⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-09 更新
AI-Driven Cytomorphology Image Synthesis for Medical Diagnostics
Authors:Jan Carreras Boada, Rao Muhammad Umer, Carsten Marr
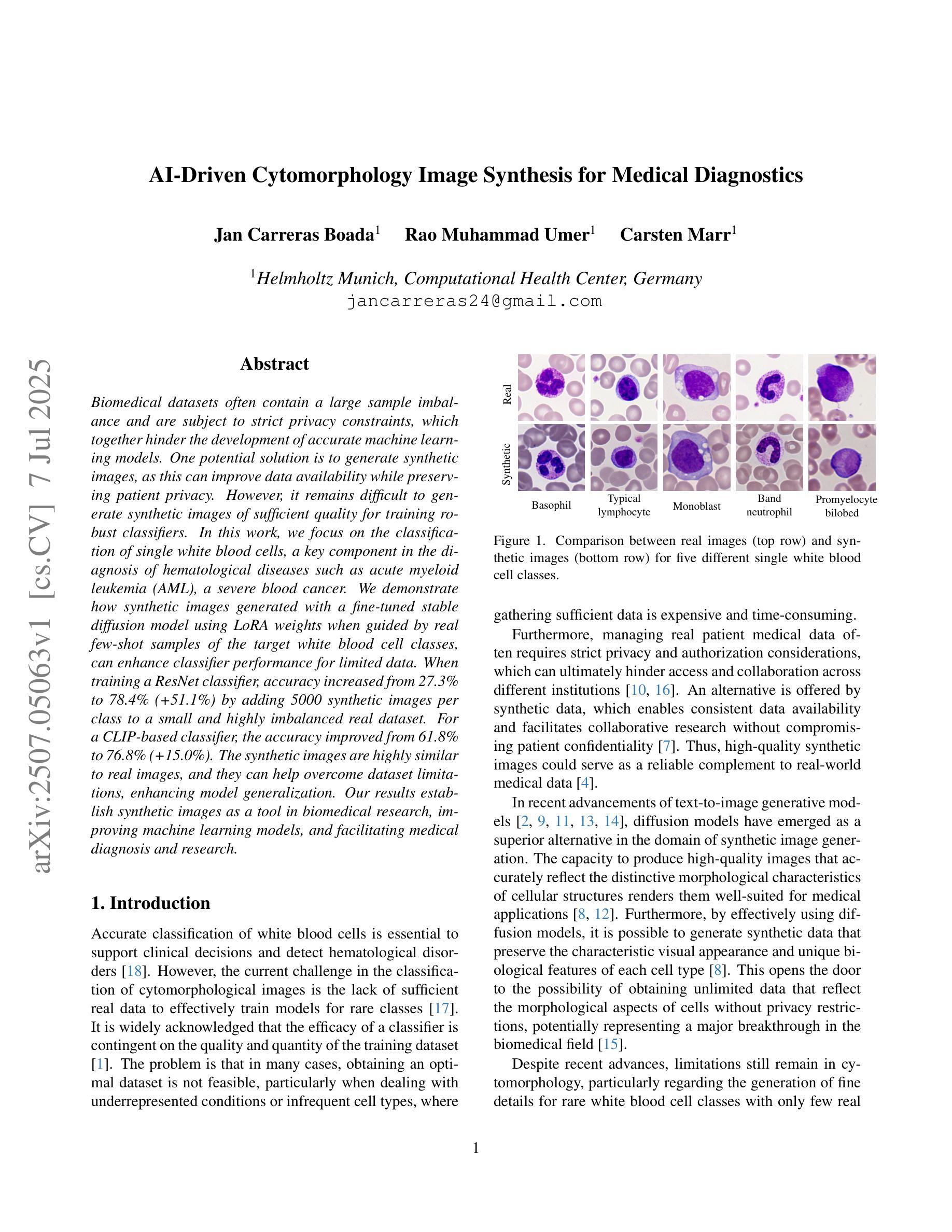
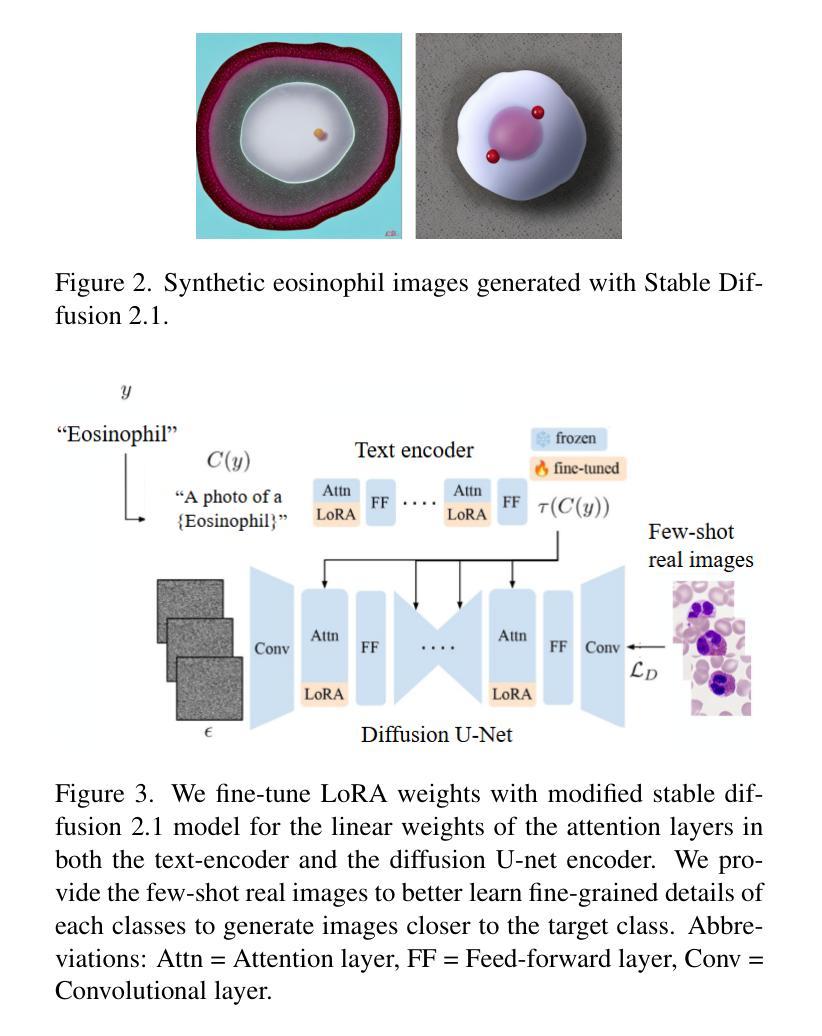
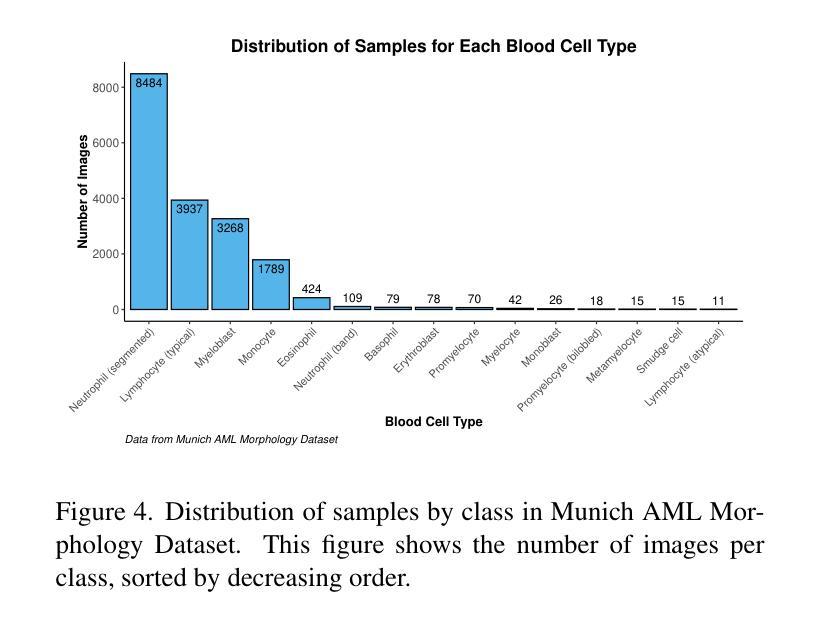
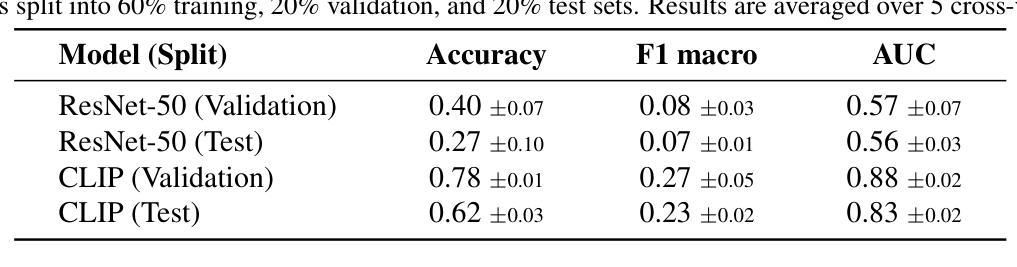
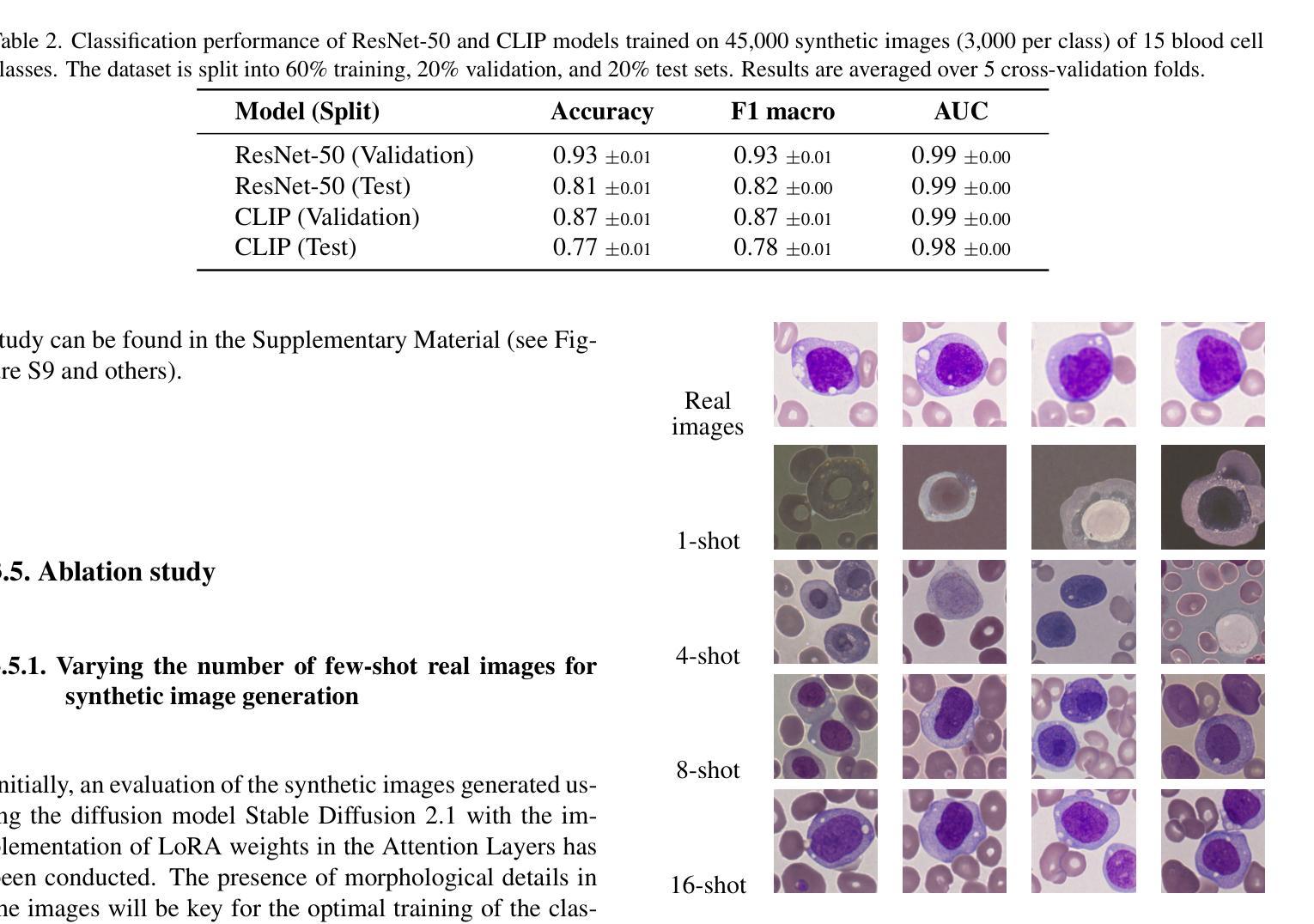
Biomedical datasets often contain a large sample imbalance and are subject to strict privacy constraints, which together hinder the development of accurate machine learning models. One potential solution is to generate synthetic images, as this can improve data availability while preserving patient privacy. However, it remains difficult to generate synthetic images of sufficient quality for training robust classifiers. In this work, we focus on the classification of single white blood cells, a key component in the diagnosis of hematological diseases such as acute myeloid leukemia (AML), a severe blood cancer. We demonstrate how synthetic images generated with a fine-tuned stable diffusion model using LoRA weights when guided by real few-shot samples of the target white blood cell classes, can enhance classifier performance for limited data. When training a ResNet classifier, accuracy increased from 27.3% to 78.4% (+51.1%) by adding 5000 synthetic images per class to a small and highly imbalanced real dataset. For a CLIP-based classifier, the accuracy improved from 61.8% to 76.8% (+15.0%). The synthetic images are highly similar to real images, and they can help overcome dataset limitations, enhancing model generalization. Our results establish synthetic images as a tool in biomedical research, improving machine learning models, and facilitating medical diagnosis and research.
生物医学数据集通常包含大量的样本不平衡问题,并受到严格的隐私约束的限制,这两者共同阻碍了准确机器学习模型的发展。一种潜在的解决方案是生成合成图像,因为这可以提高数据可用性同时保护患者隐私。然而,生成足够质量的合成图像以训练稳健的分类器仍然是一项挑战。在这项工作中,我们专注于单一白血球的分类,这是急性髓系白血病(AML)等血液癌疾病诊断的关键组成部分。我们展示了如何使用经过微调的稳定扩散模型,通过真实少量目标白血球类别的样本作为指导来生成合成图像,以提高有限数据的分类器性能。当训练ResNet分类器时,通过在高度不平衡的小型真实数据集中每类添加5000张合成图像,准确率从27.3%提高到78.4%(+51.1%)。对于基于CLIP的分类器,准确率从61.8%提高到76.8%(+15.0%)。合成图像与真实图像高度相似,有助于克服数据集限制,提高模型的泛化能力。我们的结果将合成图像确立为生物医学研究中的一种工具,可改善机器学习模型,并促进医学诊断和研究的进行。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 6 figures, 2 tables. Final Degree Project (TFG) submitted at ESCI-UPF and conducted at Helmholtz Munich
Summary
生物医学数据集中存在样本不均衡和隐私保护难题,合成图像能增加数据可用性和保护患者隐私。研究使用微调后的稳定扩散模型生成目标白细胞类别的真实少样本引导的合成图像,能提高分类器性能。使用合成图像后,分类器准确率显著提高。
Key Takeaways
- 生物医学数据集面临样本不均衡和隐私保护挑战。
- 合成图像能提高数据可用性和保护患者隐私。
- 研究使用微调稳定扩散模型生成合成图像,用于白细胞分类。
- 使用合成图像后,分类器性能显著提高,准确率增加。
- 合成图像与真实图像高度相似。
- 合成图像有助于克服数据集限制,提高模型泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图
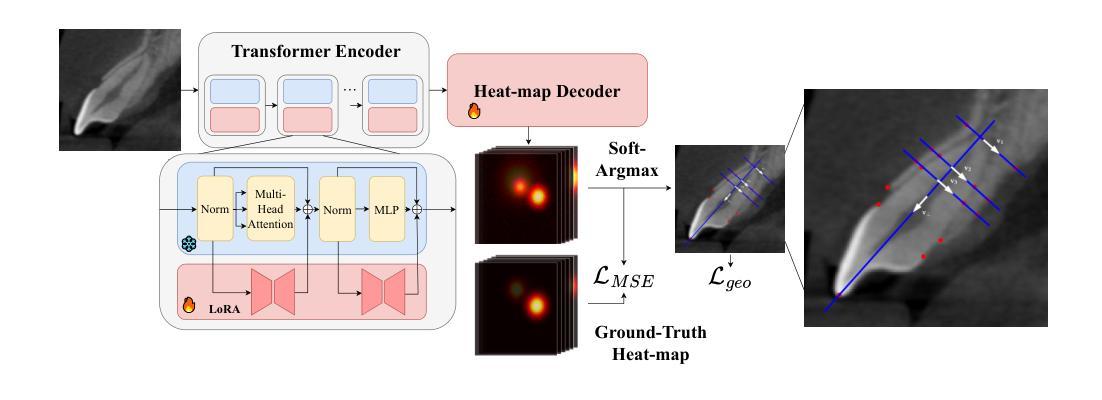
Geometric-Guided Few-Shot Dental Landmark Detection with Human-Centric Foundation Model
Authors:Anbang Wang, Marawan Elbatel, Keyuan Liu, Lizhuo Lin, Meng Lan, Yanqi Yang, Xiaomeng Li
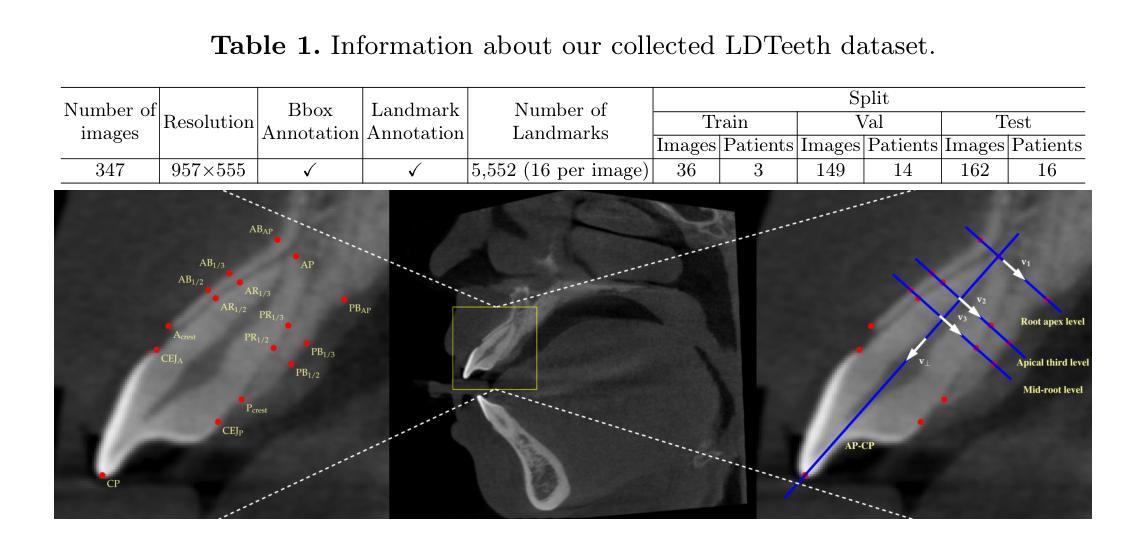
Accurate detection of anatomic landmarks is essential for assessing alveolar bone and root conditions, thereby optimizing clinical outcomes in orthodontics, periodontics, and implant dentistry. Manual annotation of landmarks on cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) by dentists is time-consuming, labor-intensive, and subject to inter-observer variability. Deep learning-based automated methods present a promising approach to streamline this process efficiently. However, the scarcity of training data and the high cost of expert annotations hinder the adoption of conventional deep learning techniques. To overcome these challenges, we introduce GeoSapiens, a novel few-shot learning framework designed for robust dental landmark detection using limited annotated CBCT of anterior teeth. Our GeoSapiens framework comprises two key components: (1) a robust baseline adapted from Sapiens, a foundational model that has achieved state-of-the-art performance in human-centric vision tasks, and (2) a novel geometric loss function that improves the model’s capacity to capture critical geometric relationships among anatomical structures. Experiments conducted on our collected dataset of anterior teeth landmarks revealed that GeoSapiens surpassed existing landmark detection methods, outperforming the leading approach by an 8.18% higher success detection rate at a strict 0.5 mm threshold-a standard widely recognized in dental diagnostics. Code is available at: https://github.com/xmed-lab/GeoSapiens.
准确检测解剖部位标志对于评估牙槽骨和牙根状况至关重要,这对于优化口腔正畸学、牙周病学和牙科植入物的临床结果至关重要。牙医在锥形束计算机断层扫描(CBCT)上对标志进行手动注释耗时且劳力密集,并存在观察者间变异。基于深度学习的自动化方法提供了一个有效优化此流程的有前途的方法。然而,训练数据的稀缺和专家注释的高成本阻碍了传统深度学习技术的采用。为了克服这些挑战,我们引入了GeoSapiens,这是一个用于稳健牙齿标志检测的新型少样本学习框架,该框架使用有限注释的上前牙CBCT数据。我们的GeoSapiens框架包含两个关键组成部分:(1)一个基于Sapiens的稳健基线,Sapiens是一个在以人为中心的任务中达到最新水平的基准模型;(2)一个新的几何损失函数,提高了模型捕捉解剖结构之间关键几何关系的能力。在我们收集的上前牙标志数据集上进行的实验表明,GeoSapiens超越了现有的标志检测方法,在严格的0.5毫米阈值标准下,成功检测率比领先的方法高出8.18%,这一标准在牙科诊断中得到了广泛认可。代码可在:https://github.com/xmed-lab/GeoSapiens获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025
Summary:
本文介绍了基于深度学习技术的GeoSapiens框架,用于通过少量标注的锥形束计算机断层扫描(CBCT)数据,实现对牙齿解剖标志点的准确、高效检测。该框架结合了强大的基线模型和新型几何损失函数,能有效捕捉解剖结构间的几何关系。在牙齿前部标志点检测数据集上的实验表明,GeoSapiens在检测成功率上超越了现有方法,达到了业界领先的性能水平。该代码已公开于GitHub上。
Key Takeaways:
- GeoSapiens框架对于牙齿解剖标志点的自动检测具有重大意义,可应用于正畸、牙周病和种植牙等领域的临床评估。
- 传统的深度学习技术因训练数据稀缺和标注成本高昂而面临挑战,GeoSapiens通过引入少样本学习技术解决了这一问题。
- GeoSapiens包含两个关键组件:基于Sapiens模型的稳健基线,以及用于增强模型捕捉几何关系能力的几何损失函数。
- 实验结果显示,GeoSapiens在牙齿前部标志点检测上取得了突破性的成果,成功检测率高于现有方法8.18%。
- 该框架的应用有助于简化锥形束计算机断层扫描数据的处理流程,提高诊断效率及准确性。
- 代码已在GitHub上公开,便于研究者使用和进一步开发。
- 该研究展示了深度学习和少样本学习在医学图像处理中的巨大潜力。
点此查看论文截图

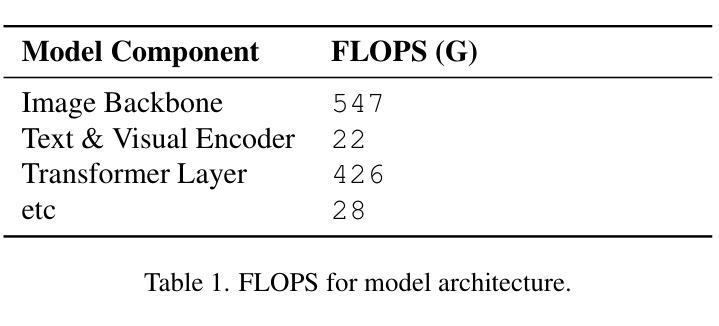
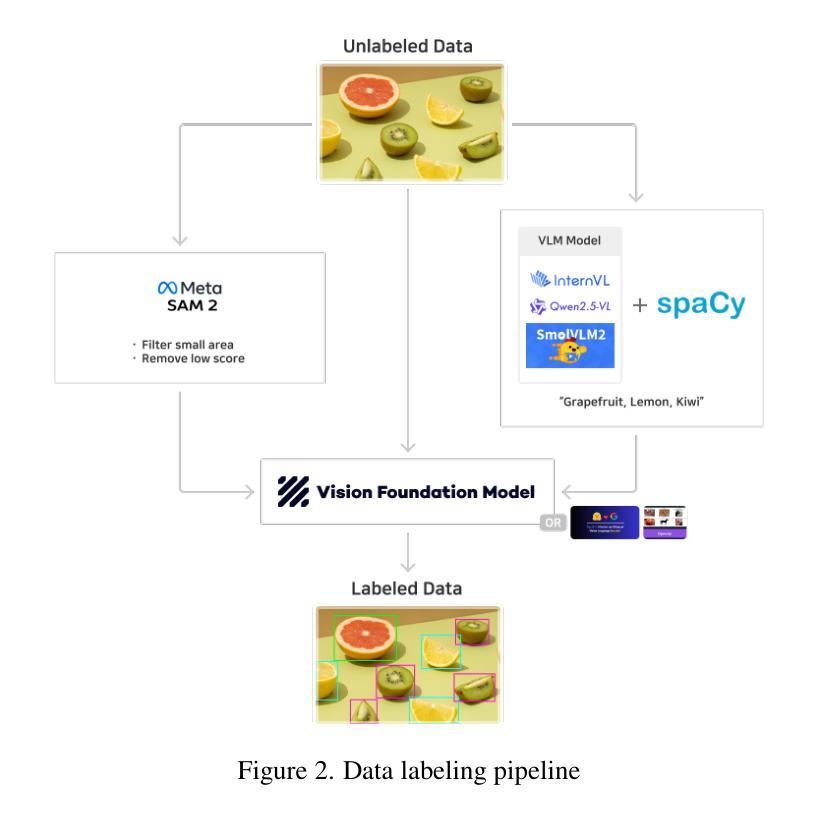
ZERO: Multi-modal Prompt-based Visual Grounding
Authors:Sangbum Choi, Kyeongryeol Go
Recent advances in artificial intelligence have led to the emergence of foundation models, large-scale pre-trained neural networks that serve as versatile starting points for a wide range of downstream tasks. In this work, we present ZERO, a zero-shot multi-prompt object detection model specifically designed for robust, production-ready deployment across diverse industrial domains. ZERO integrates direct image input with multiple user-defined prompts, which can include both textual and visual cues, and processes them through dedicated encoders to generate accurate detection outputs. The model architecture is optimized for scalability, with a total of 1.033 TFLOPS and 622.346 million parameters, and is trained using a domain-specific image database exceeding one billion images. For the CVPR 2025 Foundational Few-Shot Object Detection (FSOD) Challenge, we introduce a domain-specific fine-tuning strategy that emphasizes prompt diversity and conservative pseudo-labeling, enabling effective adaptation to new domains with minimal supervision. Our approach demonstrates practical advantages in flexibility, efficiency, and real-world applicability, achieving strong performance on the RF20VL-fsod benchmark despite limited annotation budgets. The results highlight the potential of prompt-driven, data-centric AI for scalable and adaptive object detection in dynamic industrial environments.
近期人工智能的进步催生了基础模型的出现,这些基础模型是大型预训练神经网络,可作为多种下游任务的通用起点。在这项工作中,我们推出了ZERO,这是一款零样本多提示对象检测模型,专为在各种工业领域中稳健、投入生产的部署而设计。ZERO直接整合图像输入与用户定义的多个提示,这些提示可以包括文本和视觉线索,并通过专用编码器进行处理,以生成准确的检测结果。该模型架构进行了优化,以实现可扩展性,总计1.033 TFLOPS和6.223亿个参数,并使用超过1亿张图像的专业图像数据库进行训练。针对CVPR 2025基础少样本对象检测(FSOD)挑战,我们引入了一种领域特定的微调策略,该策略强调提示多样性和保守伪标签,能够在新领域进行有效适应,监督最少。我们的方法在灵活性、效率和现实世界应用方面展现了实际优势,在RF20VL-fsod基准测试中取得了强劲的表现,尽管标注预算有限。结果突出了提示驱动、以数据为中心的AI在动态工业环境中进行可扩展和自适应对象检测的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF A solution report for CVPR2025 Foundational FSOD Challenge
Summary
基于人工智能的最新进展,出现了一种名为“ZERO”的零样本多提示目标检测模型。该模型能够跨多个工业领域进行稳健、生产就绪部署,并具有出色的灵活性和效率。它结合了直接图像输入和用户定义的多个提示(包括文本和视觉线索),通过专用编码器进行处理以生成准确的检测结果。优化的模型架构使得它能够适应大规模的数据库并具有很高的扩展性,并使用超过一亿张图片的领域特定图像数据库进行训练。此外,在CVPR 2025 Few-Shot Object Detection挑战中引入了一种特定领域的微调策略,它通过强调提示多样性和保守伪标签技术实现了对无标签环境的有效适应。该研究突显了提示驱动型数据中心人工智能在动态工业环境中实现可扩展和自适应目标检测的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- “ZERO”模型是一个用于广泛下游任务的零样本多提示目标检测模型。
- 该模型结合了直接图像输入和用户定义的提示(包括文本和视觉线索)。
- 模型架构经过优化,具有可扩展性,适用于大规模数据库和大规模训练。
- 使用超过一亿张图片的特定领域图像数据库进行训练。
- 特定领域的微调策略结合了提示多样性和保守伪标签技术以适应无标签环境。
点此查看论文截图

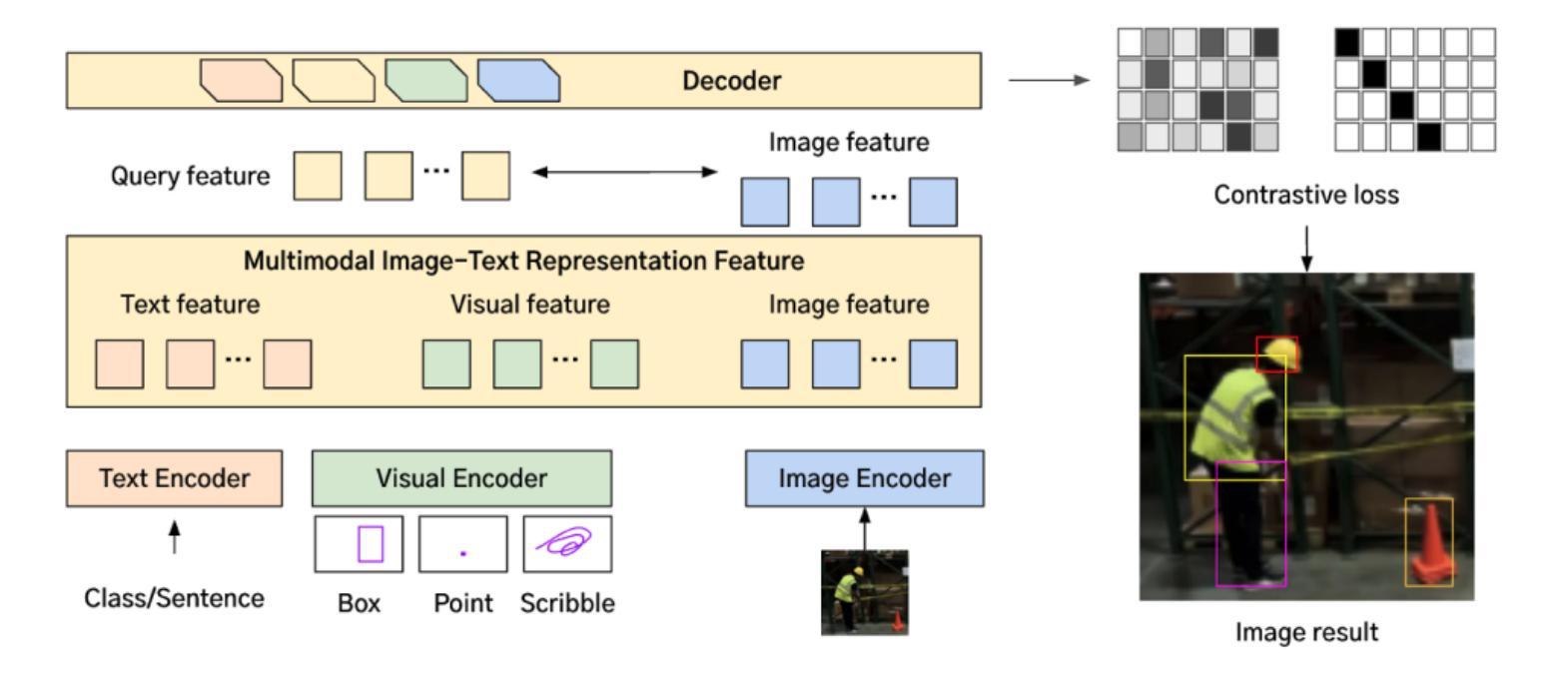
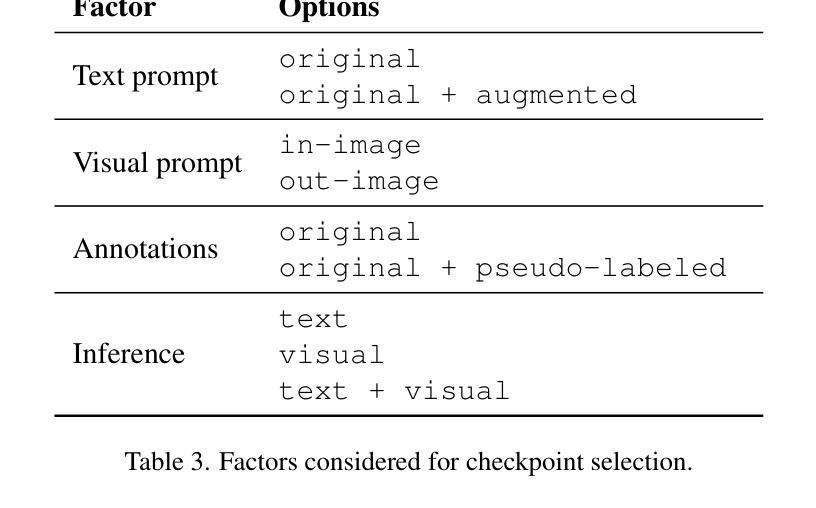
Context Tuning for In-Context Optimization
Authors:Jack Lu, Ryan Teehan, Zhenbang Yang, Mengye Ren
We introduce Context Tuning, a simple and effective method to significantly enhance few-shot adaptation of language models (LLMs) without fine-tuning model parameters. While prompt-based adaptation techniques have demonstrated the effectiveness of lightweight adaptation methods for large language models (LLMs), they typically initialize a trainable prompt or prefix with irrelevant tokens for the task at hand. In contrast, Context Tuning initializes the trainable prompt or prefix with task-specific demonstration examples, leveraging the model’s inherent In-Context Learning (ICL) ability to extract relevant information for improved few-shot learning performance. Extensive evaluations on benchmarks such as CrossFit, UnifiedQA, MMLU, BIG-Bench Hard, and ARC demonstrate that Context Tuning outperforms traditional prompt-based adaptation methods and achieves competitive accuracy to Test-Time Training with significantly higher training efficiency.
我们介绍了Context Tuning,这是一种简单有效的方法,可以在不微调模型参数的情况下显著提高语言模型的少量适应(LLMs)。虽然基于提示的适应技术已经证明了为大型语言模型(LLMs)进行轻量化适应方法的有效性,但它们通常使用与手头任务不相关的令牌来初始化可训练的提示或前缀。相比之下,Context Tuning使用任务特定的演示示例来初始化可训练的提示或前缀,利用模型固有的上下文学习(ICL)能力来提取相关信息,以提高少量学习的性能。在CrossFit、UnifiedQA、MMLU、BIG-Bench Hard和ARC等基准测试上的广泛评估表明,Context Tuning优于传统的基于提示的适应方法,其测试精度与测试时的训练相当,但训练效率更高。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF A short version of this paper has been accepted for publication in the Workshop on Test-Time Adaptation (PUT) at the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML) 2025
Summary
本文介绍了Context Tuning,这是一种简单有效的方法,可在不微调语言模型参数的情况下显著提高语言模型的少量适应性。相较于传统基于提示的适应方法使用无关任务的标记来初始化可训练提示或前缀,Context Tuning通过以任务特定演示示例来初始化可训练提示或前缀,并利用模型的固有上下文学习能力提取相关信息,以提高少样本学习的性能。在多个基准测试上的评估结果表明,Context Tuning优于传统基于提示的适应方法,并实现了与测试时间训练相当的精度,同时显著提高训练效率。
Key Takeaways
- Context Tuning是一种增强语言模型少量适应性的方法,无需微调模型参数。
- 传统基于提示的适应方法使用无关任务的标记初始化可训练提示或前缀,而Context Tuning利用任务特定演示示例进行初始化。
- Context Tuning利用语言模型的固有上下文学习能力提取相关信息,提高少样本学习性能。
- Context Tuning在多个基准测试上的表现优于传统基于提示的适应方法。
- Context Tuning实现了与测试时间训练相当的精度。
- Context Tuning显著提高训练效率。
点此查看论文截图

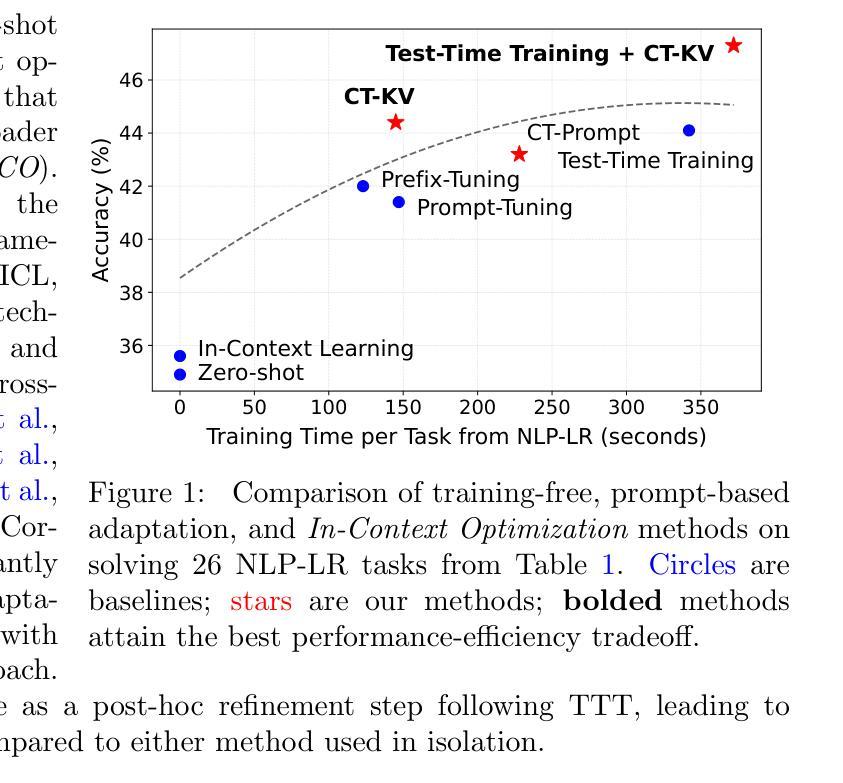
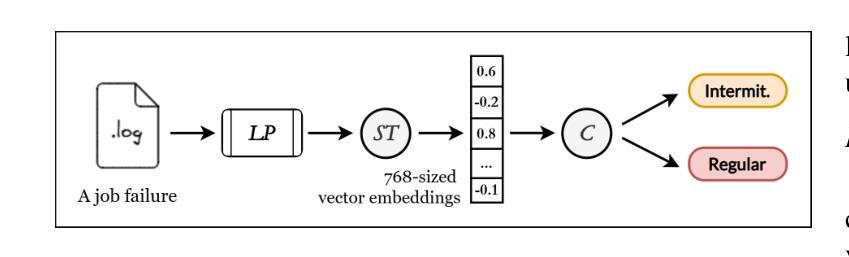
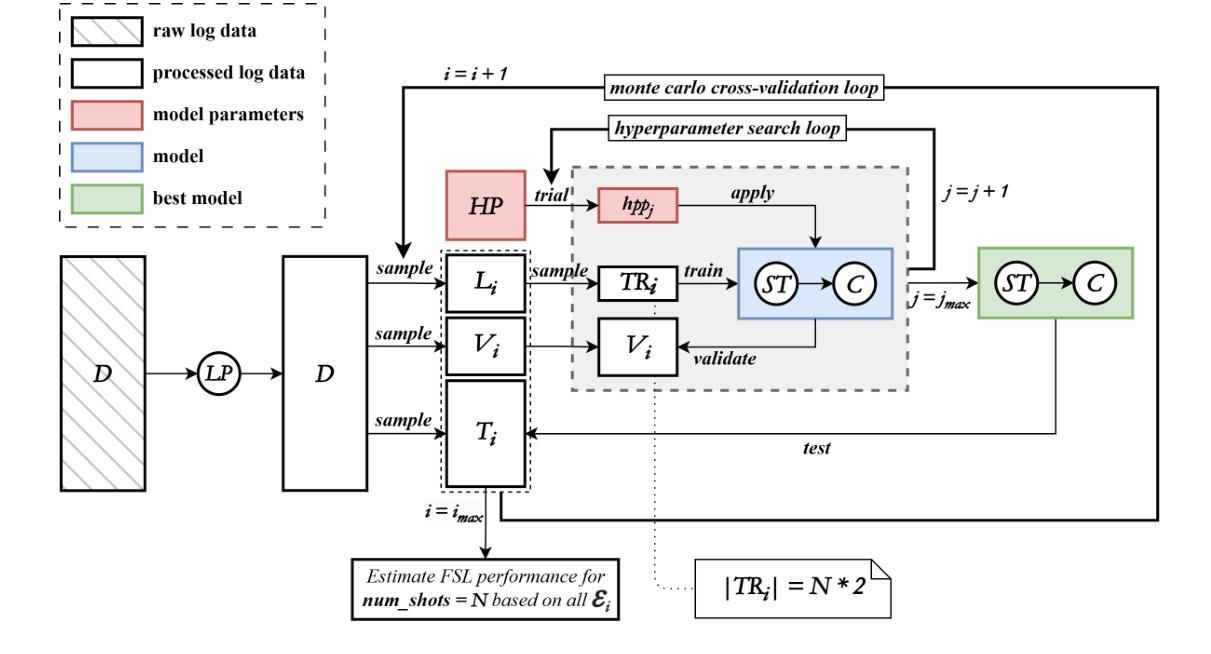
Efficient Detection of Intermittent Job Failures Using Few-Shot Learning
Authors:Henri Aïdasso, Francis Bordeleau, Ali Tizghadam
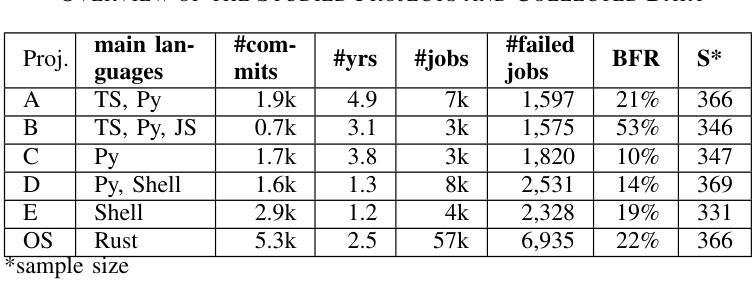
One of the main challenges developers face in the use of continuous integration (CI) and deployment pipelines is the occurrence of intermittent job failures, which result from unexpected non-deterministic issues (e.g., flaky tests or infrastructure problems) rather than regular code-related errors such as bugs. Prior studies developed machine-learning (ML) models trained on large datasets of job logs to classify job failures as either intermittent or regular. As an alternative to costly manual labeling of large datasets, the state-of-the-art (SOTA) approach leveraged a heuristic based on non-deterministic job reruns. However, this method mislabels intermittent job failures as regular in contexts where rerunning suspicious job failures is not an explicit policy, and therefore limits the SOTA’s performance in practice. In fact, our manual analysis of 2,125 job failures from 5 industrial and 1 open-source projects reveals that, on average, 32% of intermittent job failures are mislabeled as regular. To address these limitations, this paper introduces a novel approach to intermittent job failure detection using few-shot learning (FSL). Specifically, we fine-tune a small language model using a few number of manually labeled log examples to generate rich embeddings, which are then used to train an ML classifier. Our FSL-based approach achieves 70-88% F1-score with only 12 shots in all projects, outperforming the SOTA, which proved ineffective (34-52% F1-score) in 4 projects. Overall, this study underlines the importance of data quality over quantity and provides a more efficient and practical framework for the detection of intermittent job failures in organizations.
开发者在使用持续集成(CI)和部署管道时面临的主要挑战之一是间歇性作业失败的出现。这些失败是由于意外的非确定性问题(例如,测试不稳定或基础设施问题),而不是常规的代码相关错误(如错误)。先前的研究开发了经过大型作业日志数据集训练的机器学习(ML)模型,以将作业失败分类为间歇性或常规性。作为昂贵的手动标记大型数据集的替代方案,最新方法利用基于非确定性作业重跑的启发式方法。然而,在重试可疑作业失败不是明确策略的情况下,此方法会将间歇性作业失败误标记为常规性,从而限制了其在实际应用中的性能。实际上,我们对来自五个工业项目和两个开源项目的2,125个作业失败的手动分析表明,平均而言,有32%的间歇性作业失败被误标记为常规性。为了解决这些局限性,本文引入了一种使用少量学习(FSL)进行间歇性作业故障检测的新方法。具体来说,我们使用少量手动标记的日志示例对小型语言模型进行微调,以生成丰富的嵌入,然后用于训练ML分类器。基于FSL的方法在所有项目中仅使用12个样本就达到了70-88%的F1分数,优于状态最新技术(在四个项目中表现不佳,F1分数为34-52%)。总体而言,这项研究强调了数据质量比数量更重要,并提供了一种更高效且实用的框架来检测组织中的间歇性作业失败。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the 41st International Conference on Software Maintenance and Evolution - ICSME 2025, Industry Track
Summary
开发者在使用持续集成(CI)和部署管道时面临的挑战之一是间歇性作业失败。先前的研究通过训练大型作业日志数据集开发机器学习模型来对作业失败进行分类,包括间歇性失败和常规失败。最新方法基于非确定性作业重运行启发式方法,但存在误判间歇性作业失败为常规失败的缺陷。本研究通过对手动分析发现,平均有32%的间歇性作业失败被误判。为解决这一问题,本研究提出使用基于小样本学习的间歇性作业失败检测新方法,通过微调小型语言模型生成丰富的嵌入,用于训练机器学习分类器。新方法的F1分数在70-88%之间,仅在所有项目中使用12个样本即可实现,优于先前方法的34-52%。总体而言,本研究强调数据质量比数量更重要,并为组织检测间歇性作业失败提供了更实用、高效的框架。
Key Takeaways
- 开发人员在CI和部署管道中面临间歇性作业失败的挑战。
- 以往的机器学习模型通过大型作业日志数据集对作业失败进行分类,存在误判问题。
- 最新方法基于非确定性作业重运行启发式,但在某些情况下会误判间歇性作业失败为常规失败。
- 手动分析显示,平均有32%的间歇性作业失败被误判。
- 研究提出使用基于小样本学习(FSL)的新方法,通过微调小型语言模型来生成丰富的嵌入,用于训练分类器。
- 新方法在所有项目中的F1分数达到70-88%,仅使用12个样本即可实现,优于先前方法。
- 研究强调数据质量的重要性,为组织提供更实用、高效的间歇性作业失败检测框架。
点此查看论文截图

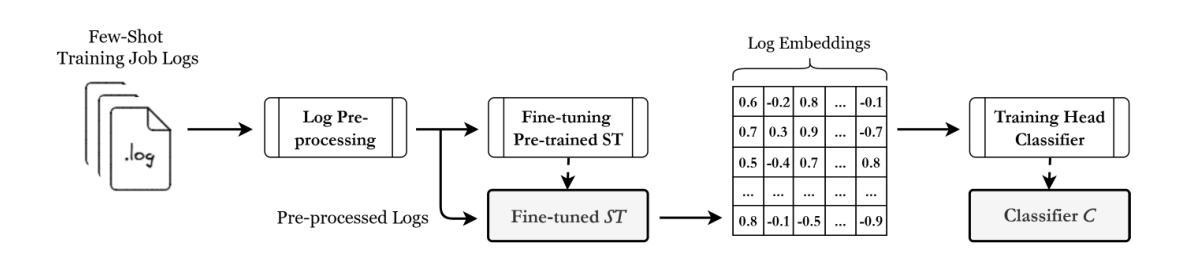
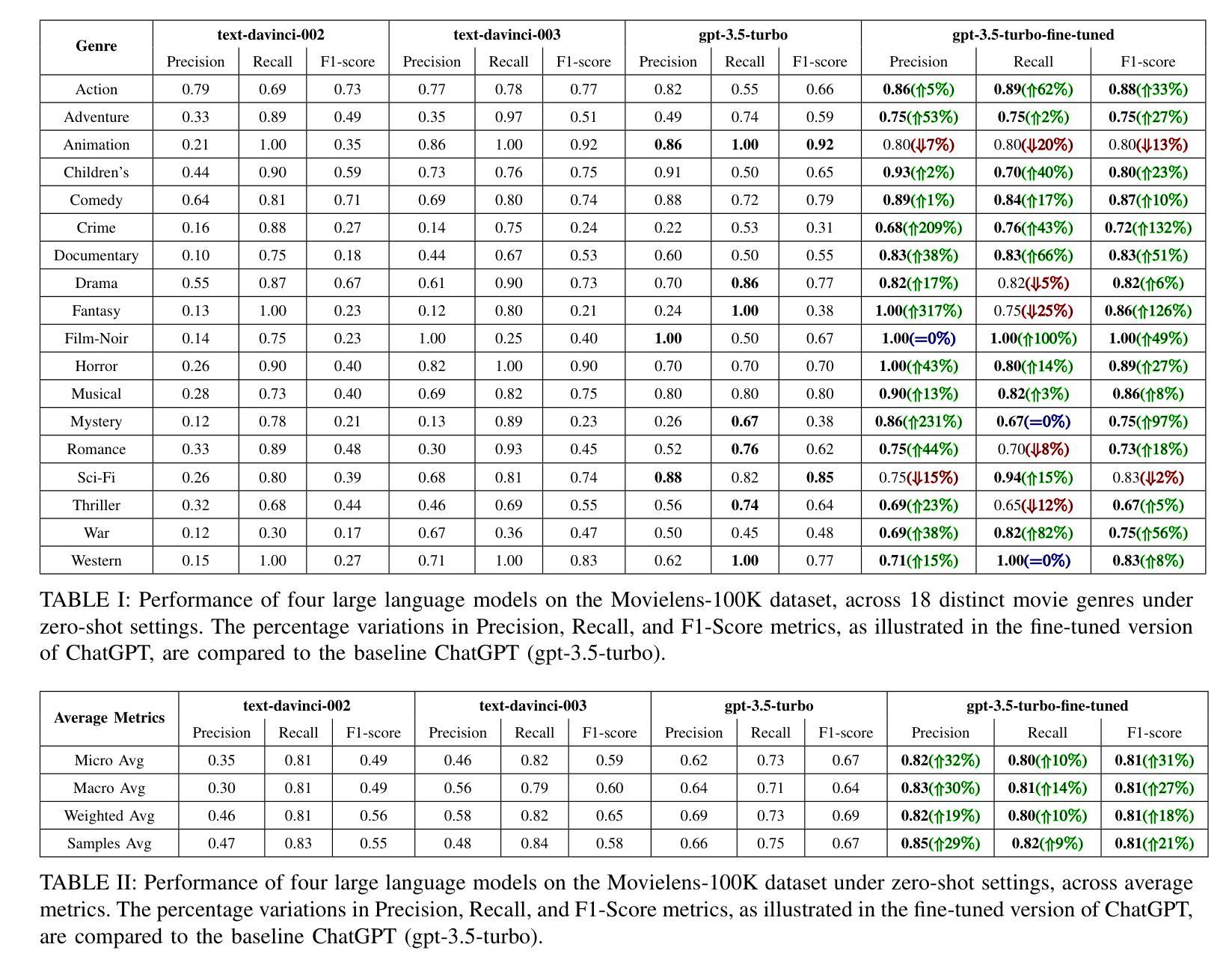
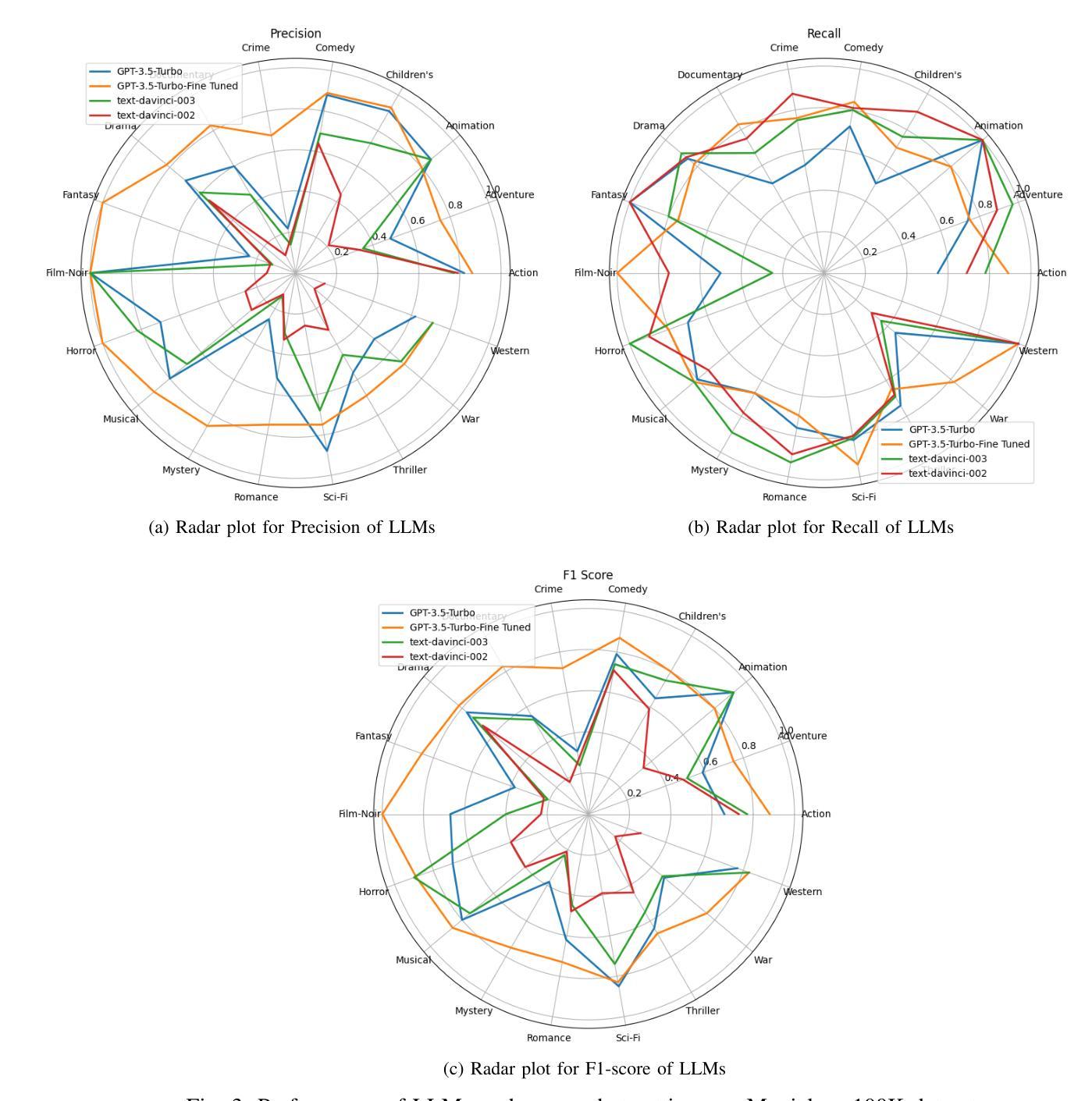
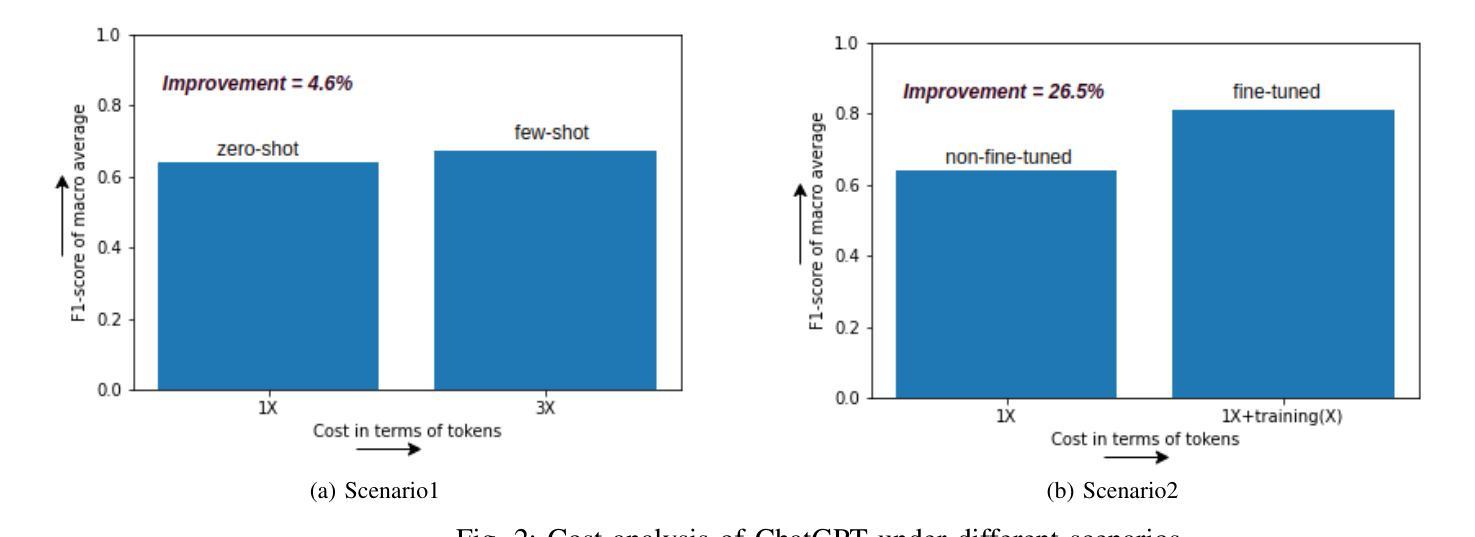
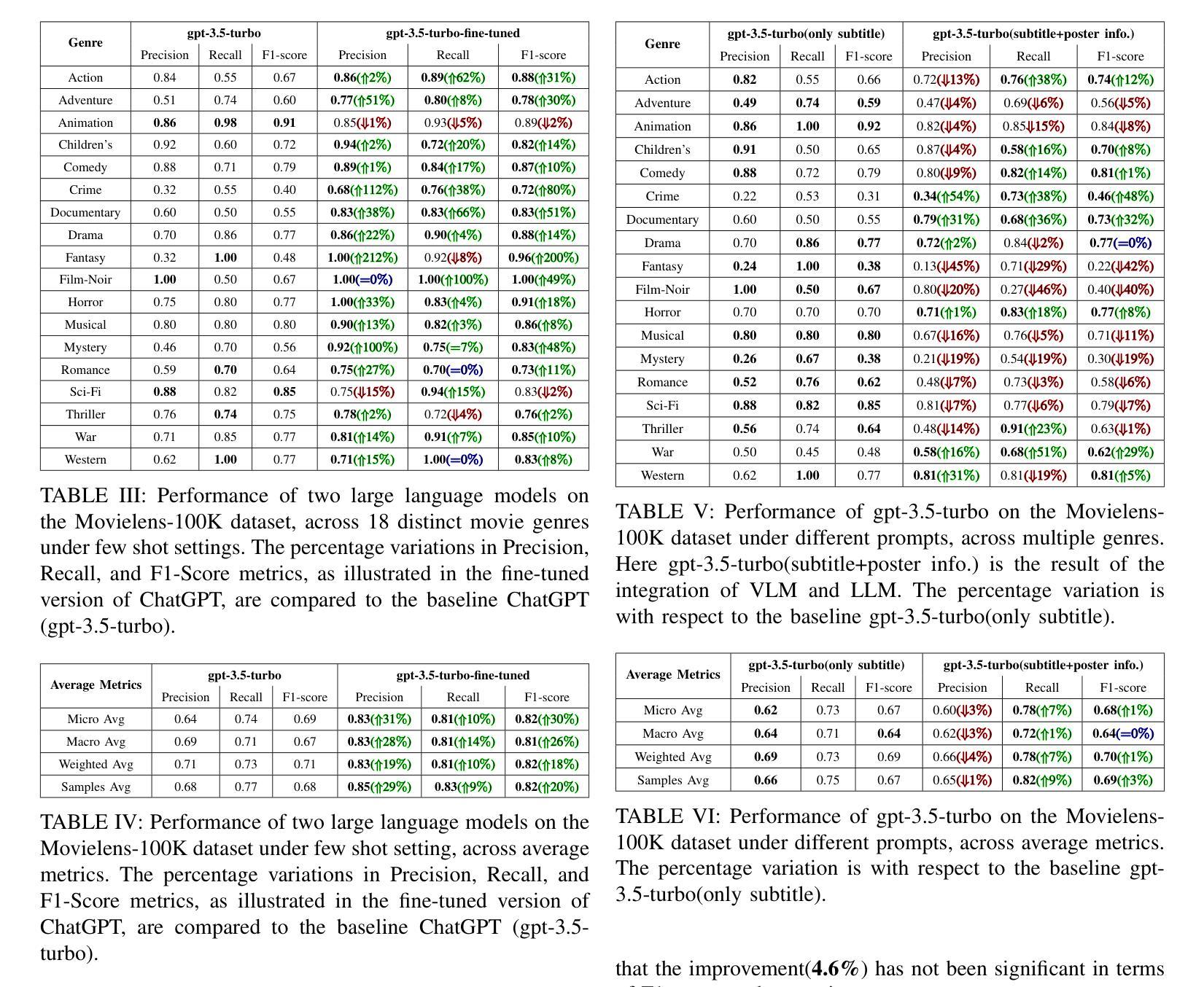
Demystifying ChatGPT: How It Masters Genre Recognition
Authors:Subham Raj, Sriparna Saha, Brijraj Singh, Niranjan Pedanekar
The introduction of ChatGPT has garnered significant attention within the NLP community and beyond. Previous studies have demonstrated ChatGPT’s substantial advancements across various downstream NLP tasks, highlighting its adaptability and potential to revolutionize language-related applications. However, its capabilities and limitations in genre prediction remain unclear. This work analyzes three Large Language Models (LLMs) using the MovieLens-100K dataset to assess their genre prediction capabilities. Our findings show that ChatGPT, without fine-tuning, outperformed other LLMs, and fine-tuned ChatGPT performed best overall. We set up zero-shot and few-shot prompts using audio transcripts/subtitles from movie trailers in the MovieLens-100K dataset, covering 1682 movies of 18 genres, where each movie can have multiple genres. Additionally, we extended our study by extracting IMDb movie posters to utilize a Vision Language Model (VLM) with prompts for poster information. This fine-grained information was used to enhance existing LLM prompts. In conclusion, our study reveals ChatGPT’s remarkable genre prediction capabilities, surpassing other language models. The integration of VLM further enhances our findings, showcasing ChatGPT’s potential for content-related applications by incorporating visual information from movie posters.
ChatGPT的引入不仅在NLP领域引起了广泛关注,而且超出了该领域。之前的研究已经证明了ChatGPT在各种下游NLP任务上的巨大进步,突出了其适应性和改变语言相关应用的可能性。然而,其在体裁预测方面的能力和局限性尚不清楚。这项工作使用MovieLens-100K数据集分析了三种大型语言模型(LLM),以评估它们的体裁预测能力。我们的研究发现,未经微调的ChatGPT在其他LLM中表现最佳,而经过微调的ChatGPT总体表现最佳。我们使用MovieLens-100K数据集中的电影预告音频转录/字幕来设置零样本和少样本提示,涵盖了18个体裁的1682部电影,每部电影可能包含多个体裁。此外,我们还通过提取IMDb电影海报并利用带有海报信息提示的视觉语言模型(VLM)来扩展我们的研究。这种精细的信息被用来增强现有的LLM提示。总之,我们的研究表明,ChatGPT在体裁预测方面表现出卓越的能力,超越了其他语言模型。视觉语言模型的整合进一步增强了我们的发现,展示了ChatGPT通过融入电影海报的视觉信息在内容相关应用中的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了ChatGPT在MovieLens-100K数据集上的电影类型预测能力,并与其他大型语言模型进行对比。实验表明,未经微调ChatGPT的预测性能优于其他大型语言模型,经过微调后表现最佳。研究还结合了视觉语言模型,利用电影海报信息增强大型语言模型的提示,进一步提高了ChatGPT的类型预测能力。
Key Takeaways
- ChatGPT在未经微调的情况下,在电影类型预测方面表现出显著的优势。
- 在使用MovieLens-100K数据集进行的实验中,ChatGPT的表现优于其他大型语言模型。
- 通过微调,ChatGPT的性能得到进一步提升,表现最佳。
- 研究结合了视觉语言模型,利用电影海报信息,提高了大型语言模型的性能。
- ChatGPT在结合视觉信息后,类型预测能力得到进一步增强。
- 该研究展示了ChatGPT在内容相关应用中的潜力。
点此查看论文截图


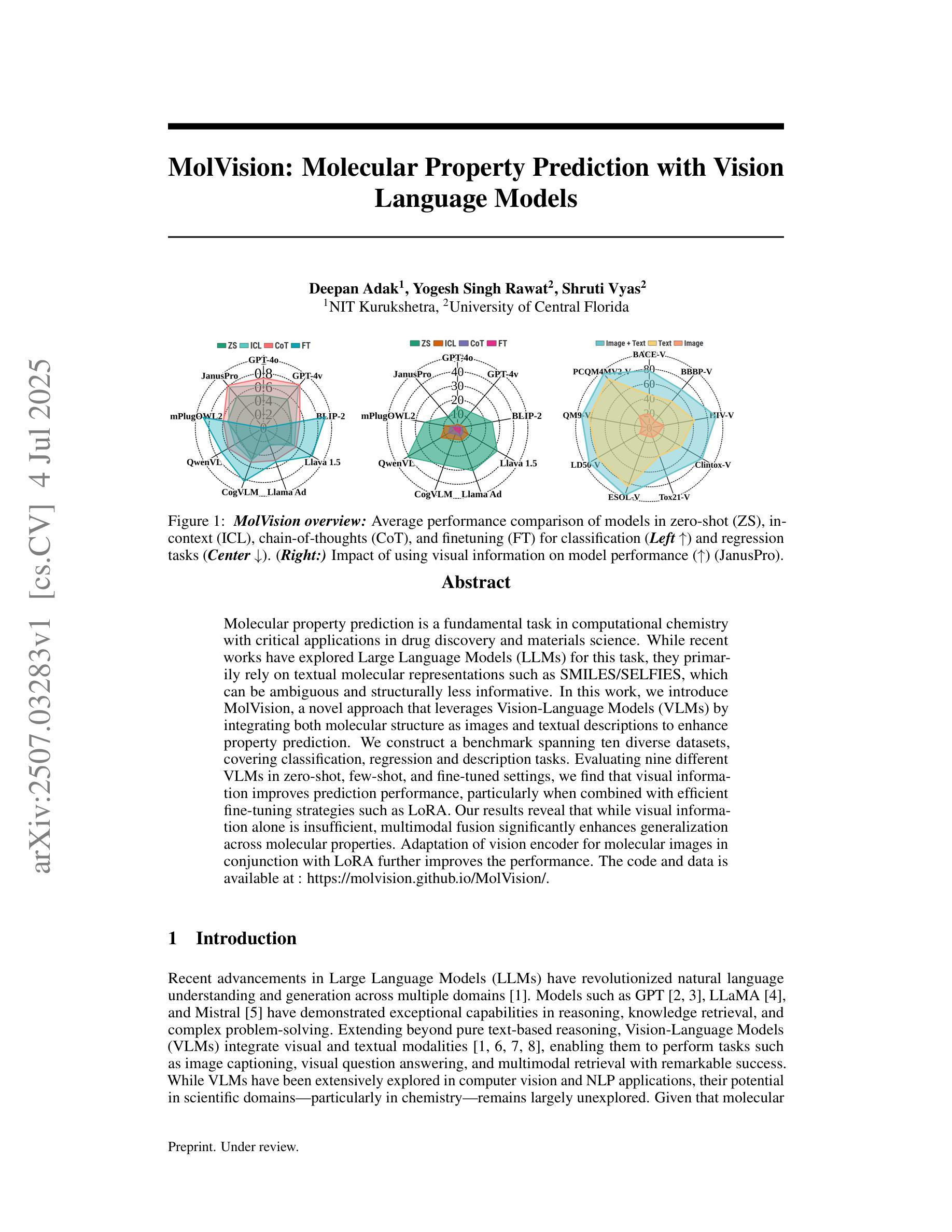
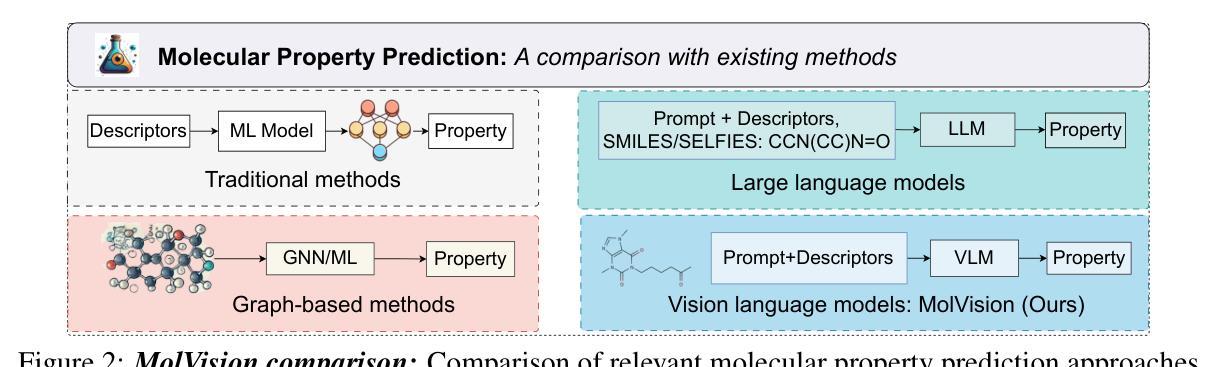
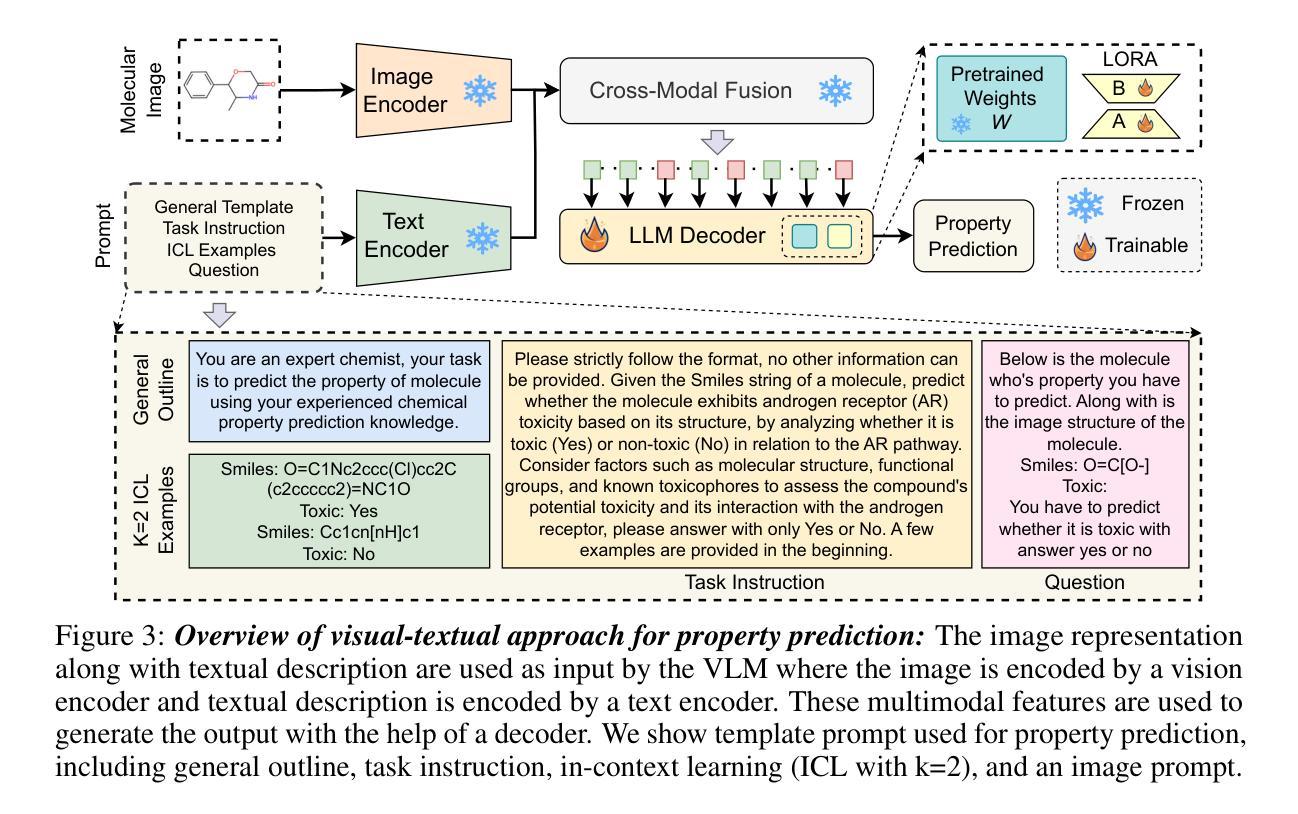
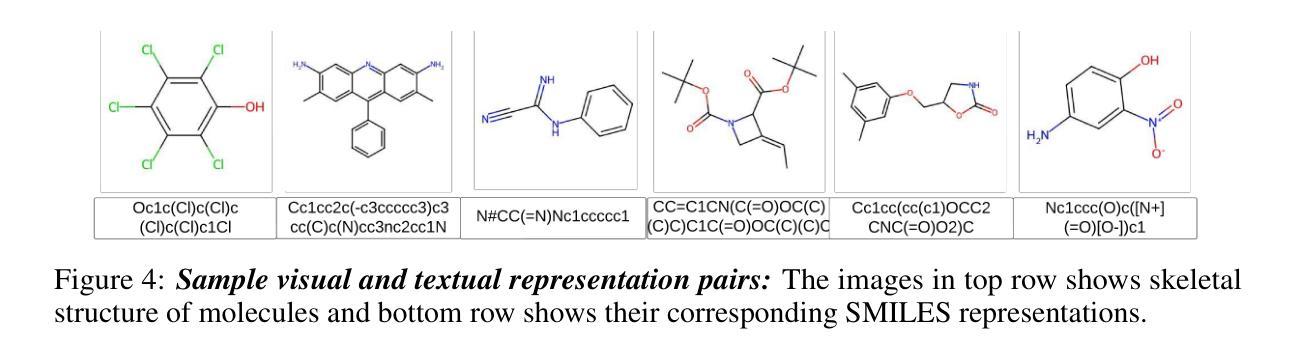
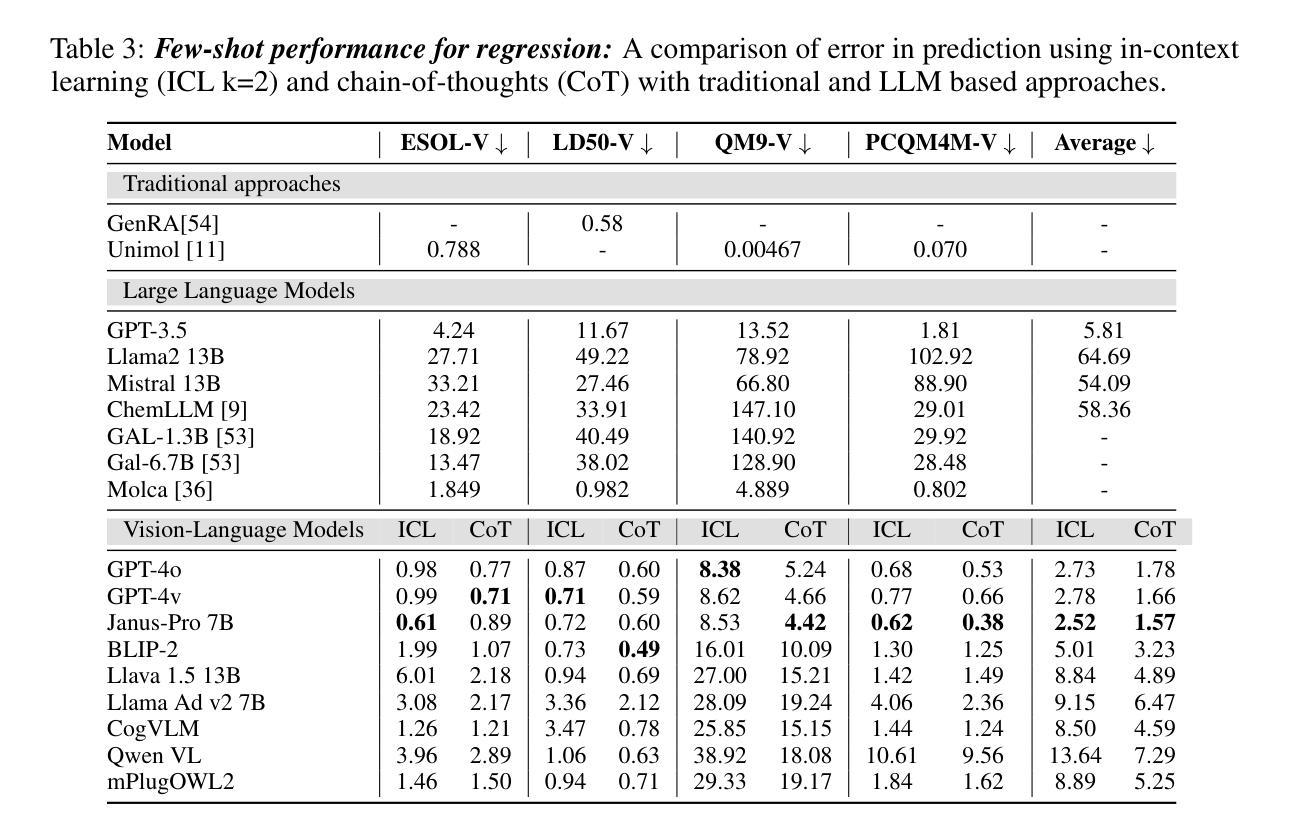
MolVision: Molecular Property Prediction with Vision Language Models
Authors:Deepan Adak, Yogesh Singh Rawat, Shruti Vyas
Molecular property prediction is a fundamental task in computational chemistry with critical applications in drug discovery and materials science. While recent works have explored Large Language Models (LLMs) for this task, they primarily rely on textual molecular representations such as SMILES/SELFIES, which can be ambiguous and structurally less informative. In this work, we introduce MolVision, a novel approach that leverages Vision-Language Models (VLMs) by integrating both molecular structure as images and textual descriptions to enhance property prediction. We construct a benchmark spanning ten diverse datasets, covering classification, regression and description tasks. Evaluating nine different VLMs in zero-shot, few-shot, and fine-tuned settings, we find that visual information improves prediction performance, particularly when combined with efficient fine-tuning strategies such as LoRA. Our results reveal that while visual information alone is insufficient, multimodal fusion significantly enhances generalization across molecular properties. Adaptation of vision encoder for molecular images in conjunction with LoRA further improves the performance. The code and data is available at : $\href{https://molvision.github.io/MolVision/}{https://molvision.github.io/MolVision/}$.
分子属性预测是计算化学中的一项基本任务,在药物发现和材料科学中有着关键的应用。虽然近期的研究已经探索了大型语言模型(LLM)在此任务中的应用,但它们主要依赖于SMILES/SELFIES等文本分子表示法,这些表示法可能具有歧义并且结构信息较少。在这项工作中,我们介绍了MolVision,这是一种新方法,它通过整合分子结构图像和文本描述来利用视觉语言模型(VLM),以增强属性预测。我们构建了一个跨越十个不同数据集的基准测试,涵盖分类、回归和描述任务。在零样本、少样本和微调设置下评估了九种不同的VLM,我们发现视觉信息提高了预测性能,特别是当与LoRA等高效的微调策略相结合时。我们的结果表明,虽然单独的视觉信息不足以进行预测,但多模式融合显著增强了跨分子属性的泛化能力。结合LoRA对分子图像视觉编码器的适应性调整进一步提高了性能。相关代码和数据集可通过以下链接获取:[https://molvision.github.io/MolVision/] 。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
MolVision结合分子结构图像和文本描述,利用视觉语言模型(VLMs)进行分子属性预测,提高了预测性能。该研究构建了一个跨越十个不同数据集的基准测试,并发现视觉信息对于预测特别是与高效微调策略结合时表现更佳。
Key Takeaways
- MolVision利用视觉语言模型(VLMs)进行分子属性预测。
- 该方法结合了分子结构图像和文本描述。
- 研究构建了包含分类、回归和描述任务的基准测试数据集。
- 视觉信息能提高预测性能,特别是与高效微调策略如LoRA结合时。
- 单一的视觉信息不足以进行准确的预测,但多模式融合能显著提高跨分子属性的泛化能力。
- 适配用于分子图像的视觉编码器与LoRA微调策略可进一步提高性能。
点此查看论文截图
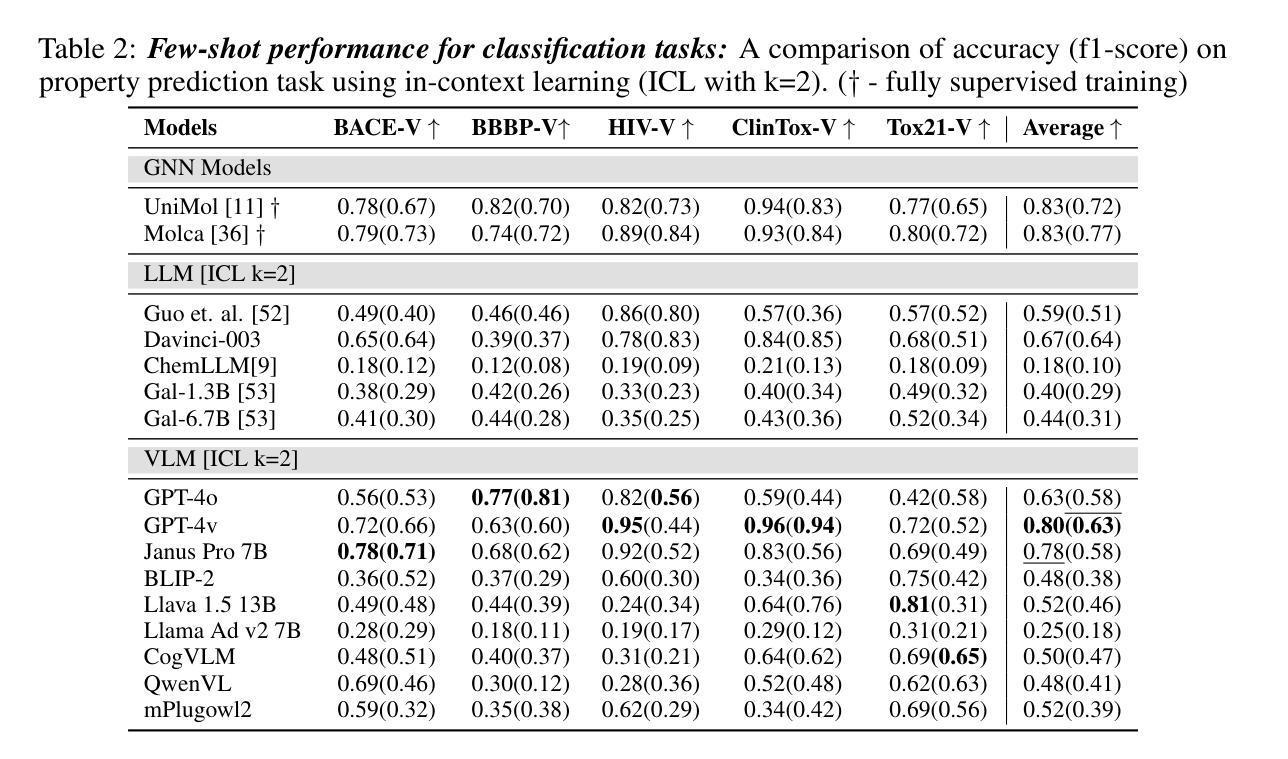
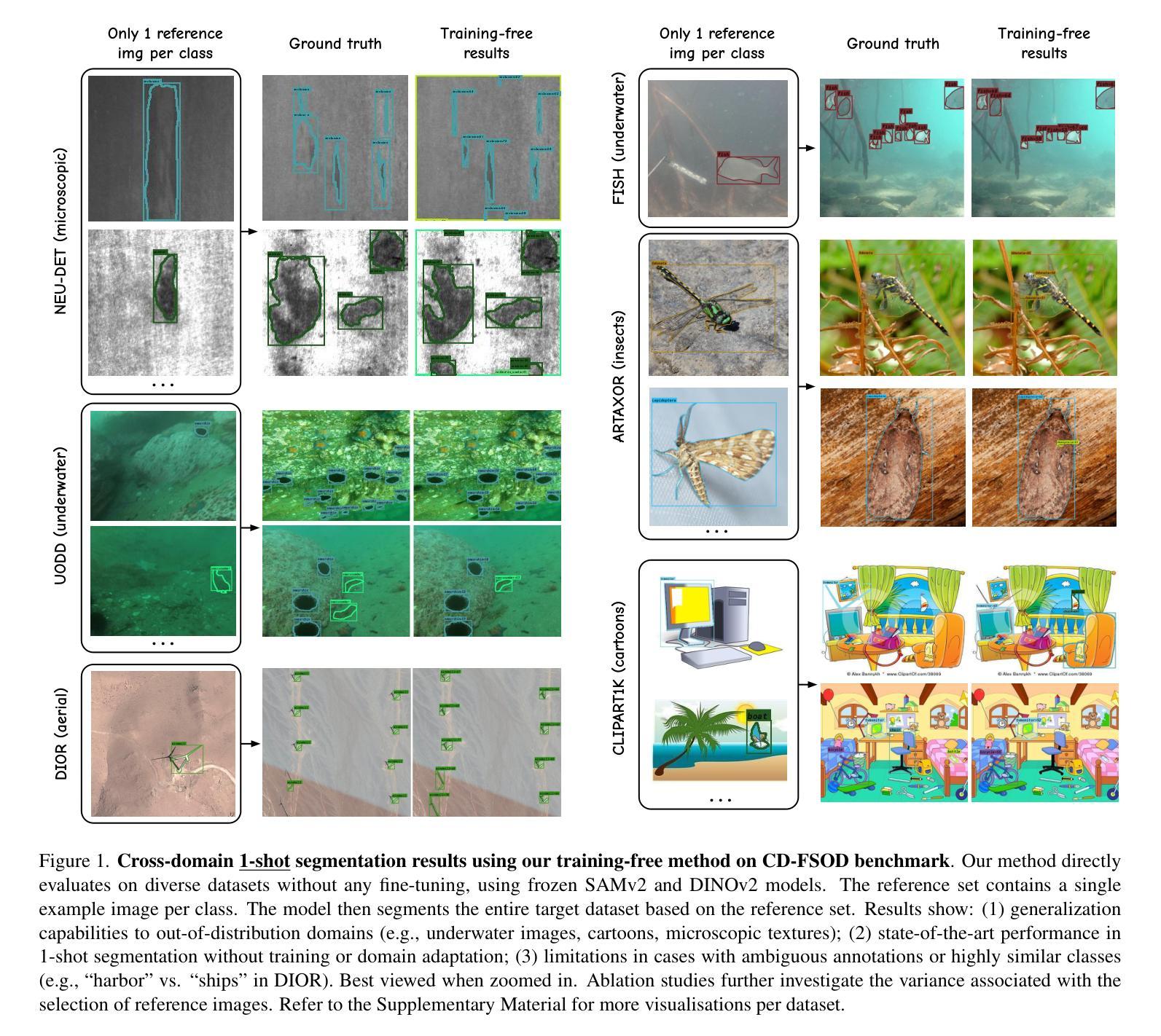
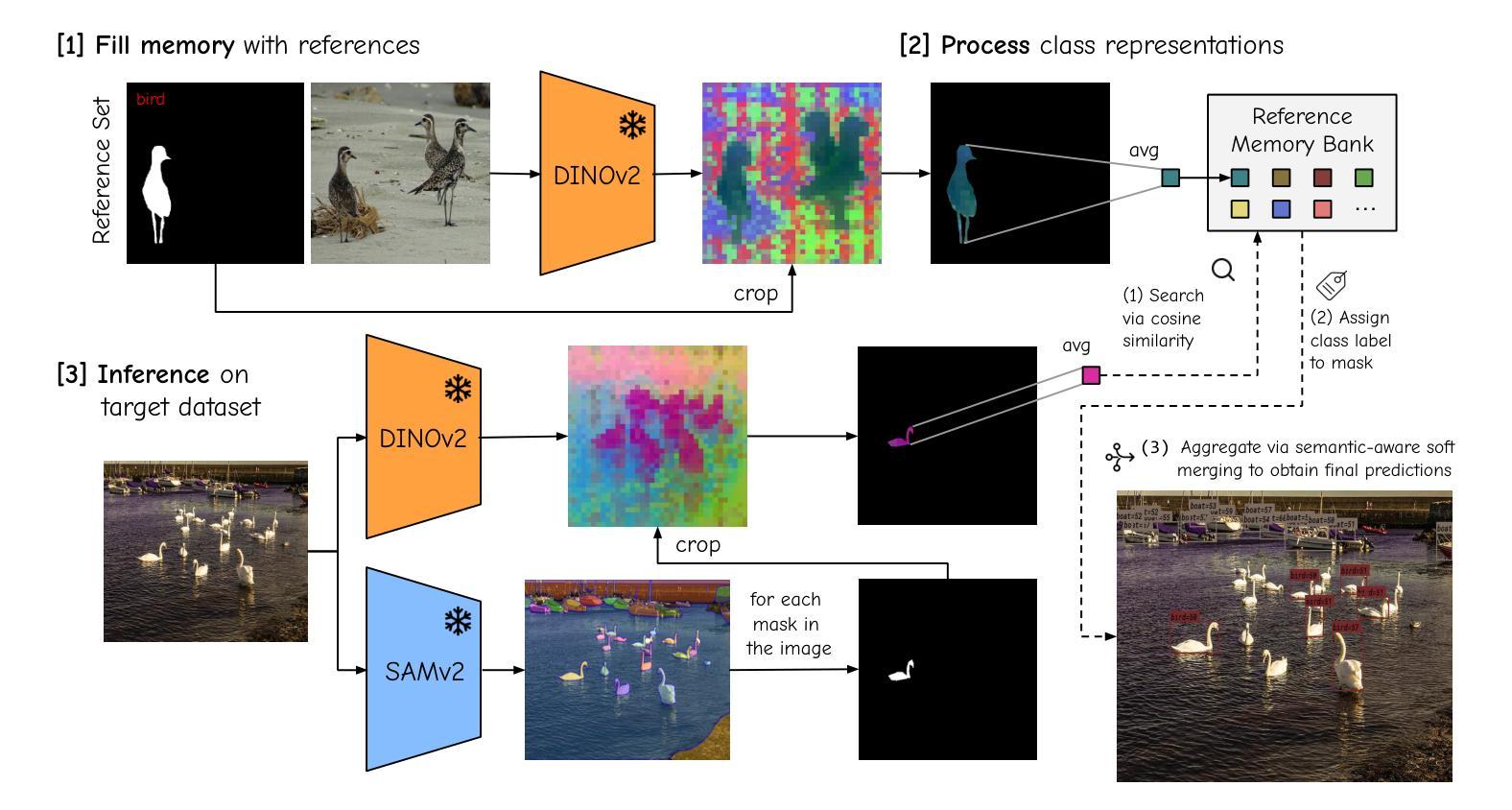
No time to train! Training-Free Reference-Based Instance Segmentation
Authors:Miguel Espinosa, Chenhongyi Yang, Linus Ericsson, Steven McDonagh, Elliot J. Crowley
The performance of image segmentation models has historically been constrained by the high cost of collecting large-scale annotated data. The Segment Anything Model (SAM) alleviates this original problem through a promptable, semantics-agnostic, segmentation paradigm and yet still requires manual visual-prompts or complex domain-dependent prompt-generation rules to process a new image. Towards reducing this new burden, our work investigates the task of object segmentation when provided with, alternatively, only a small set of reference images. Our key insight is to leverage strong semantic priors, as learned by foundation models, to identify corresponding regions between a reference and a target image. We find that correspondences enable automatic generation of instance-level segmentation masks for downstream tasks and instantiate our ideas via a multi-stage, training-free method incorporating (1) memory bank construction; (2) representation aggregation and (3) semantic-aware feature matching. Our experiments show significant improvements on segmentation metrics, leading to state-of-the-art performance on COCO FSOD (36.8% nAP), PASCAL VOC Few-Shot (71.2% nAP50) and outperforming existing training-free approaches on the Cross-Domain FSOD benchmark (22.4% nAP).
历史上,图像分割模型的性能一直受到收集大规模标注数据的高成本的限制。Segment Anything Model(SAM)通过一种可提示的、与语义无关的分割范式缓解了这一原始问题,但处理新图像时仍需要手动视觉提示或复杂的域相关提示生成规则。为了减轻这一新负担,我们的工作研究了在仅提供一小部分参考图像的情况下进行对象分割的任务。我们的关键见解是利用基础模型学到的强大语义先验知识,来识别参考图像和目标图像之间的相应区域。我们发现这种对应关系能够自动生成用于下游任务的实例级分割掩膜,并通过一个多阶段、无需训练的方法实现我们的想法,包括(1)构建内存银行;(2)表示聚合和(3)语义感知特征匹配。我们的实验显示,在分割指标上取得了显著改进,并在COCO FSOD(36.8% nAP)、PASCAL VOC Few-Shot(71.2% nAP50)上达到了最先进的性能,且在跨域FSOD基准测试上超越了现有的无训练方法(22.4% nAP)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint
Summary:
本研究通过采用可提示、语义无关的分割范式解决了大规模标注数据收集成本高的问题。但为了处理新图像,仍需手动视觉提示或复杂的特定领域提示生成规则,造成新的负担。本研究进一步探索了仅提供少量参考图像时的目标分割任务,利用基础模型学习的强语义先验知识,在参考图像和目标图像之间识别对应区域。对应性使下游任务能够自动生成实例级别的分割掩膜,并通过一个包括(1)内存库构建、(2)表示聚合和(3)语义感知特征匹配的、无需训练的多阶段方法实现了想法的实例化。实验结果显示在分割指标上有显著改善,并在COCO FSOD、PASCAL VOC Few-Shot等数据集上达到了业界领先水平,且在跨域FSOD基准测试中超越了现有的无需训练的方法。
Key Takeaways:
- Segment Anything Model (SAM) 解决了数据收集成本高的问题,但处理新图像仍需复杂操作。
- 研究探索了在仅提供少量参考图像时的目标分割任务。
- 利用基础模型学习的强语义先验知识,识别参考图像和目标图像之间的对应区域。
- 对应性有助于自动生成实例级别的分割掩膜,用于下游任务。
- 提出了一种无需训练的多阶段方法,包括内存库构建、表示聚合和语义感知特征匹配。
- 实验结果显著改进了分割指标,并在多个数据集上达到领先水平。
点此查看论文截图

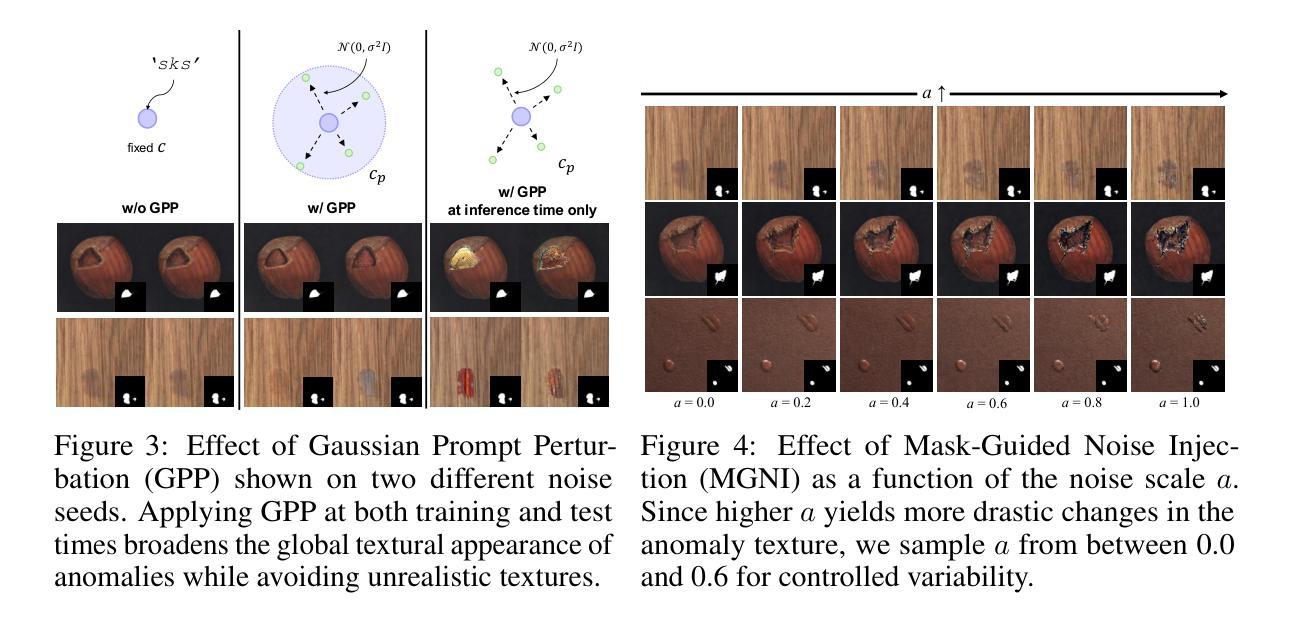
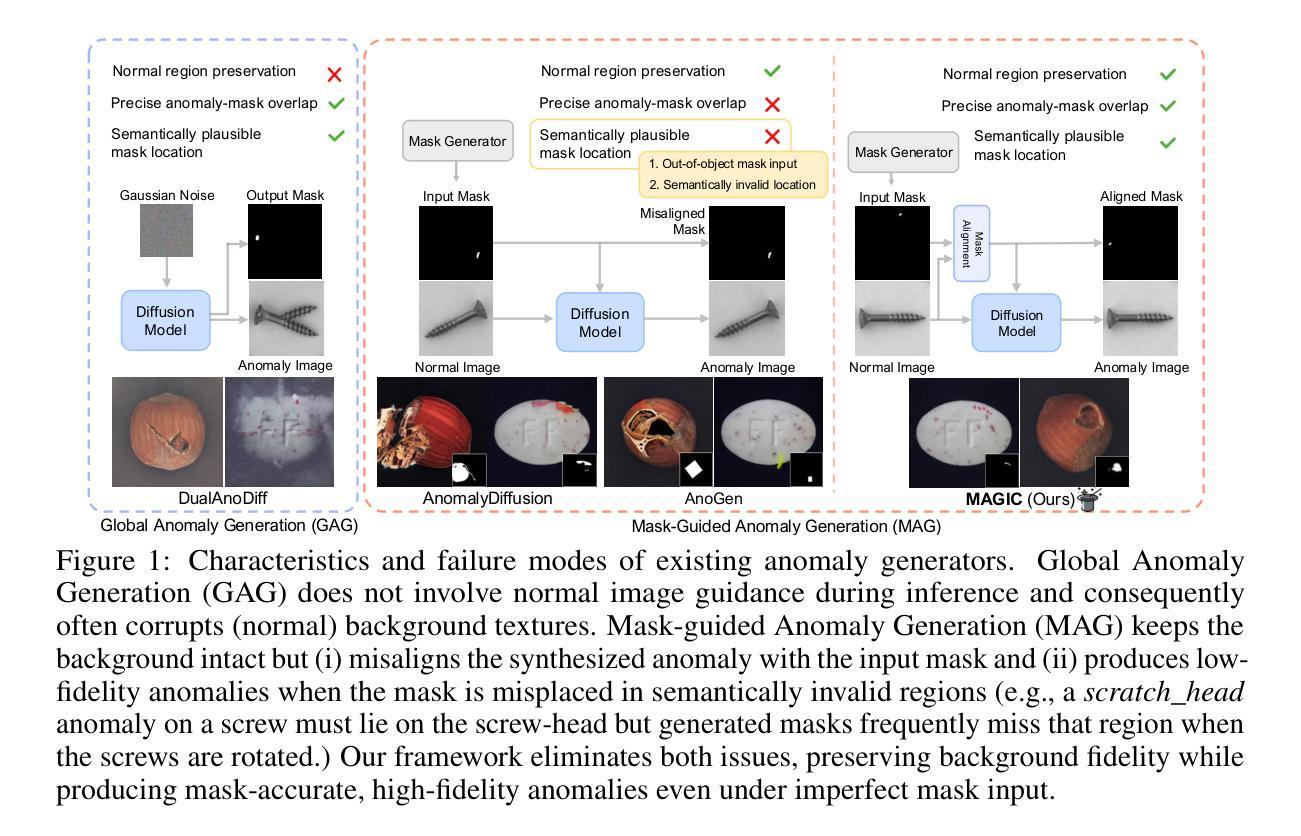
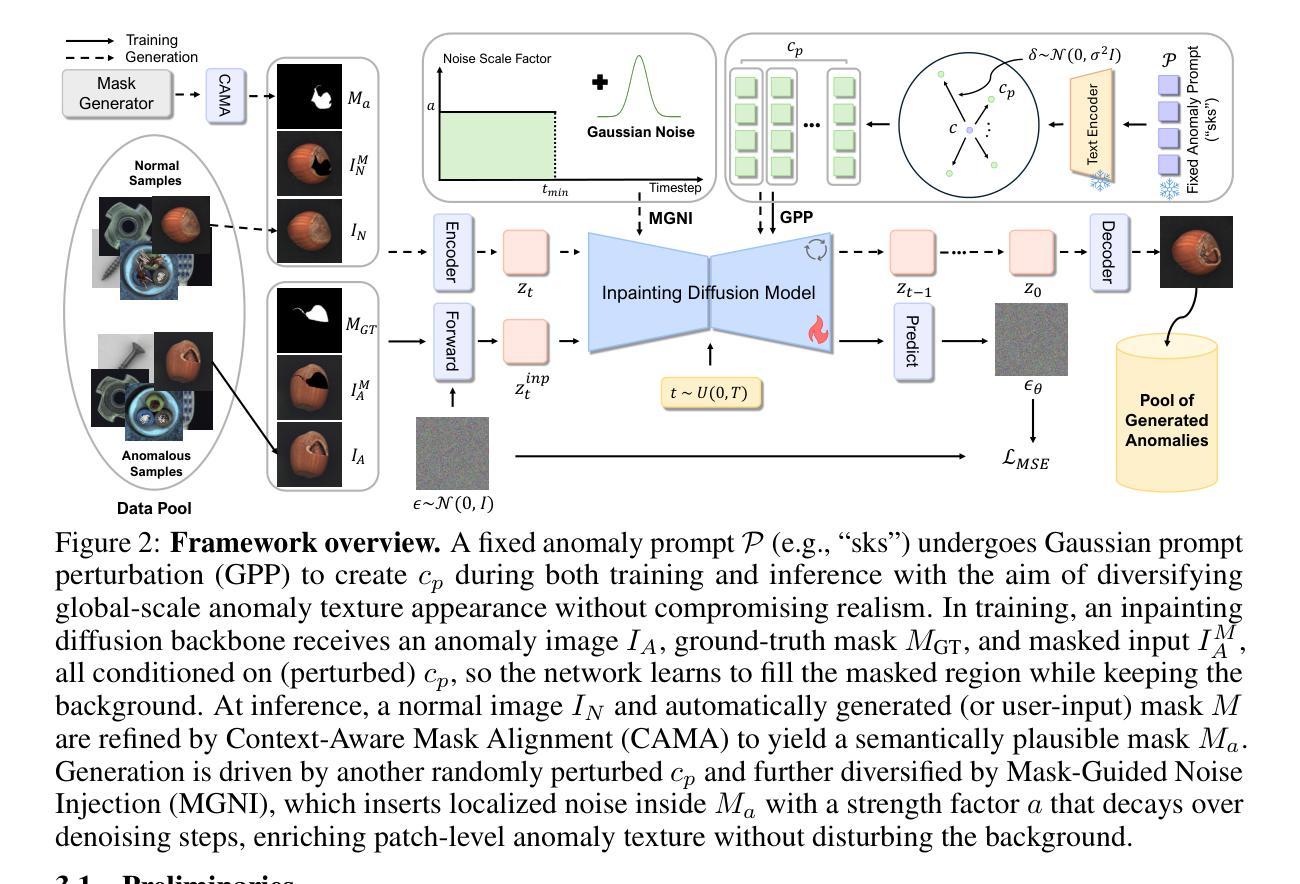
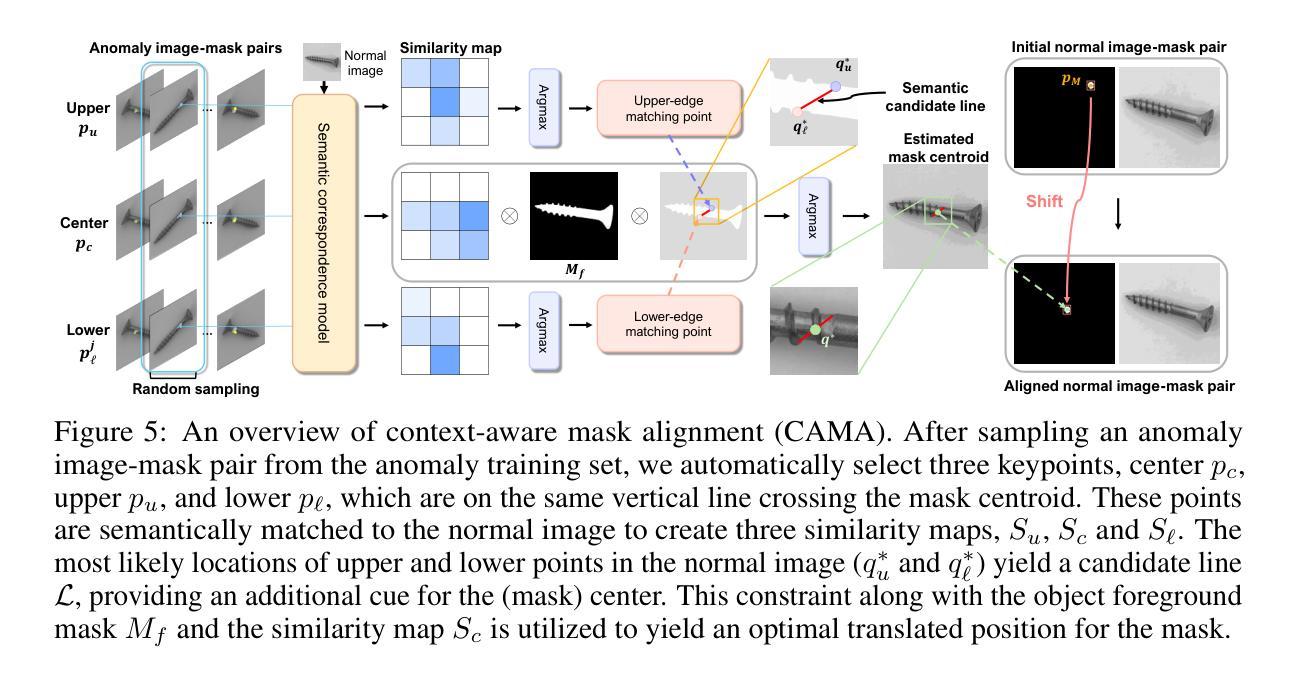
MAGIC: Mask-Guided Diffusion Inpainting with Multi-Level Perturbations and Context-Aware Alignment for Few-Shot Anomaly Generation
Authors:JaeHyuck Choi, MinJun Kim, JeHyeong Hong
Few-shot anomaly generation is emerging as a practical solution for augmenting the scarce anomaly data in industrial quality control settings. An ideal generator would meet three demands at once, namely (i) keep the normal background intact, (ii) inpaint anomalous regions to tightly overlap with the corresponding anomaly masks, and (iii) generate anomalous regions in a semantically valid location, while still producing realistic, diverse appearances from only a handful of real examples. Existing diffusion-based methods usually satisfy at most two of these requirements: global anomaly generators corrupt the background, whereas mask-guided ones often falter when the mask is imprecise or misplaced. We propose MAGIC–Mask-guided inpainting with multi-level perturbations and Context-aware alignment–to resolve all three issues. At its core, MAGIC fine-tunes a Stable Diffusion inpainting backbone that preserves normal regions and ensures strict adherence of the synthesized anomaly to the supplied mask, directly addressing background corruption and misalignment. To offset the diversity loss that fine-tuning can cause, MAGIC adds two complementary perturbation strategies: (i) Gaussian prompt-level perturbation applied during fine-tuning and inference that broadens the global appearance of anomalies while avoiding low-fidelity textual appearances, and (ii) mask-guided spatial noise injection that enriches local texture variations. Additionally, the context-aware mask alignment module forms semantic correspondences and relocates masks so that every anomaly remains plausibly contained within the host object, eliminating out-of-boundary artifacts. Under a consistent identical evaluation protocol on the MVTec-AD dataset, MAGIC outperforms previous state-of-the-arts in downstream anomaly tasks.
少数镜头异常生成(Few-shot anomaly generation)已成为工业质量控制环境中扩充稀缺异常数据的一种实用解决方案。理想的生成器需要同时满足三个要求,即(i)保持正常背景不变,(ii)将异常区域填充得与相应的异常掩膜紧密重叠,(iii)在语义有效的位置生成异常区域,同时仅从少数真实示例中生成真实、多样化的外观。现有的基于扩散的方法通常最多满足其中两个要求:全局异常生成器会破坏背景,而掩膜引导的方法在掩膜不精确或错位时常会出错。我们提出了MAGIC(带有多级扰动和上下文感知对齐的掩膜引导填充)来解决这三个问题。MAGIC的核心是微调Stable Diffusion填充主干,它保留了正常区域并确保合成的异常严格遵循提供的掩膜,直接解决了背景破坏和错位的问题。为了抵消微调可能导致的多样性损失,MAGIC增加了两种互补的扰动策略:(i)在微调期间和推理期间应用高斯提示级扰动,以扩大异常的全局外观,同时避免低保真文本外观,(ii)掩膜引导的空间噪声注入,以丰富局部纹理变化。此外,上下文感知掩膜对齐模块形成语义对应关系并重新定位掩膜,使每个异常都合理地包含在宿主对象中,消除了边界外的伪影。在MVTec-AD数据集上采用一致的评价协议,MAGIC在下游异常任务中的性能超过了以前的最先进方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 6 figures. Code: https://github.com/Jaeihk/MAGIC-Anomaly-generation
Summary
基于少样本的异常生成成为工业质量控制设置中增强稀缺异常数据的实用解决方案。现有方法存在缺陷,无法满足所有要求。本文提出MAGIC方法,通过微调Stable Diffusion模型解决背景破坏和对齐问题,并引入两种扰动策略增强多样性。在MVTec-AD数据集上,MAGIC在下游异常检测任务中表现优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- Few-shot anomaly generation是解决工业质量控制中稀缺异常数据问题的实用方法。
- 现有方法如全局异常生成和mask引导生成存在缺陷,无法满足所有要求。
- MAGIC方法通过微调Stable Diffusion模型解决背景破坏和对齐问题。
- MAGIC引入两种扰动策略:高斯提示级别扰动和mask引导的空间噪声注入,以增强多样性并避免低质量文本外观。
- 上下文感知mask对齐模块形成语义对应关系并重新定位mask,避免异常出现在边界之外。
点此查看论文截图


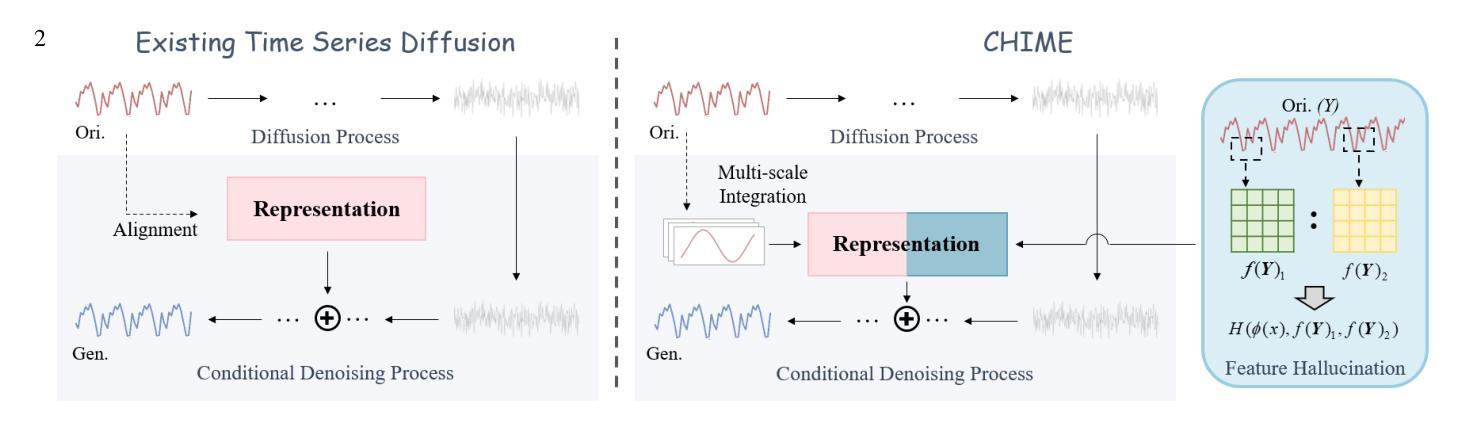
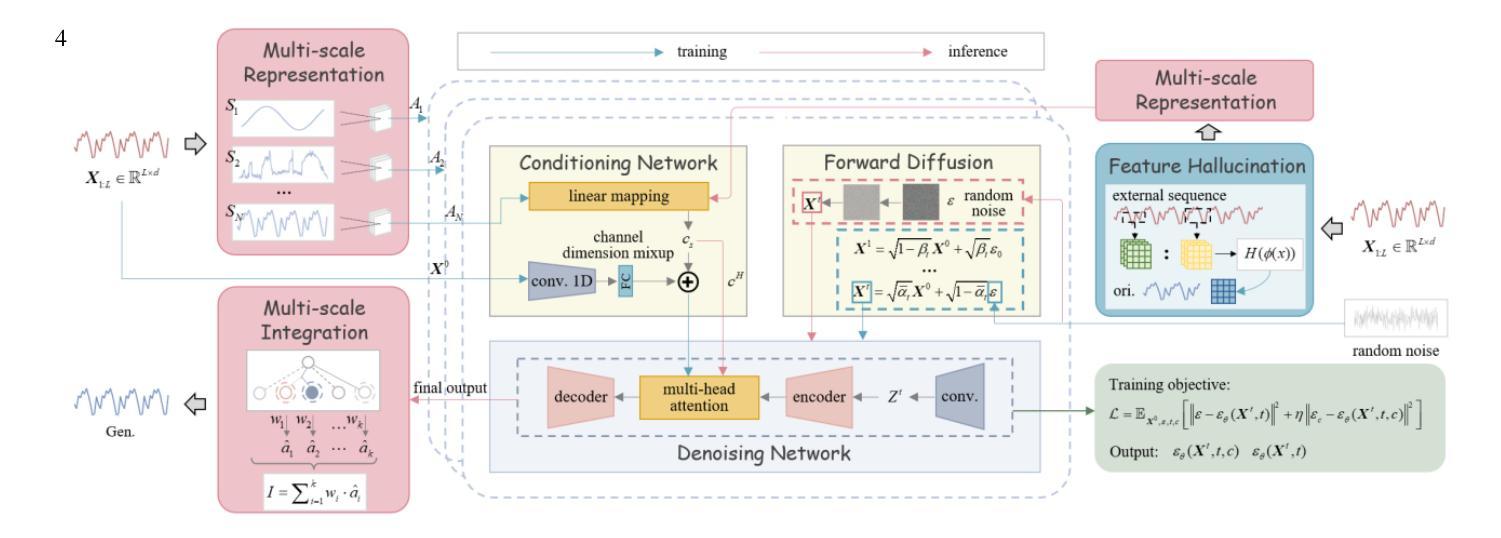
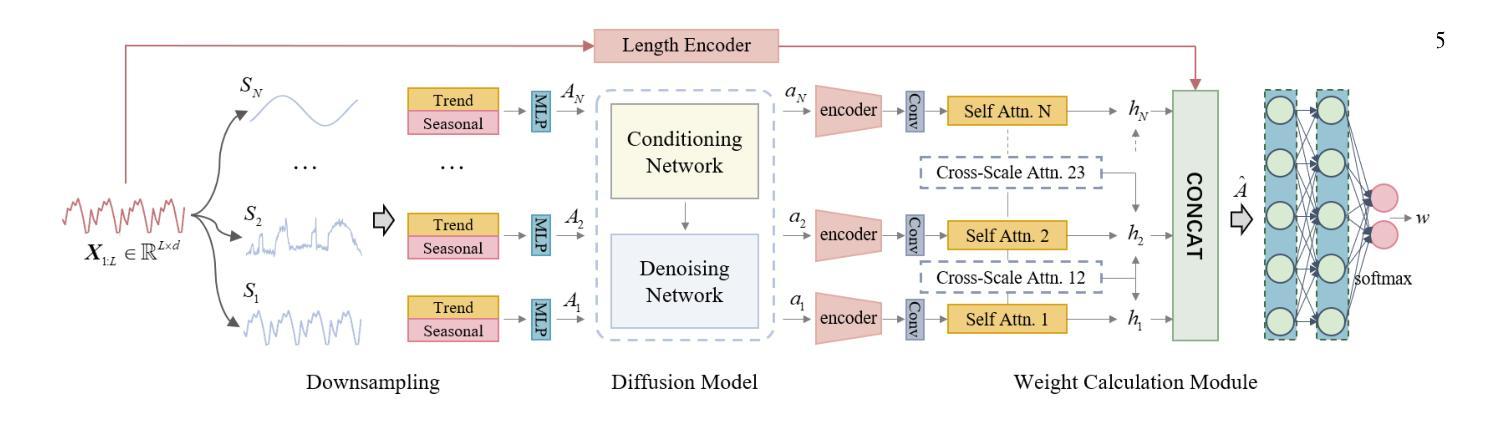
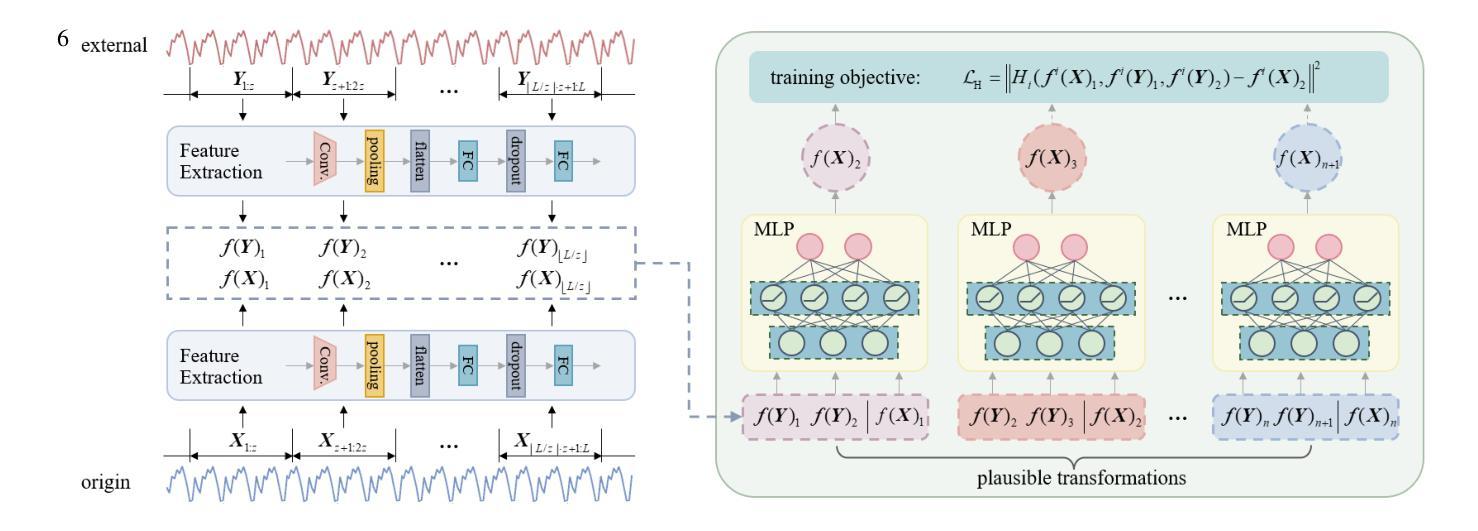
CHIME: Conditional Hallucination and Integrated Multi-scale Enhancement for Time Series Diffusion Model
Authors:Yuxuan Chen, Haipeng Xie
The denoising diffusion probabilistic model has become a mainstream generative model, achieving significant success in various computer vision tasks. Recently, there has been initial exploration of applying diffusion models to time series tasks. However, existing studies still face challenges in multi-scale feature alignment and generative capabilities across different entities and long-time scales. In this paper, we propose CHIME, a conditional hallucination and integrated multi-scale enhancement framework for time series diffusion models. By employing multi-scale decomposition and integration, CHIME captures the decomposed features of time series, achieving in-domain distribution alignment between generated and original samples. In addition, we introduce a feature hallucination module in the conditional denoising process, enabling the temporal features transfer across long-time scales. Experimental results on publicly available real-world datasets demonstrate that CHIME achieves state-of-the-art performance and exhibits excellent generative generalization capabilities in few-shot scenarios.
去噪扩散概率模型已经成为主流生成模型,在各种计算机视觉任务中取得了巨大成功。最近,人们开始探索将扩散模型应用于时间序列任务。然而,现有研究在多尺度特征对齐和跨不同实体和长时间尺度的生成能力方面仍面临挑战。在本文中,我们提出了CHIME,这是一个针对时间序列扩散模型的基于条件幻想和集成多尺度增强框架。通过采用多尺度分解和集成,CHIME能够捕获时间序列的分解特征,实现生成样本和原始样本之间的域内分布对齐。此外,我们在条件去噪过程中引入了一个特征幻觉模块,能够实现跨长时间尺度的时态特征转移。在公开的现实世界数据集上的实验结果表明,CHIME达到了最先进的性能,并在小样场景中表现出出色的生成泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散概率模型已成为主流生成模型,在计算机视觉任务中取得了巨大成功。最近,该模型开始应用于时间序列任务,但现有研究仍面临跨不同实体和长时间尺度的多尺度特征对齐和生成能力方面的挑战。本文提出了面向时间序列扩散模型的CHIME框架,采用多尺度分解与集成方法,实现了时间序列特征的分解捕获,确保了生成样本与原始样本在域内的分布对齐。此外,在条件去噪过程中引入了特征幻像模块,实现了长时间尺度下的时间特征转移。在公开的现实数据集上的实验结果表明,CHIME达到了最新技术水平,并在有限数据场景中展现出卓越的生成泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散概率模型在多种计算机视觉任务中表现优秀。
- CHIME框架被应用于时间序列扩散模型。
- CHIME解决了现有研究中跨不同实体和长时间尺度的多尺度特征对齐问题。
- CHIME采用多尺度分解与集成,实现了时间序列特征的分解捕获。
- CHIME在条件去噪过程中引入了特征幻像模块,有助于时间特征的长期转移。
- 在公开数据集上的实验表明,CHIME具有最先进的性能。
点此查看论文截图

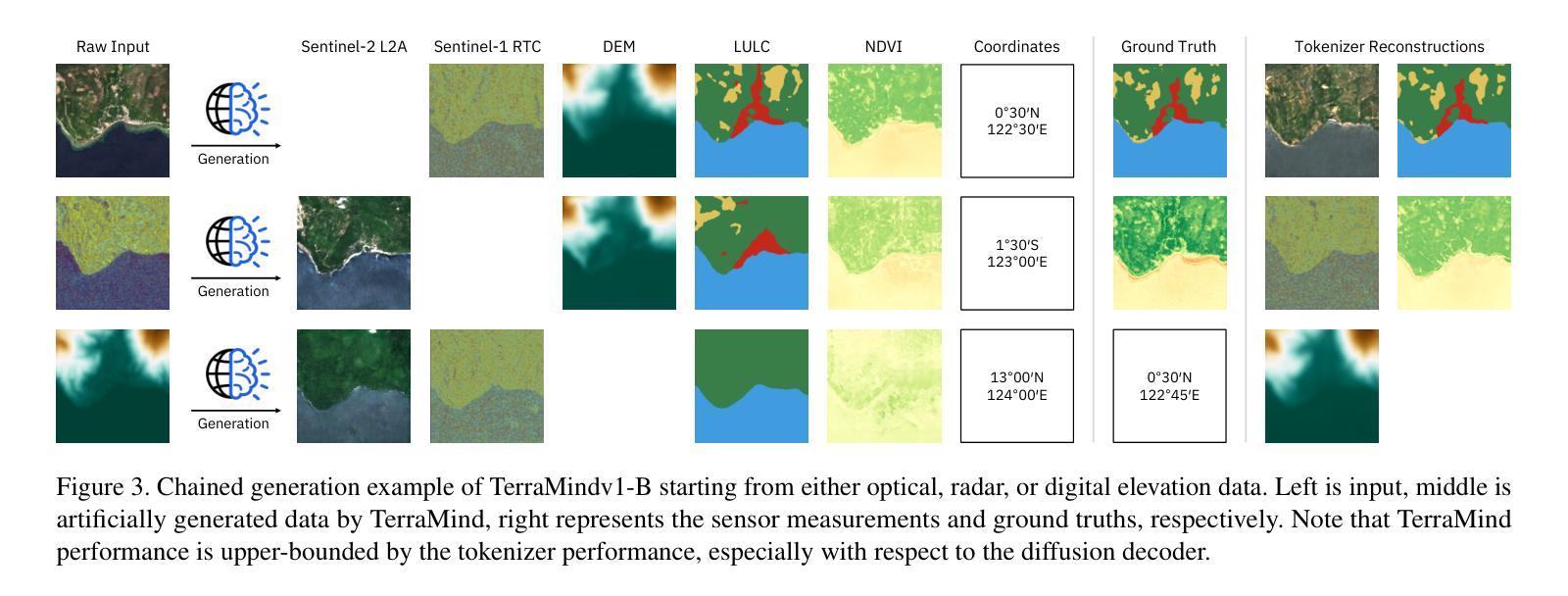
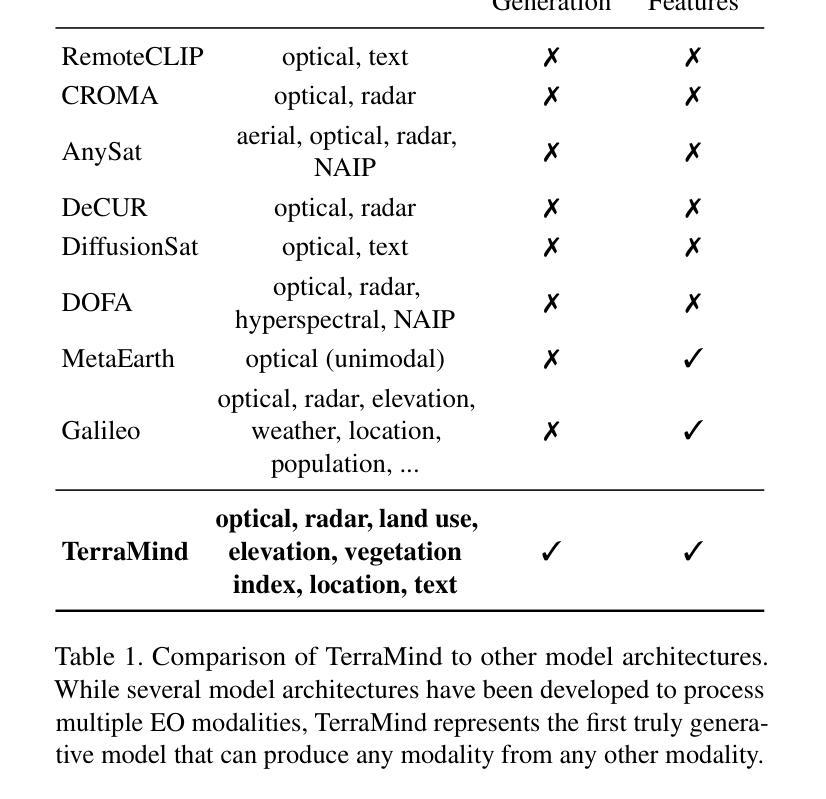
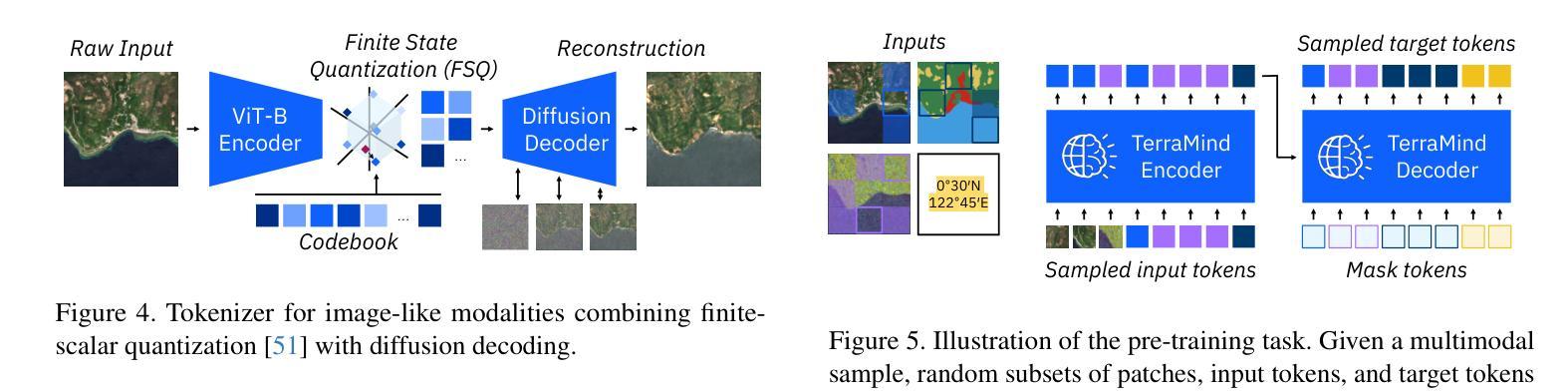
TerraMind: Large-Scale Generative Multimodality for Earth Observation
Authors:Johannes Jakubik, Felix Yang, Benedikt Blumenstiel, Erik Scheurer, Rocco Sedona, Stefano Maurogiovanni, Jente Bosmans, Nikolaos Dionelis, Valerio Marsocci, Niklas Kopp, Rahul Ramachandran, Paolo Fraccaro, Thomas Brunschwiler, Gabriele Cavallaro, Juan Bernabe-Moreno, Nicolas Longépé
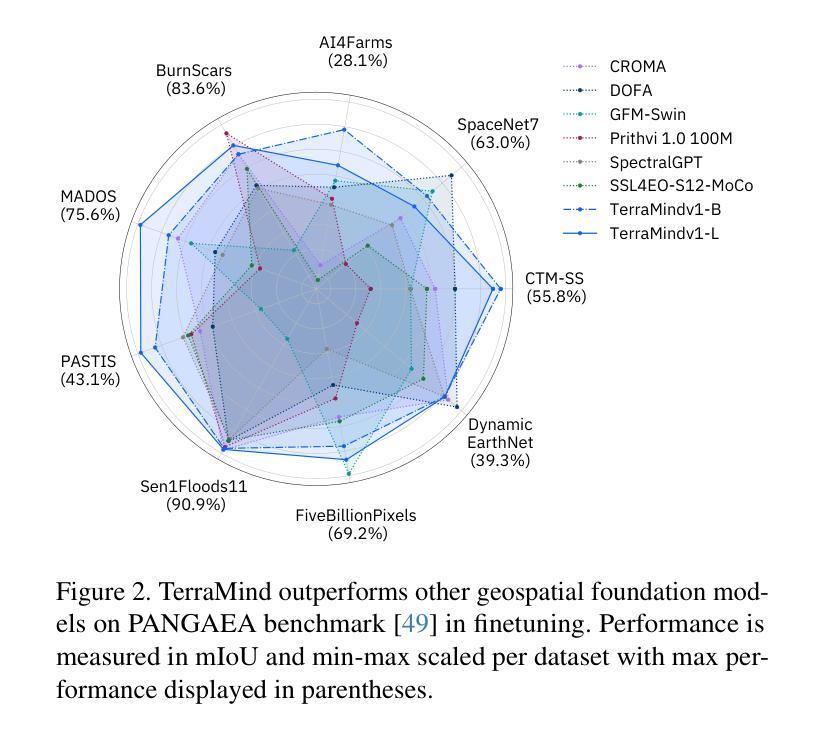
We present TerraMind, the first any-to-any generative, multimodal foundation model for Earth observation (EO). Unlike other multimodal models, TerraMind is pretrained on dual-scale representations combining both token-level and pixel-level data across modalities. On a token level, TerraMind encodes high-level contextual information to learn cross-modal relationships, while on a pixel level, TerraMind leverages fine-grained representations to capture critical spatial nuances. We pretrained TerraMind on nine geospatial modalities of a global, large-scale dataset. In this paper, we demonstrate that (i) TerraMind’s dual-scale early fusion approach unlocks a range of zero-shot and few-shot applications for Earth observation, (ii) TerraMind introduces “Thinking-in-Modalities” (TiM) – the capability of generating additional artificial data during finetuning and inference to improve the model output – and (iii) TerraMind achieves beyond state-of-the-art performance in community-standard benchmarks for EO like PANGAEA. The pretraining dataset, the model weights, and our code are open-sourced under a permissive license.
我们推出TerraMind,这是首个面向地球观测(EO)的任意到任意生成、多模式基础模型。与其他多模式模型不同,TerraMind是在双尺度表示上预训练的,结合了跨模式的令牌级别和像素级别数据。在令牌级别上,TerraMind编码高级上下文信息以学习跨模式关系,而在像素级别上,TerraMind利用精细表示来捕捉关键的空间细微差别。我们在全球大规模数据集的九个地理空间模式上预训练了TerraMind。本文中,我们证明了(i)TerraMind的双尺度早期融合方法开启了地球观测的零样本和少样本应用范围,(ii)TerraMind引入了“模态思考”(TiM)——在微调(finetuning)和推理期间生成额外的模拟数据以提高模型输出的能力,(iii)TerraMind在像PANGAEA这样的社区标准基准测试中实现了超越最新技术的性能。预训练数据集、模型权重和我们的代码都是在许可下开源的。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICCV’25
Summary
TerraMind是首个针对地球观测的任意到任意生成、多模态基础模型。它采用双尺度表示法,结合标记级别和像素级别的数据跨模态进行预训练,能学习跨模态关系并捕捉关键空间细节。TerraMind引入“模态思考”(Thinking-in-Modalities)能力,能在微调及推理过程中生成额外的人工数据,以提升模型输出效果。该模型在地球观测的社区标准基准测试中表现超越现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- TerraMind是首个地球观测的多模态基础模型。
- TerraMind采用双尺度表示法,结合标记和像素级别数据进行预训练。
- TerraMind能学习跨模态关系并捕捉关键空间细节。
- TerraMind引入“模态思考”(Thinking-in-Modalities)能力,提升模型输出效果。
- TerraMind可在零样本和少样本情况下应用。
- TerraMind在地球观测的社区标准基准测试中表现超越现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

7B Fully Open Source Moxin-LLM/VLM – From Pretraining to GRPO-based Reinforcement Learning Enhancement
Authors:Pu Zhao, Xuan Shen, Zhenglun Kong, Yixin Shen, Sung-En Chang, Arash Akbari, Timothy Rupprecht, Lei Lu, Enfu Nan, Changdi Yang, Yumei He, Weiyan Shi, Xingchen Xu, Yu Huang, Wei Jiang, Wei Wang, Yue Chen, Yong He, Yanzhi Wang
Recently, Large Language Models (LLMs) have undergone a significant transformation, marked by a rapid rise in both their popularity and capabilities. Leading this evolution are proprietary LLMs like GPT-4 and GPT-o1, which have captured widespread attention in the AI community due to their remarkable performance and versatility. Simultaneously, open-source LLMs, such as LLaMA, have made great contributions to the ever-increasing popularity of LLMs due to the ease to customize and deploy the models across diverse applications. Although open-source LLMs present unprecedented opportunities for innovation and research, the commercialization of LLMs has raised concerns about transparency, reproducibility, and safety. Many open-source LLMs fail to meet fundamental transparency requirements by withholding essential components like training code and data, which may hinder further innovations on LLMs. To mitigate this issue, we introduce Moxin 7B, a fully open-source LLM developed, adhering to principles of open science, open source, open data, and open access. We release the pre-training code and configurations, training and fine-tuning datasets, and intermediate and final checkpoints, aiming to make continuous commitments to fully open-source LLMs. After pre-training the base model, we finetune the Moxin Base model with SOTA post-training framework and instruction data to obtain Moxin Instruct model. To improve the reasoning capability, we further finetune our Instruct model with chain-of-thought data distilled from DeepSeek R1, and then use Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) following DeepSeek R1 to finetune our model, leading to the Moxin Reasoning model. Moreover, we develop our vision language model based on our Moxin model. Experiments show that our models achieve superior performance in various evaluations such as zero-shot evaluation, few-shot evaluation, and CoT evaluation.
最近,大型语言模型(LLM)经历了重大转变,其受欢迎程度和能力都迅速上升。引领这一变革的是像GPT-4和GPT-o1这样的专有大型语言模型,它们因出色的性能和多功能性而备受人工智能社区的广泛关注。同时,开源大型语言模型,如LLaMA,由于对模型进行定制和跨多种应用程序部署的便捷性,也为大型语言模型日益普及做出了巨大贡献。然而,大型语言模型的商业化引发了关于透明度、可重复性和安全的担忧。许多开源的大型语言模型未能满足基本的透明度要求,隐瞒了关键组件,如训练代码和数据,这可能阻碍大型语言模型的进一步创新。为了缓解这个问题,我们推出了Moxin 7B,这是一个遵循公开科学、开源、开放数据和开放访问原则的全开源大型语言模型。我们发布了预训练代码和配置、训练和微调数据集以及中间和最终检查点,致力于完全开源的大型语言模型的持续承诺。在预训练基础模型后,我们使用先进的后训练框架和指令数据对Moxin基础模型进行微调,以获得Moxin指令模型。为了提高推理能力,我们进一步使用从DeepSeek R1蒸馏得到的思维链数据对指令模型进行微调,然后遵循DeepSeek R1使用组相对策略优化(GRPO)对我们的模型进行微调,从而得到Moxin推理模型。此外,我们基于Moxin模型开发了我们的视觉语言模型。实验表明,我们的模型在零样本评估、少样本评估和CoT评估等各种评估中都取得了优越的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)近期经历显著变革,受到广泛关注。GPT-4和GPT-o1等专有LLM引起AI社区广泛关注,同时开源LLM如LLaMA也为LLM的普及做出贡献。然而,开源LLM的商业化引发透明度、可复制性和安全性的担忧。部分开源LLM未能满足基本透明度要求,隐藏了训练代码和数据等重要组件,可能阻碍LLM的进一步创新。为解决这一问题,我们推出完全开源的LLM——Moxin 7B,遵循公开科学、开源、开放数据和开放访问的原则。我们公开预训练代码和配置、训练和微调数据集以及中间和最终检查点。基于Moxin Base模型,使用最新后训练框架和指令数据微调得到Moxin Instruct模型。通过进一步使用来自DeepSeek R1的思维链数据优化,并使用Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO)策略微调模型,推出Moxin Reasoning模型。同时,基于Moxin模型开发视觉语言模型,实验显示模型在零样本、少样本和思维链评估中表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)近期受到广泛关注和快速发展。
- 专有LLM如GPT-4和GPT-o1引起AI社区关注,而开源LLM如LLaMA也为普及做出贡献。
- 商业化开源LLM引发透明度、可复制性和安全性的担忧。
- 部分开源LLM未能满足透明度要求,隐藏重要组件如训练代码和数据。
- 推出完全开源的LLM——Moxin 7B,遵循公开科学原则,公开预训练代码、配置、数据集和检查点。
- Moxin Instruct模型和Moxin Reasoning模型通过微调和技术优化达到优异性能。
点此查看论文截图

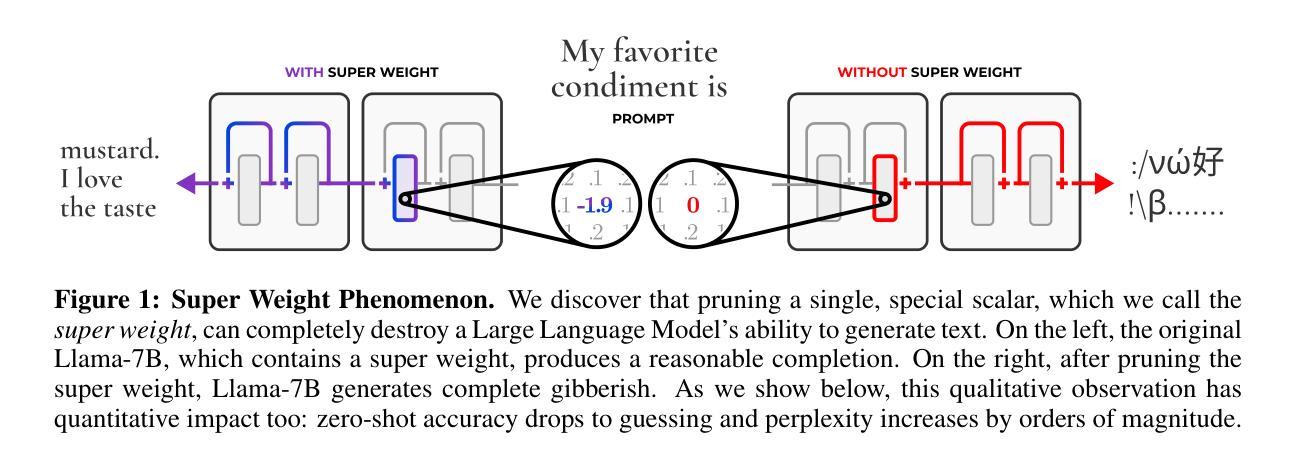
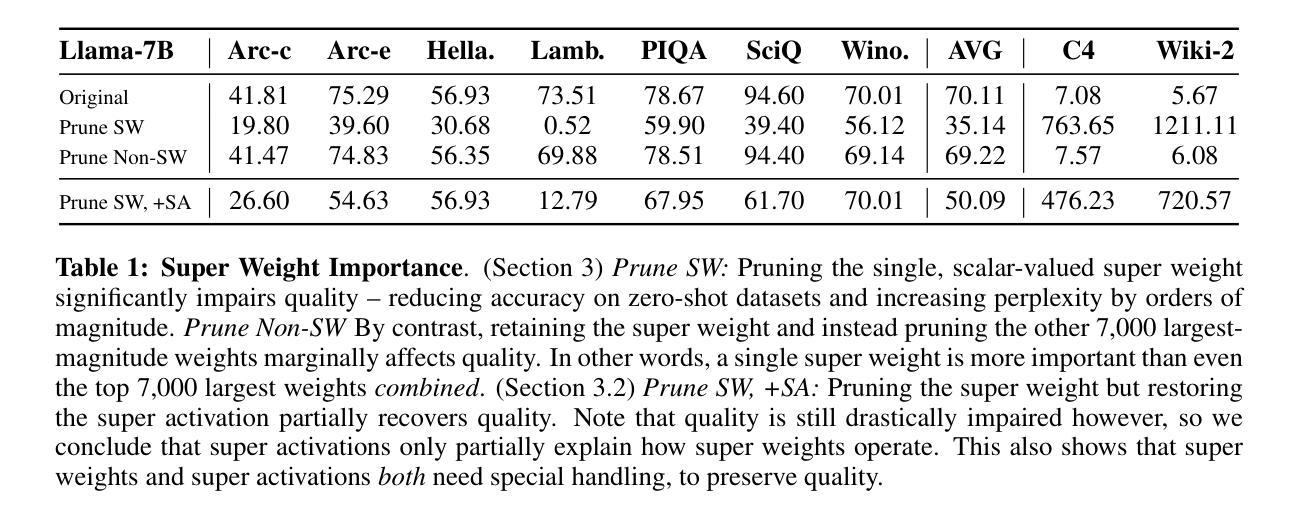
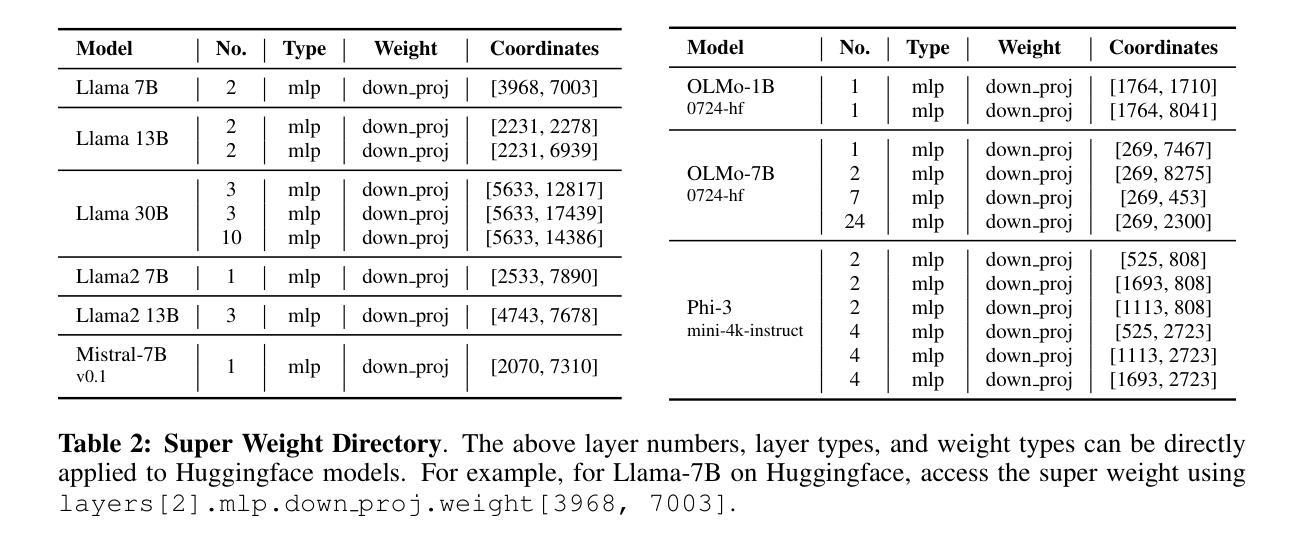
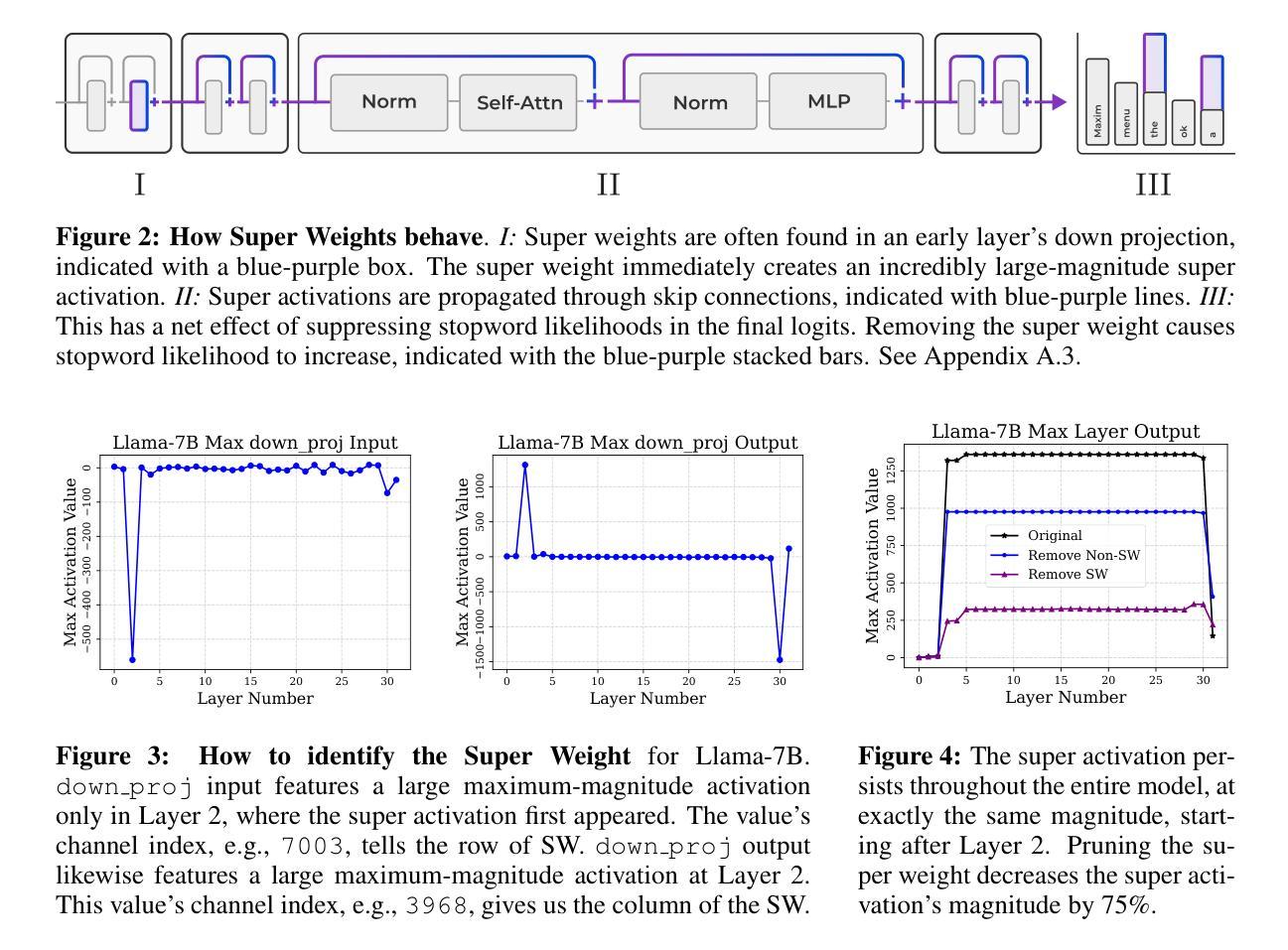
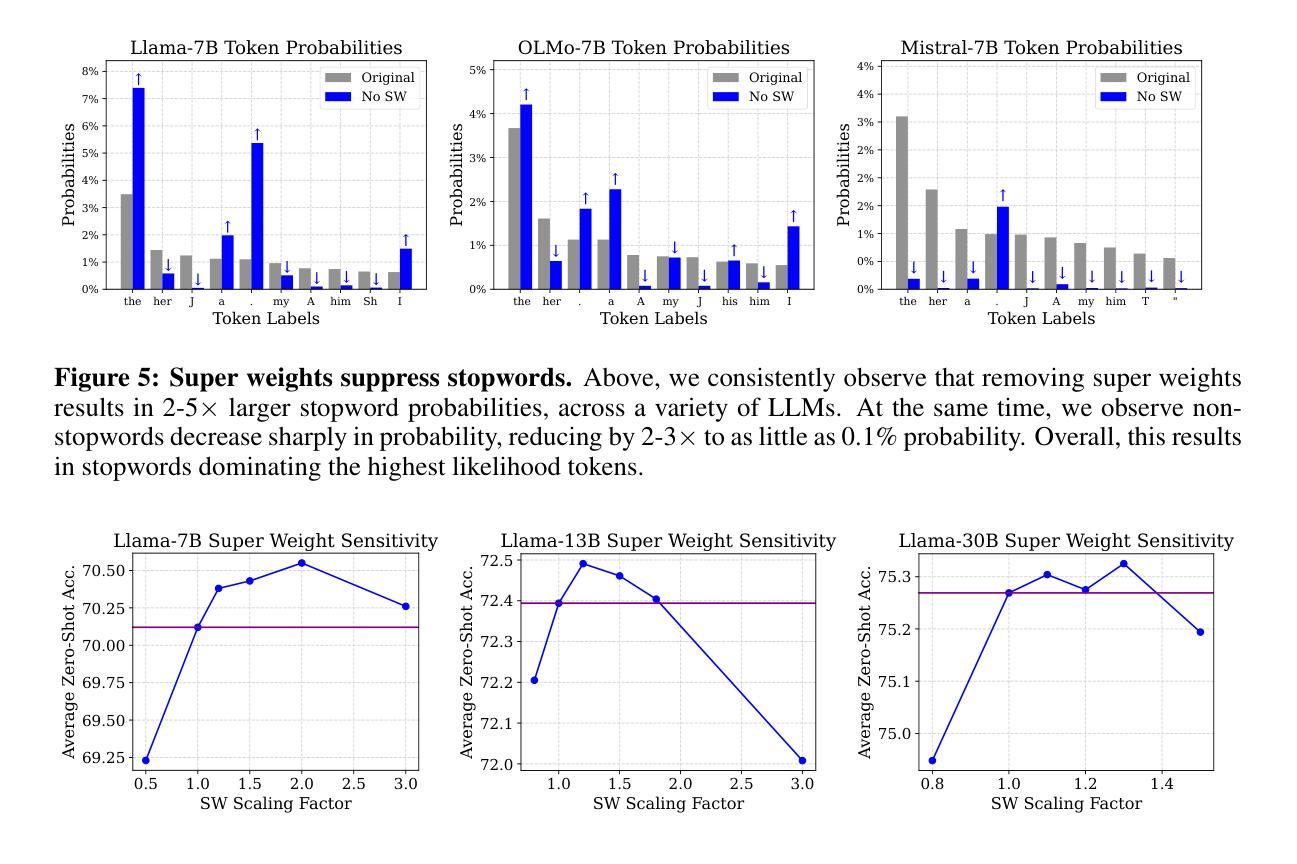
The Super Weight in Large Language Models
Authors:Mengxia Yu, De Wang, Qi Shan, Colorado J Reed, Alvin Wan
Recent works have shown a surprising result: a small fraction of Large Language Model (LLM) parameter outliers are disproportionately important to the quality of the model. LLMs contain billions of parameters, so these small fractions, such as 0.01%, translate to hundreds of thousands of parameters. In this work, we present an even more surprising finding: Pruning as few as a single parameter can destroy an LLM’s ability to generate text – increasing perplexity by 3 orders of magnitude and reducing zero-shot accuracy to guessing. We propose a data-free method for identifying such parameters, termed super weights, using a single forward pass through the model. We additionally find that these super weights induce correspondingly rare and large activation outliers, termed super activations. When preserved with high precision, super activations can improve simple round-to-nearest quantization to become competitive with state-of-the-art methods. For weight quantization, we similarly find that by preserving the super weight and clipping other weight outliers, round-to-nearest quantization can scale to much larger block sizes than previously considered. To facilitate further research into super weights, we provide an index of super weight coordinates for common, openly available LLMs.
近期的研究结果令人惊讶:大型语言模型(LLM)中的一小部分参数异常值对模型质量有着极其重要的作用。LLM包含数十亿参数,因此这些小部分,例如0.01%,相当于数十万个参数。在这项工作中,我们提出了一个更令人惊讶的发现:仅删除一个参数就能破坏LLM生成文本的能力——使困惑度增加三个数量级,并将零射击准确率降低到猜测水平。我们提出了一种无需数据的方法,通过单一的前向传递模型来识别这些参数,称为超级权重。此外,我们还发现这些超级权重会引发相应罕见的超大激活异常值,称为超级激活。当以高精确度保留时,超级激活可以改善简单的四舍五入量化方法,使其与最新技术相竞争。对于权重量化,我们也发现通过保留超级权重并剪切其他权重异常值,四舍五入量化方法可以扩展到比以往更大的块大小。为了促进对超级权重的进一步研究,我们为常见的公开LLM提供了超级权重坐标的索引。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期研究发现,大型语言模型(LLM)中的一小部分参数异常值对模型质量至关重要。通过仅修剪一个参数,LLM生成文本的能力可能被破坏,表现为困惑度增加三个数量级,零样本准确率降至猜测水平。本文提出了一种无需数据的超级权重识别方法,并发现超级权重对应产生稀有且大型激活异常值——超级激活。当精确保留超级激活时,简单的四舍五入量化方法可提高至与最新技术相当的水平。对于权重量化,通过保留超级权重并裁剪其他权重异常值,简单的四舍五入量化方法可以扩展到更大的块大小。为了方便对超级权重进行进一步研究,我们为常见的公开LLM提供了超级权重坐标索引。
Key Takeaways
- LLM中的一小部分参数异常值对模型质量至关重要。
- 仅修剪一个参数可能导致LLM生成文本能力的大幅下降。
- 提出了数据无关的超级权重识别方法。
- 超级权重会引发超级激活现象。
- 精确保留超级激活能提高量化方法的性能。
- 对于权重量化,保留超级权重并裁剪其他权重异常值能使量化方法更有效率。
点此查看论文截图

Large-scale, Independent and Comprehensive study of the power of LLMs for test case generation
Authors:Wendkûuni C. Ouédraogo, Kader Kaboré, Yinghua Li, Haoye Tian, Anil Koyuncu, Jacques Klein, David Lo, Tegawendé F. Bissyandé
Unit testing is essential for software reliability, yet manual test creation is time-consuming and often neglected. Although search-based software testing improves efficiency, it produces tests with poor readability and maintainability. Although LLMs show promise for test generation, existing research lacks comprehensive evaluation across execution-driven assessment, reasoning-based prompting, and real-world testing scenarios. This study presents the first large-scale empirical evaluation of LLM-generated unit tests at the class level, systematically analyzing four state-of-the-art models - GPT-3.5, GPT-4, Mistral 7B, and Mixtral 8x7B - against EvoSuite across 216,300 test cases from Defects4J, SF110, and CMD (a dataset mitigating LLM training data leakage). We evaluate five prompting techniques - Zero-Shot Learning (ZSL), Few-Shot Learning (FSL), Chain-of-Thought (CoT), Tree-of-Thought (ToT), and Guided Tree-of-Thought (GToT) - assessing syntactic correctness, compilability, hallucination-driven failures, readability, code coverage metrics, and fault detection capabilities. Our findings challenge prior claims that in-context learning is ineffective for test generation in code-specialized LLMs. Reasoning-based prompting - particularly GToT - significantly enhances test reliability, compilability, and structural adherence in general-purpose LLMs. However, hallucination-driven failures remain a persistent challenge, manifesting as non-existent symbol references, incorrect API calls, and fabricated dependencies, resulting in high compilation failure rates (up to 86%). Execution-based classification and mutation testing reveal that many failing tests stem from hallucinated dependencies, limiting effective fault detection.
单元测试对于软件可靠性至关重要,但手动创建测试非常耗时且经常被忽视。尽管基于搜索的软件测试提高了效率,但它产生的测试可读性较差且难以维护。虽然大型语言模型(LLMs)在测试生成方面显示出潜力,但现有研究在执行驱动评估、基于推理的提示和真实世界测试场景方面的综合评估仍然不足。本研究首次对LLM生成的类级单元测试进行大规模实证研究,系统分析了四种最先进的模型——GPT-3.5、GPT-4、Mistral 7B和Mixtral 8x7B,与EvoSuite相对比,研究对象为来自Defects4J、SF110和CMD(一种减轻LLM训练数据泄露的数据集)的216,300个测试用例。我们评估了五种提示技术——零样本学习(ZSL)、小样本学习(FSL)、思维链(CoT)、思维树(ToT)和引导思维树(GToT)——评估语法正确性、可编译性、幻觉驱动故障、可读性、代码覆盖率指标和故障检测能力。我们的研究结果质疑了先前关于上下文学习对代码专用LLM中的测试生成无效的说法。基于推理的提示——尤其是GToT——显著提高了通用LLM的测试可靠性、可编译性和结构依从性。然而,幻觉驱动故障仍然是一个持续存在的挑战,表现为不存在的符号引用、错误的API调用和虚构的依赖关系,导致高编译失败率(高达86%)。基于执行的分类和变异测试表明,许多失败的测试源于虚构的依赖关系,限制了有效的故障检测。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了LLM模型在生成单元测试方面的性能,对四种先进模型进行了大规模实证评估,探讨了五种提示技术,并发现基于推理的提示技术能显著提高测试可靠性、编译能力和结构遵循性。然而,幻想驱动故障仍然是一个持续存在的挑战,导致高编译失败率。
Key Takeaways
- LLM模型在生成单元测试时显示出潜力,但存在挑战。
- 对四种先进的LLM模型进行了大规模实证评估。
- 探讨了五种提示技术,包括Zero-Shot Learning、Few-Shot Learning等。
- 基于推理的提示技术(如GToT)能提高测试可靠性、编译能力和结构遵循性。
- 幻想驱动故障是一个持续存在的挑战,导致高编译失败率。
- 执行分类和突变测试表明,许多失败的测试源于幻想依赖。
点此查看论文截图

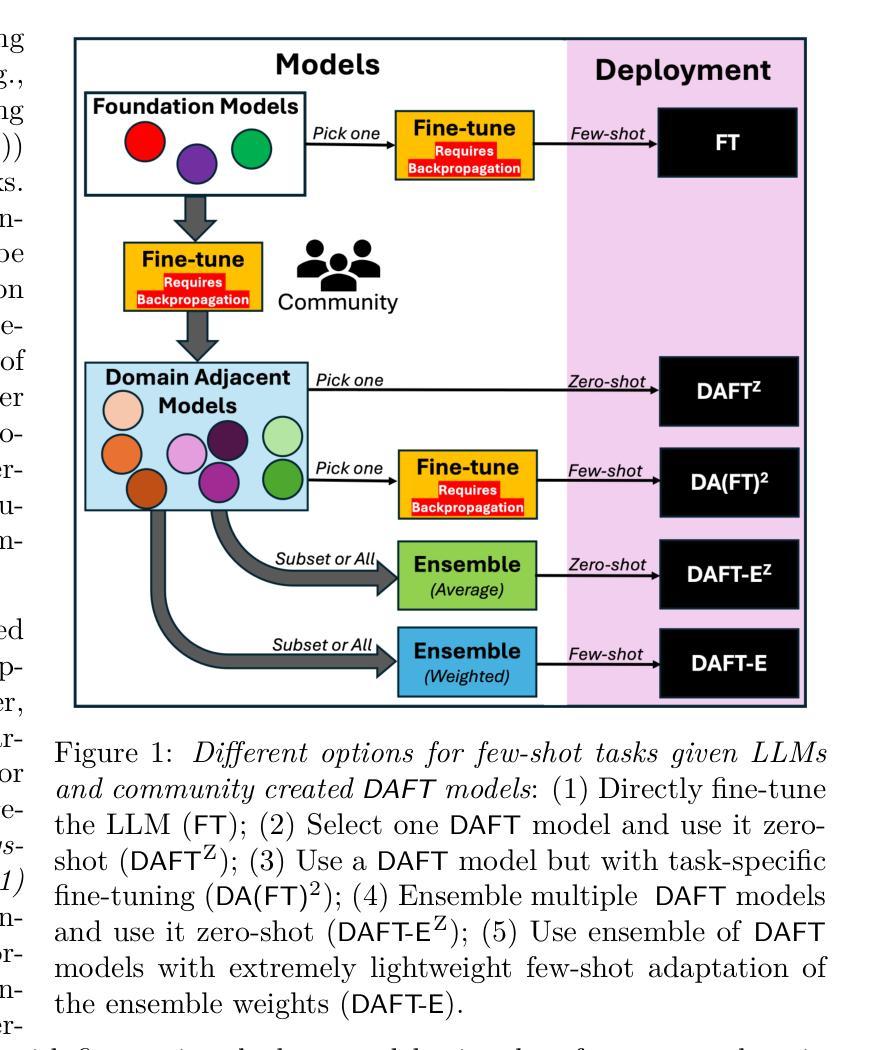
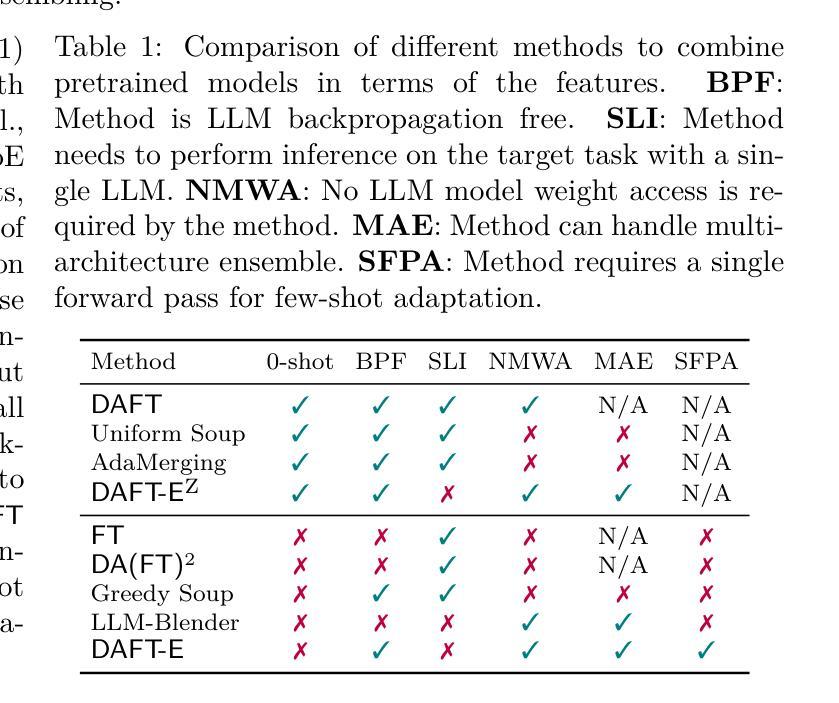
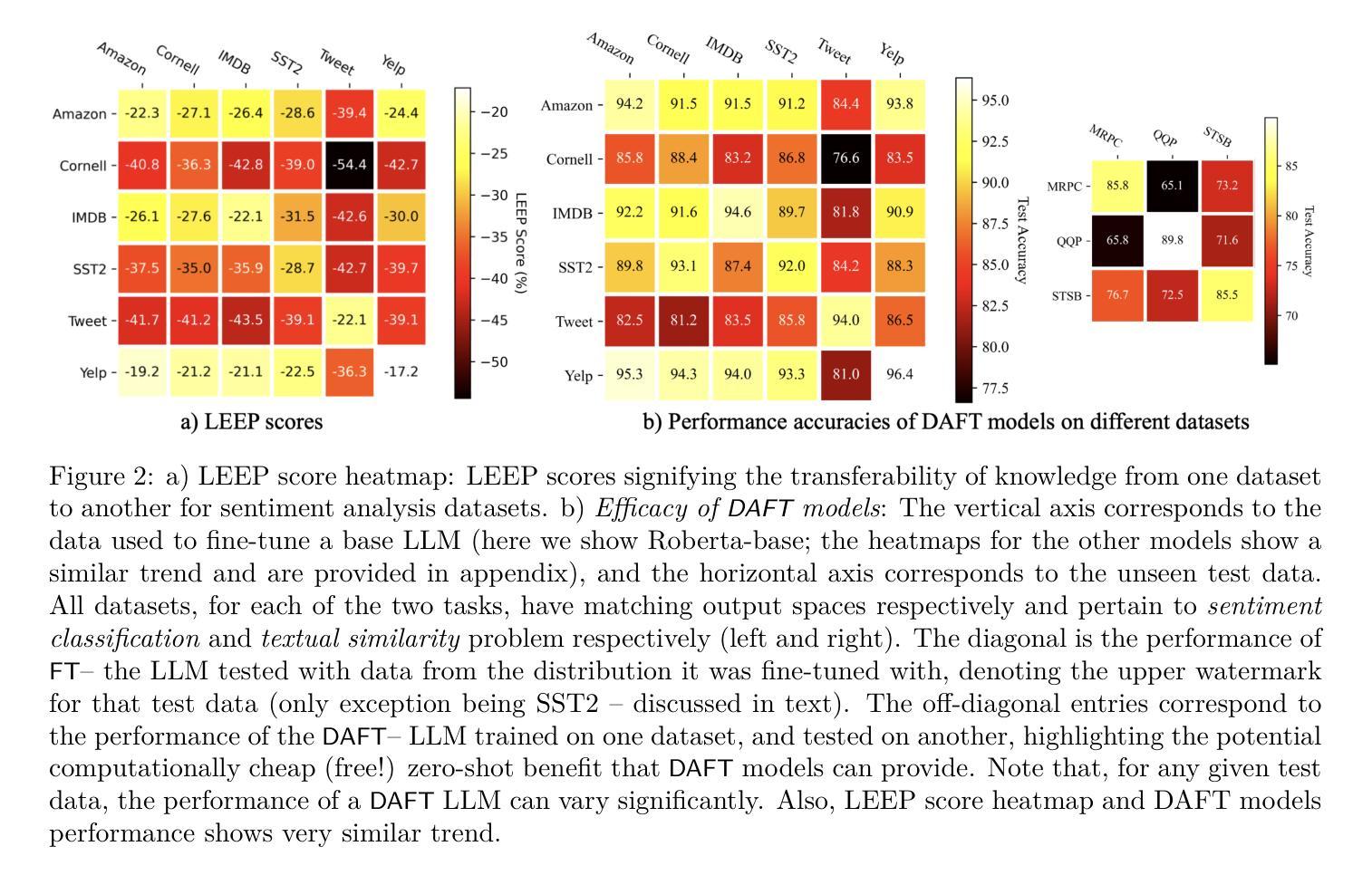
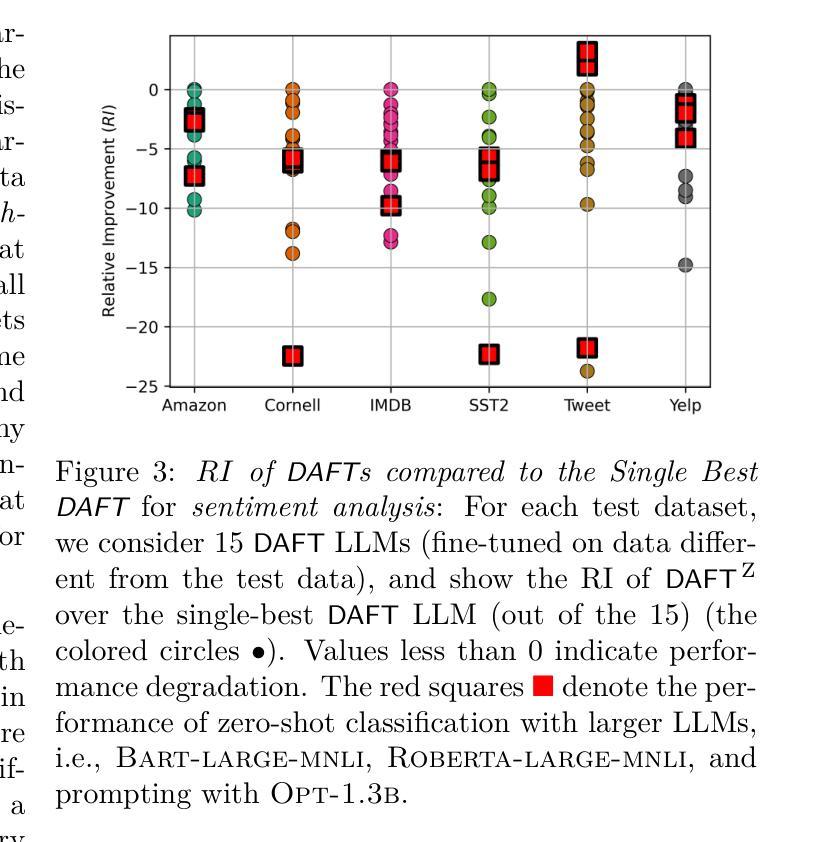
On the Utility of Domain-Adjacent Fine-Tuned Model Ensembles for Few-shot Problems
Authors:Md Ibrahim Ibne Alam, Parikshit Ram, Soham Dan, Horst Samulowitz, Koushik Kar
Large Language Models (LLMs) have been observed to perform well on a wide range of downstream tasks when fine-tuned on domain-specific data. However, such data may not be readily available in many applications, motivating zero-shot or few-shot approaches using domain-adjacent models. While several fine-tuned models for various tasks are available, finding an appropriate domain-adjacent model for a given task is often not straight forward. In this paper, we study DAFT-E, a framework that utilizes an Ensemble of Domain-Adjacent Fine-Tuned Foundation Models for few-shot problems. We show that for zero-shot problems, this ensembling method provides an accuracy performance close to that of the single best model. With few-shot problems, this performance improves further, at which point DEFT-E can outperform any single domain-adjacent model while requiring much less data for domain-specific fine-tuning.
大型语言模型(LLMs)在针对特定领域数据进行微调后,在多种下游任务上表现出良好的性能。然而,在许多应用中可能无法轻松获得此类数据,这促使人们采用使用领域相邻模型的零样本或少样本方法。虽然针对各种任务的多个微调模型是可用的,但为给定任务找到适当的领域相邻模型通常并不简单。在本文中,我们研究了DAFT-E,这是一个利用领域相邻微调基础模型的集合来解决少样本问题的框架。我们表明,对于零样本问题,这种集成方法提供的准确性表现接近单个最佳模型。对于少样本问题,性能会进一步提高,此时DEFT-E可以超越任何单个领域相邻模型,同时需要更少的数据进行领域特定微调。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Main paper is 14 pages, followed by references and appendix
Summary
大规模语言模型(LLMs)在特定领域数据上微调后,能够在各种下游任务上表现良好。但在许多应用中,此类数据可能不易获得,因此提倡使用与领域相邻的模型进行零样本或小样本方法。尽管存在多种针对各种任务的微调模型,但找到合适的与给定任务相邻的模型并不总是直接明了。本文研究了DAFT-E框架,它利用一组与领域相邻的微调基础模型(Ensemble)来解决小样本问题。我们表明,对于零样本问题,这种集成方法提供的准确率性能接近单一最佳模型。在小样本问题的情况下,性能进一步提高,此时DEFT-E可以超越任何单一的领域相邻模型,同时需要更少的数据进行领域特定微调。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs在特定领域数据上微调后,在多种下游任务上表现良好。
- 在许多应用中,特定领域数据可能难以获取,因此提倡使用零样本或小样本方法与领域相邻的模型。
- 找到与给定任务合适的领域相邻模型并不总是直接明了。
- DAFT-E框架利用一组与领域相邻的微调基础模型(Ensemble)来解决小样本问题。
- 对于零样本问题,DAFT-E集成方法的准确率性能接近单一最佳模型。
- 在小样本问题的情况下,DAFT-E性能优于单一领域相邻模型。
点此查看论文截图