⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-11 更新
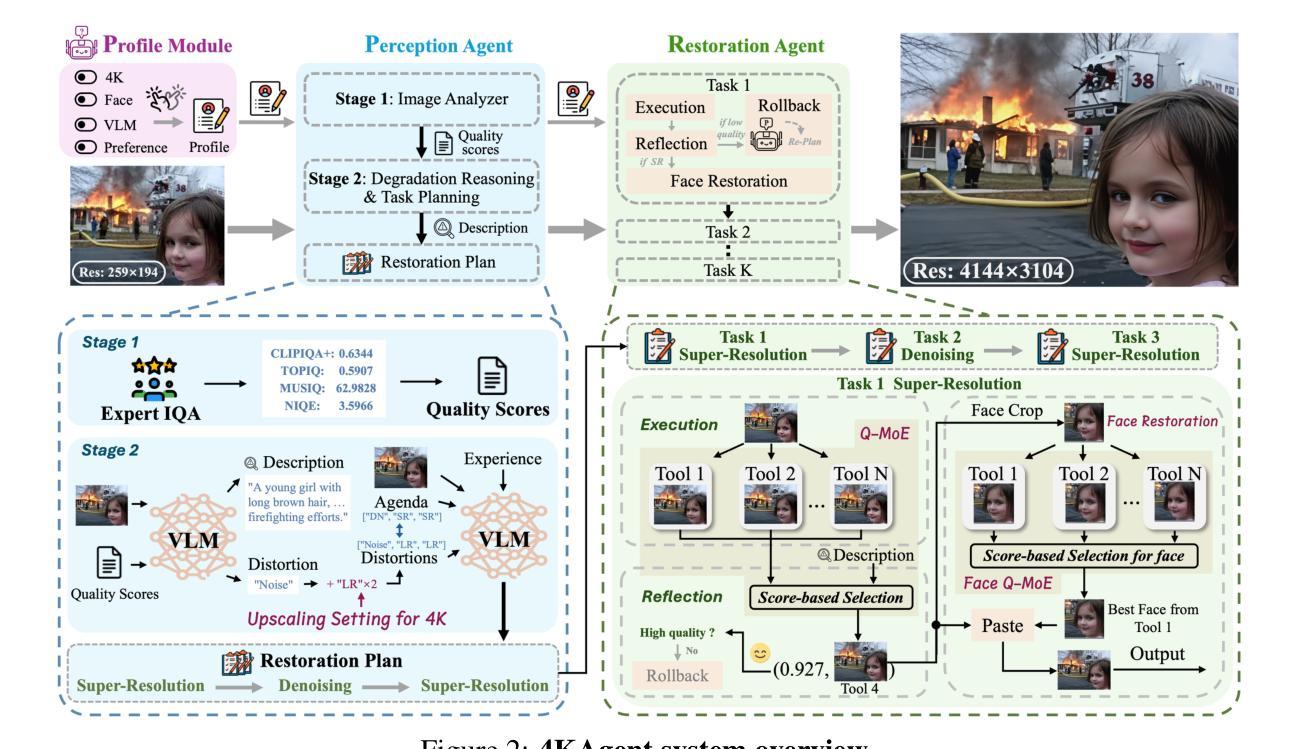
4KAgent: Agentic Any Image to 4K Super-Resolution
Authors:Yushen Zuo, Qi Zheng, Mingyang Wu, Xinrui Jiang, Renjie Li, Jian Wang, Yide Zhang, Gengchen Mai, Lihong V. Wang, James Zou, Xiaoyu Wang, Ming-Hsuan Yang, Zhengzhong Tu
We present 4KAgent, a unified agentic super-resolution generalist system designed to universally upscale any image to 4K resolution (and even higher, if applied iteratively). Our system can transform images from extremely low resolutions with severe degradations, for example, highly distorted inputs at 256x256, into crystal-clear, photorealistic 4K outputs. 4KAgent comprises three core components: (1) Profiling, a module that customizes the 4KAgent pipeline based on bespoke use cases; (2) A Perception Agent, which leverages vision-language models alongside image quality assessment experts to analyze the input image and make a tailored restoration plan; and (3) A Restoration Agent, which executes the plan, following a recursive execution-reflection paradigm, guided by a quality-driven mixture-of-expert policy to select the optimal output for each step. Additionally, 4KAgent embeds a specialized face restoration pipeline, significantly enhancing facial details in portrait and selfie photos. We rigorously evaluate our 4KAgent across 11 distinct task categories encompassing a total of 26 diverse benchmarks, setting new state-of-the-art on a broad spectrum of imaging domains. Our evaluations cover natural images, portrait photos, AI-generated content, satellite imagery, fluorescence microscopy, and medical imaging like fundoscopy, ultrasound, and X-ray, demonstrating superior performance in terms of both perceptual (e.g., NIQE, MUSIQ) and fidelity (e.g., PSNR) metrics. By establishing a novel agentic paradigm for low-level vision tasks, we aim to catalyze broader interest and innovation within vision-centric autonomous agents across diverse research communities. We will release all the code, models, and results at: https://4kagent.github.io.
我们介绍了4KAgent,这是一个统一的智能超分辨率通用系统,旨在将任何图像通用地提升到4K分辨率(如果迭代应用,甚至可以更高)。我们的系统能够转换极低分辨率且具有严重退化的图像,例如256x256的高失真输入,将其转化为清晰逼真的4K输出。4KAgent包含三个核心组件:(1)分析模块,根据特定的用例定制4KAgent管道;(2)感知代理,它利用视觉语言模型以及图像质量评估专家来分析输入图像并制定相应的恢复计划;(3)恢复代理,根据递归的执行-反思模式执行该计划,并由质量驱动的专家混合策略指导以选择每个步骤的最佳输出。此外,4KAgent嵌入了一个专门的面部恢复管道,可显着提高肖像和自拍中的面部细节。我们对4KAgent进行了严格的评估,涵盖了包括26个不同基准测试的11个不同任务类别,在广泛的成像领域上创造了最新的技术。我们的评估涵盖了自然图像、肖像照片、AI生成内容、卫星图像、荧光显微镜以及诸如眼底检查、超声波和X射线等医学影像,在感知(例如NIQE、MUSIQ)和保真度(例如PSNR)指标方面表现出卓越的性能。通过为低级视觉任务建立新的智能范式,我们旨在激发不同研究社区中对以视觉为中心的自主智能体的更广泛兴趣和创新。我们会在https://4kagent.github.io发布所有代码、模型和结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://4kagent.github.io
Summary
4KAgent是一种统一的多智能体超分辨率通用系统,可将任何图像提升到4K分辨率,甚至更高。系统包括三大核心组件:分析模块、感知智能体、恢复智能体,能够处理极端低分辨率且严重退化的图像,如高度扭曲的输入图像(分辨率为256x256),并将其转化为清晰逼真的4K输出图像。同时,系统还包括专门的面部恢复管道,能显著改善肖像和自拍中的面部细节。在涵盖广泛的图像领域进行了严格评估,包括自然图像、肖像照片、人工智能生成内容、卫星图像等,在感知和保真度指标上均表现出卓越性能。我们旨在建立低水平视觉任务的新型智能体范式,激发不同研究社区对视觉为中心的自主智能体的更广泛兴趣和创新。相关代码、模型和结果将在以下网址公开:https://4kagent.github.io。
Key Takeaways
- 4KAgent是一种统一的多智能体超分辨率系统,可将任何图像提升到至少4K分辨率。
- 系统包括三大核心组件:分析模块、感知智能体和恢复智能体。
- 能够处理极端低分辨率和严重退化的图像,并转化为清晰逼真的输出。
- 包含了专门用于增强肖像和自拍中的面部细节的面部恢复管道。
- 在多种不同领域进行了广泛的评估,包括自然图像、肖像照片等,表现出卓越性能。
- 在感知和保真度指标上都有出色的表现。
点此查看论文截图

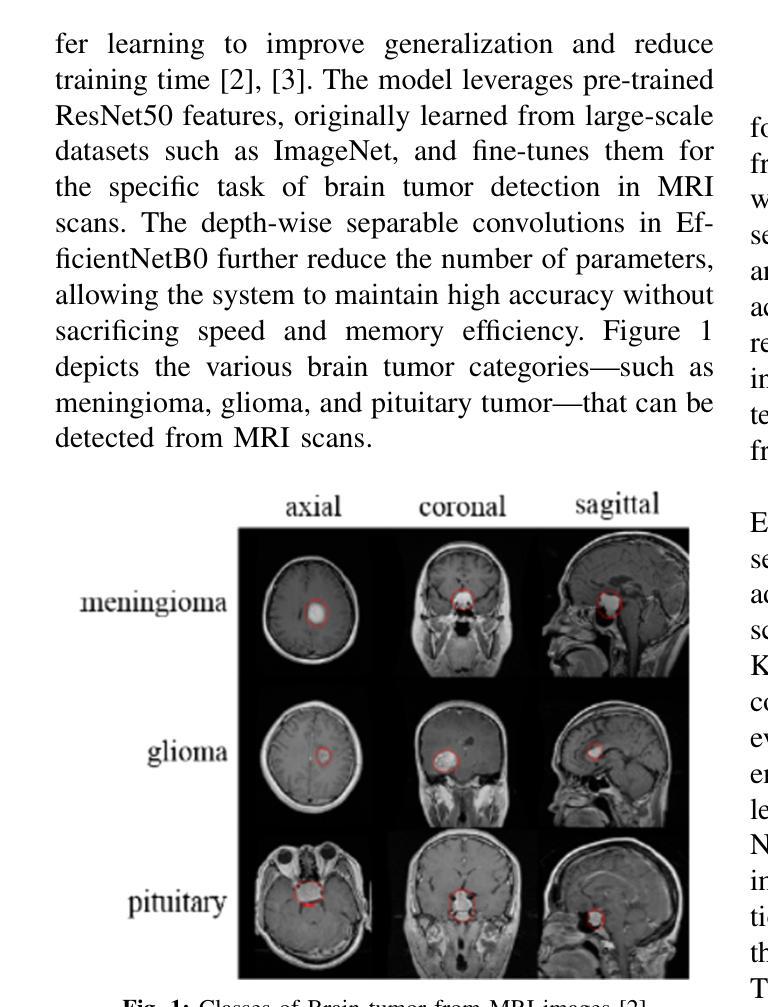
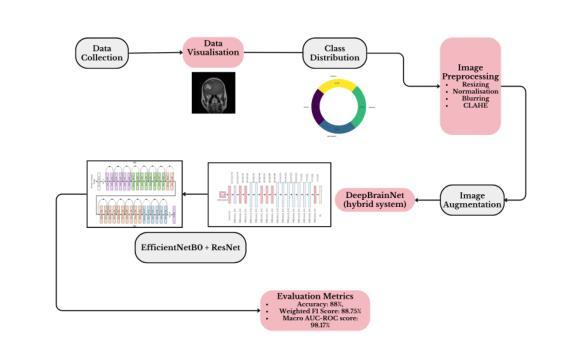
Deep Brain Net: An Optimized Deep Learning Model for Brain tumor Detection in MRI Images Using EfficientNetB0 and ResNet50 with Transfer Learning
Authors:Daniel Onah, Ravish Desai
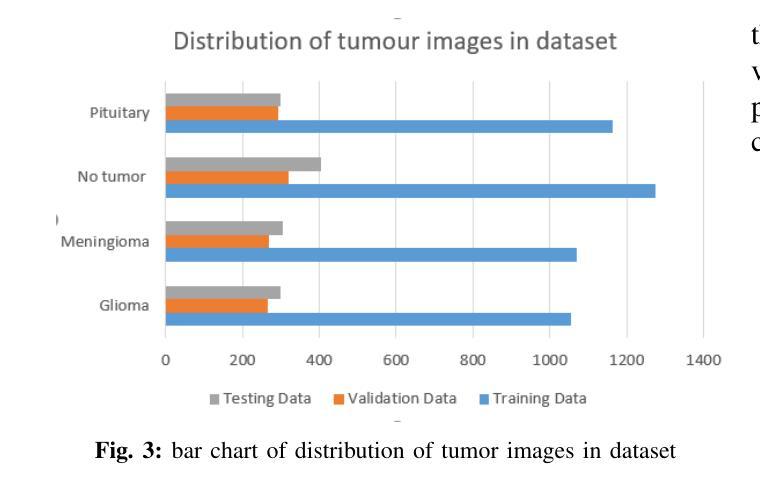
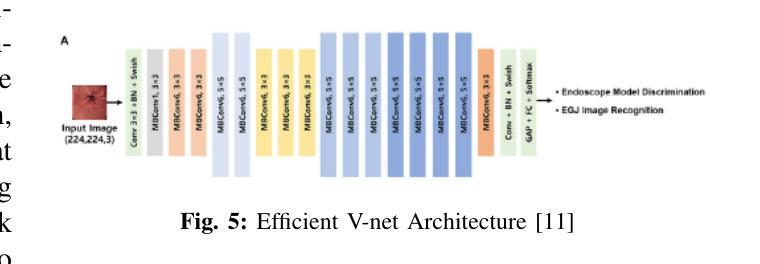
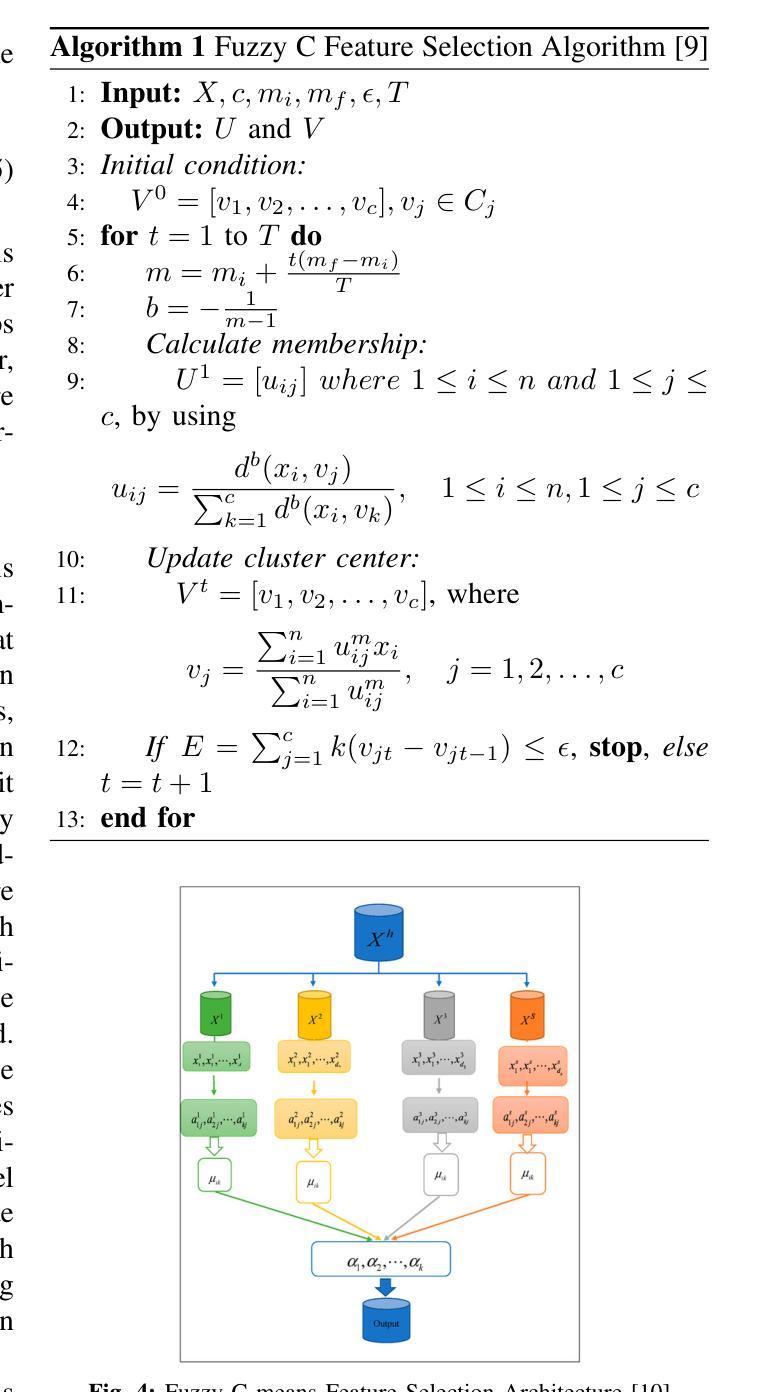
In recent years, deep learning has shown great promise in the automated detection and classification of brain tumors from MRI images. However, achieving high accuracy and computational efficiency remains a challenge. In this research, we propose Deep Brain Net, a novel deep learning system designed to optimize performance in the detection of brain tumors. The model integrates the strengths of two advanced neural network architectures which are EfficientNetB0 and ResNet50, combined with transfer learning to improve generalization and reduce training time. The EfficientNetB0 architecture enhances model efficiency by utilizing mobile inverted bottleneck blocks, which incorporate depth wise separable convolutions. This design significantly reduces the number of parameters and computational cost while preserving the ability of models to learn complex feature representations. The ResNet50 architecture, pre trained on large scale datasets like ImageNet, is fine tuned for brain tumor classification. Its use of residual connections allows for training deeper networks by mitigating the vanishing gradient problem and avoiding performance degradation. The integration of these components ensures that the proposed system is both computationally efficient and highly accurate. Extensive experiments performed on publicly available MRI datasets demonstrate that Deep Brain Net consistently outperforms existing state of the art methods in terms of classification accuracy, precision, recall, and computational efficiency. The result is an accuracy of 88 percent, a weighted F1 score of 88.75 percent, and a macro AUC ROC score of 98.17 percent which demonstrates the robustness and clinical potential of Deep Brain Net in assisting radiologists with brain tumor diagnosis.
近年来,深度学习在通过MRI图像自动检测和分类脑肿瘤方面显示出巨大潜力。然而,实现高准确性和计算效率仍然是一个挑战。在这项研究中,我们提出了Deep Brain Net,这是一个新型的深度学习系统,旨在优化脑肿瘤检测的性能。该模型融合了EfficientNetB0和ResNet50两种先进神经网络架构的优势,结合迁移学习来提高通用性和减少训练时间。EfficientNetB0架构通过利用移动倒置瓶颈块提高了模型效率,这些块结合了深度可分离卷积。这种设计显著减少了参数数量和计算成本,同时保持了模型学习复杂特征表示的能力。ResNet50架构在大型数据集(如ImageNet)上进行预训练,经过微调用于脑肿瘤分类。其残差连接的使用允许通过解决梯度消失问题和避免性能下降来训练更深的网络。这些组件的集成确保所提出的系统既计算高效又高度准确。在公共可用的MRI数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,Deep Brain Net在分类准确性、精确度、召回率和计算效率方面始终优于现有最新方法。其准确度达到88%,加权F1分数为88.75%,宏AUC ROC分数为98.17%,这证明了Deep Brain Net的稳健性和在临床辅助放射科医生诊断脑肿瘤的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 14 figures, 4 tables. To be submitted to a conference
Summary
本文介绍了深度学习在自动检测与分类脑肿瘤MRI图像中的潜力。为实现高效率与高精度,研究者提出了Deep Brain Net系统,它整合了EfficientNetB0与ResNet50两种先进的神经网络架构,并结合迁移学习来提升泛化能力并缩短训练时间。EfficientNetB0利用移动倒置瓶颈块来提升模型效率,而ResNet50则在大规模数据集上预训练,微调用于脑肿瘤分类。实验证明,Deep Brain Net在分类精度、精确率、召回率及计算效率上均超越现有先进技术,准确率达88%,加权F1分数为88.75%,宏观AUC ROC分数为98.17%,显示其在辅助放射科医生诊断脑肿瘤方面的稳健性与临床潜力。
Key Takeaways
- Deep learning在脑肿瘤MRI图像自动检测与分类方面具有巨大潜力。
- Deep Brain Net系统结合了EfficientNetB0与ResNet50两种神经网络架构,旨在提高检测脑肿瘤的性能。
- EfficientNetB0利用移动倒置瓶颈块以提高模型效率,降低参数数量和计算成本。
- ResNet50在大型数据集上预训练,并微调用于脑肿瘤分类,解决了梯度消失问题,避免了性能下降。
- Deep Brain Net在分类精度、精确率、召回率和计算效率上表现优越。
- 该系统达到了88%的准确率、88.75%的加权F1分数和98.17%的宏观AUC ROC分数。
点此查看论文截图

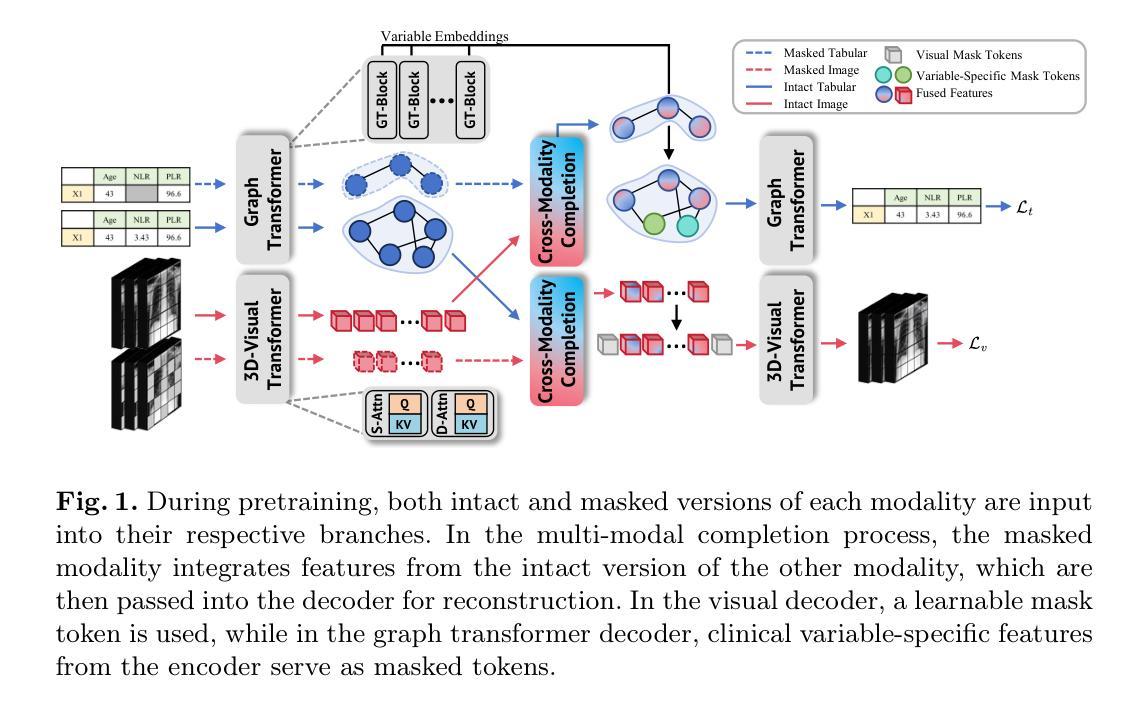
Cross-Modality Masked Learning for Survival Prediction in ICI Treated NSCLC Patients
Authors:Qilong Xing, Zikai Song, Bingxin Gong, Lian Yang, Junqing Yu, Wei Yang
Accurate prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients undergoing immunotherapy is essential for personalized treatment planning, enabling informed patient decisions, and improving both treatment outcomes and quality of life. However, the lack of large, relevant datasets and effective multi-modal feature fusion strategies pose significant challenges in this domain. To address these challenges, we present a large-scale dataset and introduce a novel framework for multi-modal feature fusion aimed at enhancing the accuracy of survival prediction. The dataset comprises 3D CT images and corresponding clinical records from NSCLC patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI), along with progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) data. We further propose a cross-modality masked learning approach for medical feature fusion, consisting of two distinct branches, each tailored to its respective modality: a Slice-Depth Transformer for extracting 3D features from CT images and a graph-based Transformer for learning node features and relationships among clinical variables in tabular data. The fusion process is guided by a masked modality learning strategy, wherein the model utilizes the intact modality to reconstruct missing components. This mechanism improves the integration of modality-specific features, fostering more effective inter-modality relationships and feature interactions. Our approach demonstrates superior performance in multi-modal integration for NSCLC survival prediction, surpassing existing methods and setting a new benchmark for prognostic models in this context.
对非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)患者进行免疫治疗时的准确预后评估对个性化治疗方案制定、患者决策信息透明以及改善治疗效果和生活质量具有重要意义。然而,缺乏相关的大型数据集和有效的多模式特征融合策略,给这一领域带来了重大挑战。为了应对这些挑战,我们推出了一个大规模数据集,并介绍了一个旨在提高生存预测准确性的多模式特征融合新框架。该数据集包含接受免疫检查点抑制剂(ICI)治疗的NSCLC患者的3D CT图像和相应的临床记录,以及无进展生存(PFS)和总生存(OS)数据。我们还提出了一种用于医学特征融合的跨模态掩膜学习方法,包括两个针对不同模态的分支:用于从CT图像中提取3D特征的Slice-Depth Transformer,以及用于学习表格数据中的节点特征和临床变量之间关系的基于图的Transformer。融合过程由掩膜模态学习策略引导,该策略使模型利用完整模态来重建缺失组件。这种机制改善了模态特定特征的集成,促进了更有效的跨模态关系和特征交互。我们的方法在NSCLC生存预测的多模态集成中展示了卓越性能,超越了现有方法,为这一背景下的预后模型设定了新的基准。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025
Summary
本文介绍了针对非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)患者接受免疫治疗时的预后准确预测的重要性,并提出一个大型数据集和一种新型多模态特征融合框架,旨在提高生存预测的准确性。该数据集包含接受免疫检查点抑制剂(ICI)治疗的NSCLC患者的3D CT图像和相关临床记录,以及无进展生存(PFS)和总生存(OS)数据。研究提出了一种跨模态掩膜学习法进行医学特征融合,包括针对CT图像和表格数据的两个定制分支。融合过程通过掩膜模态学习策略引导,提高了模态特定特征的集成。该研究在非小细胞肺癌生存预测的多模态整合中表现优越,超越了现有方法,为该领域的预后模型设定了新的基准。
Key Takeaways
- 非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)患者接受免疫治疗时的准确预后对个性化治疗计划、患者决策以及治疗结果和生活质量改善至关重要。
- 缺乏大型相关数据集和有效的多模态特征融合策略是该领域面临的挑战。
- 研究人员提出一个包含3D CT图像和临床记录的大型数据集,以及接受免疫检查点抑制剂治疗的NSCLC患者的生存数据。
- 引入了一种新型多模态特征融合框架,以提高生存预测的准确性。
- 提出了跨模态掩膜学习法,包括针对CT图像和表格数据的两个定制分支,每个分支都针对其相应的模态进行优化。
- 融合过程通过掩膜模态学习策略进行引导,改善了不同模态特征的集成。
点此查看论文截图

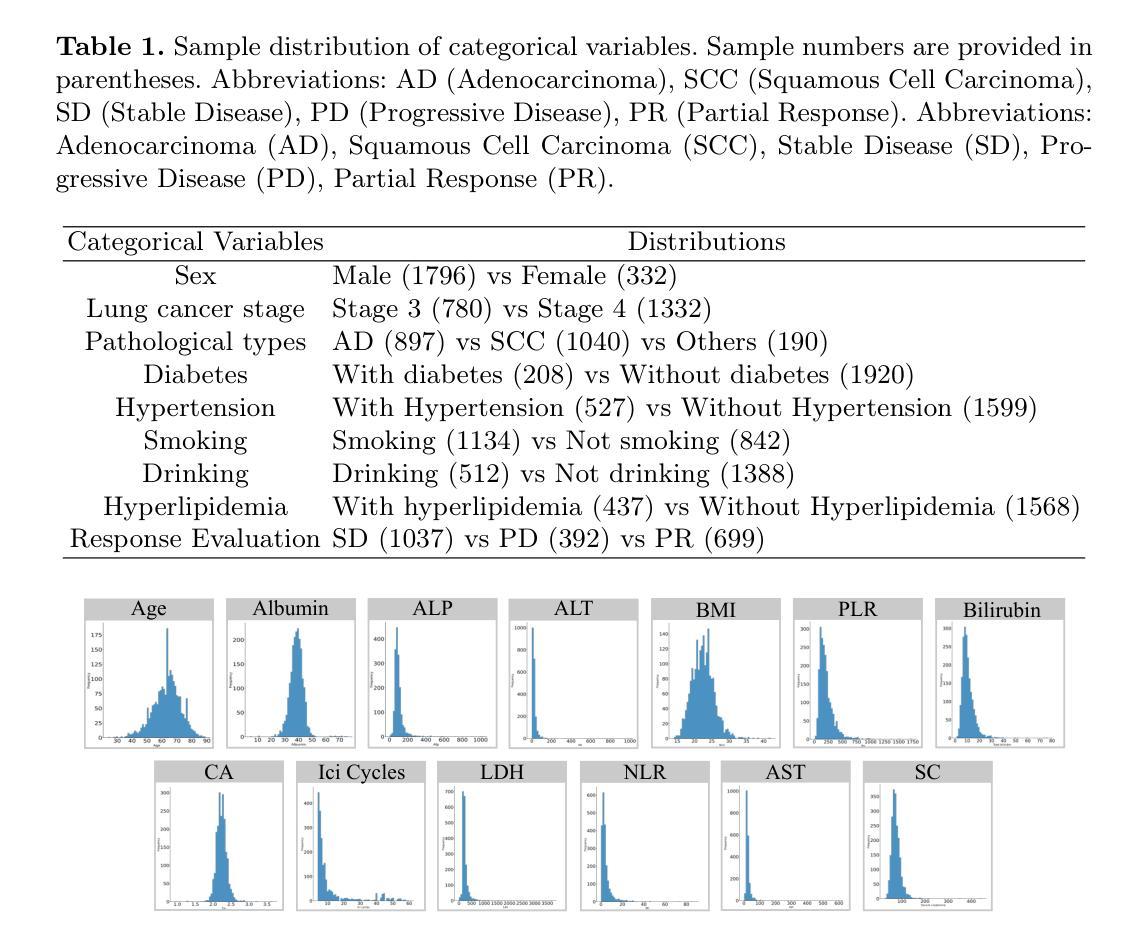
MCA-RG: Enhancing LLMs with Medical Concept Alignment for Radiology Report Generation
Authors:Qilong Xing, Zikai Song, Youjia Zhang, Na Feng, Junqing Yu, Wei Yang
Despite significant advancements in adapting Large Language Models (LLMs) for radiology report generation (RRG), clinical adoption remains challenging due to difficulties in accurately mapping pathological and anatomical features to their corresponding text descriptions. Additionally, semantic agnostic feature extraction further hampers the generation of accurate diagnostic reports. To address these challenges, we introduce Medical Concept Aligned Radiology Report Generation (MCA-RG), a knowledge-driven framework that explicitly aligns visual features with distinct medical concepts to enhance the report generation process. MCA-RG utilizes two curated concept banks: a pathology bank containing lesion-related knowledge, and an anatomy bank with anatomical descriptions. The visual features are aligned with these medical concepts and undergo tailored enhancement. We further propose an anatomy-based contrastive learning procedure to improve the generalization of anatomical features, coupled with a matching loss for pathological features to prioritize clinically relevant regions. Additionally, a feature gating mechanism is employed to filter out low-quality concept features. Finally, the visual features are corresponding to individual medical concepts, and are leveraged to guide the report generation process. Experiments on two public benchmarks (MIMIC-CXR and CheXpert Plus) demonstrate that MCA-RG achieves superior performance, highlighting its effectiveness in radiology report generation.
尽管在将大型语言模型(LLM)适应于放射学报告生成(RRG)方面取得了重大进展,但由于将病理和解剖特征准确映射到相应的文本描述中的困难,其在临床上的应用仍然具有挑战性。此外,语义无关的特征提取进一步阻碍了准确诊断报告的产生。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了医学概念对齐放射学报告生成(MCA-RG),这是一个知识驱动框架,它通过明确对齐视觉特征与独特的医学概念来增强报告生成过程。MCA-RG利用两个定制的概念库:一个病理库,包含与病灶相关的知识,和一个解剖库,包含解剖描述。视觉特征会这些医学概念进行对齐,并进行有针对性的增强。我们进一步提出了一种基于解剖学的对比学习程序,以提高解剖特征的泛化能力,结合病理特征的匹配损失来优先处理临床相关区域。此外,还采用了一种特征门控机制来过滤掉低质量的概念特征。最后,将视觉特征与单个医学概念相对应,并用于指导报告生成过程。在两个公共基准测试(MIMIC-CXR和CheXpert Plus)上的实验表明,MCA-RG取得了卓越的性能,证明了其在放射学报告生成中的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025
Summary
本文介绍了针对放射学报告生成(RRG)领域存在的问题,提出一种知识驱动框架Medical Concept Aligned Radiology Report Generation(MCA-RG)。该框架通过明确将视觉特征对应于不同的医学概念,解决在大规模语言模型(LLMs)适应放射学报告生成过程中的挑战。通过两个概念库——病理库和解剖库,MCA-RG对视觉特征进行对齐和增强。同时采用基于解剖结构的对比学习程序,提高解剖特征的泛化能力,并通过匹配损失对病理特征进行优先处理。此外,还采用特征门控机制过滤掉低质量的概念特征。实验结果表明,MCA-RG在公共数据集上取得了卓越性能,有效提升了放射学报告的生成质量。
Key Takeaways
- MCA-RG框架解决了大规模语言模型在放射学报告生成中准确映射病理和解剖特征的问题。
- 框架包含两个概念库:病理库和解剖库,用于对齐和增强视觉特征。
- 采用基于解剖结构的对比学习程序,提高解剖特征的泛化能力。
- 匹配损失用于优先处理与临床相关的病理特征。
- 特征门控机制用于过滤低质量的概念特征。
- MCA-RG通过视觉特征与医学概念的结合,指导报告生成过程。
点此查看论文截图

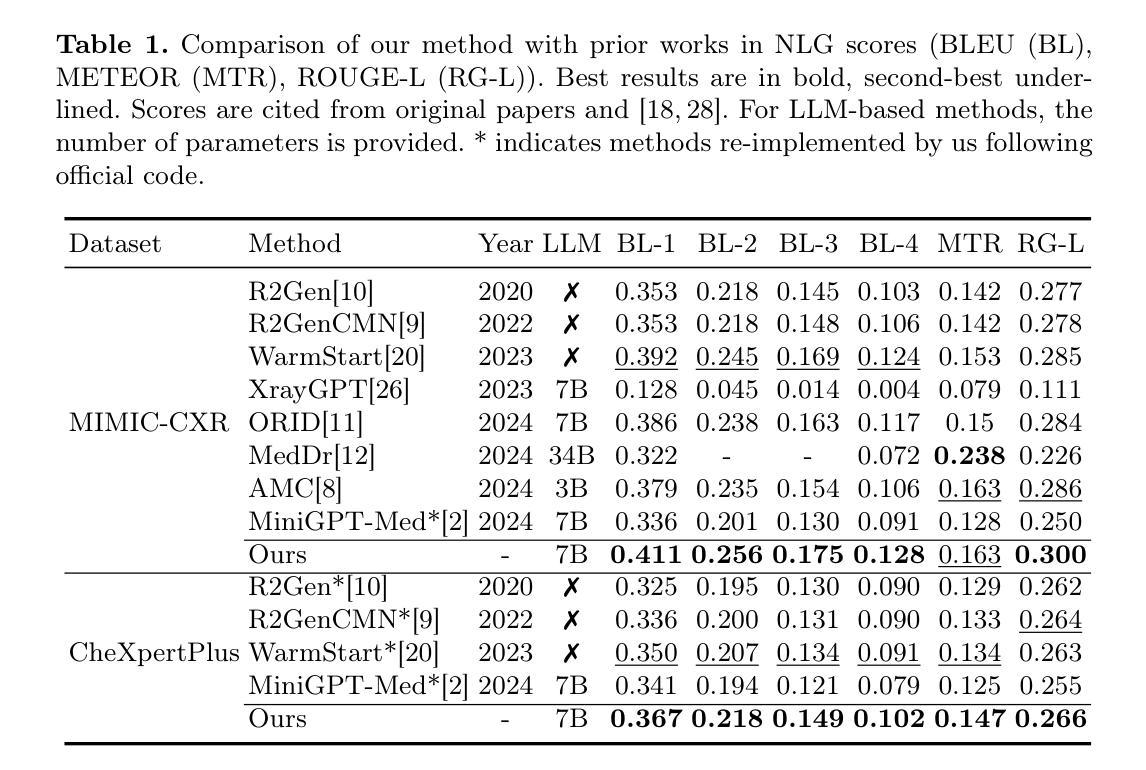
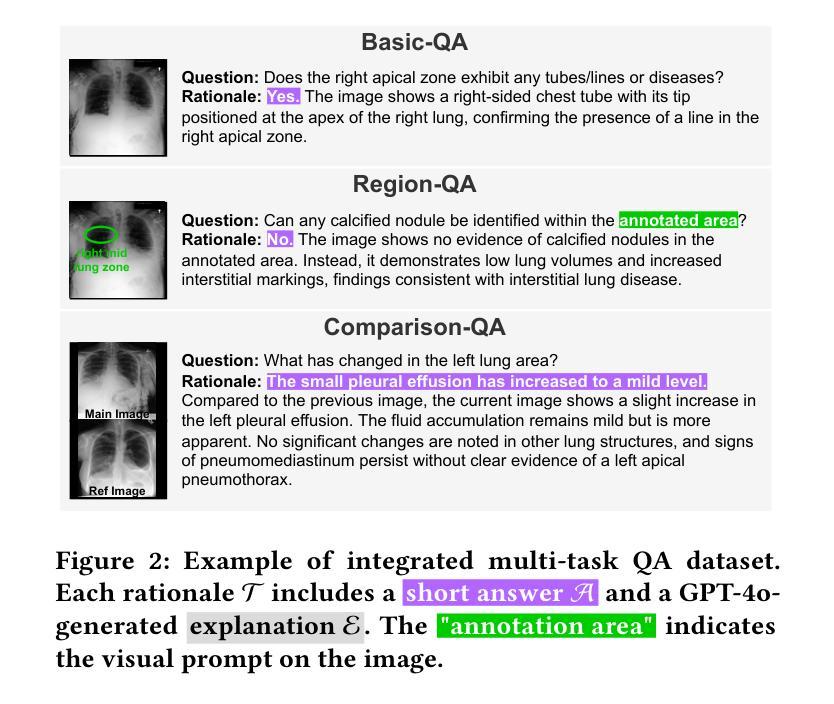
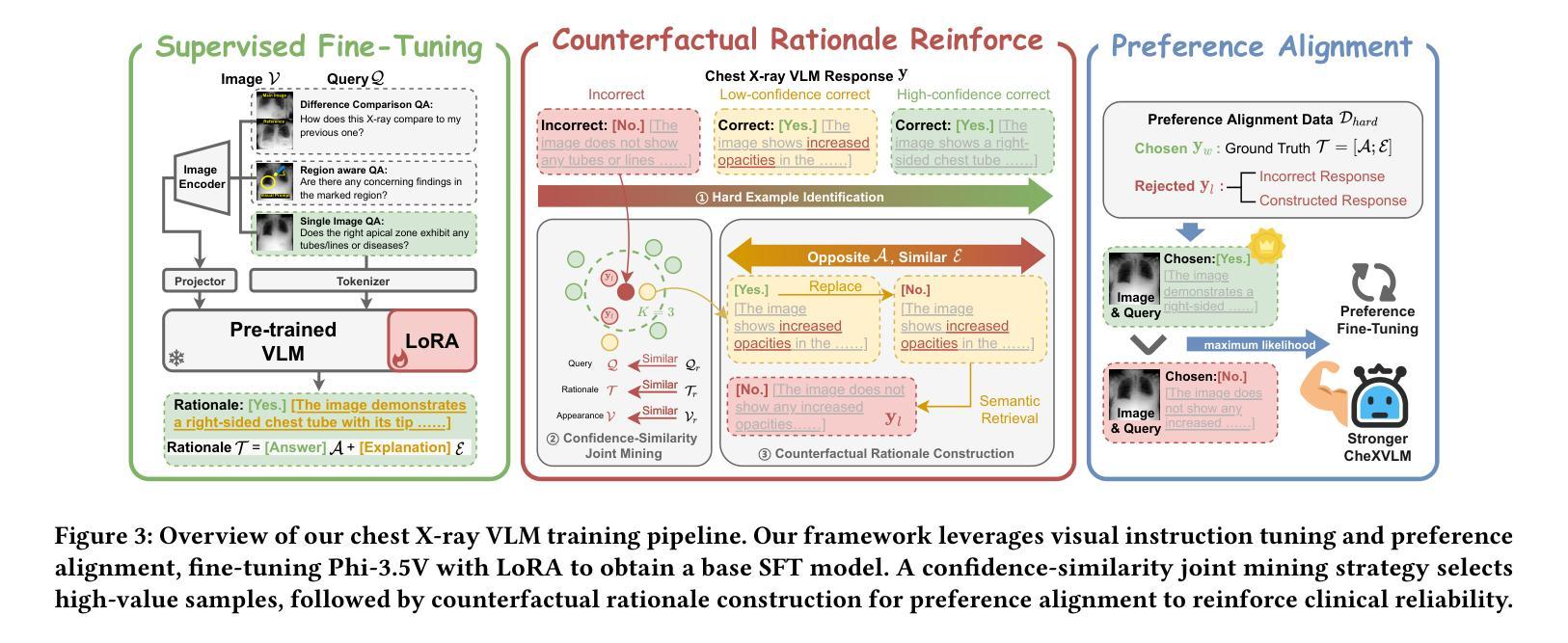
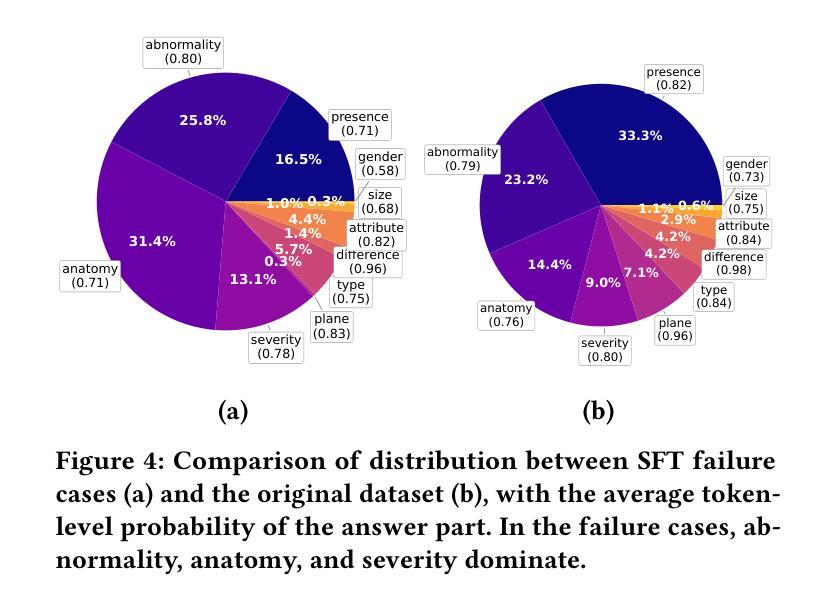
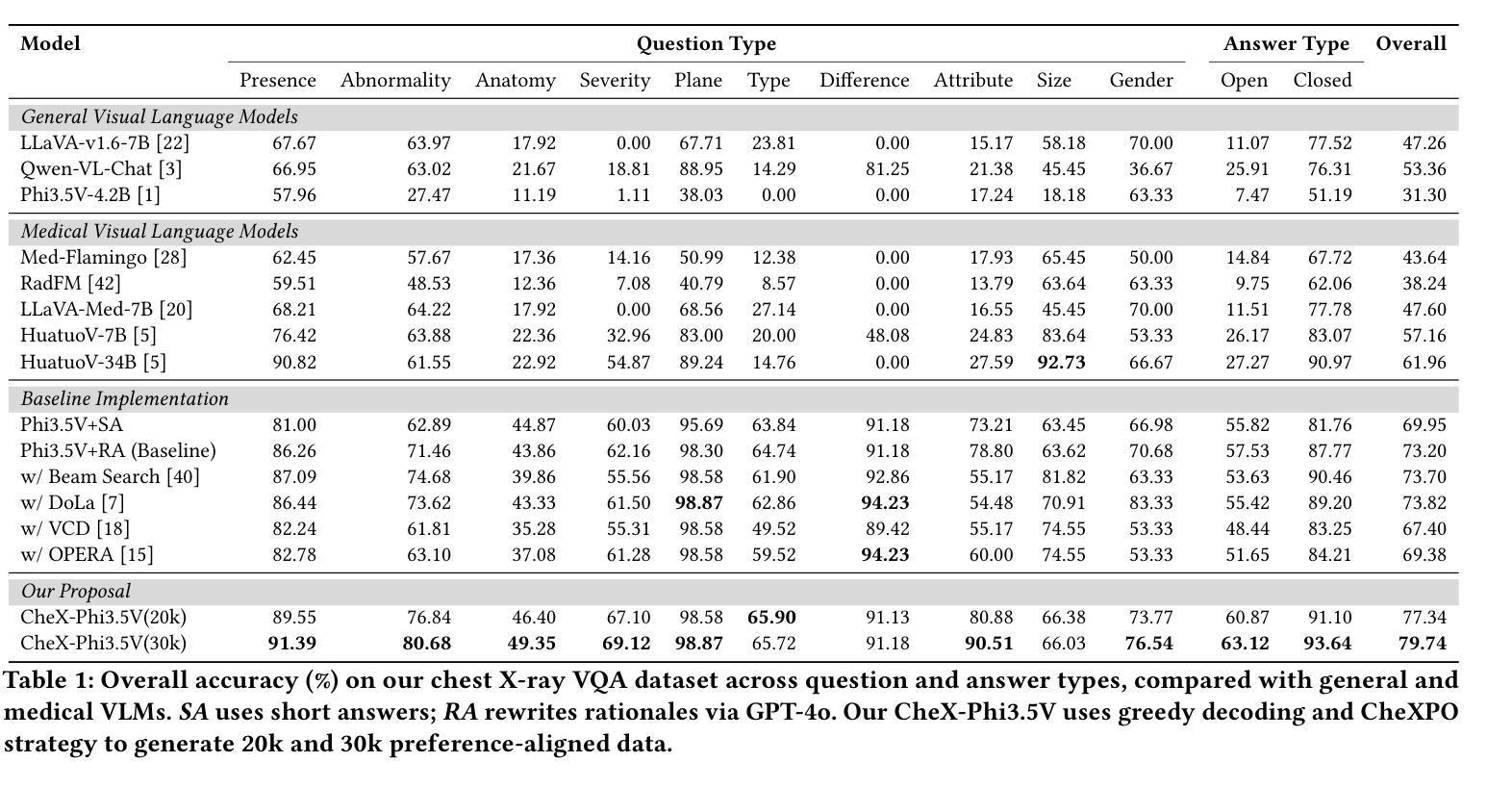
CheXPO: Preference Optimization for Chest X-ray VLMs with Counterfactual Rationale
Authors:Xiao Liang, Jiawei Hu, Di Wang, Zhi Ma, Lin Zhao, Ronghan Li, Bo Wan, Quan Wang
Vision-language models (VLMs) are prone to hallucinations that critically compromise reliability in medical applications. While preference optimization can mitigate these hallucinations through clinical feedback, its implementation faces challenges such as clinically irrelevant training samples, imbalanced data distributions, and prohibitive expert annotation costs. To address these challenges, we introduce CheXPO, a Chest X-ray Preference Optimization strategy that combines confidence-similarity joint mining with counterfactual rationale. Our approach begins by synthesizing a unified, fine-grained multi-task chest X-ray visual instruction dataset across different question types for supervised fine-tuning (SFT). We then identify hard examples through token-level confidence analysis of SFT failures and use similarity-based retrieval to expand hard examples for balancing preference sample distributions, while synthetic counterfactual rationales provide fine-grained clinical preferences, eliminating the need for additional expert input. Experiments show that CheXPO achieves 8.93% relative performance gain using only 5% of SFT samples, reaching state-of-the-art performance across diverse clinical tasks and providing a scalable, interpretable solution for real-world radiology applications.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)容易出现幻视现象,这在医疗应用中会严重损害可靠性。虽然偏好优化可以通过临床反馈来缓解这些幻视现象,但其实现面临着临床不相关训练样本、数据分布不平衡以及专家注释成本高昂等挑战。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了CheXPO,这是一种结合置信度-相似性联合挖掘和反向事实理由的胸部X光片偏好优化策略。我们的方法首先通过合成一个统一、精细粒度的多任务胸部X光片视觉指令数据集,涵盖不同类型的问题,用于有监督的微调(SFT)。然后,我们通过SFT失败的标记级置信分析来确定困难样本,并使用基于相似性的检索来扩展困难样本,以平衡偏好样本分布,同时合成反向事实理由提供精细粒度的临床偏好,无需额外的专家输入。实验表明,CheXPO仅使用5%的SFT样本就实现了8.93%的相对性能提升,在多种临床任务上达到了最先进的性能,为现实世界中的放射学应用提供了可伸缩、可解释的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对医学影像领域中的视觉语言模型(VLMs)在医学应用中的可靠性问题,提出了一种名为CheXPO的偏好优化策略。该策略通过合成一个统一的多任务胸透指令数据集来强化训练,并使用联合信心相似性挖掘以及反向假设原则来处理问题数据样本不平衡以及高难度的任务,显著提升了模型的性能表现,使其成为适合用于医学图像应用的一种可靠且可解释的解决方案。相较于专家标注的方法,该策略大大降低了成本投入。最终实验结果表明,使用CheXPO策略的模型相较于使用常规方法训练模型的性能提高了约8.93%,仅使用了大约5%的训练样本便实现了卓越的表现。这为真实世界中的医学影像诊断提供了新的思路。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉语言模型(VLMs)在医学应用中存在可靠性问题,特别是在处理医学影像时易出现幻觉。
- CheXPO策略旨在通过合成统一的多任务胸透指令数据集进行强化训练以提升模型的可靠性。数据集的设计可以应对不同类型的医学问题。
- 通过基于信心的相似性分析挖掘难以应对的实例并寻找硬实例的扩展方法,以平衡偏好样本分布。
- 合成反向假设理由的方法能够精细地反映临床偏好,减少了额外的专家输入需求。
- 实验结果显示,使用CheXPO策略的模型性能显著提高,相较于传统方法具有显著优势。仅使用少量样本即可实现卓越表现。
点此查看论文截图
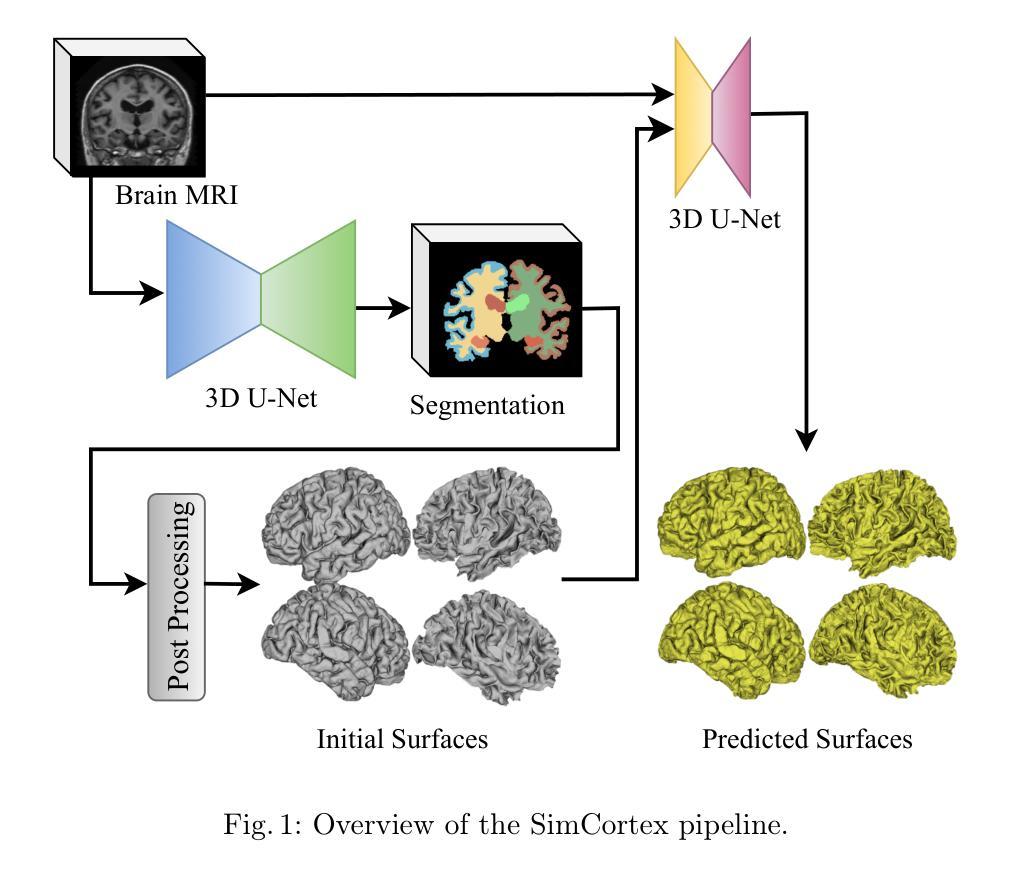
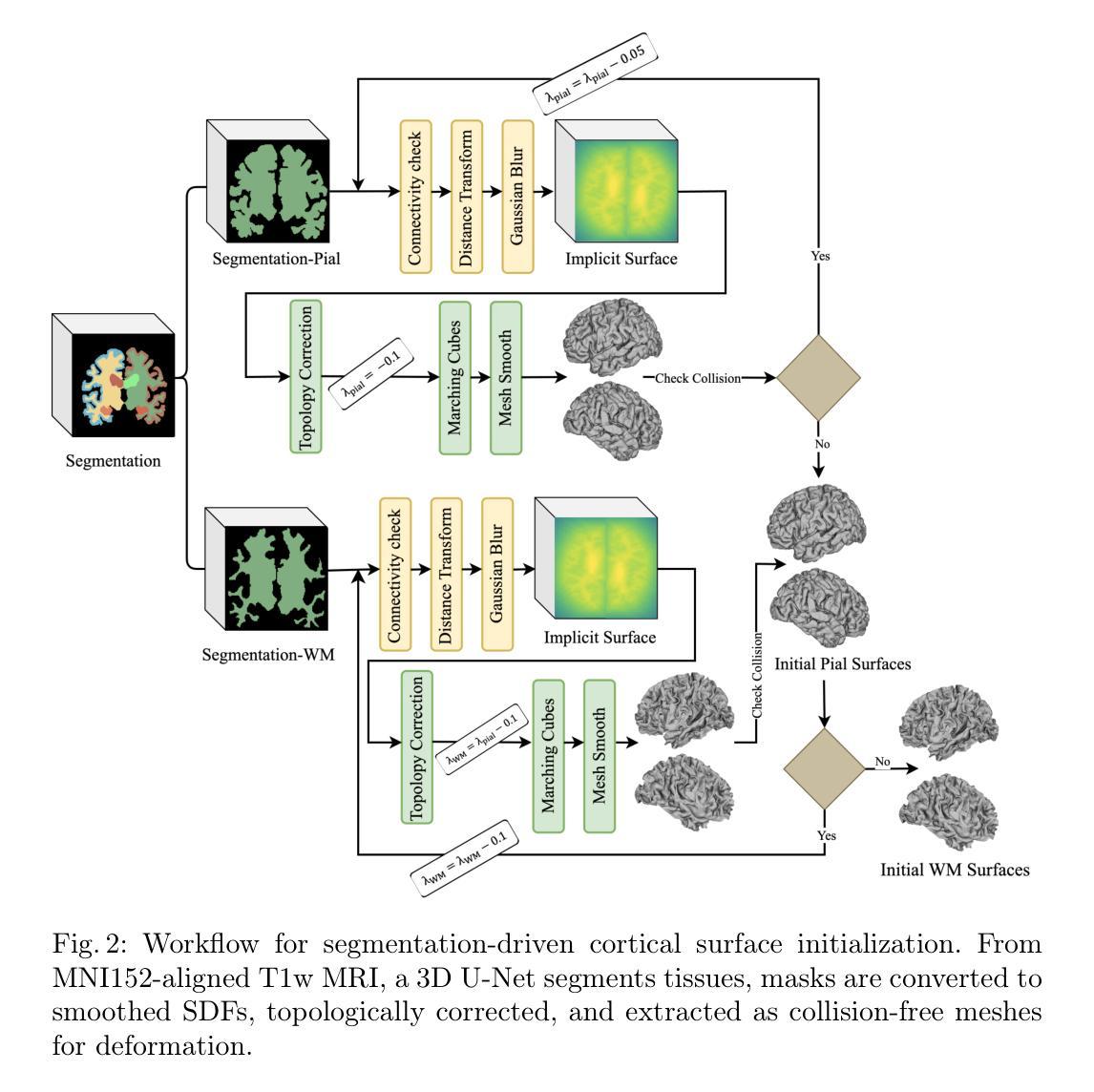
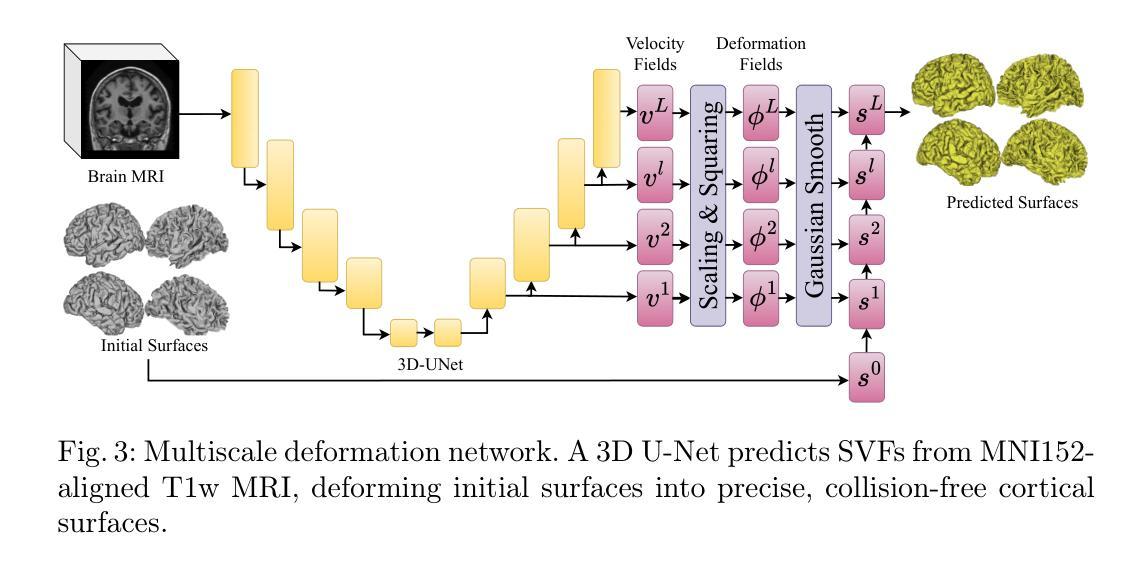
SimCortex: Collision-free Simultaneous Cortical Surfaces Reconstruction
Authors:Kaveh Moradkhani, R Jarrett Rushmore, Sylvain Bouix
Accurate cortical surface reconstruction from magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data is crucial for reliable neuroanatomical analyses. Current methods have to contend with complex cortical geometries, strict topological requirements, and often produce surfaces with overlaps, self-intersections, and topological defects. To overcome these shortcomings, we introduce SimCortex, a deep learning framework that simultaneously reconstructs all brain surfaces (left/right white-matter and pial) from T1-weighted(T1w) MRI volumes while preserving topological properties. Our method first segments the T1w image into a nine-class tissue label map. From these segmentations, we generate subject-specific, collision-free initial surface meshes. These surfaces serve as precise initializations for subsequent multiscale diffeomorphic deformations. Employing stationary velocity fields (SVFs) integrated via scaling-and-squaring, our approach ensures smooth, topology-preserving transformations with significantly reduced surface collisions and self-intersections. Evaluations on standard datasets demonstrate that SimCortex dramatically reduces surface overlaps and self-intersections, surpassing current methods while maintaining state-of-the-art geometric accuracy.
从磁共振成像(MRI)数据准确重建皮层表面对于可靠的神经解剖学分析至关重要。当前的方法必须处理复杂的皮层几何结构、严格的地形要求,并且经常产生具有重叠、自相交和地形缺陷的表面。为了克服这些缺点,我们引入了SimCortex,这是一个深度学习框架,能够同时从T1加权(T1w)MRI体积数据中重建所有大脑表面(左/右白质和皮层),同时保留地形属性。我们的方法首先将T1w图像分割成九类组织标签图。从这些分割中,我们生成了针对个体、无碰撞的初始表面网格。这些表面为后续的多尺度微分同胚变形提供了精确初始化。我们采用通过缩放和平方集成的稳态速度场(SVF),确保平滑、保持地形的变形,大大降低了表面碰撞和自相交。在标准数据集上的评估表明,SimCortex显著减少了表面重叠和自相交,超越了当前方法,同时保持了最先进的几何精度。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为SimCortex的深度学习框架,该框架可从T1加权MRI数据中准确重建所有大脑表面,同时保留拓扑属性。它通过分割T1加权图像生成初始表面网格,然后采用多尺度微分同胚变形技术,确保表面光滑且拓扑保持变换,显著减少表面碰撞和自相交。评估结果表明,SimCortex在减少表面重叠和自相交方面表现出卓越性能,同时保持几何精度处于业界领先地位。
Key Takeaways
- SimCortex是一个深度学习框架,可以从MRI数据中重建大脑表面。
- 该框架能够处理复杂的皮质几何结构和严格拓扑要求。
- SimCortex能够同时重建所有大脑表面(左右脑白质和皮层表面)。
- 通过分割T1加权图像生成初始表面网格,作为后续变形的精确初始化。
- 采用多尺度微分同胚变形技术,确保表面光滑且拓扑保持变换。
- 使用基于静止速度场的缩放和平方法,减少表面碰撞和自相交。
点此查看论文截图

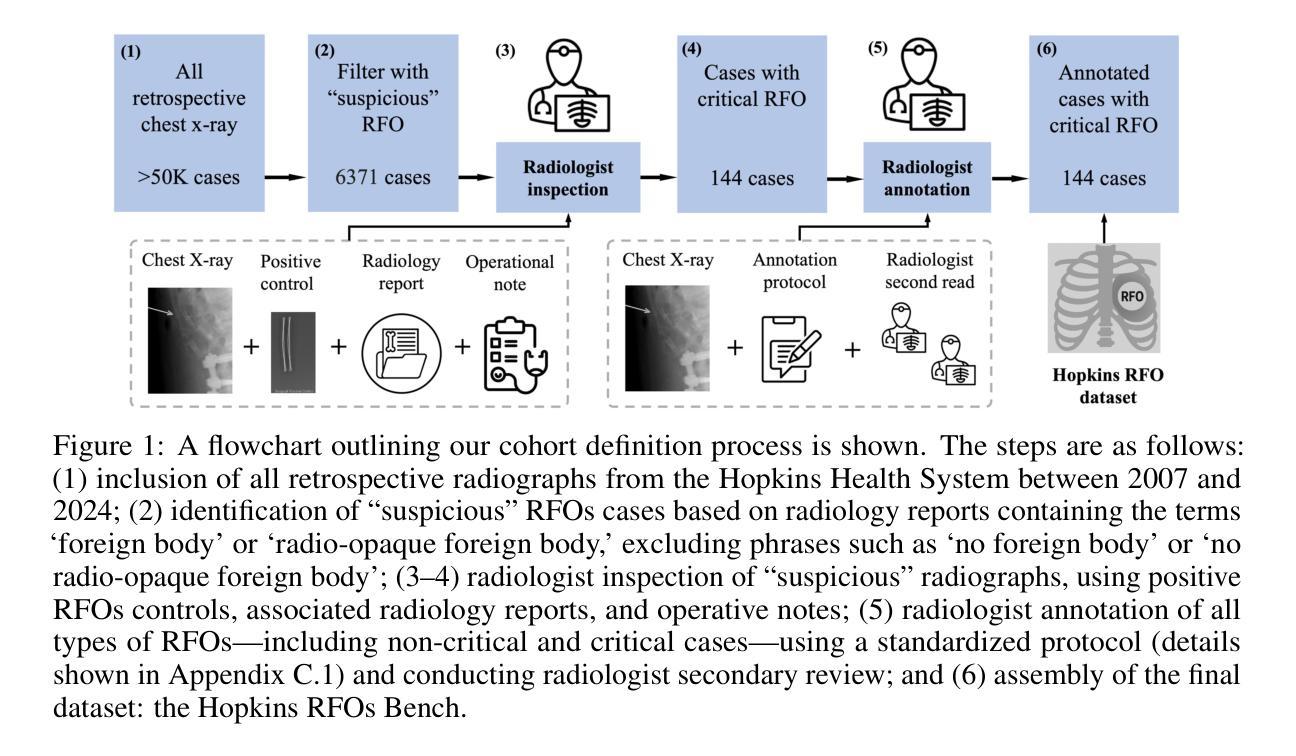
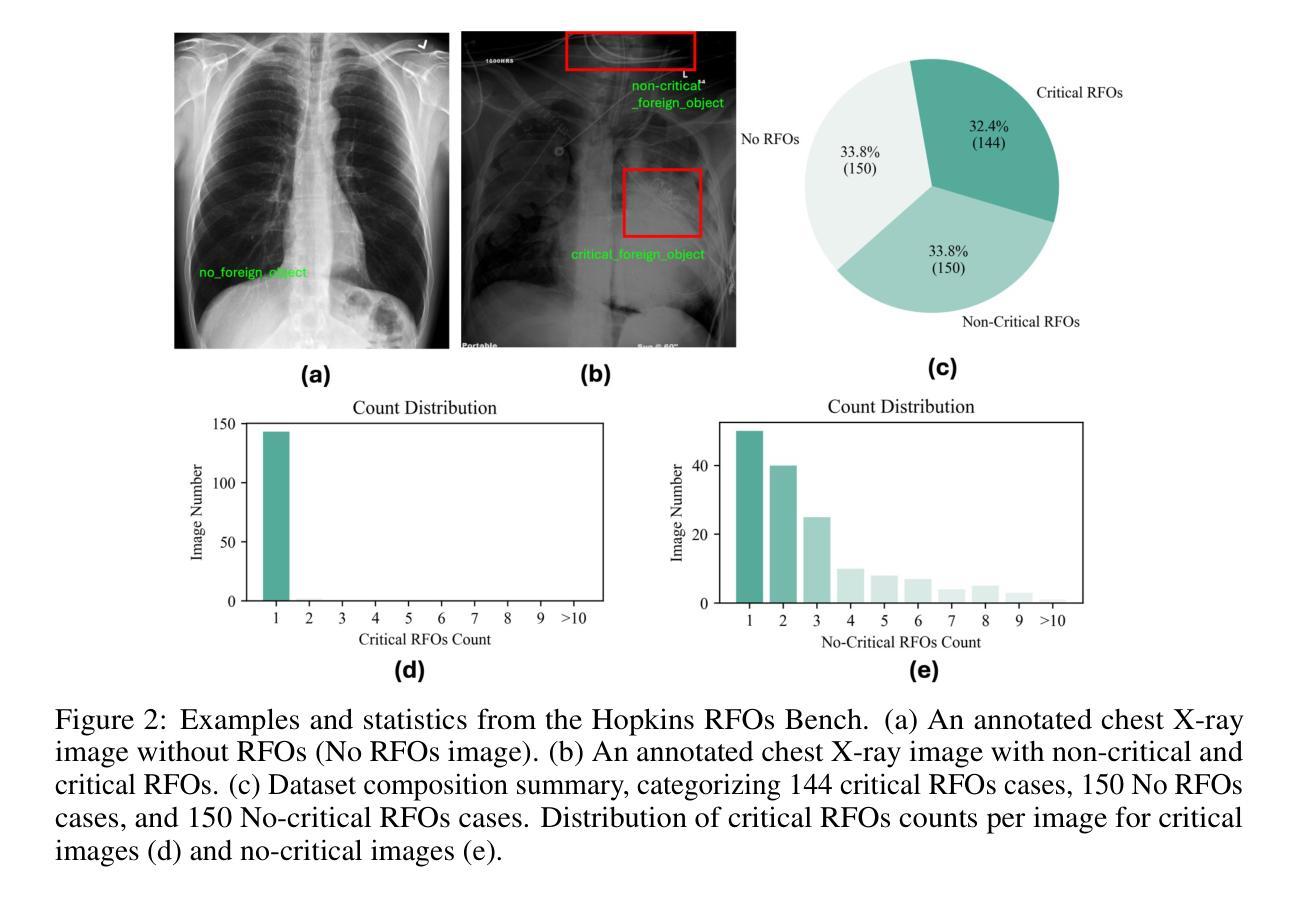
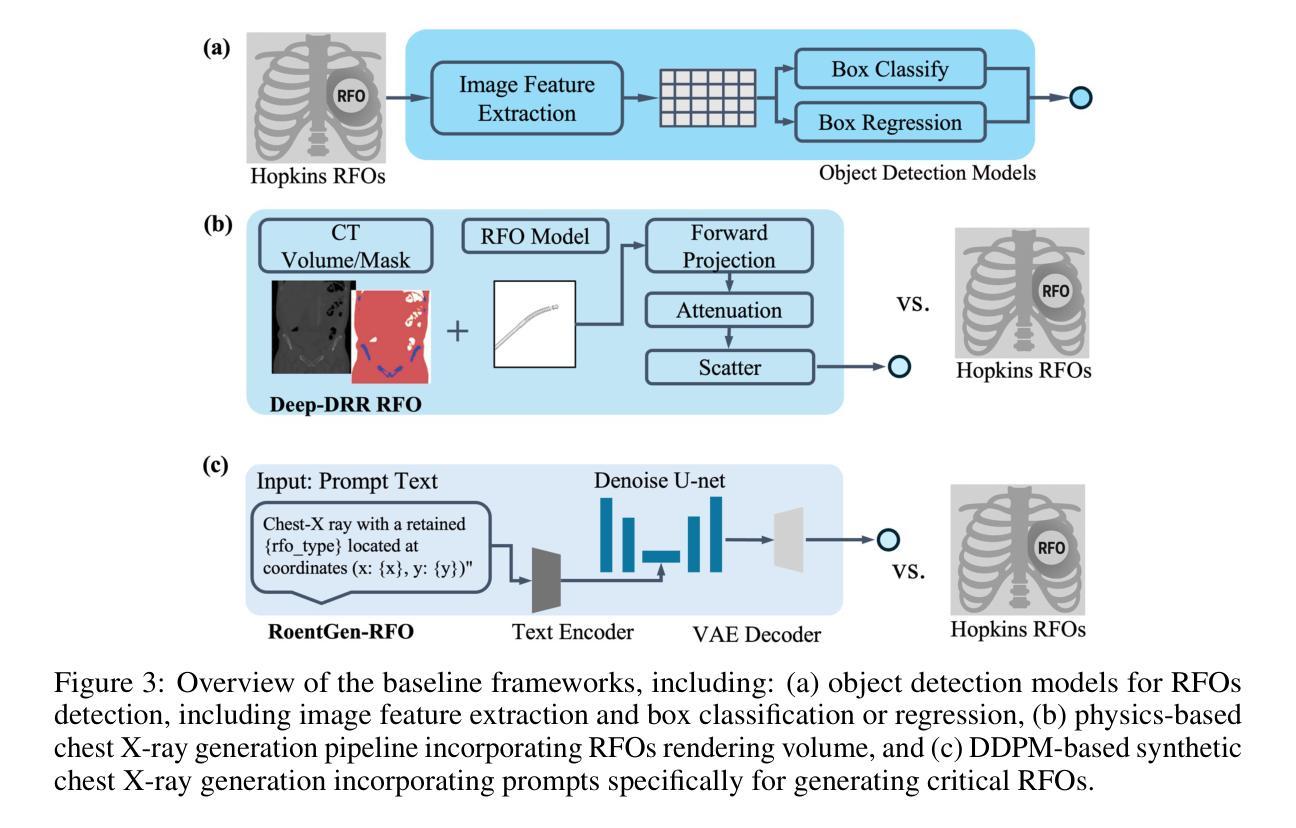
Dataset and Benchmark for Enhancing Critical Retained Foreign Object Detection
Authors:Yuli Wang, Victoria R. Shi, Liwei Zhou, Richard Chin, Yuwei Dai, Yuanyun Hu, Cheng-Yi Li, Haoyue Guan, Jiashu Cheng, Yu Sun, Cheng Ting Lin, Ihab Kamel, Premal Trivedi, Pamela Johnson, John Eng, Harrison Bai
Critical retained foreign objects (RFOs), including surgical instruments like sponges and needles, pose serious patient safety risks and carry significant financial and legal implications for healthcare institutions. Detecting critical RFOs using artificial intelligence remains challenging due to their rarity and the limited availability of chest X-ray datasets that specifically feature critical RFOs cases. Existing datasets only contain non-critical RFOs, like necklace or zipper, further limiting their utility for developing clinically impactful detection algorithms. To address these limitations, we introduce “Hopkins RFOs Bench”, the first and largest dataset of its kind, containing 144 chest X-ray images of critical RFO cases collected over 18 years from the Johns Hopkins Health System. Using this dataset, we benchmark several state-of-the-art object detection models, highlighting the need for enhanced detection methodologies for critical RFO cases. Recognizing data scarcity challenges, we further explore image synthetic methods to bridge this gap. We evaluate two advanced synthetic image methods, DeepDRR-RFO, a physics-based method, and RoentGen-RFO, a diffusion-based method, for creating realistic radiographs featuring critical RFOs. Our comprehensive analysis identifies the strengths and limitations of each synthetic method, providing insights into effectively utilizing synthetic data to enhance model training. The Hopkins RFOs Bench and our findings significantly advance the development of reliable, generalizable AI-driven solutions for detecting critical RFOs in clinical chest X-rays.
遗留的致命异物(RFOs),包括海绵、针头等手术器械,对病人安全构成严重威胁,并为医疗机构带来重大经济和法律风险。使用人工智能检测关键的RFOs是一个挑战,因为这些异物的稀有性以及专门包含关键RFOs病例的胸部X光数据集有限。现有数据集仅包含非关键的RFOs,如项链或拉链,这进一步限制了它们在开发具有临床影响力的检测算法方面的实用性。为了克服这些限制,我们推出了“霍普金斯RFOs基准测试”,这是该领域首个也是最大的数据集,包含约翰斯·霍普金斯医疗系统18年来收集的包含关键RFO病例的144张胸部X光片。使用该数据集,我们对几种最先进的物体检测模型进行了基准测试,强调了针对关键RFO病例需要提高检测方法的必要性。我们认识到数据稀缺的挑战,进一步探索图像合成方法来弥补这一差距。我们评估了两种先进的合成图像方法,一种是基于物理的DeepDRR-RFO方法,另一种是扩散基础的RoentGen-RFO方法,它们可以生成具有真实感的X光片,其中包含关键的RFOs。我们的综合分析确定了每种合成方法的优点和局限性,为有效利用合成数据以提高模型训练提供了见解。“霍普金斯RFOs基准测试”以及我们的发现极大地推动了开发可靠的、可推广的AI驱动解决方案,用于检测临床胸部X光片中的关键RFOs。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了对关键残留异物(RFOs)检测的挑战,以及如何通过霍普金斯RFOs基准数据集来解决这些问题。该数据集包含来自约翰霍普金斯医疗系统的144张胸部X光片,旨在解决关键RFO病例检测的关键挑战。同时,文章还探讨了数据稀缺问题,通过探讨合成图像方法来缩小差距。最终文章全面评估了两种先进的合成图像方法并指出了其优缺点,为有效利用合成数据提高模型训练效果提供了见解。该研究和数据集为开发可靠的AI驱动解决方案以检测临床胸部X光片中的关键RFOs提供了重要支持。
Key Takeaways
- 关键保留异物(RFOs)是医疗领域的重要问题,包括海绵和针等手术器械,对患者安全构成严重威胁。
- 霍普金斯RFOs基准数据集的推出解决了检测关键RFO病例的挑战,包含来自约翰霍普金斯医疗系统的稀有病例数据。
- 文章指出当前数据集存在局限性,即只包含非关键RFOs,因此需要开发更有效的检测算法。
- 数据稀缺问题限制了模型训练的有效性,因此探讨了合成图像方法来缩小差距。
- 文章评估了两种先进的合成图像方法——基于物理的DeepDRR-RFO和基于扩散的RoentGen-RFO方法,用以生成逼真的包含关键RFOs的放射图像。
- 研究指出了每种合成方法的优点和局限性,为有效利用合成数据增强模型训练提供了见解。
点此查看论文截图

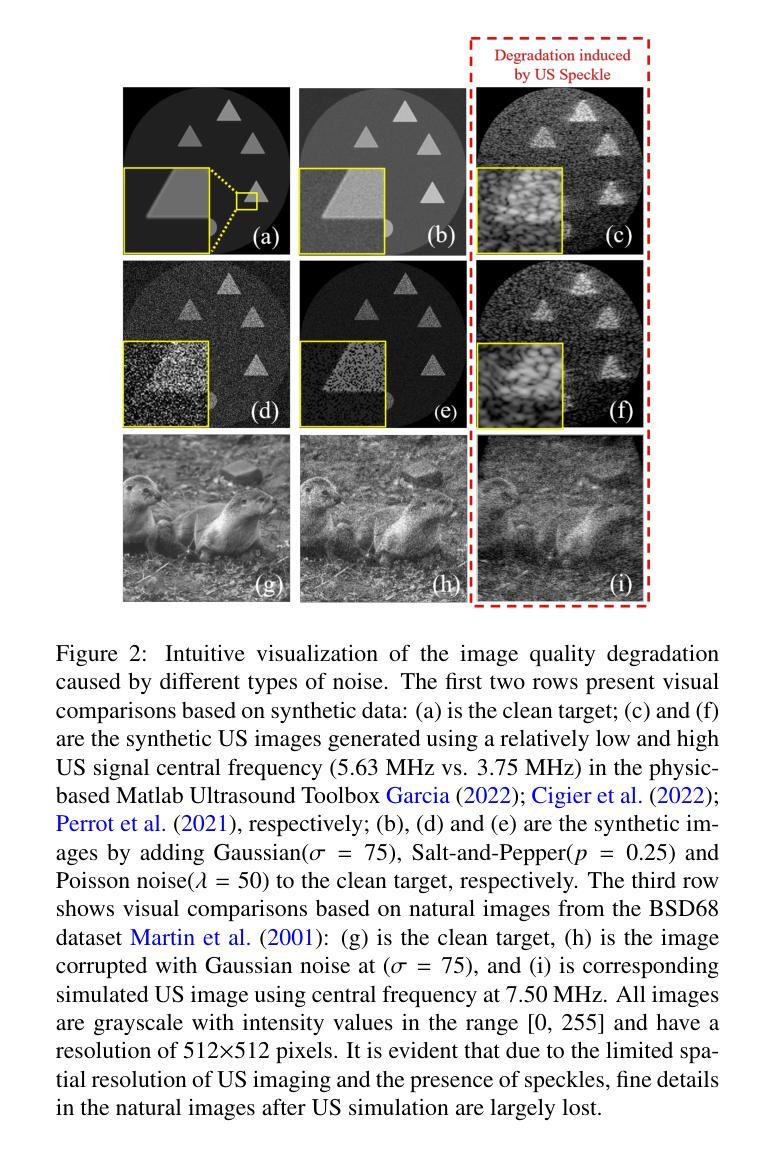
Speckle2Self: Self-Supervised Ultrasound Speckle Reduction Without Clean Data
Authors:Xuesong Li, Nassir Navab, Zhongliang Jiang
Image denoising is a fundamental task in computer vision, particularly in medical ultrasound (US) imaging, where speckle noise significantly degrades image quality. Although recent advancements in deep neural networks have led to substantial improvements in denoising for natural images, these methods cannot be directly applied to US speckle noise, as it is not purely random. Instead, US speckle arises from complex wave interference within the body microstructure, making it tissue-dependent. This dependency means that obtaining two independent noisy observations of the same scene, as required by pioneering Noise2Noise, is not feasible. Additionally, blind-spot networks also cannot handle US speckle noise due to its high spatial dependency. To address this challenge, we introduce Speckle2Self, a novel self-supervised algorithm for speckle reduction using only single noisy observations. The key insight is that applying a multi-scale perturbation (MSP) operation introduces tissue-dependent variations in the speckle pattern across different scales, while preserving the shared anatomical structure. This enables effective speckle suppression by modeling the clean image as a low-rank signal and isolating the sparse noise component. To demonstrate its effectiveness, Speckle2Self is comprehensively compared with conventional filter-based denoising algorithms and SOTA learning-based methods, using both realistic simulated US images and human carotid US images. Additionally, data from multiple US machines are employed to evaluate model generalization and adaptability to images from unseen domains. \textit{Code and datasets will be released upon acceptance.
图像去噪是计算机视觉领域的一项基本任务,特别是在医学超声(US)成像中,斑点噪声会严重降低图像质量。尽管最近深度神经网络技术的进步极大地改进了自然图像的降噪效果,但这些方法不能直接应用于超声斑点噪声,因为斑点噪声并非纯随机产生。相反,超声斑点是由体内微观结构的复杂波干涉产生的,具有组织依赖性。这种依赖性意味着获取同一场景的两个独立噪声观测结果(如Noise2Noise所要求的)并不可行。此外,由于斑点噪声的高空间依赖性,盲点网络也无法处理。为了解决这一挑战,我们引入了Speckle2Self,这是一种使用仅单个噪声观测值进行斑点减少的新型自监督算法。关键思想是应用多尺度扰动(MSP)操作,在不同尺度上引入组织依赖性的斑点图案变化,同时保留共享的解剖结构。这能够通过将清洁图像建模为低秩信号并隔离稀疏噪声成分,从而实现有效的斑点抑制。为了证明其有效性,Speckle2Self与基于传统滤波的降噪算法和基于学习的最新方法进行了全面的比较,使用了逼真的模拟超声图像和人体颈动脉超声图像。此外,还使用了多台超声机器的数据来评估模型在未见领域的图像中的通用性和适应性。\textit{代码和数据集将在接受后发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对医学超声图像中的斑点噪声问题,提出了一种新型的自监督算法Speckle2Self,仅使用单张噪声图像进行去噪。该算法通过多尺度扰动操作,在保留共享解剖结构的同时,引入组织依赖的斑点模式变化,有效抑制斑点。与基于滤波器的传统去噪算法和先进的学习型方法相比,Speckle2Self在模拟的超声图像和人体颈动脉超声图像上均表现出优异的性能,并展示了良好的跨域泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 医学超声图像中的斑点噪声是一个重要的问题,它显著降低了图像质量。
- 现有的深度神经网络去噪方法不能直接应用于超声斑点噪声,因为斑点噪声具有组织依赖性。
- Speckle2Self是一种新型自监督算法,可用于减少斑点噪声,仅使用单个噪声观察值。
- 多尺度扰动操作是Speckle2Self的关键,能在不同尺度上引入组织依赖的斑点模式变化。
- 该算法能够模拟清洁图像作为低秩信号,并隔离稀疏噪声成分,从而实现有效的斑点抑制。
- Speckle2Self在模拟和真实的超声图像上均表现出优异的性能,与现有方法相比具有优越性。
点此查看论文截图


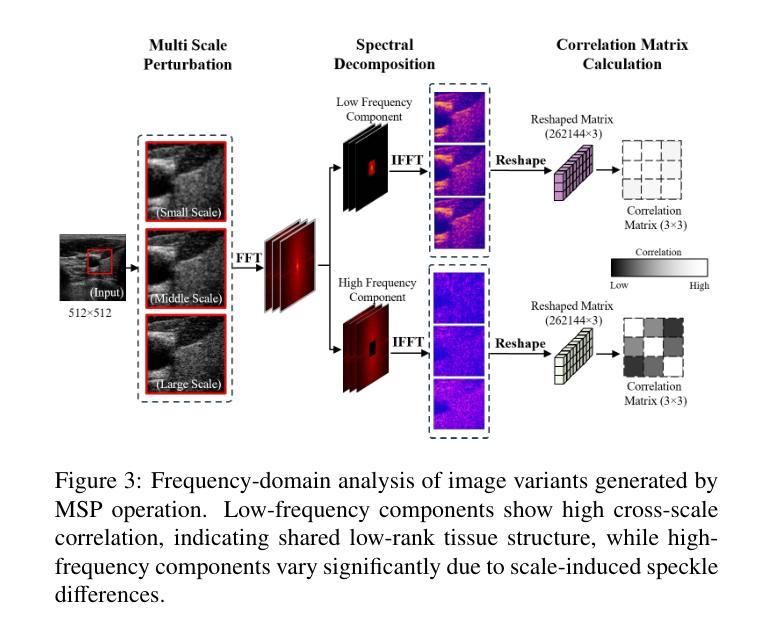
FOLC-Net: A Federated-Optimized Lightweight Architecture for Enhanced MRI Disease Diagnosis across Axial, Coronal, and Sagittal Views
Authors:Saif Ur Rehman Khan, Muhammad Nabeel Asim, Sebastian Vollmer, Andreas Dengel
The framework is designed to improve performance in the analysis of combined as well as single anatomical perspectives for MRI disease diagnosis. It specifically addresses the performance degradation observed in state-of-the-art (SOTA) models, particularly when processing axial, coronal, and sagittal anatomical planes. The paper introduces the FOLC-Net framework, which incorporates a novel federated-optimized lightweight architecture with approximately 1.217 million parameters and a storage requirement of only 0.9 MB. FOLC-Net integrates Manta-ray foraging optimization (MRFO) mechanisms for efficient model structure generation, global model cloning for scalable training, and ConvNeXt for enhanced client adaptability. The model was evaluated on combined multi-view data as well as individual views, such as axial, coronal, and sagittal, to assess its robustness in various medical imaging scenarios. Moreover, FOLC-Net tests a ShallowFed model on different data to evaluate its ability to generalize beyond the training dataset. The results show that FOLC-Net outperforms existing models, particularly in the challenging sagittal view. For instance, FOLC-Net achieved an accuracy of 92.44% on the sagittal view, significantly higher than the 88.37% accuracy of study method (DL + Residual Learning) and 88.95% of DL models. Additionally, FOLC-Net demonstrated improved accuracy across all individual views, providing a more reliable and robust solution for medical image analysis in decentralized environments. FOLC-Net addresses the limitations of existing SOTA models by providing a framework that ensures better adaptability to individual views while maintaining strong performance in multi-view settings. The incorporation of MRFO, global model cloning, and ConvNeXt ensures that FOLC-Net performs better in real-world medical applications.
该框架旨在提高MRI疾病诊断中结合以及单一解剖角度的分析性能。它特别解决了最新模型在处理轴向、冠状和矢状解剖平面时出现的性能下降问题。本文介绍了FOLC-Net框架,该框架结合了新型联邦优化轻量级架构,包含约121万参数,存储需求仅为0.9MB。FOLC-Net集成了蝠鲼觅食优化(MRFO)机制以实现高效模型结构生成、全局模型克隆以实现可扩展训练,以及ConvNeXt以增强客户端适应性。该模型在对组合多视图数据以及单独的轴向、冠状和矢状视图上进行评估,以测试其在各种医学成像场景中的稳健性。此外,FOLC-Net在不同数据上测试了ShallowFed模型,以评估其超越训练数据集的泛化能力。结果表明,FOLC-Net在具有挑战性的矢状视图方面表现优于现有模型。例如,FOLC-Net在矢状视图上的准确率达到了92.44%,显著高于研究方法(DL+残差学习)的88.37%和DL模型的88.95%。此外,FOLC-Net在所有单个视图上的准确性都有所提高,为分布式环境中的医学图像分析提供了更可靠和稳健的解决方案。FOLC-Net通过提供一个框架来解决现有最新模型在适应个别视图时性能下降的局限性,同时保持多视图环境中的强劲表现。MRFO、全局模型克隆和ConvNeXt的集成确保了FOLC-Net在真实世界医学应用中的优异性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该框架旨在提高MRI疾病诊断中对单一和多角度解剖学视角分析的性能。针对现有先进技术模型在处理轴向、冠状和矢状解剖平面时的性能下降问题,引入FOLC-Net框架。该框架结合了优化的轻量级架构、蝠鲼觅食优化机制和全局模型克隆等技术,提高了模型在多种医学成像场景中的稳健性。FOLC-Net在单视角和多视角数据上的评估结果表明,其性能优于现有模型,特别是在挑战性的矢状面上。
Key Takeaways
- FOLC-Net框架旨在提高MRI疾病诊断中解剖学视角分析的性能。
- 框架解决了现有模型在处理轴向、冠状和矢状解剖平面时的性能下降问题。
- FOLC-Net结合了优化的轻量级架构、蝠鲼觅食优化机制和全局模型克隆等技术。
- 评估结果显示,FOLC-Net在单视角和多视角数据上的性能均优于现有模型。
- 特别在矢状面上,FOLC-Net的准确率达到了92.44%,显著优于其他模型。
- FOLC-Net提供了在分布式环境中更可靠和稳健的医学图像分析解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

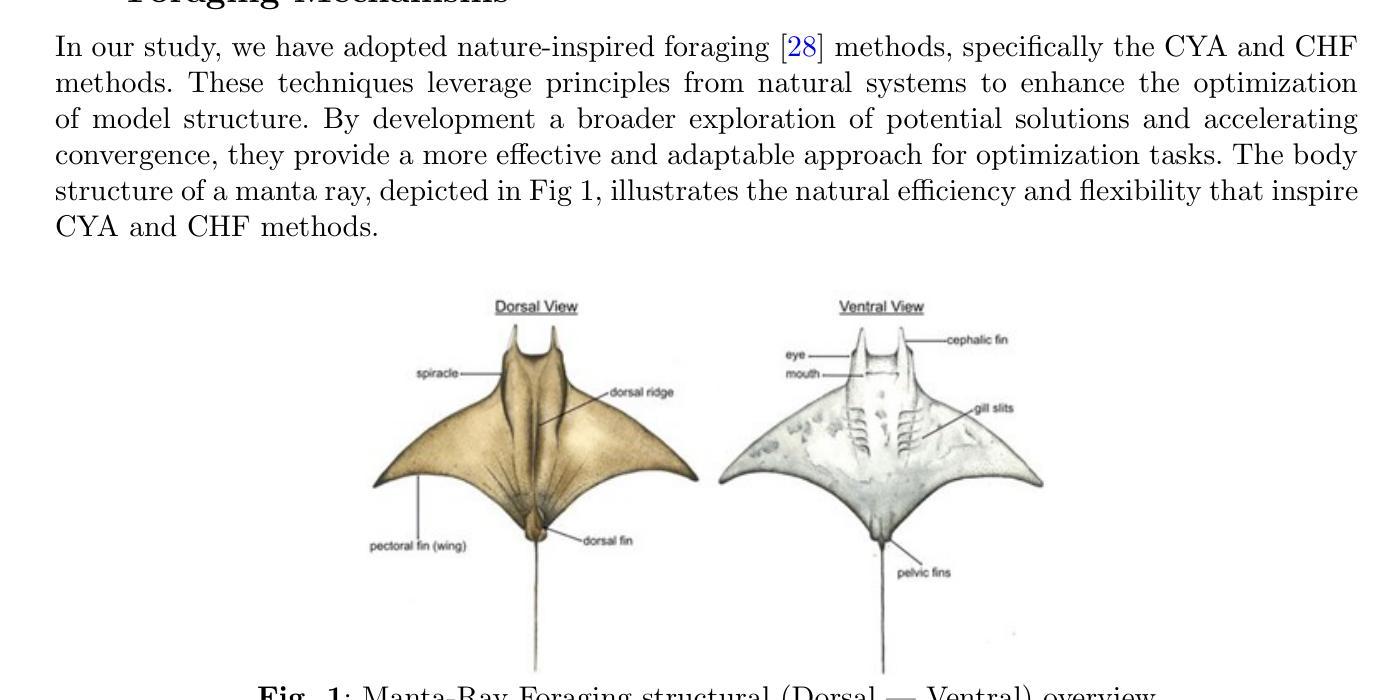
ClipGS: Clippable Gaussian Splatting for Interactive Cinematic Visualization of Volumetric Medical Data
Authors:Chengkun Li, Yuqi Tong, Kai Chen, Zhenya Yang, Ruiyang Li, Shi Qiu, Jason Ying-Kuen Chan, Pheng-Ann Heng, Qi Dou
The visualization of volumetric medical data is crucial for enhancing diagnostic accuracy and improving surgical planning and education. Cinematic rendering techniques significantly enrich this process by providing high-quality visualizations that convey intricate anatomical details, thereby facilitating better understanding and decision-making in medical contexts. However, the high computing cost and low rendering speed limit the requirement of interactive visualization in practical applications. In this paper, we introduce ClipGS, an innovative Gaussian splatting framework with the clipping plane supported, for interactive cinematic visualization of volumetric medical data. To address the challenges posed by dynamic interactions, we propose a learnable truncation scheme that automatically adjusts the visibility of Gaussian primitives in response to the clipping plane. Besides, we also design an adaptive adjustment model to dynamically adjust the deformation of Gaussians and refine the rendering performance. We validate our method on five volumetric medical data (including CT and anatomical slice data), and reach an average 36.635 PSNR rendering quality with 156 FPS and 16.1 MB model size, outperforming state-of-the-art methods in rendering quality and efficiency.
医学体积数据的可视化对于提高诊断准确性和改善手术规划和教育至关重要。电影渲染技术通过提供高质量的可视化,展现复杂的解剖细节,从而丰富这一过程,促进医学环境中的更好理解和决策。然而,高计算成本和低渲染速度限制了实际应用中对交互式可视化的需求。在本文中,我们介绍了ClipGS,这是一个支持裁剪平面交互的电影体积医学数据可视化高斯喷涂框架。为了解决动态交互带来的挑战,我们提出了一种可学习的截断方案,该方案可以自动根据裁剪平面调整高斯原始数据的可见性。此外,我们还设计了一个自适应调整模型,可以动态调整高斯变形并优化渲染性能。我们在五个医学体积数据(包括CT和解剖切片数据)上验证了我们的方法,达到了平均36.635的PSNR渲染质量,帧速率为每秒156帧,模型大小为16.1MB,在渲染质量和效率方面优于现有先进技术的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Early accepted by MICCAI 2025. Project is available at: https://med-air.github.io/ClipGS
Summary
文中介绍了体积医学数据可视化对于提高诊断准确性和改善手术规划与教育的重要性。电影渲染技术丰富了这一过程,提供了高质量的可视化表现,展示了复杂的解剖细节,有助于更好地理解和决策。针对实际应用中交互式可视化的高计算成本和低渲染速度问题,本文提出了ClipGS,一种支持裁剪平面的高斯涂抹框架,用于交互式电影渲染技术。通过提出一种可学习的截断方案和自适应调整模型,该技术在保证高质量渲染的同时提高了效率。在五个体积医学数据集上的验证显示,其平均峰值信噪比(PSNR)为36.635,帧率为每秒156帧,模型大小为16.1MB,在渲染质量和效率方面均优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 体积医学数据可视化对于诊断、手术规划和教育的重要性。
- 电影渲染技术提供高质量医学数据可视化,展示复杂解剖细节。
- 交互式可视化在实际应用中面临高计算成本和低渲染速度的挑战。
- ClipGS是一个基于高斯涂抹的框架,支持裁剪平面,用于交互式电影渲染技术。
- 提出可学习的截断方案和自适应调整模型,以提高渲染效率和质量。
- 在五个体积医学数据集上的验证结果表现优异,平均PSNR为36.635,帧率为每秒156帧。
点此查看论文截图

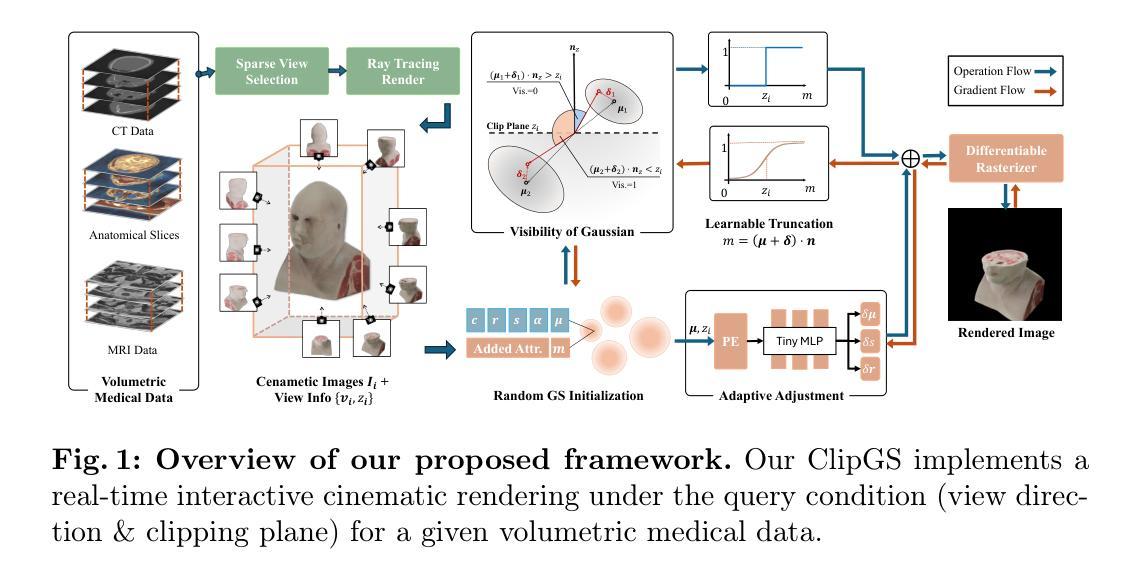
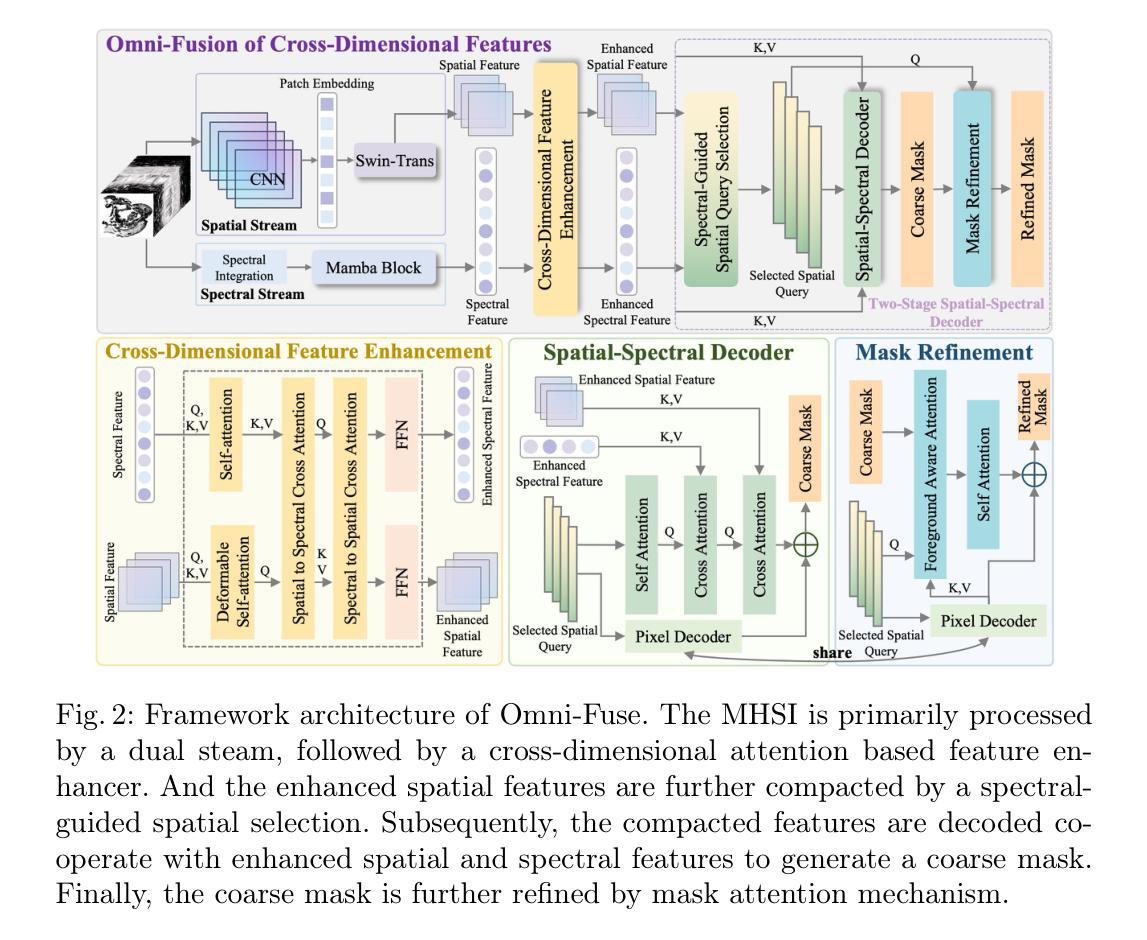
Omni-Fusion of Spatial and Spectral for Hyperspectral Image Segmentation
Authors:Qing Zhang, Guoquan Pei, Yan Wang
Medical Hyperspectral Imaging (MHSI) has emerged as a promising tool for enhanced disease diagnosis, particularly in computational pathology, offering rich spectral information that aids in identifying subtle biochemical properties of tissues. Despite these advantages, effectively fusing both spatial-dimensional and spectral-dimensional information from MHSIs remains challenging due to its high dimensionality and spectral redundancy inherent characteristics. To solve the above challenges, we propose a novel spatial-spectral omni-fusion network for hyperspectral image segmentation, named as Omni-Fuse. Here, we introduce abundant cross-dimensional feature fusion operations, including a cross-dimensional enhancement module that refines both spatial and spectral features through bidirectional attention mechanisms, a spectral-guided spatial query selection to select the most spectral-related spatial feature as the query, and a two-stage cross-dimensional decoder which dynamically guide the model to focus on the selected spatial query. Despite of numerous attention blocks, Omni-Fuse remains efficient in execution. Experiments on two microscopic hyperspectral image datasets show that our approach can significantly improve the segmentation performance compared with the state-of-the-art methods, with over 5.73 percent improvement in DSC. Code available at: https://github.com/DeepMed-Lab-ECNU/Omni-Fuse.
医学高光谱成像(MHSI)作为一种有前途的工具,在增强疾病诊断中表现出巨大的潜力,特别是在计算病理学领域。它提供了丰富的光谱信息,有助于识别组织的细微生物化学特性。尽管具有这些优势,但由于高光谱成像的高维度和光谱冗余等固有特性,有效融合空间维度和光谱维度的信息仍然是一个挑战。为了解决上述挑战,我们提出了一种用于高光谱图像分割的空间光谱全融合网络,命名为Omni-Fuse。在此,我们引入了丰富的跨维特征融合操作,包括跨维增强模块,该模块通过双向注意力机制细化空间和光谱特征、光谱引导的空间查询选择,选择最相关的光谱空间特征作为查询,以及两阶段跨维解码器,动态引导模型关注所选的空间查询。尽管存在大量的注意力块,Omni-Fuse在执行时仍保持高效。在两个显微高光谱图像数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法相较于最先进的方法可以显著提高分割性能,在DSC上提高了5.73%以上。代码可用:https://github.com/DeepMed-Lab-ECNU/Omni-Fuse。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学超光谱成像(MHSI)在疾病诊断中展现出巨大潜力,特别是在计算病理学领域。为提高超光谱图像分割效果,提出了一种名为Omni-Fuse的空间光谱全融合网络。该网络包含跨维度特征融合操作,如双向注意力机制的跨维度增强模块、光谱引导的空间查询选择及两阶段跨维度解码器。在两种显微超光谱图像数据集上的实验表明,该方法与现有技术相比能显著提高分割性能,DSC提升超过5.73%。代码已公开。
Key Takeaways
- 医学超光谱成像(MHSI)在疾病诊断中具有巨大潜力,特别是在计算病理学领域。
- Omni-Fuse是一种新型的空间光谱全融合网络,用于超光谱图像分割。
- Omni-Fuse网络包含丰富的跨维度特征融合操作,包括跨维度增强模块、光谱引导的空间查询选择和两阶段跨维度解码器。
- Omni-Fuse通过双向注意力机制优化空间及光谱特征。
- Omni-Fuse通过光谱引导选择最相关的空间特征作为查询。
- 实验表明,Omni-Fuse在两种显微超光谱图像数据集上的分割性能显著优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

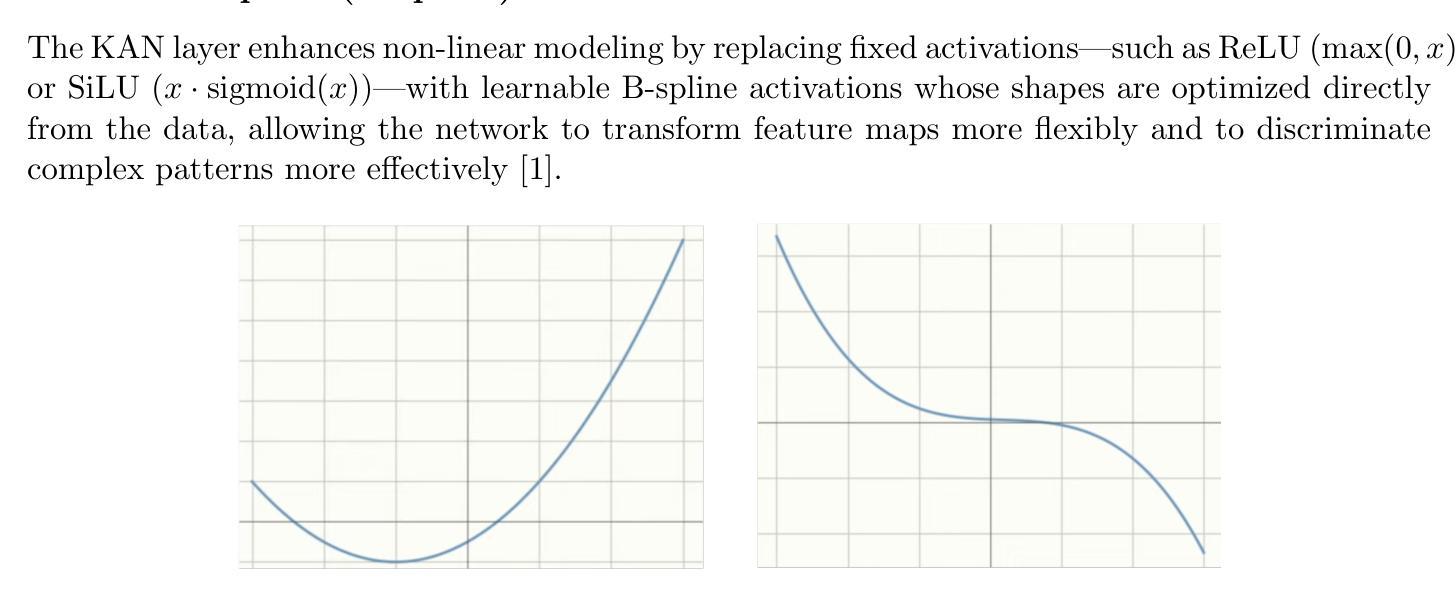
Capsule-ConvKAN: A Hybrid Neural Approach to Medical Image Classification
Authors:Laura Pituková, Peter Sinčák, László József Kovács
This study conducts a comprehensive comparison of four neural network architectures: Convolutional Neural Network, Capsule Network, Convolutional Kolmogorov–Arnold Network, and the newly proposed Capsule–Convolutional Kolmogorov–Arnold Network. The proposed Capsule-ConvKAN architecture combines the dynamic routing and spatial hierarchy capabilities of Capsule Network with the flexible and interpretable function approximation of Convolutional Kolmogorov–Arnold Networks. This novel hybrid model was developed to improve feature representation and classification accuracy, particularly in challenging real-world biomedical image data. The architectures were evaluated on a histopathological image dataset, where Capsule-ConvKAN achieved the highest classification performance with an accuracy of 91.21%. The results demonstrate the potential of the newly introduced Capsule-ConvKAN in capturing spatial patterns, managing complex features, and addressing the limitations of traditional convolutional models in medical image classification.
本研究对四种神经网络架构进行了全面比较:卷积神经网络、胶囊网络、卷积Kolmogorov-Arnold网络以及新提出的胶囊-卷积Kolmogorov-Arnold网络。所提出的Capsule-ConvKAN架构结合了胶囊网络的动态路由和空间层次结构能力,以及卷积Kolmogorov-Arnold网络的灵活和可解释函数逼近能力。该新型混合模型旨在改进特征表示和分类精度,特别是在具有挑战性的真实世界生物医学图像数据中。这些架构在病理图像数据集上进行了评估,其中Capsule-ConvKAN的分类性能最高,准确率为9 1.2 1%。结果表明,新引入的Capsule-ConvKAN在捕获空间模式、管理复杂特征以及解决医学图像分类中传统卷积模型的局限性方面具有潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint version. Accepted to IEEE SMC 2025
Summary
本文全面比较了四种神经网络架构,包括卷积神经网络、胶囊网络、卷积Kolmogorov-Arnold网络和新兴的胶囊卷积Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(Capsule-ConvKAN)。其中,Capsule-ConvKAN结合了胶囊网络的动态路由和空间层次结构能力,以及卷积Kolmogorov-Arnold网络的灵活和可解释函数逼近能力。该新型混合模型旨在改进特征表示和分类精度,特别是在具有挑战性的真实世界生物医学图像数据中。在病理图像数据集上的评估表明,Capsule-ConvKAN的分类性能最高,准确率为91.21%。这证明了Capsule-ConvKAN在捕捉空间模式、管理复杂特征以及解决医疗图像分类中传统卷积模型的局限性方面的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 四种神经网络架构进行了全面比较。
- 提出了新型的Capsule-ConvKAN架构,结合了胶囊网络和卷积Kolmogorov-Arnold网络的优点。
- Capsule-ConvKAN旨在改进特征表示和分类精度,特别是在生物医学图像数据中。
- Capsule-ConvKAN在病理图像数据集上的分类性能最高,准确率为91.21%。
- 该研究证明了Capsule-ConvKAN在捕捉空间模式和管理复杂特征方面的潜力。
- Capsule-ConvKAN解决了传统卷积模型在医疗图像分类中的局限性。
点此查看论文截图

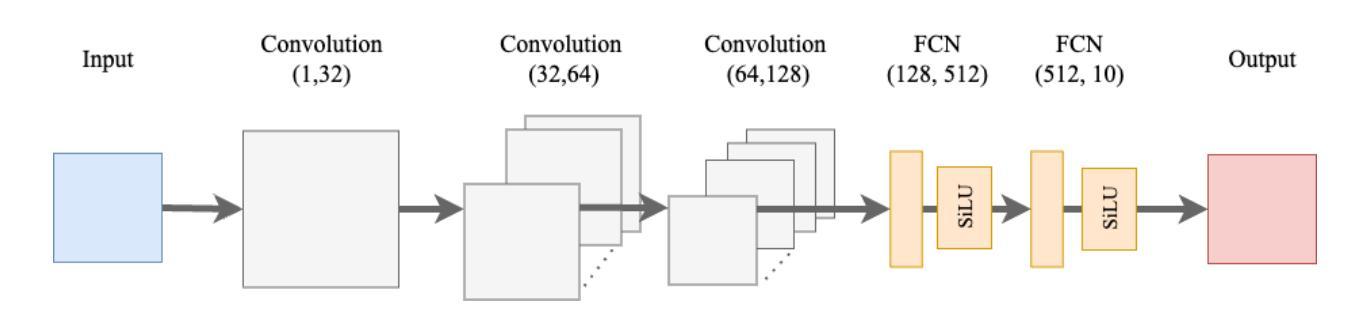
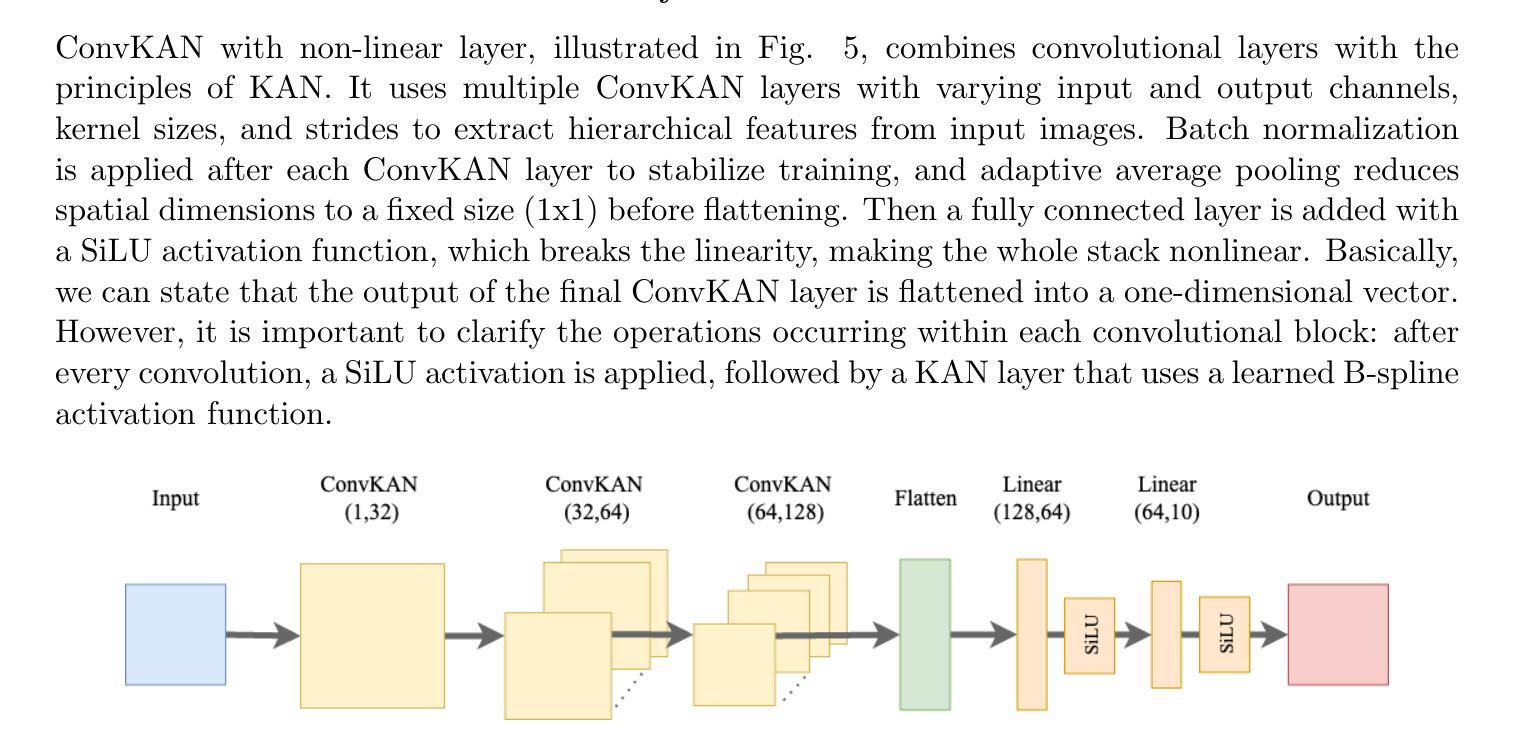
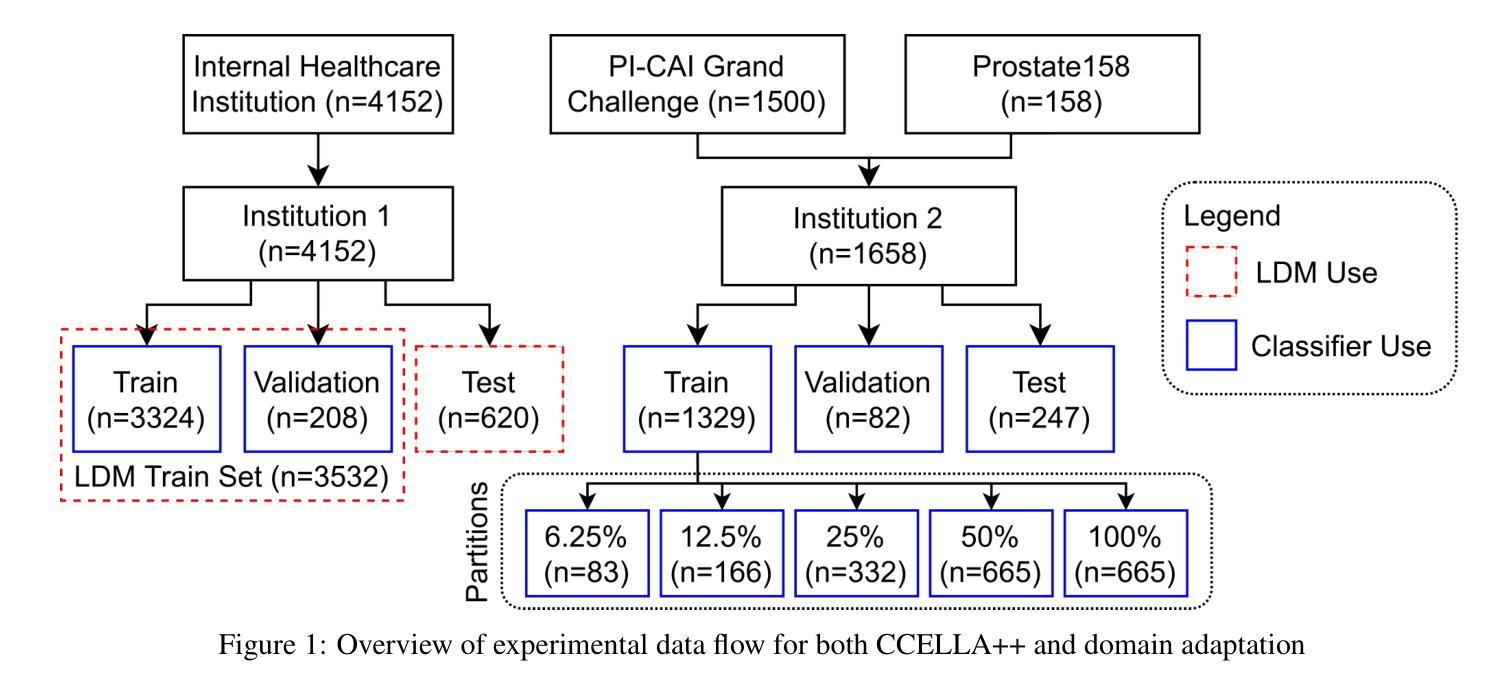
Mitigating Multi-Sequence 3D Prostate MRI Data Scarcity through Domain Adaptation using Locally-Trained Latent Diffusion Models for Prostate Cancer Detection
Authors:Emerson P. Grabke, Babak Taati, Masoom A. Haider
Objective: Latent diffusion models (LDMs) could mitigate data scarcity challenges affecting machine learning development for medical image interpretation. The recent CCELLA LDM improved prostate cancer detection performance using synthetic MRI for classifier training but was limited to the axial T2-weighted (AxT2) sequence, did not investigate inter-institutional domain shift, and prioritized radiology over histopathology outcomes. We propose CCELLA++ to address these limitations and improve clinical utility. Methods: CCELLA++ expands CCELLA for simultaneous biparametric prostate MRI (bpMRI) generation, including the AxT2, high b-value diffusion series (HighB) and apparent diffusion coefficient map (ADC). Domain adaptation was investigated by pretraining classifiers on real or LDM-generated synthetic data from an internal institution, followed with fine-tuning on progressively smaller fractions of an out-of-distribution, external dataset. Results: CCELLA++ improved 3D FID for HighB and ADC but not AxT2 (0.013, 0.012, 0.063 respectively) sequences compared to CCELLA (0.060). Classifier pretraining with CCELLA++ bpMRI outperformed real bpMRI in AP and AUC for all domain adaptation scenarios. CCELLA++ pretraining achieved highest classifier performance below 50% (n=665) external dataset volume. Conclusion: Synthetic bpMRI generated by our method can improve downstream classifier generalization and performance beyond real bpMRI or CCELLA-generated AxT2-only images. Future work should seek to quantify medical image sample quality, balance multi-sequence LDM training, and condition the LDM with additional information. Significance: The proposed CCELLA++ LDM can generate synthetic bpMRI that outperforms real data for domain adaptation with a limited target institution dataset. Our code is available at https://github.com/grabkeem/CCELLA-plus-plus
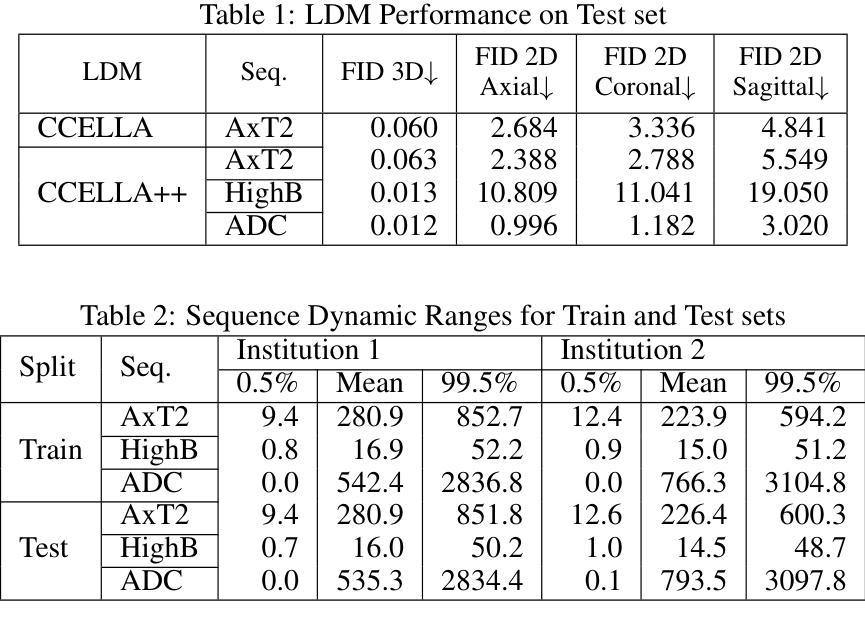
目标:潜在扩散模型(LDM)可以缓解医学图像解读机器学习开发中的数据稀缺挑战。最近的CCELLA LDM通过使用合成MRI提高了前列腺癌检测性能,用于分类器训练,但仅限于轴向T2加权(AxT2)序列,未研究跨机构领域偏移,并优先重视放射学而非组织病理学结果。我们提出CCELLA++来解决这些局限性并提高临床实用性。方法:CCELLA++扩展了CCELLA,用于同时生成双参数前列腺MRI(bpMRI),包括AxT2、高b值扩散系列(HighB)和扩散系数图(ADC)。通过用内部机构的真实数据或LDM合成数据预训练分类器,然后在逐渐较小的外部数据集部分上进行微调,来研究领域适应性问题。结果:与CCELLA相比,CCELLA++在HighB和ADC序列上改进了3D FID(分别为0.013、0.012和0.063),而AxT2序列则没有(0.060)。使用CCELLA++ bpMRI预训练的分类器在所有领域适应场景中,其AP和AUC均优于真实bpMRI。CCELLA++预训练在外部数据集体积低于50%(n=665)时达到了最高的分类器性能。结论:我们的方法生成的合成bpMRI可以改善下游分类器的泛化和性能,优于真实bpMRI或CCELLA生成的仅AxT2图像。未来的工作应该致力于量化医学图像样本质量,平衡多序列LDM训练,并用额外信息调整LDM。意义:所提出的CCELLA++ LDM可以生成合成bpMRI,在领域适应方面优于真实数据,即使目标机构数据集有限。我们的代码可在https://github.com/grabkeem/CCELLA-plus-plus找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF BT and MAH are co-senior authors on the work. This work has been submitted to the IEEE for possible publication
Summary
本文介绍了潜在扩散模型(Latent Diffusion Models,LDMs)在解决医学图像解释机器学习开发中的数据稀缺挑战方面的应用。提出的CCELLA++模型旨在解决CCELLA模型的局限性,包括仅限于轴状T2加权序列的问题,并针对不同医院数据之间的变化展开调查,并在重视放射学的同时平衡与病理组织学结果的关系。通过拓展用于同时生成双参数前列腺MRI的CCELLA++模型以及调查分类器在多个领域的适应力等方面来加强临床应用效果。该模型成功改进了某些领域的高分辨率标记表现。它结合了实际的轴状T2、高b值扩散序列和表观扩散系数图的数据来训练模型,并且成功改善了分类器的性能表现。CCELLA++模型在生成合成数据方面展现出强大的潜力,能够提高下游分类器的泛化能力和性能表现。未来研究应关注量化医学图像样本质量,平衡多序列LDM训练,并在给定额外信息的情况下调整LDM。CCELLA++模型的代码已公开发布在GitHub上供研究使用。总结为:新模型CCELLA++能生成合成双参数MRI图像,优于真实数据在特定领域适应性的表现,具有缓解医疗影像分析中数据稀缺问题的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- CCELLA++旨在扩展和改进原始CCELLA模型在医学图像领域的适用性,包括生成双参数MRI图像。
- 该模型通过结合多种MRI序列(如轴状T2加权序列、高b值扩散系列和表观扩散系数图)进行训练,提高了分类器的性能表现。
- CCELLA++通过生成合成数据提高了下游分类器的泛化能力,并在某些情况下表现出超越真实数据的性能表现。
- 模型能够适应不同医院的数据变化(即领域适应性),并且在小规模外部数据集上也能实现较好的分类器性能表现。
- 与原始CCELLA模型相比,CCELLA++在某些领域(如高b值扩散序列和表观扩散系数图)的改进效果更为显著。
点此查看论文截图

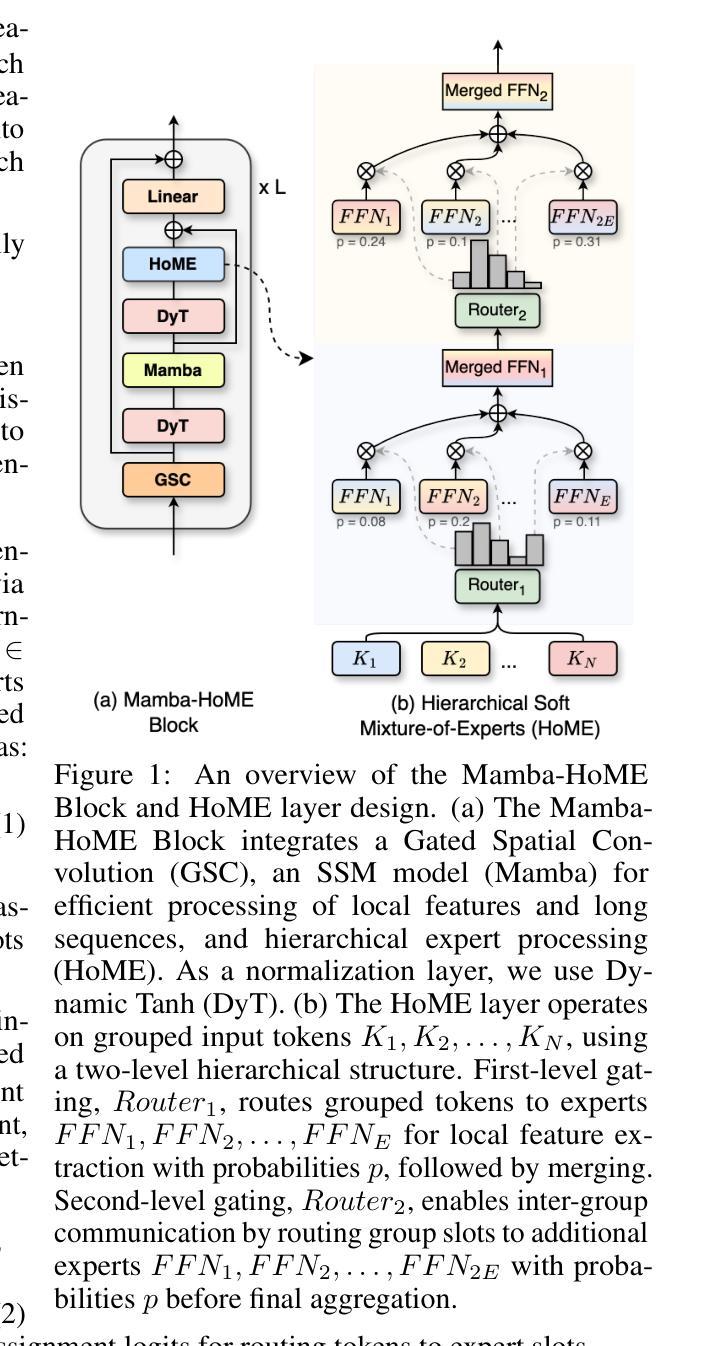
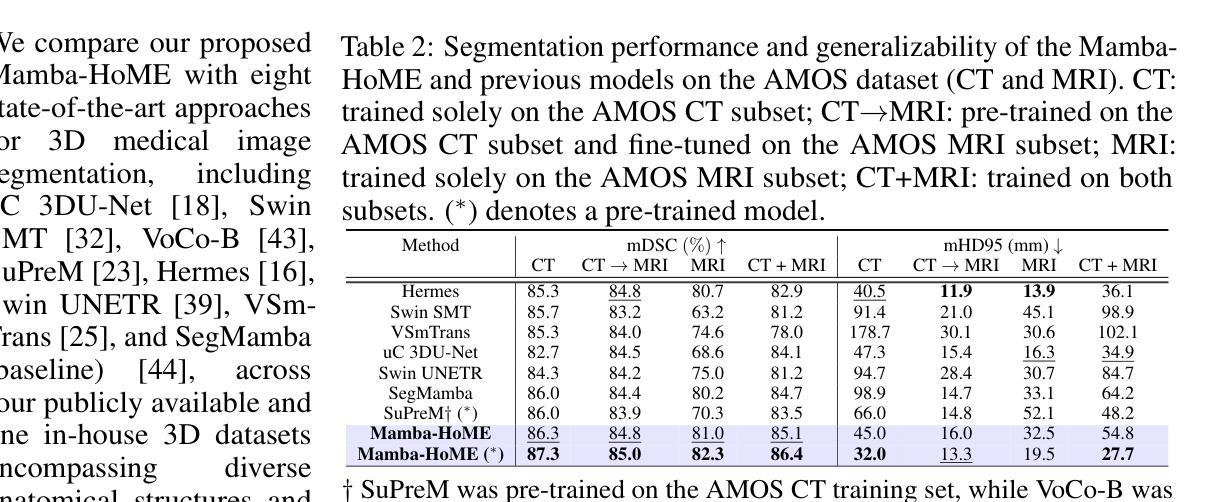
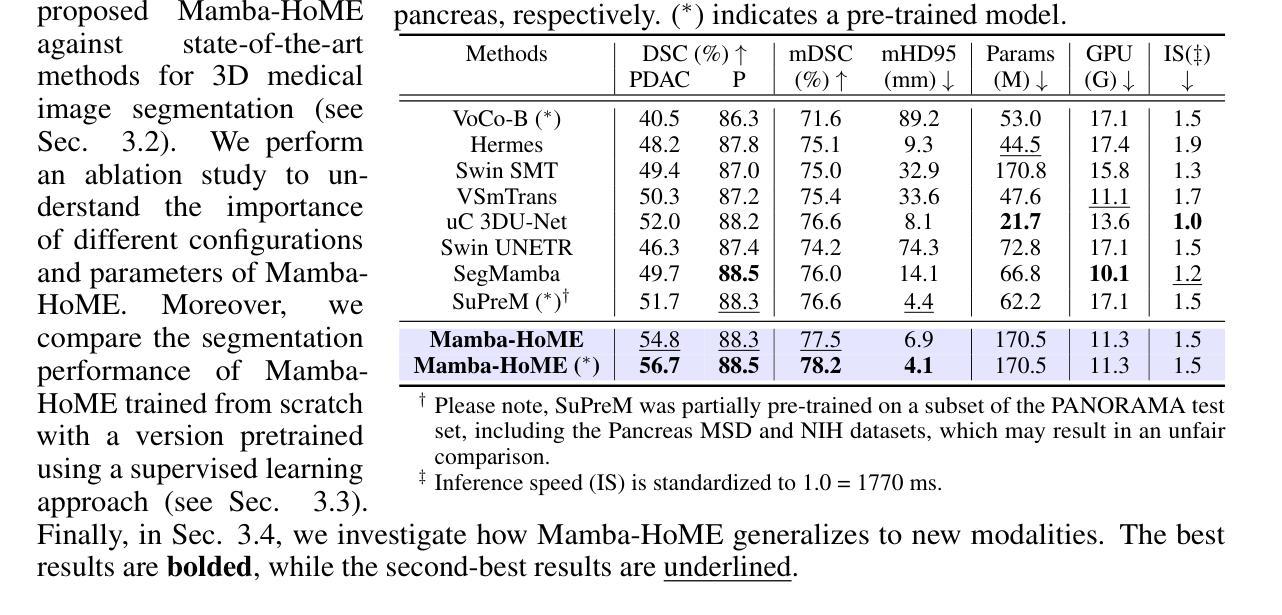
Mamba Goes HoME: Hierarchical Soft Mixture-of-Experts for 3D Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Szymon Płotka, Maciej Chrabaszcz, Gizem Mert, Ewa Szczurek, Arkadiusz Sitek
In recent years, artificial intelligence has significantly advanced medical image segmentation. However, challenges remain, including efficient 3D medical image processing across diverse modalities and handling data variability. In this work, we introduce Hierarchical Soft Mixture-of-Experts (HoME), a two-level token-routing layer for efficient long-context modeling, specifically designed for 3D medical image segmentation. Built on the Mamba state-space model (SSM) backbone, HoME enhances sequential modeling through sparse, adaptive expert routing. The first stage employs a Soft Mixture-of-Experts (SMoE) layer to partition input sequences into local groups, routing tokens to specialized per-group experts for localized feature extraction. The second stage aggregates these outputs via a global SMoE layer, enabling cross-group information fusion and global context refinement. This hierarchical design, combining local expert routing with global expert refinement improves generalizability and segmentation performance, surpassing state-of-the-art results across datasets from the three most commonly used 3D medical imaging modalities and data quality.
近年来,人工智能在医学图像分割方面取得了重大进展。然而,仍然存在挑战,包括处理不同模式的高效3D医学图像和处理数据变化。在这项工作中,我们引入了分层软混合专家(HoME),这是一种两级令牌路由层,用于高效的长上下文建模,专为3D医学图像分割而设计。建立在Mamba状态空间模型(SSM)主干网络上,HoME通过稀疏、自适应的专家路由增强了序列建模。第一阶段采用软混合专家(SMoE)层将输入序列分割成局部组,将令牌路由到针对每组的专家进行局部特征提取。第二阶段通过全局SMoE层聚合这些输出,实现跨组信息融合和全局上下文细化。这种结合局部专家路由和全局专家细化的分层设计提高了通用性和分割性能,超越了三种最常用的3D医学成像模式和数据质量的数据集上的最新结果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了基于人工智能的医学图像分割技术的最新进展,并提出了Hierarchical Soft Mixture-of-Experts(HoME)模型,该模型采用两级令牌路由层进行高效的长上下文建模,专门用于3D医学图像分割。HoME模型结合局部专家路由和全局专家细化,提高了模型的通用性和分割性能,在三种最常用的3D医学成像模态和数据质量的多个数据集上取得了优于最新技术的结果。
Key Takeaways
- 人工智能在医学图像分割方面的进展与挑战:虽然已经取得了显著的进展,但仍面临如跨不同模态的高效3D医学图像处理和数据变化处理等多方面的挑战。
- 引入HoME模型:这是一种专门为3D医学图像分割设计的两阶段模型,通过两级令牌路由层进行高效的长上下文建模。
- HoME模型的第一阶段:采用Soft Mixture-of-Experts (SMoE)层对输入序列进行局部分组,并对令牌进行路由,以进行局部特征提取。
- HoME模型的第二阶段:通过全局SMoE层聚合局部特征提取的输出,实现跨组信息融合和全局上下文细化。
- 基于Mamba状态空间模型(SSM)的HoME模型:利用SSM作为主干,增强了序列建模能力,并通过稀疏、自适应的专家路由提高性能。
- HoME模型的优点:结合局部专家路由和全局专家细化,提高了模型的通用性和分割性能。
点此查看论文截图

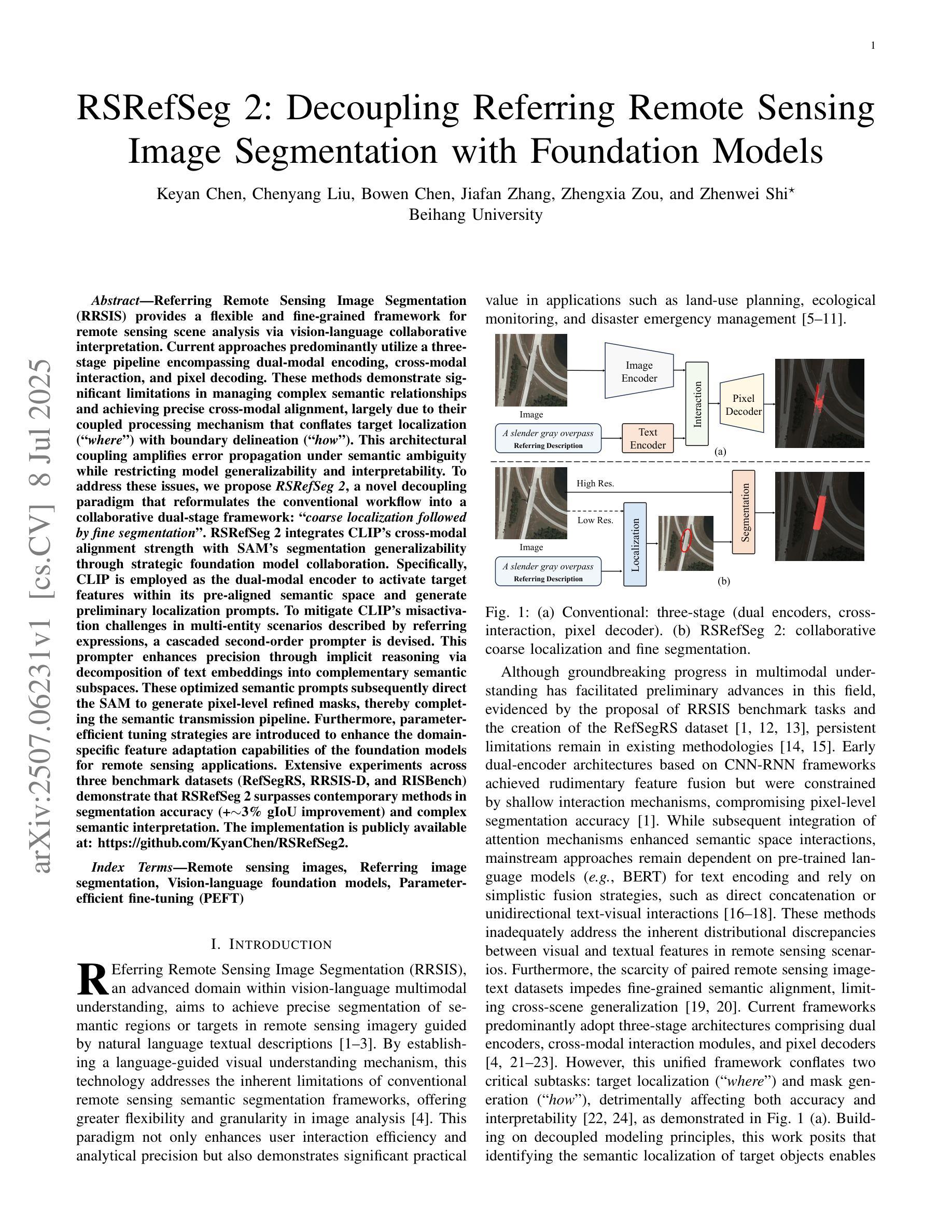
RSRefSeg 2: Decoupling Referring Remote Sensing Image Segmentation with Foundation Models
Authors:Keyan Chen, Chenyang Liu, Bowen Chen, Jiafan Zhang, Zhengxia Zou, Zhenwei Shi
Referring Remote Sensing Image Segmentation provides a flexible and fine-grained framework for remote sensing scene analysis via vision-language collaborative interpretation. Current approaches predominantly utilize a three-stage pipeline encompassing dual-modal encoding, cross-modal interaction, and pixel decoding. These methods demonstrate significant limitations in managing complex semantic relationships and achieving precise cross-modal alignment, largely due to their coupled processing mechanism that conflates target localization with boundary delineation. This architectural coupling amplifies error propagation under semantic ambiguity while restricting model generalizability and interpretability. To address these issues, we propose RSRefSeg 2, a decoupling paradigm that reformulates the conventional workflow into a collaborative dual-stage framework: coarse localization followed by fine segmentation. RSRefSeg 2 integrates CLIP’s cross-modal alignment strength with SAM’s segmentation generalizability through strategic foundation model collaboration. Specifically, CLIP is employed as the dual-modal encoder to activate target features within its pre-aligned semantic space and generate localization prompts. To mitigate CLIP’s misactivation challenges in multi-entity scenarios described by referring texts, a cascaded second-order prompter is devised, which enhances precision through implicit reasoning via decomposition of text embeddings into complementary semantic subspaces. These optimized semantic prompts subsequently direct the SAM to generate pixel-level refined masks, thereby completing the semantic transmission pipeline. Extensive experiments (RefSegRS, RRSIS-D, and RISBench) demonstrate that RSRefSeg 2 surpasses contemporary methods in segmentation accuracy (+~3% gIoU) and complex semantic interpretation. Code is available at: https://github.com/KyanChen/RSRefSeg2.
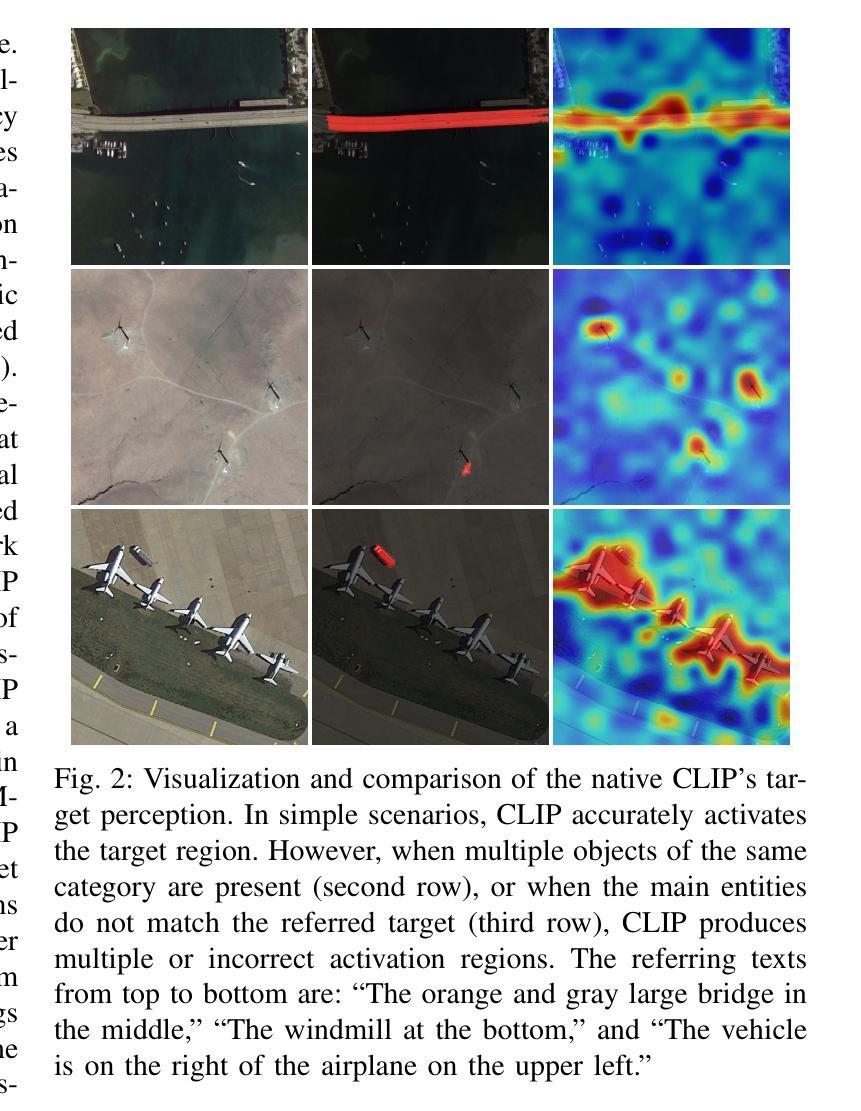
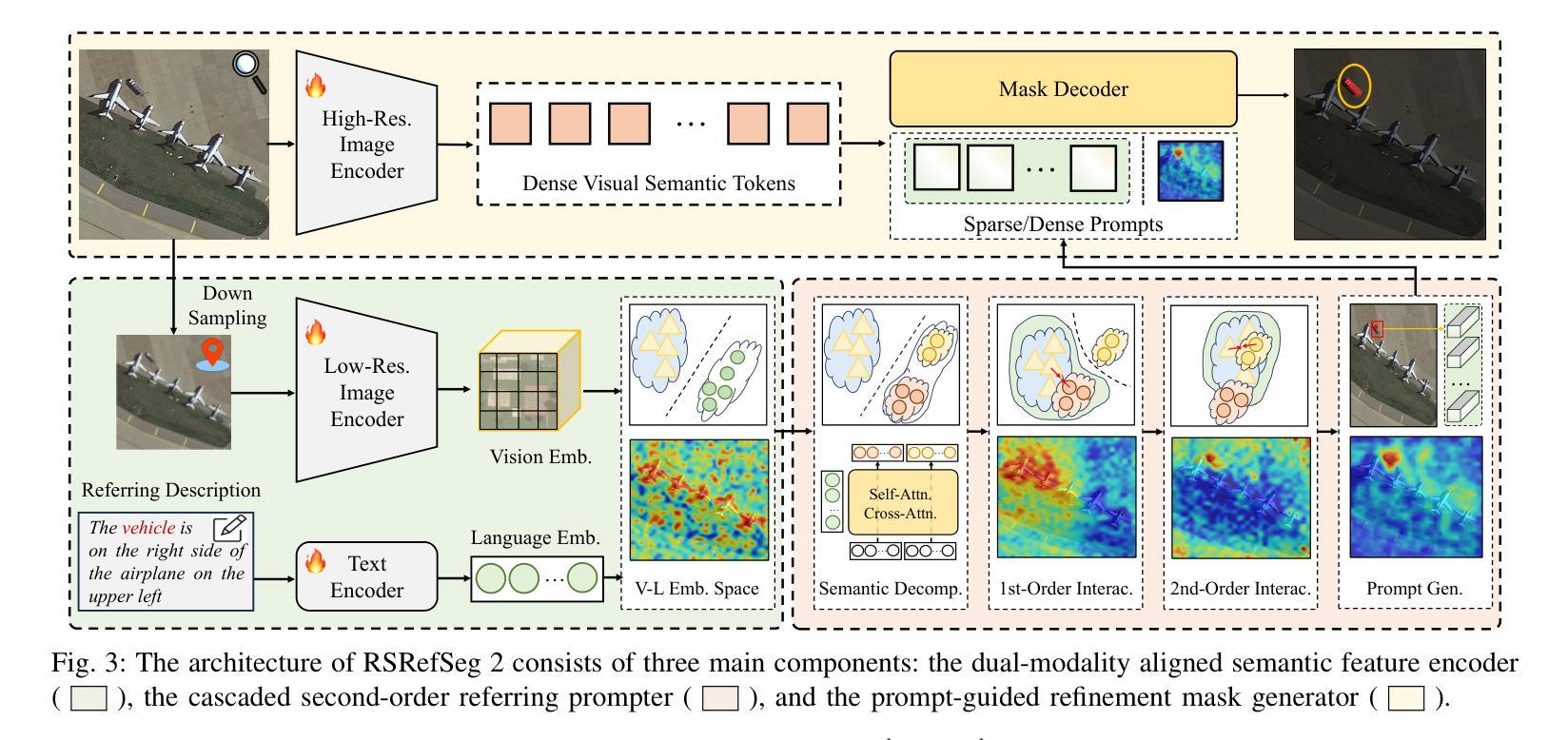
引用遥感图像分割(RSRefSeg 2)通过视觉语言协同解释提供了一种灵活、精细的框架进行遥感场景分析。目前主流的方法主要使用包含双模态编码、跨模态交互和像素解码的三阶段流程。这些方法在处理复杂的语义关系和实现精确的跨模态对齐方面存在明显的局限性,这主要是因为其耦合处理机制混淆了目标定位和边界划分。这种架构耦合在语义模糊的情况下放大了误差传播,同时限制了模型的通用性和可解释性。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了RSRefSeg 2,这是一种解耦范式,它将传统的工作流程重新设计为协同双阶段框架:先进行粗略定位,然后进行精细分割。RSRefSeg 2通过战略基础模型协作,将CLIP的跨模态对齐能力与SAM的分割通用性相结合。具体来说,CLIP被用作双模态编码器,用于激活其预对齐语义空间中的目标特征并生成定位提示。为了缓解CLIP在多实体场景中由引用文本描述的误激活挑战,设计了一种级联的二阶提示器,它通过分解文本嵌入到互补语义子空间来增强精度,并通过隐性推理实现精准提示。这些优化的语义提示随后指导SAM生成像素级细化掩码,从而完成语义传输管道。广泛的实验(RefSegRS、RRSIS-D和RISBench)表明,RSRefSeg 2在分割精度(+~3% gIoU)和复杂语义解释方面超越了当代方法。相关代码可访问于:https://github.com/KyanChen/RSRefSeg2。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了远程遥感图像分割的新方法RSRefSeg 2。该方法采用解耦范式,将传统工作流程重构为协作的双阶段框架,即先进行粗略定位,再进行精细分割。该方法结合了CLIP的跨模态对齐优势与SAM的分割泛化能力,通过战略基础模型协作,提高了遥感图像分析的灵活性和精度。
Key Takeaways
- RSRefSeg 2提出了一种新的遥感图像分割方法,采用解耦范式,分为粗定位与精细分割两个阶段。
- 方法结合了CLIP的跨模态对齐优势,有效管理复杂语义关系。
- 通过战略基础模型协作,提高了模型的泛化能力和解释性。
- 采用了SAM进行像素级精细掩膜生成,完成了语义传输管道。
- RSRefSeg 2在分割精度上超越了当代方法,达到了约3%的gIoU提升。
- 方法在RefSegRS、RRSIS-D和RISBench等多个实验中得到了验证。
点此查看论文截图
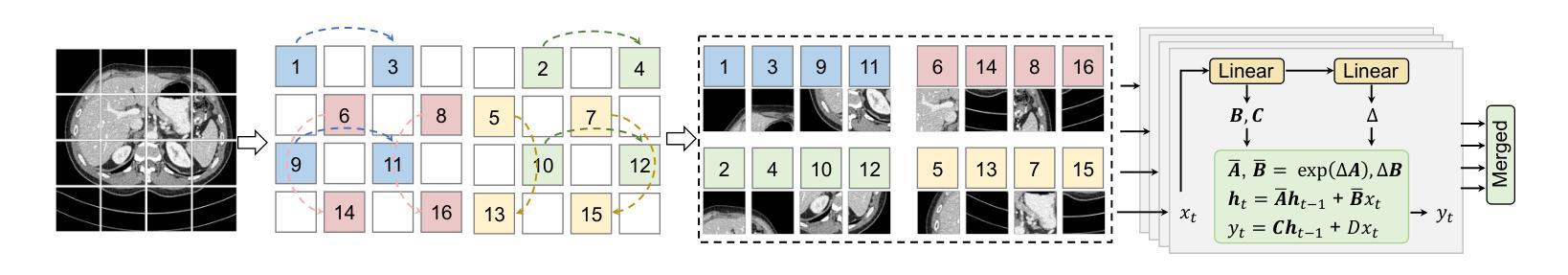
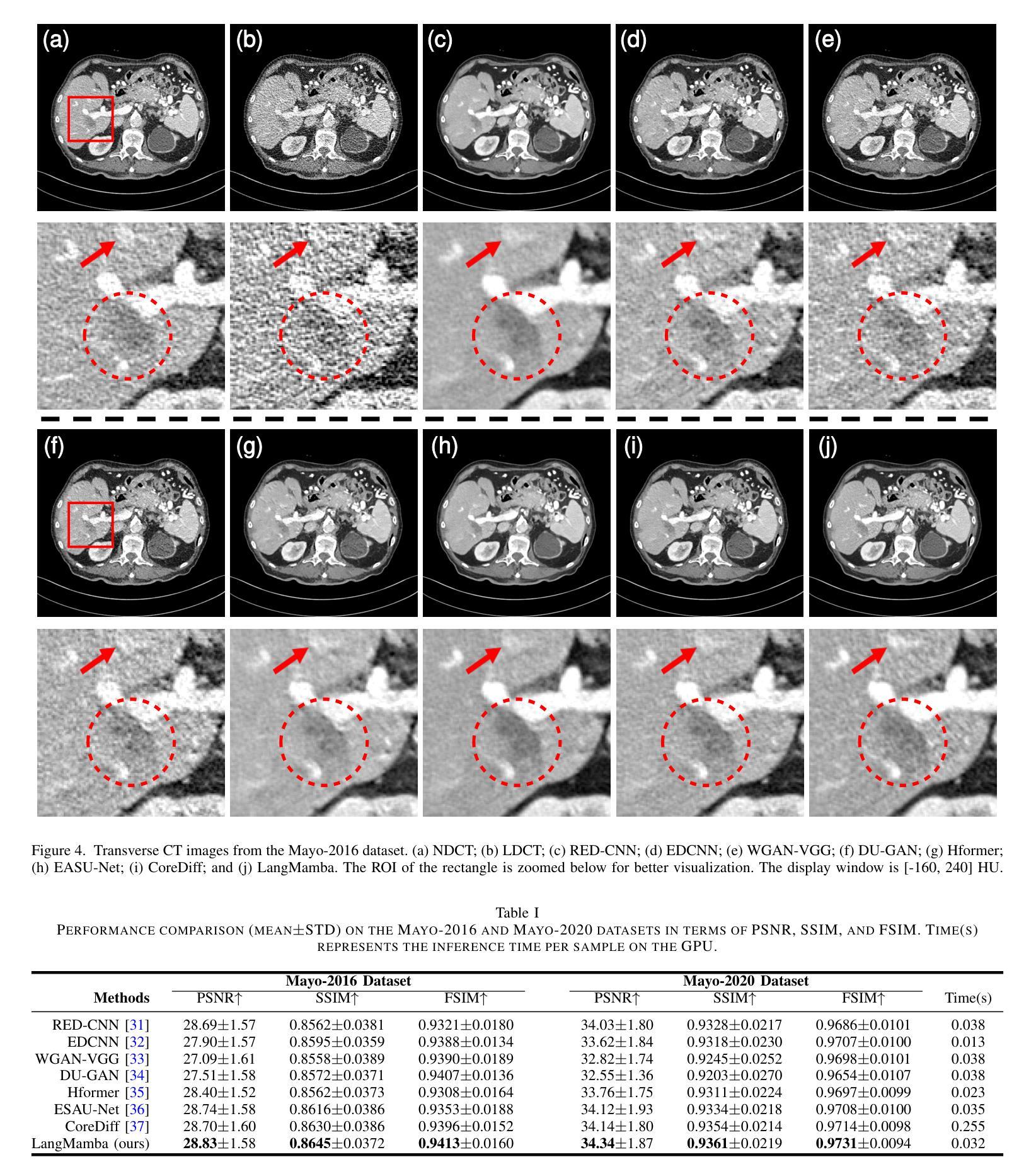
LangMamba: A Language-driven Mamba Framework for Low-dose CT Denoising with Vision-language Models
Authors:Zhihao Chen, Tao Chen, Chenhui Wang, Qi Gao, Huidong Xie, Chuang Niu, Ge Wang, Hongming Shan
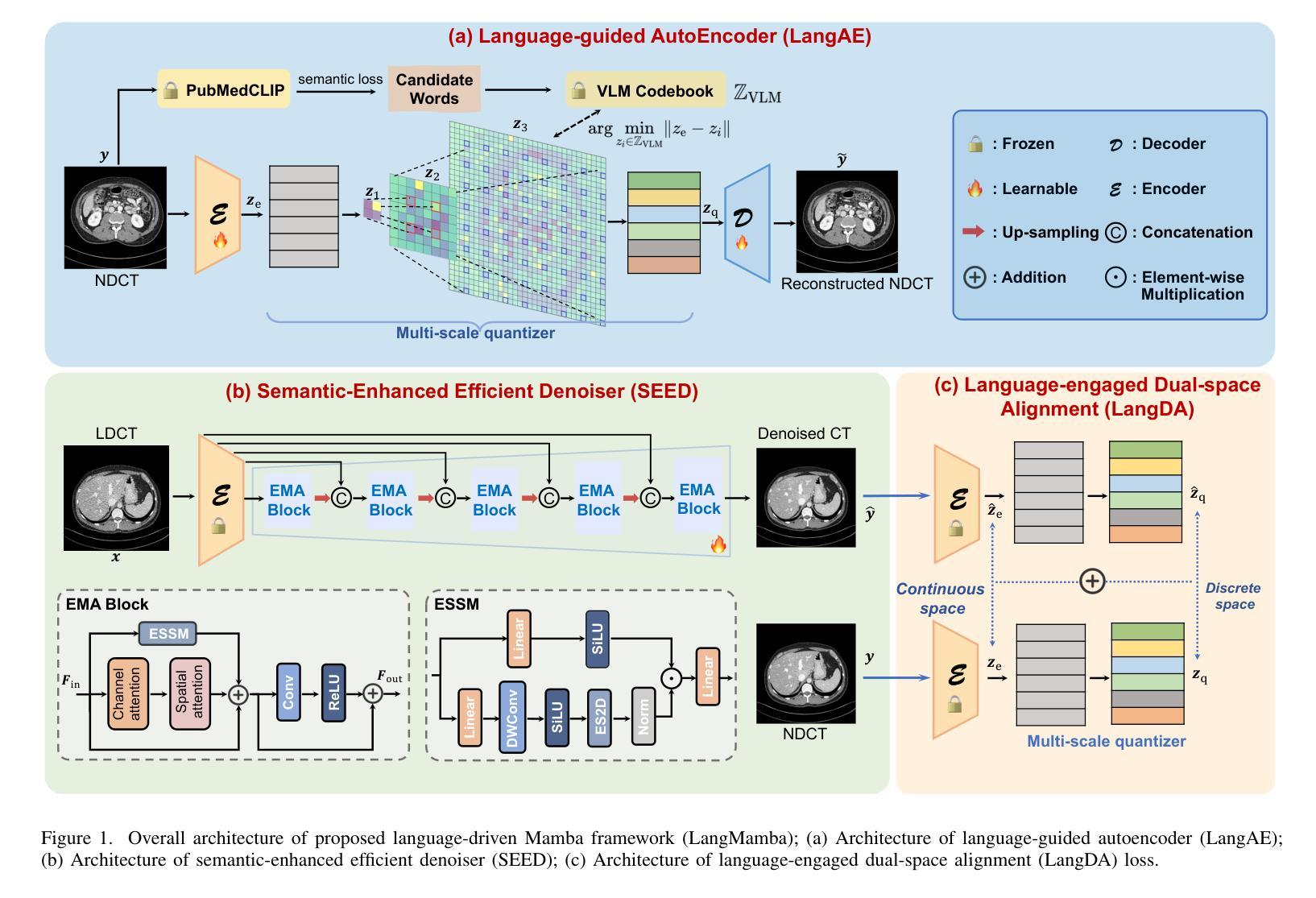
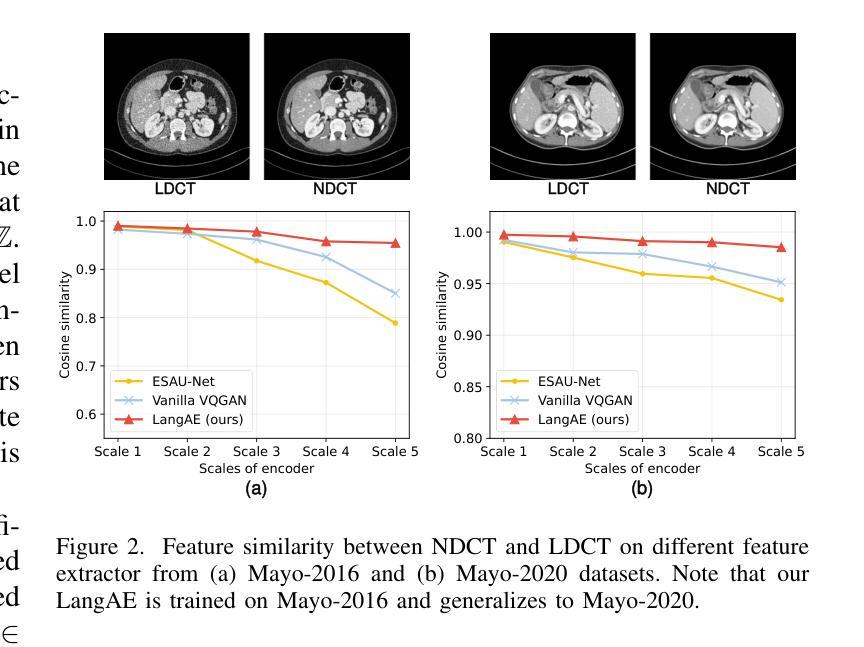
Low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) reduces radiation exposure but often degrades image quality, potentially compromising diagnostic accuracy. Existing deep learning-based denoising methods focus primarily on pixel-level mappings, overlooking the potential benefits of high-level semantic guidance. Recent advances in vision-language models (VLMs) suggest that language can serve as a powerful tool for capturing structured semantic information, offering new opportunities to improve LDCT reconstruction. In this paper, we introduce LangMamba, a Language-driven Mamba framework for LDCT denoising that leverages VLM-derived representations to enhance supervision from normal-dose CT (NDCT). LangMamba follows a two-stage learning strategy. First, we pre-train a Language-guided AutoEncoder (LangAE) that leverages frozen VLMs to map NDCT images into a semantic space enriched with anatomical information. Second, we synergize LangAE with two key components to guide LDCT denoising: Semantic-Enhanced Efficient Denoiser (SEED), which enhances NDCT-relevant local semantic while capturing global features with efficient Mamba mechanism, and Language-engaged Dual-space Alignment (LangDA) Loss, which ensures that denoised images align with NDCT in both perceptual and semantic spaces. Extensive experiments on two public datasets demonstrate that LangMamba outperforms conventional state-of-the-art methods, significantly improving detail preservation and visual fidelity. Remarkably, LangAE exhibits strong generalizability to unseen datasets, thereby reducing training costs. Furthermore, LangDA loss improves explainability by integrating language-guided insights into image reconstruction and offers a plug-and-play fashion. Our findings shed new light on the potential of language as a supervisory signal to advance LDCT denoising. The code is publicly available on https://github.com/hao1635/LangMamba.
低剂量计算机断层扫描(LDCT)降低了辐射暴露,但通常会降低图像质量,从而可能影响到诊断的准确性。现有的基于深度学习的去噪方法主要集中在像素级映射上,忽略了高级语义指导的潜在优势。最近,视觉语言模型(VLM)的进步表明,语言可以作为捕获结构化语义信息的强大工具,为改善LDCT重建提供了新的机会。在本文中,我们介绍了LangMamba,这是一种用于LDCT去噪的语言驱动Mamba框架,它利用VLM派生表示来增强正常剂量CT(NDCT)的监督。LangMamba采用两阶段学习策略。首先,我们预训练一个语言引导自动编码器(LangAE),利用冻结的VLM将NDCT图像映射到一个丰富的语义空间,其中包含解剖信息。其次,我们将LangAE与两个关键组件相结合,以指导LDCT去噪:语义增强高效去噪器(SEED),它在捕捉全局特征的同时,增强了与NDCT相关的局部语义,并使用高效的Mamba机制;以及语言参与的双空间对齐(LangDA)损失,它确保去噪图像在感知和语义空间上与NDCT对齐。在两个公共数据集上的大量实验表明,LangMamba优于传统的主流方法,显著提高了细节保留和视觉保真度。值得注意的是,LangAE对未见数据集表现出强大的泛化能力,从而降低了训练成本。此外,LangDA损失通过整合语言引导洞察到图像重建中,提高了可解释性,并以即插即用方式呈现。我们的研究为语言作为监督信号在LDCT去噪中的潜力带来了新的启示。代码已公开在https://github.com/hao1635/LangMamba。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 8 figures
Summary
本文介绍了基于语言的Mamba框架LangMamba,用于低剂量计算机断层扫描(LDCT)去噪。该方法利用视觉语言模型(VLM)的表示为正常剂量CT(NDCT)增强监督信息。LangMamba采用两阶段学习策略,首先预训练语言引导自动编码器(LangAE)将NDCT图像映射到丰富的语义空间,然后结合两个关键组件进行LDCT去噪,包括语义增强高效去噪器和语言参与双空间对齐损失。实验表明,LangMamba在细节保留和视觉保真度方面优于传统方法,且LangAE具有良好的泛化能力,降低了训练成本。此外,LangDA损失通过整合语言指导的见解来提高了解释性。
Key Takeaways
- LDCT减少辐射暴露但可能降低图像质量,影响诊断准确性。
- 现有深度学习去噪方法主要关注像素级映射,忽略了高级语义指导的潜在优势。
- LangMamba利用视觉语言模型(VLM)的表示为NDCT增强监督信息。
- LangMamba采用两阶段学习策略,包括预训练LangAE和结合两个关键组件进行LDCT去噪。
- LangMamba在细节保留和视觉保真度方面优于传统方法。
- LangAE具有良好的泛化能力,降低了训练成本。
- LangDA损失通过整合语言指导的见解提高了模型解释性。
点此查看论文截图

Just Say Better or Worse: A Human-AI Collaborative Framework for Medical Image Segmentation Without Manual Annotations
Authors:Yizhe Zhang
Manual annotation of medical images is a labor-intensive and time-consuming process, posing a significant bottleneck in the development and deployment of robust medical imaging AI systems. This paper introduces a novel Human-AI collaborative framework for medical image segmentation that substantially reduces the annotation burden by eliminating the need for explicit manual pixel-level labeling. The core innovation lies in a preference learning paradigm, where human experts provide minimal, intuitive feedback – simply indicating whether an AI-generated segmentation is better or worse than a previous version. The framework comprises four key components: (1) an adaptable foundation model (FM) for feature extraction, (2) label propagation based on feature similarity, (3) a clicking agent that learns from human better-or-worse feedback to decide where to click and with which label, and (4) a multi-round segmentation learning procedure that trains a state-of-the-art segmentation network using pseudo-labels generated by the clicking agent and FM-based label propagation. Experiments on three public datasets demonstrate that the proposed approach achieves competitive segmentation performance using only binary preference feedback, without requiring experts to directly manually annotate the images.
医学图像的手动标注是一个劳动密集且耗时的过程,这成为了开发和应用稳健的医学成像人工智能系统的重要瓶颈。本文介绍了一种用于医学图像分割的新型人机协作框架,通过消除对明确手动像素级标签的需求,极大地减轻了标注负担。核心创新点在于一种偏好学习范式,人类专家提供最小化的、直观的反馈,只需指示AI生成的分割结果是否比之前版本更好或更差。该框架包括四个关键组件:(1)用于特征提取的可适应基础模型(FM),(2)基于特征相似性的标签传播,(3)点击代理,它从人类更好或更差的反馈中学习,以决定点击哪里以及使用哪个标签,(4)多轮分割学习程序,该程序使用点击代理和基于FM的标签传播生成的伪标签来训练最先进的分割网络。在三个公共数据集上的实验表明,所提出的方法仅使用二进制偏好反馈就实现了具有竞争力的分割性能,无需专家直接手动标注图像。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 4 figures
Summary
本文介绍了一种新型人机协作框架,用于医学图像分割,通过消除对明确手动像素级标签的需求,显著减少了标注负担。核心创新点在于采用偏好学习模式,人类专家只需提供最小化的直觉反馈,即可判断人工智能生成的分割结果相较于之前版本是好还是坏。该框架包括四个关键组件:可适应的基础模型(FM)进行特征提取、基于特征相似性的标签传播、点击代理(学习人类的更好或更差反馈来决定点击位置和标签)、以及使用点击代理和FM基础标签传播生成的多轮分割学习程序来训练最新分割网络。实验表明,该方法仅使用二元偏好反馈即可实现有竞争力的分割性能,无需专家直接手动标注图像。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像的手动标注是劳动密集和时间消耗的过程,限制了医学影像AI系统的发展和部署。
- 论文提出了一种新型人机协作框架,旨在大幅减少医学图像分割的标注负担。
- 该框架采用偏好学习模式,仅需要专家的最小化直觉反馈。
- 框架包含四个关键组件:可适应的基础模型、标签传播、点击代理和多轮分割学习程序。
- 实验证明,该方法在仅使用二元偏好反馈的情况下,实现了有竞争力的分割性能。
- 该方法无需专家直接手动标注图像,降低了劳动强度和时间成本。
- 此框架对未来医学图像分割和人工智能在医疗领域的应用具有潜在的积极影响。
点此查看论文截图

From Motion to Meaning: Biomechanics-Informed Neural Network for Explainable Cardiovascular Disease Identification
Authors:Comte Valentin, Gemma Piella, Mario Ceresa, Miguel A. Gonzalez Ballester
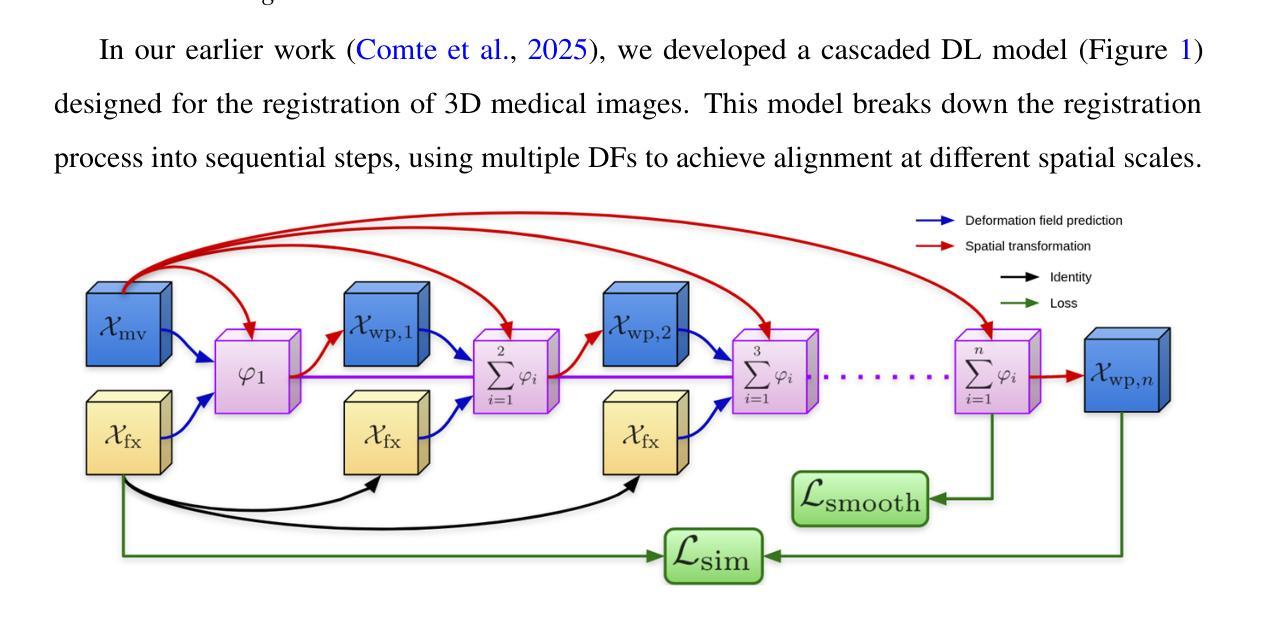
Cardiac diseases are among the leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide, which requires accurate and timely diagnostic strategies. In this study, we introduce an innovative approach that combines deep learning image registration with physics-informed regularization to predict the biomechanical properties of moving cardiac tissues and extract features for disease classification. We utilize the energy strain formulation of Neo-Hookean material to model cardiac tissue deformations, optimizing the deformation field while ensuring its physical and biomechanical coherence. This explainable approach not only improves image registration accuracy, but also provides insights into the underlying biomechanical processes of the cardiac tissues. Evaluation on the Automated Cardiac Diagnosis Challenge (ACDC) dataset achieved Dice scores of 0.945 for the left ventricular cavity, 0.908 for the right ventricular cavity, and 0.905 for the myocardium. Subsequently, we estimate the local strains within the moving heart and extract a detailed set of features used for cardiovascular disease classification. We evaluated five classification algorithms, Logistic Regression, Multi-Layer Perceptron, Support Vector Classifier, Random Forest, and Nearest Neighbour, and identified the most relevant features using a feature selection algorithm. The best performing classifier obtained a classification accuracy of 98% in the training set and 100% in the test set of the ACDC dataset. By integrating explainable artificial intelligence, this method empowers clinicians with a transparent understanding of the model’s predictions based on cardiac mechanics, while also significantly improving the accuracy and reliability of cardiac disease diagnosis, paving the way for more personalized and effective patient care.
心脏病是全球发病率和死亡率的主要原因之一,需要准确及时的诊断策略。在这项研究中,我们引入了一种创新的方法,结合深度学习图像配准和物理信息正则化,预测心脏组织运动的生物力学特性,并提取疾病分类的特征。我们使用Neo-Hookean材料的能量应变公式来模拟心脏组织变形,优化变形场的同时确保其物理和生物力学的一致性。这种可解释的方法不仅提高了图像配准的准确性,而且深入了解了心脏组织的潜在生物力学过程。在自动心脏诊断挑战(ACDC)数据集上的评估结果显示,左心室腔的Dice得分为0.945,右心室腔为0.908,心肌为0.905。随后,我们估计了心脏运动过程中的局部应变,并提取了一组详细特征用于心血管疾病分类。我们评估了五种分类算法,包括逻辑回归、多层感知器、支持向量分类器、随机森林和最近邻算法,并使用特征选择算法确定了最相关的特征。表现最佳的分类器在ACDC数据集的训练集上达到了98%的分类精度,在测试集上达到了100%的分类精度。通过集成可解释人工智能,该方法使临床医生能够基于心脏力学对模型的预测进行透明理解,同时显著提高心脏病诊断的准确性和可靠性,为更个性化和有效的患者护理铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究结合深度学习图像配准与物理信息正则化,预测心脏组织动态的生物力学特性,并提取特征进行疾病分类。采用Neo-Hookean材料的能量应变公式对心脏组织变形进行建模,优化变形场,确保物理和生物力学的一致性。此方法不仅提高了图像配准的准确度,还为心脏组织的生物力学过程提供了深入见解。在自动化心脏诊断挑战(ACDC)数据集上,对左心室腔、右心室腔和心肌的Dice评分分别达到了0.945、0.908和0.905。然后估计心脏局部应变,提取详细特征用于心血管疾病分类。评估了五种分类算法,并借助特征选择算法确定了最相关的特征。最佳分类器在ACDC数据集的训练集和测试集上的分类准确率分别达到了98%和100%。通过结合可解释的人工智能,该方法使临床医生能够透明地了解模型基于心脏机理的预测,同时显著提高心脏疾病诊断的准确性和可靠性,为更个性化和有效的患者护理铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究结合了深度学习图像配准与物理信息正则化技术,为心脏疾病的诊断提供了新的方法。
- 通过Neo-Hookean材料的能量应变公式建模心脏组织变形,提升了图像配准的准确性,并揭示了心脏组织的生物力学过程。
- 在ACDC数据集上取得了较高的图像配准效果,Dice评分达到90%以上。
- 通过估计心脏局部应变,提取了详细特征用于心血管疾病分类。
- 研究评估了多种分类算法,并找到了最相关的特征用于疾病分类。
- 最佳分类器的训练集和测试集上的分类准确率分别达到了98%和100%。
点此查看论文截图

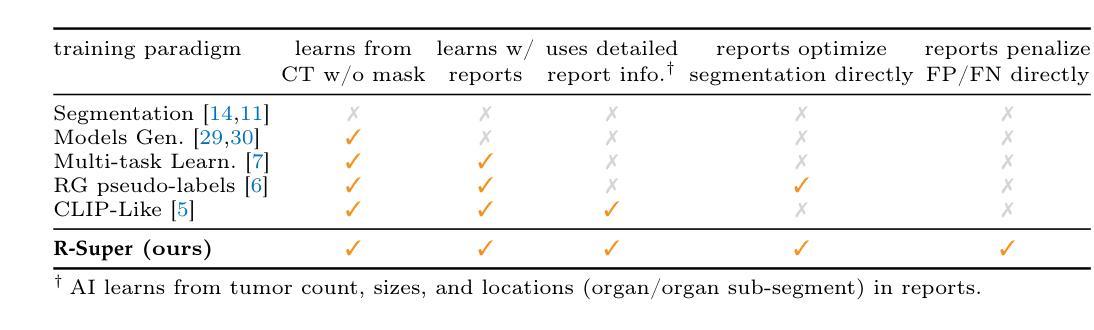
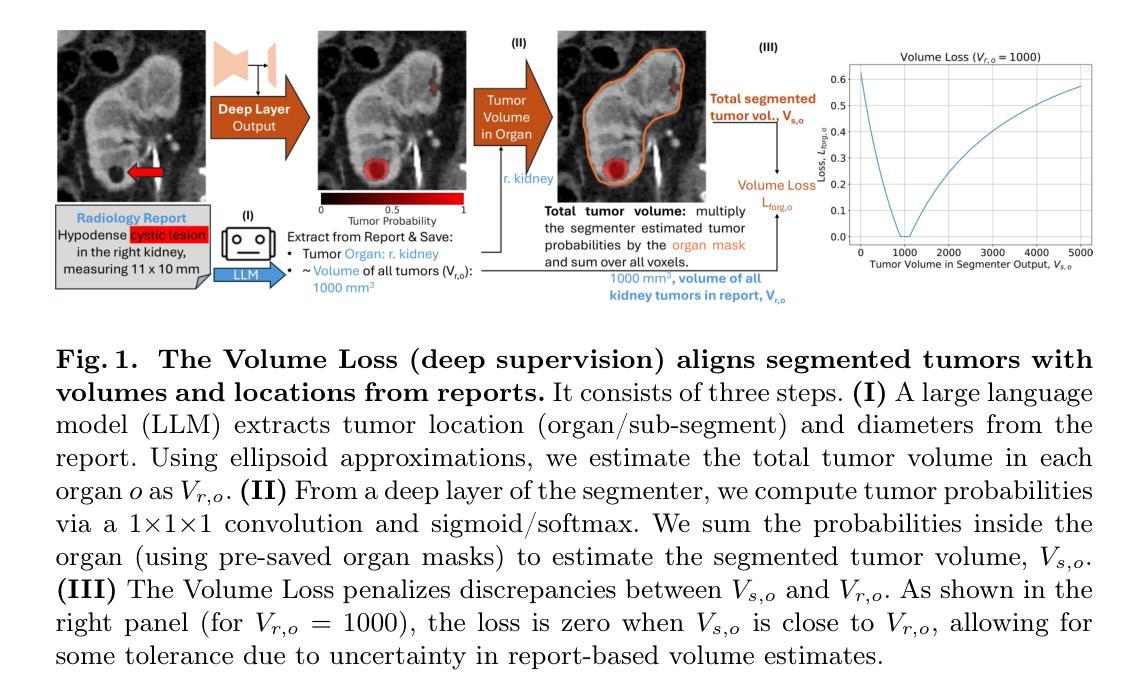
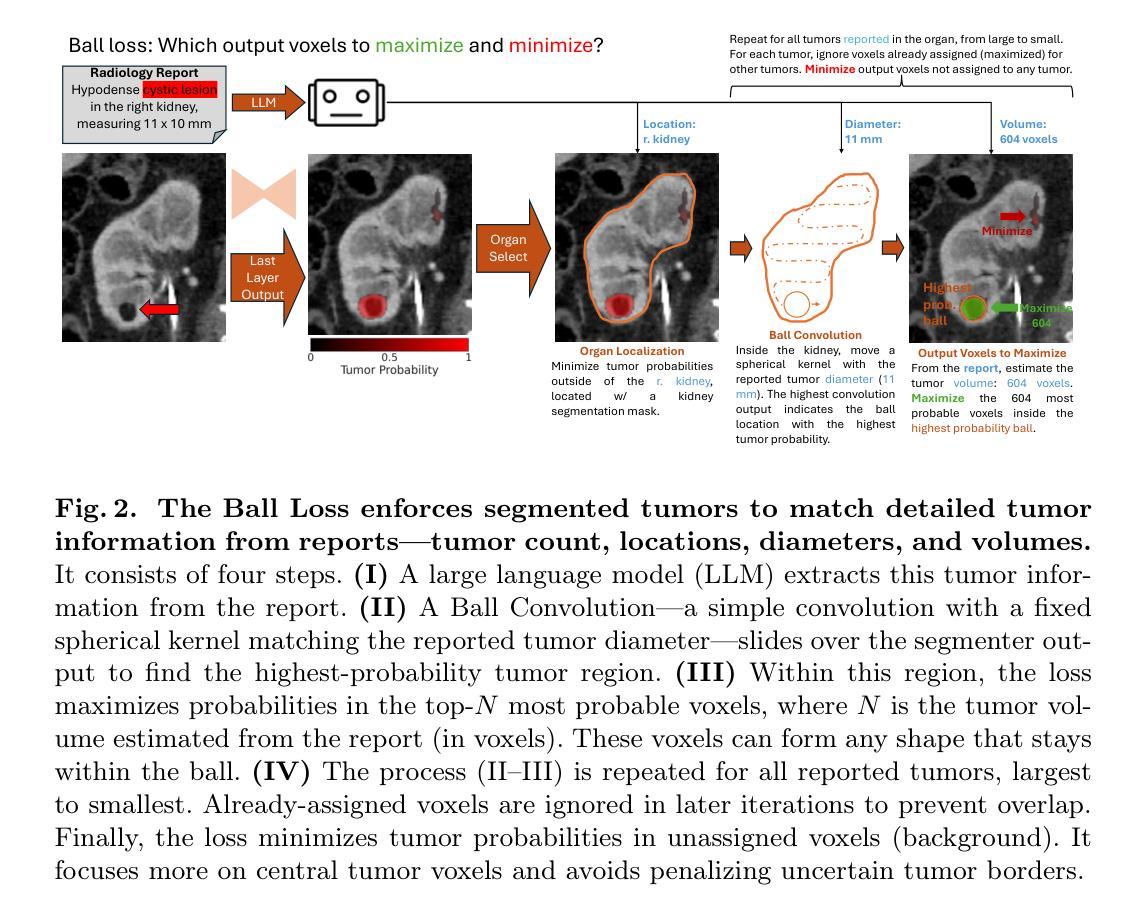
Learning Segmentation from Radiology Reports
Authors:Pedro R. A. S. Bassi, Wenxuan Li, Jieneng Chen, Zheren Zhu, Tianyu Lin, Sergio Decherchi, Andrea Cavalli, Kang Wang, Yang Yang, Alan L. Yuille, Zongwei Zhou
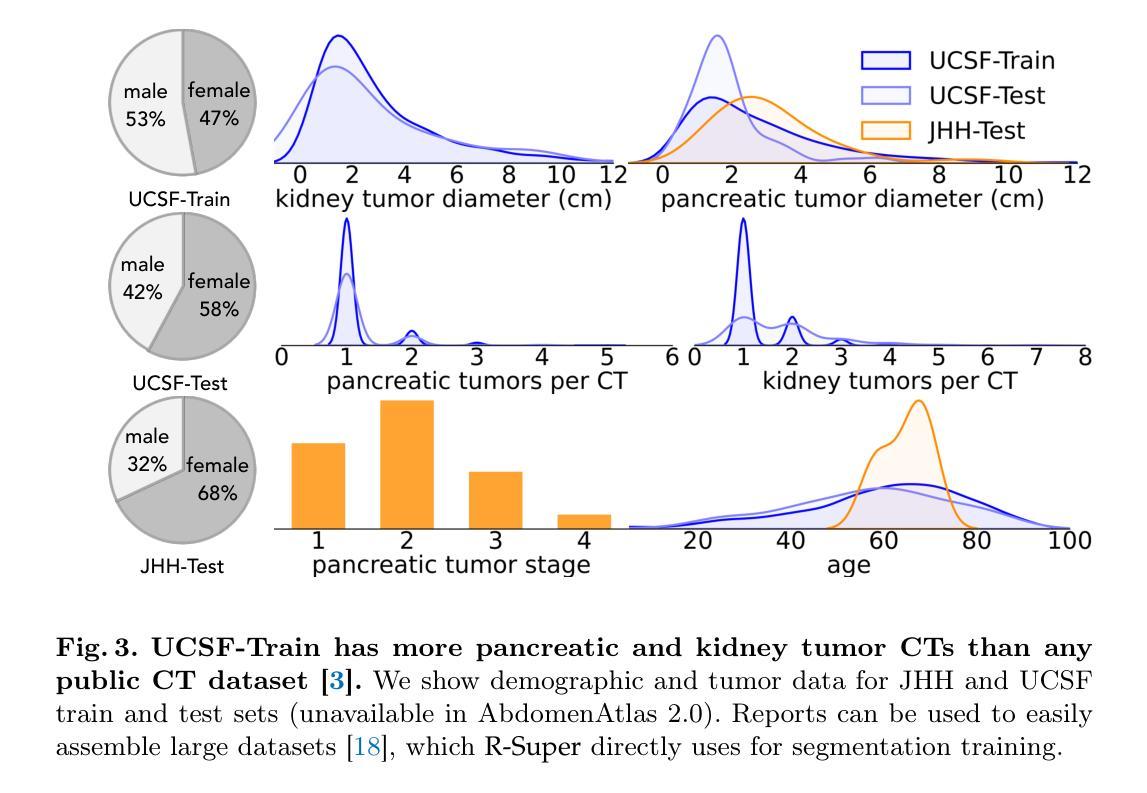
Tumor segmentation in CT scans is key for diagnosis, surgery, and prognosis, yet segmentation masks are scarce because their creation requires time and expertise. Public abdominal CT datasets have from dozens to a couple thousand tumor masks, but hospitals have hundreds of thousands of tumor CTs with radiology reports. Thus, leveraging reports to improve segmentation is key for scaling. In this paper, we propose a report-supervision loss (R-Super) that converts radiology reports into voxel-wise supervision for tumor segmentation AI. We created a dataset with 6,718 CT-Report pairs (from the UCSF Hospital), and merged it with public CT-Mask datasets (from AbdomenAtlas 2.0). We used our R-Super to train with these masks and reports, and strongly improved tumor segmentation in internal and external validation–F1 Score increased by up to 16% with respect to training with masks only. By leveraging readily available radiology reports to supplement scarce segmentation masks, R-Super strongly improves AI performance both when very few training masks are available (e.g., 50), and when many masks were available (e.g., 1.7K). Project: https://github.com/MrGiovanni/R-Super
肿瘤在CT扫描中的分割对于诊断、手术和预后至关重要,但由于其创建需要时间和专业知识,分割掩膜非常稀缺。公共腹部CT数据集有数十到数千个肿瘤掩膜,但医院有数十万个带有放射报告的肿瘤CT。因此,利用报告来改善分割是扩展的关键。在本文中,我们提出了一种报告监督损失(R-Super),它将放射学报告转化为体素级的监督,用于肿瘤分割人工智能。我们创建了包含6718个CT报告对的数据集(来自UCSF医院),并与公共CT遮罩数据集(来自AbdomenAtlas 2.0)合并。我们使用带有这些掩膜和报告的R-Super进行训练,并在内部和外部验证中显著提高了肿瘤分割效果——与仅使用掩膜进行训练相比,F1分数提高了高达16%。通过利用现成的放射学报告来补充稀缺的分割掩膜,当可用的训练掩膜很少(例如,50个)或很多(例如,1700个)时,R-Super都能极大地提高人工智能的性能。项目地址:https://github.com/MrGiovanni/R-Super
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to MICCAI 2025
Summary
本文主要研究了利用放射学报告提高肿瘤分割的AI性能。针对CT扫描中的肿瘤分割问题,提出了报告监督损失(R-Super)方法,将放射学报告转化为体素级监督信息,以改善肿瘤分割的效果。通过结合公共CT-Mask数据集和自制的CT-Report数据集进行训练,R-Super在内部和外部验证中均取得了显著的肿瘤分割效果提升,尤其是当训练掩膜数量较少时提升更为显著。
Key Takeaways
- 肿瘤分割在CT扫描中对于诊断、手术和预后评估具有重要意义,但分割掩膜的制作需要时间和专业知识,因此数量有限。
- 本文提出了报告监督损失(R-Super)方法,旨在将放射学报告转化为体素级监督信息,以改善肿瘤分割的AI性能。
- 融合了公共CT-Mask数据集和自制的CT-Report数据集进行训练,实现了在肿瘤分割上的显著改进。
- R-Super在内部和外部验证中均取得了良好的结果,与仅使用掩膜训练相比,F1分数提高了高达16%。
- R-Super方法特别适用于训练掩膜数量较少的情况,同时也能在掩膜数量较多的情况下取得良好效果。
- 该方法强化了放射学报告在AI训练中的应用价值,为利用丰富的非结构化数据资源提供了新的思路。
点此查看论文截图

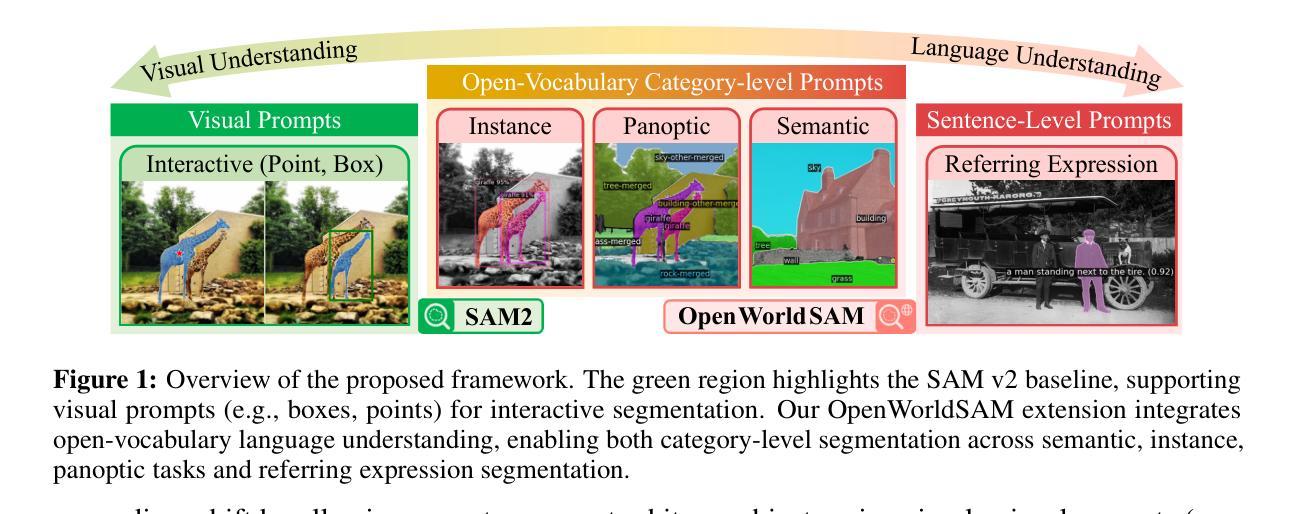
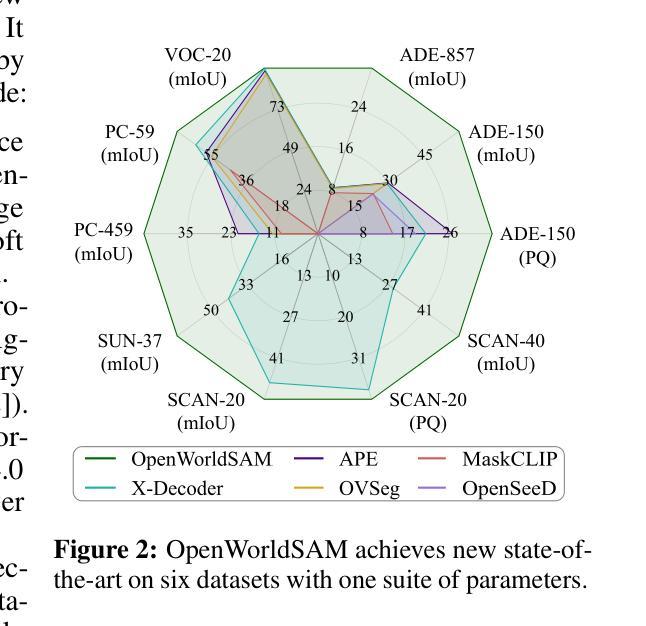
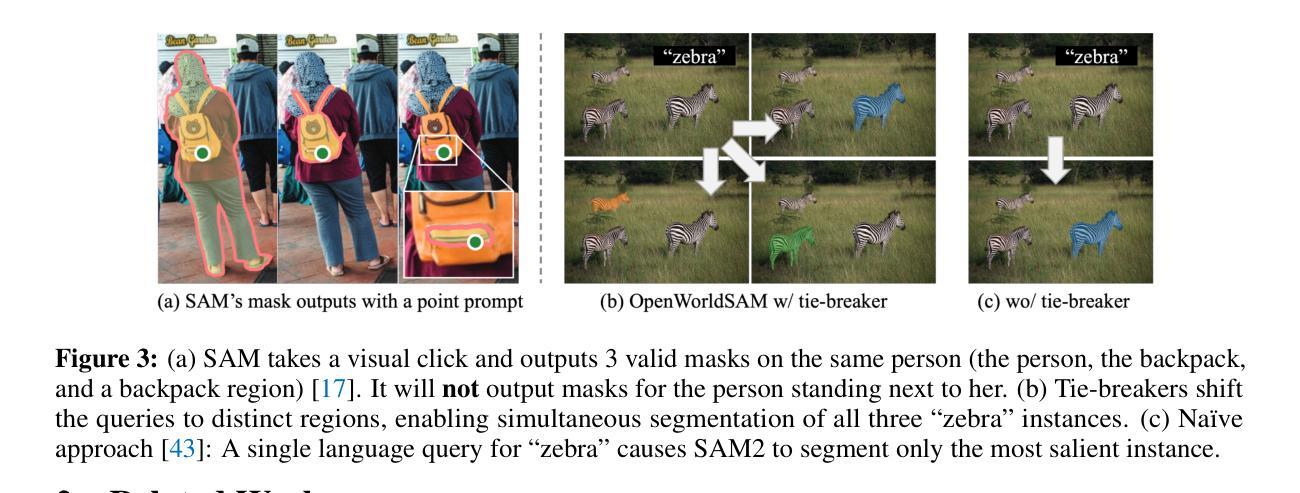
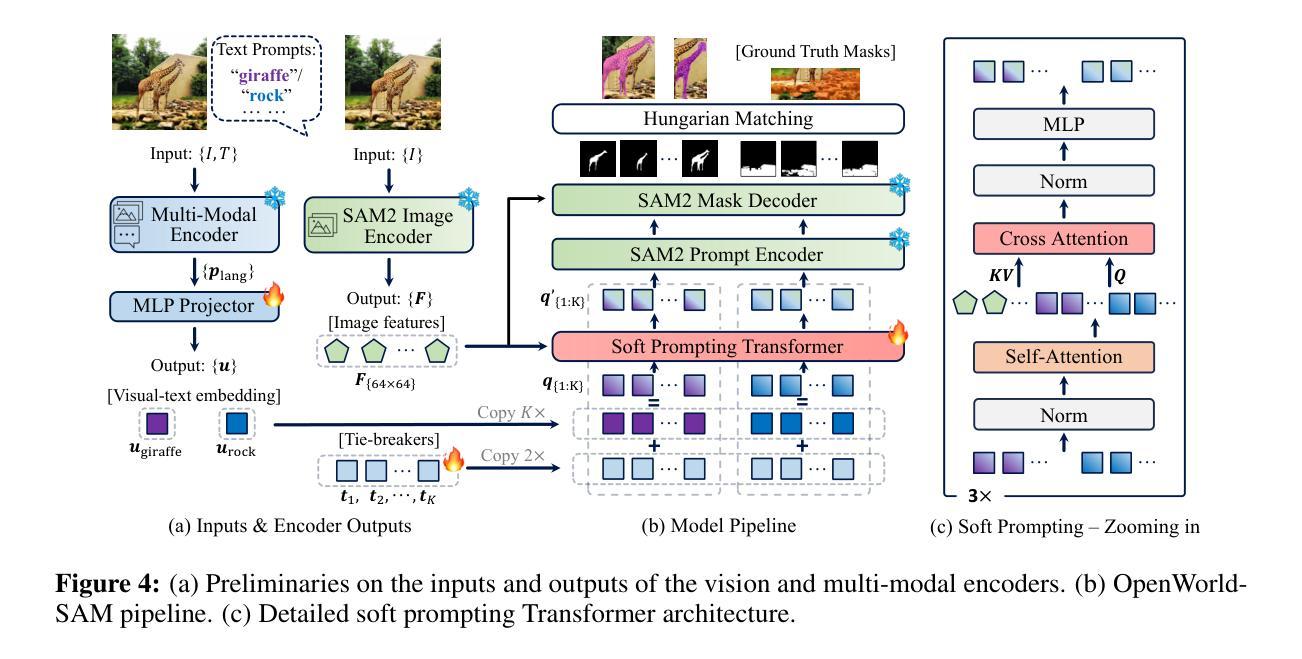
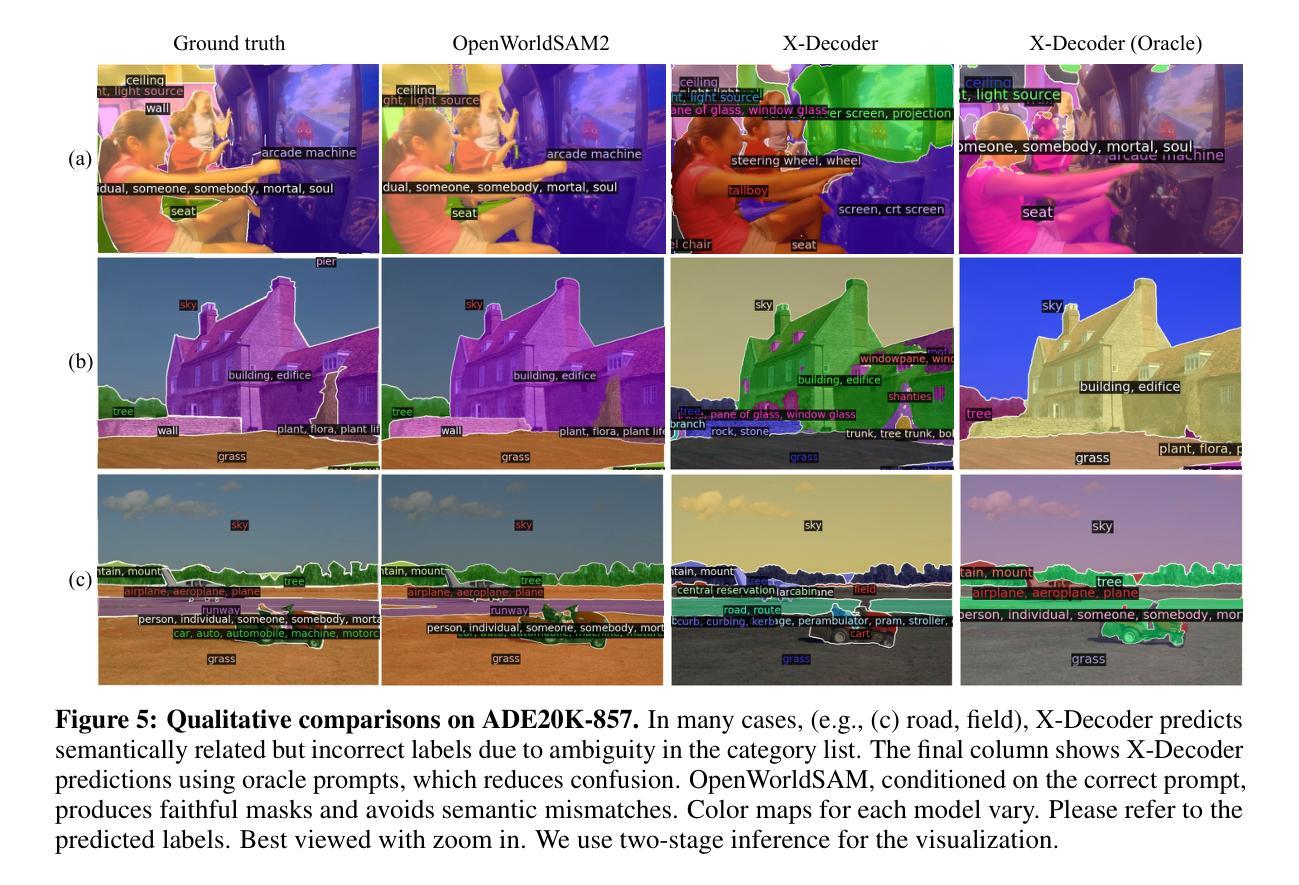
OpenWorldSAM: Extending SAM2 for Universal Image Segmentation with Language Prompts
Authors:Shiting Xiao, Rishabh Kabra, Yuhang Li, Donghyun Lee, Joao Carreira, Priyadarshini Panda
The ability to segment objects based on open-ended language prompts remains a critical challenge, requiring models to ground textual semantics into precise spatial masks while handling diverse and unseen categories. We present OpenWorldSAM, a framework that extends the prompt-driven Segment Anything Model v2 (SAM2) to open-vocabulary scenarios by integrating multi-modal embeddings extracted from a lightweight vision-language model (VLM). Our approach is guided by four key principles: i) Unified prompting: OpenWorldSAM supports a diverse range of prompts, including category-level and sentence-level language descriptions, providing a flexible interface for various segmentation tasks. ii) Efficiency: By freezing the pre-trained components of SAM2 and the VLM, we train only 4.5 million parameters on the COCO-stuff dataset, achieving remarkable resource efficiency. iii) Instance Awareness: We enhance the model’s spatial understanding through novel positional tie-breaker embeddings and cross-attention layers, enabling effective segmentation of multiple instances. iv) Generalization: OpenWorldSAM exhibits strong zero-shot capabilities, generalizing well on unseen categories and an open vocabulary of concepts without additional training. Extensive experiments demonstrate that OpenWorldSAM achieves state-of-the-art performance in open-vocabulary semantic, instance, and panoptic segmentation across multiple benchmarks, including ADE20k, PASCAL, ScanNet, and SUN-RGBD.
基于开放语言提示对物体进行分割的能力仍然是一个关键挑战,这要求模型将文本语义转化为精确的空间掩膜,同时处理多样且未知的类别。我们提出了OpenWorldSAM框架,它通过集成轻量级视觉语言模型(VLM)提取的多模式嵌入,将提示驱动的Segment Anything Model v2 (SAM2)扩展到开放词汇场景。我们的方法遵循四个关键原则:一、统一提示:OpenWorldSAM支持各种提示,包括类别级别和句子级别的语言描述,为各种分割任务提供了一个灵活的界面。二、高效性:我们通过冻结SAM2和VLM的预训练组件,只在COCO-stuff数据集上训练了450万个参数,实现了显著的资源效率。三、实例感知:我们通过新型的位置决胜嵌入和交叉注意力层增强模型的空间理解能力,实现对多个实例的有效分割。四、泛化能力:OpenWorldSAM表现出强大的零样本能力,在未见过的类别和开放的概念词汇表上无需额外训练就能很好地推广。大量实验表明,OpenWorldSAM在多个基准测试上实现了开放词汇表的语义、实例和全景分割的先进水平,包括ADE20k、PASCAL、ScanNet和SUN-RGBD。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
OpenWorldSAM框架扩展了基于文本提示进行物体分割的SAM2模型,适用于开放词汇场景。通过整合轻量级视觉语言模型的多模态嵌入,支持多种提示,实现高效、实例感知和泛化能力强的开放词汇语义、实例和全景分割。
Key Takeaways
- OpenWorldSAM框架扩展了Segment Anything Model v2(SAM2),支持开放词汇场景中的物体分割。
- 通过多模态嵌入和轻量级视觉语言模型的整合,提高模型性能。
- 统一提示:支持类别级别和句子级别的语言描述,为各种分割任务提供灵活接口。
- 高效性:通过冻结SAM2和视觉语言模型的预训练组件,仅在COCO-stuff数据集上训练4.5百万参数,实现资源高效利用。
- 实例感知:通过新型定位tie-breaker嵌入和交叉注意力层,增强模型对多个实例的空间理解,实现有效分割。
- 泛化能力强:OpenWorldSAM具有很强的零样本能力,能很好地泛化未见过的类别和开放词汇概念,无需额外训练。
点此查看论文截图