⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-10 更新
A Survey on Latent Reasoning
Authors:Rui-Jie Zhu, Tianhao Peng, Tianhao Cheng, Xingwei Qu, Jinfa Huang, Dawei Zhu, Hao Wang, Kaiwen Xue, Xuanliang Zhang, Yong Shan, Tianle Cai, Taylor Kergan, Assel Kembay, Andrew Smith, Chenghua Lin, Binh Nguyen, Yuqi Pan, Yuhong Chou, Zefan Cai, Zhenhe Wu, Yongchi Zhao, Tianyu Liu, Jian Yang, Wangchunshu Zhou, Chujie Zheng, Chongxuan Li, Yuyin Zhou, Zhoujun Li, Zhaoxiang Zhang, Jiaheng Liu, Ge Zhang, Wenhao Huang, Jason Eshraghian
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive reasoning capabilities, especially when guided by explicit chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning that verbalizes intermediate steps. While CoT improves both interpretability and accuracy, its dependence on natural language reasoning limits the model’s expressive bandwidth. Latent reasoning tackles this bottleneck by performing multi-step inference entirely in the model’s continuous hidden state, eliminating token-level supervision. To advance latent reasoning research, this survey provides a comprehensive overview of the emerging field of latent reasoning. We begin by examining the foundational role of neural network layers as the computational substrate for reasoning, highlighting how hierarchical representations support complex transformations. Next, we explore diverse latent reasoning methodologies, including activation-based recurrence, hidden state propagation, and fine-tuning strategies that compress or internalize explicit reasoning traces. Finally, we discuss advanced paradigms such as infinite-depth latent reasoning via masked diffusion models, which enable globally consistent and reversible reasoning processes. By unifying these perspectives, we aim to clarify the conceptual landscape of latent reasoning and chart future directions for research at the frontier of LLM cognition. An associated GitHub repository collecting the latest papers and repos is available at: https://github.com/multimodal-art-projection/LatentCoT-Horizon/.
大型语言模型(LLM)已经展现出令人印象深刻的推理能力,特别是在明确的思维链(CoT)推理引导下,能够口头表达中间步骤。虽然思维链提高了可解释性和准确性,但它对自然语言推理的依赖限制了模型的表达带宽。潜在推理通过完全在模型的连续隐藏状态中进行多步推理来解决这一瓶颈,从而消除了基于符号的监督。为了推动潜在推理研究的发展,这篇综述对新兴的领域提供了全面的概述。我们首先考察神经网络层作为计算基础的基石作用,强调层次化表示如何支持复杂转换。接下来,我们探索了多种潜在推理方法,包括基于激活的递归、隐藏状态传播以及微调策略等,这些策略可以压缩或内化显性推理痕迹。最后,我们讨论了先进的范式,如通过掩码扩散模型实现无限深度的潜在推理,这使得全局一致性和可逆的推理过程成为可能。通过统一这些观点,我们旨在澄清潜在推理的概念景观,并为大型语言模型认知前沿的研究指明未来方向。相关的GitHub仓库收集了最新的论文和存储库,可供访问:https://github.com/multimodal-art-projection/LatentCoT-Horizon/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)通过显式思维链(CoT)指导展现出令人印象深刻的推理能力,CoT能够表述中间步骤,提高可解释性和准确性。然而,CoT对自然语言推理的依赖限制了模型的表达带宽。潜在推理通过完全在模型的连续隐藏状态中进行多步推理来解决这一瓶颈,无需令牌级别的监督。这篇综述对潜在推理这一新兴领域进行了全面的概述,从神经网络层作为推理的计算基元出发,探讨了层次表示如何支持复杂变换。接着探索了多种潜在推理方法,包括基于激活的复发、隐藏状态传播以及精细调整策略以压缩或内化显式推理痕迹。最后讨论了通过掩模扩散模型实现无限深度潜在推理等先进范式,使全局一致性和可逆推理过程成为可能。旨在统一这些观点,澄清潜在推理的概念格局,并为LLM认知研究的前沿指明未来研究方向。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)通过显式思维链(CoT)展现出强大的推理能力,但存在表达带宽限制。
- 潜在推理方法旨在解决这一瓶颈,完全在模型的连续隐藏状态中进行多步推理,无需令牌级别的监督。
- 神经网络层作为推理的计算基元,层次表示支持复杂变换。
- 多种潜在推理方法包括基于激活的复发、隐藏状态传播以及精细调整策略。
- 无限深度潜在推理通过掩模扩散模型实现,使全局一致性和可逆推理过程成为可能。
- 综述旨在统一潜在推理的不同观点,澄清概念格局。
点此查看论文截图

Skywork-R1V3 Technical Report
Authors:Wei Shen, Jiangbo Pei, Yi Peng, Xuchen Song, Yang Liu, Jian Peng, Haofeng Sun, Yunzhuo Hao, Peiyu Wang, Yahui Zhou
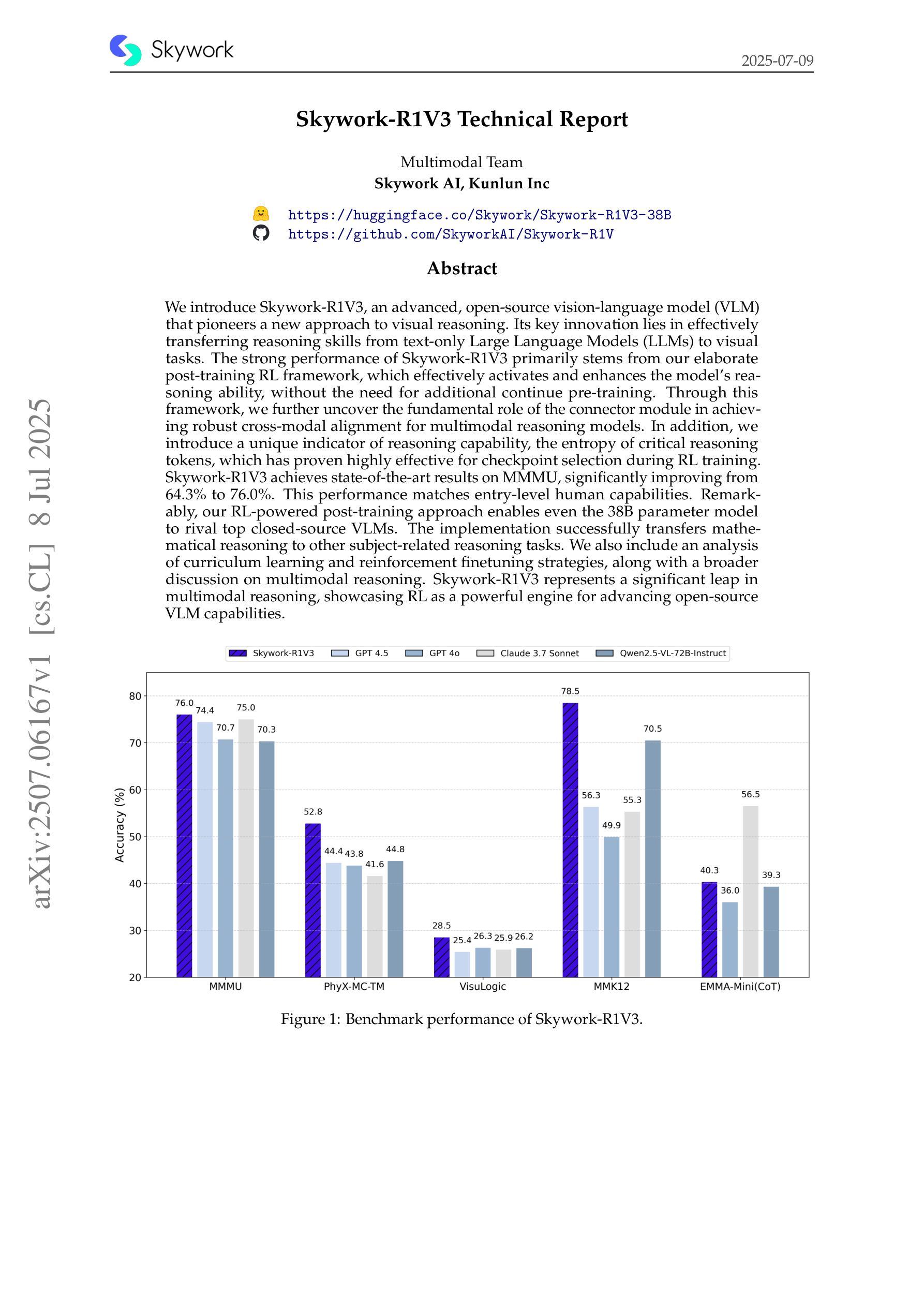
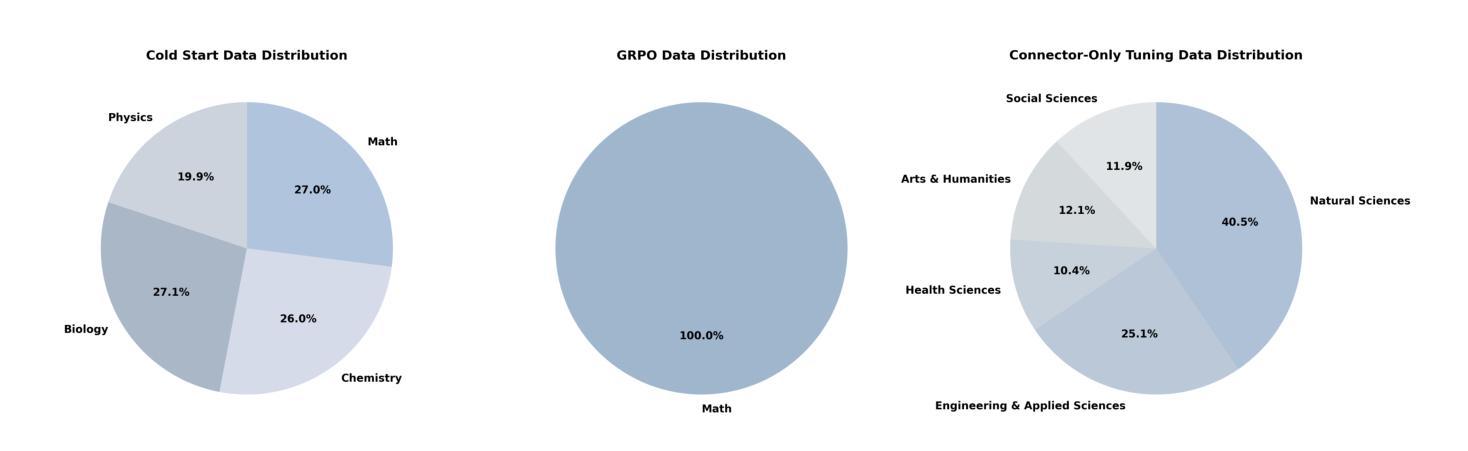
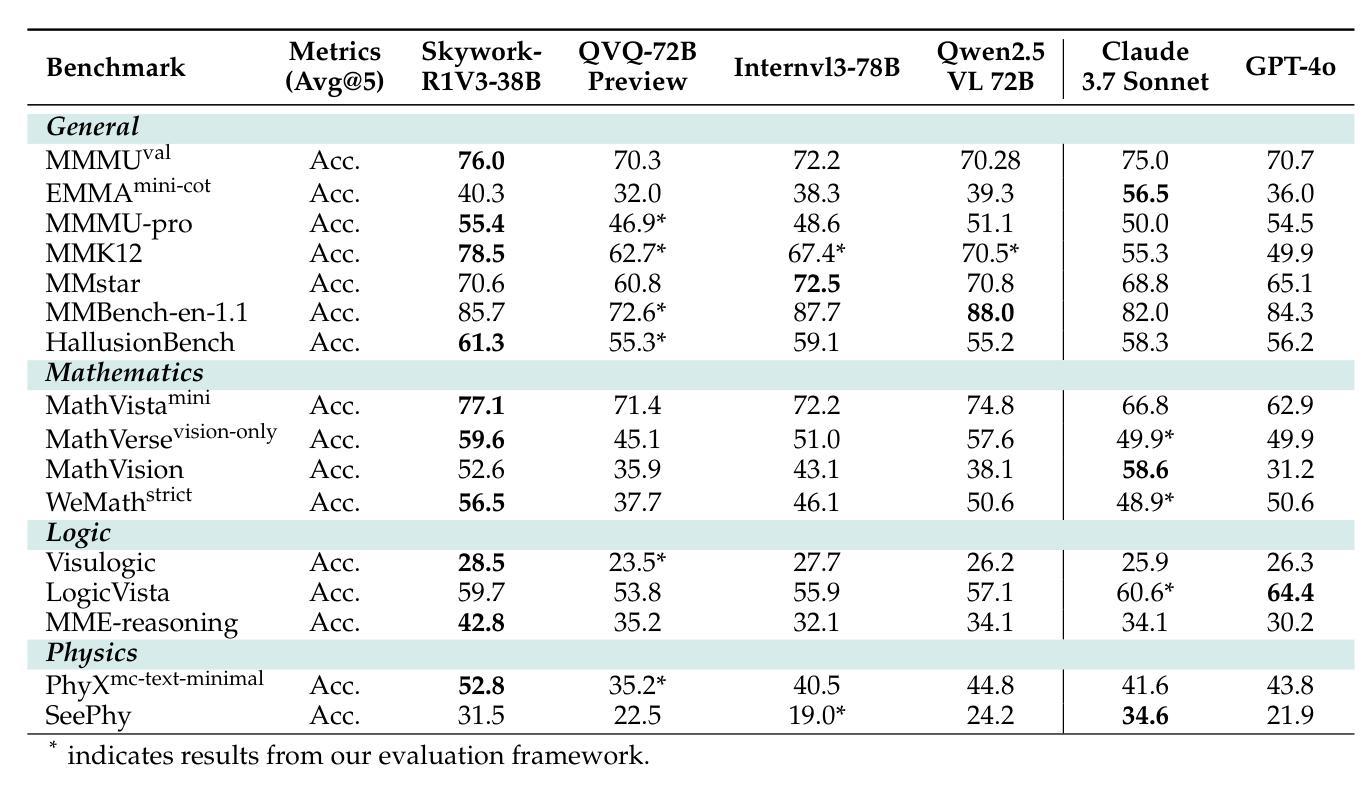
We introduce Skywork-R1V3, an advanced, open-source vision-language model (VLM) that pioneers a new approach to visual reasoning. Its key innovation lies in effectively transferring reasoning skills from text-only Large Language Models (LLMs) to visual tasks. The strong performance of Skywork-R1V3 primarily stems from our elaborate post-training RL framework, which effectively activates and enhances the model’s reasoning ability, without the need for additional continue pre-training. Through this framework, we further uncover the fundamental role of the connector module in achieving robust cross-modal alignment for multimodal reasoning models. In addition, we introduce a unique indicator of reasoning capability, the entropy of critical reasoning tokens, which has proven highly effective for checkpoint selection during RL training. Skywork-R1V3 achieves state-of-the-art results on MMMU, significantly improving from 64.3% to 76.0%. This performance matches entry-level human capabilities. Remarkably, our RL-powered post-training approach enables even the 38B parameter model to rival top closed-source VLMs. The implementation successfully transfers mathematical reasoning to other subject-related reasoning tasks. We also include an analysis of curriculum learning and reinforcement finetuning strategies, along with a broader discussion on multimodal reasoning. Skywork-R1V3 represents a significant leap in multimodal reasoning, showcasing RL as a powerful engine for advancing open-source VLM capabilities.
我们介绍了Skywork-R1V3,这是一个先进的开源视觉语言模型(VLM),它开创了一种新的视觉推理方法。其主要创新在于有效地将从文本中获取的推理能力转移到视觉任务上。Skywork-R1V3的出色表现主要源于我们精心设计的后训练强化学习(RL)框架,该框架有效地激活并增强了模型的推理能力,无需额外的继续预训练。通过这个框架,我们进一步发现了连接器模块在实现稳健的跨模态对齐中的基础作用,这对于多模态推理模型至关重要。此外,我们引入了独特的推理能力指标——关键推理代币的熵,这在强化学习训练的检查点选择中被证明是非常有效的。Skywork-R1V3在MMMU上取得了最新结果,从64.3%显著提高到76.0%。这种性能与入门级人类能力相匹配。值得注意的是,我们的基于强化学习的后训练法甚至使38B参数模型能够与顶级闭源VLM相竞争。该实现成功地将数学推理转移到其他相关推理任务上。我们还包括对课程学习和强化微调策略的分析,以及对多模态推理的更广泛讨论。Skywork-R1V3在多模态推理中代表了一个重大飞跃,展示了强化学习作为推动开源VLM能力发展的强大引擎。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
Skywork-R1V3是一款先进的开源视觉语言模型(VLM),它开创了一种新的视觉推理方法。该模型的关键创新在于有效地将纯文本大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力转移到视觉任务上。其强大的性能主要来自于精细的基于强化学习(RL)的后期训练框架,该框架能够激活并增强模型的推理能力,无需额外的连续预训练。Skywork-R1V3在MMMU上实现了最新结果,其性能与人类入门级能力相匹配。
Key Takeaways
- Skywork-R1V3是一个先进的开源视觉语言模型,具有强大的视觉推理能力。
- 该模型成功地将纯文本大型语言模型的推理能力转移到视觉任务上。
- Skywork-R1V3采用基于强化学习的后期训练框架,提高了模型的推理能力。
- 引入了推理能力的新指标——关键推理令牌熵,用于RL训练过程中的检查点选择。
- Skywork-R1V3在MMMU上的性能达到了最新水平,与人类入门级能力相匹配。
- 该模型实现了数学推理向其他相关推理任务的成功转移。
点此查看论文截图
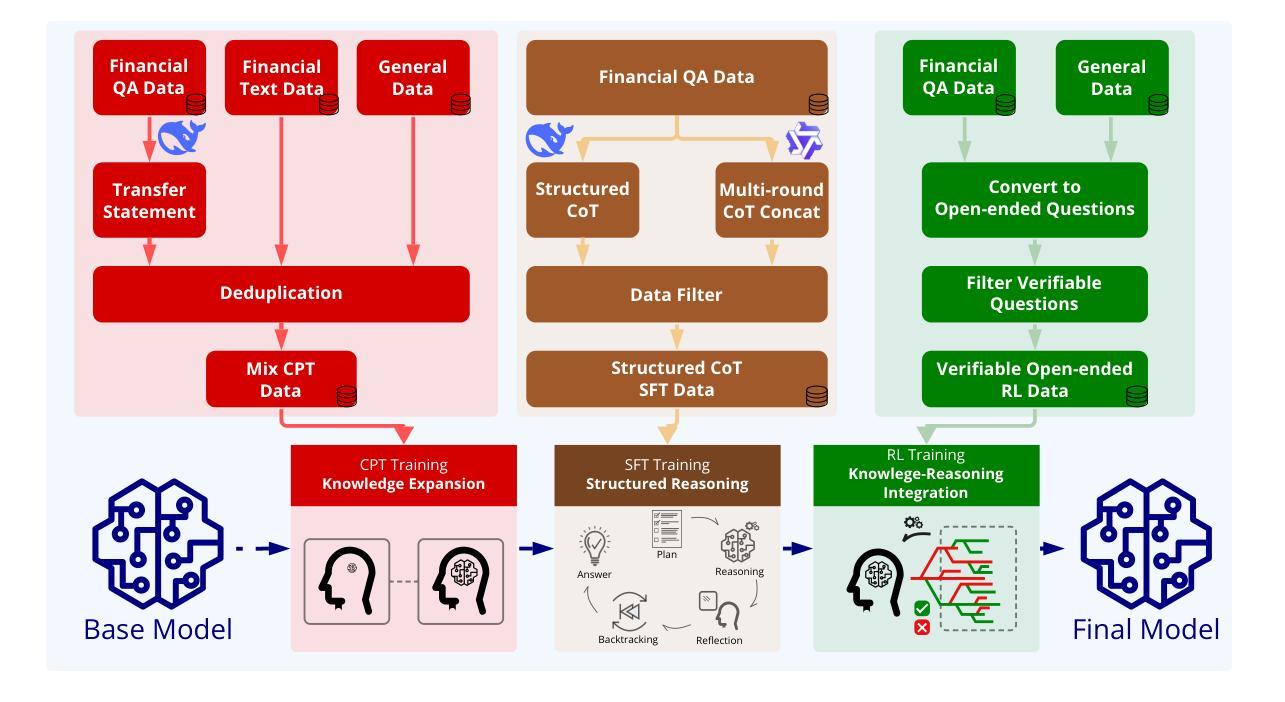
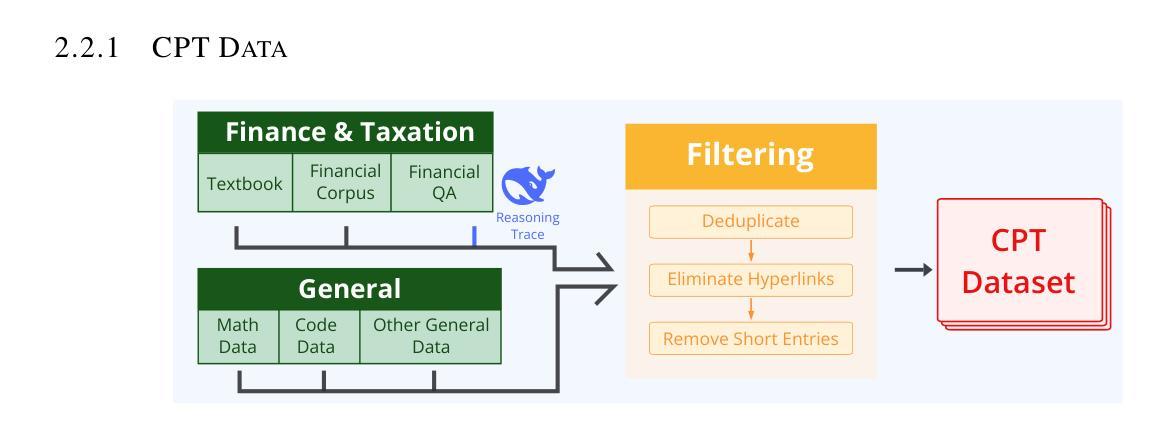
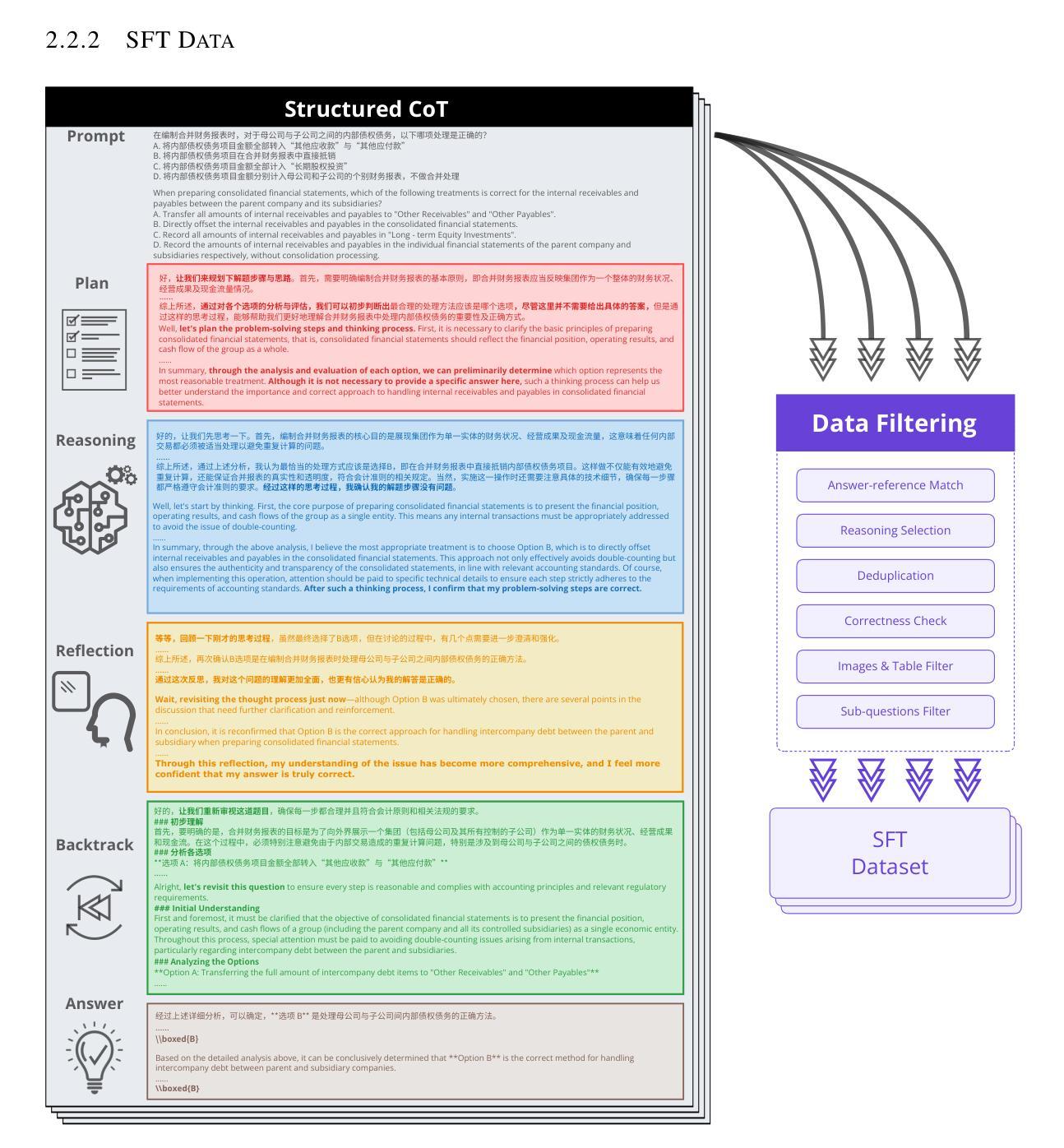
FEVO: Financial Knowledge Expansion and Reasoning Evolution for Large Language Models
Authors:Bo Pang, Yalu Ouyang, Hangfei Xu, Ziqi Jia, Panpan Li, Shengzhao Wen, Lu Wang, Shiyong Li, Yanpeng Wang
Advancements in reasoning for large language models (LLMs) have lead to significant performance improvements for LLMs in various fields such as mathematics and programming. However, research applying these advances to the financial domain, where considerable domain-specific knowledge is necessary to complete tasks, remains limited. To address this gap, we introduce FEVO (Financial Evolution), a multi-stage enhancement framework developed to enhance LLM performance in the financial domain. FEVO systemically enhances LLM performance by using continued pre-training (CPT) to expand financial domain knowledge, supervised fine-tuning (SFT) to instill structured, elaborate reasoning patterns, and reinforcement learning (RL) to further integrate the expanded financial domain knowledge with the learned structured reasoning. To ensure effective and efficient training, we leverage frontier reasoning models and rule-based filtering to curate FEVO-Train, high-quality datasets specifically designed for the different post-training phases. Using our framework, we train the FEVO series of models – C32B, S32B, R32B – from Qwen2.5-32B and evaluate them on seven benchmarks to assess financial and general capabilities, with results showing that FEVO-R32B achieves state-of-the-art performance on five financial benchmarks against much larger models as well as specialist models. More significantly, FEVO-R32B demonstrates markedly better performance than FEVO-R32B-0 (trained from Qwen2.5-32B-Instruct using only RL), thus validating the effectiveness of financial domain knowledge expansion and structured, logical reasoning distillation
在大型语言模型(LLM)的推理技术方面取得的进展,已经大大提高了LLM在数学、编程等领域中的性能。然而,将这些进展应用于金融领域的研究仍然有限,完成金融领域的任务需要大量的领域特定知识。为了弥补这一空白,我们引入了FEVO(金融进化),这是一个为增强LLM在金融领域的性能而开发的多阶段增强框架。FEVO系统通过持续预训练(CPT)来扩展金融领域知识,通过监督微调(SFT)来灌输结构化、精细的推理模式,以及通过强化学习(RL)来进一步将扩展的金融领域知识与学到的结构化推理相结合,从而提高LLM的性能。为了确保有效和高效的训练,我们利用前沿的推理模型和基于规则的过滤来创建专门为不同后训练阶段设计的FEVO-Train高质量数据集。使用我们的框架,我们训练了FEVO系列模型——C32B、S32B、R32B,它们以Qwen2.5-32B为基础,并在七个基准测试上评估它们的金融和一般能力。结果表明,FEVO-R32B在五个金融基准测试上达到了最先进的性能,与更大的模型以及专业模型相比具有优势。更重要的是,FEVO-R32B的性能明显优于FEVO-R32B-0(以Qwen2.5-32B-Instruct为基础仅使用RL进行训练),从而验证了金融领域知识扩展和结构化、逻辑推理蒸馏的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大语言模型(LLM)在推理方面的进展已经提升了其在数学、编程等领域的应用性能。然而,将这一进展应用于金融领域的研究仍然有限,金融领域需要特定的专业知识来完成任务。为解决这一空白,我们推出了FEVO(金融进化),这是一个多阶段增强框架,旨在提高LLM在金融领域的性能。通过继续预训练(CPT)来扩展金融领域知识,通过监督微调(SFT)来培养结构化、精细的推理模式,以及通过强化学习(RL)来进一步将扩展的金融领域知识与学习的结构化推理相结合,系统性地提高LLM的性能。我们训练了FEVO系列模型——C32B、S32B、R32B,并在七个基准测试上评估了它们的金融和一般能力,结果显示FEVO-R32B在五个金融基准测试上达到了最新技术性能,并且在针对更大模型和专家模型的比较中也表现出色。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在推理方面的进步已应用于多个领域,但在金融领域的应用仍然有限。
- FEVO是一个多阶段增强框架,旨在提高LLM在金融领域的性能。
- FEVO使用继续预训练(CPT)来扩展金融知识,监督微调(SFT)培养结构化推理,强化学习(RL)整合知识与推理。
- FEVO系列模型——C32B、S32B、R32B已训练,并在多个基准测试中表现优异。
- FEVO-R32B在五个金融基准测试上达到最新技术性能,并在与更大模型和专家模型的比较中表现突出。
- FEVO框架的有效性得到了验证,通过比较FEVO-R32B与仅使用RL训练的FEVO-R32B-0的性能差异。
- FEVO框架为金融领域的大语言模型应用开辟了新途径,有望推动金融领域的AI技术发展。
点此查看论文截图


CogniSQL-R1-Zero: Lightweight Reinforced Reasoning for Efficient SQL Generation
Authors:Kushal Gajjar, Harshit Sikchi, Arpit Singh Gautam, Marc Hammons, Saurabh Jha
Translating natural language into SQL (Text-to-SQL) remains a core challenge at the intersection of language understanding and structured data access. Although large language models (LLMs) have improved fluency, generating correct and executable SQL, especially for complex queries, continues to be challenging. We introduce CogniSQL-R1-Zero, a reinforcement learning (RL) framework and model that produces accurate SQL using a lightweight reward signal based on execution correctness and format-tag compliance. By avoiding intermediate supervision, hybrid pipelines and complex reward shaping, our method encourages stable learning and stronger alignment with the ultimate task objective-producing executable programs. CogniSQL-R1-Zero achieves state-of-the-art execution accuracy on Text2SQL benchmark; BIRD bench, outperforming prior supervised and instruction-tuned baselines including SFT CodeS-7B, DeepSeek-Coder 236B, and Mistral 123B-despite being trained on a significantly smaller 7B backbone. This result underscores the scalability and efficiency of our RL-based approach when trained on just four NVIDIA A100 GPUs (40 GB VRAM each). To support further research in efficient and interpretable Text-to-SQL modeling, we release two curated datasets: (i) a collection of 5,024 reasoning traces with varying context lengths, and (ii) a positive-sampled corpus of 36,356 corpus of weakly supervised queries, each annotated with six semantically diverse reasoning paths. Together, these contributions advance scalable, execution-aligned Text-to-SQL generation.
将自然语言转换为SQL(文本到SQL)仍然是语言理解与结构化数据访问交叉点上的一个核心挑战。尽管大型语言模型(LLM)提高了流畅度,但生成正确且可执行的SQL,尤其是对于复杂查询,仍然具有挑战性。我们推出了CogniSQL-R1-Zero,这是一个基于强化学习(RL)的框架和模型,它使用基于执行正确性和格式标签符合度的轻量级奖励信号来生成准确的SQL。通过避免中间监督、混合管道和复杂的奖励塑造,我们的方法鼓励稳定的学习,并与最终任务目标——产生可执行程序——更紧密地结合。CogniSQL-R1-Zero在Text2SQL基准测试上实现了最先进的执行精度;BIRD基准测试,超越了先前的监督指令调优基线,包括SFT CodeS-7B、DeepSeek-Coder 236B和Mistral 123B,尽管它是在一个显著较小的7B主干上训练的。这一结果突出了我们的基于RL的方法在仅使用四台NVIDIA A100 GPU(每台40GB VRAM)进行训练时的可扩展性和效率。为了支持在高效和可解释的文本到SQL建模方面的进一步研究,我们发布了两个精选数据集:(i)包含5024个推理轨迹,具有不同的上下文长度,(ii)一个由弱监督查询组成的积极采样语料库,每个查询都标有六条语义上不同的推理路径。这些贡献共同推动了可扩展的、与执行对齐的文本到SQL生成。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了在自然语言到SQL转换(Text-to-SQL)领域的挑战,并引入了一种新的强化学习框架——CogniSQL-R1-Zero模型。该模型能够通过执行正确性和格式标签遵守的轻量级奖励信号来生成准确的SQL。在BIRD bench上的执行准确率达到了最新水平,尽管它的训练是基于较小的7B骨架完成的。此外,还发布了两个数据集以支持进一步的Text-to-SQL建模研究。
Key Takeaways
- Text-to-SQL转换是自然语言理解和结构化数据访问的交叉点的一个重要挑战。
- 尽管大型语言模型(LLMs)提高了流畅度,但生成正确且可执行的SQL对于复杂查询仍然具有挑战性。
- 引入了一种新的强化学习框架——CogniSQL-R1-Zero模型,能够准确生成SQL。
- 该模型使用轻量级奖励信号,基于执行正确性和格式标签遵守,避免中间监督、混合管道和复杂的奖励塑形。
- CogniSQL-R1-Zero在Text2SQL基准测试上达到了最先进的执行准确率,且训练基于较小的7B骨架完成。
- 发布了两个数据集以支持进一步的Text-to-SQL建模研究,包括包含不同上下文长度的推理轨迹集合和积极样本语料库。
点此查看论文截图

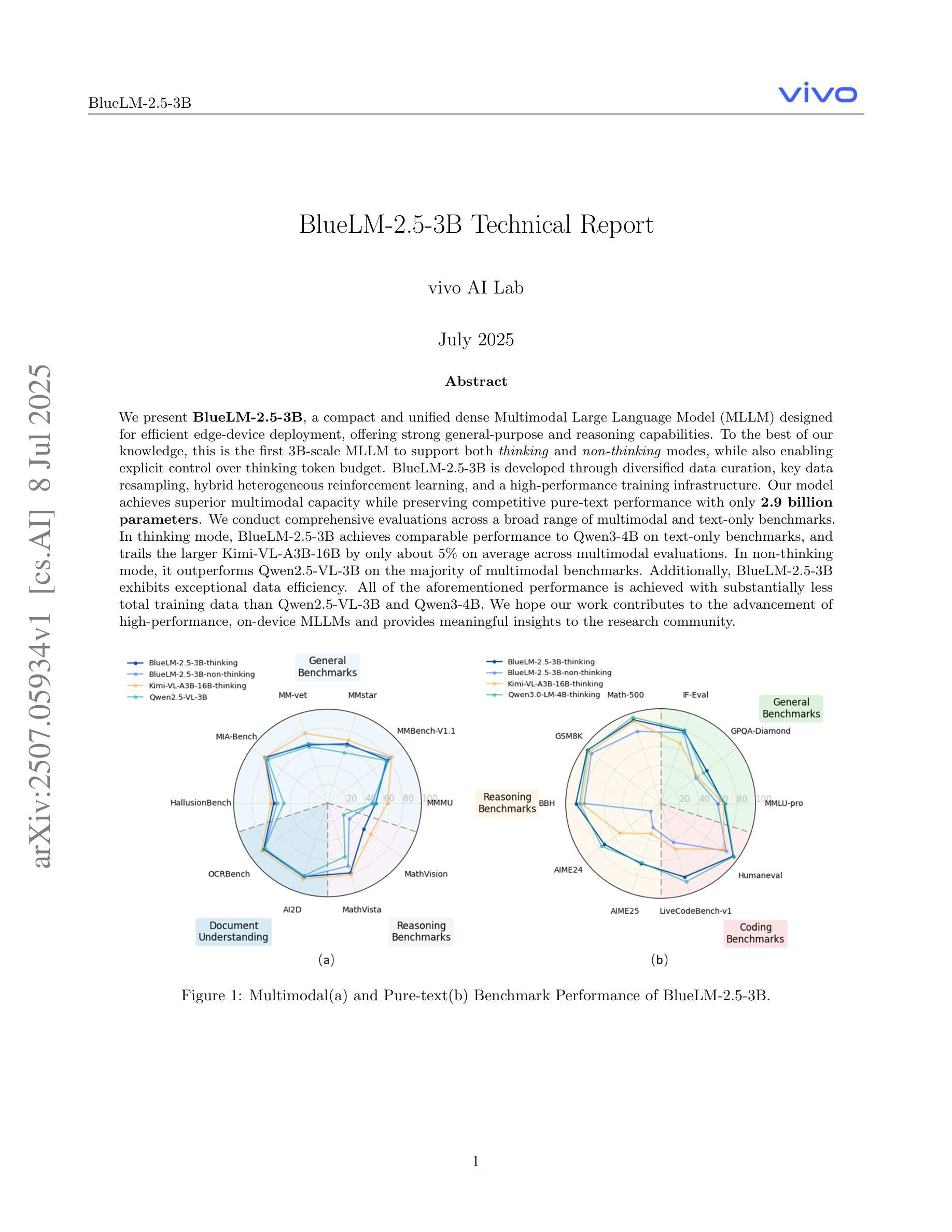
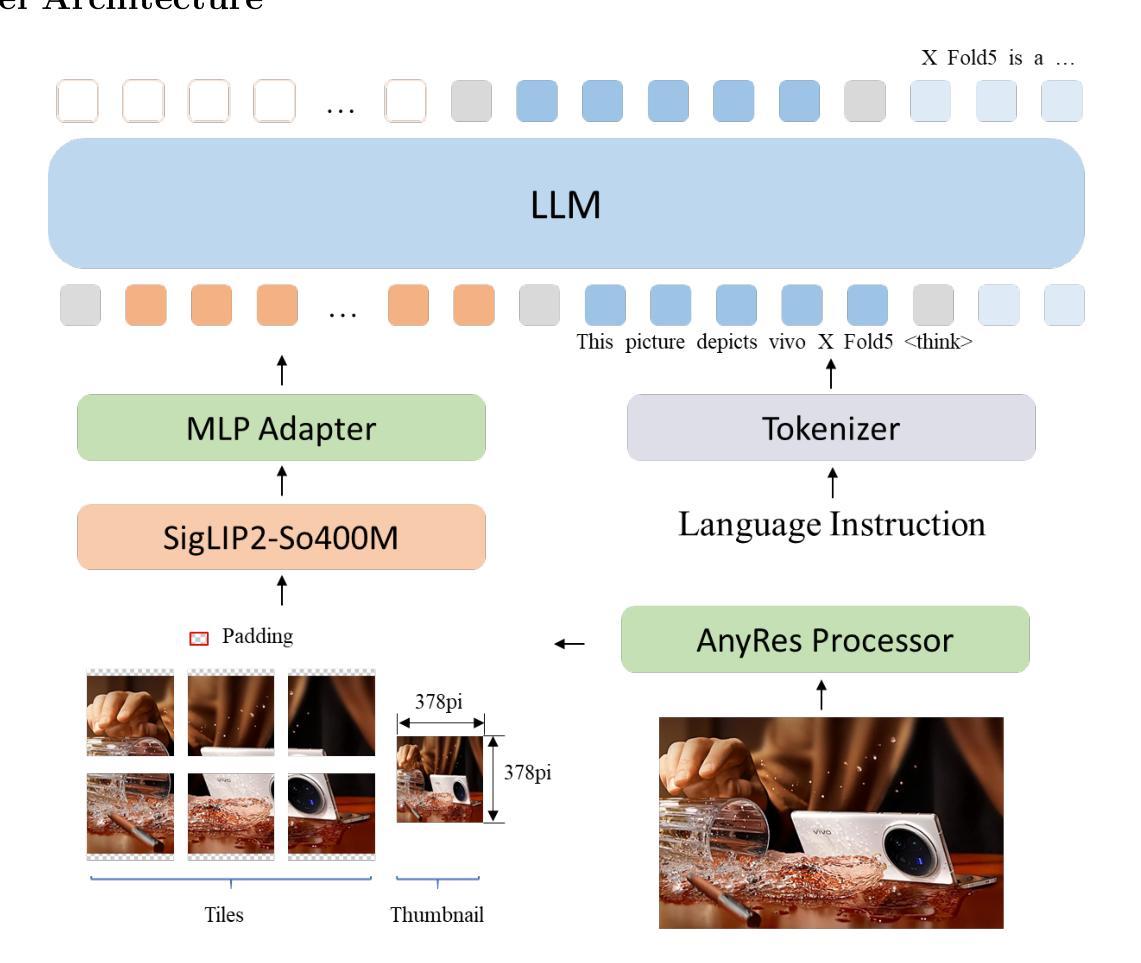
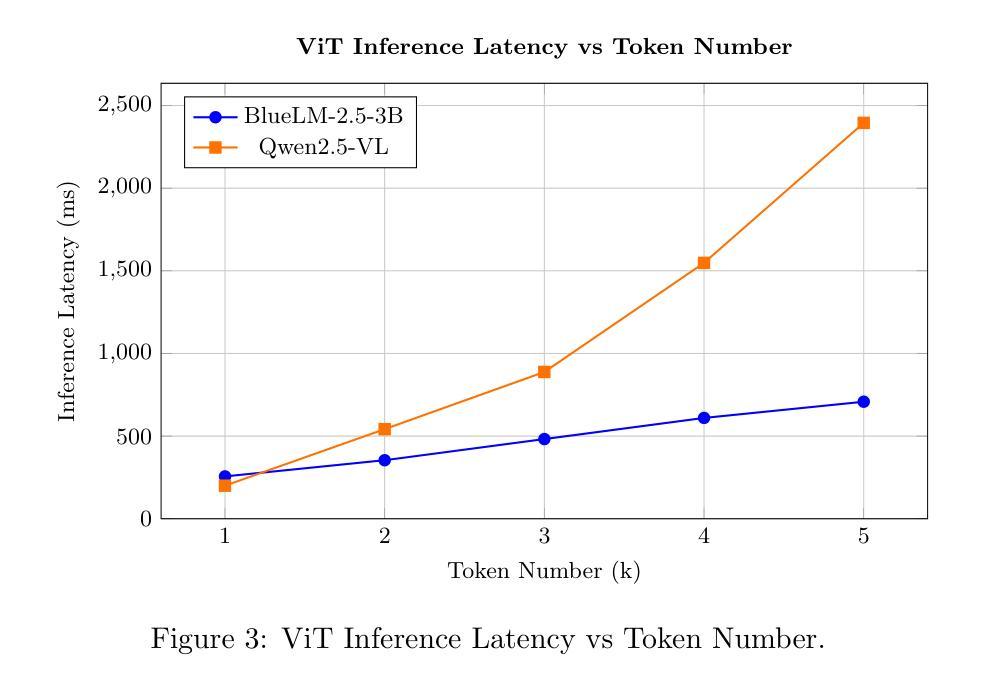
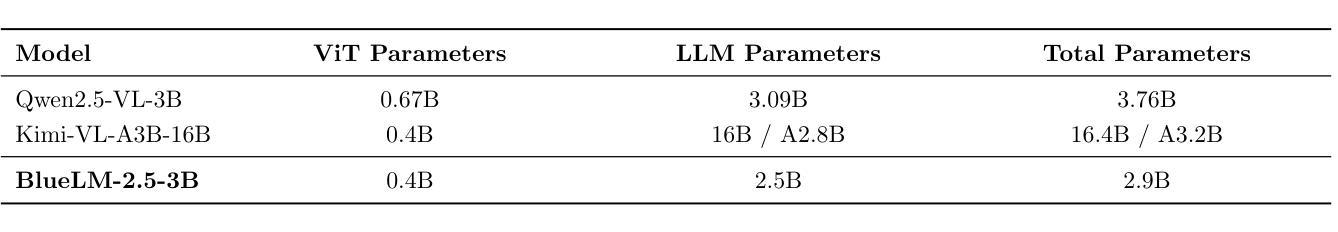
BlueLM-2.5-3B Technical Report
Authors:Baojiao Xiong, Boheng Chen, Chengzhi Wang, Daxiong Luo, Dongsheng Xu, Dongyang Liu, Fan Yang, Fangyuan Li, Fei Teng, Feng Wang, Fukang Qin, Fuquan Peng, Guanxin Tan, Guozhi Wang, Haibo Yu, Haohao Gao, Heng Liu, Hongbo Yang, Hongjian Zou, Houzheng Shen, Hu Meng, Huan Li, Hui Tan, Jiali Chen, Jianzhao Chen, Jinliang Zhu, Kai Wang, Lei Wu, Liangbing Liu, Liuyang Bian, Liyan He, Long Liu, Peiwen Li, Penggang Shi, Qi Ding, Rui Hu, Shuai Cao, Shuai Ren, Shuang Peng, Teng Xie, Weiji Chen, Weilin Xiang, Weixin Wu, Xi Yin, Xiaoxin Chen, Xu Chen, Yafei Wen, Yan Hu, Yanzhou Yang, Yina Xie, Yinghao Chen, Yixuan Liao, Yu Geng, Yuanjiang Ouyang, Yuanzhuo Yang, Yuehua He, Yushuai Peng, Zhaoxiong Wang, Zheng Wang, Zhibo Zhou, Ziyang Wu
We present BlueLM-2.5-3B, a compact and unified dense Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) designed for efficient edge-device deployment, offering strong general-purpose and reasoning capabilities. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first 3B-scale MLLM to support both thinking and non-thinking modes, while also enabling explicit control over thinking token budget. BlueLM-2.5-3B is developed through diversified data curation, key data resampling, hybrid heterogeneous reinforcement learning, and a high-performance training infrastructure. Our model achieves superior multimodal capacity while preserving competitive pure-text performance with only 2.9 billion parameters. We conduct comprehensive evaluations across a broad range of multimodal and text-only benchmarks. In thinking mode, BlueLM-2.5-3B achieves comparable performance to Qwen3-4B on text-only benchmarks, and trails the larger Kimi-VL-A3B-16B by only about 5% on average across multimodal evaluations. In non-thinking mode, it outperforms Qwen2.5-VL-3B on the majority of multimodal benchmarks. Additionally, BlueLM-2.5-3B exhibits exceptional data efficiency. All of the aforementioned performance is achieved with substantially less total training data than Qwen2.5-VL-3B and Qwen3-4B. We hope our work contributes to the advancement of high-performance, on-device MLLMs and provides meaningful insights to the research community.
我们推出BlueLM-2.5-3B,这是一款紧凑且统一的多模态大型语言模型(MLLM),专为边缘设备的有效部署而设计,具备强大的通用和推理能力。据我们所知,这是首个支持思考和非思考模式的3B规模MLLM,同时能够明确控制思考令牌预算。BlueLM-2.5-3B通过多样化数据收集、关键数据重新采样、混合异构增强学习和高性能训练基础设施而开发。我们的模型在保持仅2.9亿参数的同时,实现了卓越的多模态能力,并在多种多模态和纯文本基准测试中进行了全面评估。在思考模式下,BlueLM-2.5-3B在纯文本基准测试中的性能与Qwen3-4B相当,在多模态评估上的平均表现仅次于Kimi-VL-A3B-16B,差距约为5%。在非思考模式下,它在大多数多模态基准测试中的表现优于Qwen2.5-VL-3B。此外,BlueLM-2.5-3B表现出卓越的数据效率。上述所有性能都是在使用的总训练数据量远远少于Qwen2.5-VL-3B和Qwen3-4B的情况下实现的。我们希望我们的研究能为高性能的、设备上的MLLM做出贡献,并为研究社区提供有意义的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
我们推出了BlueLM-2.5-3B,这是一款针对边缘设备部署而设计的紧凑、统一的多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)。该模型具备强大的通用和推理能力,据我们所知,它是首个支持思考和非思考模式的同时还能控制思考令牌预算的3B规模MLLM。通过多样化数据收集、关键数据重采样、混合异构增强学习以及高性能训练基础设施,BlueLM-2.5-3B实现了卓越的多模态能力,同时保持仅有2.9亿参数时的文本性能竞争力。在广泛的跨多模态和文本基准测试中进行了全面评估,其性能令人瞩目。
Key Takeaways:
- BlueLM-2.5-3B是一个适用于边缘设备部署的多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)。
- 该模型具备强大的通用和推理能力。
- BlueLM-2.5-3B支持思考和非思考两种模式,并可以控制思考令牌预算。
- 该模型通过多样化数据收集、关键数据重采样等技术实现卓越的多模态能力。
- BlueLM-2.5-3B在文本基准测试中的性能与Qwen3-4B相当,并在多模态评估中仅落后Kimi-VL-A3B-16B约5%。
- 在非思考模式下,BlueLM-2.5-3B在大多数多模态基准测试中优于Qwen2.5-VL-3B。
- BlueLM-2.5-3B展现出卓越的数据效率,使用的数据量远低于Qwen2.5-VL-3B和Qwen3-4B。
点此查看论文截图
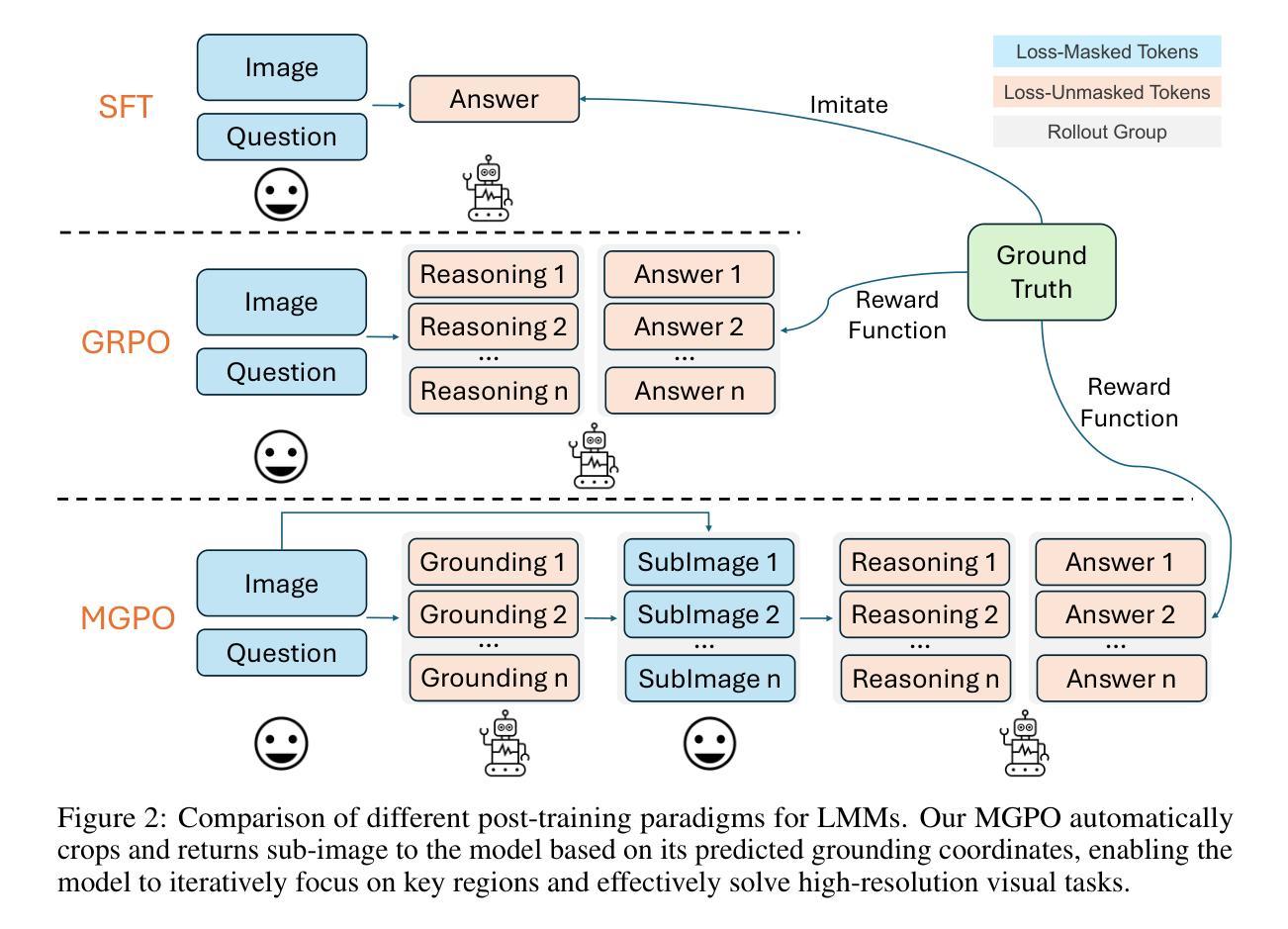
High-Resolution Visual Reasoning via Multi-Turn Grounding-Based Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Xinyu Huang, Yuhao Dong, Weiwei Tian, Bo Li, Rui Feng, Ziwei Liu
State-of-the-art large multi-modal models (LMMs) face challenges when processing high-resolution images, as these inputs are converted into enormous visual tokens, many of which are irrelevant to the downstream task. In this paper, we propose Multi-turn Grounding-based Policy Optimization (MGPO), an end-to-end reinforcement learning (RL) framework that enables LMMs to iteratively focus on key visual regions by automatically cropping sub-images, based on model-predicted grounding coordinates within a multi-turn conversation framework. Compared to supervised fine-tuning (SFT), which requires costly additional grounding annotations, our approach highlights that LMMs can emerge robust grounding abilities during the RL training process, leveraging only a binary reward function derived from the correctness of the final answer. Additionally, we observe that LMMs struggle to autonomously trigger visual grounding during the rollout process. To address this cold start problem, we design a multi-turn conversational template and restrict policy loss computation to model outputs generated across multiple dialogue rounds, thereby promoting stable optimization. Extensive experiments demonstrate that, when trained on standard visual-question-short answering data without grounding annotations, MGPO effectively elicits stronger grounding capabilities compared to GRPO, leading to 5.4% improvement on in-distribution MME-Realworld and 5.2% improvement on the challenging out-of-distribution (OOD) V* Bench. Notably, MGPO post-training on Qwen2.5-VL-7B with 21K samples surpasses OpenAI’s o1 and GPT-4o models on the OOD V* Bench. Codes are available at https://github.com/EvolvingLMMs-Lab/MGPO.
当前先进的大型多模态模型(LMMs)在处理高分辨率图像时面临挑战,因为这些输入会被转化为巨大的视觉令牌,其中许多与下游任务无关。在本文中,我们提出了基于多轮定位的策略优化(MGPO),这是一种端到端的强化学习(RL)框架,它使LMMs能够通过自动裁剪子图像,在多轮对话框架内基于模型预测的定位坐标来迭代关注关键视觉区域。与需要昂贵额外定位注释的监督微调(SFT)相比,我们的方法强调,LMMs可以在RL训练过程中形成稳健的定位能力,仅利用基于最终答案正确性的二元奖励函数。此外,我们观察到LMMs在滚动过程中自主触发视觉定位方面存在困难。为了解决冷启动问题,我们设计了一个多轮对话模板,并将政策损失计算限制在多个对话轮次中生成的模型输出上,从而促进稳定优化。大量实验表明,在标准视觉问答简短回答数据上进行训练时,无需定位注释的MGPO能有效地引发更强的定位能力,与GRPO相比,在内部分布MME-Realworld上提高了5.4%,在具有挑战性的外部分布(OOD)V* Bench上提高了5.2%。值得注意的是,MGPO在Qwen2.5-VL-7B模型上使用21K样本进行后训练,在OOD V* Bench上超越了OpenAI的o1和GPT-4o模型。代码可在https://github.com/EvolvingLMMs-Lab/MGPO中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于强化学习的大型多模态模型(LMMs)视觉定位策略优化方法——多轮定位基础策略优化(MGPO)。该方法能够在无需额外定位标注的情况下,通过端到端的强化学习过程,使LMMs在对话框架内自动裁剪子图像,并基于模型预测的定位坐标进行迭代优化。为解决冷启动问题,设计多轮对话模板并限制策略损失计算在多轮对话输出中,促进稳定优化。实验结果显示,在无需定位标注的标准视觉问答数据集上训练的MGPO,相对于传统方法,能够有效提升模型的定位能力,并在具有挑战性的未见数据集上取得显著效果。代码已公开。
Key Takeaways
- MGPO是一个基于强化学习的框架,旨在使大型多模态模型在处理高分辨率图像时能够自动裁剪和关注关键视觉区域。
- MGPO通过模型预测的定位坐标进行迭代优化,无需额外的定位标注。
- LMMs在自主触发视觉定位方面存在冷启动问题,MGPO通过多轮对话模板和策略损失计算的方式解决这一问题。
- 实验证明MGPO在标准视觉问答数据集上的定位能力优于传统方法,且在未见数据集上有显著效果。
- MGPO在Qwen2.5-VL-7B数据集上的表现优于OpenAI的o1和GPT-4o模型。
- MGPO方法已公开源代码,便于研究者和开发者使用。
点此查看论文截图



Video Event Reasoning and Prediction by Fusing World Knowledge from LLMs with Vision Foundation Models
Authors:L’ea Dubois, Klaus Schmidt, Chengyu Wang, Ji-Hoon Park, Lin Wang, Santiago Munoz
Current video understanding models excel at recognizing “what” is happening but fall short in high-level cognitive tasks like causal reasoning and future prediction, a limitation rooted in their lack of commonsense world knowledge. To bridge this cognitive gap, we propose a novel framework that synergistically fuses a powerful Vision Foundation Model (VFM) for deep visual perception with a Large Language Model (LLM) serving as a knowledge-driven reasoning core. Our key technical innovation is a sophisticated fusion module, inspired by the Q-Former architecture, which distills complex spatiotemporal and object-centric visual features into a concise, language-aligned representation. This enables the LLM to effectively ground its inferential processes in direct visual evidence. The model is trained via a two-stage strategy, beginning with large-scale alignment pre-training on video-text data, followed by targeted instruction fine-tuning on a curated dataset designed to elicit advanced reasoning and prediction skills. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our model achieves state-of-the-art performance on multiple challenging benchmarks. Notably, it exhibits remarkable zero-shot generalization to unseen reasoning tasks, and our in-depth ablation studies validate the critical contribution of each architectural component. This work pushes the boundary of machine perception from simple recognition towards genuine cognitive understanding, paving the way for more intelligent and capable AI systems in robotics, human-computer interaction, and beyond.
当前视频理解模型在识别“发生了什么”方面表现出色,但在高级认知任务(如因果推理和未来预测)方面存在不足,这一局限性源于它们缺乏常识世界知识。为了弥补这一认知鸿沟,我们提出了一种新型框架,该框架协同融合了用于深度视觉感知的强大视觉基础模型(VFM)和作为知识驱动推理核心的大型语言模型(LLM)。我们的关键技术创新在于一个复杂的融合模块,该模块受到Q-Former架构的启发,将复杂的时空和对象中心的视觉特征蒸馏成简洁、与语言对齐的表示形式。这使LLM能够有效地将其推理过程直接建立在视觉证据上。该模型采用两阶段策略进行训练,首先在大规模视频文本数据上进行对齐预训练,然后在专门设计的数据集上进行有针对性的指令微调,以激发高级推理和预测技能。大量实验表明,我们的模型在多个具有挑战性的基准测试上达到了最先进的性能。值得注意的是,它对未见过的推理任务表现出了显著的零样本泛化能力,我们的深度消融研究验证了每个架构组件的关键贡献。这项工作将机器感知的边界从简单的识别推向了真正的认知理解,为机器人、人机交互等领域的更智能、更强大的AI系统铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 22 pages, 4 figures
Summary
多媒体视频理解的现状是模型主要识别“发生了什么”,但在因果推理和未来预测等高级认知任务上表现不足,缺乏常识性世界知识。为弥补这一认知差距,我们提出了一个融合强大的视觉基础模型(VFM)和知识驱动推理核心的大型语言模型(LLM)的新框架。受Q-Former架构启发的复杂融合模块可将复杂的时空和对象中心视觉特征蒸馏成简洁、与语言对齐的表示形式。模型采用两阶段训练策略,首先在视频文本数据上进行大规模对齐预训练,然后在定制数据集上进行针对性指令微调,以激发高级推理和预测技能。实验表明,该模型在多个具有挑战性的基准测试上取得了最新性能。尤其是,它在未见过的推理任务上展现出卓越的零样本泛化能力。此工作推动了多媒体视频理解的进步,迈向真正的认知理解,为机器人技术、人机交互等领域更智能、更强大的AI系统铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways
- 当前视频理解模型的局限性在于缺乏高级认知任务和常识性世界知识。
- 提出融合视觉基础模型(VFM)与大型语言模型(LLM)的新框架来弥补认知差距。
- 引入复杂融合模块,将视觉特征转化为语言对齐的表示形式。
- 模型采用两阶段训练策略,包括大规模对齐预训练和指令微调。
- 模型在多个基准测试上表现优异,尤其是零样本泛化能力突出。
- 融合框架有助于实现多媒体视频理解的真正认知水平。
点此查看论文截图

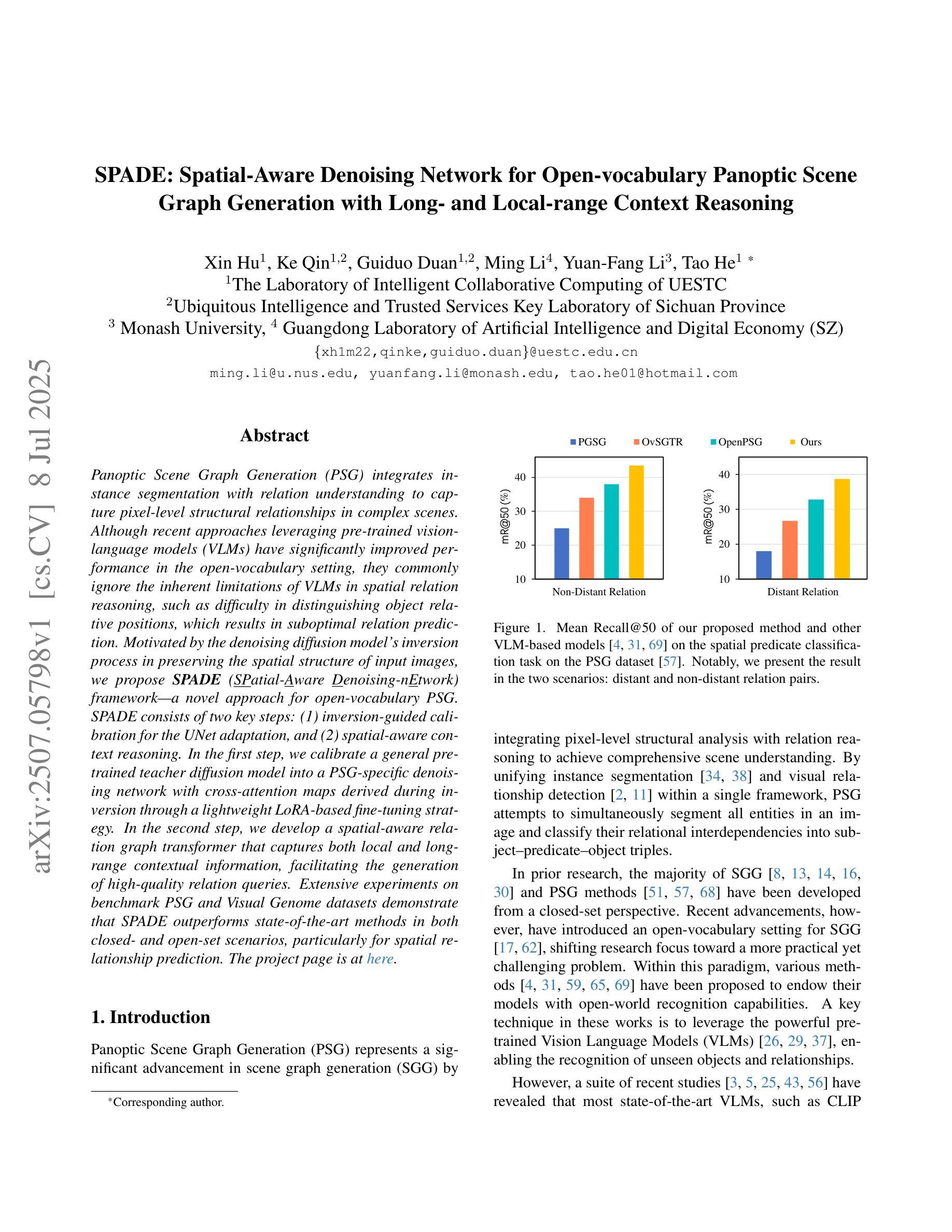
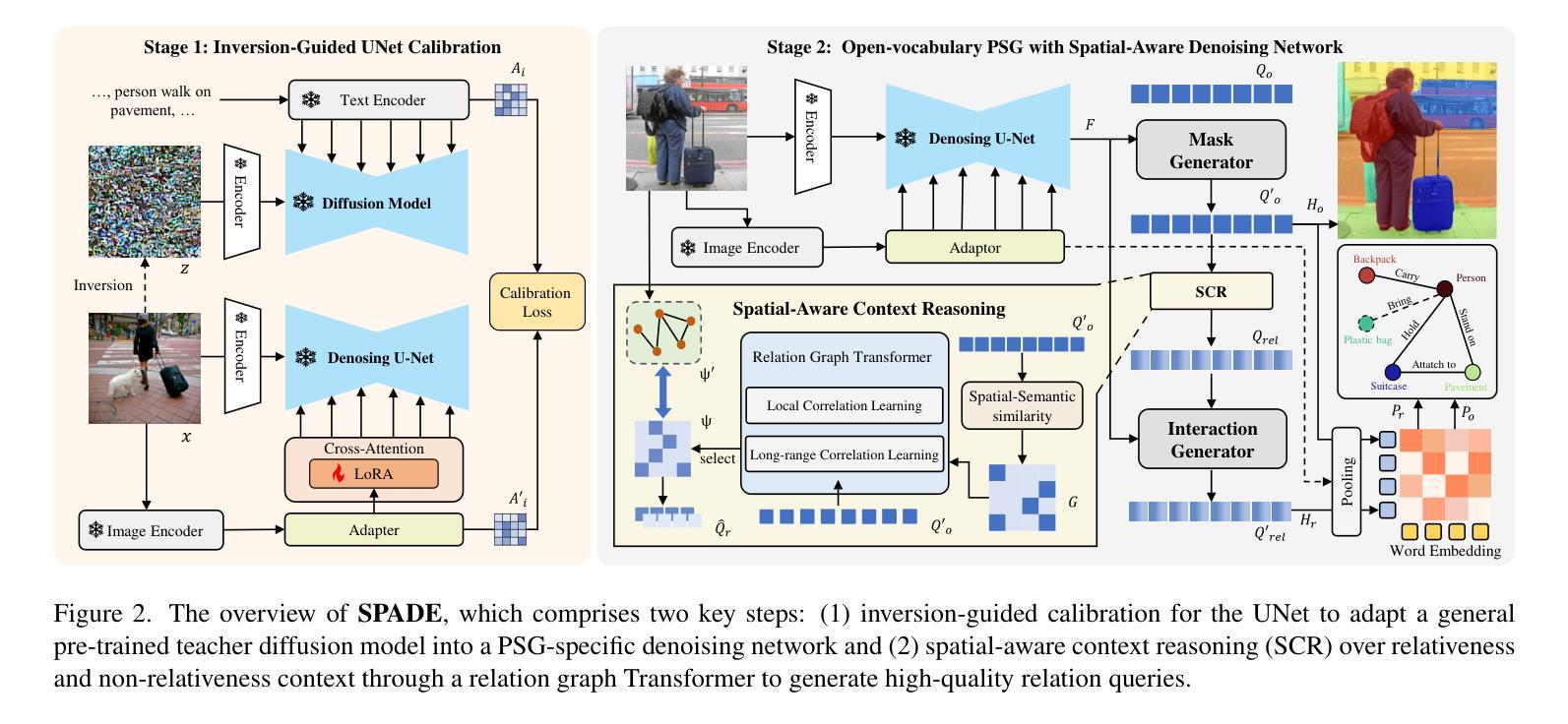
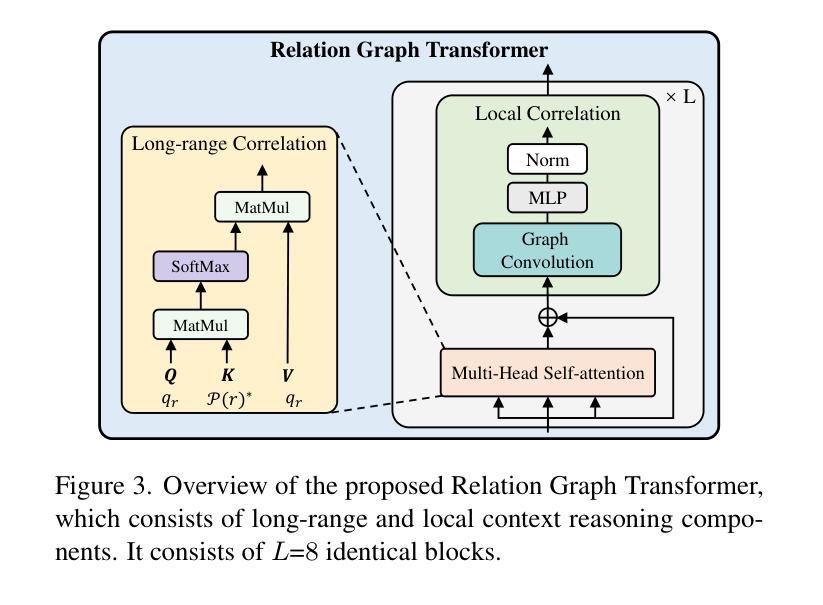
SPADE: Spatial-Aware Denoising Network for Open-vocabulary Panoptic Scene Graph Generation with Long- and Local-range Context Reasoning
Authors:Xin Hu, Ke Qin, Guiduo Duan, Ming Li, Yuan-Fang Li, Tao He
Panoptic Scene Graph Generation (PSG) integrates instance segmentation with relation understanding to capture pixel-level structural relationships in complex scenes. Although recent approaches leveraging pre-trained vision-language models (VLMs) have significantly improved performance in the open-vocabulary setting, they commonly ignore the inherent limitations of VLMs in spatial relation reasoning, such as difficulty in distinguishing object relative positions, which results in suboptimal relation prediction. Motivated by the denoising diffusion model’s inversion process in preserving the spatial structure of input images, we propose SPADE (SPatial-Aware Denoising-nEtwork) framework – a novel approach for open-vocabulary PSG. SPADE consists of two key steps: (1) inversion-guided calibration for the UNet adaptation, and (2) spatial-aware context reasoning. In the first step, we calibrate a general pre-trained teacher diffusion model into a PSG-specific denoising network with cross-attention maps derived during inversion through a lightweight LoRA-based fine-tuning strategy. In the second step, we develop a spatial-aware relation graph transformer that captures both local and long-range contextual information, facilitating the generation of high-quality relation queries. Extensive experiments on benchmark PSG and Visual Genome datasets demonstrate that SPADE outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both closed- and open-set scenarios, particularly for spatial relationship prediction.
全景场景图生成(PSG)结合了实例分割和关系理解,以捕捉复杂场景中的像素级结构关系。尽管最近利用预训练的视觉语言模型(VLM)的方法在开放词汇设置中的性能显著提高,但它们通常忽略了VLM在空间关系推理方面的固有局限性,例如难以区分对象的相对位置,导致关系预测不理想。受去噪扩散模型在保留输入图像空间结构时的反转过程的启发,我们提出了SPADE(空间感知去噪网络)框架——一种用于开放词汇PSG的新方法。SPADE由两个关键步骤组成:(1)反转引导校准用于UNet适应,(2)空间感知上下文推理。在第一步中,我们通过轻量化LoRA微调策略将通用的预训练教师扩散模型校准为PSG特定的去噪网络,在此过程中使用反转时产生的交叉注意力图。在第二步中,我们开发了一种空间感知关系图转换器,能够捕捉局部和长距离上下文信息,有助于生成高质量的关系查询。在基准PSG和Visual Genome数据集上的大量实验表明,SPADE在封闭和开放场景中均优于最先进的方法,特别是在空间关系预测方面。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICCV 2025
Summary
本文介绍了Panoptic Scene Graph Generation(PSG)技术,该技术结合了实例分割和关系理解,以捕捉复杂场景中的像素级结构关系。虽然利用预训练的语言视觉模型(VLM)的方法在开放词汇环境中显著提高了性能,但它们通常忽略了VLM在空间关系推理方面的固有局限性,如难以区分对象的相对位置,导致关系预测不佳。为此,本文提出了SPADE(空间感知去噪网络)框架,包括两个关键步骤:反转引导校准的UNet适应性和空间感知上下文推理。SPADE通过轻量化LoRA技术微调策略,将一般预训练的老师扩散模型校准为PSG特定的去噪网络,并开发了一个空间感知关系图转换器,以捕捉本地和远程上下文信息,从而生成高质量的关系查询。在PSG和Visual Genome数据集上的实验表明,SPADE在封闭和开放场景中均优于最新方法,特别是在空间关系预测方面。
Key Takeaways
- PSG技术结合了实例分割和关系理解,用于捕捉复杂场景的像素级结构关系。
- 尽管预训练的视觉语言模型(VLM)在开放词汇环境中表现良好,但它们在空间关系推理方面存在局限性。
- SPADE框架由两个关键步骤组成:反转引导校准的UNet适应性和空间感知上下文推理。
- SPADE通过轻量化LoRA技术将预训练的扩散模型校准为PSG特定的去噪网络。
- SPADE开发了一个空间感知关系图转换器,能捕捉本地和远程上下文信息,提高关系预测的质量。
- 在PSG和Visual Genome数据集上的实验表明,SPADE在封闭和开放场景中均表现优异。
点此查看论文截图
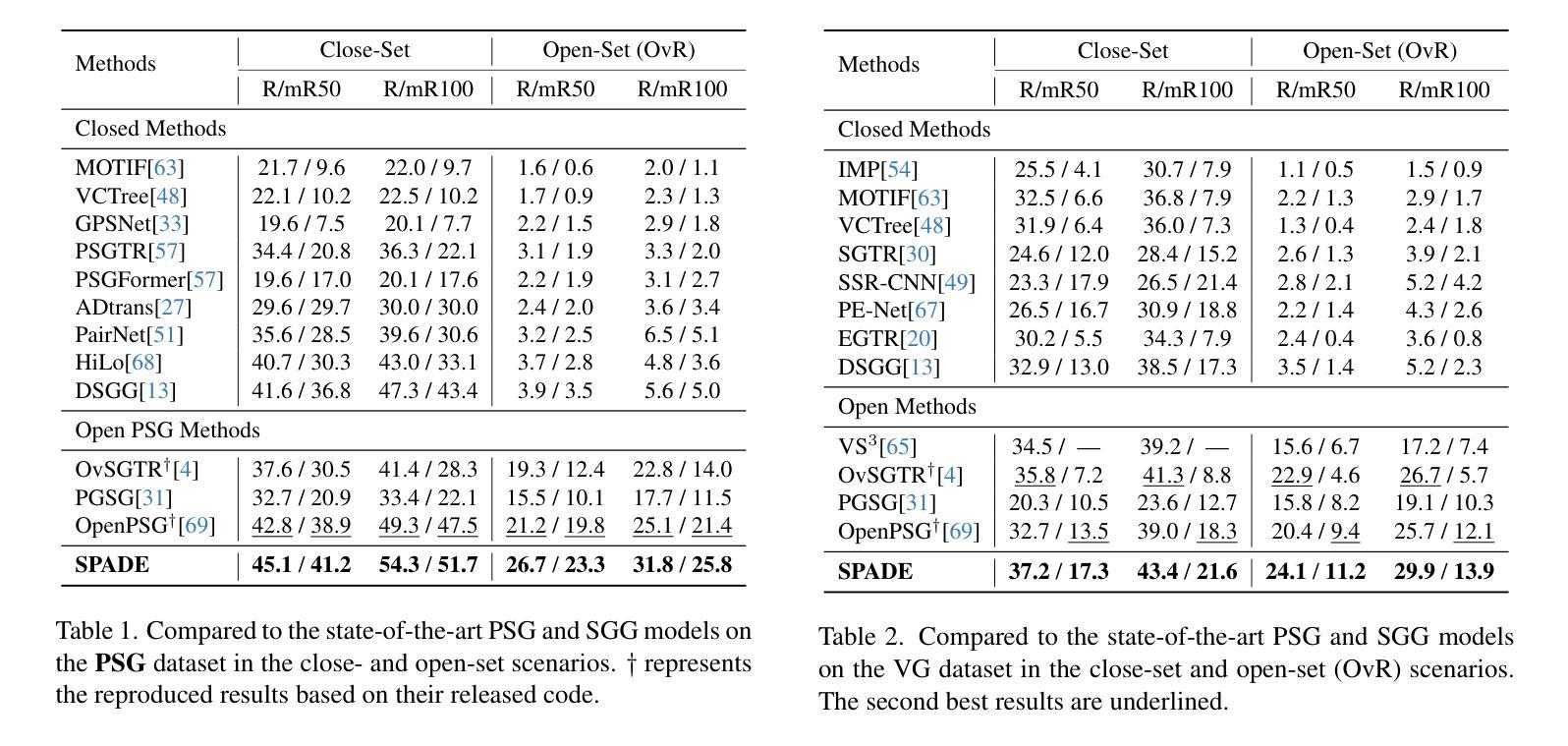
Agentic-R1: Distilled Dual-Strategy Reasoning
Authors:Weihua Du, Pranjal Aggarwal, Sean Welleck, Yiming Yang
Current long chain-of-thought (long-CoT) models excel at mathematical reasoning but rely on slow and error-prone natural language traces. Tool-augmented agents address arithmetic via code execution, but often falter on complex logical tasks. We introduce a fine-tuning framework, DualDistill, that distills complementary reasoning strategies from multiple teachers into a unified student model. Using this approach, we train Agentic-R1, which dynamically selects the optimal strategy for each query, invoking tools for arithmetic and algorithmic problems, and using text-based reasoning for abstract ones. Our method improves accuracy across a range of tasks, including both computation-intensive and standard benchmarks, demonstrating the effectiveness of multi-strategy distillation in achieving robust and efficient reasoning. Our project is available at https://github.com/StigLidu/DualDistill
当前的长思维链(long-CoT)模型擅长数学推理,但依赖于缓慢且易出错的自然语言轨迹。工具增强型代理通过代码执行来解决算术问题,但在复杂的逻辑任务中常常遇到困难。我们引入了一种微调框架,名为DualDistill,该框架从多个教师模型中提炼出互补的推理策略,并将其融合到一个统一的学生模型中。通过这种方法,我们训练了Agentic-R1,该模型能够针对每个查询动态选择最佳策略,对算术和算法问题调用工具,对抽象问题则采用基于文本的推理。我们的方法在多种任务上提高了准确性,包括计算密集型任务和标准基准测试,证明了多策略蒸馏在实现稳健高效推理方面的有效性。我们的项目可在https://github.com/StigLidu/DualDistill上查看。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint. 15 pages. Project available at https://github.com/StigLidu/DualDistill
Summary
该文本介绍了当前长链思维模型在处理数学推理方面表现出色,但面对自然语言推理存在反应缓慢、容易出错的问题。此外,通过工具增强的智能代理通常专注于解决算术问题但可能面临复杂的逻辑挑战。针对这些挑战,我们提出一个称为DualDistill的精调框架,它能够从不同的教师模型中提炼互补推理策略并将其融入学生模型中。在此基础上,我们训练出Agentic-R1模型,它能针对每个查询动态选择最佳策略,为算法问题和算术问题调用工具并使用文本进行抽象推理。此方法提高了各种任务的准确性,包括计算密集型任务和标准基准测试,展示了多元策略融合在实现稳健高效推理方面的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 当前长链思维模型擅长数学推理,但在自然语言推理方面存在局限性。
- 工具增强代理可以解决算术问题,但在复杂逻辑任务上可能表现不足。
- 引入DualDistill精调框架,能够从多个教师模型中提炼互补推理策略。
- Agentic-R1模型能够动态选择最佳策略来处理不同类型的推理任务。
- Agentic-R1模型结合了工具使用和文本推理,提高了处理各种任务的准确性。
- 该方法在处理计算密集型任务和标准基准测试方面表现出色。
点此查看论文截图


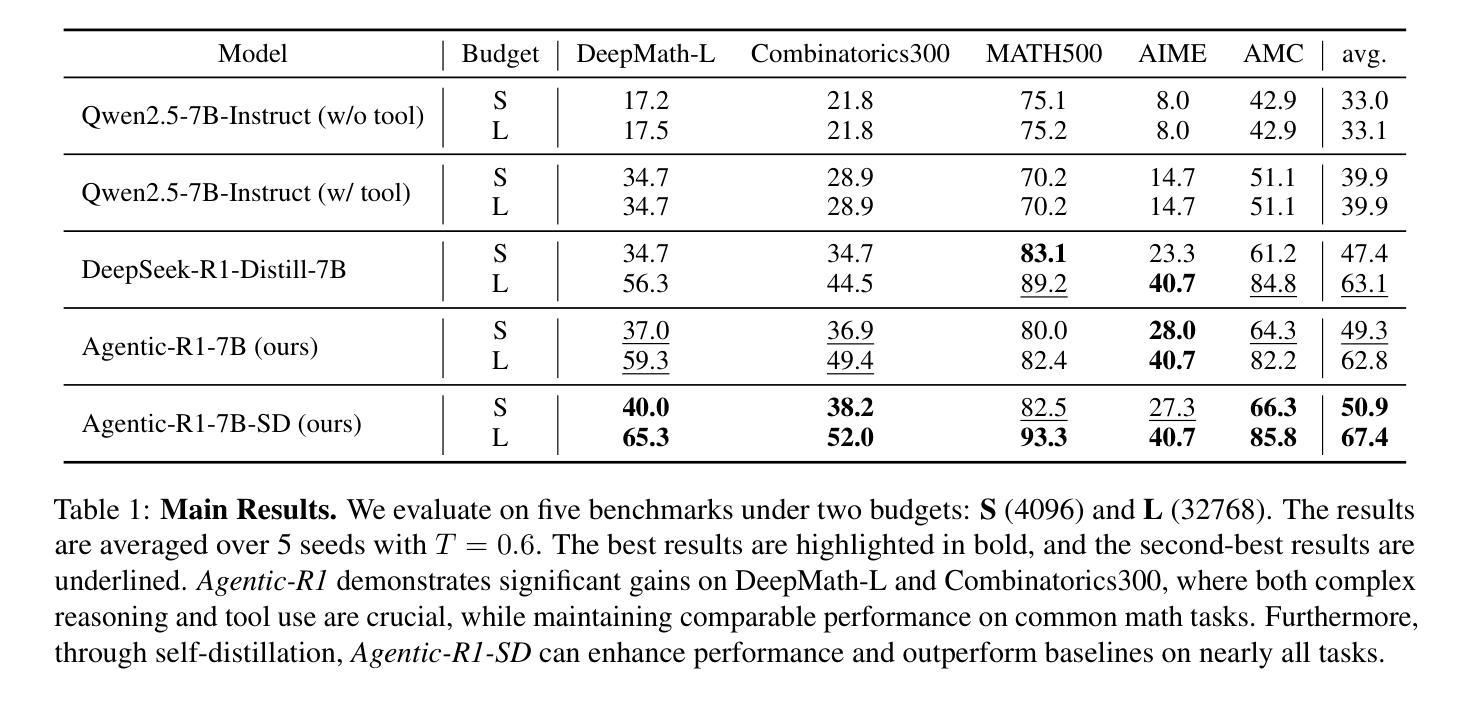
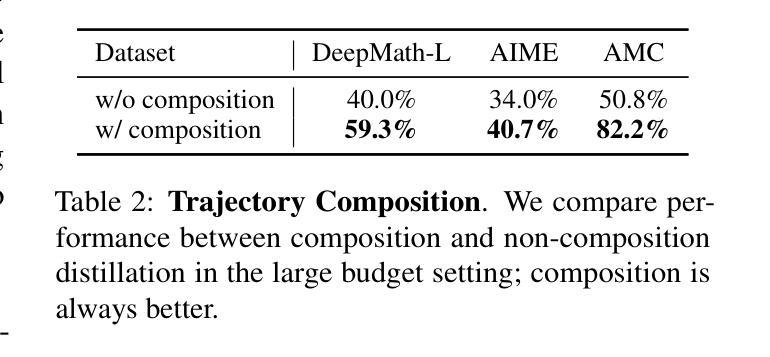
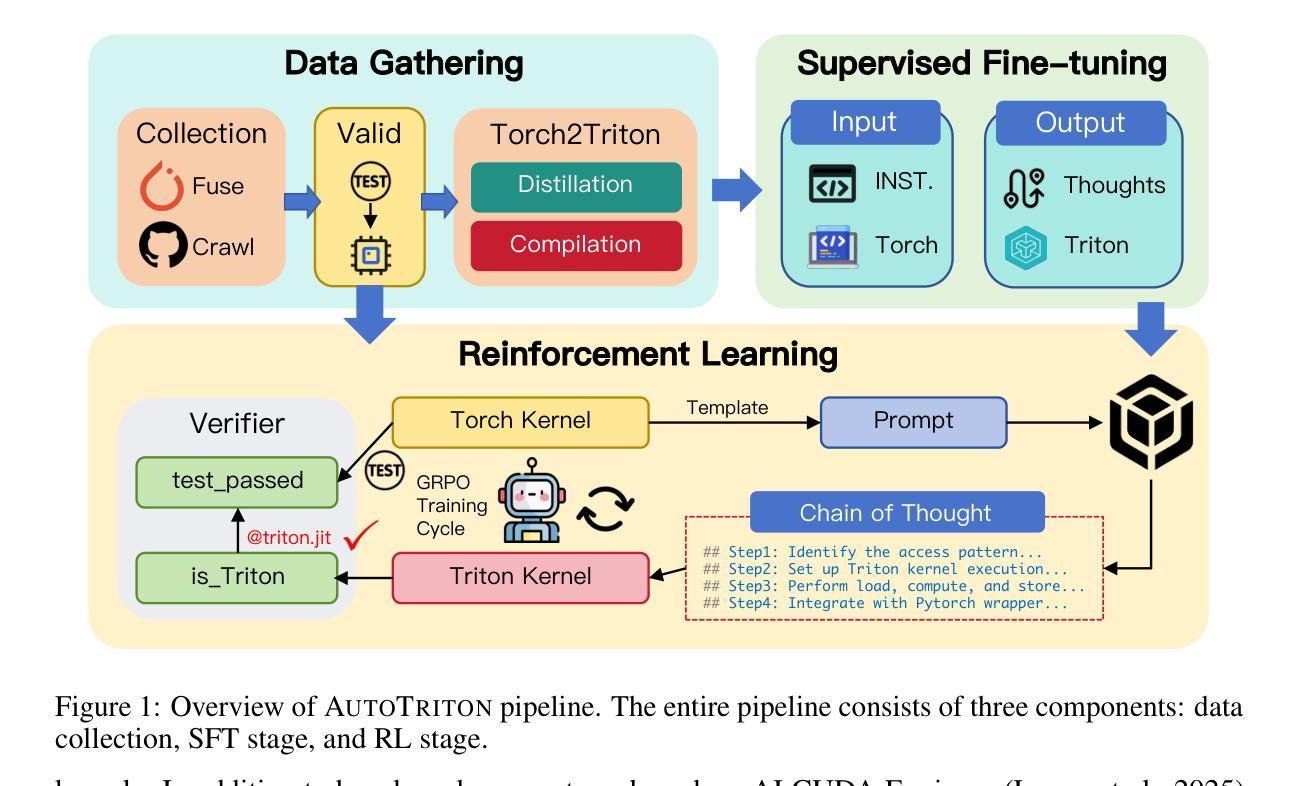
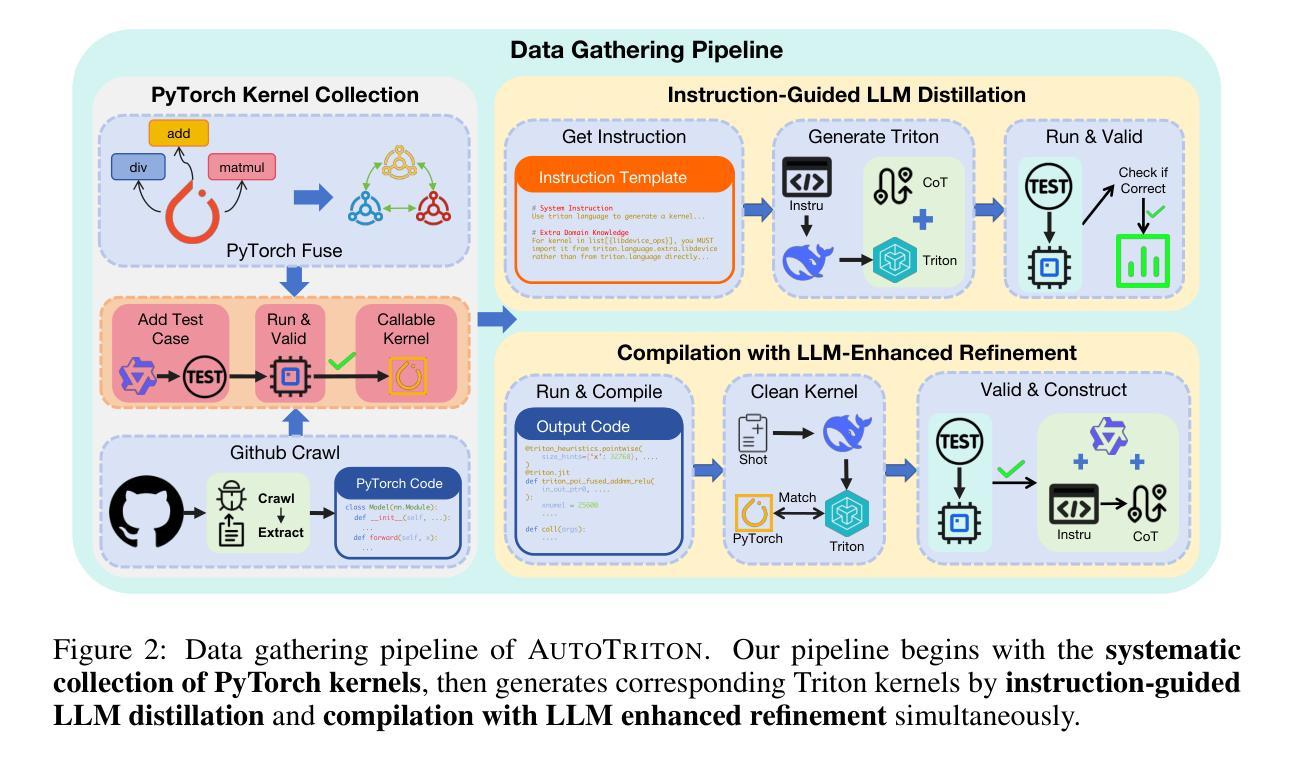
AutoTriton: Automatic Triton Programming with Reinforcement Learning in LLMs
Authors:Shangzhan Li, Zefan Wang, Ye He, Yuxuan Li, Qi Shi, Jianling Li, Yonggang Hu, Wanxiang Che, Xu Han, Zhiyuan Liu, Maosong Sun
Kernel development in deep learning requires optimizing computational units across hardware while balancing memory management, parallelism, and hardware-specific optimizations through extensive empirical tuning. Although domain-specific languages like Triton simplify GPU programming by abstracting low-level details, developers must still manually tune critical parameters such as tile sizes and memory access patterns through iterative experimentation, creating substantial barriers to optimal performance and wider adoption. In this work, we introduce AutoTriton, the first model dedicated to Triton programming powered by reinforcement learning (RL). AutoTriton performs supervised fine-tuning (SFT) to be equipped with essential Triton programming expertise using a high-quality data gathering pipeline, and conducts RL with Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) algorithm, combining a rule-based reward and an execution-based reward to further improve Triton programming ability, sequentially. Experiments across five evaluation channels of TritonBench and KernelBench illustrate that our 8B model AutoTriton achieves performance comparable to mainstream large models, including Claude-4-Sonnet and DeepSeek-R1-0528. Further experimental analysis demonstrates the crucial role of each module within AutoTriton, including the SFT stage, the RL stage, and the reward design strategy. These findings underscore the promise of RL for automatically generating high-performance kernels, and since high-performance kernels are core components of AI systems, this breakthrough establishes an important foundation for building more efficient AI systems. The model and code will be available at https://github.com/AI9Stars/AutoTriton.
内核深度学习的发展需要在硬件上优化计算单元,同时平衡内存管理、并行性和硬件特定优化,这需要通过大量的经验调整来实现。虽然像Triton这样的领域特定语言通过抽象底层细节来简化GPU编程,但开发者仍然需要手动调整关键参数,如瓦片大小和内存访问模式,通过迭代实验,这给达到最佳性能和更广泛的应用造成了重大障碍。在这项工作中,我们引入了AutoTriton,这是由强化学习(RL)驱动的首个专门用于Triton编程的模型。AutoTriton通过高质量的数据收集管道进行有监督的微调(SFT),从而具备基本的Triton编程专业知识,并结合基于规则的奖励和基于执行的奖励,采用群体相对策略优化(GRPO)算法进行强化学习,以进一步提高Triton编程能力。在TritonBench和KernelBench的五个评估通道上的实验表明,我们的8B模型AutoTriton的性能与主流大型模型(包括Claude-4-Sonnet和DeepSeek-R1-0528)相当。进一步的实验分析证明了AutoTriton中每个模块的重要作用,包括SFT阶段、RL阶段和奖励设计策略。这些发现突显了强化学习在自动生成高性能内核方面的潜力,由于高性能内核是AI系统的核心组件,这一突破为构建更高效的AI系统奠定了重要基础。模型和代码将在https://github.com/AI9Stars/AutoTriton上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:该研究引入了基于强化学习(RL)的AutoTriton模型,该模型用于简化内核开发的GPU编程过程。AutoTriton通过监督微调(SFT)获得Triton编程专业知识,并采用基于规则的奖励和执行奖励的Group Relative Policy Optimization(GRPO)算法优化内核开发过程。实验结果验证了该模型相较于主流模型的竞争力。模型的推出将提升人工智能系统的性能与效率。其模型和数据将会公开发布于github平台供用户自由获取。该工作简化GPU编程复杂性的关键组件进一步改善了高性能AI系统的建设进程。模型的卓越性能展现了其潜力与前景。
Key Takeaways:
- AutoTriton模型采用强化学习技术优化内核开发过程,实现GPU编程自动化。
- 该模型通过监督微调(SFT)获得Triton编程专业知识,并采用Group Relative Policy Optimization(GRPO)算法提升性能。
- 实验结果显示AutoTriton模型性能与主流大型模型相当,并在多个评估渠道表现出色。
- 模型在奖励设计策略上采用了结合基于规则的奖励和执行奖励的方法。实验证明这种方法提高了模型的性能优化能力。
点此查看论文截图

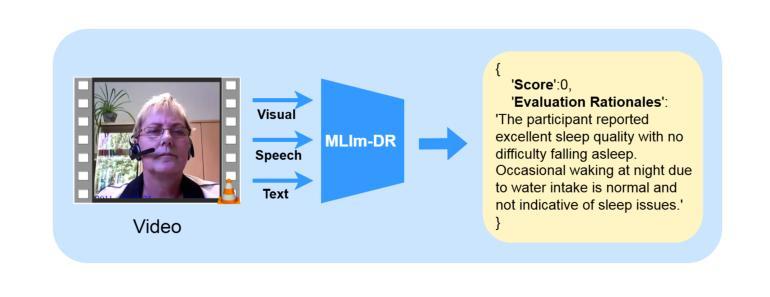
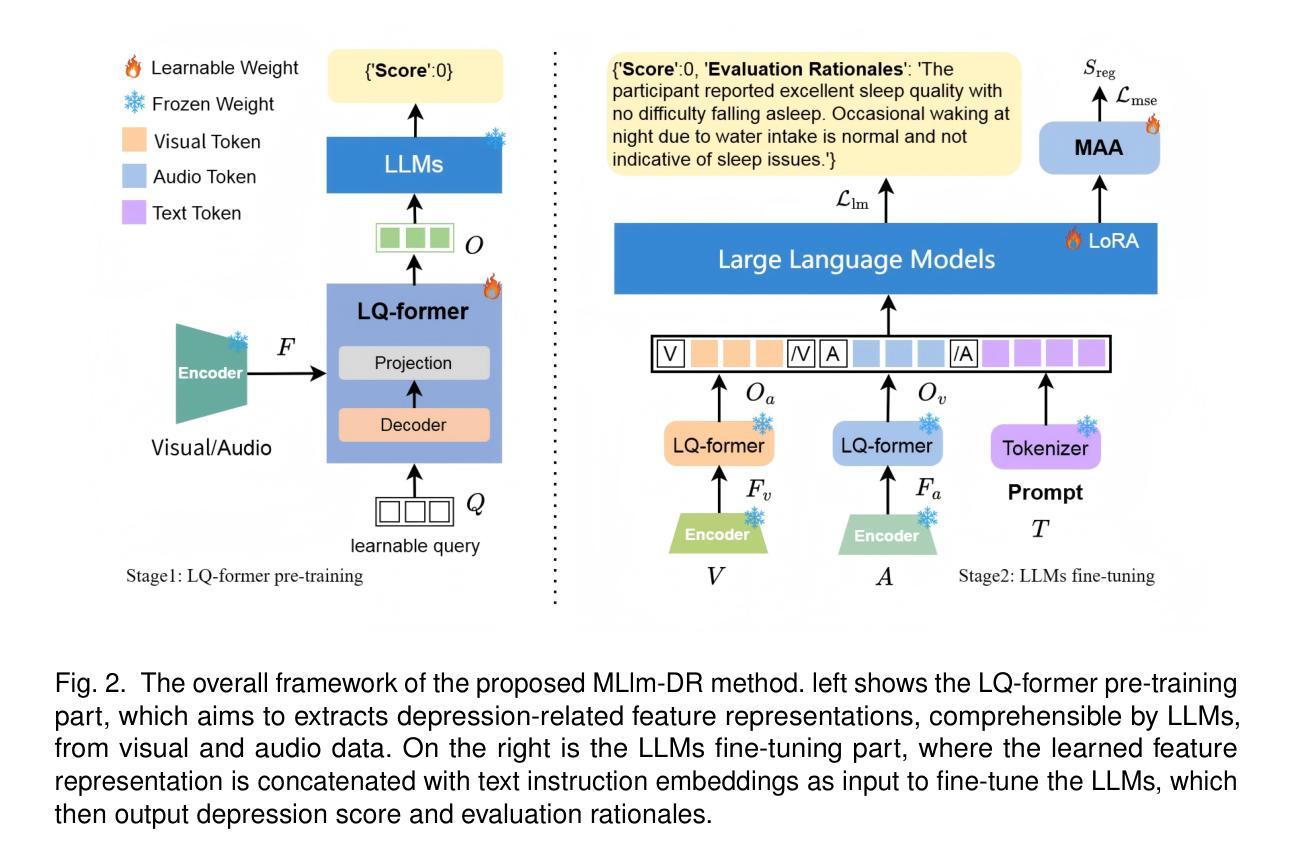
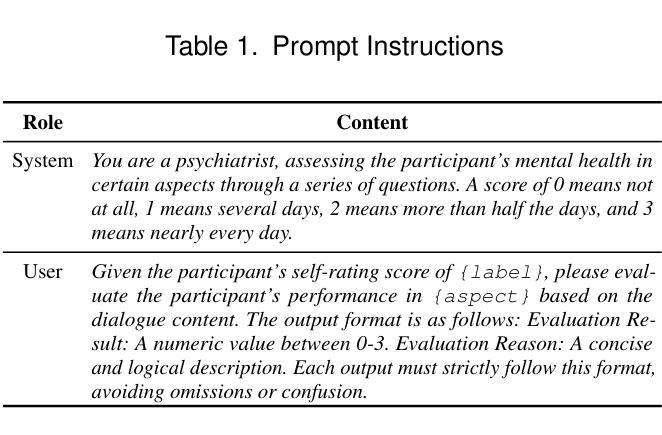
MLlm-DR: Towards Explainable Depression Recognition with MultiModal Large Language Models
Authors:Wei Zhang, Juan Chen, En Zhu, Wenhong Cheng, YunPeng Li, Yanbo J. Wang
Automated depression diagnosis aims to analyze multimodal information from interview videos to predict participants’ depression scores. Previous studies often lack clear explanations of how these scores were determined, limiting their adoption in clinical practice. While the advent of LLMs provides a possible pathway for explainable depression diagnosis, current LLMs capable of processing multimodal data lack training on interview data, resulting in poor diagnostic performance when used directly. In this paper, we propose a novel multimodal large language model (MLlm-DR) that can understand multimodal information inputs and supports explainable depression diagnosis. MLlm-DR integrates a smaller LLMs and a lightweight query module (LQ-former). Specifically, the smaller LLMs is designed to generate depression scores and corresponding evaluation rationales. To enhance its logical reasoning for domain-specific tasks while maintaining practicality, we constructed a robust training dataset to fine-tune it. Meanwhile, the LQ-former captures depression-related features from speech and visual data, aiding the model’s ability to process multimodal information, to achieve comprehensive depression diagnosis. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art results on two interview-based benchmark datasets, CMDC and E-DAIC-WOZ, demonstrating its effectiveness and superiority.
自动化抑郁症诊断旨在分析访谈视频中的多模态信息,以预测参与者的抑郁评分。以往的研究往往缺乏这些评分如何确定的明确解释,限制了它们在临床实践中的应用。虽然大型语言模型(LLMs)的出现为可解释的抑郁症诊断提供了可能的途径,但目前能够处理多模态数据的大型语言模型缺乏访谈数据的训练,导致在实际应用中的诊断性能较差。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型的多模态大型语言模型(MLlm-DR),能够理解多模态信息输入并支持可解释的抑郁症诊断。MLlm-DR集成了较小的大型语言模型(LLMs)和一个轻量级的查询模块(LQ-former)。具体来说,较小的LLMs被设计用于生成抑郁评分和相应的评估依据。为了提高其在特定任务中的逻辑推理能力并保持实用性,我们构建了一个稳健的训练数据集对其进行微调。同时,LQ-former通过捕捉语音和视觉数据中的抑郁症相关特征,辅助模型处理多模态信息的能力,实现全面的抑郁症诊断。我们的方法在基于访谈的两个基准数据集CMDC和E-DAIC-WOZ上取得了最新成果,证明了其有效性和优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于视频访谈的多模态信息,自动化抑郁症诊断旨在预测参与者的抑郁程度分数。以往研究缺乏确定这些分数的明确解释,限制了其在临床实践中的应用。本文提出一种新型的多模态大型语言模型(MLlm-DR),能了解多模态信息输入并支持可解释的抑郁症诊断。该模型融合了较小的语言模型和轻量级查询模块(LQ-former)。语言模型用于生成抑郁程度分数和相应的评估依据,而LQ-former则能捕捉语音和视觉数据的抑郁相关特征,协助模型处理多模态信息,实现全面的抑郁症诊断。在CMDC和E-DAIC-WOZ两个基于访谈的基准数据集上,该方法取得了最佳结果,证明了其有效性和优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 自动化抑郁症诊断通过分析视频访谈的多模态信息来预测参与者的抑郁程度分数。
- 以往研究缺乏明确的分数判定依据,限制了其在临床实践中的应用。
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLlm-DR)能处理多模态信息并支持可解释的抑郁症诊断。
- MLlm-DR融合了较小的语言模型和轻量级查询模块(LQ-former)。
- 语言模型负责生成抑郁程度分数和相应的评估依据。
- LQ-former能从语音和视觉数据中捕捉抑郁相关特征,增强了模型的诊断能力。
点此查看论文截图

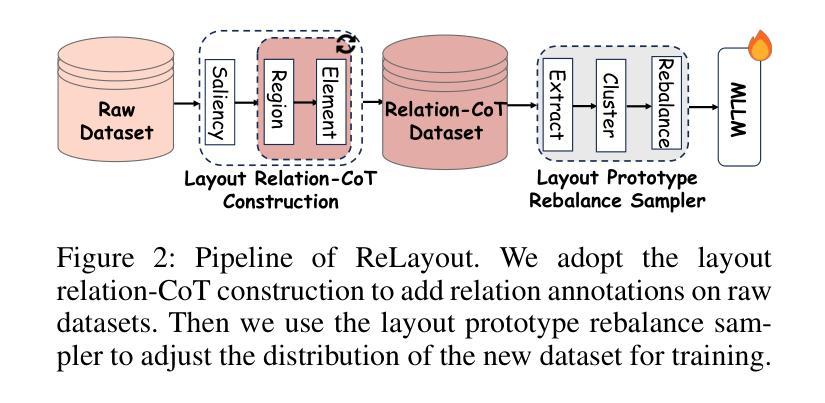
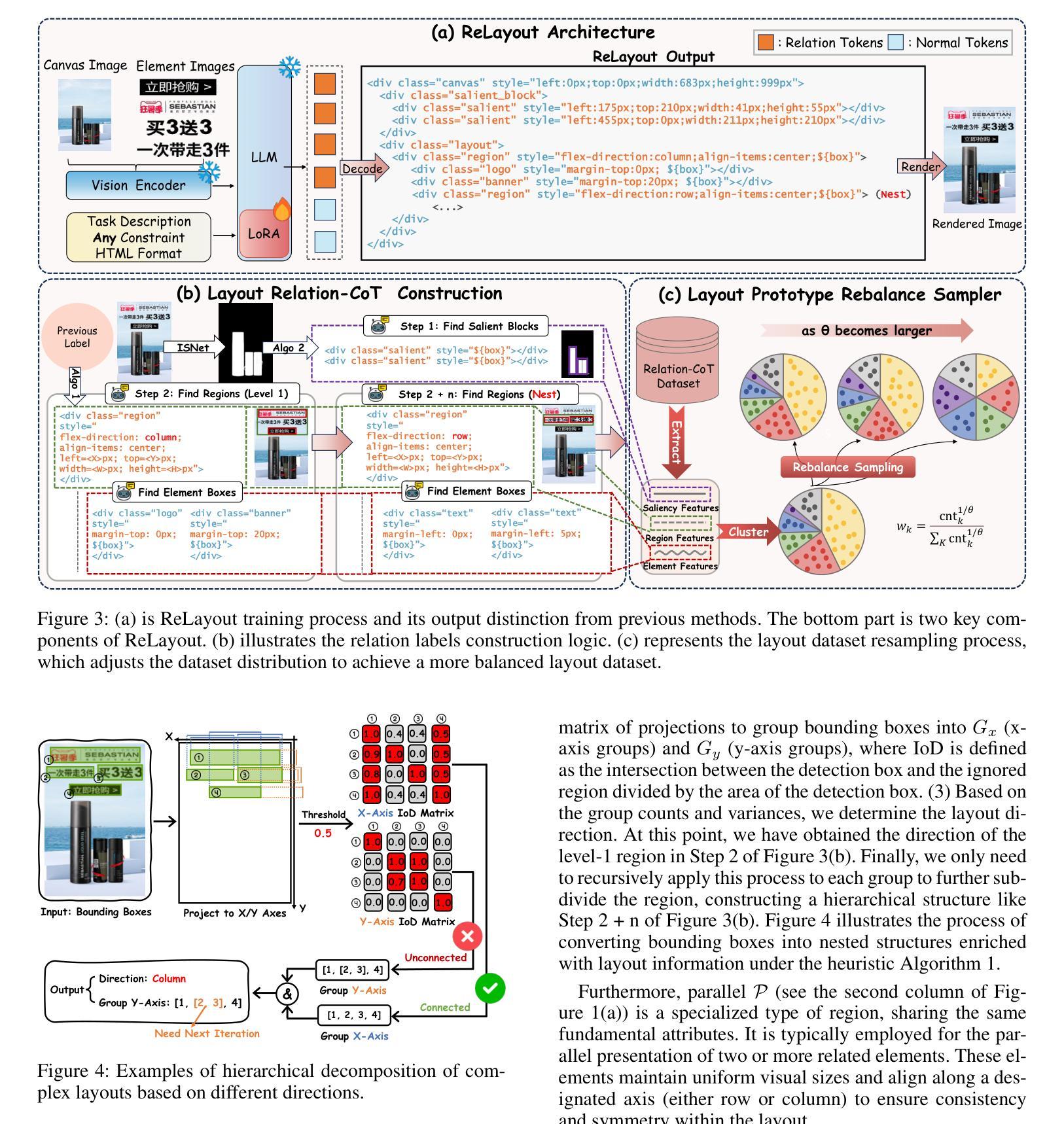
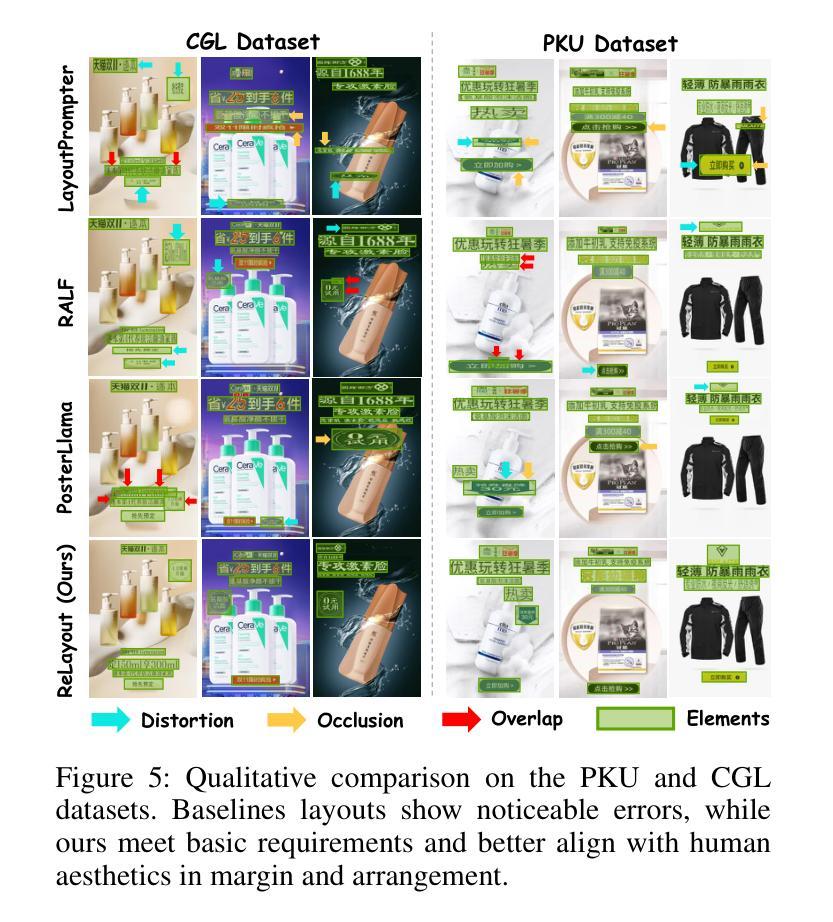
ReLayout: Integrating Relation Reasoning for Content-aware Layout Generation with Multi-modal Large Language Models
Authors:Jiaxu Tian, Xuehui Yu, Yaoxing Wang, Pan Wang, Guangqian Guo, Shan Gao
Content-aware layout aims to arrange design elements appropriately on a given canvas to convey information effectively. Recently, the trend for this task has been to leverage large language models (LLMs) to generate layouts automatically, achieving remarkable performance. However, existing LLM-based methods fail to adequately interpret spatial relationships among visual themes and design elements, leading to structural and diverse problems in layout generation. To address this issue, we introduce ReLayout, a novel method that leverages relation-CoT to generate more reasonable and aesthetically coherent layouts by fundamentally originating from design concepts. Specifically, we enhance layout annotations by introducing explicit relation definitions, such as region, salient, and margin between elements, with the goal of decomposing the layout into smaller, structured, and recursive layouts, thereby enabling the generation of more structured layouts. Furthermore, based on these defined relationships, we introduce a layout prototype rebalance sampler, which defines layout prototype features across three dimensions and quantifies distinct layout styles. This sampler addresses uniformity issues in generation that arise from data bias in the prototype distribution balance process. Extensive experimental results verify that ReLayout outperforms baselines and can generate structural and diverse layouts that are more aligned with human aesthetics and more explainable.
内容感知布局旨在合理安排给定画布上的设计元素,以有效地传达信息。最近,针对此任务的趋势是借助大型语言模型(LLM)自动生成布局,并取得了显著的性能。然而,基于LLM的现有方法无法充分解释视觉主题和设计元素之间的空间关系,导致布局生成中存在结构和多样化问题。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了ReLayout,这是一种新的方法,它通过利用关系-CoT从根本上源于设计概念来生成更合理和美学上连贯的布局。具体来说,我们通过引入明确的关联定义来增强布局注释,如区域、显著性和元素之间的边缘,旨在将布局分解成更小、更结构化和递归的布局,从而能够生成更结构化的布局。此外,基于这些定义的关系,我们引入了布局原型平衡采样器,它在三个维度上定义了布局原型特征并量化了不同的布局风格。该采样器解决了在原型分布平衡过程中因数据偏差而产生的生成均匀性问题。大量的实验结果证实,ReLayout优于基线方法,并能生成更符合人类审美和更具解释性的结构和多样化的布局。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于内容感知的布局旨在合理安排设计元素以有效传达信息。当前趋势是利用大型语言模型(LLMs)自动生成布局,并取得显著性能。然而,现有基于LLM的方法在解读视觉主题和设计元素之间的空间关系方面存在不足,导致布局生成中存在结构和多样化问题。为解决这一问题,我们提出了ReLayout方法,该方法利用关系认知建模生成更合理、美学上更连贯的布局。通过引入明确的关系定义增强布局注释,如区域、显著性和元素间的间距,将布局分解为更小、更结构化的递归布局,从而实现更结构化布局的生成。此外,基于这些定义的关系,我们引入了布局原型平衡采样器,该采样器在三个维度上定义布局原型特征并量化不同的布局风格。实验结果验证,ReLayout优于基线方法,并能生成更符合人类审美和更可解释的结构化和多样化布局。
Key Takeaways
- 内容感知布局旨在有效传达信息,通过合理安排设计元素在给定画布上的位置。
- 现有基于大型语言模型的布局生成方法存在解读空间关系不足的问题。
- ReLayout方法利用关系认知建模生成更合理和美学上连贯的布局。
- 通过引入明确的关系定义(如区域、显著性和元素间距)增强布局注释。
- ReLayout将布局分解为更小、结构化的递归布局,实现更结构化布局的生成。
- 布局原型平衡采样器的引入解决了因数据偏见而产生的布局生成均匀性问题。
点此查看论文截图


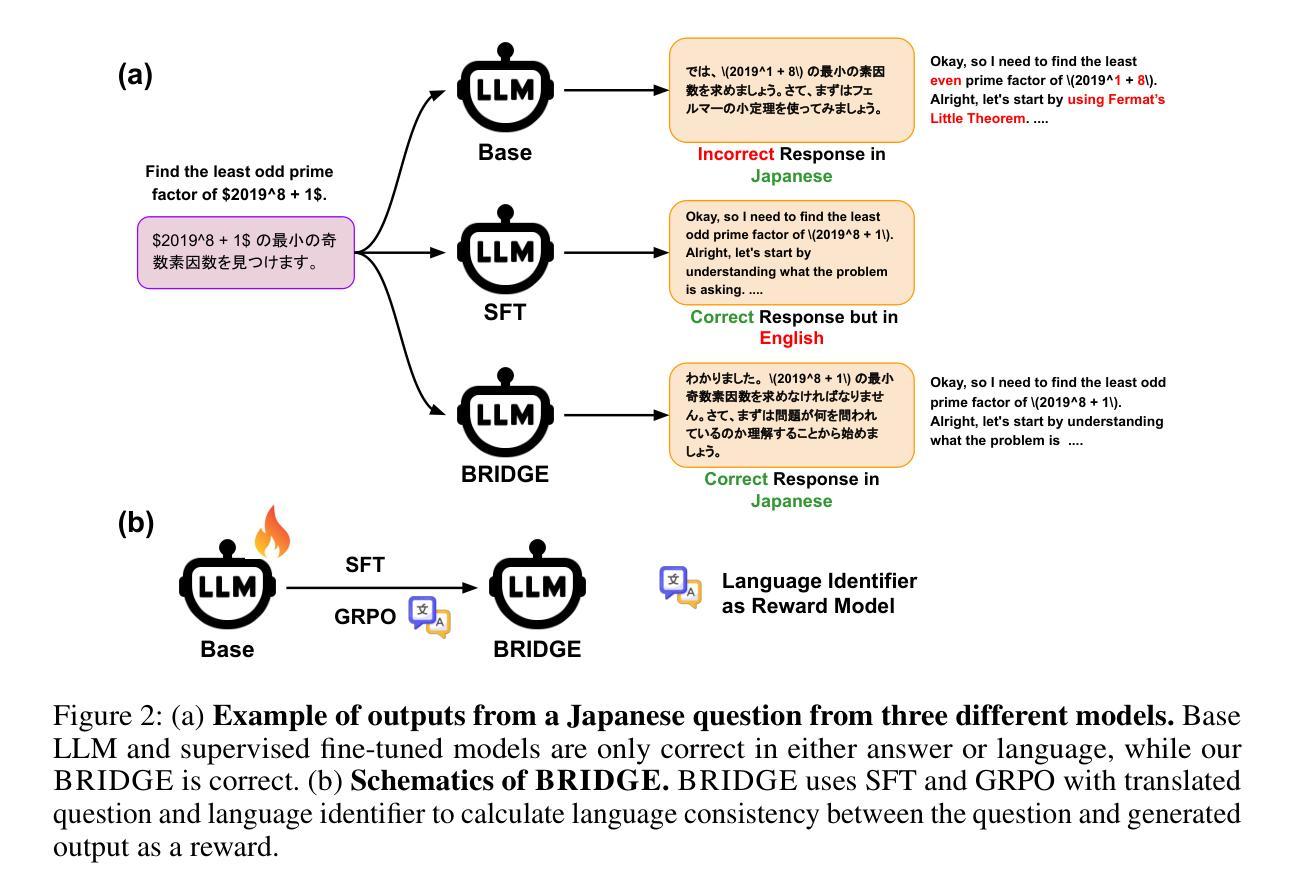
Learn Globally, Speak Locally: Bridging the Gaps in Multilingual Reasoning
Authors:Jaedong Hwang, Kumar Tanmay, Seok-Jin Lee, Ayush Agrawal, Hamid Palangi, Kumar Ayush, Ila Fiete, Paul Pu Liang
Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved strong performance in domains like mathematics, factual QA, and code generation, yet their multilingual reasoning capabilities in these tasks remain underdeveloped. Especially for low-resource languages such as Swahili or Thai, LLMs can often misinterpret prompts or default to reasoning in English. This implicit bias toward high-resource languages undermines factual accuracy, interpretability, and trust. Current multilingual benchmarks focus only on final answers, overlooking whether models actually reason in the target language. To address this gap, we introduce GeoFact-X, a geography-based multilingual factual reasoning benchmark with annotated reasoning traces in five languages: English, Hindi, Japanese, Swahili, and Thai. We further propose BRIDGE, a novel training method that guides supervised fine-tuning and test-time reinforcement learning with a language-consistency reward to align reasoning with the input language. Finally, we develop an automatic evaluation protocol using LLM-as-a-judge to assess answer correctness and the quality and language consistency of reasoning traces, enabling nuanced and scalable analysis beyond surface-level metrics. Our results show that BRIDGE significantly enhances multilingual reasoning fidelity, demonstrating that reasoning-aware multilingual reinforcement learning is crucial for robust cross-lingual generalization. https://jd730.github.io/projects/GeoFact-X_BRIDGE
大型语言模型(LLM)在数学、事实问答和代码生成等领域表现出强大的性能,但它们在这些任务中的多语种推理能力仍待发展。特别是对于斯瓦希里语或泰语等低资源语言,LLM经常误解提示或默认以英语进行推理。这种对高资源语言的隐性偏好会损害事实准确性、可解释性和信任度。当前的多语种基准测试仅关注最终答案,忽视模型是否以目标语言进行推理。为了弥补这一空白,我们引入了GeoFact-X,这是一个基于地理的多语种事实推理基准测试,包含五种语言的注释推理轨迹:英语、印地语、日语、斯瓦希里语和泰语。此外,我们提出了一种新的训练方法BRIDGE,该方法通过监督微调与测试时的强化学习,以语言一致性奖励来引导推理与输入语言对齐。最后,我们开发了一种自动评估协议,利用LLM-as-a-judge来评估答案的正确性、推理轨迹的质量和语言一致性,从而实现超越表面层次的指标的微妙和可扩展分析。我们的结果表明,BRIDGE显著提高了多语种推理的保真度,证明推理感知的多语种强化学习对于稳健的跨语言泛化至关重要。详情请见https://jd730.github.io/projects/GeoFact-X_BRIDGE。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在数学、事实问答和代码生成等领域表现出强大的性能,但在多语种推理能力方面仍有待提升。特别是对于斯瓦希里语或泰语等低资源语言,LLMs容易误解提示或默认以英语进行推理。这种对高资源语言的隐性偏好会影响事实准确性、可解释性和信任度。当前的多语种基准测试主要关注最终答案,忽视模型是否目标语言进行推理。为解决这一差距,我们推出GeoFact-X,一个基于地理的多语种事实推理基准测试,包含五种语言的推理轨迹标注:英语、印地语、日语、斯瓦希里语和泰语。我们还提出BRIDGE,一种新型训练方式,通过指导监督微调与测试时的强化学习,以语言一致性奖励来使推理与输入语言对齐。最后,我们开发了一种自动评估协议,利用LLM-as-a-judge评估答案的正确性以及推理轨迹的质量和语言一致性,以进行超越表面层次的细致和规模化分析。研究表明,BRIDGE显著提高了多语种推理的忠实度,证明以推理为核心的多语种强化学习对于跨语言泛化至关重要。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在多语种推理方面存在挑战,特别是在低资源语言领域。
- 当前多语种基准测试主要关注最终答案,忽视模型是否真正在目标语言进行推理。
- 推出GeoFact-X基准测试,涵盖多种语言的推理轨迹标注。
- 提出BRIDGE训练方式,通过监督微调与强化学习提高多语种推理能力。
- 开发自动评估协议,评估答案及推理轨迹的质量和语言一致性。
- BRIDGE训练显著提高了多语种推理的忠实度。
点此查看论文截图


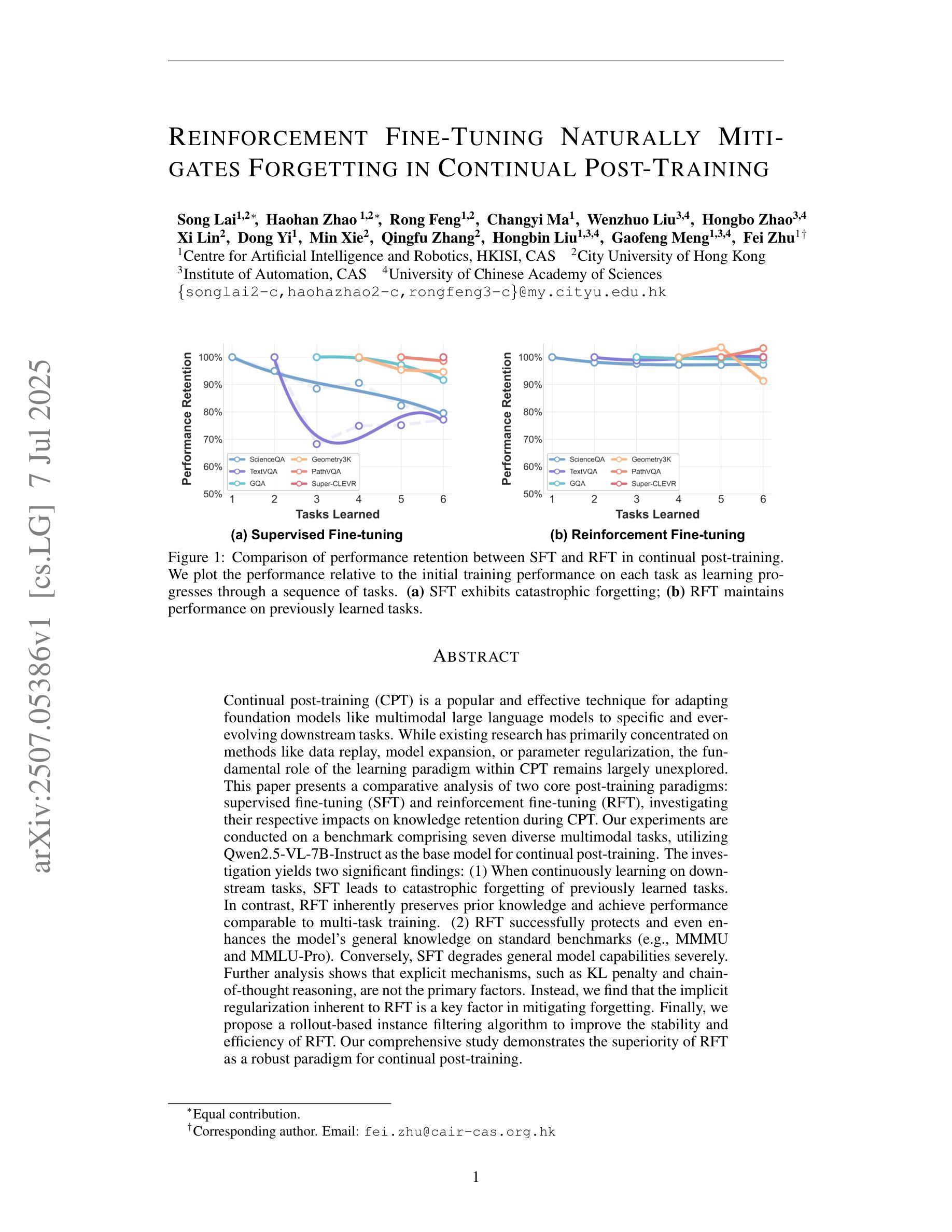
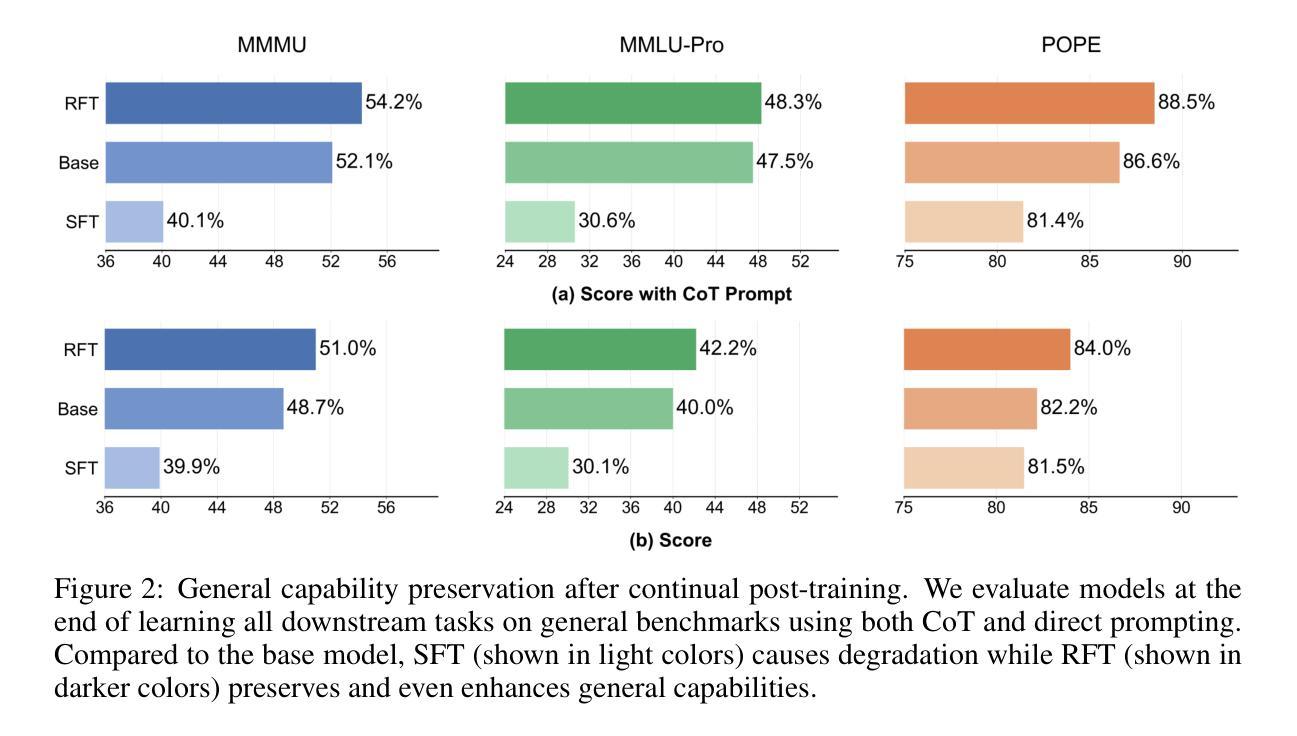
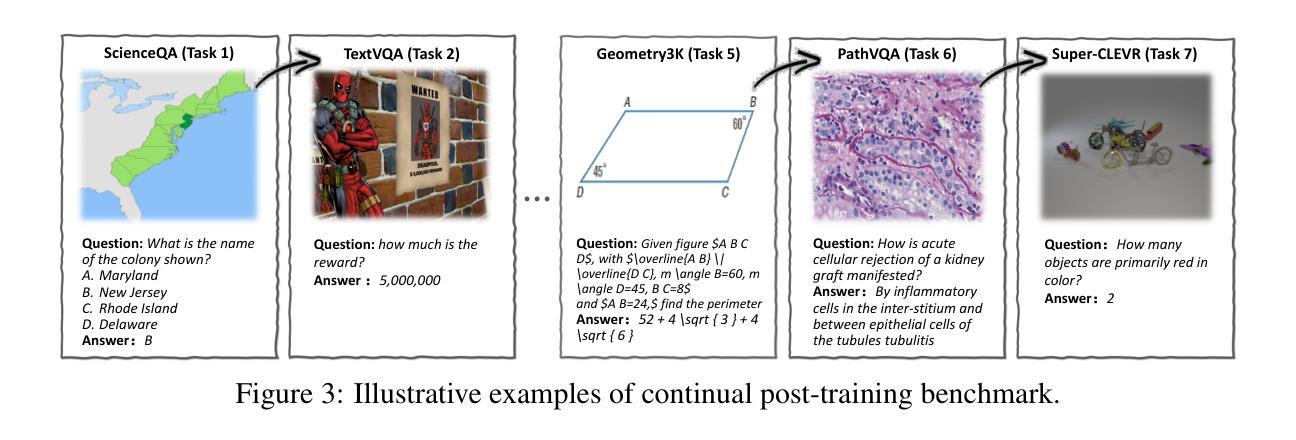
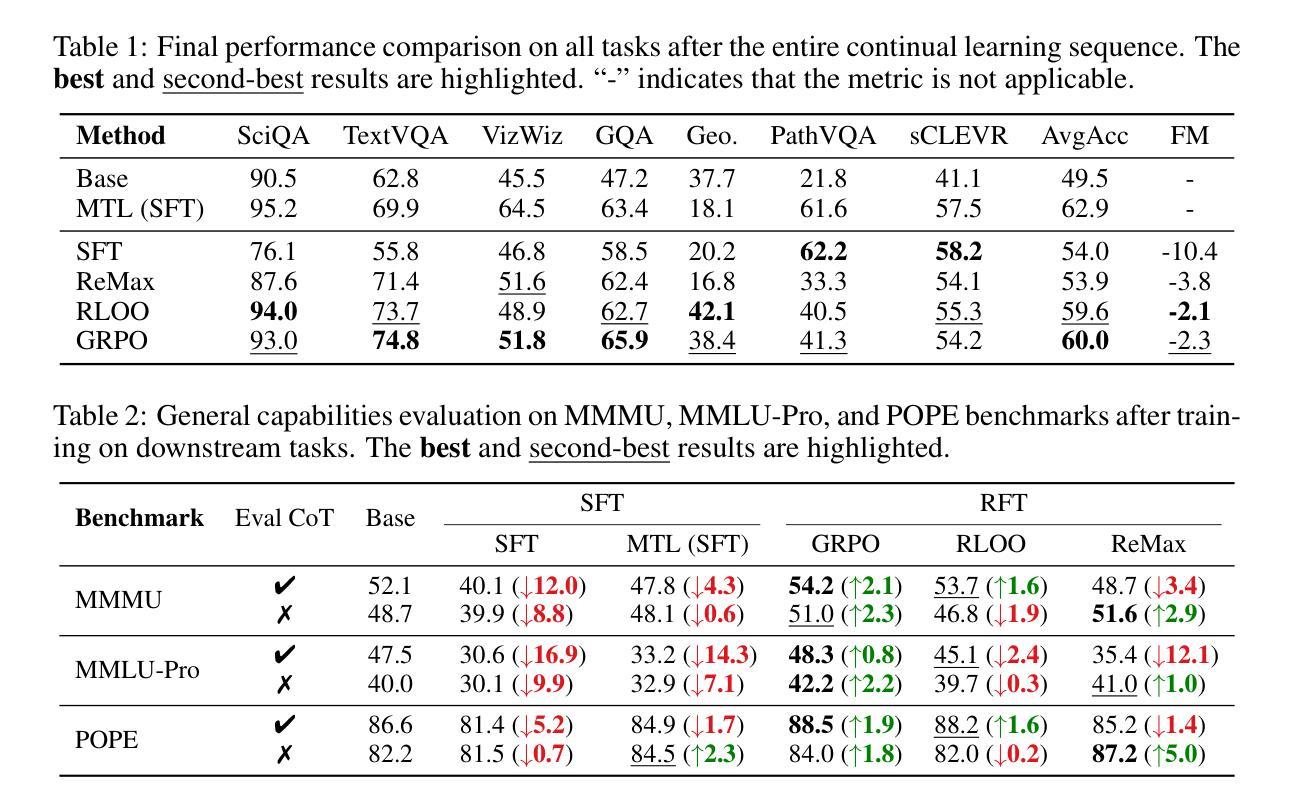
Reinforcement Fine-Tuning Naturally Mitigates Forgetting in Continual Post-Training
Authors:Song Lai, Haohan Zhao, Rong Feng, Changyi Ma, Wenzhuo Liu, Hongbo Zhao, Xi Lin, Dong Yi, Min Xie, Qingfu Zhang, Hongbin Liu, Gaofeng Meng, Fei Zhu
Continual post-training (CPT) is a popular and effective technique for adapting foundation models like multimodal large language models to specific and ever-evolving downstream tasks. While existing research has primarily concentrated on methods like data replay, model expansion, or parameter regularization, the fundamental role of the learning paradigm within CPT remains largely unexplored. This paper presents a comparative analysis of two core post-training paradigms: supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and reinforcement fine-tuning (RFT), investigating their respective impacts on knowledge retention during CPT. Our experiments are conducted on a benchmark comprising seven diverse multimodal tasks, utilizing Qwen2.5-VL-7B-Instruct as the base model for continual post-training. The investigation yields two significant findings: (1) When continuously learning on downstream tasks, SFT leads to catastrophic forgetting of previously learned tasks. In contrast, RFT inherently preserves prior knowledge and achieve performance comparable to multi-task training. (2) RFT successfully protects and even enhances the model’s general knowledge on standard benchmarks (e.g., MMMU and MMLU-Pro). Conversely, SFT degrades general model capabilities severely. Further analysis shows that explicit mechanisms, such as KL penalty and chain-of-thought reasoning, are not the primary factors. Instead, we find that the implicit regularization inherent to RFT is a key factor in mitigating forgetting. Finally, we propose a rollout-based instance filtering algorithm to improve the stability and efficiency of RFT. Our comprehensive study demonstrates the superiority of RFT as a robust paradigm for continual post-training.
持续后训练(CPT)是一种适应基础模型(如多模态大型语言模型)到特定且不断发展的下游任务的流行且有效的技术。尽管现有研究主要集中在数据回放、模型扩展或参数正则化等方法上,但CPT中学习范式的基本作用仍未得到充分探索。本文对比分析两种核心后训练范式:有监督微调(SFT)和强化微调(RFT),研究它们对CPT期间知识保留的各自影响。我们的实验是在包含七个不同多模态任务的基准测试集上进行的,并利用Qwen2.5-VL-7B-Instruct作为持续后训练的基础模型。调查产生了两个重要发现:(1)在下游任务上进行持续学习时,SFT会导致先前学习任务的灾难性遗忘。相比之下,RFT固有地保留先前知识,并实现与多任务训练相当的性能。(2)RFT成功保护甚至提高了模型在标准基准测试集(例如MMMU和MMLU-Pro)上的通用知识。相反,SFT严重降低了模型的通用能力。进一步分析表明,明确的机制(如KL惩罚和链式思维推理)并不是主要因素。相反,我们发现RFT所固有的隐式正则化是缓解遗忘的关键因素。最后,我们提出了一种基于rollout的实例过滤算法,以提高RFT的稳定性和效率。我们的综合研究证明了RFT作为持续后训练的稳健范式的优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本论文对持续训练后的两种核心范式——监督微调(SFT)和强化微调(RFT)进行了比较分析,探究了它们在持续训练过程中对知识保留的影响。实验以Qwen2.5-VL-7B-Instruct为基础模型,在七个不同的多模态任务上进行。研究发现,在进行下游任务持续学习时,SFT会导致先前学习任务的灾难性遗忘,而RFT则能够保留先验知识并实现与多任务训练相当的性能。此外,RFT能够保护甚至提高模型在标准基准测试(如MMMU和MMLU-Pro)上的通用知识,而SFT则会严重降低模型的通用能力。进一步分析表明,明确的机制(如KL惩罚和链式思维推理)并不是主要因素,而RFT中固有的隐式正则化是缓解遗忘的关键。最后,论文提出了一种基于rollout的实例过滤算法,以提高RFT的稳定性和效率。综合研究表明,RFT作为一种稳健的持续训练范式具有优越性。
关键见解
- 论文对比分析了监督微调(SFT)和强化微调(RFT)两种核心持续训练范式。
- SFT在持续学习下游任务时会导致先前学习任务的灾难性遗忘。
- RFT能够保留先验知识,实现与多任务训练相当的性能。
- RFT能够保护并提升模型在标准基准测试上的通用知识。
- 明确的机制(如KL惩罚和链式思维推理)在缓解遗忘方面不是主要因素。
- RFT中的隐式正则化是缓解遗忘的关键。
- 论文提出了一种基于rollout的实例过滤算法,以提高RFT的稳定性和效率。
点此查看论文截图
A Comparative Study of Specialized LLMs as Dense Retrievers
Authors:Hengran Zhang, Keping Bi, Jiafeng Guo
While large language models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed as dense retrievers, the impact of their domain-specific specialization on retrieval effectiveness remains underexplored. This investigation systematically examines how task-specific adaptations in LLMs influence their retrieval capabilities, an essential step toward developing unified retrievers capable of handling text, code, images, and multimodal content. We conduct extensive experiments with eight Qwen2.5 7B LLMs, including base, instruction-tuned, code/math-specialized, long reasoning, and vision-language models across zero-shot retrieval settings and the supervised setting. For the zero-shot retrieval settings, we consider text retrieval from the BEIR benchmark and code retrieval from the CoIR benchmark. Further, to evaluate supervised performance, all LLMs are fine-tuned on the MS MARCO dataset. We find that mathematical specialization and the long reasoning capability cause consistent degradation in three settings, indicating conflicts between mathematical reasoning and semantic matching. The vision-language model and code-specialized LLMs demonstrate superior zero-shot performance compared to other LLMs, even surpassing BM25 on the code retrieval task, and maintain comparable performance to base LLMs in supervised settings. These findings suggest promising directions for the unified retrieval task leveraging cross-domain and cross-modal fusion.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)越来越多地被部署为密集检索器,其领域特定专业化对检索效果的影响尚未得到充分探索。这项研究系统地探讨了LLM中的任务特定适应如何影响其检索能力,这是朝着开发能够处理文本、代码、图像和多模式内容的统一检索器迈出的重要一步。我们在八个Qwen2.5 7B LLM上进行了广泛实验,包括基础、指令调优、代码/数学专业化、长期推理和视觉语言模型,涵盖了零射击检索设置和有监督设置。对于零射击检索设置,我们考虑从BEIR基准测试中进行文本检索,并从CoIR基准测试中进行代码检索。此外,为了评估监督性能,所有LLM都在MS MARCO数据集上进行微调。我们发现数学专业化和长期推理能力会导致三种环境下的持续退化,表明数学推理和语义匹配之间存在冲突。视觉语言模型和代码专业化的LLM在零射击性能上表现出色,与其他LLM相比具有优势,甚至在代码检索任务上超越了BM25,在有监督环境下保持与基础LLM相当的性能。这些发现表明,利用跨域和跨模态融合的统一检索任务大有希望。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CCIR25 and published by Springer LNCS or LNAI
Summary:大型语言模型(LLM)在密集检索器中的应用越来越广泛,但其针对特定领域的专业化对检索效果的影响尚未得到充分探索。本研究系统地探讨了LLM的任务特定适应性对其检索能力的影响,这是开发能够处理文本、代码、图像和多模态内容的统一检索器的关键步骤。通过对八种不同专业化的LLM进行广泛的实验,包括基础模型、指令调优、代码/数学专业、逻辑推理和视觉语言模型等,研究发现在三种设置中数学专业化和逻辑推理能力的一致性下降表明数学推理和语义匹配之间的冲突。视觉语言模型和针对代码专业的LLM在零射击设置中的表现优于其他LLM,甚至在代码检索任务上超越了BM25,在监督设置中的性能也与其他基础LLM相当。这些发现表明,利用跨域和跨模态融合的统一检索任务具有广阔的发展前景。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在密集检索中的应用逐渐普及,但其针对特定领域的专业化对检索效果影响尚待研究。
- LLM的任务特定适应性对其检索能力有系统性影响,这是开发统一检索器的重要步骤。
- 在不同设置中,数学专业化和逻辑推理能力的一致性下降表明数学推理和语义匹配之间存在冲突。
- 视觉语言模型和针对代码专业的LLM在零射击设置中的表现优于其他LLM。
- 针对代码专业的LLM在代码检索任务上的表现甚至超越了BM25。
- 在监督设置中,视觉语言模型和针对代码专业的LLM的性能与其他基础LLM相当。
点此查看论文截图

Enhancing Adaptive Behavioral Interventions with LLM Inference from Participant-Described States
Authors:Karine Karine, Benjamin M. Marlin
The use of reinforcement learning (RL) methods to support health behavior change via personalized and just-in-time adaptive interventions is of significant interest to health and behavioral science researchers focused on problems such as smoking cessation support and physical activity promotion. However, RL methods are often applied to these domains using a small collection of context variables to mitigate the significant data scarcity issues that arise from practical limitations on the design of adaptive intervention trials. In this paper, we explore an approach to significantly expanding the state space of an adaptive intervention without impacting data efficiency. The proposed approach enables intervention participants to provide natural language descriptions of aspects of their current state. It then leverages inference with pre-trained large language models (LLMs) to better align the policy of a base RL method with these state descriptions. To evaluate our method, we develop a novel physical activity intervention simulation environment that generates text-based state descriptions conditioned on latent state variables using an auxiliary LLM. We show that this approach has the potential to significantly improve the performance of online policy learning methods.
使用强化学习(RL)方法,通过个性化的即时适应性干预来支持健康行为改变,对于专注于戒烟支持和体育活动推广等问题的健康和行为科学研究者来说,具有极大的兴趣。然而,由于适应干预试验设计的实际限制所导致的严重数据稀缺问题,RL方法通常应用于这些领域,使用少量上下文变量来缓解。在本文中,我们探索了一种在不影响数据效率的情况下大幅扩展适应性干预状态空间的方法。所提出的方法使干预参与者能够提供对当前状态方面的自然语言描述。然后,它利用与预训练的大型语言模型(LLM)进行推断,以更好地将基础RL方法的策略与这些状态描述对齐。为了评估我们的方法,我们开发了一个新型体育活动干预模拟环境,该环境使用辅助LLM根据潜在状态变量生成文本状态描述。我们表明,这种方法有可能显著改善在线策略学习方法的表现。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at Machine Learning for Healthcare (MLHC) 2025
Summary
强化学习(RL)方法被用于支持健康行为改变,通过个性化及时适应性干预来促进戒烟支持和身体活动推广等问题,备受健康和行为科学研究者关注。然而,实际应用中常常面临数据稀缺问题,限制了适应性干预试验的设计。本文提出了一种显著扩展适应性干预状态空间的方法,通过让参与者提供当前状态的自然语言描述,并利用预训练的大型语言模型进行推理,更好地将基础强化学习方法的策略与这些状态描述对齐。通过开发新型身体活动干预模拟环境,我们证明了该方法在改善在线策略学习方法的性能上具有巨大潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 强化学习在健康行为改变中的应用重要且受到广泛关注。
- 数据稀缺是应用强化学习时面临的问题之一。
- 允许参与者提供当前状态的自然语言描述是解决数据稀缺问题的一种有效方法。
- 预训练的大型语言模型用于推理可以更好地匹配强化学习策略的当前状态描述。
- 提出的新型物理活动干预模拟环境用于评估此方法的有效性。
- 该方法有望显著提高在线策略学习方法的性能。
点此查看论文截图

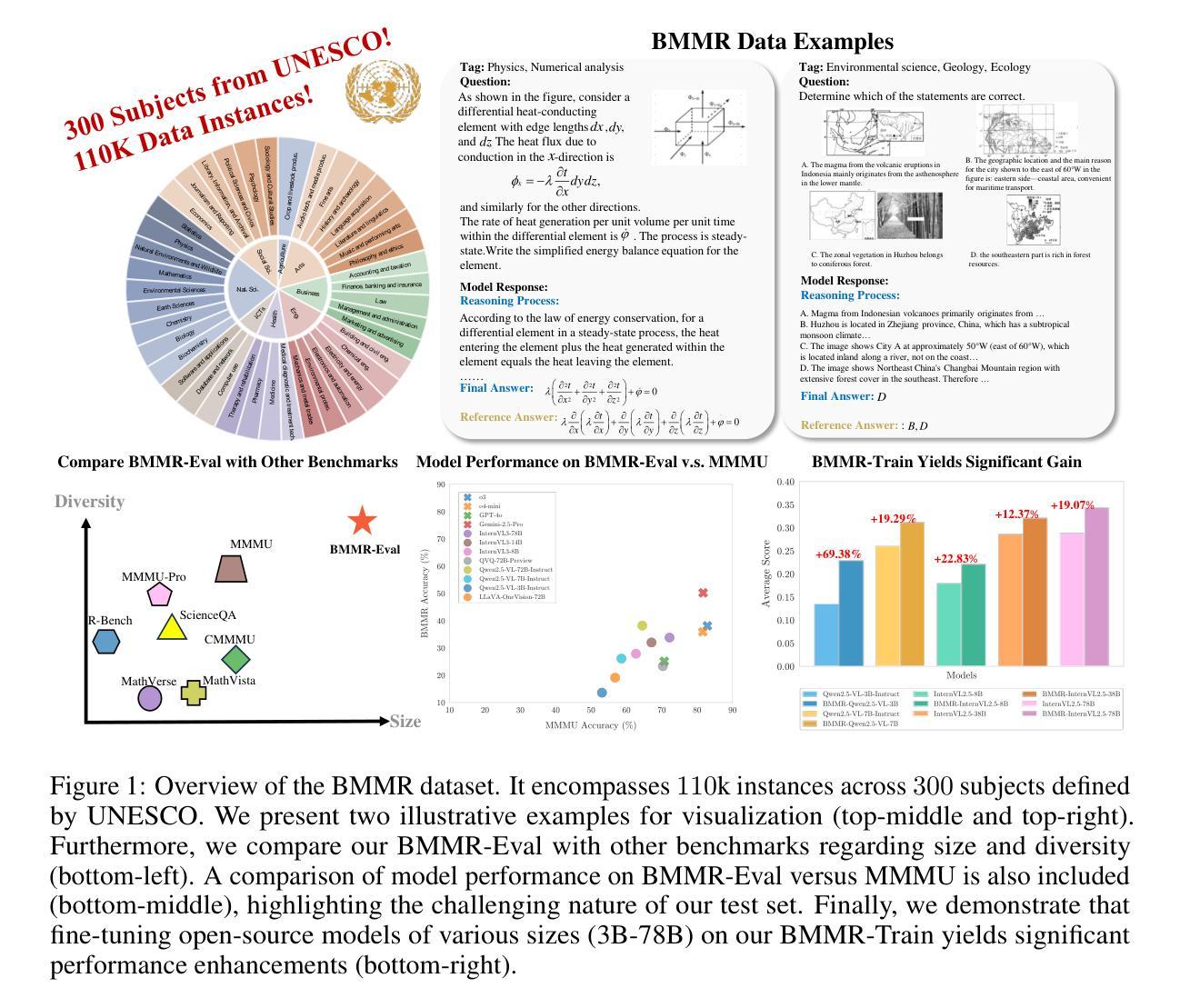
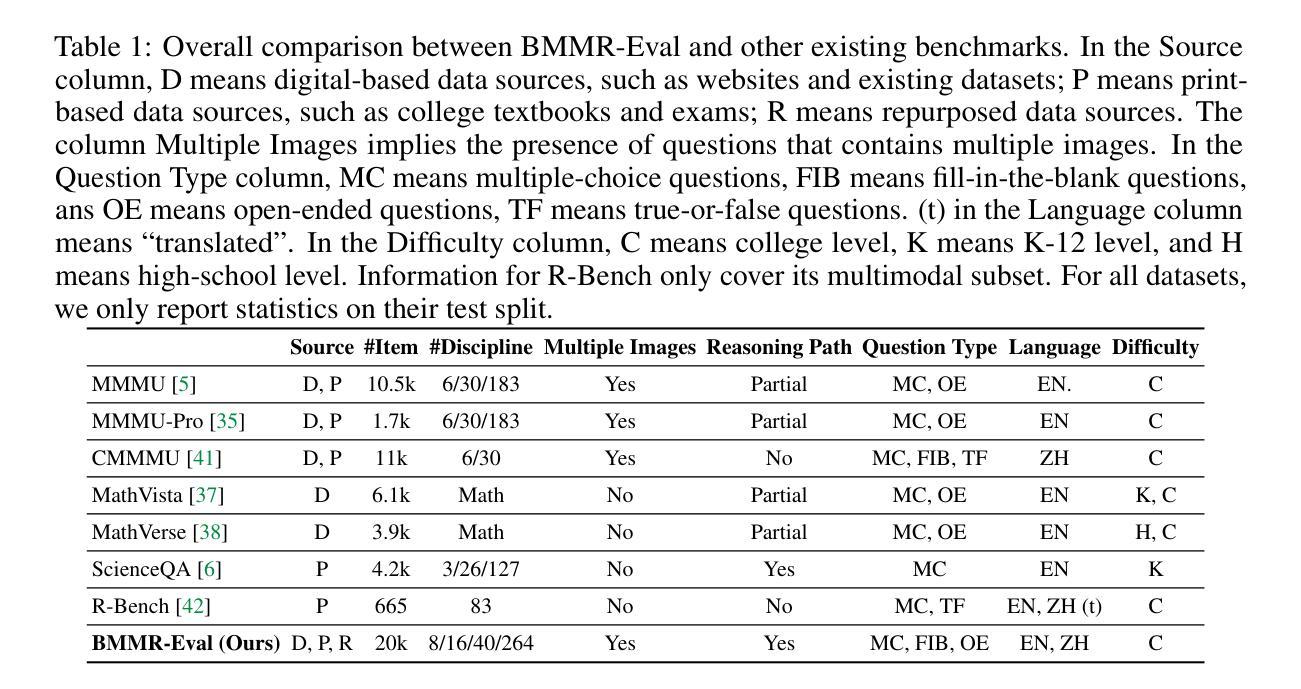
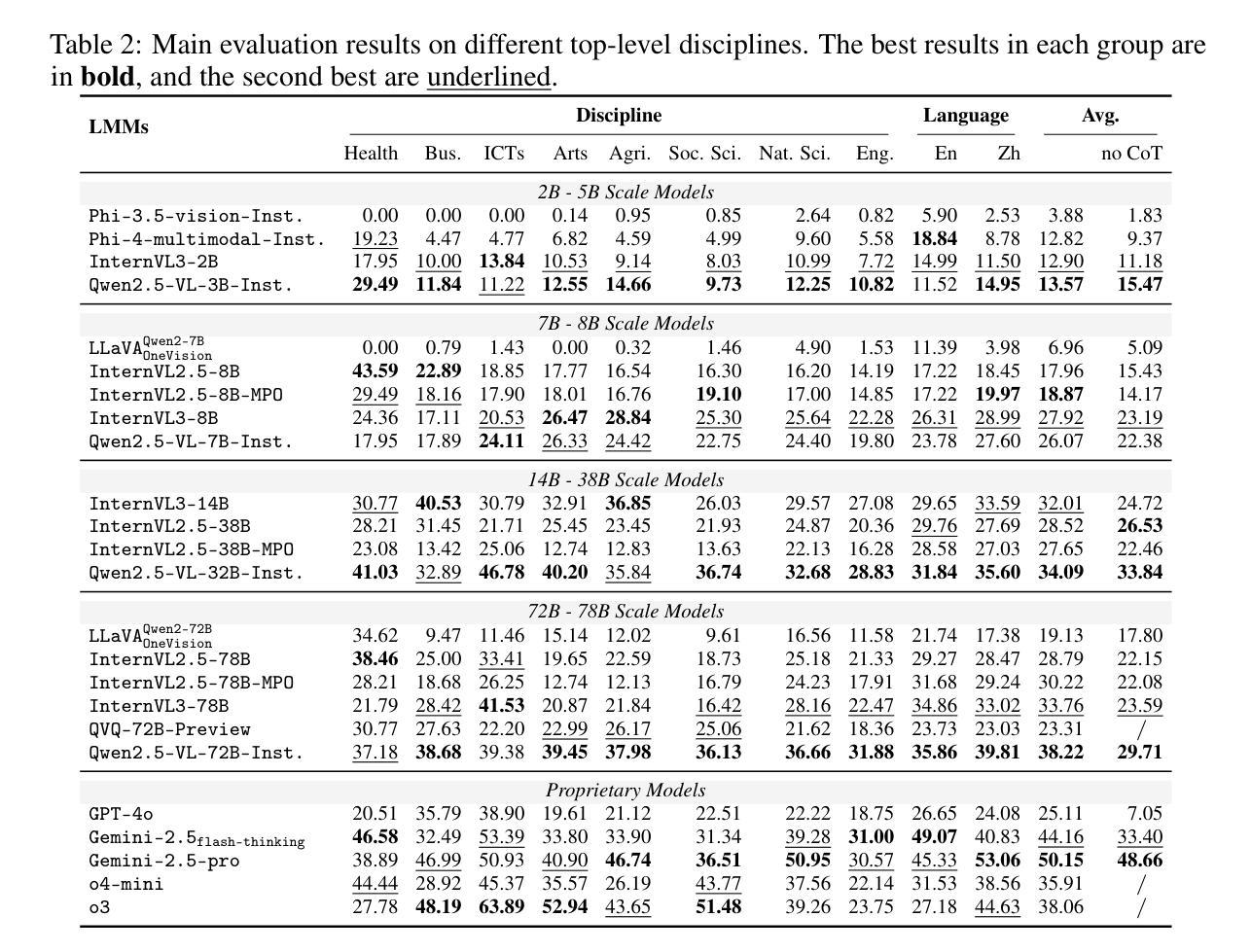
BMMR: A Large-Scale Bilingual Multimodal Multi-Discipline Reasoning Dataset
Authors:Zhiheng Xi, Guanyu Li, Yutao Fan, Honglin Guo, Yufang Liu, Xiaoran Fan, Jiaqi Liu, Jingchao Ding, Wangmeng Zuo, Zhenfei Yin, Lei Bai, Tao Ji, Tao Gui, Qi Zhang, Philip Torr, Xuanjing Huang
In this paper, we introduce BMMR, a large-scale bilingual, multimodal, multi-disciplinary reasoning dataset for the community to develop and evaluate large multimodal models (LMMs). BMMR comprises 110k college-level questions spanning 300 UNESCO-defined subjects, spanning diverse formats-multiple-choice, fill-in-the-blank, and open-ended QA-and sourced from both print and digital media such as books, exams, and quizzes. All data are curated and filtered via a human-in-the-loop and scalable framework, and each instance is paired with a high-quality reasoning path. The dataset is organized into two parts: BMMR-Eval that comprises 20,458 high-quality instances to comprehensively assess LMMs’ knowledge and reasoning across multiple disciplines in both Chinese and English; and BMMR-Train that contains 88,991 instances to support further research and development, extending the current focus on mathematical reasoning to diverse disciplines and domains. In addition, we propose the process-based multi-discipline verifier (i.e., BMMR-Verifier) for accurate and fine-grained evaluation of reasoning paths. Extensive experiments on 24 models reveal that (i) even SOTA models (e.g., o3 and Gemini-2.5-Pro) leave substantial headroom on BMMR-Eval; (ii) reasoning models exhibit discipline bias and outperform LMMs only on specific subjects; (iii) open-source models still trail their proprietary counterparts; and (iv) fine-tuning on BMMR-Train narrows this gap. Additionally, we conduct reasoning-chain analyses using BMMR-Verifier and other in-depth studies, uncovering the challenges LMMs currently face in multidisciplinary reasoning. We will release the data, and we hope our work can offer insights and contributions to the community.
本文介绍了BMMR,这是一个大规模的双语、多模态、多学科推理数据集,供社区用于开发和评估大型多模态模型(LMMs)。BMMR包含涉及联合国教科文组织定义的300个学科的11万道大学级别问题,涵盖多种题型,如选择题、填空题和开放式的问答题,来源于书籍、考试和测验等纸质和数字媒体。所有数据都是通过人机循环和可扩展的框架进行筛选和过滤的,每个实例都配有一条高质量推理路径。该数据集分为两部分:BMMR-Eval包含2万零458个高质量实例,旨在全面评估LMMs在中英文多个学科的知识和推理能力;BMMR-Train包含8万零991个实例,用于支持进一步的研究和开发,从当前对数学推理的关注扩展到多个学科领域。此外,我们提出了基于过程的跨学科验证器(即BMMR-Verifier),对推理路径进行准确细致的评估。对24个模型的广泛实验表明:(i)即使在BMMR-Eval上,即使是最先进的技术模型(如o3和Gemini-2.5-Pro)仍有很大的提升空间;(ii)推理模型存在学科偏见,仅在特定学科上优于LMMs;(iii)开源模型仍然落后于专有模型;(iv)在BMMR-Train上进行微调可以缩小这一差距。此外,我们使用BMMR-Verifier进行推理链分析以及其他深入研究,揭示了LMMs当前在多学科推理方面所面临的挑战。我们将发布这些数据,希望我们的工作能为社区提供见解和贡献。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint
摘要
本文介绍了一个大规模的双语、多模态、多学科推理数据集BMMR,供社区用于开发和评估大型多模态模型(LMMs)。BMMR包含110k道涉及300个联合国教科文组织定义学科的大学级别问题,涵盖多种题型,如选择题、填空题和开放问答,来源于书籍、考试和测验等印刷和数字媒体。数据集通过人机协作和可扩展框架进行筛选和过滤,每个实例都配备高质量推理路径。数据集分为两部分:BMMR-Eval包含20,458道高质量实例,旨在全面评估LMMs在多学科中的知识和推理能力(包括中文和英文);BMMR-Train包含88,991个实例,用于支持进一步的研究和开发,扩展当前对数学推理的关注,涵盖多个学科和领域。此外,本文提出了基于过程的跨学科验证器(即BMMR-Verifier)进行推理路径的精确和细致评估。对24个模型的广泛实验表明:(i)即使在BMMR-Eval上,现有顶尖模型仍有提升空间;(ii)推理模型在某些特定学科上表现优于LMMs,但存在学科偏见;(iii)开源模型仍落后于专有模型;(iv)在BMMR-Train上进行微调缩小了这一差距。此外,通过BMMR-Verifier和其他深入的分析研究,揭示了LMMs在多学科推理方面所面临的挑战。我们将发布这些数据集,希望我们的工作能为社区提供见解和贡献。
关键见解
- 引入大规模双语、多模态、多学科推理数据集BMMR,用于开发和评估大型多模态模型(LMMs)。
- 数据集包含多种题型和来源,涵盖广泛的学科领域。
- 提出基于过程的跨学科验证器(BMMR-Verifier)进行精细的推理路径评估。
- 实验表明现有顶尖模型在BMMR-Eval上仍有提升空间。
- 推理模型表现存在学科偏见,某些特定学科上表现较好。
- 开源模型在性能上仍落后于专有模型。
点此查看论文截图

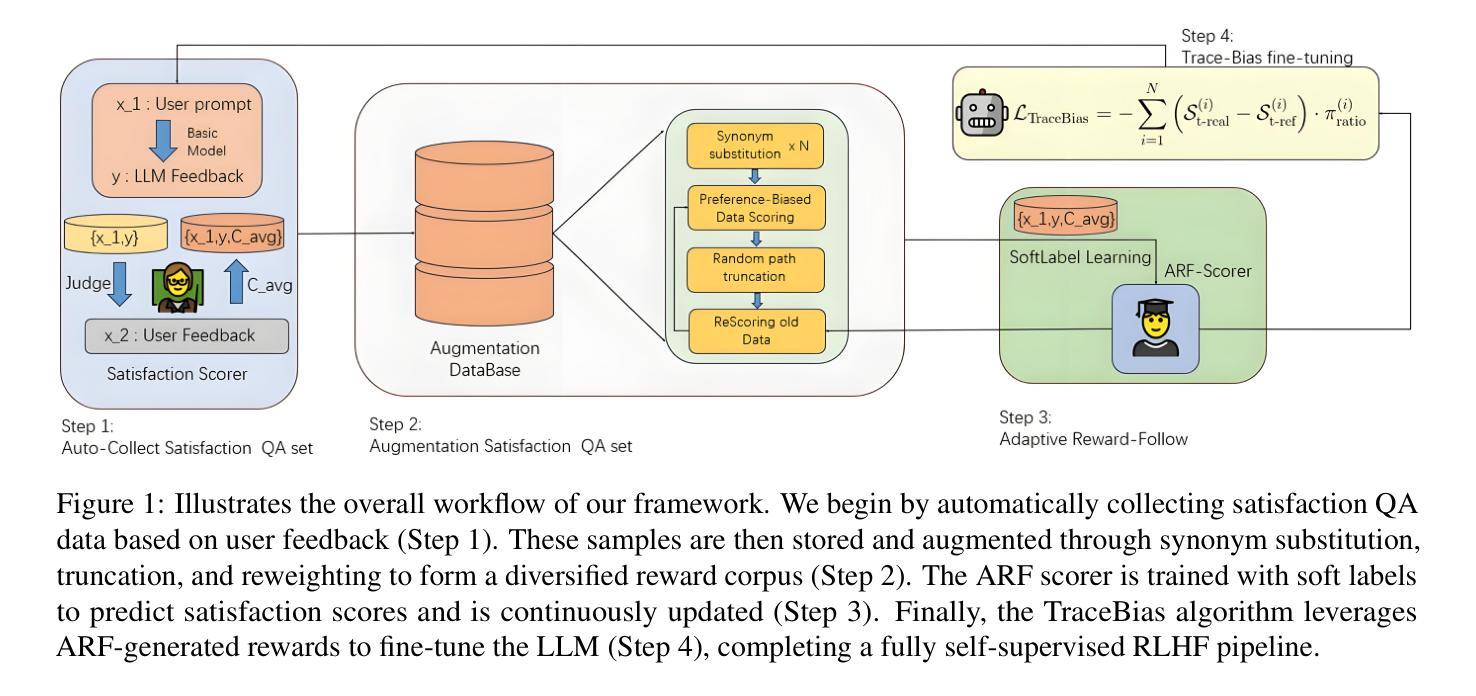
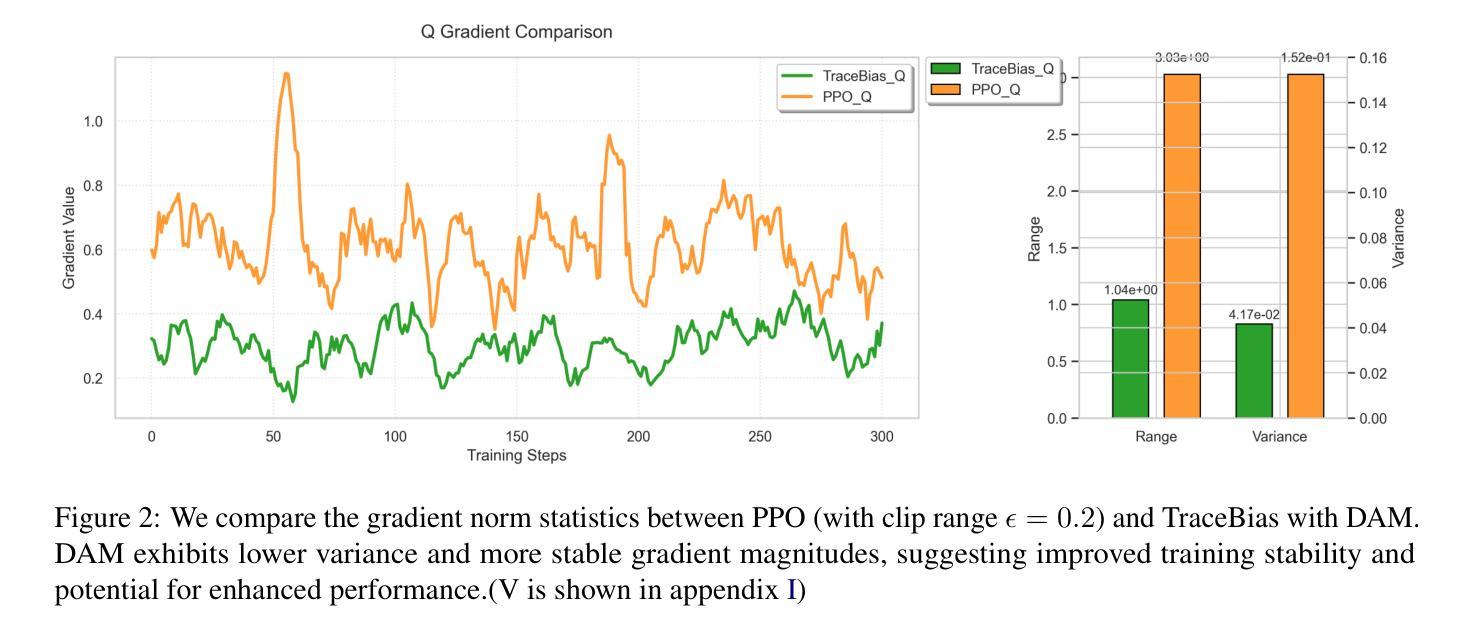
ARF-RLHF: Adaptive Reward-Following for RLHF through Emotion-Driven Self-Supervision and Trace-Biased Dynamic Optimization
Authors:YuXuan Zhang
With the rapid advancement of Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) and autoregressive transformers, state-of-the-art models such as GPT-4.0, DeepSeek R1, and Llama 3.3 increasingly emphasize answer depth and personalization. However, most existing RLHF approaches (e.g., PPO, DPO) still rely on a binary-preference (BT) paradigm, which, while reducing annotation costs, still requires substantial human effort and captures only group-level tendencies rather than individual preferences. To overcome these limitations, we propose Adaptive Reward-Following (ARF), a self-assessment framework that leverages a high-precision emotion analyzer achieving over 70% accuracy on GoEmotions, Sentiment140, and DailyDialog to convert free-form user feedback into continuous preference scores. We further enrich and debias these signals through lightweight data augmentations, including synonym replacement, random trace truncation, and score bias annotation algorithm. A Dynamic Adapter Preference Tracker continuously models evolving user tastes in real time, enabling our novel Trace Bias (TB) fine-tuning algorithm to optimize directly on these tracked rewards instead of coarse binary labels. Experiments on Qwen-2/2.5, Gemma-2, and Llama-3.2 across four preference domains demonstrate that ARF achieves an improvement of 3.3% over PPO and 7.6% over DPO. Moreover, TB preserves theoretical alignment with PPO and DPO objectives. Overall, ARF presents a scalable, personalized, and cost-effective approach to RLHF LLMs through autonomous reward modeling.
随着强化学习从人类反馈(RLHF)和自回归变压器的快速发展,最先进的模型如GPT-4.0、DeepSeek R1和Llama 3.3越来越强调答案的深度和个性化。然而,现有的大多数RLHF方法(如PPO、DPO)仍然依赖于二元偏好(BT)范式,虽然降低了标注成本,但仍需要大量的人力投入,并且只能捕捉群体层面的趋势,而非个人偏好。
为了克服这些限制,我们提出了自适应奖励跟踪(ARF),这是一个自我评估框架,它利用高精度情绪分析器(在GoEmotions、Sentiment140和DailyDialog上的准确率超过7宁”),将自由形式的用户反馈转化为连续偏好分数。我们还通过轻量级的数据增强来丰富和去偏置这些信号,包括同义词替换、随机轨迹截断和评分偏差注释算法。动态适配器偏好跟踪器实时建模不断变化的用户品味,使我们的新型轨迹偏差(TB)微调算法可以直接在这些跟踪的奖励上进行优化,而不是粗略的二元标签。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint under review
Summary
基于强化学习人类反馈(RLHF)、自回归变压器以及先进模型如GPT-4.0、DeepSeek R1和Llama 3.3的快速发展,回答的深度和个性化越来越受到重视。然而,现有的RLHF方法仍然依赖于二元偏好(BT)模式,需要大量人力并仅捕捉群体偏好而非个体偏好。为此,本文提出了自适应奖励跟踪(ARF)这一自我评估框架,利用高精度情绪分析器将自由形式的用户反馈转化为连续偏好分数,并通过轻量级数据增强和动态适配器偏好跟踪技术来丰富和去偏这些信号。实验表明,ARF在四个偏好领域均优于PPO和DPO,实现了可规模化、个性化和成本效益高的LLM强化学习人类反馈方法。
Key Takeaways
- 先进模型如GPT-4.0等强调答案的深度和个性化。
- 现有RLHF方法依赖二元偏好模式,需要大量人力并仅捕捉群体偏好。
- ARF框架利用高精度情绪分析器转化用户反馈为连续偏好分数。
- 通过轻量级数据增强技术丰富和去偏用户反馈信号。
- 动态适配器偏好跟踪技术实时建模用户口味变化。
- ARF通过自主奖励建模实现了可规模化、个性化和成本效益高的RLHF方法。
点此查看论文截图

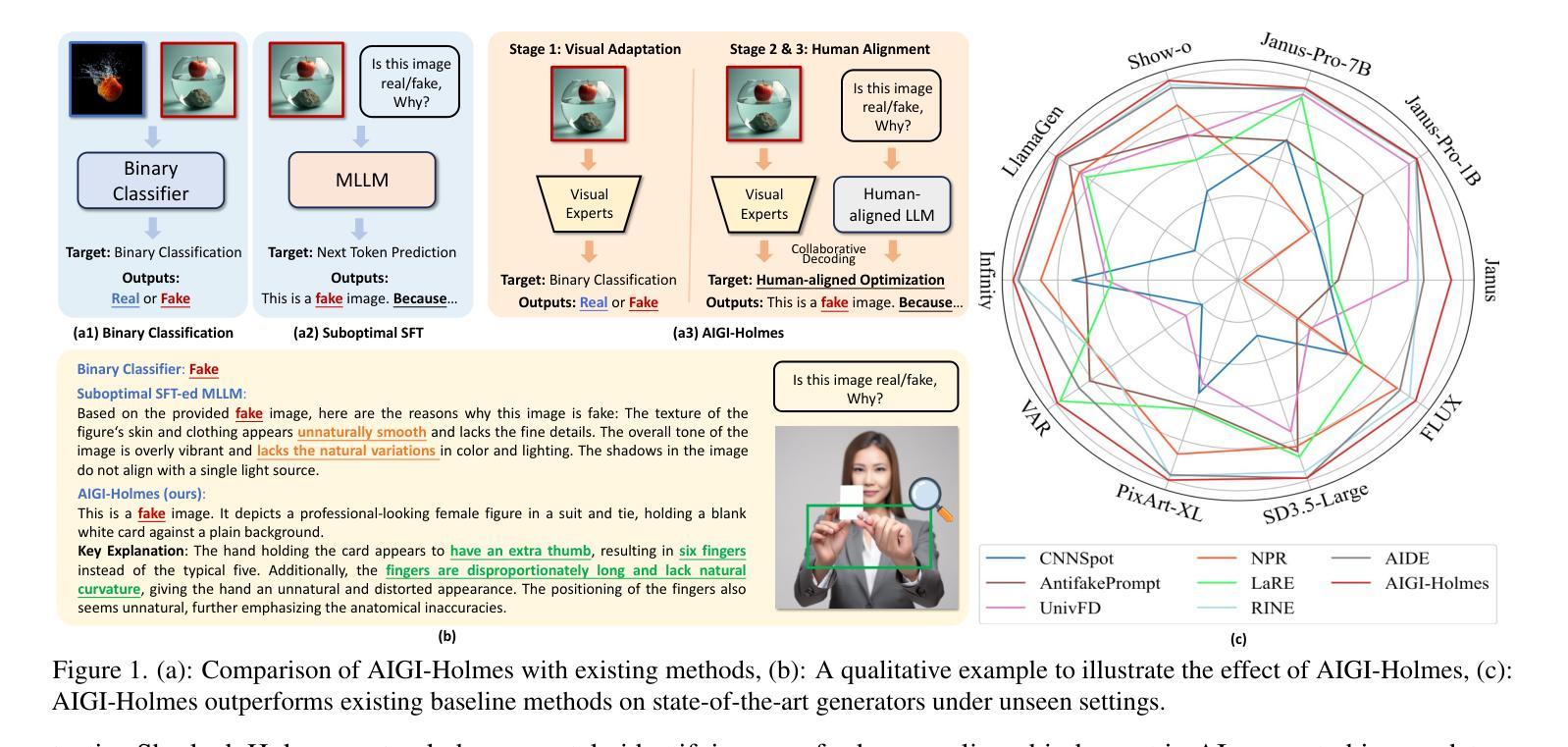
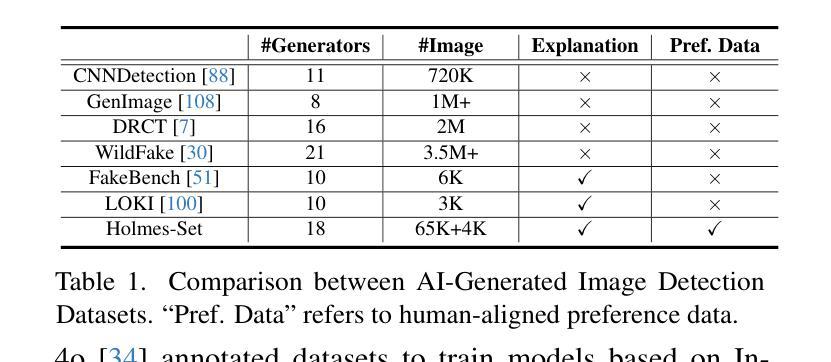
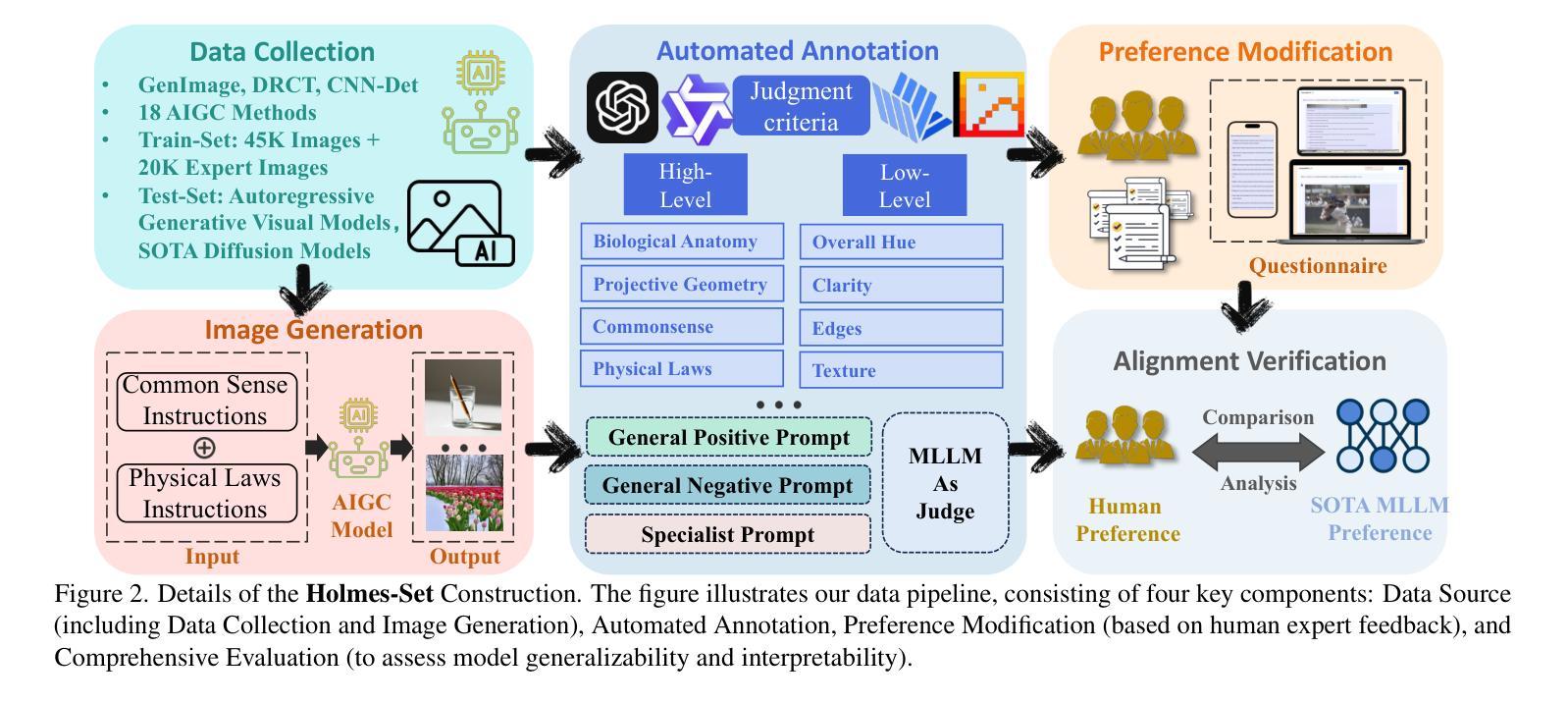
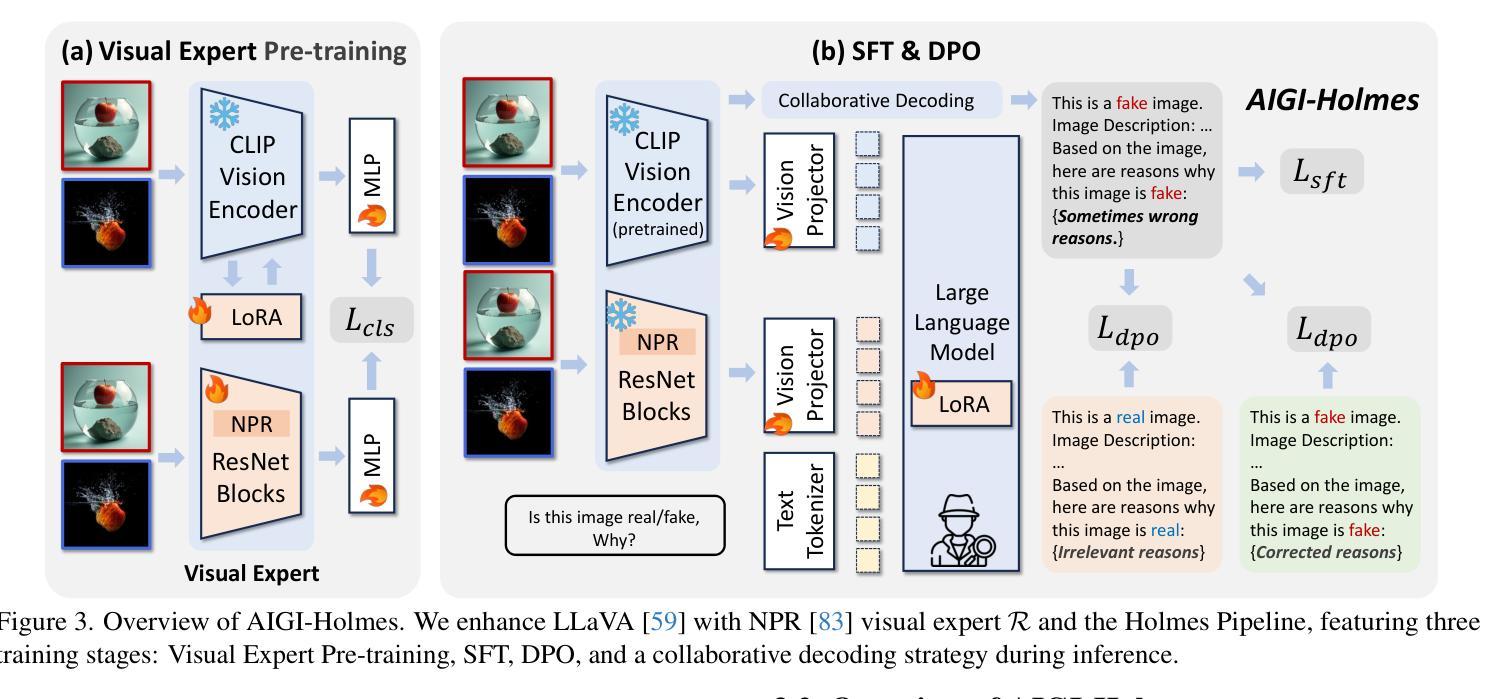
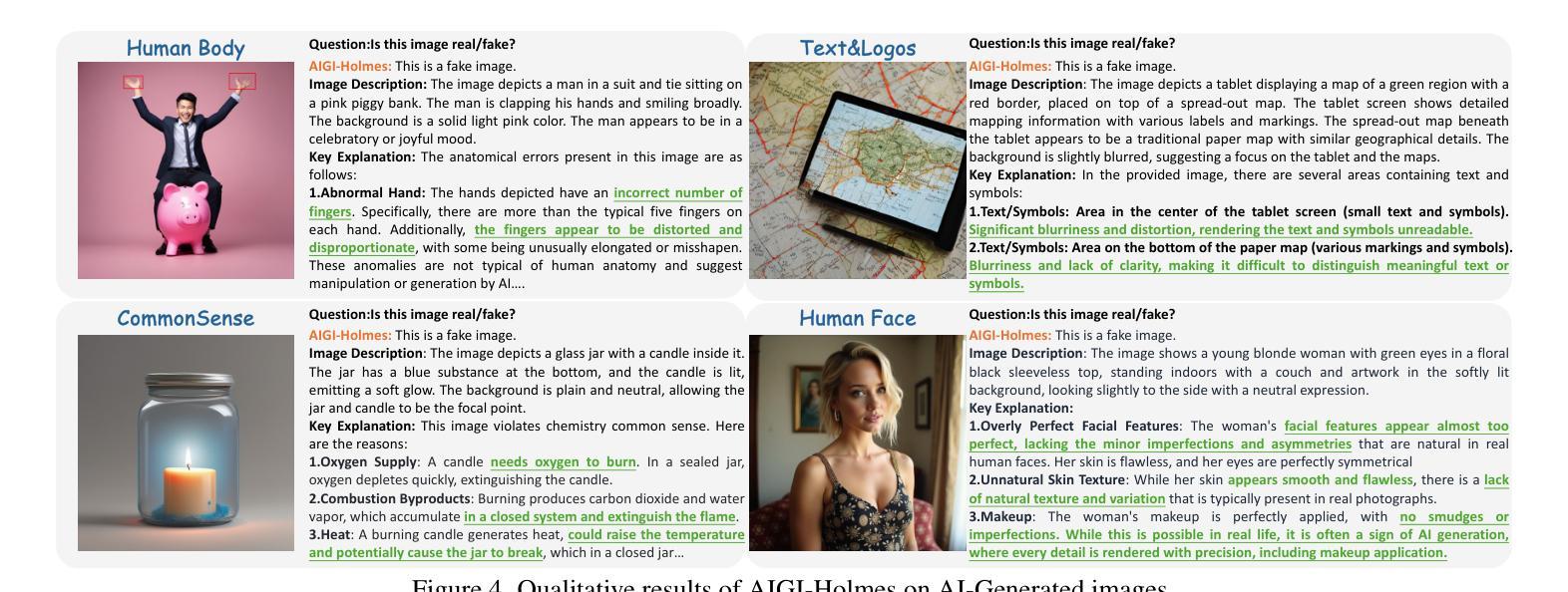
AIGI-Holmes: Towards Explainable and Generalizable AI-Generated Image Detection via Multimodal Large Language Models
Authors:Ziyin Zhou, Yunpeng Luo, Yuanchen Wu, Ke Sun, Jiayi Ji, Ke Yan, Shouhong Ding, Xiaoshuai Sun, Yunsheng Wu, Rongrong Ji
The rapid development of AI-generated content (AIGC) technology has led to the misuse of highly realistic AI-generated images (AIGI) in spreading misinformation, posing a threat to public information security. Although existing AIGI detection techniques are generally effective, they face two issues: 1) a lack of human-verifiable explanations, and 2) a lack of generalization in the latest generation technology. To address these issues, we introduce a large-scale and comprehensive dataset, Holmes-Set, which includes the Holmes-SFTSet, an instruction-tuning dataset with explanations on whether images are AI-generated, and the Holmes-DPOSet, a human-aligned preference dataset. Our work introduces an efficient data annotation method called the Multi-Expert Jury, enhancing data generation through structured MLLM explanations and quality control via cross-model evaluation, expert defect filtering, and human preference modification. In addition, we propose Holmes Pipeline, a meticulously designed three-stage training framework comprising visual expert pre-training, supervised fine-tuning, and direct preference optimization. Holmes Pipeline adapts multimodal large language models (MLLMs) for AIGI detection while generating human-verifiable and human-aligned explanations, ultimately yielding our model AIGI-Holmes. During the inference stage, we introduce a collaborative decoding strategy that integrates the model perception of the visual expert with the semantic reasoning of MLLMs, further enhancing the generalization capabilities. Extensive experiments on three benchmarks validate the effectiveness of our AIGI-Holmes.
人工智能生成内容(AIGC)技术的快速发展导致了高度逼真的AI生成图像(AIGI)被滥用,用于传播错误信息,对公众信息安全构成威胁。尽管现有的AIGI检测技术通常有效,但它们面临两个问题:一是缺乏可验证的人为解释,二是在最新技术中缺乏泛化能力。为了解决这两个问题,我们引入了一个大规模且全面的数据集Holmes-Set,其中包括Holmes-SFTSet(一个带有关于图像是否由AI生成解释的指令调整数据集)和Holmes-DPOSet(一个人为对齐的偏好数据集)。我们的工作引入了一种高效的数据标注方法,称为“多元专家陪审团”,通过结构化的MLLM解释和质量控制来增强数据生成,质量控制包括跨模型评估、专家缺陷过滤和人为偏好修正。此外,我们提出了精心设计的三阶段训练框架Holmes Pipeline,包括视觉专家预训练、监督微调以及直接偏好优化。Holmes Pipeline适应于多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)用于检测AIGI,同时生成可验证和人为对齐的解释,最终得到我们的模型AIGI-Holmes。在推理阶段,我们引入了一种协同解码策略,将视觉专家的模型感知与MLLMs的语义推理相结合,进一步提高了泛化能力。在三个基准上的大量实验验证了我们的AIGI-Holmes的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICCV 2025
Summary
人工智能生成内容(AIGC)技术的快速发展导致AI生成图像(AIGI)被滥用,传播错误信息,威胁公众信息安全。现有AIGI检测技术虽普遍有效,但存在缺乏可验证的人类解释和新技术普及的泛化能力不足的问题。为解决这些问题,研究团队引入大规模综合数据集Holmes-Set,包括带有图像是否AI生成解释的指令调整数据集Holmes-SFTSet和人类对齐偏好数据集Holmes-DPOSet。该研究采用多专家评审的高效数据标注方法,通过结构化MLLM解释和质量控制措施提高数据生成质量。同时提出Holmes Pipeline三阶段训练框架,包括视觉专家预训练、监督微调及直接偏好优化等。实验证明,新模型AIGI-Holmes能有效检测AIGI并生成可验证的人类对齐解释,同时具有良好的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- AI生成内容(AIGC)技术快速发展,导致AI生成图像(AIGI)被滥用传播错误信息,威胁公众信息安全。
- 现有AIGI检测技术面临缺乏可验证的人类解释和新技术普及的泛化能力不足的问题。
- 研究团队引入大规模综合数据集Holmes-Set,包括带有解释的指令调整数据集和人类对齐偏好数据集。
- 采用多专家评审的数据标注方法提高数据质量,包括结构化MLLM解释和质量控制措施。
- 提出Holmes Pipeline三阶段训练框架,包括视觉专家预训练、监督微调及直接偏好优化等。
- AIGI检测模型生成的人类对齐解释具有可验证性。
点此查看论文截图

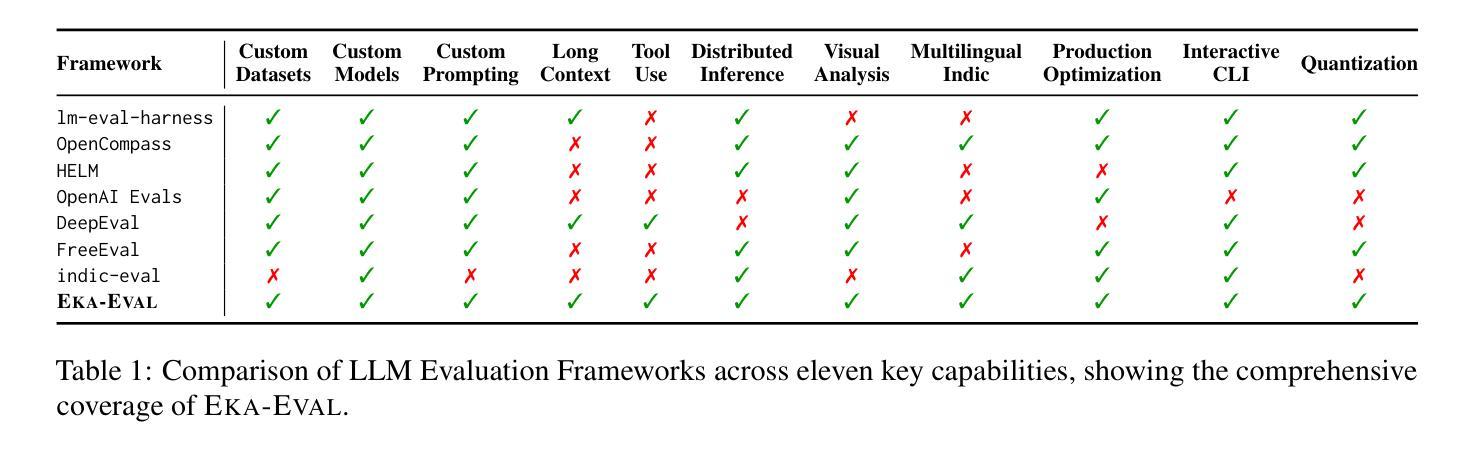
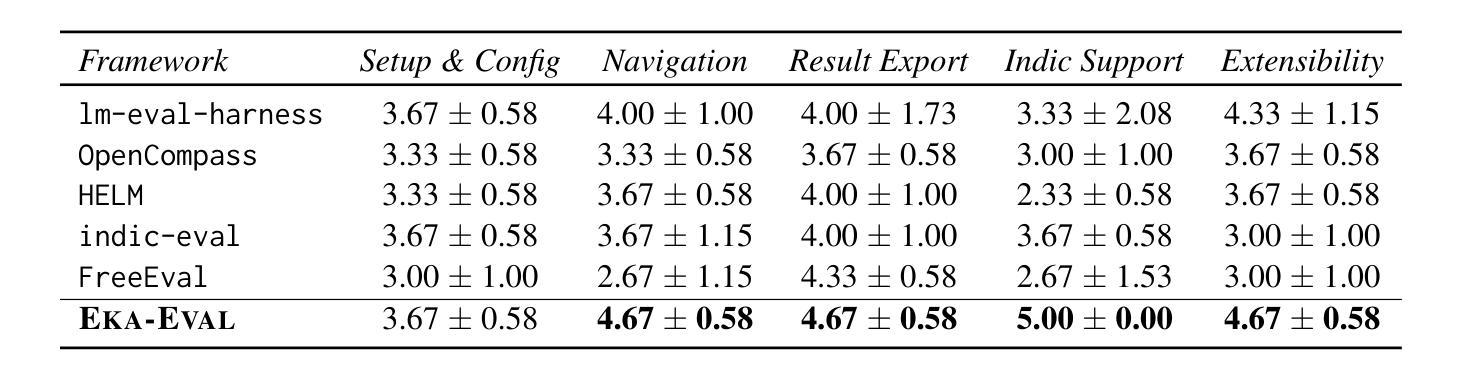
Eka-Eval : A Comprehensive Evaluation Framework for Large Language Models in Indian Languages
Authors:Samridhi Raj Sinha, Rajvee Sheth, Abhishek Upperwal, Mayank Singh
The rapid advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs) has intensified the need for evaluation frameworks that address the requirements of linguistically diverse regions, such as India, and go beyond English-centric benchmarks. We introduce EKA-EVAL, a unified evaluation framework that integrates over 35+ benchmarks (including 10 Indic benchmarks) across nine major evaluation categories. The framework provides broader coverage than existing Indian language evaluation tools, offering 11 core capabilities through a modular architecture, seamless integration with Hugging Face and proprietary models, and plug-and-play usability. As the first end-to-end suite for scalable, multilingual LLM benchmarking, the framework combines extensive benchmarks, modular workflows, and dedicated support for low-resource Indian languages to enable inclusive assessment of LLM capabilities across diverse domains. We conducted extensive comparisons against five existing baselines, demonstrating that EKA-EVAL achieves the highest participant ratings in four out of five categories. The framework is open-source and publicly available at: https://github.com/lingo-iitgn/eka-eval.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展,需要强化评估框架的需求,以满足印度等语言多样化的地区需求,并超越以英语为中心的基准测试。我们介绍了EKA-EVAL这一统一评估框架,它集成了超过35项基准测试(包括10项印度语言基准测试),涵盖九大主要评估类别。该框架提供了比现有印度语言评估工具更广泛的覆盖范围,通过模块化架构提供11项核心能力,与Hugging Face和专有模型无缝集成,以及即插即用的易用性。作为首个端到端、可伸缩的多语种LLM基准测试套件,该框架结合了广泛的基准测试、模块化工作流程以及对低资源印度语言的专项支持,以实现对不同领域LLM能力的全面评估。我们与五个现有基线进行了广泛比较,结果表明,在五个类别中,EKA-EVAL在四个类别中获得了最高参与者评分。该框架是开源的,可在以下网址公开获取:https://github.com/lingo-iitgn/eka-eval 。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展加剧了对评估框架的需求,这些评估框架需要满足语言多样化地区(如印度)的要求,并超越英语中心的基准测试。我们介绍了EKA-EVAL,这是一个统一评估框架,整合了35个以上的基准测试(包括10个印度语言基准测试),涵盖九大主要评估类别。该框架提供比现有印度语言评估工具更广泛的覆盖,通过模块化架构提供11项核心能力,与Hugging Face和专有模型无缝集成,以及即插即用的易用性。作为首个端到端、可伸缩、多语言LLM基准测试套件,该框架结合了广泛的基准测试、模块化工作流程以及对低资源印度语言的专门支持,以实现对LLM在各种领域能力的包容性评估。
Key Takeaways
- EKA-EVAL是一个统一评估框架,满足大型语言模型(LLM)的评估需求。
- 该框架考虑到了语言多样性,特别包括印度语言。
- EKA-EVAL整合了超过35个基准测试,涵盖九大评估类别。
- 相比其他印度语言评估工具,EKA-EVAL提供更广泛的覆盖。
- 框架具有模块化架构、易于与Hugging Face和专有模型集成等特点。
- EKA-EVAL在五个类别中的四个获得了最高参与者评分。
点此查看论文截图