⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-10 更新
Differentiable Reward Optimization for LLM based TTS system
Authors:Changfeng Gao, Zhihao Du, Shiliang Zhang
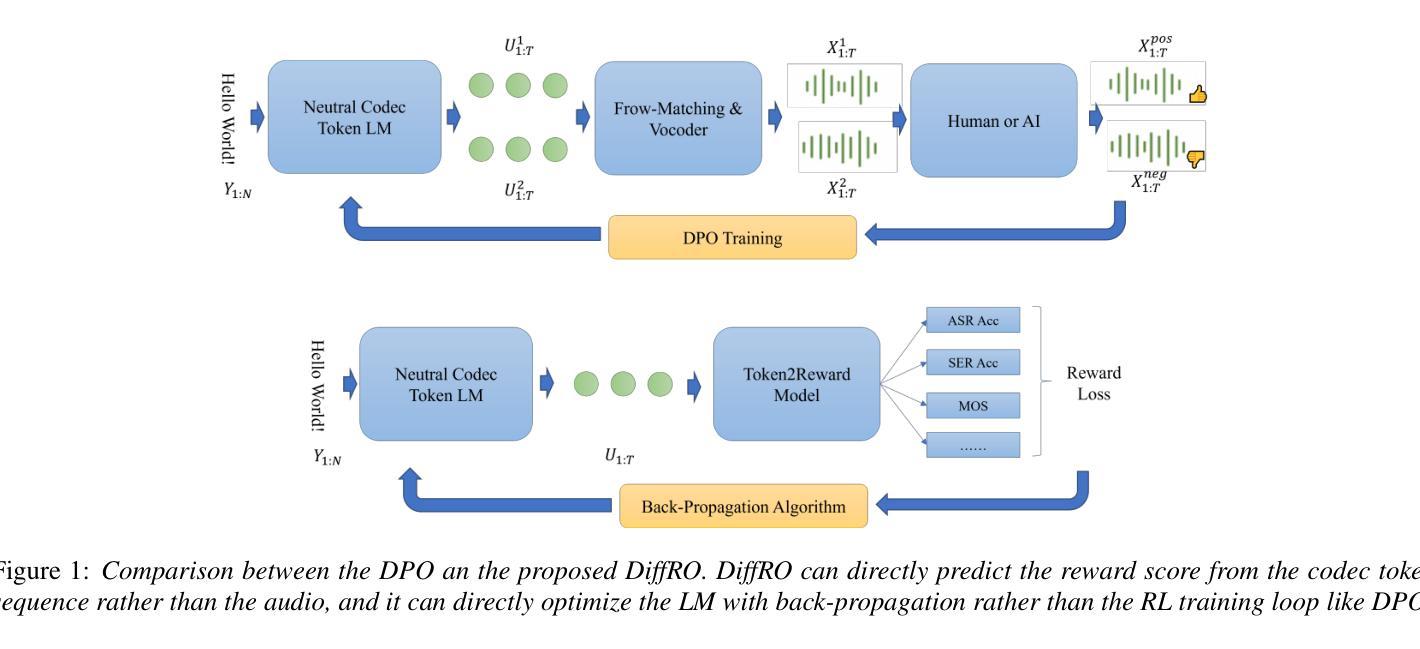
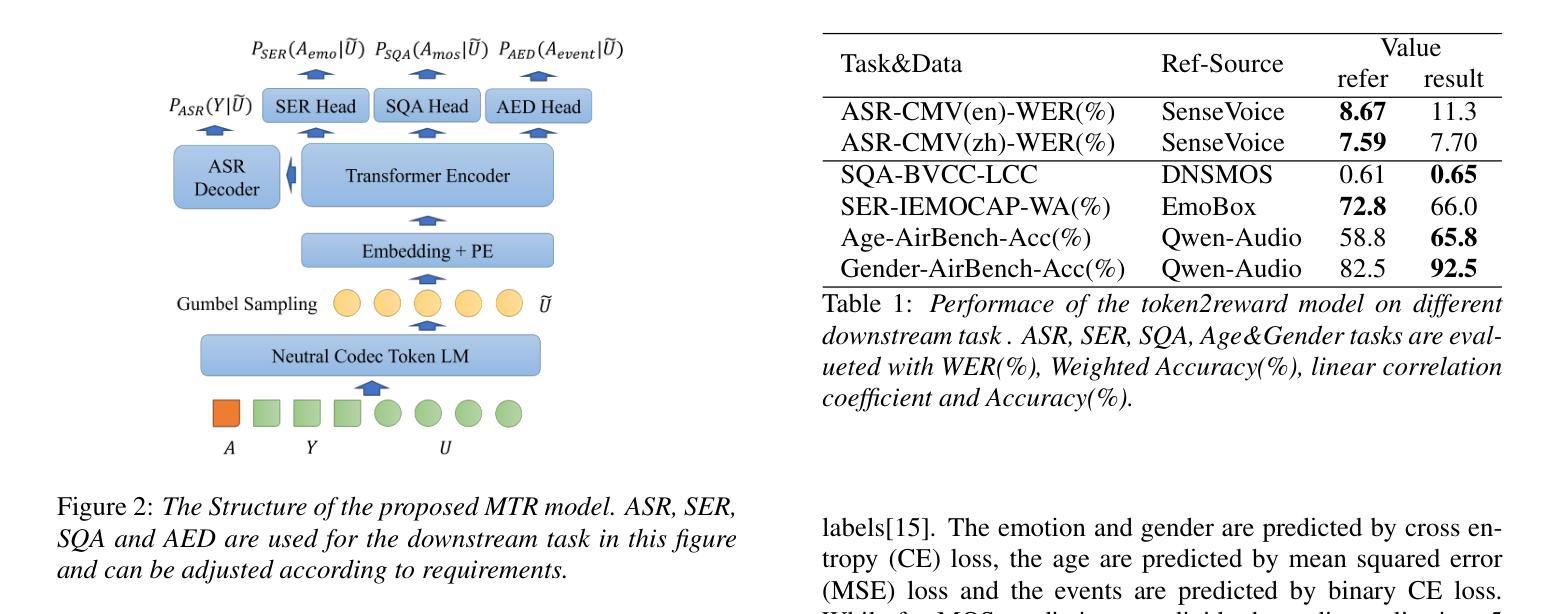
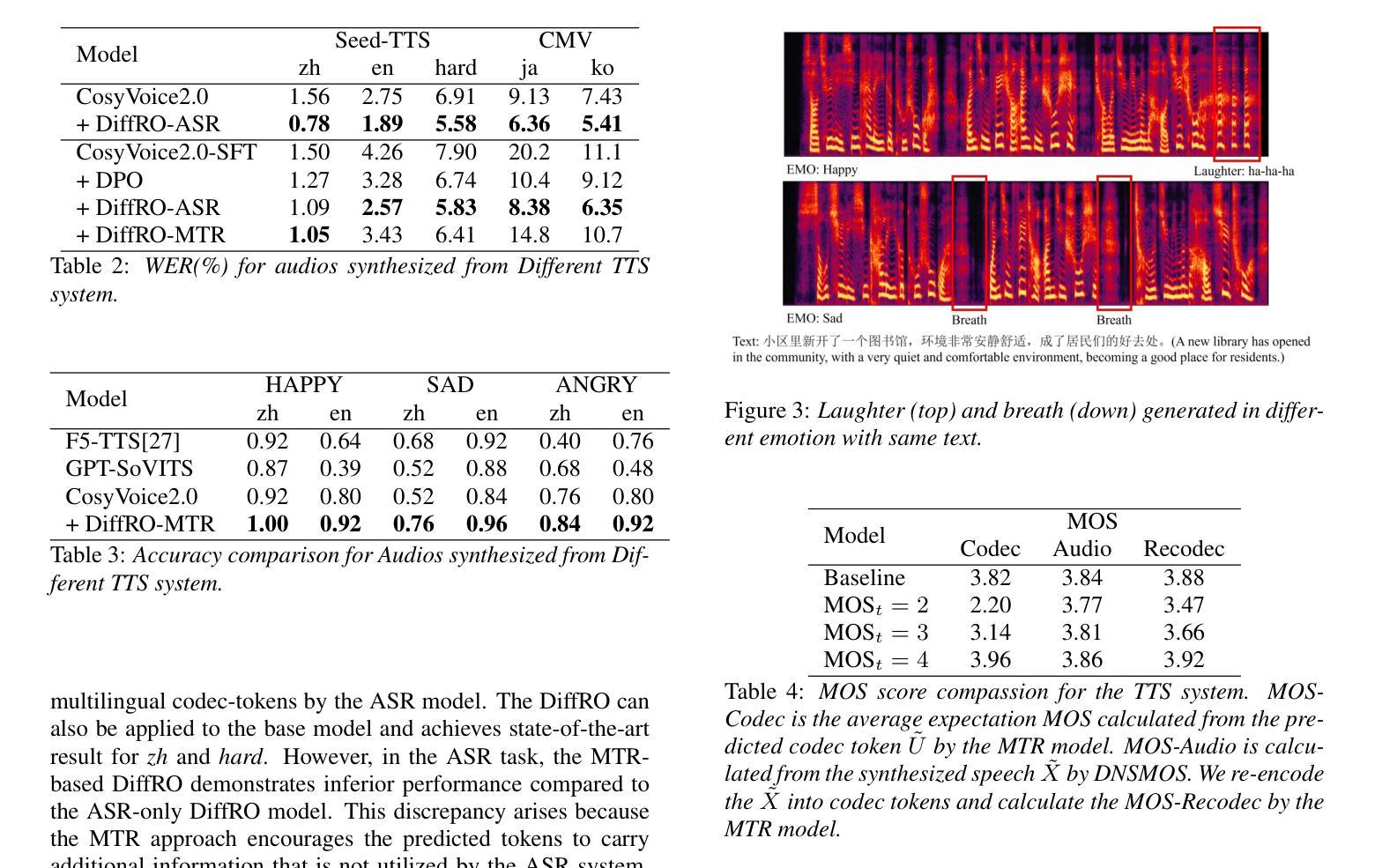
This paper proposes a novel Differentiable Reward Optimization (DiffRO) method aimed at enhancing the performance of neural codec language models based text-to-speech (TTS) systems. In contrast to conventional reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) approaches applied to TTS, DiffRO directly compute the rewards based on neural codec tokens, rather than relying on synthesized audio. Furthermore, we employ the Gumbel-Softmax technique to render the reward function differentiable, thereby streamlining the RLHF training process. Additionally, we introduce a multi-task reward (MTR) model which can provide feedback from different perspectives and find that it can augment the system’s capability to follow instructions effectively.Experimental results indicate that DiffRO significantly improves the pronunciation accuracy of the TTS system, achieving state-of-the-art (SOTA) WER results on the seed-tts-eval benchmark. Moreover, with the integration of the MTR model, we demonstrate the ability to control emotional and quality attributes in a zero-shot manner.
本文提出了一种新型的可微分奖励优化(DiffRO)方法,旨在提高基于神经编码语言模型的文本到语音(TTS)系统的性能。与传统的应用于TTS的人反馈强化学习(RLHF)方法相比,DiffRO直接基于神经编码令牌计算奖励,而不是依赖于合成音频。此外,我们采用Gumbel-Softmax技术使奖励函数可微分,从而简化了RLHF训练过程。我们还引入了一个多任务奖励(MTR)模型,可以从不同的角度提供反馈,并发现它可以增强系统有效遵循指令的能力。实验结果表明,DiffRO显著提高了TTS系统的发音准确性,在seed-tts-eval基准测试中实现了最先进的词错误率(WER)结果。而且,通过整合MTR模型,我们展示了零样本方式控制情感和品质属性的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种名为可微奖励优化(DiffRO)的新方法,旨在提高基于神经编码语言模型的文本到语音(TTS)系统的性能。与常规的应用于TTS的基于人类反馈的强化学习(RLHF)方法不同,DiffRO直接基于神经编码令牌计算奖励,而不是依赖于合成的音频。此外,本文采用Gumbel-Softmax技术使奖励函数可微,从而简化了RLHF训练过程。同时,引入多任务奖励(MTR)模型,可从不同角度提供反馈,提高了系统遵循指令的有效性。实验结果表明,DiffRO显著提高了TTS系统的发音准确性,在seed-tts-eval基准测试中实现了最先进的词错误率(WER)结果。而且,通过整合MTR模型,我们展示了零样本方式控制情感和品质属性的能力。
Key Takeaways
- DiffRO方法被提出以提高基于神经编码语言模型的TTS系统性能。
- 与传统RLHF方法不同,DiffRO直接基于神经编码令牌计算奖励。
- Gumbel-Softmax技术被用于使奖励函数可微,简化了RLHF训练过程。
- 引入多任务奖励(MTR)模型,从不同角度提供反馈,提高系统遵循指令的能力。
- DiffRO显著提高TTS系统的发音准确性,达到最先进的WER结果。
- MTR模型的整合使系统能够零样本方式控制情感和品质属性。
点此查看论文截图

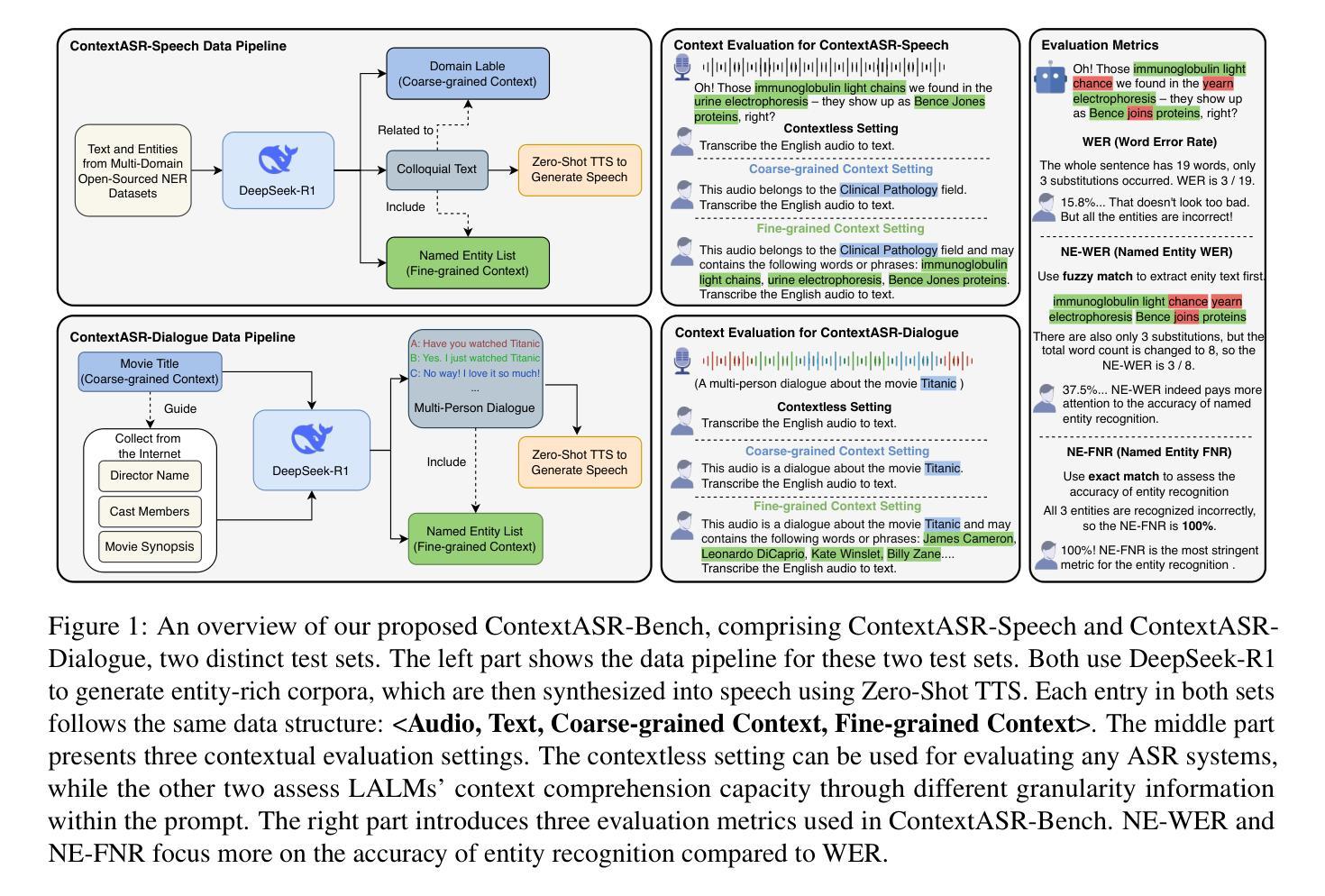
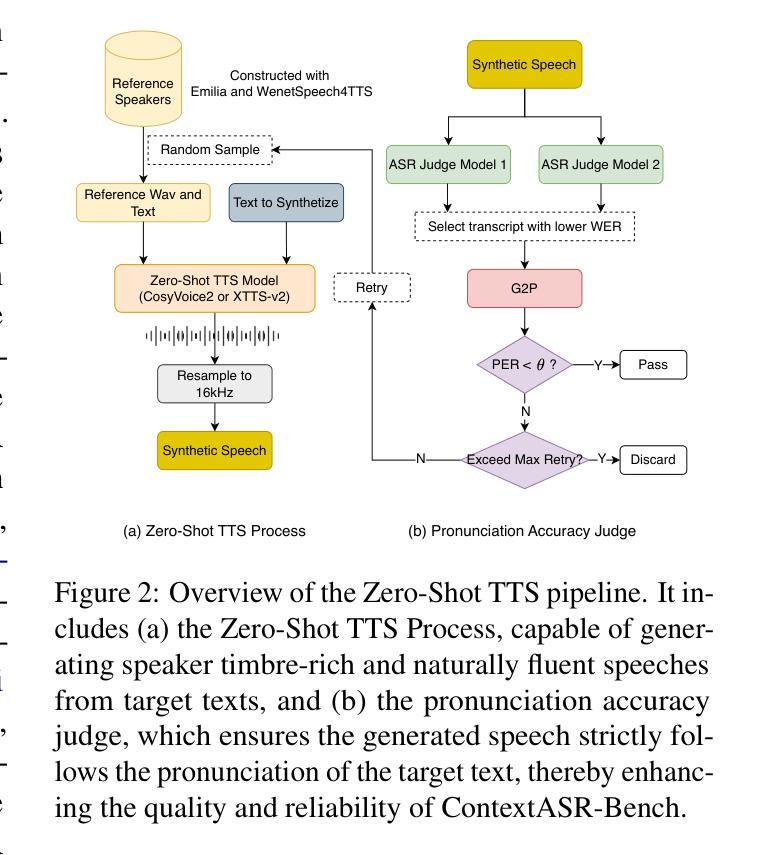
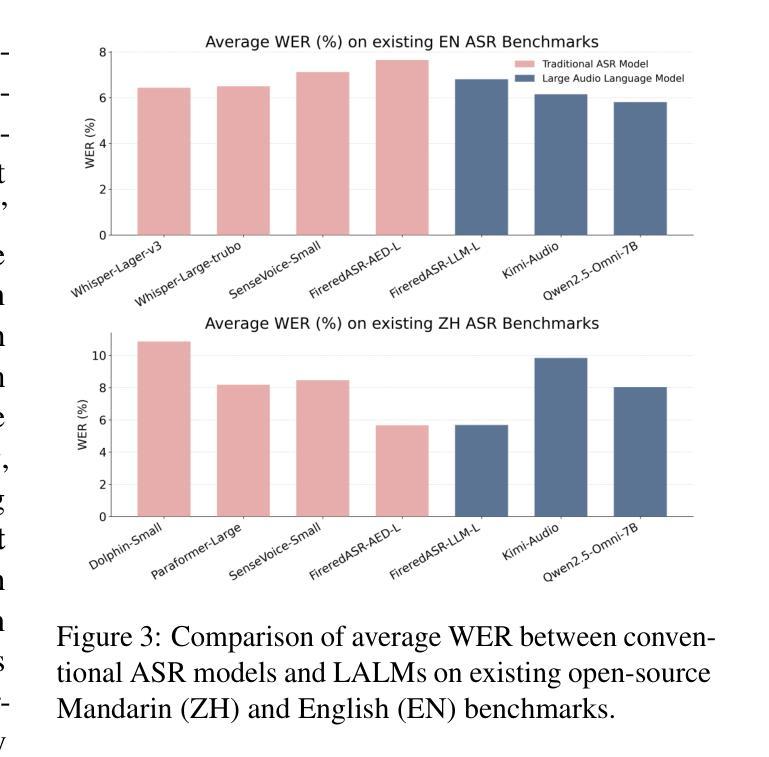
ContextASR-Bench: A Massive Contextual Speech Recognition Benchmark
Authors:He Wang, Linhan Ma, Dake Guo, Xiong Wang, Lei Xie, Jin Xu, Junyang Lin
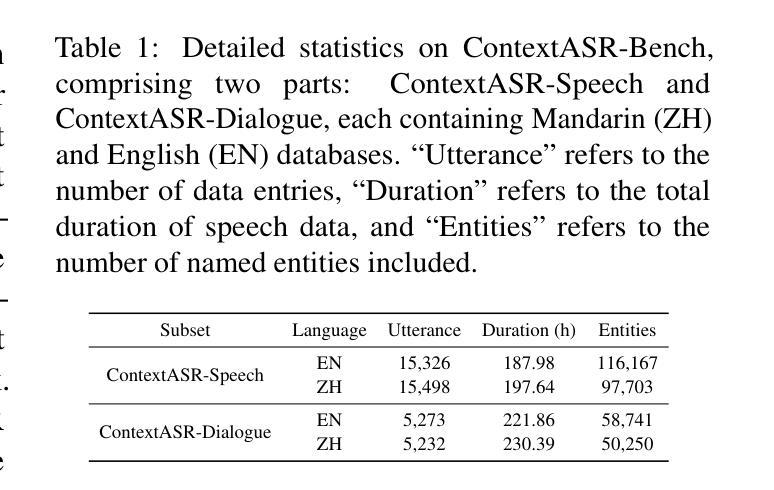
Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) has been extensively investigated, yet prior evaluative efforts have largely been restricted to contextless paradigms. This constraint stems from the limited proficiency of conventional ASR models in context modeling and their deficiency in memory and reasoning based on world knowledge. Recent breakthroughs in the development of Large Language Models (LLMs) and corresponding Large Audio Language Models (LALMs) have markedly enhanced the visibility of general artificial intelligence capabilities. Consequently, there exists a compelling need for a benchmark that can evaluate both the generality and intelligence of ASR systems. To address this gap, we propose ContextASR-Bench: a comprehensive, large-scale benchmark designed to assess contextual speech recognition. This benchmark encompasses up to 40,000 data entries across over 10 domains, enabling a thorough evaluation of model performance in scenarios that omit or incorporate coarse-grained or fine-grained contextual information. Moreover, diverging from conventional ASR evaluations, our benchmark includes an analysis of model efficacy in recognizing named entities mentioned within the auditory input. Our extensive evaluation highlights that LALMs, with strong world knowledge and context learning capabilities, outperform conventional ASR models by a large margin. The dataset and evaluation code have been released at https://github.com/MrSupW/ContextASR-Bench.
自动语音识别(ASR)已经得到了广泛的研究,但之前的评估工作大多局限于无上下文的模式。这一限制源于传统ASR模型在上下文建模方面的有限能力,以及它们在基于世界知识的记忆和推理方面的不足。最近,大型语言模型(LLM)和相应的大型音频语言模型(LALM)的发展取得了突破,显著提高了通用人工智能能力可见度。因此,存在一种迫切需要对能够评估ASR系统通用性和智能性的基准测试。为解决这一空白,我们提出了ContextASR-Bench:一个全面、大规模的基准测试,旨在评估上下文语音识别。该基准测试包含超过10个领域的多达4万个数据条目,能够在省略或包含粗粒度或细粒度上下文信息的场景中彻底评估模型性能。此外,与传统的ASR评估不同,我们的基准测试还包括对模型识别听觉输入中提到的命名实体的功效的分析。我们的广泛评估强调,具有强大世界知识和上下文学习能力的LALM在性能上大大超过了传统ASR模型。数据集和评估代码已发布在https://github.com/MrSupW/ContextASR-Bench。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 4 figures
Summary
本文介绍了自动语音识别(ASR)的新挑战,传统ASR模型在语境建模方面的局限性使其缺乏记忆和基于世界知识的推理能力。随着大型语言模型(LLM)和大型音频语言模型(LALM)的发展,有必要建立一个能够评估ASR系统的通用性和智能性的基准测试。为此,提出了ContextASR-Bench基准测试,该测试包含多达4万个数据条目,跨越10个领域,并包括在包含或排除粗粒度或细粒度上下文信息的场景中对模型性能的综合评估。分析发现,具有强大世界知识和上下文学习能力的LALM明显优于传统ASR模型。
Key Takeaways
- 传统ASR模型在语境建模方面存在局限性,缺乏记忆和基于世界知识的推理能力。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)和大型音频语言模型(LALM)的发展为ASR系统带来了新的可能性。
- ContextASR-Bench基准测试是为了评估ASR系统的通用性和智能性而提出的。
- ContextASR-Bench包含多达4万个数据条目,跨越10个领域,可全面评估模型性能。
- ContextASR-Bench包括在包含或排除上下文信息的场景中对模型性能的分析。
- LALM在模型性能上明显优于传统ASR模型。
点此查看论文截图

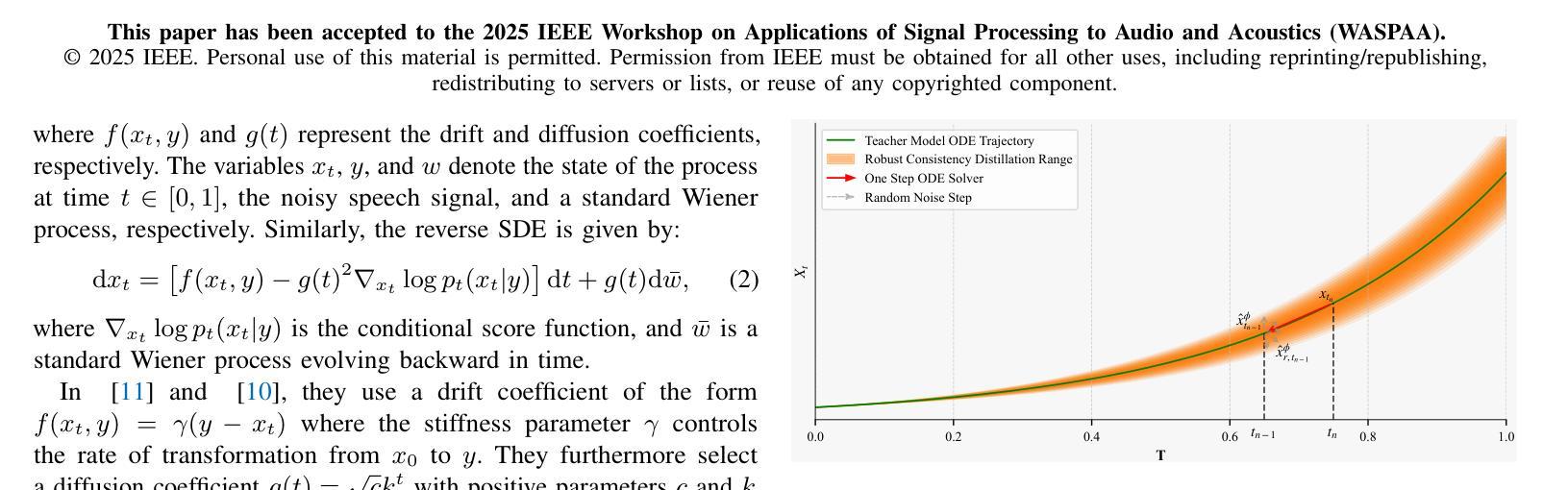
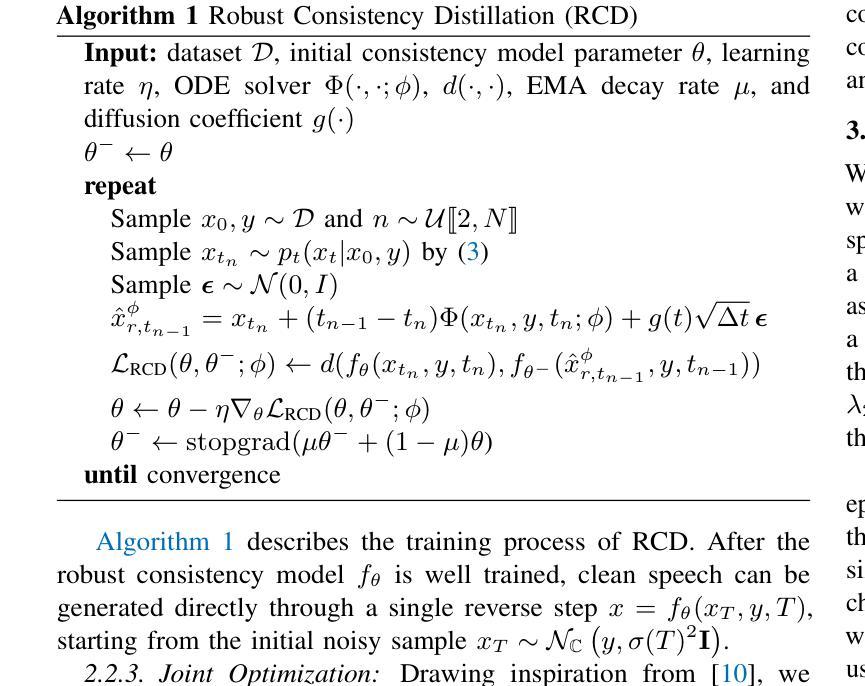
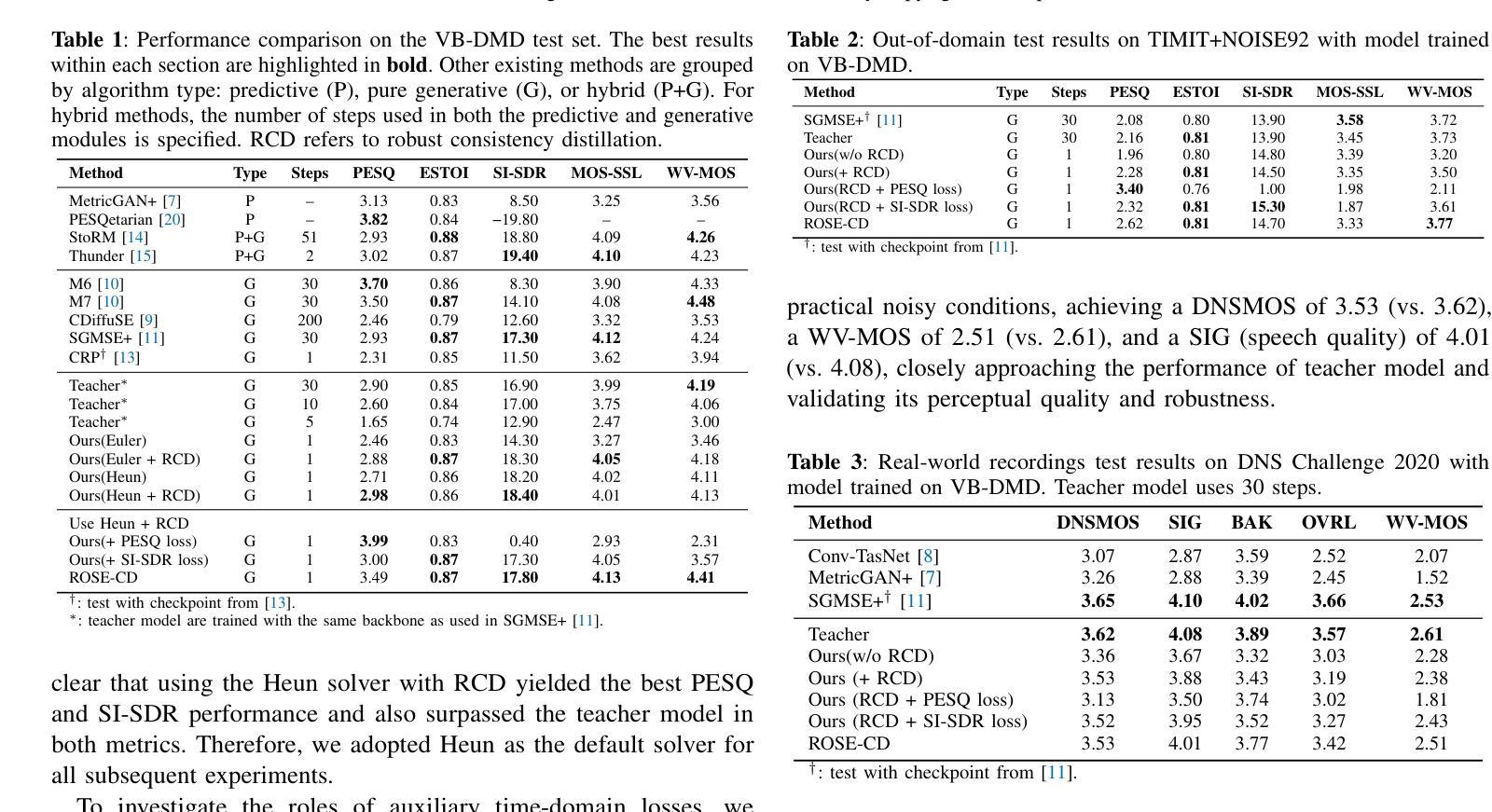
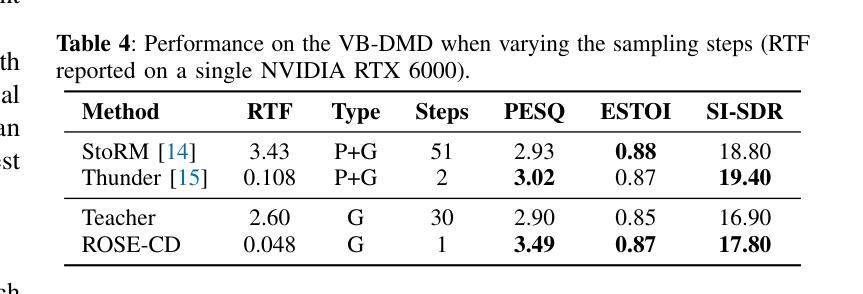
Robust One-step Speech Enhancement via Consistency Distillation
Authors:Liang Xu, Longfei Felix Yan, W. Bastiaan Kleijn
Diffusion models have shown strong performance in speech enhancement, but their real-time applicability has been limited by multi-step iterative sampling. Consistency distillation has recently emerged as a promising alternative by distilling a one-step consistency model from a multi-step diffusion-based teacher model. However, distilled consistency models are inherently biased towards the sampling trajectory of the teacher model, making them less robust to noise and prone to inheriting inaccuracies from the teacher model. To address this limitation, we propose ROSE-CD: Robust One-step Speech Enhancement via Consistency Distillation, a novel approach for distilling a one-step consistency model. Specifically, we introduce a randomized learning trajectory to improve the model’s robustness to noise. Furthermore, we jointly optimize the one-step model with two time-domain auxiliary losses, enabling it to recover from teacher-induced errors and surpass the teacher model in overall performance. This is the first pure one-step consistency distillation model for diffusion-based speech enhancement, achieving 54 times faster inference speed and superior performance compared to its 30-step teacher model. Experiments on the VoiceBank-DEMAND dataset demonstrate that the proposed model achieves state-of-the-art performance in terms of speech quality. Moreover, its generalization ability is validated on both an out-of-domain dataset and real-world noisy recordings.
扩散模型在语音增强方面表现出强大的性能,但其实时应用性受到多步迭代采样的限制。近期,一致性蒸馏作为一种有前景的替代方案崭露头角,它通过从基于多步扩散的教师模型中蒸馏出一步一致性模型。然而,蒸馏出的一致性模型本质上偏向于教师模型的采样轨迹,导致其对噪声的鲁棒性较低,并容易继承教师模型的误差。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了ROSE-CD:通过一致性蒸馏实现稳健的一步语音增强。这是一种蒸馏一步一致性模型的新方法。具体来说,我们引入随机学习轨迹来提高模型对噪声的鲁棒性。此外,我们还通过两个时域辅助损失联合优化一步模型,使其能够从教师引发的错误中恢复,并在总体性能上超越教师模型。这是首个用于基于扩散的语音增强纯一步一致性蒸馏模型,其推理速度达到教师模型的54倍,且性能更为优越。在VoiceBank-DEMAND数据集上的实验表明,该模型在语音质量方面达到了最先进的性能。此外,其在域外数据集和真实世界噪声记录上的泛化能力也得到了验证。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to IEEE WASPAA 2025. 6 pages, 1 figures
Summary
本文提出了一种基于一致性蒸馏的鲁棒一步语音增强方法(ROSE-CD),用于解决扩散模型在语音增强中的实时应用问题。通过引入随机学习轨迹和联合优化一步模型与两个时域辅助损失,提高了模型的抗噪声能力和从教师模型诱导的错误中恢复的能力。实验结果表明,该模型在语音质量方面达到了最先进的性能,具有出色的泛化能力和快速推理速度。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在语音增强中表现出强大的性能,但实时应用受到多步迭代采样的限制。
- 一致性蒸馏是一种新兴的有前途的替代方法,通过蒸馏一步一致性模型从多步扩散教师模型中。
- 蒸馏的一致性模型偏向于教师模型的采样轨迹,对噪声的鲁棒性较低,并可能继承教师模型的不准确之处。
- ROSE-CD方法通过引入随机学习轨迹来提高模型的抗噪声能力。
- ROSE-CD通过联合优化一步模型与两个时域辅助损失,使模型能够从教师模型诱导的错误中恢复并超越教师模型的整体性能。
- ROSE-CD是在扩散语音增强中首次提出的纯一步一致性蒸馏模型,具有快速推理速度和卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图

ADMC: Attention-based Diffusion Model for Missing Modalities Feature Completion
Authors:Wei Zhang, Juan Chen, Yanbo J. Wang, En Zhu, Xuan Yang, Yiduo Wang
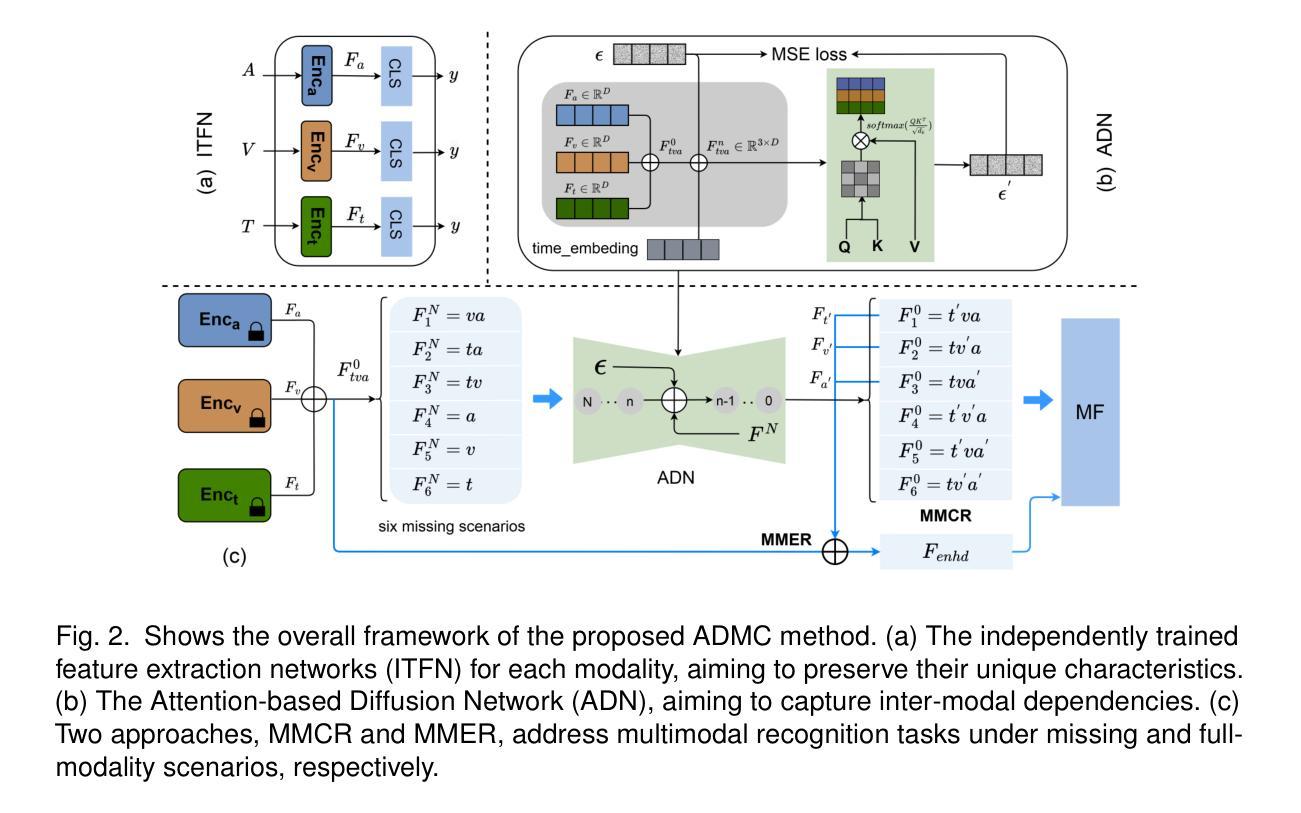
Multimodal emotion and intent recognition is essential for automated human-computer interaction, It aims to analyze users’ speech, text, and visual information to predict their emotions or intent. One of the significant challenges is that missing modalities due to sensor malfunctions or incomplete data. Traditional methods that attempt to reconstruct missing information often suffer from over-coupling and imprecise generation processes, leading to suboptimal outcomes. To address these issues, we introduce an Attention-based Diffusion model for Missing Modalities feature Completion (ADMC). Our framework independently trains feature extraction networks for each modality, preserving their unique characteristics and avoiding over-coupling. The Attention-based Diffusion Network (ADN) generates missing modality features that closely align with authentic multimodal distribution, enhancing performance across all missing-modality scenarios. Moreover, ADN’s cross-modal generation offers improved recognition even in full-modality contexts. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art results on the IEMOCAP and MIntRec benchmarks, demonstrating its effectiveness in both missing and complete modality scenarios.
多模态情感与意图识别是自动化人机交互的核心,其目标是通过分析用户的语音、文本和视觉信息来预测其情感或意图。面临的挑战之一是传感器故障或数据不完整导致的模态缺失。传统的方法试图重建缺失的信息,但常常受到过度耦合和不精确生成过程的影响,导致结果不理想。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了基于注意力的扩散模型(ADMC)进行缺失模态特征补全。我们的框架独立训练每种模态的特征提取网络,保留其独特特性,避免过度耦合。基于注意力的扩散网络(ADN)生成缺失模态的特征,这些特征紧密符合真实的多模态分布,提高了所有缺失模态场景的性能。此外,ADN的跨模态生成甚至在完整模态上下文中也提供了改进的识别能力。我们的方法在IEMOCAP和MIntRec基准测试中取得了最新结果,证明了它在缺失和完整模态场景中的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多模态情感与意图识别在自动化人机交互中至关重要。它通过用户的语音、文本和视觉信息分析来预测用户的情感或意图。面对传感器故障或数据不完整导致的缺失模态问题,传统方法往往存在过度耦合和不精确生成过程的问题,导致结果不佳。为此,我们引入了基于注意力的扩散模型用于缺失模态特征补全(ADMC)。我们的框架独立训练每种模态的特征提取网络,保留其独特性并避免过度耦合。基于注意力的扩散网络(ADN)生成的缺失模态特征能与真实的多模态分布紧密对齐,提升各种缺失模态场景的性能。此外,ADN的跨模态生成能力在全模态上下文中也能提供改进后的识别效果。我们的方法在IEMOCAP和MIntRec基准测试中取得了最新成果,证明了它在缺失和完整模态场景中的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态情感与意图识别在自动化人机交互中的重要性。
- 缺失模态是自动化识别的一个挑战,传统方法存在过度耦合和不精确生成的问题。
- 引入基于注意力的扩散模型用于缺失模态特征补全(ADMC)。
- ADMC框架独立训练每种模态的特征提取网络,避免过度耦合。
- 基于注意力的扩散网络(ADN)生成的缺失模态特征与真实多模态分布对齐,提升性能。
- ADN的跨模态生成能力在全模态上下文中也能提供改进后的识别效果。
点此查看论文截图


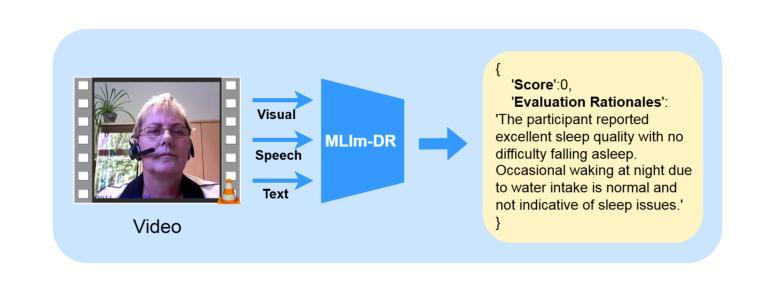
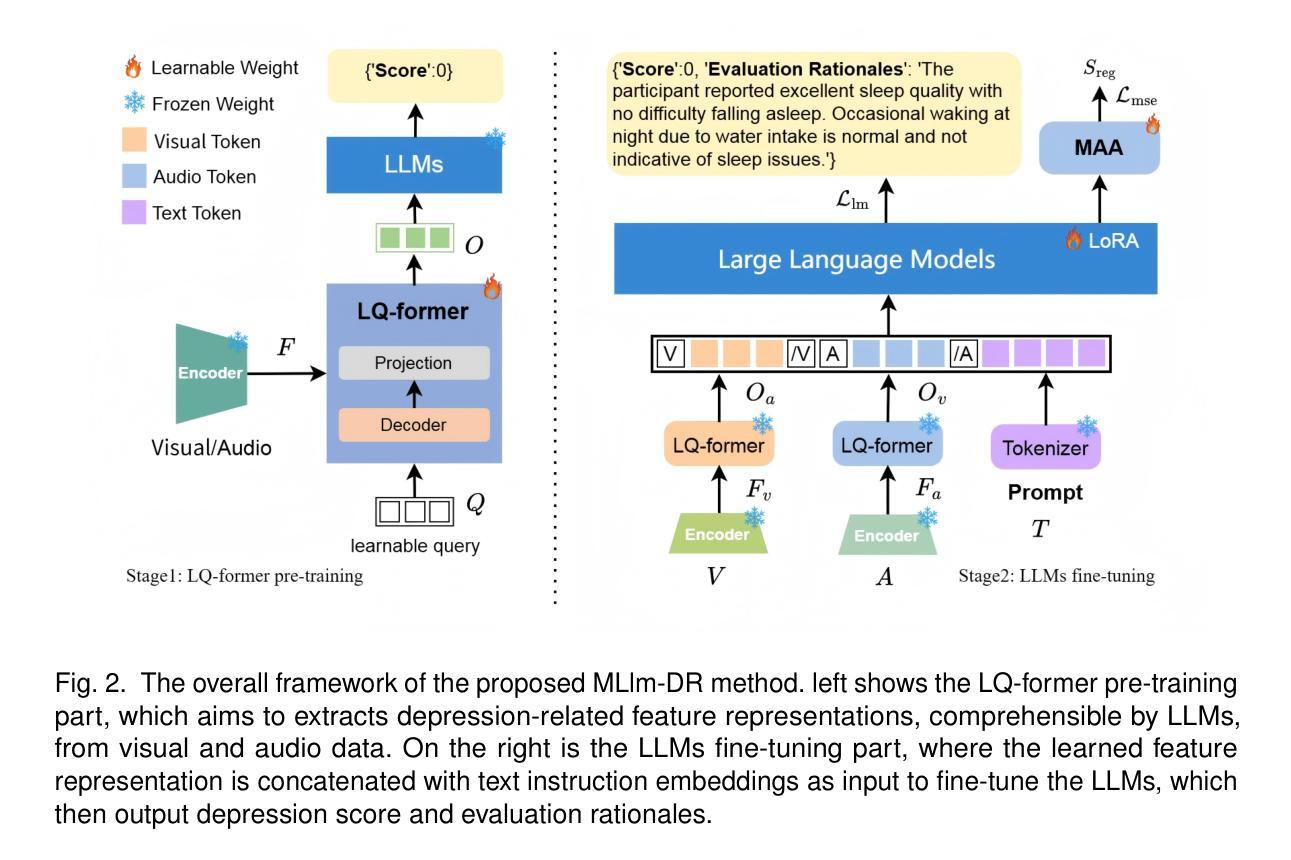
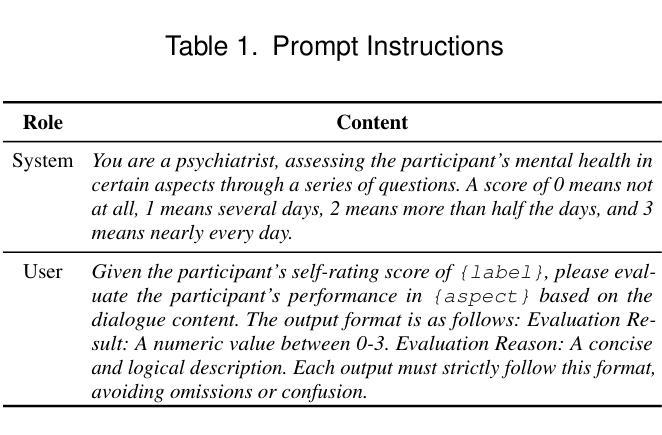
MLlm-DR: Towards Explainable Depression Recognition with MultiModal Large Language Models
Authors:Wei Zhang, Juan Chen, En Zhu, Wenhong Cheng, YunPeng Li, Yanbo J. Wang
Automated depression diagnosis aims to analyze multimodal information from interview videos to predict participants’ depression scores. Previous studies often lack clear explanations of how these scores were determined, limiting their adoption in clinical practice. While the advent of LLMs provides a possible pathway for explainable depression diagnosis, current LLMs capable of processing multimodal data lack training on interview data, resulting in poor diagnostic performance when used directly. In this paper, we propose a novel multimodal large language model (MLlm-DR) that can understand multimodal information inputs and supports explainable depression diagnosis. MLlm-DR integrates a smaller LLMs and a lightweight query module (LQ-former). Specifically, the smaller LLMs is designed to generate depression scores and corresponding evaluation rationales. To enhance its logical reasoning for domain-specific tasks while maintaining practicality, we constructed a robust training dataset to fine-tune it. Meanwhile, the LQ-former captures depression-related features from speech and visual data, aiding the model’s ability to process multimodal information, to achieve comprehensive depression diagnosis. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art results on two interview-based benchmark datasets, CMDC and E-DAIC-WOZ, demonstrating its effectiveness and superiority.
自动化抑郁症诊断旨在分析访谈视频中的多模式信息,以预测参与者的抑郁评分。之前的研究往往缺乏关于这些评分如何确定的明确解释,这限制了它们在临床实践中的应用。虽然大型语言模型(LLMs)的出现为可解释的抑郁症诊断提供了一条可能的途径,但目前能够处理多模式数据的大型语言模型缺乏访谈数据的训练,导致当直接使用时诊断性能较差。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型的多模式大型语言模型(MLlm-DR),能够理解多模式信息输入并支持可解释的抑郁症诊断。MLlm-DR整合了较小的大型语言模型(LLMs)和一个轻量级的查询模块(LQ-former)。具体来说,较小的LLMs被设计用来生成抑郁评分和相应的评估依据。为了增强其在特定领域的逻辑推理能力同时保持实用性,我们构建了一个稳健的训练数据集对其进行微调。同时,LQ-former从语音和视觉数据中捕获与抑郁症相关的特征,帮助模型处理多模式信息,以实现全面的抑郁症诊断。我们的方法在基于访谈的两个基准数据集CMDC和E-DAIC-WOZ上取得了最新成果,证明了其有效性和优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
自动化抑郁症诊断旨在通过分析访谈视频中的多模态信息来预测参与者的抑郁程度。然而,先前的研究往往缺乏明确解释这些分数的确定方式,限制了其在临床实践中的应用。本文提出了一种新型的多模态大型语言模型(MLlm-DR),能够处理多模态信息输入并支持可解释的抑郁症诊断。该模型结合了较小的语言模型和轻量级查询模块(LQ-former),以生成抑郁分数和相应的评估依据,并通过构建稳健的训练数据集进行微调,提高其领域特定任务的逻辑推理能力,同时保持实用性。LQ-former有助于模型处理多模态信息,在两种基于访谈的基准数据集CMDC和E-DAIC-WOZ上取得了最先进的成果,证明了其有效性和优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 自动化抑郁症诊断通过分析访谈视频中的多模态信息预测参与者的抑郁程度。
- 先前研究缺乏明确的诊断分数解释,限制了其在临床实践中的应用。
- 提出了一种新型的多模态大型语言模型(MLlm-DR)用于支持可解释的抑郁症诊断。
- MLlm-DR结合了较小的语言模型和轻量级查询模块(LQ-former)。
- 较小的语言模型用于生成抑郁分数和评估依据。
- 通过构建稳健的训练数据集对模型进行微调,提高领域任务的逻辑推理能力并维持实用性。
点此查看论文截图

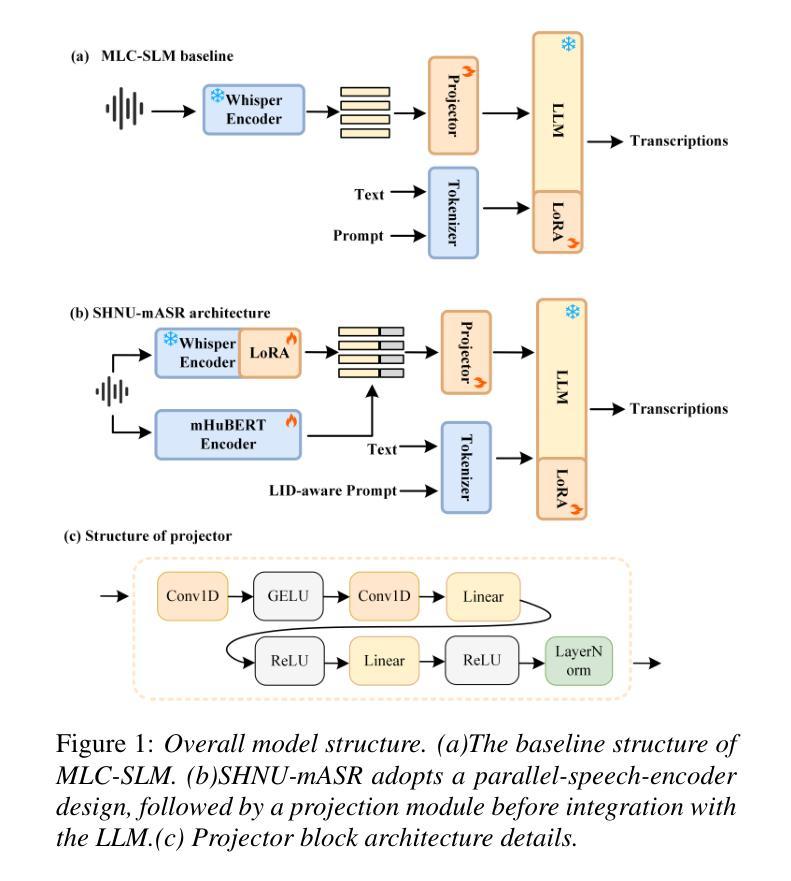
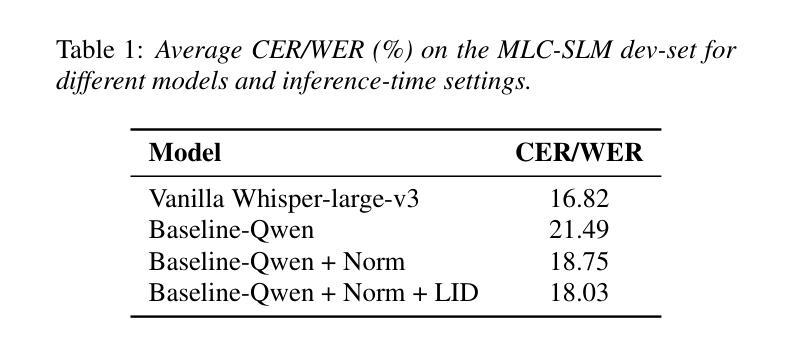
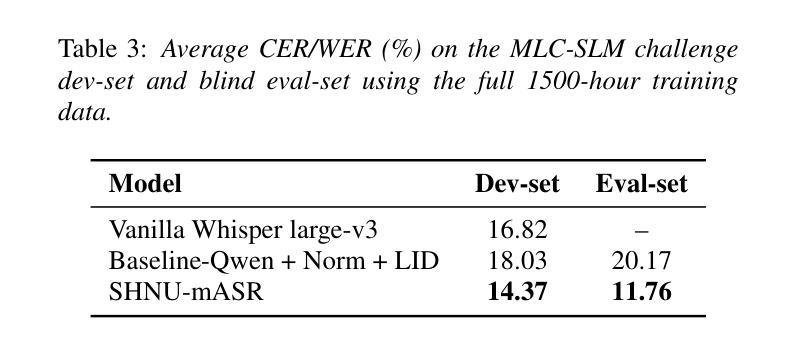
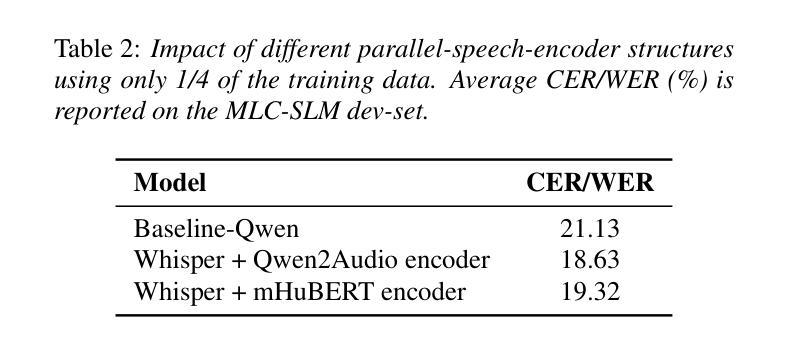
SHNU Multilingual Conversational Speech Recognition System for INTERSPEECH 2025 MLC-SLM Challenge
Authors:Yuxiang Mei, Yuang Zheng, Dongxing Xu, Yanhua Long
This paper describes SHNU multilingual conversational speech recognition system (SHNU-mASR, team name-“maybe”), submitted to Track 1 of the INTERSPEECH 2025 MLC-SLM Challenge. Our system integrates a parallel-speech-encoder architecture with a large language model (LLM) to form a unified multilingual ASR framework. The parallel-speech-encoder consists of two pre-trained encoders, the Whisper-large-v3 encoder and mHuBERT-147 encoder. Their output embeddings are concatenated and fed into the LLM, enabling the model to leverage complementary acoustic and linguistic knowledge and achieve competitive performance. Moreover, we adopt a tri-stage training strategy to jointly update the low-rank adaptation modules and projector parameters of both the speech encoders and the LLM. In addition, we incorporate an additional language-aware prompt at the LLM input to enhance language-specific text generation. The SHNU-mASR system achieves an overall character/word error rate (CER/WER) of 11.76% on the blind evaluation set of the challenge, outperforming the official MLC-SLM baseline by 8.41 absolute CER/WER, without increasing the baseline training data.
本文介绍了SHNU多语种对话语音识别系统(SHNU-mASR,团队名为“maybe”),该系统提交至INTERSPEECH 2025 MLC-SLM Challenge的Track 1。我们的系统将并行语音编码器架构与大型语言模型(LLM)集成在一起,形成一个统一的多语种ASR框架。并行语音编码器由两个预训练编码器组成,即Whisper-large-v3编码器和mHuBERT-147编码器。他们的输出嵌入进行拼接,并输入到LLM中,使模型能够利用互补的声学知识和语言知识,实现有竞争力的性能。此外,我们采用三阶段训练策略,联合更新低秩适应模块和语音编码器和LLM的投影仪参数。另外,我们在LLM的输入端增加了一个额外的语言感知提示,以增强特定语言的文本生成。SHNU-mASR系统在挑战盲评数据集上实现了11.76%的整体字符/单词错误率(CER/WER),相较于官方MLC-SLM基线提高了8.41个绝对CER/WER,且没有增加基线训练数据。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by Interspeech 2025 MLC-SLM workshop
Summary
本文介绍了SHNU的多语种对话语音识别系统(SHNU-mASR),该系统参与了INTERSPEECH 2025 MLC-SLM Challenge的Track 1挑战。该系统结合了并行语音编码器架构和大型语言模型(LLM),形成一个统一的多语种ASR框架。采用预训练的Whisper-large-v3和mHuBERT-147编码器,其输出嵌入通过连接并输入到LLM中,使得模型能够利用互补的声学知识和语言知识,实现了良好的性能。通过采用三阶段训练策略,对低阶适应模块和投影参数进行联合更新,进一步增强了系统的性能。在挑战的无标注评估集上,SHNU-mASR系统的字符/词错误率(CER/WER)达到了11.76%,相较于官方MLC-SLM基线提高了8.41个绝对CER/WER,且未增加基线训练数据。
Key Takeaways
- SHNU团队提出了一种多语种对话语音识别系统SHNU-mASR,针对INTERSPEECH 2025 MLC-SLM Challenge的Track 1进行了挑战。
- 系统集成了并行语音编码器架构和大型语言模型(LLM),形成统一的多语种ASR框架。
- 采用预训练的Whisper-large-v3和mHuBERT-147编码器,使模型能够利用互补的声学知识和语言知识。
- 通过三阶段训练策略联合更新低阶适应模块和投影参数,增强了系统性能。
- SHNU-mASR系统实现了较低的字符/词错误率(CER/WER),相较于官方基线有显著的提升。
- 该提升是在不增加基线训练数据的情况下实现的。
点此查看论文截图

Evaluating Logit-Based GOP Scores for Mispronunciation Detection
Authors:Aditya Kamlesh Parikh, Cristian Tejedor-Garcia, Catia Cucchiarini, Helmer Strik
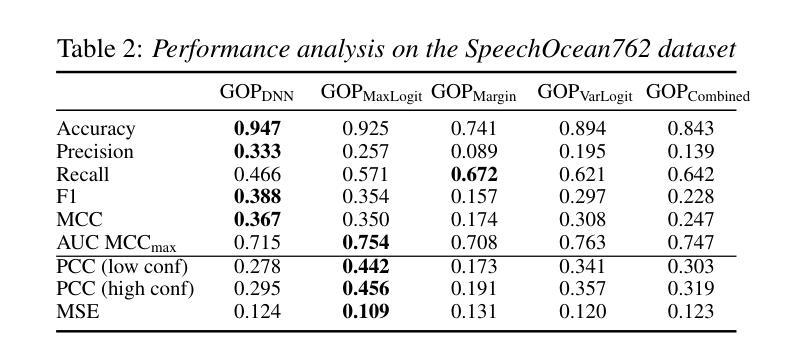
Pronunciation assessment relies on goodness of pronunciation (GOP) scores, traditionally derived from softmax-based posterior probabilities. However, posterior probabilities may suffer from overconfidence and poor phoneme separation, limiting their effectiveness. This study compares logit-based GOP scores with probability-based GOP scores for mispronunciation detection. We conducted our experiment on two L2 English speech datasets spoken by Dutch and Mandarin speakers, assessing classification performance and correlation with human ratings. Logit-based methods outperform probability-based GOP in classification, but their effectiveness depends on dataset characteristics. The maximum logit GOP shows the strongest alignment with human perception, while a combination of different GOP scores balances probability and logit features. The findings suggest that hybrid GOP methods incorporating uncertainty modeling and phoneme-specific weighting improve pronunciation assessment.
发音评估依赖于发音质量(GOP)分数,这些分数传统上是从基于softmax的后验概率中得出的。然而,后验概率可能会受到过度自信和音素分离不良的影响,从而限制了其有效性。本研究对比了基于对数几率(logit)的GOP分数与基于概率的GOP分数在发音错误检测方面的表现。我们在由荷兰语和普通话发音的两组英语二语语音数据集上进行了实验,评估了分类性能和与人类评分的相关性。基于对数几率的方法在分类上优于基于概率的GOP,但其有效性取决于数据集的特性。最大对数几率GOP与人的感知一致性最强,而结合不同的GOP分数则平衡了概率和对数几率特征。研究结果表明,采用不确定性建模和音素特定权重的混合GOP方法能改善发音评估效果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to Interspeech 2025. This publication is part of the project Responsible AI for Voice Diagnostics (RAIVD) with file number NGF.1607.22.013 of the research programme NGF AiNed Fellowship Grants which is financed by the Dutch Research Council (NWO)
总结
本文主要探讨了发音评估中的好发音(GOP)得分计算方法。研究发现基于logit的GOP得分计算方法相较于传统的基于概率的得分计算方法能更好地用于发音错误的检测。此外,不同数据集下基于对数概率得分方法的最佳应用方式也进行了研究,发现最大对数概率得分与人的感知最为一致,而结合不同GOP得分的方法可以平衡概率和对数概率特征。研究还表明,结合不确定性建模和音素特定权重的混合GOP方法能提高发音评估的准确度。
关键见解
- 基于对数概率(logit)的GOP得分计算方法相较于基于概率的方法在发音评估中表现更优。
- 最大对数概率GOP得分与人的感知最为一致。
- 结合不同GOP得分的混合方法能够平衡概率和对数概率特征,提高评估准确性。
- 数据集特性会影响基于对数概率方法的性能。
- 基于不确定性建模的混合GOP方法能进一步提高发音评估的精确度。
- 音素特定权重在发音评估中起到重要作用。
点此查看论文截图

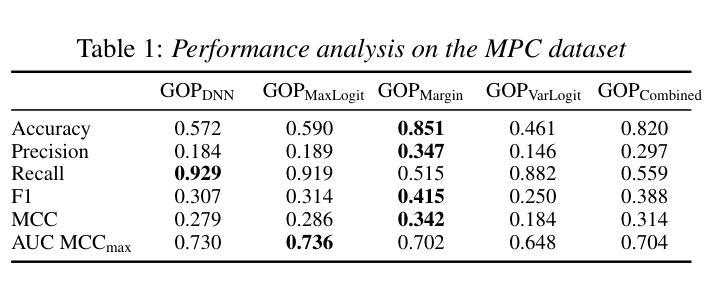
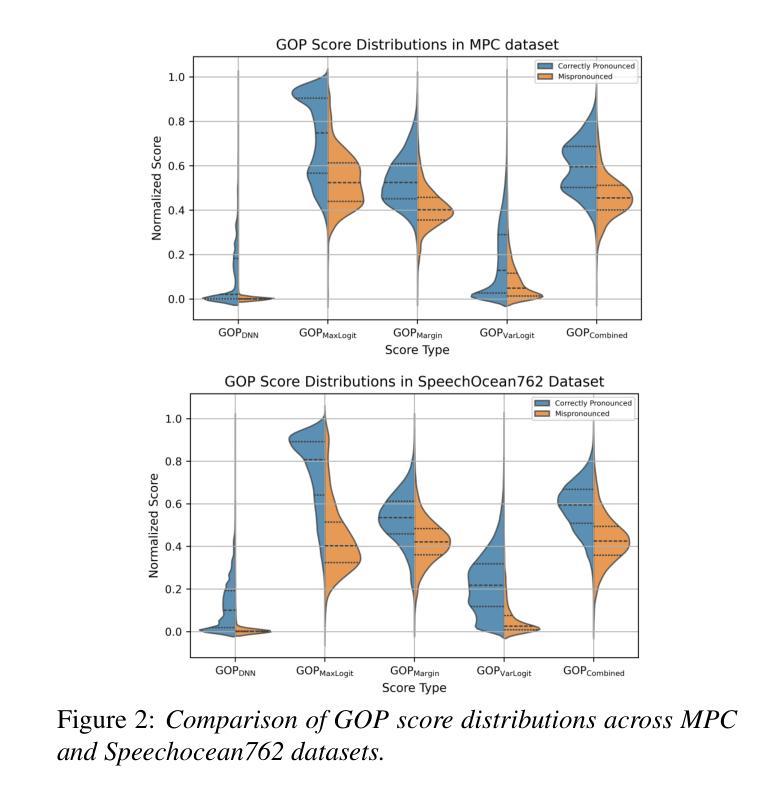
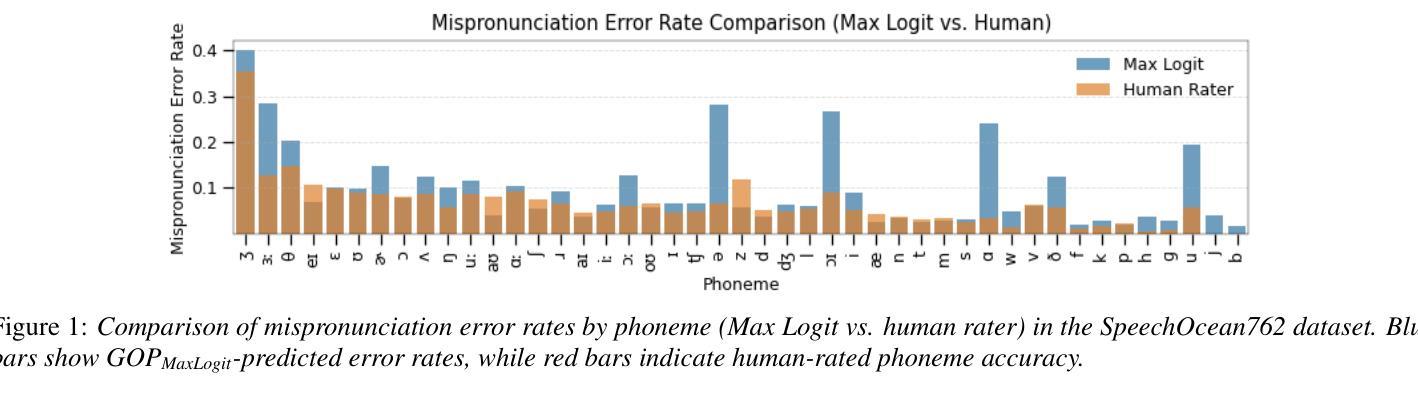
Enhancing GOP in CTC-Based Mispronunciation Detection with Phonological Knowledge
Authors:Aditya Kamlesh Parikh, Cristian Tejedor-Garcia, Catia Cucchiarini, Helmer Strik
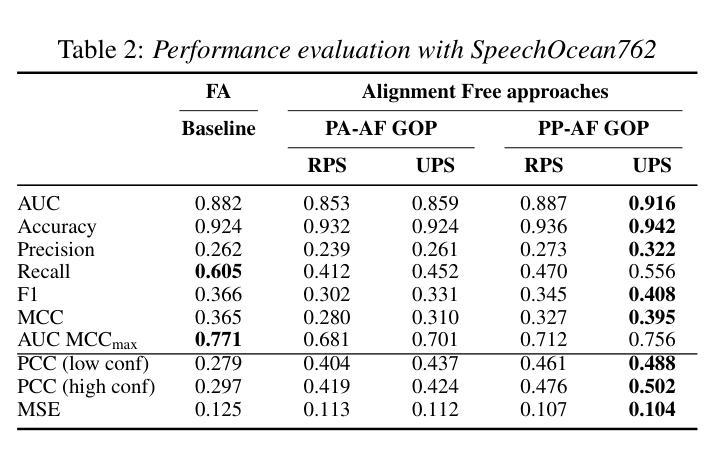
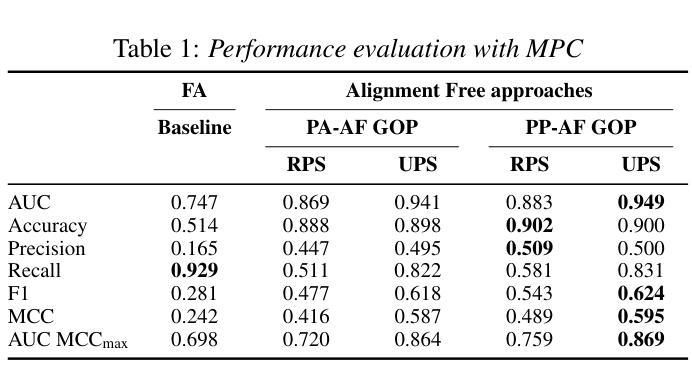
Computer-Assisted Pronunciation Training (CAPT) systems employ automatic measures of pronunciation quality, such as the goodness of pronunciation (GOP) metric. GOP relies on forced alignments, which are prone to labeling and segmentation errors due to acoustic variability. While alignment-free methods address these challenges, they are computationally expensive and scale poorly with phoneme sequence length and inventory size. To enhance efficiency, we introduce a substitution-aware alignment-free GOP that restricts phoneme substitutions based on phoneme clusters and common learner errors. We evaluated our GOP on two L2 English speech datasets, one with child speech, My Pronunciation Coach (MPC), and SpeechOcean762, which includes child and adult speech. We compared RPS (restricted phoneme substitutions) and UPS (unrestricted phoneme substitutions) setups within alignment-free methods, which outperformed the baseline. We discuss our results and outline avenues for future research.
计算机辅助发音训练(CAPT)系统采用发音质量自动测量,如发音质量(GOP)指标。GOP依赖于强制对齐,由于声学变化,它容易受到标记和分段错误的影响。虽然无对齐方法解决了这些挑战,但它们在计算上很昂贵,随着音素序列长度和库存大小的增加,性能下降。为了提高效率,我们引入了一种基于音素聚类和学习者常见错误的替代感知无对齐GOP。我们在两个英语二级语音数据集上评估了我们的GOP,其中一个数据集包含儿童语音My Pronunciation Coach(MPC),另一个数据集包含儿童和成人语音的SpeechOcean762。我们在无对齐方法中比较了RPS(受限音素替代)和UPS(非受限音素替代)设置,它们优于基线水平。我们讨论了我们的结果并概述了未来研究的方向。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to Interspeech 2025. This publication is part of the project Responsible AI for Voice Diagnostics (RAIVD) with file number NGF.1607.22.013 of the research programme NGF AiNed Fellowship Grants which is financed by the Dutch Research Council (NWO)
Summary
本文介绍了计算机辅助发音训练(CAPT)系统采用基于强制对齐的发音质量评估方法,如发音质量评估(GOP)指标。然而,由于声学变化导致的标签和分段误差影响了强制对齐方法的准确性。为了解决这个问题,研究者提出了一种基于音素聚类和常见学习者错误的替代感知对齐无关的GOP方法,以提高效率。该方法在两种英语二语语音数据集上的表现优于基线方法,包括针对儿童语音的My Pronunciation Coach数据集和包含儿童和成人语音的SpeechOcean762数据集。本文探讨了结果并展望了未来研究方向。
Key Takeaways
- 计算机辅助发音训练(CAPT)系统使用自动评估发音质量的方法,如发音质量评估(GOP)指标。
- 传统GOP依赖强制对齐,易受到声学变化的标签和分段误差影响。
- 提出了基于音素聚类和常见学习者错误的替代感知对齐无关的GOP方法,以提高效率。
- 该方法在两种英语二语语音数据集上的表现优于基线方法。
- 研究对比了受限音素替代(RPS)和无限制音素替代(UPS)的设定。
- 结果显示,对齐无关的方法在语音数据集上的性能优于基线方法。
点此查看论文截图

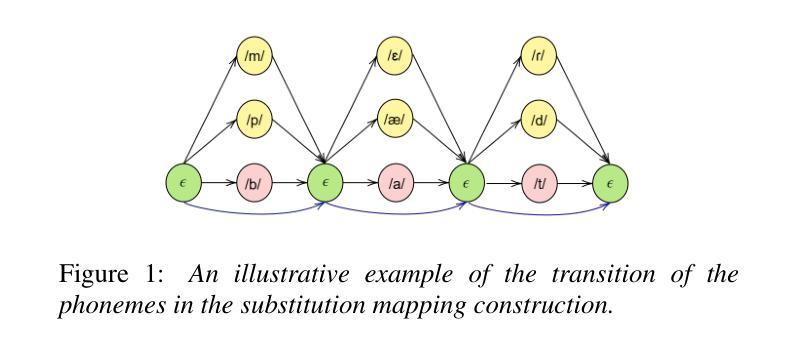
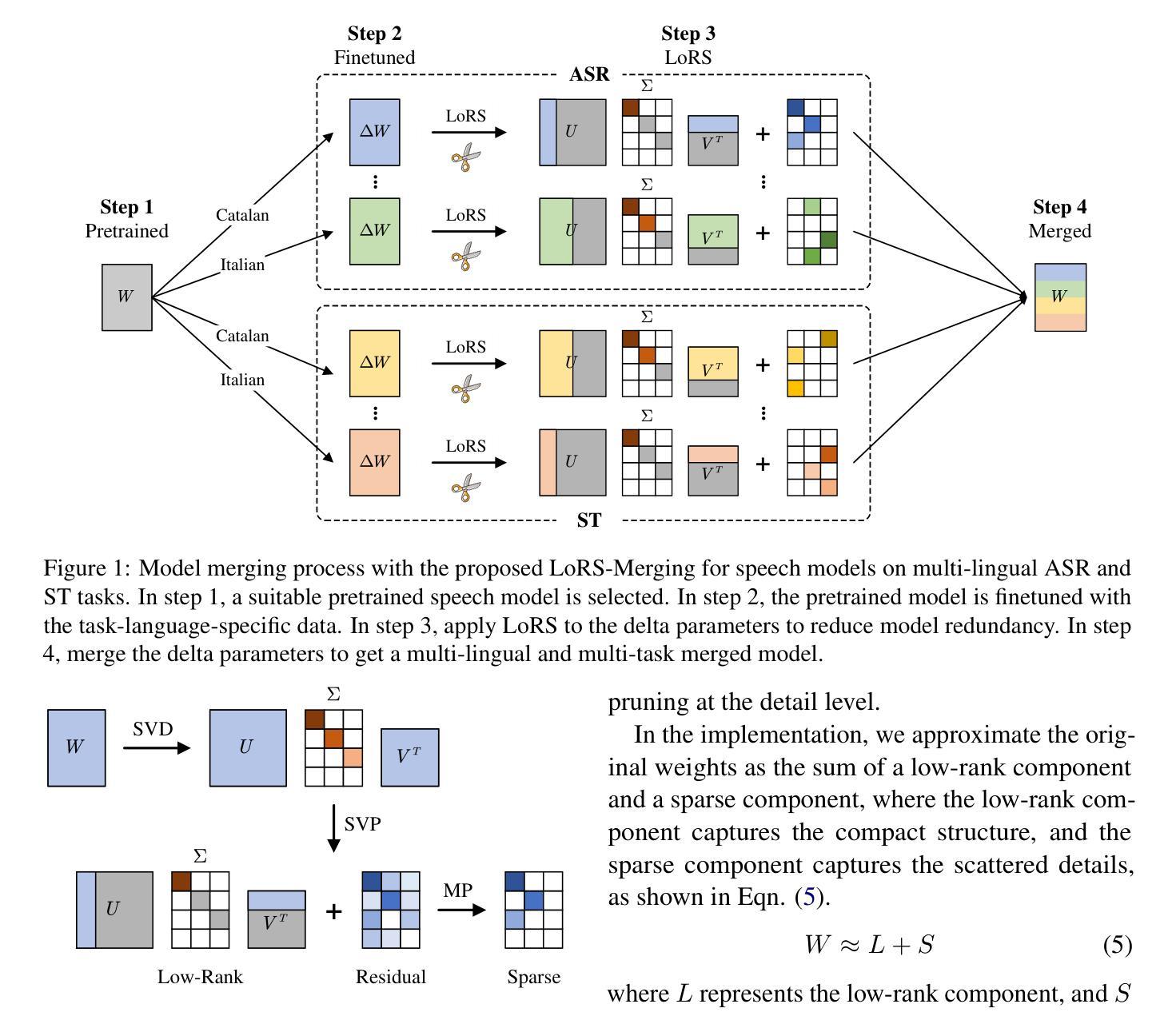
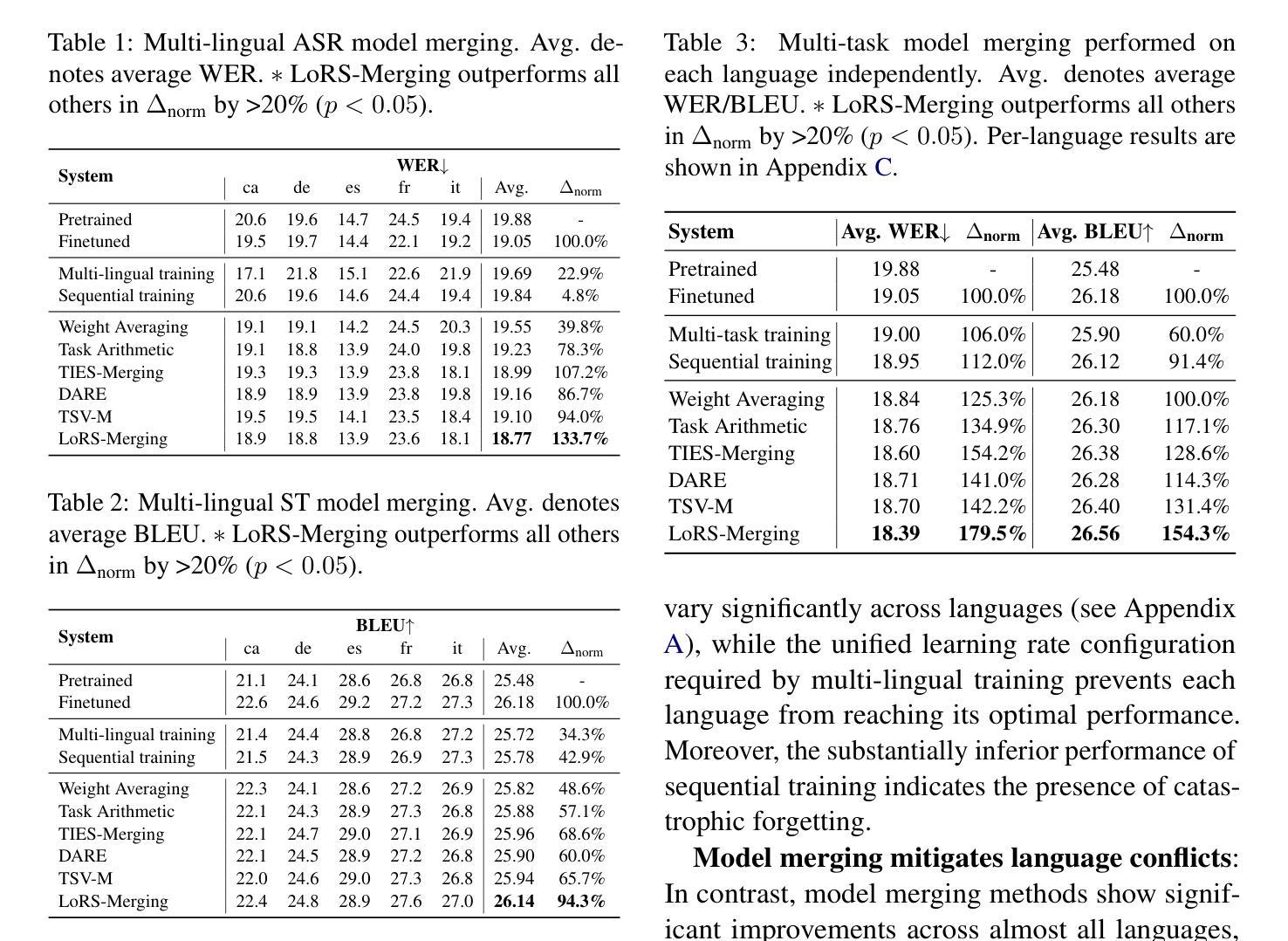
Low-Rank and Sparse Model Merging for Multi-Lingual Speech Recognition and Translation
Authors:Qiuming Zhao, Guangzhi Sun, Chao Zhang
Language diversity presents a significant challenge in speech-to-text (S2T) tasks, such as automatic speech recognition and translation. Traditional multi-lingual multi-task training approaches aim to address this by jointly optimising multiple speech recognition and translation tasks across various languages. While models like Whisper, built on these strategies, demonstrate strong performance, they still face issues of high computational cost, language interference, suboptimal training configurations, and limited extensibility. To overcome these challenges, we introduce LoRS-Merging (low-rank and sparse model merging), a novel technique designed to efficiently integrate models trained on different languages or tasks while preserving performance and reducing computational overhead. LoRS-Merging combines low-rank and sparse pruning to retain essential structures while eliminating redundant parameters, mitigating language interference, and enhancing extensibility. Experimental results across 10 languages demonstrate that LoRS-Merging significantly outperforms multi-lingual multi-task training, sequential training, and other merging methods, achieving over 20% improvement in normalised performance. Our findings suggest that model merging, particularly LoRS-Merging, is a scalable and effective complement to traditional multi-lingual training strategies for S2T applications.
语言多样性在语音到文本(S2T)的任务中,如自动语音识别和翻译,构成了一个重大挑战。传统多语言多任务训练的方法旨在通过联合优化多种语言的语音识别和翻译任务来解决这一问题。虽然基于这些策略构建的模型(如whisper)表现出强大的性能,但它们仍然面临计算成本高、语言干扰、训练配置不佳和扩展性有限等问题。为了克服这些挑战,我们引入了LoRS-Merging(低秩和稀疏模型合并),这是一种旨在高效集成在不同语言或任务上训练的模型的新技术,同时保留性能并降低计算开销。LoRS-Merging结合了低秩和稀疏剪枝技术,以保留重要结构的同时消除冗余参数,减轻语言干扰并增强扩展性。在10种语言上的实验结果表明,LoRS-Merging显著优于多语言多任务训练、顺序训练和其他合并方法,在标准化性能上提高了超过20%。我们的研究结果表明,模型合并,特别是LoRS-Merging,是S2T应用中传统多语言训练策略的可扩展和有效的补充。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages
Summary
语言多样性在语音转文本(S2T)任务中,如自动语音识别和翻译中,带来了重大挑战。传统的多语言多任务训练旨在通过联合优化多种语言和任务的语音识别和翻译任务来解决这一问题。尽管基于这些策略构建的模型如Whisper表现出强大的性能,但它们仍然面临计算成本高、语言干扰、训练配置不佳和扩展性有限等问题。为了克服这些挑战,我们引入了LoRS-Merging(低阶和稀疏模型合并)技术,它是专门设计用来有效整合不同语言或任务训练过的模型,同时保持性能并减少计算开销。通过低阶和稀疏修剪相结合,LoRS-Merging保留了关键结构并消除了冗余参数,减轻了语言干扰并提高了扩展性。在10种语言上的实验结果表明,LoRS-Merging显著优于多语言多任务训练、顺序训练和其他合并方法,在标准化性能上提高了超过20%。我们的研究结果表明,模型合并,尤其是LoRS-Merging,是S2T应用中传统多语言训练策略的可扩展和有效的补充。
Key Takeaways
- 语言多样性对语音转文本任务提出了挑战。
- 传统多语言多任务训练旨在应对这一挑战,但仍存在计算成本高、语言干扰等问题。
- LoRS-Merging技术通过整合不同语言或任务的模型来提高效率。
- LoRS-Merging结合了低阶和稀疏修剪,以消除冗余参数并保留关键结构。
- LoRS-Merging在多种语言上的实验表现优于其他训练方法。
- LoRS-Merging提高了模型的扩展性,并可作为传统多语言训练策略的有效补充。
点此查看论文截图