⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-11 更新
Towards Multimodal Understanding via Stable Diffusion as a Task-Aware Feature Extractor
Authors:Vatsal Agarwal, Matthew Gwilliam, Gefen Kohavi, Eshan Verma, Daniel Ulbricht, Abhinav Shrivastava
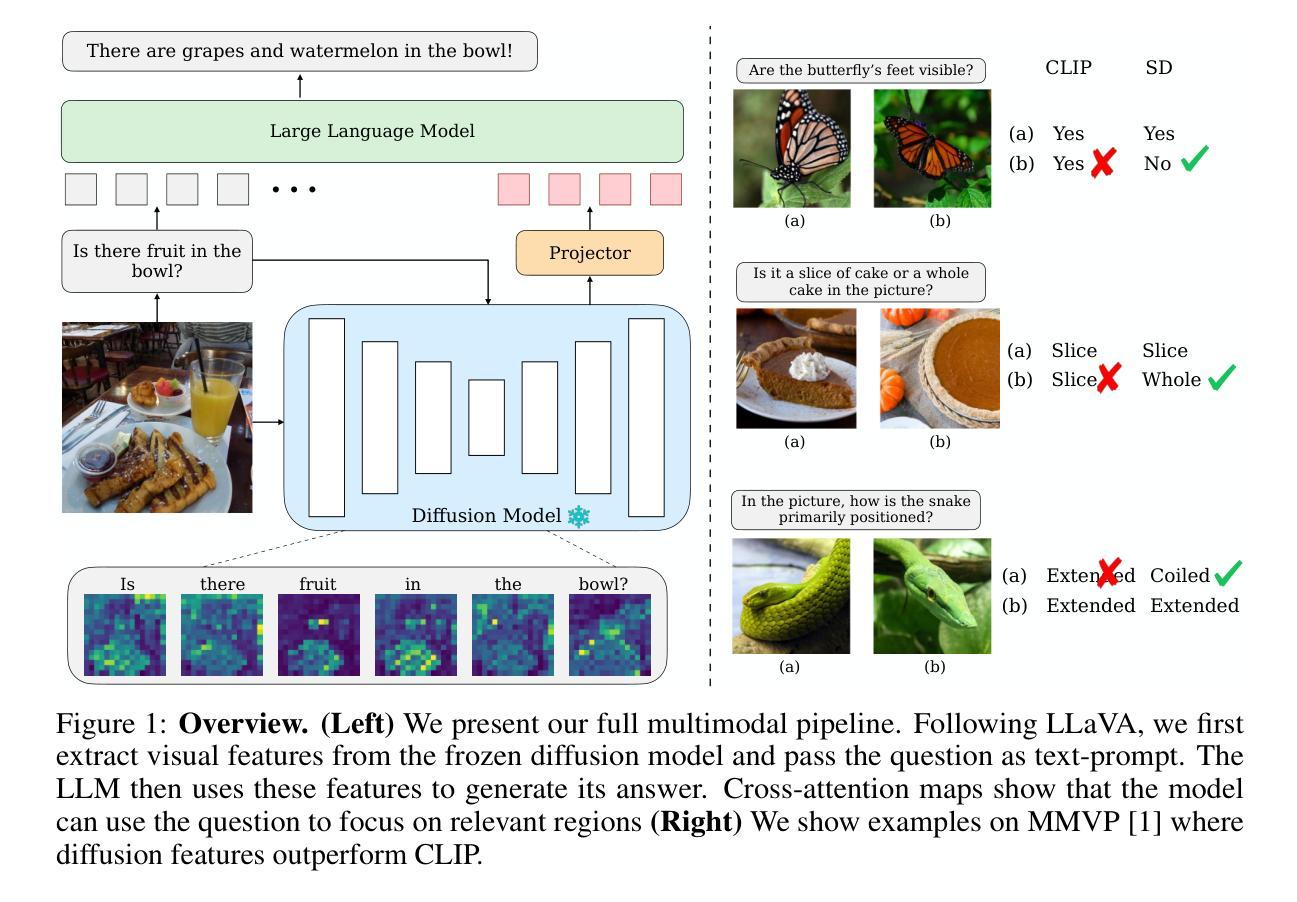
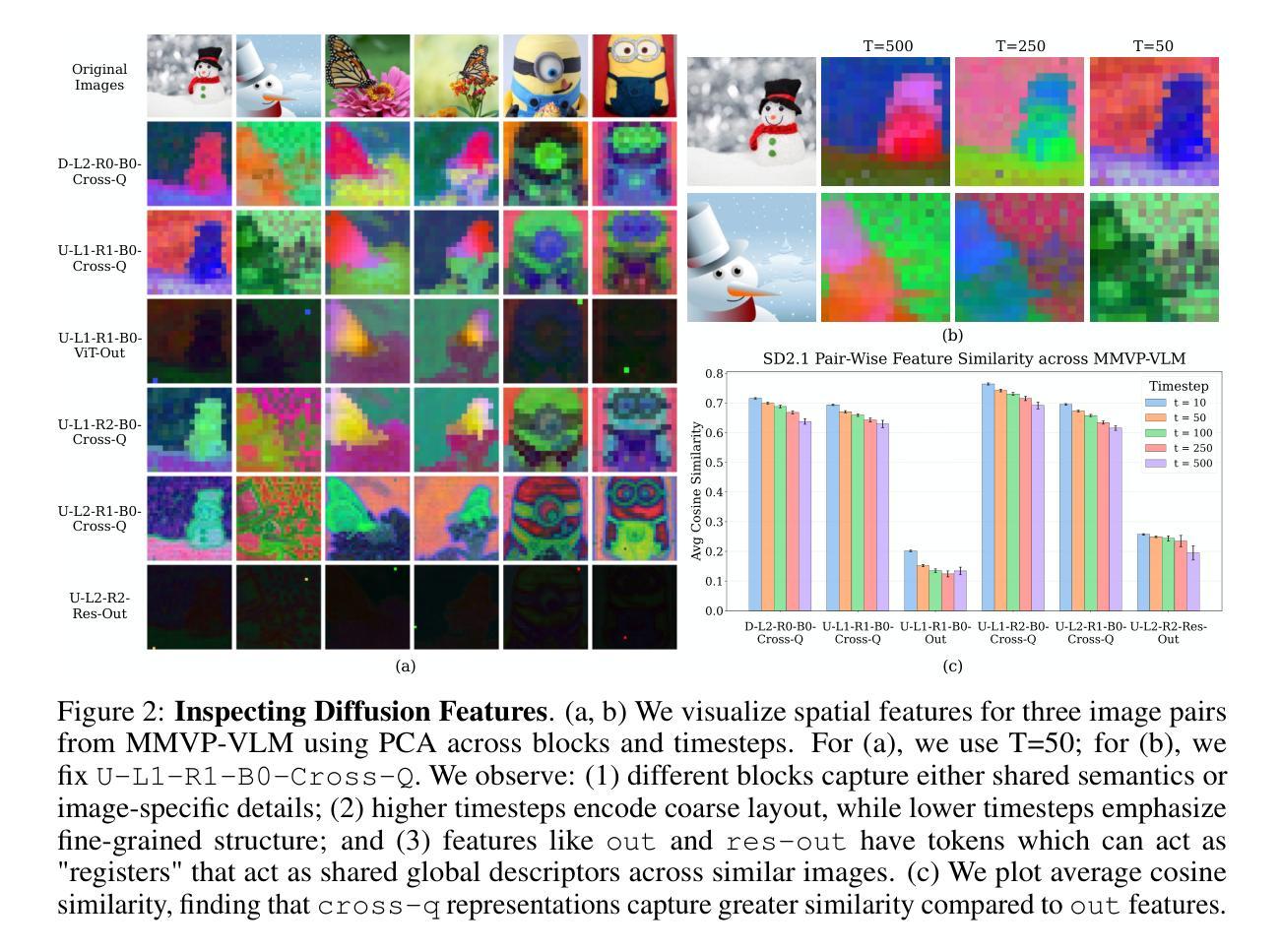
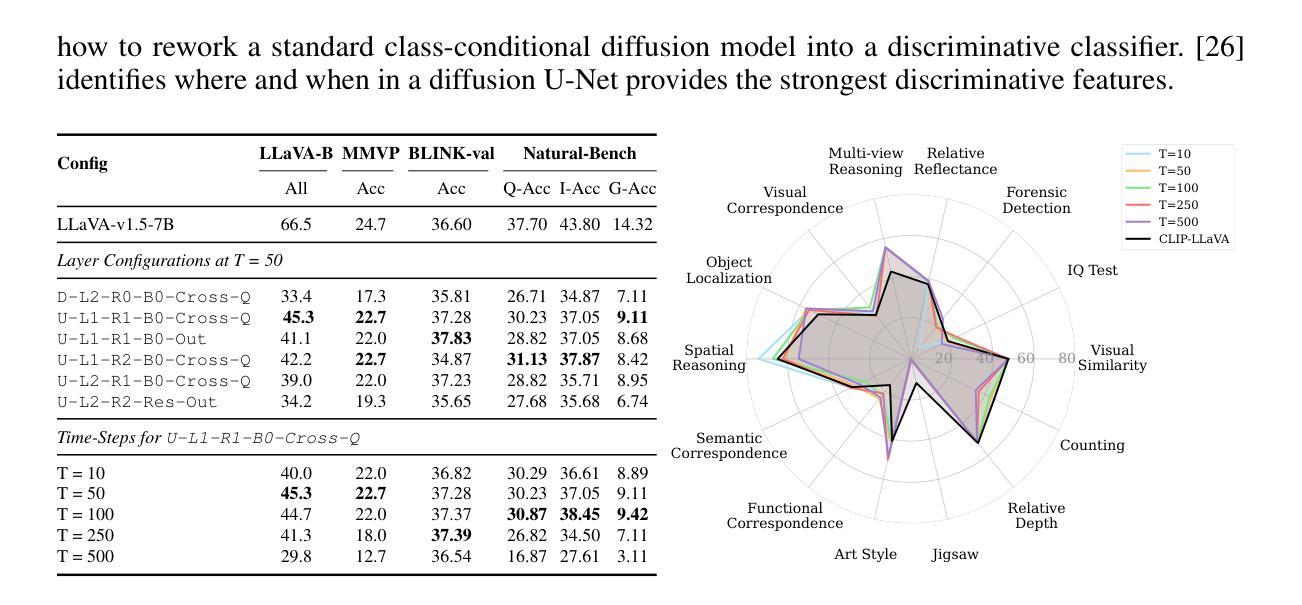
Recent advances in multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have enabled image-based question-answering capabilities. However, a key limitation is the use of CLIP as the visual encoder; while it can capture coarse global information, it often can miss fine-grained details that are relevant to the input query. To address these shortcomings, this work studies whether pre-trained text-to-image diffusion models can serve as instruction-aware visual encoders. Through an analysis of their internal representations, we find diffusion features are both rich in semantics and can encode strong image-text alignment. Moreover, we find that we can leverage text conditioning to focus the model on regions relevant to the input question. We then investigate how to align these features with large language models and uncover a leakage phenomenon, where the LLM can inadvertently recover information from the original diffusion prompt. We analyze the causes of this leakage and propose a mitigation strategy. Based on these insights, we explore a simple fusion strategy that utilizes both CLIP and conditional diffusion features. We evaluate our approach on both general VQA and specialized MLLM benchmarks, demonstrating the promise of diffusion models for visual understanding, particularly in vision-centric tasks that require spatial and compositional reasoning. Our project page can be found https://vatsalag99.github.io/mustafar/.
近期多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的进步已经实现了基于图像的问答功能。然而,一个关键限制是使用CLIP作为视觉编码器;虽然它可以捕捉粗糙的全局信息,但它经常会错过与输入查询相关的细微细节。为了解决这些缺点,这项工作研究了预训练文本到图像扩散模型是否可以作为指令感知的视觉编码器。通过对它们内部表示的分析,我们发现扩散特征既丰富语义,又能编码强大的图像文本对齐。此外,我们发现可以利用文本条件来使模型关注与输入问题相关的区域。然后,我们研究了如何将这些特征与大型语言模型对齐,并发现了一个泄露现象,其中LLM可能无意中从原始的扩散提示中恢复信息。我们分析了泄露的原因并提出了缓解策略。基于这些见解,我们探索了一种简单的融合策略,利用CLIP和条件扩散特征。我们在通用的VQA和专门的MLLM基准上评估了我们的方法,证明了扩散模型在视觉理解方面的潜力,特别是在需要空间和理解组合推理的以视觉为中心的任务中。我们的项目页面可在https://vatsalag99.github.io/mustafar/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Website: see https://vatsalag99.github.io/mustafar/
Summary
最新研究利用预训练的文本到图像扩散模型作为指令感知视觉编码器,以改进基于图像的问答系统。研究发现扩散模型特征丰富,既可进行图像文本对齐,又能通过文本条件使模型关注与输入问题相关的区域。然而,存在信息泄露现象,大型语言模型可能无意中从扩散提示中恢复信息。研究提出了缓解策略,并探索了结合CLIP和条件扩散特征的方法。该策略在一般问答和特定的大型语言模型基准测试中表现优异,显示出扩散模型在视觉理解方面的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)已具备图像问答能力,但使用CLIP作为视觉编码器存在局限性。
- 扩散模型特征丰富,可进行图像文本对齐。
- 通过文本条件使模型关注与输入问题相关的区域。
- 大型语言模型可能会从扩散提示中恢复信息,存在信息泄露现象。
- 研究提出了信息泄露的缓解策略。
- 结合CLIP和条件扩散特征的方法在视觉理解方面表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

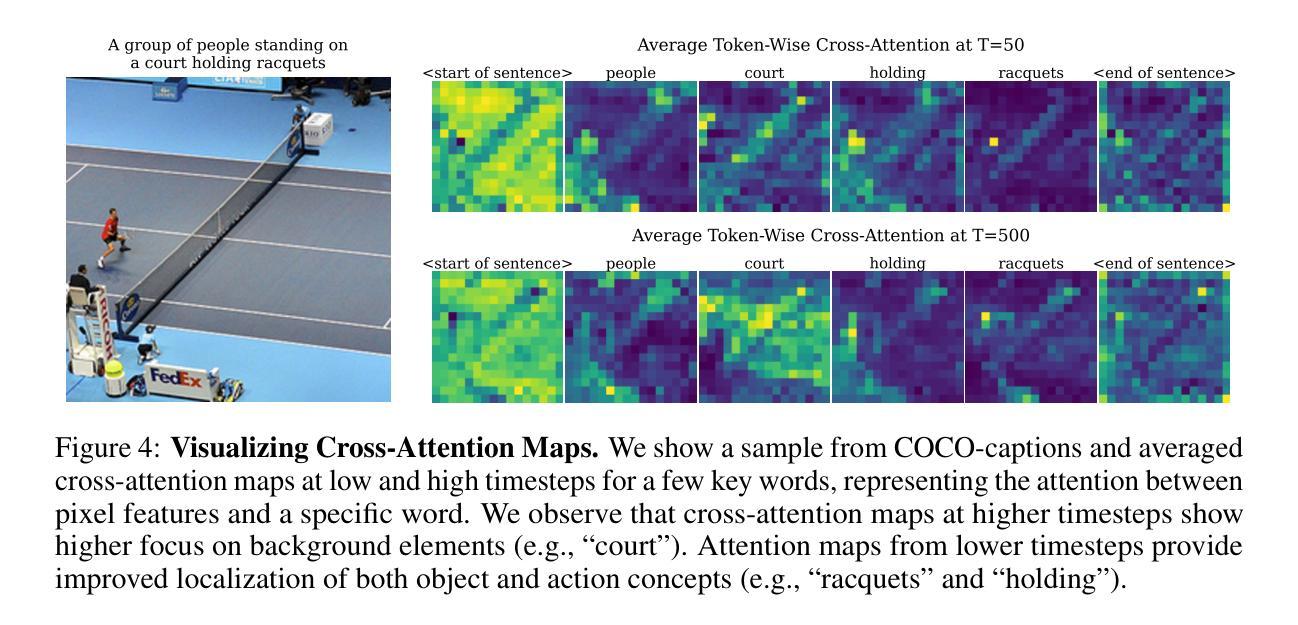
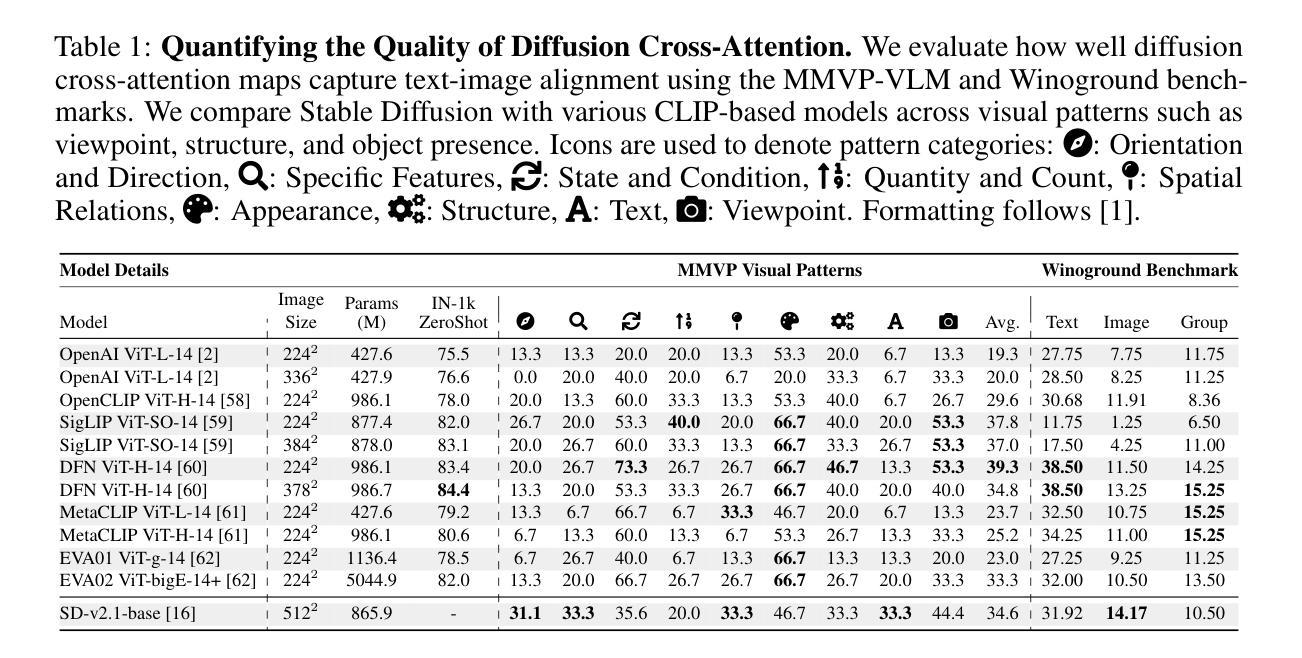
Vision-Language-Vision Auto-Encoder: Scalable Knowledge Distillation from Diffusion Models
Authors:Tiezheng Zhang, Yitong Li, Yu-cheng Chou, Jieneng Chen, Alan Yuille, Chen Wei, Junfei Xiao
Building state-of-the-art Vision-Language Models (VLMs) with strong captioning capabilities typically necessitates training on billions of high-quality image-text pairs, requiring millions of GPU hours. This paper introduces the Vision-Language-Vision (VLV) auto-encoder framework, which strategically leverages key pretrained components: a vision encoder, the decoder of a Text-to-Image (T2I) diffusion model, and subsequently, a Large Language Model (LLM). Specifically, we establish an information bottleneck by regularizing the language representation space, achieved through freezing the pretrained T2I diffusion decoder. Our VLV pipeline effectively distills knowledge from the text-conditioned diffusion model using continuous embeddings, demonstrating comprehensive semantic understanding via high-quality reconstructions. Furthermore, by fine-tuning a pretrained LLM to decode the intermediate language representations into detailed descriptions, we construct a state-of-the-art (SoTA) captioner comparable to leading models like GPT-4o and Gemini 2.0 Flash. Our method demonstrates exceptional cost-efficiency and significantly reduces data requirements; by primarily utilizing single-modal images for training and maximizing the utility of existing pretrained models (image encoder, T2I diffusion model, and LLM), it circumvents the need for massive paired image-text datasets, keeping the total training expenditure under $1,000 USD.
构建具有强大描述功能的最先进的视觉语言模型(VLM)通常需要训练数十亿个高质量的图片文本对,这需要数百万的GPU小时。本文介绍了视觉语言视觉(VLV)自动编码器框架,该框架战略性地利用了关键预训练组件:视觉编码器、文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型的解码器,以及随后的大型语言模型(LLM)。具体来说,我们通过正则化语言表示空间来建立信息瓶颈,这是通过冻结预训练的T2I扩散解码器来实现的。我们的VLV管道有效地从文本条件扩散模型中蒸馏知识,使用连续嵌入来展示高质量重构的综合语义理解。此外,我们通过微调预训练的大型语言模型来解码中间语言表示形式以生成详细描述,从而构建了一个与GPT-4o和Gemini 2.0 Flash等领先模型相当的最先进的描述器。我们的方法展示了卓越的成本效益,大大降低了数据要求;主要通过使用单模态图像进行训练并最大限度地利用现有的预训练模型(图像编码器、T2I扩散模型和LLM),从而避免了大规模配对图像文本数据集的需求,将总训练费用保持在1000美元以下。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了Vision-Language-Vision(VLV)自编码器框架,通过战略性地利用关键预训练组件,如视觉编码器、文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型的解码器以及大型语言模型(LLM),实现了具有强大描述能力的先进视觉语言模型(VLM)的构建。该方法通过正则化语言表示空间建立信息瓶颈,利用文本条件扩散模型的知识蒸馏,并通过微调LLM来解码中间语言表示,从而生成详细的描述。此方法具有卓越的成本效益,显著减少了数据需求,主要使用单模态图像进行训练,并最大限度地利用现有预训练模型,无需大规模配对图像文本数据集,总训练费用低于1000美元。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了Vision-Language-Vision(VLV)自编码器框架,实现了具有强大描述能力的视觉语言模型(VLM)。
- 利用预训练组件:视觉编码器、文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型的解码器和大型语言模型(LLM)。
- 通过正则化语言表示空间建立信息瓶颈,提高模型性能。
- 利用文本条件扩散模型的知识蒸馏。
- 通过微调LLM生成高质量描述。
- 方法具有卓越的成本效益,显著减少数据需求。
点此查看论文截图

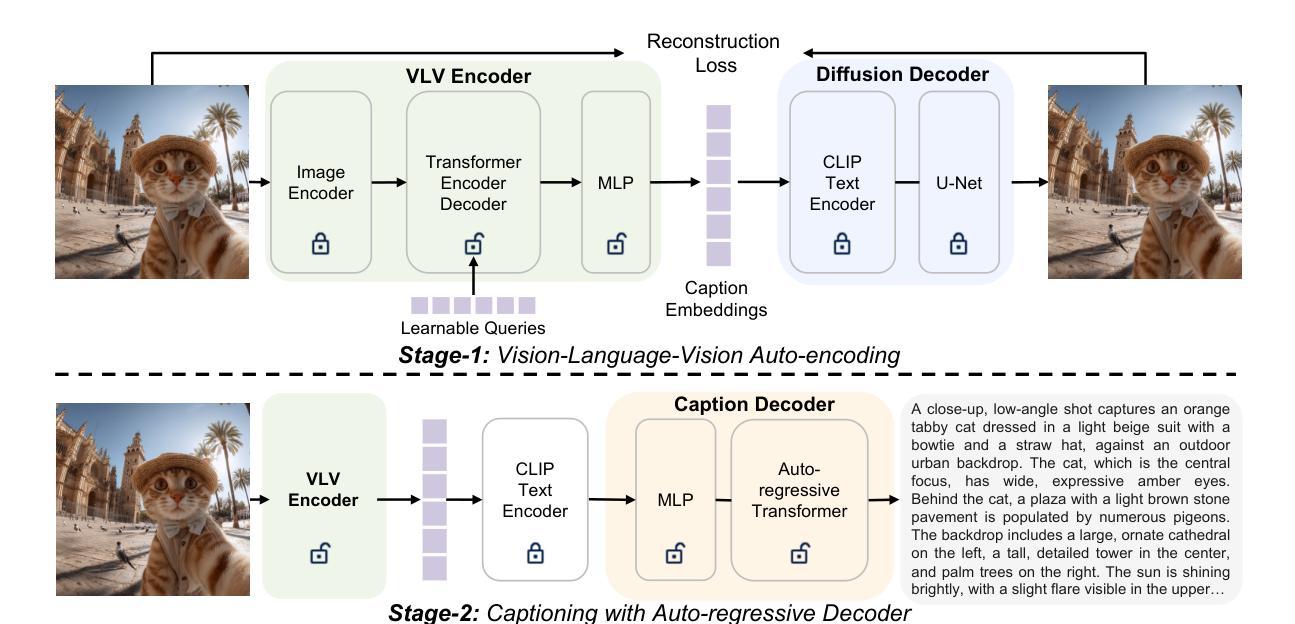

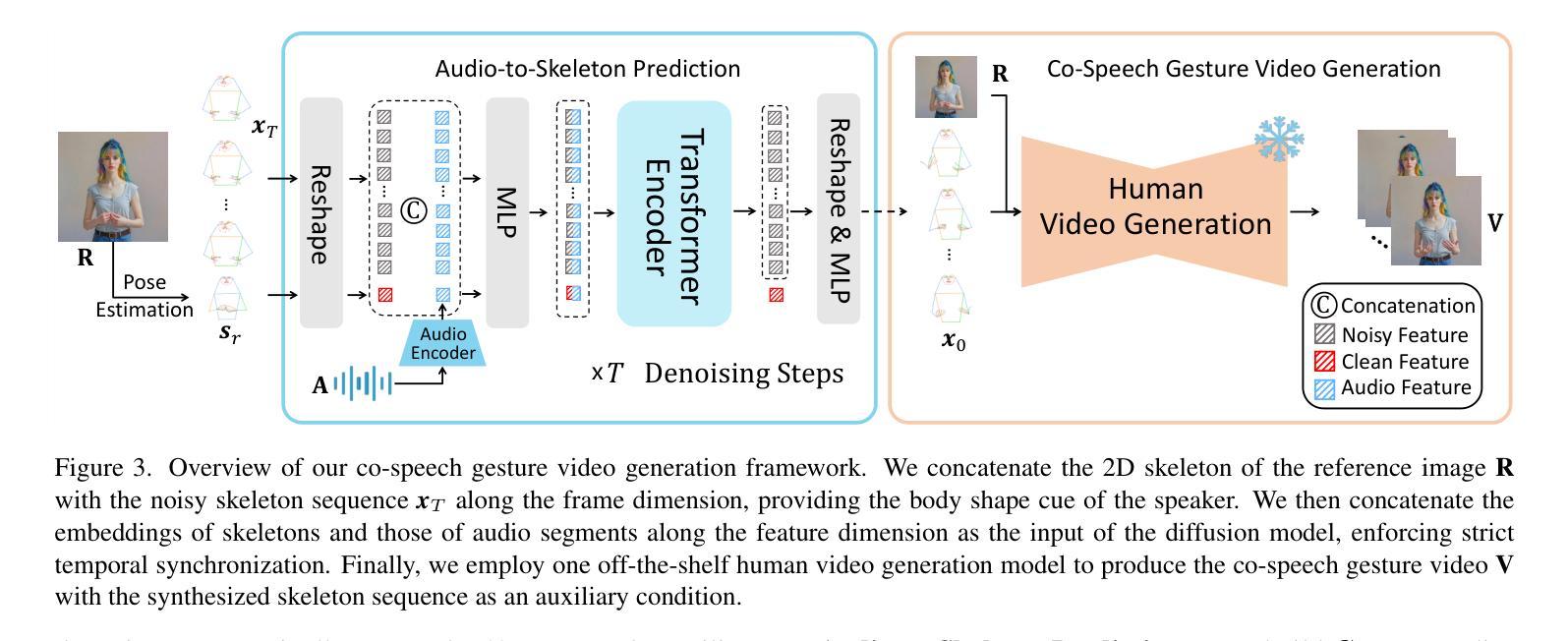
Democratizing High-Fidelity Co-Speech Gesture Video Generation
Authors:Xu Yang, Shaoli Huang, Shenbo Xie, Xuelin Chen, Yifei Liu, Changxing Ding
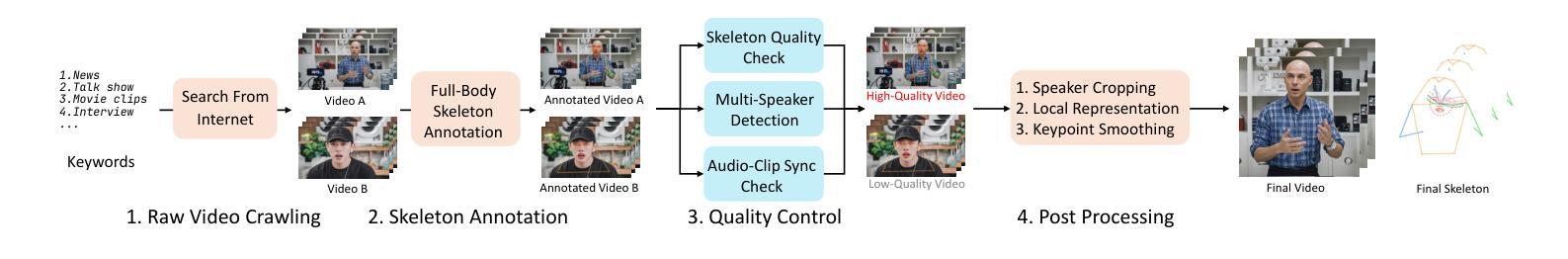
Co-speech gesture video generation aims to synthesize realistic, audio-aligned videos of speakers, complete with synchronized facial expressions and body gestures. This task presents challenges due to the significant one-to-many mapping between audio and visual content, further complicated by the scarcity of large-scale public datasets and high computational demands. We propose a lightweight framework that utilizes 2D full-body skeletons as an efficient auxiliary condition to bridge audio signals with visual outputs. Our approach introduces a diffusion model conditioned on fine-grained audio segments and a skeleton extracted from the speaker’s reference image, predicting skeletal motions through skeleton-audio feature fusion to ensure strict audio coordination and body shape consistency. The generated skeletons are then fed into an off-the-shelf human video generation model with the speaker’s reference image to synthesize high-fidelity videos. To democratize research, we present CSG-405-the first public dataset with 405 hours of high-resolution videos across 71 speech types, annotated with 2D skeletons and diverse speaker demographics. Experiments show that our method exceeds state-of-the-art approaches in visual quality and synchronization while generalizing across speakers and contexts.
协同语音手势视频生成旨在合成与音频对齐的逼真视频,包含说话者的面部表情和体态动作。此任务面临挑战,原因在于音频和视觉内容之间的一到多映射关系,再加上大规模公开数据集的稀缺和高计算需求。我们提出了一个轻量级的框架,利用2D全身骨架作为有效的辅助条件来连接音频信号和视觉输出。我们的方法引入了一个扩散模型,该模型根据精细的音频片段和从说话者的参考图像中提取的骨架进行条件处理,通过骨架音频特征融合来预测骨骼运动,以确保严格的音频协调和身体形状一致性。生成的骨架然后输入到带有说话者参考图像的人像视频生成模型中,合成高保真视频。为了推动研究民主化,我们推出了CSG-405数据集——第一个公共数据集,包含71种语音类型的405小时高分辨率视频,标注了2D骨架和多样的说话者人口统计数据。实验表明,我们的方法在视觉质量和同步方面超过了最先进的方法,并且在跨说话者和上下文方面具有很好的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025
Summary
本文提出一种基于扩散模型的协同语音手势视频生成框架,利用二维全身骨骼作为辅助条件,将音频信号与视觉输出相连接。该方法通过精细音频片段和从参考图像中提取的骨骼进行特征融合,预测骨骼运动,确保严格的音频协调和体态一致性。生成的骨骼数据将输入到现成的视频生成模型中,结合参考图像合成高质量视频。为推进研究,本文还发布了首个公共数据集CSG-405,包含405小时的高分辨率视频,涵盖71种语音类型,并标注了二维骨骼和多样的演讲者特征。实验表明,该方法在视觉质量和同步性方面超过了现有技术,并在不同演讲者和语境中具有良好的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 协同语音手势视频生成旨在合成与音频同步的、逼真的视频,包括面部表达和体态。
- 该任务面临音频与视觉内容之间一对一映射的难题,以及大规模公共数据集缺乏和计算需求高的挑战。
- 提出了一个基于扩散模型的轻量级框架,利用二维全身骨骼作为音频和视觉之间的桥梁。
- 框架通过精细音频片段和参考图像中的骨骼特征融合来预测骨骼运动。
- 发布了首个公共数据集CSG-405,包含标注的二维骨骼和多样的演讲者特征。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在视觉质量和同步性能上超越现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

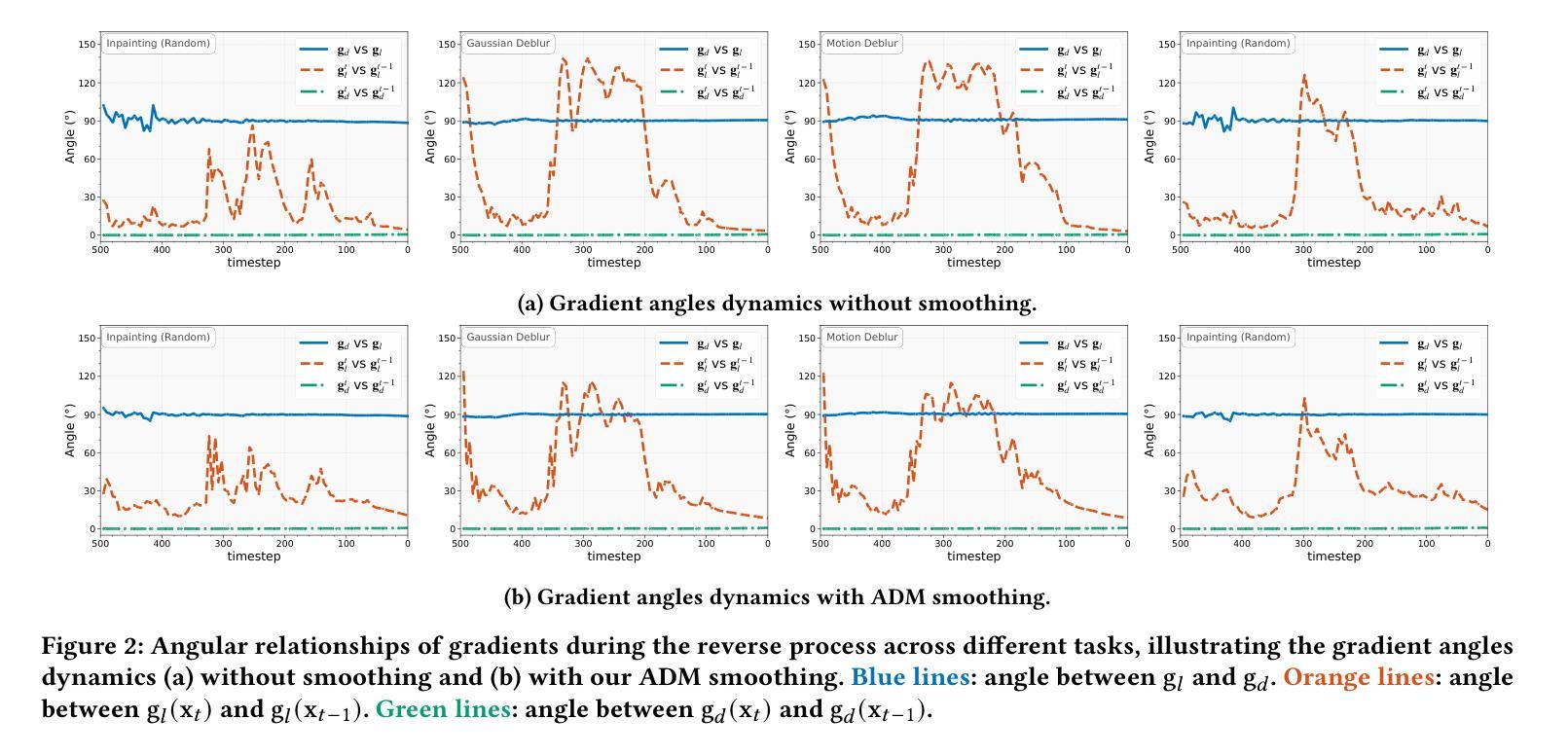
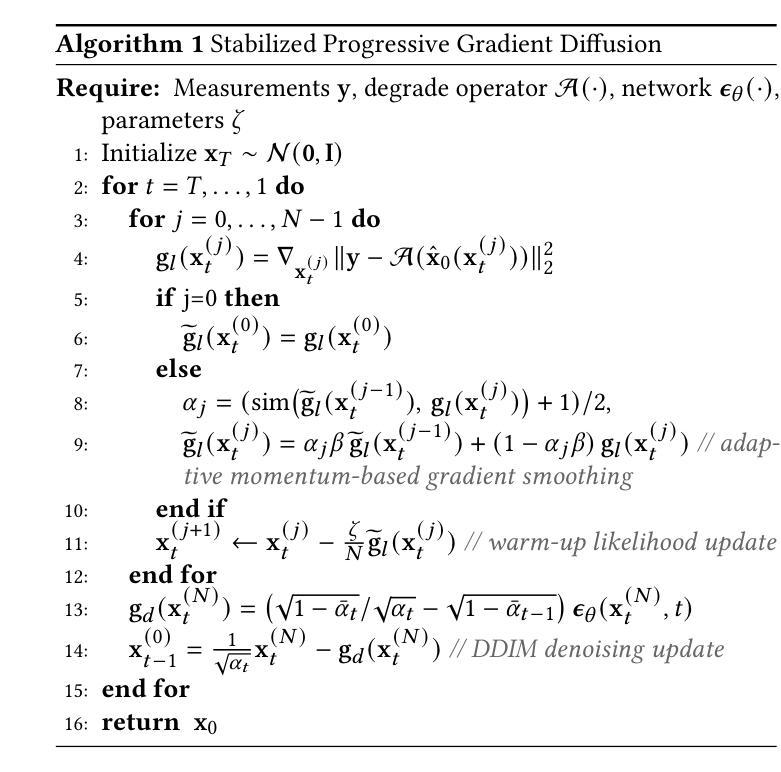
Enhancing Diffusion Model Stability for Image Restoration via Gradient Management
Authors:Hongjie Wu, Mingqin Zhang, Linchao He, Ji-Zhe Zhou, Jiancheng Lv
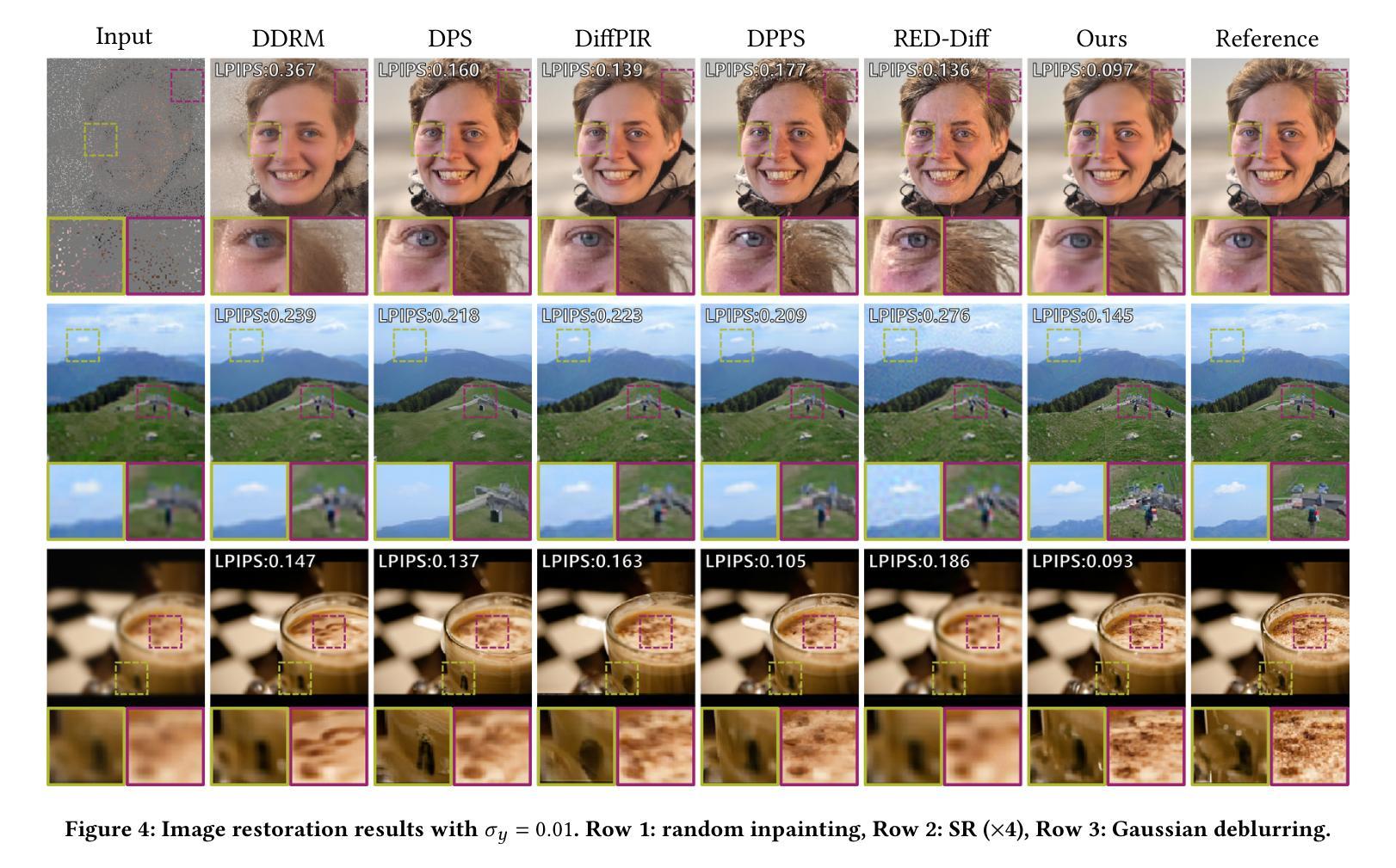
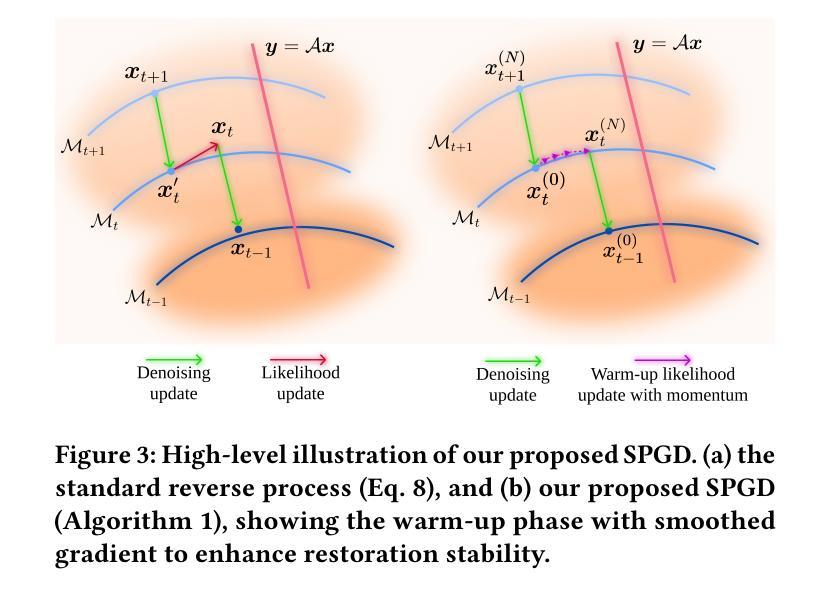
Diffusion models have shown remarkable promise for image restoration by leveraging powerful priors. Prominent methods typically frame the restoration problem within a Bayesian inference framework, which iteratively combines a denoising step with a likelihood guidance step. However, the interactions between these two components in the generation process remain underexplored. In this paper, we analyze the underlying gradient dynamics of these components and identify significant instabilities. Specifically, we demonstrate conflicts between the prior and likelihood gradient directions, alongside temporal fluctuations in the likelihood gradient itself. We show that these instabilities disrupt the generative process and compromise restoration performance. To address these issues, we propose Stabilized Progressive Gradient Diffusion (SPGD), a novel gradient management technique. SPGD integrates two synergistic components: (1) a progressive likelihood warm-up strategy to mitigate gradient conflicts; and (2) adaptive directional momentum (ADM) smoothing to reduce fluctuations in the likelihood gradient. Extensive experiments across diverse restoration tasks demonstrate that SPGD significantly enhances generation stability, leading to state-of-the-art performance in quantitative metrics and visually superior results. Code is available at \href{https://github.com/74587887/SPGD}{here}.
扩散模型通过利用强大的先验信息在图像修复领域展现出巨大的潜力。显著的方法通常在贝叶斯推断框架下构建修复问题,该框架迭代地将去噪步骤与似然引导步骤相结合。然而,生成过程中这两个组件之间的交互仍然未被充分探索。在本文中,我们分析了这些组件的底层梯度动态,并识别出重大不稳定因素。具体来说,我们展示了先验和似然梯度方向之间的冲突,以及似然梯度本身的暂时波动。我们表明,这些不稳定因素破坏了生成过程并影响了修复性能。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了稳定的渐进梯度扩散(SPGD),这是一种新型的梯度管理技术。SPGD集成两个协同组件:(1)渐进的似然预热策略,以缓解梯度冲突;(2)自适应方向动量(ADM)平滑,以减少似然梯度的波动。在多种修复任务上的广泛实验表明,SPGD显著提高了生成稳定性,在定量指标上达到了最先进的性能,并在视觉上产生了更优质的结果。代码可在https://github.com/74587887/SPGD获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ACM Multimedia 2025. Preprint version
Summary
本文探讨了扩散模型在图像修复中的潜力,分析了现有方法中的梯度动态问题,并提出了稳定的渐进梯度扩散(SPGD)技术来解决这些问题。通过采用渐进可能性预热策略和自适应方向动量平滑技术,SPGD增强了生成过程的稳定性,显著提高了图像修复的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型利用先验知识在图像修复中展现出巨大潜力。
- 现有方法通常在贝叶斯推断框架下解决修复问题,结合去噪和似然性指导步骤。
- 论文分析了现有方法中的梯度动态问题,特别是先验和似然性梯度方向的冲突,以及似然性梯度本身的时空波动。
- 这些问题会破坏生成过程并影响修复性能。
- 为了解决这些问题,论文提出了稳定的渐进梯度扩散(SPGD)技术。
- SPGD包括两个协同组件:渐进的似然性预热策略,用于缓解梯度冲突;自适应方向动量(ADM)平滑,用于减少似然性梯度波动。
点此查看论文截图


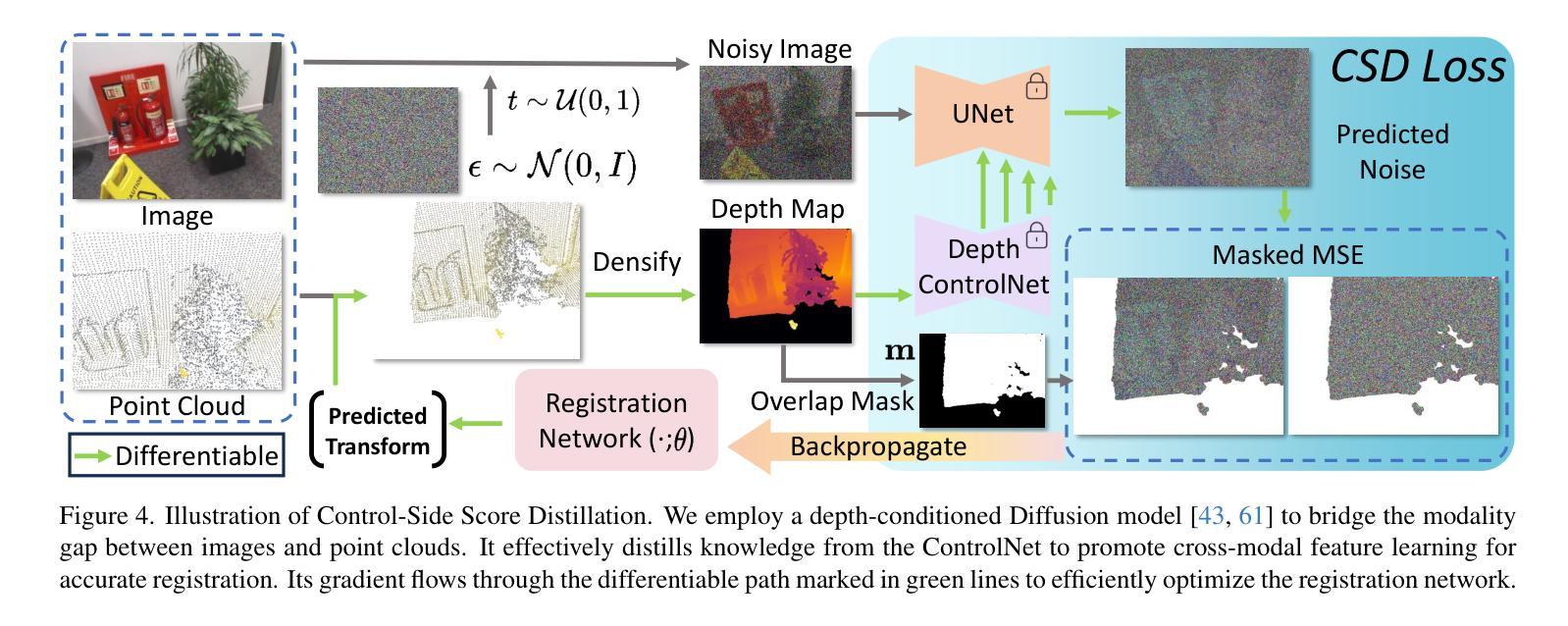
Diff$^2$I2P: Differentiable Image-to-Point Cloud Registration with Diffusion Prior
Authors:Juncheng Mu, Chengwei Ren, Weixiang Zhang, Liang Pan, Xiao-Ping Zhang, Yue Gao
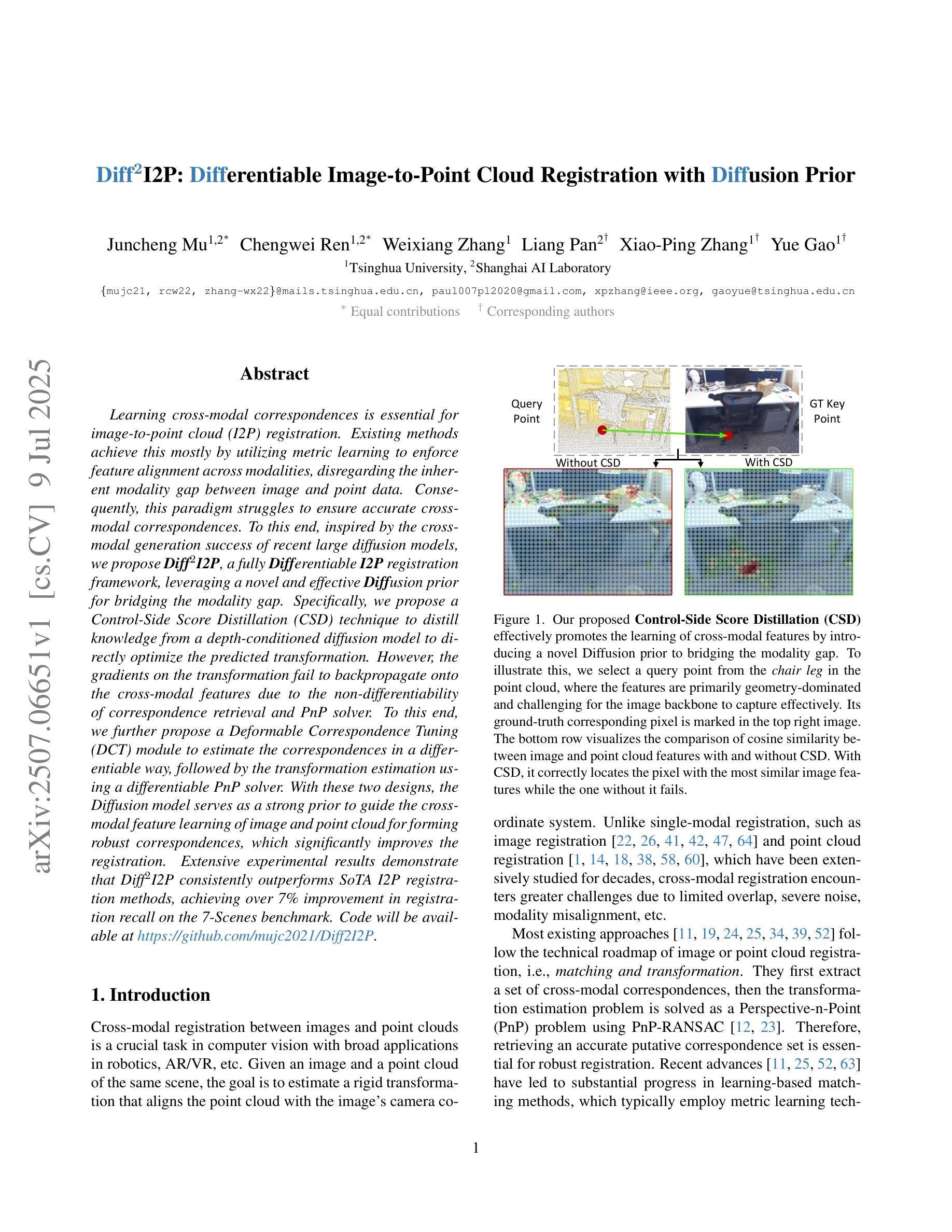
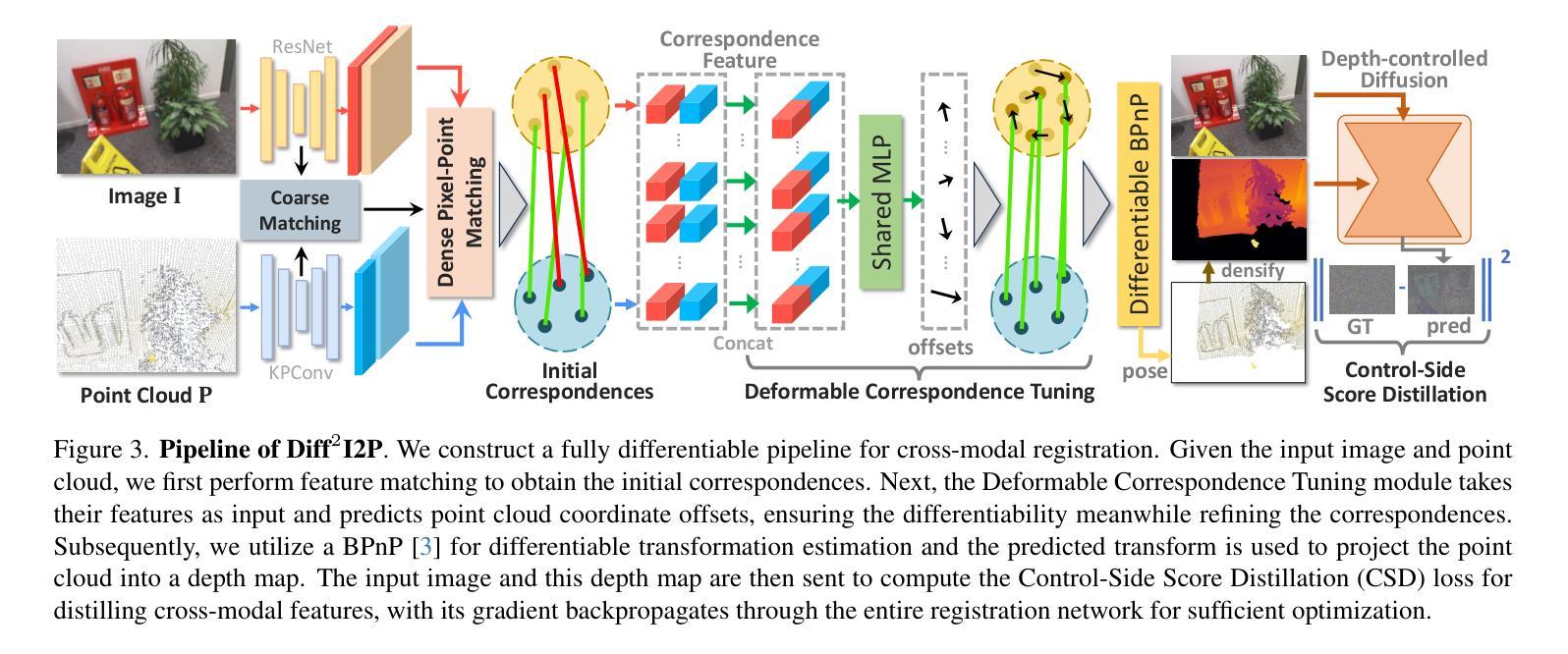
Learning cross-modal correspondences is essential for image-to-point cloud (I2P) registration. Existing methods achieve this mostly by utilizing metric learning to enforce feature alignment across modalities, disregarding the inherent modality gap between image and point data. Consequently, this paradigm struggles to ensure accurate cross-modal correspondences. To this end, inspired by the cross-modal generation success of recent large diffusion models, we propose Diff$^2$I2P, a fully Differentiable I2P registration framework, leveraging a novel and effective Diffusion prior for bridging the modality gap. Specifically, we propose a Control-Side Score Distillation (CSD) technique to distill knowledge from a depth-conditioned diffusion model to directly optimize the predicted transformation. However, the gradients on the transformation fail to backpropagate onto the cross-modal features due to the non-differentiability of correspondence retrieval and PnP solver. To this end, we further propose a Deformable Correspondence Tuning (DCT) module to estimate the correspondences in a differentiable way, followed by the transformation estimation using a differentiable PnP solver. With these two designs, the Diffusion model serves as a strong prior to guide the cross-modal feature learning of image and point cloud for forming robust correspondences, which significantly improves the registration. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that Diff$^2$I2P consistently outperforms SoTA I2P registration methods, achieving over 7% improvement in registration recall on the 7-Scenes benchmark.
学习跨模态对应关系对于图像到点云(I2P)注册至关重要。现有方法主要通过利用度量学习来强制执行跨模态的特征对齐来实现这一目标,忽略了图像和点数据之间固有的模态差距。因此,这种范式难以确保准确的跨模态对应关系。鉴于此,受近期大型扩散模型在跨模态生成方面成功的启发,我们提出了Diff$^2$I2P,这是一个完全可微分的I2P注册框架,利用新型有效的扩散先验来弥合模态差距。具体来说,我们提出了一种控制侧分数蒸馏(CSD)技术,从深度条件扩散模型中提炼知识以直接优化预测的变换。然而,由于对应检索和PnP求解器的不可微性,变换上的梯度无法反向传播到跨模态特征。为此,我们进一步提出了可变形对应调整(DCT)模块,以可微分的方式估计对应,然后使用可微分PnP求解器进行变换估计。通过这两种设计,扩散模型充当了一个强大的先验来指导图像和点云的跨模态特征学习,形成稳健的对应关系,这显著提高了注册效果。大量实验结果表明,Diff$^2$I2P持续超越最新技术I2P注册方法,在7场景基准测试上注册召回率提高了超过7%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025
Summary
本文为了解决图像到点云(I2P)注册中的跨模态对应问题,提出了Diff$^2$I2P框架。该框架利用扩散模型作为强先验,通过Control-Side Score Distillation(CSD)技术优化预测转换。为解决对应检索和PnP求解器的不可微性,进一步提出了Deformable Correspondence Tuning(DCT)模块以可微方式估计对应关系,并使用可微PnP求解器进行转换估计。该框架在跨模态特征学习中实现了稳健的对应关系,显著提高了注册性能,并在7-Scenes基准测试中实现了超过现有技术7%的注册召回率提升。
Key Takeaways
- 解决图像到点云(I2P)注册中的跨模态对应问题是关键。
- 现有方法主要通过度量学习实现特征对齐,但忽略了模态间的固有差距。
- Diff$^2$I2P框架利用扩散模型作为强先验,通过CSD技术优化预测转换。
- DCT模块以可微方式估计对应关系,解决对应检索和PnP求解器的不可微性问题。
- 扩散模型在跨模态特征学习中起到重要作用,形成稳健的对应关系。
- 该框架在注册性能上显著优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图
FedPhD: Federated Pruning with Hierarchical Learning of Diffusion Models
Authors:Qianyu Long, Qiyuan Wang, Christos Anagnostopoulos, Daning Bi
Federated Learning (FL), as a distributed learning paradigm, trains models over distributed clients’ data. FL is particularly beneficial for distributed training of Diffusion Models (DMs), which are high-quality image generators that require diverse data. However, challenges such as high communication costs and data heterogeneity persist in training DMs similar to training Transformers and Convolutional Neural Networks. Limited research has addressed these issues in FL environments. To address this gap and challenges, we introduce a novel approach, FedPhD, designed to efficiently train DMs in FL environments. FedPhD leverages Hierarchical FL with homogeneity-aware model aggregation and selection policy to tackle data heterogeneity while reducing communication costs. The distributed structured pruning of FedPhD enhances computational efficiency and reduces model storage requirements in clients. Our experiments across multiple datasets demonstrate that FedPhD achieves high model performance regarding Fr'echet Inception Distance (FID) scores while reducing communication costs by up to $88%$. FedPhD outperforms baseline methods achieving at least a $34%$ improvement in FID, while utilizing only $56%$ of the total computation and communication resources.
联邦学习(FL)作为一种分布式学习范式,能够在分布式客户端数据上训练模型。对于需要多样化数据的扩散模型(DMs)的高质量图像生成来说,FL特别有益。然而,与训练Transformer和卷积神经网络类似,训练DMs也存在高通信成本和数据异质性的挑战。针对联邦学习环境中的这些问题进行的研究有限。为了解决这一空白以及面临的挑战,我们引入了一种新型方法FedPhD,旨在在联邦学习环境中有效地训练DMs。FedPhD利用分层联邦学习、同质性感知模型聚合和选择策略来解决数据异质性问题,同时降低通信成本。FedPhD的分布式结构化剪枝提高了计算效率,降低了客户端的模型存储需求。我们在多个数据集上的实验表明,FedPhD在降低通信成本高达88%的同时,实现了高水平的模型性能,在Fréchet Inception Distance(FID)得分方面表现出色。FedPhD优于基线方法,在FID上至少提高了34%,同时仅使用56%的总计算和通信资源。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 8 figures, 5 tables. This paper introduces FedPhD, a novel hierarchical federated learning framework for training diffusion models that addresses data heterogeneity and communication costs through homogeneity-aware aggregation and structured pruning. Submitted to IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics and is under review
Summary
在分布式环境下,Federated Learning(FL)为训练Diffusion Models(DMs)提供了有效方案,尤其对于需要多样化数据的高品质图像生成器来说。然而,FL环境中训练DMs面临高通信成本和数据异构性的挑战。为解决这些问题,我们提出了FedPhD方法,它通过利用分层FL和同构感知模型聚合与选择策略来应对数据异构性并降低通信成本。实验证明,FedPhD在降低通信成本的同时,实现了高模型性能,并显著优于基线方法。
Key Takeaways
- Federated Learning (FL) 在训练Diffusion Models (DMs)时具有优势,特别是对于需要多样化数据的高品质图像生成器。
- FL环境中训练DMs面临高通信成本和数据异构性的挑战。
- FedPhD方法旨在高效地在FL环境中训练DMs。
- FedPhD利用分层FL和同构感知模型聚合与选择策略来解决数据异构性问题并降低通信成本。
- FedPhD通过分布式结构化剪枝提高计算效率并减少客户端的模型存储需求。
- 实验证明FedPhD在降低通信成本的同时,实现了高模型性能。
点此查看论文截图


Mitigating Multi-Sequence 3D Prostate MRI Data Scarcity through Domain Adaptation using Locally-Trained Latent Diffusion Models for Prostate Cancer Detection
Authors:Emerson P. Grabke, Babak Taati, Masoom A. Haider
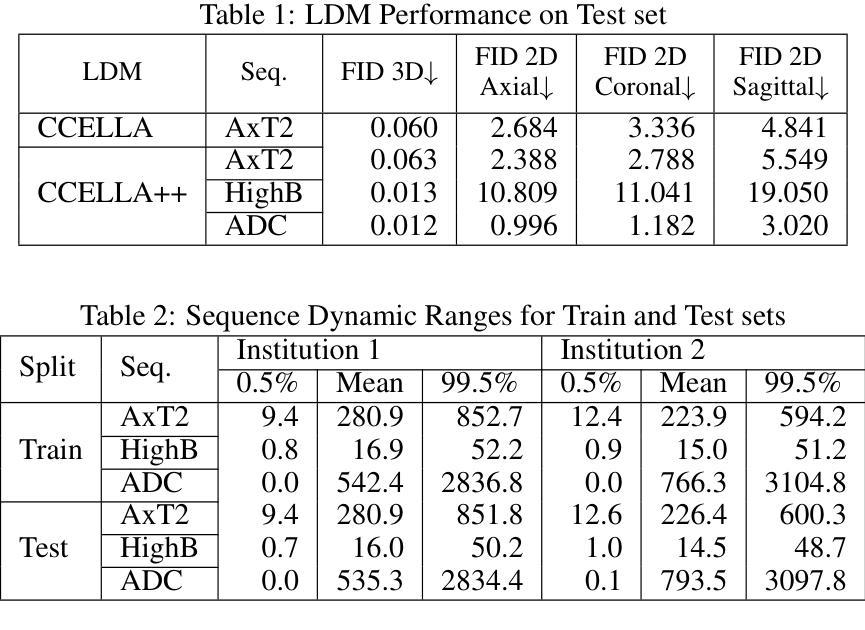
Objective: Latent diffusion models (LDMs) could mitigate data scarcity challenges affecting machine learning development for medical image interpretation. The recent CCELLA LDM improved prostate cancer detection performance using synthetic MRI for classifier training but was limited to the axial T2-weighted (AxT2) sequence, did not investigate inter-institutional domain shift, and prioritized radiology over histopathology outcomes. We propose CCELLA++ to address these limitations and improve clinical utility. Methods: CCELLA++ expands CCELLA for simultaneous biparametric prostate MRI (bpMRI) generation, including the AxT2, high b-value diffusion series (HighB) and apparent diffusion coefficient map (ADC). Domain adaptation was investigated by pretraining classifiers on real or LDM-generated synthetic data from an internal institution, followed with fine-tuning on progressively smaller fractions of an out-of-distribution, external dataset. Results: CCELLA++ improved 3D FID for HighB and ADC but not AxT2 (0.013, 0.012, 0.063 respectively) sequences compared to CCELLA (0.060). Classifier pretraining with CCELLA++ bpMRI outperformed real bpMRI in AP and AUC for all domain adaptation scenarios. CCELLA++ pretraining achieved highest classifier performance below 50% (n=665) external dataset volume. Conclusion: Synthetic bpMRI generated by our method can improve downstream classifier generalization and performance beyond real bpMRI or CCELLA-generated AxT2-only images. Future work should seek to quantify medical image sample quality, balance multi-sequence LDM training, and condition the LDM with additional information. Significance: The proposed CCELLA++ LDM can generate synthetic bpMRI that outperforms real data for domain adaptation with a limited target institution dataset. Our code is available at https://github.com/grabkeem/CCELLA-plus-plus
目标:潜在扩散模型(LDM)可以缓解影响医学图像解释机器学习发展的数据稀缺挑战。最近的CCELLA LDM使用合成MRI提高了前列腺癌检测性能,用于分类器训练,但仅限于轴T2加权(AxT2)序列,没有研究跨机构领域转移,并优先于放射学而非组织病理学结果。我们提出CCELLA++来解决这些限制并提高临床实用性。方法:CCELLA++扩展了CCELLA,用于同时生成双参数前列腺MRI(bpMRI),包括AxT2、高b值扩散系列(HighB)和扩散系数图(ADC)。通过预训练分类器在内部机构的真实或LDM生成合成数据上,然后在逐渐较小的外部数据集部分上进行微调,来研究领域适应性问题。结果:与CCELLA相比,CCELLA++改进了HighB和ADC的3D FID(分别为0.013和0.012),而AxT2序列没有改进(为0.063)。使用CCELLA++ bpMRI预训练的分类器在所有领域适应场景中,其AP和AUC均优于真实bpMRI。当外部数据集体积低于50%(n=665)时,CCELLA++预训练达到最佳分类器性能。结论:通过我们的方法生成的合成bpMRI可以提高下游分类器的泛化和性能,超越了真实bpMRI或CCELLA生成的仅AxT2图像。未来的工作应致力于量化医学图像样本质量,平衡多序列LDM训练,并用额外信息调整LDM。意义:所提出的CCELLA++ LDM可以生成合成bpMRI,在有限的特定机构数据集上实现领域适应性的超越真实数据表现。我们的代码可在https://github.com/grabkeem/CCELLA-plus-plus找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF BT and MAH are co-senior authors on the work. This work has been submitted to the IEEE for possible publication
Summary
本文介绍了潜在扩散模型(Latent Diffusion Models,简称LDMs)在解决医学影像解读中数据稀缺挑战方面的应用。针对原有CCELLA模型在前列腺癌症检测中的局限性,提出了CCELLA++模型。该模型不仅扩展了原有的单序列生成能力,实现了双参数前列腺MRI(bpMRI)的生成,并进行了跨机构域适应性的研究。实验结果表明,CCELLA++生成的合成bpMRI在分类器预训练中的表现超越了真实bpMRI数据,特别是在外部数据集体积较小的情况下。该模型的代码已公开于GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- CCELLA++扩展了原有的CCELLA模型,实现了双参数前列腺MRI(bpMRI)的生成,包括AxT2、HighB和ADC序列。
- CCELLA++进行了跨机构域适应性的研究,通过预训练分类器以适应不同机构的数据集。
- 实验结果表明,CCELLA++生成的合成bpMRI数据在分类器预训练中的表现优于真实bpMRI数据。
- 在外部数据集体积较小的情况下,CCELLA++预训练的分类器性能最佳。
- CCELLA++模型公开的代码可供其他研究者使用。
- 未来的研究应关注量化医学图像样本质量,平衡多序列LDM训练,以及通过额外信息调整LDM。
- LDM的引入有助于解决医学影像解读中数据稀缺的问题,具有潜在的临床应用价值。
点此查看论文截图

CultureCLIP: Empowering CLIP with Cultural Awareness through Synthetic Images and Contextualized Captions
Authors:Yuchen Huang, Zhiyuan Fan, Zhitao He, Sandeep Polisetty, Wenyan Li, Yi R. Fung
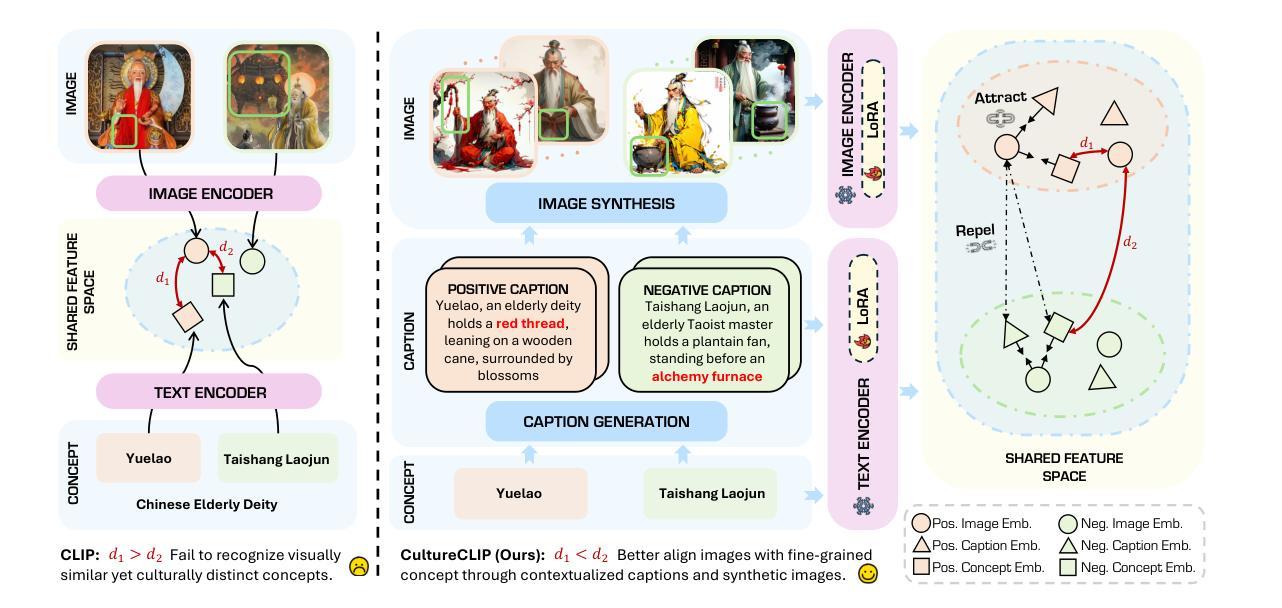
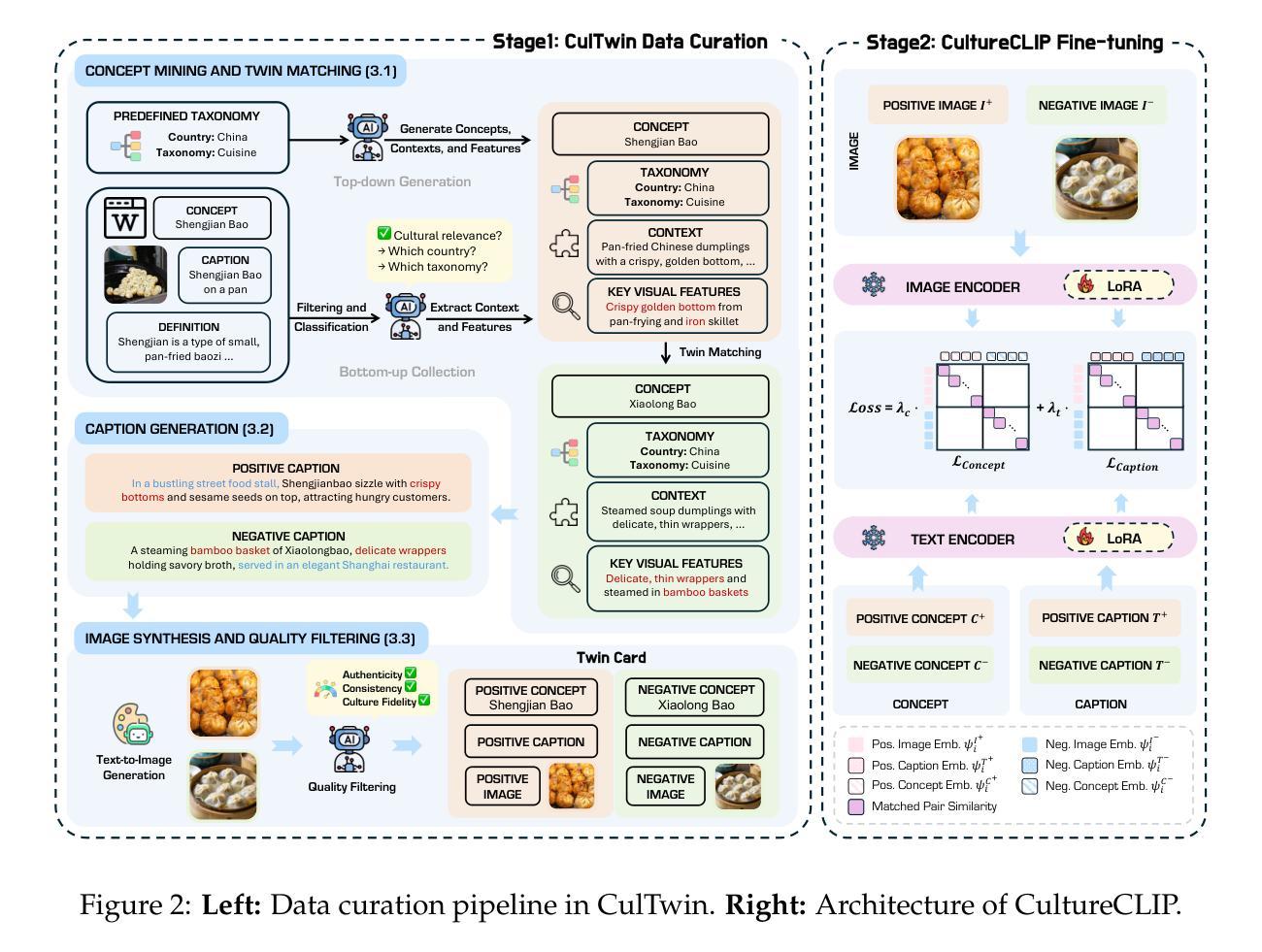
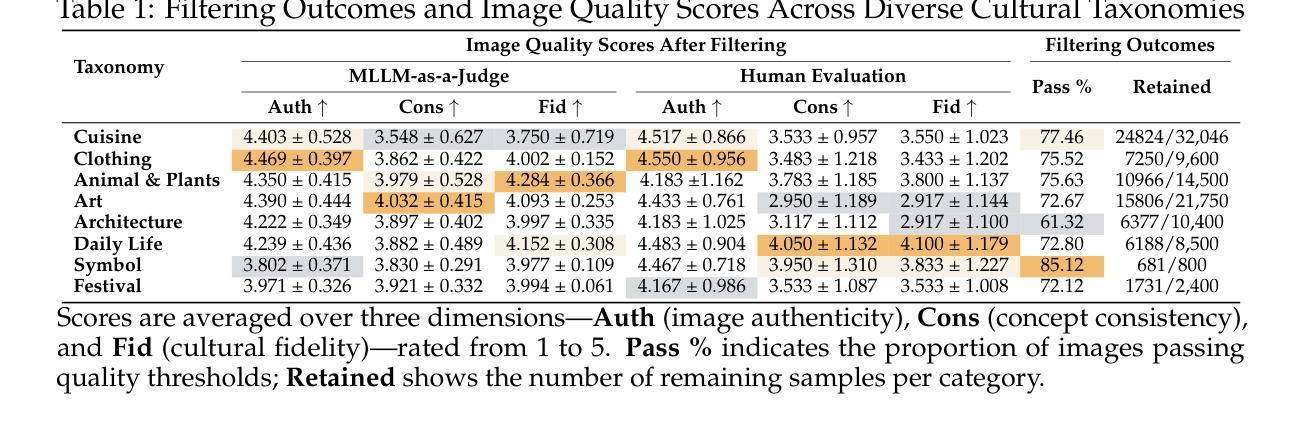
Pretrained vision-language models (VLMs) such as CLIP excel in multimodal understanding but struggle with contextually relevant fine-grained visual features, making it difficult to distinguish visually similar yet culturally distinct concepts. This limitation stems from the scarcity of high-quality culture-specific datasets, the lack of integrated contextual knowledge, and the absence of hard negatives highlighting subtle distinctions. To address these challenges, we first design a data curation pipeline that leverages open-sourced VLMs and text-to-image diffusion models to construct CulTwin, a synthetic cultural dataset. This dataset consists of paired concept-caption-image triplets, where concepts visually resemble each other but represent different cultural contexts. Then, we fine-tune CLIP on CulTwin to create CultureCLIP, which aligns cultural concepts with contextually enhanced captions and synthetic images through customized contrastive learning, enabling finer cultural differentiation while preserving generalization capabilities. Experiments on culturally relevant benchmarks show that CultureCLIP outperforms the base CLIP, achieving up to a notable 5.49% improvement in fine-grained concept recognition on certain tasks, while preserving CLIP’s original generalization ability, validating the effectiveness of our data synthesis and VLM backbone training paradigm in capturing subtle cultural distinctions.
预训练视觉语言模型(如CLIP)在多媒体理解方面表现出色,但在与上下文相关的精细视觉特征方面却表现挣扎,难以区分视觉上相似但文化上迥异的概念。这一局限性源于高质量的文化特定数据集的稀缺、缺乏集成化的上下文知识以及缺乏强调细微区别的硬阴性样本。为了解决这些挑战,我们首先设计了一条数据整理管道,利用开源的VLMs和文本到图像扩散模型来构建CulTwin,一个合成文化数据集。该数据集包含配对的概念-字幕-图像三元组,其中概念在视觉上相互类似,但代表了不同的文化背景。然后,我们在CulTwin上对CLIP进行微调,创建了CultureCLIP,它通过定制对比学习,将文化概念与上下文增强的字幕和合成图像对齐,从而实现更精细的文化区分能力,同时保留泛化能力。在相关文化基准上的实验表明,CultureCLIP优于基础CLIP,在某些任务上实现了高达5.49%的精细概念识别改进,同时保留了CLIP的原始泛化能力,验证了我们的数据合成和VLM主干训练范式在捕捉微妙文化区别方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 25 pages, COLM 2025
Summary
预训练视觉语言模型(如CLIP)在多模态理解方面表现出色,但在区分视觉相似但文化不同的概念时遇到困难。为解决此问题,研究团队设计了一个数据收集流程,利用开源的VLMs和文本到图像扩散模型构建了一个名为CulTwin的文化数据集。此数据集包含配对概念、标题和图像三元组,概念视觉相似但代表不同文化背景。通过对CLIP在CulTwin数据集上的微调,研究团队创建了CultureCLIP,通过定制对比学习,使文化概念与上下文增强的标题和合成图像对齐,实现更精细的文化区分,同时保持泛化能力。实验表明,CultureCLIP在特定任务上的精细概念识别能力较基础CLIP有显著提升,提升幅度达5.49%,同时保持了CLIP的原始泛化能力,验证了数据合成和VLM骨干训练模式在捕捉微妙文化差异方面的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 预训练视觉语言模型(如CLIP)在区分视觉相似但文化不同的概念时存在挑战。
- 数据集稀缺和文化特定知识的缺乏是影响模型性能的主要原因。
- 研究团队通过设计数据收集流程并构建合成文化数据集CulTwin来应对这一挑战。
- CulTwin数据集包含配对概念、标题和图像三元组,旨在体现不同文化背景下的视觉相似性。
- 通过在CulTwin数据集上微调CLIP,创建了CultureCLIP模型。
- CultureCLIP通过定制对比学习实现对文化概念的精细区分,同时保持模型的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图


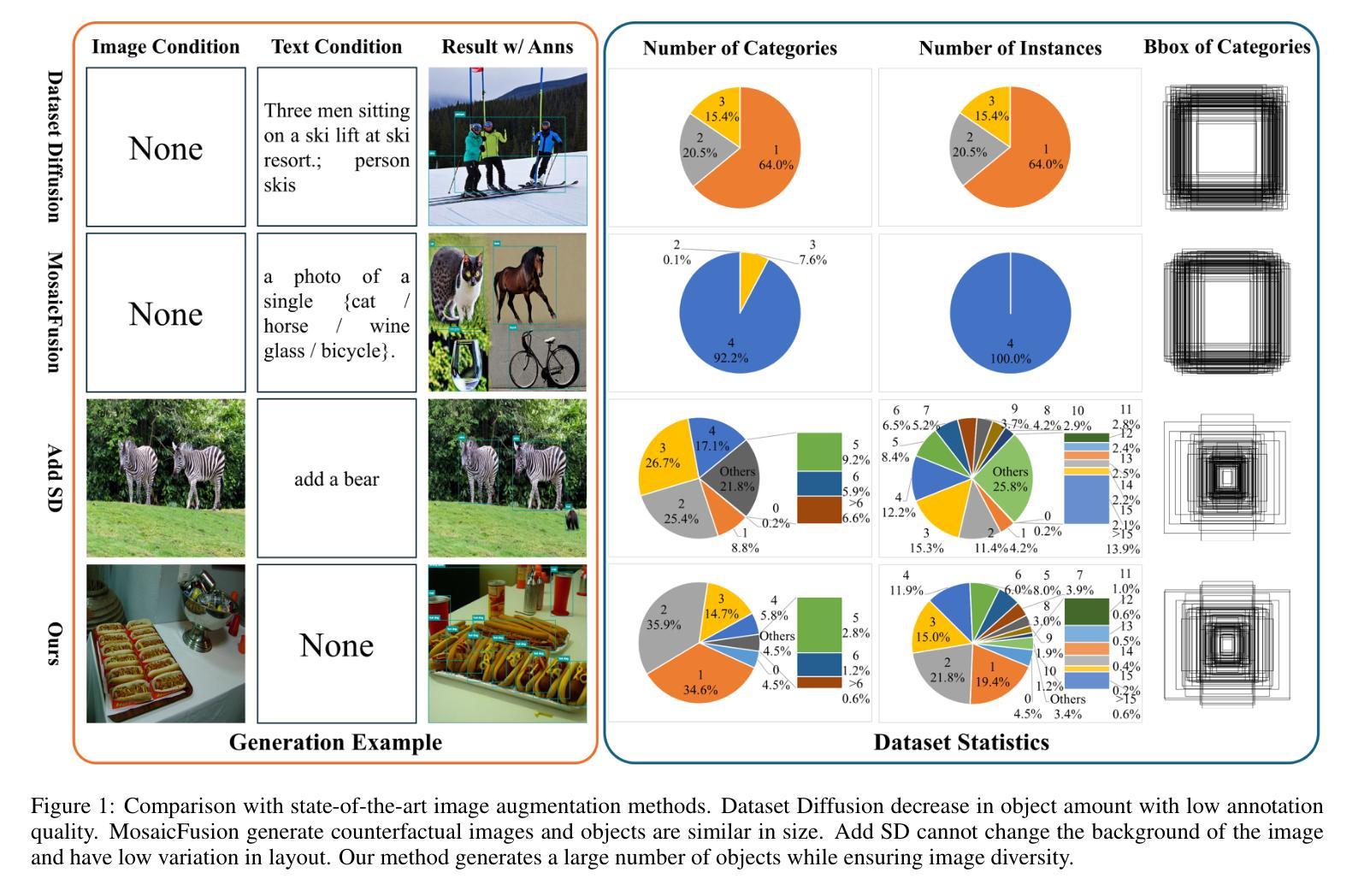
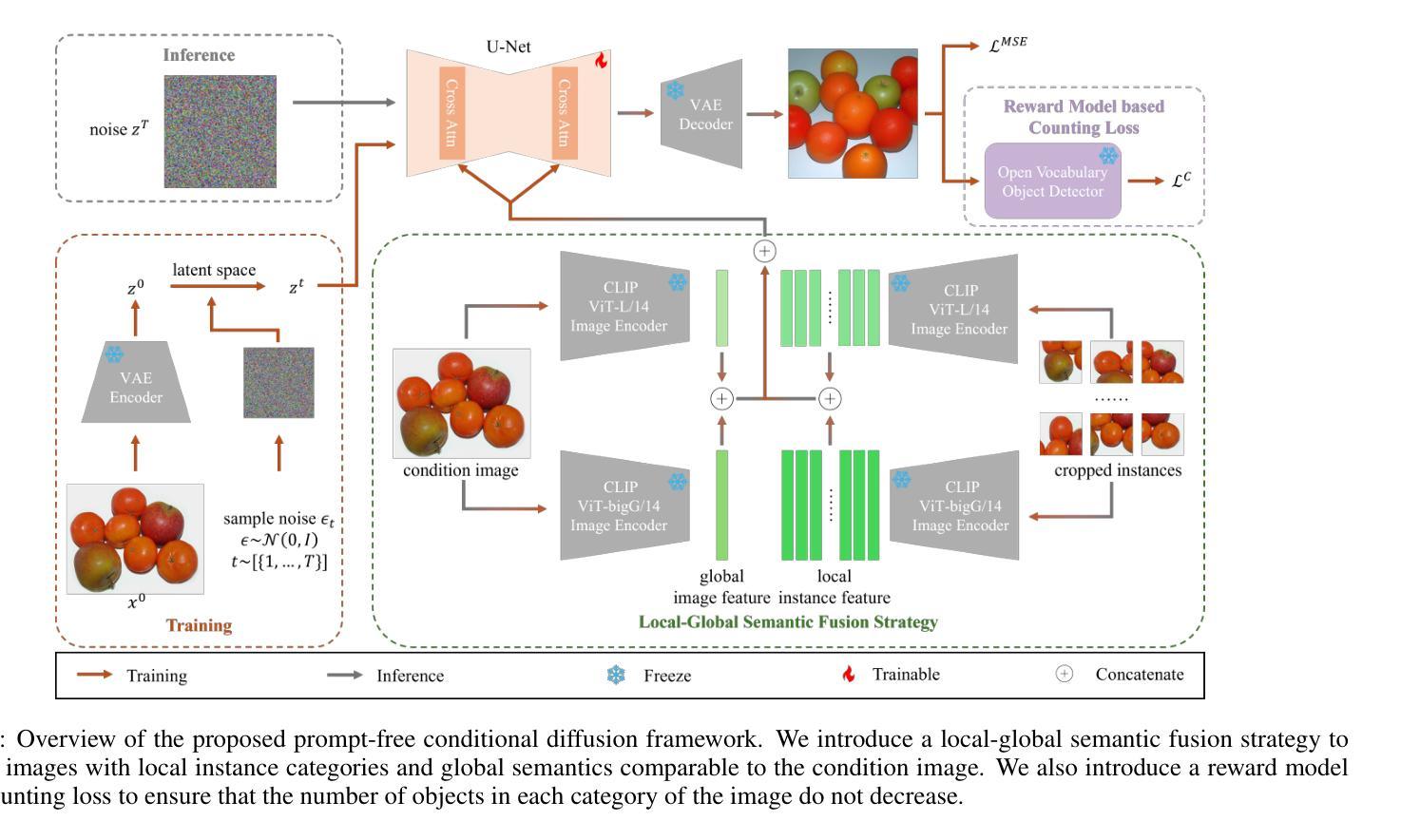
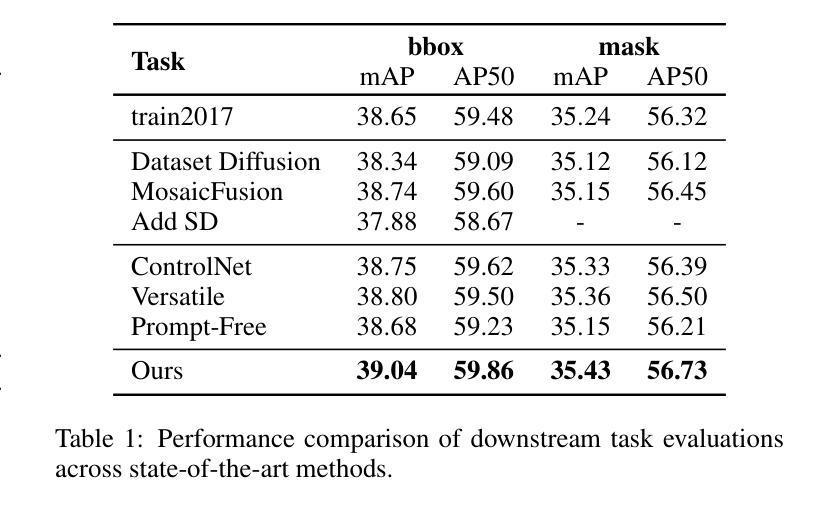
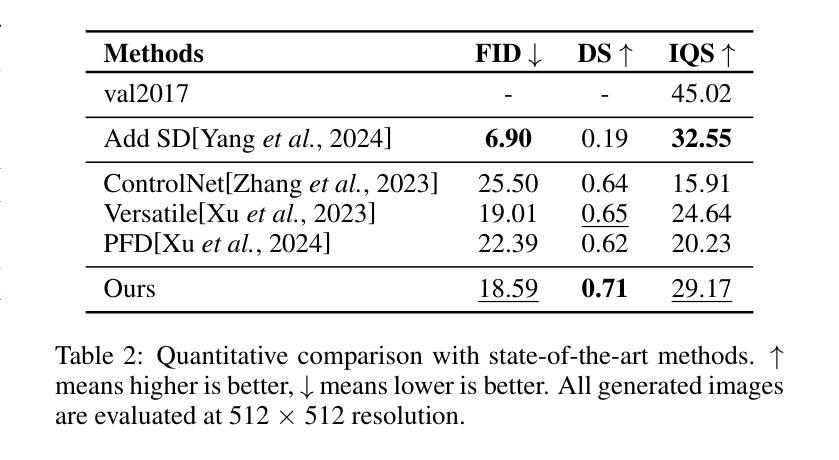
Prompt-Free Conditional Diffusion for Multi-object Image Augmentation
Authors:Haoyu Wang, Lei Zhang, Wei Wei, Chen Ding, Yanning Zhang
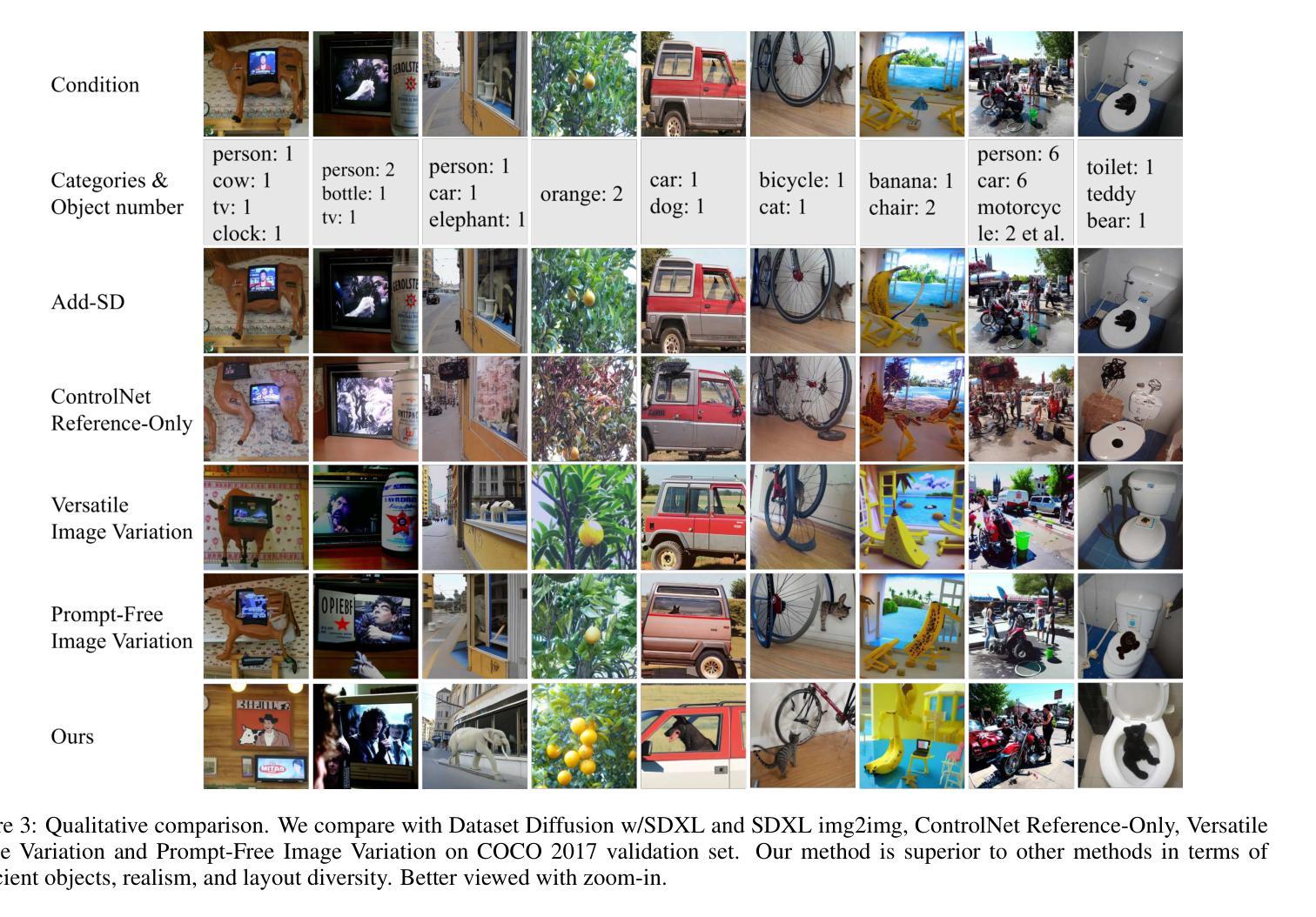
Diffusion models has underpinned much recent advances of dataset augmentation in various computer vision tasks. However, when involving generating multi-object images as real scenarios, most existing methods either rely entirely on text condition, resulting in a deviation between the generated objects and the original data, or rely too much on the original images, resulting in a lack of diversity in the generated images, which is of limited help to downstream tasks. To mitigate both problems with one stone, we propose a prompt-free conditional diffusion framework for multi-object image augmentation. Specifically, we introduce a local-global semantic fusion strategy to extract semantics from images to replace text, and inject knowledge into the diffusion model through LoRA to alleviate the category deviation between the original model and the target dataset. In addition, we design a reward model based counting loss to assist the traditional reconstruction loss for model training. By constraining the object counts of each category instead of pixel-by-pixel constraints, bridging the quantity deviation between the generated data and the original data while improving the diversity of the generated data. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method over several representative state-of-the-art baselines and showcase strong downstream task gain and out-of-domain generalization capabilities. Code is available at \href{https://github.com/00why00/PFCD}{here}.
扩散模型为各种计算机视觉任务中的数据集增强提供了许多最新的进展支持。然而,在涉及生成多对象图像作为真实场景时,大多数现有方法要么完全依赖于文本条件,导致生成的对象与原始数据之间存在偏差,要么过于依赖原始图像,导致生成的图像缺乏多样性,对下游任务帮助有限。为了用一个方法同时解决这两个问题,我们提出了一个无需提示的多对象图像增强条件扩散框架。具体来说,我们引入了一种局部全局语义融合策略,从图像中提取语义来替代文本,并通过LoRA将知识注入扩散模型,以减轻原始模型与目标数据集之间的类别偏差。此外,我们设计了一种基于奖励模型的计数损失来辅助传统重建损失进行模型训练。通过约束每个类别的对象计数,而不是逐像素约束,我们缩小了生成数据与原始数据之间的数量偏差,同时提高了生成数据的多样性。实验结果表明,该方法优于几种具有代表性的最新基线方法,并展示了强大的下游任务增益和跨域泛化能力。代码可从https://github.com/00why00/PFCD此处获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at IJCAI 2025
Summary
本文探讨了扩散模型在多目标图像增强方面的应用。针对现有方法中存在的问题,提出了一种无提示条件扩散框架,通过引入局部全局语义融合策略和基于计数的奖励模型,解决了生成目标与原始数据之间的偏差和生成图像缺乏多样性两个问题。该方法在多个代表性基准测试中表现优异,并展示了强大的下游任务增益和跨域泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在多目标图像增强方面取得重要进展。
- 现有方法存在生成目标与原始数据偏差、生成图像缺乏多样性等问题。
- 引入无提示条件扩散框架,结合局部全局语义融合策略,解决上述问题。
- 通过LoRA注入知识到扩散模型中,减轻原始模型与目标数据集之间的类别偏差。
- 设计基于计数的奖励模型,辅助传统重建损失进行模型训练。
- 通过约束每类对象计数而非逐像素约束,缩小生成数据与原始数据之间的数量偏差,提高生成数据多样性。
点此查看论文截图


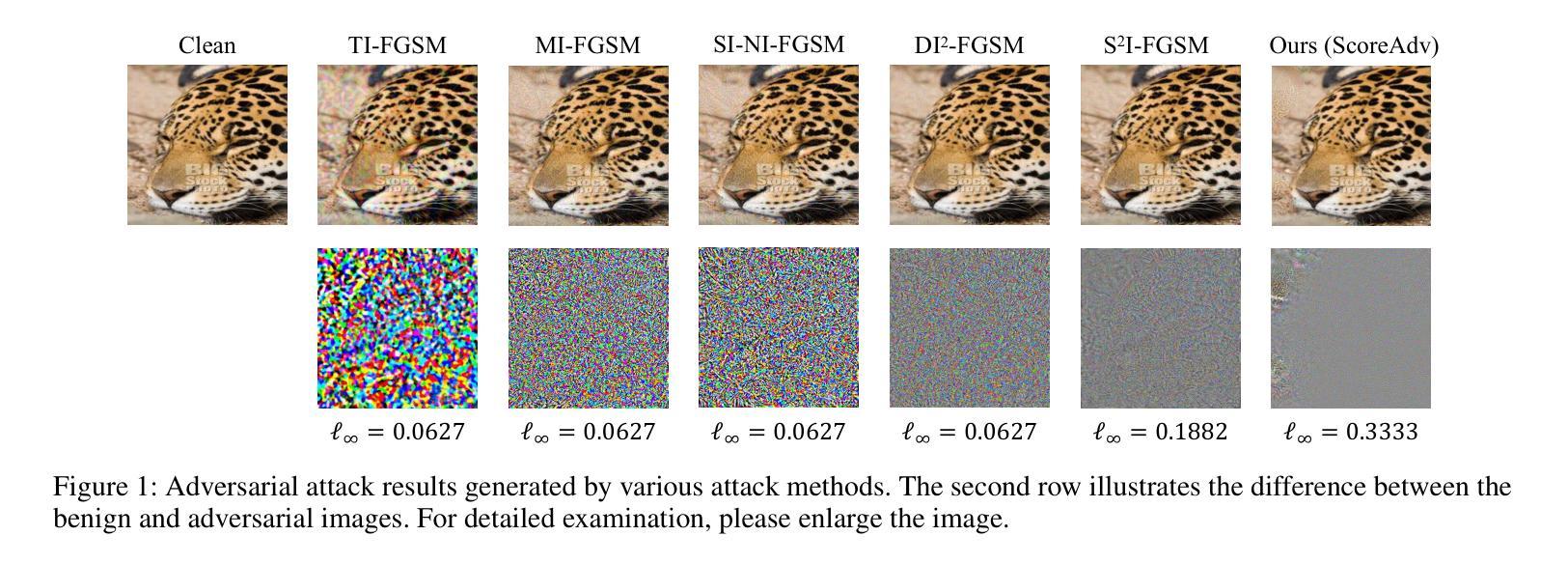
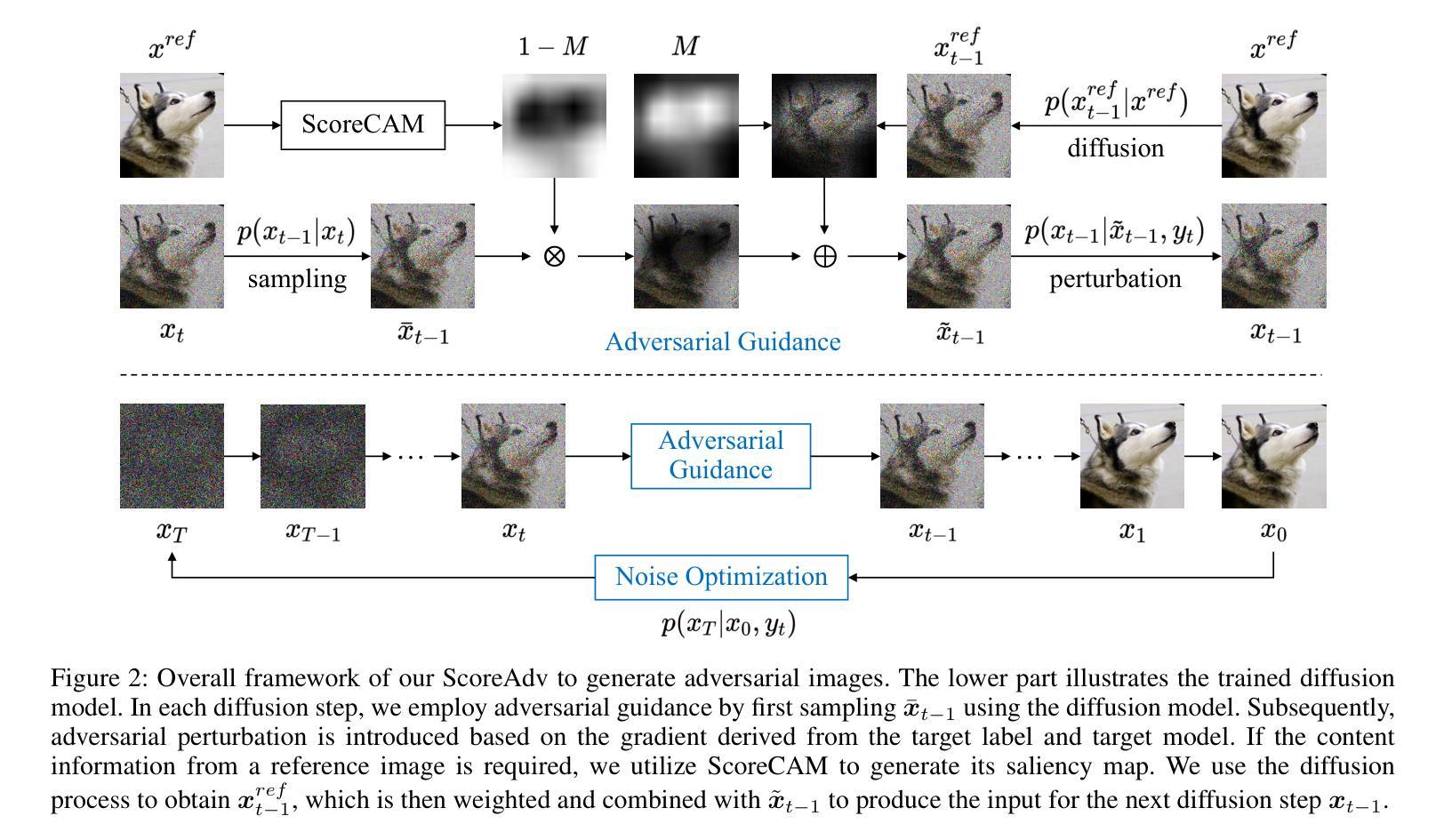
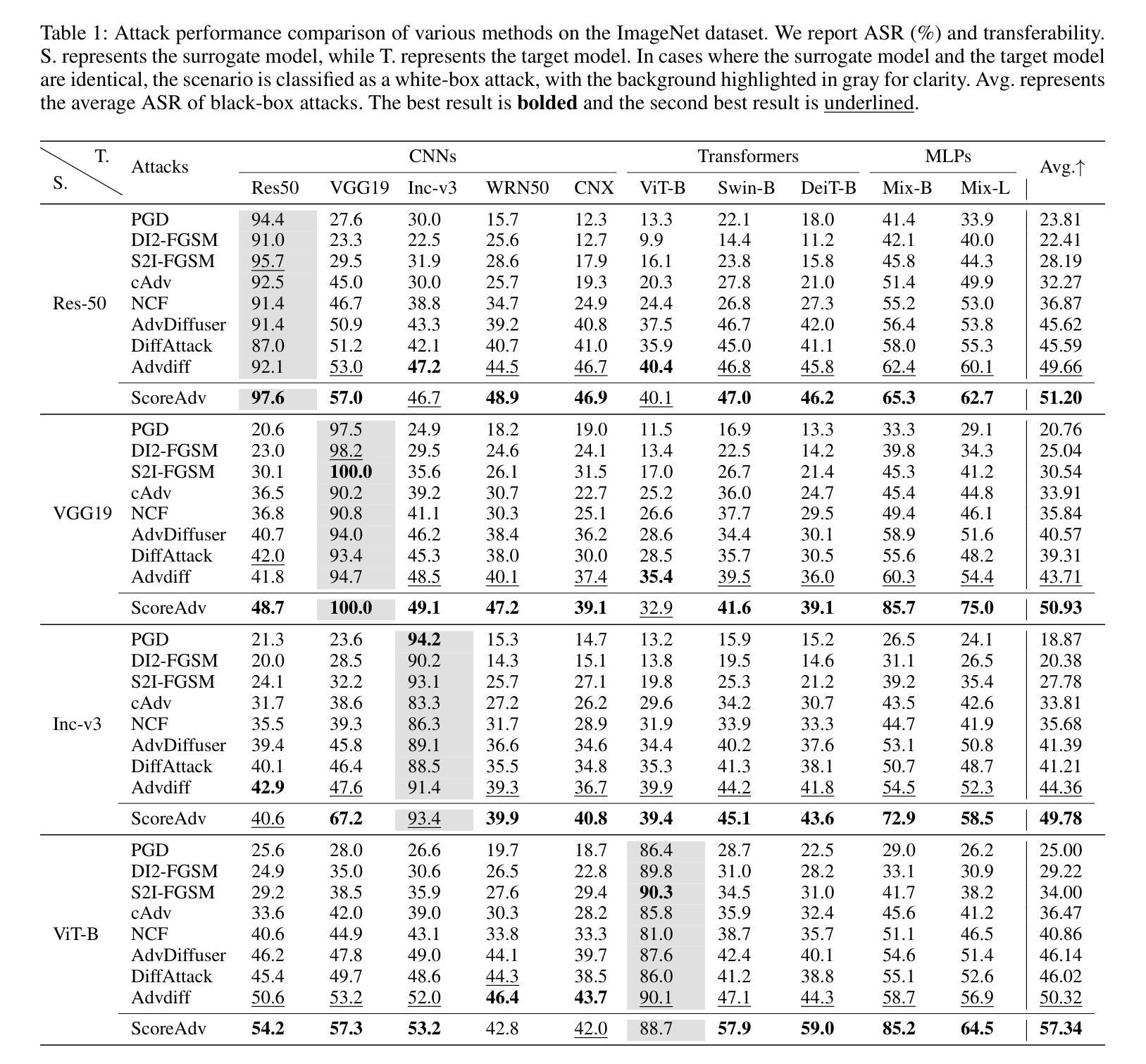
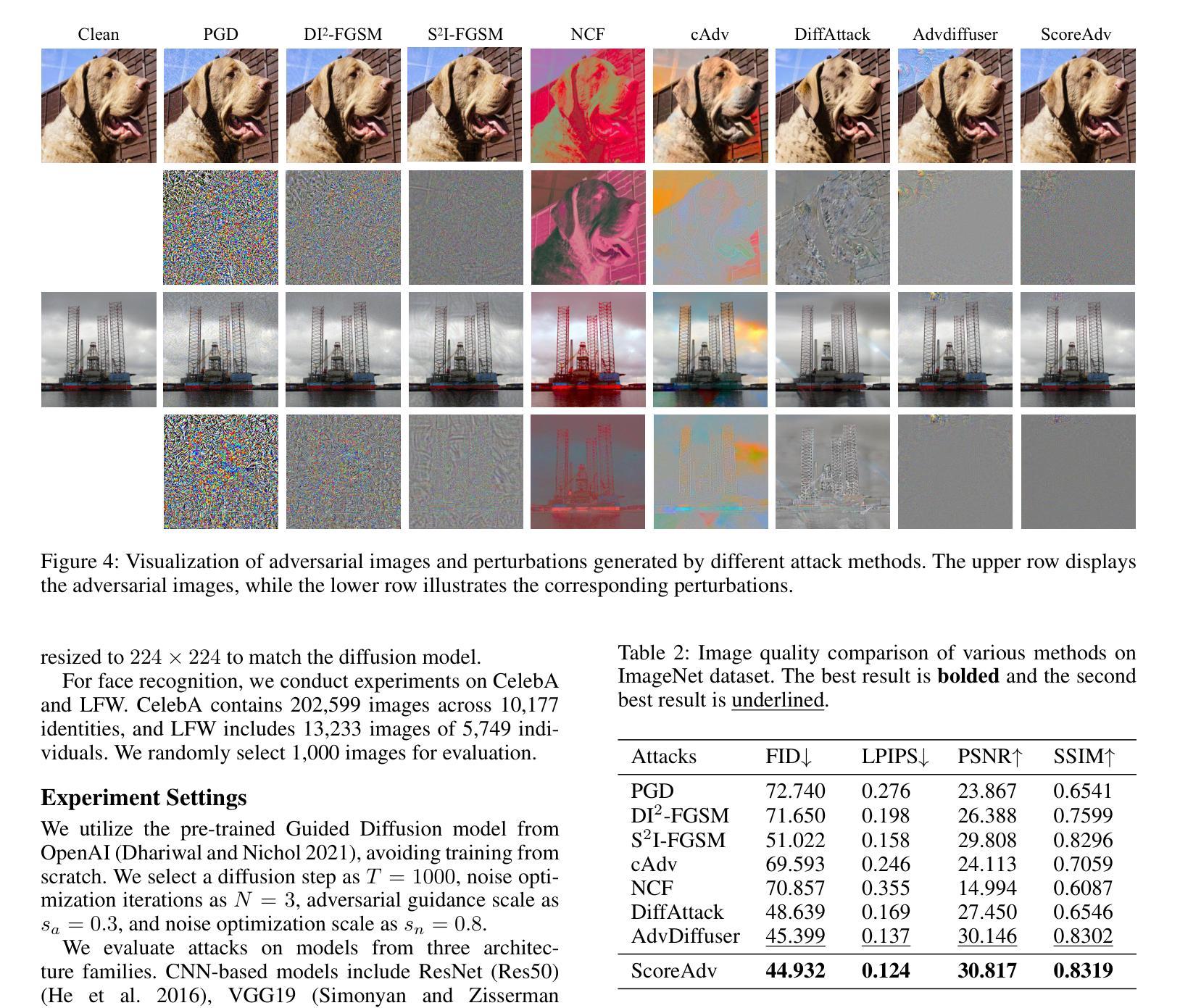
ScoreAdv: Score-based Targeted Generation of Natural Adversarial Examples via Diffusion Models
Authors:Chihan Huang, Hao Tang
Despite the success of deep learning across various domains, it remains vulnerable to adversarial attacks. Although many existing adversarial attack methods achieve high success rates, they typically rely on $\ell_{p}$-norm perturbation constraints, which do not align with human perceptual capabilities. Consequently, researchers have shifted their focus toward generating natural, unrestricted adversarial examples (UAEs). GAN-based approaches suffer from inherent limitations, such as poor image quality due to instability and mode collapse. Meanwhile, diffusion models have been employed for UAE generation, but they still rely on iterative PGD perturbation injection, without fully leveraging their central denoising capabilities. In this paper, we introduce a novel approach for generating UAEs based on diffusion models, named ScoreAdv. This method incorporates an interpretable adversarial guidance mechanism to gradually shift the sampling distribution towards the adversarial distribution, while using an interpretable saliency map to inject the visual information of a reference image into the generated samples. Notably, our method is capable of generating an unlimited number of natural adversarial examples and can attack not only classification models but also retrieval models. We conduct extensive experiments on ImageNet and CelebA datasets, validating the performance of ScoreAdv across ten target models in both black-box and white-box settings. Our results demonstrate that ScoreAdv achieves state-of-the-art attack success rates and image quality. Furthermore, the dynamic balance between denoising and adversarial perturbation enables ScoreAdv to remain robust even under defensive measures.
尽管深度学习在各个领域的成功应用,它仍然容易受到对抗性攻击的威胁。虽然许多现有的对抗性攻击方法达到了高成功率,但它们通常依赖于$\ell_{p}$-norm扰动约束,这些约束并不符合人类的感知能力。因此,研究者们开始关注生成自然、无限制的对抗样本(UAEs)。基于GAN的方法存在固有的局限性,例如由于不稳定和模式崩溃导致的图像质量差。同时,扩散模型已被用于UAE生成,但它们仍然依赖于迭代PGD扰动注入,并未充分利用其核心的降噪能力。在本文中,我们介绍了一种基于扩散模型生成UAEs的新型方法,名为ScoreAdv。该方法采用可解释的对抗性指导机制,逐步将采样分布转向对抗性分布,同时使用可解释的显著性图将参考图像的可视信息注入生成的样本中。值得注意的是,我们的方法可以生成无限数量的自然对抗样本,并且可以攻击不仅是分类模型,还有检索模型。我们在ImageNet和CelebA数据集上进行了大量实验,验证了ScoreAdv在黑白盒设置中对十个目标模型的性能。结果表明,ScoreAdv达到了最先进的攻击成功率和图像质量。此外,降噪和对抗性扰动之间的动态平衡使ScoreAdv在防御措施下仍能保持稳定。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于扩散模型的新型生成无限制对抗样本的方法,名为ScoreAdv。该方法通过可解释的对抗性引导机制逐步将采样分布转向对抗性分布,同时使用可解释的显著性图将参考图像的可视信息注入生成的样本中。ScoreAdv能在不限数量的自然对抗样本上生成攻击,并能在黑箱和白箱设置中攻击分类模型和检索模型。实验结果显示,ScoreAdv在攻击成功率和图像质量上均达到领先水平,且在防御措施下仍能保持稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- 现有深度学习模型易受基于$\ell_{p}$-范数的对抗攻击影响,这不符合人类感知能力。因此,研究者开始专注于生成自然无限制的对抗样本(UAEs)。
- 生成对抗样本的现有方法主要依赖于迭代PGD扰动注入,没有充分利用扩散模型的中心去噪能力。
- ScoreAdv方法基于扩散模型提出,结合了可解释的对抗引导机制和显著性图注入参考图像信息。
- ScoreAdv能生成无限数量的自然对抗样本,并能攻击分类模型和检索模型。
- ScoreAdv在ImageNet和CelebA数据集上的实验结果表明其在攻击成功率和图像质量上达到了先进水平。
- ScoreAdv通过动态平衡去噪和对抗扰动,在防御措施下仍能保持稳健性。
点此查看论文截图



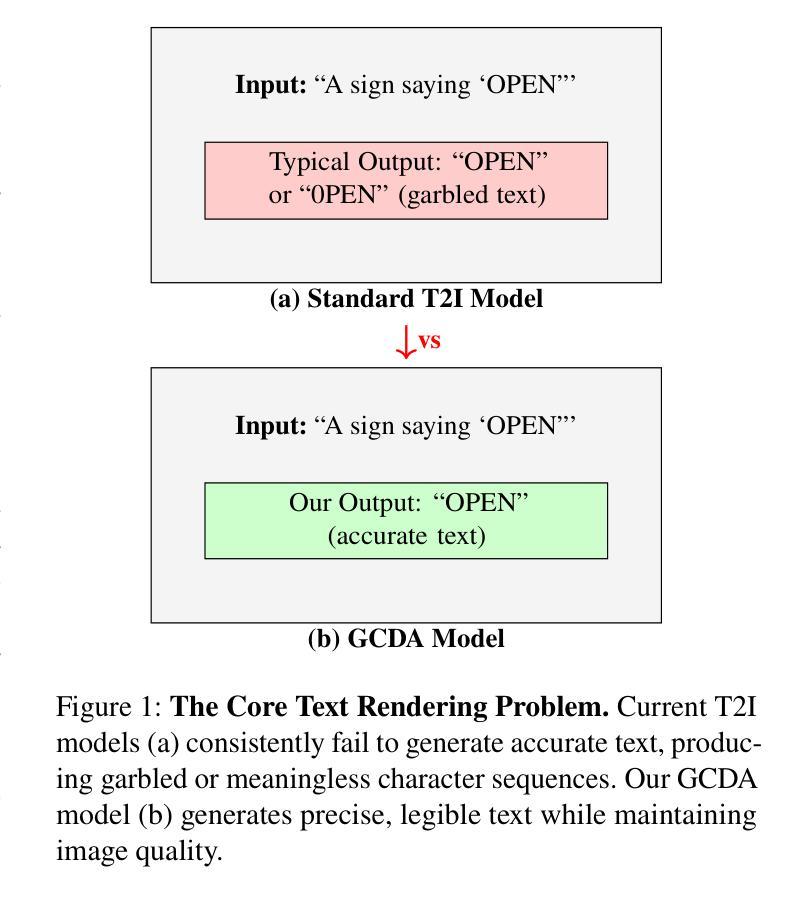
TextPixs: Glyph-Conditioned Diffusion with Character-Aware Attention and OCR-Guided Supervision
Authors:Syeda Anshrah Gillani, Mirza Samad Ahmed Baig, Osama Ahmed Khan, Shahid Munir Shah, Umema Mujeeb, Maheen Ali
The modern text-to-image diffusion models boom has opened a new era in digital content production as it has proven the previously unseen ability to produce photorealistic and stylistically diverse imagery based on the semantics of natural-language descriptions. However, the consistent disadvantage of these models is that they cannot generate readable, meaningful, and correctly spelled text in generated images, which significantly limits the use of practical purposes like advertising, learning, and creative design. This paper introduces a new framework, namely Glyph-Conditioned Diffusion with Character-Aware Attention (GCDA), using which a typical diffusion backbone is extended by three well-designed modules. To begin with, the model has a dual-stream text encoder that encodes both semantic contextual information and explicit glyph representations, resulting in a character-aware representation of the input text that is rich in nature. Second, an attention mechanism that is aware of the character is proposed with a new attention segregation loss that aims to limit the attention distribution of each character independently in order to avoid distortion artifacts. Lastly, GCDA has an OCR-in-the-loop fine-tuning phase, where a full text perceptual loss, directly optimises models to be legible and accurately spell. Large scale experiments to benchmark datasets, such as MARIO-10M and T2I-CompBench, reveal that GCDA sets a new state-of-the-art on all metrics, with better character based metrics on text rendering (Character Error Rate: 0.08 vs 0.21 for the previous best; Word Error Rate: 0.15 vs 0.25), human perception, and comparable image synthesis quality on high-fidelity (FID: 14.3).
现代文本到图像扩散模型的繁荣开启了数字内容生产的新时代,因为它证明了基于自然语言描述的语义生成摄影逼真且风格多样的图像的能力。然而,这些模型一直存在一个缺点,那就是它们无法生成可读、有意义、拼写正确的文本图像,这极大地限制了它们在广告、学习和创意设计等实用场合的应用。本文介绍了一个新框架,即带有字符感知注意力机制的Glyph条件扩散(GCDA),该框架通过使用三个精心设计的模块扩展了典型的扩散主干。首先,该模型具有一个双流文本编码器,该编码器编码语义上下文信息和明确的字形表示,从而得到输入文本的自然丰富字符感知表示。其次,提出了一种字符感知的注意力机制,通过新的注意力分割损失来限制每个字符的独立注意力分布,以避免失真伪影。最后,GCDA有一个OCR循环微调阶段,其中全文本感知损失直接优化模型,使其可读且拼写准确。大规模实验在MARIO-10M和T2I-CompBench等基准数据集上进行,表明GCDA在所有指标上均达到最新水平,文本渲染的字符基础指标表现更好(字符错误率:0.08对比之前最佳的0.21;单词错误率:0.15对比之前的最佳值0.25),在人类感知和高保真图像合成质量上表现相当(FID为14.3)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 30 pages
Summary
文本到图像扩散模型的进步开启了数字内容生产的新时代,展现出基于自然语言描述的语义生成逼真且风格多样的图像的能力。然而,这些模型无法生成可读、有意义且拼写正确的文本图像,这限制了其在广告、学习和创意设计等实用领域的运用。本文提出一种新的框架——Glyph-Conditioned Diffusion with Character-Aware Attention(GCDA),通过三个精心设计模块扩展典型的扩散主干。该模型具备双文本编码器,编码语义上下文信息和明确的字形表示,形成丰富的字符感知文本表示。此外,提出字符感知注意力机制,通过新的注意力分割损失来独立限制每个字符的注意力分布,避免失真伪影。最后,GCDA具有OCR闭环微调阶段,通过全文感知损失直接优化模型的可读性和拼写准确性。大规模实验结果表明,GCDA在各项指标上均达到最新水平,文字渲染的字符基础指标表现更佳(字符错误率:0.08对比之前最佳的0.21;词错误率:0.15对比0.25),人类感知与图像合成质量也相当出色(FID:14.3)。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像扩散模型的新时代:展示了基于自然语言描述的语义生成高质量图像的能力。
- 当前模型的主要限制:无法生成可读、有意义且拼写正确的文本图像。
- GCDA框架的引入:通过三个模块扩展典型的扩散模型,包括双文本编码器、字符感知注意力机制和OCR闭环微调阶段。
- 双文本编码器:编码语义上下文和字形表示,形成丰富的字符感知文本表示。
- 字符感知注意力机制:通过注意力分割损失独立限制每个字符的注意力分布。
- OCR闭环微调阶段:通过全文感知损失优化模型的可读性和拼写准确性。
点此查看论文截图

T-LoRA: Single Image Diffusion Model Customization Without Overfitting
Authors:Vera Soboleva, Aibek Alanov, Andrey Kuznetsov, Konstantin Sobolev
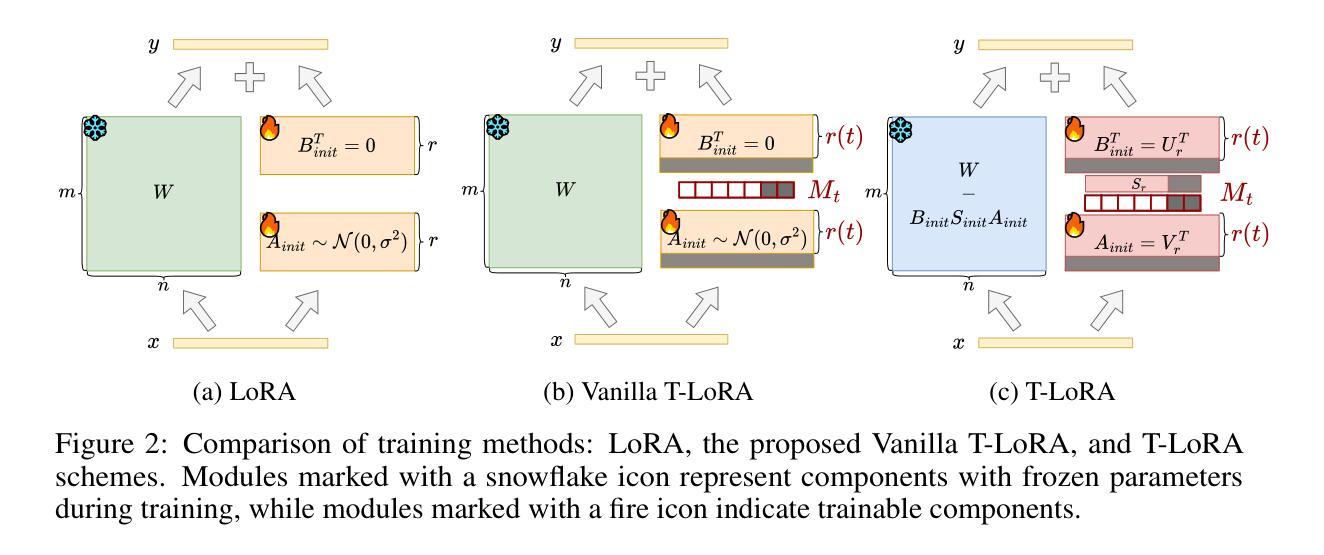
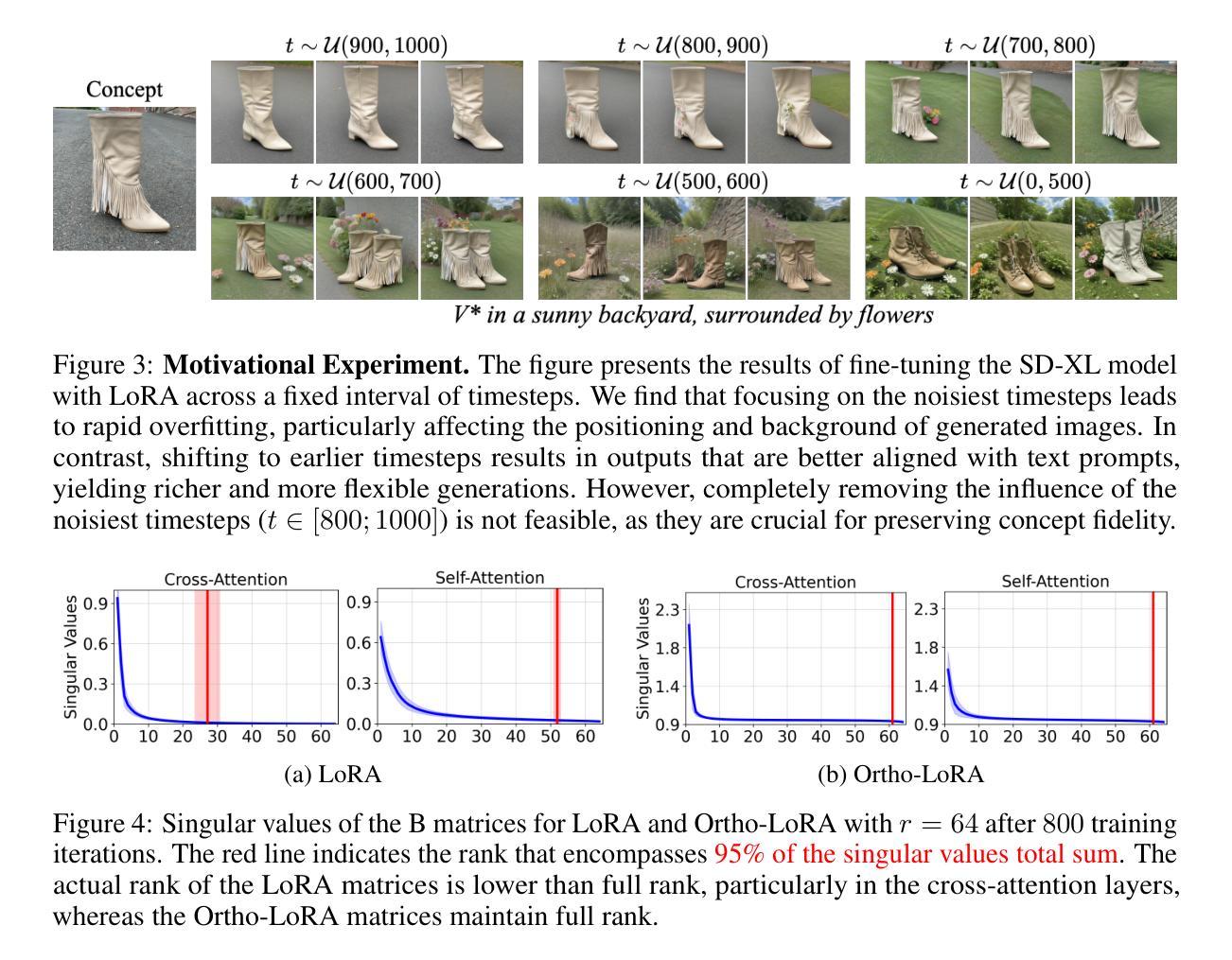
While diffusion model fine-tuning offers a powerful approach for customizing pre-trained models to generate specific objects, it frequently suffers from overfitting when training samples are limited, compromising both generalization capability and output diversity. This paper tackles the challenging yet most impactful task of adapting a diffusion model using just a single concept image, as single-image customization holds the greatest practical potential. We introduce T-LoRA, a Timestep-Dependent Low-Rank Adaptation framework specifically designed for diffusion model personalization. In our work we show that higher diffusion timesteps are more prone to overfitting than lower ones, necessitating a timestep-sensitive fine-tuning strategy. T-LoRA incorporates two key innovations: (1) a dynamic fine-tuning strategy that adjusts rank-constrained updates based on diffusion timesteps, and (2) a weight parametrization technique that ensures independence between adapter components through orthogonal initialization. Extensive experiments show that T-LoRA and its individual components outperform standard LoRA and other diffusion model personalization techniques. They achieve a superior balance between concept fidelity and text alignment, highlighting the potential of T-LoRA in data-limited and resource-constrained scenarios. Code is available at https://github.com/ControlGenAI/T-LoRA.
扩散模型微调提供了一种强大的方法来定制预训练模型以生成特定对象,但当训练样本有限时,它经常遭受过拟合的问题,这损害了其泛化能力和输出多样性。本文解决了使用仅一个概念图像适应扩散模型的具有挑战性和影响力的任务,因为单图像定制具有最大的实际应用潜力。我们引入了T-LoRA,这是一个专门用于扩散模型个性化的时序依赖低秩适应框架。我们的工作表明,较高的扩散时间步比低的时间步更容易出现过拟合,这需要一种对时间步敏感的微调策略。T-LoRA包含两个关键创新点:(1)一种动态微调策略,根据扩散时间步长调整秩约束更新;(2)一种权重参数化技术,通过正交初始化确保适配器组件之间的独立性。大量实验表明,T-LoRA及其各个组件的性能超过了标准的LoRA和其他扩散模型个性化技术。他们在概念保真度和文本对齐之间达到了出色的平衡,突显了T-LoRA在数据有限和资源受限场景中的潜力。代码可在https://github.com/ControlGenAI/T-LoRA中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型微调虽然能够针对预训练模型进行个性化定制以生成特定对象,但在训练样本有限的情况下常常会出现过拟合问题,影响模型的泛化能力和输出多样性。本文引入T-LoRA框架,采用时间步依赖的低秩适应策略,针对扩散模型的个性化定制提出解决方案。实验表明,T-LoRA及其组件在概念保真度和文本对齐方面实现了卓越平衡,具有数据有限和资源受限场景下的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型微调在有限训练样本时容易过拟合,影响模型的泛化能力和输出多样性。
- T-LoRA框架被设计用于扩散模型的个性化定制。
- T-LoRA采用时间步依赖的低秩适应策略。
- 扩散模型中的高时间步长比低时间步长更容易过拟合,需要一种时间步敏感的微调策略。
- T-LoRA框架包括两个关键创新点:动态微调策略和权重参数化技术。
- 动态微调策略根据扩散时间步长调整等级约束更新。
- T-LoRA及其组件在概念保真度和文本对齐方面表现出卓越性能,具有在数据有限和资源受限场景下的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

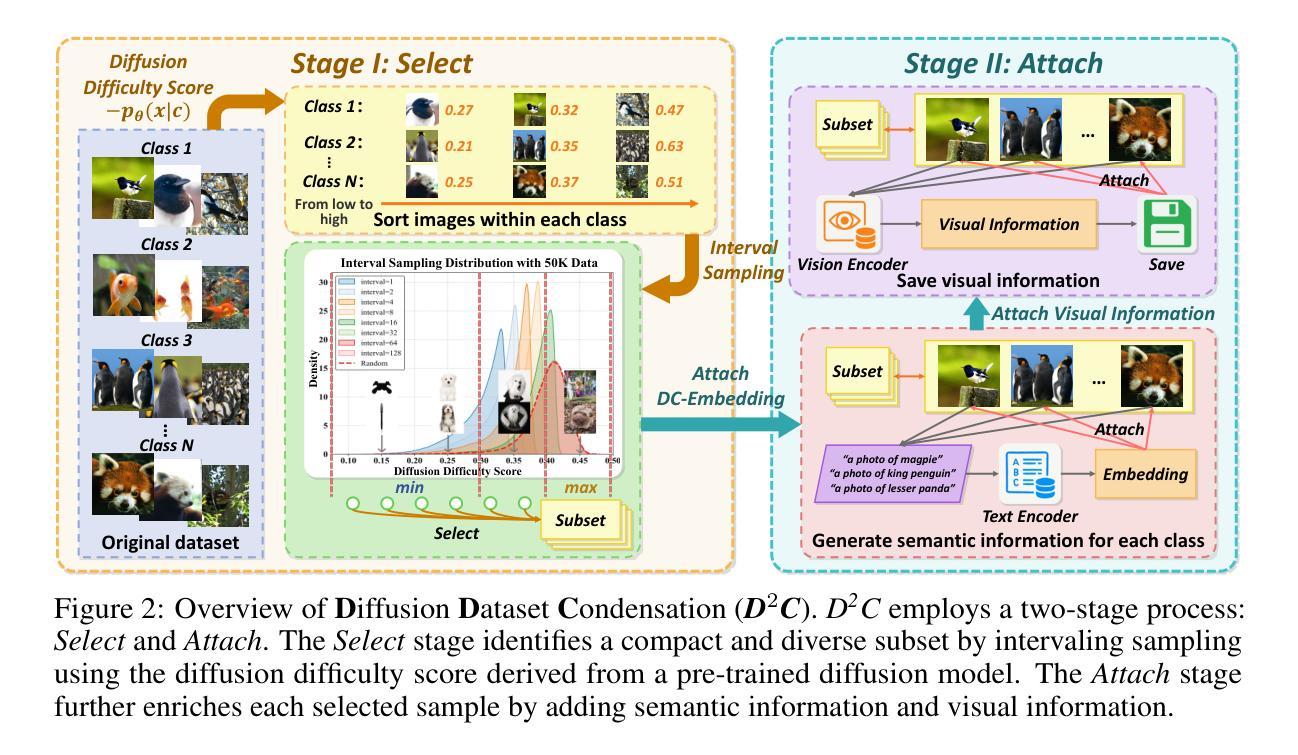
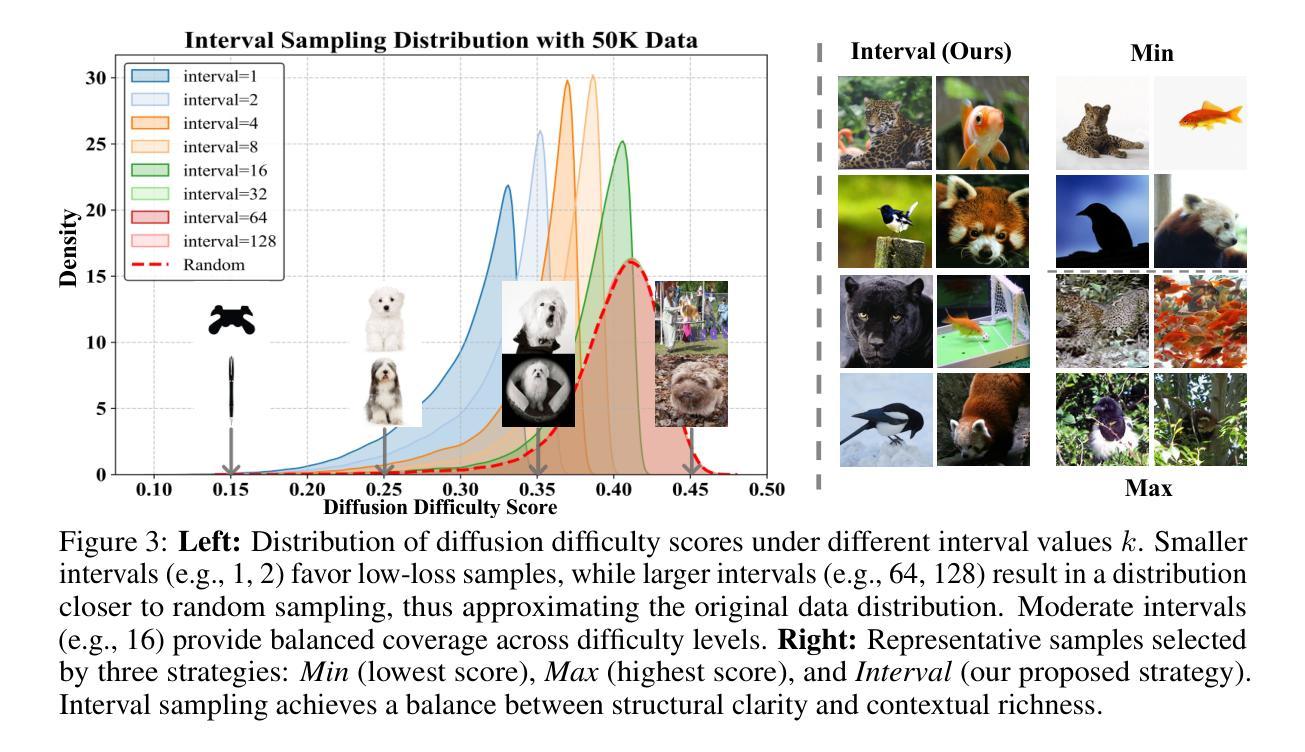
Diffusion Dataset Condensation: Training Your Diffusion Model Faster with Less Data
Authors:Rui Huang, Shitong Shao, Zikai Zhou, Pukun Zhao, Hangyu Guo, Tian Ye, Lichen Bai, Shuo Yang, Zeke Xie
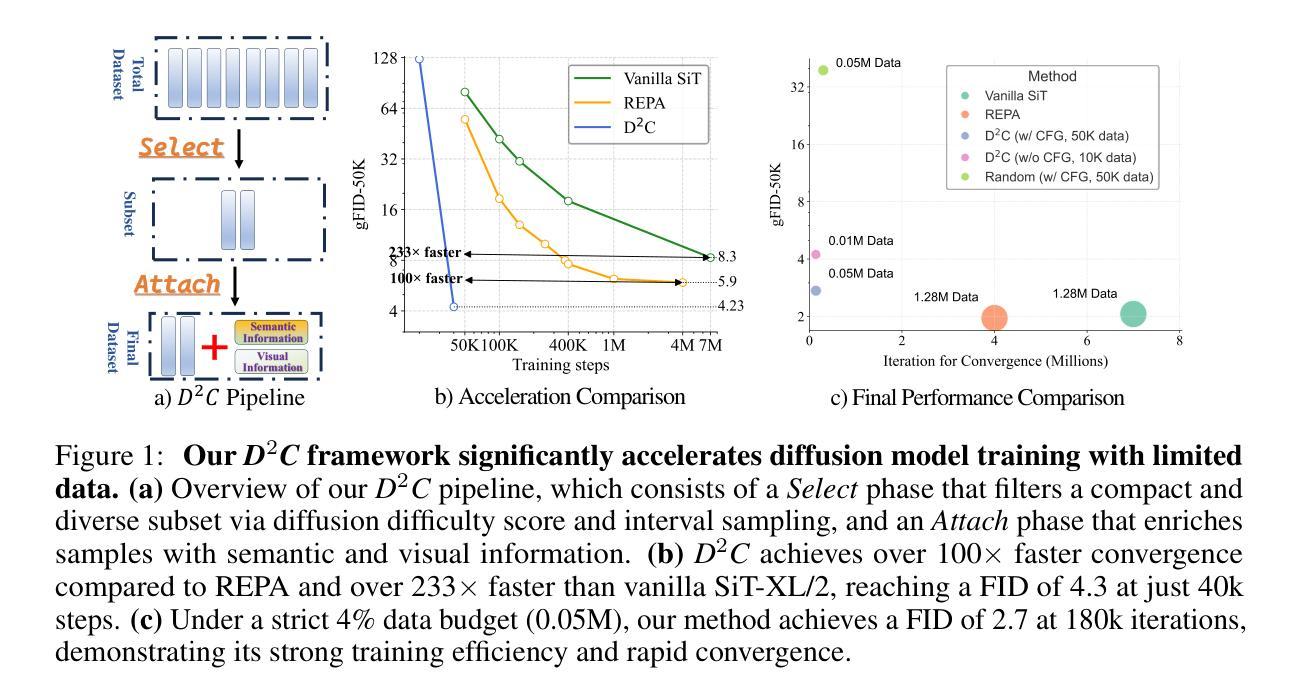
Diffusion models have achieved remarkable success in various generative tasks, but training them remains highly resource-intensive, often requiring millions of images and many days of GPU computation. From a data-centric perspective addressing this limitation, we study diffusion dataset condensation as a new and challenging problem setting. The goal is to construct a “synthetic” sub-dataset with significantly fewer samples than the original dataset, enabling high-quality diffusion model training with greatly reduced cost. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to formally investigate dataset condensation for diffusion models, whereas prior work focused on training discriminative models. To tackle this new challenge, we propose a novel Diffusion Dataset Condensation (D2C) framework, which consists of two phases: Select and Attach. The Select phase identifies a compact and diverse subset using a diffusion difficulty score and interval sampling. The Attach phase enhances the selected subset by attaching rich semantic and visual representations to strengthen the conditional signals. Extensive experiments across various dataset sizes, model architectures, and resolutions show that our D2C framework enables significantly faster diffusion model training with dramatically fewer data, while preserving high visual quality. Notably, for the SiT-XL/2 architecture, D2C achieves a 100x training speed-up, reaching a FID score of 4.3 in just 40k steps using only 0.8% of the training data.
扩散模型在各种生成任务中取得了显著的成功,但其训练仍然需要大量资源,通常需要数百万张图像和数天的GPU计算。从数据中心的视角来解决这一限制,我们研究扩散数据集凝聚作为一个新的有挑战性的设置。目标是构建一个与原始数据集相比样本数量显著较少的“合成”子数据集,从而实现高质量扩散模型的低成本训练。据我们所知,我们是首次正式研究扩散模型的数据集凝聚,而之前的工作主要集中在训练判别模型上。为了应对这一新挑战,我们提出了一种新颖的扩散数据集凝聚(D2C)框架,它分为两个阶段:选择和附加。选择阶段使用扩散难度分数和间隔采样来确定紧凑且多样化的子集。附加阶段通过为所选子集添加丰富的语义和视觉表示来增强条件信号。在不同数据集大小、模型架构和分辨率的大量实验表明,我们的D2C框架能够在显著减少数据的同时实现更快的扩散模型训练,同时保持较高的视觉质量。值得注意的是,对于SiT-XL/2架构,D2C实现了100倍的加速训练速度,仅使用0.8%的训练数据在短短4万步内达到了FID分数为4.3。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Iintroduces D2C: a novel framework for diffusion dataset condensation
Summary
扩散模型在各种生成任务中取得了显著的成功,但其训练仍然需要大量的资源和计算。为了解决这一问题,本文研究了扩散数据集压缩这一新的难题。目标是构建一个与原始数据集相比样本数量显著减少的“合成”子集,从而以大幅降低的成本实现高质量的扩散模型训练。本文首次正式研究扩散模型的数据集压缩问题,而之前的工作主要集中在判别模型的训练上。为了解决这一新挑战,本文提出了Diffusion Dataset Condensation (D2C)框架,该框架包括Select和Attach两个阶段。Select阶段使用扩散难度分数和间隔采样来识别紧凑且多样化的子集。Attach阶段通过为所选子集添加丰富的语义和视觉表示来加强条件信号。实验表明,D2C框架能够在大幅减少数据的同时,实现更快的扩散模型训练,并保持较高的视觉质量。特别是在SiT-XL/2架构上,使用D2C方法实现了训练速度的百倍加速,在仅使用0.8%的训练数据的情况下,达到了FID分数为4.3的优异表现。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在生成任务中表现优秀,但训练需要大量资源和计算成本。
- 扩散数据集压缩旨在构建含有较少样本的合成子集,降低扩散模型的训练成本。
- Diffusion Dataset Condensation (D2C)框架包括Select和Attach两个阶段来解决扩散数据集压缩问题。
- Select阶段通过识别一个紧凑且多样化的子集以压缩数据集规模。
- Attach阶段强化了条件信号,通过为所选子集添加丰富的语义和视觉表示来提高模型性能。
- 实验证明D2C框架能显著加速扩散模型的训练速度并减少数据使用量。
点此查看论文截图


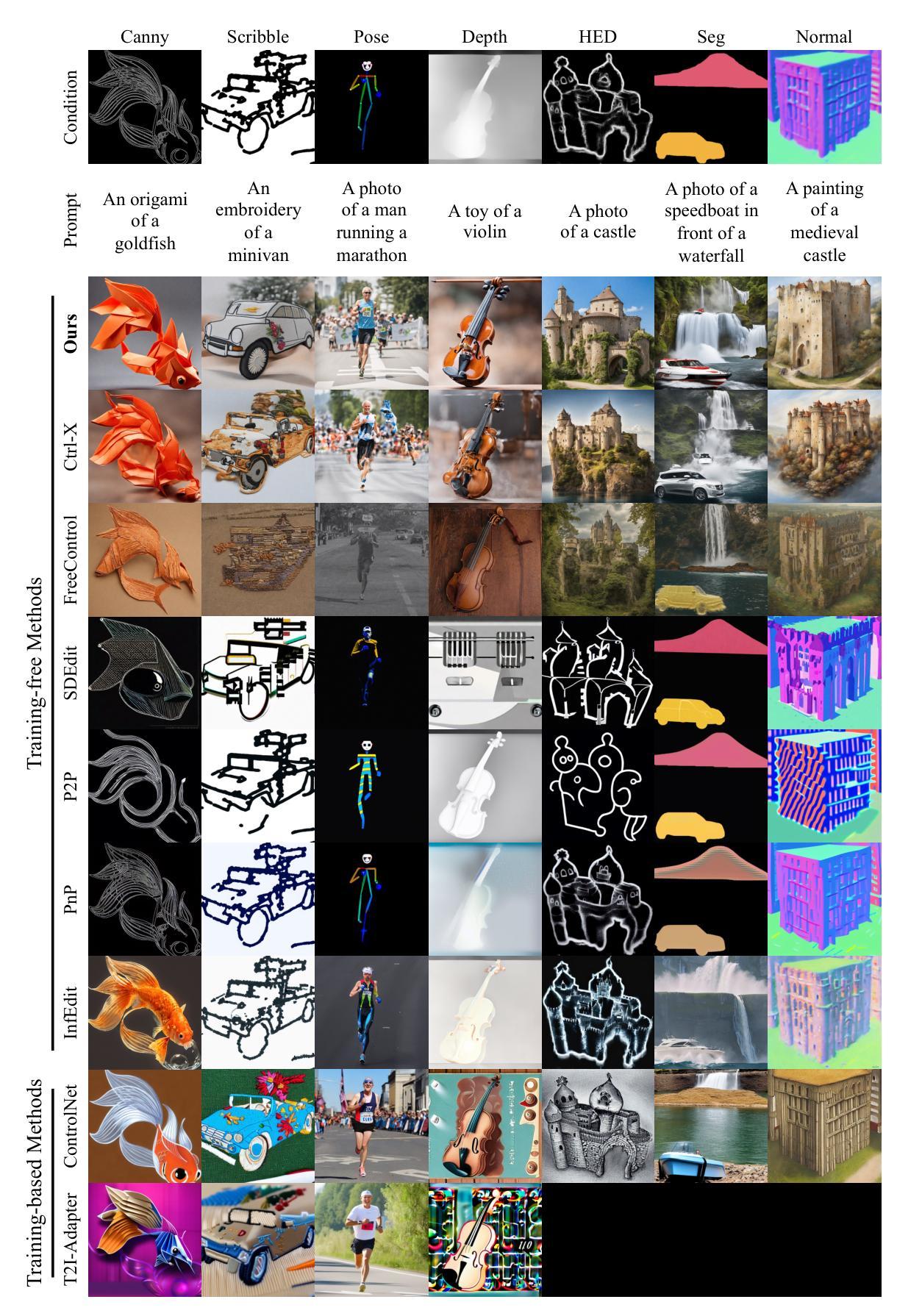
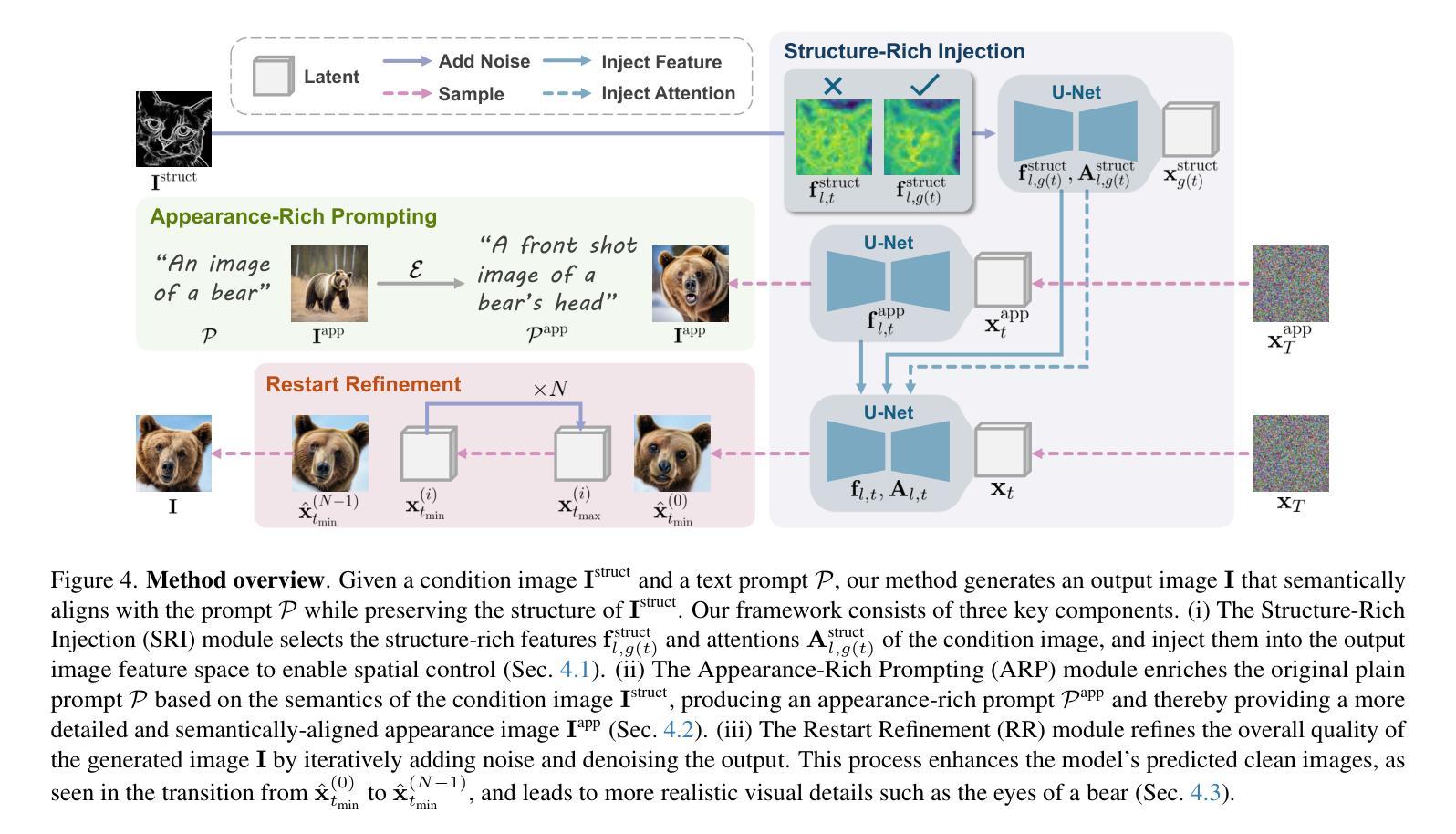
RichControl: Structure- and Appearance-Rich Training-Free Spatial Control for Text-to-Image Generation
Authors:Liheng Zhang, Lexi Pang, Hang Ye, Xiaoxuan Ma, Yizhou Wang
Text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models have shown remarkable success in generating high-quality images from text prompts. Recent efforts extend these models to incorporate conditional images (e.g., depth or pose maps) for fine-grained spatial control. Among them, feature injection methods have emerged as a training-free alternative to traditional fine-tuning approaches. However, they often suffer from structural misalignment, condition leakage, and visual artifacts, especially when the condition image diverges significantly from natural RGB distributions. By revisiting existing methods, we identify a core limitation: the synchronous injection of condition features fails to account for the trade-off between domain alignment and structural preservation during denoising. Inspired by this observation, we propose a flexible feature injection framework that decouples the injection timestep from the denoising process. At its core is a structure-rich injection module, which enables the model to better adapt to the evolving interplay between alignment and structure preservation throughout the diffusion steps, resulting in more faithful structural generation. In addition, we introduce appearance-rich prompting and a restart refinement strategy to further enhance appearance control and visual quality. Together, these designs enable training-free generation that is both structure-rich and appearance-rich. Extensive experiments show that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance across diverse zero-shot conditioning scenarios.
文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型在根据文本提示生成高质量图像方面取得了显著的成功。最近的研究努力将这些模型扩展到结合条件图像(例如深度或姿态图)以实现精细的空间控制。其中,特征注入方法作为一种无需训练的传统微调方法的替代方案而出现。然而,它们常常遭受结构错位、条件泄露和视觉伪影等问题,尤其是当条件图像与自然RGB分布相差较大时。通过对现有方法的重新审视,我们确定了一个核心限制:条件特征的同步注入未能考虑到去噪过程中的域对齐与结构保持之间的权衡。受此观察的启发,我们提出了一种灵活的特征注入框架,该框架将注入时间与去噪过程解耦。其核心是一个结构丰富的注入模块,使模型能够更好地适应扩散步骤中对齐与结构保持之间的不断变化的相互作用,从而实现更忠实的结构生成。此外,我们还引入了丰富的外观提示和重启细化策略,以进一步增强外观控制和视觉质量。这些设计共同实现了无需训练即可生成既丰富结构又丰富外观的图像。大量实验表明,我们的方法在多种零样本条件场景下达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2406.07540 by other authors
摘要
文本转图像(T2I)扩散模型通过文本提示生成高质量图像,取得了显著的成功。近期研究尝试将条件图像(如深度或姿态图)融入这些模型,以实现精细的空间控制。特征注入方法作为一种无需训练的传统微调方法的替代方案应运而生。然而,当条件图像与自然的RGB分布差异较大时,它们常面临结构错位、条件泄露和视觉伪影等问题。本文通过重新审视现有方法,发现核心限制在于同步注入条件特征时,未能考虑域对齐与结构保留之间的权衡。基于此观察,本文提出一种灵活的特征注入框架,将注入时间与去噪过程解耦。其核心的结构丰富注入模块使模型能够更好地适应扩散步骤中域对齐与结构保留之间的不断变化的权衡,从而实现更忠实于原结构的生成。此外,本文还引入外观丰富的提示和重启细化策略,进一步增强了外观控制和视觉质量。总的来说,这些设计实现了无需训练的结构丰富和外观丰富的生成。大量实验表明,本文方法在不同零样本条件场景下面向应用获得了最佳性能。
关键见解
- 文本转图像(T2I)扩散模型能够通过文本提示生成高质量图像。
- 近期研究尝试融入条件图像以实现更精细的空间控制。
- 特征注入方法作为一种无需训练的微调方法的替代方案受到关注。
- 特征注入面临的核心挑战是结构错位、条件泄露和视觉伪影等问题。
- 现有方法同步注入条件特征时未充分权衡域对齐与结构保留。
- 本文提出的灵活特征注入框架能够解耦注入时间与去噪过程,实现更忠实于原结构的生成。
点此查看论文截图

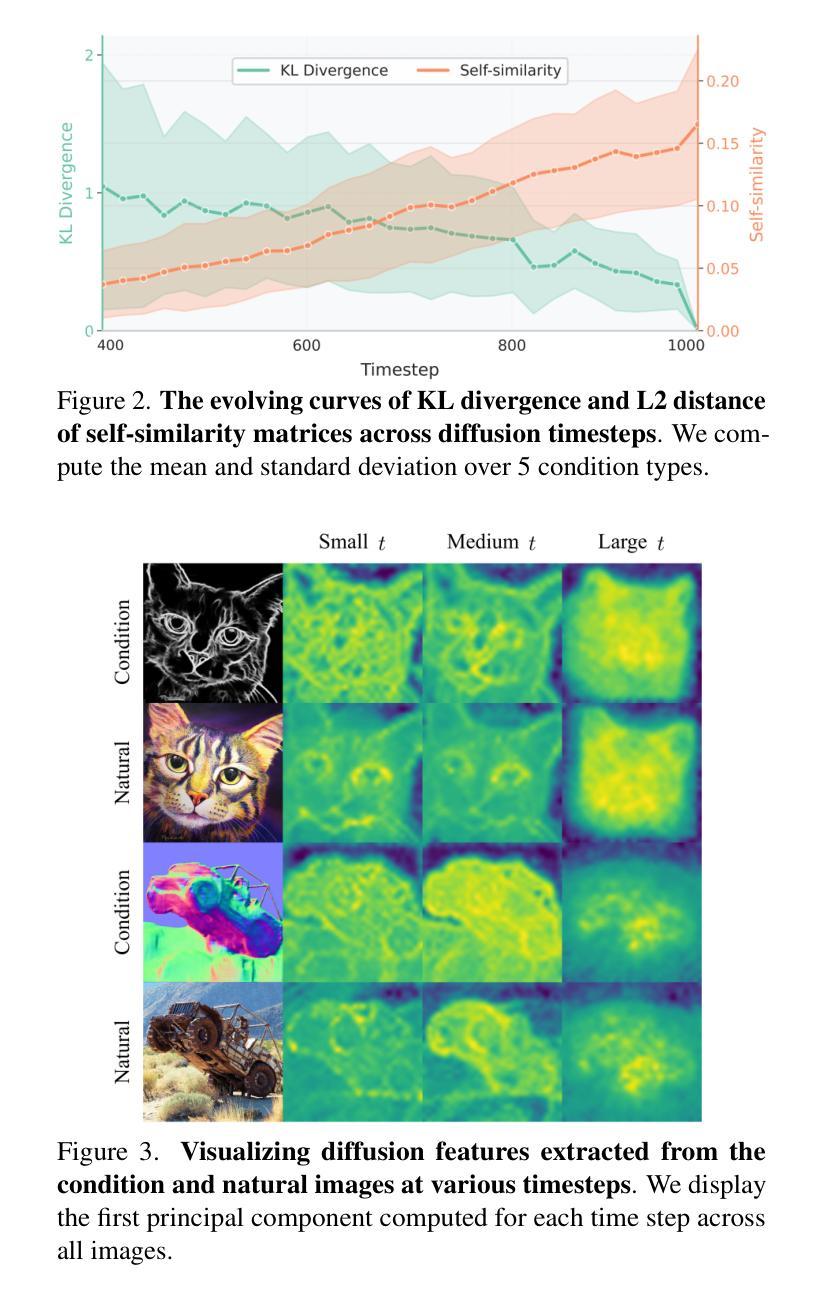

CaO$_2$: Rectifying Inconsistencies in Diffusion-Based Dataset Distillation
Authors:Haoxuan Wang, Zhenghao Zhao, Junyi Wu, Yuzhang Shang, Gaowen Liu, Yan Yan
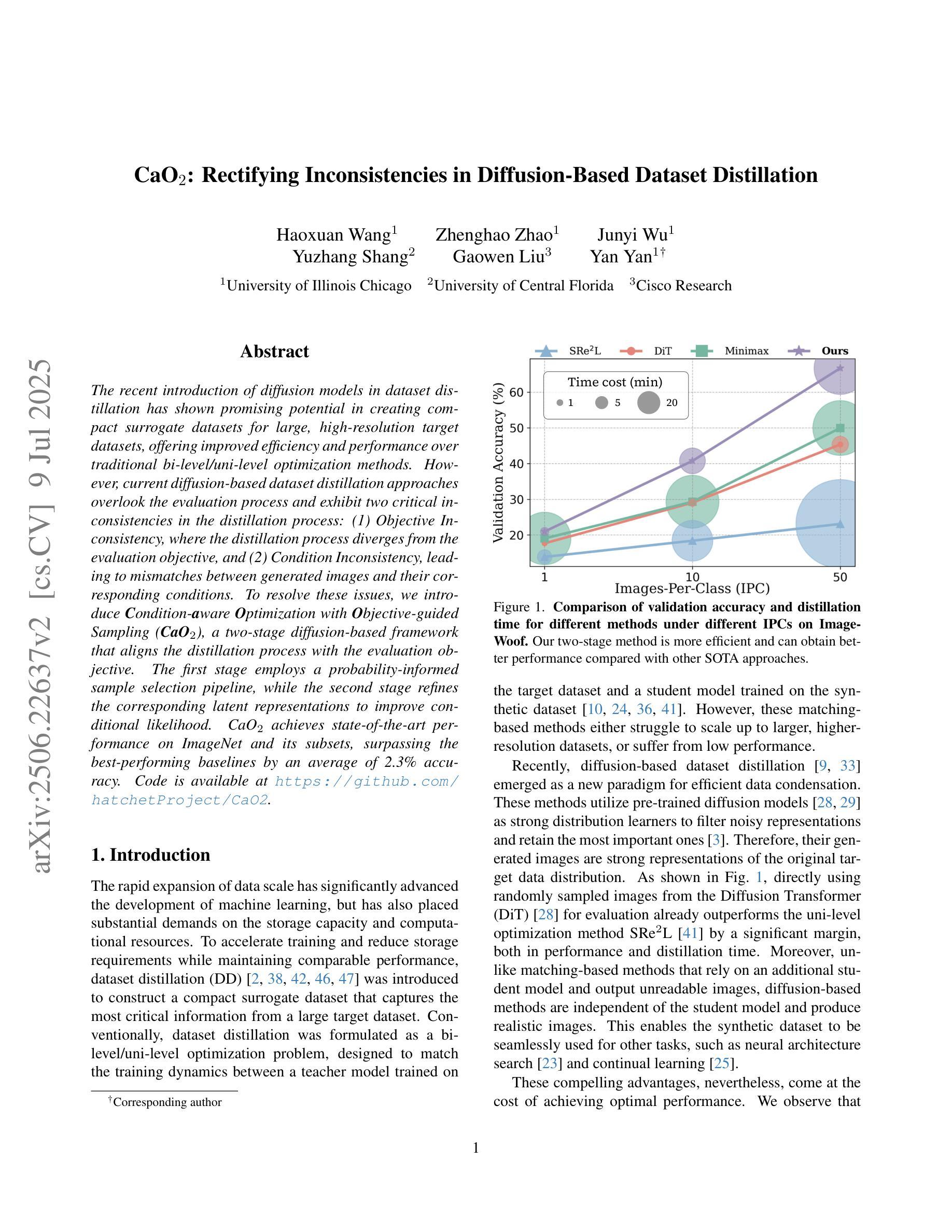
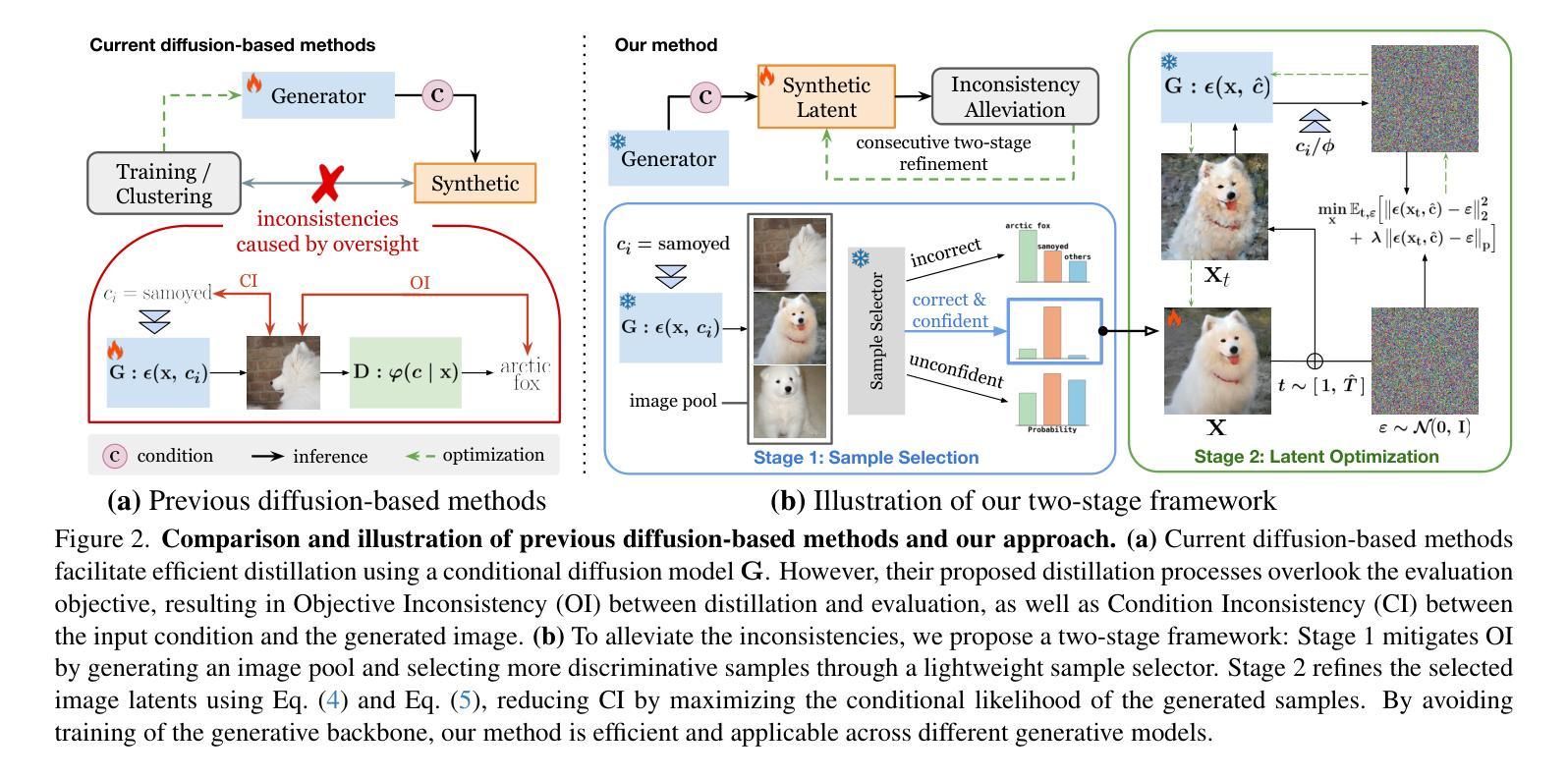
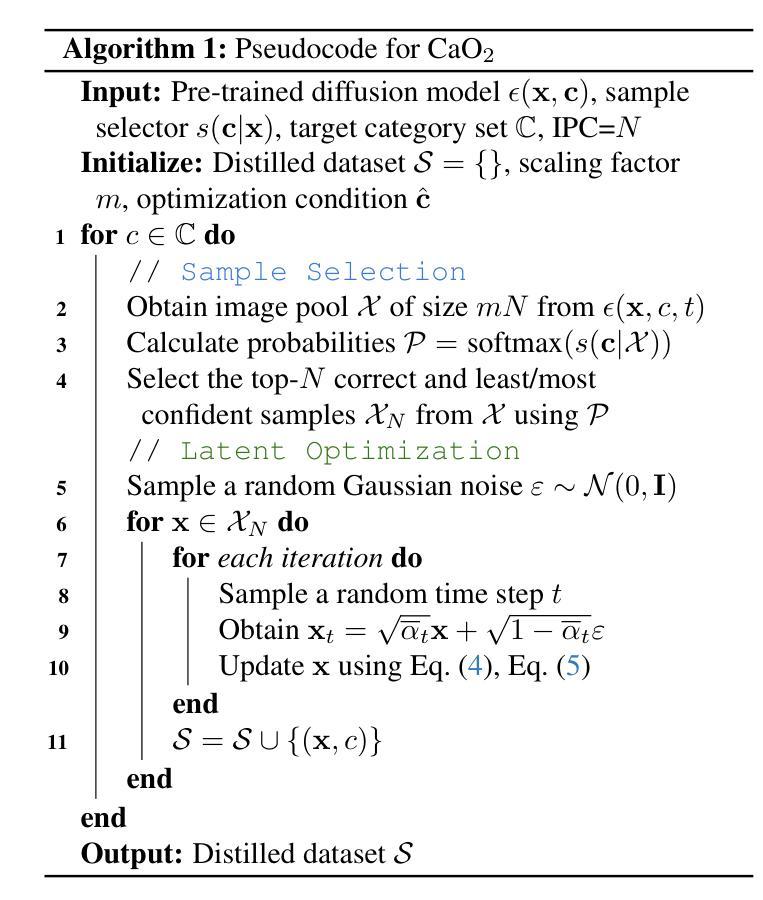
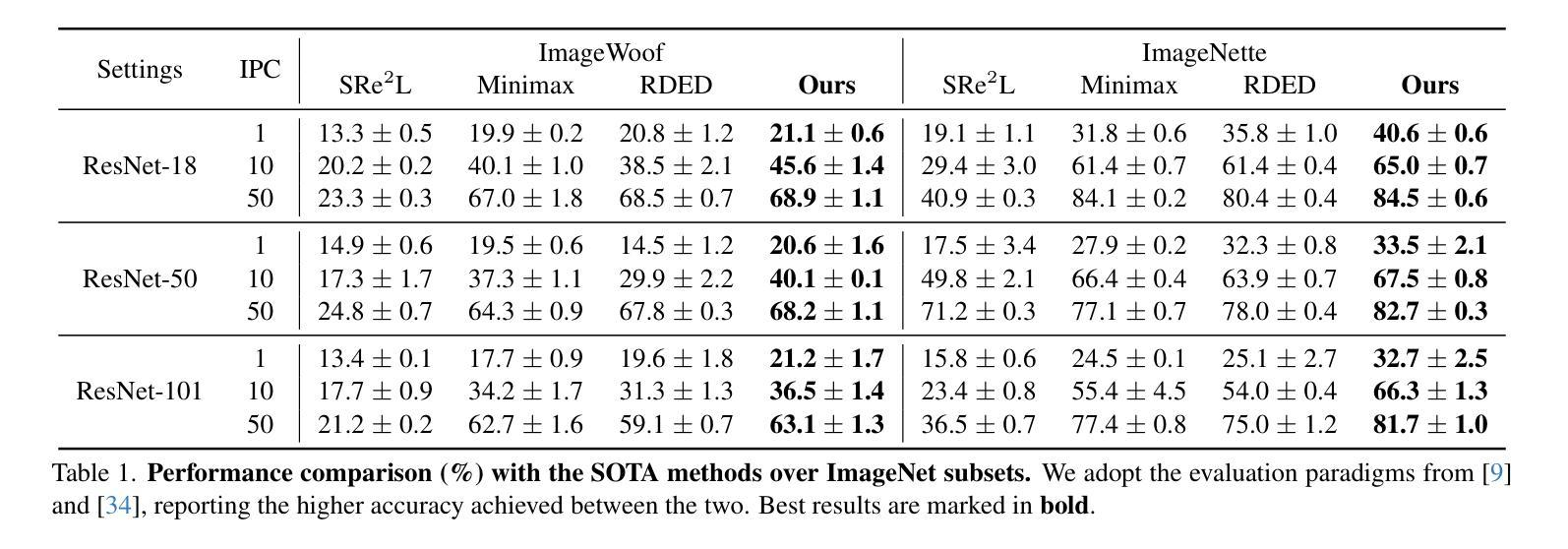
The recent introduction of diffusion models in dataset distillation has shown promising potential in creating compact surrogate datasets for large, high-resolution target datasets, offering improved efficiency and performance over traditional bi-level/uni-level optimization methods. However, current diffusion-based dataset distillation approaches overlook the evaluation process and exhibit two critical inconsistencies in the distillation process: (1) Objective Inconsistency, where the distillation process diverges from the evaluation objective, and (2) Condition Inconsistency, leading to mismatches between generated images and their corresponding conditions. To resolve these issues, we introduce Condition-aware Optimization with Objective-guided Sampling (CaO$_2$), a two-stage diffusion-based framework that aligns the distillation process with the evaluation objective. The first stage employs a probability-informed sample selection pipeline, while the second stage refines the corresponding latent representations to improve conditional likelihood. CaO$_2$ achieves state-of-the-art performance on ImageNet and its subsets, surpassing the best-performing baselines by an average of 2.3% accuracy.
在数据集蒸馏中最近引入的扩散模型显示出在为目标的大型高分辨率数据集创建紧凑替代数据集方面的巨大潜力,相较于传统的双向或单向优化方法,它提高了效率和性能。然而,当前的基于扩散的数据集蒸馏方法忽略了评估过程,并在蒸馏过程中表现出两个关键的不一致性:(1)目标不一致性,即蒸馏过程与评估目标相偏离;(2)条件不一致性,导致生成的图像与其对应的条件不匹配。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了基于条件感知优化与目标导向采样(CaO$_2$)的两阶段扩散框架,使蒸馏过程与评估目标保持一致。第一阶段采用基于概率的样本选择管道,而第二阶段则对相应的潜在表示进行微调,以提高条件概率。CaO$_2$在ImageNet及其子集上实现了最先进的性能,平均准确率高于最佳基线2.3%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025. Code is available at https://github.com/hatchetProject/CaO2
Summary
扩散模型在数据集蒸馏中的最新引入,为创建针对大型高分辨率目标数据集的高效紧凑替代数据集展示了潜力。然而,现有的基于扩散的数据集蒸馏方法忽视了评估过程,并在蒸馏过程中表现出两个关键的不一致性:目标不一致和条件不一致。为解决这些问题,我们提出了基于目标引导采样的条件感知优化(CaO2)的两阶段扩散框架,使蒸馏过程与评估目标保持一致。CaO2在ImageNet及其子集上实现了最先进的性能,平均准确率比最佳基线高出2.3%。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在数据集蒸馏中展现出潜力,能创建针对大型高分辨率目标数据集的紧凑替代数据集。
- 当前扩散模型在蒸馏过程中存在两个关键的不一致性:目标不一致和条件不一致。
- 条件感知优化(CaO2)是一个两阶段的扩散框架,旨在解决这两个不一致性问题。
- CaO2通过概率信息采样管道的第一阶段和第二阶段改进潜在表示,提高条件概率的精度。
- CaO2在ImageNet及其子集上实现了最先进的性能表现。
- CaO2相比最佳基线,平均准确率提高了2.3%。
点此查看论文截图
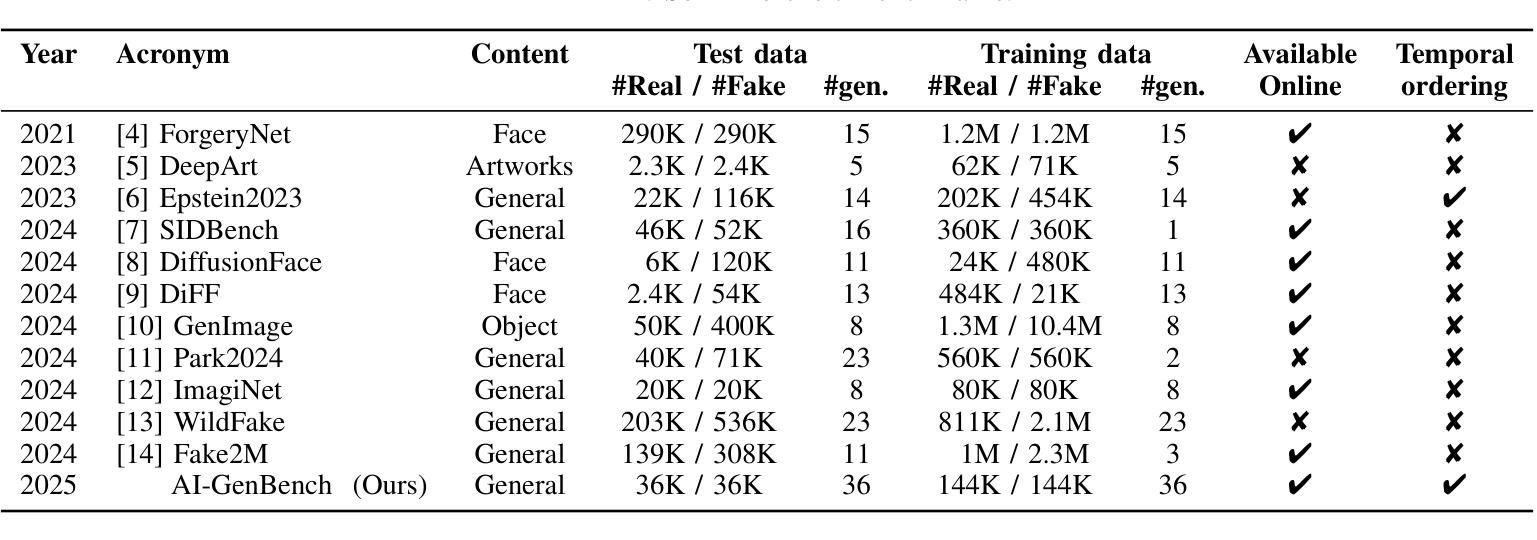
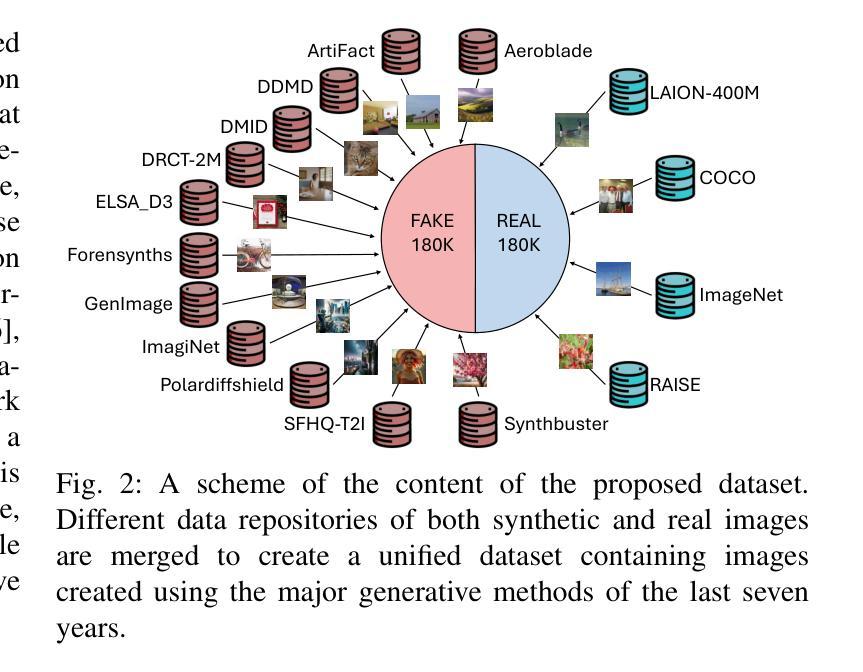
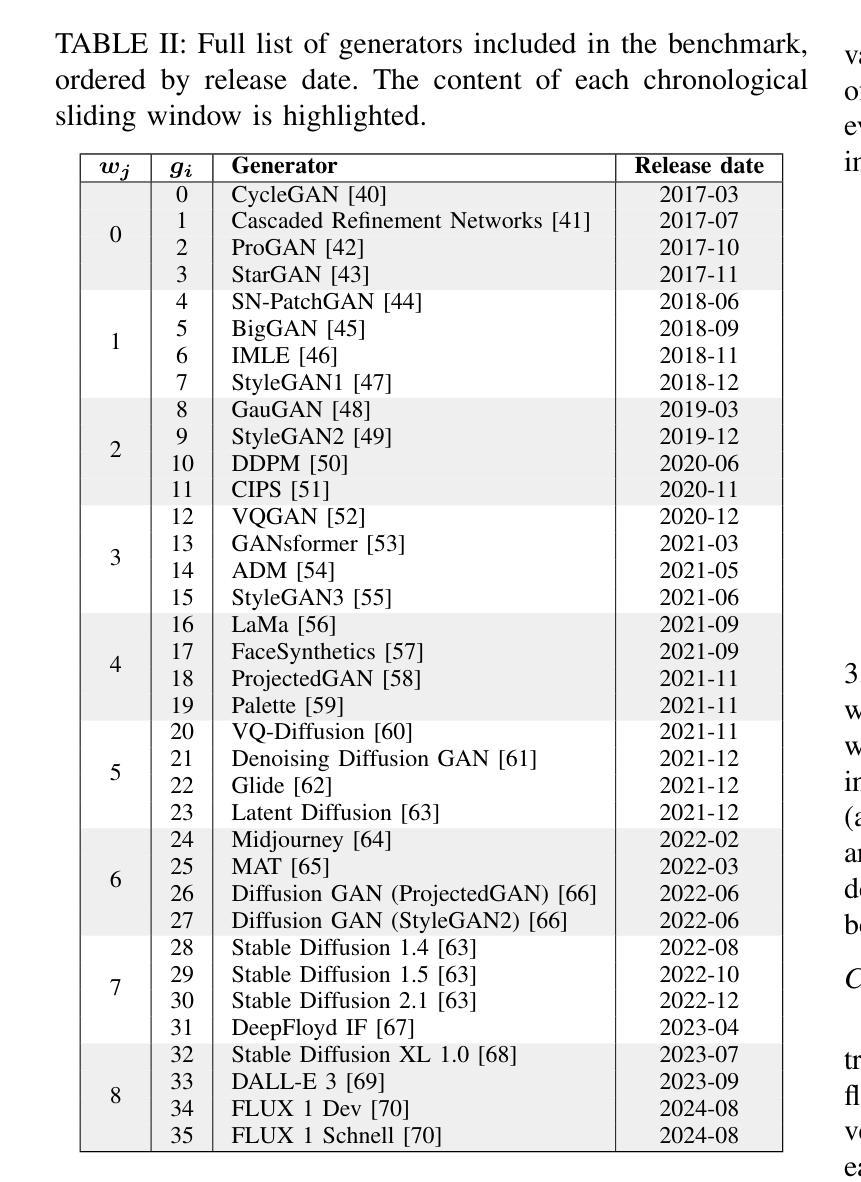
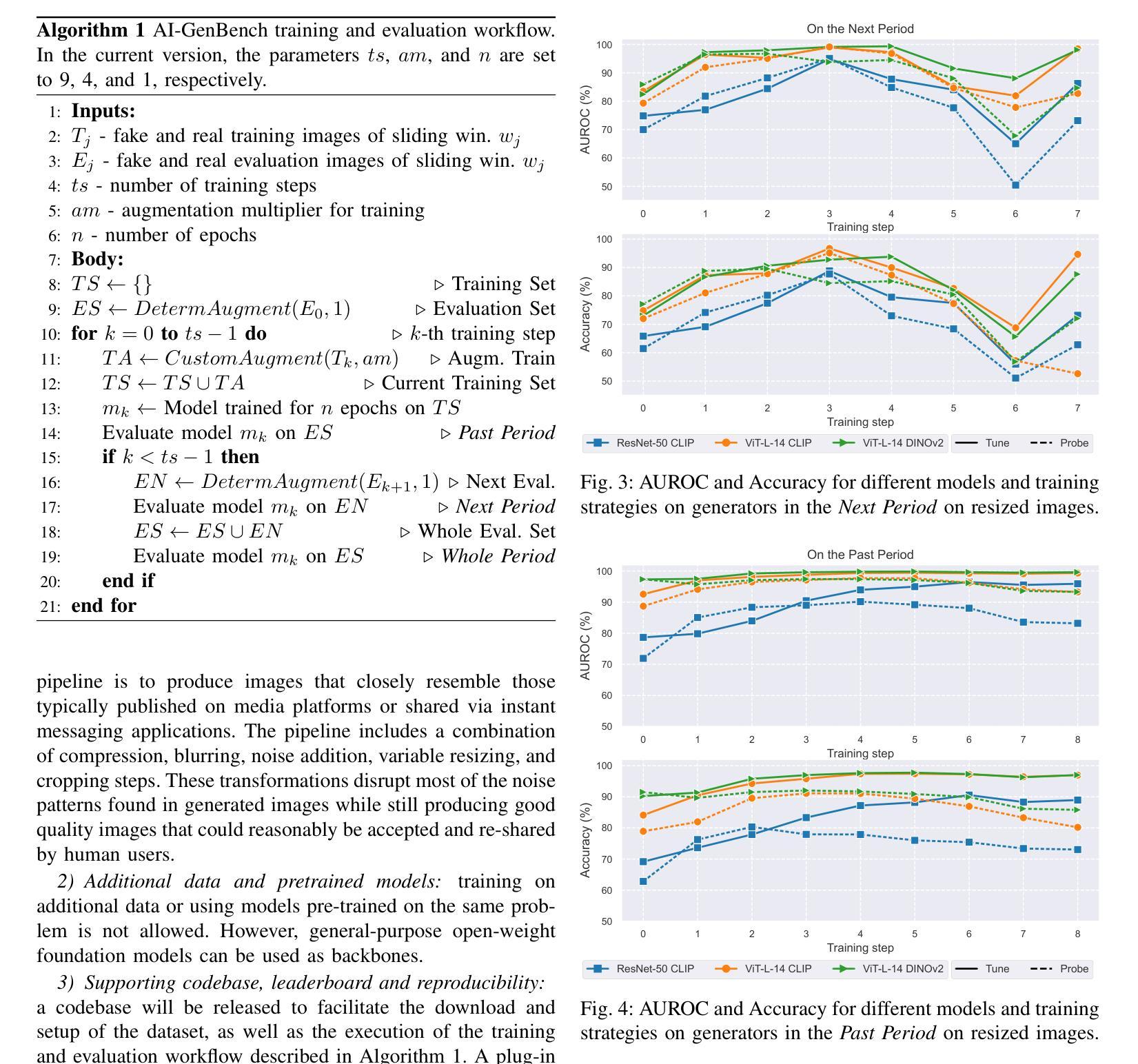
AI-GenBench: A New Ongoing Benchmark for AI-Generated Image Detection
Authors:Lorenzo Pellegrini, Davide Cozzolino, Serafino Pandolfini, Davide Maltoni, Matteo Ferrara, Luisa Verdoliva, Marco Prati, Marco Ramilli
The rapid advancement of generative AI has revolutionized image creation, enabling high-quality synthesis from text prompts while raising critical challenges for media authenticity. We present Ai-GenBench, a novel benchmark designed to address the urgent need for robust detection of AI-generated images in real-world scenarios. Unlike existing solutions that evaluate models on static datasets, Ai-GenBench introduces a temporal evaluation framework where detection methods are incrementally trained on synthetic images, historically ordered by their generative models, to test their ability to generalize to new generative models, such as the transition from GANs to diffusion models. Our benchmark focuses on high-quality, diverse visual content and overcomes key limitations of current approaches, including arbitrary dataset splits, unfair comparisons, and excessive computational demands. Ai-GenBench provides a comprehensive dataset, a standardized evaluation protocol, and accessible tools for both researchers and non-experts (e.g., journalists, fact-checkers), ensuring reproducibility while maintaining practical training requirements. By establishing clear evaluation rules and controlled augmentation strategies, Ai-GenBench enables meaningful comparison of detection methods and scalable solutions. Code and data are publicly available to ensure reproducibility and to support the development of robust forensic detectors to keep pace with the rise of new synthetic generators.
人工智能生成的图像生成技术的快速发展,已经彻底改变了图像创作的面貌,使得可以根据文字提示生成高质量图像,同时也为媒体真实性带来了重大挑战。我们提出了Ai-GenBench,这是一个新型基准测试,旨在解决现实场景中检测AI生成图像的需求的迫切问题。与现有在静态数据集上评估模型的方法不同,Ai-GenBench引入了一个时间评估框架,该框架按生成模型的顺序逐步训练检测算法,以测试其适应新生成模型的能力,例如从生成对抗网络(GANs)到扩散模型的过渡。我们的基准测试侧重于高质量、多样化的视觉内容,并克服了当前方法的关键局限性,包括任意的数据集分割、不公平的比较和过高的计算需求。Ai-GenBench为研究人员和非专业人士(例如记者、事实核查人员)提供了综合数据集、标准化的评估协议和易于使用的工具,确保实际训练的实用性同时保持可重复性。通过制定明确的评估规则和控制的增强策略,Ai-GenBench使得检测方法的比较和可扩展解决方案变得更有意义。代码和数据公开可用,以确保可重复性并支持稳健的取证检测器的开发,以跟上新的合成生成器的步伐。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at Verimedia workshop, IJCNN 2025. 9 pages, 6 figures, 4 tables, code available: https://github.com/MI-BioLab/AI-GenBench
Summary
生成式AI的快速进步为图像创作带来了革命性的变化,实现了基于文本提示的高质量合成,同时对媒体真实性提出了严峻挑战。我们推出了Ai-GenBench,这是一个新型基准测试平台,旨在解决现实场景中检测AI生成图像的需求。不同于现有仅在静态数据集上评估模型的解决方案,Ai-GenBench引入了一个临时评估框架,该框架按生成模型的顺序逐步对合成图像进行训练,以测试其适应新生成模型的能力,如从生成对抗网络(GANs)向扩散模型过渡。我们的基准测试平台侧重于高质量、多样化的视觉内容,并克服了当前方法的关键局限性,包括任意数据集分割、不公平比较和过高的计算需求。Ai-GenBench为研究人员和非专家(如记者、事实核查人员)提供了综合数据集、标准化评估协议和可用工具,确保了可重复性并满足了实际的训练需求。通过制定明确的评估规则和受控的增强策略,Ai-GenBench使得检测方法的比较和可扩展解决方案变得更有意义。代码和数据公开可用,以确保可重复性和支持稳健的取证检测器的开发,以应对新的合成生成器的崛起。
Key Takeaways
- 生成式AI的进步推动了图像创作的革命,实现了基于文本的高质量图像合成。
- Ai-GenBench是一个新型基准测试平台,旨在解决现实场景中检测AI生成图像的需求。
- 不同于其他解决方案,Ai-GenBench采用临时评估框架来测试模型适应新生成模型的能力。
- Ai-GenBench侧重于高质量、多样化的视觉内容,并克服了当前方法的局限性。
- 平台为研究人员和非专家提供了综合数据集、标准化评估协议和工具。
- Ai-GenBench建立了明确的评估规则和受控的增强策略,便于检测方法的比较。
点此查看论文截图

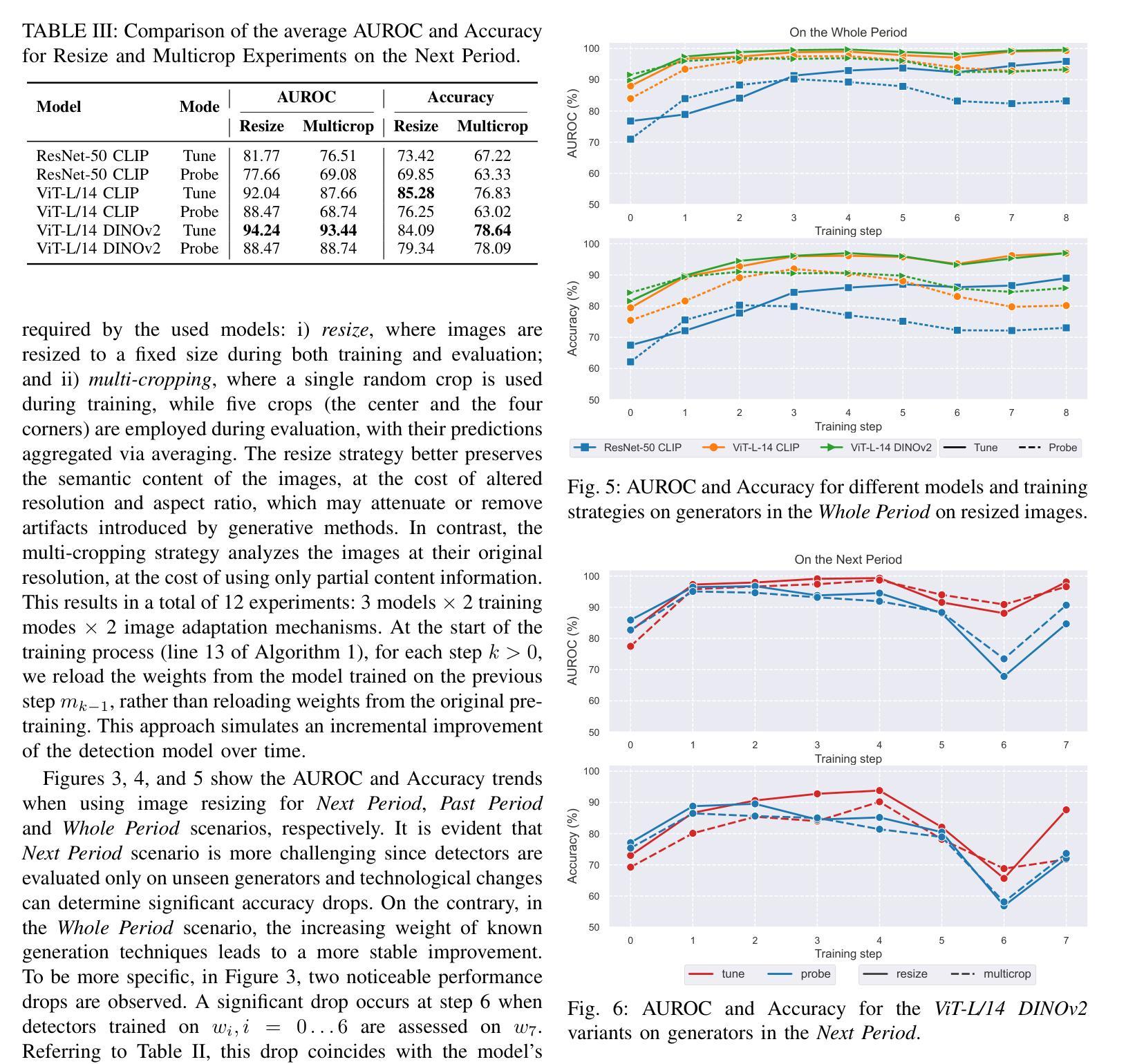
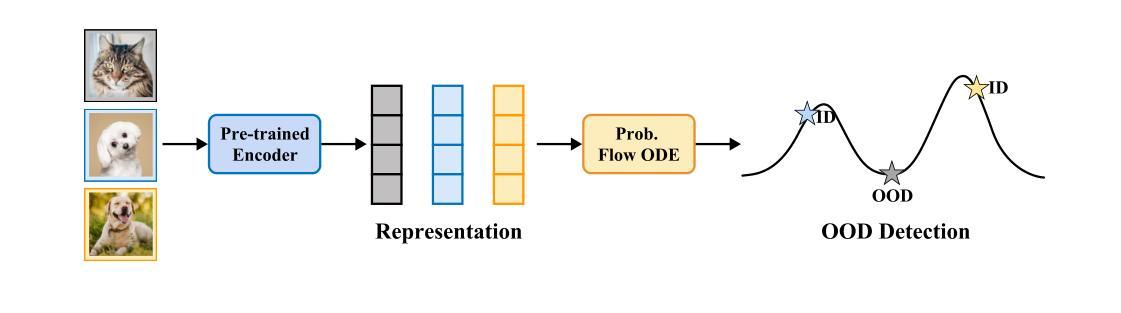
Revisiting Likelihood-Based Out-of-Distribution Detection by Modeling Representations
Authors:Yifan Ding, Arturas Aleksandraus, Amirhossein Ahmadian, Jonas Unger, Fredrik Lindsten, Gabriel Eilertsen
Out-of-distribution (OOD) detection is critical for ensuring the reliability of deep learning systems, particularly in safety-critical applications. Likelihood-based deep generative models have historically faced criticism for their unsatisfactory performance in OOD detection, often assigning higher likelihood to OOD data than in-distribution samples when applied to image data. In this work, we demonstrate that likelihood is not inherently flawed. Rather, several properties in the images space prohibit likelihood as a valid detection score. Given a sufficiently good likelihood estimator, specifically using the probability flow formulation of a diffusion model, we show that likelihood-based methods can still perform on par with state-of-the-art methods when applied in the representation space of pre-trained encoders. The code of our work can be found at $\href{https://github.com/limchaos/Likelihood-OOD.git}{\texttt{https://github.com/limchaos/Likelihood-OOD.git}}$.
异常检测(OOD)对于确保深度学习系统的可靠性至关重要,特别是在安全关键应用中。基于可能性的深度生成模型在历史上面临着在异常检测中表现不佳的批评,在应用于图像数据时,它们往往会给异常数据分配更高的可能性,而不是分配给内部数据样本。在这项工作中,我们证明了可能性本身并没有缺陷。相反,图像空间中的几个属性禁止将可能性作为有效的检测分数。给定一个足够好的可能性估计器,特别是使用扩散模型的概率流公式,我们表明在应用于预训练编码器的表示空间时,基于可能性的方法仍然可以与最先进的方法相媲美。我们工作的代码可以在https://github.com/limchaos/Likelihood-OOD.git找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Scandinavian Conference on Image Analysis 2025 (oral)
Summary
本工作指出,对于图像数据,利用预训练编码器的表示空间,利用概率流公式的扩散模型作为好的可能性估计器,基于可能性的方法仍能与最先进的OOD检测方法表现相当。以往对基于可能性的深度生成模型在OOD检测中的表现不佳的批评并非源于其本质缺陷。相反,图像空间中的某些特性阻碍了可能性作为有效的检测分数。因此,在合适的条件下,利用扩散模型改进后的可能性评估机制能够提高模型的可靠性。相关代码可通过链接访问。
Key Takeaways
- 重要性:OOD检测对于确保深度学习系统的可靠性至关重要,特别是在安全关键应用中。
- 基于可能性的深度生成模型在过去因其在OOD检测中的表现不佳而受到批评。但在特定条件下(例如使用适当的可能性估计器),其性能可以得到提升。
- 图像空间的某些特性可能会妨碍基于可能性的检测方法在OOD识别方面的表现。然而,在预训练编码器的表示空间中应用这些方法时,可能获得更好的结果。
- 使用扩散模型的概率流公式作为可能性估计器是本文的一个关键创新点。这表明适当的模型架构改进可以显著提高基于可能性的方法的性能。
- 基于可能性的方法与最先进的OOD检测方法表现相当,表明在合适的条件下,这些方法具有潜在的优越性。这为未来开发更为可靠的深度学习系统提供了重要的参考方向。
- 在实验和测试中应注意良好的可能性估计器的有效性以及图像空间特性的影响。通过优化这些因素,可以提高基于可能性的方法在OOD检测中的性能。
点此查看论文截图

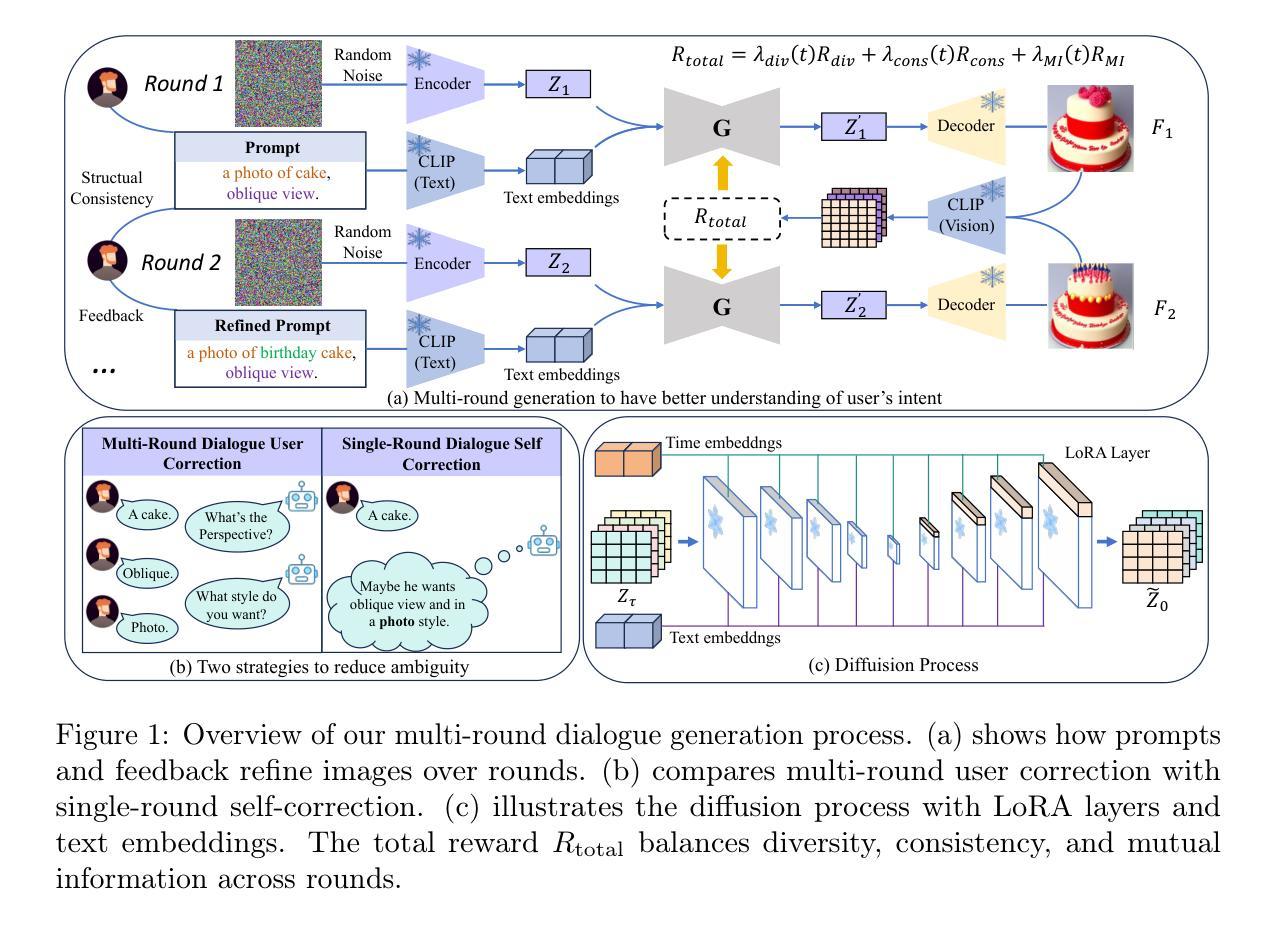
OMR-Diffusion:Optimizing Multi-Round Enhanced Training in Diffusion Models for Improved Intent Understanding
Authors:Kun Li, Jianhui Wang, Miao Zhang, Xueqian Wang
Generative AI has significantly advanced text-driven image generation, but it still faces challenges in producing outputs that consistently align with evolving user preferences and intents, particularly in multi-turn dialogue scenarios. In this research, We present a Visual Co-Adaptation (VCA) framework that incorporates human-in-the-loop feedback, utilizing a well-trained reward model specifically designed to closely align with human preferences. Using a diverse multi-turn dialogue dataset, the framework applies multiple reward functions (such as diversity, consistency, and preference feedback) to refine the diffusion model through LoRA, effectively optimizing image generation based on user input. We also constructed multi-round dialogue datasets with prompts and image pairs that well-fit user intent. Experiments show the model achieves 508 wins in human evaluation, outperforming DALL-E 3 (463 wins) and others. It also achieves 3.4 rounds in dialogue efficiency (vs. 13.7 for DALL-E 3) and excels in metrics like LPIPS (0.15) and BLIP (0.59). Various experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method over state-of-the-art baselines, with significant improvements in image consistency and alignment with user intent.
生成式人工智能在文本驱动图像生成方面取得了显著进展,但在持续生成符合不断变化的用户偏好和意图的输出方面仍面临挑战,特别是在多轮对话场景中。本研究提出了一种视觉协同适应(VCA)框架,该框架引入了人类反馈循环,并利用专门训练有素的奖励模型,以与人类偏好紧密对齐。使用多样化的多轮对话数据集,该框架应用多个奖励函数(如多样性、一致性和偏好反馈)来通过LoRA细化扩散模型,有效地根据用户输入优化图像生成。我们还构建了多轮对话数据集,带有符合用户意图的提示和图像对。实验表明,该模型在人工评估中取得4次胜出,超过DALL-E 3(赢得对手四次胜出),并展现出出色的表现。它在对话效率方面也取得了较高的表现(对比对手需要轮询交流;但与此模型比对话只需要将近三秒钟左右)。它也在指标如LPIPS(相似度为达到领先的得分0.15)和BLIP(得分为接近满分,即大约接近一个水平为高的分数线)等方面表现出色。各种实验表明,与最先进的基线相比,所提出的方法具有显著优势,在图像一致性和符合用户意图方面取得了重大改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文介绍了基于视觉协同适应(VCA)框架的研究,该框架结合了人类反馈和奖励模型,优化了文本驱动图像生成的多轮对话场景。通过应用多个奖励函数,如多样性、一致性和偏好反馈,该框架能够基于用户输入优化扩散模型。实验表明,该模型在人类评价中胜出次数更多,对话效率更高,且在图像一致性与用户意图对齐方面表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 研究提出了一个名为Visual Co-Adaptation(VCA)的框架,用于改进文本驱动的图像生成。
- VCA框架结合了人类反馈和奖励模型,以更好地适应用户偏好和意图。
- 该框架应用多个奖励函数,包括多样性、一致性和偏好反馈,以优化扩散模型。
- 通过使用多轮对话数据集和适当的提示和图像对,该模型可以更好地适应用户意图。
- 实验结果显示,该模型在人类评价和对话效率方面均优于其他模型。
- 该模型在图像一致性和与用户意图对齐方面表现出显著改进。
点此查看论文截图

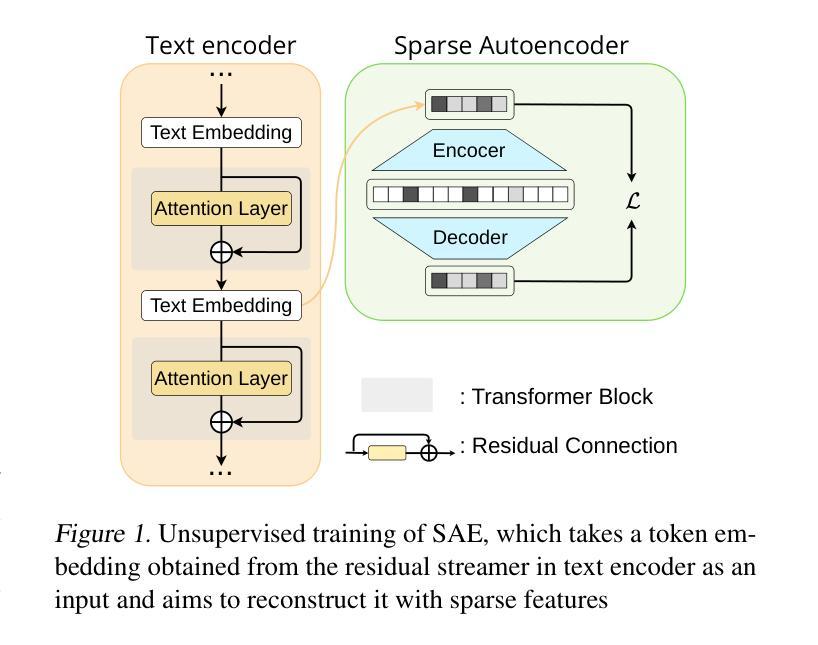
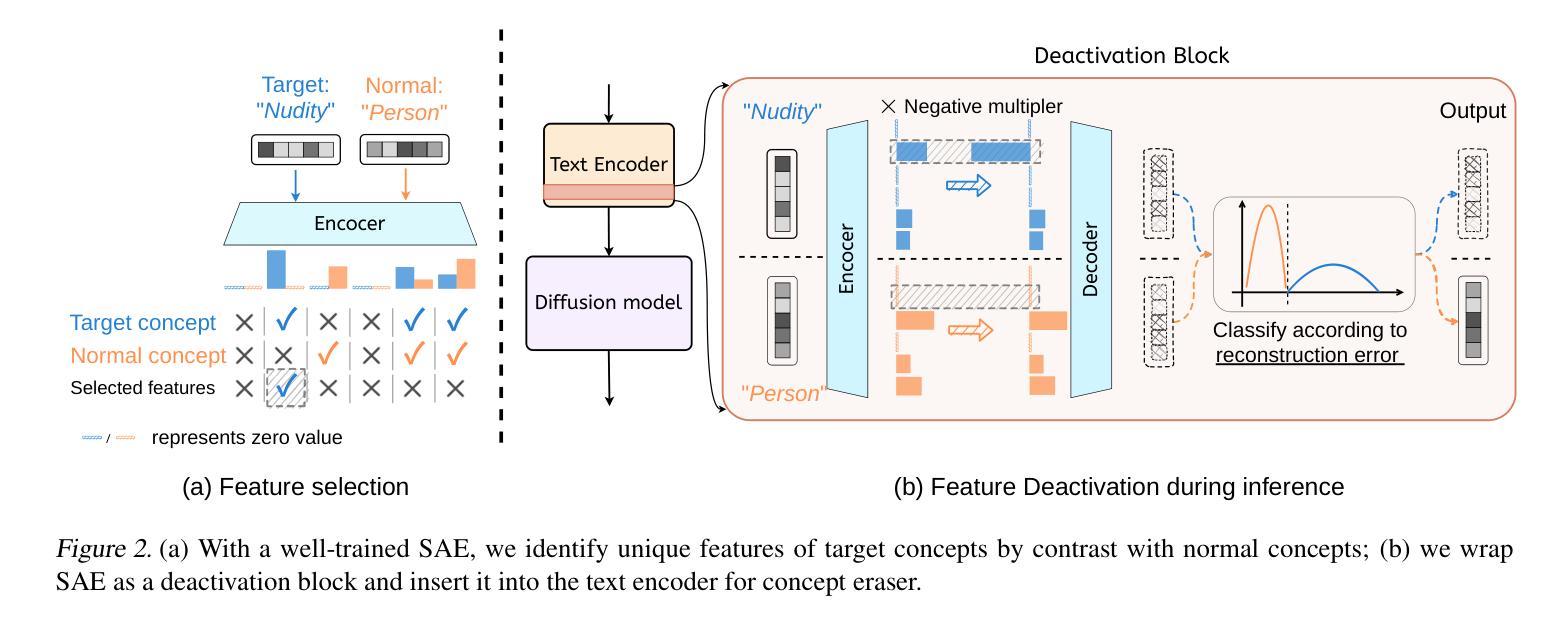
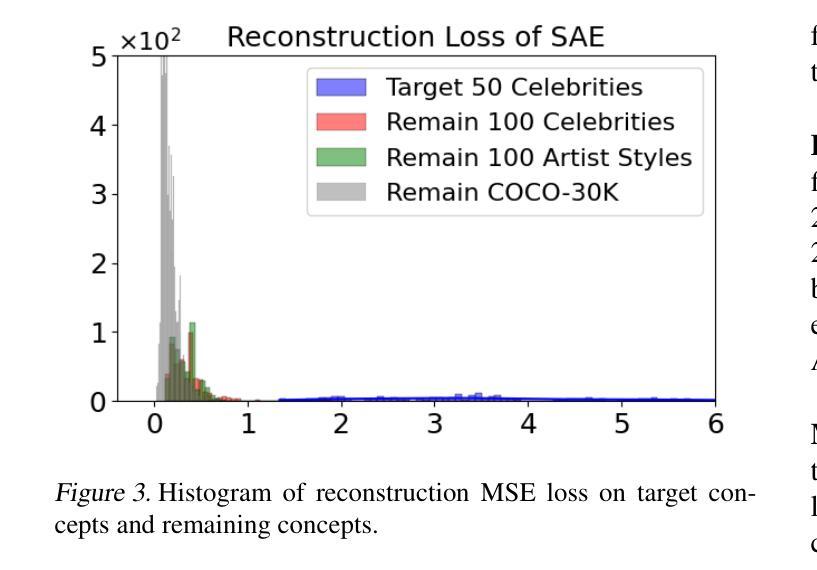
Sparse Autoencoder as a Zero-Shot Classifier for Concept Erasing in Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Authors:Zhihua Tian, Sirun Nan, Ming Xu, Shengfang Zhai, Wenjie Qu, Jian Liu, Ruoxi Jia, Jiaheng Zhang
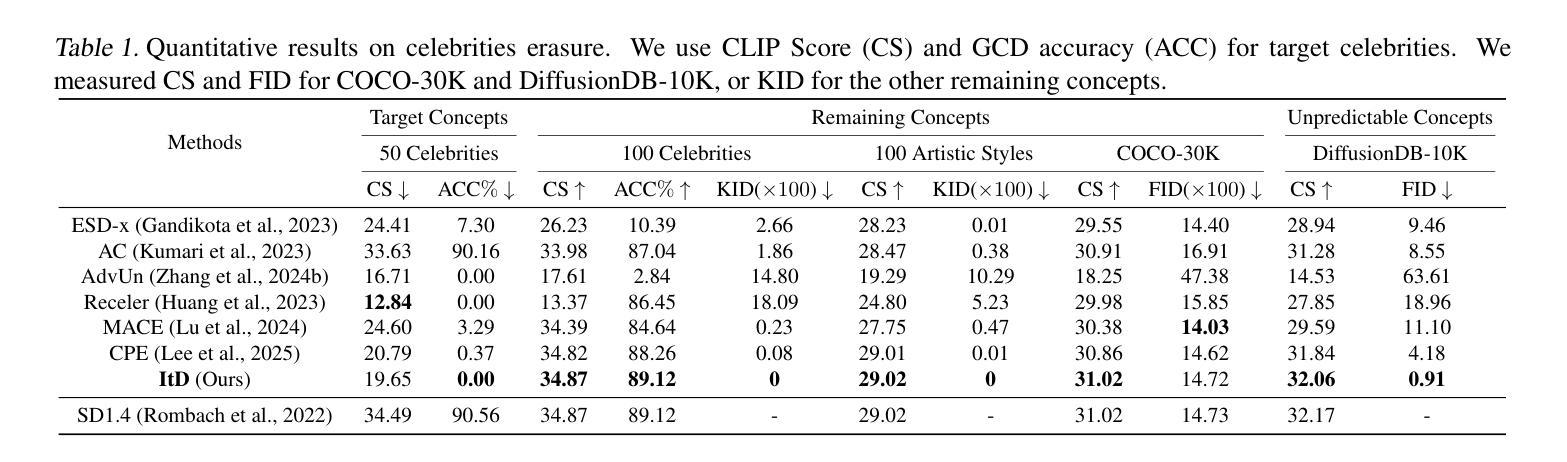
Text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models have achieved remarkable progress in generating high-quality images but also raise people’s concerns about generating harmful or misleading content. While extensive approaches have been proposed to erase unwanted concepts without requiring retraining from scratch, they inadvertently degrade performance on normal generation tasks. In this work, we propose Interpret then Deactivate (ItD), a novel framework to enable precise concept removal in T2I diffusion models while preserving overall performance. ItD first employs a sparse autoencoder (SAE) to interpret each concept as a combination of multiple features. By permanently deactivating the specific features associated with target concepts, we repurpose SAE as a zero-shot classifier that identifies whether the input prompt includes target concepts, allowing selective concept erasure in diffusion models. Moreover, we demonstrate that ItD can be easily extended to erase multiple concepts without requiring further training. Comprehensive experiments across celebrity identities, artistic styles, and explicit content demonstrate ItD’s effectiveness in eliminating targeted concepts without interfering with normal concept generation. Additionally, ItD is also robust against adversarial prompts designed to circumvent content filters. Code is available at: https://github.com/NANSirun/Interpret-then-deactivate.
文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型在生成高质量图像方面取得了显著的进步,但也引发了人们对生成有害或误导性内容的担忧。虽然已提出广泛的方法在不重新训练的情况下消除不需要的概念,但它们会无意中降低正常生成任务的性能。在这项工作中,我们提出了“先解释后停用”(ItD)这一新框架,能够在T2I扩散模型中实现精确的概念去除,同时保持整体性能。ItD首先采用稀疏自动编码器(SAE)来解释每个概念是多个特征的组合。通过永久停用与目标概念相关的特定特征,我们将SAE重新定位为一种零射击分类器,可以识别输入提示是否包含目标概念,从而在扩散模型中实现选择性概念删除。此外,我们证明ItD可以很容易地扩展到删除多个概念,而无需进一步训练。在名人身份、艺术风格和明确内容方面的综合实验证明了ItD在消除目标概念方面的有效性,而不会干扰正常的概念生成。此外,ItD对于设计用于规避内容过滤器的对抗性提示也具有鲁棒性。代码可在:https://github.com/NANSirun/Interpret-then-deactivate找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 25 pages
Summary
文本提出一种名为Interpret then Deactivate(ItD)的新框架,用于在文本转图像(T2I)扩散模型中实现精确的概念去除,同时保留整体性能。该框架通过稀疏自动编码器(SAE)解释每个概念,并永久停用与目标概念相关的特定特征,实现选择性概念删除。同时,该框架能够扩展到删除多个概念而无需进一步训练,且对对抗性提示具有鲁棒性。
Key Takeaways
- ItD框架能够在不损害整体性能的前提下,精确地从文本转图像(T2I)扩散模型中移除有害或误导性的概念。
- ItD利用稀疏自动编码器(SAE)解释每个概念,并将其视为多个特征的组合。
- 通过永久停用与目标概念相关的特定特征,ItD能够实现选择性概念删除,并允许对扩散模型进行精确调控。
- ItD框架能够轻松扩展到删除多个概念,无需进一步训练。
- 实验表明,ItD在消除特定概念的同时,不会干扰正常的概念生成任务。
- ItD框架对于对抗性的提示具有鲁棒性,能够有效避免内容过滤的绕过。
点此查看论文截图

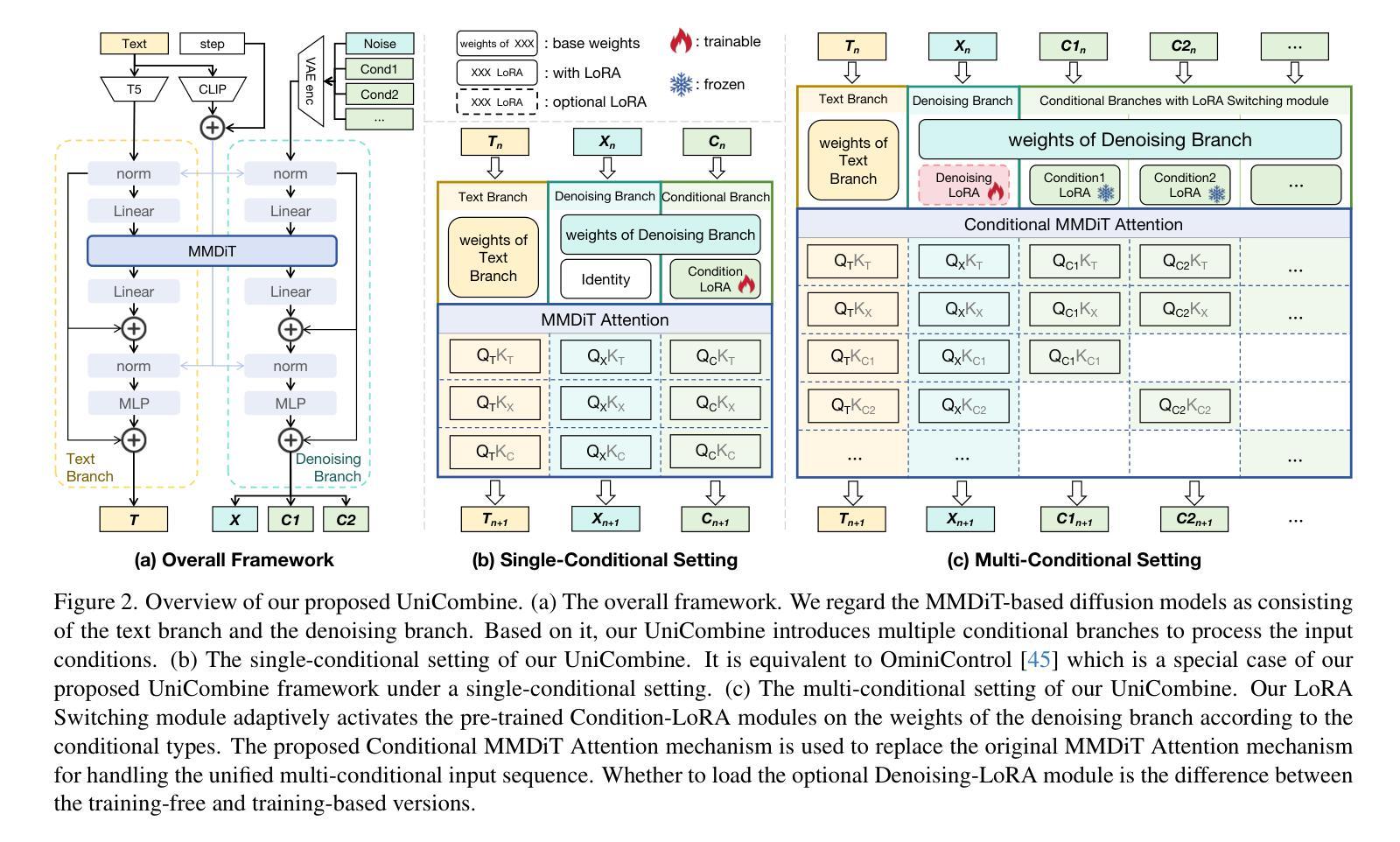
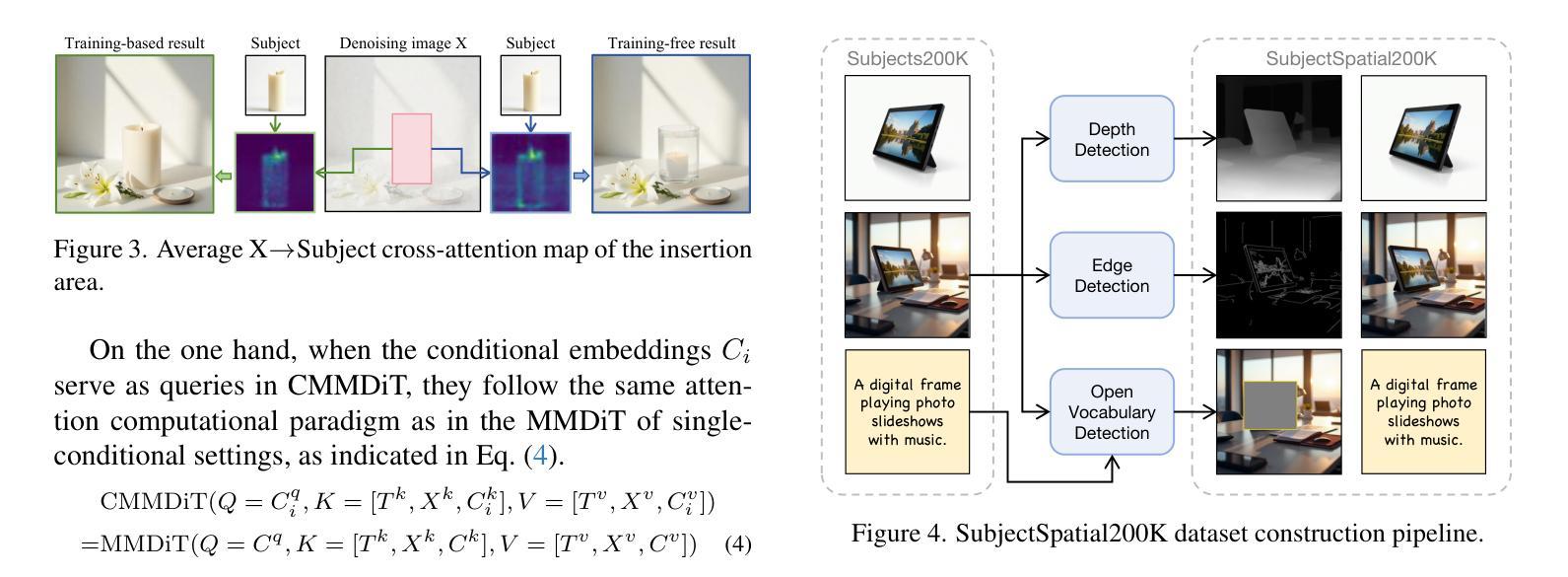
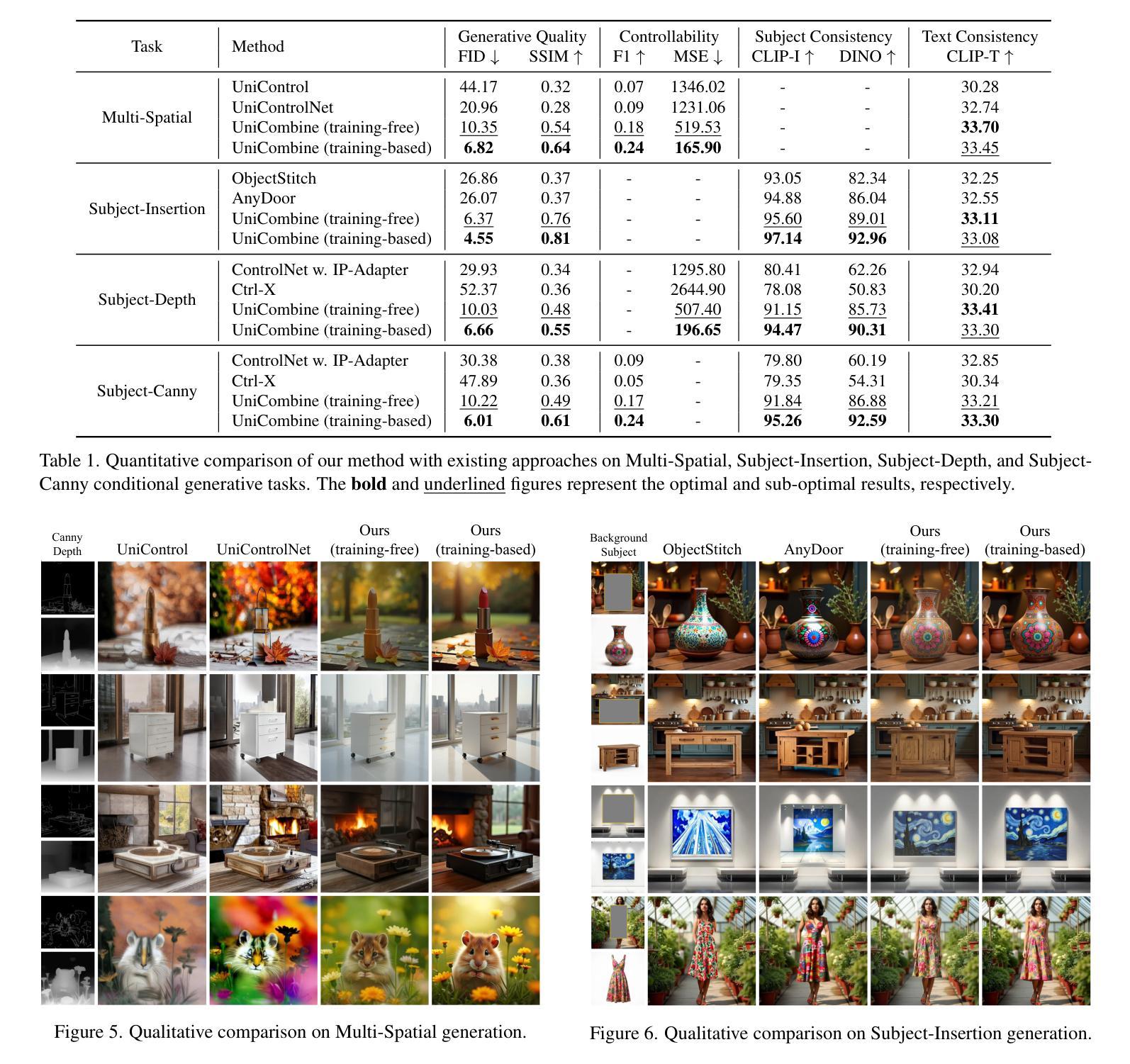
UniCombine: Unified Multi-Conditional Combination with Diffusion Transformer
Authors:Haoxuan Wang, Jinlong Peng, Qingdong He, Hao Yang, Ying Jin, Jiafu Wu, Xiaobin Hu, Yanjie Pan, Zhenye Gan, Mingmin Chi, Bo Peng, Yabiao Wang
With the rapid development of diffusion models in image generation, the demand for more powerful and flexible controllable frameworks is increasing. Although existing methods can guide generation beyond text prompts, the challenge of effectively combining multiple conditional inputs while maintaining consistency with all of them remains unsolved. To address this, we introduce UniCombine, a DiT-based multi-conditional controllable generative framework capable of handling any combination of conditions, including but not limited to text prompts, spatial maps, and subject images. Specifically, we introduce a novel Conditional MMDiT Attention mechanism and incorporate a trainable LoRA module to build both the training-free and training-based versions. Additionally, we propose a new pipeline to construct SubjectSpatial200K, the first dataset designed for multi-conditional generative tasks covering both the subject-driven and spatially-aligned conditions. Extensive experimental results on multi-conditional generation demonstrate the outstanding universality and powerful capability of our approach with state-of-the-art performance.
随着扩散模型在图像生成领域的快速发展,对更强大、更灵活的可控框架的需求也在增加。尽管现有方法可以在文本提示之外引导生成,但如何有效地结合多个条件输入并保持与所有条件的一致性仍是未解决的问题。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了UniCombine,这是一个基于DiT的多条件可控生成框架,能够处理任何组合的条件,包括但不限于文本提示、空间地图和主题图像。具体来说,我们引入了一种新型的Conditional MMDiT Attention机制,并融入了一个可训练的LoRA模块,以构建免训练和基础训练两个版本。此外,我们提出了一种新的流程来构建SubjectSpatial200K数据集,这是专门为多条件生成任务设计的第一个数据集,涵盖了主题驱动和空间对齐的条件。在多条件生成方面的广泛实验结果表明,我们的方法具有出色的通用性和强大的能力,并达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着扩散模型在图像生成领域的快速发展,对更强大、更灵活的可控框架的需求不断增加。现有方法虽然能够超越文本提示引导生成,但如何有效结合多种条件输入,同时保持与所有输入的一致性仍是未解决的问题。为此,我们提出了UniCombine,一个基于DiT的多条件可控生成框架,能够处理各种条件组合,包括但不限于文本提示、空间地图和主题图像。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在图像生成领域的应用快速发展,对更先进、更灵活的可控框架的需求增加。
- 现有方法在结合多种条件输入时面临挑战,无法有效维持所有输入的一致性。
- UniCombine是一个基于DiT的多条件可控生成框架,能够处理各种条件组合。
- 提出了新型的Conditional MMDiT Attention机制,增强了框架的性能。
- 引入了可训练的LoRA模块,用于构建无需训练和需要训练的两个版本。
- 构建了SubjectSpatial200K数据集,专为多条件生成任务设计,涵盖主题驱动和空间对齐条件。
点此查看论文截图