⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-09 更新
Music2Palette: Emotion-aligned Color Palette Generation via Cross-Modal Representation Learning
Authors:Jiayun Hu, Yueyi He, Tianyi Liang, Changbo Wang, Chenhui Li
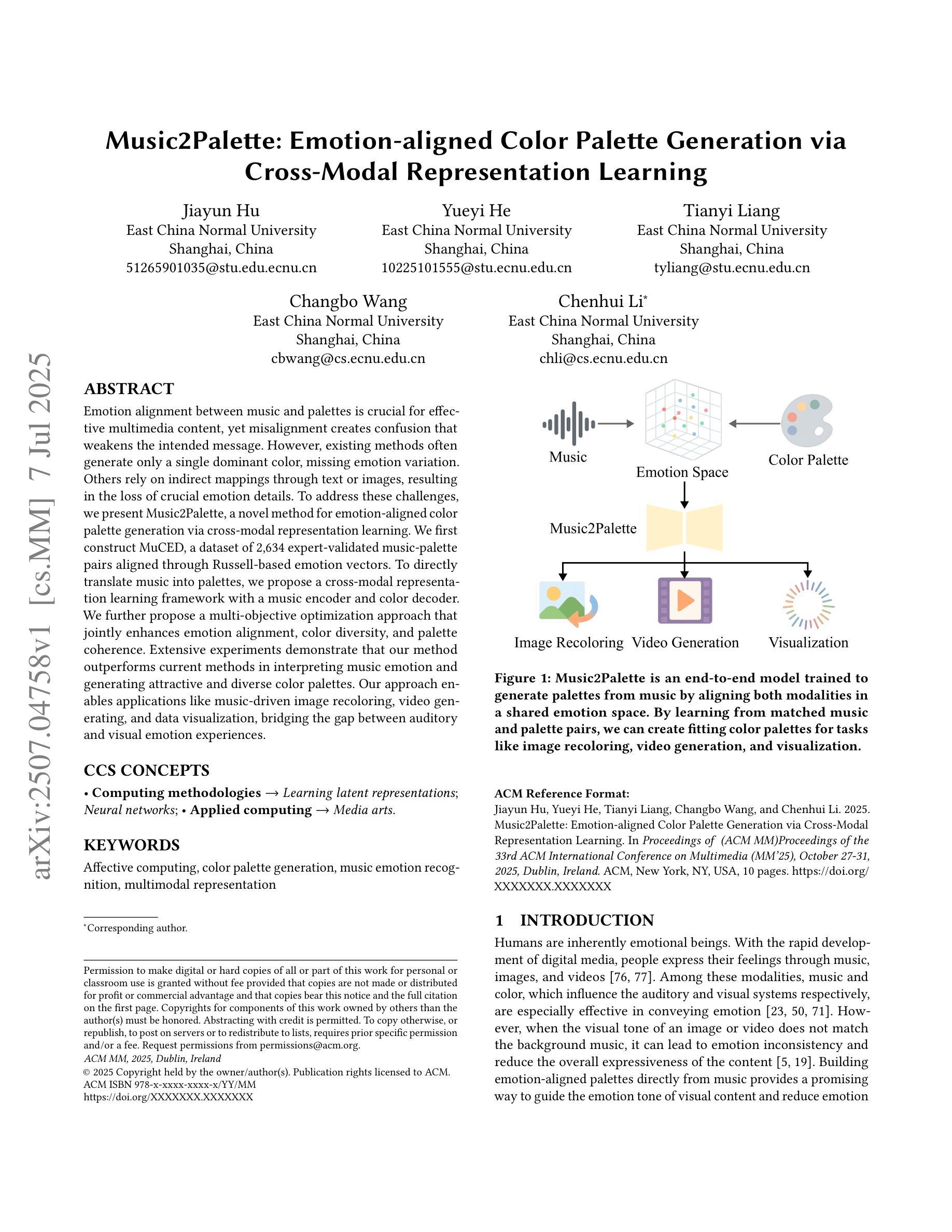
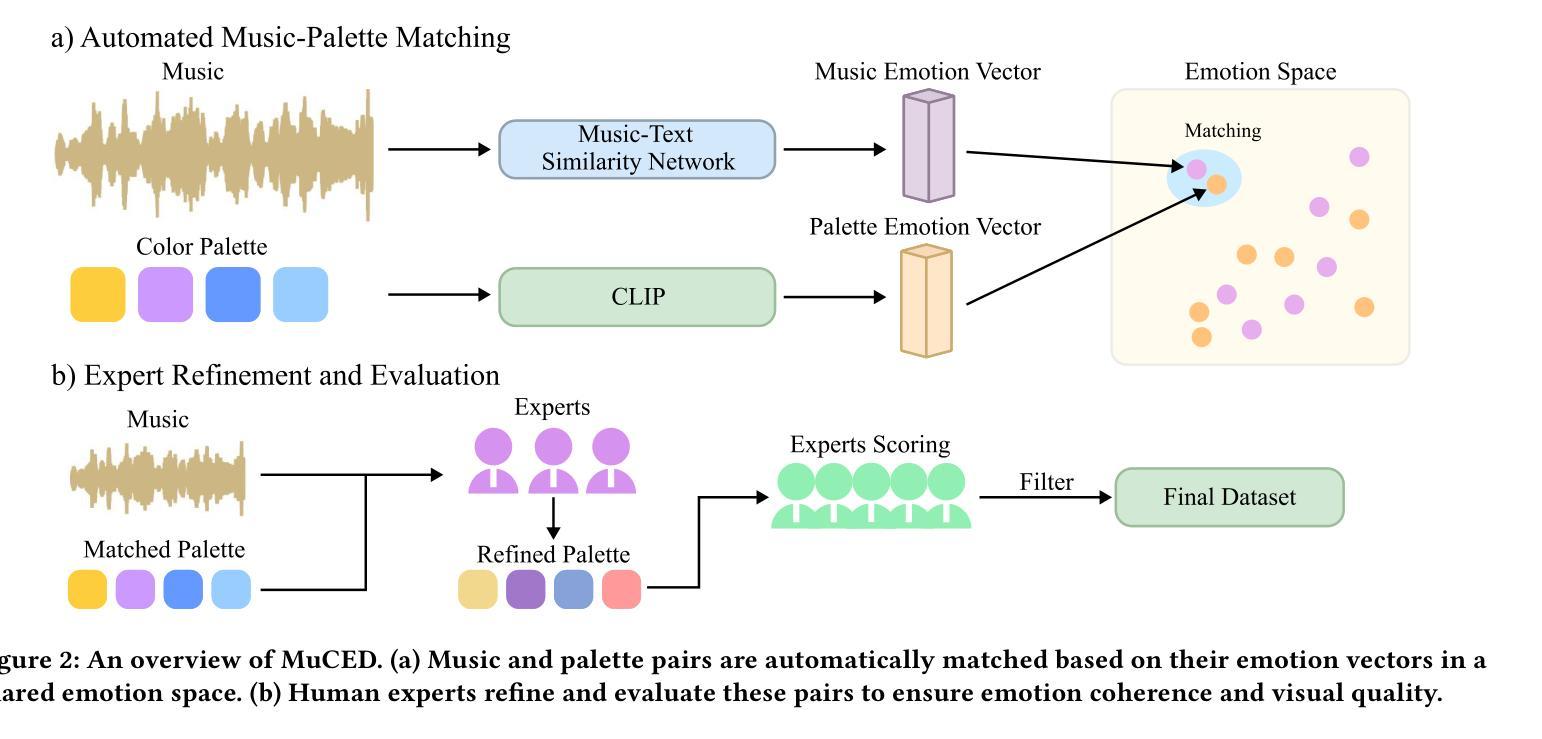
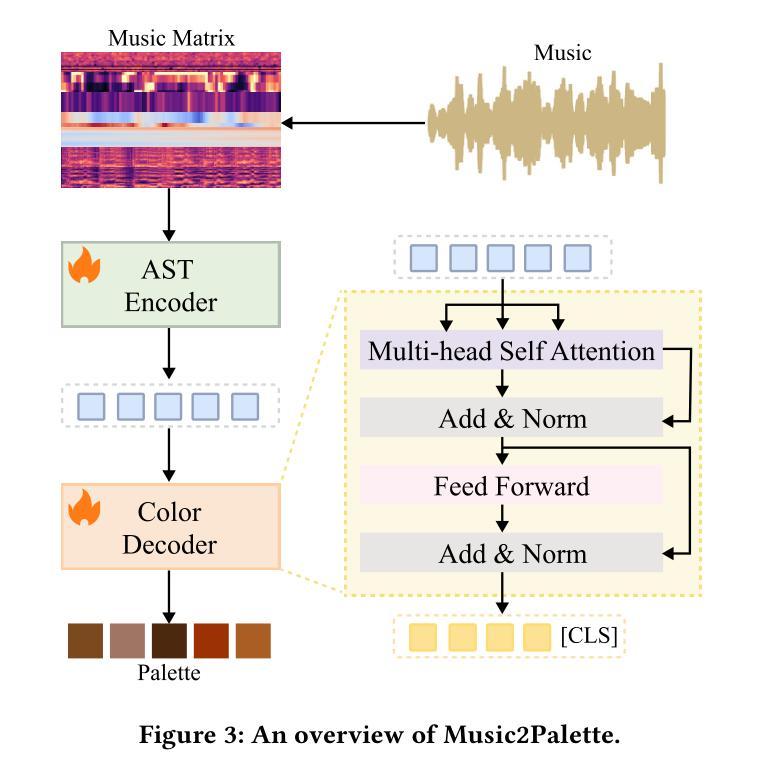
Emotion alignment between music and palettes is crucial for effective multimedia content, yet misalignment creates confusion that weakens the intended message. However, existing methods often generate only a single dominant color, missing emotion variation. Others rely on indirect mappings through text or images, resulting in the loss of crucial emotion details. To address these challenges, we present Music2Palette, a novel method for emotion-aligned color palette generation via cross-modal representation learning. We first construct MuCED, a dataset of 2,634 expert-validated music-palette pairs aligned through Russell-based emotion vectors. To directly translate music into palettes, we propose a cross-modal representation learning framework with a music encoder and color decoder. We further propose a multi-objective optimization approach that jointly enhances emotion alignment, color diversity, and palette coherence. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms current methods in interpreting music emotion and generating attractive and diverse color palettes. Our approach enables applications like music-driven image recoloring, video generating, and data visualization, bridging the gap between auditory and visual emotion experiences.
音乐与调色板之间的情感对齐对于有效的多媒体内容至关重要,然而,错位会产生削弱预期信息的混乱。然而,现有方法通常只生成一种主要的颜色,忽略了情感变化。其他方法依赖于文本或图像的间接映射,导致情感细节丢失。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了Music2Palette,这是一种通过跨模态表示学习进行情感对齐的颜色调色板生成的新方法。我们首先构建了MuCED数据集,其中包含2634对专家验证的音乐调色板组合,通过对齐Russell情绪向量进行对齐。为了直接将音乐翻译成调色板,我们提出了一个音乐编码器与颜色解码器的跨模态表示学习框架。我们还提出了一种多目标优化方法,该方法可以联合增强情感对齐、颜色多样性和调色板一致性。大量实验表明,我们的方法在解读音乐情感和生成有吸引力的多样化颜色调色板方面优于当前方法。我们的方法能够应用于音乐驱动图像重新着色、视频生成和数据可视化等应用,缩小听觉和视觉情感体验之间的差距。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
音乐与调色板之间的情感对齐对于有效的多媒体内容至关重要,而情感的不对齐会削弱预期的信息传递。为解决现有方法单一颜色生成与依赖文本或图像间接映射导致的情感细节缺失问题,本文提出了一种新颖的方法——Music2Palette。通过跨模态表示学习技术,直接转换音乐到调色板。实验证明,该方法在解释音乐情感、生成吸引人的多样化调色板方面优于当前方法。此技术可应用于音乐驱动图像重新着色、视频生成和数据可视化等领域,缩小听觉和视觉情感体验之间的鸿沟。
Key Takeaways
- 情感对齐在多媒体内容中的重要性及其影响。
- 音乐与调色板情感不匹配带来的问题。
- 现有方法的不足及其局限性(如单一颜色生成和依赖文本或图像间接映射)。
- Music2Palette方法介绍及特点。
- 使用跨模态表示学习直接转换音乐的策略。
- 多目标优化方法在提高情感对齐、色彩多样性和调色板一致性方面的作用。
点此查看论文截图

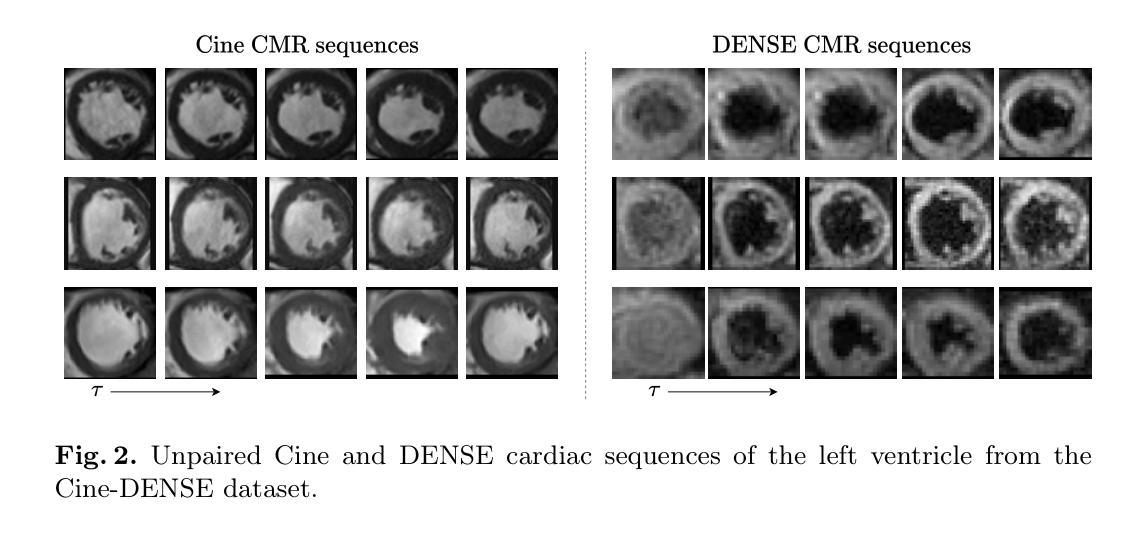
Unsupervised Cardiac Video Translation Via Motion Feature Guided Diffusion Model
Authors:Swakshar Deb, Nian Wu, Frederick H. Epstein, Miaomiao Zhang
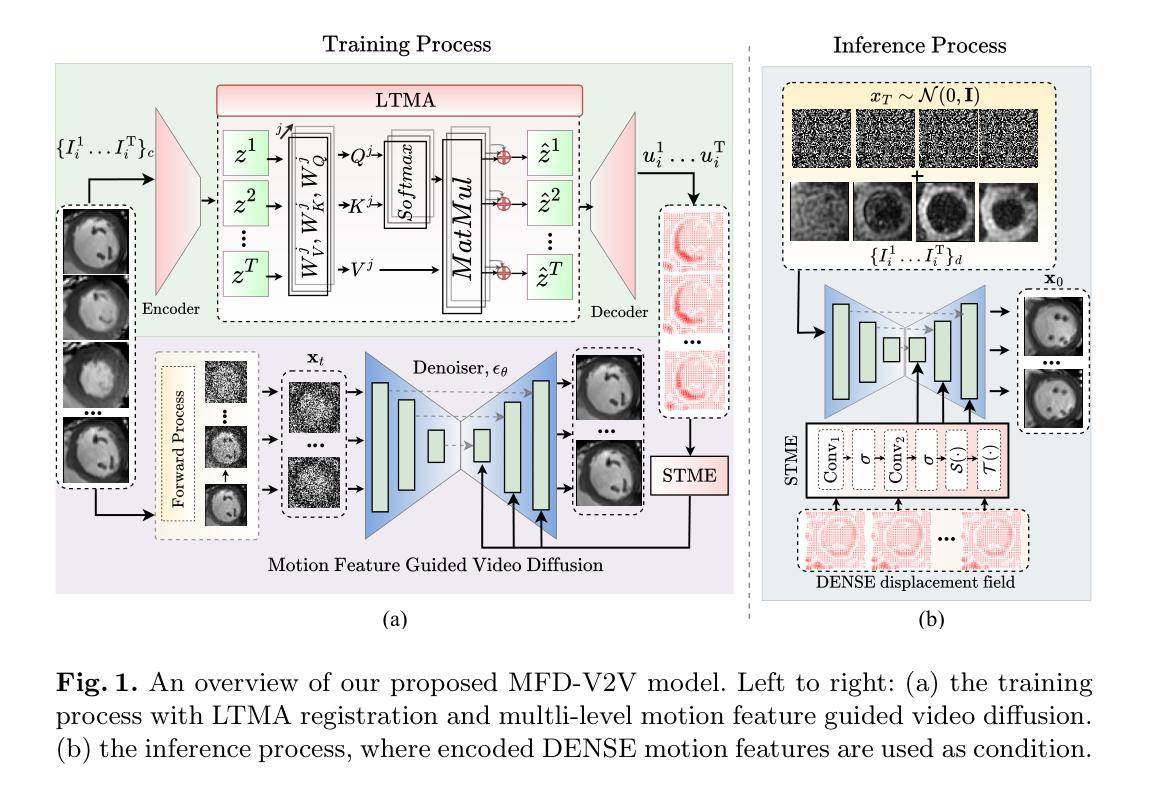
This paper presents a novel motion feature guided diffusion model for unpaired video-to-video translation (MFD-V2V), designed to synthesize dynamic, high-contrast cine cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) from lower-contrast, artifact-prone displacement encoding with stimulated echoes (DENSE) CMR sequences. To achieve this, we first introduce a Latent Temporal Multi-Attention (LTMA) registration network that effectively learns more accurate and consistent cardiac motions from cine CMR image videos. A multi-level motion feature guided diffusion model, equipped with a specialized Spatio-Temporal Motion Encoder (STME) to extract fine-grained motion conditioning, is then developed to improve synthesis quality and fidelity. We evaluate our method, MFD-V2V, on a comprehensive cardiac dataset, demonstrating superior performance over the state-of-the-art in both quantitative metrics and qualitative assessments. Furthermore, we show the benefits of our synthesized cine CMRs improving downstream clinical and analytical tasks, underscoring the broader impact of our approach. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/SwaksharDeb/MFD-V2V.
本文提出了一种新型的运动特征引导扩散模型(MFD-V2V),用于无配对视频到视频的转换,旨在从低对比度、易产生伪影的位移编码激发回声(DENSE)CMR序列中合成动态、高对比度的电影心脏磁共振(CMR)。为实现这一目标,我们首先引入了一个潜在时间多注意力(LTMA)注册网络,该网络可以有效地从电影CMR图像视频中学习更准确且一致的心脏运动。然后,我们开发了一个多级运动特征引导扩散模型,配备了一个专门的时空运动编码器(STME),以提取精细的运动条件,以提高合成质量和保真度。我们在综合心脏数据集上评估了我们的MFD-V2V方法,在定量指标和定性评估方面都表现出了卓越的性能。此外,我们还展示了我们的合成电影CMR对下游临床和分析任务的益处,强调了我们的方法更广泛的影响。我们的代码可在[https://github.com/SwaksharDeb/MFD-V2V公开获取。]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This work has been accepted for presentation at the 28th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2025)
Summary
该论文提出了一种新型的运动特征引导扩散模型(MFD-V2V),用于无配对视频到视频的转换。该模型旨在从低对比度、易产生伪影的位移编码激发回声(DENSE)CMR序列中合成动态、高对比度的电影心脏磁共振成像(Cine CMR)。为达到这一目标,论文首先引入了潜伏时间多注意力(LTMA)注册网络,有效地从电影CMR图像视频中学习更准确、一致的心脏运动。随后开发了一种多级别运动特征引导扩散模型,配备了一种特殊的时空运动编码器(STME),以提取精细的运动条件,以提高合成质量和保真度。评估方法MFD-V2V在全面的心脏数据集上表现优越,并在定量指标和定性评估上均优于现有技术。此外,论文展示了合成的电影CMR对下游临床和分析任务的益处,强调了方法更广泛的影响。代码已公开于 https://github.com/SwaksharDeb/MFD-V2V。
Key Takeaways
- 论文提出了一种新的运动特征引导扩散模型(MFD-V2V),用于从DENSE CMR序列合成动态、高对比度的电影心脏磁共振成像(Cine CMR)。
- 引入了潜伏时间多注意力(LTMA)注册网络,学习更准确、一致的心脏运动。
- 开发了一种多级别运动特征引导扩散模型,配备时空运动编码器(STME),提高合成质量和保真度。
- 在全面的心脏数据集上评估,表现优于现有技术。
- 合成的电影CMR对下游临床和分析任务有积极影响。
- 模型代码已公开,便于他人使用和研究。
- 该方法具有潜力改善心脏疾病的诊断和治疗。
点此查看论文截图

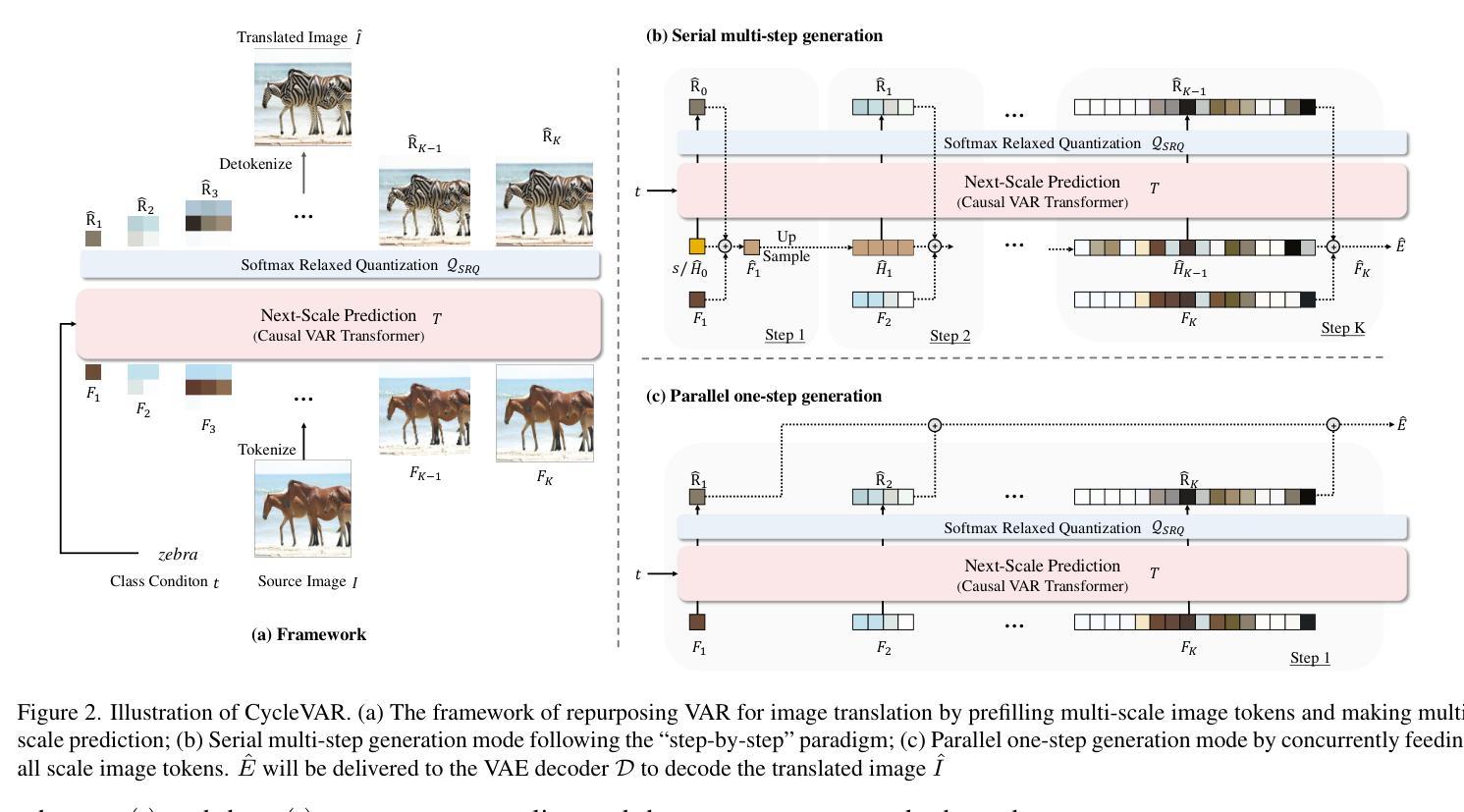
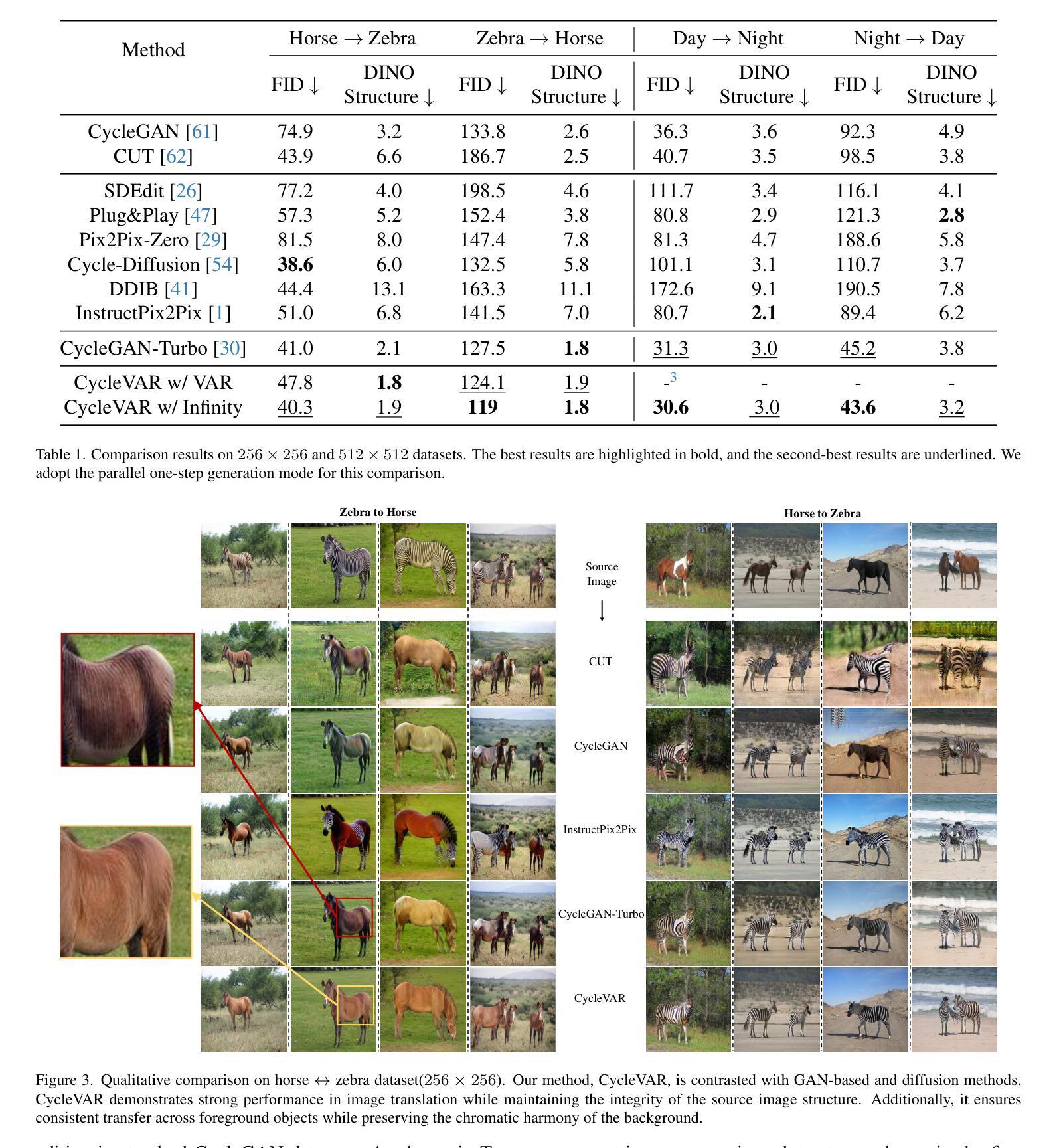
CycleVAR: Repurposing Autoregressive Model for Unsupervised One-Step Image Translation
Authors:Yi Liu, Shengqian Li, Zuzeng Lin, Feng Wang, Si Liu
The current conditional autoregressive image generation methods have shown promising results, yet their potential remains largely unexplored in the practical unsupervised image translation domain, which operates without explicit cross-domain correspondences. A critical limitation stems from the discrete quantization inherent in traditional Vector Quantization-based frameworks, which disrupts gradient flow between the Variational Autoencoder decoder and causal Transformer, impeding end-to-end optimization during adversarial training in image space. To tackle this issue, we propose using Softmax Relaxed Quantization, a novel approach that reformulates codebook selection as a continuous probability mixing process via Softmax, thereby preserving gradient propagation. Building upon this differentiable foundation, we introduce CycleVAR, which reformulates image-to-image translation as image-conditional visual autoregressive generation by injecting multi-scale source image tokens as contextual prompts, analogous to prefix-based conditioning in language models. CycleVAR exploits two modes to generate the target image tokens, including (1) serial multi-step generation, enabling iterative refinement across scales, and (2) parallel one-step generation synthesizing all resolution outputs in a single forward pass. Experimental findings indicate that the parallel one-step generation mode attains superior translation quality with quicker inference speed than the serial multi-step mode in unsupervised scenarios. Furthermore, both quantitative and qualitative results indicate that CycleVAR surpasses previous state-of-the-art unsupervised image translation models, \textit{e}.\textit{g}., CycleGAN-Turbo.
当前的条件自回归图像生成方法已经显示出有前景的结果,但在实际的无监督图像翻译领域,其潜力在很大程度上尚未被探索,这一领域的工作不需要明确的跨域对应关系。一个关键的限制来自于传统基于向量量化的框架所固有的离散量化,它破坏了变分自编码器解码器和因果变压器之间的梯度流,阻碍了图像空间对抗训练期间的端到端优化。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了Softmax松弛量化这一新方法,它通过Softmax将码本选择重新定义为连续的概率混合过程,从而保留梯度传播。基于这个可微分的基础,我们引入了CycleVAR,它将图像到图像的翻译重新定义为图像条件视觉自回归生成,通过注入多尺度源图像令牌作为上下文提示,类似于语言模型中的前缀条件。CycleVAR利用两种模式来生成目标图像令牌,包括(1)串行多步生成,实现跨尺度的迭代细化;(2)并行一步生成,一次前向传递中合成所有分辨率的输出。实验结果表明,在无人监督的情况下,并行一步生成模式具有更高的翻译质量和更快的推理速度,优于串行多步模式。此外,定量和定性的结果都表明,CycleVAR超越了先前的最先进的无监督图像翻译模型,例如CycleGAN-Turbo。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICCV 2025. Code available at: https://github.com/IamCreateAI/CycleVAR
Summary
本文探讨了当前条件自回归图像生成方法在无监督图像翻译领域的应用。针对传统基于向量量化的框架中存在的离散量化问题,提出了Softmax Relaxed Quantization方法,将代码本选择重构为连续的概率混合过程。在此基础上,引入了CycleVAR方法,将图像到图像的翻译重构为图像条件视觉自回归生成,并通过两种生成模式实现了高质量的无监督图像翻译。
Key Takeaways
- 当前条件自回归图像生成方法在无监督图像翻译领域应用潜力巨大。
- 传统基于向量量化的框架存在离散量化问题,影响梯度流和端到端优化。
- Softmax Relaxed Quantization方法将代码本选择重构为连续的概率混合过程。
- CycleVAR将图像到图像的翻译重构为图像条件视觉自回归生成。
- CycleVAR采用两种生成模式:串行多步生成和并行一步生成。
- 并行一步生成模式在无监督场景中实现了更高的翻译质量和更快的推理速度。
点此查看论文截图

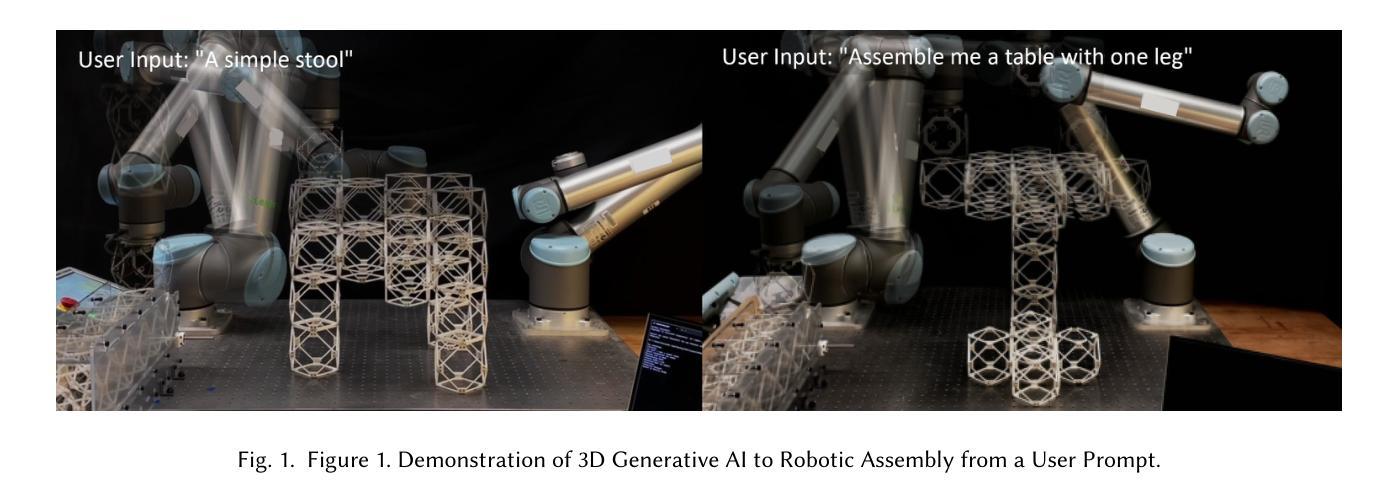
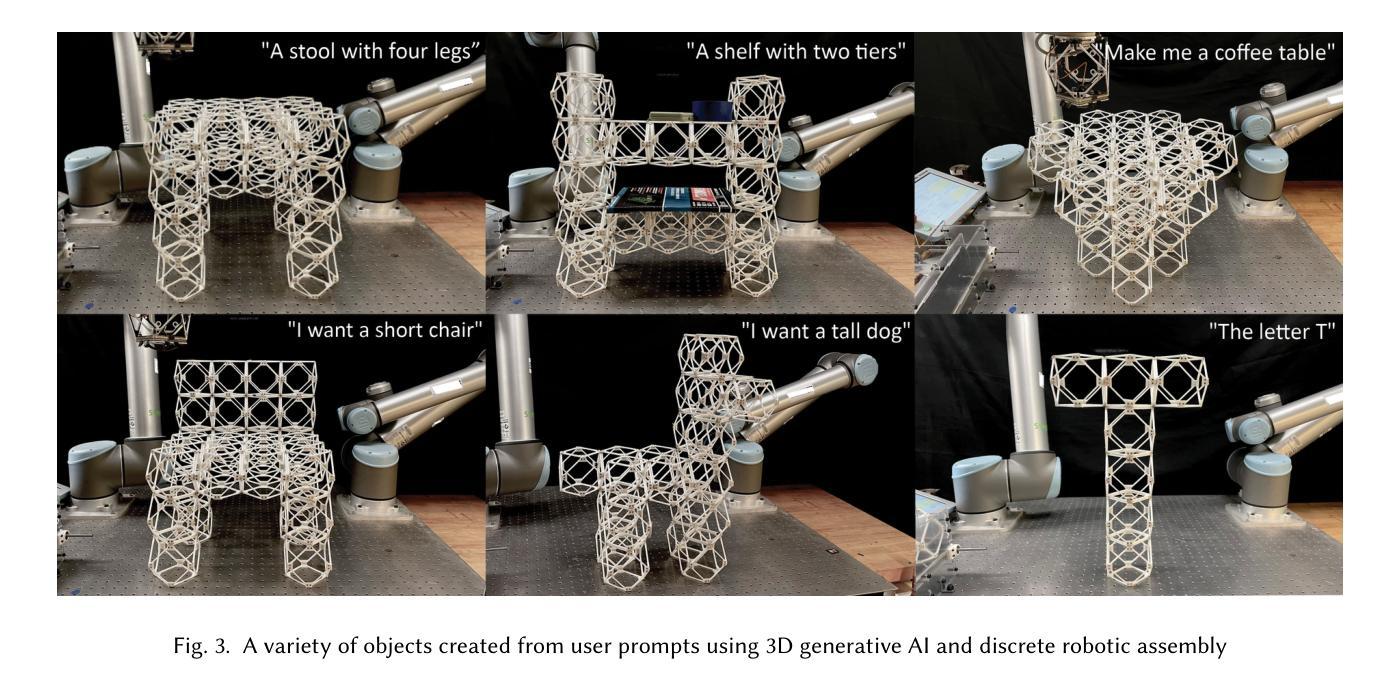
Making Physical Objects with Generative AI and Robotic Assembly: Considering Fabrication Constraints, Sustainability, Time, Functionality, and Accessibility
Authors:Alexander Htet Kyaw, Se Hwan Jeon, Miana Smith, Neil Gershenfeld
3D generative AI enables rapid and accessible creation of 3D models from text or image inputs. However, translating these outputs into physical objects remains a challenge due to the constraints in the physical world. Recent studies have focused on improving the capabilities of 3D generative AI to produce fabricable outputs, with 3D printing as the main fabrication method. However, this workshop paper calls for a broader perspective by considering how fabrication methods align with the capabilities of 3D generative AI. As a case study, we present a novel system using discrete robotic assembly and 3D generative AI to make physical objects. Through this work, we identified five key aspects to consider in a physical making process based on the capabilities of 3D generative AI. 1) Fabrication Constraints: Current text-to-3D models can generate a wide range of 3D designs, requiring fabrication methods that can adapt to the variability of generative AI outputs. 2) Time: While generative AI can generate 3D models in seconds, fabricating physical objects can take hours or even days. Faster production could enable a closer iterative design loop between humans and AI in the making process. 3) Sustainability: Although text-to-3D models can generate thousands of models in the digital world, extending this capability to the real world would be resource-intensive, unsustainable and irresponsible. 4) Functionality: Unlike digital outputs from 3D generative AI models, the fabrication method plays a crucial role in the usability of physical objects. 5) Accessibility: While generative AI simplifies 3D model creation, the need for fabrication equipment can limit participation, making AI-assisted creation less inclusive. These five key aspects provide a framework for assessing how well a physical making process aligns with the capabilities of 3D generative AI and values in the world.
3D生成式AI能够从文本或图像输入中快速创建可访问的3D模型。然而,由于物理世界的限制,将这些输出转化为实物仍然是一个挑战。最近的研究主要集中在提高3D生成式AI的可制造输出能力,以3D打印为主要制造方法。然而,本研讨会的论文呼吁从更广泛的视角来思考制造方法与3D生成式AI的能力如何相匹配。作为案例研究,我们展示了一个使用离散机器人装配和3D生成式AI制造实物的系统。通过这项工作,我们确定了基于3D生成式AI的能力的物理制造过程中要考虑的五个关键方面。1)制造约束:目前的文本到3D模型可以生成广泛的3D设计,需要能够适应生成式AI输出的可变性的制造方法。2)时间:虽然生成式AI可以在几秒内生成3D模型,但制造实物可能需要数小时甚至数天的时间。更快的生产速度可以使人类和AI在设计过程中的迭代更加紧密。3)可持续性:虽然文本到3D模型可以在数字世界中生成数千个模型,但如果将这种能力扩展到现实世界将会消耗大量资源,是不可持续的,也是不负责任的。4)功能性:与来自3D生成式AI模型的数字输出不同,制造方法对于实物的可用性起着至关重要的作用。5)可访问性:虽然生成式AI简化了3D模型的创建,但对制造设备的需求可能会限制参与程度,使得AI辅助创作变得不那么包容。这五个方面提供了一个框架,用于评估物理制造过程与3D生成式AI的能力以及世界价值观之间的匹配程度。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Presented at the CHI 2025 Workshop on Generative AI and HCI
Summary
本文讨论了基于文本或图像输入的3D生成AI在创建快速可访问的3D模型方面的能力,但由于现实世界中的限制,将这些输出转化为实物仍具有挑战性。文章提出需要考虑与三维生成AI的能力相对应的制造方法,并介绍了一种利用离散机器人组装和三维生成AI制造物体的新系统。通过这项工作,确定了基于三维生成AI能力的实体制造过程需要考虑的五个关键方面,包括制造约束、时间、可持续性、功能性和可及性。
Key Takeaways
- 3D generative AI能快速从文本或图像创建3D模型,但转化为实体面临挑战。
- 制造方法与三维生成AI的能力对应,对制造实体至关重要。
- 新系统利用离散机器人组装和三维生成AI制造物体。
- 基于三维生成AI能力的实体制造过程需要考虑五个关键方面:制造约束、时间、可持续性、功能性和可及性。
+ 制造约束:需要适应由生成AI产生的多变输出。
+ 时间:虽然AI能快速生成模型,但实体制造需要时间,追求更快的生产流程有助于缩小人与AI的设计迭代差距。
+ 可持续性:从数字世界扩展到现实世界需要考虑到资源消耗和环境影响。
+ 功能性:制造方法对实体物体的实用性至关重要。
点此查看论文截图

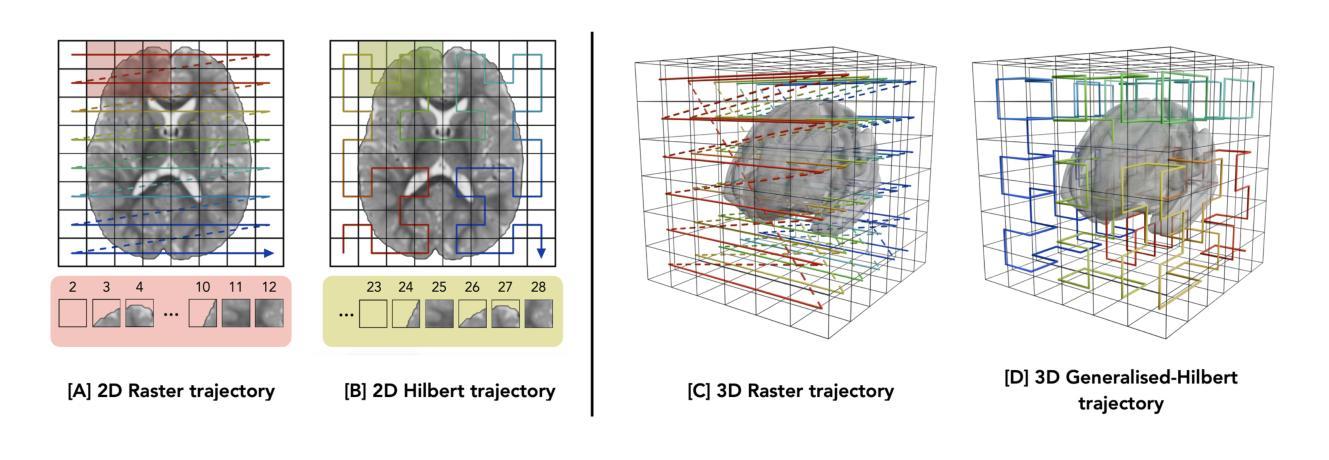
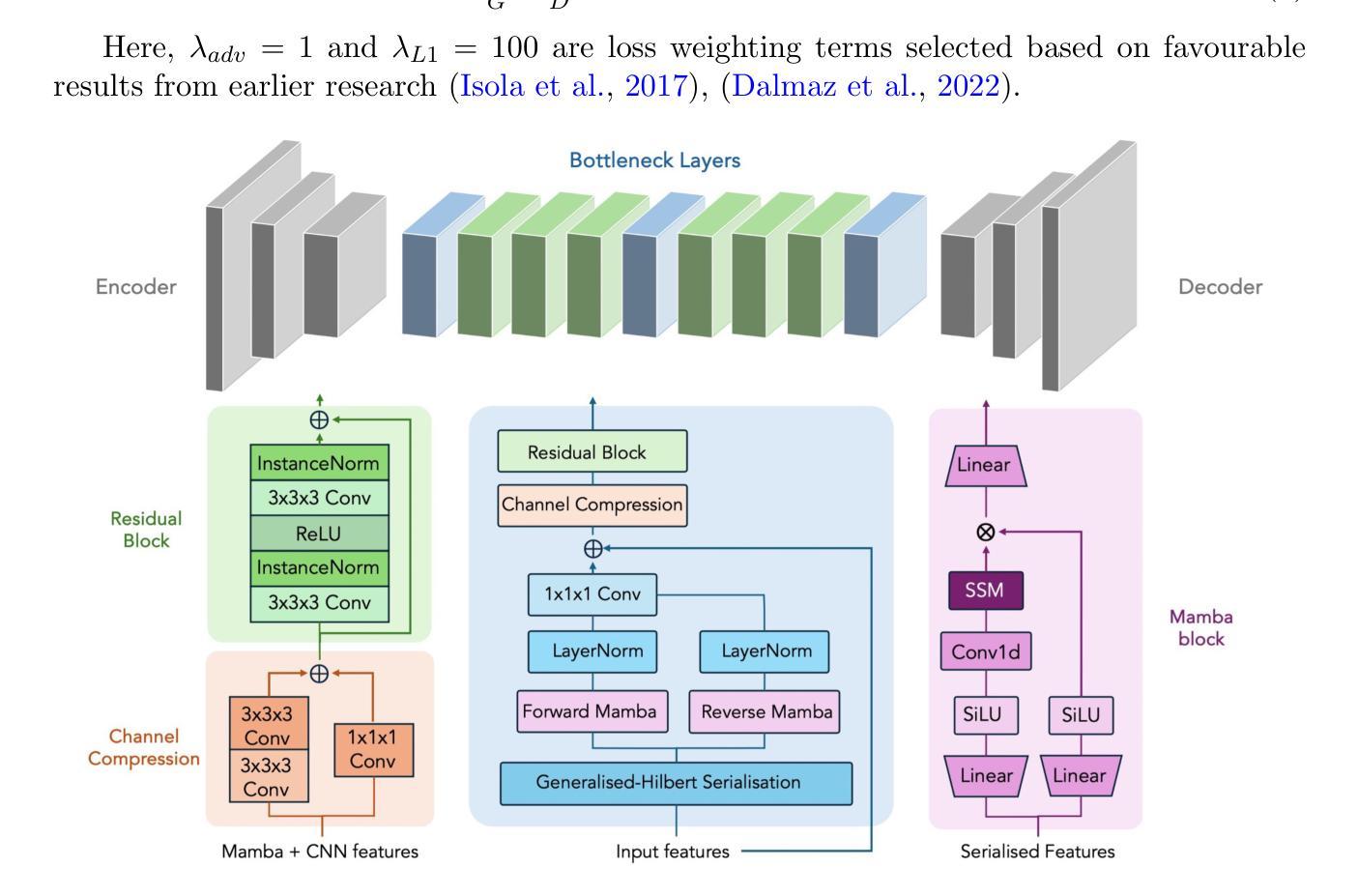
GAMBAS: Generalised-Hilbert Mamba for Super-resolution of Paediatric Ultra-Low-Field MRI
Authors:Levente Baljer, Ula Briski, Robert Leech, Niall J. Bourke, Kirsten A. Donald, Layla E. Bradford, Simone R. Williams, Sadia Parkar, Sidra Kaleem, Salman Osmani, Sean C. L. Deoni, Steven C. R. Williams, Rosalyn J. Moran, Emma C. Robinson, Frantisek Vasa
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is critical for neurodevelopmental research, however access to high-field (HF) systems in low- and middle-income countries is severely hindered by their cost. Ultra-low-field (ULF) systems mitigate such issues of access inequality, however their diminished signal-to-noise ratio limits their applicability for research and clinical use. Deep-learning approaches can enhance the quality of scans acquired at lower field strengths at no additional cost. For example, Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) fused with transformer modules have demonstrated a remarkable ability to capture both local information and long-range context. Unfortunately, the quadratic complexity of transformers leads to an undesirable trade-off between long-range sensitivity and local precision. We propose a hybrid CNN and state-space model (SSM) architecture featuring a novel 3D to 1D serialisation (GAMBAS), which learns long-range context without sacrificing spatial precision. We exhibit improved performance compared to other state-of-the-art medical image-to-image translation models.
磁共振成像(MRI)对神经发育研究至关重要,但在中低收入国家,高场(HF)系统的获取因其成本而受到严重阻碍。超低场(ULF)系统缓解了获取不平等的问题,但其信噪比降低限制了其在研究和临床使用中的应用。深度学习的方法可以在不增加成本的情况下提高低场强扫描的质量。例如,与变压器模块融合的卷积神经网络(CNNs)表现出捕捉局部信息和长远语境的显著能力。然而,变压器的二次复杂性导致了长远敏感性和局部精度之间不理想权衡。我们提出了一种混合CNN和状态空间模型(SSM)架构,采用新型3D到1D序列化(GAMBAS),可在不牺牲空间精度的情况下学习长远语境。与其他最先进的医疗图像到图像翻译模型相比,我们表现出了更好的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication at MIDL 2025, 21 pages, 8 figures
Summary
MRI在神经发育研究中至关重要,但低收入和中等收入国家的高场系统存在访问困难的问题。超低频系统缓解了此类问题,但其信噪比降低限制了其在研究和临床使用中的应用。深度学习可通过提高低场强扫描的质量来解决这一问题,而不会增加成本。例如,卷积神经网络(CNN)与变压器模块的融合可以捕捉局部信息和长距离上下文信息。然而,变压器存在二次复杂性问题,可能导致长距离敏感性和局部精确性之间的权衡。为此,本文提出了一种混合CNN和状态空间模型(SSM)架构,采用新型三维到一维序列化(GAMBAS),可在不牺牲空间精度的情况下学习长距离上下文信息。其性能优于其他先进的医学图像到图像翻译模型。
Key Takeaways
- 核磁共振成像(MRI)在神经发育研究中具有重要价值,但高场系统在某些国家的获取成本极高,阻碍了研究发展。
- 超低频系统可能为解决不平等访问提供了一种途径,但其信噪比降低限制了其在研究和临床中的应用。
- 深度学习可通过无额外成本的方式提高低场强扫描的质量。
- 卷积神经网络(CNN)与变压器模块结合具有捕捉局部信息和长距离上下文信息的能力。
- 变压器存在二次复杂性,导致长距离敏感性和局部精确性之间的权衡问题。
- 一种新型的混合CNN和状态空间模型(SSM)架构被提出,其通过新型三维到一维序列化(GAMBAS)学习长距离上下文信息而不牺牲空间精度。
点此查看论文截图