⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-09 更新
SV-DRR: High-Fidelity Novel View X-Ray Synthesis Using Diffusion Model
Authors:Chun Xie, Yuichi Yoshii, Itaru Kitahara
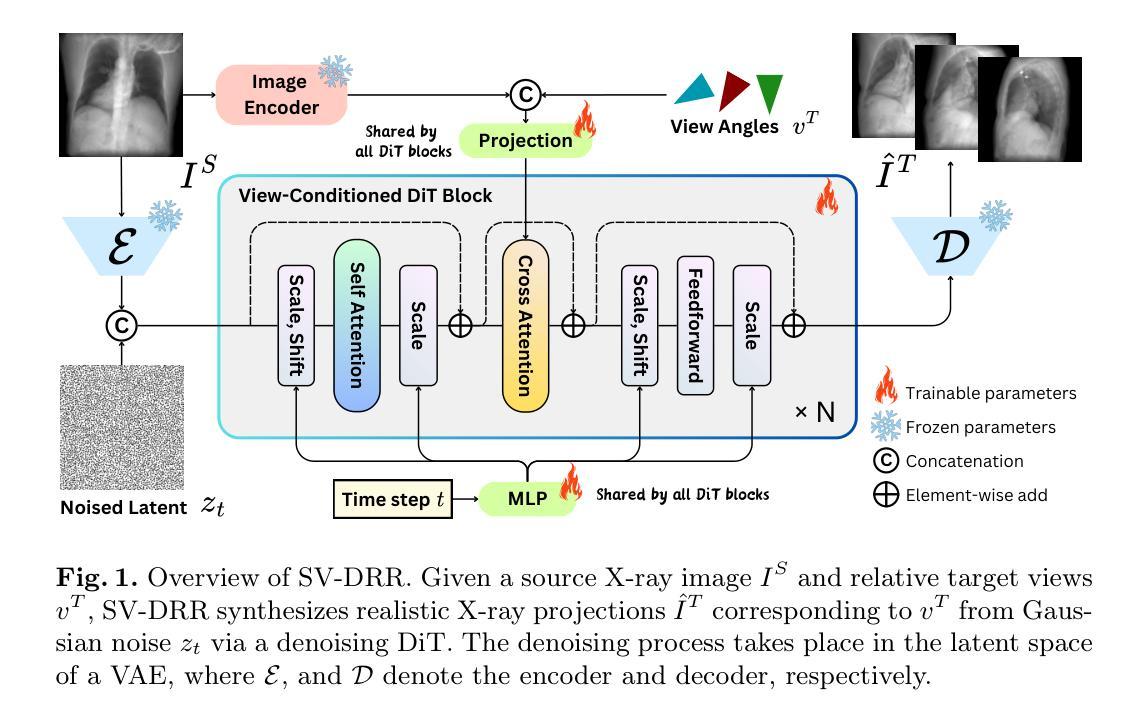
X-ray imaging is a rapid and cost-effective tool for visualizing internal human anatomy. While multi-view X-ray imaging provides complementary information that enhances diagnosis, intervention, and education, acquiring images from multiple angles increases radiation exposure and complicates clinical workflows. To address these challenges, we propose a novel view-conditioned diffusion model for synthesizing multi-view X-ray images from a single view. Unlike prior methods, which are limited in angular range, resolution, and image quality, our approach leverages the Diffusion Transformer to preserve fine details and employs a weak-to-strong training strategy for stable high-resolution image generation. Experimental results demonstrate that our method generates higher-resolution outputs with improved control over viewing angles. This capability has significant implications not only for clinical applications but also for medical education and data extension, enabling the creation of diverse, high-quality datasets for training and analysis. Our code is available at GitHub.
X射线成像是一种快速且经济实惠的工具,可用于可视化人体内部结构。虽然多视角X射线成像提供了增强诊断、干预和教育的补充信息,但从多个角度获取图像会增加辐射暴露并复杂化临床工作流程。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种基于视图调节的扩散模型,该模型可从单个视角合成多视角X射线图像。不同于在角度范围、分辨率和图像质量上有所局限的先前方法,我们的方法利用扩散变压器来保留细节,并采用从弱到强的训练策略来进行稳定的高分辨率图像生成。实验结果表明,我们的方法生成了更高分辨率的输出,对观察角度有更好的控制。这项能力不仅对临床应用有重要意义,而且对医学教育和数据扩展也有重要意义,能够创建用于培训和分析的多样、高质量数据集。我们的代码可在GitHub上获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by MICCAI2025
Summary
多视角X射线成像能够提供互补信息,提高诊断、治疗和教育的效果,但辐射暴露增加及临床操作复杂化的问题也随之而来。为解决这些问题,我们提出了一种基于扩散模型的新型单视角合成多视角X射线图像方法。与传统方法相比,我们的方法使用扩散变压器保存精细细节并采用由弱至强的训练策略以生成稳定的高分辨率图像。实验结果显示,该方法生成的图像分辨率更高,对视角的控制更为精准。这不仅对临床应用有重要意义,还对提高医学教育和数据扩展的效率有积极影响,能够创建多样且高质量的数据集以供分析和训练。
Key Takeaways
- 多视角X射线成像可以提供更全面的内部结构信息以增强诊断效果和患者治疗干预的精确性。然而,它会增加辐射暴露并复杂化临床工作流程。
- 提出了一种基于扩散模型的全新方法,能够从单一视角合成多视角X射线图像。
- 与传统方法相比,新方法使用扩散变压器技术,可以更好地保存图像中的精细细节。
- 采用由弱至强的训练策略,确保稳定的高分辨率图像生成。
- 实验验证显示新方法生成的图像分辨率更高,对视角控制更为精准。
- 该技术不仅有助于临床应用,还能促进医学教育和数据扩展的进步。
点此查看论文截图

VERITAS: Verification and Explanation of Realness in Images for Transparency in AI Systems
Authors:Aadi Srivastava, Vignesh Natarajkumar, Utkarsh Bheemanaboyna, Devisree Akashapu, Nagraj Gaonkar, Archit Joshi
The widespread and rapid adoption of AI-generated content, created by models such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Diffusion Models, has revolutionized the digital media landscape by allowing efficient and creative content generation. However, these models also blur the difference between real images and AI-generated synthetic images, raising concerns regarding content authenticity and integrity. While many existing solutions to detect fake images focus solely on classification and higher-resolution images, they often lack transparency in their decision-making, making it difficult for users to understand why an image is classified as fake. In this paper, we present VERITAS, a comprehensive framework that not only accurately detects whether a small (32x32) image is AI-generated but also explains why it was classified that way through artifact localization and semantic reasoning. VERITAS produces human-readable explanations that describe key artifacts in synthetic images. We show that this architecture offers clear explanations of the basis of zero-shot synthetic image detection tasks. Code and relevant prompts can be found at https://github.com/V-i-g-n-e-s-h-N/VERITAS .
由生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型等模型生成的AI生成内容得到广泛且迅速的采纳,这通过允许高效和有创意的内容生成,已经彻底改变了数字媒体领域。然而,这些模型也模糊了真实图像和AI生成的合成图像之间的差异,引发了人们对内容真实性和完整性的担忧。虽然许多现有的检测虚假图像解决方案只关注分类和更高分辨率的图像,但它们在做决策时往往缺乏透明度,使得用户难以理解为何某图像会被归类为虚假图像。在本文中,我们提出了VERITAS,这是一个全面的框架,不仅准确检测小到(32x32)的图像是否是AI生成的,而且还通过伪影定位和语义推理来解释将其分类为虚假的原因。VERITAS产生人类可读的解释,描述合成图像中的关键伪影。我们证明该架构在零样本合成图像检测任务中提供了清晰的解释。代码和相关提示可在https://github.com/V-i-g-n-e-s-h-N/VERITAS找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
人工智能生成的内容,如通过生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型创建的,已经彻底改变了数字媒体领域,实现了高效且富有创意的内容生成。然而,这些模型也模糊了真实图像和人工智能生成的合成图像之间的差异,引发了关于内容真实性和完整性的担忧。VERITAS框架不仅能准确检测小到(32x32)的图像是否由人工智能生成,还能通过伪影定位和语义推理解释分类原因,为用户提供可读的解释。该架构为基于零样本的合成图像检测任务提供了清晰的解释基础。有关代码和相关提示,请访问:链接地址。
Key Takeaways
- AI生成的内容已经改变了数字媒体领域,带来了高效和创造性的内容生成方式。
- AI模型(如GANs和Diffusion Models)生成的图像与真实图像之间的界限模糊,引发对内容真实性的关注。
- VERITAS框架能准确检测小到(32x32)的图像是否由AI生成。
- VERITAS不仅检测图像,还能通过伪影定位和语义推理解释检测结果,为用户提供清晰的可读解释。
- VERITAS框架在合成图像检测任务中提供了清晰的解释基础。
- 该论文提供了一个GitHub链接,其中包含代码和相关提示,便于用户访问和使用VERITAS框架。
点此查看论文截图



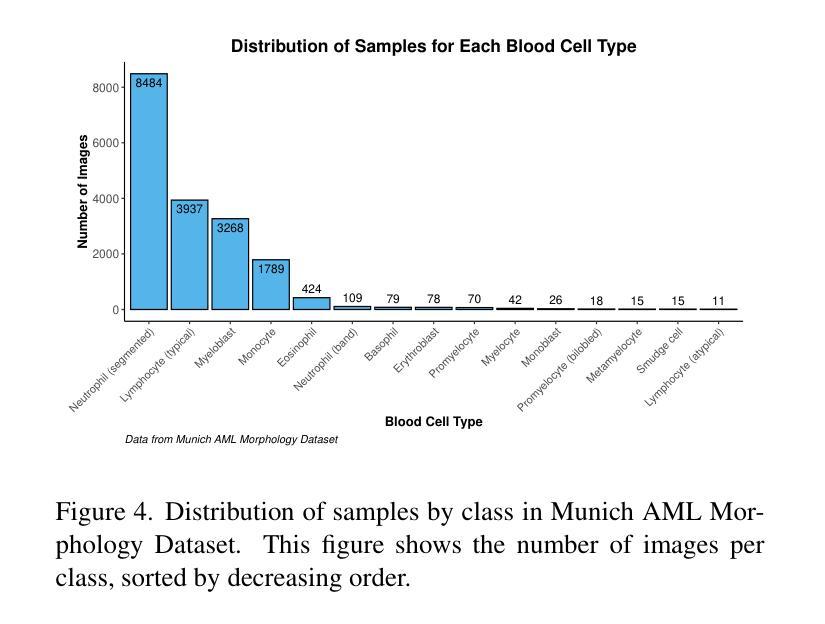
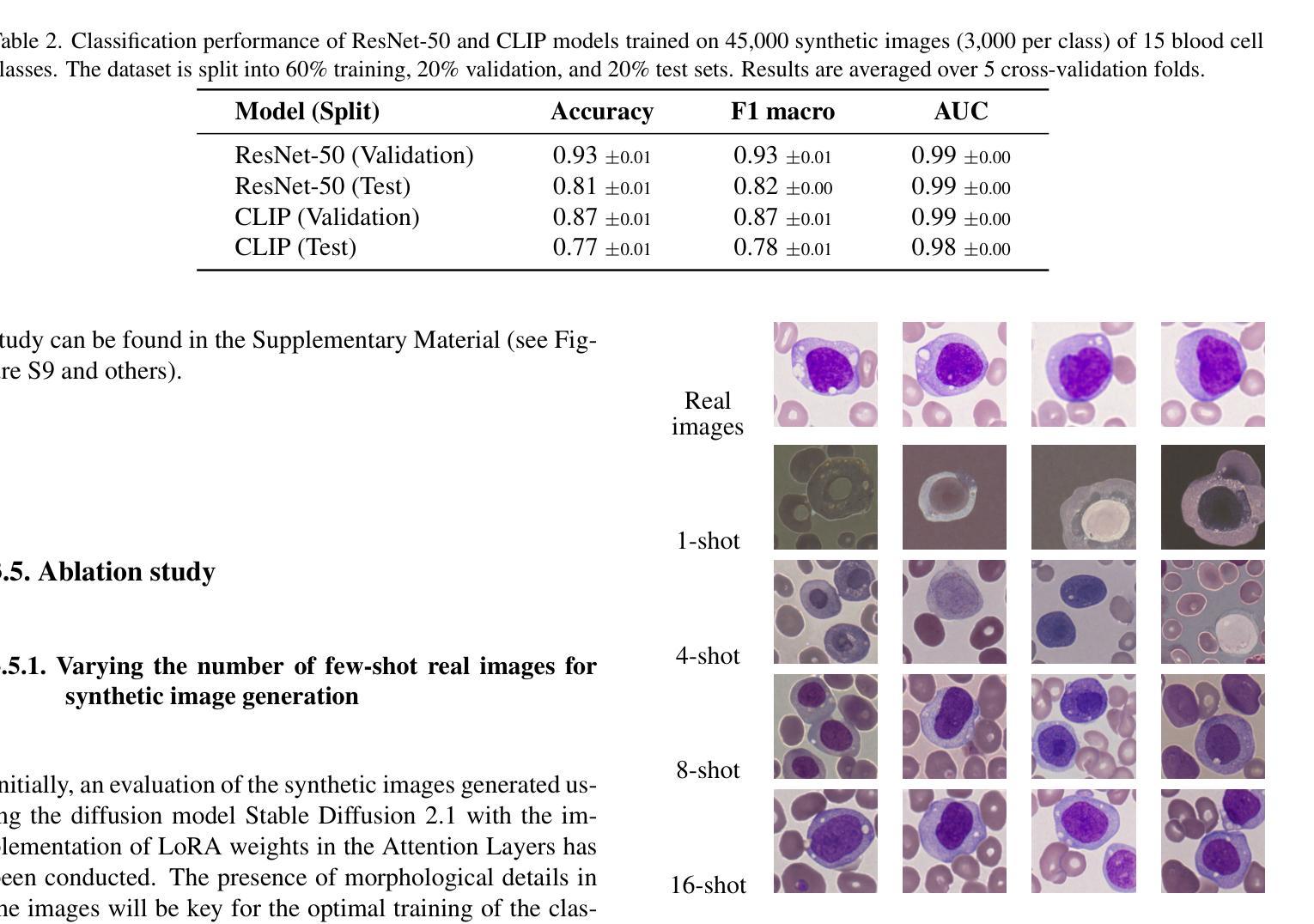
AI-Driven Cytomorphology Image Synthesis for Medical Diagnostics
Authors:Jan Carreras Boada, Rao Muhammad Umer, Carsten Marr
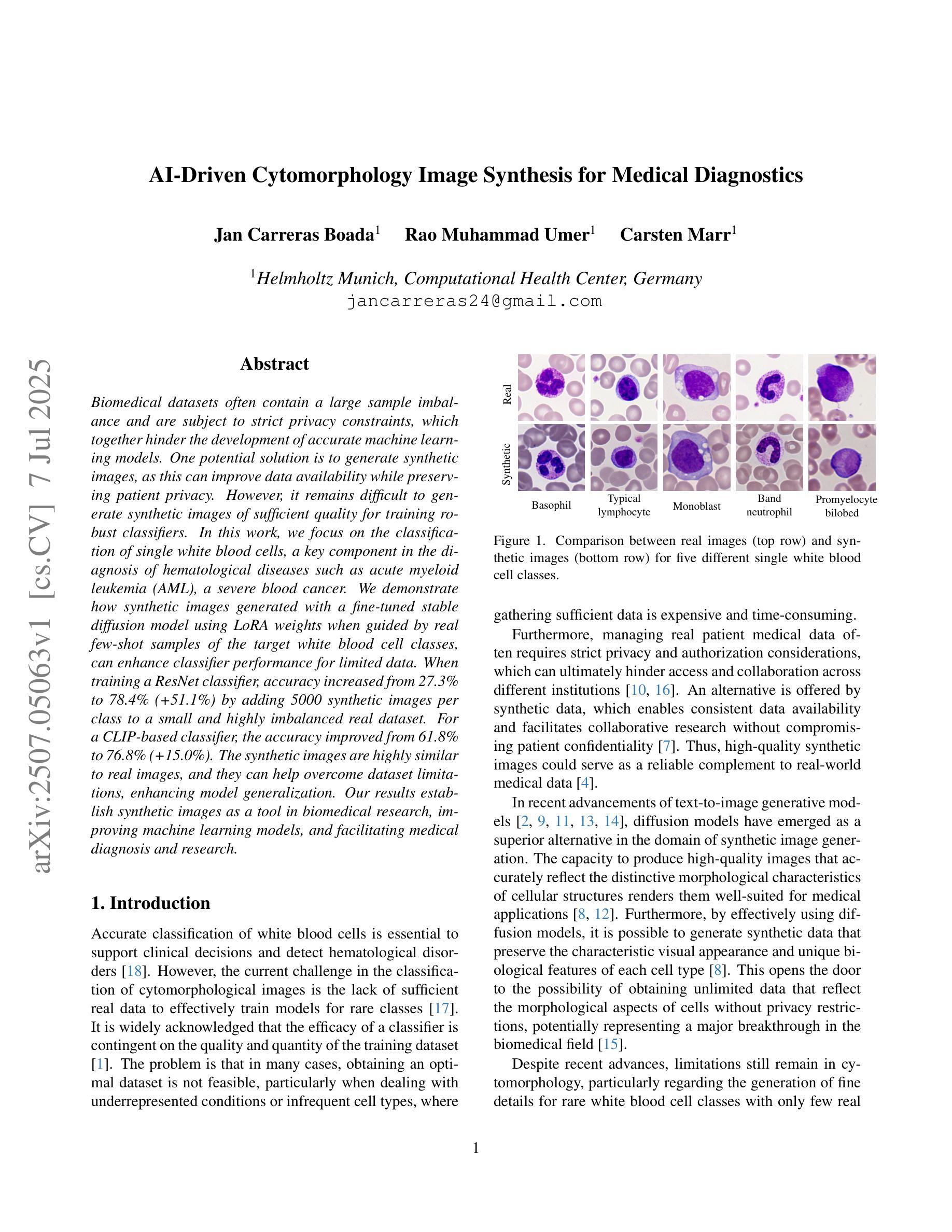
Biomedical datasets often contain a large sample imbalance and are subject to strict privacy constraints, which together hinder the development of accurate machine learning models. One potential solution is to generate synthetic images, as this can improve data availability while preserving patient privacy. However, it remains difficult to generate synthetic images of sufficient quality for training robust classifiers. In this work, we focus on the classification of single white blood cells, a key component in the diagnosis of hematological diseases such as acute myeloid leukemia (AML), a severe blood cancer. We demonstrate how synthetic images generated with a fine-tuned stable diffusion model using LoRA weights when guided by real few-shot samples of the target white blood cell classes, can enhance classifier performance for limited data. When training a ResNet classifier, accuracy increased from 27.3% to 78.4% (+51.1%) by adding 5000 synthetic images per class to a small and highly imbalanced real dataset. For a CLIP-based classifier, the accuracy improved from 61.8% to 76.8% (+15.0%). The synthetic images are highly similar to real images, and they can help overcome dataset limitations, enhancing model generalization. Our results establish synthetic images as a tool in biomedical research, improving machine learning models, and facilitating medical diagnosis and research.
生物医学数据集常常包含大量的样本不均衡问题,并受到严格的隐私约束的限制,这两者共同阻碍了准确机器学习模型的发展。一种潜在的解决方案是生成合成图像,因为这可以改善数据可用性同时保护病人隐私。然而,生成足够质量的合成图像以训练稳健的分类器仍然是一项挑战。在这项工作中,我们专注于单一白血球的分类,这是急性髓系白血病(AML)等血液疾病诊断的关键组成部分,这是一种严重的血液癌症。我们展示了如何使用微调后的稳定扩散模型,结合目标白血球类别的真实少量样本作为指导,生成合成图像,以提高有限数据的分类器性能。当对ResNet分类器进行训练时,通过向一个小而高度不平衡的真实数据集添加每类5000张合成图像,准确率从27.3%提高到78.4%(+51.1%)。对于基于CLIP的分类器,准确率从61.8%提高到76.8%(+15.0%)。合成图像与真实图像高度相似,有助于克服数据集限制,提高模型的泛化能力。我们的结果将合成图像确立为生物医学研究中的一种工具,可改善机器学习模型,促进医学诊断和研究的进行。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 6 figures, 2 tables. Final Degree Project (TFG) submitted at ESCI-UPF and conducted at Helmholtz Munich
Summary
生物医学数据集中存在样本不平衡和隐私保护限制的问题,影响了机器学习模型的准确性。本研究通过利用微调后的稳定扩散模型生成合成图像,结合真实样本训练分类器,提高了对白血病细胞的分类性能。合成图像在增加有限数据的同时,提高了分类器的准确率,并有助于克服数据集限制,增强模型的泛化能力。这为生物医学研究中的机器学习模型和医疗诊断提供了新的工具。
Key Takeaways
- 生物医学数据集面临样本不平衡和隐私保护限制的挑战。
- 合成图像生成是解决这些问题的一种潜在解决方案。
- 利用微调后的稳定扩散模型和真实样本引导,可以生成高质量合成图像。
- 合成图像可提高分类器的性能,特别是对于有限数据的情况。
- 在使用ResNet分类器的情况下,添加合成图像使准确率从27.3%提高到78.4%(+51.1%)。
- 对于基于CLIP的分类器,准确率从61.8%提高到76.8%(+15.0%)。
点此查看论文截图
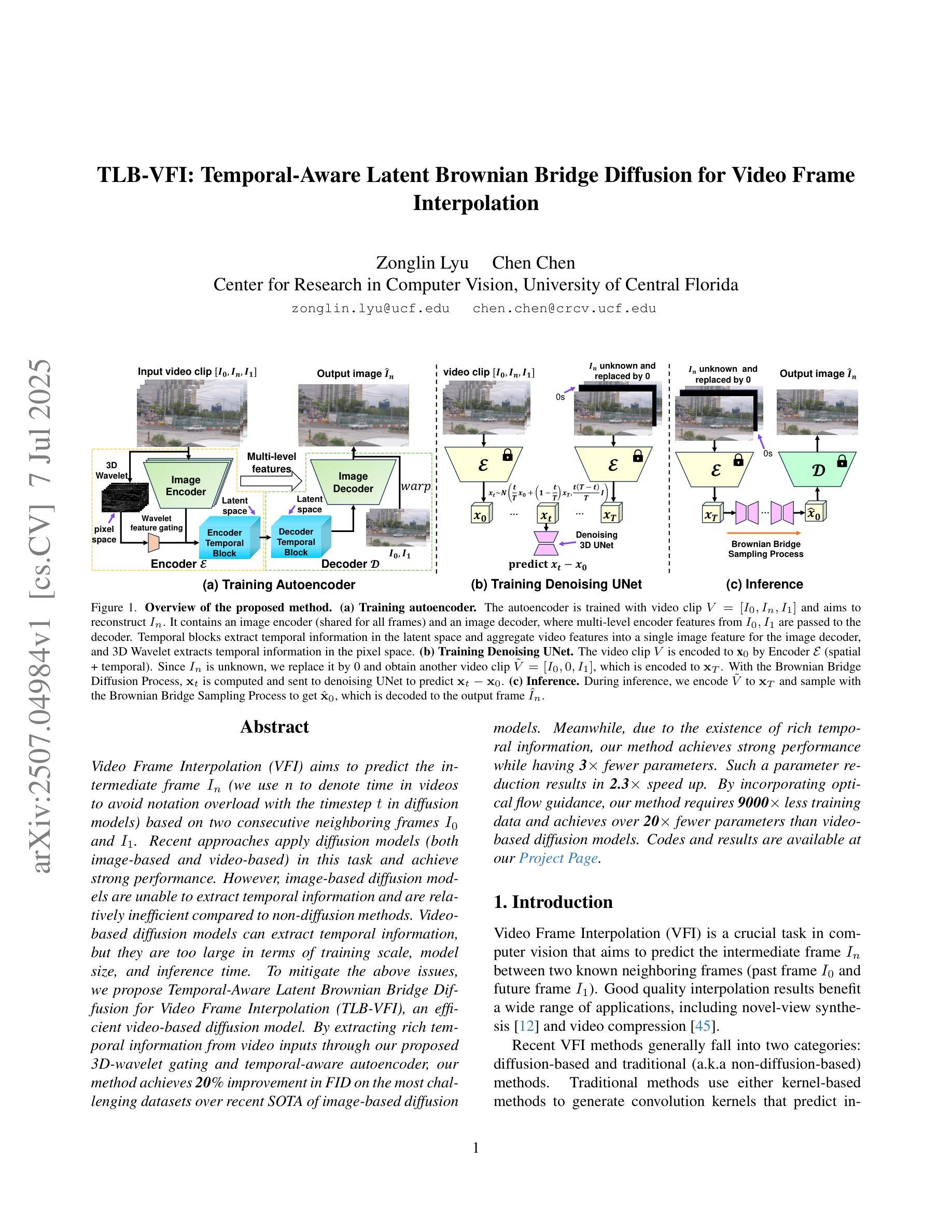
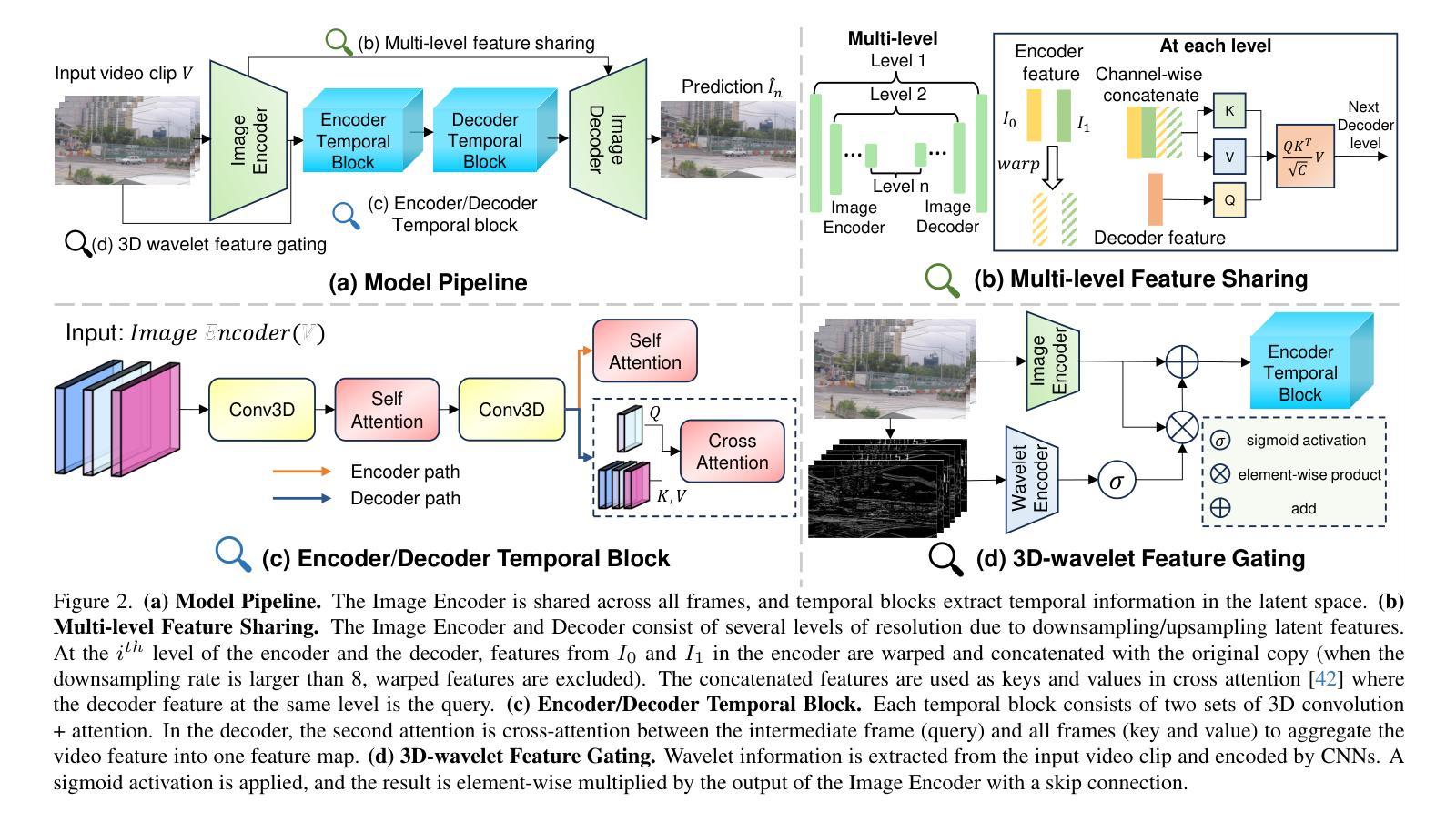
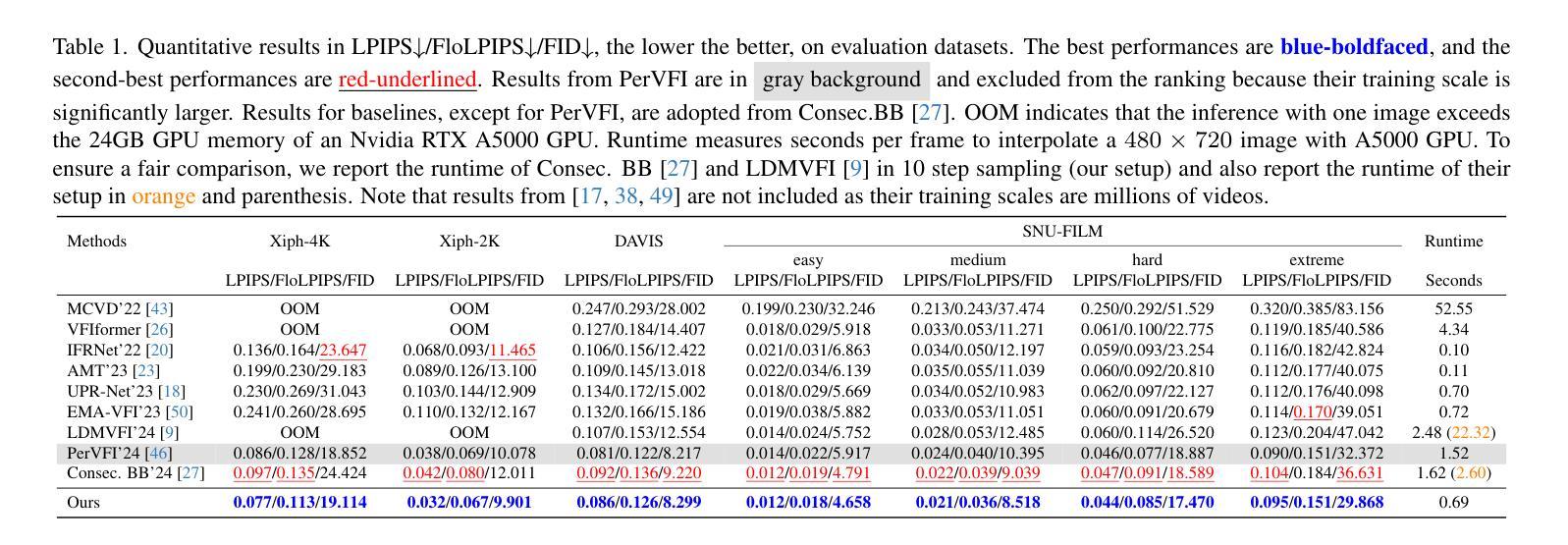
TLB-VFI: Temporal-Aware Latent Brownian Bridge Diffusion for Video Frame Interpolation
Authors:Zonglin Lyu, Chen Chen
Video Frame Interpolation (VFI) aims to predict the intermediate frame $I_n$ (we use n to denote time in videos to avoid notation overload with the timestep $t$ in diffusion models) based on two consecutive neighboring frames $I_0$ and $I_1$. Recent approaches apply diffusion models (both image-based and video-based) in this task and achieve strong performance. However, image-based diffusion models are unable to extract temporal information and are relatively inefficient compared to non-diffusion methods. Video-based diffusion models can extract temporal information, but they are too large in terms of training scale, model size, and inference time. To mitigate the above issues, we propose Temporal-Aware Latent Brownian Bridge Diffusion for Video Frame Interpolation (TLB-VFI), an efficient video-based diffusion model. By extracting rich temporal information from video inputs through our proposed 3D-wavelet gating and temporal-aware autoencoder, our method achieves 20% improvement in FID on the most challenging datasets over recent SOTA of image-based diffusion models. Meanwhile, due to the existence of rich temporal information, our method achieves strong performance while having 3times fewer parameters. Such a parameter reduction results in 2.3x speed up. By incorporating optical flow guidance, our method requires 9000x less training data and achieves over 20x fewer parameters than video-based diffusion models. Codes and results are available at our project page: https://zonglinl.github.io/tlbvfi_page.
视频帧插值(VFI)旨在基于两个连续相邻帧$I_0$和$I_1$来预测中间帧$I_n$(我们用n来表示视频中的时间,以避免与扩散模型中的时间步长t的符号过载)。最近的方法在该任务中应用了扩散模型(基于图像和基于视频的),并取得了强大的性能。然而,基于图像的扩散模型无法提取时间信息,与非扩散方法相比效率相对较低。基于视频的扩散模型可以提取时间信息,但在训练规模、模型大小和推理时间方面过于庞大。为了缓解上述问题,我们提出了用于视频帧插值的时序感知潜在布朗桥扩散(TLB-VFI),一种高效的基于视频扩散模型。通过我们提出的3D小波门控和时序感知自动编码器从视频输入中提取丰富的时间信息,我们的方法在最具挑战性的数据集上的FID提高了20%,超过了最近的基于图像的扩散模型的最先进方法。同时,由于存在丰富的时间信息,我们的方法在参数更少的情况下实现了强大的性能,参数减少了三倍。这种参数减少导致了2.3倍的加速。通过结合光流引导,我们的方法需要9000倍更少的训练数据,并且与基于视频的扩散模型相比,参数减少了超过20倍。相关代码和结果可在我们的项目页面查看:https://zonglinl.github.io/tlbvfi_page。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文介绍了针对视频帧插值(VFI)任务的Temporal-Aware Latent Brownian Bridge Diffusion模型(TLB-VFI)。该模型能够有效结合图像与视频扩散模型的优点,解决了现有模型在提取时间信息和效率方面的问题。通过引入3D-wavelet门控机制和时空感知自动编码器,TLB-VFI在最具挑战性的数据集上实现了比当前先进的图像扩散模型更低的FID得分,性能提升20%。同时,由于充分提取了时间信息,该模型在减少参数的同时保持了强大的性能,参数减少三倍,速度提升2.3倍。通过引入光流引导机制,TLB-VFI进一步减少了训练数据需求,与传统视频扩散模型相比,参数减少了超过20倍。相关代码和结果可访问项目页面查看。
关键见解
- 视频帧插值(VFI)任务旨在基于两个连续帧预测中间帧。
- 现有图像扩散模型无法有效提取时间信息,效率较低。
- 视频扩散模型虽能提取时间信息,但训练规模、模型大小和推理时间成本较高。
4.TLB-VFI模型结合了图像与视频扩散模型的优点,解决了上述问题。 - 通过引入3D-wavelet门控机制和时空感知自动编码器,TLB-VFI实现了性能提升。
- 在最具挑战性的数据集上实现了参数减少和速度提升的优化。
点此查看论文截图
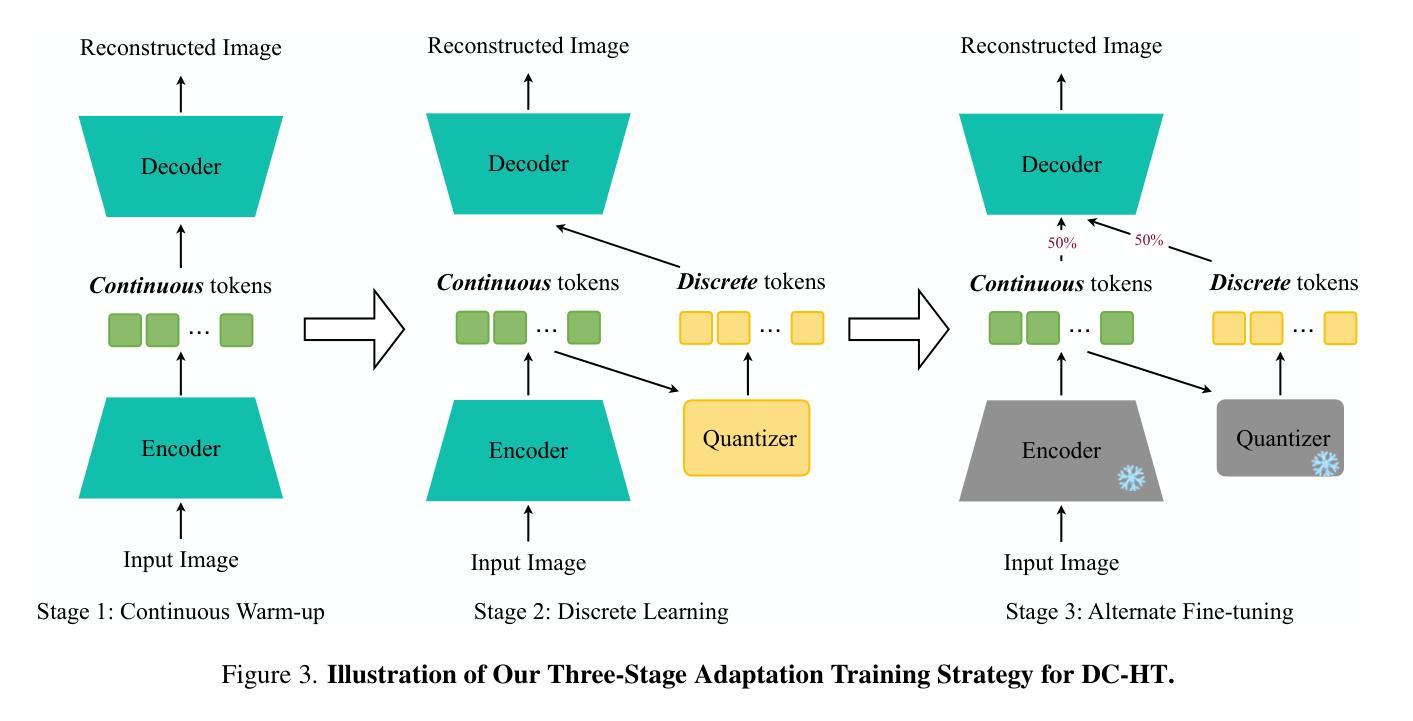
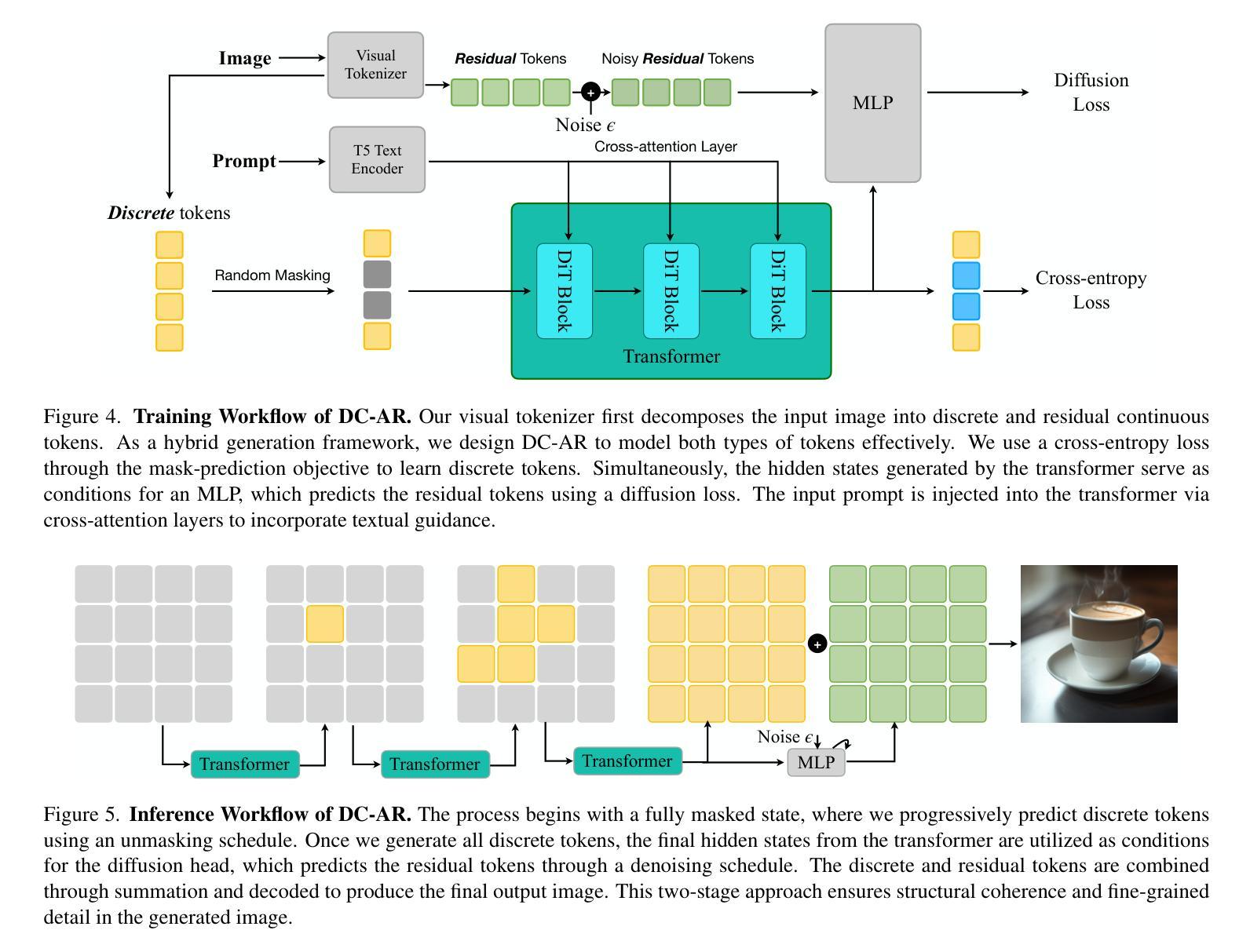
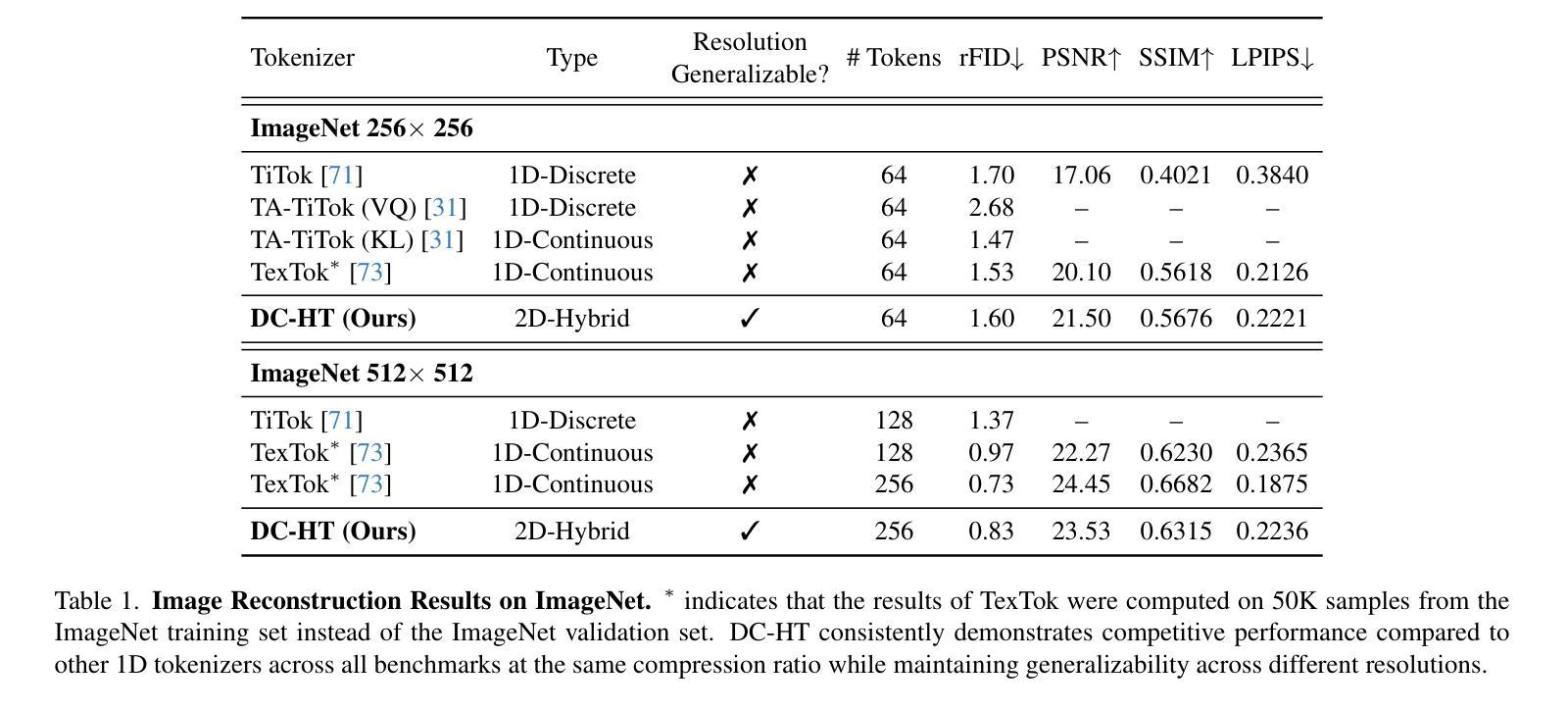
DC-AR: Efficient Masked Autoregressive Image Generation with Deep Compression Hybrid Tokenizer
Authors:Yecheng Wu, Junyu Chen, Zhuoyang Zhang, Enze Xie, Jincheng Yu, Junsong Chen, Jinyi Hu, Yao Lu, Song Han, Han Cai
We introduce DC-AR, a novel masked autoregressive (AR) text-to-image generation framework that delivers superior image generation quality with exceptional computational efficiency. Due to the tokenizers’ limitations, prior masked AR models have lagged behind diffusion models in terms of quality or efficiency. We overcome this limitation by introducing DC-HT - a deep compression hybrid tokenizer for AR models that achieves a 32x spatial compression ratio while maintaining high reconstruction fidelity and cross-resolution generalization ability. Building upon DC-HT, we extend MaskGIT and create a new hybrid masked autoregressive image generation framework that first produces the structural elements through discrete tokens and then applies refinements via residual tokens. DC-AR achieves state-of-the-art results with a gFID of 5.49 on MJHQ-30K and an overall score of 0.69 on GenEval, while offering 1.5-7.9x higher throughput and 2.0-3.5x lower latency compared to prior leading diffusion and autoregressive models.
我们介绍了DC-AR,这是一种新型的面罩自回归(AR)文本到图像生成框架,它以出色的计算效率提供了卓越的图像生成质量。由于标记器的限制,先前的面罩自回归模型在质量或效率方面落后于扩散模型。我们通过引入DC-HT——一种为AR模型设计的深度压缩混合标记器来克服这一限制,它在保持高重建保真度和跨分辨率泛化能力的同时,实现了32倍的空间压缩比。基于DC-HT,我们扩展了MaskGIT,并创建了一个新的混合面罩自回归图像生成框架,该框架首先通过离散令牌生成结构元素,然后通过剩余令牌进行微调。DC-AR在MJHQ-30K上的gFID为5.49,在GenEval上的总体得分为0.69,同时与先前的领先扩散和自回归模型相比,提供1.5-7.9倍的高吞吐量以及2.0-3.5倍的低延迟。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025
Summary
我们推出了DC-AR,这是一种新型的面具自回归(AR)文本到图像生成框架,它以卓越的计算效率提供了优质的图像生成质量。由于令牌器的限制,先前的掩模AR模型在质量或效率方面落后于扩散模型。通过引入DC-HT——一种实现32倍空间压缩比的深度压缩混合令牌器,我们克服了这一限制,同时保持了高重建保真度和跨分辨率的通用性。基于DC-HT,我们扩展了MaskGIT,创建了一个新的混合掩模自回归图像生成框架,该框架首先通过离散令牌生成结构元素,然后通过残差令牌进行细化。DC-AR在MJHQ-30K上实现了5.49的gFID和GenEval上的0.69的综合得分,同时与先前的领先扩散和自回归模型相比,提供了1.5-7.9倍的更高吞吐量以及2.0-3.5倍更低的延迟。
Key Takeaways
- DC-AR是一个新型的文本到图像生成框架,基于掩模自回归(AR)技术。
- 相比其他模型,DC-AR在图像生成质量和计算效率上表现更优秀。
- DC-HT是DC-AR的一个重要组成部分,是一种深度压缩混合令牌器,可以实现高压缩比同时保持重建质量。
- DC-AR框架结合了离散令牌和残差令牌,首先生成结构元素再进行细化。
- DC-AR在多个评估指标上达到了先进水平,包括MJHQ-30K上的gFID和GenEval的综合得分。
- DC-AR相比其他领先模型,提供了更高的吞吐量和更低的延迟。
点此查看论文截图

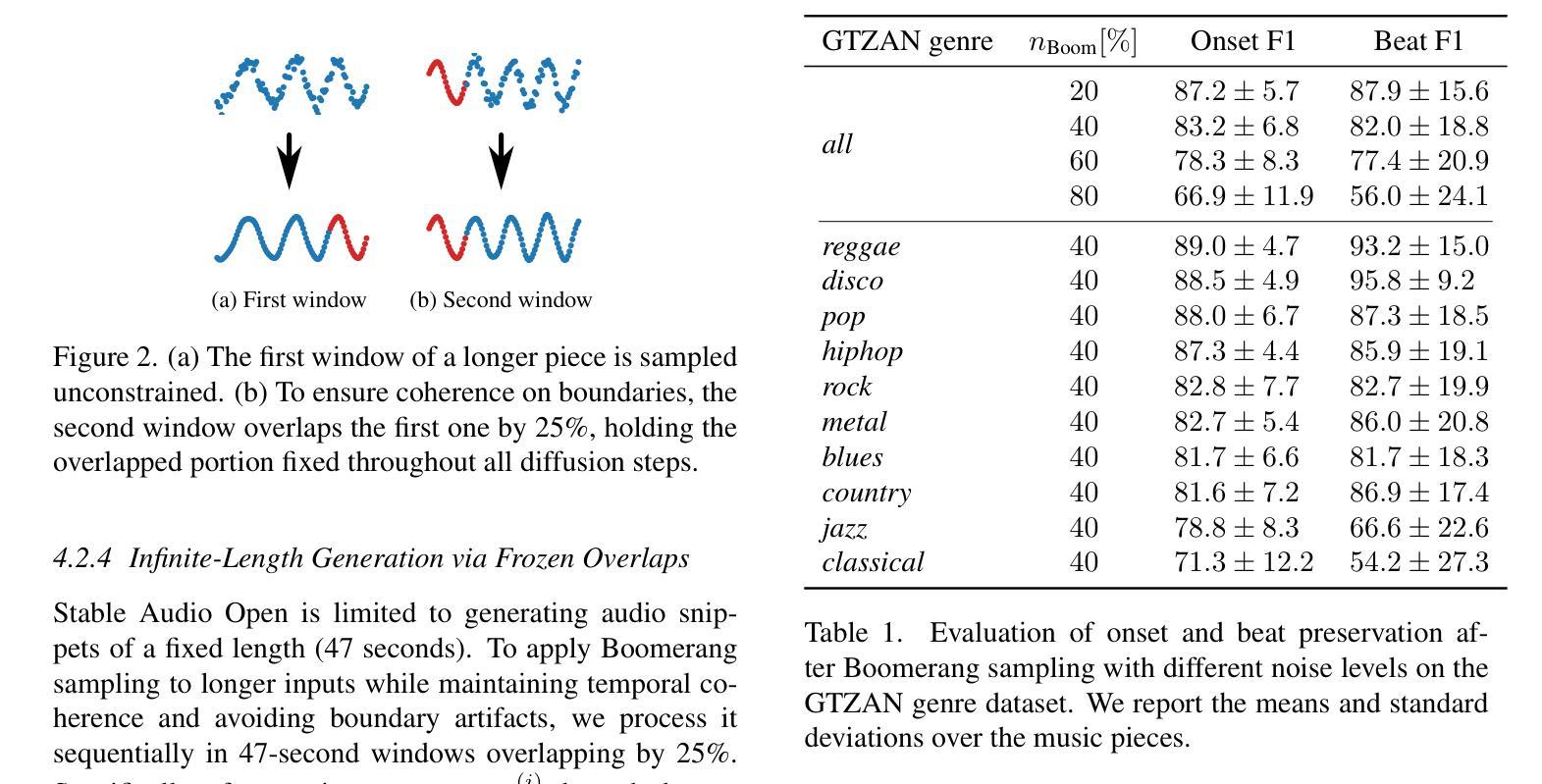
Music Boomerang: Reusing Diffusion Models for Data Augmentation and Audio Manipulation
Authors:Alexander Fichtinger, Jan Schlüter, Gerhard Widmer
Generative models of music audio are typically used to generate output based solely on a text prompt or melody. Boomerang sampling, recently proposed for the image domain, allows generating output close to an existing example, using any pretrained diffusion model. In this work, we explore its application in the audio domain as a tool for data augmentation or content manipulation. Specifically, implementing Boomerang sampling for Stable Audio Open, we augment training data for a state-of-the-art beat tracker, and attempt to replace musical instruments in recordings. Our results show that the rhythmic structure of existing examples is mostly preserved, that it improves performance of the beat tracker, but only in scenarios of limited training data, and that it can accomplish text-based instrument replacement on monophonic inputs. We publish our implementation to invite experiments on data augmentation in other tasks and explore further applications.
音乐音频的生成模型通常仅基于文本提示或旋律来生成输出。最近为图像领域提出的Boomerang采样允许使用任何预训练的扩散模型来生成接近现有示例的输出。在这项工作中,我们探索其在音频领域作为数据增强或内容操作工具的应用。具体来说,我们为Stable Audio Open实现了Boomerang采样,为最先进的节拍跟踪器增加了训练数据,并尝试在录音中替换乐器。我们的结果表明,现有示例的节奏结构大多得以保留,它提高了在训练数据有限场景下的节拍跟踪器性能,并且能够在单声道输入上实现基于文本的乐器替换。我们发布我们的实现,以邀请其他任务的实验对增强的数据进行探索并进一步研究其应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at SMC 2025. Code at https://malex1106.github.io/boomify/
Summary
本文探索了Boomerang采样在音频领域的应用,利用预训练的扩散模型生成接近现有样本的输出,用于数据增强或内容操纵。实验表明,该采样方法可以保留现有示例的节奏结构,提升打拍器在有限训练数据场景下的性能,并能在单声道输入上实现基于文本的乐器替换。
Key Takeaways
- Boomerang采样被引入到音频领域,允许使用预训练的扩散模型生成接近现有样本的输出。
- 该方法主要用于数据增强和内容操纵。
- 实施Boomerang采样后,可以保留现有示例的节奏结构。
- 在有限训练数据场景下,Boomerang采样可以提升打拍器的性能。
- Boomerang采样能够实现基于文本的乐器替换。
- 该研究公开了实施方法,邀请其他任务进行数据增强实验。
点此查看论文截图

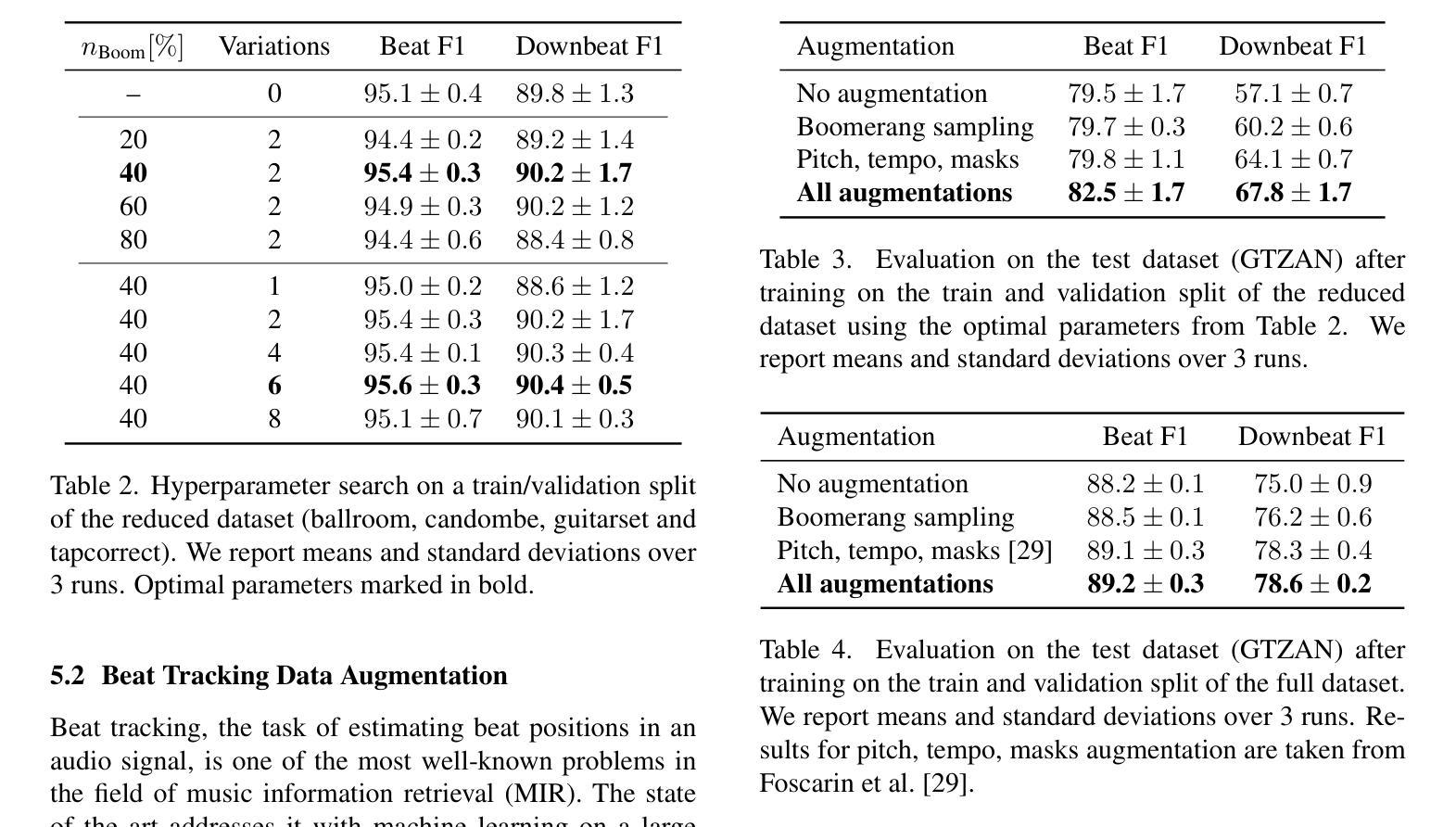
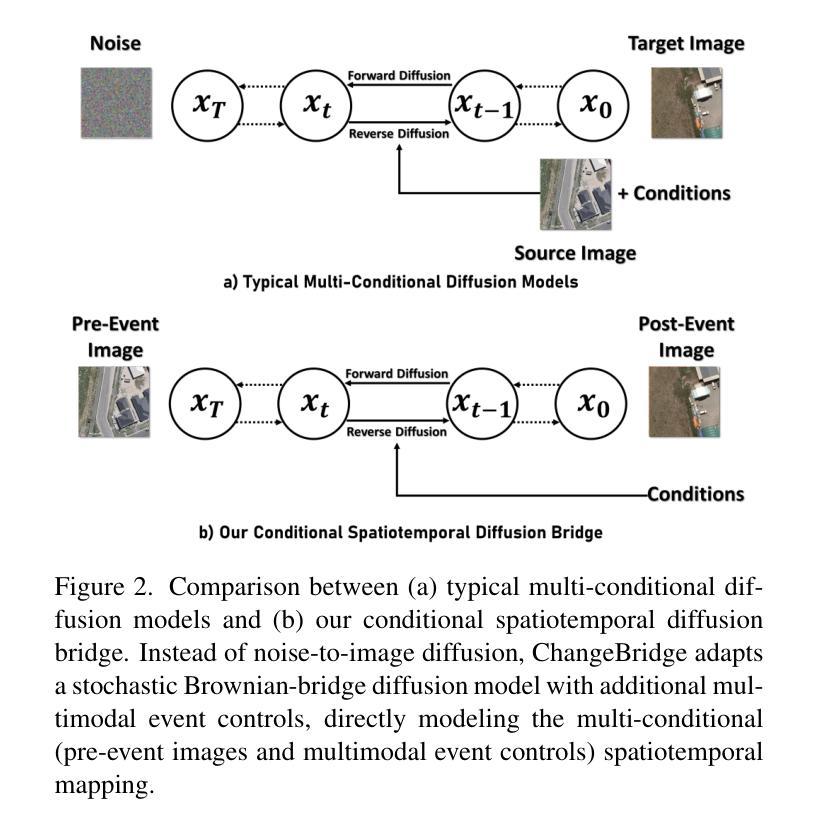
ChangeBridge: Spatiotemporal Image Generation with Multimodal Controls for Remote Sensing
Authors:Zhenghui Zhao, Chen Wu, Di Wang, Hongruixuan Chen, Zhuo Zheng
Recent advancements in generative methods, especially diffusion models, have made great progress in remote sensing image synthesis. Despite these advancements, existing methods have not explored the simulation of future scenarios based on given scenario images. This simulation capability has wide applications for urban planning, land managementChangeBridge: Spatiotemporal Image Generation with Multimodal Controls, and beyond. In this work, we propose ChangeBridge, a conditional spatiotemporal diffusion model. Given pre-event images and conditioned on multimodal spatial controls (e.g., text prompts, instance layouts, and semantic maps), ChangeBridge can synthesize post-event images. The core idea behind ChangeBridge is to modeling the noise-to-image diffusion model, as a pre-to-post diffusion bridge. Conditioned on multimodal controls, ChangeBridge leverages a stochastic Brownian-bridge diffusion, directly modeling the spatiotemporal evolution between pre-event and post-event states. To the best of our knowledge, ChangeBridge is the first spatiotemporal generative model with multimodal controls for remote sensing. Experimental results demonstrate that ChangeBridge can simulate high-fidelity future scenarios aligned with given conditions, including event and event-driven background variations. Code will be available.
近年来,生成方法,尤其是扩散模型,在遥感图像合成方面取得了巨大进展。尽管有这些进展,现有方法尚未探索基于给定场景图像模拟未来情景的能力。这种模拟能力在城市规划、土地管理和更广泛的应用中具有广泛的应用。在这项工作中,我们提出了ChangeBridge,一个条件性的时空扩散模型。给定预事件图像,并基于多模式空间控制(如文本提示、实例布局和语义地图),ChangeBridge可以合成后事件图像。ChangeBridge的核心思想是将噪声到图像的扩散模型作为预到后扩散的桥梁。基于多模式控制,ChangeBridge利用随机布朗桥扩散,直接模拟预事件和后事件状态之间的时空演化。据我们所知,ChangeBridge是遥感领域中具有多模式控制的第一个时空生成模型。实验结果表明,ChangeBridge可以模拟与给定条件相符的高保真未来情景,包括事件和事件驱动的背景变化。代码将可用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型在遥感图像合成领域取得了显著进展,但现有方法尚未探索基于给定场景图像模拟未来情景的能力。本文提出ChangeBridge,一种条件时空扩散模型,给定预事件图像和多模态空间控制(如文本提示、实例布局和语义地图),可合成后事件图像。其核心思想是将噪声到图像的扩散模型作为预到后扩散桥梁。实验结果证明,ChangeBridge能够模拟与给定条件高度一致的高保真未来情景,包括事件和事件驱动的背景变化。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在遥感图像合成中取得重大进展。
- 现有方法未充分探索基于给定场景图像的模拟未来情景能力。
- ChangeBridge是一种条件时空扩散模型,能合成后事件图像。
- ChangeBridge的核心思想是将噪声到图像的扩散模型作为预到后扩散桥梁。
- ChangeBridge支持多模态控制,包括文本提示、实例布局和语义地图。
- ChangeBridge是首个具有多模态控制的时空遥感生成模型。
点此查看论文截图


Information-Guided Diffusion Sampling for Dataset Distillation
Authors:Linfeng Ye, Shayan Mohajer Hamidi, Guang Li, Takahiro Ogawa, Miki Haseyama, Konstantinos N. Plataniotis
Dataset distillation aims to create a compact dataset that retains essential information while maintaining model performance. Diffusion models (DMs) have shown promise for this task but struggle in low images-per-class (IPC) settings, where generated samples lack diversity. In this paper, we address this issue from an information-theoretic perspective by identifying two key types of information that a distilled dataset must preserve: ($i$) prototype information $\mathrm{I}(X;Y)$, which captures label-relevant features; and ($ii$) contextual information $\mathrm{H}(X | Y)$, which preserves intra-class variability. Here, $(X,Y)$ represents the pair of random variables corresponding to the input data and its ground truth label, respectively. Observing that the required contextual information scales with IPC, we propose maximizing $\mathrm{I}(X;Y) + \beta \mathrm{H}(X | Y)$ during the DM sampling process, where $\beta$ is IPC-dependent. Since directly computing $\mathrm{I}(X;Y)$ and $\mathrm{H}(X | Y)$ is intractable, we develop variational estimations to tightly lower-bound these quantities via a data-driven approach. Our approach, information-guided diffusion sampling (IGDS), seamlessly integrates with diffusion models and improves dataset distillation across all IPC settings. Experiments on Tiny ImageNet and ImageNet subsets show that IGDS significantly outperforms existing methods, particularly in low-IPC regimes. The code will be released upon acceptance.
数据集蒸馏旨在创建一个紧凑的数据集,该数据集在保持模型性能的同时保留关键信息。扩散模型(DMs)在此任务中显示出潜力,但在每类图像(IPC)较少的设置中面临挑战,生成的样本缺乏多样性。本文从信息论的角度解决了这个问题,确定了蒸馏数据集必须保留的两种关键类型的信息:(i)原型信息I(X;Y),这捕获了与标签相关的特征;(ii)上下文信息H(X|Y),这保留了类内变异性。在这里,(X,Y)代表与输入数据及其真实标签对应的随机变量对。观察到所需的上下文信息随IPC而变化,我们建议在DM采样过程中最大化I(X;Y)+βH(X|Y),其中β取决于IPC。由于直接计算I(X;Y)和H(X|Y)是不可行的,我们通过数据驱动的方法紧密地估算这些量的下限。我们的方法,信息引导扩散采样(IGDS),可以无缝地与扩散模型集成,并在所有IPC设置中都改善了数据集蒸馏的效果。在Tiny ImageNet和ImageNet子集上的实验表明,IGDS显著优于现有方法,特别是在低IPC环境中。代码将在接受后发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了基于信息理论的扩散模型数据集蒸馏方法,旨在解决在低图像每类别(IPC)设置下生成样本缺乏多样性的挑战。文章指出,蒸馏数据集必须保留两种关键信息:原型信息和上下文信息。文章还提出了一种新的方法——信息引导扩散采样(IGDS),该方法通过最大化这两种信息的组合来改进扩散模型的数据集蒸馏效果,并在Tiny ImageNet和ImageNet子集上的实验证明了其显著优势。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型用于数据集蒸馏,旨在创建保留关键信息的紧凑数据集。
- 在低图像每类别(IPC)设置下,扩散模型生成的样本缺乏多样性。
- 蒸馏数据集必须保留两种关键信息:原型信息和上下文信息。
- 原型信息捕获与标签相关的特征,而上下文信息保留类内变异性。
- 提出了信息引导扩散采样(IGDS)方法,通过最大化原型信息和上下文信息的组合来改善扩散模型的数据集蒸馏效果。
- IGDS方法通过数据驱动的方式紧密地估算并最大化信息组合。
点此查看论文截图


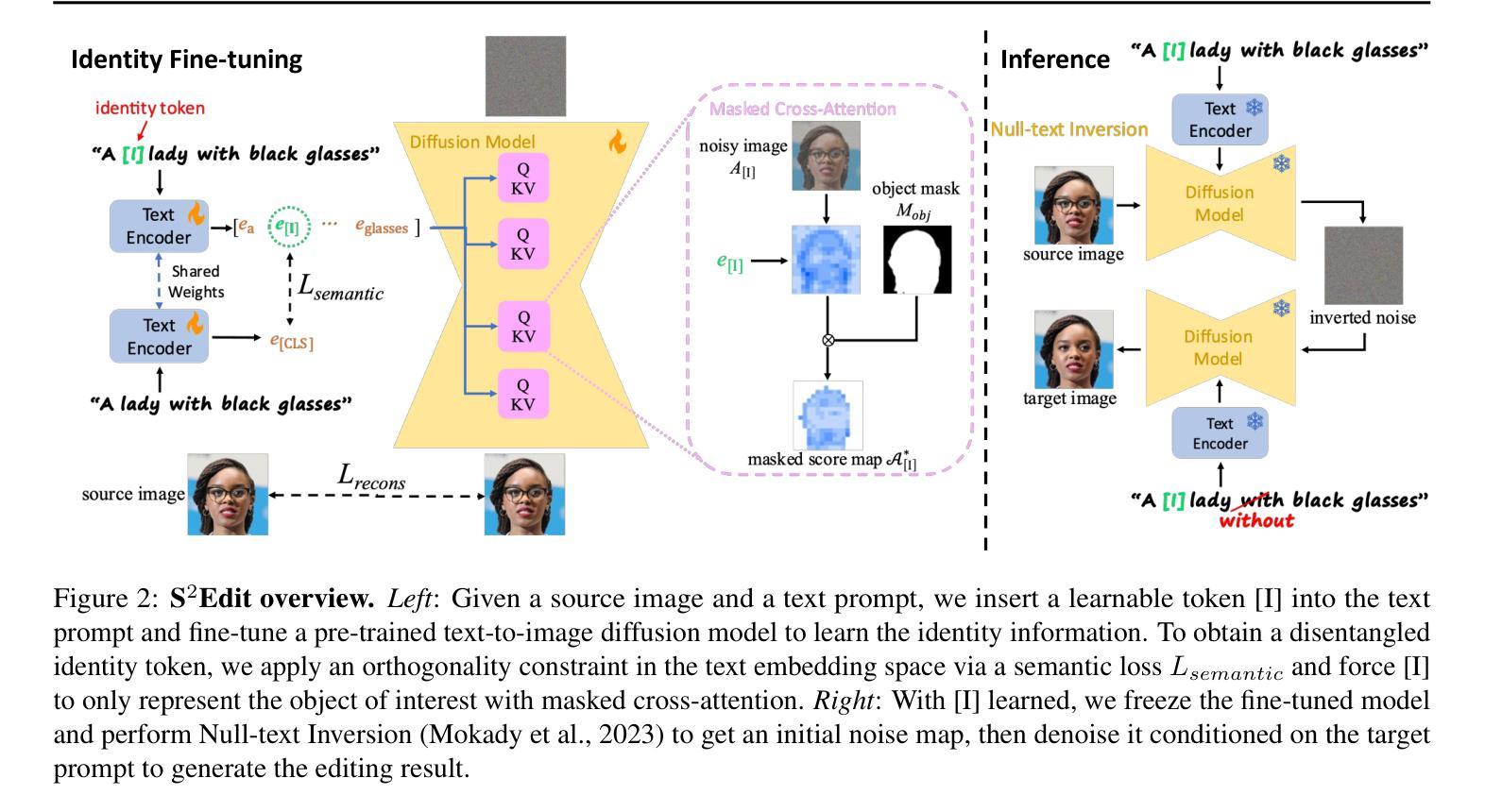
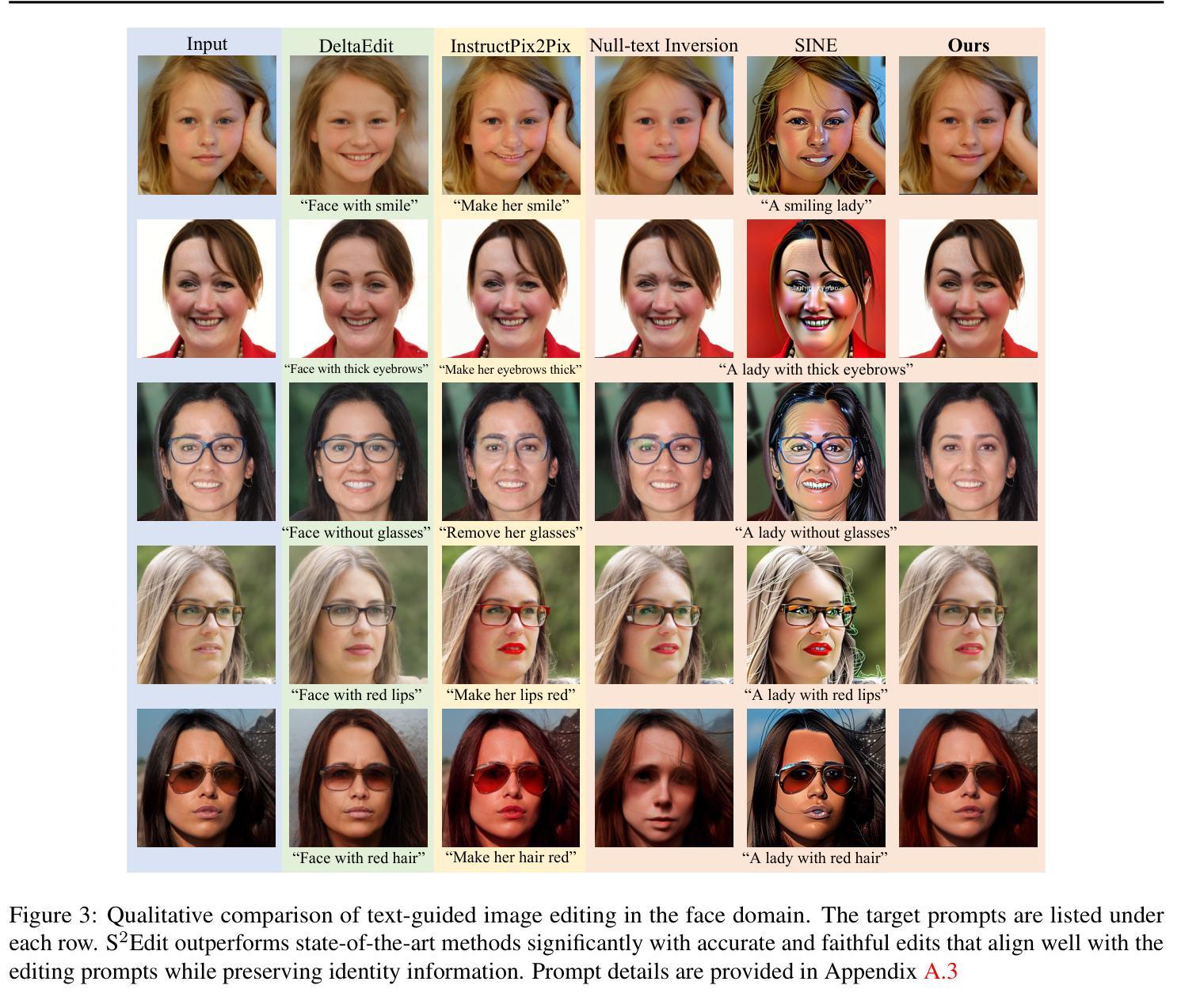
S$^2$Edit: Text-Guided Image Editing with Precise Semantic and Spatial Control
Authors:Xudong Liu, Zikun Chen, Ruowei Jiang, Ziyi Wu, Kejia Yin, Han Zhao, Parham Aarabi, Igor Gilitschenski
Recent advances in diffusion models have enabled high-quality generation and manipulation of images guided by texts, as well as concept learning from images. However, naive applications of existing methods to editing tasks that require fine-grained control, e.g., face editing, often lead to suboptimal solutions with identity information and high-frequency details lost during the editing process, or irrelevant image regions altered due to entangled concepts. In this work, we propose S$^2$Edit, a novel method based on a pre-trained text-to-image diffusion model that enables personalized editing with precise semantic and spatial control. We first fine-tune our model to embed the identity information into a learnable text token. During fine-tuning, we disentangle the learned identity token from attributes to be edited by enforcing an orthogonality constraint in the textual feature space. To ensure that the identity token only affects regions of interest, we apply object masks to guide the cross-attention maps. At inference time, our method performs localized editing while faithfully preserving the original identity with semantically disentangled and spatially focused identity token learned. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of S$^2$Edit over state-of-the-art methods both quantitatively and qualitatively. Additionally, we showcase several compositional image editing applications of S$^2$Edit such as makeup transfer.
最近扩散模型的技术进步已经能够实现由文本引导的高质量图像生成和操纵,以及从图像中进行概念学习。然而,将现有方法直接应用于需要精细控制的编辑任务(例如面部编辑),通常会导致次优解决方案,编辑过程中会丢失身份信息和高频细节,或者由于概念纠缠而改变无关的图像区域。在这项工作中,我们提出了S^2Edit,这是一种基于预训练的文本到图像扩散模型的新方法,能够实现个性化的精确语义和空间控制编辑。我们首先对我们的模型进行微调,将身份嵌入到一个可学习的文本令牌中。在微调过程中,我们通过强制文本特征空间中的正交性约束,将学习到的身份令牌与要编辑的属性分开。为了确保身份令牌只影响感兴趣区域,我们应用对象掩码来引导交叉注意力图。在推理阶段,我们的方法能够执行局部编辑,同时忠实保留原始身份,并学习到语义上解耦和空间上集中的身份令牌。大量实验表明,S^2Edit在定量和定性方面均优于现有先进技术。此外,我们还展示了S^2Edit在化妆转移等组合图像编辑方面的几个应用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了基于预训练文本到图像扩散模型的S^2Edit方法,可实现个性化编辑,具有精确语义和空间控制。通过微调模型将身份信息处理为可学习的文本令牌,并在文本特征空间中通过正交约束进行解耦,确保身份令牌只影响感兴趣区域。S^2Edit能进行局部编辑,同时忠实保留原始身份,并通过对象蒙版引导跨注意力图实现空间聚焦。实验证明,S^2Edit在定量和定性上均优于现有方法,并展示了化妆转移等图像编辑应用。
Key Takeaways
- S^2Edit利用扩散模型实现高质量图像生成和文本引导编辑。
- 通过微调模型,将身份信息处理为可学习的文本令牌。
- 在文本特征空间中通过正交约束解耦身份令牌和要编辑的属性。
- 应用对象蒙版来引导跨注意力图,确保身份令牌仅影响感兴趣区域。
- S^2Edit能实现局部编辑,同时保留原始身份。
- 实验结果证明S^2Edit在性能上优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图



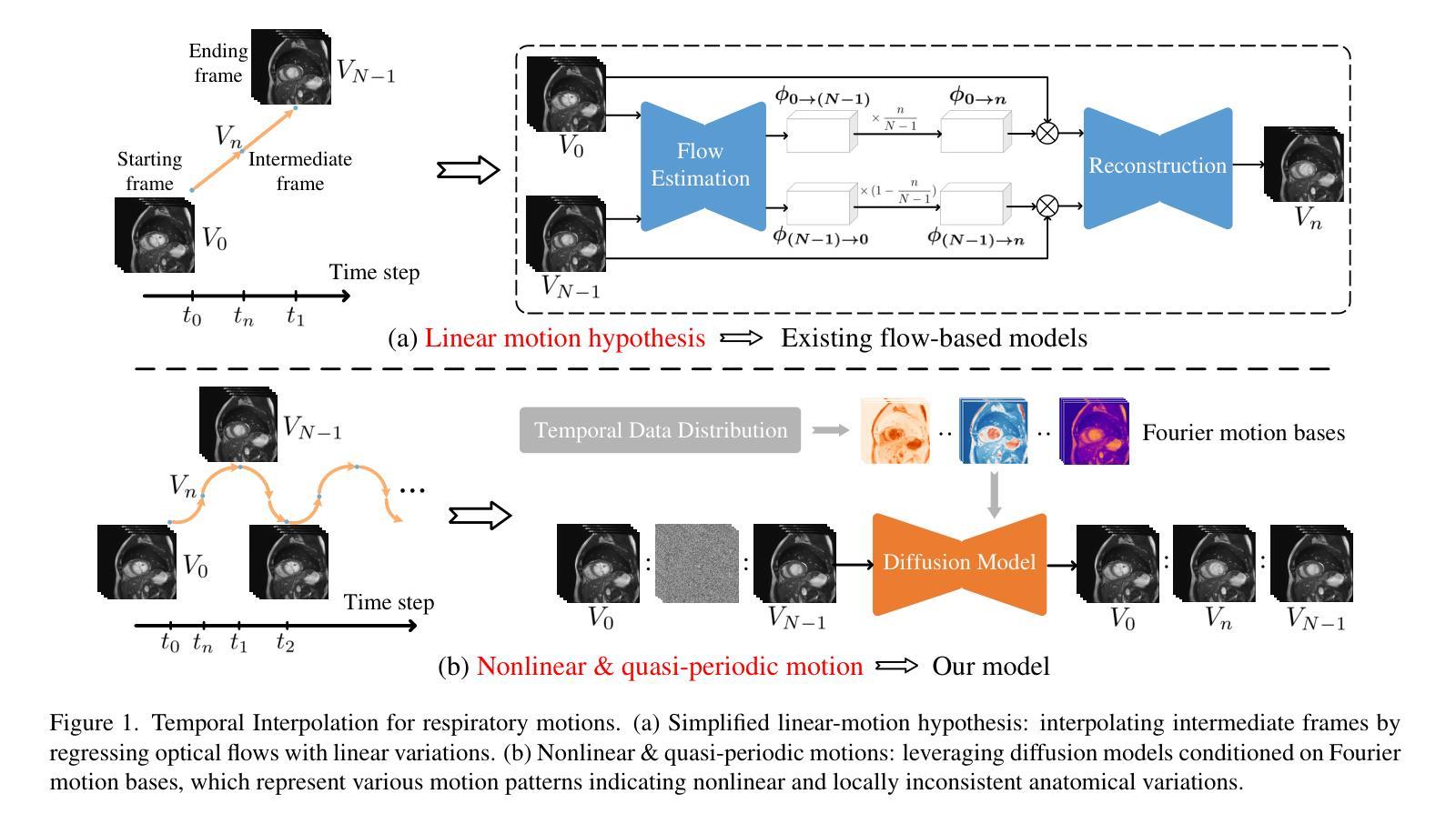
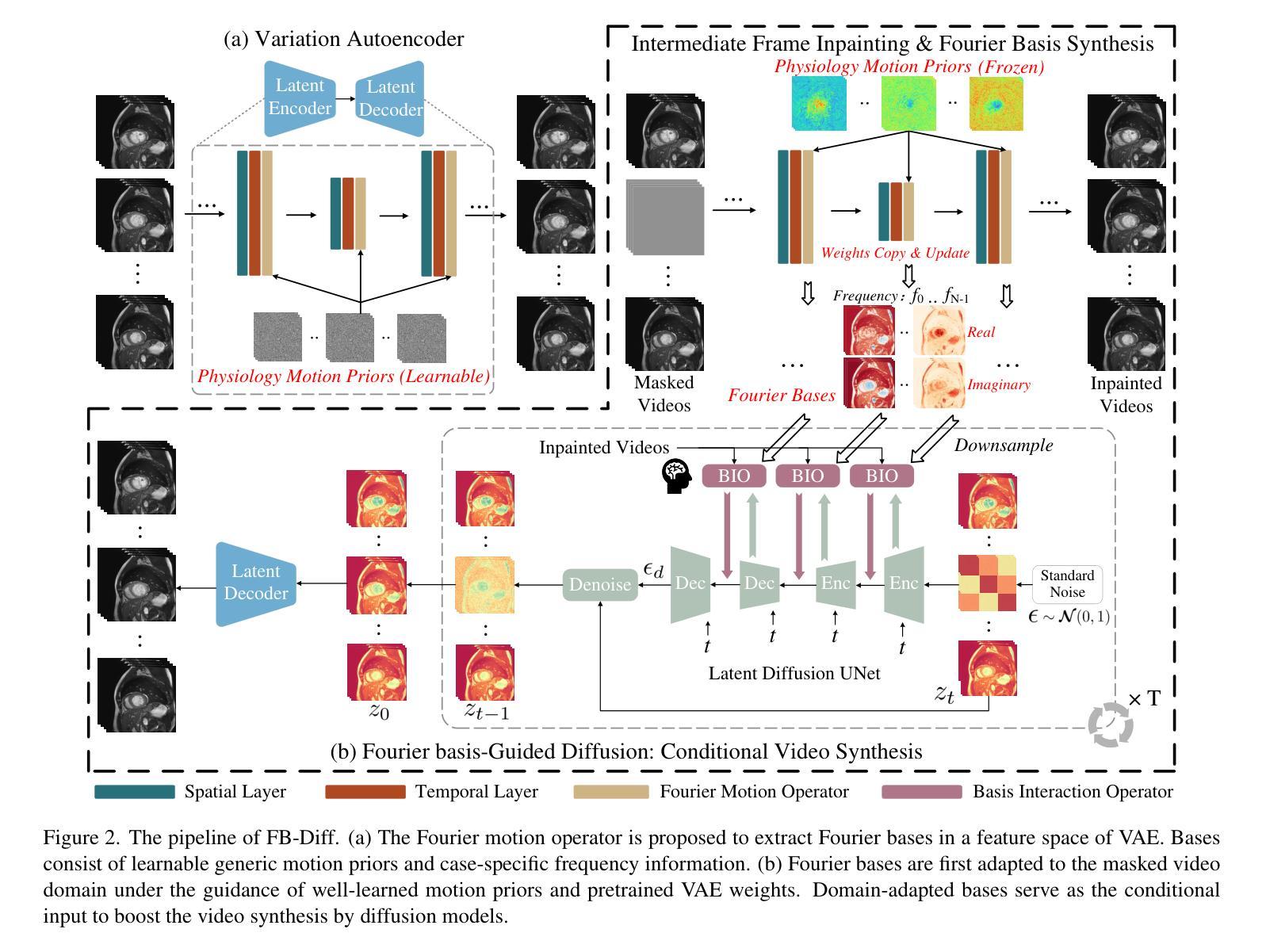
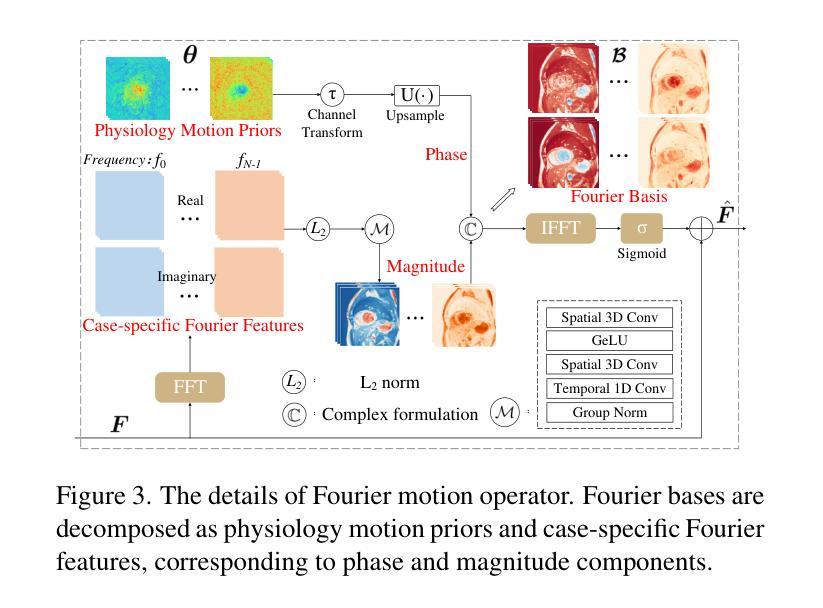
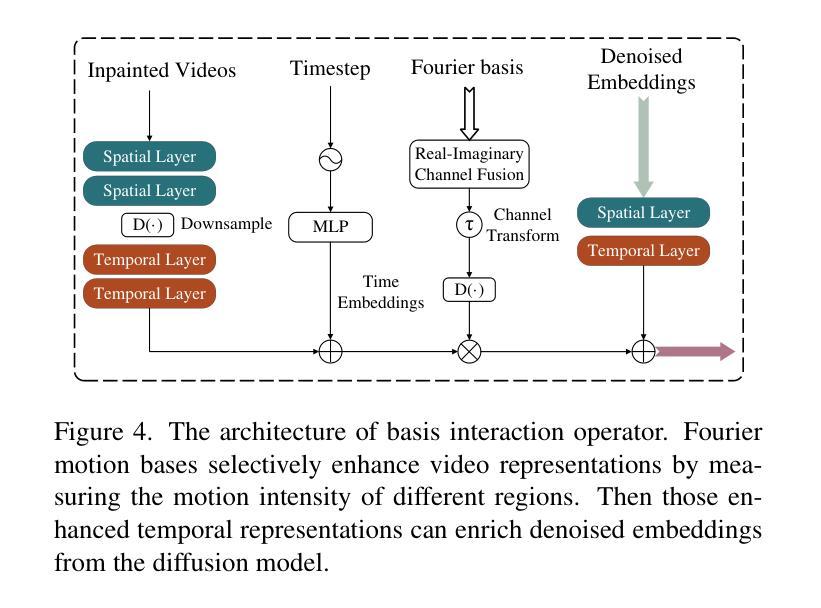
FB-Diff: Fourier Basis-guided Diffusion for Temporal Interpolation of 4D Medical Imaging
Authors:Xin You, Runze Yang, Chuyan Zhang, Zhongliang Jiang, Jie Yang, Nassir Navab
The temporal interpolation task for 4D medical imaging, plays a crucial role in clinical practice of respiratory motion modeling. Following the simplified linear-motion hypothesis, existing approaches adopt optical flow-based models to interpolate intermediate frames. However, realistic respiratory motions should be nonlinear and quasi-periodic with specific frequencies. Intuited by this property, we resolve the temporal interpolation task from the frequency perspective, and propose a Fourier basis-guided Diffusion model, termed FB-Diff. Specifically, due to the regular motion discipline of respiration, physiological motion priors are introduced to describe general characteristics of temporal data distributions. Then a Fourier motion operator is elaborately devised to extract Fourier bases by incorporating physiological motion priors and case-specific spectral information in the feature space of Variational Autoencoder. Well-learned Fourier bases can better simulate respiratory motions with motion patterns of specific frequencies. Conditioned on starting and ending frames, the diffusion model further leverages well-learned Fourier bases via the basis interaction operator, which promotes the temporal interpolation task in a generative manner. Extensive results demonstrate that FB-Diff achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) perceptual performance with better temporal consistency while maintaining promising reconstruction metrics. Codes are available.
在四维医学成像的时间插值任务中,对于呼吸运动建模的临床实践起着至关重要的作用。遵循简化的线性运动假设,现有方法采用基于光学流的模型进行中间帧插值。然而,实际的呼吸运动应该是非线性、准周期性的,并具有特定的频率。基于这一特性,我们从频率角度解决时间插值问题,并提出了一种傅里叶基础引导的扩散模型,称为FB-Diff。具体来说,由于呼吸的常规运动规律,我们引入生理运动先验来描述时间数据分布的一般特征。然后精心设计了一个傅里叶运动算子,通过结合生理运动先验和案例特定的光谱信息,在变分自动编码器的特征空间中提取傅里叶基础。学习良好的傅里叶基础能更好地模拟具有特定频率的运动模式。基于起始帧和结束帧的条件,扩散模型进一步利用学习良好的傅里叶基础,通过基础交互算子,以生成的方式促进时间插值任务。大量结果表明,FB-Diff达到了最先进的感知性能,具有较好的时间一致性,同时保持了有希望的重建指标。相关代码已公开。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025
Summary
本文提出了一个基于傅里叶基础的扩散模型(FB-Diff),用于解决四维医学成像中的时间插值问题。该模型结合生理运动先验和变分自编码器的特征空间,从频率角度解决时间插值问题。通过引入傅里叶运动算子,提取傅里叶基础,模拟具有特定频率的运动模式,实现生成式的时间插值任务,取得了最佳感知性能和良好的时间一致性。
Key Takeaways
- 4D医学成像中的时间插值任务对呼吸运动建模的临床实践至关重要。
- 现有方法采用基于光学流动的模型进行插值,但忽略了呼吸运动的非线性、准周期性特点。
- 本文从频率角度解决时间插值问题,提出FB-Diff模型。
- 该模型引入生理运动先验来描述时间数据分布的一般特征。
- 通过傅里叶运动算子提取傅里叶基础,结合生理运动先验和特定光谱信息。
- FB-Diff模型能够实现生成式的时间插值任务,达到最佳感知性能,保持良好的时间一致性。
点此查看论文截图

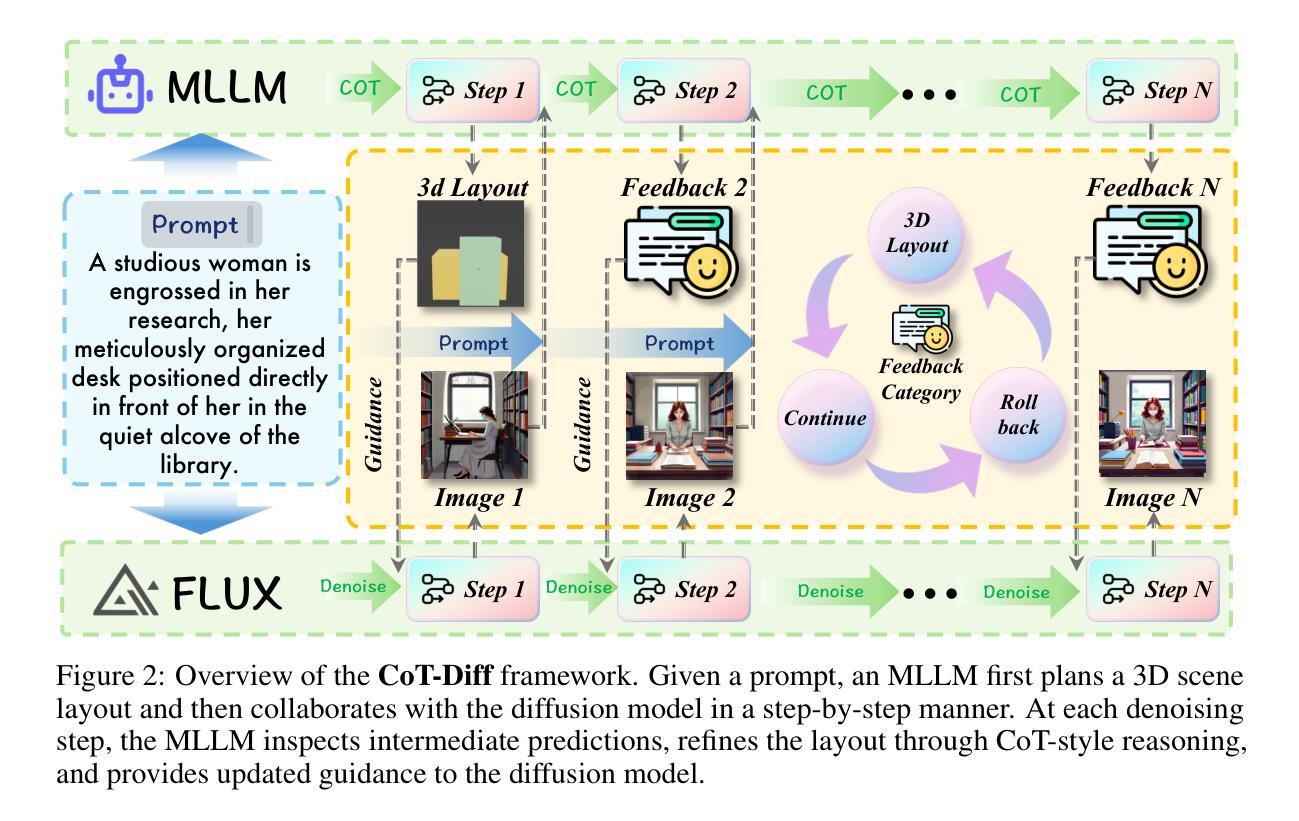
CoT-lized Diffusion: Let’s Reinforce T2I Generation Step-by-step
Authors:Zheyuan Liu, Munan Ning, Qihui Zhang, Shuo Yang, Zhongrui Wang, Yiwei Yang, Xianzhe Xu, Yibing Song, Weihua Chen, Fan Wang, Li Yuan
Current text-to-image (T2I) generation models struggle to align spatial composition with the input text, especially in complex scenes. Even layout-based approaches yield suboptimal spatial control, as their generation process is decoupled from layout planning, making it difficult to refine the layout during synthesis. We present CoT-Diff, a framework that brings step-by-step CoT-style reasoning into T2I generation by tightly integrating Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM)-driven 3D layout planning with the diffusion process. CoT-Diff enables layout-aware reasoning inline within a single diffusion round: at each denoising step, the MLLM evaluates intermediate predictions, dynamically updates the 3D scene layout, and continuously guides the generation process. The updated layout is converted into semantic conditions and depth maps, which are fused into the diffusion model via a condition-aware attention mechanism, enabling precise spatial control and semantic injection. Experiments on 3D Scene benchmarks show that CoT-Diff significantly improves spatial alignment and compositional fidelity, and outperforms the state-of-the-art method by 34.7% in complex scene spatial accuracy, thereby validating the effectiveness of this entangled generation paradigm.
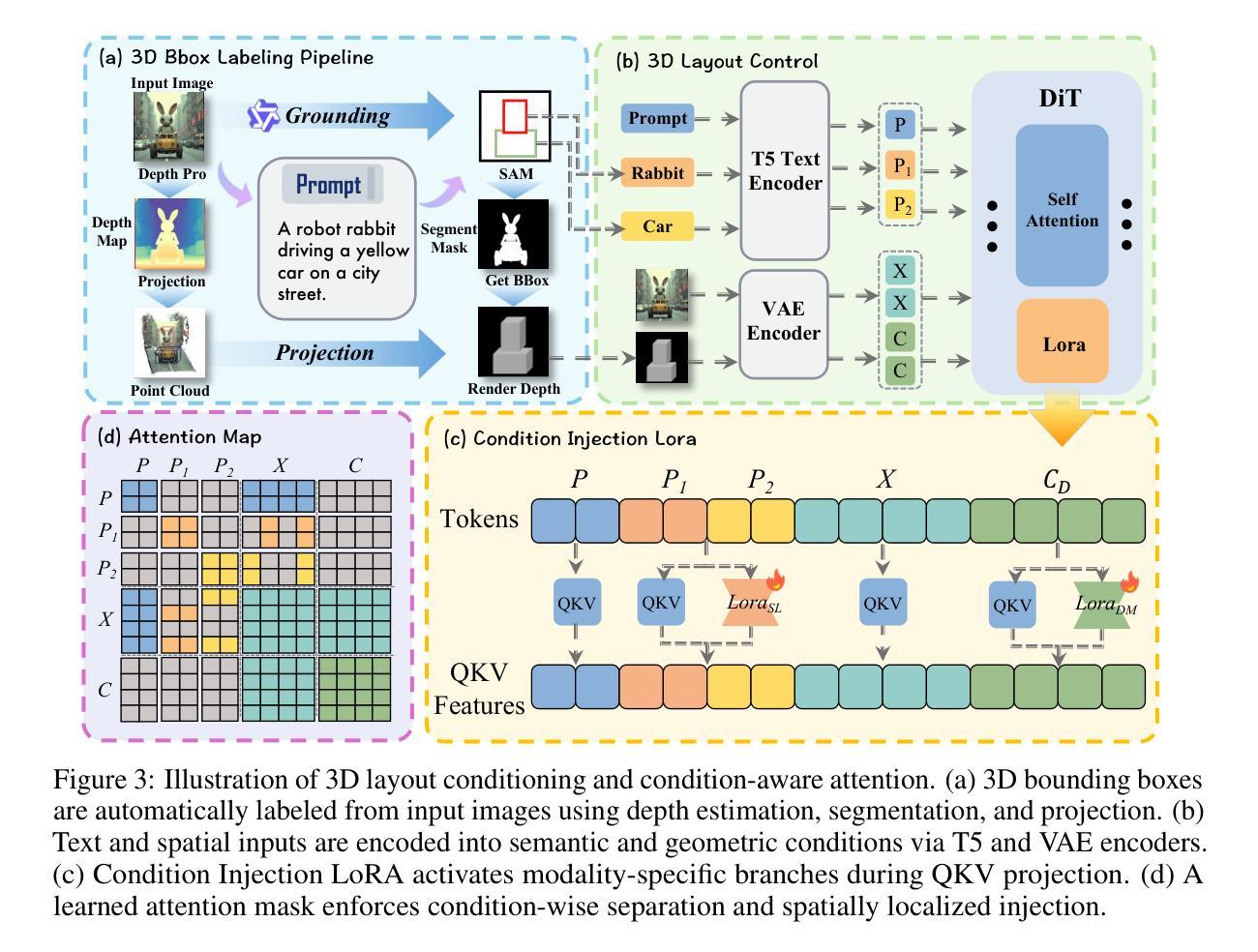
当前文本到图像(T2I)生成模型在复杂的场景中很难将空间构图与输入文本对齐。即使是基于布局的方法也会产生次优的空间控制,因为它们的生成过程与布局规划是分离的,使得在合成过程中难以调整布局。我们提出了CoT-Diff框架,它通过紧密结合多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)驱动的3D布局规划与扩散过程,将分步的CoT风格推理带入T2I生成。CoT-Diff使布局感知推理能够在单个扩散回合内完成:在每个去噪步骤中,MLLM评估中间预测,动态更新3D场景布局,并持续指导生成过程。更新的布局被转换为语义条件和深度图,通过条件感知注意力机制融合到扩散模型中,实现了精确的空间控制和语义注入。在3D场景基准测试上的实验表明,CoT-Diff在空间和组成保真度方面显著提高,并且在复杂场景的空间准确性方面比现有技术领先了34.7%,从而验证了这种纠缠生成模式的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了当前文本到图像生成模型在复杂场景中的空间布局对齐问题。为此,提出了一种名为CoT-Diff的新框架,该框架通过紧密结合多模态大型语言模型驱动的3D布局规划与扩散过程,将分步的CoT风格推理引入T2I生成。CoT-Diff使布局感知推理能够在单个扩散回合内完成:在每个去噪步骤中,MLLM评估中间预测,动态更新3D场景布局,并连续指导生成过程。实验表明,CoT-Diff在复杂场景中显著提高了空间对齐和组合保真度,并优于当前最先进的方法,提高了34.7%的空间精度。验证了这种纠缠生成模式的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 当前文本到图像生成模型在复杂场景中的空间布局对齐存在挑战。
- CoT-Diff框架通过结合多模态大型语言模型和扩散过程来解决这个问题。
- CoT-Diff实现了布局感知推理,在每个扩散回合中动态更新3D场景布局。
- MLLM在中间预测阶段评估并指导生成过程。
- CoT-Diff通过条件感知注意力机制将更新的布局融合到扩散模型中。
- 实验表明,CoT-Diff在复杂场景中显著提高了空间对齐和组合保真度。
点此查看论文截图

Sat2City: 3D City Generation from A Single Satellite Image with Cascaded Latent Diffusion
Authors:Tongyan Hua, Lutao Jiang, Ying-Cong Chen, Wufan Zhao
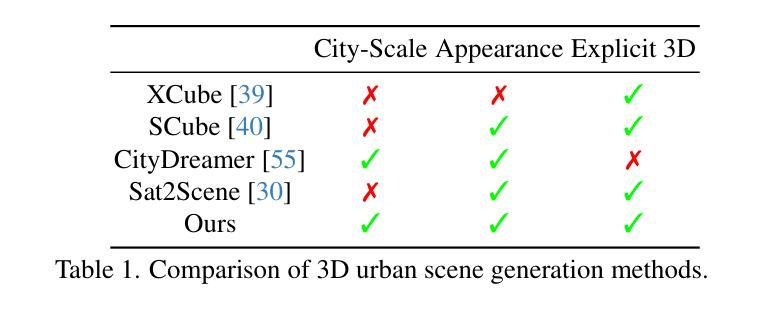
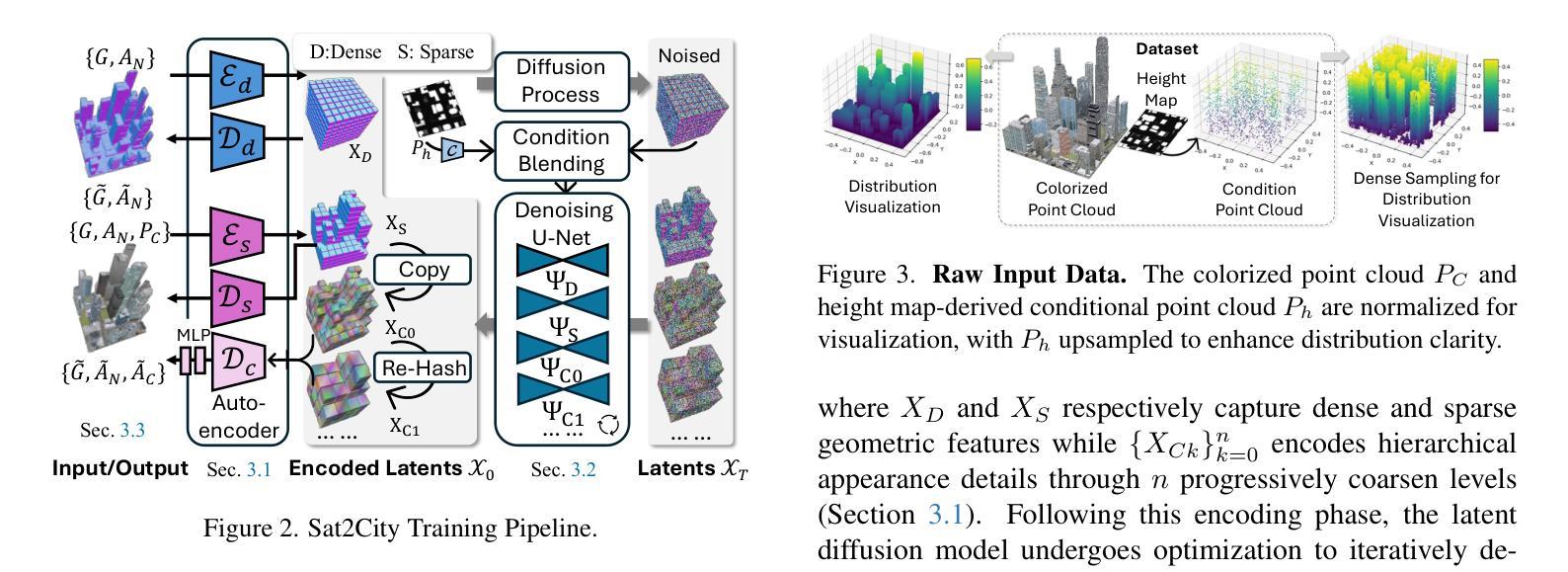
Recent advancements in generative models have enabled 3D urban scene generation from satellite imagery, unlocking promising applications in gaming, digital twins, and beyond. However, most existing methods rely heavily on neural rendering techniques, which hinder their ability to produce detailed 3D structures on a broader scale, largely due to the inherent structural ambiguity derived from relatively limited 2D observations. To address this challenge, we propose Sat2City, a novel framework that synergizes the representational capacity of sparse voxel grids with latent diffusion models, tailored specifically for our novel 3D city dataset. Our approach is enabled by three key components: (1) A cascaded latent diffusion framework that progressively recovers 3D city structures from satellite imagery, (2) a Re-Hash operation at its Variational Autoencoder (VAE) bottleneck to compute multi-scale feature grids for stable appearance optimization and (3) an inverse sampling strategy enabling implicit supervision for smooth appearance transitioning.To overcome the challenge of collecting real-world city-scale 3D models with high-quality geometry and appearance, we introduce a dataset of synthesized large-scale 3D cities paired with satellite-view height maps. Validated on this dataset, our framework generates detailed 3D structures from a single satellite image, achieving superior fidelity compared to existing city generation models.
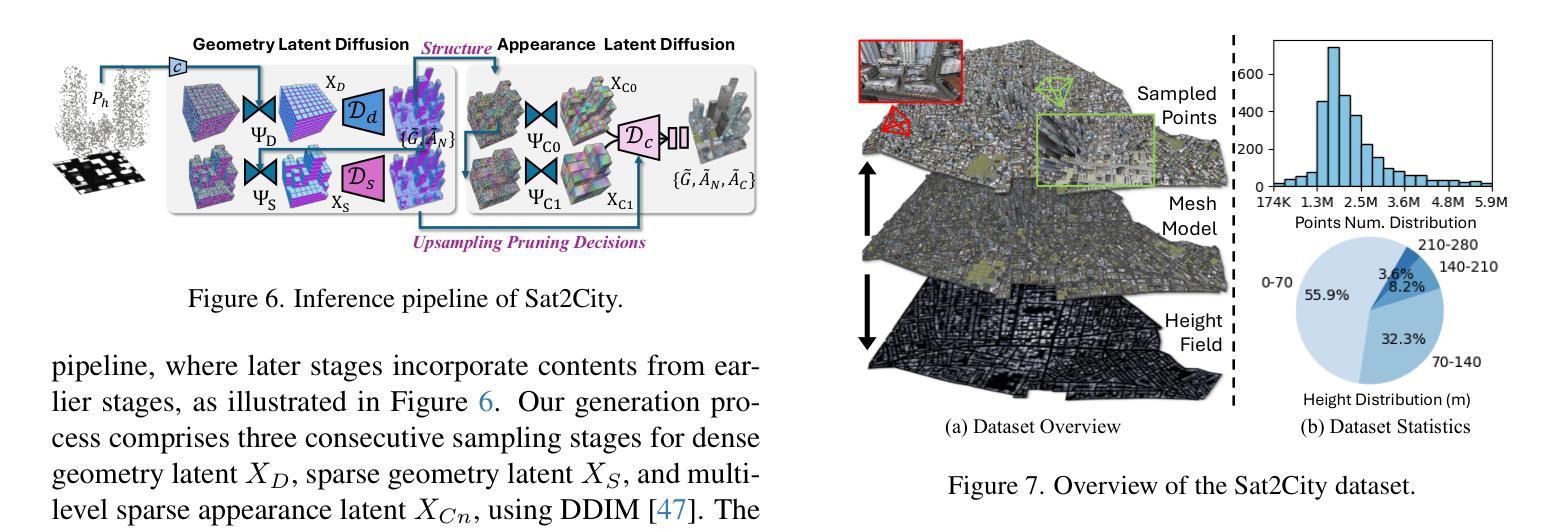
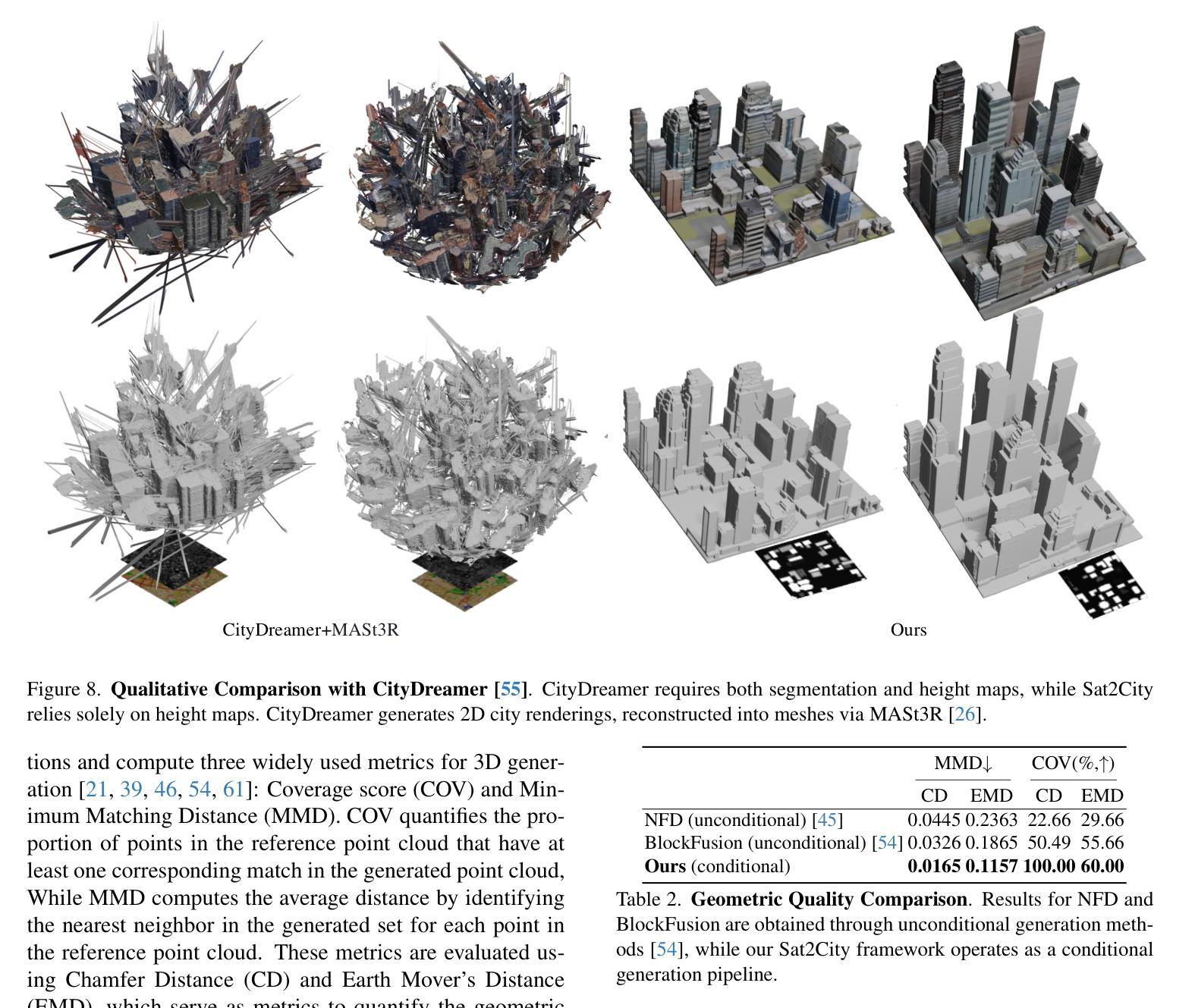
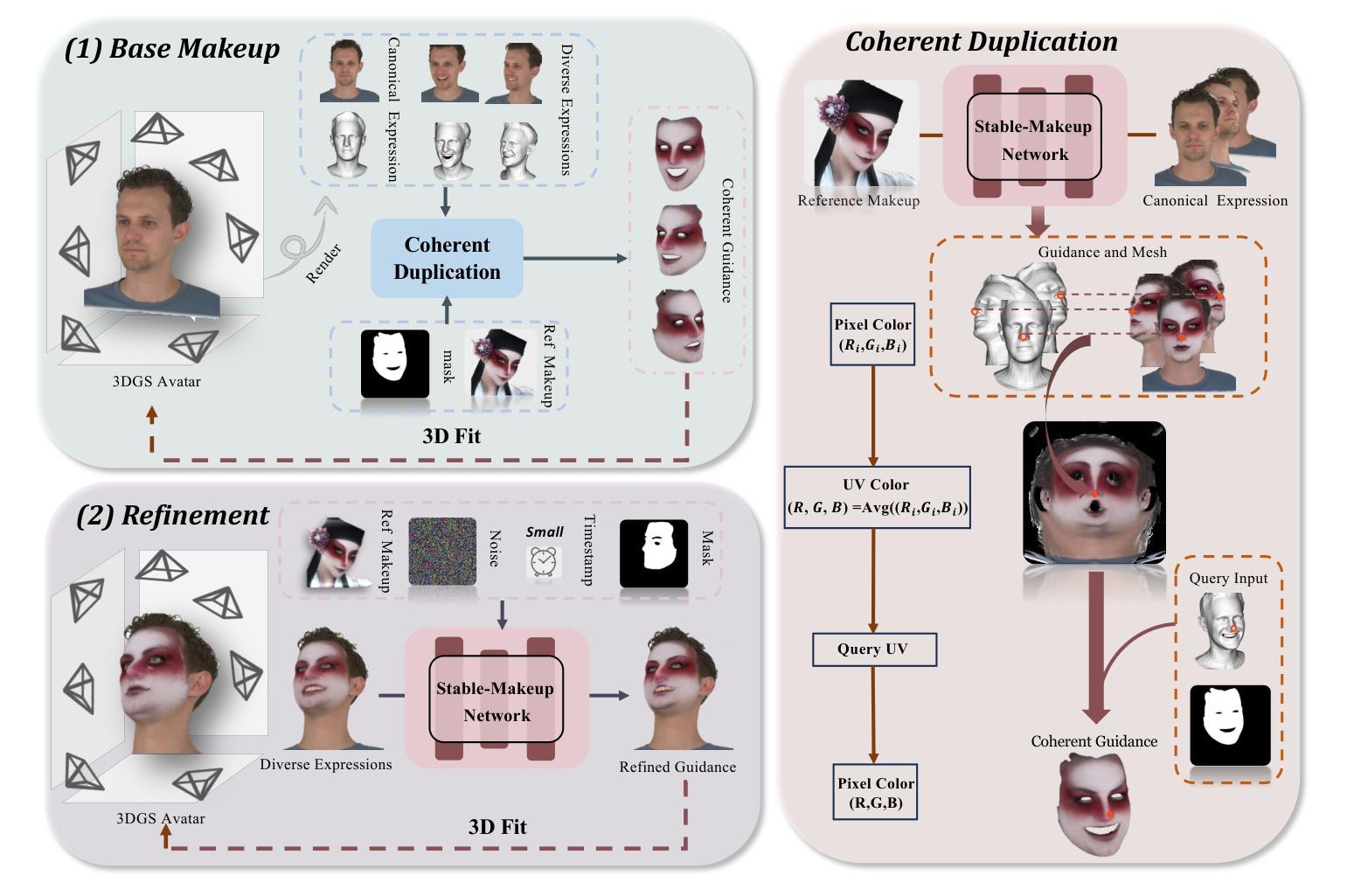
最近生成模型的进展使得从卫星图像生成三维城市场景成为可能,这在游戏、数字孪生等领域具有广阔的应用前景。然而,大多数现有方法严重依赖于神经渲染技术,这限制了它们在更大规模上生成详细三维结构的能力,这主要是由于相对有限的二维观测所固有的结构模糊性。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了Sat2City框架,该框架结合了稀疏体素网格的表示能力与潜在扩散模型,专门用于我们新的三维城市数据集。我们的方法由三个关键组件提供支持:(1)级联潜在扩散框架,该框架从卫星图像逐步恢复三维城市结构;(2)在其变分自动编码器(VAE)瓶颈处进行Re-Hash操作,以计算用于稳定外观优化的多尺度特征网格;(3)反向采样策略,实现对平滑外观过渡的隐式监督。为了克服收集具有高质量几何和外观的现实世界城市规模三维模型的挑战,我们引入了一个合成的大规模三维城市数据集,该数据集配有卫星视图的高度图。在我们的数据集上进行验证,我们的框架能够从单张卫星图像生成详细的三维结构,与现有的城市生成模型相比,具有更高的保真度。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025
Summary
近期生成模型的技术进步能够实现从卫星图像生成三维城市场景,为游戏、数字孪生等领域带来应用前景。但现有方法多依赖神经渲染技术,难以在更大规模上生成详细的三维结构。为此,本文提出Sat2City框架,结合稀疏体素网格的表示能力与潜在扩散模型,通过三个关键组件解决挑战。该框架在新型三维城市数据集上表现优越,能从单张卫星图像生成高精度三维结构。
Key Takeaways
- 生成模型最新进展实现了从卫星图像生成三维城市场景,应用于游戏、数字孪生等领域。
- 现有方法主要依赖神经渲染技术,难以在更大规模上生成详细的三维结构。
- Sat2City框架结合稀疏体素网格与潜在扩散模型,解决现有挑战。
- 框架包含三个关键组件:级联潜在扩散框架、重哈希操作和逆向采样策略。
- 新型三维城市数据集配备卫星视图高度图。
- 该框架在新型数据集上表现优越,实现单张卫星图像生成高精度三维结构。
点此查看论文截图

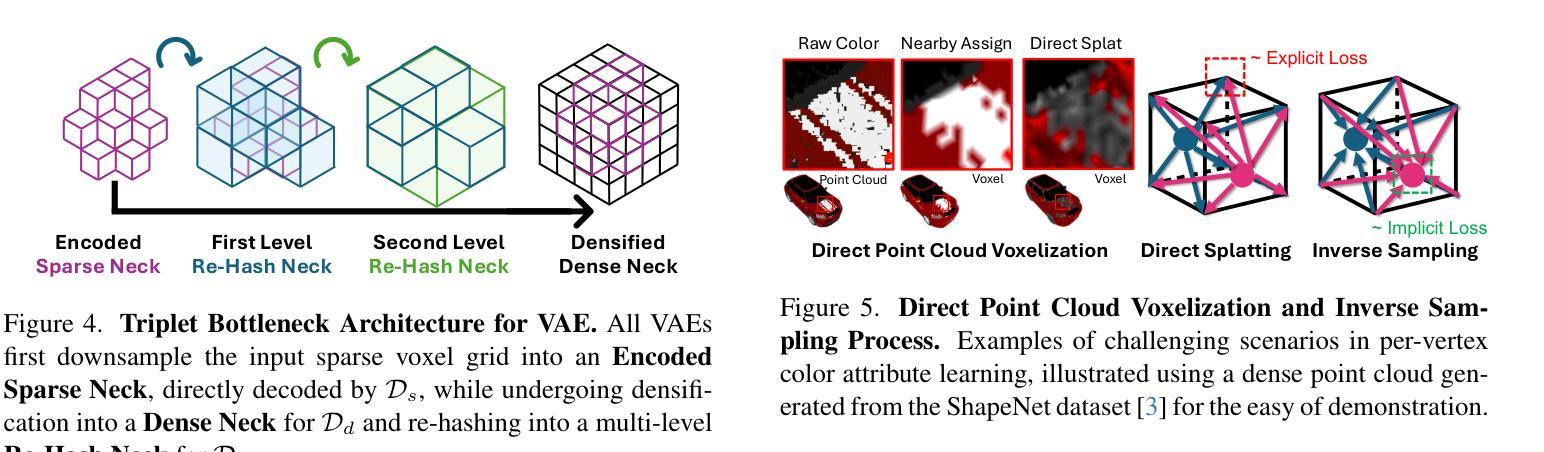
AvatarMakeup: Realistic Makeup Transfer for 3D Animatable Head Avatars
Authors:Yiming Zhong, Xiaolin Zhang, Ligang Liu, Yao Zhao, Yunchao Wei
Similar to facial beautification in real life, 3D virtual avatars require personalized customization to enhance their visual appeal, yet this area remains insufficiently explored. Although current 3D Gaussian editing methods can be adapted for facial makeup purposes, these methods fail to meet the fundamental requirements for achieving realistic makeup effects: 1) ensuring a consistent appearance during drivable expressions, 2) preserving the identity throughout the makeup process, and 3) enabling precise control over fine details. To address these, we propose a specialized 3D makeup method named AvatarMakeup, leveraging a pretrained diffusion model to transfer makeup patterns from a single reference photo of any individual. We adopt a coarse-to-fine idea to first maintain the consistent appearance and identity, and then to refine the details. In particular, the diffusion model is employed to generate makeup images as supervision. Due to the uncertainties in diffusion process, the generated images are inconsistent across different viewpoints and expressions. Therefore, we propose a Coherent Duplication method to coarsely apply makeup to the target while ensuring consistency across dynamic and multiview effects. Coherent Duplication optimizes a global UV map by recoding the averaged facial attributes among the generated makeup images. By querying the global UV map, it easily synthesizes coherent makeup guidance from arbitrary views and expressions to optimize the target avatar. Given the coarse makeup avatar, we further enhance the makeup by incorporating a Refinement Module into the diffusion model to achieve high makeup quality. Experiments demonstrate that AvatarMakeup achieves state-of-the-art makeup transfer quality and consistency throughout animation.
与现实生活中的面部美容类似,3D虚拟化身需要个性化定制以增强其视觉吸引力,但这个领域仍然没有得到足够的探索。虽然当前的3D高斯编辑方法可以适应面部化妆的目的,但这些方法未能满足实现真实化妆效果的基本要求:1)在可驱动的表情中保持外观的一致性,2)在化妆过程中保持身份识别,以及3)对细节进行精确控制。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种专门的3D化妆方法,名为AvatarMakeup,它利用预训练的扩散模型从任何个人的单张参考照片中转移化妆模式。我们采用由粗到细的理念,首先保持外观和身份的的一致性,然后细化细节。特别是,扩散模型被用于生成化妆图像作为监督。由于扩散过程中的不确定性,生成的图像在不同的视角和表情下存在不一致性。因此,我们提出了一种连贯复制方法,对目标进行粗略化妆,同时确保动态和多视角效果的一致性。连贯复制通过重新编码生成化妆图像之间的平均面部属性来优化全局UV地图。通过查询全局UV地图,它很容易合成来自任意视图和表情的连贯化妆指导,以优化目标化身。给定粗略的化妆化身,我们进一步通过将细化模块融入扩散模型中,提高化妆效果,以实现高质量的化妆。实验表明,AvatarMakeup在动画中实现了最先进的化妆转移质量和一致性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本描述了一种名为AvatarMakeup的3D虚拟角色化妆方法。此方法借助预训练的扩散模型,从单一参考照片转移妆容。为确保妆容在动态和多种视角下的连贯性,提出了Coherent Duplication方法。此外,还加入了一个细化模块来提升妆容质量。
Key Takeaways
- 现有3D高斯编辑方法在虚拟角色化妆方面存在局限性,不能满足真实妆容效果的要求。
- AvatarMakeup方法利用预训练的扩散模型,从单一参考照片转移妆容,实现了个性化的化妆。
- Coherent Duplication方法用于确保妆容在动态和多种视角下的连贯性。
- 扩散模型生成妆容图像作为监督。
- 生成妆容图像在不同视角和表情下的不一致性,通过Coherent Duplication方法进行优化。
- 通过查询全局UV地图,可以轻松合成任意视角和表情的连贯妆容指导。
- 引入细化模块进一步提升妆容质量,实现了高水平的化妆效果。
点此查看论文截图


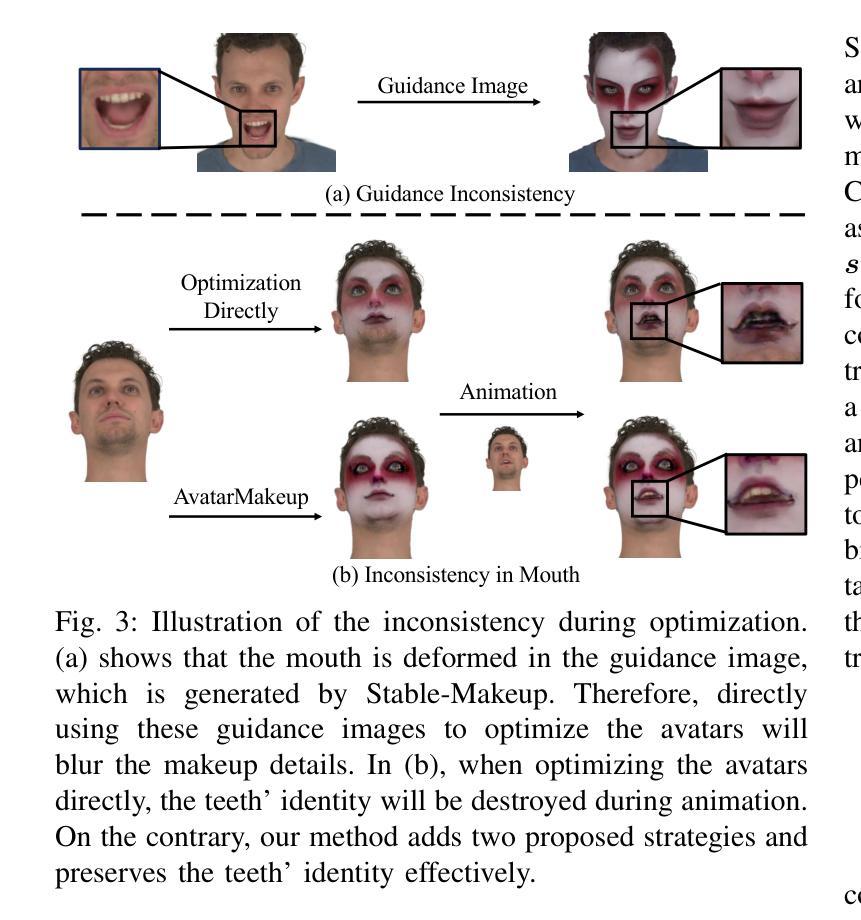

AniCrafter: Customizing Realistic Human-Centric Animation via Avatar-Background Conditioning in Video Diffusion Models
Authors:Muyao Niu, Mingdeng Cao, Yifan Zhan, Qingtian Zhu, Mingze Ma, Jiancheng Zhao, Yanhong Zeng, Zhihang Zhong, Xiao Sun, Yinqiang Zheng
Recent advances in video diffusion models have significantly improved character animation techniques. However, current approaches rely on basic structural conditions such as DWPose or SMPL-X to animate character images, limiting their effectiveness in open-domain scenarios with dynamic backgrounds or challenging human poses. In this paper, we introduce \textbf{AniCrafter}, a diffusion-based human-centric animation model that can seamlessly integrate and animate a given character into open-domain dynamic backgrounds while following given human motion sequences. Built on cutting-edge Image-to-Video (I2V) diffusion architectures, our model incorporates an innovative ‘’avatar-background’’ conditioning mechanism that reframes open-domain human-centric animation as a restoration task, enabling more stable and versatile animation outputs. Experimental results demonstrate the superior performance of our method. Codes are available at https://github.com/MyNiuuu/AniCrafter.
视频扩散模型的最新进展极大地改进了角色动画技术。然而,当前的方法依赖于基本结构条件,如DWPose或SMPL-X来驱动角色图像,这在具有动态背景或复杂人类姿态的开放场景中限制了其有效性。在本文中,我们介绍了AniCrafter,这是一个基于扩散的人类中心动画模型,可以无缝集成并驱动给定的角色进入开放领域的动态背景,同时遵循给定的人类运动序列。我们的模型建立在最先进的图像到视频(I2V)扩散架构上,融入了一种创新的“化身背景”条件机制,将开放领域的人类中心动画重新构建为恢复任务,从而实现更稳定和更通用的动画输出。实验结果证明了我们的方法的优越性。代码可在https://github.com/MyNiuuu/AniCrafter获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Homepage: https://myniuuu.github.io/AniCrafter ; Codes: https://github.com/MyNiuuu/AniCrafter
Summary
近期视频扩散模型的进步显著提升了角色动画技术。然而,当前方法依赖于基本结构条件(如DWPose或SMPL-X)来驱动角色图像,这在开放域动态背景或复杂人类姿势的场景中效果有限。本文介绍了一款基于扩散的人类中心动画模型——AniCrafter,它能无缝集成并驱动给定角色进入开放域动态背景,同时遵循给定的人类运动序列。该模型采用先进的图像到视频(I2V)扩散架构,引入了一种创新的“Avatar-背景”条件机制,将开放域人类中心动画重构为恢复任务,从而实现更稳定和多样化的动画输出。实验结果证明了该方法的卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 近期视频扩散模型的进步已经显著提高了角色动画技术。
- 当前的角色动画方法受限于基本结构条件,难以处理开放域动态背景和复杂人类姿势。
- 论文提出了基于扩散的人类中心动画模型——AniCrafter。
- AniCrafter能够无缝集成并驱动给定角色进入开放域动态背景,遵循给定的人类运动序列。
- AniCrafter采用先进的图像到视频(I2V)扩散架构。
- AniCrafter引入了创新的“Avatar-背景”条件机制,将动画重构为恢复任务。
点此查看论文截图

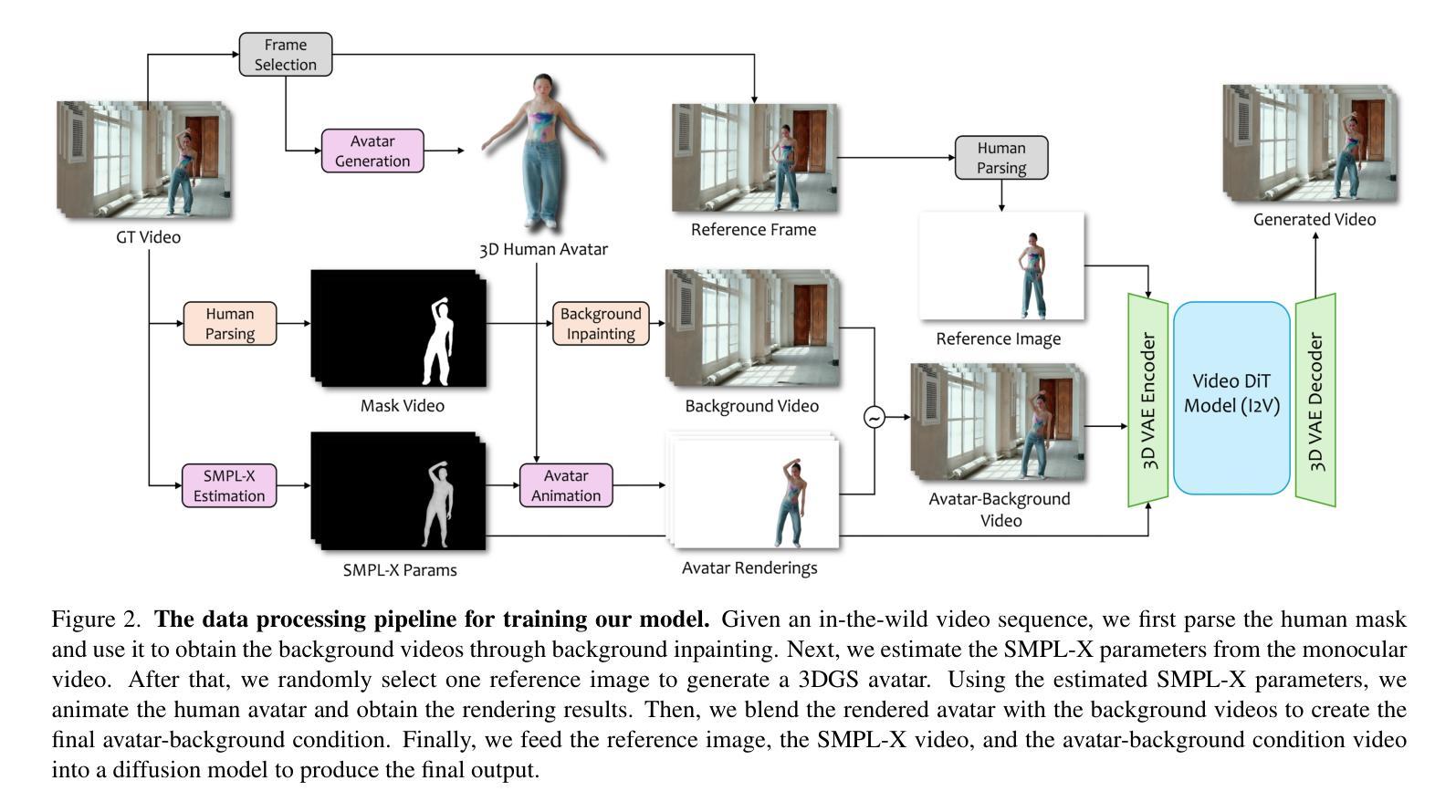
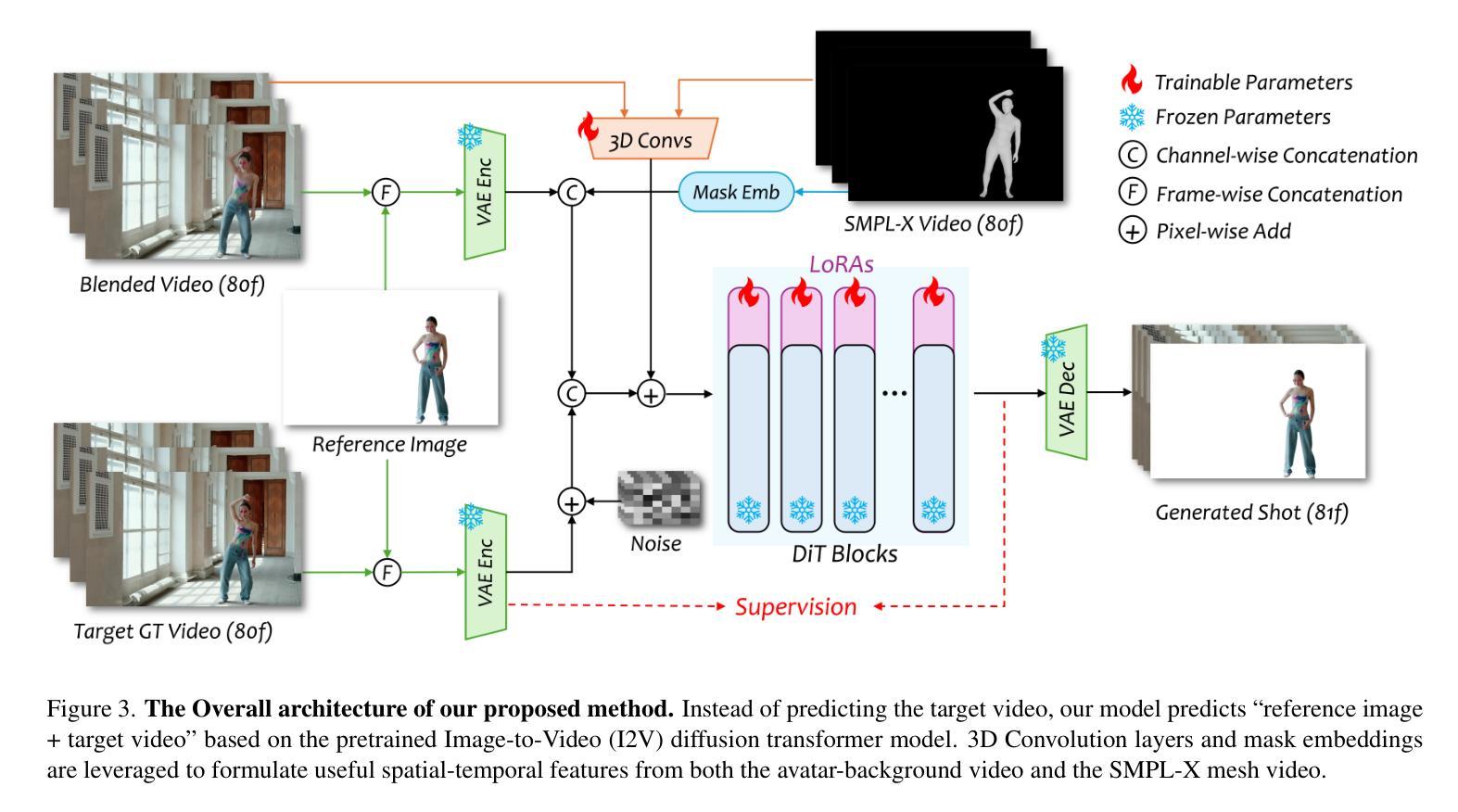
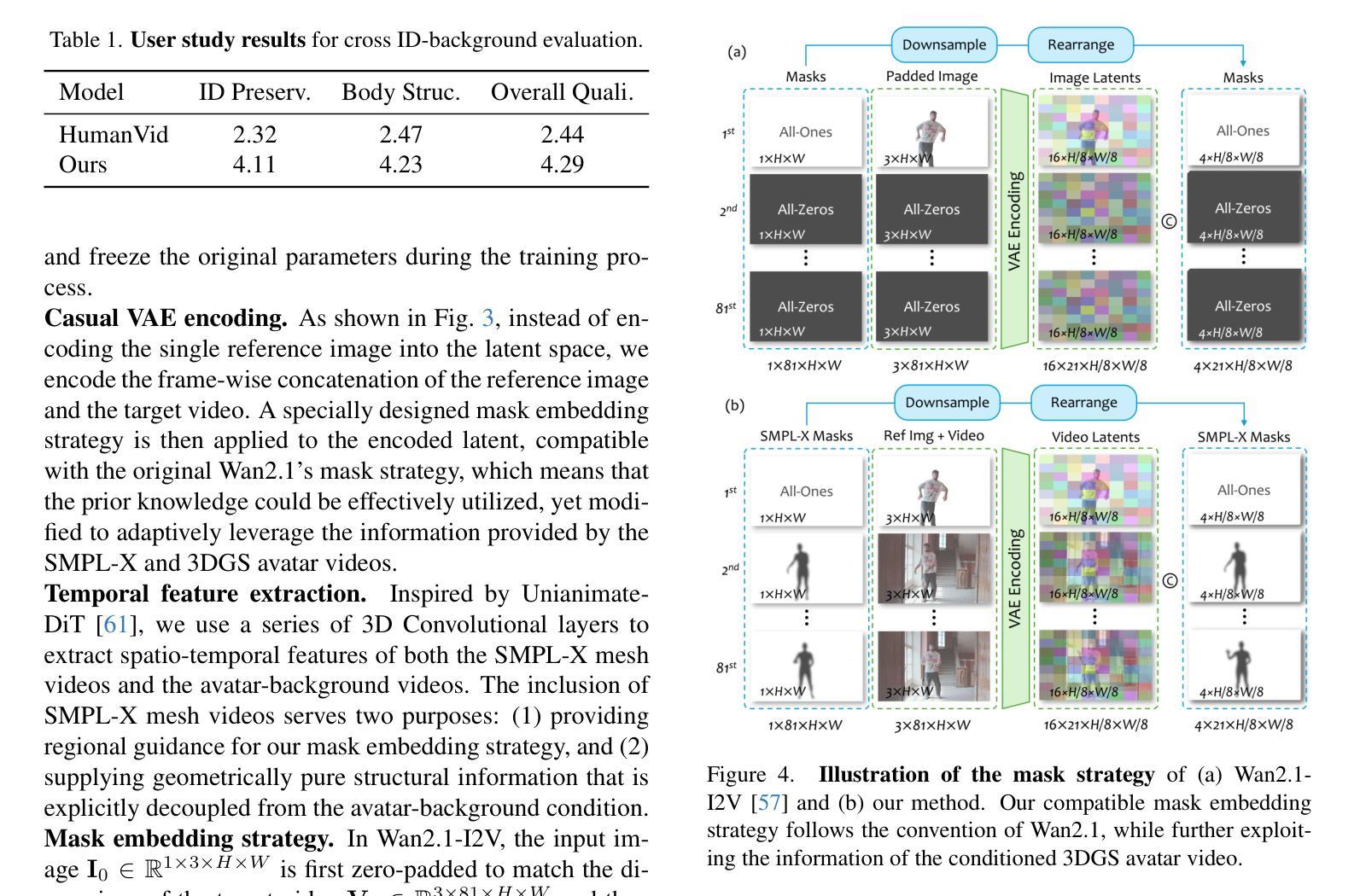

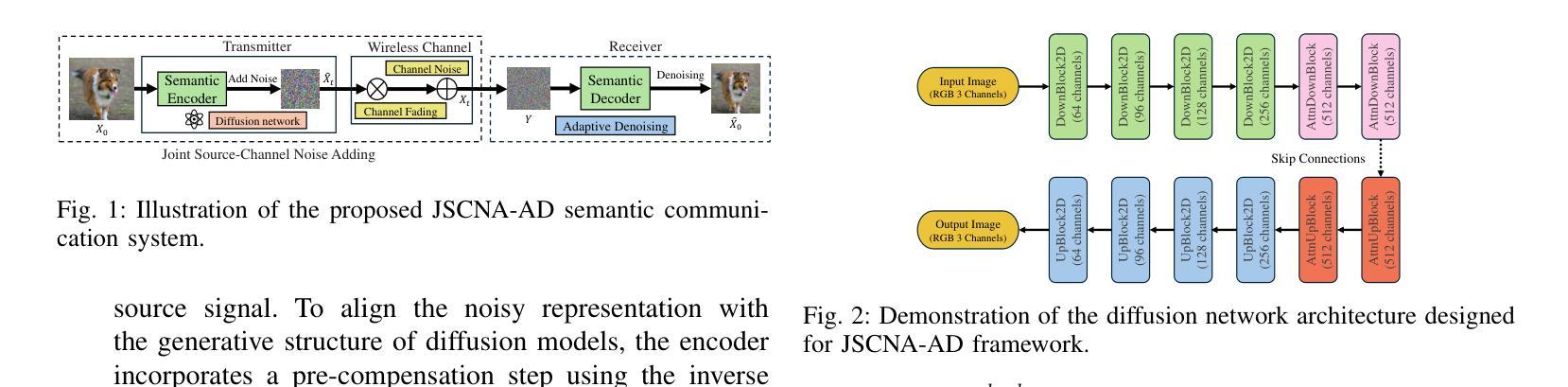
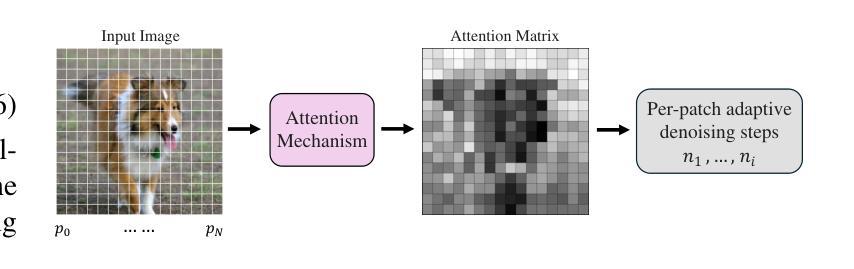
Joint Source-Channel Noise Adding with Adaptive Denoising for Diffusion-Based Semantic Communications
Authors:Chengyang Liang, Dong Li
Semantic communication (SemCom) aims to convey the intended meaning of messages rather than merely transmitting bits, thereby offering greater efficiency and robustness, particularly in resource-constrained or noisy environments. In this paper, we propose a novel framework which is referred to as joint source-channel noise adding with adaptive denoising (JSCNA-AD) for SemCom based on a diffusion model (DM). Unlike conventional encoder-decoder designs, our approach intentionally incorporates the channel noise during transmission, effectively transforming the harmful channel noise into a constructive component of the diffusion-based semantic reconstruction process. Besides, we introduce an attention-based adaptive denoising mechanism, in which transmitted images are divided into multiple regions, and the number of denoising steps is dynamically allocated based on the semantic importance of each region. This design effectively balances the reception quality and the inference latency by prioritizing the critical semantic information. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms existing SemCom schemes under various noise conditions, underscoring the potential of diffusion-based models in next-generation communication systems.
语义通信(SemCom)旨在传达信息的意图,而不仅仅是传输比特,从而提供更高效和稳健的通信,特别是在资源受限或嘈杂的环境中。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于扩散模型(DM)的语义通信的新型框架,称为联合源信道噪声添加与自适应去噪(JSCNA-AD)。与传统的编码器-解码器设计不同,我们的方法故意在传输过程中加入信道噪声,有效地将有害的信道噪声转化为扩散语义重建过程的建设性组成部分。此外,我们引入了一种基于注意力的自适应去噪机制,其中传输的图像被分割成多个区域,并根据每个区域的语义重要性动态分配去噪步骤的数量。这种设计通过优先处理关键的语义信息,有效地平衡了接收质量和推理延迟。大量实验表明,在各种噪声条件下,我们的方法显著优于现有的SemCom方案,突显了扩散模型在下一代通信系统中的应用潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于扩散模型的语义通信新型框架研究。该框架通过联合源信道噪声添加和自适应去噪技术,将有害的信道噪声转化为建设性成分,优化了语义重建过程。引入注意力机制自适应去噪机制,根据图像区域的语义重要性动态分配去噪步骤,提升接收质量和降低推理延迟。实验证明,该方法在各种噪声条件下显著优于现有语义通信方案。
Key Takeaways
- SemCom旨在传达消息的意图意义,而非仅传输比特,从而提高效率和稳健性,尤其在资源受限或嘈杂环境中。
- 提出基于扩散模型的新型JSCNA-AD框架,故意将信道噪声纳入传输过程,转化为建设性成分。
- 引入注意力机制自适应去噪技术,根据图像区域的语义重要性动态调整去噪步骤。
- 该设计有效平衡接收质量和推理延迟,优先处理关键语义信息。
- 实验证明,该框架在各种噪声条件下显著优于现有SemCom方案。
- 扩散模型在下一代通信系统中具有潜在应用价值。
点此查看论文截图


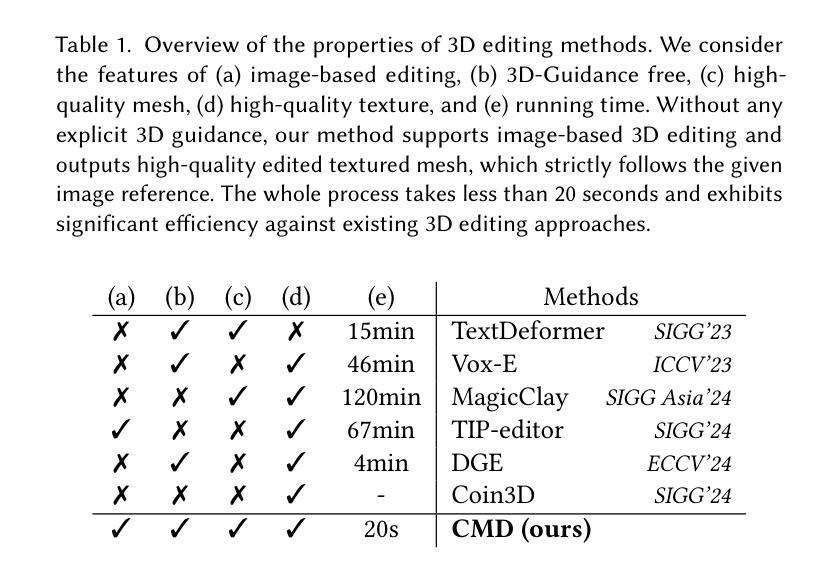
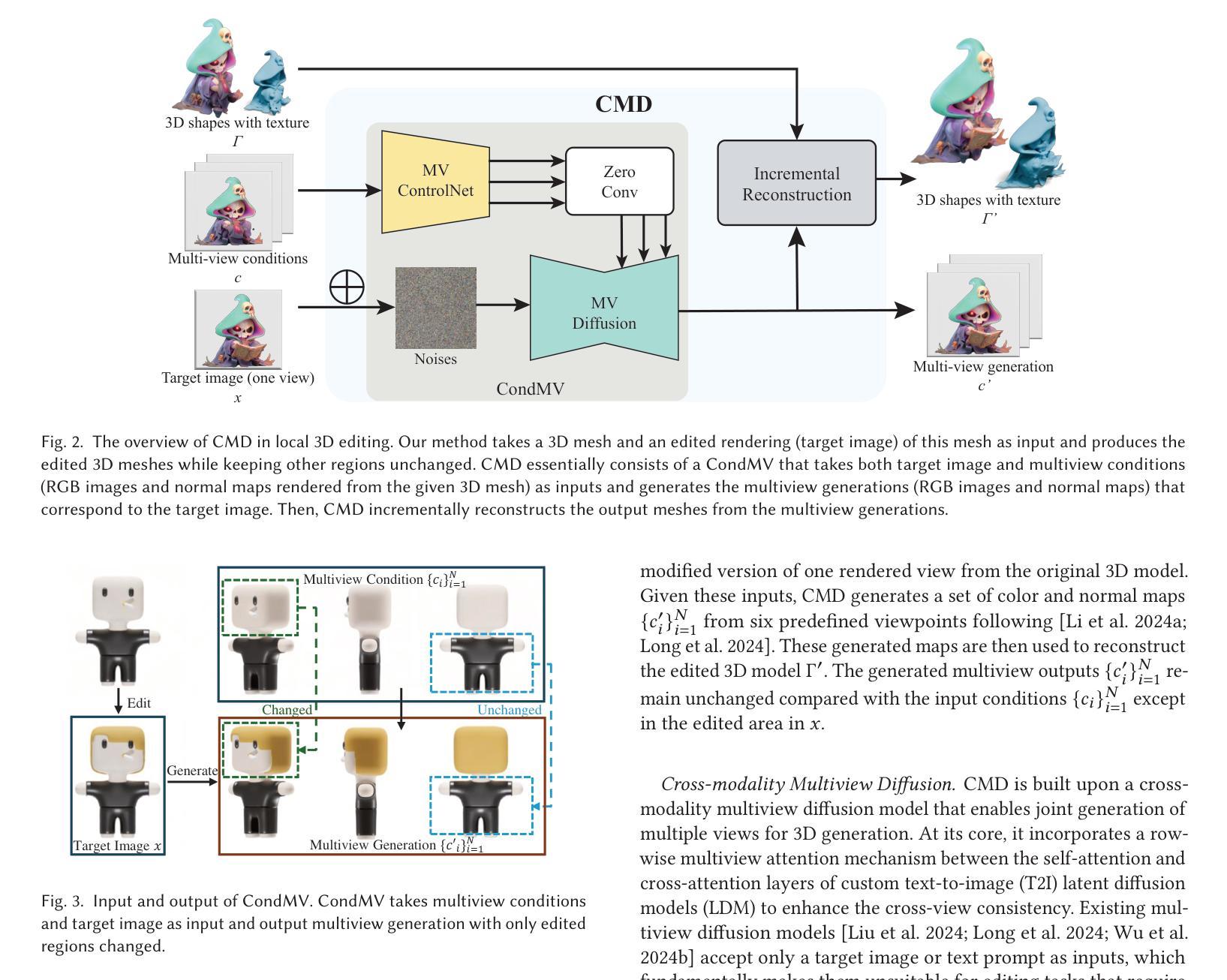
CMD: Controllable Multiview Diffusion for 3D Editing and Progressive Generation
Authors:Peng Li, Suizhi Ma, Jialiang Chen, Yuan Liu, Congyi Zhang, Wei Xue, Wenhan Luo, Alla Sheffer, Wenping Wang, Yike Guo
Recently, 3D generation methods have shown their powerful ability to automate 3D model creation. However, most 3D generation methods only rely on an input image or a text prompt to generate a 3D model, which lacks the control of each component of the generated 3D model. Any modifications of the input image lead to an entire regeneration of the 3D models. In this paper, we introduce a new method called CMD that generates a 3D model from an input image while enabling flexible local editing of each component of the 3D model. In CMD, we formulate the 3D generation as a conditional multiview diffusion model, which takes the existing or known parts as conditions and generates the edited or added components. This conditional multiview diffusion model not only allows the generation of 3D models part by part but also enables local editing of 3D models according to the local revision of the input image without changing other 3D parts. Extensive experiments are conducted to demonstrate that CMD decomposes a complex 3D generation task into multiple components, improving the generation quality. Meanwhile, CMD enables efficient and flexible local editing of a 3D model by just editing one rendered image.
最近,3D生成方法已经显示出其自动化创建3D模型的强大能力。然而,大多数3D生成方法仅依赖于输入图像或文本提示来生成3D模型,这缺乏对生成3D模型各个组件的控制。输入图像的任何修改都会导致3D模型的整个重新生成。在本文中,我们介绍了一种新方法CMD,它可以从输入图像生成3D模型,同时实现对生成3D模型的各个组件进行灵活局部编辑。在CMD中,我们将3D生成制定为条件多视图扩散模型,以现有或已知部分作为条件,生成编辑或添加的组件。这种条件多视图扩散模型不仅允许逐个部分地生成3D模型,而且能够在不改变其他3D部分的情况下,根据输入图像的局部修订对3D模型进行局部编辑。大量实验表明,CMD将复杂的3D生成任务分解为多个组件,提高了生成质量。同时,CMD通过仅编辑一个渲染图像就能实现对3D模型的高效和灵活局部编辑。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF SIGGRAPH 2025, Page: https://penghtyx.github.io/CMD/
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为CMD的新方法,能够从输入图像生成3D模型,并实现对模型各组件的灵活局部编辑。该方法采用条件多视角扩散模型进行建模,以现有部分作为条件生成编辑或添加的组件。这种模型不仅能够分步骤生成3D模型,而且能够根据输入图像的局部修改进行局部编辑,而不会影响到其他部分的3D模型。实验证明,CMD方法能够提高生成质量,并能高效灵活地编辑3D模型。
Key Takeaways
- CMD方法能够从输入图像生成3D模型,并允许对生成的模型进行灵活局部编辑。
- CMD采用条件多视角扩散模型进行建模,将现有部分作为条件来生成新的组件。
- 该方法能够将复杂的3D生成任务分解为多个组件,提高了生成质量。
- CMD通过仅编辑一个渲染图像就能实现对3D模型的局部高效灵活编辑。
- 实验证明了CMD方法的优越性能,包括生成质量和编辑效率等方面。
- CMD方法为解决当前3D生成方法中缺乏组件控制的问题提供了新的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

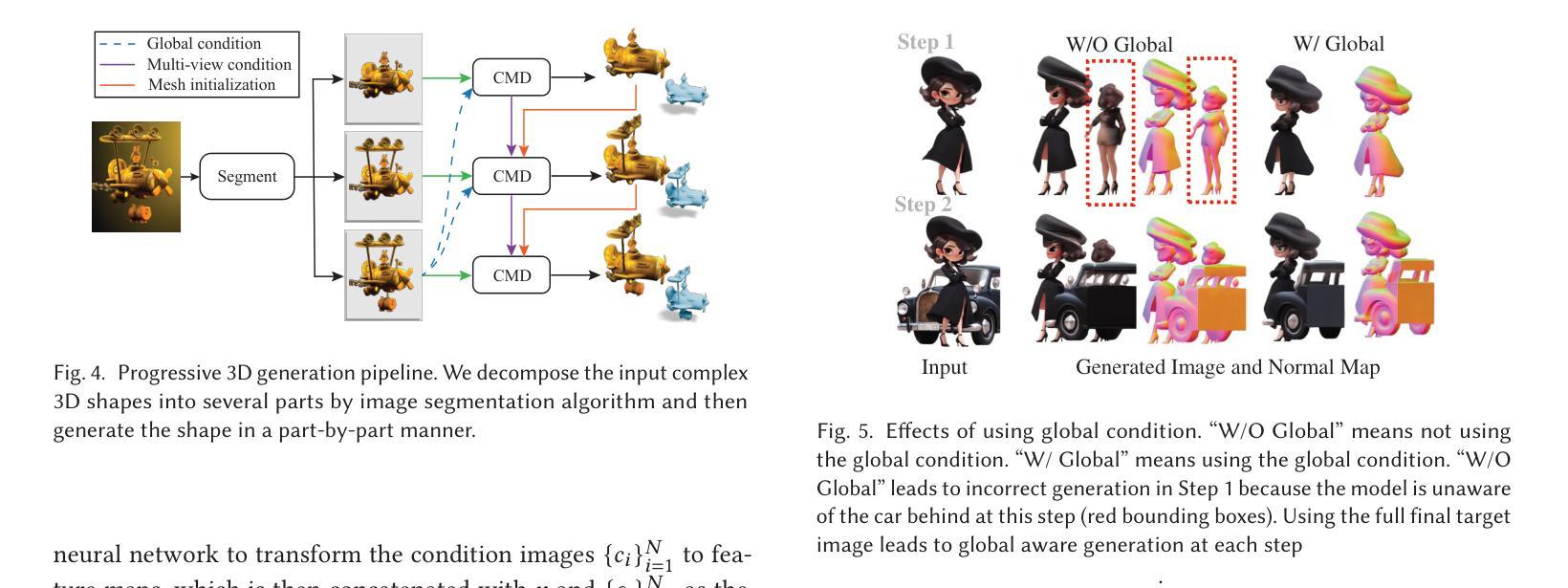

Diffusion-based Adversarial Identity Manipulation for Facial Privacy Protection
Authors:Liqin Wang, Qianyue Hu, Wei Lu, Xiangyang Luo
The success of face recognition (FR) systems has led to serious privacy concerns due to potential unauthorized surveillance and user tracking on social networks. Existing methods for enhancing privacy fail to generate natural face images that can protect facial privacy. In this paper, we propose diffusion-based adversarial identity manipulation (DiffAIM) to generate natural and highly transferable adversarial faces against malicious FR systems. To be specific, we manipulate facial identity within the low-dimensional latent space of a diffusion model. This involves iteratively injecting gradient-based adversarial identity guidance during the reverse diffusion process, progressively steering the generation toward the desired adversarial faces. The guidance is optimized for identity convergence towards a target while promoting semantic divergence from the source, facilitating effective impersonation while maintaining visual naturalness. We further incorporate structure-preserving regularization to preserve facial structure consistency during manipulation. Extensive experiments on both face verification and identification tasks demonstrate that compared with the state-of-the-art, DiffAIM achieves stronger black-box attack transferability while maintaining superior visual quality. We also demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach for commercial FR APIs, including Face++ and Aliyun.
人脸识别(FR)系统的成功引发了严重的隐私担忧,因为可能存在未经授权的监督和社会网络上的用户跟踪。现有的增强隐私的方法无法生成能够保护面部隐私的自然面部图像。在本文中,我们提出了基于扩散的对抗身份操纵(DiffAIM)方法,以生成自然且高度可转移的对抗面部图像,对抗恶意FR系统。具体来说,我们在扩散模型的低维潜在空间中操作面部身份。这涉及在反向扩散过程中迭代地注入基于梯度的对抗性身份指导,逐步引导生成走向所需的对抗性面部图像。该指导针对身份收敛到目标进行优化,同时促进与源之间的语义发散,从而在保持视觉自然性的同时实现有效的伪装。我们进一步结合了结构保持正则化,以保持面部结构一致性在操纵过程中。对面部验证和识别任务的广泛实验表明,与最新技术相比,DiffAIM实现了更强的黑盒攻击转移能力,同时保持了较高的视觉质量。我们还证明了所提出方法在包括Face++和阿里云在内的商业FR API上的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ACM MM 2025
Summary
本文提出了基于扩散模型的对抗性身份操纵技术(DiffAIM),用于生成自然的、高度可迁移的对抗性面部图像,以保护面部隐私并对抗恶意人脸识别(FR)系统。通过操纵低维潜在空间中的面部身份,并在反向扩散过程中逐步引导生成面向目标对抗性面部,实现有效伪装同时保持视觉自然性。结合结构保持正则化,保持面部结构一致性。实验表明,与现有技术相比,DiffAIM在人脸识别和身份验证任务上实现了更强的黑盒攻击迁移性和更高的视觉质量。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型用于生成对抗性面部图像。
- 通过操纵低维潜在空间中的面部身份来生成自然的面部图像。
- 在反向扩散过程中注入基于梯度的对抗性身份指导。
- 优化指导以实现身份收敛并促进语义发散。
- 结合结构保持正则化以保持面部结构一致性。
- 相对于现有技术,DiffAIM具有更强的黑盒攻击迁移性并保持优越的视觉质量。
点此查看论文截图

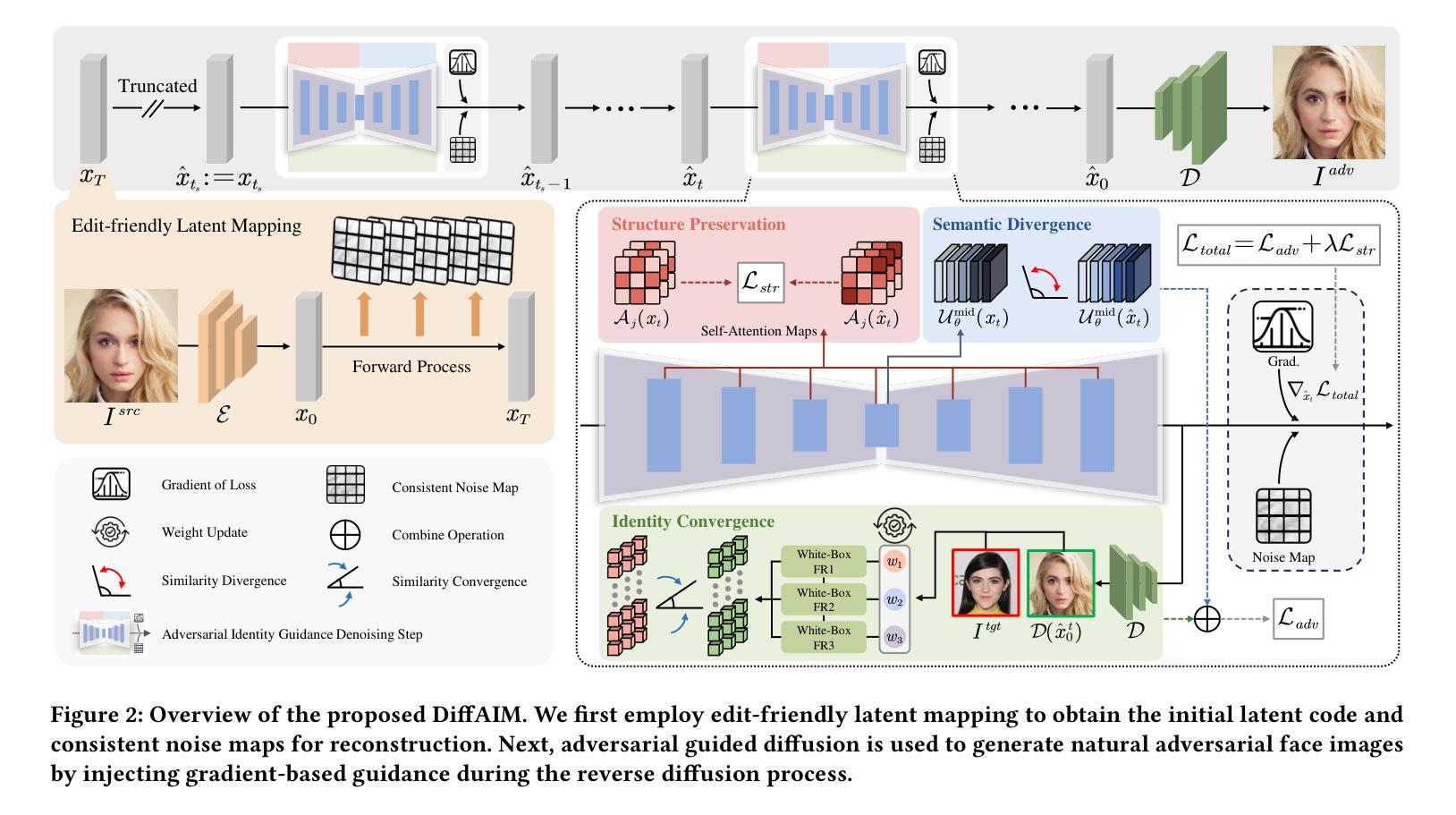
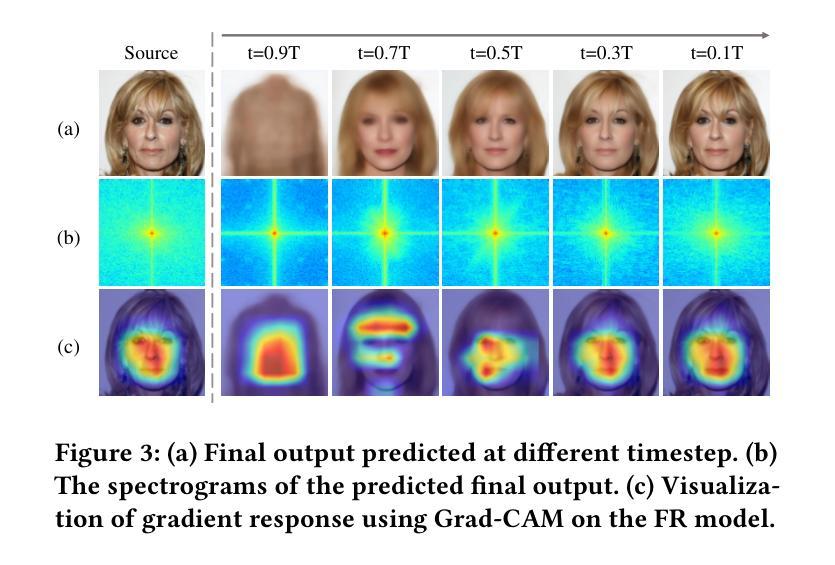
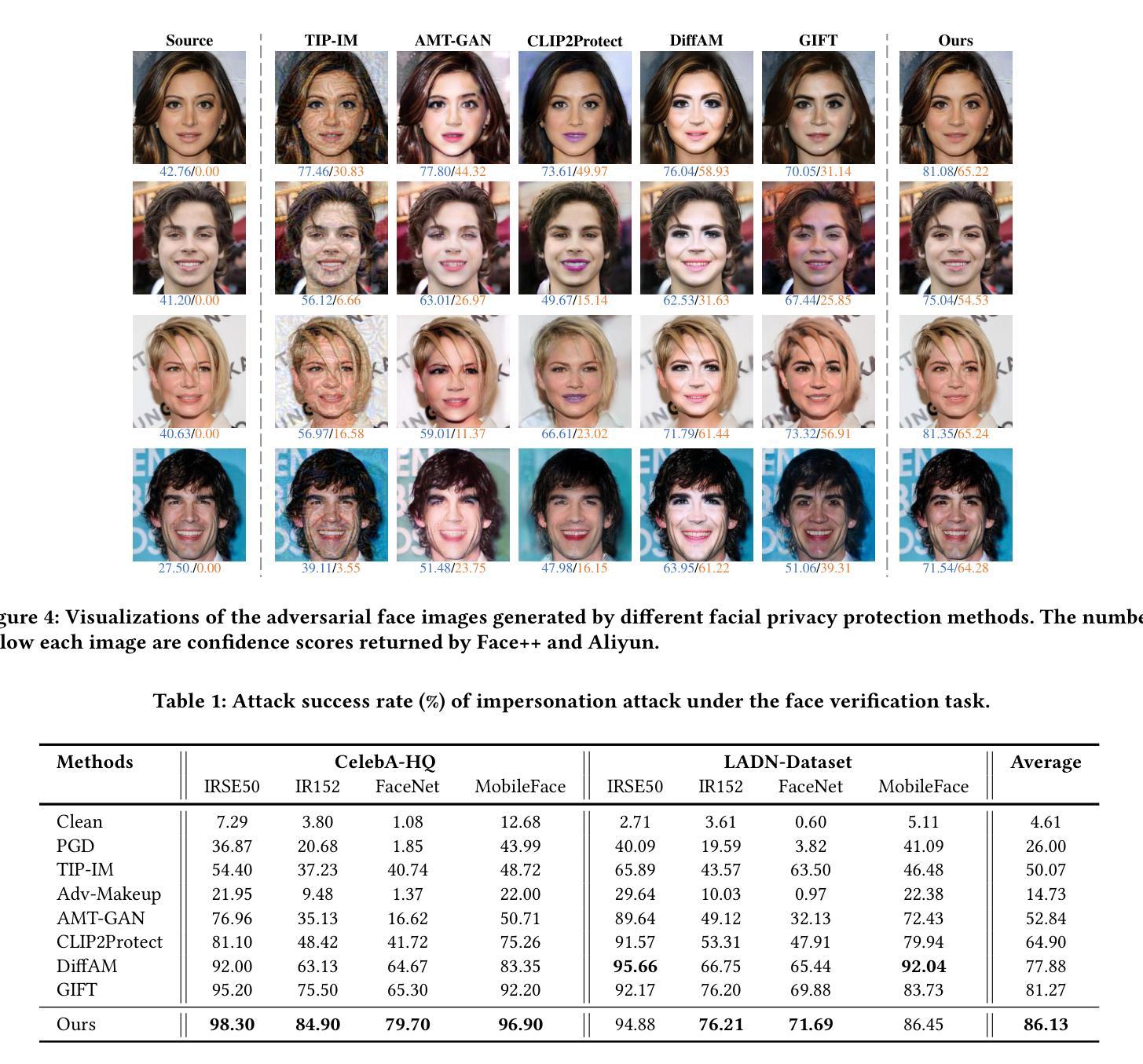
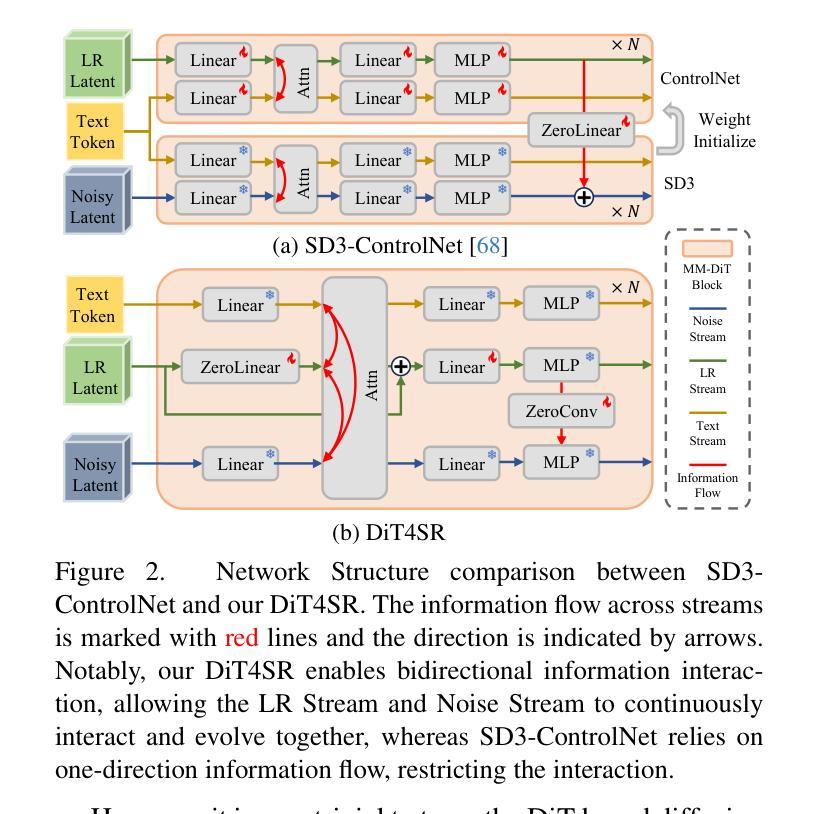
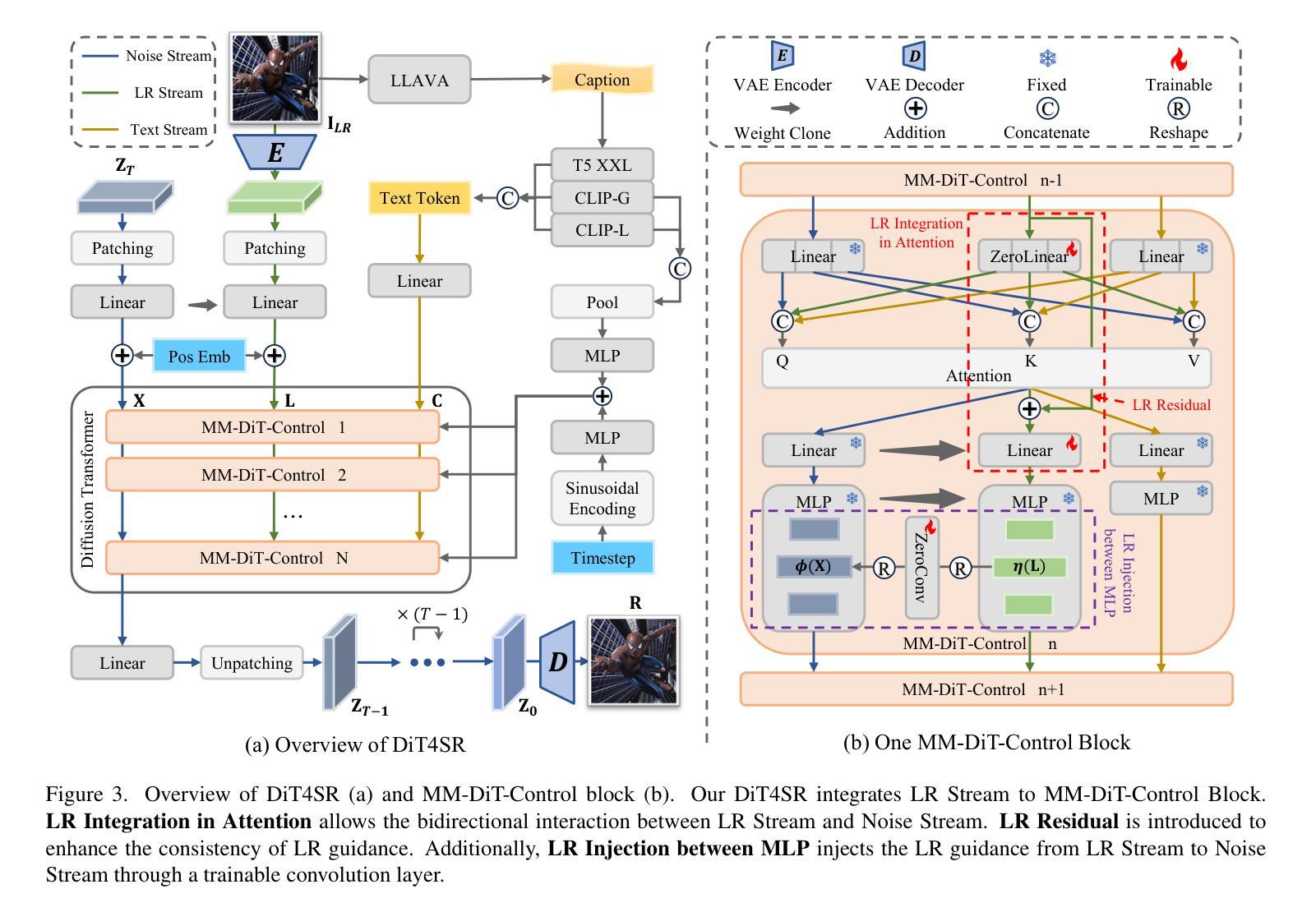
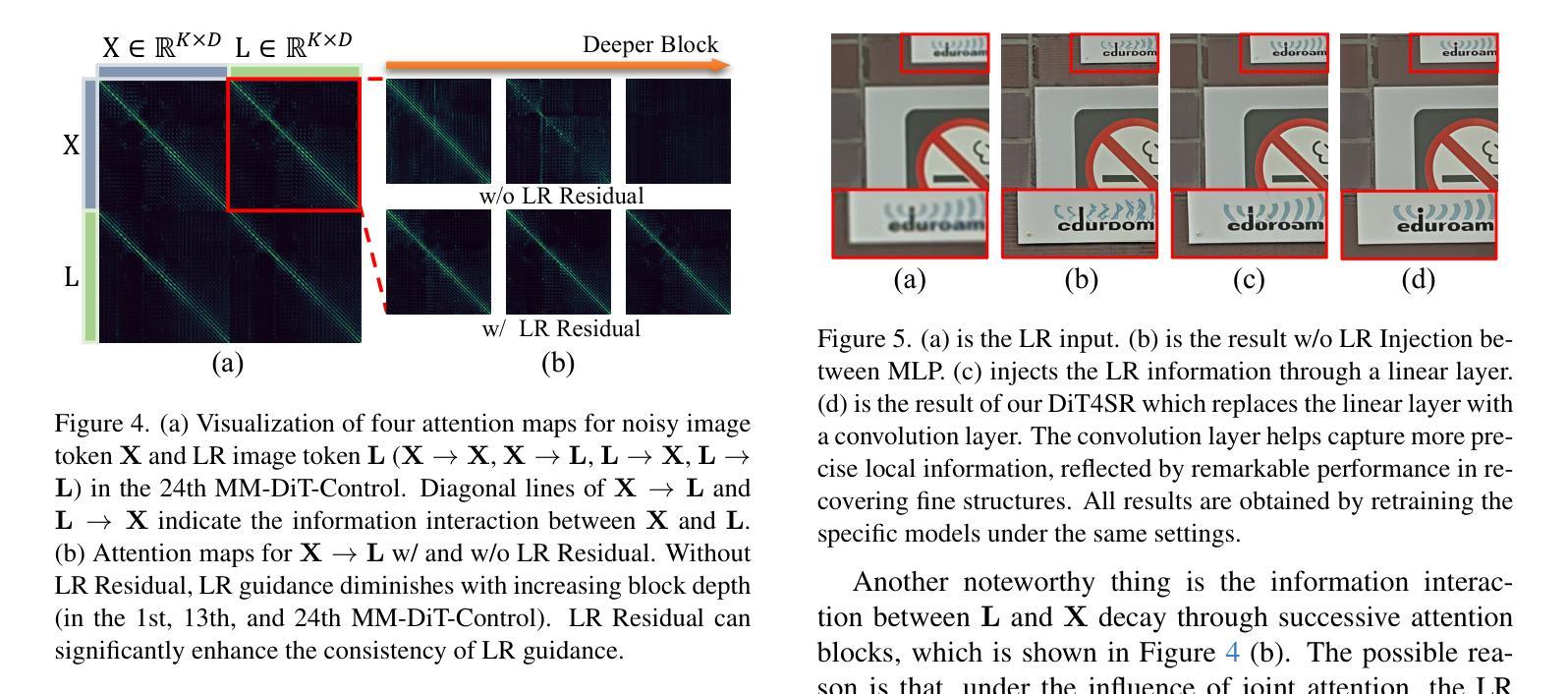
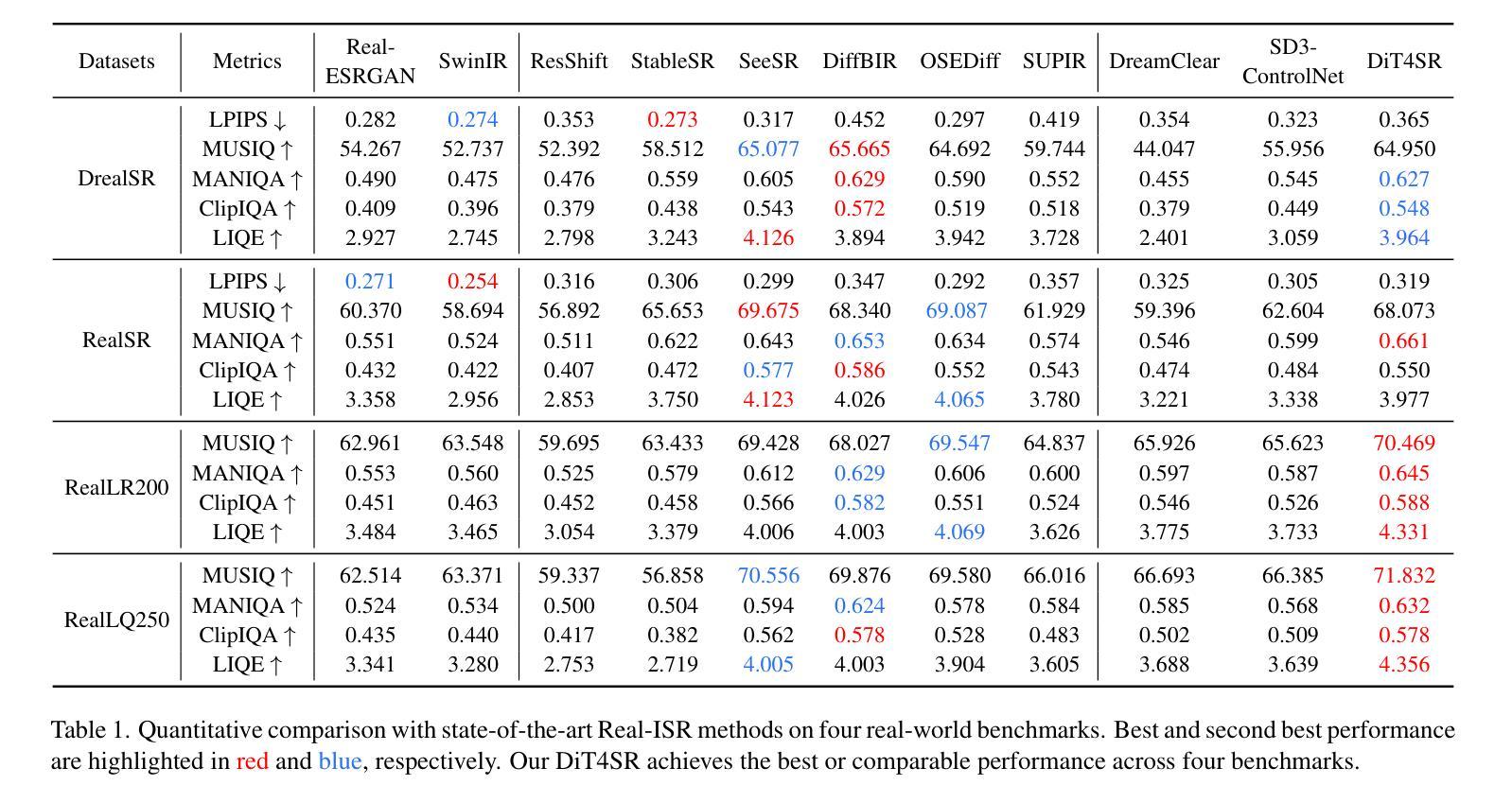
DiT4SR: Taming Diffusion Transformer for Real-World Image Super-Resolution
Authors:Zheng-Peng Duan, Jiawei Zhang, Xin Jin, Ziheng Zhang, Zheng Xiong, Dongqing Zou, Jimmy S. Ren, Chun-Le Guo, Chongyi Li
Large-scale pre-trained diffusion models are becoming increasingly popular in solving the Real-World Image Super-Resolution (Real-ISR) problem because of their rich generative priors. The recent development of diffusion transformer (DiT) has witnessed overwhelming performance over the traditional UNet-based architecture in image generation, which also raises the question: Can we adopt the advanced DiT-based diffusion model for Real-ISR? To this end, we propose our DiT4SR, one of the pioneering works to tame the large-scale DiT model for Real-ISR. Instead of directly injecting embeddings extracted from low-resolution (LR) images like ControlNet, we integrate the LR embeddings into the original attention mechanism of DiT, allowing for the bidirectional flow of information between the LR latent and the generated latent. The sufficient interaction of these two streams allows the LR stream to evolve with the diffusion process, producing progressively refined guidance that better aligns with the generated latent at each diffusion step. Additionally, the LR guidance is injected into the generated latent via a cross-stream convolution layer, compensating for DiT’s limited ability to capture local information. These simple but effective designs endow the DiT model with superior performance in Real-ISR, which is demonstrated by extensive experiments. Project Page: https://adam-duan.github.io/projects/dit4sr/.
大规模预训练扩散模型由于其丰富的生成先验,在解决现实图像超分辨率(Real-ISR)问题上越来越受欢迎。最近的扩散变压器(DiT)的发展在图像生成方面已经超越了传统的基于UNet的架构,这也引发了一个问题:我们可以采用先进的基于DiT的扩散模型进行Real-ISR吗?为此,我们提出了DiT4SR,这是首批尝试将大规模DiT模型用于Real-ISR的工作之一。不同于ControlNet直接注入从低分辨率(LR)图像中提取的嵌入,我们将LR嵌入集成到DiT的原始注意机制中,允许LR潜伏和生成潜伏之间的双向信息流。这两个流的充分交互使LR流随着扩散过程而发展,产生逐步精细的指导,更好地与每个扩散步骤中的生成潜伏对齐。此外,通过跨流卷积层将LR指导注入到生成的潜伏中,弥补了DiT捕捉局部信息能力的不足。这些简单而有效的设计使得DiT模型在Real-ISR方面的性能卓越,这已通过大量实验得到证明。项目页面:https://adam-duan.github.io/projects/dit4sr/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于扩散模型的DiT架构在图像生成领域表现出强大的性能优势,为此研究者提出DiT4SR模型,旨在将大型DiT模型应用于解决现实图像超分辨率问题(Real-ISR)。DiT4SR将低分辨率(LR)嵌入整合到DiT的原生注意力机制中,实现了LR潜值与生成潜值之间的双向信息流。此外,通过跨流卷积层将LR指导注入生成潜值中,增强了DiT捕捉局部信息的能力。这些设计使得DiT模型在Real-ISR任务上表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 大型预训练扩散模型在解决现实图像超分辨率(Real-ISR)问题上日益普及,归功于其丰富的生成先验。
- DiT架构在图像生成领域表现出卓越性能,激发了将其应用于Real-ISR问题的探索。
- DiT4SR模型实现了低分辨率(LR)与生成潜值之间的双向信息流,通过整合LR嵌入到DiT的注意力机制中。
- 跨流卷积层用于将LR指导注入生成潜值中,以补偿DiT捕捉局部信息的局限性。
- DiT4SR模型设计简洁但有效,在Real-ISR任务上展现出卓越性能。
- 该研究通过广泛实验验证了DiT4SR模型的性能优势。
点此查看论文截图

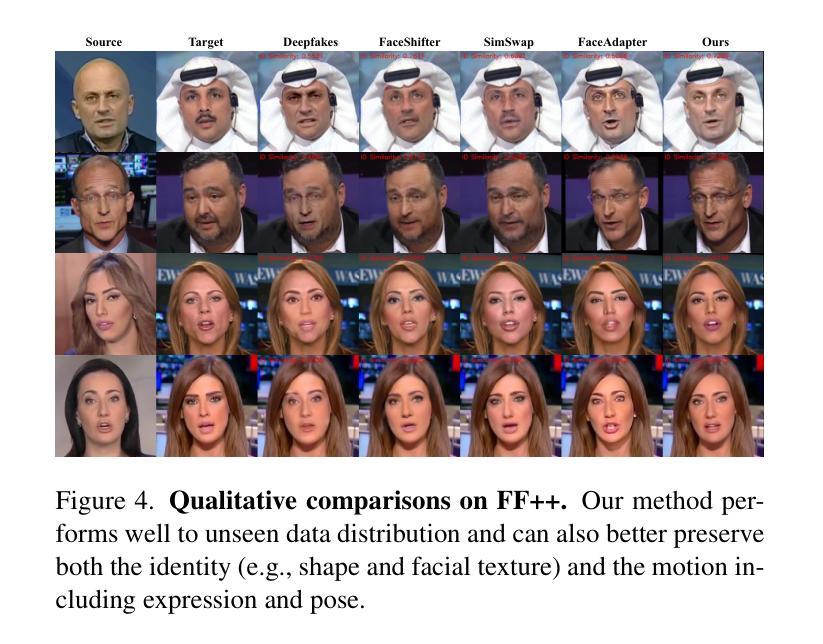
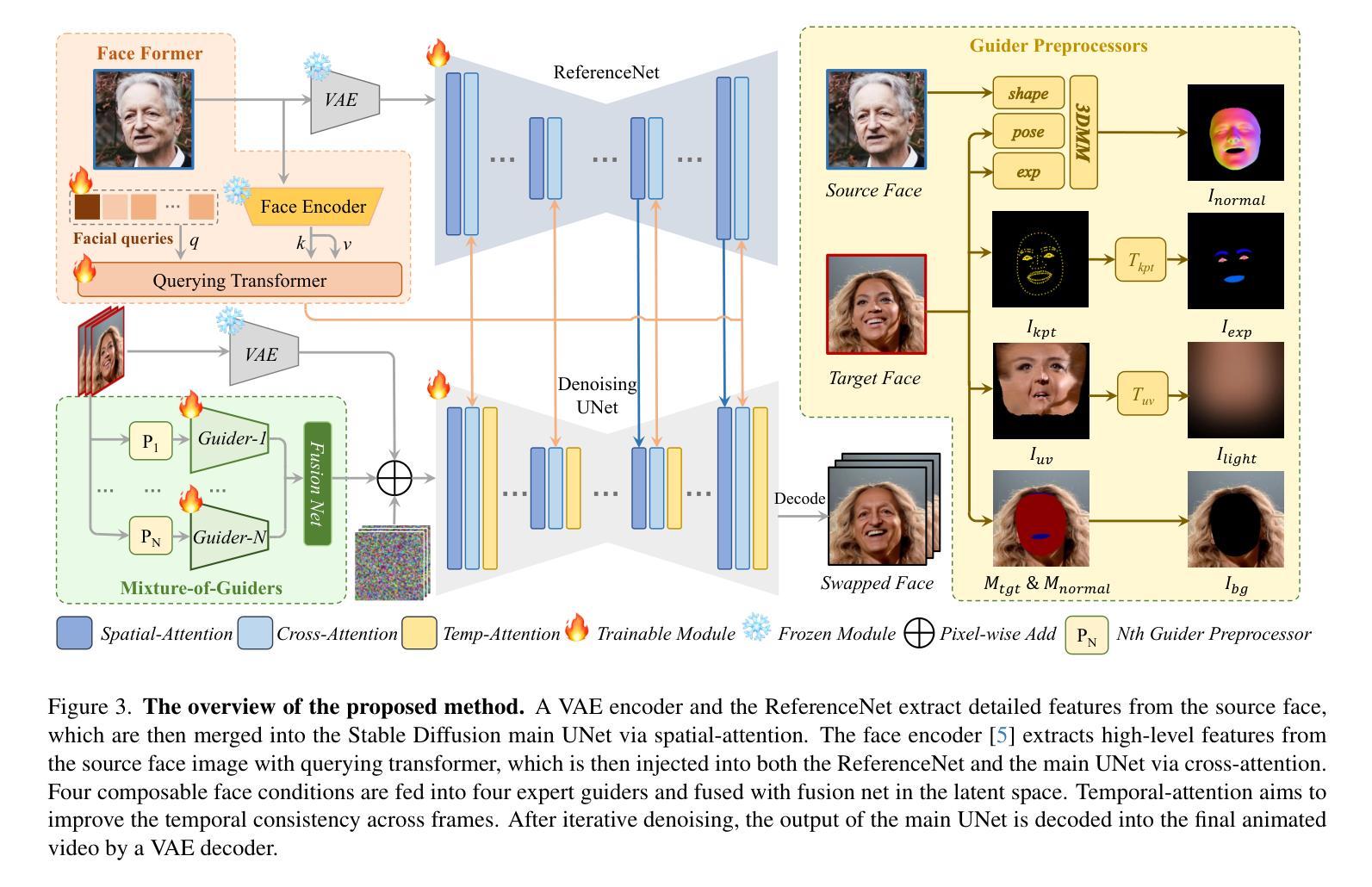
DynamicFace: High-Quality and Consistent Face Swapping for Image and Video using Composable 3D Facial Priors
Authors:Runqi Wang, Yang Chen, Sijie Xu, Tianyao He, Wei Zhu, Dejia Song, Nemo Chen, Xu Tang, Yao Hu
Face swapping transfers the identity of a source face to a target face while retaining the attributes like expression, pose, hair, and background of the target face. Advanced face swapping methods have achieved attractive results. However, these methods often inadvertently transfer identity information from the target face, compromising expression-related details and accurate identity. We propose a novel method DynamicFace that leverages the power of diffusion models and plug-and-play adaptive attention layers for image and video face swapping. First, we introduce four fine-grained facial conditions using 3D facial priors. All conditions are designed to be disentangled from each other for precise and unique control. Then, we adopt Face Former and ReferenceNet for high-level and detailed identity injection. Through experiments on the FF++ dataset, we demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art results in face swapping, showcasing superior image quality, identity preservation, and expression accuracy. Our framework seamlessly adapts to both image and video domains. Our code and results will be available on the project page: https://dynamic-face.github.io/
面部替换技术将源面部的身份转移到目标面部,同时保留目标面部的表情、姿态、发型和背景等属性。先进的面部替换方法已经取得了吸引人的结果。然而,这些方法常常会在不经意间从目标面部转移身份信息,从而损失表情相关的细节和准确的身份。我们提出了一种新的方法DynamicFace,它利用扩散模型的强大功能和即插即用的自适应注意力层进行图像和视频面部替换。首先,我们引入四种精细的面部条件,使用3D面部先验。所有条件都被设计成相互独立,以实现精确和独特的控制。然后,我们采用Face Former和ReferenceNet进行高级和详细的身份注入。通过在FF++数据集上的实验,我们证明我们的方法在面部替换方面达到了最新水平,展示了卓越的图片质量、身份保留和表情准确性。我们的框架可以无缝适应图像和视频领域。我们的代码和结果将在项目页面上进行公开:https://dynamic-face.github.io/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025. Project page: https://dynamic-face.github.io/
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于扩散模型的新型动态面部替换方法,该方法利用精细面部条件和自适应注意力层,在图像和视频面部替换中实现了出色的表现。通过实验结果展示,该方法在面部替换领域达到了最先进的水平,具有高质量图像、身份保留和精确表达等特点。此外,该方法还可以轻松适应图像和视频领域。
Key Takeaways
- 文中提出了一种新的动态面部替换方法,名为DynamicFace,该方法结合了扩散模型和自适应注意力层技术。
- 该方法引入了四种精细面部条件,利用3D面部先验进行设计,以实现精确且独特的控制。
- 采用Face Former和ReferenceNet进行高级和详细的身份注入,以提高面部替换的质量和准确性。
- 在FF++数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法在面部替换领域达到了最先进的水平,具有优秀的图像质量、身份保留和表达准确性。
- DynamicFace框架可以无缝适应图像和视频领域,为多媒体内容创作提供更大的灵活性。
- 该方法通过利用扩散模型的强大能力,有效解决了传统面部替换方法中身份信息转移的问题。
点此查看论文截图




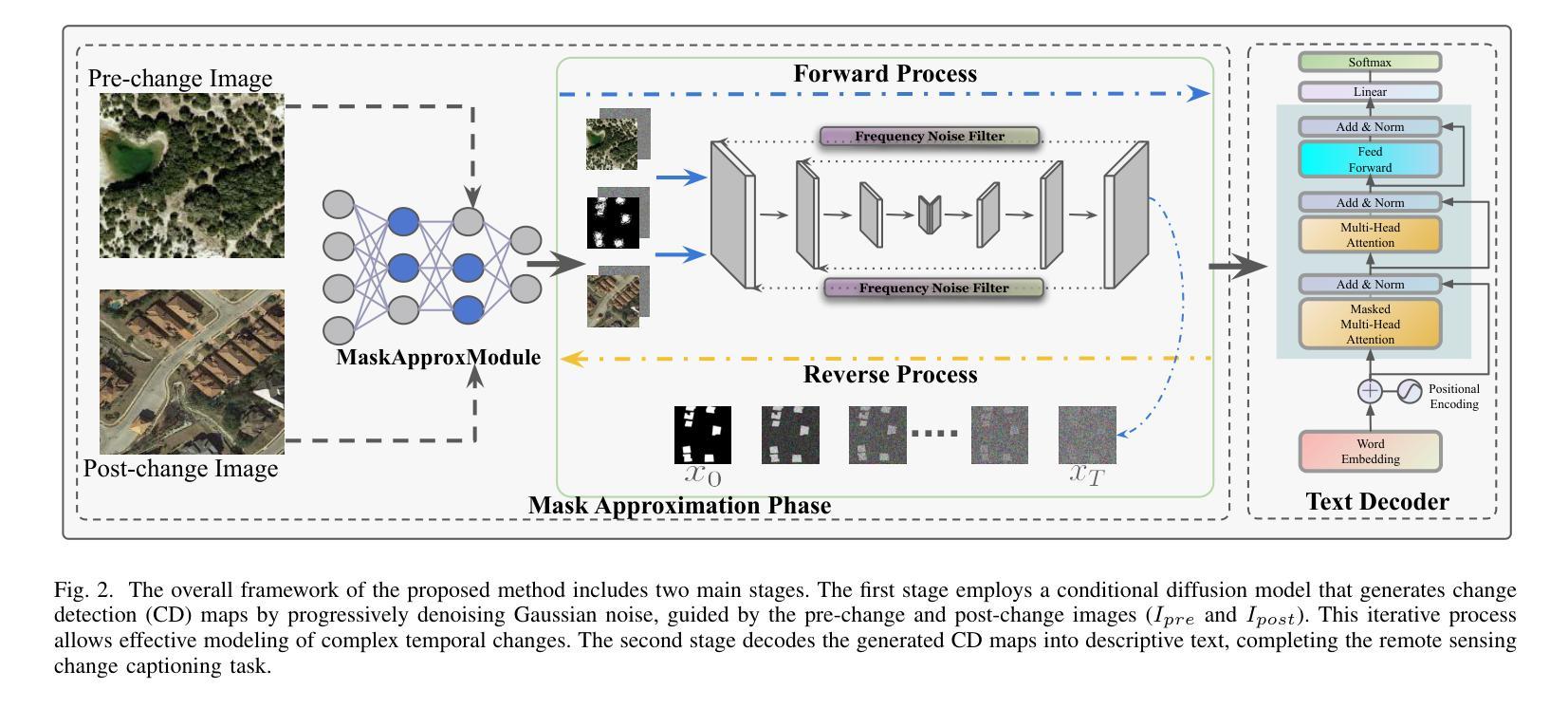
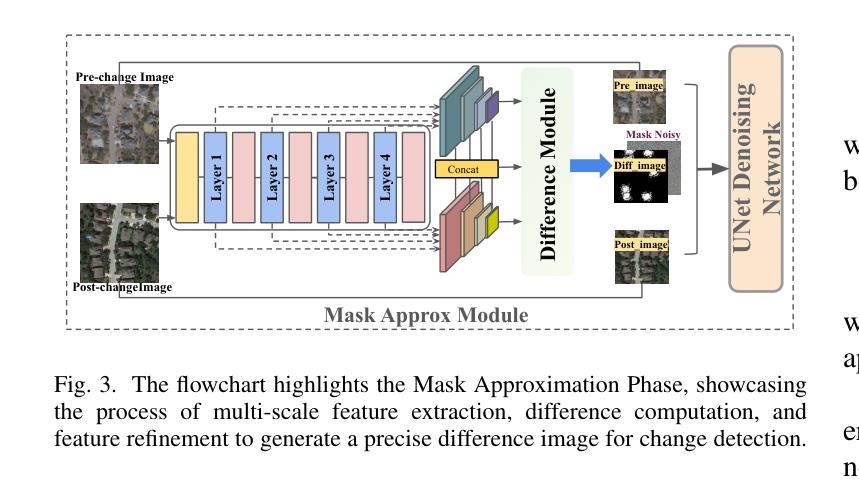
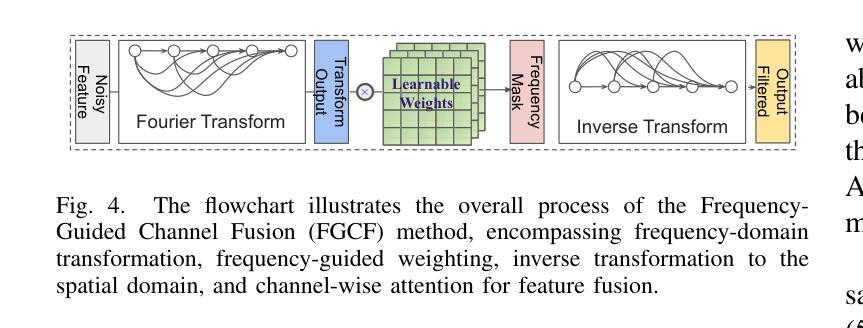
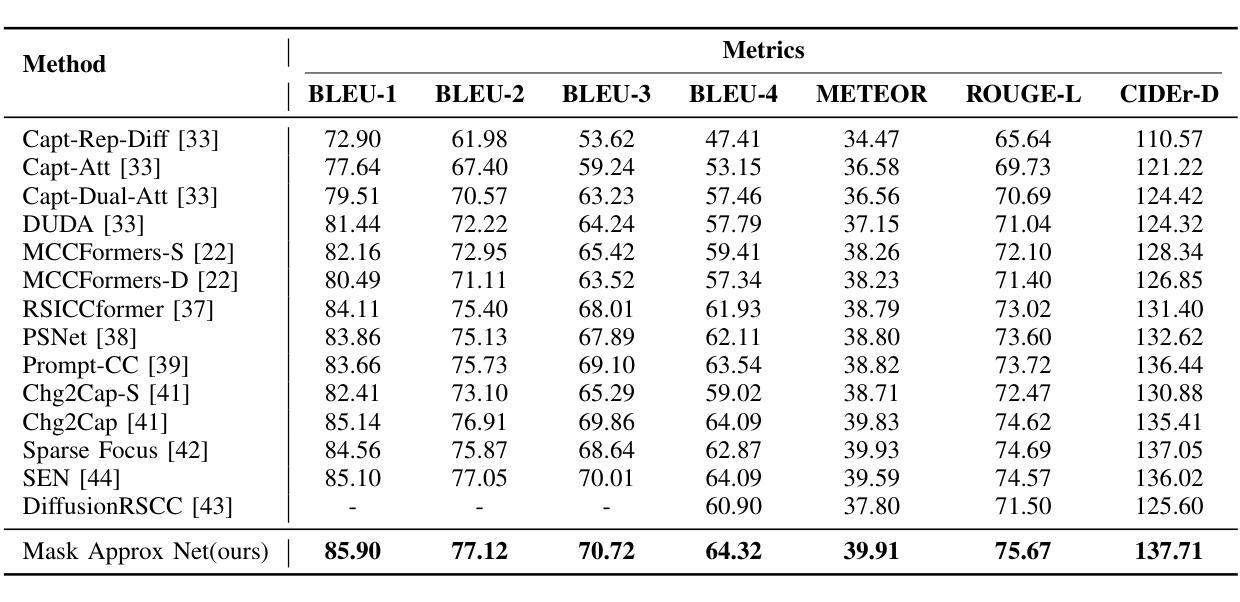
Mask Approximation Net: A Novel Diffusion Model Approach for Remote Sensing Change Captioning
Authors:Dongwei Sun, Jing Yao, Wu Xue, Changsheng Zhou, Pedram Ghamisi, Xiangyong Cao
Remote sensing image change description represents an innovative multimodal task within the realm of remote sensing processing.This task not only facilitates the detection of alterations in surface conditions, but also provides comprehensive descriptions of these changes, thereby improving human interpretability and interactivity.Current deep learning methods typically adopt a three stage framework consisting of feature extraction, feature fusion, and change localization, followed by text generation. Most approaches focus heavily on designing complex network modules but lack solid theoretical guidance, relying instead on extensive empirical experimentation and iterative tuning of network components. This experience-driven design paradigm may lead to overfitting and design bottlenecks, thereby limiting the model’s generalizability and adaptability.To address these limitations, this paper proposes a paradigm that shift towards data distribution learning using diffusion models, reinforced by frequency-domain noise filtering, to provide a theoretically motivated and practically effective solution to multimodal remote sensing change description.The proposed method primarily includes a simple multi-scale change detection module, whose output features are subsequently refined by a well-designed diffusion model.Furthermore, we introduce a frequency-guided complex filter module to boost the model performance by managing high-frequency noise throughout the diffusion process. We validate the effectiveness of our proposed method across several datasets for remote sensing change detection and description, showcasing its superior performance compared to existing techniques. The code will be available at \href{https://github.com/sundongwei}{MaskApproxNet}.
遥感图像变化描述是遥感处理领域的一项创新的多模式任务。这项任务不仅有助于检测地表条件的变化,而且提供了对这些变化的全面描述,从而提高了人类可解释性和交互性。当前的深度学习方法通常采用一个三阶段的框架,包括特征提取、特征融合和变化定位,然后是文本生成。大多数方法过于注重设计复杂的网络模块,但缺乏坚实的理论指导,而是依赖于大量的经验实验和网络组件的迭代调整。这种经验驱动的设计范式可能导致过度拟合和设计瓶颈,从而限制了模型的通用性和适应性。为了解决这些局限性,本文提出了一种基于扩散模型的数据分布学习范式,辅以频域噪声滤波,为多模式遥感变化描述提供理论驱动和实践有效的解决方案。该方法主要包括一个简单的多尺度变化检测模块,其输出特征随后由一个设计精良的扩散模型进行细化。此外,我们引入了一个频率引导复杂滤波器模块,通过管理扩散过程中的高频噪声来提高模型性能。我们在多个遥感变化检测和描述的数据集上验证了所提出方法的有效性,展示了其相较于现有技术的卓越性能。代码将在MaskApproxNet(https://github.com/sundongwei)上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
远程遥感图像变化描述是一项新颖的跨模态任务。传统深度学习方法通常采用三阶段框架,包括特征提取、特征融合和变化定位,然后进行文本生成。然而,这些方法主要依赖于经验实验和组件迭代调整,缺乏坚实的理论基础。为解决这些问题,本文提出了基于扩散模型的数据分布学习范式,并结合频域噪声滤波,为跨模态遥感变化描述提供了理论和实践上的解决方案。该方法包括一个简单多尺度变化检测模块和一个精心设计扩散模型,通过频率引导复杂滤波器模块提升性能。本文的方法在多数据集上进行了验证,展现出对现有的优越性。相关代码可通过链接查看。
Key Takeaways
- 远程遥感图像变化描述是一项重要的跨模态任务,有助于表面条件变化的检测和描述。
- 传统深度学习方法采用三阶段框架处理这个任务,但存在过度依赖经验实验和组件调整的问题。
- 本文提出基于扩散模型的解决方案,强调数据分布学习,以改善模型的泛化和适应性。
- 方法包括简单多尺度变化检测模块和扩散模型,其中扩散模型经过精心设计以优化性能。
- 为提升性能引入了频率引导复杂滤波器模块,管理扩散过程中的高频噪声。
- 在多个数据集上的验证显示,本文提出的方法在遥感变化检测和描述方面表现出卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图