⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-10 更新
EC-Flow: Enabling Versatile Robotic Manipulation from Action-Unlabeled Videos via Embodiment-Centric Flow
Authors:Yixiang Chen, Peiyan Li, Yan Huang, Jiabing Yang, Kehan Chen, Liang Wang
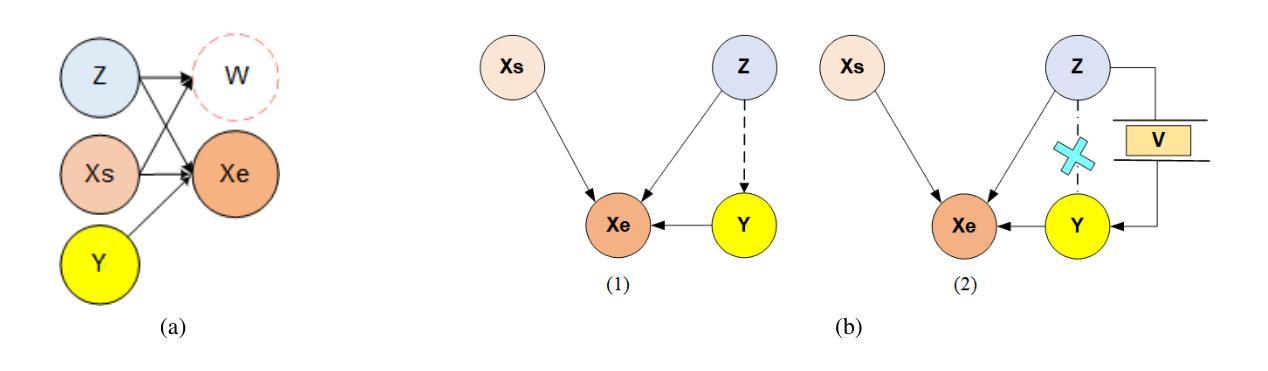
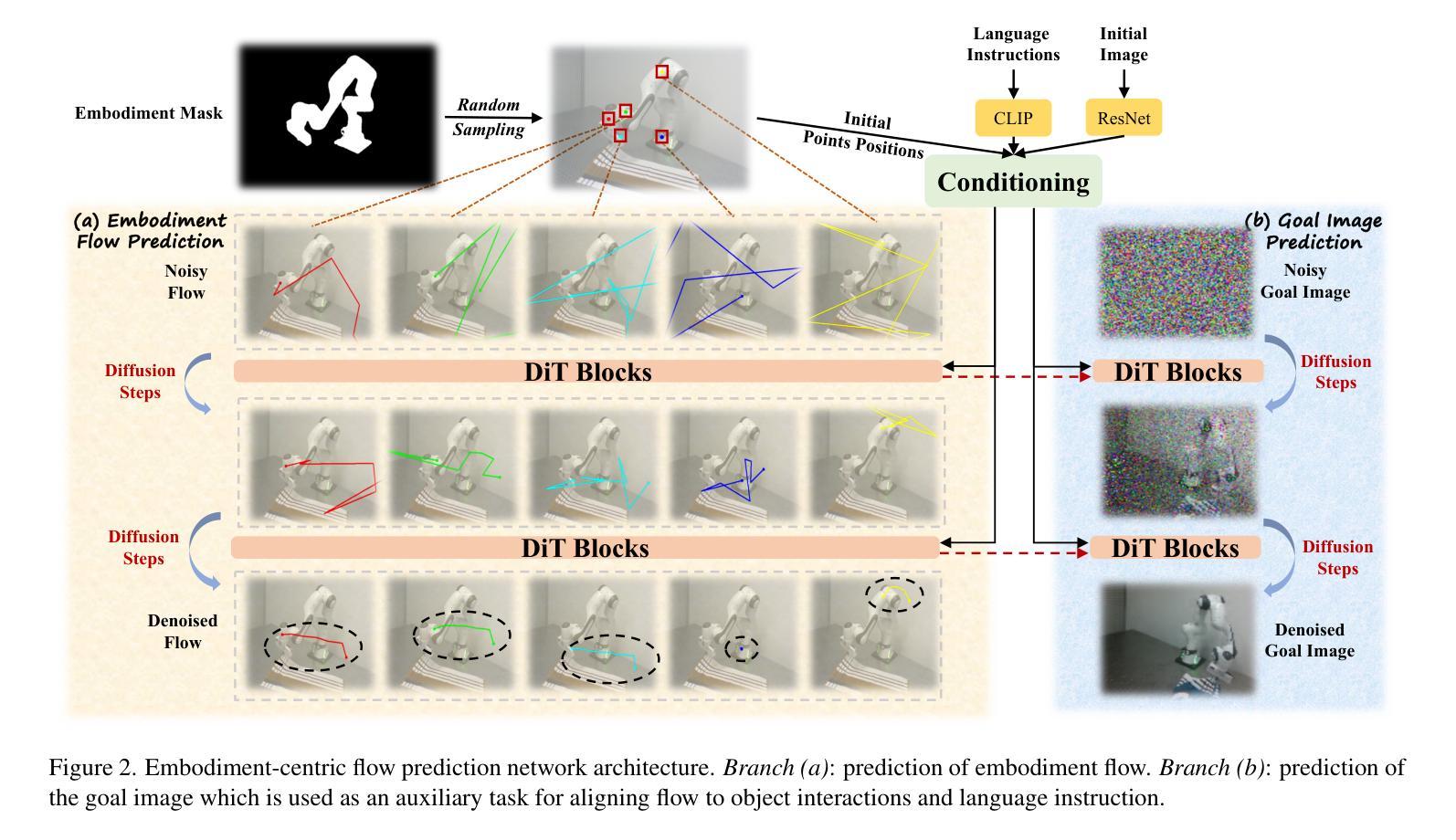
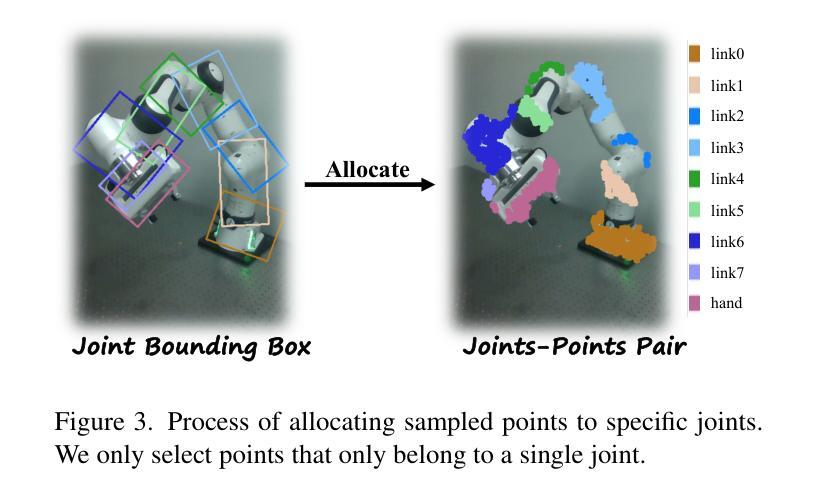
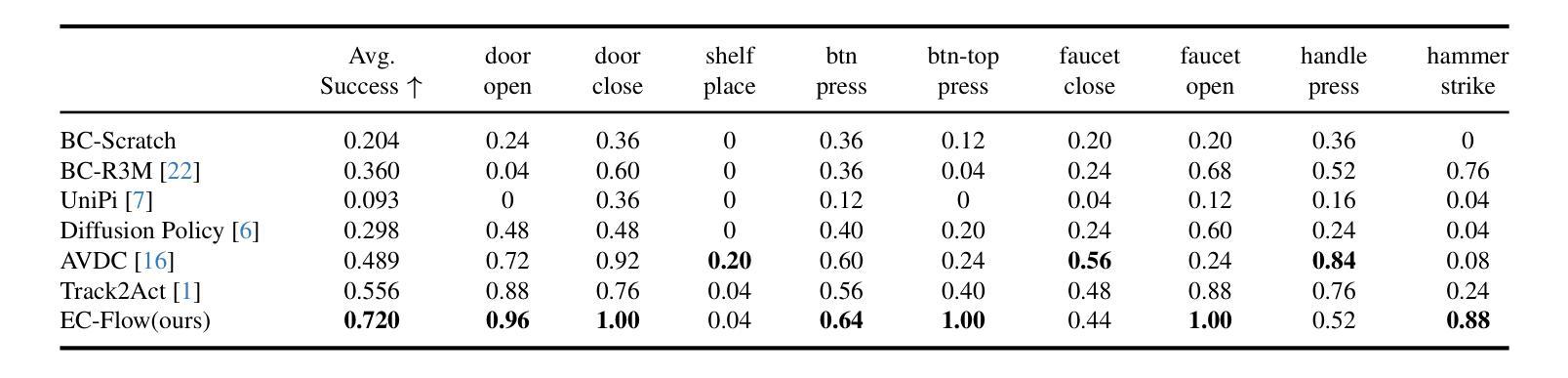
Current language-guided robotic manipulation systems often require low-level action-labeled datasets for imitation learning. While object-centric flow prediction methods mitigate this issue, they remain limited to scenarios involving rigid objects with clear displacement and minimal occlusion. In this work, we present Embodiment-Centric Flow (EC-Flow), a framework that directly learns manipulation from action-unlabeled videos by predicting embodiment-centric flow. Our key insight is that incorporating the embodiment’s inherent kinematics significantly enhances generalization to versatile manipulation scenarios, including deformable object handling, occlusions, and non-object-displacement tasks. To connect the EC-Flow with language instructions and object interactions, we further introduce a goal-alignment module by jointly optimizing movement consistency and goal-image prediction. Moreover, translating EC-Flow to executable robot actions only requires a standard robot URDF (Unified Robot Description Format) file to specify kinematic constraints across joints, which makes it easy to use in practice. We validate EC-Flow on both simulation (Meta-World) and real-world tasks, demonstrating its state-of-the-art performance in occluded object handling (62% improvement), deformable object manipulation (45% improvement), and non-object-displacement tasks (80% improvement) than prior state-of-the-art object-centric flow methods. For more information, see our project website at https://ec-flow1.github.io .
当前的语言引导型机器人操纵系统通常需要低级的动作标注数据集来进行模仿学习。虽然以物体为中心的运动预测方法缓解了这个问题,但它们仍然局限于涉及刚性物体、位移清晰、遮挡较少的场景。在这项工作中,我们提出了Embodiment-Centric Flow(EC-Flow)框架,它可以直接从动作未标注的视频中学习操纵技能,通过预测embodiment-centric flow来实现。我们的关键见解是,融入主体本身的内在运动学可以极大地提高在各种操纵场景中的通用性,包括变形物体的处理、遮挡以及非物体位移任务。为了将EC-Flow与语言指令和物体交互连接起来,我们进一步引入了一个目标对齐模块,通过联合优化动作一致性和目标图像预测来实现。此外,将EC-Flow转换为可执行的机器人动作只需要一个标准的机器人URDF(统一机器人描述格式)文件来指定关节间的运动学约束,这使得它在实践中易于使用。我们在模拟(Meta-World)和真实世界任务中都验证了EC-Flow的有效性,表明其在处理遮挡物体(提高62%)、变形物体操作(提高45%)和非物体位移任务(提高80%)方面的性能均处于最新水平,超越了现有的以物体为中心的运动预测方法。更多信息请参见我们的项目网站:https://ec-flow1.github.io。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICCV 2025
Summary
本文提出一种名为Embodiment-Centric Flow(EC-Flow)的框架,能够直接从未标注动作的视频中学习操控技能。该框架结合机器人本身的运动学特性,提高了对各种操控场景的泛化能力,如处理可变形的物体、遮挡物以及非物体位移任务。此外,还引入了一个目标对齐模块,通过联合优化动作一致性和目标图像预测,将EC-Flow与语言指令和物体交互连接起来。该框架易于实践应用,只需标准的机器人URDF文件即可将EC-Flow转化为可执行的机器人动作。在模拟和真实任务中的验证显示,EC-Flow在遮挡物处理、可变形物体操控和非物体位移任务上的表现均达到或超越了最新水平。
Key Takeaways
- EC-Flow框架直接从未标注动作的视频中学习操控技能,无需低级别的动作标注数据集。
- 框架结合机器人本身的运动学特性,提高对各种操控场景的泛化能力。
- 引入目标对齐模块,联合优化动作一致性和目标图像预测,将EC-Flow与语言指令和物体交互连接。
- EC-Flow易于实践应用,通过标准的机器人URDF文件即可将框架转化为可执行的机器人动作。
- 在模拟和真实任务中的验证显示,EC-Flow在遮挡物处理、可变形物体操控和非物体位移任务上的表现优异。
- 与先前的对象中心流方法相比,EC-Flow在特定任务上有显著改进,如遮挡物处理改进了62%、可变形物体操控改进了45%、非物体位移任务改进了80%。
点此查看论文截图

NeoBabel: A Multilingual Open Tower for Visual Generation
Authors:Mohammad Mahdi Derakhshani, Dheeraj Varghese, Marzieh Fadaee, Cees G. M. Snoek
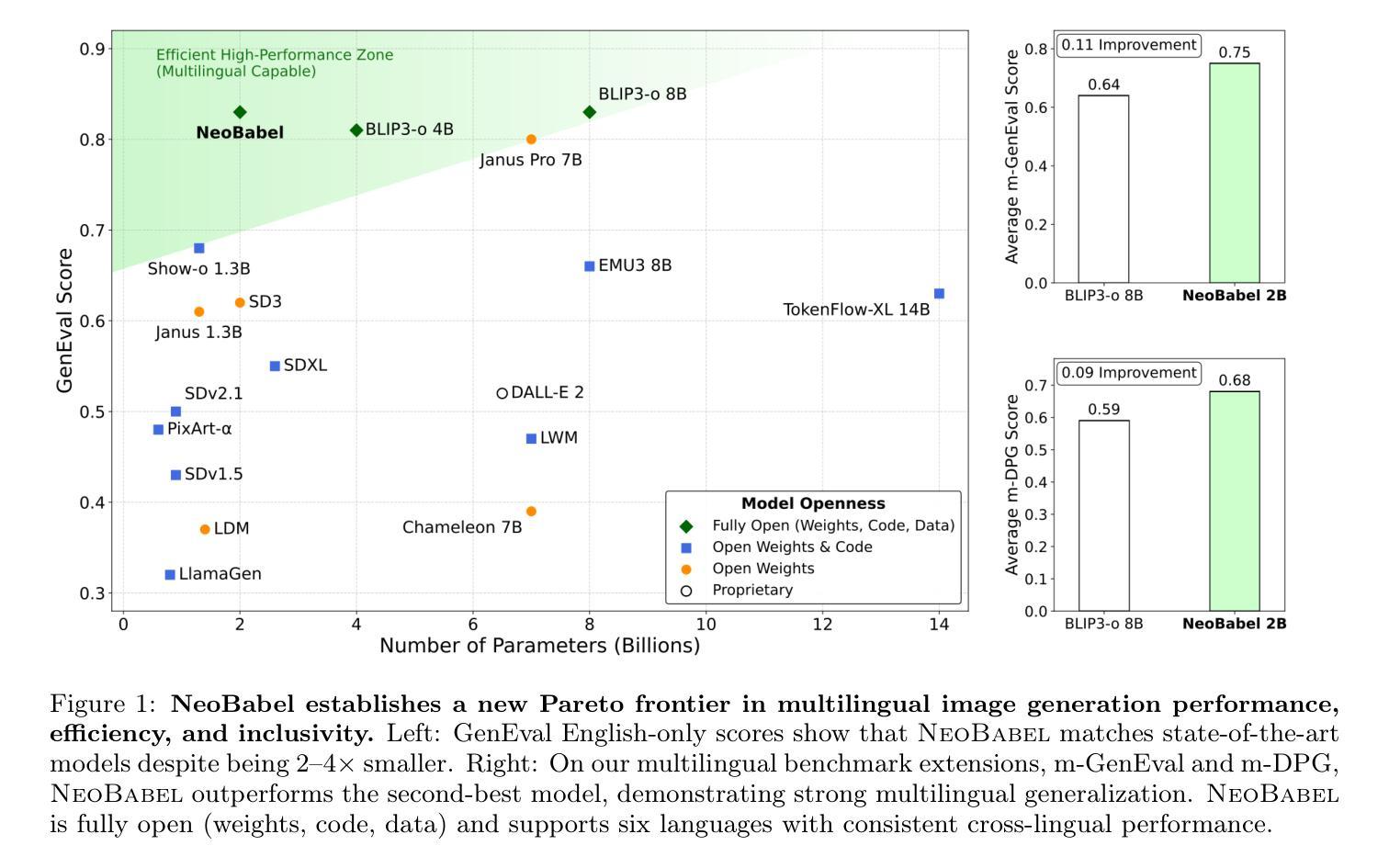
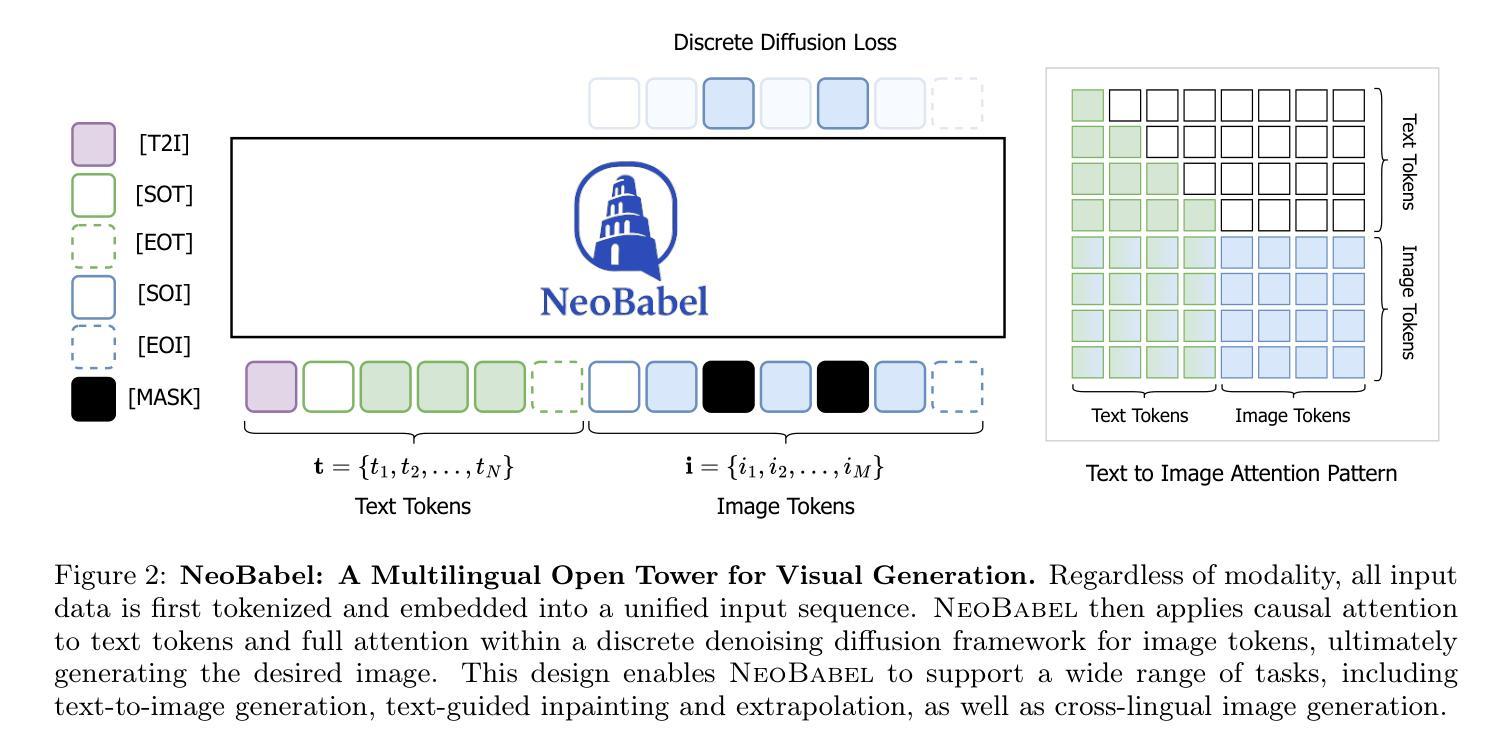
Text-to-image generation advancements have been predominantly English-centric, creating barriers for non-English speakers and perpetuating digital inequities. While existing systems rely on translation pipelines, these introduce semantic drift, computational overhead, and cultural misalignment. We introduce NeoBabel, a novel multilingual image generation framework that sets a new Pareto frontier in performance, efficiency and inclusivity, supporting six languages: English, Chinese, Dutch, French, Hindi, and Persian. The model is trained using a combination of large-scale multilingual pretraining and high-resolution instruction tuning. To evaluate its capabilities, we expand two English-only benchmarks to multilingual equivalents: m-GenEval and m-DPG. NeoBabel achieves state-of-the-art multilingual performance while retaining strong English capability, scoring 0.75 on m-GenEval and 0.68 on m-DPG. Notably, it performs on par with leading models on English tasks while outperforming them by +0.11 and +0.09 on multilingual benchmarks, even though these models are built on multilingual base LLMs. This demonstrates the effectiveness of our targeted alignment training for preserving and extending crosslingual generalization. We further introduce two new metrics to rigorously assess multilingual alignment and robustness to code-mixed prompts. Notably, NeoBabel matches or exceeds English-only models while being 2-4x smaller. We release an open toolkit, including all code, model checkpoints, a curated dataset of 124M multilingual text-image pairs, and standardized multilingual evaluation protocols, to advance inclusive AI research. Our work demonstrates that multilingual capability is not a trade-off but a catalyst for improved robustness, efficiency, and cultural fidelity in generative AI.
文本到图像生成技术的进步主要以英语为中心,为非英语使用者创造了障碍,并加剧了数字不平等现象。尽管现有系统依赖于翻译管道,但这些管道会引发语义漂移、计算开销和文化不匹配等问题。我们推出了NeoBabel,这是一个新的多语言图像生成框架,在性能、效率和包容性方面树立了新的帕累托边界,支持六种语言:英语、中文、荷兰语、法语、印地语和波斯语。该模型通过大规模多语言预训练和高分辨率指令调整的结合进行训练。为了评估其能力,我们将两个仅适用于英语的基准测试扩展到了多语言版本:m-GenEval和m-DPG。NeoBabel在保持强大英语能力的同时,实现了最新的多语言性能,在m-GenEval上得分为0.75,在m-DPG上得分为0.68。值得注意的是,它在英语任务上的表现与领先模型持平,在多语言基准测试上的得分比它们高出+0.11和+0.09,尽管这些模型是基于多语言基础LLM构建的。这证明了我们有针对性的对齐训练在保留和扩展跨语言泛化方面的有效性。我们还引入了两个新指标来严格评估多语言对齐和对抗混合提示的稳健性。值得注意的是,NeoBabel匹配或超越了仅适用于英语的模型,同时体积缩小了2-4倍。我们发布了一个开放工具包,包括所有代码、模型检查点、1.24亿多语言文本图像对组成的精选数据集以及标准化多语言评估协议,以促进包容性人工智能研究。我们的工作表明,多语言能力并不是一种权衡,而是提高生成式人工智能的稳健性、效率和文化忠实度的催化剂。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 34 pages, 12 figures
Summary
文本到图像生成技术主要围绕英语展开,对非英语人群存在数字鸿沟。现有系统依赖翻译管道,存在语义漂移、计算冗余和文化不匹配问题。我们推出NeoBabel,支持六种语言的新多语言图像生成框架,通过大规模多语言预训练和高分辨率指令调整实现性能、效率和包容性的新帕累托前沿。它在多语言基准测试上表现卓越,同时保留强大的英语能力。我们进一步引入两个新指标来严格评估多语言对齐和代码混合提示的稳健性。NeoBabel匹配或超过英语模型表现,同时模型体积更小,为推进包容性人工智能研究发布开放工具包。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像生成技术存在语言中心化问题,主要为英语设计,对非英语人群存在数字鸿沟。
- 现有系统依赖翻译管道,存在语义漂移、计算冗余和文化不匹配等缺点。
- NeoBabel是一个支持六种语言的多语言图像生成框架,具有出色的性能、效率和包容性。
- NeoBabel实现了在多语言基准测试上的卓越表现,同时保持强大的英语能力。
- 引入两个新指标以评估多语言对齐和代码混合提示的稳健性。
- NeoBabel性能与英语模型相当或更好,且模型体积更小。
点此查看论文截图

Enhancing Synthetic CT from CBCT via Multimodal Fusion and End-To-End Registration
Authors:Maximilian Tschuchnig, Lukas Lamminger, Philipp Steininger, Michael Gadermayr
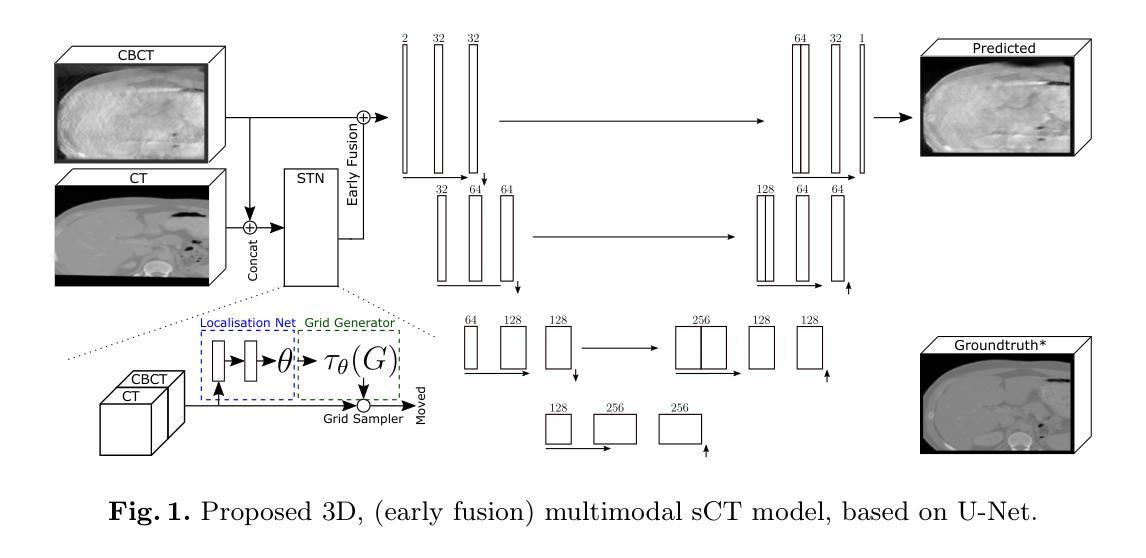
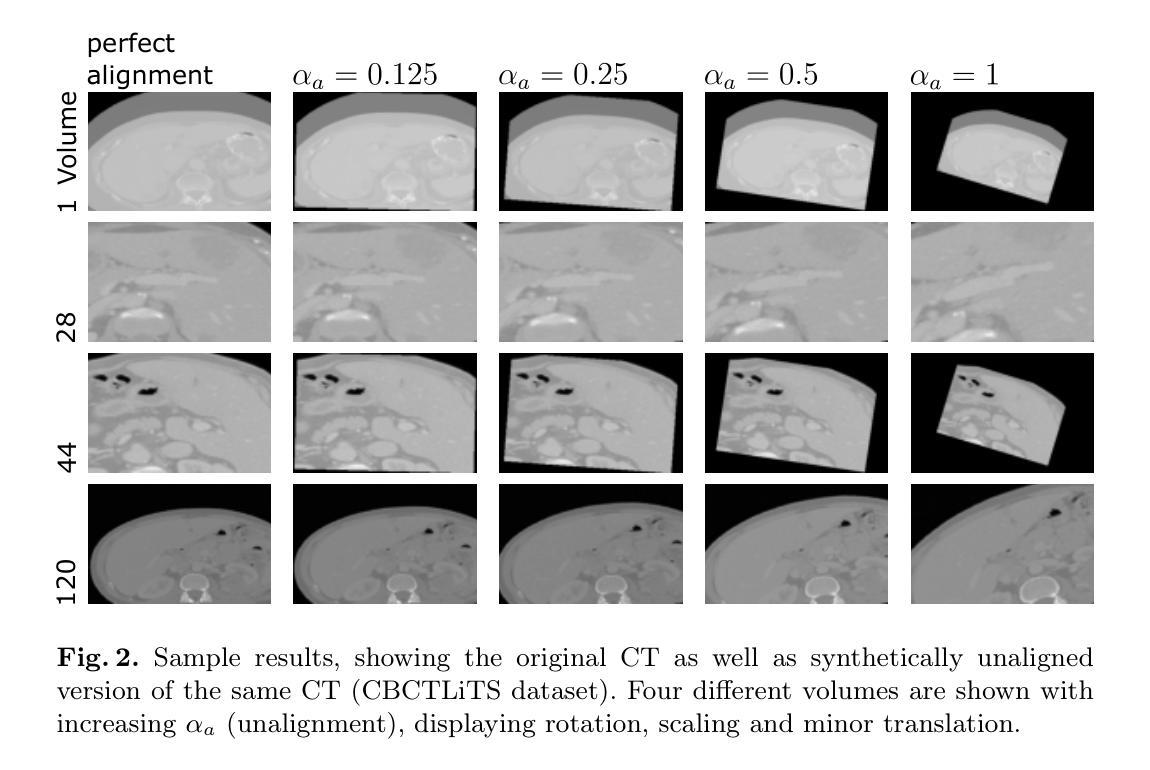
Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) is widely used for intraoperative imaging due to its rapid acquisition and low radiation dose. However, CBCT images typically suffer from artifacts and lower visual quality compared to conventional Computed Tomography (CT). A promising solution is synthetic CT (sCT) generation, where CBCT volumes are translated into the CT domain. In this work, we enhance sCT generation through multimodal learning by jointly leveraging intraoperative CBCT and preoperative CT data. To overcome the inherent misalignment between modalities, we introduce an end-to-end learnable registration module within the sCT pipeline. This model is evaluated on a controlled synthetic dataset, allowing precise manipulation of data quality and alignment parameters. Further, we validate its robustness and generalizability on two real-world clinical datasets. Experimental results demonstrate that integrating registration in multimodal sCT generation improves sCT quality, outperforming baseline multimodal methods in 79 out of 90 evaluation settings. Notably, the improvement is most significant in cases where CBCT quality is low and the preoperative CT is moderately misaligned.
锥束计算机断层扫描(CBCT)因其快速采集和低辐射剂量而广泛应用于术中成像。然而,与常规计算机断层扫描(CT)相比,CBCT图像通常存在伪影和视觉质量较低的问题。一种有前途的解决方案是生成合成CT(sCT),将CBCT体积转换为CT域。在这项工作中,我们通过多模态学习增强sCT生成,联合利用术中CBCT和术前CT数据。为了克服不同模态之间固有的不匹配问题,我们在sCT管道内引入了一个端到端可学习的注册模块。该模型在受控的合成数据集上进行评估,允许精确操纵数据质量和对齐参数。此外,我们在两个真实世界的临床数据集上验证了其稳健性和通用性。实验结果表明,在多功能sCT生成中集成注册功能可以提高sCT质量,在90个评估设置中,优于基线多功能方法79次。值得注意的是,在CBCT质量较低且术前CT中度错位的情况下,改进效果最为显著。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at CAIP 2025. arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2506.08716
Summary
基于锥形束计算机断层扫描(CBCT)的术中成像因快速采集和低辐射剂量而广泛应用,但其图像通常存在伪影和视觉质量较低的问题。本研究通过多模态学习增强合成CT(sCT)生成,利用术中CBCT和术前CT数据。为解决不同模态间固有的不匹配问题,我们在sCT管道中引入了端到端的可学习注册模块。该模型在合成数据集上进行了评估,允许精确操控数据质量和对齐参数。在两项真实世界临床数据集上的验证显示,其在多模态sCT生成中整合注册功能提高了sCT质量,在90个评估设置中,多模态基线方法被超越79次。在CBCT质量较低且术前CT中度错位的情况下,改进最为显著。
Key Takeaways
- CBCT广泛应用于术中成像,但图像质量低于传统CT。
- 多模态学习用于增强合成CT(sCT)生成。
- 解决不同模态间不匹配问题,引入端到端的可学习注册模块。
- 在合成数据集上评估模型性能,可精确控制数据质量和对齐参数。
- 模型在真实世界临床数据集上验证其稳健性和通用性。
- 实验结果表明,整合注册功能的多模态sCT生成能提高sCT质量。
点此查看论文截图

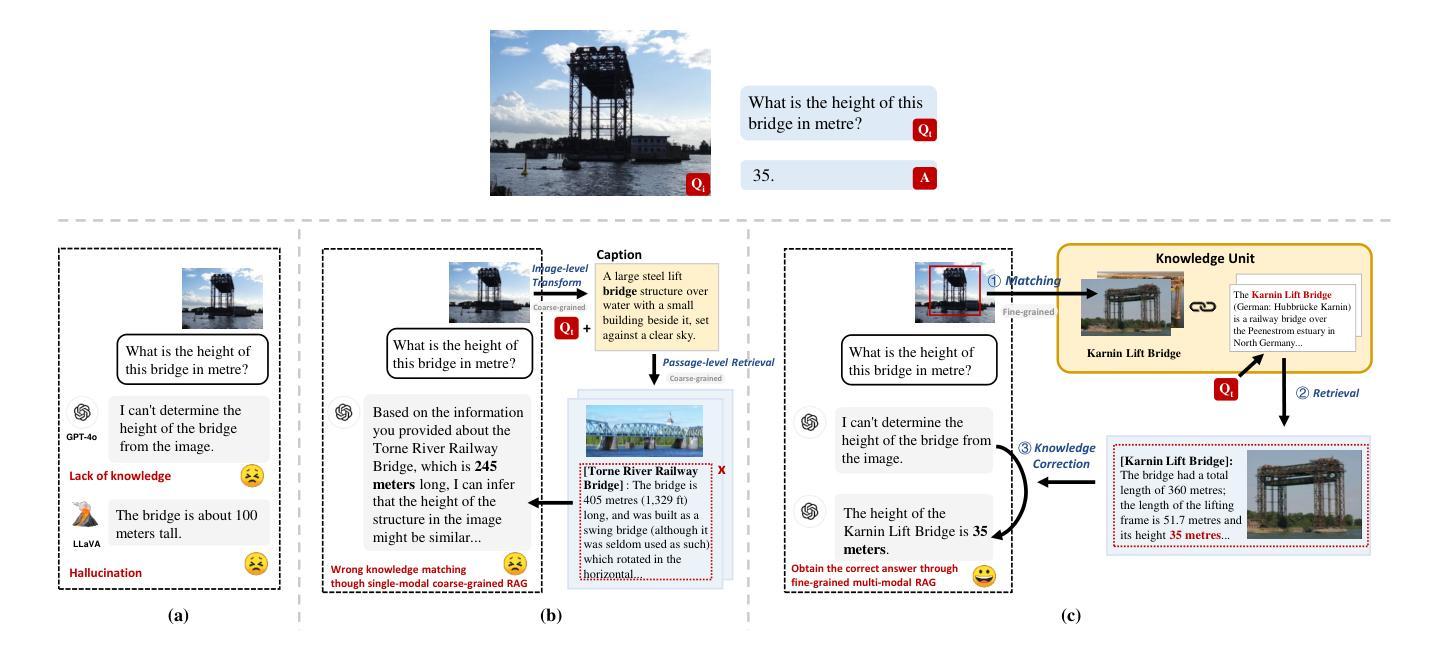
Fine-Grained Knowledge Structuring and Retrieval for Visual Question Answering
Authors:Zhengxuan Zhang, Yin Wu, Yuyu Luo, Nan Tang
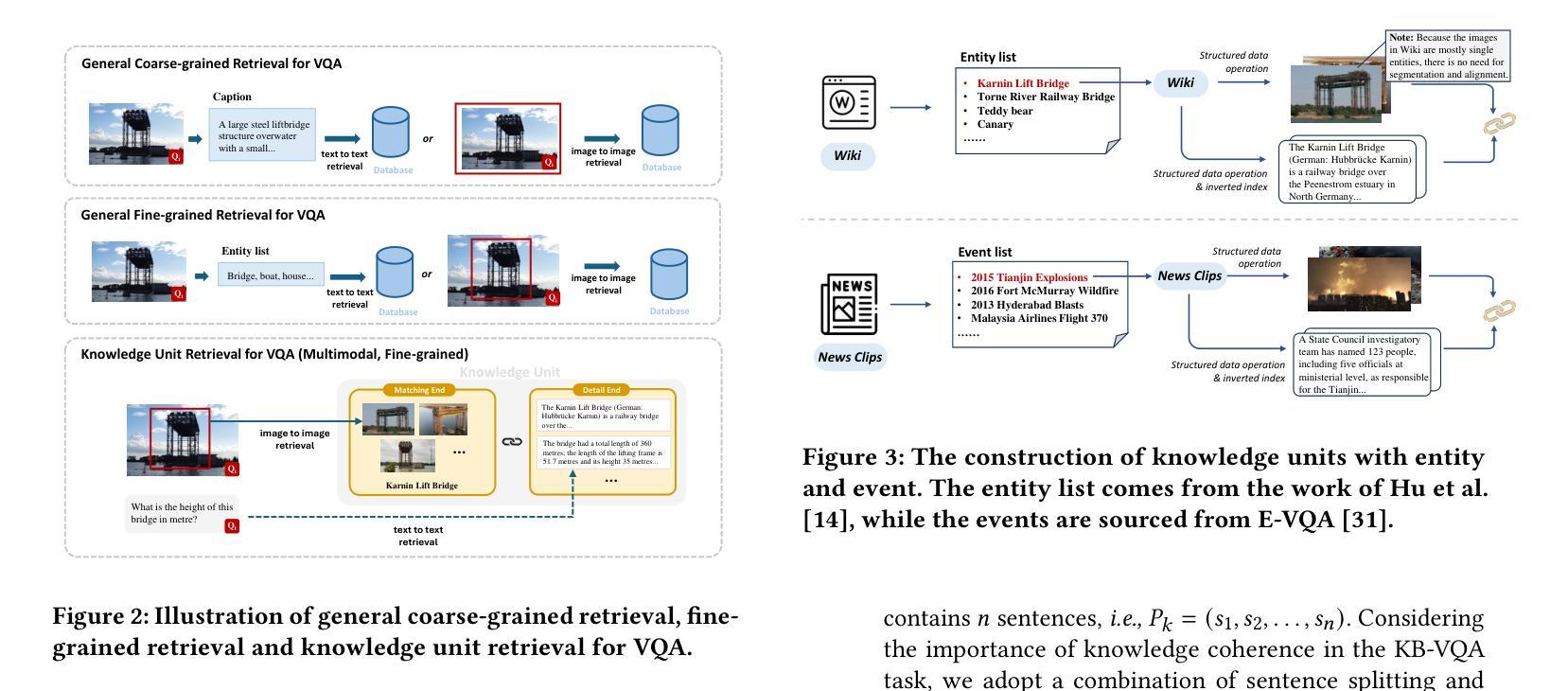
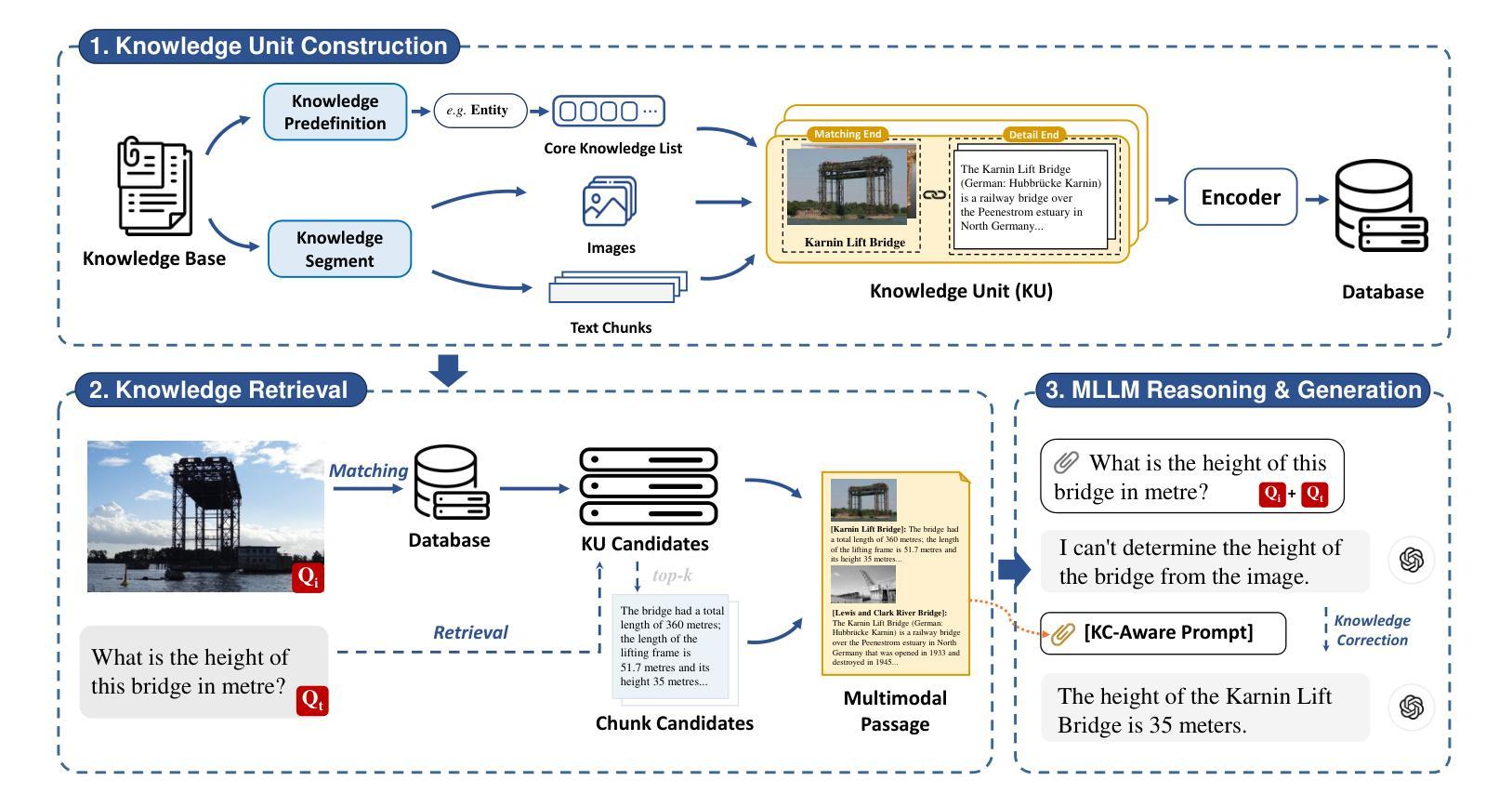
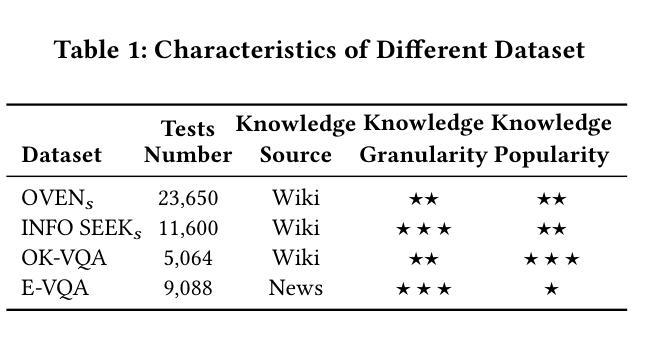
Visual Question Answering (VQA) focuses on providing answers to natural language questions by utilizing information from images. Although cutting-edge multimodal large language models (MLLMs) such as GPT-4o achieve strong performance on VQA tasks, they frequently fall short in accessing domain-specific or the latest knowledge. To mitigate this issue, retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) leveraging external knowledge bases (KBs), referred to as KB-VQA, emerges as a promising approach. Nevertheless, conventional unimodal retrieval techniques, which translate images into textual descriptions, often result in the loss of critical visual details. To address these challenges, this study presents two key innovations. First, we introduce fine-grained knowledge units that consist of multimodal data fragments (e.g. text fragments, entity images, and so on) in a structured manner. Rather than merely refining retrieval mechanisms, we prioritize the systematic organization and management of these knowledge units, ensuring that the structuring process itself enhances retrieval quality. Second, we propose a knowledge unit retrieval-augmented generation framework (KU-RAG) that seamlessly integrates fine-grained retrieval with MLLMs. Our KU-RAG framework not only ensures precise retrieval of relevant knowledge but also enhances reasoning capabilities through a knowledge correction chain. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms existing KB-VQA methods across four benchmarks, achieving an average improvement of approximately 3% and up to 11% in the best case.
视觉问答(VQA)专注于通过利用图像中的信息来提供对自然语言问题的答案。尽管最前沿的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)如GPT-4o在VQA任务上表现出强大的性能,但它们通常在访问特定领域或最新知识时显得不足。为了缓解这个问题,利用外部知识库(KBs)的检索增强生成(RAG)技术,被称为KB-VQA,作为一种有前途的方法而出现。然而,传统的单模态检索技术将图像翻译成文本描述,往往会导致关键视觉细节的丢失。为了应对这些挑战,本研究提出了两个关键的创新点。首先,我们引入了精细粒度的知识单元,它们由多模态数据片段(如文本片段、实体图像等)以结构化的方式组成。我们优先重视这些知识单元的系统组织和管理,确保结构化过程本身提高检索质量,而不仅仅是改进检索机制。其次,我们提出了一个知识单元检索增强生成框架(KU-RAG),该框架无缝集成了精细粒度的检索与MLLMs。我们的KU-RAG框架不仅确保精确检索相关知识,而且通过知识校正链增强推理能力。实验结果表明,我们的方法在所有四个基准测试中始终优于现有的KB-VQA方法,平均提高了约3%的性能,在最佳情况下提高了高达11%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了视觉问答(VQA)领域的一个研究,该研究针对当前多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在访问特定领域或最新知识方面的不足,提出了利用外部知识库的检索增强生成(RAG)方法。研究中引入了精细知识单元和多模态数据片段的结构化组织,提出了一种知识单元检索增强生成框架(KU-RAG),该框架不仅确保了相关知识的精确检索,而且通过知识校正链增强了推理能力。实验结果表明,该方法在四个基准测试中均优于现有的KB-VQA方法,平均提高了约3%,最高提高了11%。
Key Takeaways
- VQA领域关注通过图像信息回答自然语言问题。
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在VQA任务上表现出强大的性能,但在访问特定领域或最新知识方面存在不足。
- 引入知识单元(fine-grained knowledge units)和多模态数据片段的结构化组织来解决挑战。
- 提出知识单元检索增强生成框架(KU-RAG),结合了精细检索和MLLMs。
- KU-RAG确保了相关知识的精确检索并增强了推理能力。
- 实验结果显示KU-RAG在四个基准测试中表现优异,平均提升约3%,最高提升达11%。
- 该研究为VQA领域提供了一个新的、有效的解决方案,特别是在处理特定领域或最新知识时。
点此查看论文截图

A Comprehensive Solution for Whole-Brain multi-pool CEST Imaging at 3T based on single-shot True FISP readout: Towards Homogeneous, Multi-Parameter and High Repeatability
Authors:Yupeng Wu, Siyuan Fang, Siyuan Wang, Caixia Fu, Jianqi Li
Purpose: To develop and validate a comprehensive, rapid, and reproducible solution for whole-brain, multi-pool CEST imaging at 3T, overcoming key barriers to clinical translation such as long acquisition times and inaccuracies from field inhomogeneities. Methods: This study integrated a single-shot 3D True FISP readout sequence for efficient whole-brain CEST data acquisition. A streamlined workflow was developed to acquire B0, B1, and T1 maps for correction. To overcome the time-consuming nature of traditional B1 correction, we implemented a machine learning-based method to perform rapid B1 correction using data from a single B1 power acquisition. Data were analyzed using a four-pool Lorentzian model to derive quantitative metrics, including MTRLD and the AREX. The method’s accuracy was validated in phantoms and its test-retest reproducibility was assessed in healthy volunteers across 96 brain regions. Results: The True FISP sequence acquired high-quality, whole-brain images free of major artifacts. The neural network accurately replicated the gold-standard three-point B1 correction, achieving excellent intraclass correlation (ICC > 0.97) in human subjects. The AREX metric successfully corrected for T1 and MT confounders, reducing the CV from 35.4% to 9.2% in phantoms. The complete pipeline, including Z-spectrum and correction maps, took approximately 9 minutes. The method demonstrated high region-level reproducibility, with the average CV for APT_AREX under 10% for most brain regions across test-retest scans. Conclusion: This study presents a validated, end-to-end solution for whole-brain, multi-pool CEST imaging. By combining an efficient sequence with a rapid, AI-driven correction pipeline and robust quantitative analysis, our method delivers high-fidelity, reproducible, and quantitative multi-parameter maps of brain metabolism in a clinically acceptable timeframe.
目的:旨在开发并验证一种全面、快速、可重复的3T全脑多池CEST成像解决方案,克服临床翻译中的关键障碍,如长时间的采集时间和由场不均匀性引起的不准确。方法:本研究结合了单发射3D True FISP读出序列,以实现高效的全脑CEST数据采集。为了获取B0、B1和T1图进行校正,开发了一个简化的工作流程。为了克服传统的B1校正耗时长的缺点,我们实施了一种基于机器学习的方法进行快速B1校正,使用单个B1功率采集的数据。数据使用四池洛伦兹模型进行分析,以得出定量指标,包括MTRLD和AREX。该方法的准确性在幻影中得到了验证,其在96个脑区的测试再测试重现性也在健康志愿者中得到了评估。结果:True FISP序列获取了高质量的全脑图像,无主要伪影。神经网络准确地复制了金标准三点B1校正,在人类受试者中达到了很高的组内相关系数(ICC> 0.97)。AREX指标成功地校正了T1和MT干扰因素,将幻影中的变异系数从35.4%降低到9.2%。完整的流程,包括Z光谱和校正映射图,大约需要9分钟。该方法表现出高度的区域重现性,大多数脑区在测试再测试扫描中APT_AREX的平均变异系数低于10%。结论:本研究提出了一种经过验证的全脑多池CEST成像端到端解决方案。通过将高效的序列与快速、人工智能驱动的校正管道和稳健的定量分析相结合,我们的方法能够在临床上可接受的时间内提供高保真、可重复和定量的脑代谢多参数图。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Keywords: CEST, whole-brain, multi-pool, true fast imaging with steady-state precession (True FISP), balanced steady state free precession (bSSFP)
Summary
本研究旨在开发并验证一种全面、快速、可重复的针对全脑多池化学交换饱和转移成像(CEST)的解决策略,该策略在3T环境下克服了长采集时间和场不均匀性所带来的关键临床翻译障碍。通过结合高效序列、快速的人工智能驱动校正管道和稳健的定量分析,该方法提供了高保真、可重复和定量的脑代谢多参数地图,在可接受的临床时间内实现全脑成像。
Key Takeaways
- 研究目的是开发并验证一种针对全脑多池CEST成像的快速、全面且可重复的解决方案。
- 通过整合单发射3D True FISP读出序列,实现了高效的全脑CEST数据采集。
- 研究开发了一种简化的工作流程,用于获取B0、B1和T1地图以进行校正。
- 实施了一种基于机器学习的方法,使用单次B1功率采集数据进行快速B1校正,克服了传统B1校正的时间消耗。
- 利用四池洛伦兹模型对数据进行分析,得出包括MTRLD和AREX在内的定量指标。
- 在 Phantom 和健康志愿者中的96个脑区进行了方法的准确性和测试再测试可重复性的验证。
点此查看论文截图