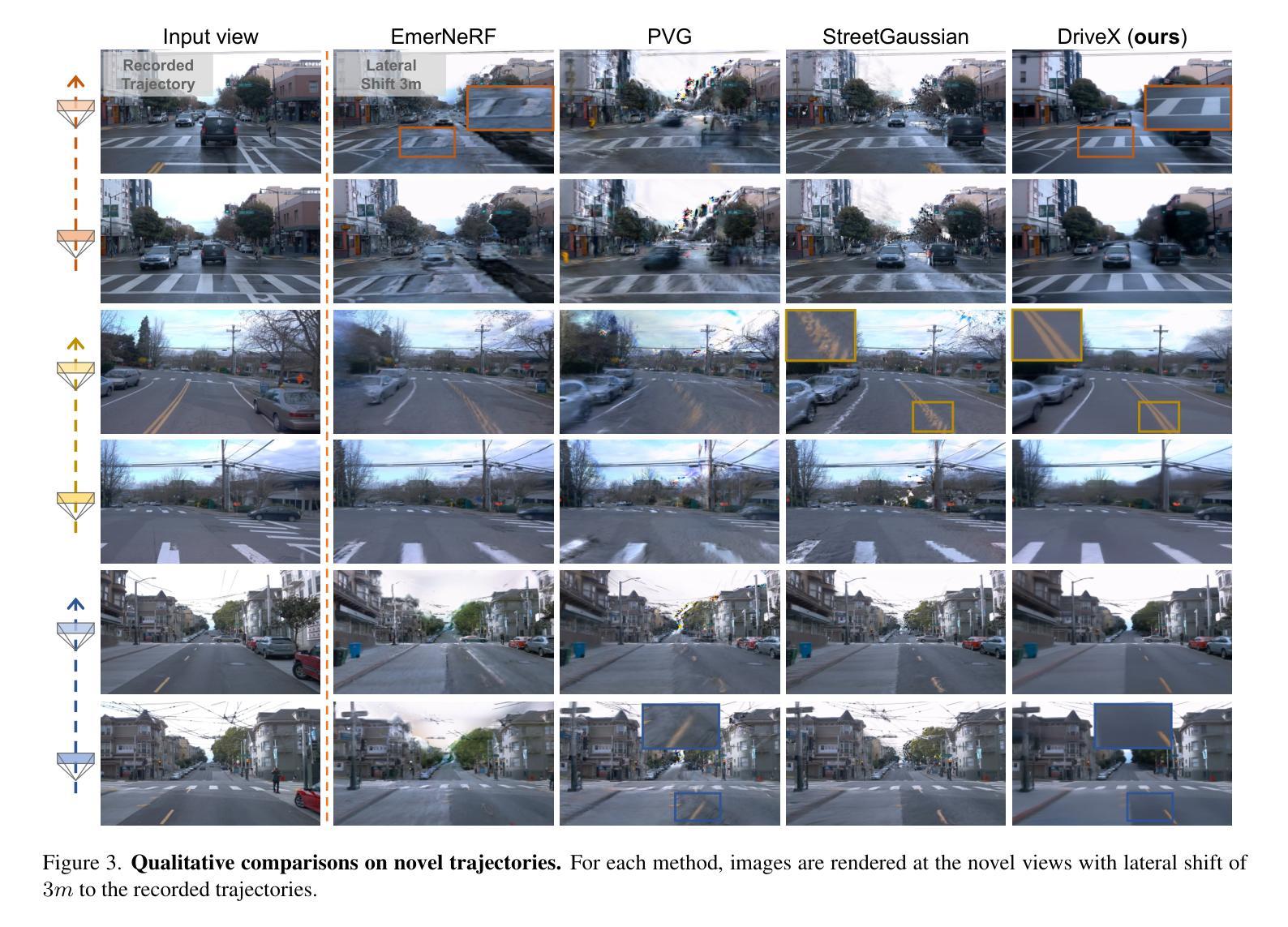
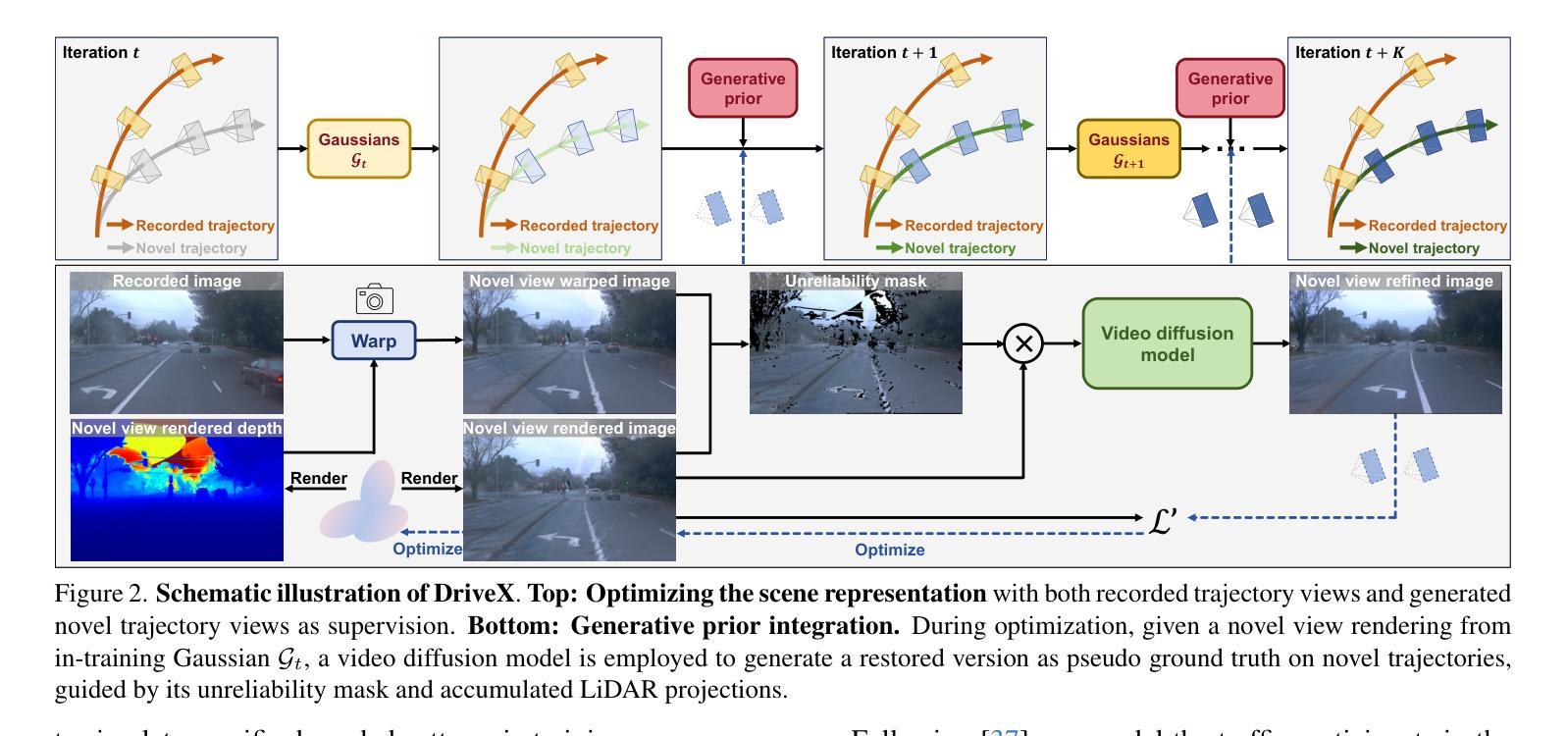
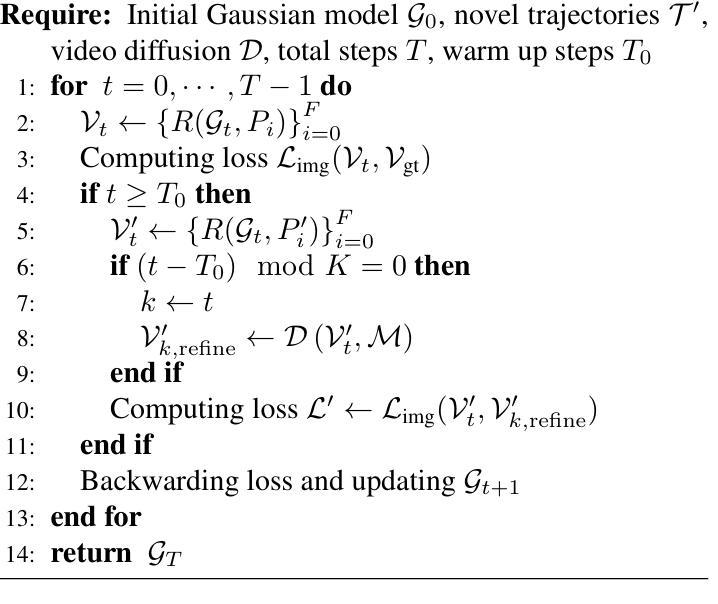
DriveX: Driving View Synthesis on Free-form Trajectories with Generative Prior
Authors:Zeyu Yang, Zijie Pan, Yuankun Yang, Xiatian Zhu, Li Zhang
Driving view synthesis along free-form trajectories is essential for realistic driving simulations, enabling closed-loop evaluation of end-to-end driving policies. Existing methods excel at view interpolation along recorded paths but struggle to generalize to novel trajectories due to limited viewpoints in driving videos. To tackle this challenge, we propose DriveX, a novel free-form driving view synthesis framework, that progressively distills generative prior into the 3D Gaussian model during its optimization. Within this framework, we utilize a video diffusion model to refine the degraded novel trajectory renderings from the in-training Gaussian model, while the restored videos in turn serve as additional supervision for optimizing the 3D Gaussian. Concretely, we craft an inpainting-based video restoration task, which can disentangle the identification of degraded regions from the generative capability of the diffusion model and remove the need of simulating specific degraded pattern in the training of the diffusion model. To further enhance the consistency and fidelity of generated contents, the pseudo ground truth is progressively updated with gradually improved novel trajectory rendering, allowing both components to co-adapt and reinforce each other while minimizing the disruption on the optimization. By tightly integrating 3D scene representation with generative prior, DriveX achieves high-quality view synthesis beyond recorded trajectories in real time–unlocking new possibilities for flexible and realistic driving simulations on free-form trajectories.
驾驶视角的合成沿着自由形式的轨迹对于真实的驾驶模拟至关重要,它能够实现端到端驾驶策略的闭环评估。现有方法在沿着记录路径的视图插值方面表现出色,但由于驾驶视频中观点有限,很难推广到新的轨迹。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了DriveX,这是一种新型的自由形式驾驶视角合成框架,它能在优化过程中逐步将生成先验知识提炼到3D高斯模型中。在这个框架内,我们利用视频扩散模型来完善训练中的高斯模型产生的退化新轨迹渲染,同时恢复的视频反过来作为优化3D高斯模型的额外监督。具体来说,我们制定了一项基于图像补全的视频恢复任务,该任务能够从扩散模型的生成能力中识别出退化区域,从而在训练扩散模型时无需模拟特定的退化模式。为了进一步提高生成内容的一致性和保真度,伪地面真实值会随逐渐改进的新轨迹渲染而逐步更新,使两个组件能够相互适应和强化,同时最小化对优化的干扰。通过紧密集成3D场景表示和生成先验知识,DriveX在实时条件下实现了超越记录轨迹的高质量视角合成,为自由形式轨迹上的灵活和真实驾驶模拟开启了新的可能性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025
Summary
该文针对驾驶模拟中的轨迹合成问题,提出了一种名为DriveX的新型自由轨迹驾驶视图合成框架。该框架利用生成先验逐步提炼3D高斯模型,并利用视频扩散模型对训练中的高斯模型产生的退化新轨迹渲染进行细化。通过结合3D场景表示和生成先验,DriveX实现了超越记录轨迹的高质量实时视图合成,为灵活和逼真的驾驶模拟提供了新的可能性。
Key Takeaways
- DriveX框架解决了驾驶模拟中沿自由轨迹的视图合成问题,这对于实现端到端的驾驶策略闭环评估至关重要。
- 该框架利用生成先验逐步优化3D高斯模型,提高了视图合成的质量。
- 使用视频扩散模型细化新轨迹渲染,进一步提高合成视图的逼真度。
- 提出了一种基于图像补全的视频恢复任务,提高了扩散模型的生成能力和对退化区域的识别能力。
- 通过逐步更新伪地面真实和逐渐改进的新轨迹渲染,增强了生成内容的连贯性和保真度。
- DriveX框架实现了实时的高质量视图合成,超越了以往的记录轨迹,为驾驶模拟提供了更大的灵活性。
点此查看论文截图



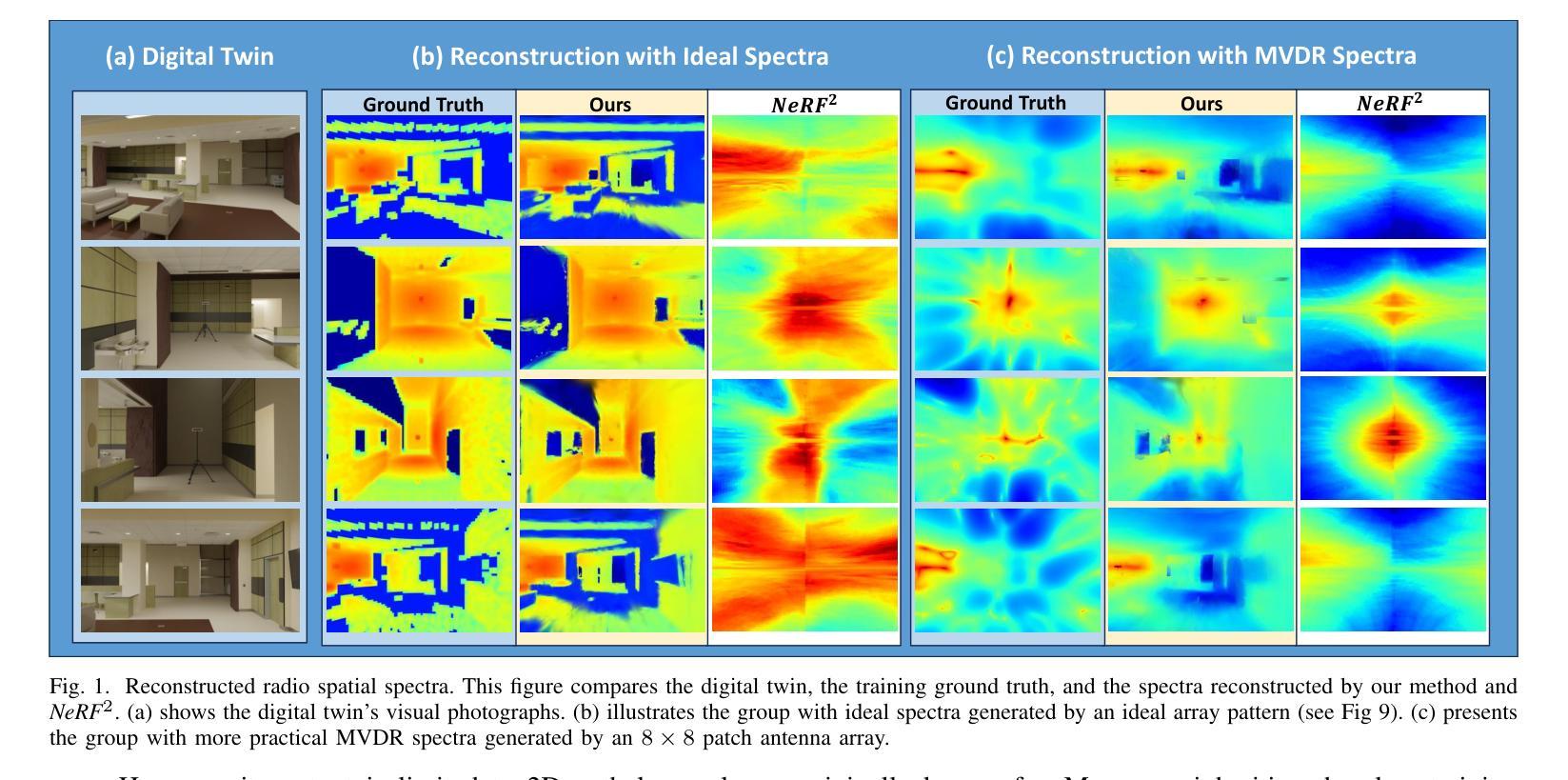
RF-3DGS: Wireless Channel Modeling with Radio Radiance Field and 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Lihao Zhang, Haijian Sun, Samuel Berweger, Camillo Gentile, Rose Qingyang Hu
Precisely modeling radio propagation in complex environments has been a significant challenge, especially with the advent of 5G and beyond networks, where managing massive antenna arrays demands more detailed information. Traditional methods, such as empirical models and ray tracing, often fall short, either due to insufficient details or because of challenges for real-time applications. Inspired by the newly proposed 3D Gaussian Splatting method in the computer vision domain, which outperforms other methods in reconstructing optical radiance fields, we propose RF-3DGS, a novel approach that enables precise site-specific reconstruction of radio radiance fields from sparse samples. RF-3DGS can render radio spatial spectra at arbitrary positions within 2 ms following a brief 3-minute training period, effectively identifying dominant propagation paths. Furthermore, RF-3DGS can provide fine-grained Spatial Channel State Information (Spatial-CSI) of these paths, including the channel gain, the delay, the angle of arrival (AoA), and the angle of departure (AoD). Our experiments, calibrated through real-world measurements, demonstrate that RF-3DGS not only significantly improves reconstruction quality, training efficiency, and rendering speed compared to state-of-the-art methods, but also holds great potential for supporting wireless communication and advanced applications such as Integrated Sensing and Communication (ISAC). Code and dataset will be available at https://github.com/SunLab-UGA/RF-3DGS.
对复杂环境中的无线电传播进行精确建模一直是一个巨大的挑战,尤其是随着5G及以后网络的出现,管理大规模天线阵列需要更详细的信息。传统的方法,如经验模型和射线追踪,往往因为缺乏细节或实时应用方面的挑战而达不到预期效果。受计算机视觉领域新提出的3D高斯喷涂法(3DGS)的启发,该方法在重建光学辐射场方面表现出卓越性能,我们提出了RF-3DGS,这是一种能够从稀疏样本中进行精确的站场重建无线电辐射场的新方法。RF-3DGS可以在短暂的3分钟训练期后,在2毫秒内渲染任意位置的无线电频谱,有效地识别出主要的传播路径。此外,RF-3DGS还可以提供这些路径的精细空间信道状态信息(Spatial-CSI),包括信道增益、延迟、到达角(AoA)和离开角(AoD)。我们的实验通过真实世界的测量进行了校准,证明RF-3DGS不仅显著提高了重建质量、训练效率和渲染速度,与最新技术相比具有巨大的优势,而且在大力支持无线通信和集成传感与通信(ISAC)等高级应用方面也具有巨大潜力。代码和数据集将在https://github.com/SunLab-UGA/RF-3DGS上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF in submission to IEEE journals
Summary
针对复杂环境中的电波传播精确建模一直是重大挑战,尤其是5G及以后网络,管理大规模天线阵列需要更详细的信息。受计算机视觉领域新提出的3D高斯喷涂法启发,我们提出RF-3DGS新方法,能从稀疏样本中重建精确的无线电辐射场。RF-3DGS可在短暂的3分钟训练后,在2毫秒内渲染任意位置的无线电频谱,有效识别主要的传播路径。此外,RF-3DGS还能提供这些路径的精细空间信道状态信息,包括信道增益、延迟、到达角(AoA)和离开角(AoD)。实验证明,RF-3DGS不仅显著提高了重建质量、训练效率和渲染速度,而且具有支持无线通信和集成传感通信(ISAC)等先进应用的巨大潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 建模复杂环境中的电波传播一直存在挑战,特别是大规模天线阵列的管理需求日益增加。
- 传统建模方法如经验模型和射线追踪法存在局限性。
- 受计算机视觉中3D高斯喷涂法的启发,提出了RF-3DGS新方法。
- RF-3DGS能精确重建无线电辐射场,从稀疏样本中生成详细的无线电空间频谱。
- RF-3DGS能迅速渲染任意位置的无线电频谱,并有效识别主要的传播路径。
- RF-3DGS提供精细的空间信道状态信息,包括信道增益、延迟、到达角和离开角等。
点此查看论文截图


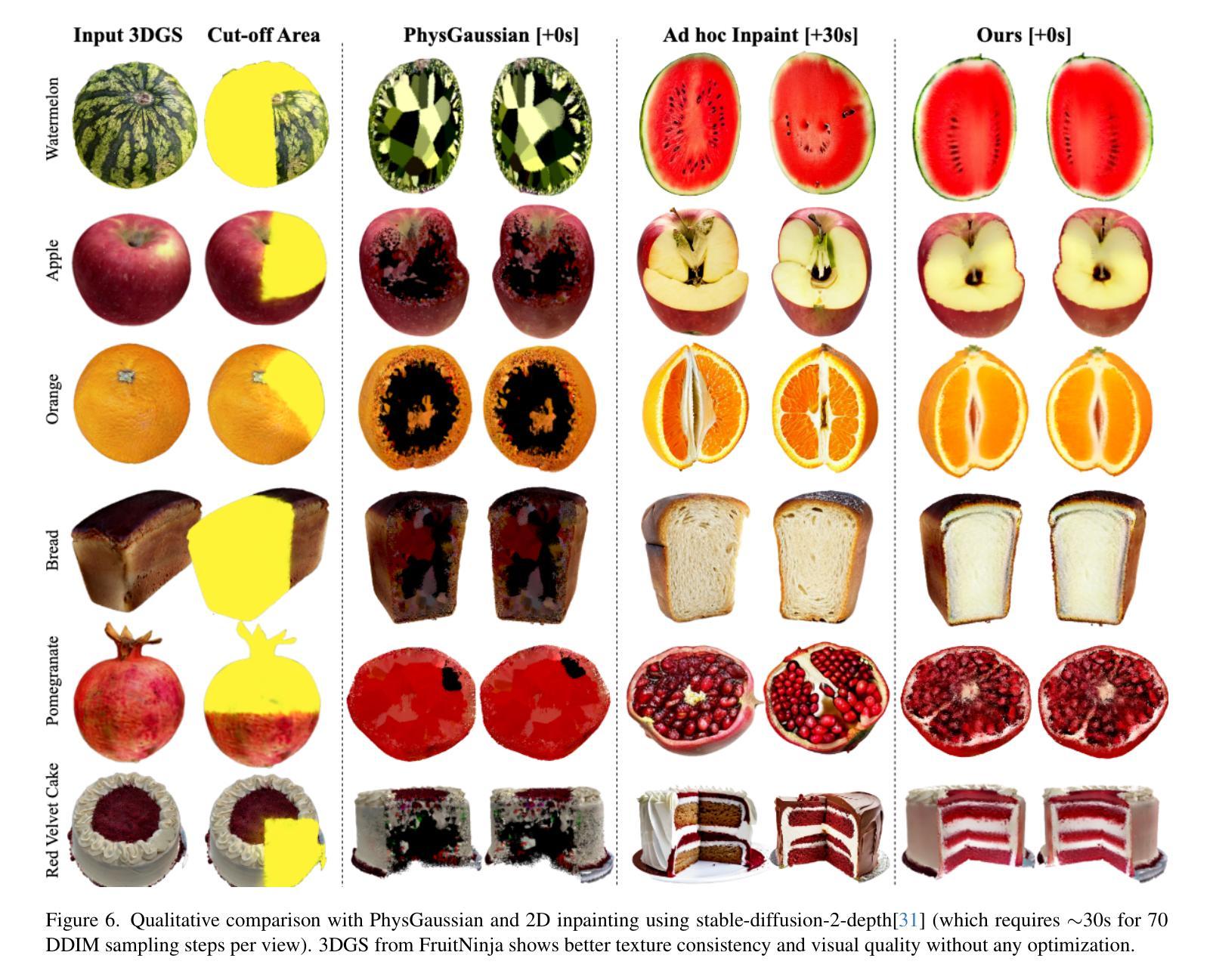
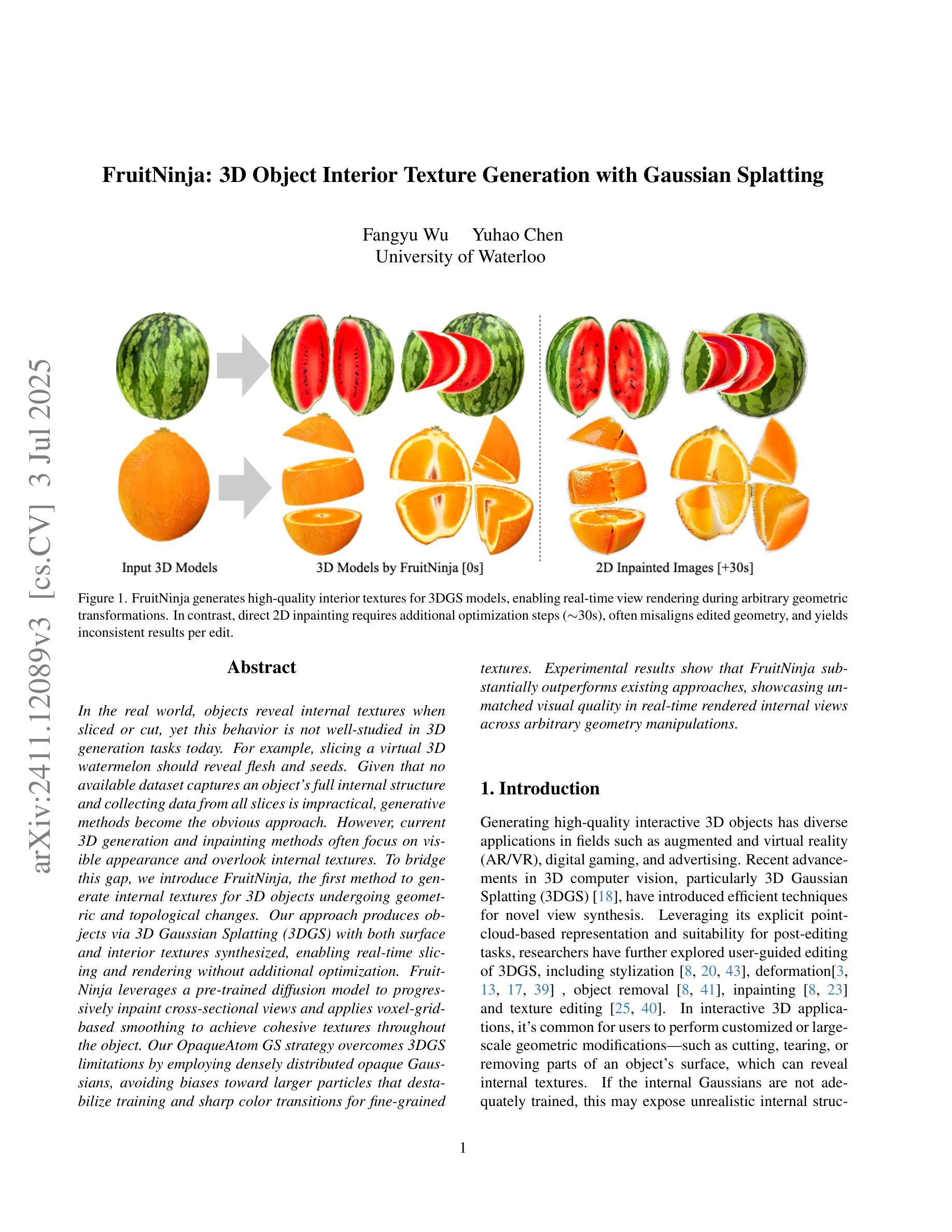
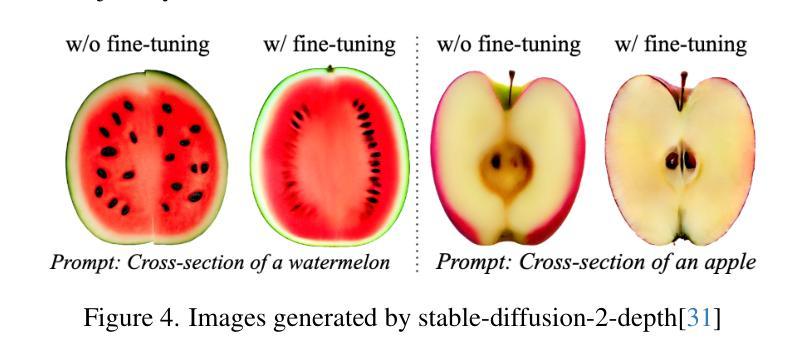
FruitNinja: 3D Object Interior Texture Generation with Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Fangyu Wu, Yuhao Chen
In the real world, objects reveal internal textures when sliced or cut, yet this behavior is not well-studied in 3D generation tasks today. For example, slicing a virtual 3D watermelon should reveal flesh and seeds. Given that no available dataset captures an object’s full internal structure and collecting data from all slices is impractical, generative methods become the obvious approach. However, current 3D generation and inpainting methods often focus on visible appearance and overlook internal textures. To bridge this gap, we introduce FruitNinja, the first method to generate internal textures for 3D objects undergoing geometric and topological changes. Our approach produces objects via 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) with both surface and interior textures synthesized, enabling real-time slicing and rendering without additional optimization. FruitNinja leverages a pre-trained diffusion model to progressively inpaint cross-sectional views and applies voxel-grid-based smoothing to achieve cohesive textures throughout the object. Our OpaqueAtom GS strategy overcomes 3DGS limitations by employing densely distributed opaque Gaussians, avoiding biases toward larger particles that destabilize training and sharp color transitions for fine-grained textures. Experimental results show that FruitNinja substantially outperforms existing approaches, showcasing unmatched visual quality in real-time rendered internal views across arbitrary geometry manipulations.
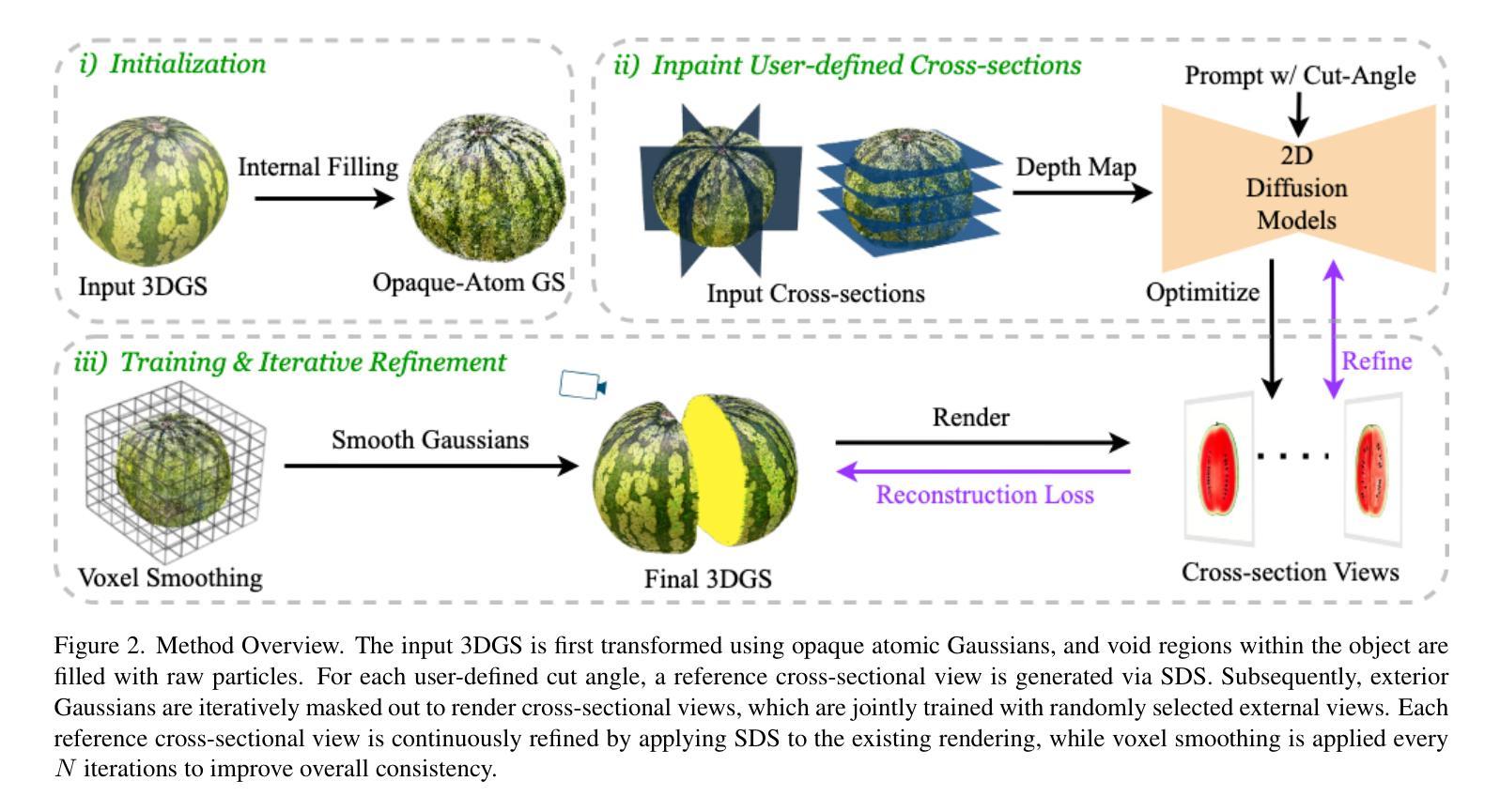
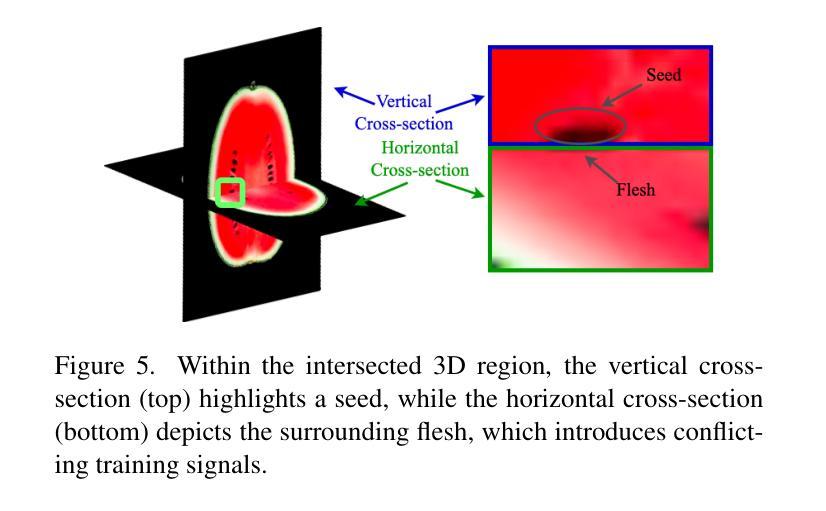
在真实世界中,物体在被切割时会显示出内部纹理,然而这一行为在当前的3D生成任务中并未得到很好的研究。例如,切割虚拟的3D西瓜应该能够显示出瓜瓤和瓜籽。由于目前没有数据集能够捕捉物体的完整内部结构,并且从所有切片收集数据并不实际,因此生成方法成为了一个显而易见的选择。然而,当前的3D生成和补全方法通常侧重于可见的外观,而忽略了内部纹理。为了填补这一空白,我们引入了FruitNinja,这是第一种能够为经历几何和拓扑变化的3D对象生成内部纹理的方法。我们的方法通过3D高斯展开(3DGS)生成对象,同时合成表面和内部纹理,能够实现实时切片和渲染,无需额外的优化。FruitNinja利用预训练的扩散模型来逐步填充横截面视图,并应用基于体素网格的平滑处理,以实现整个对象中的连贯纹理。我们的OpaqueAtom GS策略通过采用密集分布的不透明高斯分布来克服3DGS的局限性,避免了偏向较大粒子导致的训练不稳定和精细纹理的尖锐色彩过渡问题。实验结果表明,FruitNinja显著优于现有方法,在任意几何操作的实时渲染内部视图中展现出无与伦比的视觉品质。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted in CVPR 2025, project page https://fanguw.github.io/FruitNinja3D
Summary
本文提出一种名为FruitNinja的方法,利用三维高斯点投影技术(3DGS),生成在几何和拓扑变化下的三维对象内部纹理。该方法通过预训练的扩散模型逐步填充横截面视图,并利用体素网格平滑技术实现对象内外部纹理的连贯性。通过采用密集分布的遮罩高斯方法克服3DGS的局限性,避免大型粒子导致的训练不稳定和精细纹理的尖锐色彩过渡问题。实验结果显示FruitNinja在实时渲染内部视图方面显著优于现有方法,具有出色的视觉效果。
Key Takeaways
- FruitNinja是一种基于三维高斯点投影技术(3DGS)的方法,旨在生成三维对象的内部纹理。
- 当前的三维生成和补全方法往往关注可见外观,忽略了内部纹理。FruitNinja填补了这一空白。
- FruitNinja使用预训练的扩散模型逐步填充横截面视图,实现内外部纹理的连贯性。
- 通过采用密集分布的遮罩高斯方法(OpaqueAtom GS),克服了3DGS的局限性。
- 该方法避免了因大型粒子导致的训练不稳定和精细纹理的尖锐色彩过渡问题。
- 实验结果显示FruitNinja在实时渲染内部视图方面显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图