⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-09 更新
Spatio-Temporal LLM: Reasoning about Environments and Actions
Authors:Haozhen Zheng, Beitong Tian, Mingyuan Wu, Zhenggang Tang, Klara Nahrstedt, Alex Schwing
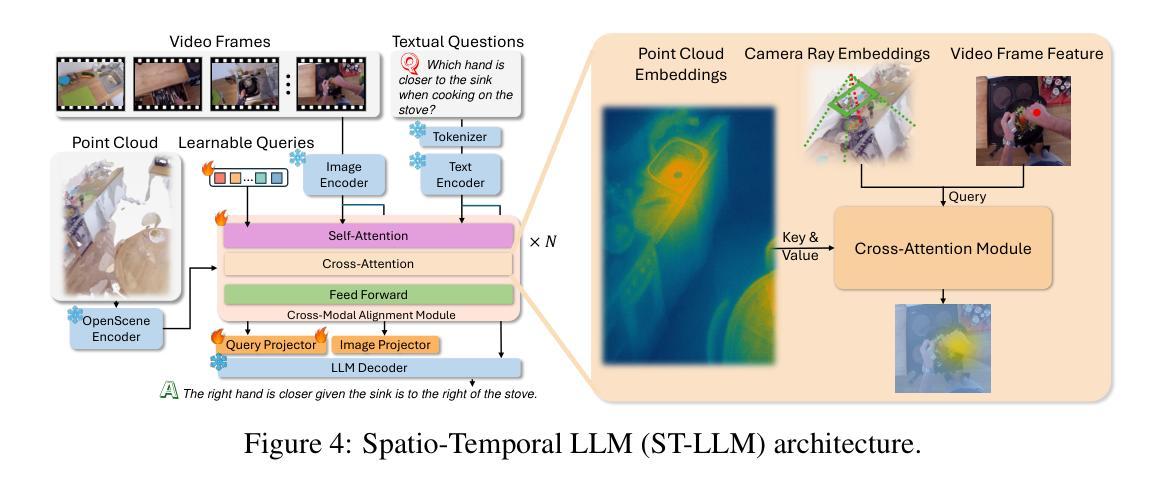
Despite the significant recent progress of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), MLLMs still struggle to correctly answer prompts that require a holistic spatio-temporal understanding. Specifically, it is challenging to address prompts that refer to 1) the entirety of an environment that an agent equipped with an MLLM can operate in; and simultaneously also refer to 2) recent actions that just happened and are encoded in a video clip. However, such a holistic spatio-temporal understanding is important for agents operating in the real world. To address this issue, we first develop a framework to collect a large-scale dataset. Using the collected “Reasoning about Environments and Actions” (REA) dataset, we show that recent methods indeed struggle to correctly answer the prompts. To improve, we develop a “spatio-temporal LLM” (ST-LLM), a model equipped with projectors to improve both spatial understanding of an environment and temporal understanding of recent observations. On the collected REA data, we show that the proposed method significantly improves results compared to prior work. Code and data are available at https://zoezheng126.github.io/STLLM-website/.
尽管最近多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)取得了重大进展,但在需要全面时空理解的任务提示中,MLLMs仍然难以正确回答问题。具体来说,解决涉及以下两个方面的提示具有挑战性:1)MLLMs所在代理可以操作的整体环境;同时涉及2)刚刚发生并被编码在视频剪辑中的最近动作。然而,这种全面的时空理解对于在现实世界中操作的代理很重要。为了解决这个问题,我们首先开发了一个框架来收集大规模数据集。“关于环境和行动的思考”(REA)数据集显示,最近的方法确实难以正确回答提示。为了改进,我们开发了一种“时空LLM”(ST-LLM),这是一种配备投影仪的模型,可以提高对环境的空间理解和最近观察的时间理解。在收集的REA数据上,我们证明所提出的方法与先前的工作相比,结果显著改进。代码和数据可在 https://zoezheng126.github.io/STLLM-website/ 找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code and data are available at https://zoezheng126.github.io/STLLM-website/
Summary
文章介绍了尽管最近的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)取得了显著进展,但在应对需要全面时空理解能力的提示时仍面临挑战。针对这种情况,研究人员开发了一个框架来收集大规模数据集,即“环境与行为推理”(REA)数据集,并在此基础上提出了一个名为“时空LLM”(ST-LLM)的模型来改善环境和最新观察的时序理解问题。研究结果显示,该方法显著提高了与之前工作的结果对比。代码和数据可以在网上找到。
Key Takeaways
- MLLMs在应对需要全面时空理解的提示时存在挑战。
- 环境和最新行为的时空理解对现实世界的智能体操作至关重要。
- 研究人员通过开发框架创建了大规模的“环境与行为推理”(REA)数据集。
- 在REA数据集上,现有方法的表现并不理想。
- 为了改善这种情况,提出了“时空LLM”(ST-LLM)模型,该模型配备了投影仪以提高对环境和最新观察的理解。
- 在REA数据集上进行的实验表明,ST-LLM模型的结果显著优于先前的工作。
点此查看论文截图

Open Vision Reasoner: Transferring Linguistic Cognitive Behavior for Visual Reasoning
Authors:Yana Wei, Liang Zhao, Jianjian Sun, Kangheng Lin, Jisheng Yin, Jingcheng Hu, Yinmin Zhang, En Yu, Haoran Lv, Zejia Weng, Jia Wang, Chunrui Han, Yuang Peng, Qi Han, Zheng Ge, Xiangyu Zhang, Daxin Jiang, Vishal M. Patel
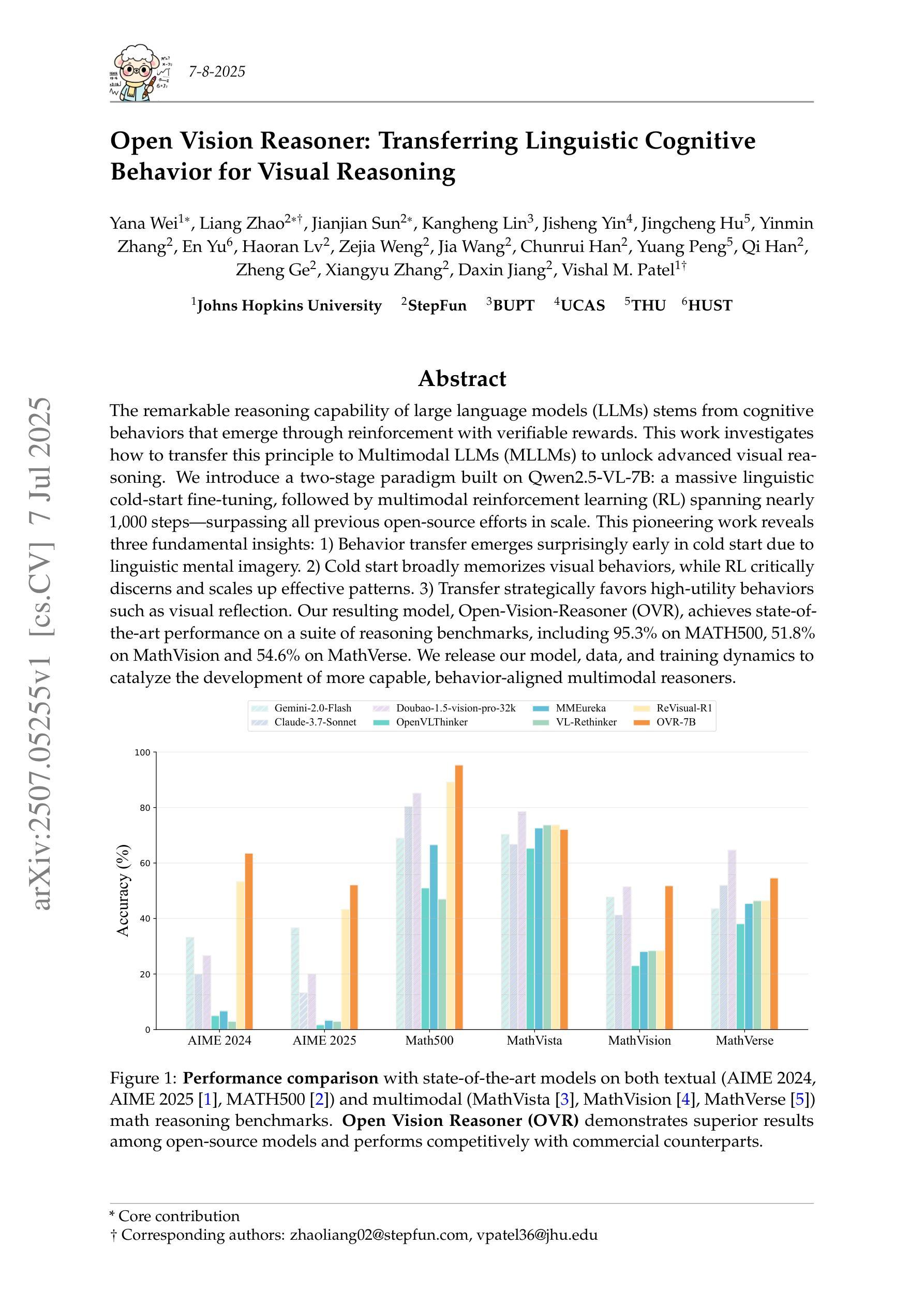
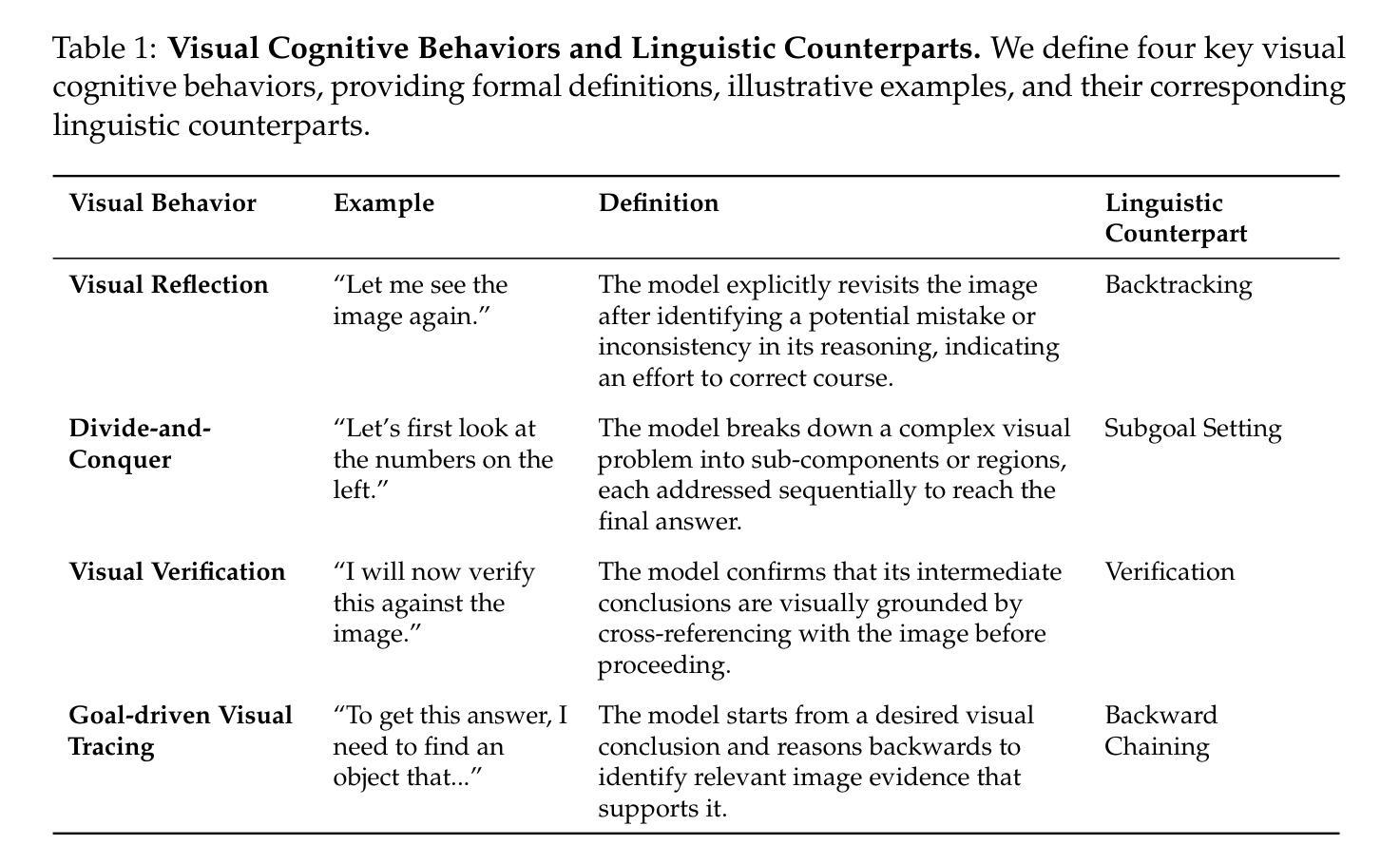
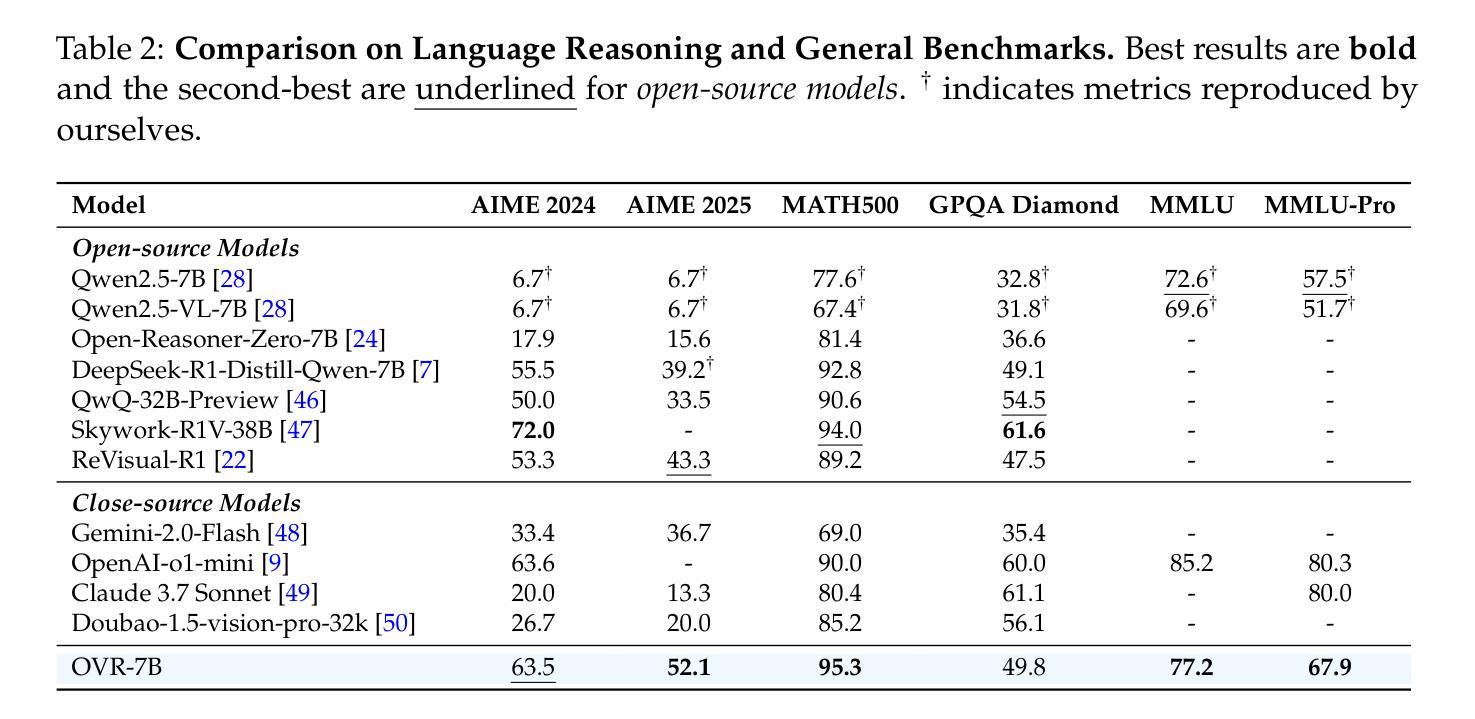
The remarkable reasoning capability of large language models (LLMs) stems from cognitive behaviors that emerge through reinforcement with verifiable rewards. This work investigates how to transfer this principle to Multimodal LLMs (MLLMs) to unlock advanced visual reasoning. We introduce a two-stage paradigm built on Qwen2.5-VL-7B: a massive linguistic cold-start fine-tuning, followed by multimodal reinforcement learning (RL) spanning nearly 1,000 steps, surpassing all previous open-source efforts in scale. This pioneering work reveals three fundamental insights: 1) Behavior transfer emerges surprisingly early in cold start due to linguistic mental imagery. 2) Cold start broadly memorizes visual behaviors, while RL critically discerns and scales up effective patterns. 3) Transfer strategically favors high-utility behaviors such as visual reflection. Our resulting model, Open-Vision-Reasoner (OVR), achieves state-of-the-art performance on a suite of reasoning benchmarks, including 95.3% on MATH500, 51.8% on MathVision and 54.6% on MathVerse. We release our model, data, and training dynamics to catalyze the development of more capable, behavior-aligned multimodal reasoners.
大型语言模型的卓越推理能力来源于通过可验证的奖励进行强化后出现的认知行为。本研究旨在探索如何将这一原理应用于多模态大型语言模型,以解锁高级视觉推理能力。我们基于Qwen2.5-VL-7B引入了一个两阶段的范式:首先是大规模语言冷启动微调,其次是涵盖近1000步的多模态强化学习。这项工作规模超过了之前所有开源工作的规模。这一开创性研究揭示了三个基本观点:1)由于语言心理图像,行为转移在冷启动的早期阶段就会出现;2)冷启动广泛记忆视觉行为,而强化学习则能辨别并扩大有效模式;3)转移策略有利于高实用性的行为,如视觉反射。我们得到的模型——Open-Vision-Reasoner(OVR)在一系列推理基准测试中达到了最先进的性能,包括MATH500上的95.3%,MathVision上的51.8%和MathVerse上的54.6%。我们发布我们的模型、数据和训练动态,以推动开发更具能力、更符合行为的多模态推理器。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型的卓越推理能力来源于通过可验证的奖励进行强化后所展现的认知行为。本研究探索如何将这一原则应用于多模态大型语言模型,以解锁高级视觉推理能力。本研究引入了一个基于Qwen2.5-VL-7B的两阶段范式,先进行大规模语言冷启动微调,然后进行近1000步的多模态强化学习。本研究揭示了三个关键见解,并成功开发出一个名为Open-Vision-Reasoner(OVR)的模型,该模型在多个推理基准测试上达到最新水平。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型的推理能力来源于通过可验证奖励进行强化后所展现的认知行为。
- 通过两阶段范式(基于Qwen2.5-VL-7B的冷启动微调和多模态强化学习)将强化学习原则应用于多模态大型语言模型,以解锁高级视觉推理能力。
- 行为转移在冷启动阶段由于语言心理图像而意外地早期出现。
- 冷启动广泛记忆视觉行为,而强化学习则关键地区分和扩大有效模式。
- 转移策略有利于高实用性的行为,如视觉反射。
- 开发的Open-Vision-Reasoner(OVR)模型在多个推理基准测试上达到最新水平,包括MATH500的95.3%、MathVision的51.8%和MathVerse的54.6%。
点此查看论文截图

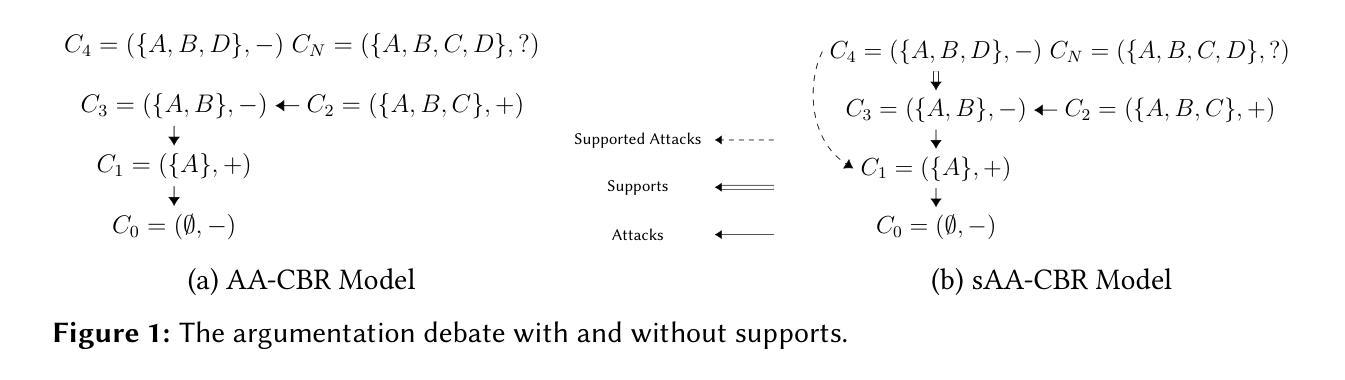
Supported Abstract Argumentation for Case-Based Reasoning
Authors:Adam Gould, Gabriel de Olim Gaul, Francesca Toni
We introduce Supported Abstract Argumentation for Case-Based Reasoning (sAA-CBR), a binary classification model in which past cases engage in debates by arguing in favour of their labelling and attacking or supporting those with opposing or agreeing labels. With supports, sAA-CBR overcomes the limitation of its precursor AA-CBR, which can contain extraneous cases (or spikes) that are not included in the debates. We prove that sAA-CBR contains no spikes, without trading off key model properties
我们介绍了基于案例推理的支持抽象论证(sAA-CBR)方法,这是一种二分类模型,过去案例中会展开辩论来为自身标签辩护,并攻击或支持那些持有反对或相同标签的案例。有了这些支持,sAA-CBR克服了其前身AA-CBR的局限性,后者可能包含未参与辩论的额外案例(或峰值)。我们证明sAA-CBR不包含峰值,不会牺牲关键模型属性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to IARML@ICJAI2025: Workshop on the Interactions between Analogical Reasoning and Machine Learning
Summary:介绍了基于案例推理的支持抽象论证(sAA-CBR)二元分类模型,它通过支持过去的案例辩论,对标签进行论证或攻击或支持那些具有对立或相同标签的案例。相较于AA-CBR模型,sAA-CBR通过支持克服了包含额外案例(或峰值)的局限性,同时证明其不包含峰值且不会牺牲关键模型属性。
Key Takeaways:
- sAA-CBR是一种二元分类模型,利用过去的案例进行辩论。
- 它通过支持或攻击案例标签来进行分类。
- sAA-CBR克服了AA-CBR模型的局限性,即包含额外案例(或峰值)。
- sAA-CBR在保证模型关键属性的情况下消除了峰值问题。
- 该模型通过对辩论的支持来改善案例的标注过程。
- sAA-CBR能够更有效地处理包含对立或相同标签的案例之间的辩论。
点此查看论文截图

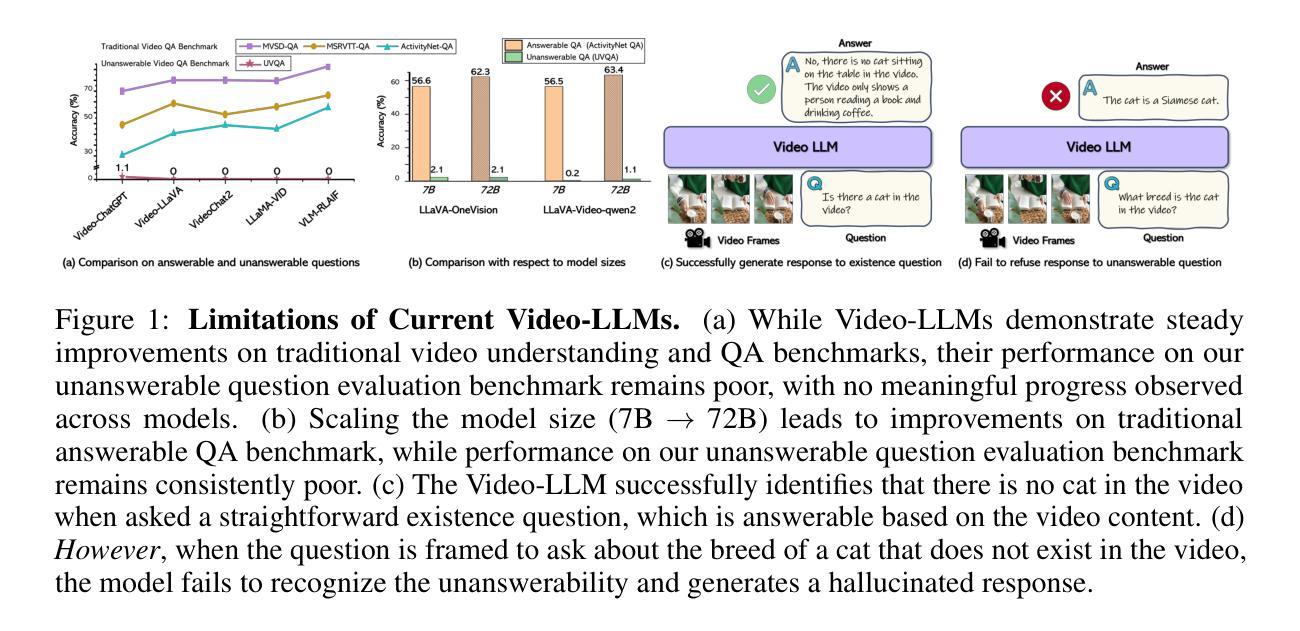
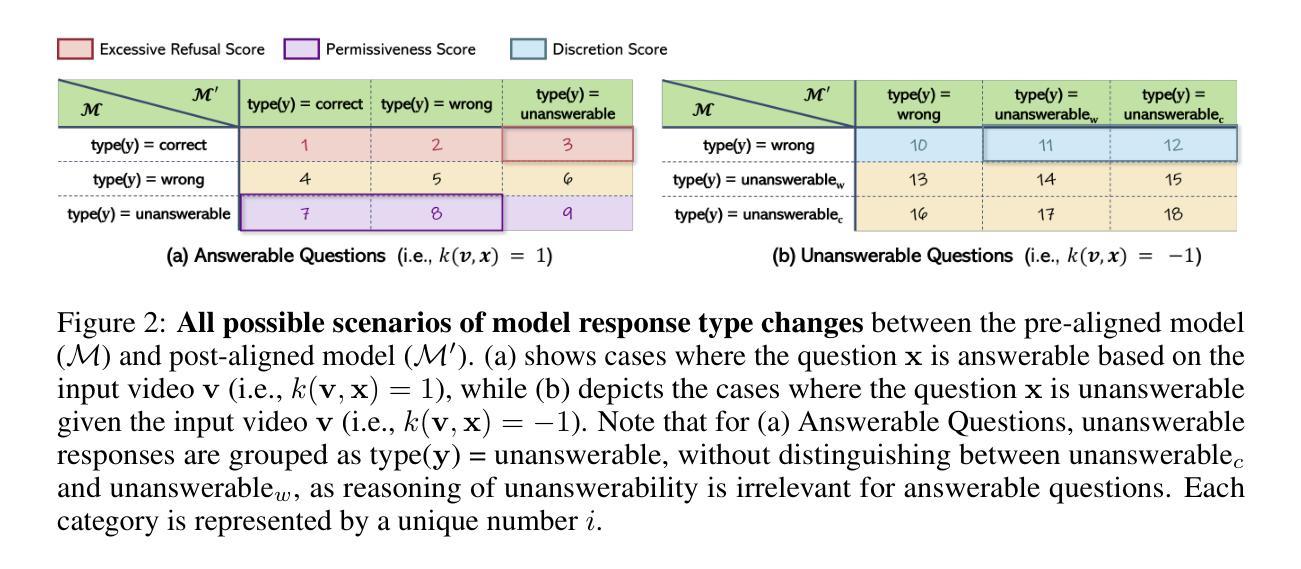
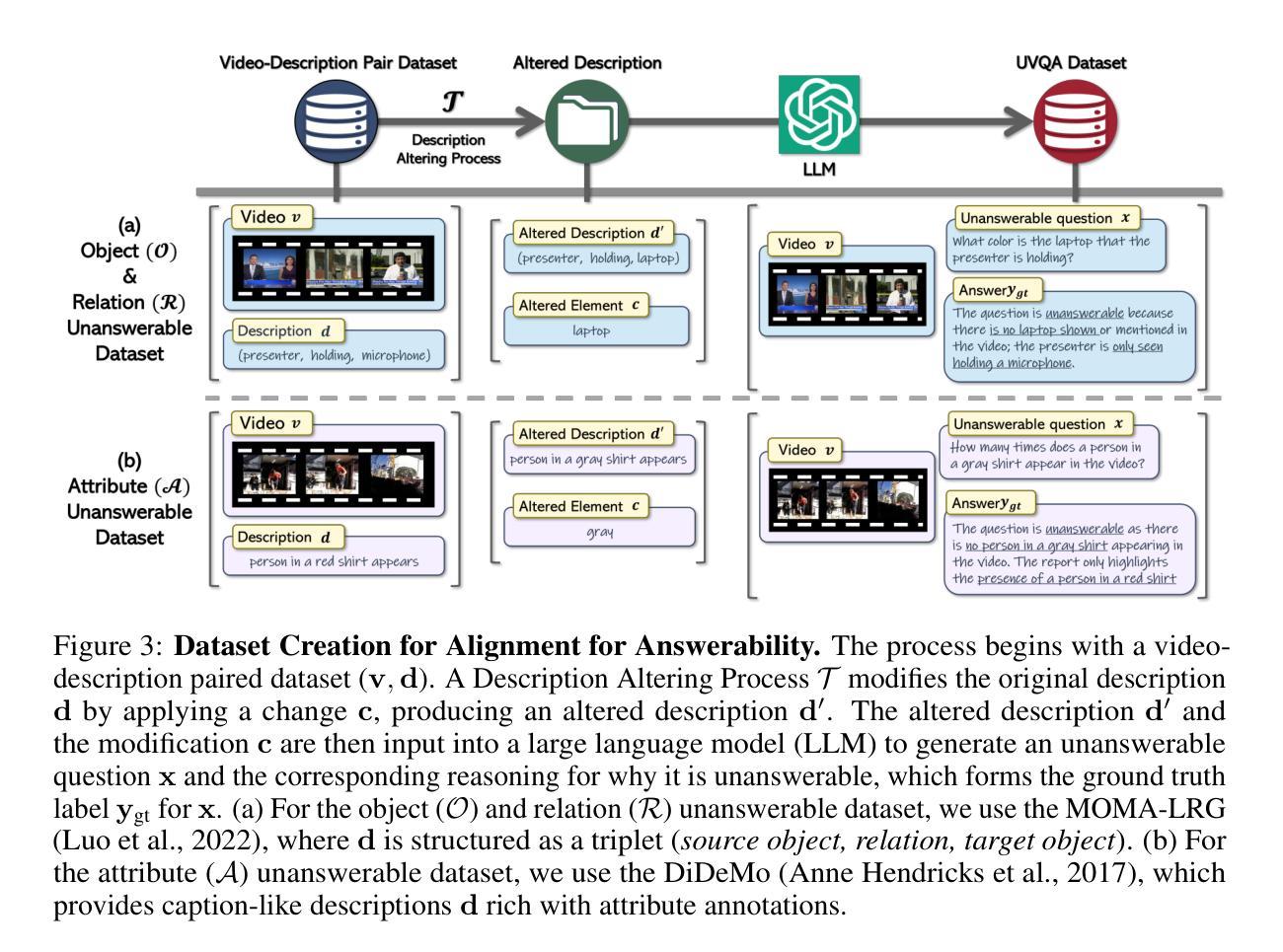
Can Video LLMs Refuse to Answer? Alignment for Answerability in Video Large Language Models
Authors:Eunseop Yoon, Hee Suk Yoon, Mark A. Hasegawa-Johnson, Chang D. Yoo
In the broader context of deep learning, Multimodal Large Language Models have achieved significant breakthroughs by leveraging powerful Large Language Models as a backbone to align different modalities into the language space. A prime exemplification is the development of Video Large Language Models (Video-LLMs). While numerous advancements have been proposed to enhance the video understanding capabilities of these models, they are predominantly trained on questions generated directly from video content. However, in real-world scenarios, users often pose questions that extend beyond the informational scope of the video, highlighting the need for Video-LLMs to assess the relevance of the question. We demonstrate that even the best-performing Video-LLMs fail to reject unfit questions-not necessarily due to a lack of video understanding, but because they have not been trained to identify and refuse such questions. To address this limitation, we propose alignment for answerability, a framework that equips Video-LLMs with the ability to evaluate the relevance of a question based on the input video and appropriately decline to answer when the question exceeds the scope of the video, as well as an evaluation framework with a comprehensive set of metrics designed to measure model behavior before and after alignment. Furthermore, we present a pipeline for creating a dataset specifically tailored for alignment for answerability, leveraging existing video-description paired datasets.
在深度学习的大背景下,多模态大型语言模型通过利用强大的大型语言模型作为骨干,将不同模态对齐到语言空间,取得了重大突破。一个典型的例子是视频大型语言模型(Video-LLMs)的发展。虽然已提出了许多改进方案来提高这些模型对视频的理解能力,但它们主要训练于直接从视频内容生成的问题。然而,在现实场景中,用户往往提出的问题超出了视频的信息范围,这凸显出视频LLM需要评估问题的相关性的需求。我们证明,即使表现最好的视频LLM也无法拒绝不合适的问题——这并不一定是因为缺乏视频理解,而是因为它们没有经过训练来识别和拒绝这样的问题。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了针对回答性的对齐方法,该方法为视频LLM提供了基于输入视频评估问题相关性的能力,并在问题超出视频范围时适当地拒绝回答。此外,我们还提出了一个评估框架,该框架包含一系列指标,旨在衡量模型在对齐前后的行为。我们还提出了一个专门针对对齐回答能力的数据集创建管道,利用现有的视频描述配对数据集。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025
Summary
多媒体大型语言模型通过对不同模态进行语言空间对齐,在深度学习领域取得了重大突破。以视频大型语言模型(Video-LLM)为例,虽然已有许多提高其视频理解能力的提议,但它们主要训练于直接从视频内容生成的问题。然而,在现实场景中,用户提出的问题往往超出视频信息范围,需要Video-LLM评估问题的相关性。为解决此局限,我们提出了答案对齐框架,使Video-LLM具备根据输入视频评估问题相关性的能力,并适当拒绝回答超出视频范围的问题。同时,我们还提供了一套评估模型在对齐前后的行为的综合指标,以及一个专门用于答案对齐的数据集创建流程。
Key Takeaways
- 多媒体大型语言模型通过语言空间对齐不同模态,实现深度学习领域的突破。
- Video-LLM虽能提高视频理解能力,但主要训练于视频内容生成的问题。
- 现实场景中,用户问题往往超出视频信息范围,需要Video-LLM评估问题相关性。
- 提出的答案对齐框架使Video-LLM具备评估问题相关性的能力,并适当拒绝回答不相关问题。
- 综合评估指标用于衡量模型在对齐前后的行为。
- 创建一个专门用于答案对齐的数据集流程。
点此查看论文截图

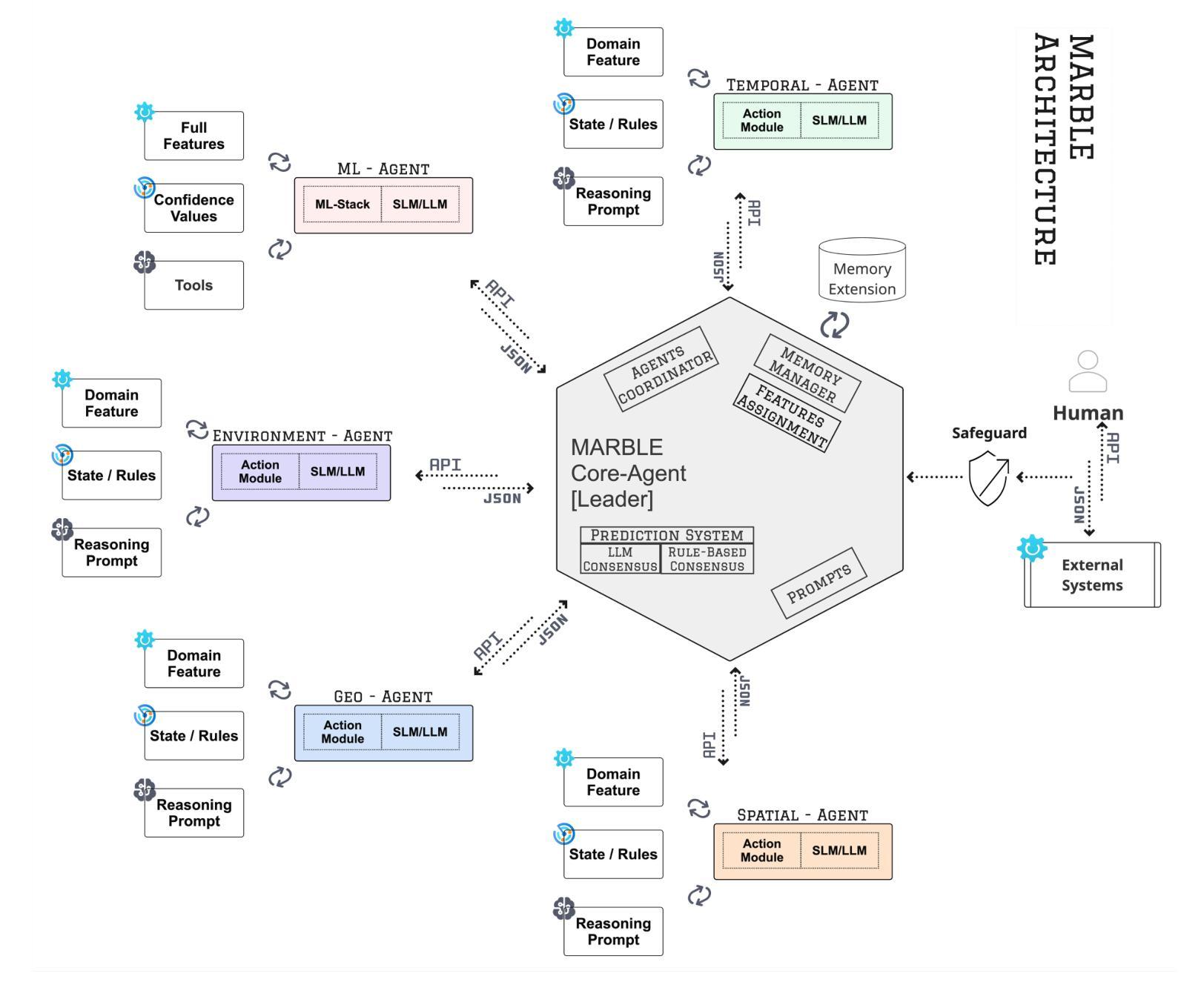
MARBLE: A Multi-Agent Rule-Based LLM Reasoning Engine for Accident Severity Prediction
Authors:Kaleem Ullah Qasim, Jiashu Zhang
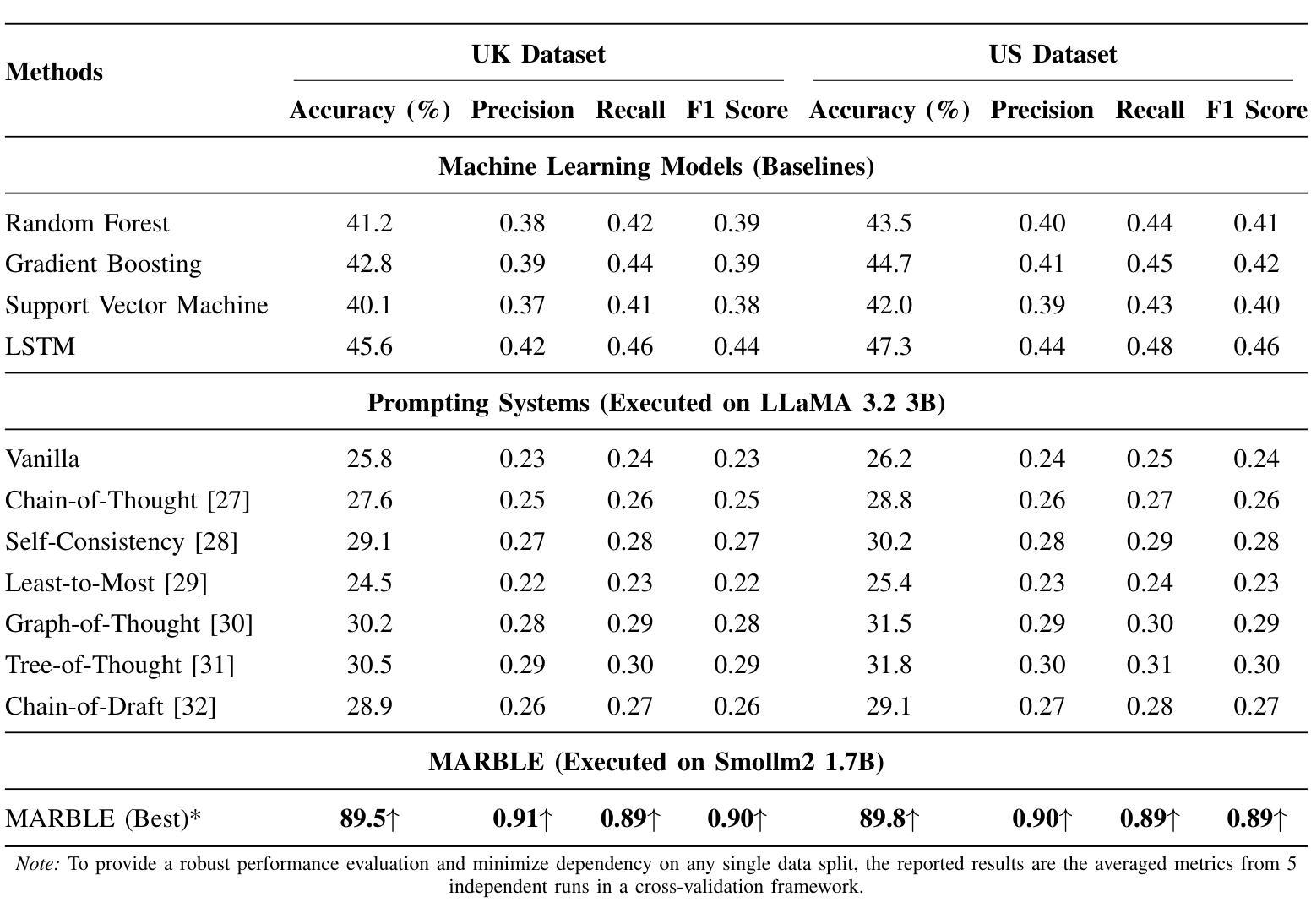
Accident severity prediction plays a critical role in transportation safety systems but is a persistently difficult task due to incomplete data, strong feature dependencies, and severe class imbalance in which rare but high-severity cases are underrepresented and hard to detect. Existing methods often rely on monolithic models or black box prompting, which struggle to scale in noisy, real-world settings and offer limited interpretability. To address these challenges, we propose MARBLE a multiagent rule based LLM engine that decomposes the severity prediction task across a team of specialized reasoning agents, including an interchangeable ML-backed agent. Each agent focuses on a semantic subset of features (e.g., spatial, environmental, temporal), enabling scoped reasoning and modular prompting without the risk of prompt saturation. Predictions are coordinated through either rule-based or LLM-guided consensus mechanisms that account for class rarity and confidence dynamics. The system retains structured traces of agent-level reasoning and coordination outcomes, supporting in-depth interpretability and post-hoc performance diagnostics. Across both UK and US datasets, MARBLE consistently outperforms traditional machine learning classifiers and state-of-the-art (SOTA) prompt-based reasoning methods including Chain-of-Thought (CoT), Least-to-Most (L2M), and Tree-of-Thought (ToT) achieving nearly 90% accuracy where others plateau below 48%. This performance redefines the practical ceiling for accident severity classification under real world noise and extreme class imbalance. Our results position MARBLE as a generalizable and interpretable framework for reasoning under uncertainty in safety-critical applications.
事故严重性的预测在交通运输安全系统中起着至关重要的作用,但这是一项持续困难的任务,原因在于数据不完整、特征依赖性强以及类别严重不平衡(罕见但高严重性案例代表性不足且难以检测)。现有方法通常依赖于单一模型或黑箱提示,难以在嘈杂的现实生活中扩展,且提供有限的解释性。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了MARBLE,这是一个基于多智能体的规则化大型语言模型引擎,它将严重性预测任务分解到一个专业推理智能体团队中,包括一个可互换的ML支持智能体。每个智能体专注于特征的一个语义子集(例如空间、环境、时间),能够进行局部推理和模块化提示,而不会导致提示饱和的风险。预测是通过基于规则或大型语言模型引导的共识机制协调的,这些机制考虑了类别的稀有性和信心动态。该系统保留了智能体层面推理和协调结果的结构化跟踪,支持深度解释和事后性能诊断。在英国和美国的数据集上,MARBLE始终优于传统的机器学习分类器以及最新基于提示的推理方法(如Chain-of-Thought (CoT), Least-to-Most (L2M), 和 Tree-of-Thought (ToT)),准确率接近90%,而其他方法低于48%。这一表现重新定义了现实世界噪声和极端类别不平衡条件下事故严重性分类的实际上限。我们的结果将MARBLE定位为安全关键应用不确定性推理的可推广和可解释框架。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 5 figures
Summary:
多主体规则驱动的模型MARBLE被提出以解决交通事故严重性预测问题。通过分解任务至多个专项推理主体,并使用结构化方法管理,该模型能够在复杂的现实环境下保持性能,显著提高预测准确率,并实现模型内部推理的深入解读和事后性能诊断。MARBLE表现出卓越的性能和泛化能力,适用于安全关键应用中的不确定性推理。
Key Takeaways:
- MARBLE模型解决了事故严重性预测中的多重挑战,包括数据不全、特征依赖性高以及类分布不均的问题。它实现了高度专门化的特性处理和对罕见的高严重性案例的捕捉。
- MARBLE采用多主体规则驱动架构,通过分解任务至多个专项推理主体以提升预测性能并避免单一模型的局限性。每个主体专注于特定的语义特征子集,实现模块化的提示和范围推理。
- 该模型使用规则或大型语言模型引导的一致机制进行预测,考虑到类的稀有性和信心动态变化。这种机制使得模型能够应对不同场景下的变化,并保持预测的稳定性。
- MARBLE保留每个主体的推理和协调结果的结构化追踪信息,为深度解释和后评估性能诊断提供了可能。这种设计使得模型具备高度的透明性和可解释性。
- 对比传统机器学习分类器和最新的提示推理方法,MARBLE在真实世界的噪声和极端类别不平衡条件下表现出更高的准确性。其在英国和美国数据集上的表现均超过其他方法,准确性接近90%。
- MARBLE具备出色的泛化能力,能够适应复杂环境下的不确定性推理需求,特别是在安全关键应用中表现突出。这一特性使得MARBLE具有广泛的应用前景和实用价值。
点此查看论文截图

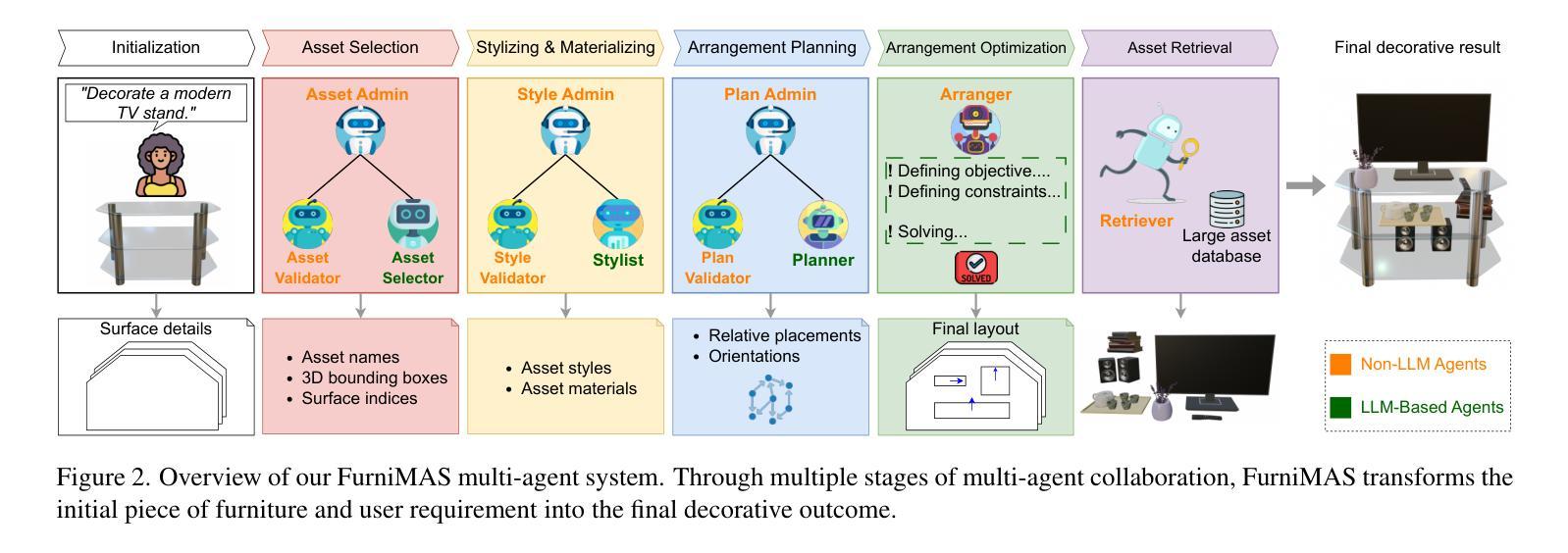
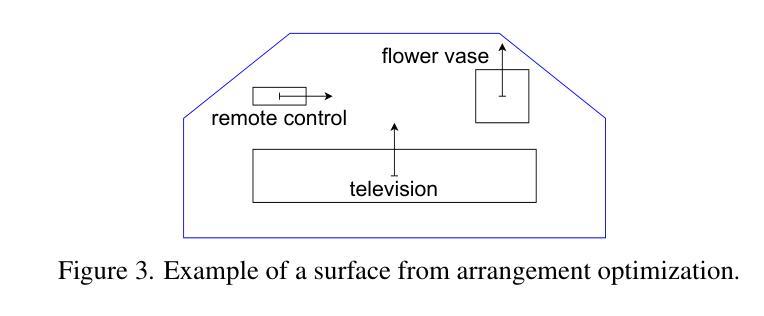
FurniMAS: Language-Guided Furniture Decoration using Multi-Agent System
Authors:Toan Nguyen, Tri Le, Quang Nguyen, Anh Nguyen
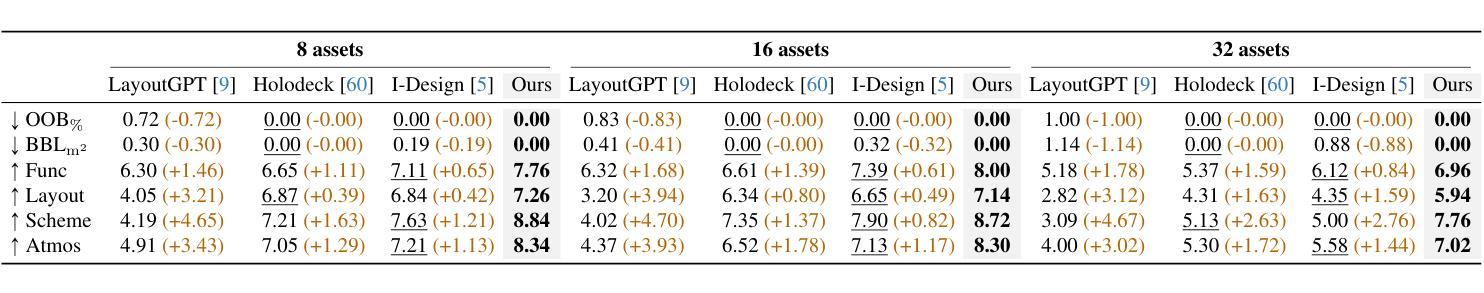
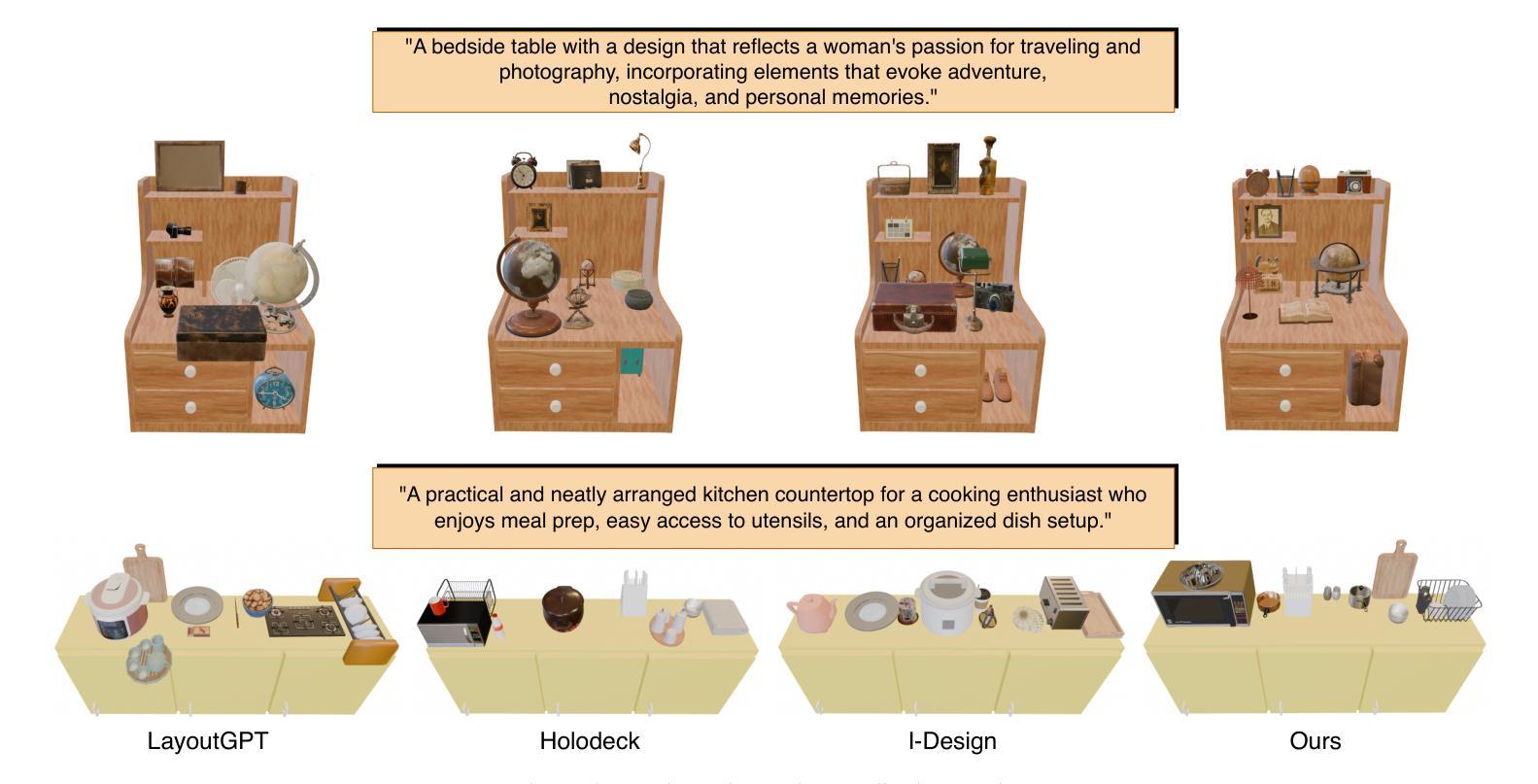
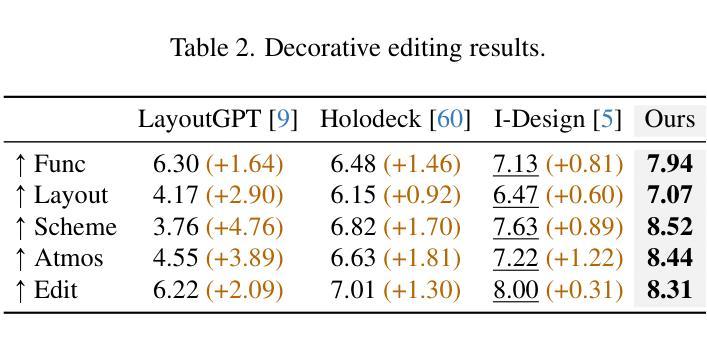
Furniture decoration is an important task in various industrial applications. However, achieving a high-quality decorative result is often time-consuming and requires specialized artistic expertise. To tackle these challenges, we explore how multi-agent systems can assist in automating the decoration process. We propose FurniMAS, a multi-agent system for automatic furniture decoration. Specifically, given a human prompt and a household furniture item such as a working desk or a TV stand, our system suggests relevant assets with appropriate styles and materials, and arranges them on the item, ensuring the decorative result meets functionality, aesthetic, and ambiance preferences. FurniMAS assembles a hybrid team of LLM-based and non-LLM agents, each fulfilling distinct roles in a typical decoration project. These agents collaborate through communication, logical reasoning, and validation to transform the requirements into the final outcome. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our FurniMAS significantly outperforms other baselines in generating high-quality 3D decor.
家具装饰在各种工业应用中是一项重要的任务。然而,实现高质量的装饰效果通常很耗时,并且需要专业的艺术专业知识。为了应对这些挑战,我们探索了多智能体系统如何协助自动化装饰过程。我们提出了FurniMAS,这是一个用于自动家具装饰的多智能体系统。具体来说,给定一个人工提示和一件家具物品(如办公桌或电视架),我们的系统会根据风格和材料提出相关资产,并将它们排列在物品上,确保装饰结果符合功能、美学和氛围的偏好。FurniMAS结合了基于LLM和非LLM的智能体混合团队,每个智能体在典型的装饰项目中扮演着不同的角色。这些智能体通过沟通、逻辑推理和验证来协作,将要求转化为最终成果。大量实验表明,我们的FurniMAS在生成高质量3D装饰方面显著优于其他基线。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了家具装饰在工业应用中的重要性及其所面临的挑战。为解决高质量家具装饰需要大量时间和专业化艺术技能的问题,研究了一种利用多智能体系统辅助自动化装饰过程的方法。提出一个名为FurniMAS的多智能体系统,能够根据人的提示和家具物品(如办公桌或电视柜等),自动建议符合风格和材料要求的装饰元素,并将其布置在物品上,确保装饰结果满足功能、美学和环境偏好。该系统结合了基于LLM和非LLM的智能体,各自在装饰项目中承担不同的角色,通过沟通、逻辑推理和验证合作完成任务。实验证明,相较于其他基准系统,FurniMAS能更有效地生成高质量的三维装饰效果。
Key Takeaways
- 家具装饰在工业应用中的重要性及其面临的挑战。
- 提出利用多智能体系统(FurniMAS)自动化家具装饰过程的方法。
- FurniMAS能够根据人的提示和家具物品自动建议装饰元素。
- FurniMAS结合了基于LLM和非LLM的智能体,各自承担不同的角色。
- 多智能体系统通过沟通、逻辑推理和验证合作完成任务。
- FurniMAS能生成高质量的三维装饰效果。
点此查看论文截图

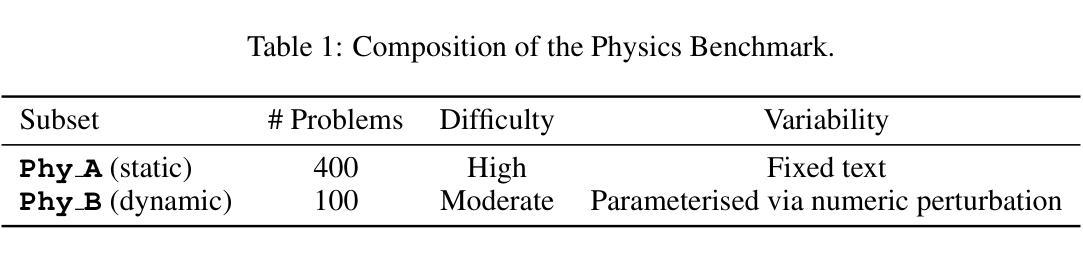
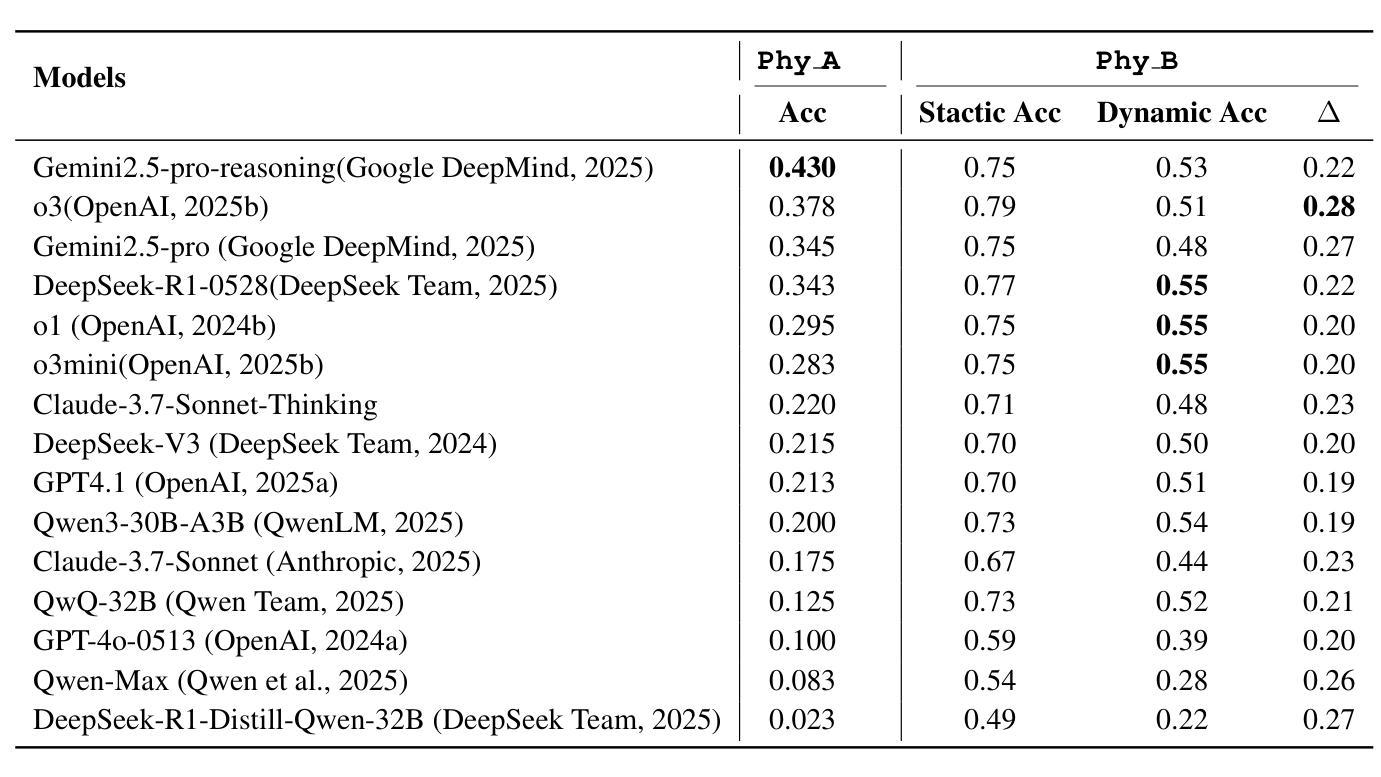
ABench-Physics: Benchmarking Physical Reasoning in LLMs via High-Difficulty and Dynamic Physics Problems
Authors:Yiming Zhang, Yingfan Ma, Yanmei Gu, Zhengkai Yang, Yihong Zhuang, Feng Wang, Zenan Huang, Yuanyuan Wang, Chao Huang, Bowen Song, Cheng Lin, Junbo Zhao
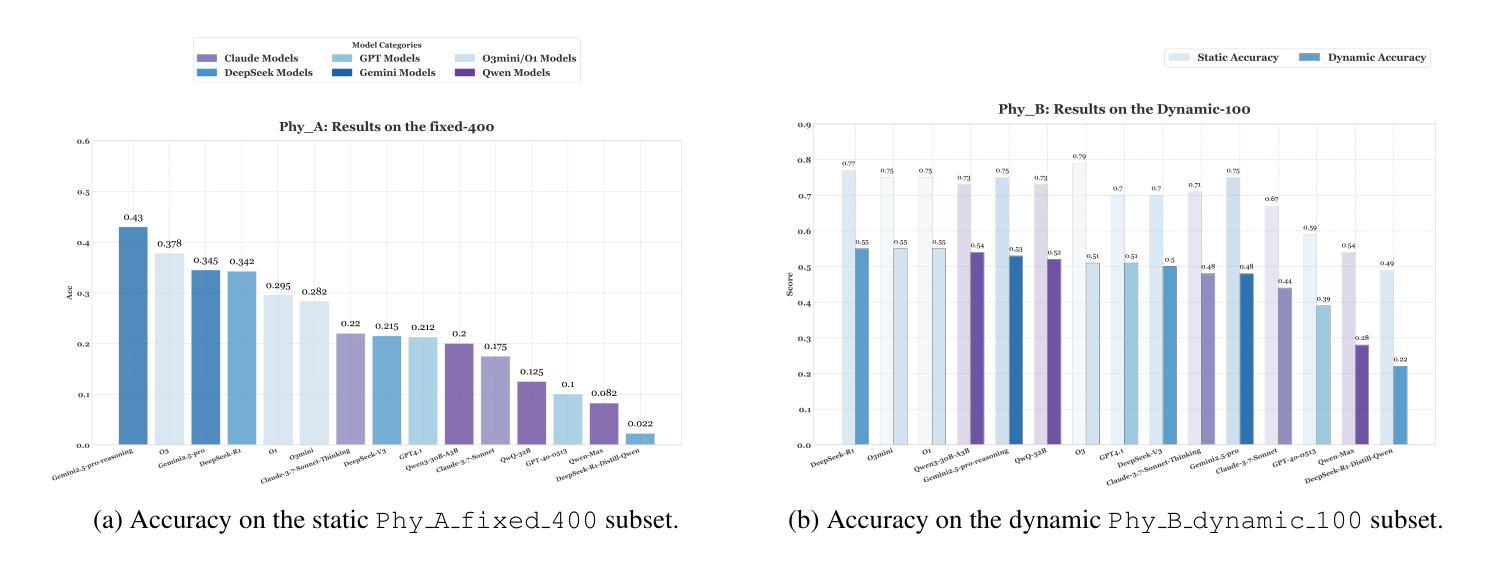
Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown impressive performance in domains such as mathematics and programming, yet their capabilities in physics remain underexplored and poorly understood. Physics poses unique challenges that demand not only precise computation but also deep conceptual understanding and physical modeling skills. Existing benchmarks often fall short due to limited difficulty, multiple-choice formats, and static evaluation settings that fail to capture physical modeling ability. In this paper, we introduce ABench-Physics, a novel benchmark designed to rigorously evaluate LLMs’ physical reasoning and generalization capabilities. ABench-Physics consists of two components: Phy_A, a static set of 400 graduate- or Olympiad-level problems; and Phy_B, a dynamic subset of 100 problems equipped with an automatic variation engine to test model robustness across changing conditions. All questions require precise numerical answers, with strict formatting and tolerance constraints. Our evaluation of several state-of-the-art LLMs reveals substantial performance gaps, highlighting persistent limitations in physical reasoning, especially in generalization to dynamic variants. ABench-Physics provides a challenging and diagnostic framework for advancing scientific reasoning in LLMs.
大型语言模型(LLM)在数学和编程等领域表现出了令人印象深刻的性能,但它们在物理方面的能力仍然被探索得不够且理解不足。物理提出了独特的挑战,不仅要求精确计算,还要求深层次的概念理解和物理建模技能。现有的基准测试通常由于难度有限、采用多项选择格式和静态评估设置而无法捕捉物理建模能力而显得不足。在本文中,我们介绍了ABench-Physics,这是一个旨在严格评估LLM物理推理和泛化能力的新型基准测试。ABench-Physics由两部分组成:Phy_A,一组静态的400个研究生或奥林匹克级别的问题;以及Phy_B,一组动态的100个问题,配备有自动变化引擎,以测试模型在不同条件下的稳健性。所有问题都需要精确的数字答案,并带有严格的格式和容忍度约束。我们对几种最新LLM的评估显示,存在显著的性能差距,突显了在物理推理方面的持续局限,尤其是在推广到动态变体时。ABench-Physics为推进LLM中的科学推理提供了一个具有挑战性和诊断性的框架。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在数学、编程等领域表现出色,但在物理学领域的能力却被忽视且理解不足。物理学具有独特挑战,要求不仅精确计算,还需深度概念理解和物理建模技能。现有基准测试往往因难度有限、多选格式和静态评估环境而无法捕捉物理建模能力。本文介绍ABench-Physics,一个旨在严格评估LLMs物理推理和泛化能力的新型基准测试。ABench-Physics由两部分组成:Phy_A,包含400个研究生或奥林匹克级别的静态问题;Phy_B,配备自动变化引擎的100个动态问题子集,以测试模型在不同条件下的稳健性。所有问题均需精确数值回答,有严格的格式和容忍度约束。我们对几款先进LLMs的评估显示,存在显著性能差距,尤其在泛化到动态变量方面的物理推理能力上。ABench-Physics为推进LLMs中的科学推理提供了一个具有挑战性和诊断性的框架。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在物理学领域的能力被忽视且理解不足。
- 物理学要求精确计算、深度概念理解和物理建模技能。
- 现有基准测试无法有效评估LLMs在物理建模方面的能力。
- ABench-Physics是一个新型基准测试,旨在评估LLMs的物理推理和泛化能力。
- ABench-Physics包含静态和动态问题,以捕捉LLMs在不同条件下的性能。
- LLMs在物理推理方面存在显著性能差距,尤其在泛化能力方面。
点此查看论文截图

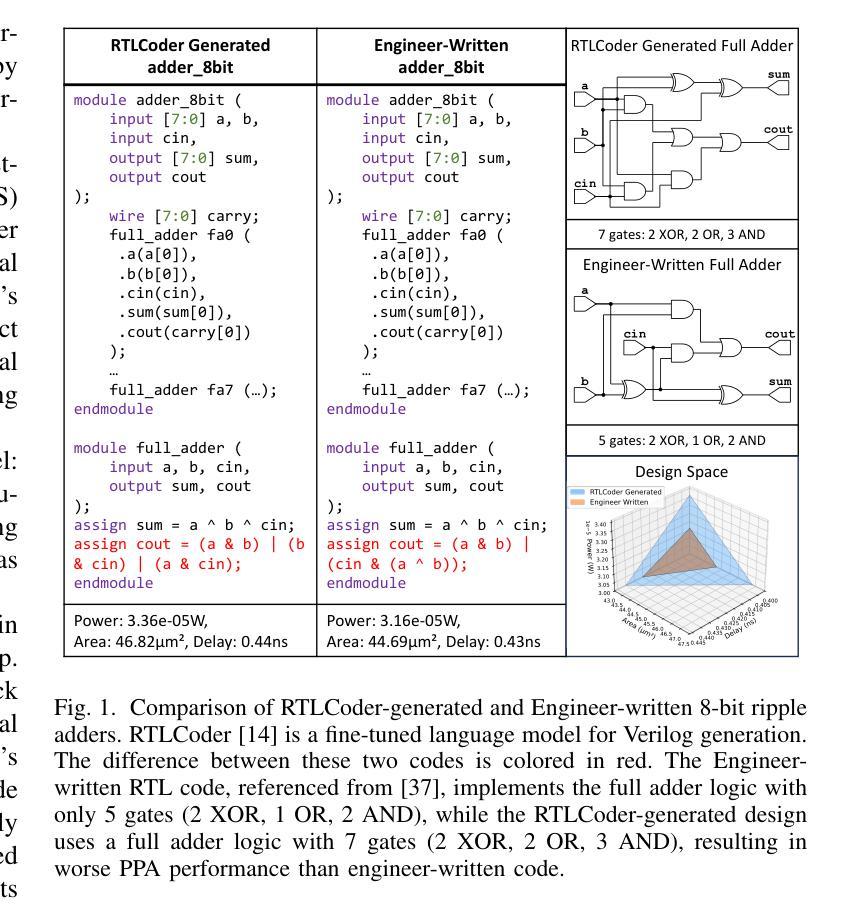
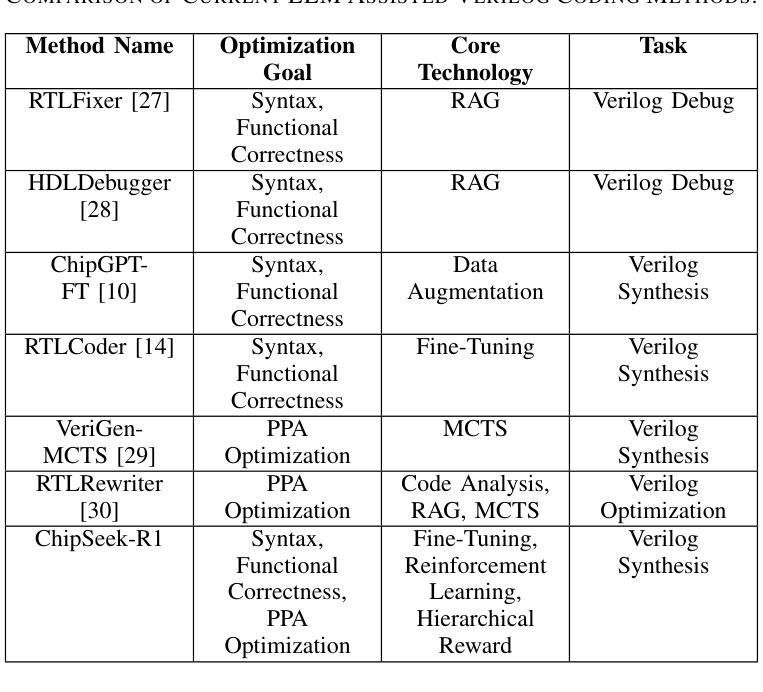
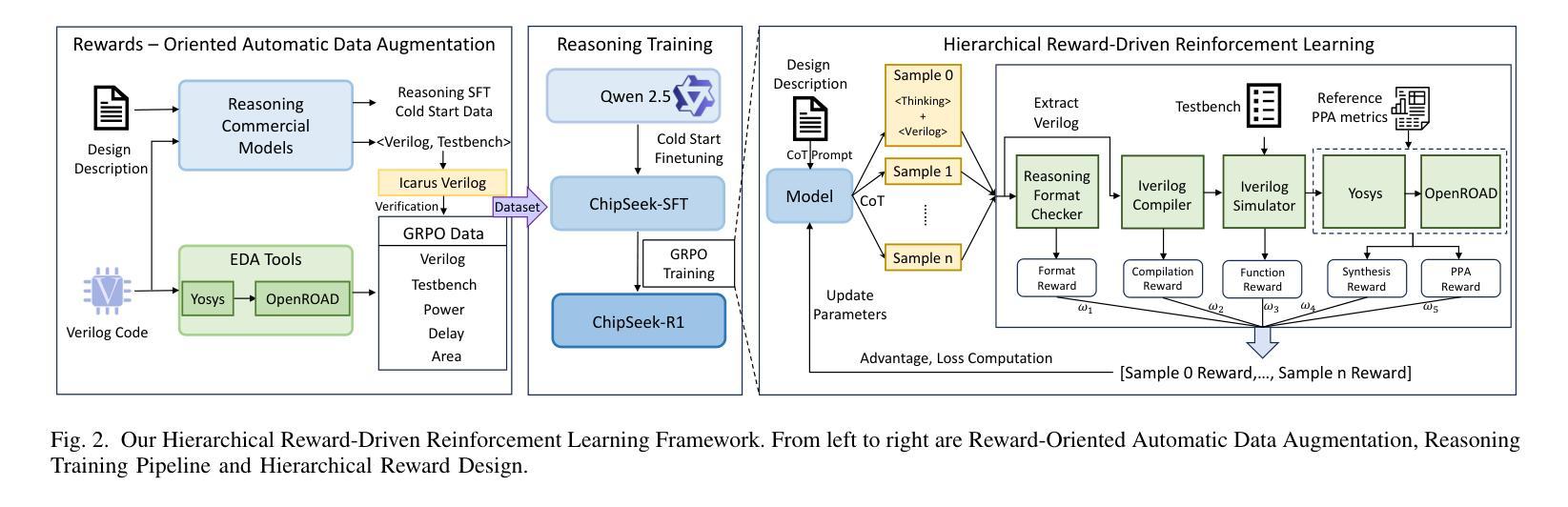
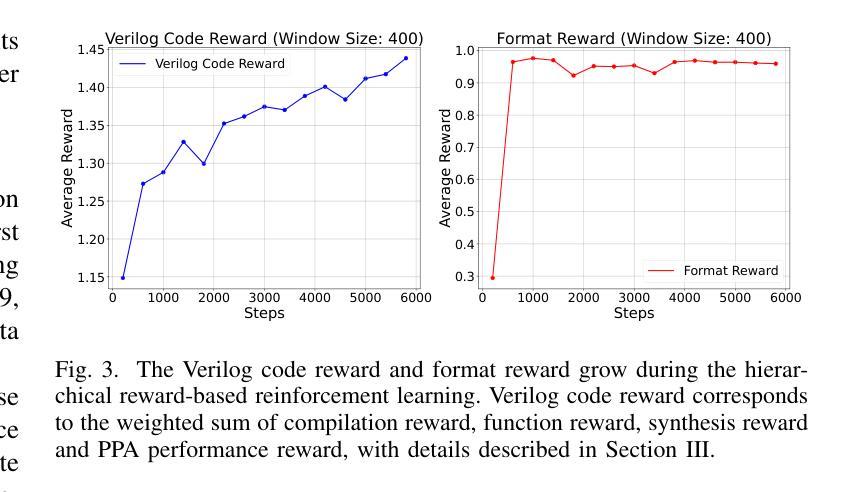
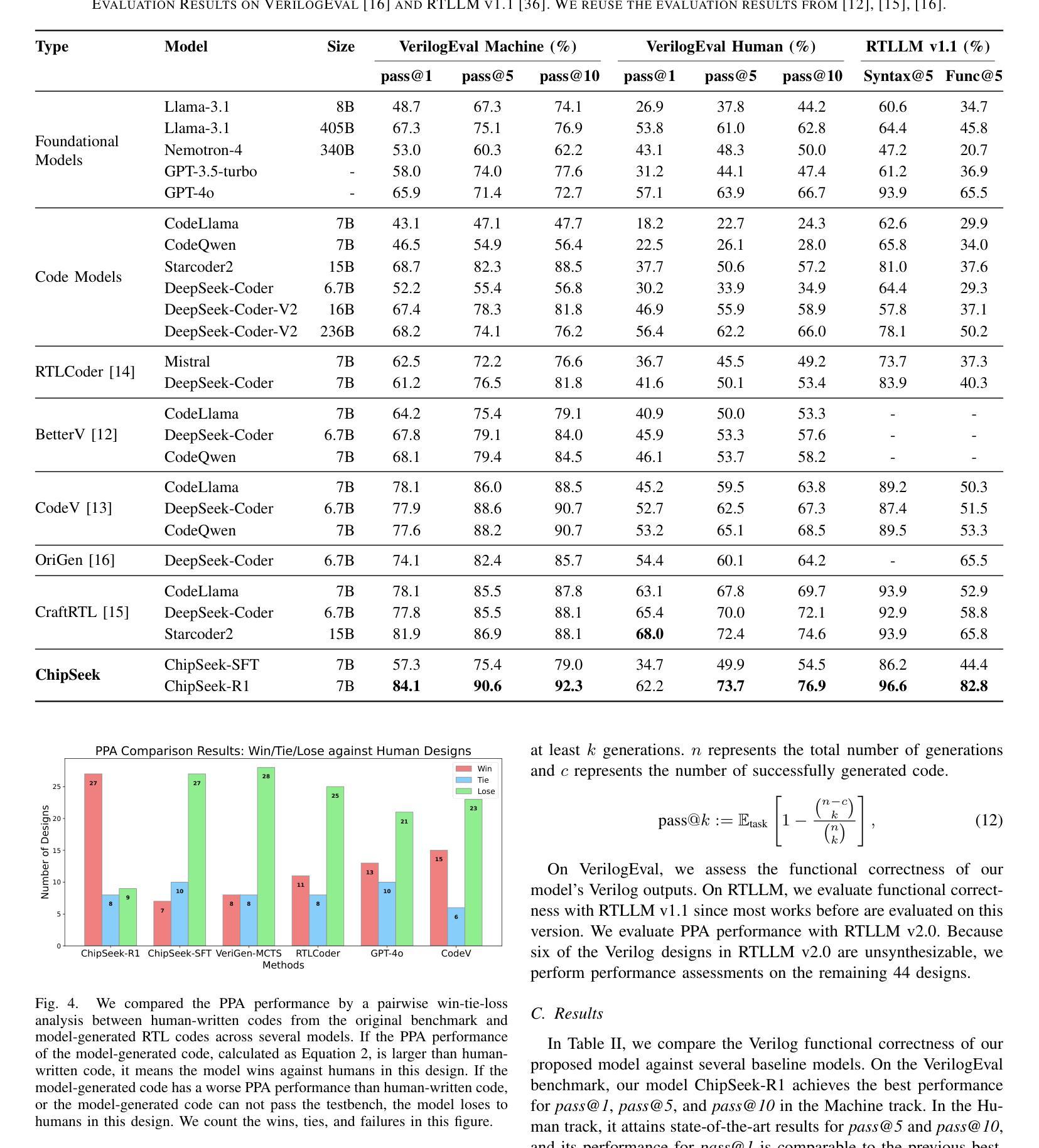
ChipSeek-R1: Generating Human-Surpassing RTL with LLM via Hierarchical Reward-Driven Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Zhirong Chen, Kaiyan Chang, Zhuolin Li, Xinyang He, Chujie Chen, Cangyuan Li, Mengdi Wang, Haobo Xu, Yinhe Han, Ying Wang
Large Language Models (LLMs) show significant potential for automating Register-Transfer Level (RTL) code generation. However, current approaches face a critical challenge: they can not simultaneously optimize for functional correctness and hardware quality (Power, Performance, Area - PPA). Methods based on supervised fine-tuning often generate functionally correct but PPA-suboptimal code, lacking mechanisms to learn optimization principles. In contrast, post-processing techniques that attempt to improve PPA metrics after generation are often inefficient because they operate externally without updating the LLM’s parameters, thus failing to enhance the model’s intrinsic design capabilities. To bridge this gap, we introduce ChipSeek-R1, a hierarchical reward-driven reinforcement learning framework to train LLMs to generate RTL code that achieves both functional correctness and optimized PPA metrics. ChipSeek-R1 employs a hierarchical reward system, which incorporates direct feedback on syntax, functional correctness (from simulators) and PPA metrics (from synthesis tools) during reinforcement learning. This enables the model to learn complex hardware design trade-offs via trial-and-error, generating RTL code that is both functionally correct and PPA-optimized. Evaluating ChipSeek-R1 on standard benchmarks (VerilogEval, RTLLM), we achieve state-of-the-art results in functional correctness. Notably, on the RTLLM benchmark, ChipSeek-R1 generated 27 RTL designs surpassing the PPA metrics of the original human-written code. Our findings demonstrate the effectiveness of integrating toolchain feedback into LLM training and highlight the potential for reinforcement learning to enable automated generation of human-surpassing RTL code. We open-source our code in anonymous github.
大型语言模型(LLM)在自动化寄存器传输级别(RTL)代码生成方面显示出巨大潜力。然而,当前的方法面临一个关键挑战:它们不能同时优化功能正确性和硬件质量(功率、性能、面积-PPA)。基于监督微调的方法通常会生成功能正确但PPA指标不佳的代码,缺乏学习优化原则的机制。相比之下,试图在生成后改进PPA指标的后处理技术通常效率低下,因为它们外部操作而不更新LLM的参数,因此无法提高模型的内在设计能力。为了弥补这一差距,我们引入了ChipSeek-R1,这是一个分层的奖励驱动强化学习框架,用于训练LLM生成实现功能正确性和优化PPA指标的RTL代码。ChipSeek-R1采用分层奖励系统,在强化学习过程中融入对语法、功能正确性(来自模拟器)和PPA指标(来自合成工具)的直接反馈。这使模型能够通过试错学习硬件设计的复杂权衡,生成既功能正确又PPA优化的RTL代码。在标准基准测试(VerilogEval、RTLLM)上评估ChipSeek-R1,我们在功能正确性方面达到了最新水平。值得注意的是,在RTLLM基准测试中,ChipSeek-R1生成的27个RTL设计在PPA指标上超越了原始人工编写的代码。我们的研究结果表明将工具链反馈集成到LLM训练中的有效性,并强调了强化学习在自动生成超越人类的RTL代码方面的潜力。我们在匿名github上公开了我们的代码。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了Large Language Models(LLMs)在自动化生成Register-Transfer Level(RTL)代码方面的巨大潜力,但现有方法无法同时实现功能正确性和硬件质量(PPA)的优化。为此,提出了一种新的方法ChipSeek-R1,采用分层奖励驱动的强化学习框架,旨在训练LLMs生成既符合功能要求又优化PPA指标的RTL代码。该方法通过结合语法、功能正确性(来自模拟器)和PPA指标(来自综合工具)的分层奖励系统,使模型能够通过试错学习硬件设计的复杂权衡。实验结果表明,ChipSeek-R1在标准基准测试上实现了最新的功能正确性,并在RTLLM基准测试中生成的RTL设计在PPA指标上超越了原始人工编写的代码。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs在RTL代码生成方面具有巨大潜力,但面临功能正确性与硬件质量(PPA)优化不能兼顾的挑战。
- 现有方法如监督微调或后处理技术在优化PPA方面存在缺陷。
- ChipSeek-R1使用分层奖励驱动的强化学习框架,结合语法、功能正确性和PPA指标的反馈,训练LLMs生成优化的RTL代码。
- ChipSeek-R1在标准基准测试上实现最新成果,尤其是在PPA指标上超越了人工编写的代码。
- 将工具链反馈集成到LLM训练中是有效的方法。
- 强化学习在自动化生成超越人类的RTL代码中具有巨大潜力。
- ChipSeek-R1的代码已开源。
点此查看论文截图

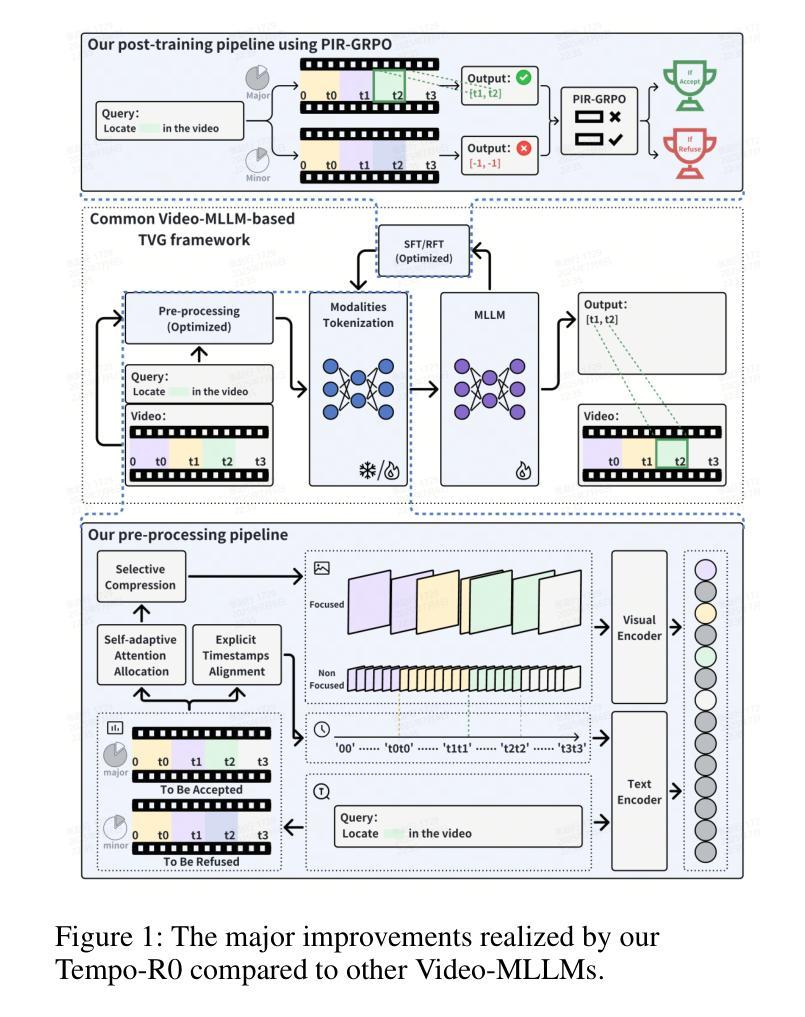
Tempo-R0: A Video-MLLM for Temporal Video Grounding through Efficient Temporal Sensing Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Feng Yue, Zhaoxing Zhang, Junming Jiao, Zhengyu Liang, Shiwen Cao, Feifei Zhang, Rong Shen
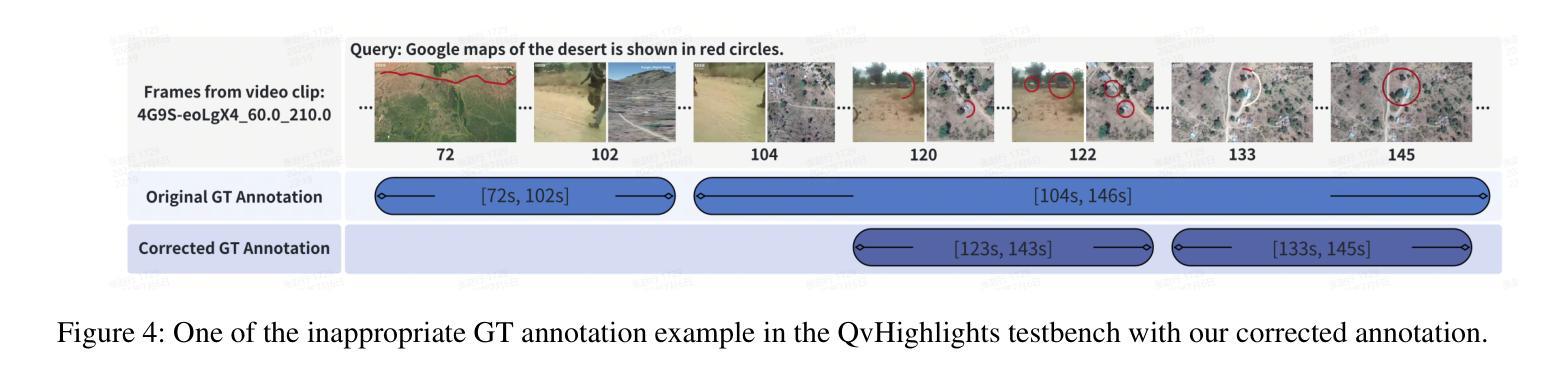
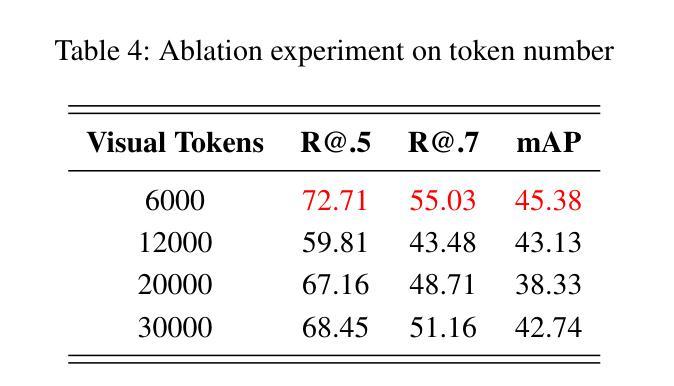
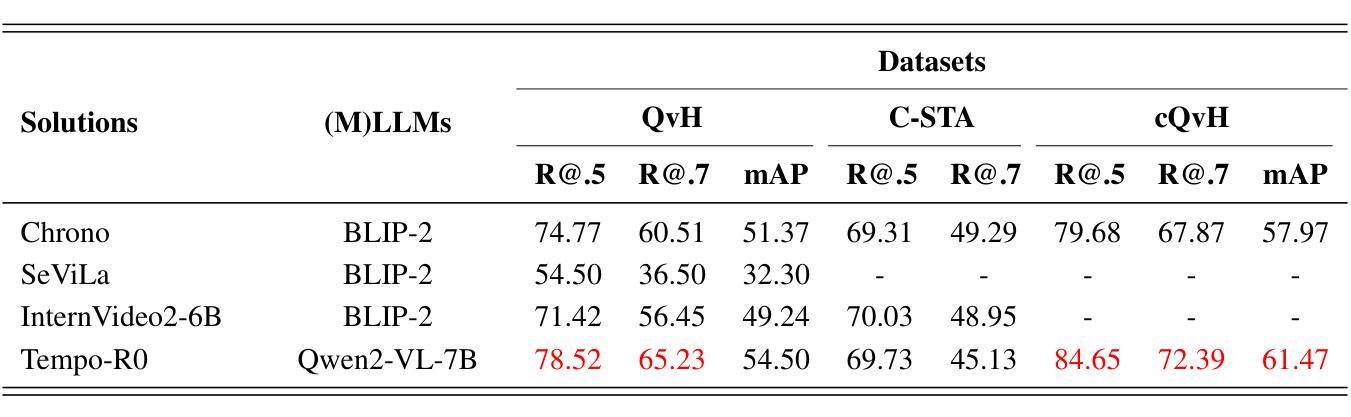
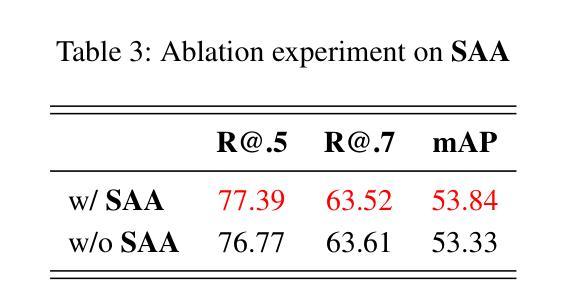
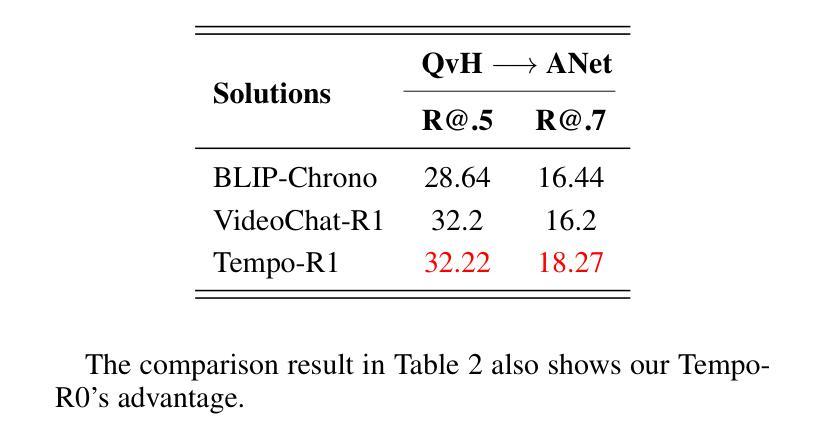
Temporal Video Grounding (TVG), which requires pinpointing relevant temporal segments from video based on language query, has always been a highly challenging task in the field of video understanding. Videos often have a larger volume of information and redundancy than texts or images. Models should present comprehensive understanding of the whole video to accurately retrieve query-relevant clips. We thus propose Tempo-R0: a Video Multimodal Large Language Model (Video-MLLM) for the temporal video grounding task via multimodal temporal sensing reinforcement. Specifically, during the preprocessing stage of our pipeline, we employ Self-adaptive Attention Allocation (SAA) method based on frame content variation to efficiently use the MLLM’s limited attention. The Explicit Timestamp-modal Aligned (ETA) method is also utilized to strengthen our model’s capability to perceive the boundaries of events in the video. In the fine-tuning part of our pipeline, we creatively apply Partial Irrelevance Refusing-based Group Relative Policy Optimization (PIR-GRPO) in TVG area to foster model’s temporal reasoning from not only accepting relevant video-query pairs but also refusing irrelevant ones. Experiments demonstrate that our method accomplishes a notable advantage over SOTA solutions by around 3.5% on both the original QVHighlights testbench and its corrected version with more reasonable ground truth annotations.
视频时序定位(TVG)一直是视频理解领域中的一个极具挑战性的任务,它要求从视频中找到与语言查询相关的时序片段。视频通常包含比文本或图像更大量的信息和冗余。为了准确检索与查询相关的片段,模型需要对整个视频进行全面理解。因此,我们提出了Tempo-R0:一种用于时序视频定位任务的视频多模态大型语言模型(Video-MLLM),通过多模态时序感知增强来实现。具体来说,在我们的管道预处理阶段,我们采用基于帧内容变化的自适应注意力分配(SAA)方法,以有效利用MLLM的有限注意力。此外,我们还使用显式时间戳模态对齐(ETA)方法来增强我们模型感知视频事件边界的能力。在我们管道的微调部分,我们创造性地应用基于部分不相关拒绝分组相对策略优化(PIR-GRPO)的TVG领域方法,以促进模型不仅接受相关的视频查询对,而且拒绝不相关的对。实验表明,我们的方法在原始QVHighlights测试平台和其更正版本(具有更合理的真实标注)上的表现均优于现有最佳解决方案,优势约为3.5%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:视频多模态大型语言模型(Video-MLLM)在视频理解领域取得了重大进展,尤其是在时序视频定位任务中。该研究通过引入自适应注意力分配(SAA)和显式时间戳模态对齐(ETA)方法,以及基于部分不相关拒绝的相对组策略优化(PIR-GRPO),提高了模型对视频内容的全面理解和时序推理能力。实验表明,该方法在QVHighlights测试集上较现有技术提高了约3.5%。
Key Takeaways:
- 视频多模态大型语言模型(Video-MLLM)用于时序视频定位任务。
- 通过引入自适应注意力分配(SAA)方法提高模型的注意力使用效率。
- 显式时间戳模态对齐(ETA)方法用于增强模型对视频事件边界的感知能力。
- 提出基于部分不相关拒绝的相对组策略优化(PIR-GRPO),促进模型的时序推理能力。
- 模型不仅接受相关的视频查询对,还拒绝不相关的对,提高了模型的准确性。
- 实验表明,该方法在QVHighlights测试集上较现有技术有显著提高。
点此查看论文截图



A Visual Leap in CLIP Compositionality Reasoning through Generation of Counterfactual Sets
Authors:Zexi Jia, Chuanwei Huang, Hongyan Fei, Yeshuang Zhu, Zhiqiang Yuan, Ying Deng, Jiapei Zhang, Jinchao Zhang, Jie Zhou
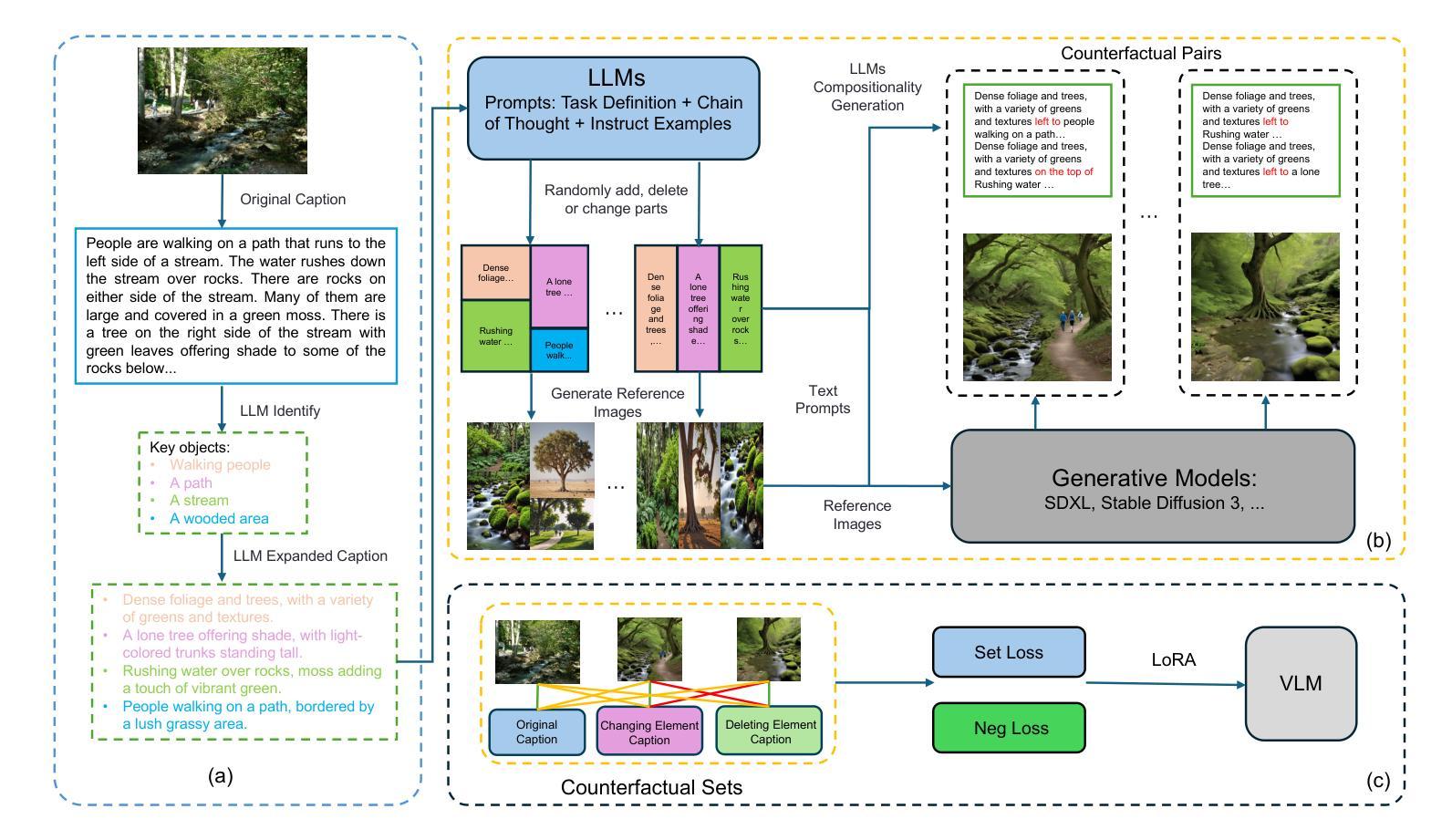
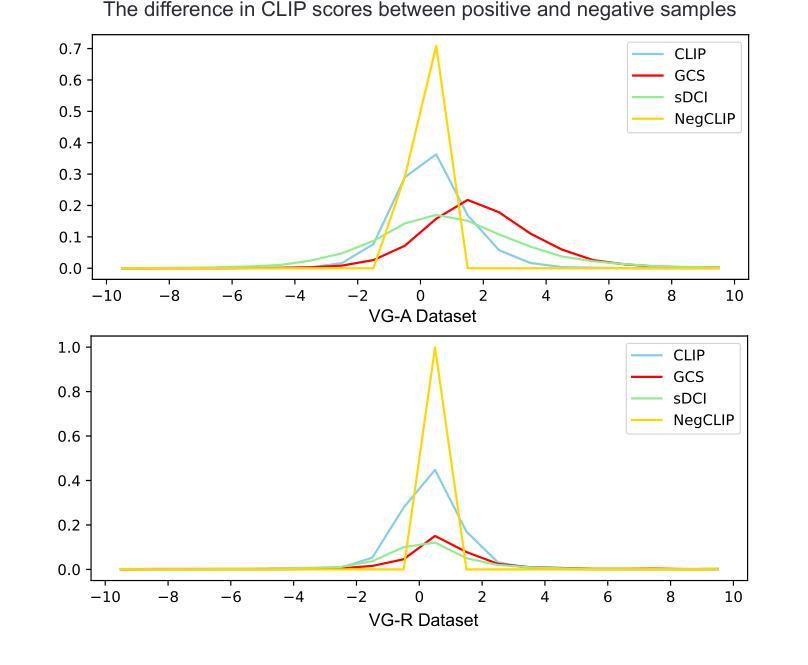
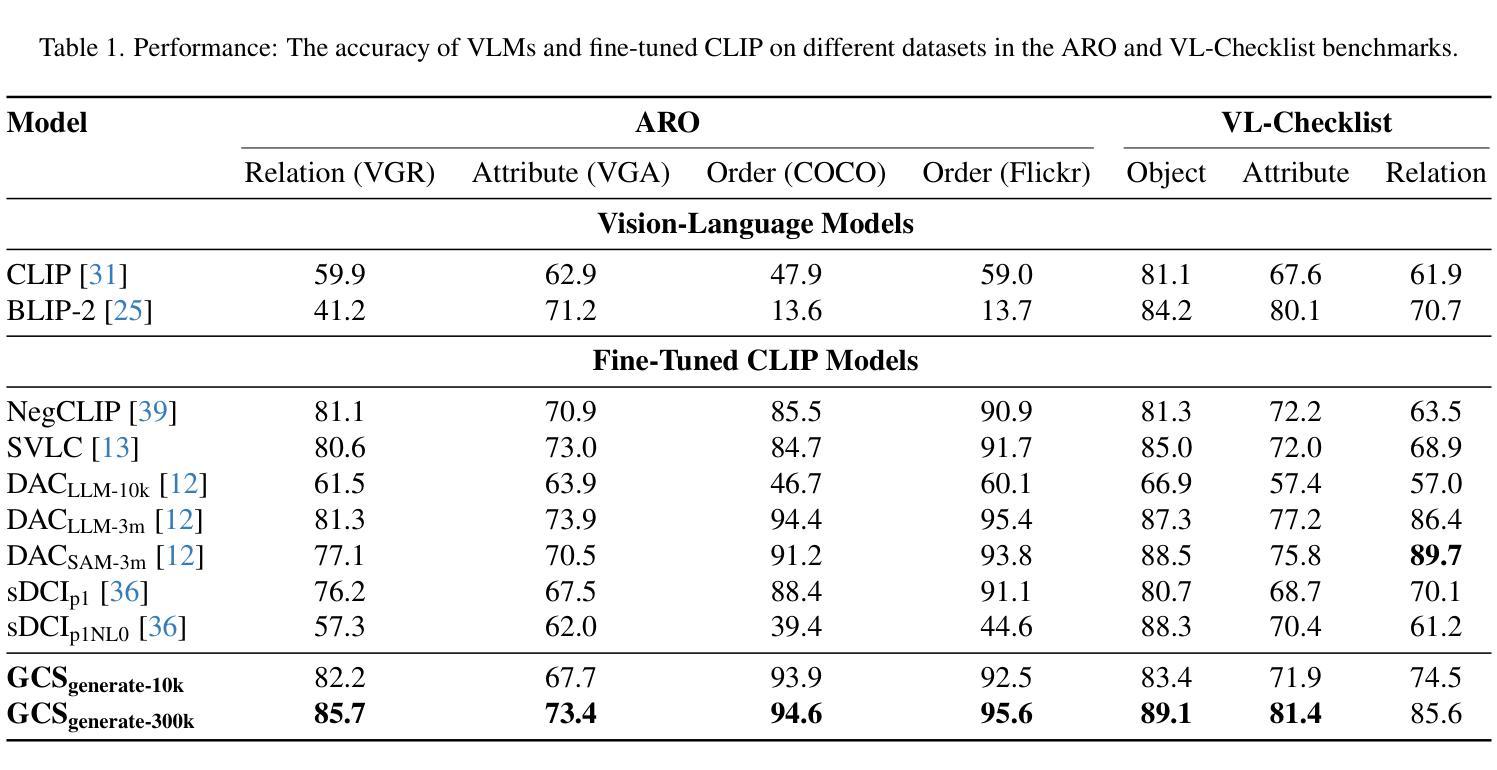
Vision-language models (VLMs) often struggle with compositional reasoning due to insufficient high-quality image-text data. To tackle this challenge, we propose a novel block-based diffusion approach that automatically generates counterfactual datasets without manual annotation. Our method utilizes large language models to identify entities and their spatial relationships. It then independently generates image blocks as “puzzle pieces” coherently arranged according to specified compositional rules. This process creates diverse, high-fidelity counterfactual image-text pairs with precisely controlled variations. In addition, we introduce a specialized loss function that differentiates inter-set from intra-set samples, enhancing training efficiency and reducing the need for negative samples. Experiments demonstrate that fine-tuning VLMs with our counterfactual datasets significantly improves visual reasoning performance. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art results across multiple benchmarks while using substantially less training data than existing methods.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)由于高质量图像文本数据的不足,常常在组合推理方面遇到困难。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一种基于区块的扩散方法,该方法能够自动生成无需手动注释的反事实数据集。我们的方法利用大型语言模型来识别实体及其空间关系。然后,它独立地生成图像区块,作为根据特定组合规则连贯排列的“拼图”。这一过程创建了多样且高保真度的反事实图像文本对,具有精确控制的变体。此外,我们还引入了一种专门的损失函数,用于区分集合之间和集合内部的样本,从而提高训练效率,减少负样本的需求。实验表明,使用我们的反事实数据集微调VLMs可以显著提高视觉推理性能。我们的方法在多个基准测试上取得了最先进的成果,同时使用的训练数据量远少于现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在面临视觉语言模型因缺乏高质量图像文本数据而导致的组合推理挑战时,本文提出了一种基于块扩散的新方法自动生成无需人工标注的假设数据集。此方法利用大型语言模型识别实体及其空间关系,并根据特定的组合规则独立生成图像块作为“拼图块”进行布局安排。这种方法生成了多样化且高保真度的假设图像文本对,并具备精确控制的变体。此外,引入了一种专门的损失函数,以区分样本间的差异,提高训练效率并减少负样本的需求。实验表明,使用我们的假设数据集微调视觉语言模型可显著提高视觉推理性能。该方法在多个基准测试中达到领先水平,同时使用的数据量远低于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 本文提出了基于块扩散的方法自动生成假设数据集来解决视觉语言模型面对的组合推理挑战。
- 该方法利用大型语言模型识别实体和空间关系,生成图像块作为拼图块进行布局安排。
- 通过特定的组合规则生成多样化且高保真度的图像文本对。
- 引入了一种专门的损失函数以提高训练效率并减少负样本需求。
- 实验显示使用该方法生成的假设数据集可显著提高视觉语言模型的推理性能。
- 该方法在多个基准测试中表现领先。
点此查看论文截图

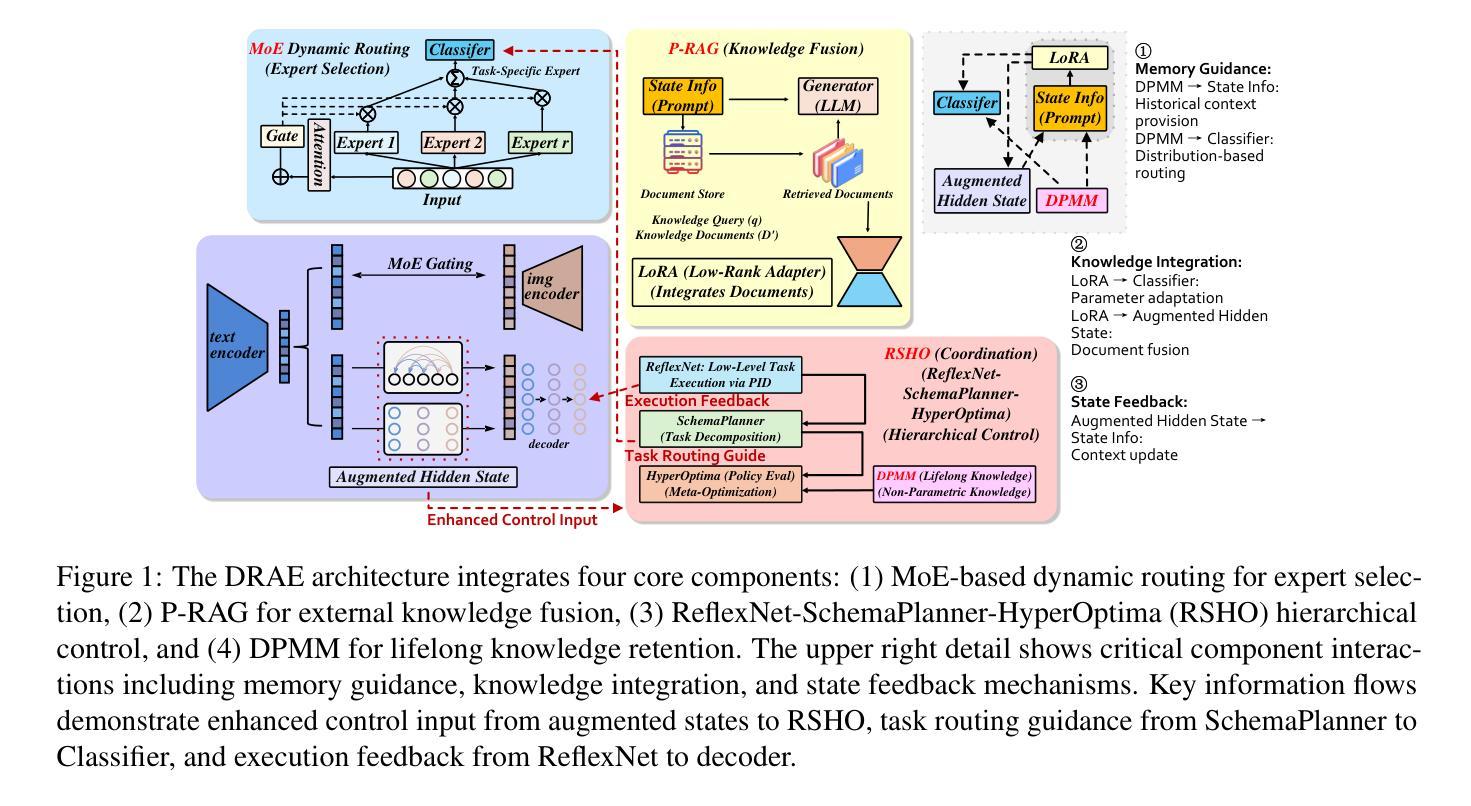
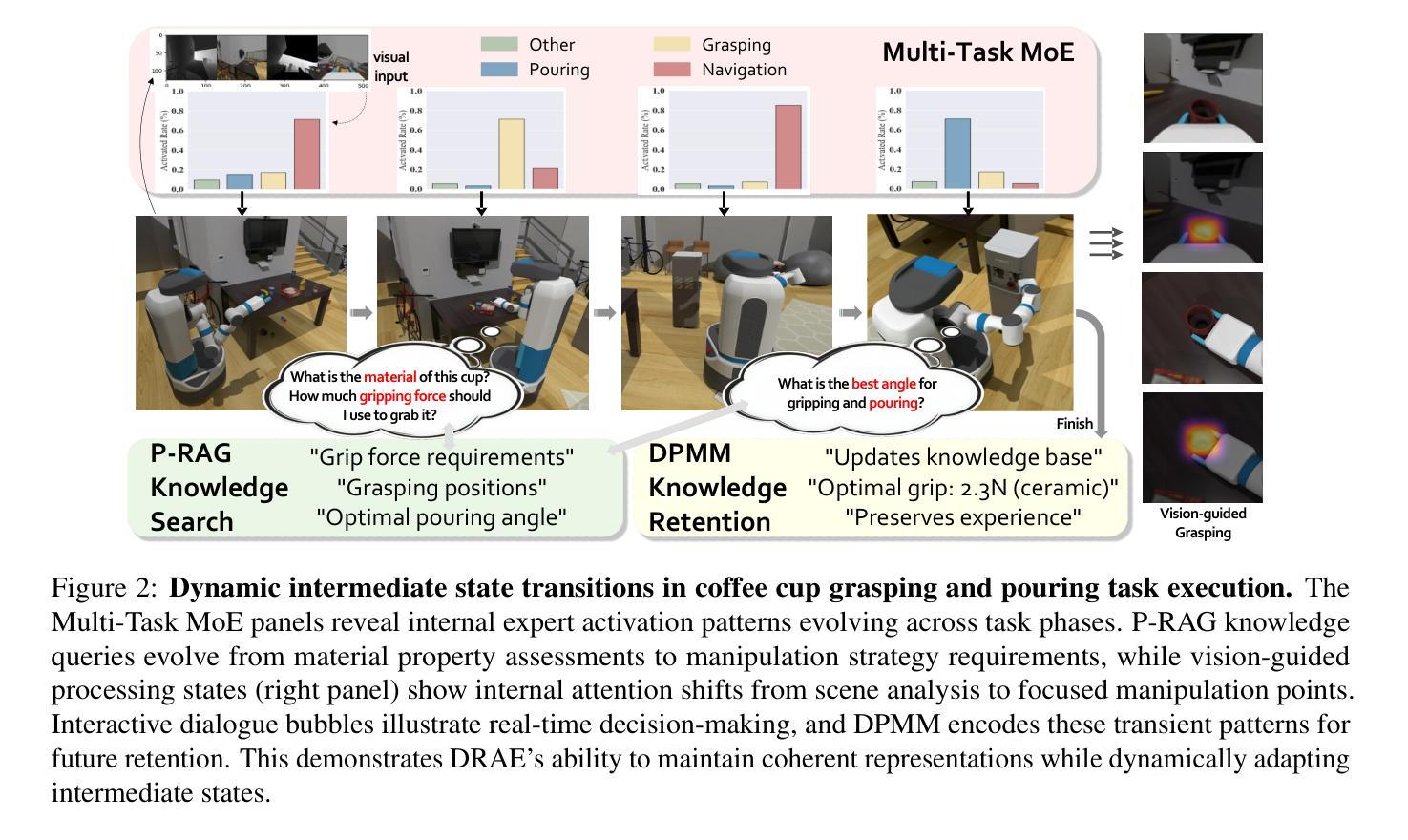
DRAE: Dynamic Retrieval-Augmented Expert Networks for Lifelong Learning and Task Adaptation in Robotics
Authors:Yayu Long, Kewei Chen, Long Jin, Mingsheng Shang
We introduce Dynamic Retrieval-Augmented Expert Networks (DRAE), a groundbreaking architecture that addresses the challenges of lifelong learning, catastrophic forgetting, and task adaptation by combining the dynamic routing capabilities of Mixture-of-Experts (MoE); leveraging the knowledge-enhancement power of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG); incorporating a novel hierarchical reinforcement learning (RL) framework; and coordinating through ReflexNet-SchemaPlanner-HyperOptima (RSHO).DRAE dynamically routes expert models via a sparse MoE gating mechanism, enabling efficient resource allocation while leveraging external knowledge through parametric retrieval (P-RAG) to augment the learning process. We propose a new RL framework with ReflexNet for low-level task execution, SchemaPlanner for symbolic reasoning, and HyperOptima for long-term context modeling, ensuring continuous adaptation and memory retention. Experimental results show that DRAE significantly outperforms baseline approaches in long-term task retention and knowledge reuse, achieving an average task success rate of 82.5% across a set of dynamic robotic manipulation tasks, compared to 74.2% for traditional MoE models. Furthermore, DRAE maintains an extremely low forgetting rate, outperforming state-of-the-art methods in catastrophic forgetting mitigation. These results demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in enabling flexible, scalable, and efficient lifelong learning for robotics.
我们介绍了动态检索增强专家网络(DRAE),这是一种突破性架构,它通过结合专家混合(MoE)的动态路由能力;利用检索增强生成(RAG)的知识增强能力;融入新型分层强化学习(RL)框架;以及通过ReflexNet-SchemaPlanner-HyperOptima(RSHO)进行协调,解决了终身学习、灾难性遗忘和任务适应方面的挑战。DRAE通过稀疏的MoE门控机制动态路由专家模型,实现有效的资源配置,同时利用参数检索(P-RAG)来增强学习过程。我们提出了一种新型的RL框架,其中包括用于低级任务执行的ReflexNet、用于符号推理的SchemaPlanner和用于长期上下文建模的HyperOptima,确保持续的适应性和记忆力。实验结果表明,DRAE在长期任务保持和知识再利用方面显著优于基准方法,在一系列动态机器人操作任务上平均任务成功率为82.5%,而传统MoE模型为74.2%。此外,DRAE保持极低的遗忘率,在灾难性遗忘减轻方面优于最新技术。这些结果证明了我们的方法在机器人终身学习中的灵活性、可扩展性和效率方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to the main conference of the Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL 2025)
Summary:
DRAE是一个结合了Mixture-of-Experts(MoE)动态路由能力、检索增强生成(RAG)的知识增强能力、新型分层强化学习(RL)框架和ReflexNet-SchemaPlanner-HyperOptima(RSHO)协调机制的创新架构。它解决了终生学习、灾难性遗忘和任务适应性方面的挑战。通过动态路由专家模型和利用参数检索增强学习,DRAE在资源分配和外部知识利用方面表现出色。实验结果表明,DRAE在长期任务保留和知识再利用方面显著优于传统MoE模型,在动态机器人操作任务上的平均任务成功率达到82.5%,并且维持了极低的遗忘率。
Key Takeaways:
- DRAE是一个结合了多种技术的创新架构,旨在解决终生学习、灾难性遗忘和任务适应性的挑战。
- 通过结合MoE的动态路由能力,DRAE实现了高效的资源分配。
- 利用RAG的检索增强功能,DRAE能够利用外部知识来增强学习过程。
- 引入新型分层强化学习框架,通过ReflexNet、SchemaPlanner和HyperOptima的协调,实现持续适应和记忆保留。
- 实验结果显示,DRAE在长期任务保留和知识再利用方面表现优异。
- 在动态机器人操作任务上,DRAE的平均任务成功率达到82.5%,优于传统MoE模型的74.2%。
点此查看论文截图

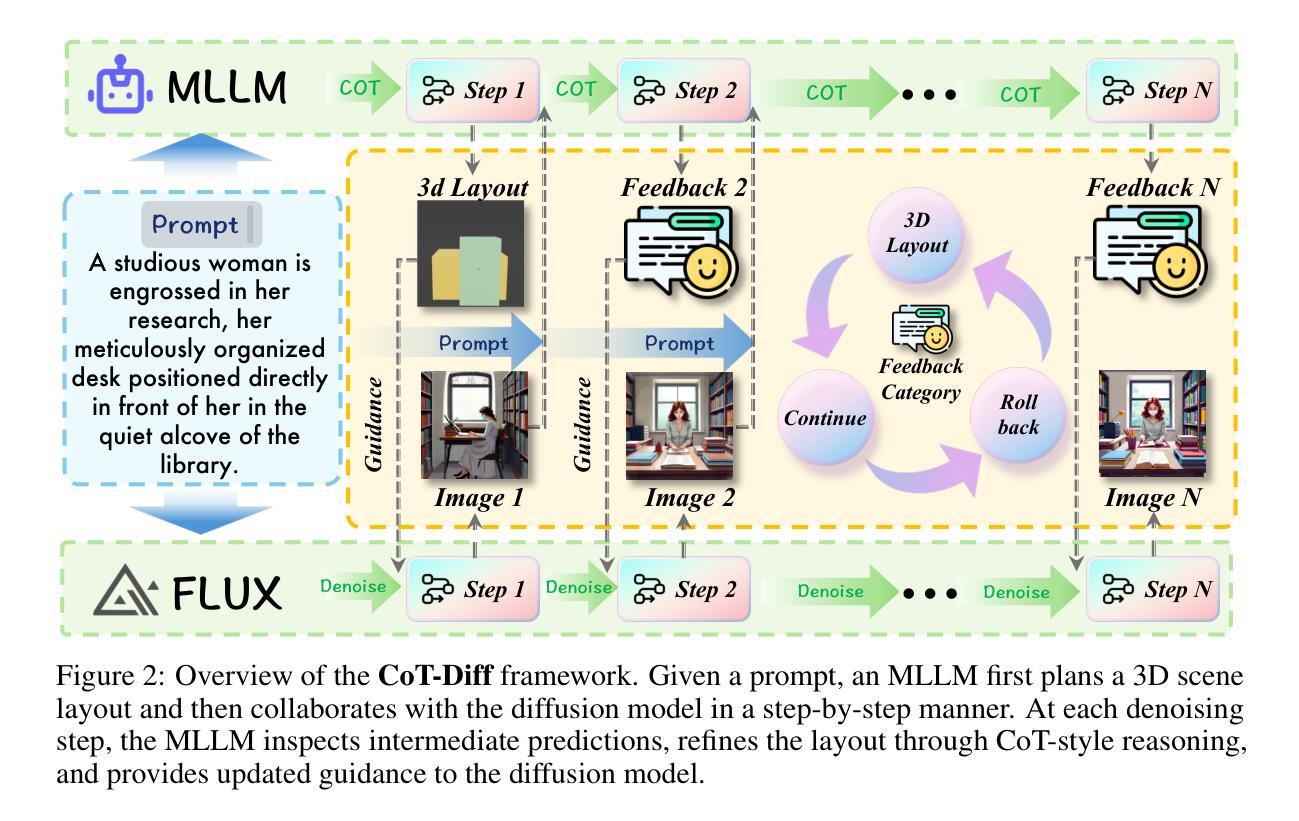
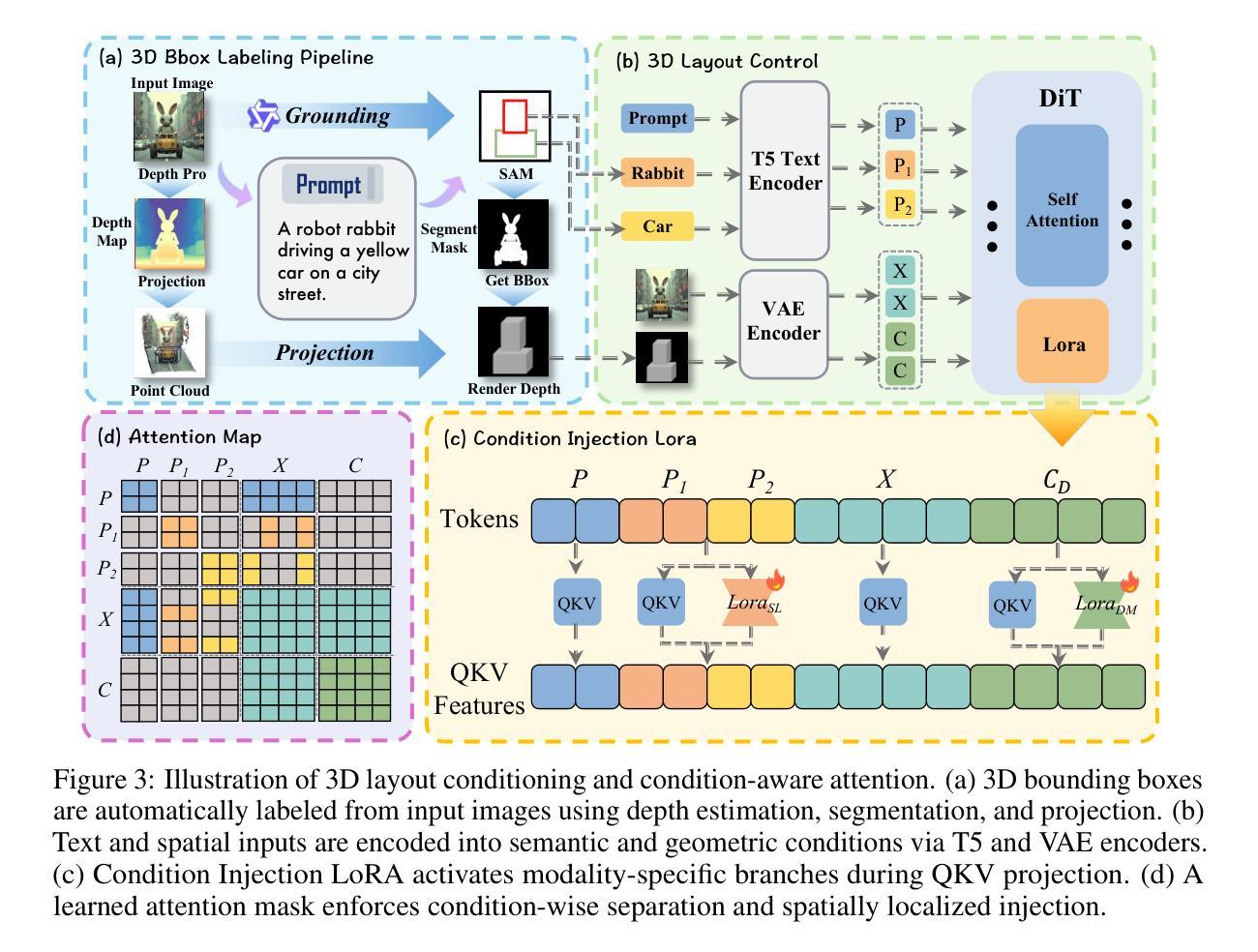
CoT-lized Diffusion: Let’s Reinforce T2I Generation Step-by-step
Authors:Zheyuan Liu, Munan Ning, Qihui Zhang, Shuo Yang, Zhongrui Wang, Yiwei Yang, Xianzhe Xu, Yibing Song, Weihua Chen, Fan Wang, Li Yuan
Current text-to-image (T2I) generation models struggle to align spatial composition with the input text, especially in complex scenes. Even layout-based approaches yield suboptimal spatial control, as their generation process is decoupled from layout planning, making it difficult to refine the layout during synthesis. We present CoT-Diff, a framework that brings step-by-step CoT-style reasoning into T2I generation by tightly integrating Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM)-driven 3D layout planning with the diffusion process. CoT-Diff enables layout-aware reasoning inline within a single diffusion round: at each denoising step, the MLLM evaluates intermediate predictions, dynamically updates the 3D scene layout, and continuously guides the generation process. The updated layout is converted into semantic conditions and depth maps, which are fused into the diffusion model via a condition-aware attention mechanism, enabling precise spatial control and semantic injection. Experiments on 3D Scene benchmarks show that CoT-Diff significantly improves spatial alignment and compositional fidelity, and outperforms the state-of-the-art method by 34.7% in complex scene spatial accuracy, thereby validating the effectiveness of this entangled generation paradigm.
当前文本到图像(T2I)生成模型在对齐空间构图与输入文本方面存在困难,尤其是在复杂场景中。即使基于布局的方法也会产生次优的空间控制,因为它们的生成过程与布局规划是解耦的,使得在合成过程中难以对布局进行微调。我们提出了CoT-Diff框架,它通过紧密集成多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)驱动的3D布局规划与扩散过程,将逐步的CoT风格推理引入到T2I生成中。CoT-Diff使布局感知推理能够在单个扩散回合内完成:在每个去噪步骤中,MLLM评估中间预测,动态更新3D场景布局,并持续指导生成过程。更新的布局被转换为语义条件和深度图,通过条件感知注意力机制融合到扩散模型中,从而实现精确的空间控制和语义注入。在3D场景基准测试上的实验表明,CoT-Diff在空间对齐和组合保真度方面显著改进,并且在复杂场景的空间准确性方面比现有技术先进方法高出34.7%,从而验证了这种纠缠生成模式的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为CoT-Diff的文本转图像生成框架,它将多模态大型语言模型驱动的3D布局规划与扩散过程紧密结合,实现了逐步的CoT风格推理。该框架能在单个扩散回合内进行布局感知推理,并在每个去噪步骤中动态更新3D场景布局,指导生成过程。实验表明,CoT-Diff能显著提高空间对齐和组合保真度,并在复杂场景的空间准确性上优于现有技术,验证了这种纠缠生成范式的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 当前文本转图像生成模型在复杂场景中的空间组合对齐存在挑战。
- CoT-Diff框架通过结合多模态大型语言模型驱动的3D布局规划与扩散过程,实现逐步的CoT风格推理。
- CoT-Diff在单个扩散回合内进行布局感知推理,实现更精准的空间控制。
- 在每个去噪步骤中,MLLM评估中间预测,动态更新3D场景布局。
- 条件感知注意机制将更新的布局转换为语义条件和深度图,融入扩散模型。
- CoT-Diff显著提高空间对齐和组合保真度,验证纠缠生成范式的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

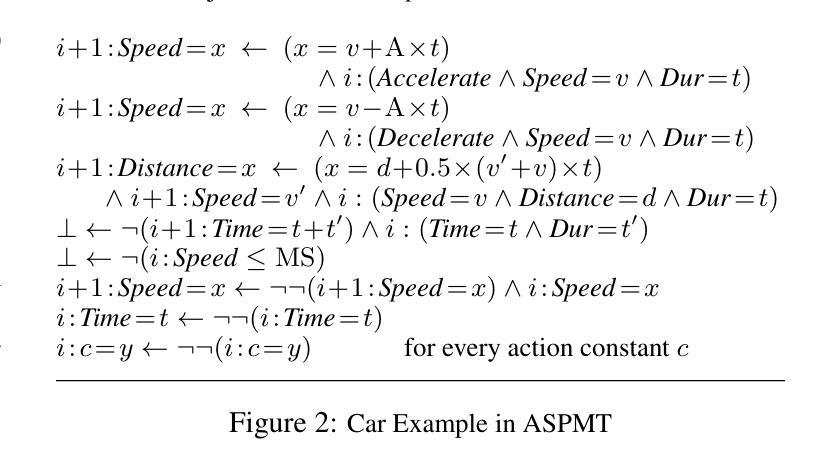
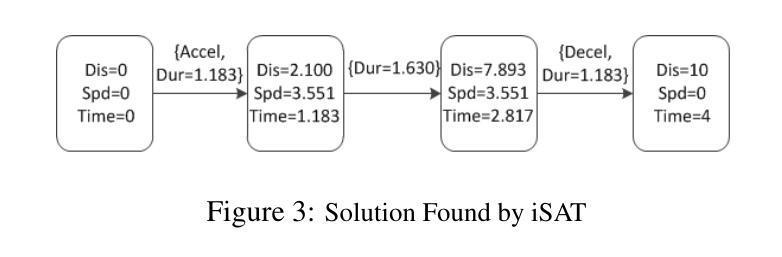
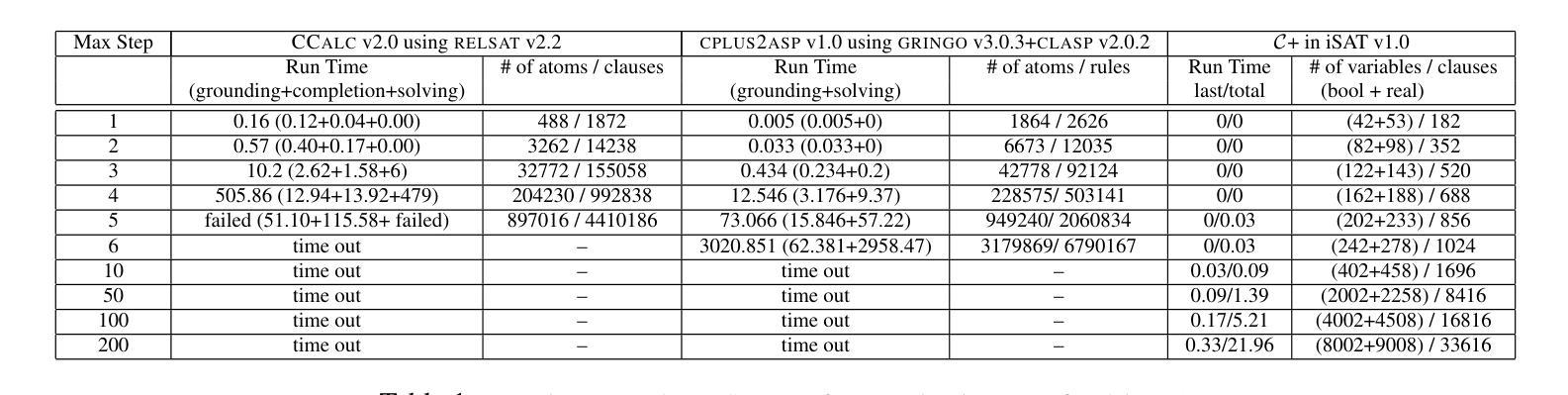
Answer Set Programming Modulo Theories and Reasoning about Continuous Changes
Authors:Joohyung Lee, Yunsong Meng
Answer Set Programming Modulo Theories (ASPMT) is a new framework of tight integration of answer set programming (ASP) and satisfiability modulo theories (SMT). Similar to the relationship between first-order logic and SMT, it is based on a recent proposal of the functional stable model semantics by fixing interpretations of background theories. Analogously to a known relationship between ASP and SAT, ``tight’’ ASPMT programs can be translated into SMT instances. We demonstrate the usefulness of ASPMT by enhancing action language C+ to handle continuous changes as well as discrete changes. We reformulate the semantics of C+ in terms ofASPMT, and show that SMT solvers can be used to compute the language. We also show how the language can represent cumulative effects on continuous resources.
答案集规划模论(ASPMT)是答案集规划(ASP)和可满足性模论(SMT)紧密集成的全新框架。它类似于一阶逻辑与SMT之间的关系,基于背景理论的解释固定功能稳定模型语义的最新提议。与ASP和SAT之间的已知关系类似,“紧密”的ASPMT程序可以转换为SMT实例。我们通过增强动作语言C+来处理连续变化和离散变化,展示了ASPMT的实用性。我们根据ASPMT重新定义了C+的语义,并展示了SMT求解器可以用于计算该语言。我们还展示了该语言如何表示对连续资源的累积影响。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF In Proceedings of the 23rd International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI 2013), pages 990-996, 2013
Summary
ASPMT(答案集编程模理论)是答案集编程(ASP)和可满足性模理论(SMT)紧密结合的新框架。它基于最近提出的功能稳定模型语义,通过解释背景理论来实现与SMT的关联。类似于ASP与SAT之间的关系,紧密的ASPMT程序可以转化为SMT实例。通过增强动作语言C+来处理连续变化和离散变化,展示了ASPMT的实用性。我们以ASPMT重新表述了C+的语义,并展示了如何使用SMT求解器来计算语言。同时,展示了该语言如何表示对连续资源的累积影响。
Key Takeaways
- ASPMT是ASP和SMT的紧密结合框架。
- ASPMT基于功能稳定模型语义,解释背景理论。
- 紧密的ASPMT程序可转化为SMT实例。
- C+语言通过ASPMT得到增强,能处理连续和离散变化。
- 使用SMT求解器计算基于ASPMT的语言。
- 该语言能表示对连续资源的累积影响。
点此查看论文截图


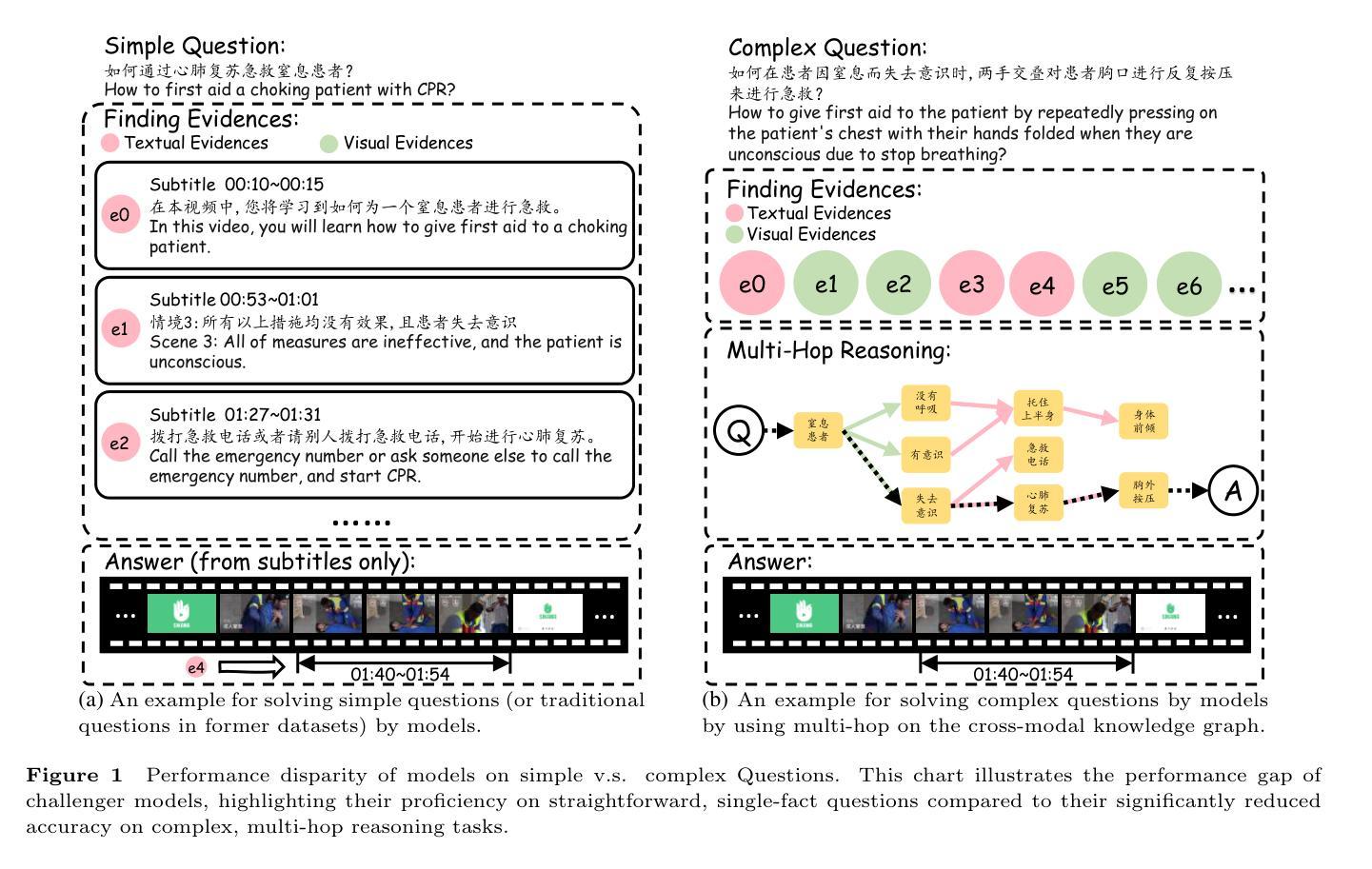
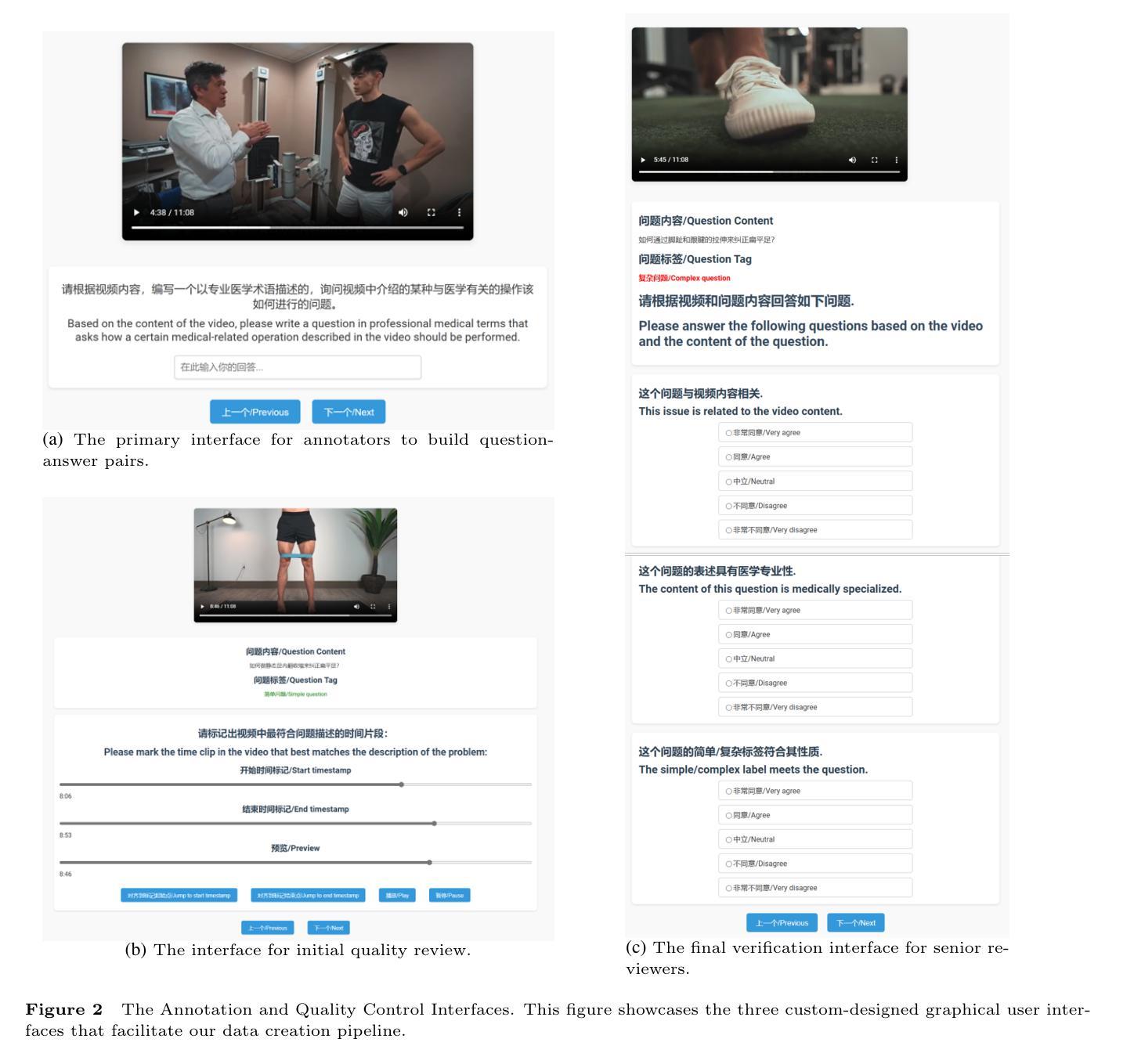
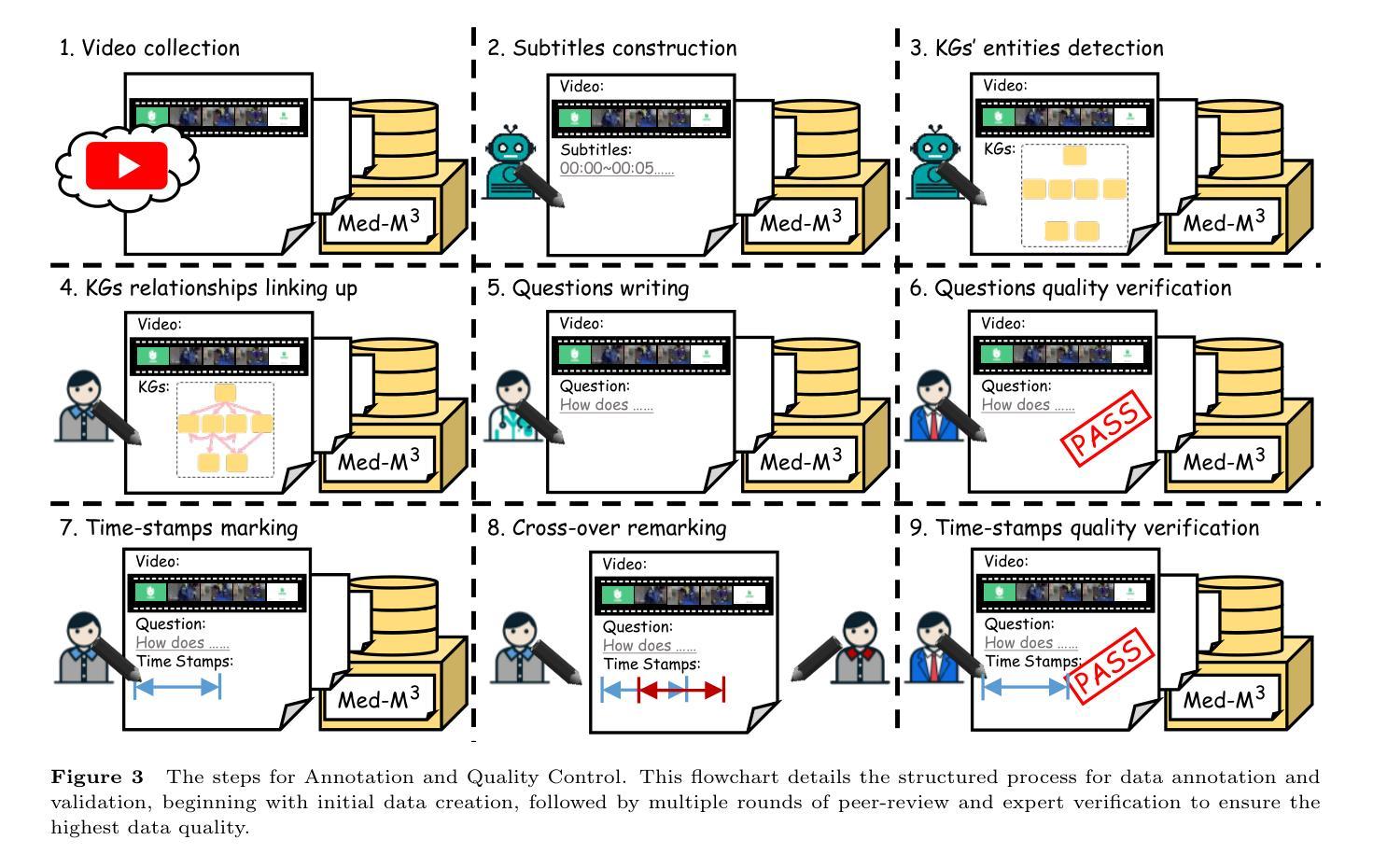
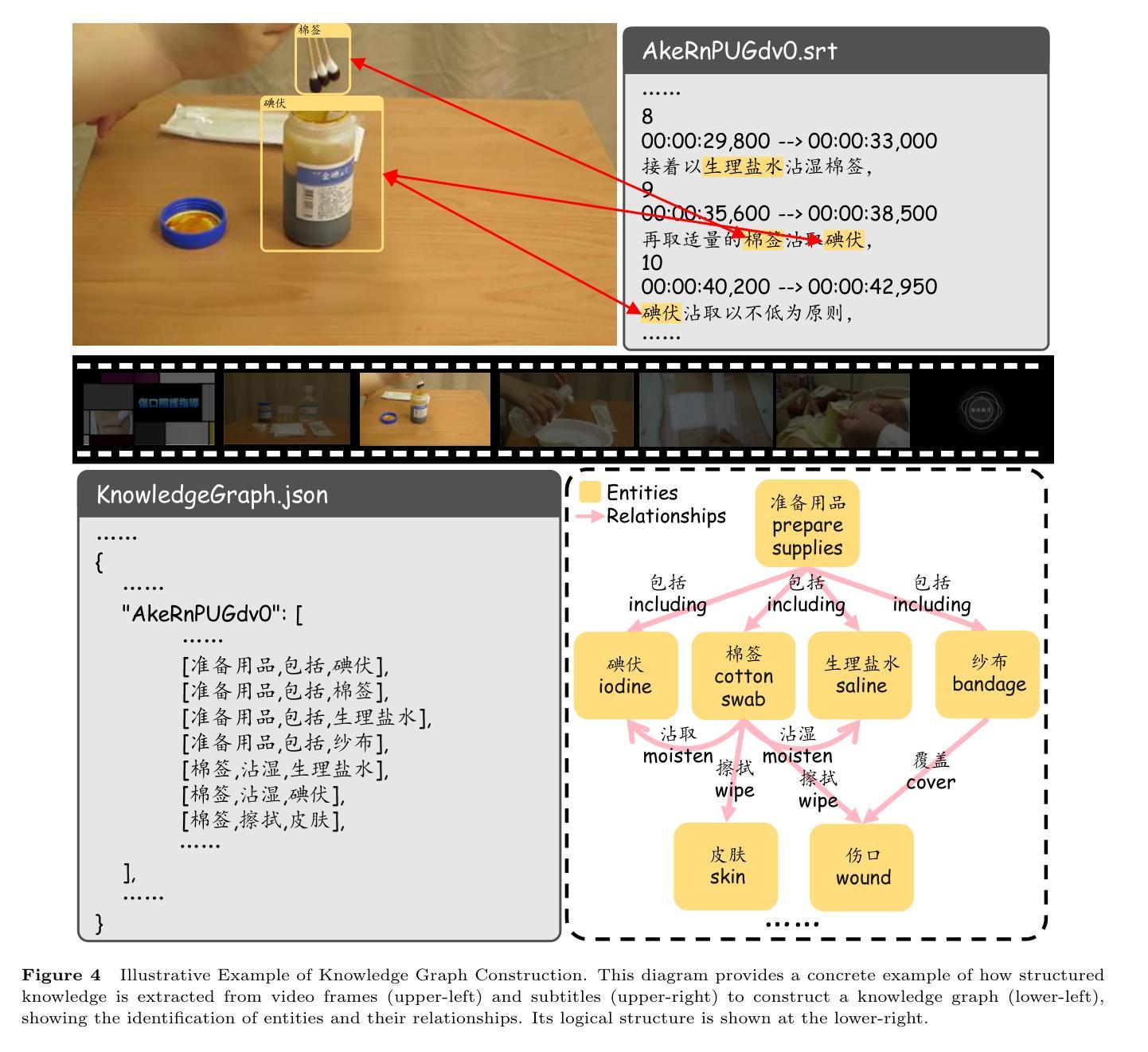
M$^3$-Med: A Benchmark for Multi-lingual, Multi-modal, and Multi-hop Reasoning in Medical Instructional Video Understanding
Authors:Shenxi Liu, Kan Li, Mingyang Zhao, Yuhang Tian, Bin Li, Shoujun Zhou, Hongliang Li, Fuxia Yang
With the rapid progress of artificial intelligence (AI) in multi-modal understanding, there is increasing potential for video comprehension technologies to support professional domains such as medical education. However, existing benchmarks suffer from two primary limitations: (1) Linguistic Singularity: they are largely confined to English, neglecting the need for multilingual resources; and (2) Shallow Reasoning: their questions are often designed for surface-level information retrieval, failing to properly assess deep multi-modal integration. To address these limitations, we present M3-Med, the first benchmark for Multi-lingual, Multi-modal, and Multi-hop reasoning in Medical instructional video understanding. M3-Med consists of medical questions paired with corresponding video segments, annotated by a team of medical experts. A key innovation of M3-Med is its multi-hop reasoning task, which requires a model to first locate a key entity in the text, then find corresponding visual evidence in the video, and finally synthesize information across both modalities to derive the answer. This design moves beyond simple text matching and poses a substantial challenge to a model’s deep cross-modal understanding capabilities. We define two tasks: Temporal Answer Grounding in Single Video (TAGSV) and Temporal Answer Grounding in Video Corpus (TAGVC). We evaluated several state-of-the-art models and Large Language Models (LLMs) on M3-Med. The results reveal a significant performance gap between all models and human experts, especially on the complex multi-hop questions where model performance drops sharply. M3-Med effectively highlights the current limitations of AI models in deep cross-modal reasoning within specialized domains and provides a new direction for future research.
随着人工智能在多模态理解方面的快速发展,视频理解技术在医疗教育等专业领域的应用潜力越来越大。然而,现有的基准测试存在两个主要局限性:(1)语言单一性:它们大多仅限于英语,忽视了多语言资源的需求;(2)浅层推理:它们的问题往往是为了表面信息的检索而设计的,无法适当地评估深度多模态融合。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了M3-Med,这是医疗教学视频理解中多语言、多模态、多跳推理的首个基准测试。M3-Med由医疗问题及其对应的视频片段组成,由医疗专家团队进行注释。M3-Med的关键创新之处在于其多跳推理任务,这需要模型首先定位文本中的关键实体,然后在视频中找到相应的视觉证据,最后融合两种模式的信息来得出答案。这种设计超越了简单的文本匹配,对模型的跨模态深度理解能力提出了实质性的挑战。我们定义了两个任务:单视频时序答案定位(TAGSV)和视频语料库时序答案定位(TAGVC)。我们在M3-Med上评估了几种最前沿的模型和大语言模型(LLMs)。结果表明,所有模型与人类专家之间存显著的性能差距,尤其是在复杂的多跳问题上,模型性能急剧下降。M3-Med有效地突出了人工智能模型在专业领域的深度跨模态推理方面的当前局限性,并为未来的研究提供了新的方向。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 8 figures, 7 tables
Summary
随着人工智能在多模态理解方面的快速发展,视频理解技术在医疗教育等职业领域的应用潜力日益增强。然而,现有的基准测试主要存在两个局限性:一是语言单一性,大部分局限于英语,忽视了多语言资源的需要;二是浅层推理,问题设计往往只针对表面信息的检索,无法恰当评估深度多模态融合。为解决这个问题,我们推出了M3-Med,这是首个针对医疗教学视频理解的多语言、多模态、多跳推理的基准测试。M3-Med由医疗问题及其对应的视频片段组成,由医疗专家团队进行注释。其关键创新在于多跳推理任务,需要模型首先在文本中找到关键实体,然后在视频中找到相应的视觉证据,最后融合两种模式的信息得出答案。我们定义了两个任务:单视频中的时间答案定位(TAGSV)和视频语料库中的时间答案定位(TAGVC)。我们对一些最先进的模型和大语言模型在M3-Med上进行了评估。结果显示,在所有模型中,与人类的专家相比,模型的性能仍存在显著差距,特别是在复杂的多跳问题上,模型性能急剧下降。M3-Med有效地指出了当前人工智能模型在特定领域的深度跨模态推理方面的局限性,并为未来的研究提供了新的方向。
Key Takeaways
- 人工智能在多模态理解方面取得进展,视频理解技术在医疗教育等领域有潜力。
- 现有基准测试存在局限性:主要面向英语人群和注重浅层信息检索的问题设计。
- M3-Med是首个针对医疗教学视频理解的多语言、多模态、多跳推理的基准测试。
- M3-Med包括两个任务:单视频中的时间答案定位(TAGSV)和视频语料库中的时间答案定位(TAGVC)。测试任务涉及找到关键实体和对应的视觉证据以及融合信息得出答案的过程。
- 当前人工智能模型在深度跨模态推理方面仍落后于人类专家,特别是在复杂问题上表现欠佳。
- M3-Med揭示了人工智能模型在特定领域的局限性并为未来的研究提供了新的方向。
点此查看论文截图

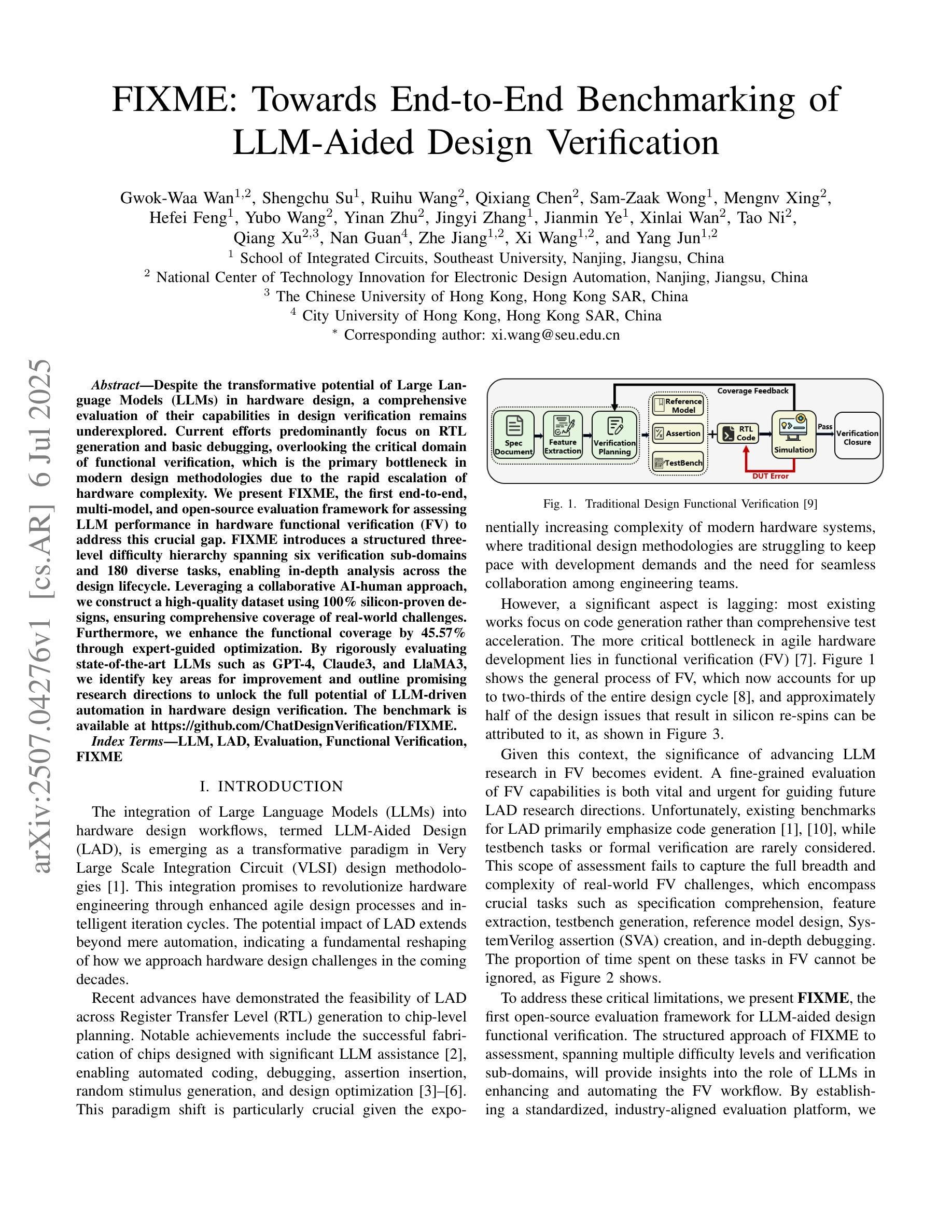
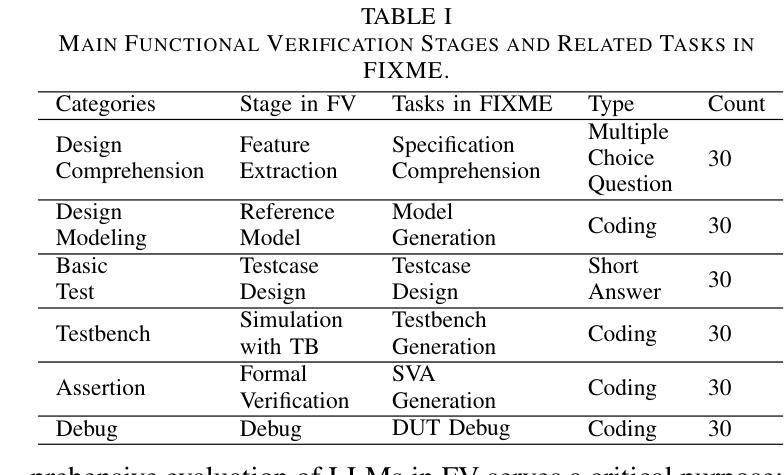
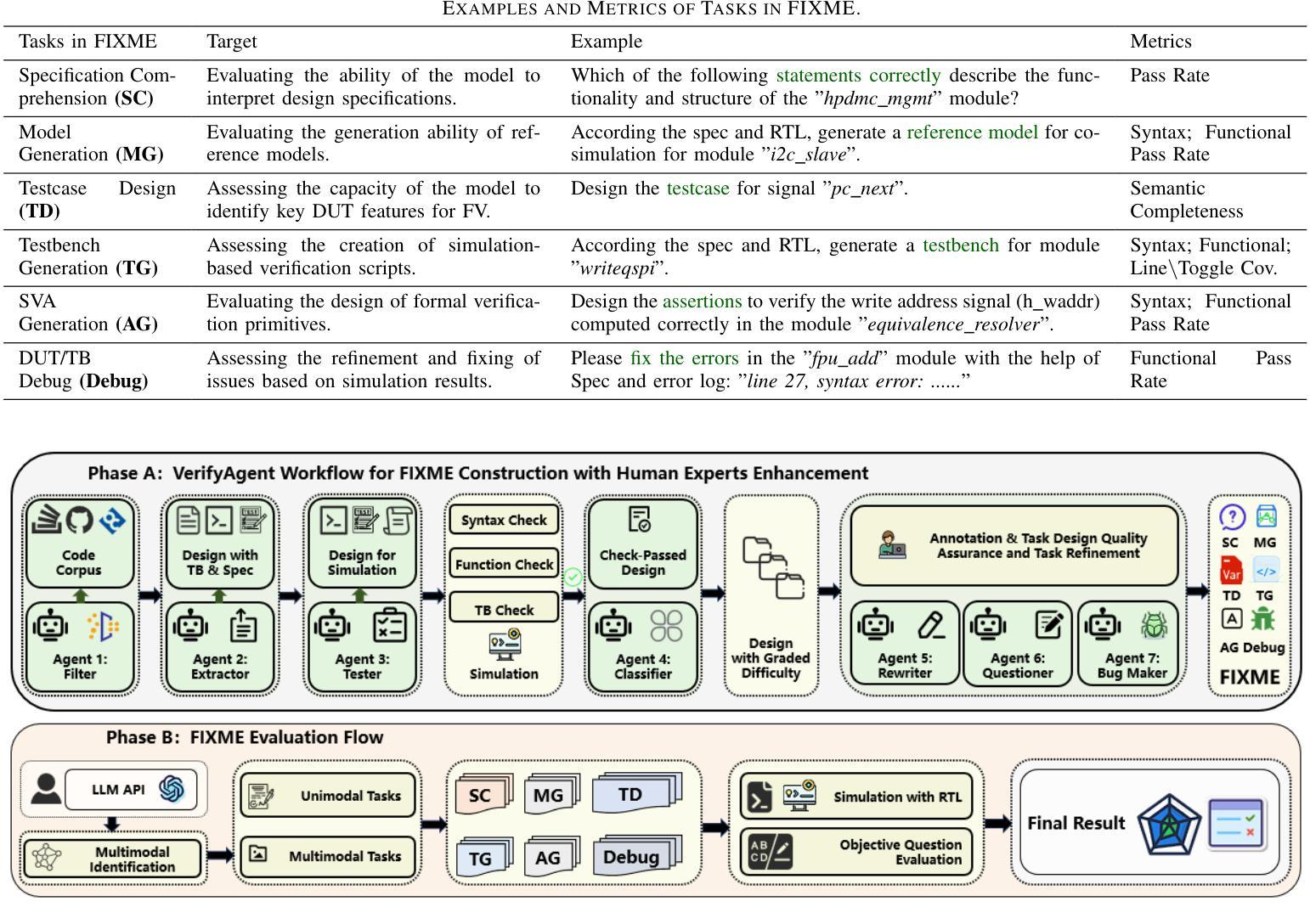
FIXME: Towards End-to-End Benchmarking of LLM-Aided Design Verification
Authors:Gwok-Waa Wan, Shengchu Su, Ruihu Wang, Qixiang Chen, Sam-Zaak Wong, Mengnv Xing, Hefei Feng, Yubo Wang, Yinan Zhu, Jingyi Zhang, Jianmin Ye, Xinlai Wan, Tao Ni, Qiang Xu, Nan Guan, Zhe Jiang, Xi Wang, Yang Jun
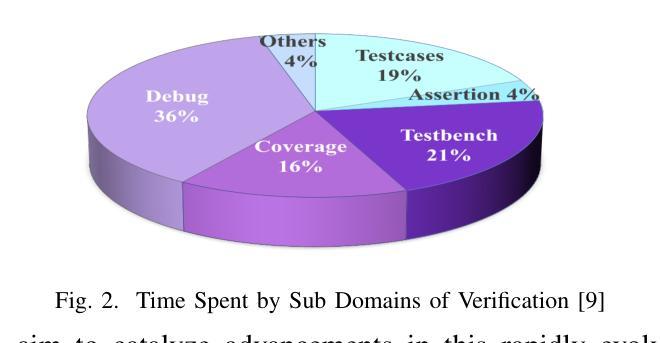
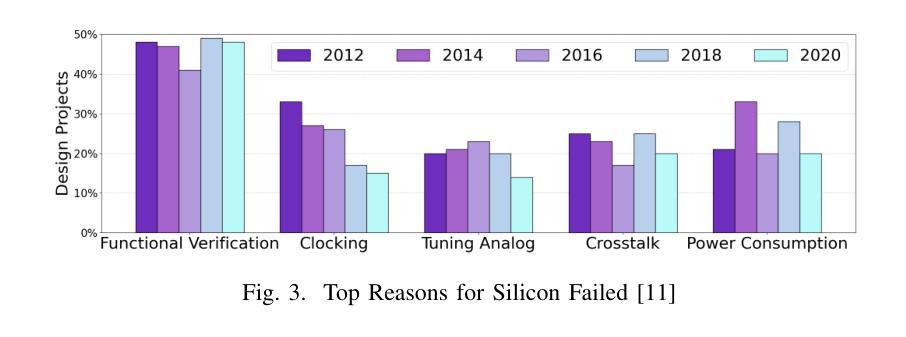
Despite the transformative potential of Large Language Models (LLMs) in hardware design, a comprehensive evaluation of their capabilities in design verification remains underexplored. Current efforts predominantly focus on RTL generation and basic debugging, overlooking the critical domain of functional verification, which is the primary bottleneck in modern design methodologies due to the rapid escalation of hardware complexity. We present FIXME, the first end-to-end, multi-model, and open-source evaluation framework for assessing LLM performance in hardware functional verification (FV) to address this crucial gap. FIXME introduces a structured three-level difficulty hierarchy spanning six verification sub-domains and 180 diverse tasks, enabling in-depth analysis across the design lifecycle. Leveraging a collaborative AI-human approach, we construct a high-quality dataset using 100% silicon-proven designs, ensuring comprehensive coverage of real-world challenges. Furthermore, we enhance the functional coverage by 45.57% through expert-guided optimization. By rigorously evaluating state-of-the-art LLMs such as GPT-4, Claude3, and LlaMA3, we identify key areas for improvement and outline promising research directions to unlock the full potential of LLM-driven automation in hardware design verification. The benchmark is available at https://github.com/ChatDesignVerification/FIXME.
尽管大型语言模型(LLM)在硬件设计方面具有变革性潜力,但对其在设计验证方面的能力进行全面评估的研究仍然不足。目前的研究主要集中寄存器传输级别(RTL)生成和基本调试上,忽视了功能验证这一关键领域。由于硬件复杂性迅速升级,功能验证已成为现代设计方法论中的主要瓶颈。为了弥补这一关键空白,我们提出了FIXME,这是一个端到端、多模式、开源的评估框架,旨在评估LLM在硬件功能验证(FV)中的性能。FIXME引入了一个结构化的三级难度层次结构,涵盖六个验证子域和180个多样化任务,从而能够在整个设计生命周期中进行深入分析。通过协作的人机方法,我们使用经过硅验证的100%设计构建了一个高质量数据集,确保全面覆盖现实世界中的挑战。此外,通过专家指导的优化,我们提高了功能覆盖率45.57%。我们严格评估了最先进的LLM,如GPT-4、Claude3和LlaMA3等,确定了改进的关键领域,并指出了有前景的研究方向,以释放LLM驱动自动化在硬件设计验证中的全部潜力。该基准测试可在https://github.com/ChatDesignVerification/FIXME获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
大型语言模型(LLM)在硬件设计方面具有变革性潜力,但在设计验证方面的能力评估仍然不足。针对此问题,我们提出了FIXME评估框架,该框架旨在评估LLM在硬件功能验证(FV)方面的性能。FIXME引入了一个结构化三级难度层次结构,涵盖六个验证子域和180个不同任务,实现设计生命周期的深度分析。通过利用协作式人工智能与人类的方法,我们构建了一个高质量的数据集,确保全面覆盖现实挑战。对最前沿的LLM如GPT-4、Claude3和LlaMA3进行严格评估,我们确定了关键改进领域,并指出了在硬件设计验证中解锁LLM驱动自动化的潜力方向。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在硬件设计领域具有巨大潜力,特别是在设计验证方面。
- 当前对LLM在硬件功能验证方面的能力评估仍然不足,需要更多的研究关注。
- FIXME是首个针对硬件功能验证评估LLM性能的全流程、多模型、开源框架。
- FIXME引入了一个结构化难度层次结构,涵盖多个验证子域和不同任务,以进行全面分析。
- 该框架采用协作式人工智能与人类的方法,利用高质量数据集,确保现实挑战的全面覆盖。
- 对现有LLM的评估确定了关键改进领域,并指出了未来研究的方向。
- 该评估框架有助于解锁LLM在硬件设计验证中的全潜力。
点此查看论文截图
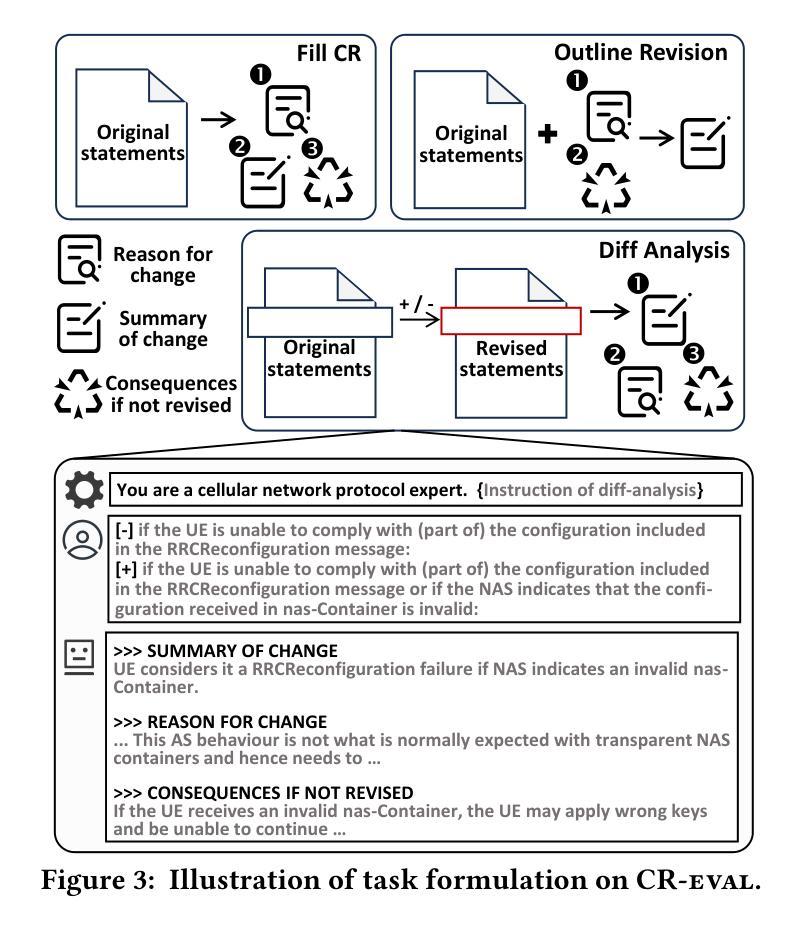
Can Large Language Models Automate the Refinement of Cellular Network Specifications?
Authors:Jianshuo Dong, Tianyi Zhang, Feng Yan, Yuanjie Li, Hewu Li, Han Qiu
Cellular networks serve billions of users globally, yet concerns about reliability and security persist due to weaknesses in 3GPP standards. However, traditional analysis methods, including manual inspection and automated tools, struggle with increasingly expanding cellular network specifications. This paper investigates the feasibility of Large Language Models (LLMs) for automated cellular network specification refinement. To advance it, we leverage 200,000+ approved 3GPP Change Requests (CRs) that document specification revisions, constructing a valuable dataset for domain tasks. We introduce CR-eval, a principled evaluation framework, and benchmark 16 state-of-the-art LLMs, demonstrating that top models can discover security-related weaknesses in over 127 out of 200 test cases within five trials. To bridge potential gaps, we explore LLM specialization techniques, including fine-tuning an 8B model to match or surpass advanced LLMs like GPT-4o and DeepSeek-R1. Evaluations on 30 cellular attacks identify open challenges for achieving full automation. These findings confirm that LLMs can automate the refinement of cellular network specifications and provide valuable insights to guide future research in this direction.
全球范围内,蜂窝网络为数亿用户提供服务,但由于对第三代合作伙伴计划(3GPP)标准的弱点,关于可靠性和安全的担忧依然存在。然而,传统分析方法,包括手动检查和自动化工具,在处理不断扩展的蜂窝网络规格时遇到了困难。本文研究了大型语言模型(LLM)在自动蜂窝网络规格优化方面的可行性。为了推进这一研究,我们利用超过二十万份经过批准的3GPP变更请求(CR),这些变更请求记录了规格修订情况,构建了针对领域任务的宝贵数据集。我们介绍了CR评估原则框架CR-eval,并对16款最新大型语言模型进行了基准测试。结果表明,顶级模型在五轮测试中能在超过127个测试案例中找出与安全性相关的弱点。为了弥合潜在差距,我们探索了大型语言模型的特殊化技术,包括微调一个拥有庞大规模的大型语言模型模型来达到或超越诸如GPT-4o和DeepSeek-R等尖端大型语言模型的水平。通过对三十种蜂窝攻击的评价发现实现完全自动化的开放挑战。这些发现证实大型语言模型能够自动化蜂窝网络规格的完善工作,并为未来这一方向的研究提供了宝贵的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
随着全球用户数量的增长,对蜂窝网络可靠性及安全性的担忧也在增加,特别是在3GPP标准上的弱点。传统分析方法如手动检查和自动化工具已无法满足日益扩大的蜂窝网络规格的需求。本研究利用大型语言模型(LLMs)探索自动化蜂窝网络规格优化的可行性。我们使用了超过二十万份批准的3GPP更改请求(CRs),构建了宝贵的数据集,为任务领域提供支持。我们引入了CR-eval评估框架,并对十六种最新的大型语言模型进行了基准测试。结果显示,顶级模型在五轮测试中能在超过一百二十七例测试案例中发现了安全相关的弱点。为了缩小潜在差距,我们探索了大型语言模型的特殊化技术,包括微调大型语言模型以适应或超越先进的模型如GPT-4o和DeepSeek-R1。对三十种蜂窝攻击的评价指出了实现全面自动化的挑战。这些发现证实大型语言模型能够自动化蜂窝网络规格的完善,为未来在这一方向的研究提供了宝贵的见解。
Key Takeaways:
- 蜂窝网络面临可靠性及安全性问题,尤其是涉及3GPP标准的弱点问题亟待解决。
- 传统分析方法在处理大规模蜂窝网络规格时面临挑战。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在自动化蜂窝网络规格优化方面具有潜力。
- 利用大量批准的3GPP更改请求构建了数据集用于训练和优化大型语言模型。
- 顶级的大型语言模型能够发现大量安全相关的弱点,显示其在识别安全性问题方面的效能。
- 存在潜在的缺陷和改进空间,可能需要特定的精细化调整或更深入的技术改进以应对所有蜂窝网络规格优化的问题。例如需要进一步探索如何改进大型语言模型的特殊化技术,以便适应不同领域需求,特别是面对特定的安全问题时如何实现更好的优化效果。同时还需要解决实现全面自动化的挑战。
点此查看论文截图
LVLM-Composer’s Explicit Planning for Image Generation
Authors:Spencer Ramsey, Jeffrey Lee, Amina Grant
The burgeoning field of generative artificial intelligence has fundamentally reshaped our approach to content creation, with Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) standing at its forefront. While current LVLMs have demonstrated impressive capabilities in text-to-image generation, they often falter when confronted with complex textual descriptions demanding precise compositional understanding and visual planning. This limitation particularly impacts the accurate rendering of multiple objects, their attributes, spatial relationships, and specific poses within intricate scenes, as evidenced by benchmarks like LongBench-T2I. To address these challenges, we introduce LVLM-Composer, a novel 10-billion parameter scale LVLM specifically engineered for enhanced compositional image synthesis. Our method incorporates a Hierarchical Semantic Planning Module for structured prompt decomposition and a Fine-Grained Feature Alignment Mechanism for precise visual guidance during generation. We propose a multi-stage training paradigm, featuring Hierarchical Semantic-Visual Grounding Pre-training and Compositional Planning Reinforcement Learning with Self-Correction, to instill robust compositional reasoning. Extensive experiments on the LongBench-T2I benchmark, utilizing automatic evaluation by Gemini-2.0-Flash and InternVL3-78B, demonstrate LVLM-Composer’s superior performance across critical compositional dimensions including object accuracy, composition fidelity, and pose accuracy, significantly outperforming state-of-the-art baselines. An in-depth ablation study further validates the indispensable contribution of our proposed modules, while human evaluations confirm the perceptual superiority of our generated images. LVLM-Composer represents a significant step towards truly controllable and compositionally accurate open-ended text-to-image generation.
生成人工智能领域蓬勃发展,从根本上改变了我们的内容创作方式,大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)处于其前沿地位。虽然当前的LVLMs在文本到图像生成方面表现出了令人印象深刻的能力,但它们在面对复杂的文本描述时,往往会在需要精确的组合理解和视觉规划方面遇到困难。这一局限性特别影响了在复杂场景中多个物体、属性、空间关系和特定姿态的准确呈现,LongBench-T2I等基准测试证明了这一点。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了LVLM-Composer,这是一个专门为增强组合图像合成而设计的新型10亿参数规模LVLM。我们的方法结合了分层语义规划模块进行结构化提示分解和精细特征对齐机制,以在生成过程中提供精确的视觉指导。我们提出了一种多阶段训练范式,包括分层语义-视觉接地预训练以及组合规划强化学习与自我校正,以灌输稳健的组合推理。在LongBench-T2I基准测试上进行的广泛实验,使用Gemini-2.0-Flash和InternVL3-78B进行自动评估,证明LVLM-Composer在关键组合维度上的卓越性能,包括目标准确性、组合保真度和姿态准确性,显著优于最新技术基线。深入的消融研究进一步验证了我们所提出模块的不可或缺贡献,而人类评估则证实了我们生成图像的可观感知优越性。LVLM-Composer是朝着真正可控和组合准确的开放式文本到图像生成迈出的重要一步。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在生成式人工智能领域,大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)已经成为内容创作方法革新的前沿。当前LVLMs在文本到图像生成方面展现出卓越能力,但在处理复杂文本描述时面临挑战,尤其是在呈现多个对象、属性、空间关系和特定姿态的复杂场景时表现欠佳。为应对这些挑战,我们推出LVLM-Composer模型,该模型具备增强的组合图像合成能力。通过分层语义规划模块和精细特征对齐机制,以及多阶段训练模式,该模型在关键评估标准上表现出卓越性能。实验证明,LVLM-Composer在对象准确性、组合保真度和姿态准确性等方面显著优于现有技术基线。
Key Takeaways
- 生成式人工智能领域中,大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)推动内容创作革新。
- 当前LVLMs在处理复杂文本描述时面临挑战,特别是在呈现多个对象的复杂场景时。
- LVLM-Composer模型具备增强的组合图像合成能力。
- LVLM-Composer通过分层语义规划模块和精细特征对齐机制进行结构化提示分解和精确视觉引导生成。
- 多阶段训练模式强化组合推理能力。
- LVLM-Composer在关键评估标准上表现出卓越性能,显著优于现有技术基线。
- 实验结果经自动评估工具确认,并通过深度剖析研究验证模型各组成部分的贡献。
点此查看论文截图

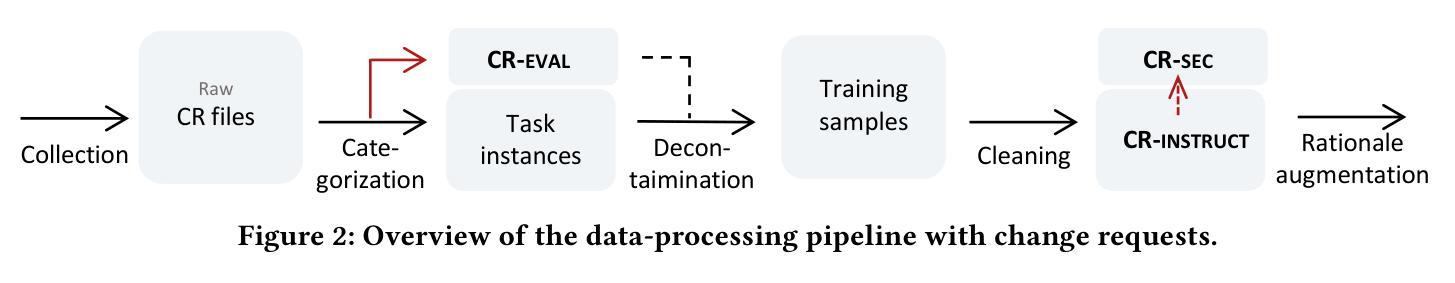
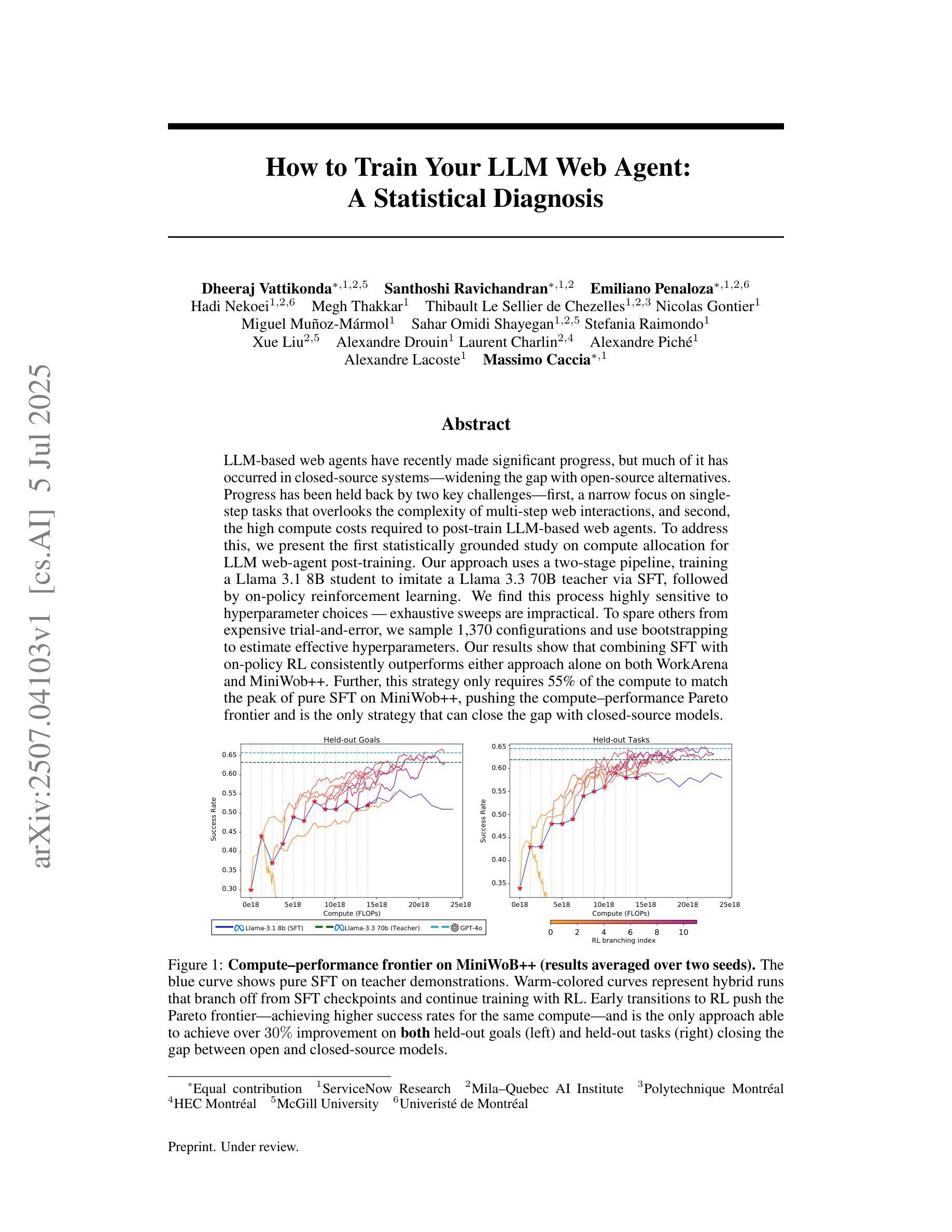
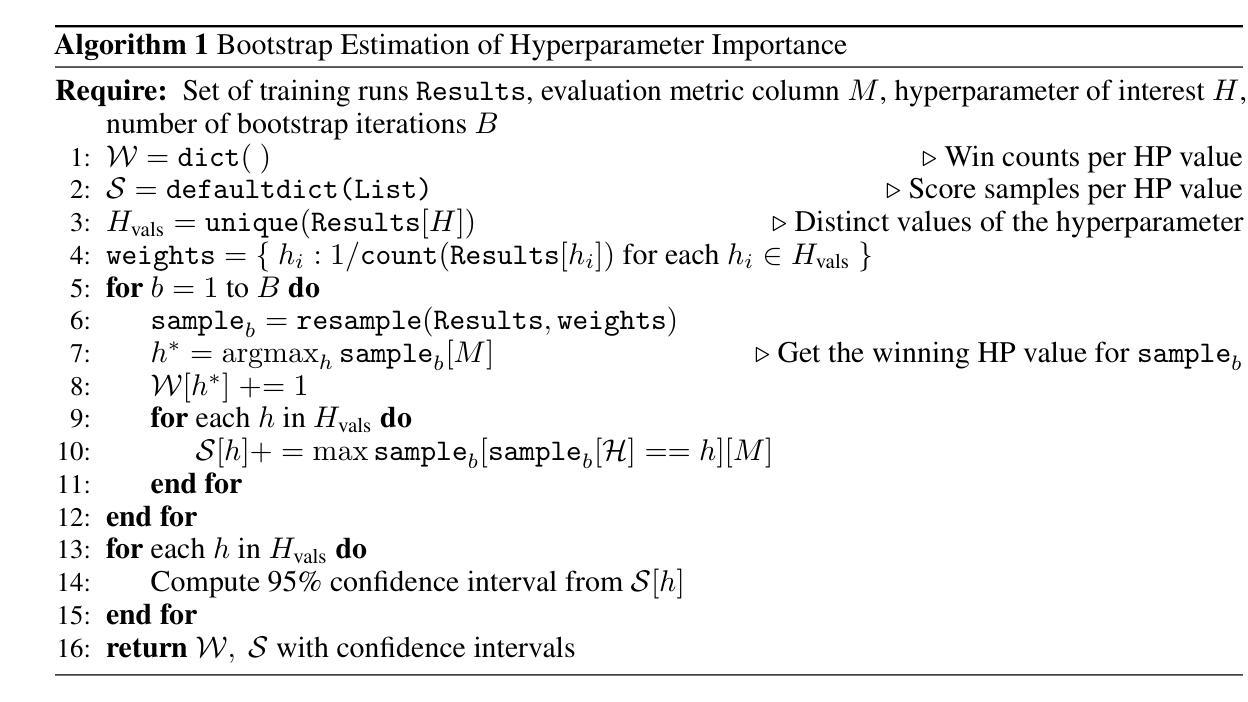
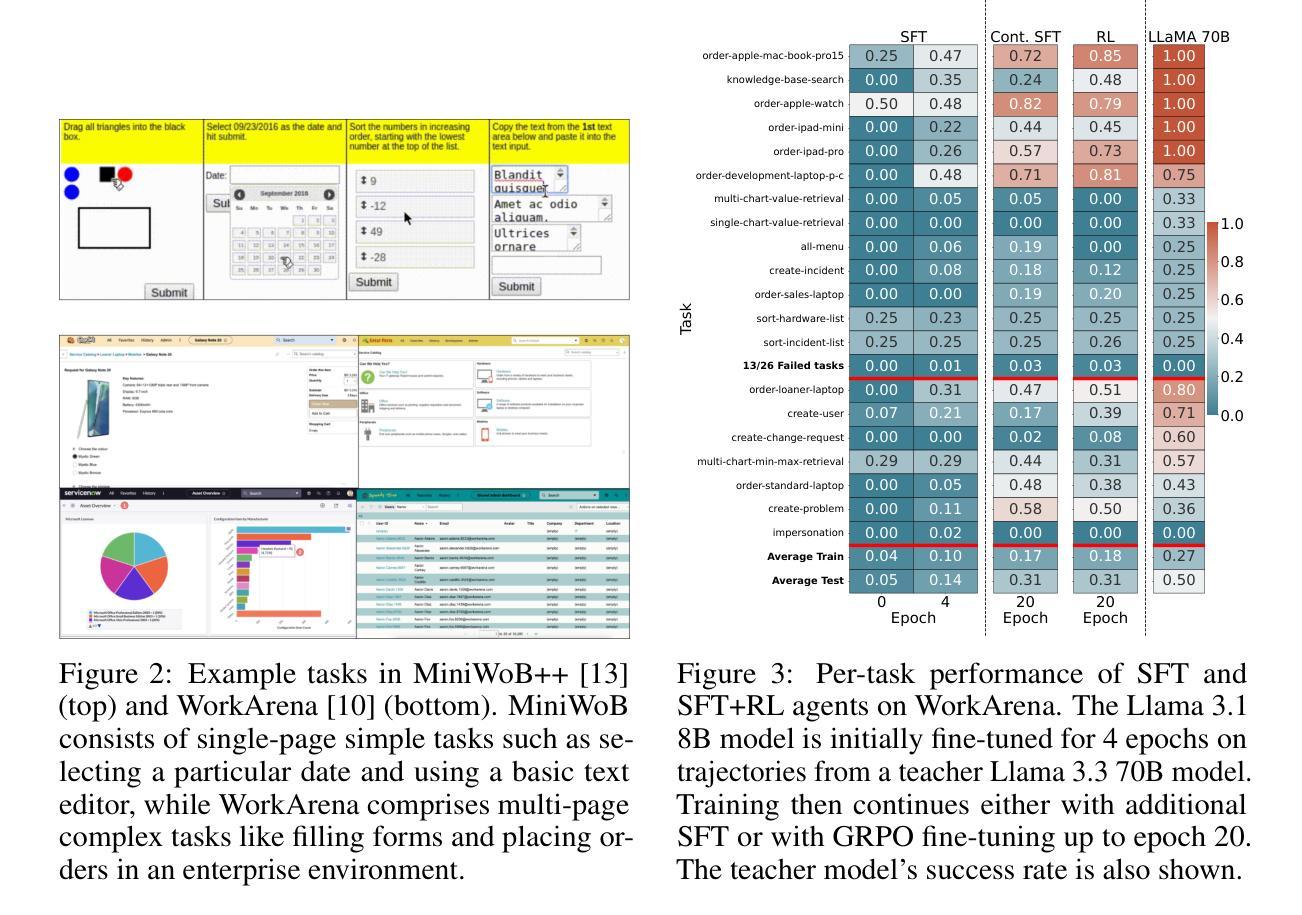
How to Train Your LLM Web Agent: A Statistical Diagnosis
Authors:Dheeraj Vattikonda, Santhoshi Ravichandran, Emiliano Penaloza, Hadi Nekoei, Megh Thakkar, Thibault Le Sellier de Chezelles, Nicolas Gontier, Miguel Muñoz-Mármol, Sahar Omidi Shayegan, Stefania Raimondo, Xue Liu, Alexandre Drouin, Laurent Charlin, Alexandre Piché, Alexandre Lacoste, Massimo Caccia
LLM-based web agents have recently made significant progress, but much of it has occurred in closed-source systems, widening the gap with open-source alternatives. Progress has been held back by two key challenges: first, a narrow focus on single-step tasks that overlooks the complexity of multi-step web interactions; and second, the high compute costs required to post-train LLM-based web agents. To address this, we present the first statistically grounded study on compute allocation for LLM web-agent post-training. Our approach uses a two-stage pipeline, training a Llama 3.1 8B student to imitate a Llama 3.3 70B teacher via supervised fine-tuning (SFT), followed by on-policy reinforcement learning. We find this process highly sensitive to hyperparameter choices, making exhaustive sweeps impractical. To spare others from expensive trial-and-error, we sample 1,370 configurations and use bootstrapping to estimate effective hyperparameters. Our results show that combining SFT with on-policy RL consistently outperforms either approach alone on both WorkArena and MiniWob++. Further, this strategy requires only 55% of the compute to match the peak performance of pure SFT on MiniWob++, effectively pushing the compute-performance Pareto frontier, and is the only strategy that can close the gap with closed-source models.
基于LLM的Web代理最近取得了重大进展,但大部分进展出现在闭源系统中,与开源替代方案的差距被拉大。进展受到两个主要挑战的限制:首先,对单步任务的狭窄关注,忽视了多步Web交互的复杂性;其次,基于LLM的Web代理后训练所需的计算成本很高。为了解决这个问题,我们对LLM Web代理后训练的计算分配进行了首次统计研究。我们的方法采用两阶段管道,训练一个Llama 3.1 8B学生模型通过监督微调(SFT)来模仿Llama 3.3 70B教师模型,随后进行策略性强化学习。我们发现这个过程对超参数选择非常敏感,使全面的扫描变得不切实际。为了节省他人昂贵的试错过程,我们对1370种配置进行采样,并使用自助法来估计有效的超参数。我们的结果表明,结合SFT和策略性RL在工作竞技场(WorkArena)和MiniWob++上的表现始终优于单独采用任何一种方法。此外,该策略仅需55%的计算量即可达到纯SFT在MiniWob++上的峰值性能,有效地推动了计算性能帕累托前沿,而且是唯一能够缩小与闭源模型差距的策略。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
近期,LLM(大型语言模型)基础的web代理在封闭源代码系统中取得显著进展,但仍面临多种挑战,导致开源替代方案的差距扩大。主要挑战包括:一是过于关注单步骤任务,忽视了多步骤web交互的复杂性;二是LLM基础web代理后训练的计算成本高昂。为解决这一问题,我们首次进行了关于LLM web代理后训练的计算分配统计研究。我们采用两阶段管道方法,通过监督微调(SFT)训练Llama 3.1 8B学生模型以模仿Llama 3.3 70B教师模型,随后进行基于策略强化学习。我们发现这一过程对超参数选择高度敏感,使得全面扫描不切实际。为节省他人昂贵的试错成本,我们对1370个配置进行采样,并使用bootstrap估计有效超参数。结果显示,结合SFT和基于策略的强化学习始终优于单一方法,在工作竞技场(WorkArena)和MiniWob++上的表现尤为明显。此外,该策略仅需55%的计算量即可达到纯SFT在MiniWob++上的峰值性能,有效推动了计算性能帕累托前沿,是唯一能够缩小与封闭源代码模型差距的策略。
Key Takeaways:
- LLM-based web代理在封闭源代码系统中取得进展,但开源替代方案差距扩大。
- 主要面临两个挑战:关注单步骤任务忽视多步骤交互的复杂性和高计算成本。
- 采用两阶段管道方法解决此问题,包括监督微调(SFT)和基于策略的强化学习。
- 发现过程对超参数选择高度敏感,全面扫描不切实际。
- 结合SFT和基于策略的强化学习表现优于单一方法,在工作竞技场和MiniWob++上表现显著。
- 该策略降低计算需求,有效推动计算性能帕累托前沿。
点此查看论文截图
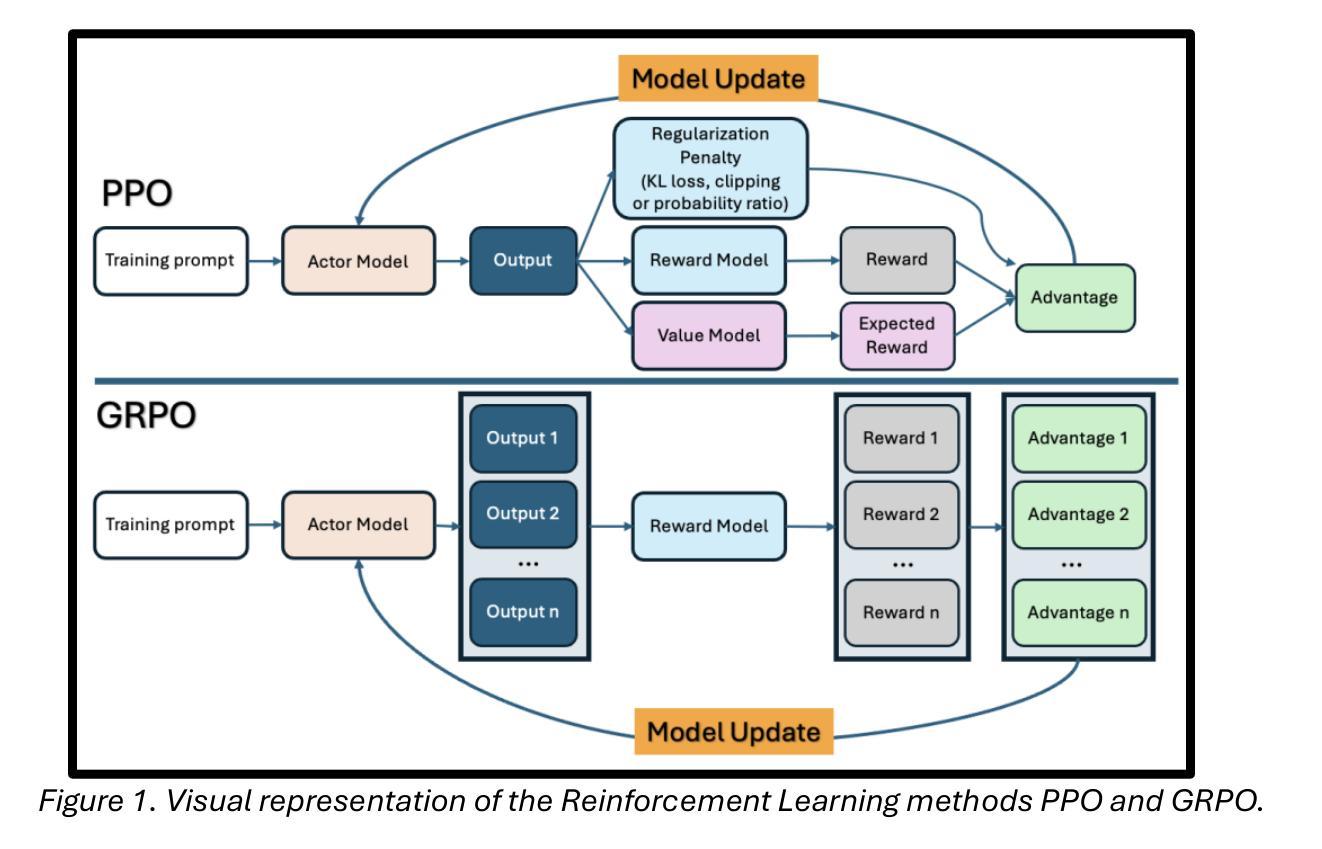
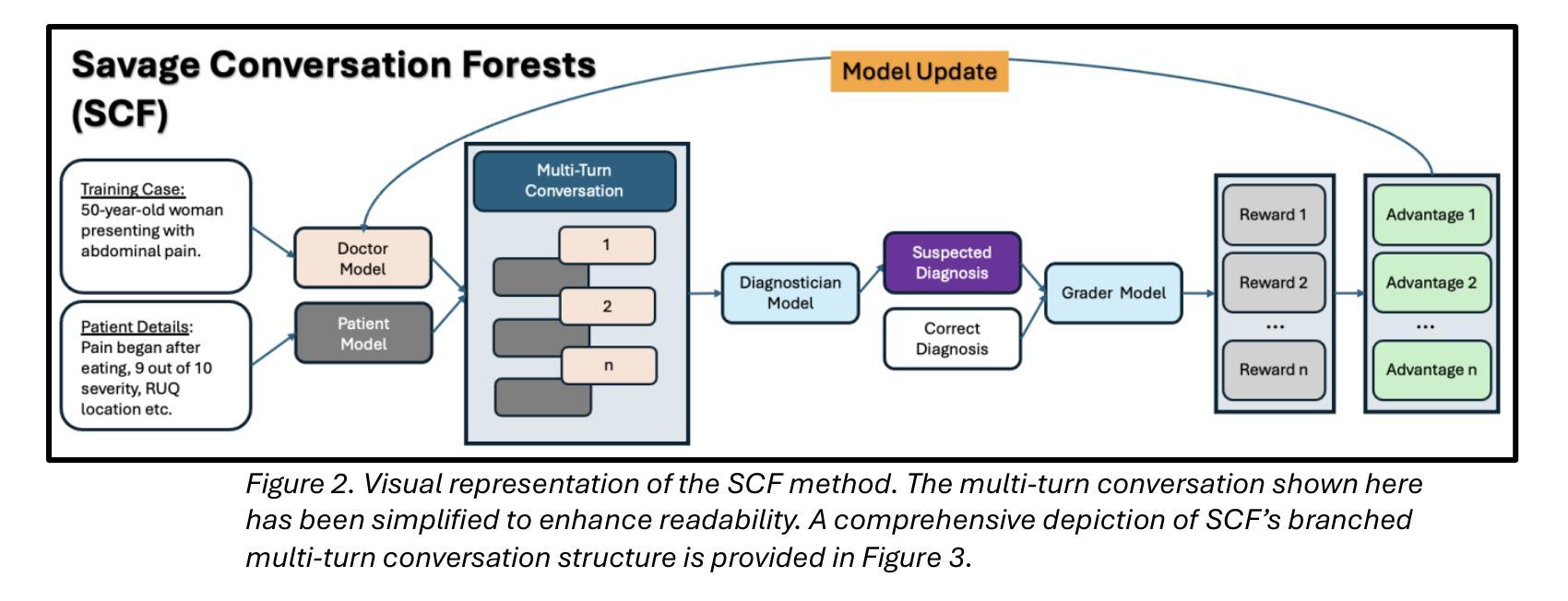
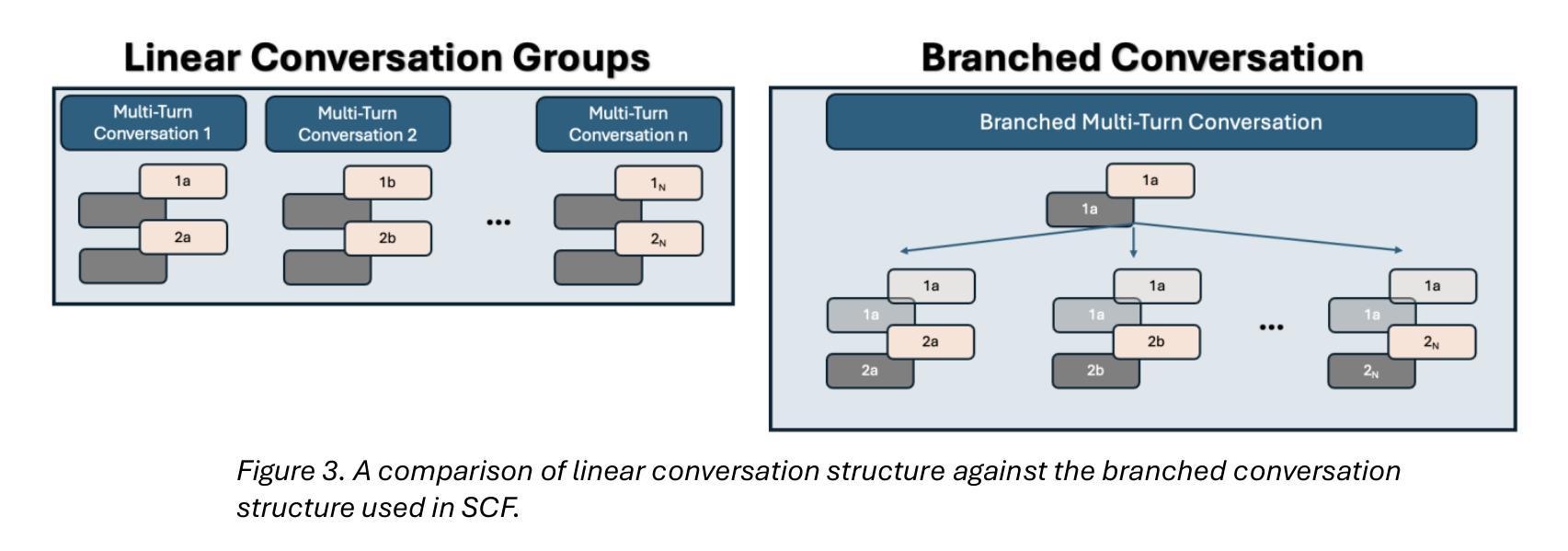
Conversation Forests: The Key to Fine Tuning Large Language Models for Multi-Turn Medical Conversations is Branching
Authors:Thomas Savage
Fine-tuning methods such as Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) and Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) have demonstrated success in training large language models (LLMs) for single-turn tasks. However, these methods fall short in multi-turn applications, such as diagnostic patient interviewing, where understanding how early conversational turns influence downstream completions and outcomes is essential. In medicine, a multi-turn perspective is critical for learning diagnostic schemas and better understanding conversation dynamics. To address this gap, I introduce Savage Conversation Forests (SCF), a reinforcement learning framework that leverages a branched conversation architecture to fine-tune LLMs for multi-turn dialogue. SCF generates multiple possible conversation continuations at each turn, enabling the model to learn how different early responses affect downstream interactions and diagnostic outcomes. In experiments simulating doctor-patient conversations, SCF with branching outperforms linear conversation architectures on diagnostic accuracy. I hypothesize that SCF’s improvements stem from its ability to provide richer, interdependent training signals across conversation turns. These results suggest that a branched training architecture is an important strategy for fine tuning LLMs in complex multi-turn conversational tasks.
微调方法,如直接偏好优化(DPO)和组相对策略优化(GRPO),在针对单轮任务的训练大型语言模型(LLM)方面取得了成功。然而,这些方法在多轮应用方面表现不足,比如在诊断病人访谈中,理解早期对话轮次如何影响下游完成和结果至关重要。在医学领域,多轮视角对于学习诊断模式和更好地了解对话动态至关重要。为了解决这一差距,我引入了野蛮对话森林(SCF),这是一个利用分支对话架构的强化学习框架,用于对多轮对话进行微调的大型语言模型。SCF在每一轮生成多个可能的对话延续,使模型能够学习不同的早期回应如何影响下游互动和诊断结果。在模拟医患对话的实验中,带有分支的SCF在诊断准确性方面优于线性对话架构。我假设SCF的改进源于其在对话轮次之间提供丰富、相互依存训练信号的能力。这些结果表明,分支训练架构是微调复杂多轮对话任务中大型语言模型的重要策略。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在单回合任务中通过直接偏好优化(DPO)和群体相对策略优化(GRPO)等微调方法取得了成功。但在多回合应用,如诊断病人访谈中,这些方法存在不足。为此,引入野蛮对话森林(SCF)这一强化学习框架,采用分支对话架构微调LLM,用于多回合对话。SCF在模拟医患对话的实验中,以分支方式在诊断准确性上优于线性对话架构。预计SCF的改进源于其提供跨对话回合的丰富、相互依赖的训练信号的能力。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在单回合任务中已有成功应用。
- 在多回合对话任务中,如诊断病人访谈,现有微调方法存在局限性。
- 野蛮对话森林(SCF)是一个强化学习框架,采用分支对话架构来微调LLM。
- SCF能够生成每一回合的多种可能对话延续。
- SCF通过学习不同早期回应对后续互动和诊断结果的影响来提高诊断准确性。
- SCF在模拟医患对话的实验中表现优于线性对话架构。
- SCF的改进得益于其在不同对话回合提供丰富、相互依赖的训练信号的能力。
点此查看论文截图

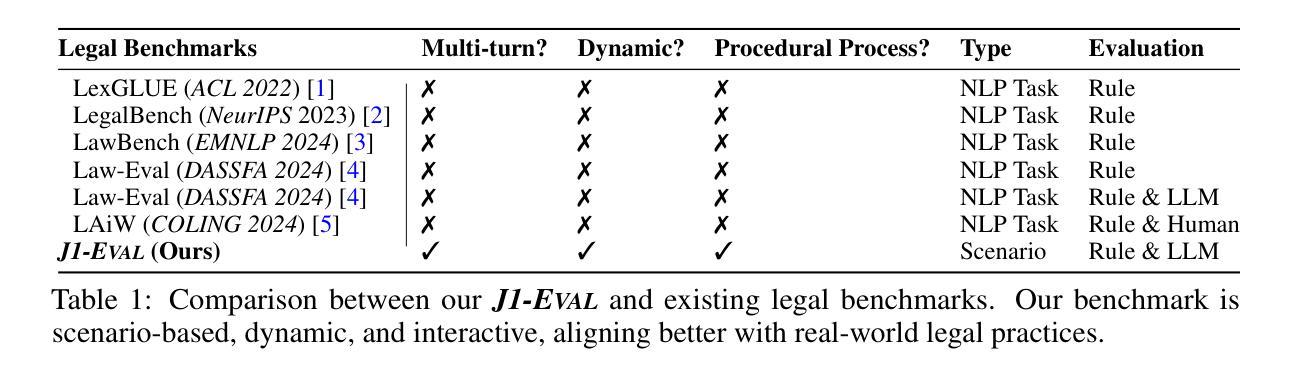
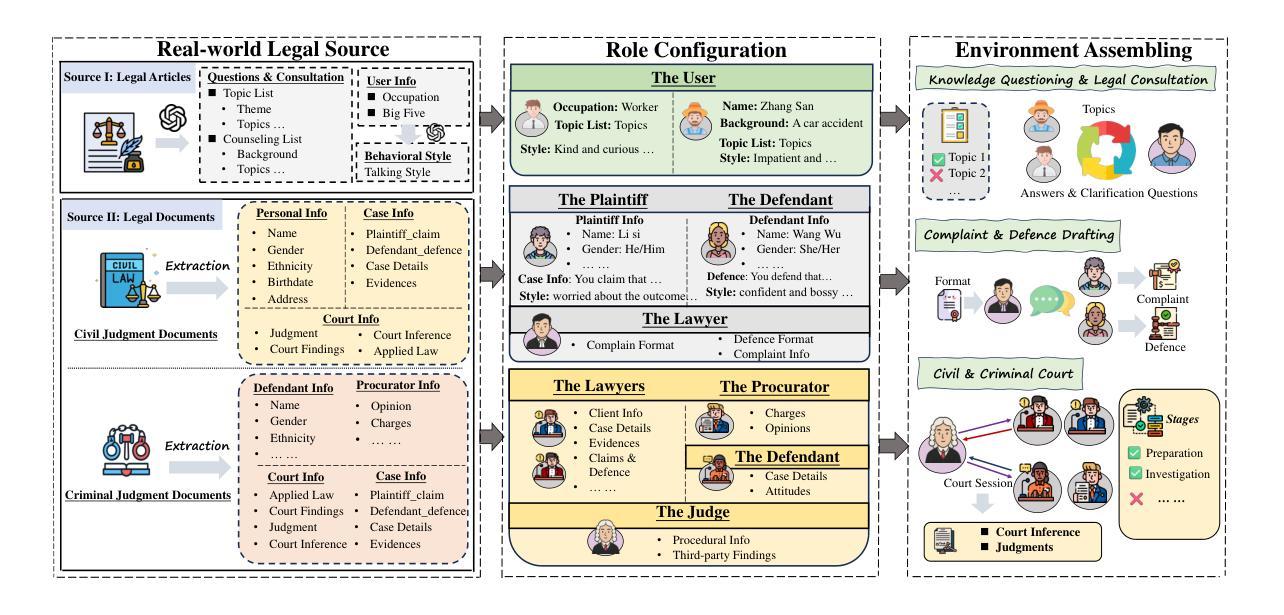
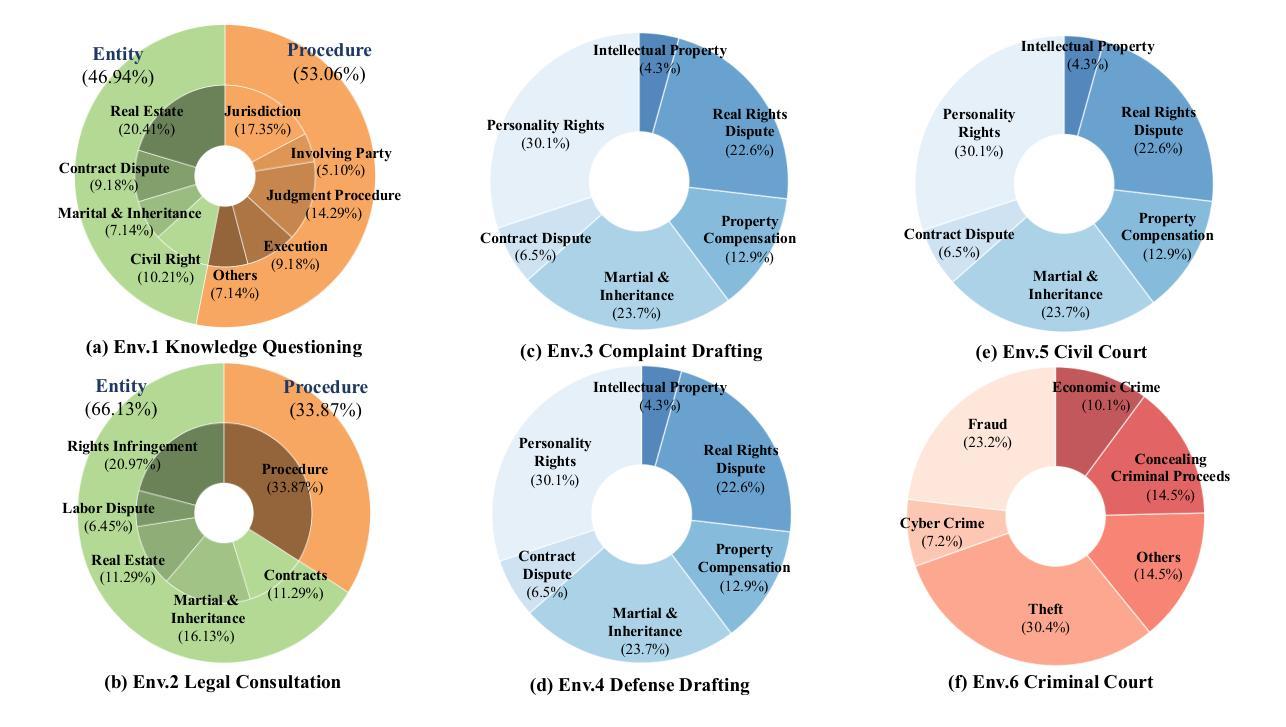
Ready Jurist One: Benchmarking Language Agents for Legal Intelligence in Dynamic Environments
Authors:Zheng Jia, Shengbin Yue, Wei Chen, Siyuan Wang, Yidong Liu, Yun Song, Zhongyu Wei
The gap between static benchmarks and the dynamic nature of real-world legal practice poses a key barrier to advancing legal intelligence. To this end, we introduce J1-ENVS, the first interactive and dynamic legal environment tailored for LLM-based agents. Guided by legal experts, it comprises six representative scenarios from Chinese legal practices across three levels of environmental complexity. We further introduce J1-EVAL, a fine-grained evaluation framework, designed to assess both task performance and procedural compliance across varying levels of legal proficiency. Extensive experiments on 17 LLM agents reveal that, while many models demonstrate solid legal knowledge, they struggle with procedural execution in dynamic settings. Even the SOTA model, GPT-4o, falls short of 60% overall performance. These findings highlight persistent challenges in achieving dynamic legal intelligence and offer valuable insights to guide future research.
静态基准测试与真实世界法律实践的动态性质之间的差距是推进法律智能的主要障碍。为此,我们引入了J1-ENVS,这是第一个针对大型语言模型(LLM)代理量身定制的互动式动态法律环境。在专家指导下,它涵盖了中国法律实践中三个不同环境复杂程度等级的六个典型场景。我们还引入了J1-EVAL这一精细的评估框架,旨在评估不同法律专业水平的任务执行情况和程序合规性。对17个大型语言模型代理进行的广泛实验表明,虽然许多模型展现出坚实的法律知识基础,但在动态环境中执行程序方面却遇到了困难。即使是目前最先进的模型GPT-4o,总体性能也不足60%。这些发现突显了实现动态法律智能所面临的持久挑战,并为未来的研究提供了宝贵的指导。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
静态基准与真实世界法律实践的动态性质之间存在差距,这是推进法律智能的主要障碍。为此,我们推出了J1-ENVS,这是第一个针对LLM代理设计的交互式动态法律环境。它由法律专家引导,包含中国法律实践中三个不同环境复杂程度层次的六个代表性场景。我们还引入了J1-EVAL,这是一个精细的评价框架,旨在评估不同法律熟练度等级的任务执行情况和程序合规性。对17个LLM代理的广泛实验表明,尽管许多模型展现出坚实的法律知识,但在动态环境中执行程序时却遇到了困难。即使是最先进的模型GPT-4o,总体性能也不到60%。这些发现突显了实现动态法律智能的持久挑战,并为未来的研究提供了宝贵的指导。
Key Takeaways:
- 静态基准与真实世界法律实践的动态性质之间的差距是推进法律智能的主要障碍。
- J1-ENVS是首个针对LLM代理设计的交互式动态法律环境,包含六个代表中国法律实践的典型场景。
- J1-EVAL是一个评估LLM代理在任务执行和程序合规性方面的表现的评价框架。
- 广泛实验显示,尽管LLM模型具备法律知识,但在动态环境中执行程序时仍面临困难。
- 现有模型在动态法律智能方面性能不佳,即使是最先进的模型GPT-4o也是如此。
- 实验结果突显了实现动态法律智能的持久挑战。
点此查看论文截图