⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-09 更新
VERITAS: Verification and Explanation of Realness in Images for Transparency in AI Systems
Authors:Aadi Srivastava, Vignesh Natarajkumar, Utkarsh Bheemanaboyna, Devisree Akashapu, Nagraj Gaonkar, Archit Joshi
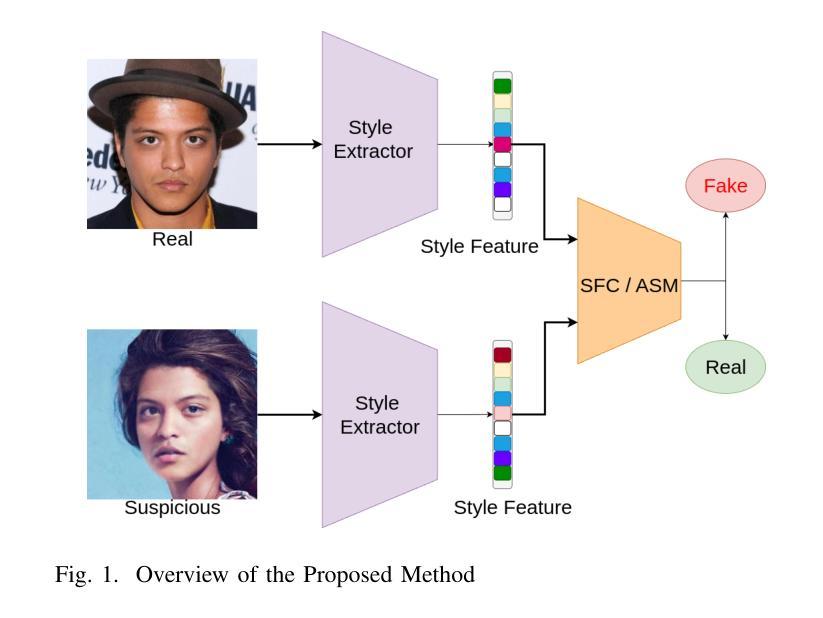
The widespread and rapid adoption of AI-generated content, created by models such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Diffusion Models, has revolutionized the digital media landscape by allowing efficient and creative content generation. However, these models also blur the difference between real images and AI-generated synthetic images, raising concerns regarding content authenticity and integrity. While many existing solutions to detect fake images focus solely on classification and higher-resolution images, they often lack transparency in their decision-making, making it difficult for users to understand why an image is classified as fake. In this paper, we present VERITAS, a comprehensive framework that not only accurately detects whether a small (32x32) image is AI-generated but also explains why it was classified that way through artifact localization and semantic reasoning. VERITAS produces human-readable explanations that describe key artifacts in synthetic images. We show that this architecture offers clear explanations of the basis of zero-shot synthetic image detection tasks. Code and relevant prompts can be found at https://github.com/V-i-g-n-e-s-h-N/VERITAS .
由生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型等模型生成的AI生成内容得到广泛而迅速采纳,它通过实现高效创意的内容生成,为数字媒体领域带来了革命性变化。然而,这些模型也模糊了真实图像和AI生成的合成图像之间的差异,引发了人们对内容真实性和完整性的担忧。虽然许多现有检测虚假图像的方法只关注分类和更高分辨率的图像,但它们在决策制定上往往缺乏透明度,使得用户难以理解为何某图像会被归类为虚假图像。在本文中,我们提出了VERITAS,这是一个全面的框架,不仅能够准确检测小到(32x32)的图像是否是AI生成的,而且能够通过伪影定位和语义推理来解释为何将其归类为AI生成。VERITAS产生人类可读的解释,描述合成图像中的关键伪影。我们表明,该架构为无样本合成图像检测任务提供了明确的解释。代码和相关提示可在https://github.com/V-i-g-n-e-s-h-N/VERITAS找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
人工智能生成的内容如通过生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型等创造的内容正快速广泛地被采纳,这不仅为数字媒体领域带来了创新和高效的内容生成方式,但同时也使得真实图像和AI生成的合成图像之间的界限变得模糊,引发了关于内容真实性和完整性的担忧。现有的图像检测假图解决方案主要集中在分类和高分辨率图像上,但它们的决策过程缺乏透明度,使得用户难以理解为何某图像被判定为假。本文提出了VERITAS框架,不仅能准确检测小到(32x32)的图像是否由AI生成,还能通过伪影定位和语义推理解释分类的原因,产生人类可读的解释,描述合成图像中的关键伪影。该架构为无射击合成图像检测任务提供了清晰的解释依据。相关代码和提示可在相关网站找到。
Key Takeaways
- AI生成的内容如GANs和扩散模型等已经革命化了数字媒体领域的创意和效率。
- AI生成的图像与真实图像的界限模糊引发了内容真实性的担忧。
- 当前假图检测方案虽可分类图像并适应高分辨率图像,但缺乏决策透明度。
- VERITAS框架不仅可以准确检测小型图像是否由AI生成,还可以解释检测结果的依据。
- VERITAS提供了清晰的伪影定位以及合成图像的关键语义推理,通过人类可读的解释帮助用户理解判断原因。
- 该架构为零射式合成图像检测任务提供了透明且可理解的解释基础。
点此查看论文截图



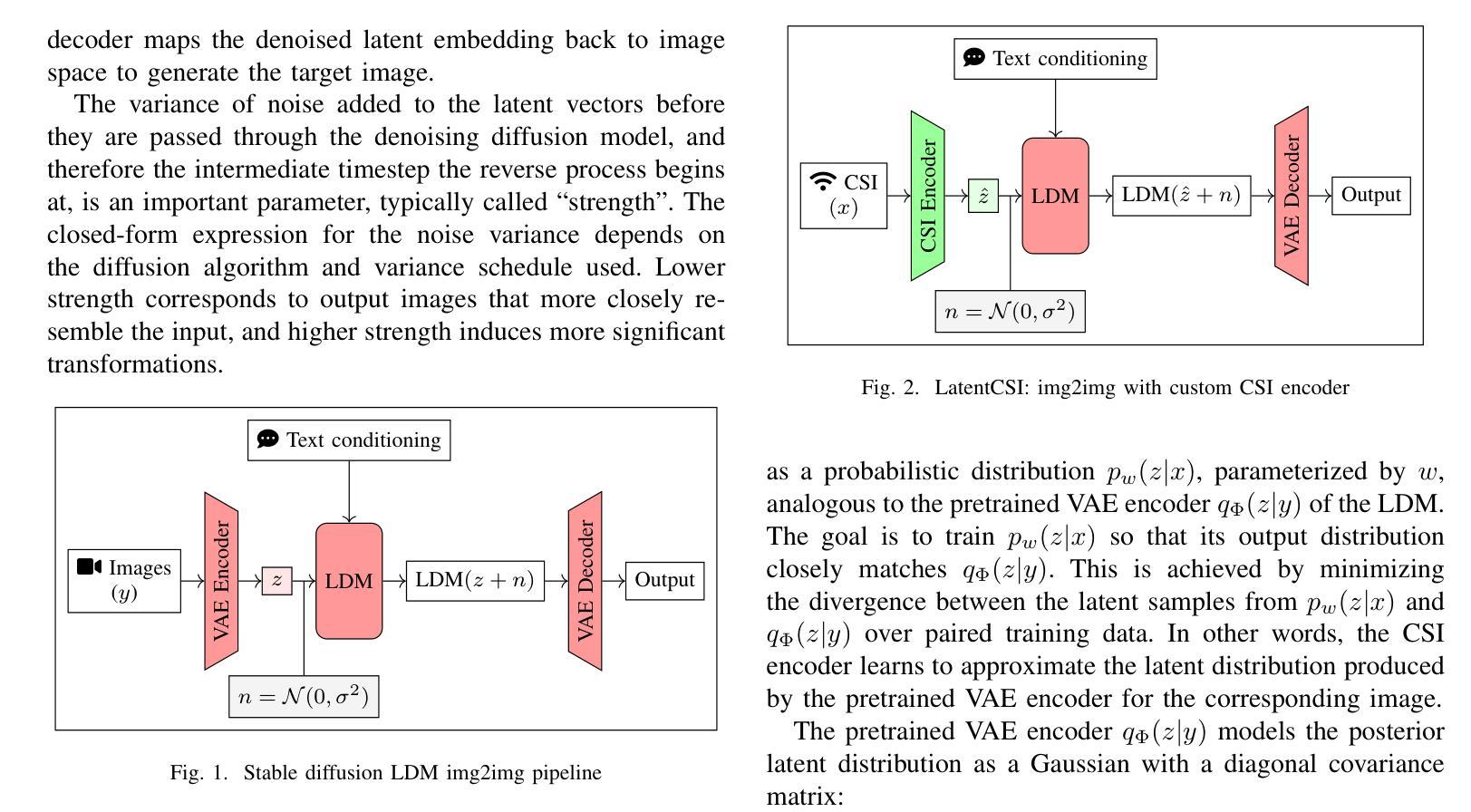
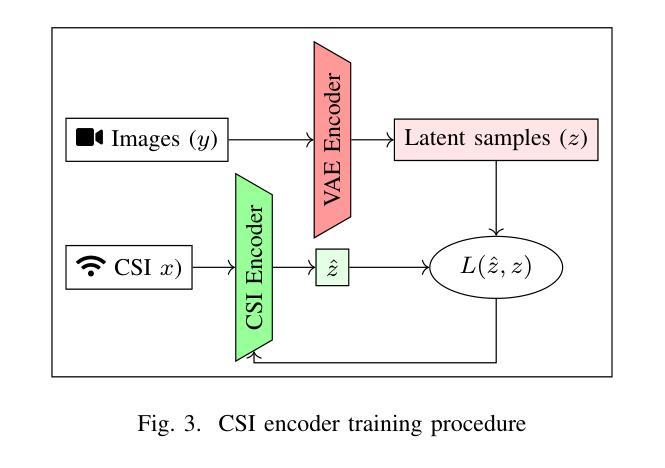
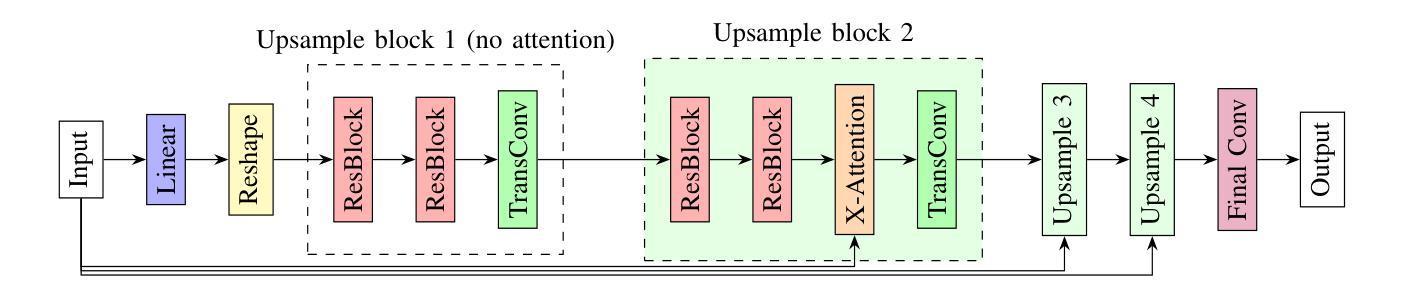
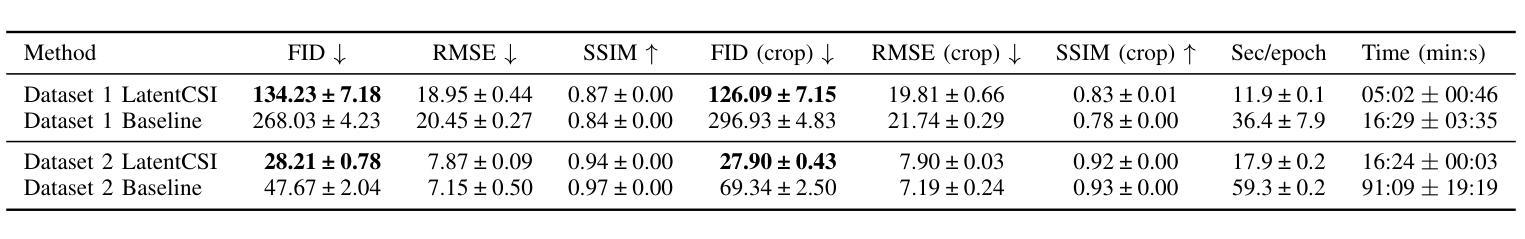
High-resolution efficient image generation from WiFi CSI using a pretrained latent diffusion model
Authors:Eshan Ramesh, Takayuki Nishio
We present LatentCSI, a novel method for generating images of the physical environment from WiFi CSI measurements that leverages a pretrained latent diffusion model (LDM). Unlike prior approaches that rely on complex and computationally intensive techniques such as GANs, our method employs a lightweight neural network to map CSI amplitudes directly into the latent space of an LDM. We then apply the LDM’s denoising diffusion model to the latent representation with text-based guidance before decoding using the LDM’s pretrained decoder to obtain a high-resolution image. This design bypasses the challenges of pixel-space image generation and avoids the explicit image encoding stage typically required in conventional image-to-image pipelines, enabling efficient and high-quality image synthesis. We validate our approach on two datasets: a wide-band CSI dataset we collected with off-the-shelf WiFi devices and cameras; and a subset of the publicly available MM-Fi dataset. The results demonstrate that LatentCSI outperforms baselines of comparable complexity trained directly on ground-truth images in both computational efficiency and perceptual quality, while additionally providing practical advantages through its unique capacity for text-guided controllability.
我们提出了LatentCSI,这是一种从WiFi CSI测量中生成物理环境图像的新型方法,它利用预先训练的潜在扩散模型(LDM)。不同于以往依赖复杂且计算密集的技术(如GANs)的方法,我们的方法采用轻量级的神经网络将CSI振幅直接映射到LDM的潜在空间。然后,我们对潜在表示应用LDM的去噪声扩散模型,在解码之前使用基于文本的指导来获得高分辨率图像。这种设计绕过了像素空间图像生成的挑战,避免了传统图像到图像管道中通常需要的显式图像编码阶段,从而实现了高效的高质量图像合成。我们在两个数据集上验证了我们的方法:一个是我们使用现成的WiFi设备和相机收集的宽带CSI数据集;另一个是公共可用的MM-Fi数据集的子集。结果表明,LatentCSI在计算效率和感知质量上均优于直接在地面上训练的同等复杂度的基线图像,此外,它还通过独特的文本指导可控性提供了实际优势。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 4 figures
Summary
基于WiFi CSI测量的物理环境图像生成新方法LatentCSI的研究介绍。该方法利用预训练的潜在扩散模型(LDM),通过轻量级神经网络将CSI振幅映射到LDM的潜在空间,再应用LDM的降噪扩散模型进行图像生成。此方法绕过像素空间图像生成的挑战,避免传统图像到图像的管道中通常需要的显式图像编码阶段,实现高效高质量图像合成。
Key Takeaways
- LatentCSI是一种基于WiFi CSI测量的物理环境图像生成新方法。
- 该方法利用预训练的潜在扩散模型(LDM)。
- LatentCSI使用轻量级神经网络将CSI振幅映射到LDM的潜在空间。
- 方法应用LDM的降噪扩散模型进行图像生成。
- 此方法绕过像素空间图像生成的挑战,实现高效高质量图像合成。
- LatentCSI在宽频CSI数据集和公开可用的MM-Fi数据集上进行了验证。
点此查看论文截图



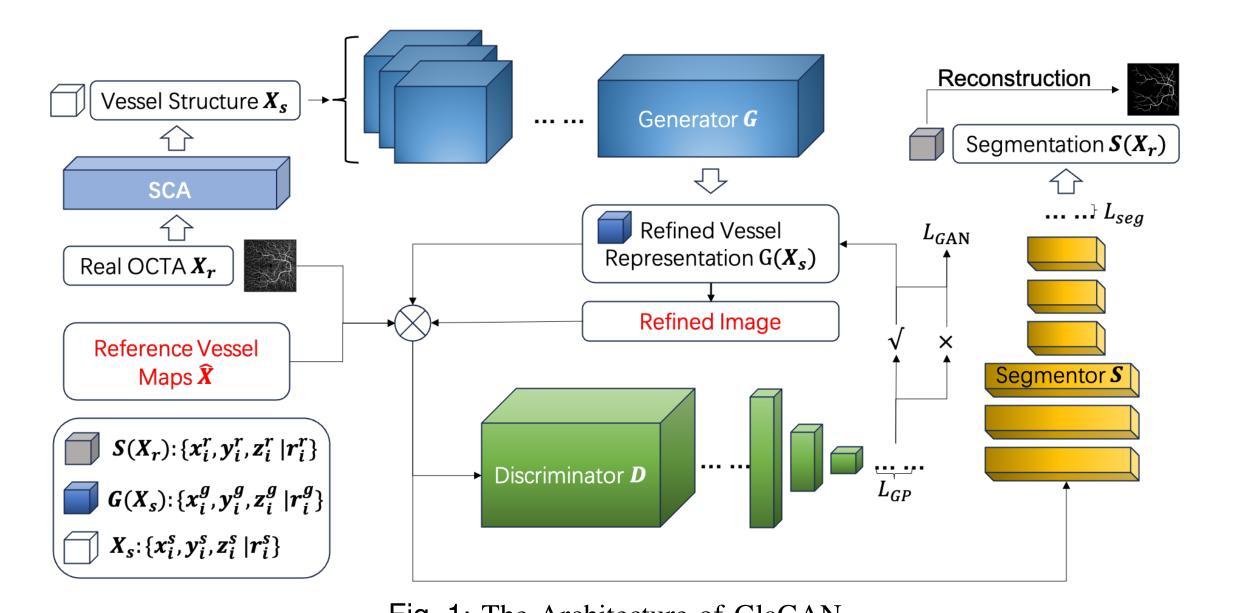
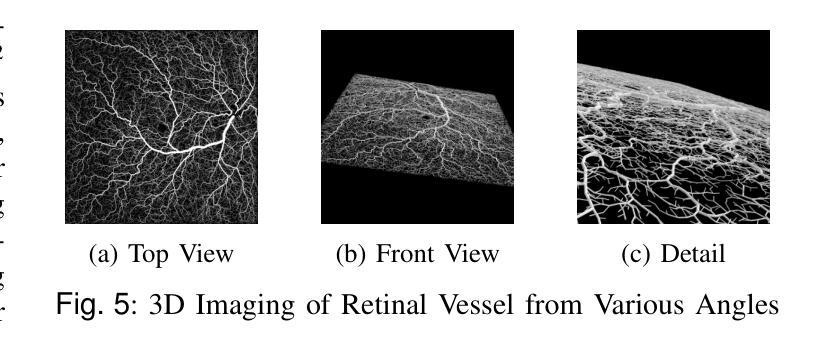
GlaGAN: A Generative Unsupervised Model for High-Precision Segmentation of Retinal Main Vessels toward Early Detection of Glaucoma
Authors:Cheng Huang, Weizheng Xie, Tsengdar J. Lee, Jui-Kai Wang, Karanjit Kooner, Ning Zhang, Jia Zhang
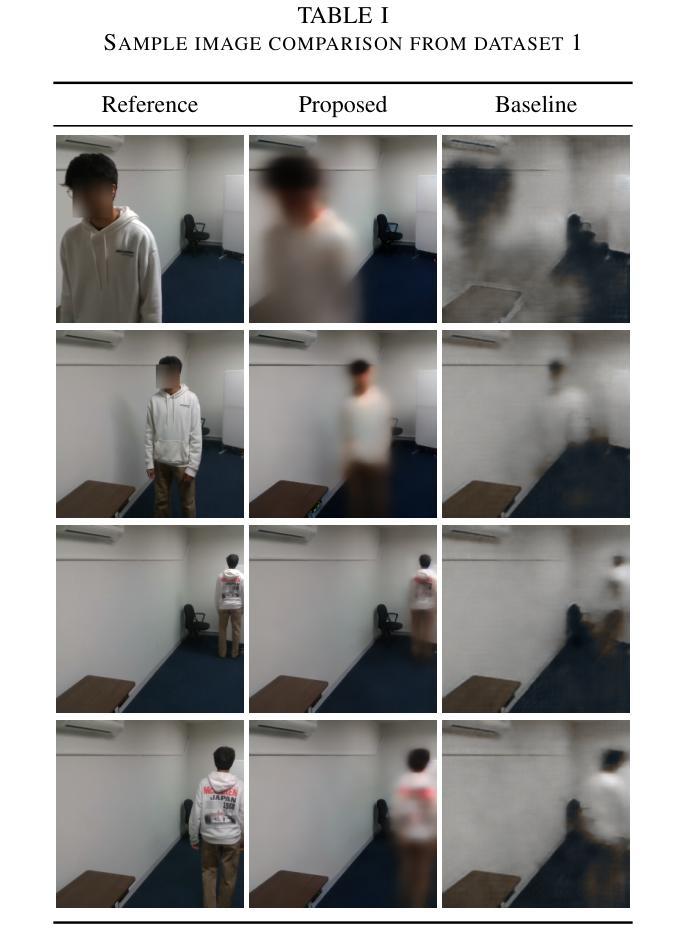
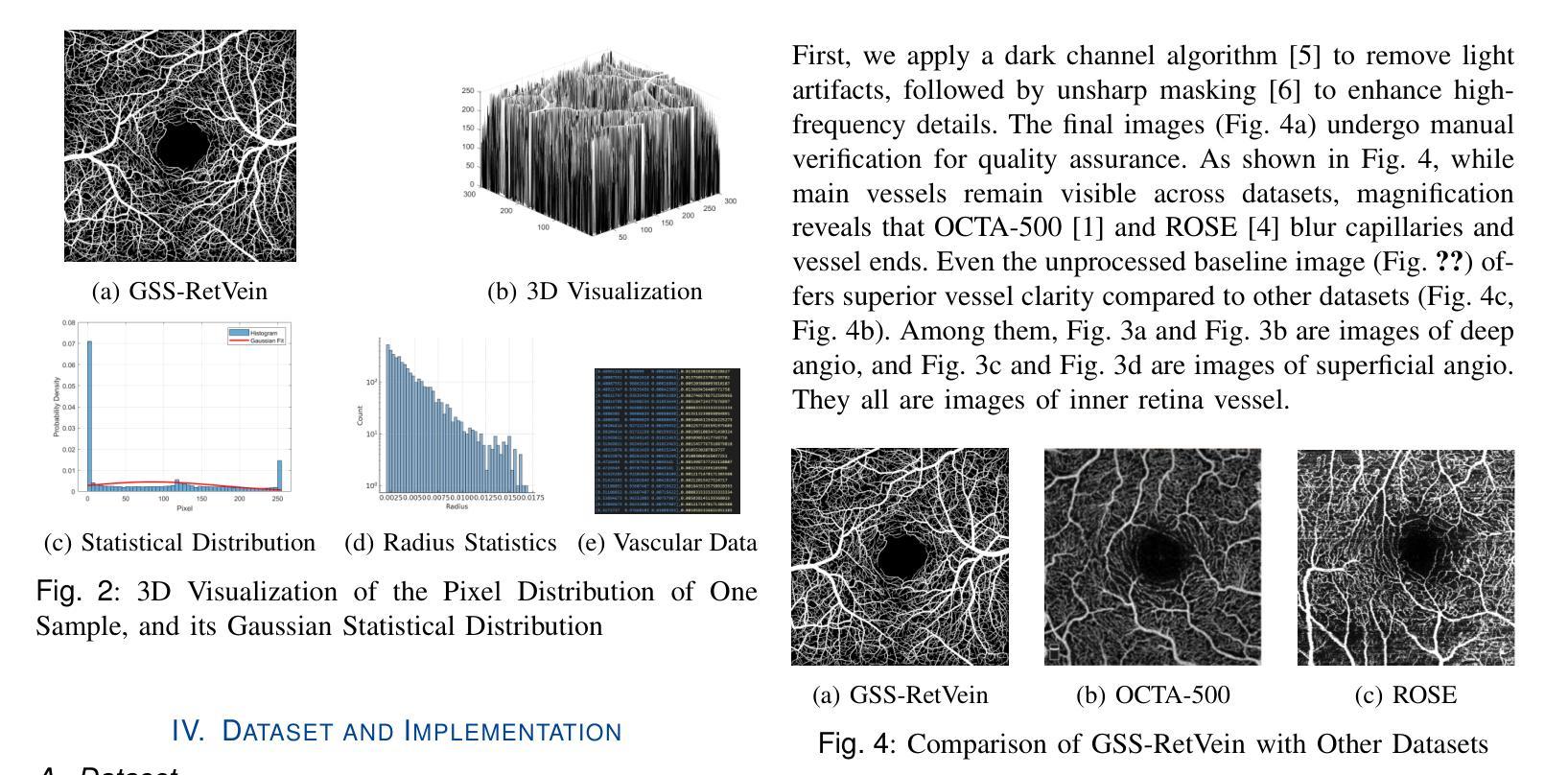
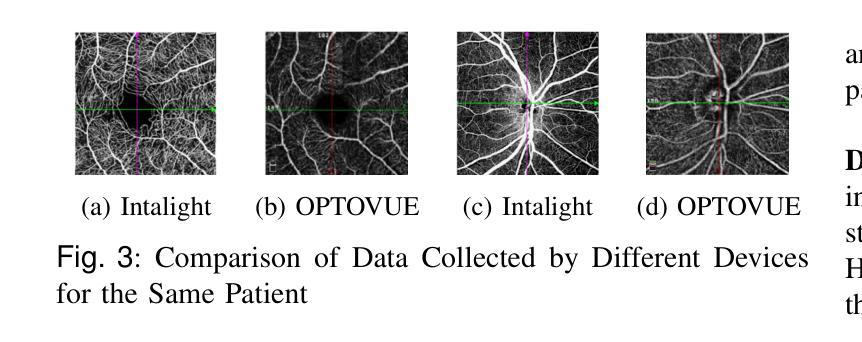
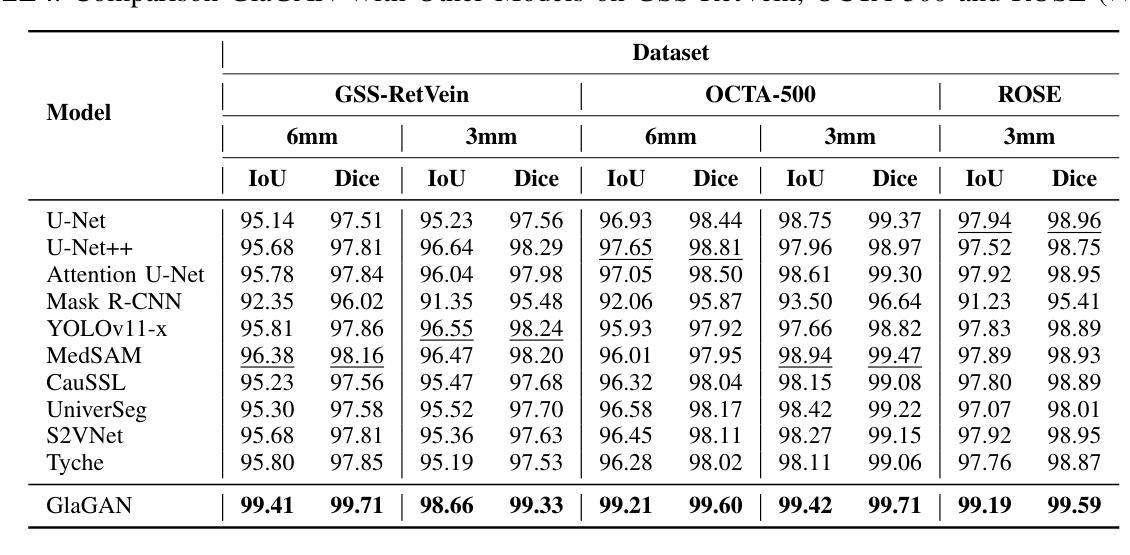
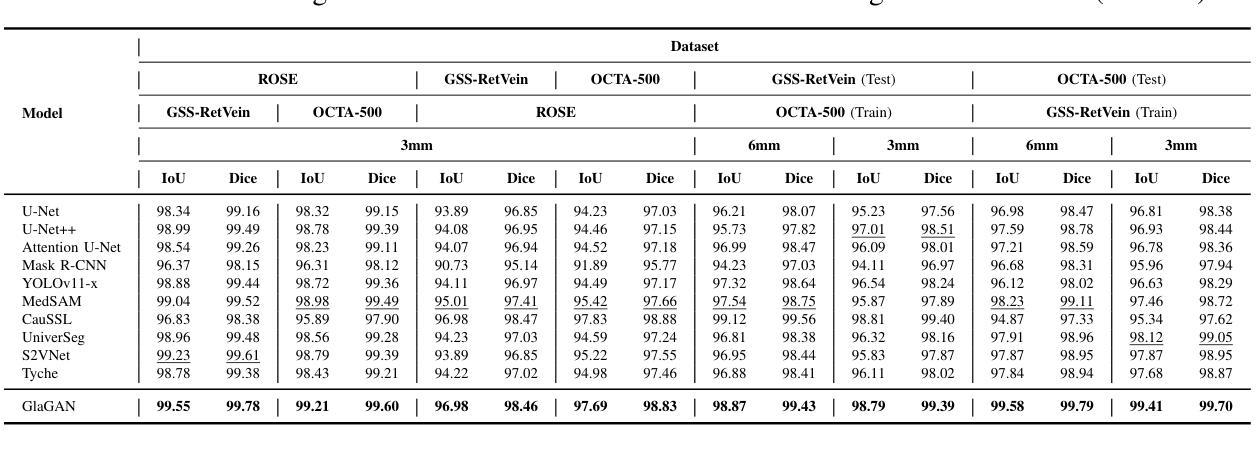
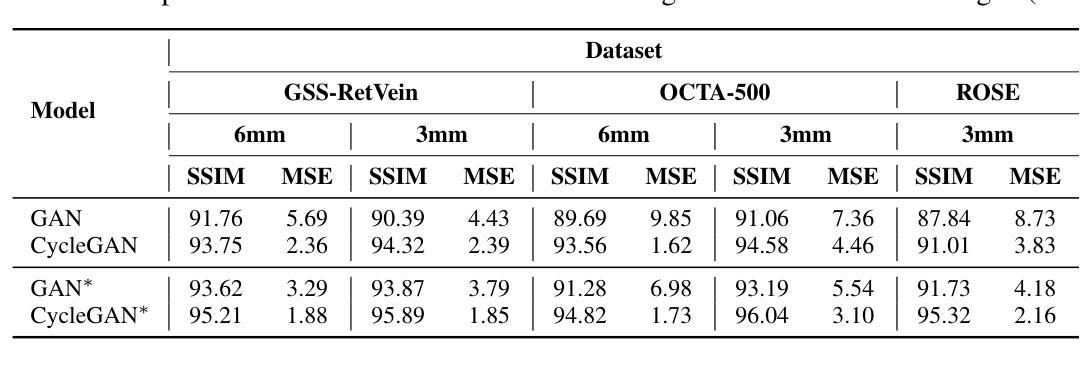
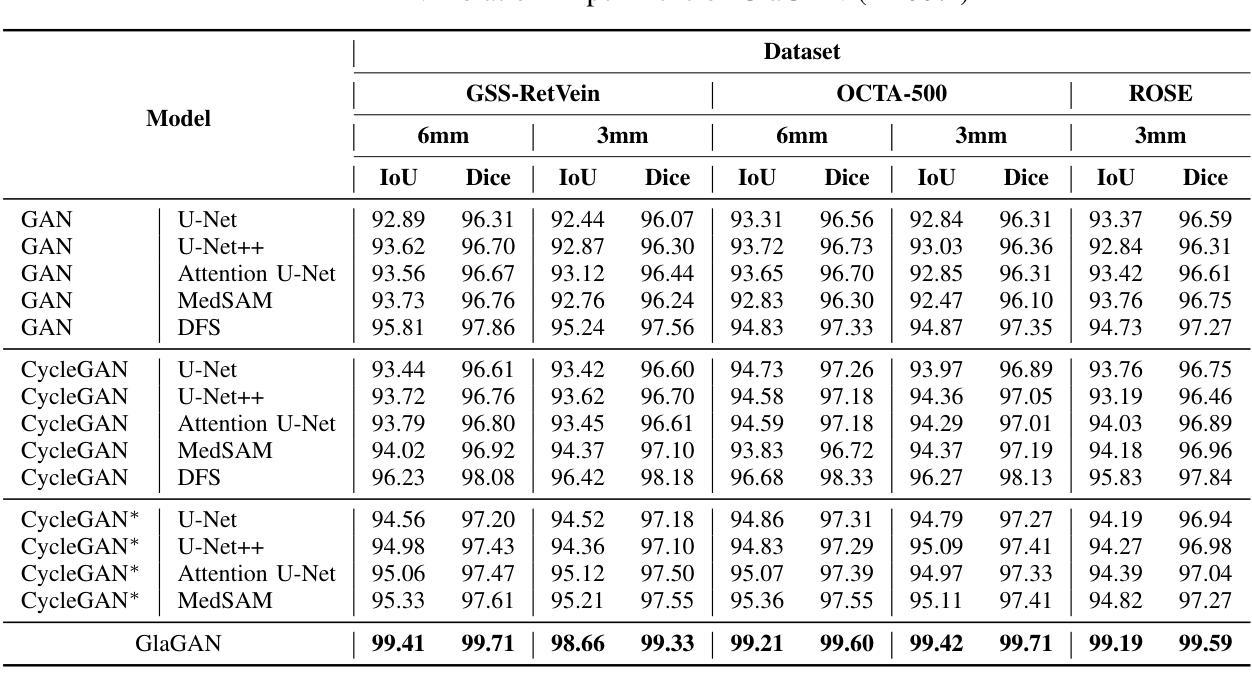
Structural changes in the main retinal blood vessels are critical biomarkers for glaucoma onset and progression. Identifying these vessels is essential for vascular modeling yet highly challenging. This paper introduces GlaGAN, an unsupervised generative AI model for segmenting main blood vessels in Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography (OCTA) images. The process begins with the Space Colonization Algorithm (SCA) to rapidly generate vessel skeletons, including radius estimations. By synergistically integrating generative adversarial networks (GANs) with biostatistical modeling of vessel radii, GlaGAN efficiently reconstructs 2D and 3D representations, achieving nearly 100% segmentation accuracy without requiring labeled data or high-performance computing resources. To address data scarcity, we also present GSS-RetVein, a high-definition mixed 2D/3D glaucoma retinal dataset featuring clear capillary structures. Designed for robustness testing, GSS-RetVein incorporates controlled noise while maintaining sharp capillary boundaries in 2D and enhancing 3D vascular reconstruction for blood flow prediction and glaucoma progression simulations. Experimental results demonstrate GSS-RetVein outperforms existing datasets in evaluating main vessel segmentation. Code and dataset are available: https://github.com/VikiXie/SatMar8.
视网膜主血管结构的变化是青光眼发生和发展的重要生物标志物。识别这些血管对血管建模至关重要,但极具挑战性。本文介绍了GlaGAN,这是一种用于在光学相干断层扫描血管造影(OCTA)图像中分割主血管的无监督生成式人工智能模型。流程始于空间殖民算法(SCA),该算法能够快速生成血管骨架,包括半径估算。通过协同整合生成对抗网络(GANs)与血管半径的生物统计建模,GlaGAN能够高效地重建二维和三维表示,在不使用标记数据或高性能计算资源的情况下实现接近100%的分割精度。为了解决数据稀缺问题,我们还推出了GSS-RetVein,这是一个高清混合二维/三维青光眼视网膜数据集,具有清晰的毛细血管结构。设计用于稳健性测试,GSS-RetVein在二维中保持了清晰的毛细血管边界,同时增强了三维血管重建,用于血流预测和青光眼进展模拟。实验结果表明,在评估主血管分割方面,GSS-RetVein优于现有数据集。代码和数据集可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/VikiXie/SatMar8。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文介绍了一种用于光学相干断层扫描血管造影(OCTA)图像中主要血管分割的无监督生成人工智能模型——GlaGAN。该模型结合了空间殖民算法(SCA)和生成对抗网络(GANs),对血管半径进行生物统计学建模,实现了高效的二维和三维重建,无需标注数据和高性能计算资源即可达到近百分之百的分割精度。为解决数据稀缺问题,还推出了GSS-RetVein混合二维/三维青光眼视网膜数据集,用于测试模型的稳健性,并优化了血管重建,用于血流预测和青光眼进展模拟。
关键见解
- 主视网膜血管结构变化是青光眼发生和进展的重要生物标志物。
- GlaGAN是一种无监督生成AI模型,用于在OCTA图像中分割主要血管。
- GlaGAN采用SCA算法生成血管骨架,并估算半径。
- GlaGAN结合GANs和血管半径生物统计建模,实现高效二维和三维重建。
- GlaGAN达到近百分之百的分割精度,无需标注数据和高性能计算资源。
- 为了解决数据稀缺问题,引入了GSS-RetVein混合二维/三维青光眼视网膜数据集。
- GSS-RetVein数据集用于测试模型的稳健性,并优化血管重建,支持血流预测和青光眼进展模拟。
点此查看论文截图

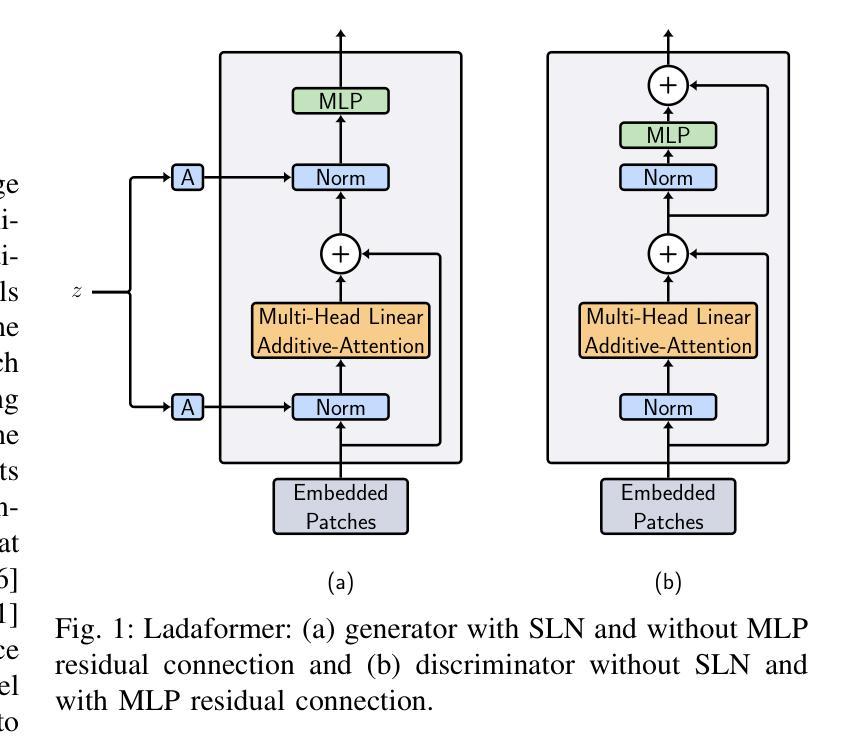
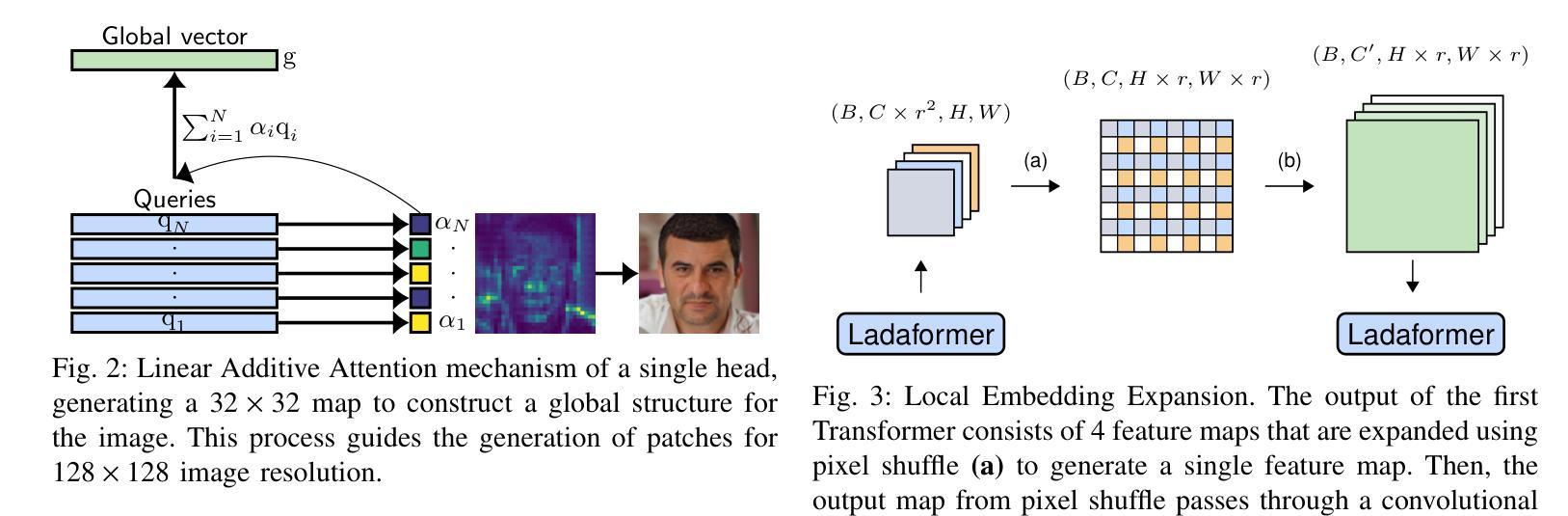
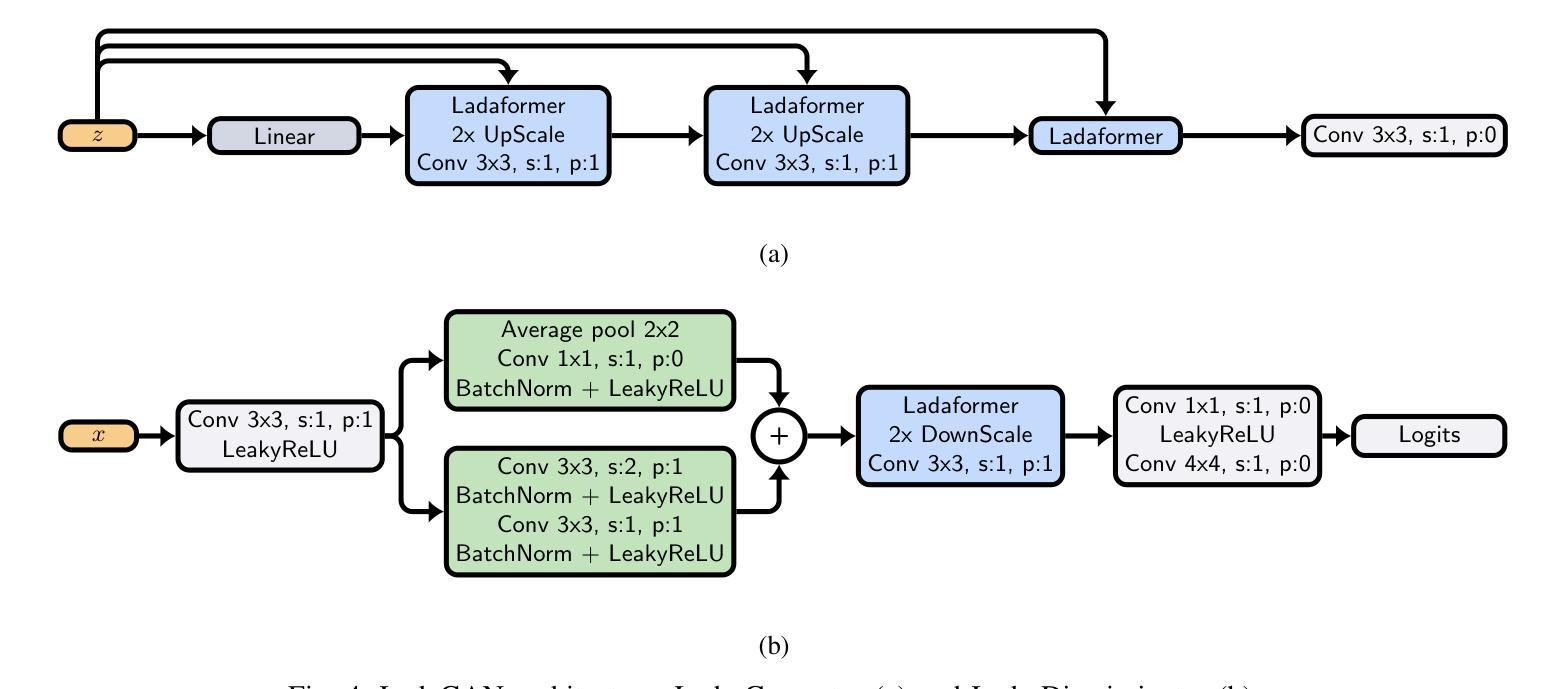
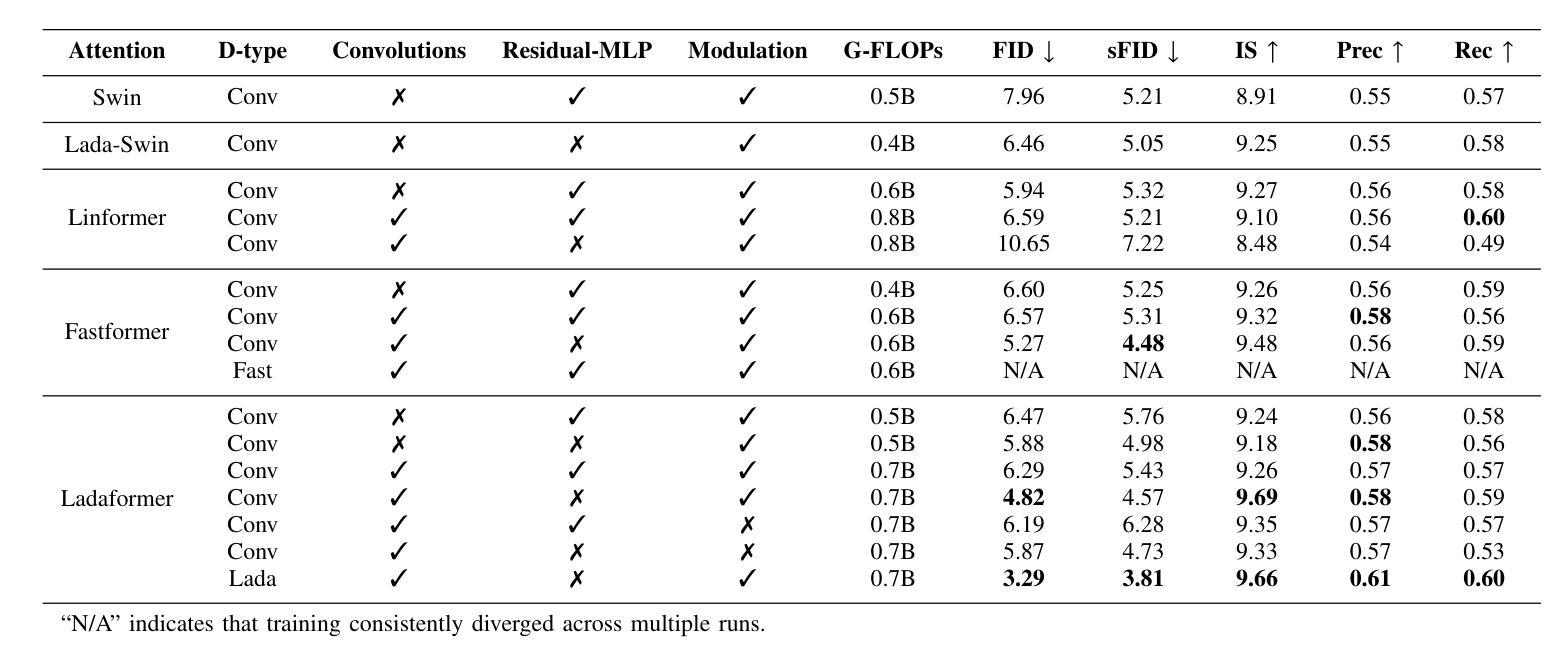
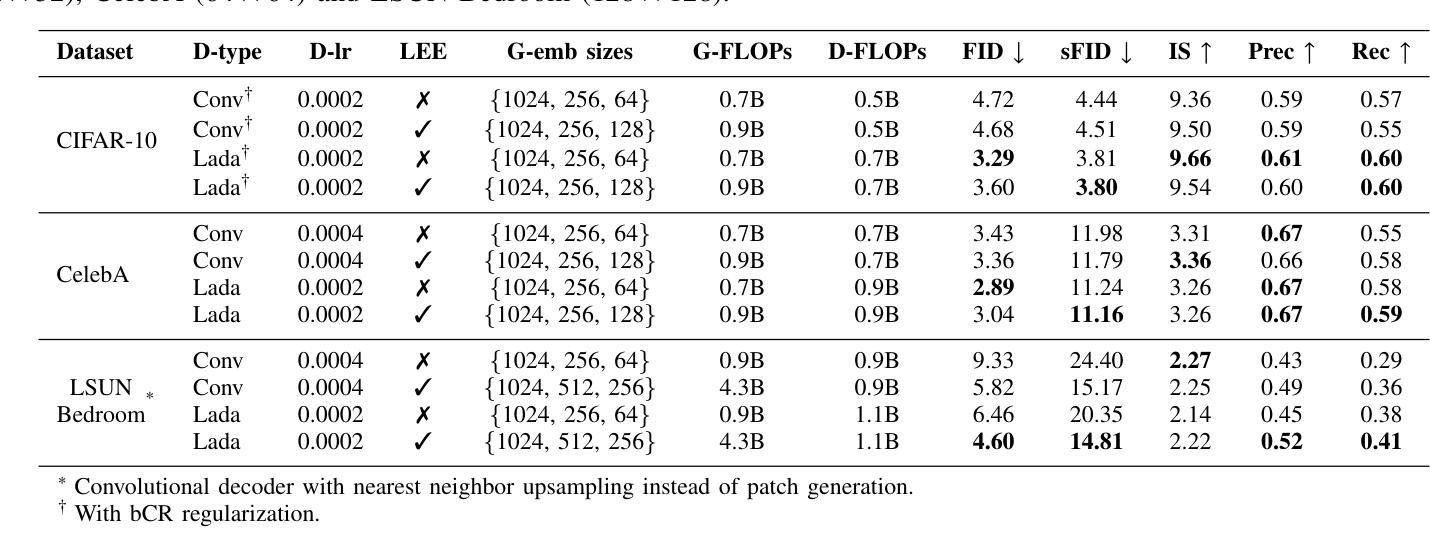
Efficient generative adversarial networks using linear additive-attention Transformers
Authors:Emilio Morales-Juarez, Gibran Fuentes-Pineda
Although the capacity of deep generative models for image generation, such as Diffusion Models (DMs) and Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), has dramatically improved in recent years, much of their success can be attributed to computationally expensive architectures. This has limited their adoption and use to research laboratories and companies with large resources, while significantly raising the carbon footprint for training, fine-tuning, and inference. In this work, we present a novel GAN architecture which we call LadaGAN. This architecture is based on a linear attention Transformer block named Ladaformer. The main component of this block is a linear additive-attention mechanism that computes a single attention vector per head instead of the quadratic dot-product attention. We employ Ladaformer in both the generator and discriminator, which reduces the computational complexity and overcomes the training instabilities often associated with Transformer GANs. LadaGAN consistently outperforms existing convolutional and Transformer GANs on benchmark datasets at different resolutions while being significantly more efficient. Moreover, LadaGAN shows competitive performance compared to state-of-the-art multi-step generative models (e.g. DMs) using orders of magnitude less computational resources.
尽管深度生成模型(如扩散模型(DMs)和生成对抗网络(GANs))在图像生成方面的能力近年来得到了显著提升,但它们的大部分成功归功于计算成本高昂的架构。这限制了其在拥有大量资源的研究实验室和公司中的应用和使用,同时显著提高了训练、微调及推理的碳足迹。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新型的GAN架构,我们称之为LadaGAN。该架构基于名为Ladaformer的线性注意力Transformer块。该块的主要组件是线性加法注意力机制,它为每个头计算一个单独的注意力向量,而不是二次点积注意力。我们在生成器和判别器中都使用了Ladaformer,这降低了计算复杂性,并克服了通常与Transformer GANs相关的训练不稳定问题。LadaGAN在基准数据集上始终优于现有的卷积和Transformer GANs,支持不同分辨率,同时效率更高。此外,与使用大量计算资源的最新多步生成模型(例如DMs)相比,LadaGAN显示出具有竞争力的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 8 figures
Summary
近年深度生成模型如Diffusion Models和GAN在图像生成方面能力显著提升,但其计算成本高昂的架构限制了其应用,并增加了训练、微调及推理的碳足迹。本研究提出一种新型GAN架构LadaGAN,基于线性注意力Transformer块Ladaformer,采用线性加法注意力机制,降低计算复杂度并克服Transformer GANs的训练不稳定性。LadaGAN在基准数据集上表现优异,相较于卷积和Transformer GANs更高效,与多步生成模型相比使用更少的计算资源。
Key Takeaways
- 深度生成模型如Diffusion Models和GAN在图像生成方面取得显著进步。
- 计算成本高昂限制了这些模型的广泛应用,并增加了碳足迹。
- 新型GAN架构LadaGAN被提出,基于线性注意力Transformer块Ladaformer。
- LadaGAN采用线性加法注意力机制,降低计算复杂度。
- LadaGAN克服了Transformer GANs的训练不稳定性。
- LadaGAN在基准数据集上表现优异,相较于其他GAN架构更高效。
点此查看论文截图