⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-10 更新
Automatic Synthesis of High-Quality Triplet Data for Composed Image Retrieval
Authors:Haiwen Li, Delong Liu, Zhaohui Hou, Zhicheng Zhao, Fei Su
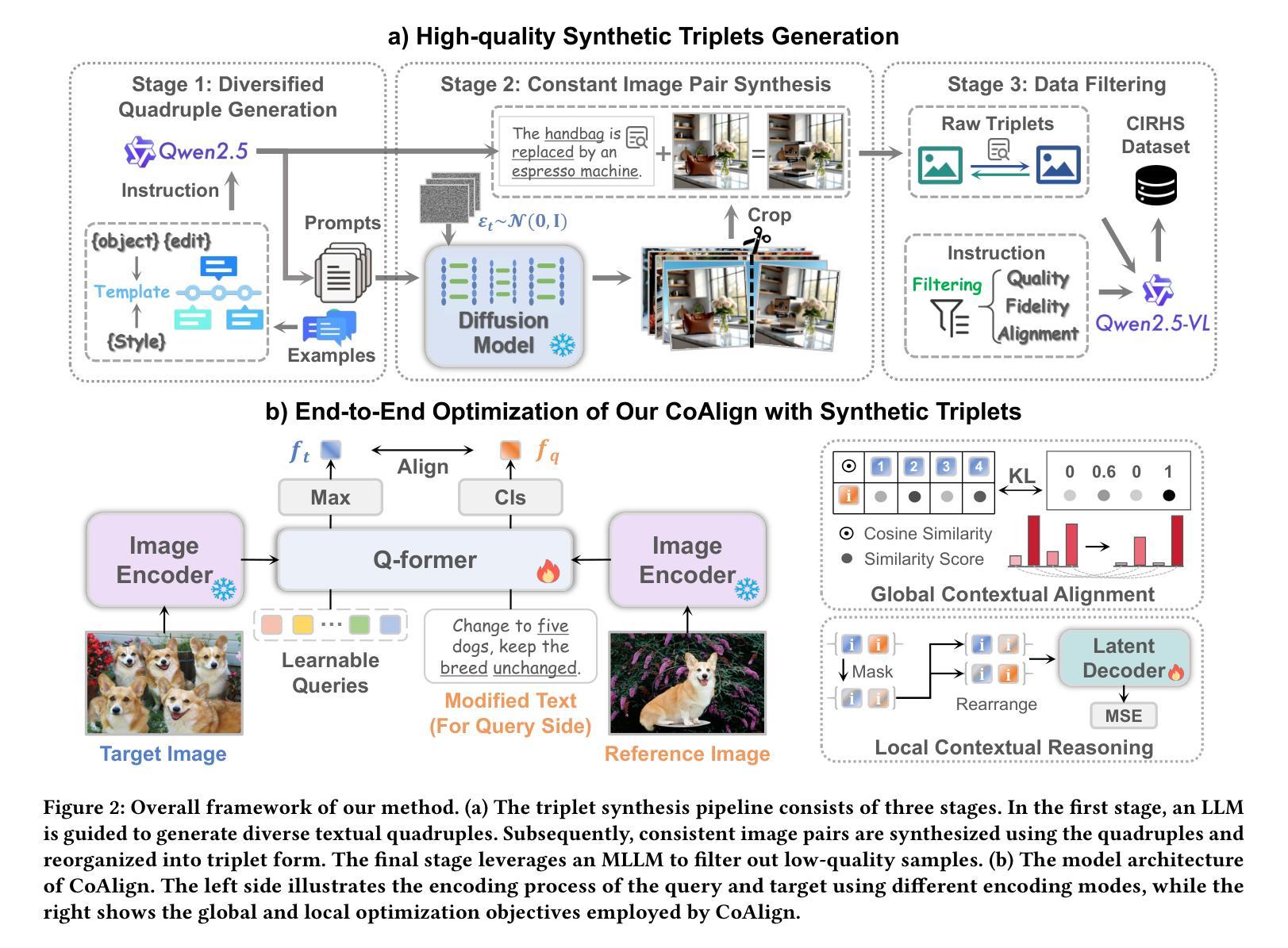
As a challenging vision-language (VL) task, Composed Image Retrieval (CIR) aims to retrieve target images using multimodal (image+text) queries. Although many existing CIR methods have attained promising performance, their reliance on costly, manually labeled triplets hinders scalability and zero-shot capability. To address this issue, we propose a scalable pipeline for automatic triplet generation, along with a fully synthetic dataset named Composed Image Retrieval on High-quality Synthetic Triplets (CIRHS). Our pipeline leverages a large language model (LLM) to generate diverse prompts, controlling a text-to-image generative model to produce image pairs with identical elements in each pair, which are then filtered and reorganized to form the CIRHS dataset. In addition, we introduce Hybrid Contextual Alignment (CoAlign), a novel CIR framework, which can accomplish global alignment and local reasoning within a broader context, enabling the model to learn more robust and informative representations. By utilizing the synthetic CIRHS dataset, CoAlign achieves outstanding zero-shot performance on three commonly used benchmarks, demonstrating for the first time the feasibility of training CIR models on a fully synthetic dataset. Furthermore, under supervised training, our method outperforms all the state-of-the-art supervised CIR approaches, validating the effectiveness of our proposed retrieval framework. The code and the CIRHS dataset will be released soon.
作为具有挑战性的视觉语言(VL)任务,组合图像检索(CIR)旨在使用多模态(图像+文本)查询来检索目标图像。尽管许多现有的CIR方法已经取得了有前景的性能,但它们对成本高昂的手动标记三元组的依赖阻碍了可扩展性和零样本学习能力。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了用于自动三元组生成的可扩展管道,以及一个名为“基于高质量合成三元组的组合图像检索(CIRHS)”的完全合成数据集。我们的管道利用大型语言模型(LLM)生成各种提示,控制文本到图像的生成模型,以产生具有相同元素的图像对,然后对它们进行过滤和重组以形成CIRHS数据集。此外,我们介绍了混合上下文对齐(CoAlign),这是一种新型的CIR框架,可以在更广泛的上下文范围内完成全局对齐和局部推理,使模型能够学习更健壮和富有信息量的表示。通过利用合成的CIRHS数据集,CoAlign在三个常用基准测试上取得了出色的零样本性能表现,首次证明了在完全合成数据集上训练CIR模型的可行性。此外,在监督训练下,我们的方法优于所有最新的监督型CIR方法,验证了我们所提出的检索框架的有效性。代码和CIRHS数据集将很快发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper was originally submitted to ACM MM 2025 on April 12, 2025
Summary
本文提出一种用于自动生成三元组的可扩展管道,并构建了一个名为CIRHS的合成数据集,用于图像检索任务。利用大型语言模型生成不同提示,控制文本到图像生成模型产生具有相同元素的图像对,经过筛选和重组形成CIRHS数据集。同时,引入Hybrid Contextual Alignment(CoAlign)这一新型图像检索框架,实现全局对齐和局部推理,学习更稳健和更具信息量的表示。在三个常用基准测试上,CoAlign利用合成CIRHS数据集实现了出色的零样本性能,并在监督训练下超越了所有最先进的监督图像检索方法。
Key Takeaways
- Composed Image Retrieval (CIR) 是一项重要的视觉语言任务,旨在使用多模态查询(图像+文本)检索目标图像。
- 现有CIR方法虽然性能有保证,但依赖手动标注的三元组数据,限制了可扩展性和零样本能力。
- 提出一种自动三元组生成的管道,构建了一个名为CIRHS的合成数据集。
- 利用大型语言模型生成提示,控制文本到图像生成模型产生图像对。
- 引入Hybrid Contextual Alignment(CoAlign)框架,实现全局对齐和局部推理。
- CoAlign在零样本场景下表现出卓越性能,并在三个常用基准测试中超越现有方法。
点此查看论文截图



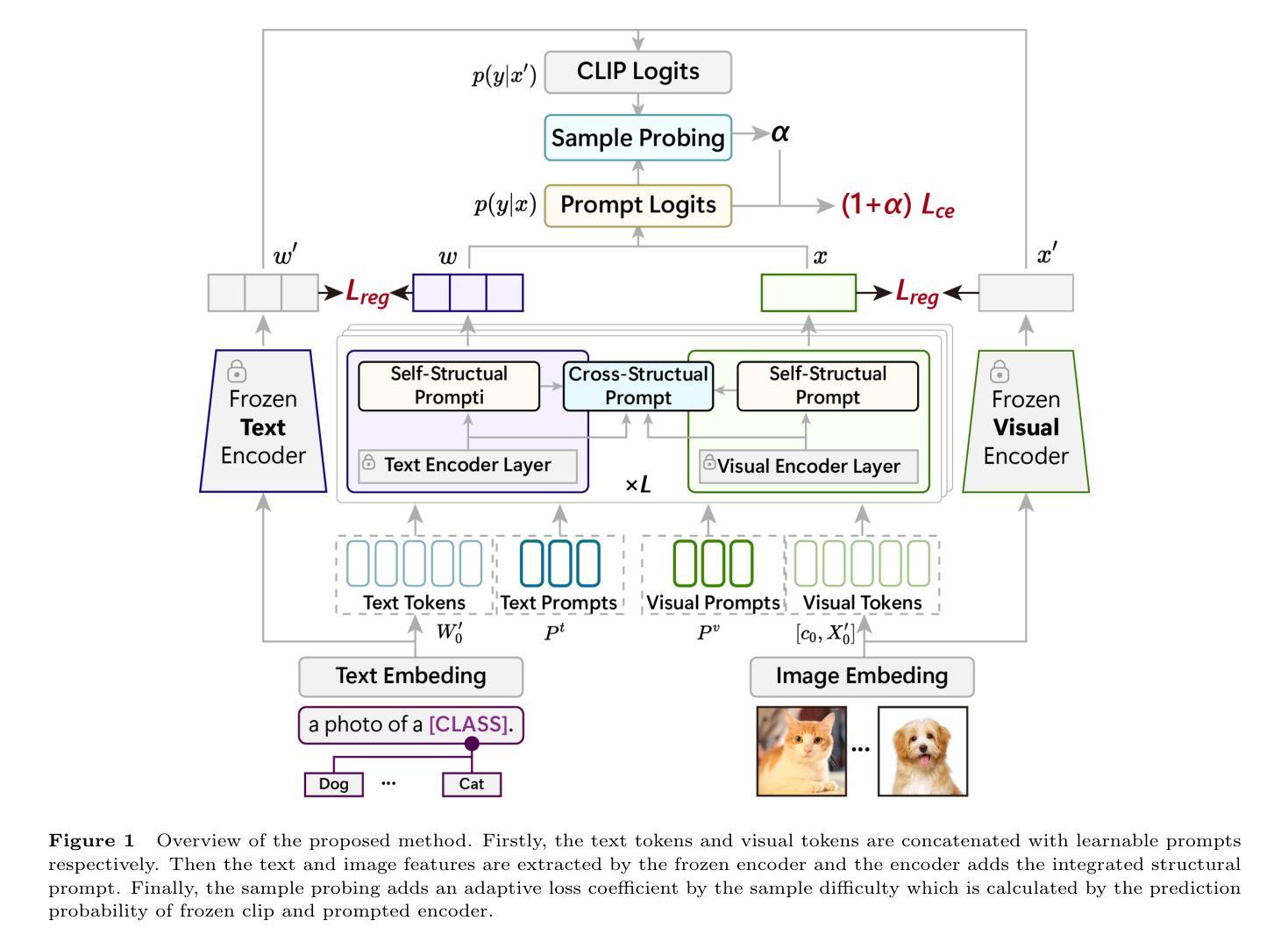
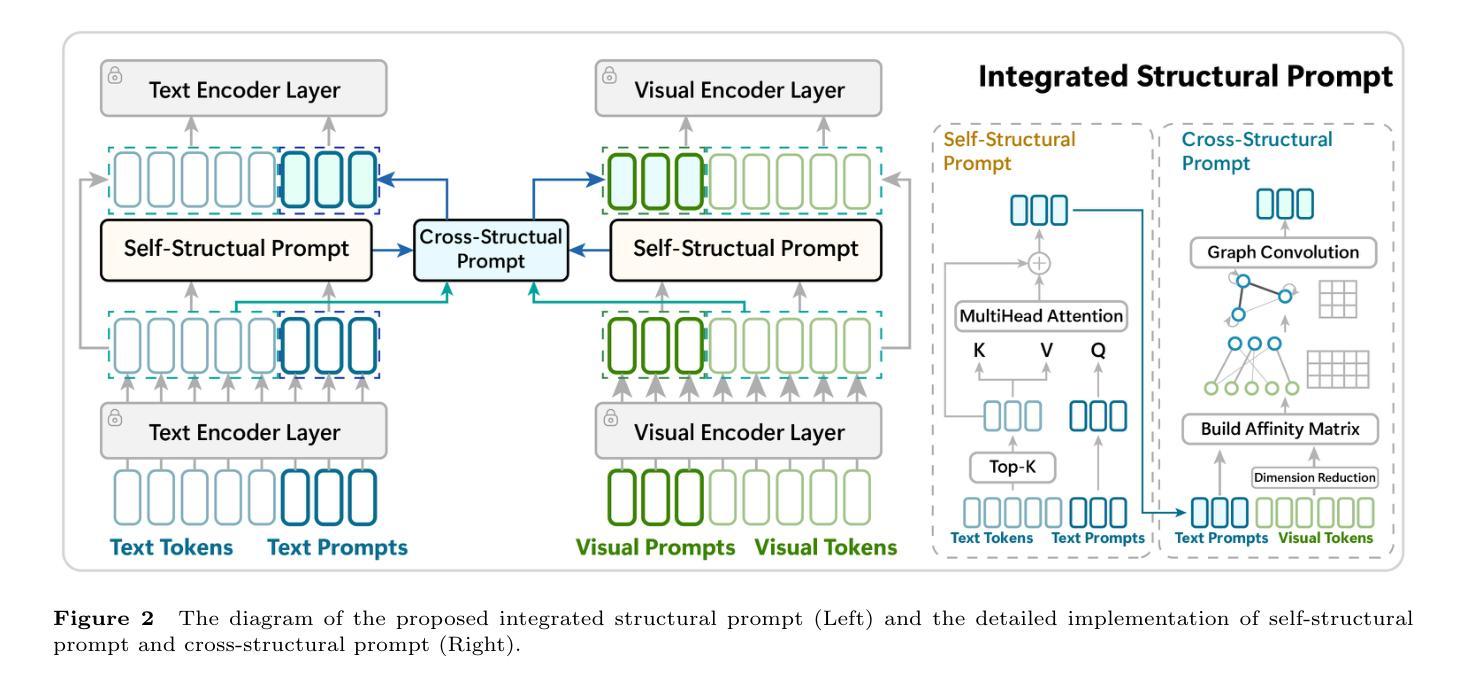
Integrated Structural Prompt Learning for Vision-Language Models
Authors:Jiahui Wang, Qin Xu, Bo Jiang, Bin Luo
Prompt learning methods have significantly extended the transferability of pre-trained Vision-Language Models (VLMs) like CLIP for various downstream tasks. These methods adopt handcraft templates or learnable vectors to provide text or image instructions in fine-tuning VLMs. However, most existing works ignore the structural relationships between learnable prompts and tokens within and between modalities. Moreover, balancing the performance of base and new classes remains a significant challenge. In this paper, we propose an Integrated Structural Prompt (ISP) for VLMs to enhance the interaction of information representations between the text and image branches. ISP introduces self-structural and cross-structural prompt modules to model the structural relationships between learnable prompts and frozen tokens within and across modalities. This enables efficient information transfer while preserving feature stability. Additionally, we propose a sample probing module that dynamically adjusts loss coefficients based on sample difficulty, preventing the mode from overfitting to simple samples and improving generalization ability to new classes. Extensive experiments on three widely used settings: base-to-new generalization, cross-dataset evaluation, and domain generalization demonstrate that the proposed ISP achieves competitive performance against state-of-the-art methods.
提示学习方法已显著扩展了预训练视觉语言模型(如CLIP)在各种下游任务上的可迁移性。这些方法采用手工模板或可学习向量,在微调VLM时提供文本或图像指令。然而,大多数现有工作忽略了可学习提示与模态内和跨模态标记之间的结构关系。此外,平衡基础类别和新类别的性能仍然是一个巨大的挑战。在本文中,我们提出了一种用于VLM的集成结构提示(ISP),以增强文本和图像分支之间信息表示的交互。ISP引入了自我结构和跨结构提示模块,以建模可学习提示与模态内和跨模态冻结标记之间的结构关系。这可以在保持特征稳定性的同时实现有效的信息传输。此外,我们提出了一种样本探测模块,该模块根据样本难度动态调整损失系数,防止模型过度拟合简单样本,提高对新类别的泛化能力。在三种广泛应用场景下的大量实验:基础到新类别的泛化、跨数据集评估和域泛化,证明所提出的ISP在竞争性能上达到了最先进的方法水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
预训练视觉语言模型(如CLIP)的迁移能力通过Prompt学习法得到显著提高,用于下游任务。此方法通过手工模板或可学习向量提供文本或图像指令以微调模型。然而,现有工作忽视了可学习提示与模态内和模态间标记之间的结构关系。此外,平衡基础类别和新类别的性能仍然是一个挑战。本文提出了用于视觉语言模型的集成结构提示(ISP),以增强文本和图像分支之间信息表示的交互。ISP引入自结构和跨结构提示模块,对可学习提示与模态内和跨模态冻结标记之间的结构关系进行建模。这可以在保持特征稳定性的同时实现高效的信息传输。此外,还提出了样本探针模块,根据样本难度动态调整损失系数,防止模型过度拟合简单样本,提高对新类别的泛化能力。在三种广泛使用的设置下进行了大量实验:基础到新类别的推广、跨数据集评估和域推广,证明所提出的ISP在竞争方法中表现出卓越的性能。
Key Takeaways
以下是七个关于给定文本的见解要点:
- Prompt学习法增强了预训练视觉语言模型(如CLIP)在下游任务中的迁移能力。
- 通过手工模板或可学习向量提供文本或图像指令以微调模型是当前的常见方法。
- 目前的工作忽略了可学习提示与模态内和模态间标记之间的结构关系的重要性。
- 在使用预训练模型时,平衡基础类别和新类别的性能是一个重要挑战。
- 集成结构提示(ISP)通过增强文本和图像分支之间的信息交互提高了视觉语言模型的性能。
- ISP通过引入自结构和跨结构提示模块,建模可学习提示与冻结标记之间的结构关系。
点此查看论文截图

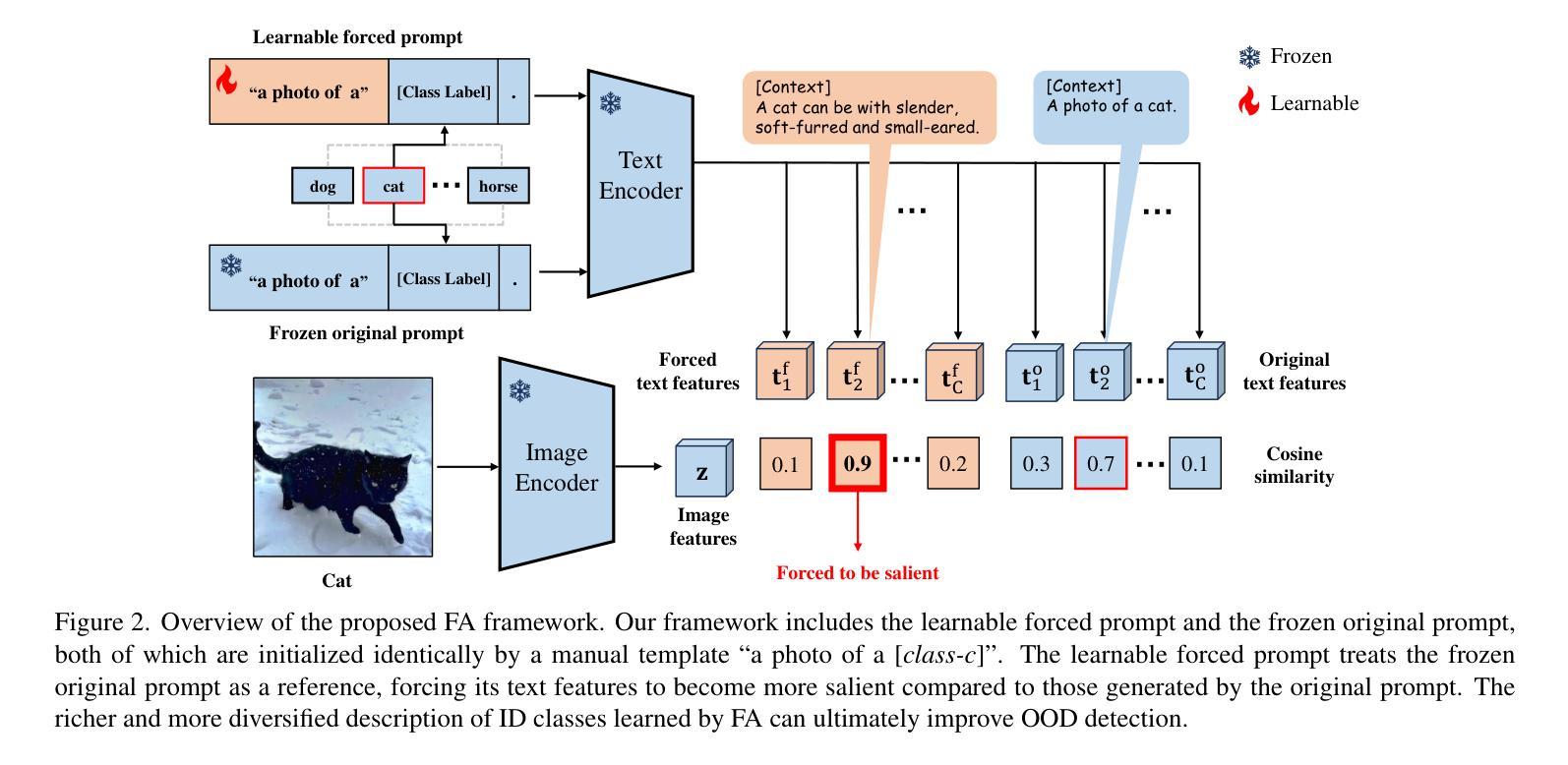
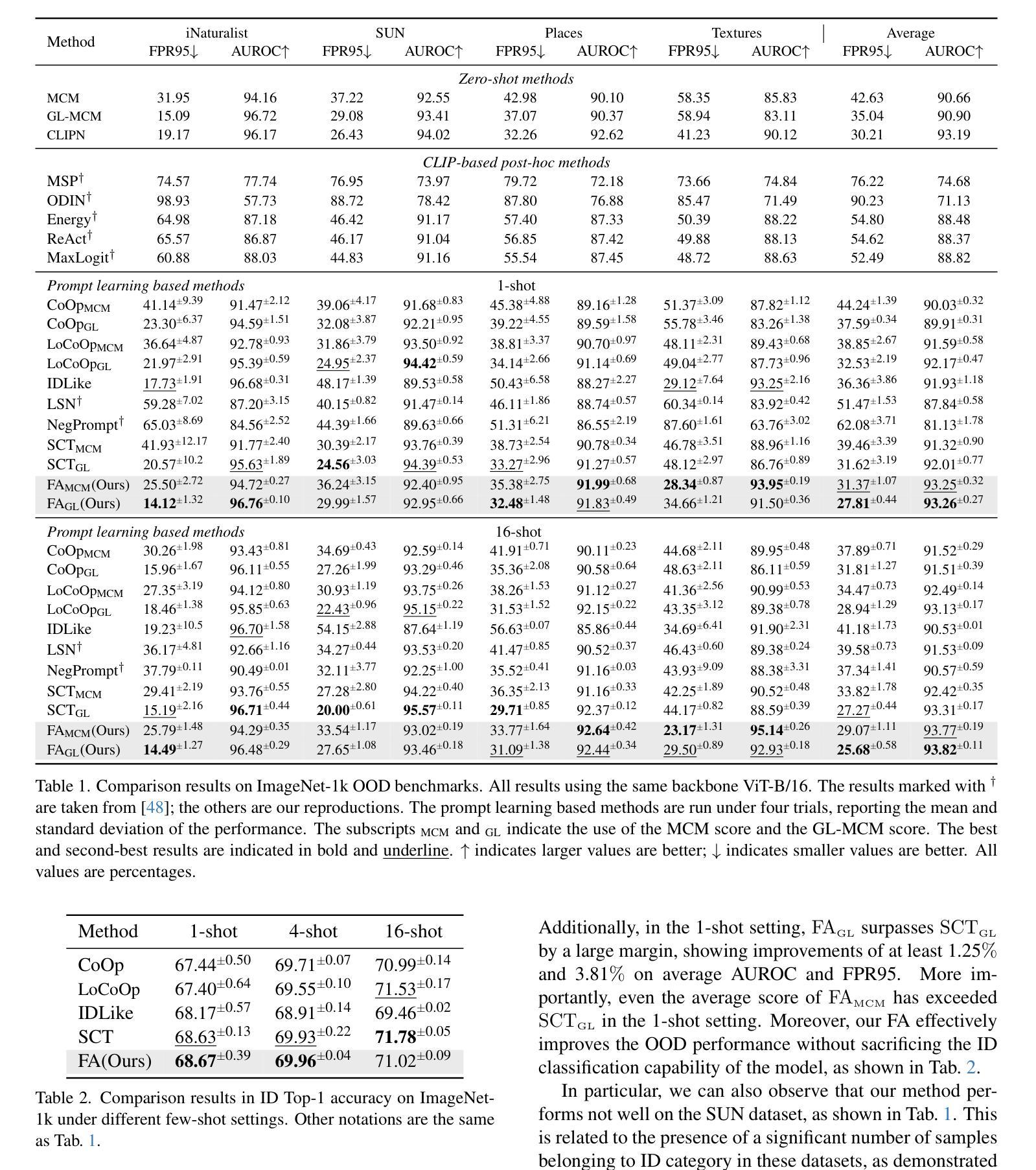
FA: Forced Prompt Learning of Vision-Language Models for Out-of-Distribution Detection
Authors:Xinhua Lu, Runhe Lai, Yanqi Wu, Kanghao Chen, Wei-Shi Zheng, Ruixuan Wang
Pre-trained vision-language models (VLMs) have advanced out-of-distribution (OOD) detection recently. However, existing CLIP-based methods often focus on learning OOD-related knowledge to improve OOD detection, showing limited generalization or reliance on external large-scale auxiliary datasets. In this study, instead of delving into the intricate OOD-related knowledge, we propose an innovative CLIP-based framework based on Forced prompt leArning (FA), designed to make full use of the In-Distribution (ID) knowledge and ultimately boost the effectiveness of OOD detection. Our key insight is to learn a prompt (i.e., forced prompt) that contains more diversified and richer descriptions of the ID classes beyond the textual semantics of class labels. Specifically, it promotes better discernment for ID images, by forcing more notable semantic similarity between ID images and the learnable forced prompt. Moreover, we introduce a forced coefficient, encouraging the forced prompt to learn more comprehensive and nuanced descriptions of the ID classes. In this way, FA is capable of achieving notable improvements in OOD detection, even when trained without any external auxiliary datasets, while maintaining an identical number of trainable parameters as CoOp. Extensive empirical evaluations confirm our method consistently outperforms current state-of-the-art methods. Code is available at https://github.com/0xFAFA/FA.
预训练视觉语言模型(VLMs)最近在异常分布(OOD)检测方面取得了进展。然而,现有的基于CLIP的方法通常专注于学习OOD相关知识以提高OOD检测能力,显示出有限的泛化能力或对外部大规模辅助数据集的依赖。本研究中,我们并未深入研究复杂的OOD相关知识,而是提出了一种基于强制提示学习(FA)的创新的CLIP框架,旨在充分利用内部分布(ID)知识,并最终提高OOD检测的有效性。我们的关键见解是学习一种提示(即强制提示),其中包含超越类别标签文本语义的ID类别的更多样化和丰富的描述。具体来说,它通过强制ID图像和可学习的强制提示之间更显著的语义相似性,促进了对ID图像的更佳辨别。此外,我们引入了一个强制系数,鼓励强制提示学习更全面、微妙的ID类别描述。通过这种方式,即使在没有任何外部辅助数据集的情况下进行训练,FA也能在OOD检测方面实现显著的改进,同时保持与CoOp相同数量的可训练参数。大量的经验评估证明我们的方法始终优于当前最先进的方法。代码可用在https://github.com/0xFAFA/FA。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 4 figures, Accepted by ICCV2025
Summary
本文提出了一种基于CLIP的强制提示学习(FA)框架,旨在充分利用分布内(ID)知识,提高异常检测效果。通过强制提示学习,模型能够学习包含超过类标签文本语义的更多样化和丰富的描述,从而改进对分布内图像的识别,实现在无需外部辅助数据集的情况下显著提升异常检测性能。代码已发布在相应GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 强制提示学习(FA)是一种基于CLIP的新框架,旨在利用分布内(ID)知识提高异常检测性能。
- 该方法通过强制提示学习更多样化和丰富的描述来改进对分布内图像的识别。
- 引入强制系数来鼓励模型学习更全面、微妙的分布内类描述。
- 该方法无需外部辅助数据集即可实现显著的性能提升。
- 该框架在保持与CoOp相同数量的可训练参数的同时,实现了性能的提升。
- 通过广泛的实验评估,证明该方法在异常检测方面表现优于当前最先进的方法。
点此查看论文截图

Visual Adaptive Prompting for Compositional Zero-Shot Learning
Authors:Kyle Stein, Arash Mahyari, Guillermo Francia, Eman El-Sheikh
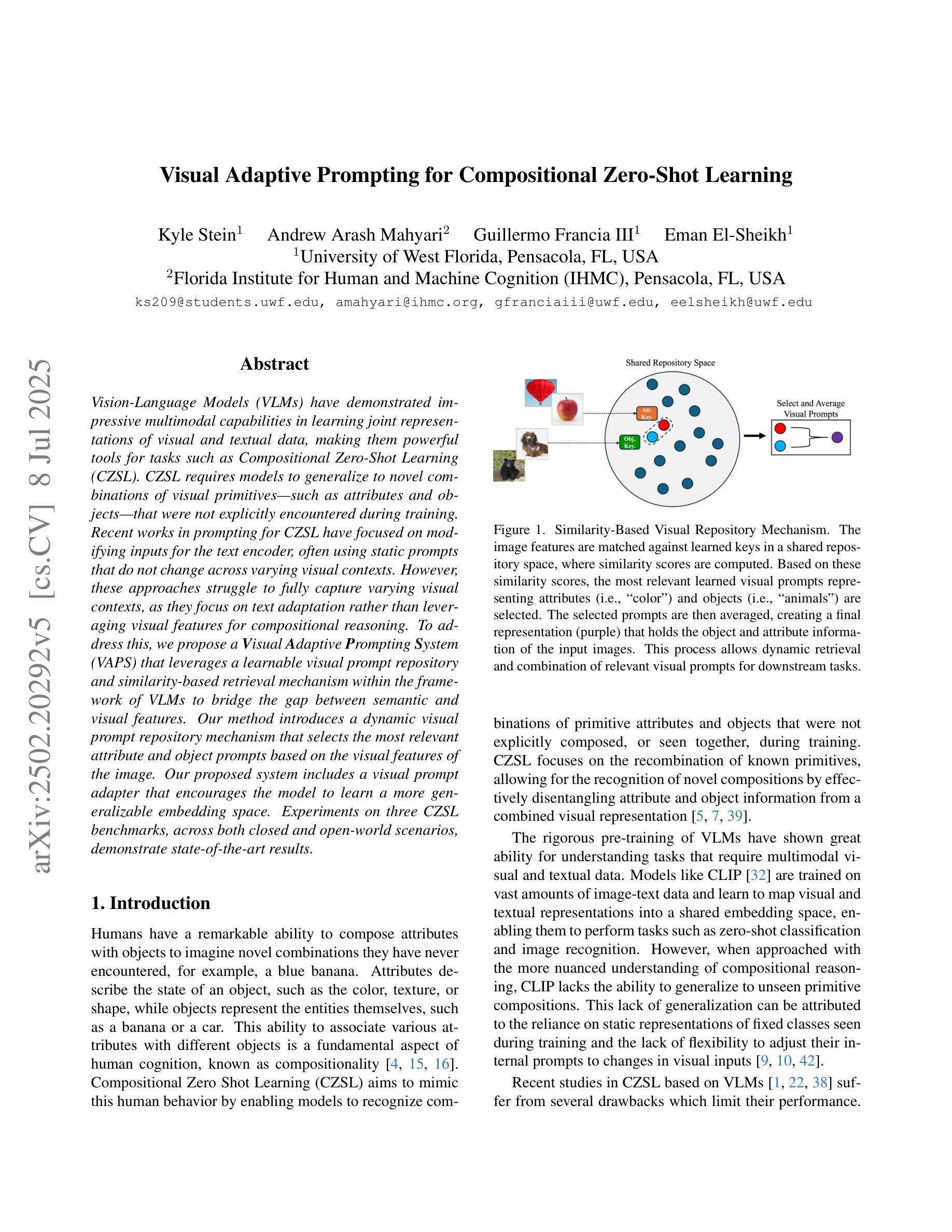
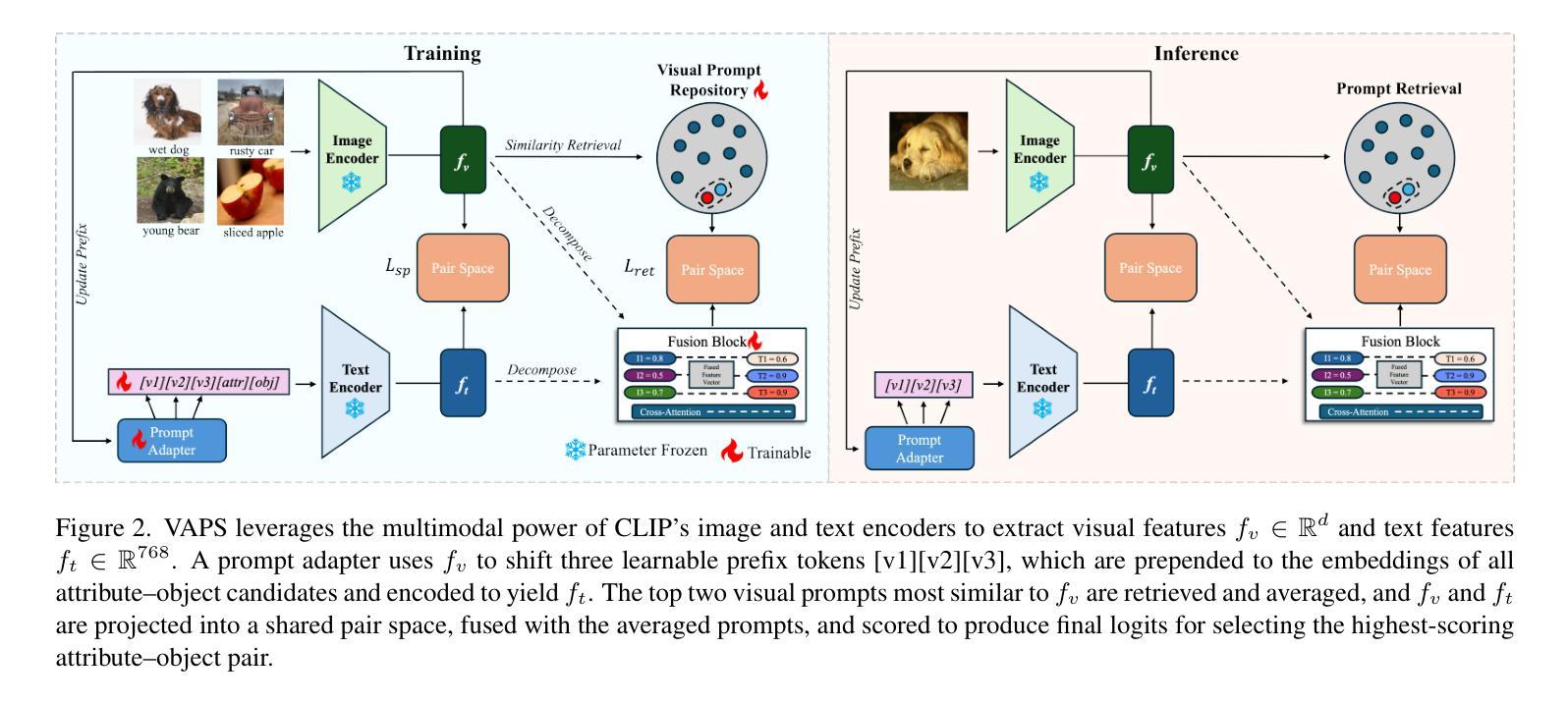
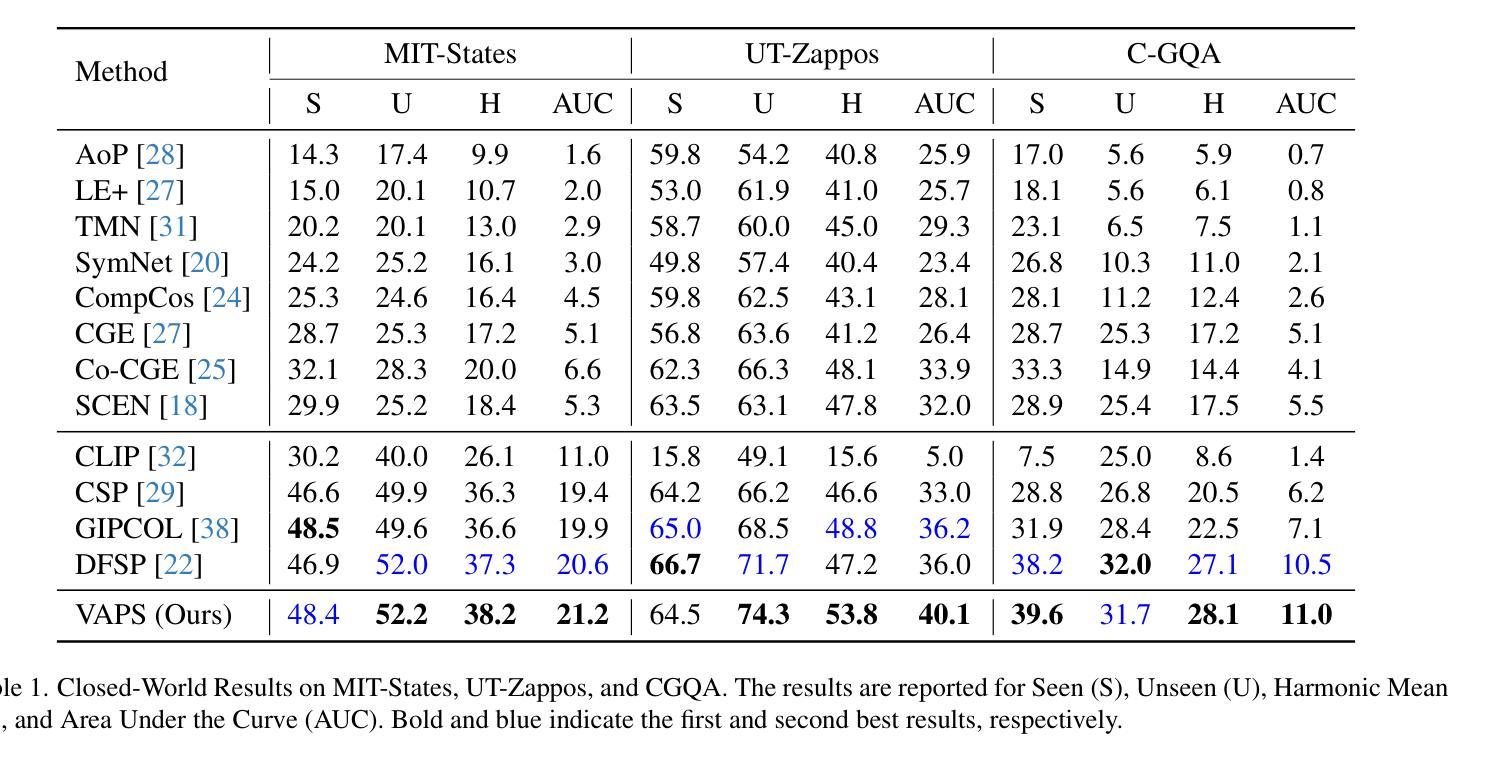
Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have demonstrated impressive multimodal capabilities in learning joint representations of visual and textual data, making them powerful tools for tasks such as Compositional Zero-Shot Learning (CZSL). CZSL requires models to generalize to novel combinations of visual primitives–such as attributes and objects–that were not explicitly encountered during training. Recent works in prompting for CZSL have focused on modifying inputs for the text encoder, often using static prompts that do not change across varying visual contexts. However, these approaches struggle to fully capture varying visual contexts, as they focus on text adaptation rather than leveraging visual features for compositional reasoning. To address this, we propose a Visual Adaptive Prompting System (VAPS) that leverages a learnable visual prompt repository and similarity-based retrieval mechanism within the framework of VLMs to bridge the gap between semantic and visual features. Our method introduces a dynamic visual prompt repository mechanism that selects the most relevant attribute and object prompts based on the visual features of the image. Our proposed system includes a visual prompt adapter that encourages the model to learn a more generalizable embedding space. Experiments on three CZSL benchmarks, across both closed and open-world scenarios, demonstrate state-of-the-art results.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)在联合表示视觉和文本数据方面表现出了令人印象深刻的跨模态能力,使其成为完成组合零射击学习(CZSL)等任务的有力工具。CZSL要求模型能够泛化到在训练期间未明确遇到的新组合的视觉元素,如属性和对象。关于CZSL的提示方法主要集中在修改文本编码器的输入,通常使用静态提示,这些提示不会随着不同的视觉上下文而改变。然而,这些方法在捕捉多变的视觉上下文方面存在困难,因为它们侧重于文本适应,而不是利用视觉特征进行组合推理。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种视觉自适应提示系统(VAPS),该系统利用可学习的视觉提示存储库和视觉语言模型框架内的基于相似性的检索机制来弥合语义和视觉特征之间的差距。我们的方法引入了一种动态视觉提示存储库机制,该机制根据图像视觉特征选择最相关的属性和对象提示。我们提出的系统包括一个视觉提示适配器,鼓励模型学习一个更具泛化能力的嵌入空间。在三个CZSL基准测试上的实验,无论是在封闭世界还是开放世界场景中,都取得了最先进的成果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
视觉语言模型(VLMs)在视觉和文本数据的联合表示学习上表现出强大的多模态能力,适用于组合零射击学习(CZSL)等任务。针对CZSL中的视觉上下文变化问题,本文提出一种视觉自适应提示系统(VAPS),通过引入可学习的视觉提示库和基于相似度的检索机制,缩小语义和视觉特征之间的差距。该系统包括一个视觉提示适配器,鼓励模型学习更具通用性的嵌入空间。在三个CZSL基准测试上的实验表明,该方法在封闭和开放世界场景下均达到最新技术水平。
Key Takeaways
- VLMs在多模态学习中表现强大,特别是在CZSL任务中。
- 现有方法主要通过文本编码器的输入提示来处理CZSL,但这种方式无法完全捕捉视觉上下文的差异。
- 本文提出一种视觉自适应提示系统(VAPS),利用可学习的视觉提示库和基于相似度的检索机制来改进这一状况。
- VAPS通过动态选择最相关的属性对象提示来适应图像视觉特征。
- VAPS包括一个视觉提示适配器,有助于模型学习更通用的嵌入空间。
- 在三个CZSL基准测试上的实验表明,VAPS在封闭和开放世界场景下均取得最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图
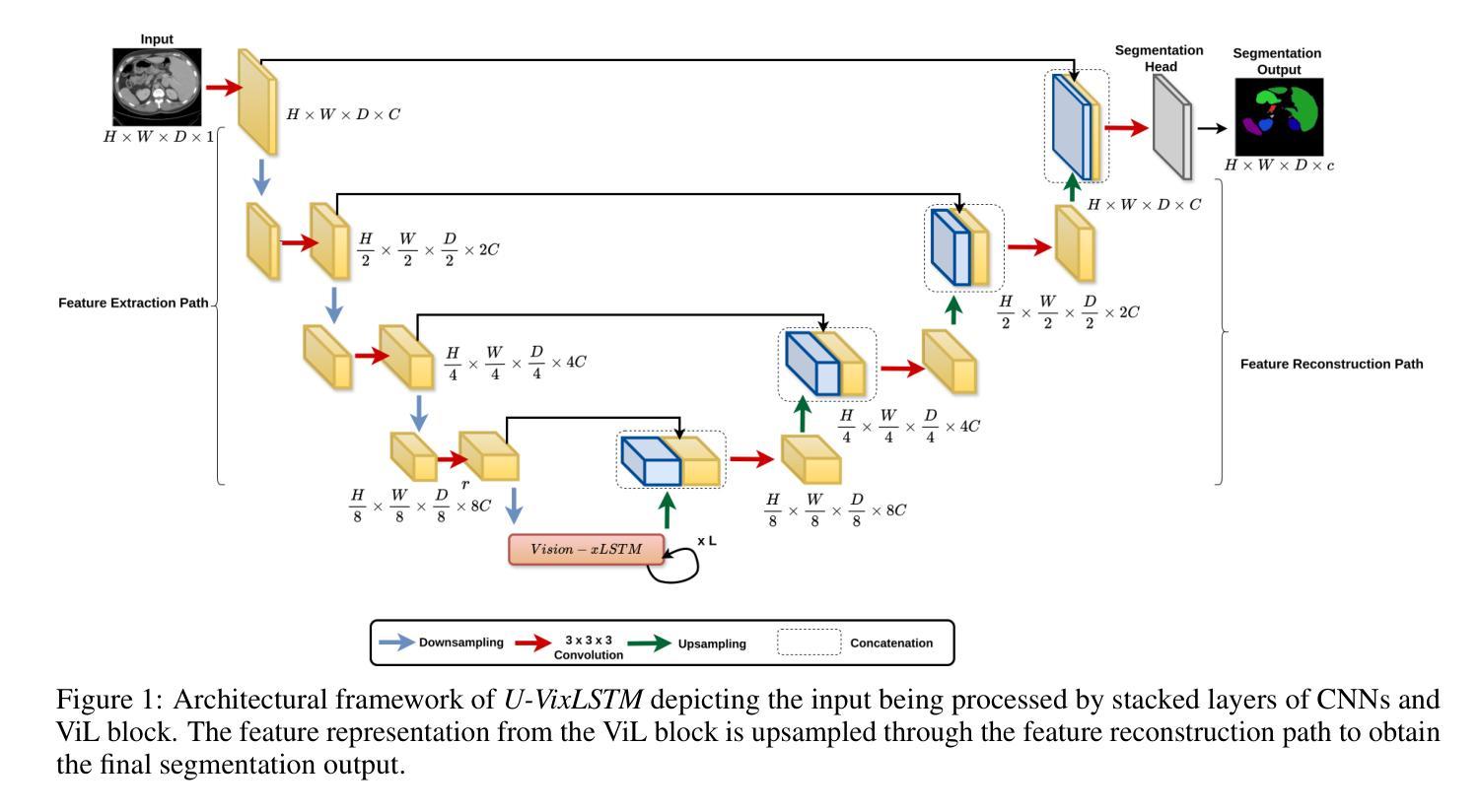
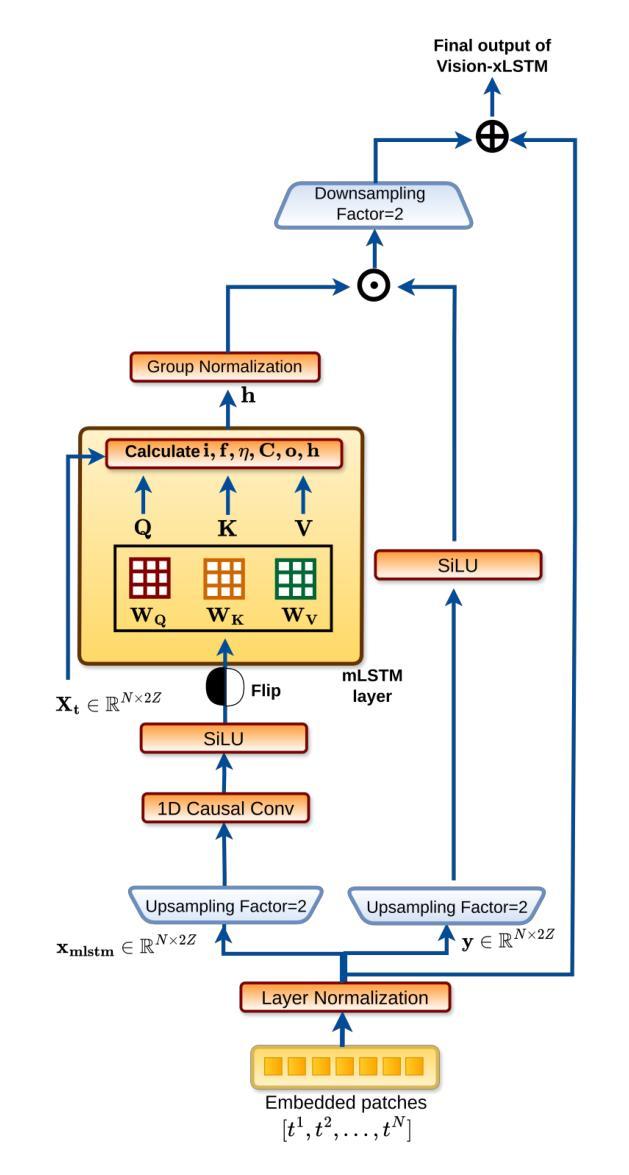
Are Vision xLSTM Embedded UNet More Reliable in Medical 3D Image Segmentation?
Authors:Pallabi Dutta, Soham Bose, Swalpa Kumar Roy, Sushmita Mitra
The development of efficient segmentation strategies for medical images has evolved from its initial dependence on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) to the current investigation of hybrid models that combine CNNs with Vision Transformers (ViTs). There is an increasing focus on creating architectures that are both high-performing and computationally efficient, capable of being deployed on remote systems with limited resources. Although transformers can capture global dependencies in the input space, they face challenges from the corresponding high computational and storage expenses involved. This research investigates the integration of CNNs with Vision Extended Long Short-Term Memory (Vision-xLSTM)s by introducing the novel U-VixLSTM. The Vision-xLSTM blocks capture the temporal and global relationships within the patches extracted from the CNN feature maps. The convolutional feature reconstruction path upsamples the output volume from the Vision-xLSTM blocks to produce the segmentation output. Our primary objective is to propose that Vision-xLSTM forms an appropriate backbone for medical image segmentation, offering excellent performance with reduced computational costs. The U-VixLSTM exhibits superior performance compared to the state-of-the-art networks in the publicly available Synapse, ISIC and ACDC datasets. Code provided: https://github.com/duttapallabi2907/U-VixLSTM
医疗图像分割策略的发展已经从最初依赖于卷积神经网络(CNNs)演变为现在对结合CNN和Vision Transformers(ViTs)的混合模型的研究。目前,人们越来越关注创建既高性能又计算效率高的架构,能够部署在资源有限的远程系统上。虽然Transformer可以捕获输入空间中的全局依赖性,但它们面临着高昂的计算和存储成本所带来的挑战。本研究通过引入新型的U-VixLSTM,探讨了CNN与Vision Extended Long Short-Term Memory(Vision-xLSTM)的结合。Vision-xLSTM块捕获来自CNN特征图提取的补丁中的时间和全局关系。卷积特征重建路径对Vision-xLSTM块的输出体积进行上采样,以产生分割输出。我们的主要目标是提出Vision-xLSTM是医疗图像分割的合适骨干网,能在降低计算成本的同时提供出色的性能。U-VixLSTM在公开的Synapse、ISIC和ACDC数据集上表现出优于最新网络的性能。相关代码链接:https://github.com/duttapallabi2907/U-VixLSTM
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了医疗图像分割策略的发展,从最初依赖卷积神经网络(CNNs)到当前对结合CNN与Vision Transformer(ViTs)的混合模型的探索。研究重点在创建既高性能又计算效率高的架构,能在资源有限的远程系统上部署。文章提出了结合CNN与Vision-xLSTM的新模型U-VixLSTM,该模型能捕捉CNN特征图中斑块内的时序和全局关系,并通过卷积特征重建路径产生分割输出。U-VixLSTM在公开数据集Synapse、ISIC和ACDC上的表现优于现有顶尖网络。
Key Takeaways
- 医疗图像分割策略从CNN转向混合模型,结合CNN与Vision Transformer(ViTs)。
- 新型模型U-VixLSTM结合了CNN和Vision-xLSTM,旨在实现高效和性能优异的医疗图像分割。
- U-VixLSTM模型可以捕捉CNN特征图中的时序和全局关系。
- U-VixLSTM模型通过卷积特征重建路径产生分割输出。
- U-VixLSTM在多个公开数据集上的表现超越了现有的顶尖网络。
- 该研究提供的代码可在GitHub上访问。
点此查看论文截图