⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-09 更新
Multi-modal Representations for Fine-grained Multi-label Critical View of Safety Recognition
Authors:Britty Baby, Vinkle Srivastav, Pooja P. Jain, Kun Yuan, Pietro Mascagni, Nicolas Padoy
The Critical View of Safety (CVS) is crucial for safe laparoscopic cholecystectomy, yet assessing CVS criteria remains a complex and challenging task, even for experts. Traditional models for CVS recognition depend on vision-only models learning with costly, labor-intensive spatial annotations. This study investigates how text can be harnessed as a powerful tool for both training and inference in multi-modal surgical foundation models to automate CVS recognition. Unlike many existing multi-modal models, which are primarily adapted for multi-class classification, CVS recognition requires a multi-label framework. Zero-shot evaluation of existing multi-modal surgical models shows a significant performance gap for this task. To address this, we propose CVS-AdaptNet, a multi-label adaptation strategy that enhances fine-grained, binary classification across multiple labels by aligning image embeddings with textual descriptions of each CVS criterion using positive and negative prompts. By adapting PeskaVLP, a state-of-the-art surgical foundation model, on the Endoscapes-CVS201 dataset, CVS-AdaptNet achieves 57.6 mAP, improving over the ResNet50 image-only baseline (51.5 mAP) by 6 points. Our results show that CVS-AdaptNet’s multi-label, multi-modal framework, enhanced by textual prompts, boosts CVS recognition over image-only methods. We also propose text-specific inference methods, that helps in analysing the image-text alignment. While further work is needed to match state-of-the-art spatial annotation-based methods, this approach highlights the potential of adapting generalist models to specialized surgical tasks. Code: https://github.com/CAMMA-public/CVS-AdaptNet
对安全性的批判性观点(CVS)对于安全的腹腔镜胆囊切除术至关重要,但评估CVS标准仍然是一个复杂且具有挑战性的任务,即使是专家也是如此。传统的CVS识别模型依赖于仅视觉模型的学习,这需要昂贵的、劳动密集的空间注释。本研究探讨了文本如何成为多模态手术基础模型中训练和推理的强大工具,以自动化CVS识别。与许多现有的多模态模型不同,CVS识别需要多标签框架,而不是主要适应于多类分类。对现有多模态手术模型的零样本评估显示,此任务存在显著的性能差距。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了CVS-AdaptNet,这是一种多标签适应策略,通过利用正面和负面提示,将图像嵌入与每个CVS标准的文本描述对齐,从而增强跨多个标签的精细二进制分类。通过适应最先进的手术基础模型PeskaVLP和在Endoscapes-CVS201数据集上,CVS-AdaptNet达到了57.6的mAP,比仅使用ResNet50图像的基线(51.5 mAP)提高了6个百分点。我们的结果表明,CVS-AdaptNet的多标签、多模态框架通过文本提示而增强,在仅使用图像的方法上推动了CVS识别。我们还提出了文本特定的推理方法,有助于分析图像文本对齐。虽然需要进一步的工作才能匹配基于空间注释的先进方法,但这种方法突显了将通用模型适应专门手术任务的潜力。代码:https://github.com/CAMMA-public/CVS-AdaptNet
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
安全视图中对于腹腔镜胆囊切除术的关键观察点(CVS)评估非常重要但又非常复杂和具有挑战性,特别是对于专家来说。传统CVS识别模型依赖于视觉模型进行昂贵和繁琐的空间注释学习。本研究探讨了文本如何作为多模态手术基础模型的训练和推理的强大工具,以自动进行CVS识别。与许多现有的多模态模型不同,CVS识别需要多标签框架。对现有多模态手术模型的零样本评估显示,该任务存在显著的性能差距。为解决这一问题,我们提出了CVS-AdaptNet,这是一种多标签适应策略,通过图像嵌入与每个CVS标准的文本描述对齐,使用正面和负面提示来增强跨多个标签的精细粒度二进制分类。通过在Endoscapes-CVS数据集上适应先进的手术基础模型PeskaVLP,CVS-AdaptNet实现了57.6的mAP,比仅使用ResNet的图像基线(mAP为51.5)提高了六个百分点。我们的结果表明,通过文本提示增强的多标签多模态框架CVS-AdaptNet在图像方法上推动了CVS识别的进步。我们还提出了文本特定的推理方法,有助于分析图像和文本的匹配度。尽管需要进一步的工作来匹配基于空间注释的方法的最先进水平,但这种方法突出了将通用模型适应于特殊手术任务的潜力。具体代码实现已在Github上进行公开:https://github.com/CAMMA-public/CVS-AdaptNet 。
总结简短并且不超过要求长度,表述简洁且易于理解即可。本段研究针对在腹腔镜胆囊切除术中关于关键观察点的安全视图评估的挑战性任务展开研究。该研究提出了一种新的多模态模型CVS-AdaptNet,通过结合图像和文本信息提高自动化识别关键观察点的精度并展现了对评估的安全视图的进一步了解的方法和流程已在GitHub公开交流促进技术讨论分享推广及其在现实情况下的改进实现作用;但技术的极限仍有待探索改进和拓展推广的潜力。其优点在于利用了多模态信息以提高识别精度和适应不同任务需求。虽然还需要进一步的研究和改进以达到最先进的技术水平但同时也推动了技术的普及和推广的前景 简要总结起来便如下:新型模型实现高效跨模态处理复杂识别挑战与高级技术的深入探索和改进还有广阔潜力可挖掘实现更好的安全性和性能表现。
点此查看论文截图

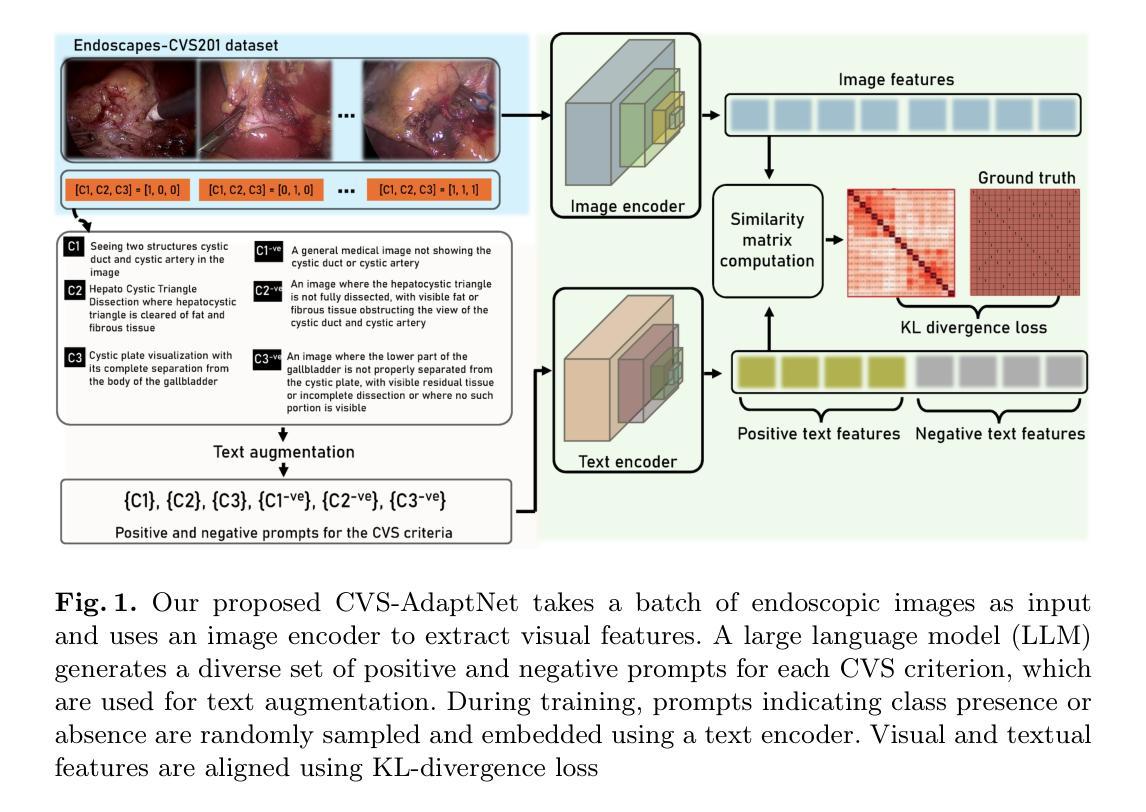
HiLa: Hierarchical Vision-Language Collaboration for Cancer Survival Prediction
Authors:Jiaqi Cui, Lu Wen, Yuchen Fei, Bo Liu, Luping Zhou, Dinggang Shen, Yan Wang
Survival prediction using whole-slide images (WSIs) is crucial in cancer re-search. Despite notable success, existing approaches are limited by their reliance on sparse slide-level labels, which hinders the learning of discriminative repre-sentations from gigapixel WSIs. Recently, vision language (VL) models, which incorporate additional language supervision, have emerged as a promising solu-tion. However, VL-based survival prediction remains largely unexplored due to two key challenges. First, current methods often rely on only one simple lan-guage prompt and basic cosine similarity, which fails to learn fine-grained associ-ations between multi-faceted linguistic information and visual features within WSI, resulting in inadequate vision-language alignment. Second, these methods primarily exploit patch-level information, overlooking the intrinsic hierarchy of WSIs and their interactions, causing ineffective modeling of hierarchical interac-tions. To tackle these problems, we propose a novel Hierarchical vision-Language collaboration (HiLa) framework for improved survival prediction. Specifically, HiLa employs pretrained feature extractors to generate hierarchical visual features from WSIs at both patch and region levels. At each level, a series of language prompts describing various survival-related attributes are constructed and aligned with visual features via Optimal Prompt Learning (OPL). This ap-proach enables the comprehensive learning of discriminative visual features cor-responding to different survival-related attributes from prompts, thereby improv-ing vision-language alignment. Furthermore, we introduce two modules, i.e., Cross-Level Propagation (CLP) and Mutual Contrastive Learning (MCL) to maximize hierarchical cooperation by promoting interactions and consistency be-tween patch and region levels. Experiments on three TCGA datasets demonstrate our SOTA performance.
使用全切片图像(WSI)进行生存预测在癌症研究中至关重要。尽管已有显著的成功,但现有方法受限于对稀疏切片级别标签的依赖,这阻碍了从千兆像素WSI中学习判别表示。最近,融入额外语言监督的视觉语言(VL)模型的出现作为一种有前途的解决方案。然而,基于VL的生存预测仍然因两个关键挑战而未被充分探索。首先,当前的方法通常仅依赖于一个简单的语言提示和基本的余弦相似性,这无法学习WSI内多面语言信息和视觉特征之间的精细关联,导致视觉语言对齐不足。其次,这些方法主要利用补丁级别的信息,忽略了WSI的内在层次及其相互作用,导致层次交互的建模无效。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种用于改进生存预测的新型分层视觉语言协作(HiLa)框架。具体来说,HiLa使用预训练的特征提取器从WSI生成层次化的视觉特征,这些特征既包含补丁级别又包含区域级别。在每个级别上,构建了一系列描述与生存相关属性的语言提示,并通过最佳提示学习(OPL)与视觉特征对齐。这种方法能够全面学习对应于不同生存相关属性的判别性视觉特征,从而提高视觉语言对齐。此外,我们引入了跨级传播(CLP)和相互对比学习(MCL)两个模块,通过促进补丁和区域级别之间的交互和一致性,以最大化层次协作。在三个TCGA数据集上的实验证明了我们的性能处于SOTA水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by MICCAI2025
Summary
在癌症研究中,基于全幻灯片图像(WSI)的生存预测至关重要。现有方法受限于稀疏的幻灯片级标签,难以从吉像素WSI中学习判别表示。新兴的视觉语言(VL)模型通过引入额外的语言监督解决了这个问题。然而,基于VL的生存预测仍面临两大挑战。为解决这些问题,我们提出了分层视觉语言协作(HiLa)框架,以改进生存预测。HiLa使用预训练的特征提取器生成层次化的视觉特征,并通过最佳提示学习(OPL)与语言提示对齐。此外,我们还引入了跨层次传播(CLP)和相互对比学习(MCL)两个模块,以最大化层次间的合作与一致性。在三个TCGA数据集上的实验证明了该方法的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 基于全幻灯片图像(WSI)的生存预测在癌症研究中很重要。
- 当前方法受限于稀疏的标签,难以从WSI中学习判别特征。
- 视觉语言(VL)模型通过引入语言监督来解决这个问题,但基于VL的生存预测面临挑战。
- 提出的HiLa框架通过生成层次化的视觉特征和使用最佳提示学习(OPL)解决这些问题。
- HiLa框架引入了跨层次传播(CLP)和相互对比学习(MCL)模块,以最大化层次间的合作与一致性。
- 实验证明HiLa框架在三个TCGA数据集上的性能优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

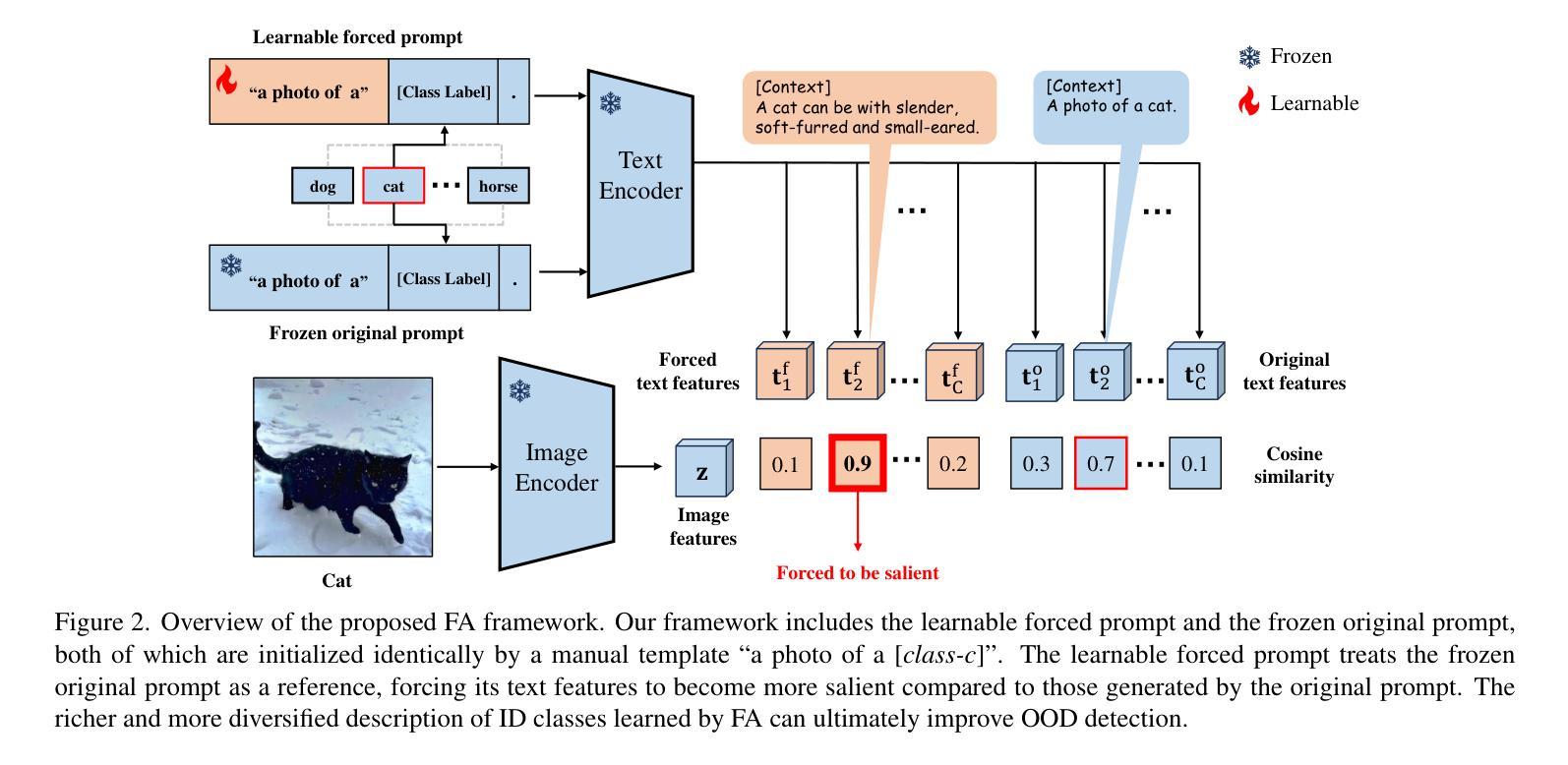
FA: Forced Prompt Learning of Vision-Language Models for Out-of-Distribution Detection
Authors:Xinhua Lu, Runhe Lai, Yanqi Wu, Kanghao Chen, Wei-Shi Zheng, Ruixuan Wang
Pre-trained vision-language models (VLMs) have advanced out-of-distribution (OOD) detection recently. However, existing CLIP-based methods often focus on learning OOD-related knowledge to improve OOD detection, showing limited generalization or reliance on external large-scale auxiliary datasets. In this study, instead of delving into the intricate OOD-related knowledge, we propose an innovative CLIP-based framework based on Forced prompt leArning (FA), designed to make full use of the In-Distribution (ID) knowledge and ultimately boost the effectiveness of OOD detection. Our key insight is to learn a prompt (i.e., forced prompt) that contains more diversified and richer descriptions of the ID classes beyond the textual semantics of class labels. Specifically, it promotes better discernment for ID images, by forcing more notable semantic similarity between ID images and the learnable forced prompt. Moreover, we introduce a forced coefficient, encouraging the forced prompt to learn more comprehensive and nuanced descriptions of the ID classes. In this way, FA is capable of achieving notable improvements in OOD detection, even when trained without any external auxiliary datasets, while maintaining an identical number of trainable parameters as CoOp. Extensive empirical evaluations confirm our method consistently outperforms current state-of-the-art methods. Code is available at https://github.com/0xFAFA/FA.
预训练视觉语言模型(VLMs)最近在离群值检测(OOD)方面取得了进展。然而,现有的基于CLIP的方法通常侧重于学习OOD相关知识以提高OOD检测能力,显示出有限的泛化能力或对外部大规模辅助数据集的依赖。本研究中,我们并没有深入研究复杂的OOD相关知识,而是提出了一种基于强制提示学习(FA)的CLIP框架,旨在充分利用分布内(ID)知识,并最终提高OOD检测的有效性。我们的关键见解是学习一种包含超过类别标签文本语义的更具多样化和丰富描述的提示(即强制提示)。具体来说,它通过强制ID图像和可学习的强制提示之间更显著的语义相似性,促进了对ID图像的更佳辨别力。此外,我们引入了一个强制系数,鼓励强制提示学习更全面、更微妙的ID类别描述。通过这种方式,即使在没有任何外部辅助数据集进行训练的情况下,FA也能在OOD检测方面实现显著的改进,同时保持与CoOp相同数量的可训练参数。大量的经验评估证明我们的方法始终优于当前最先进的方法。代码可在https://github.com/0xFAFA/FA找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:基于预训练的语言视觉模型,该研究提出了一种新的CLIP框架,名为基于强制提示学习(FA)的方法,旨在充分利用分布内(ID)知识,从而提高异常检测效果。该方法通过强制学习更丰富的描述来区分分布内图像,且无需依赖外部大规模辅助数据集。在无需额外数据集的情况下,该方法在异常检测方面取得了显著改进,与当前的最优方法相比有明显优势。
Key Takeaways:
- 预训练的语言视觉模型(VLMs)已经促进了异常检测技术的发展。
- 当前CLIP方法侧重于学习异常检测相关知识以提高检测效果,但泛化性受限并依赖外部大规模数据集。
- 研究提出基于强制提示学习(FA)的CLIP框架,充分利用分布内(ID)知识提高异常检测效果。
- 通过强制学习包含更丰富描述的提示信息,增强了分布内图像的辨识能力。
- 引入强制系数来鼓励学习更全面的描述信息。
- 该方法在不使用外部辅助数据集的情况下实现了显著的异常检测性能提升。
点此查看论文截图

LVLM-Composer’s Explicit Planning for Image Generation
Authors:Spencer Ramsey, Jeffrey Lee, Amina Grant
The burgeoning field of generative artificial intelligence has fundamentally reshaped our approach to content creation, with Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) standing at its forefront. While current LVLMs have demonstrated impressive capabilities in text-to-image generation, they often falter when confronted with complex textual descriptions demanding precise compositional understanding and visual planning. This limitation particularly impacts the accurate rendering of multiple objects, their attributes, spatial relationships, and specific poses within intricate scenes, as evidenced by benchmarks like LongBench-T2I. To address these challenges, we introduce LVLM-Composer, a novel 10-billion parameter scale LVLM specifically engineered for enhanced compositional image synthesis. Our method incorporates a Hierarchical Semantic Planning Module for structured prompt decomposition and a Fine-Grained Feature Alignment Mechanism for precise visual guidance during generation. We propose a multi-stage training paradigm, featuring Hierarchical Semantic-Visual Grounding Pre-training and Compositional Planning Reinforcement Learning with Self-Correction, to instill robust compositional reasoning. Extensive experiments on the LongBench-T2I benchmark, utilizing automatic evaluation by Gemini-2.0-Flash and InternVL3-78B, demonstrate LVLM-Composer’s superior performance across critical compositional dimensions including object accuracy, composition fidelity, and pose accuracy, significantly outperforming state-of-the-art baselines. An in-depth ablation study further validates the indispensable contribution of our proposed modules, while human evaluations confirm the perceptual superiority of our generated images. LVLM-Composer represents a significant step towards truly controllable and compositionally accurate open-ended text-to-image generation.
生成人工智能领域日新月异,已经从根本上改变了我们的内容创作方式,大视觉语言模型(LVLMs)正处于这一领域的前沿。尽管当前的LVLMs在文本到图像生成方面展现出了令人印象深刻的能力,但当面对复杂的文本描述,需要精确的组合理解和视觉规划时,它们往往会遇到困难。这一局限性对在复杂场景中准确呈现多个物体、其属性、空间关系以及特定姿态产生了显著影响,LongBench-T2I等基准测试证明了这一点。为了应对这些挑战,我们推出了LVLM-Composer,这是一个新型的大型视觉语言模型,专门针对增强组合图像合成而设计,规模达到10亿参数级别。我们的方法融入了分层语义规划模块,用于结构化提示分解和精细特征对齐机制,以在生成过程中提供精确的视觉指导。我们提出了一种多阶段训练范式,包含分层语义视觉定位预训练以及组合规划强化学习与自我修正,以建立稳健的组合推理。在LongBench-T2I基准测试上进行的广泛实验,采用Gemini-2.0-Flash和InternVL3-78B进行自动评估,证明LVLM-Composer在关键组合维度上表现出卓越性能,包括物体准确性、组合保真度和姿态准确性,显著优于最新基线。深入的消融研究进一步验证了我们所提出模块的不可或缺作用,而人类评估则证实了我们生成图像的感觉优越性。LVLM-Composer是朝着真正可控和组合准确的开放式文本到图像生成迈出的重要一步。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本主要介绍了生成式人工智能领域的蓬勃发展及其在内容创作方面的革命性变革。文章重点介绍了大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在文本生成图像领域的突出表现及其面临的挑战。文章还介绍了一种新型的大型视觉语言模型——LVLM-Composer,它通过一系列的创新技术和训练方法,增强了结构化提示分解和精细特征对齐机制,从而提高了复杂场景中的多物体、属性、空间关系和姿态的准确渲染能力。实验结果显示,LVLM-Composer在关键指标上超越了现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 生成式人工智能已彻底改变了内容创作方式,其中大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)处于前沿地位。
- 当前LVLMs在处理复杂文本描述时存在挑战,尤其是在准确渲染多个物体及其属性、空间关系和特定姿态方面。
- LVLM-Composer是一种新型的大型视觉语言模型,具有增强的结构化提示分解和精细特征对齐机制,旨在解决上述问题。
- LVLM-Composer通过多阶段训练范式,包括分层语义视觉定位预训练和组合规划强化学习进行自我校正,以灌输强大的组合推理能力。
- 实验结果表明,LVLM-Composer在关键指标上显著优于现有技术,如对象准确性、组合保真度和姿态准确性。
- 深入的分析研究验证了LVLM-Composer中提出的模块不可或缺的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

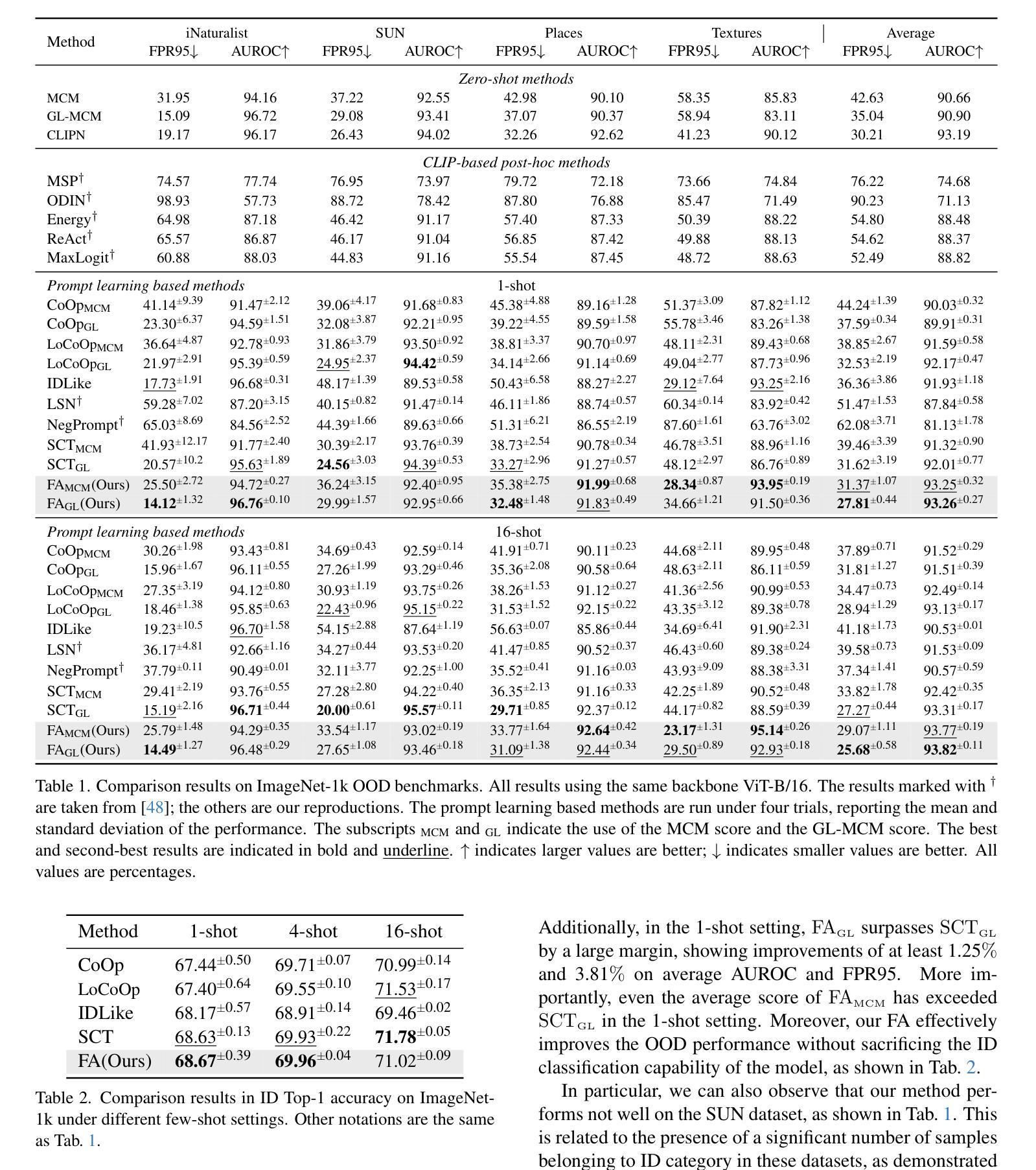
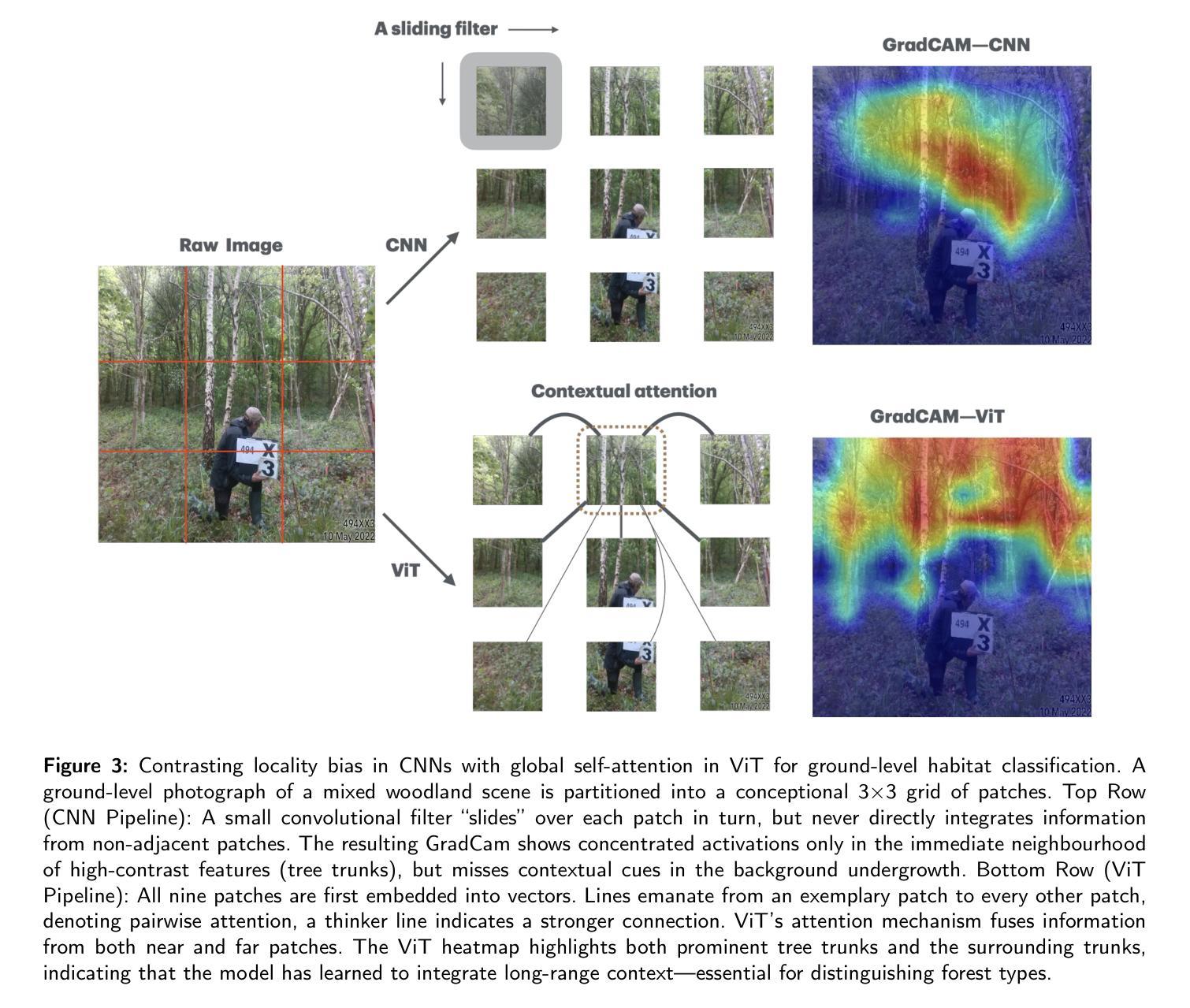
Habitat Classification from Ground-Level Imagery Using Deep Neural Networks
Authors:Hongrui Shi, Lisa Norton, Lucy Ridding, Simon Rolph, Tom August, Claire M Wood, Lan Qie, Petra Bosilj, James M Brown
Habitat assessment at local scales – critical for enhancing biodiversity and guiding conservation priorities – often relies on expert field survey that can be costly, motivating the exploration of AI-driven tools to automate and refine this process. While most AI-driven habitat mapping depends on remote sensing, it is often constrained by sensor availability, weather, and coarse resolution. In contrast, ground-level imagery captures essential structural and compositional cues invisible from above and remains underexplored for robust, fine-grained habitat classification. This study addresses this gap by applying state-of-the-art deep neural network architectures to ground-level habitat imagery. Leveraging data from the UK Countryside Survey covering 18 broad habitat types, we evaluate two families of models – convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and vision transformers (ViTs) – under both supervised and supervised contrastive learning paradigms. Our results demonstrate that ViTs consistently outperform state-of-the-art CNN baselines on key classification metrics (Top-3 accuracy = 91%, MCC = 0.66) and offer more interpretable scene understanding tailored to ground-level images. Moreover, supervised contrastive learning significantly reduces misclassification rates among visually similar habitats (e.g., Improved vs. Neutral Grassland), driven by a more discriminative embedding space. Finally, our best model performs on par with experienced ecological experts in habitat classification from images, underscoring the promise of expert-level automated assessment. By integrating advanced AI with ecological expertise, this research establishes a scalable, cost-effective framework for ground-level habitat monitoring to accelerate biodiversity conservation and inform land-use decisions at the national scale.
生境评估在本地尺度上对于增强生物多样性和指导保护优先事项至关重要,通常依赖于昂贵的专家实地调查,这激发了人们探索使用人工智能工具来自动化和完善这一过程。虽然大多数人工智能驱动的生境地图制作依赖于遥感技术,但它通常受到传感器可用性、天气和分辨率粗糙的限制。相比之下,地面水平的图像捕捉了从上面看不见的至关重要的结构和组成线索,并且对于稳健的、精细的生境分类仍然未被充分探索。本研究通过应用最新深度神经网络架构进行地面生境图像分析来解决这一空白。我们利用覆盖18种广泛生境类型的英国乡村调查数据,评估了两种模型家族,即卷积神经网络(CNN)和视觉变压器(ViT),这两种模型在监督学习和监督对比学习范式下进行了评估。我们的结果表明,视觉变压器在关键分类指标上始终优于最新的CNN基准测试(前三名准确率= 91%,MCC = 0.66),并且提供更针对地面水平图像的可解释场景理解。此外,监督对比学习显著降低了视觉上相似生境之间的误分类率(例如,改良草地与中性草地),这得益于更具区分性的嵌入空间。最后,我们最好的模型在图像生境分类方面与经验丰富的生态专家表现相当,这突显了专家级自动化评估的潜力。通过整合先进的人工智能和生态专业知识,这项研究建立了一个可扩展的、成本效益高的地面生境监测框架,以加速生物多样性保护并为全国尺度的土地利用决策提供信息。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 26 pages, 12 figures, 6 tables
Summary
基于深度神经网络架构和地面级图像数据,本研究实现了对地面级栖息地精细分类的自动化评估。通过对比卷积神经网络(CNN)和视觉转换器(ViT)两种模型,发现ViT在关键分类指标上表现更优秀,具有更高的可解释性和适用性。同时,该研究也通过监督对比学习减少了视觉相似栖息地之间的误分类率。此研究结合先进的人工智能技术和生态专业知识,为地面级栖息地监测提供了一个可扩展、成本效益高的框架,有助于加速生物多样性保护和土地利用决策。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究使用AI工具自动化评估地面级栖息地分类,降低专家现场调查成本。
- 通过对比CNN和ViT模型,发现ViT在精细栖息地分类方面表现更优秀。
- ViT模型提供更高的分类准确性,并且具有更好的可解释性。
- 监督对比学习提高了模型对视觉相似栖息地的区分能力。
- 本研究结合AI技术与生态专业知识,为地面级栖息地监测提供有效框架。
- 该框架有助于实现大规模、成本效益高的栖息地监测。
点此查看论文截图


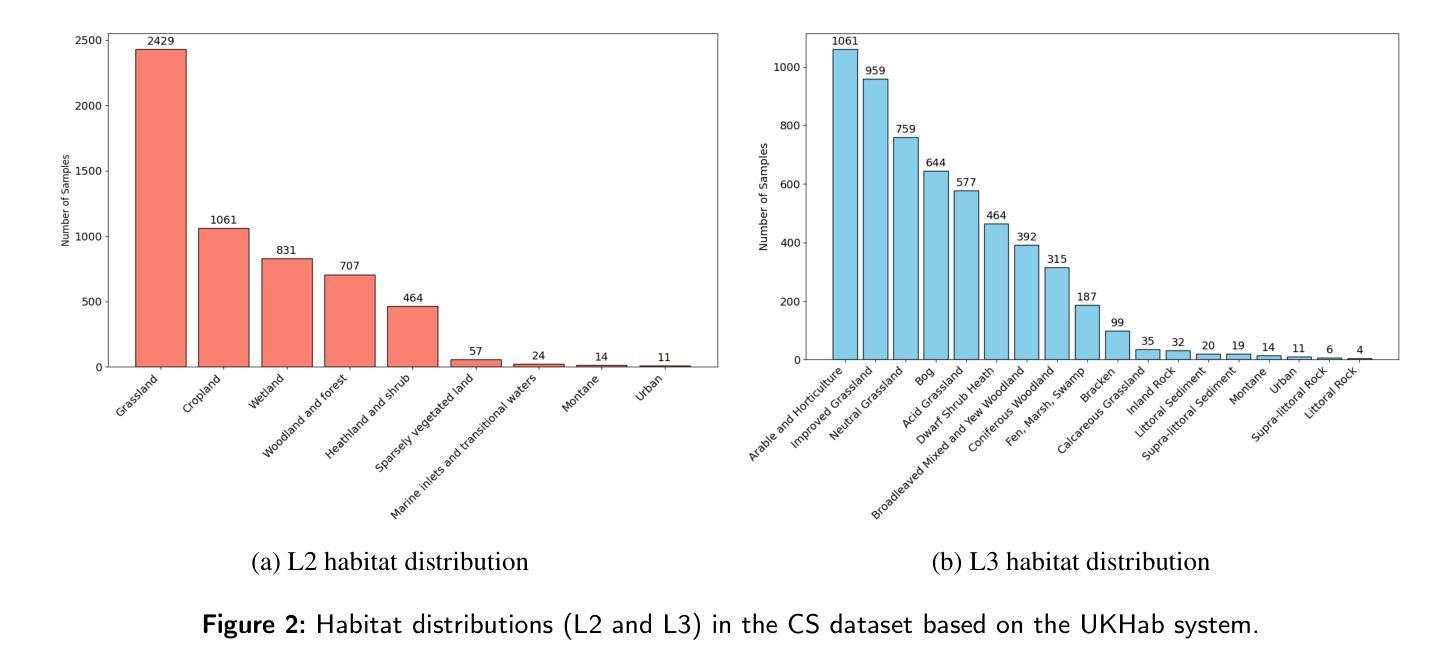

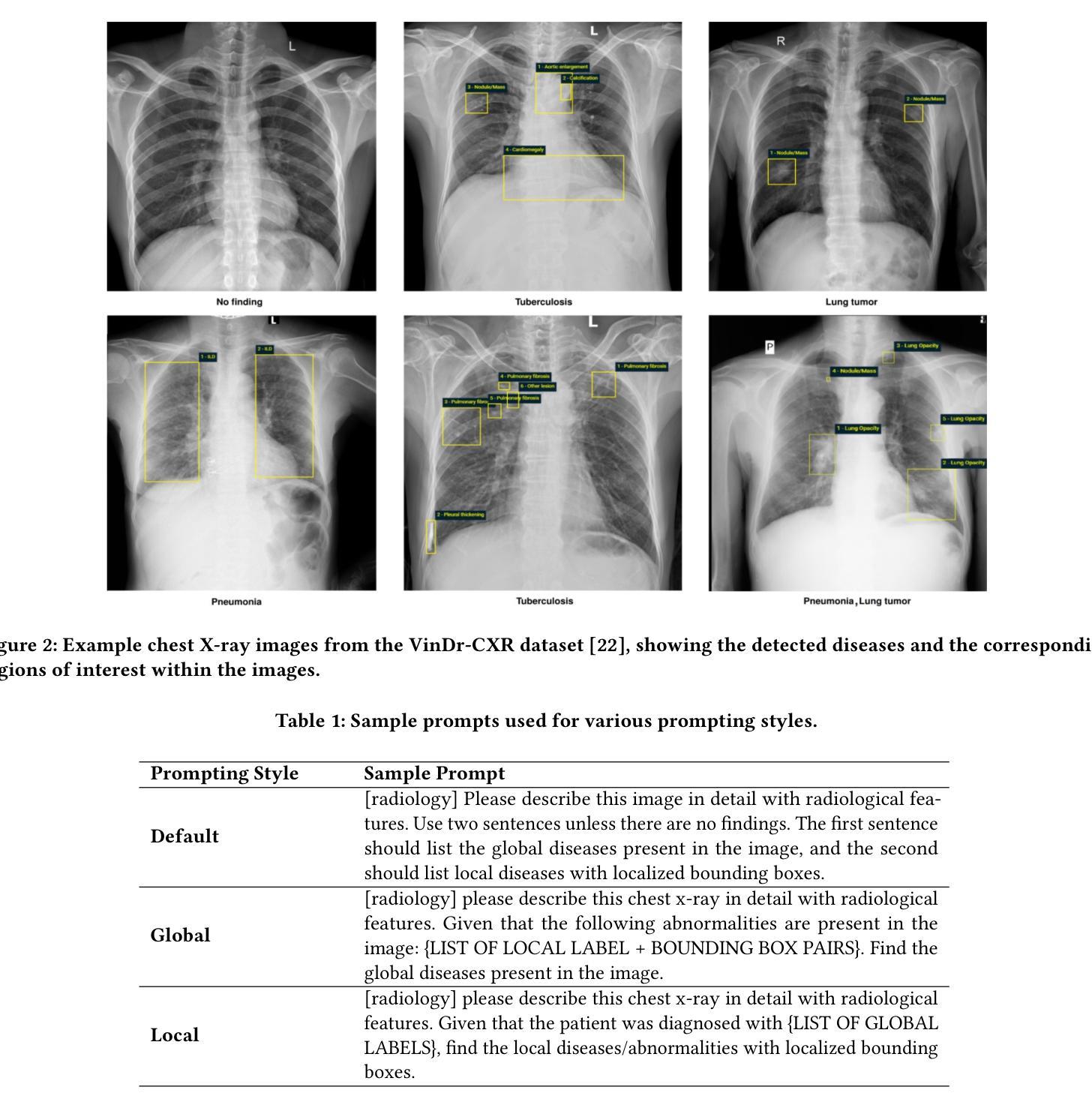
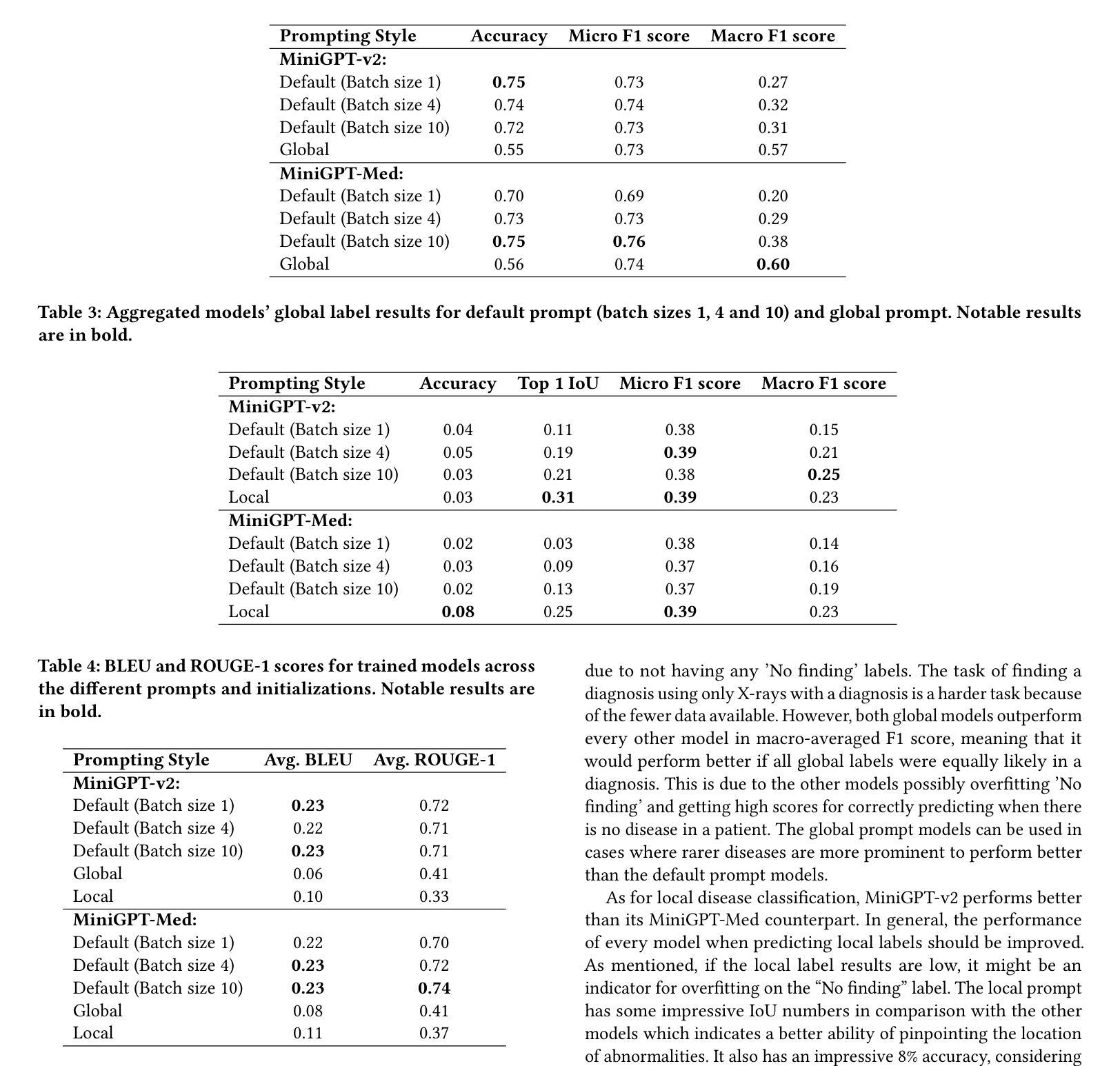
ChestGPT: Integrating Large Language Models and Vision Transformers for Disease Detection and Localization in Chest X-Rays
Authors:Shehroz S. Khan, Petar Przulj, Ahmed Ashraf, Ali Abedi
The global demand for radiologists is increasing rapidly due to a growing reliance on medical imaging services, while the supply of radiologists is not keeping pace. Advances in computer vision and image processing technologies present significant potential to address this gap by enhancing radiologists’ capabilities and improving diagnostic accuracy. Large language models (LLMs), particularly generative pre-trained transformers (GPTs), have become the primary approach for understanding and generating textual data. In parallel, vision transformers (ViTs) have proven effective at converting visual data into a format that LLMs can process efficiently. In this paper, we present ChestGPT, a deep-learning framework that integrates the EVA ViT with the Llama 2 LLM to classify diseases and localize regions of interest in chest X-ray images. The ViT converts X-ray images into tokens, which are then fed, together with engineered prompts, into the LLM, enabling joint classification and localization of diseases. This approach incorporates transfer learning techniques to enhance both explainability and performance. The proposed method achieved strong global disease classification performance on the VinDr-CXR dataset, with an F1 score of 0.76, and successfully localized pathologies by generating bounding boxes around the regions of interest. We also outline several task-specific prompts, in addition to general-purpose prompts, for scenarios radiologists might encounter. Overall, this framework offers an assistive tool that can lighten radiologists’ workload by providing preliminary findings and regions of interest to facilitate their diagnostic process.
由于医疗成像服务日益增长的依赖,对放射科医师的全球需求迅速增加,而放射科医师的供给却跟不上这一需求。计算机视觉和图像处理技术的进步在增强放射科医师的能力和提高诊断准确性方面展现出巨大的潜力来解决这一差距。大型语言模型(LLM)特别是预训练生成式转换器(GPT)已成为理解和生成文本数据的主要方法。同时,视觉转换器(ViT)已证明在将视觉数据转换为LLM可以高效处理的形式方面非常有效。在本文中,我们提出了ChestGPT,这是一个深度学习框架,它将EVA ViT与Llama 2 LLM相结合,用于对胸部X射线图像中的疾病进行分类并定位感兴趣区域。ViT将X射线图像转换为令牌,然后连同工程提示一起输入到LLM中,实现了疾病的联合分类和定位。这种方法结合了迁移学习技术,提高了可解释性和性能。所提出的方法在VinDr-CXR数据集上取得了强大的全球疾病分类性能,F1分数为0.76,并成功定位了病理,在感兴趣区域周围生成了边界框。我们还概述了除通用提示之外针对特定任务的提示,用于应对放射科医生可能遇到的场景。总的来说,这个框架提供了一个辅助工具,通过提供初步检查结果和感兴趣区域来减轻放射科医生的工作量,从而促进其诊断过程。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 5 figures, 4 tables
Summary
随着医疗成像服务的依赖度增加,全球对放射科医生的需求迅速增长,而放射科医生的供应却跟不上这一速度。计算机视觉和图像处理技术的进展为解决这一差距提供了巨大潜力,通过增强放射科医生的能力和提高诊断准确性来实现。本研究提出了一种名为ChestGPT的深度学习框架,它结合了EVA Vision Transformer(ViT)和Llama 2大型语言模型(LLM),用于对胸部X射线图像进行疾病分类和感兴趣区域定位。该框架利用迁移学习技术,提高了可解释性和性能,在VinDr-CXR数据集上实现了强大的全局疾病分类性能,F1分数为0.76,并成功定位了病理区域。总体而言,该框架为放射科医生提供了一种辅助工具,可以通过提供初步发现和感兴趣区域来减轻他们的工作量,从而有助于诊断过程。
Key Takeaways
- 医学成像服务的依赖度增加导致对放射科医生的需求迅速增长。
- 放射科医生的供应无法满足日益增长的需求。
- 计算机视觉和图像处理技术有潜力通过增强放射科医生的能力和提高诊断准确性来解决这一差距。
- ChestGPT是一个结合EVA Vision Transformer(ViT)和Llama 2大型语言模型(LLM)的深度学习框架。
- ChestGPT能够实现疾病分类和胸部X射线图像中的感兴趣区域定位。
- 该框架利用迁移学习技术,提高了性能和可解释性。
- 在VinDr-CXR数据集上,ChestGPT实现了F1分数0.76的强效全局疾病分类性能。
点此查看论文截图

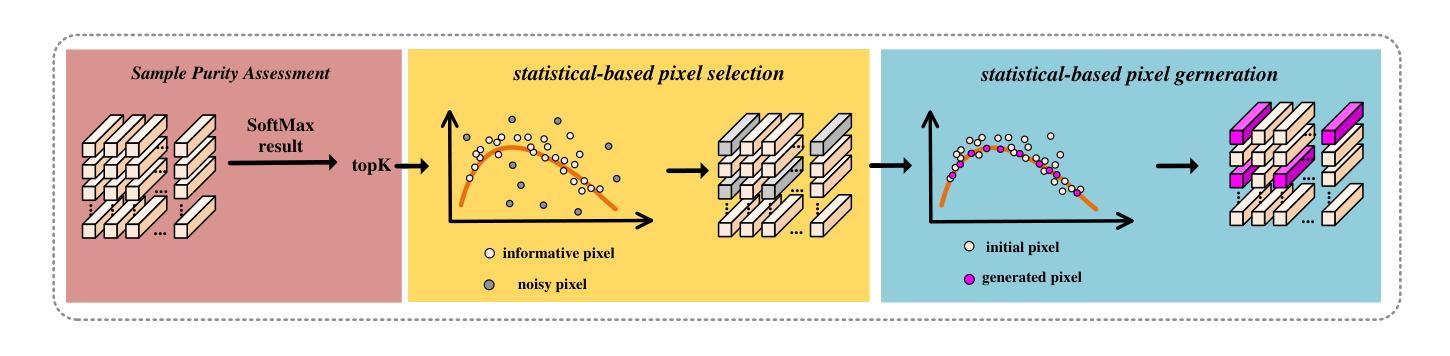
Dual-frequency Selected Knowledge Distillation with Statistical-based Sample Rectification for PolSAR Image Classification
Authors:Xinyue Xin, Ming Li, Yan Wu, Xiang Li, Peng Zhang, Dazhi Xu
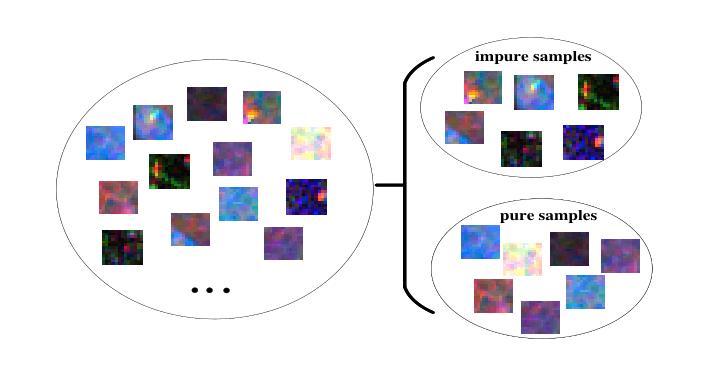
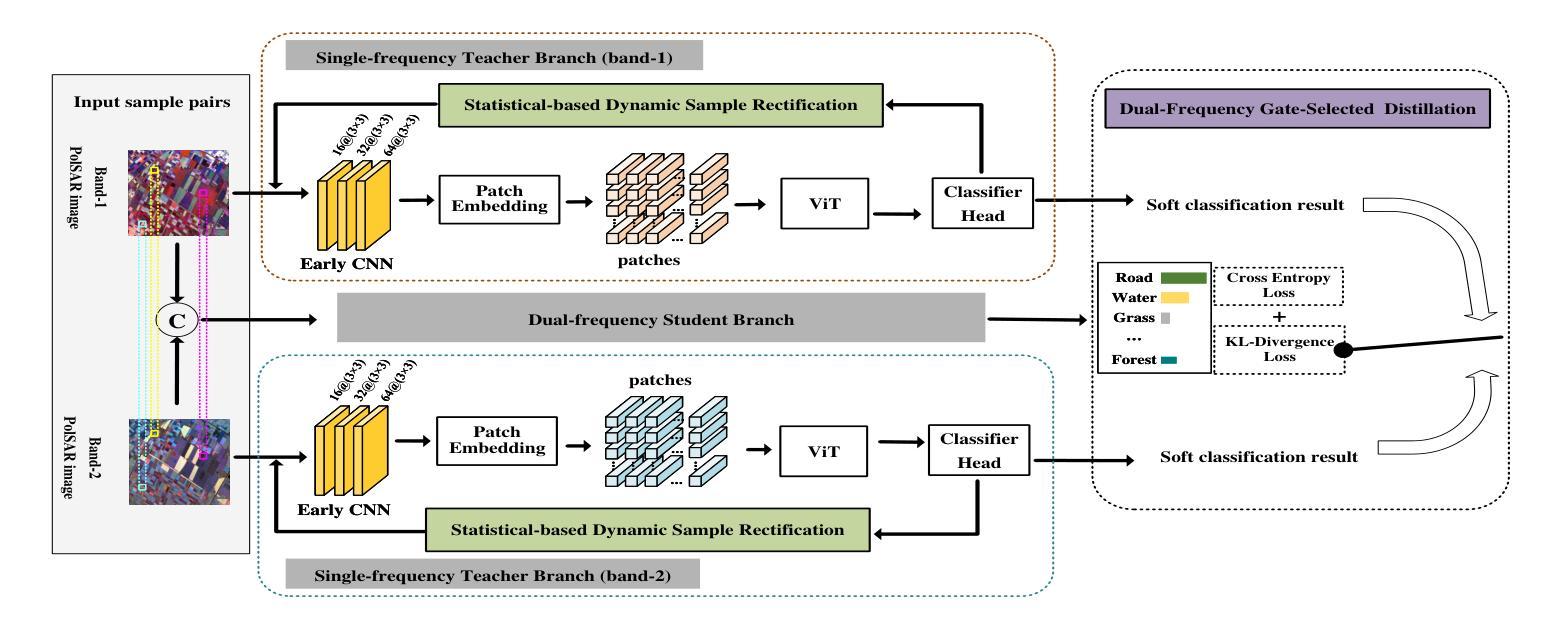
The collaborative classification of dual-frequency PolSAR images is a meaningful but also challenging research. The effect of regional consistency on classification information learning and the rational use of dual-frequency data are two main difficulties for dual-frequency collaborative classification. To tackle these problems, a selected knowledge distillation network with statistical-based sample rectification (SKDNet-SSR) is proposed in this article. First, in addition to applying CNN and ViT as local and global feature extractors, a statistical-based dynamic sample rectification (SDSR) module is designed to avoid the impact of poor regional consistency on spatial information learning process. Specifically, based on the fact that the PolSAR covariance matrix conforms to the complex Wishart distribution, SDSR first dynamically evaluates the sample purity, and then performs pixel selection and pixel generation to remove noisy pixels, thereby avoiding the feature interaction between informative pixels and noisy pixels and improving the classification feature extraction process. Next, a dual-frequency gate-selected distillation (DGSD) module is constructed to emphasize the advantages of different frequency bands and perform complementary learning on dual-frequency data. It uses the dominant single-frequency branch on each sample as teacher model to train the dual-frequency student model, enabling the student model to learn the optimal results and realizing complementary utilization of dual-frequency data on different terrain objects. Comprehensive experiments on four measured dual-frequency PolSAR data demonstrate that the proposed SKDNet-SSR outperforms other related methods.
双频PolSAR图像协同分类是一项有意义但也具有挑战性的研究。区域一致性对分类信息学习的影响以及如何合理利用双频数据是双频协同分类的两个主要难题。为了解决这些问题,本文提出了一种基于统计样本修正的选择知识蒸馏网络(SKDNet-SSR)。首先,除了使用CNN和ViT作为局部和全局特征提取器外,还设计了一个基于统计的动态样本修正(SDSR)模块,以避免区域一致性差对空间信息学习过程的影响。具体而言,基于PolSAR协方差矩阵符合复杂Wishart分布的事实,SDSR首先动态评估样本纯度,然后进行像素选择和像素生成,以去除噪声像素,从而避免信息像素和噪声像素之间的特征交互,改进分类特征提取过程。接下来,构建了一个双频门选蒸馏(DGSD)模块,以强调不同频段的优点,并对双频数据进行互补学习。它使用每个样本上的主导单频分支作为教师模型来训练双频学生模型,使学生模型能够学习最佳结果,并在不同地形对象上实现双频数据的互补利用。在四个实测双频PolSAR数据上的综合实验表明,所提出的SKDNet-SSR优于其他相关方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在协同分类极化SAR图像的研究中,存在因区域一致性和有效利用双频数据所带来的挑战。本文提出了一种结合统计样本校正的知识蒸馏网络(SKDNet-SSR)来应对这些挑战。该网络不仅使用CNN和ViT作为局部和全局特征提取器,还设计了一个基于统计的动态样本校正(SDSR)模块,以避免不良区域一致性对空间信息学习过程的影响。此外,还构建了一个双频门选蒸馏(DGSD)模块,以强调不同频段的优点并对双频数据进行互补学习。实验证明,SKDNet-SSR方法相比其他相关方法具有优势。
Key Takeaways
- 协同分类双频极化SAR图像研究具有意义和挑战性。
- 区域一致性和有效利用双频数据是两大难题。
- 提出了一种结合统计样本校正的知识蒸馏网络(SKDNet-SSR)。
- SKDNet-SSR使用CNN和ViT作为特征提取器。
- 设计了基于统计的动态样本校正(SDSR)模块,以提高分类特征提取过程。
- 构建双频门选蒸馏(DGSD)模块,实现不同频段的互补学习。
点此查看论文截图

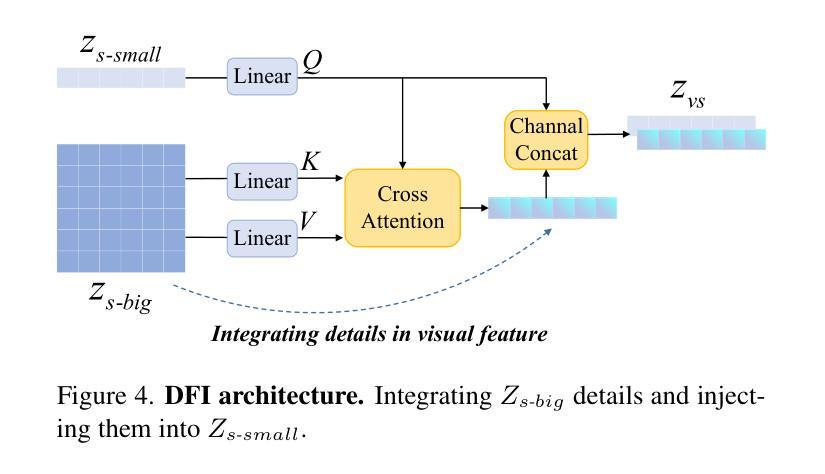
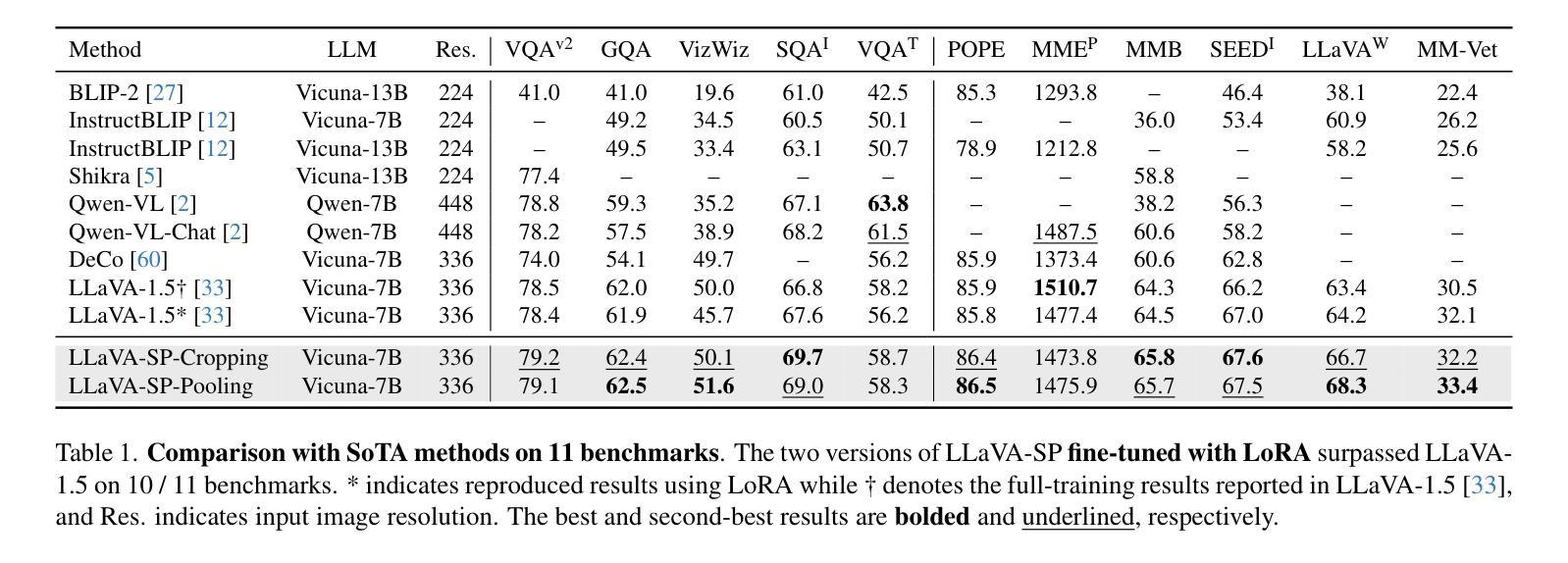
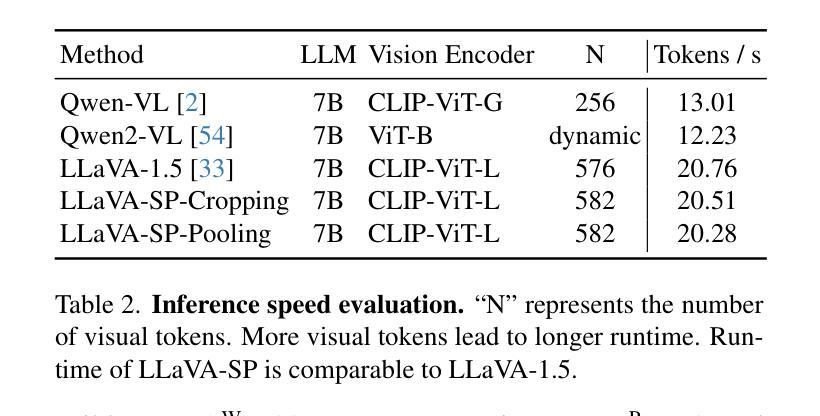
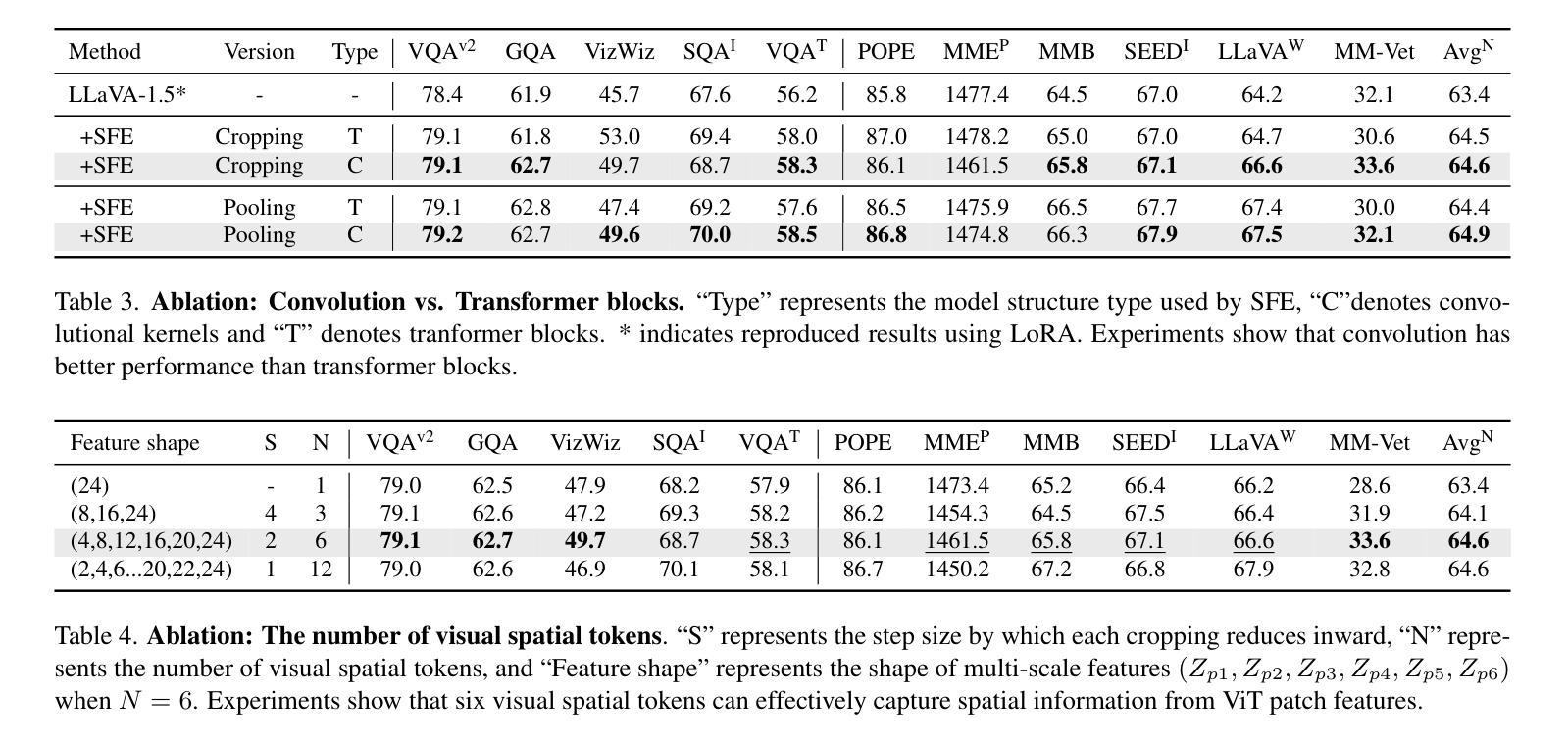
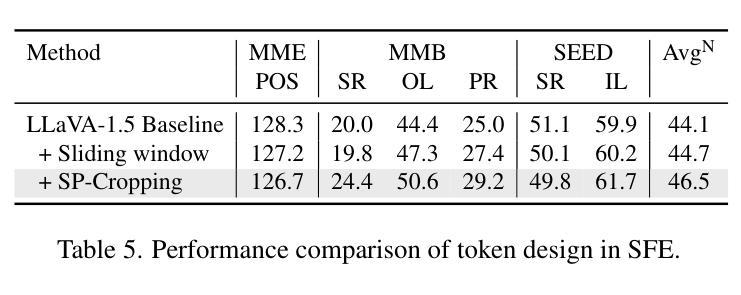
LLaVA-SP: Enhancing Visual Representation with Visual Spatial Tokens for MLLMs
Authors:Haoran Lou, Chunxiao Fan, Ziyan Liu, Yuexin Wu, Xinliang Wang
The architecture of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) commonly connects a vision encoder, often based on CLIP-ViT, to a large language model. While CLIP-ViT works well for capturing global image features, it struggles to model local relationships between adjacent patches, leading to weaker visual representation, which in turn affects the detailed understanding ability of MLLMs. To solve this, we propose LLaVA-SP, which only adds six spatial visual tokens to the original visual tokens to enhance the visual representation. Our approach offers three key advantages: 1) We propose a novel Projector, which uses convolutional kernels to derive visual spatial tokens from ViT patch features, simulating two visual spatial ordering approaches: “from central region to global” and “from abstract to specific”. Then, a cross-attention mechanism is applied to fuse fine-grained visual information, enriching the overall visual representation. 2) We present two model variants: LLaVA-SP-Cropping, which focuses on detail features through progressive cropping, and LLaVA-SP-Pooling, which captures global semantics through adaptive pooling, enabling the model to handle diverse visual understanding tasks. 3) Extensive experiments show that LLaVA-SP, fine-tuned with LoRA, achieves significant performance improvements across various multimodal benchmarks, outperforming the state-of-the-art LLaVA-1.5 model in multiple tasks with nearly identical inference latency. The code and models are available at https://github.com/CnFaker/LLaVA-SP.
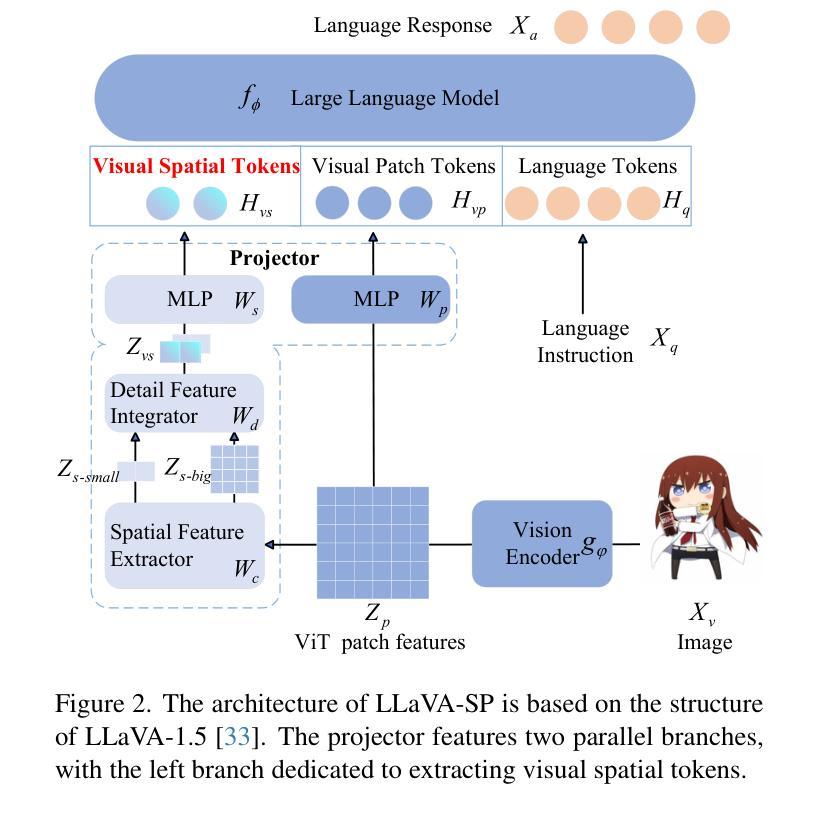
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的架构通常将基于CLIP-ViT的视觉编码器与大型语言模型相连接。虽然CLIP-ViT在捕获全局图像特征方面表现良好,但在对相邻补丁之间的局部关系进行建模时遇到困难,导致视觉表示较弱,进而影响了MLLMs的详细理解能力。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了LLaVA-SP,它只在原始视觉令牌上添加六个空间视觉令牌,以增强视觉表示。我们的方法提供了三个关键优势:
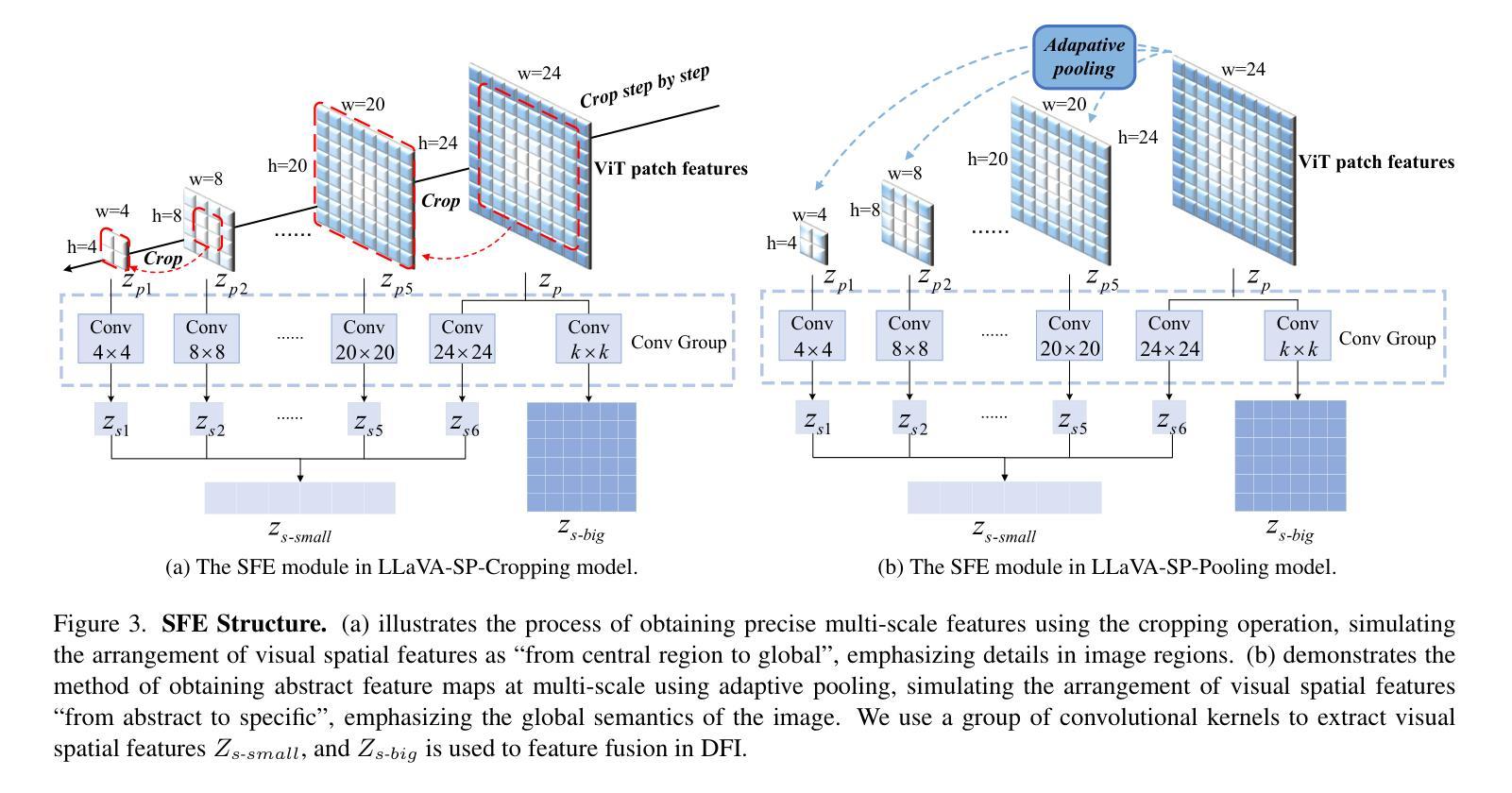
1)我们提出了一个使用卷积核从ViT补丁特征中推导出视觉空间令牌的新型投影仪,模拟两种视觉空间排序方法:“从中心区域到全局”和“从抽象到具体”。然后,应用交叉注意力机制融合细粒度视觉信息,丰富总体视觉表示。
2)我们推出了两个模型变体:LLaVA-SP-Cropping,它通过逐步裁剪关注细节特征;以及LLaVA-SP-Pooling,它通过自适应池化捕获全局语义,使模型能够处理各种视觉理解任务。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICCV 2025
Summary
多模态大型语言模型的架构通常将基于CLIP-ViT的视觉编码器与大型语言模型相连接。CLIP-ViT在捕捉全局图像特征方面表现良好,但在建模相邻补丁之间的局部关系方面存在困难,导致视觉表征较弱,进而影响MLLLM的详细理解能力。为解决此问题,我们提出了LLaVA-SP,它仅添加六个空间视觉令牌来增强原始视觉令牌的视觉表征。该方法具有三个关键优势。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLLM)结合视觉编码器(如CLIP-ViT)与大型语言模型。
- CLIP-ViT在捕捉全局图像特征上表现良好,但在建模局部关系方面存在缺陷。
- LLaVA-SP通过添加空间视觉令牌增强视觉表征。
- LLaVA-SP使用卷积核衍生视觉空间令牌,模拟两种视觉空间排序方法。
- LLaVA-SP提供两种模型变体:LLaVA-SP-Cropping和LLaVA-SP-Pooling,分别关注细节特征和全局语义。
- LLaVA-SP经过LoRA微调后,在多种多模态基准测试中实现了显著的性能改进。
点此查看论文截图
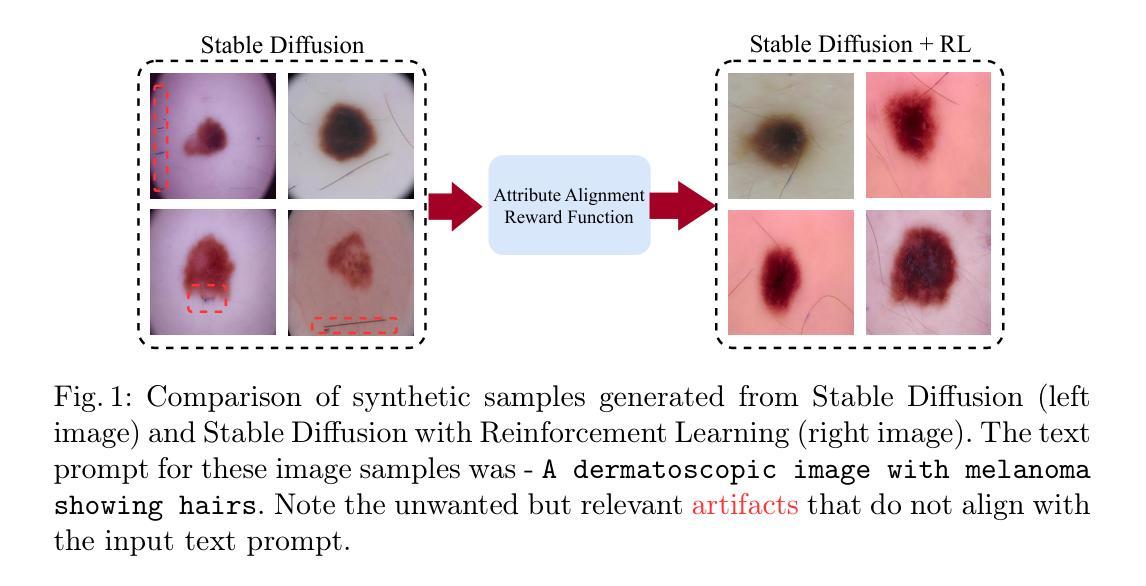
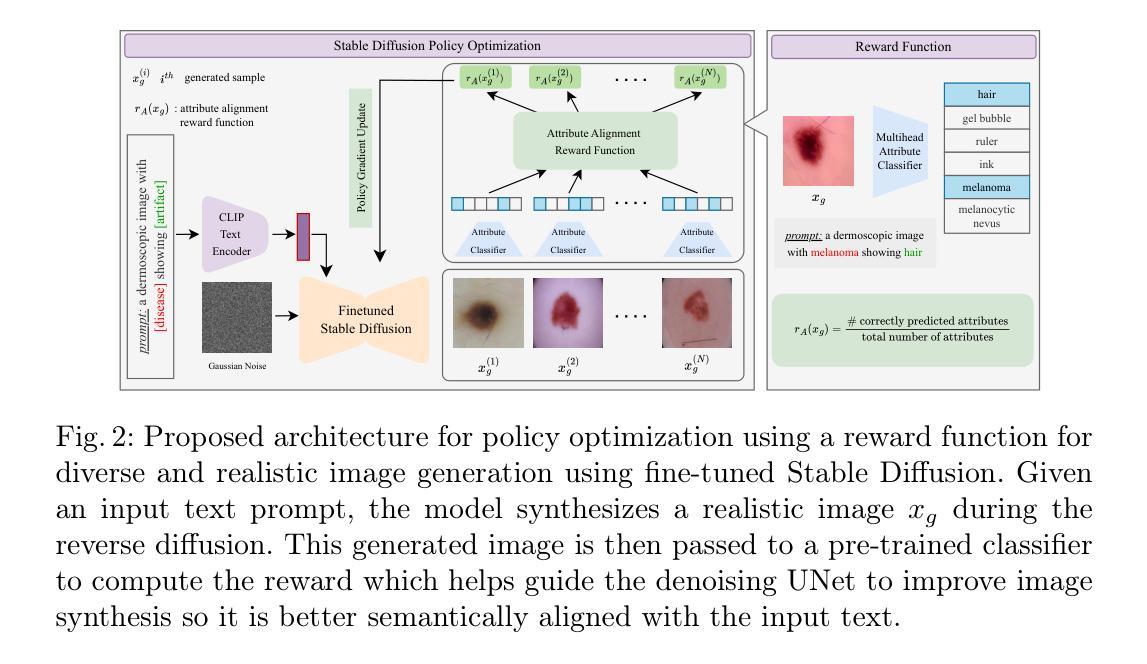
RL4Med-DDPO: Reinforcement Learning for Controlled Guidance Towards Diverse Medical Image Generation using Vision-Language Foundation Models
Authors:Parham Saremi, Amar Kumar, Mohamed Mohamed, Zahra TehraniNasab, Tal Arbel
Vision-Language Foundation Models (VLFM) have shown a tremendous increase in performance in terms of generating high-resolution, photorealistic natural images. While VLFMs show a rich understanding of semantic content across modalities, they often struggle with fine-grained alignment tasks that require precise correspondence between image regions and textual descriptions, a limitation in medical imaging, where accurate localization and detection of clinical features are essential for diagnosis and analysis. To address this issue, we propose a multi-stage architecture where a pre-trained VLFM (e.g. Stable Diffusion) provides a cursory semantic understanding, while a reinforcement learning (RL) algorithm refines the alignment through an iterative process that optimizes for understanding semantic context. The reward signal is designed to align the semantic information of the text with synthesized images. Experiments on the public ISIC2019 skin lesion dataset demonstrate that the proposed method improves (a) the quality of the generated images, and (b) the alignment with the text prompt over the original fine-tuned Stable Diffusion baseline. We also show that the synthesized samples could be used to improve disease classifier performance for underrepresented subgroups through augmentation. Our code is accessible through the project website: https://parhamsaremi.github.io/rl4med-ddpo
视觉语言基础模型(VLFM)在生成高分辨率、逼真自然图像方面的性能得到了极大的提升。虽然VLFM在多模态的语义内容理解方面表现出丰富的能力,但在需要图像区域和文本描述之间精确对应的精细对齐任务中,它们常常会遇到困难。在医学成像领域,准确定位和检测临床特征是诊断和治疗的关键,这一限制尤为重要。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种多阶段架构,其中预训练的VLFM(例如Stable Diffusion)提供基本的语义理解,而强化学习(RL)算法通过优化语义上下文理解的迭代过程来精细对齐。奖励信号被设计为将文本与合成图像的语义信息对齐。在公开的ISIC2019皮肤病变数据集上的实验表明,所提出的方法改进了(a)生成图像的质量和(b)与文本提示的对齐程度,超过了原始微调过的Stable Diffusion基线。我们还表明,合成的样本可以通过增强来改善代表性不足的子群体的疾病分类器性能。我们的代码可通过项目网站获取:https://parhamsaremi.github.io/rl4med-ddpo
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于视觉语言基础模型(VLFM)的强大性能,本文提出了一种多阶段架构,旨在解决医学图像中精细粒度对齐任务的挑战。通过预训练的VLFM提供初步语义理解,并使用强化学习算法通过迭代过程进行精细化对齐。该研究使用公共的ISIC2019皮肤病变数据集进行实验验证,证明该方法提高了图像生成质量和文本对齐度。此外,合成的样本可用于提高代表性不足的亚组疾病分类器的性能。代码已上传至项目网站供公众访问。
Key Takeaways
- VLFM在生成高分辨率、逼真的自然图像方面表现出卓越的性能,但在医学成像中的精细粒度对齐任务上存在局限性。
- 提出了一种多阶段架构,结合预训练的VLFM和强化学习算法,以提高图像与文本之间的对齐精度。
- 在ISIC2019皮肤病变数据集上的实验验证了该方法的有效性,提高了图像生成质量和文本对齐度。
- 合成的样本可用于增强代表性不足的亚组疾病分类器的性能。
- 该方法的代码已上传至项目网站供公众访问和使用。
点此查看论文截图

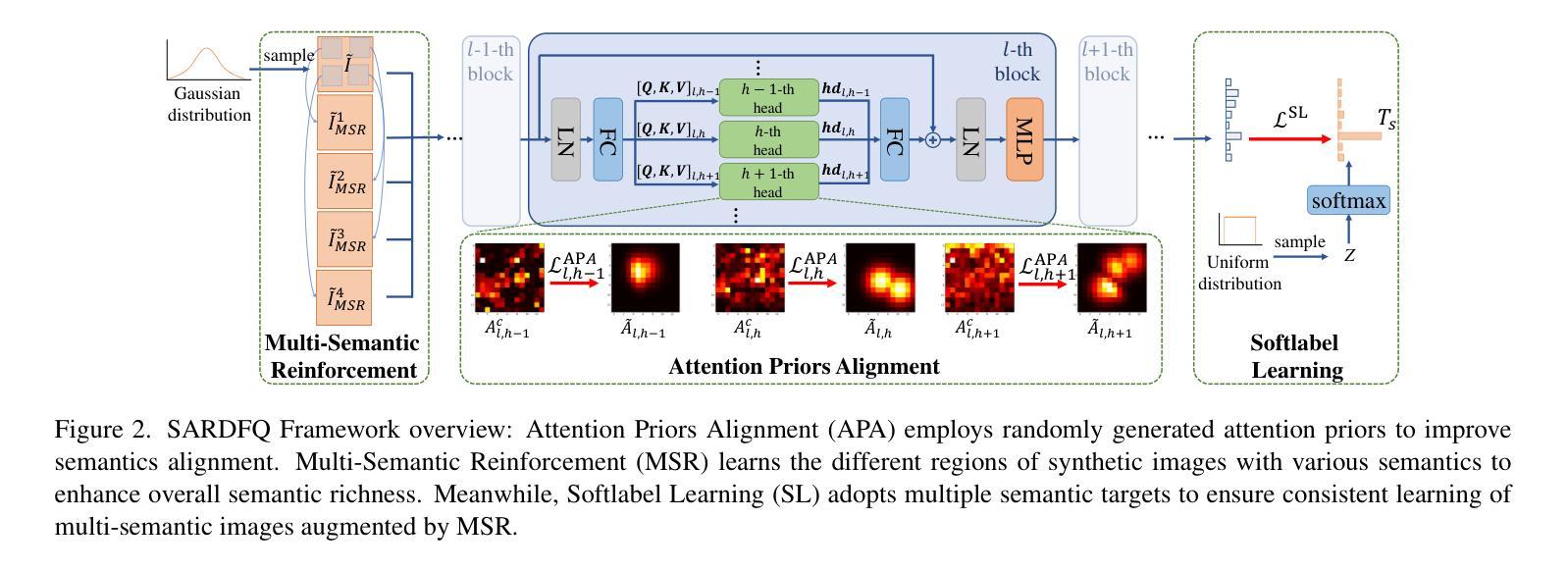
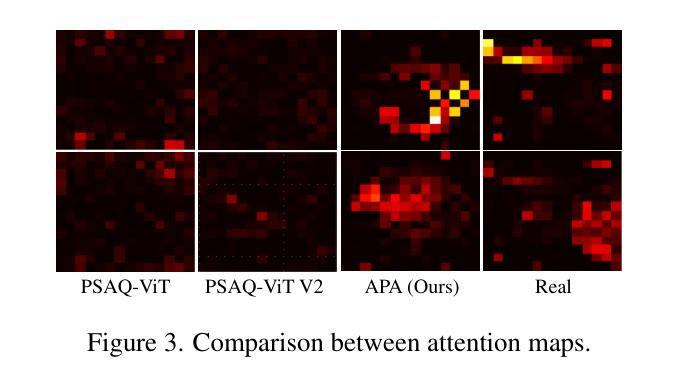
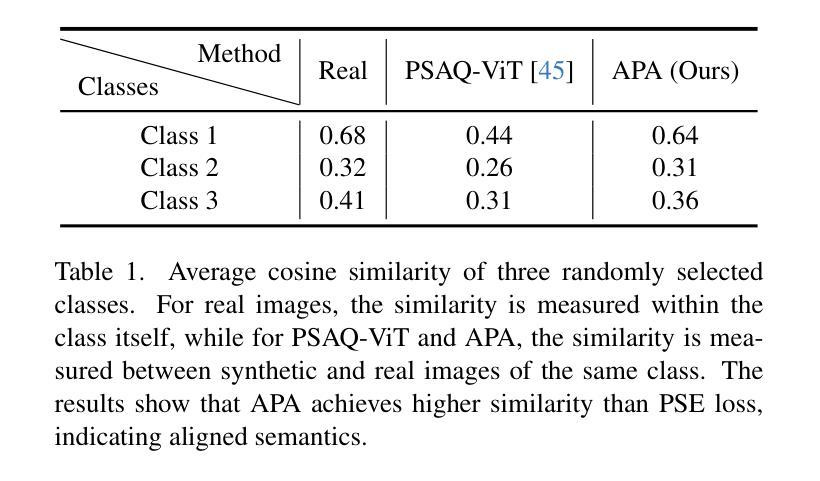
Semantic Alignment and Reinforcement for Data-Free Quantization of Vision Transformers
Authors:Yunshan Zhong, Yuyao Zhou, Yuxin Zhang, Wanchen Sui, Shen Li, Yong Li, Fei Chao, Rongrong Ji
Data-free quantization (DFQ) enables model quantization without accessing real data, addressing concerns regarding data security and privacy. With the growing adoption of Vision Transformers (ViTs), DFQ for ViTs has garnered significant attention. However, existing DFQ methods exhibit two limitations: (1) semantic distortion, where the semantics of synthetic images deviate substantially from those of real images, and (2) semantic inadequacy, where synthetic images contain extensive regions with limited content and oversimplified textures, leading to suboptimal quantization performance. To address these limitations, we propose SARDFQ, a novel Semantics Alignment and Reinforcement Data-Free Quantization method for ViTs. To address semantic distortion, SARDFQ incorporates Attention Priors Alignment (APA), which optimizes synthetic images to follow randomly generated structure attention priors. To mitigate semantic inadequacy, SARDFQ introduces Multi-Semantic Reinforcement (MSR), leveraging localized patch optimization to enhance semantic richness across synthetic images. Furthermore, SARDFQ employs Soft-Label Learning (SL), wherein multiple semantic targets are adapted to facilitate the learning of multi-semantic images augmented by MSR. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of SARDFQ, significantly surpassing existing methods. For example, SARDFQ improves top-1 accuracy on ImageNet by 15.52% for W4A4 ViT-B. The code is at https://github.com/zysxmu/SARDFQ.
无数据量化(DFQ)能够在不访问真实数据的情况下实现模型量化,解决了对数据安全和隐私的担忧。随着视觉变压器(ViT)的广泛应用,ViT的无数据量化(DFQ)已引起广泛关注。然而,现有的DFQ方法存在两个局限性:(1)语义失真,即合成图像的语义与真实图像的语义存在较大偏差;(2)语义不足,合成图像包含大量内容有限、纹理过于简单的区域,导致量化性能不佳。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了SARDFQ,一种新型的用于视觉变压器的语义对齐和强化无数据量化方法。为解决语义失真问题,SARDFQ引入了注意力先验对齐(APA),优化合成图像以遵循随机生成的结构注意力先验。为了缓解语义不足的问题,SARDFQ引入了多语义强化(MSR),利用局部补丁优化来增强合成图像中的语义丰富性。此外,SARDFQ还采用了软标签学习(SL),适应多个语义目标,以促进由MSR增强的多语义图像的学习。大量实验证明了SARDFQ的有效性,显著超越了现有方法。例如,SARDFQ在ImageNet上的top-1准确率提高了15.52%,适用于W4A4 ViT-B。代码地址为:https://github.com/zysxmu/SARDFQ。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV2025
Summary
数据无关量化(DFQ)可在不接触真实数据的情况下实现模型量化,关注数据安全和隐私保护。针对视觉变压器(ViTs)的DFQ存在语义失真和语义不足的问题。为此,我们提出了SARDFQ,一种新颖的语义对齐和强化数据无关量化方法。它通过Attention Prior Alignment优化合成图像以遵循随机生成的结构注意力先验来解决语义失真问题。此外,SARDFQ采用多语义强化和多语义图像学习来解决语义不足的问题。实验表明,SARDFQ效果显著,在ImageNet上,W4A4 ViT-B的top-1准确率提高了15.52%。
Key Takeaways
- 数据无关量化(DFQ)可以在不接触真实数据的情况下实现模型量化,重视数据安全和隐私保护。
- 现有DFQ方法存在语义失真和语义不足的问题。
- SARDFQ是一种针对视觉变压器(ViTs)的新的DFQ方法,通过Attention Prior Alignment解决语义失真问题。
- SARDFQ采用多语义强化(MSR)和软标签学习(SL)来解决语义不足的问题,提高合成图像的语义丰富性。
- SARDFQ通过优化合成图像的结构和语义,实现了对现有方法的显著超越。
- 在ImageNet上,SARDFQ对W4A4 ViT-B的top-1准确率提高了15.52%。
- SARDFQ的代码已公开在https://github.com/zysxmu/SARDFQ。
点此查看论文截图