⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-11 更新
Exploring LLMs for Predicting Tutor Strategy and Student Outcomes in Dialogues
Authors:Fareya Ikram, Alexander Scarlatos, Andrew Lan
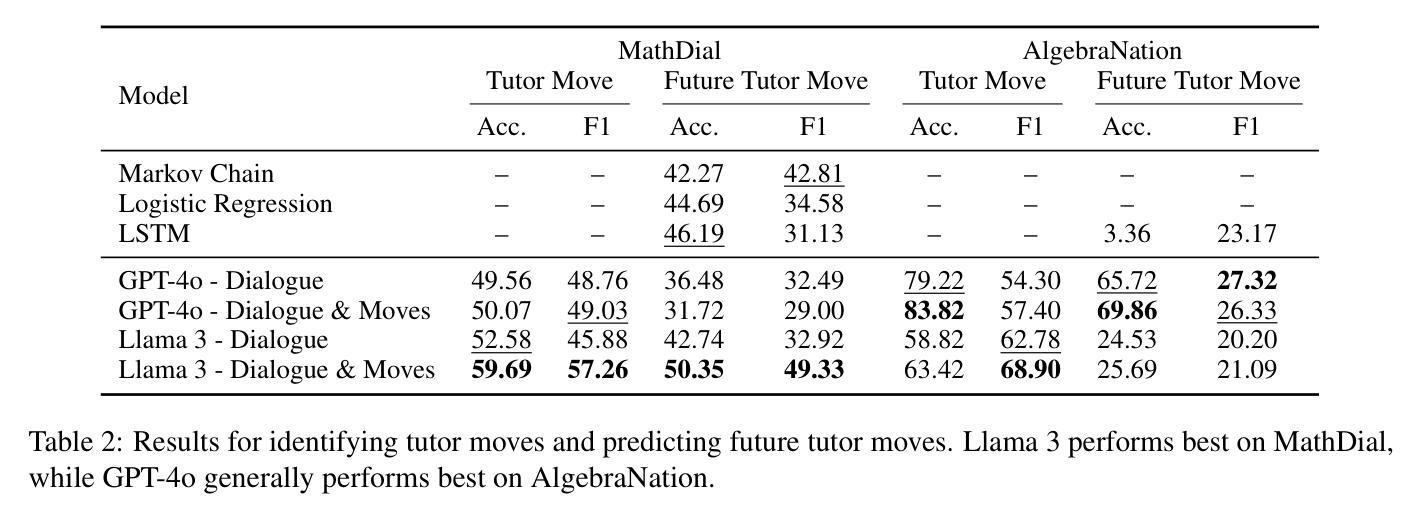
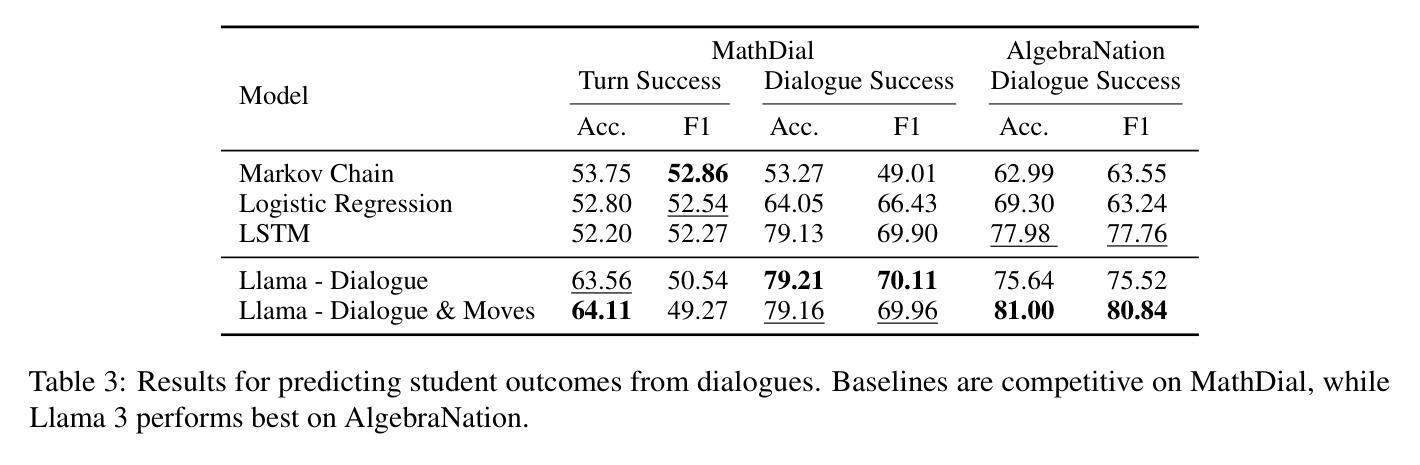
Tutoring dialogues have gained significant attention in recent years, given the prominence of online learning and the emerging tutoring abilities of artificial intelligence (AI) agents powered by large language models (LLMs). Recent studies have shown that the strategies used by tutors can have significant effects on student outcomes, necessitating methods to predict how tutors will behave and how their actions impact students. However, few works have studied predicting tutor strategy in dialogues. Therefore, in this work we investigate the ability of modern LLMs, particularly Llama 3 and GPT-4o, to predict both future tutor moves and student outcomes in dialogues, using two math tutoring dialogue datasets. We find that even state-of-the-art LLMs struggle to predict future tutor strategy while tutor strategy is highly indicative of student outcomes, outlining a need for more powerful methods to approach this task.
近年来,随着在线学习的普及以及由大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的人工智能(AI)代理的辅导能力的发展,辅导对话引起了人们的广泛关注。最近的研究表明,导师使用的策略对学生的成果有重大影响,因此需要预测导师的行为及其行为对学生影响的方法。然而,很少有研究关注对话中预测导师策略的工作。因此,在这项工作中,我们研究了现代大型语言模型(特别是Llama 3和GPT-4o)在对话中预测未来导师动作和学生成果的能力,使用了两个数学辅导对话数据集。我们发现,即使是最先进的大型语言模型也很难预测未来的导师策略,而导师策略对学生的成果具有很强的预示性,这突显了需要更强大的方法来应对这项任务。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in BEA 2025: 20th Workshop on Innovative Use of NLP for Building Educational Applications
Summary
基于近年来在线学习的盛行以及由大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的人工智能(AI)辅导能力的崛起,辅导对话已引起广泛关注。本研究探讨了现代LLM在预测对话中辅导人员的未来行动以及学生结果的能力,发现即使是最先进的LLM在预测未来辅导策略时也会遇到困难,而辅导策略对学生的结果具有高度的预示性。
Key Takeaways
- 辅导对话近年来受到广泛关注,主要因为在线学习的普及和AI辅导能力的崛起。
- LLMs,特别是Llama 3和GPT-4o,被用于预测对话中辅导人员的未来行动和学生结果。
- 发现现有的LLMs在预测未来辅导策略方面存在困难。
- 辅导策略对学生的结果具有高度的预示性。
- 需要更强大的方法来应对这一任务。
- 本研究使用了两个数学辅导对话数据集进行实证研究。
点此查看论文截图

Analysis of Reaction-Diffusion Predator-Prey System under Random Switching
Authors:Nguyen H. Du, Nhu N. Nguyen
This paper investigates the long-term dynamics of a reaction-diffusion predator-prey system subject to random environmental fluctuations modeled by Markovian switching. The model is formulated as a hybrid system of partial differential equations (PDEs), where the switching between different ecological regimes captures the randomness in environmental conditions. We derive a critical threshold parameter that determines whether the predator species will eventually go extinct or persist. We further characterize the system’s asymptotic behavior by providing a detailed pathwise description of the omega-limit set of solutions. This analysis reveals how the effects of random switching shape the distribution and long-term coexistence of the species. Numerical simulations are provided to validate and illustrate the theoretical findings, highlighting transitions between different dynamical regimes. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work that rigorously analyzes a spatially diffusive predator-prey model under Markovian switching, thereby bridging the gap between spatial ecology and stochastic hybrid PDE systems.
本文研究了受马尔可夫开关模型模拟的随机环境波动影响的反应扩散捕食者-猎物系统的长期动态。该模型被制定为一组偏微分方程(PDE)的混合系统,其中不同生态状态之间的转换捕捉了环境条件的随机性。我们推导出了一个临界阈值参数,这个参数决定了捕食者物种最终会灭绝还是持续存在。我们进一步通过提供解的ω极限集的详细路径描述来刻画系统的渐近行为。这个分析揭示了随机转换如何影响物种的分布和长期共存。提供了数值模拟来验证和说明理论发现,突出了不同动态状态之间的过渡。据我们所知,这是首次对马尔可夫开关下的空间扩散捕食者-猎物模型进行严谨分析,从而填补了空间生态学和随机混合PDE系统之间的空白。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了具有马尔可夫切换的随机环境波动下的反应扩散捕食者-被捕食者系统的长期动态。模型被表述为偏微分方程(PDEs)的混合系统,其中不同生态状态之间的切换捕捉了环境条件的随机性。我们推导出了一个关键阈值参数,该参数决定了捕食者物种最终会灭绝还是持续存在。我们还通过提供解决方案的omega极限集的详细路径描述来表征系统的渐近行为。这种分析揭示了随机切换如何影响物种的分布和长期共存。数值模拟用于验证和说明理论发现,突出了不同动态状态之间的过渡。据我们所知,这是首次对马尔可夫切换下的空间扩散捕食者-被捕食者模型进行严谨分析,从而填补了空间生态学和随机混合PDE系统之间的鸿沟。
Key Takeaways
- 该模型研究了反应扩散捕食者-被捕食者系统在随机环境波动下的长期动态,环境波动由马尔可夫切换来模拟。
- 该模型是一个混合系统,包含偏微分方程(PDEs),能够捕捉不同生态状态间的转换。
- 推导出一个关键阈值参数,决定捕食者物种的最终存亡。
- 通过详细路径描述系统的omega极限集,揭示了系统的渐近行为。
- 随机切换影响物种的分布和长期共存。
- 数值模拟验证了理论发现,展示了不同动态状态之间的过渡。
点此查看论文截图

DocTalk: Scalable Graph-based Dialogue Synthesis for Enhancing LLM Conversational Capabilities
Authors:Jing Yang Lee, Hamed Bonab, Nasser Zalmout, Ming Zeng, Sanket Lokegaonkar, Colin Lockard, Binxuan Huang, Ritesh Sarkhel, Haodong Wang
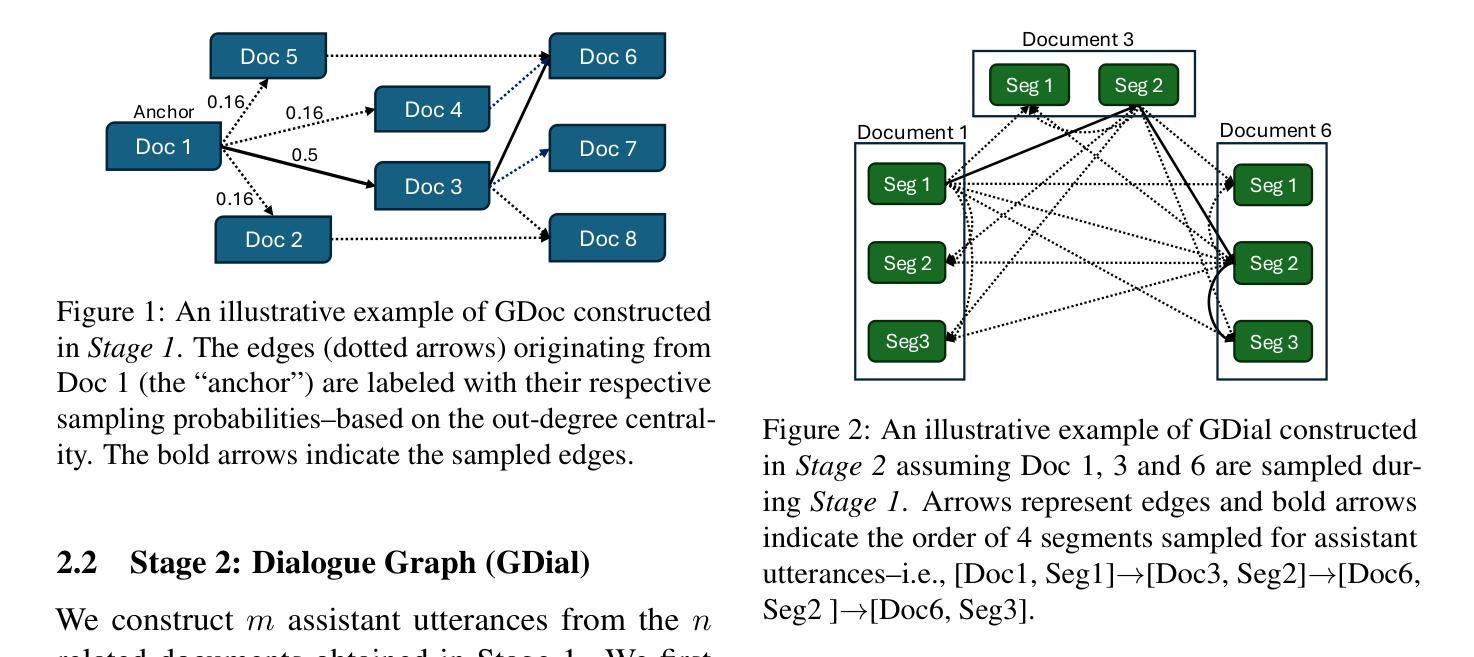
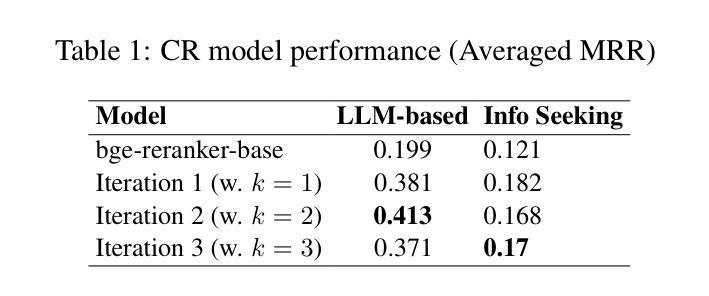
Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly employed in multi-turn conversational tasks, yet their pre-training data predominantly consists of continuous prose, creating a potential mismatch between required capabilities and training paradigms. We introduce a novel approach to address this discrepancy by synthesizing conversational data from existing text corpora. We present a pipeline that transforms a cluster of multiple related documents into an extended multi-turn, multi-topic information-seeking dialogue. Applying our pipeline to Wikipedia articles, we curate DocTalk, a multi-turn pre-training dialogue corpus consisting of over 730k long conversations. We hypothesize that exposure to such synthesized conversational structures during pre-training can enhance the fundamental multi-turn capabilities of LLMs, such as context memory and understanding. Empirically, we show that incorporating DocTalk during pre-training results in up to 40% gain in context memory and understanding, without compromising base performance. DocTalk is available at https://huggingface.co/datasets/AmazonScience/DocTalk.
大型语言模型(LLM)在多轮对话任务中的使用越来越广泛,但它们的预训练数据主要由连续的散文构成,导致所需的能力和训练范式之间产生潜在的不匹配。我们引入了一种通过合成现有文本语料库中的对话数据来解决这一差异的新方法。我们展示了一条将多个相关文档集群转化为扩展的多轮、多话题信息搜索对话的流水线。将我们的流水线应用于维基百科文章,我们整理了DocTalk,这是一个多轮预训练对话语料库,包含超过73万篇长对话。我们假设,在预训练期间接触这种合成的对话结构可以提高LLM的多轮能力,如上下文记忆和理解。实际上,我们表明,在预训练过程中融入DocTalk可以在不损害基础性能的情况下,提高上下文的记忆和理解能力高达40%。DocTalk可在https://huggingface.co/datasets/AmazonScience/DocTalk获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at SIGDIAL 2025
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在多轮对话任务中的应用日益广泛,但其预训练数据主要由连续散文构成,可能导致所需能力与训练模式之间的不匹配。本文提出了一种通过合成对话数据来解决这一差异的新方法。我们展示了从现有文本语料库中提取信息的管道,能够将多个相关文档转化为多轮、多话题的信息搜寻对话。我们应用此管道到维基百科文章上,精心制作了DocTalk对话预训练语料库,其中包含超过73万条长对话。假设这种合成的对话结构在预训练期间的曝光能够增强LLM的多轮对话能力,如上下文记忆和理解。实验表明,在预训练中加入DocTalk可以提高高达40%的上下文记忆和理解能力,且不会降低基本性能。DocTalk可以在链接https://huggingface.co/datasets/AmazonScience/DocTalk中访问到。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在多轮对话任务中的使用增加,但其预训练数据主要由连续散文组成,这可能导致与对话任务需求的不匹配。
- 提出了一种新的方法来解决这一问题,即通过合成对话数据来模拟真实的对话环境。
- 通过维基百科文章构建了一个名为DocTalk的预训练对话语料库,包含了大量丰富的对话数据。
- DocTalk可以提高LLM的上下文记忆和理解能力,提升幅度最高可达40%。
- 这种提升并不会对模型的基本性能造成影响。
- DocTalk语料库可通过公开链接访问以供研究使用。
点此查看论文截图


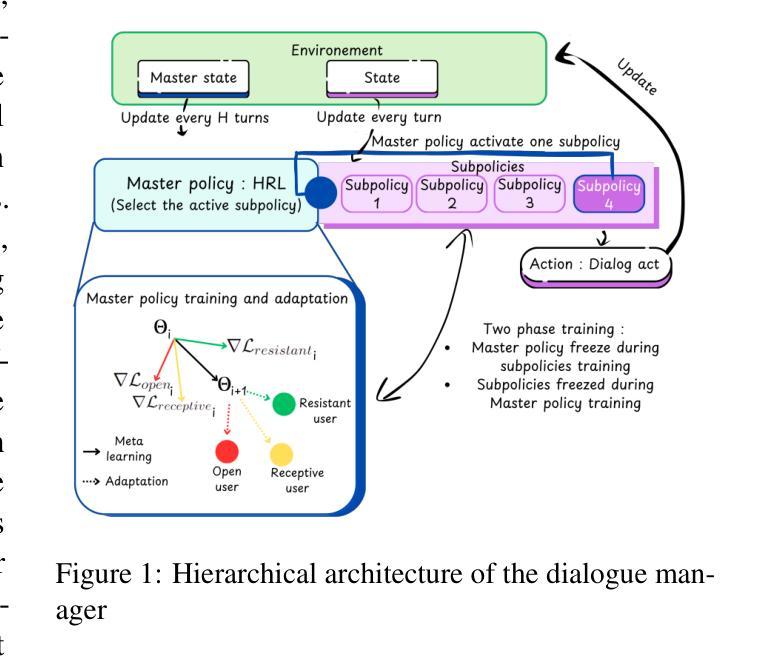
Tailored Conversations beyond LLMs: A RL-Based Dialogue Manager
Authors:Lucie Galland, Catherine Pelachaud, Florian Pecune
In this work, we propose a novel framework that integrates large language models (LLMs) with an RL-based dialogue manager for open-ended dialogue with a specific goal. By leveraging hierarchical reinforcement learning to model the structured phases of dialogue and employ meta-learning to enhance adaptability across diverse user profiles, our approach enhances adaptability and efficiency, enabling the system to learn from limited data, transition fluidly between dialogue phases, and personalize responses to heterogeneous patient needs. We apply our framework to Motivational Interviews, aiming to foster behavior change, and demonstrate that the proposed dialogue manager outperforms a state-of-the-art LLM baseline in terms of reward, showing a potential benefit of conditioning LLMs to create open-ended dialogue systems with specific goals.
在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新型框架,该框架将大型语言模型(LLM)与基于强化学习的对话管理器相结合,用于实现具有特定目标的开放对话。我们借助分层强化学习来模拟对话的结构化阶段,并利用元学习来提高对不同用户配置的适应性。我们的方法提高了适应性和效率,使系统能够在有限的数据中学习,流畅地过渡到不同的对话阶段,并对不同的患者需求做出个性化回应。我们将该框架应用于动机访谈,旨在促进行为改变,并证明所提出的对话管理器在奖励方面优于最新的LLM基准测试,显示出将LLM设置为实现具有特定目标的开放对话系统的潜在优势。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本工作提出一种新型框架,整合大型语言模型与基于强化学习的对话管理器,用于实现具有特定目标的开放式对话。通过利用分层强化学习对对话的结构阶段进行建模,并借助元学习提高对不同用户特征的适应性,该方法增强了系统的适应性和效率,使系统能从有限数据中学习、流畅地转换对话阶段,并对不同患者的需求进行个性化回应。本研究将框架应用于动机面试,旨在促进行为改变,并证明所提出的对话管理器在奖励方面优于当前主流的大型语言模型基准测试,展示了在条件大型语言模型以创建具有特定目标的开放式对话系统的潜在优势。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新型框架,整合大型语言模型(LLMs)与强化学习(RL)对话管理器。
- 利用分层强化学习建模对话的结构阶段。
- 通过元学习提高对不同用户特征的适应性。
- 系统能从有限数据中学习,流畅转换对话阶段。
- 框架可以个性化回应不同患者的需求。
- 将框架应用于动机面试,促进行为改变。
点此查看论文截图


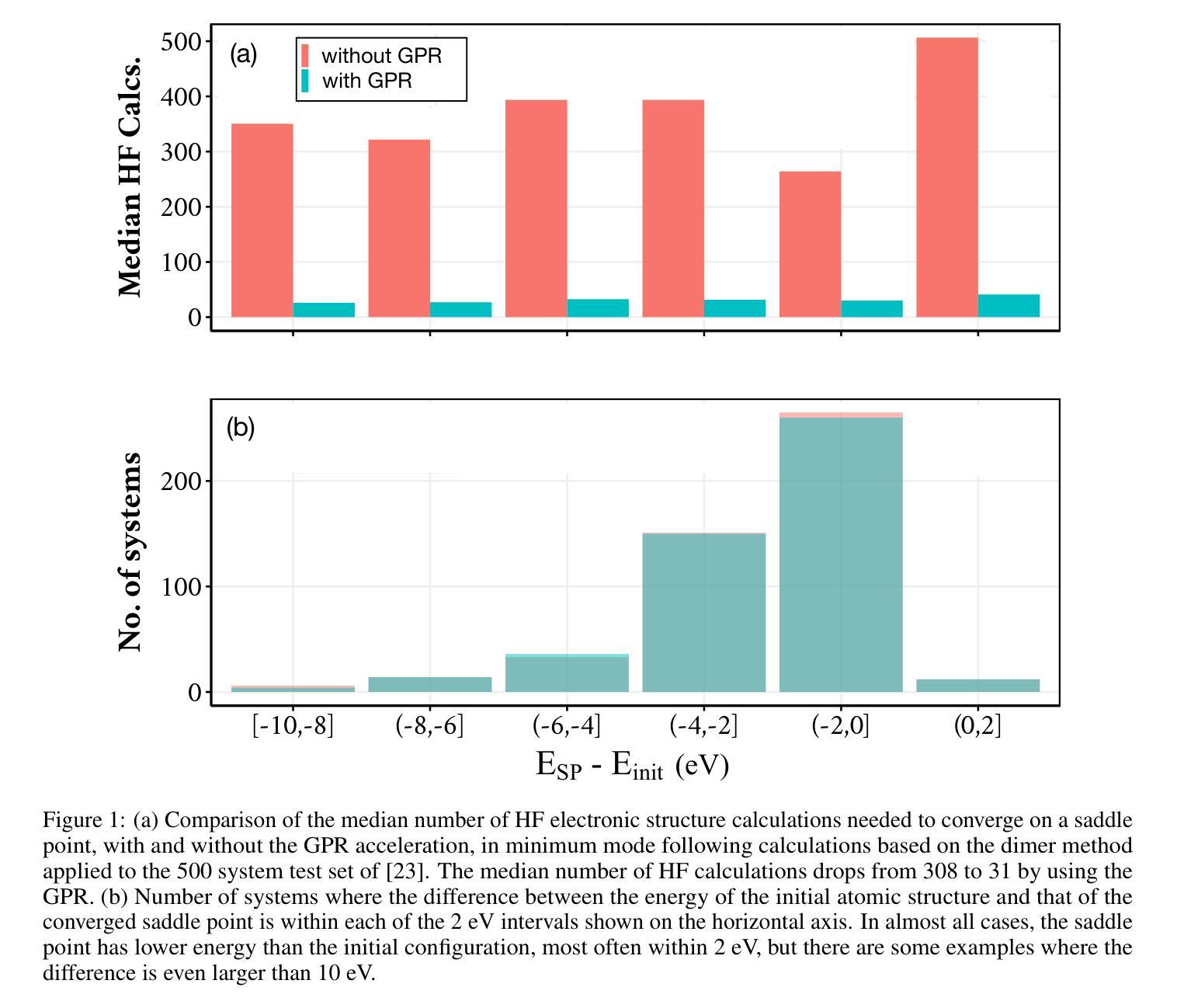
Efficient Implementation of Gaussian Process Regression Accelerated Saddle Point Searches with Application to Molecular Reactions
Authors:Rohit Goswami, Maxim Masterov, Satish Kamath, Alejandro Peña-Torres, Hannes Jónsson
The task of locating first order saddle points on high-dimensional surfaces describing the variation of energy as a function of atomic coordinates is an essential step for identifying the mechanism and estimating the rate of thermally activated events within the harmonic approximation of transition state theory. When combined directly with electronic structure calculations, the number of energy and atomic force evaluations needed for convergence is a primary issue. Here, we describe an efficient implementation of Gaussian process regression (GPR) acceleration of the minimum mode following method where a dimer is used to estimate the lowest eigenmode of the Hessian. A surrogate energy surface is constructed and updated after each electronic structure calculation. The method is applied to a test set of 500 molecular reactions previously generated by Hermez and coworkers [J. Chem. Theory Comput. 18, 6974 (2022)]. An order of magnitude reduction in the number of electronic structure calculations needed to reach the saddle point configurations is obtained by using the GPR compared to the dimer method. Despite the wide range in stiffness of the molecular degrees of freedom, the calculations are carried out using Cartesian coordinates and are found to require similar number of electronic structure calculations as an elaborate internal coordinate method implemented in the Sella software package. The present implementation of the GPR surrogate model in C++ is efficient enough for the wall time of the saddle point searches to be reduced in 3 out of 4 cases even though the calculations are carried out at a low Hartree-Fock level.
定位描述能量随原子坐标变化的高维表面上的一阶鞍点,是在谐近似过渡态理论中识别机制和估计热激活事件速率的必要步骤。当直接与电子结构计算相结合时,达到收敛所需的能量和原子力评估次数是主要问题。在这里,我们描述了一种高效的高斯过程回归(GPR)加速最小模式跟随方法的实现,其中二聚体用于估计海森矩阵的最低本征模式。在每次电子结构计算后,构建并更新替代能量表面。该方法应用于Hermez和同事之前生成的500个分子反应的测试集(J. Chem. Theory Comput. 18, 6974 (2022))。与二聚体方法相比,通过使用GPR,达到鞍点配置所需的电子结构计算次数减少了一个数量级。尽管分子自由度的刚度范围很广,但计算是采用笛卡尔坐标进行的,并且发现与在Sella软件包中实现的复杂内部坐标方法所需的电子结构计算次数相似。目前用C++实现的GPR替代模型足够高效,在四种情况下有三种情况的鞍点搜索壁时间有所减少,尽管这些计算是在哈特里-福克低级水平进行的。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 4 figures
Summary
本文描述了一种使用高斯过程回归(GPR)加速寻找高维表面上的一阶鞍点的方法。该方法结合了电子结构计算和最低本征模式估计,用于估计能量变化。应用于Hermez和同事生成的500个分子反应测试集,与二聚体方法相比,使用GPR减少了达到鞍点配置所需的电子结构计算数量。计算采用笛卡尔坐标,与Sella软件包中的复杂内部坐标方法相比,所需电子结构计算次数相似。
Key Takeaways
- 文章介绍了一种高效的高斯过程回归(GPR)方法,用于加速寻找描述能量变化的高维表面上的第一阶鞍点。
- 该方法结合了电子结构计算和最低本征模式的估计。
- 对Hermez和同事生成的分子反应测试集的应用显示,与使用二聚体方法相比,使用GPR减少了达到鞍点配置所需的电子结构计算数量。
- 计算是在笛卡尔坐标下进行的,与Sella软件包的复杂内部坐标方法相比,所需电子结构计算次数相当。
- GPR方法的实施是有效的,能够在3/4的情况下减少鞍点搜索的墙时间。
- 该方法的实施是在C++中进行的,即使在低Hartree-Fock水平下也能实现较好的效率。
点此查看论文截图

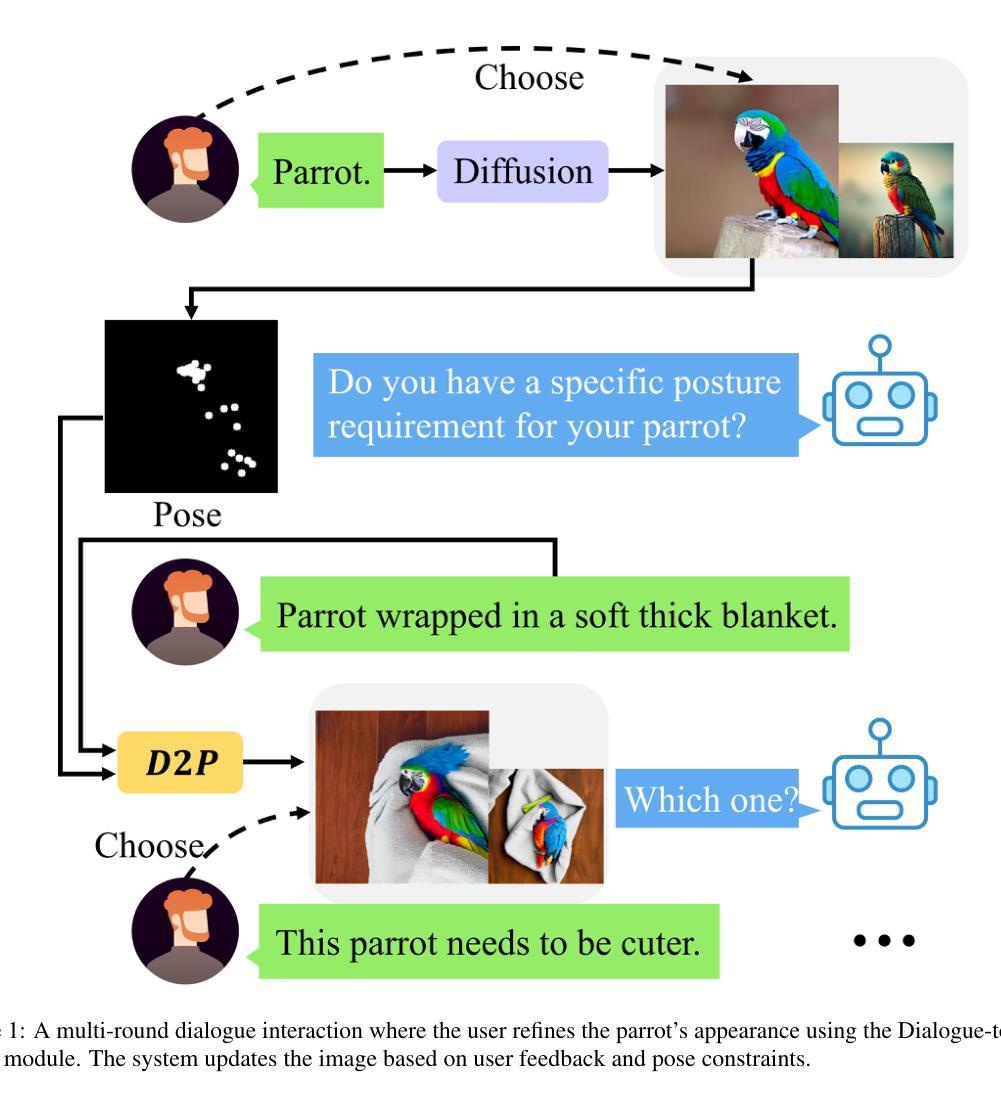
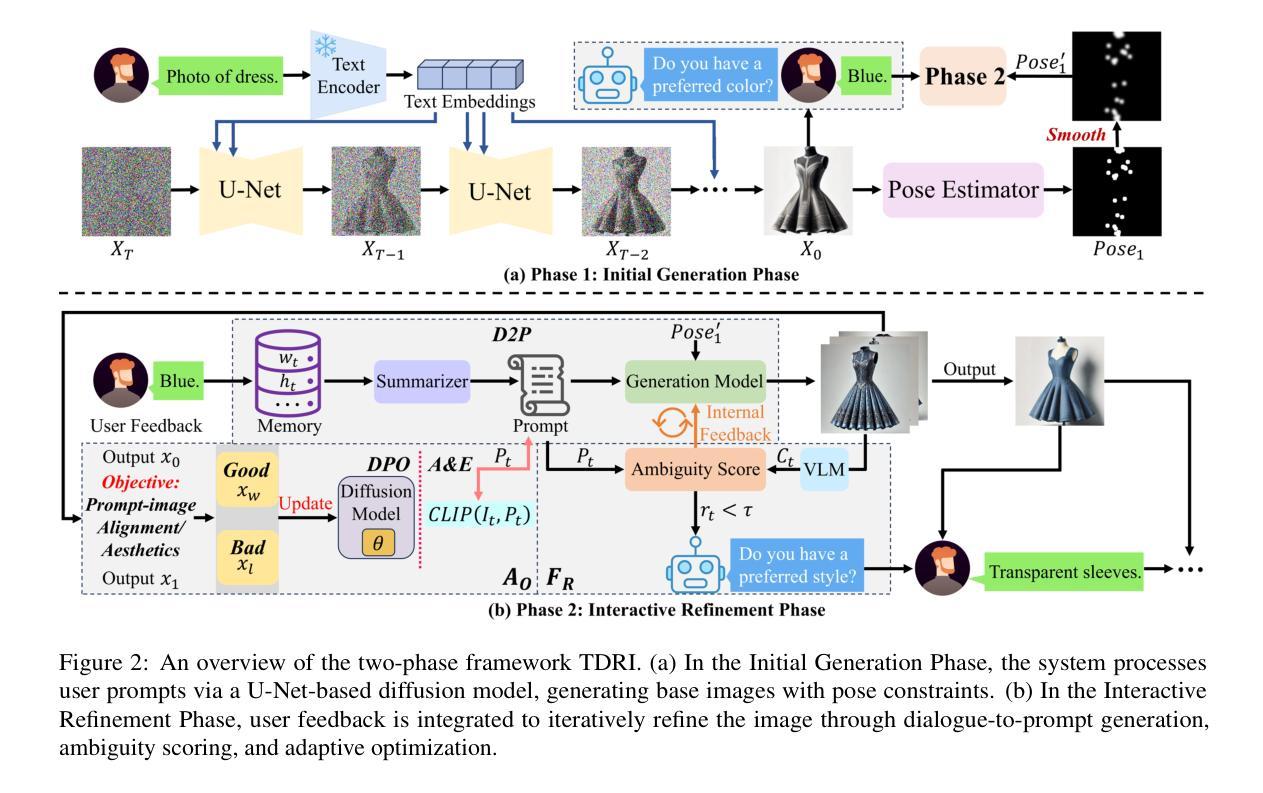
TDRI: Two-Phase Dialogue Refinement and Co-Adaptation for Interactive Image Generation
Authors:Yuheng Feng, Jianhui Wang, Kun Li, Sida Li, Tianyu Shi, Haoyue Han, Miao Zhang, Xueqian Wang
Although text-to-image generation technologies have made significant advancements, they still face challenges when dealing with ambiguous prompts and aligning outputs with user intent.Our proposed framework, TDRI (Two-Phase Dialogue Refinement and Co-Adaptation), addresses these issues by enhancing image generation through iterative user interaction. It consists of two phases: the Initial Generation Phase, which creates base images based on user prompts, and the Interactive Refinement Phase, which integrates user feedback through three key modules. The Dialogue-to-Prompt (D2P) module ensures that user feedback is effectively transformed into actionable prompts, which improves the alignment between user intent and model input. By evaluating generated outputs against user expectations, the Feedback-Reflection (FR) module identifies discrepancies and facilitates improvements. In an effort to ensure consistently high-quality results, the Adaptive Optimization (AO) module fine-tunes the generation process by balancing user preferences and maintaining prompt fidelity. Experimental results show that TDRI outperforms existing methods by achieving 33.6% human preference, compared to 6.2% for GPT-4 augmentation, and the highest CLIP and BLIP alignment scores (0.338 and 0.336, respectively). In iterative feedback tasks, user satisfaction increased to 88% after 8 rounds, with diminishing returns beyond 6 rounds. Furthermore, TDRI has been found to reduce the number of iterations and improve personalization in the creation of fashion products. TDRI exhibits a strong potential for a wide range of applications in the creative and industrial domains, as it streamlines the creative process and improves alignment with user preferences
尽管文本到图像生成技术已经取得了重大进展,但在处理模糊提示以及将输出与用户意图对齐时仍面临挑战。我们提出的框架TDRI(两阶段对话细化与协同适应)通过迭代用户交互增强图像生成来解决这些问题。它分为两个阶段:初始生成阶段,根据用户提示创建基础图像;以及交互细化阶段,通过三个关键模块集成用户反馈。对话到提示(D2P)模块确保用户反馈有效地转化为可操作提示,这改善了用户意图与模型输入之间的对齐。通过评估生成输出与用户期望之间的对比,反馈反射(FR)模块识别差异并促进改进。为了始终确保高质量的结果,自适应优化(AO)模块通过平衡用户偏好并保持提示的忠实性来微调生成过程。实验结果表明,TDRI在达到人类偏好33.6%的情况下优于现有方法,而GPT-4增强的方法仅为6.2%,并且具有最高的CLIP和BLIP对齐分数(分别为0.338和0.336)。在迭代反馈任务中,经过8轮后用户满意度提高到88%,超过6轮后的回报递减。此外,还发现TDRI减少了迭代次数,并改善了时尚产品的个性化创建。TDRI在创意和工业领域具有广泛的应用潜力,因为它简化了创意过程并改善了与用户偏好的对齐。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本转图像生成技术虽有进展,但仍面临模糊提示和用户意图对齐的挑战。提出的TDRI框架通过迭代用户交互增强图像生成,分为初始生成阶段和交互细化阶段。TDRI框架表现出强大的潜力,适用于创意和工业领域的广泛应用,可优化创意流程,提高与用户偏好的对齐度。
Key Takeaways
- TDRI框架旨在解决文本转图像生成技术在处理模糊提示和用户意图对齐方面面临的挑战。
- TDRI框架包含两个阶段:初始生成阶段和交互细化阶段。
- 通过集成用户反馈的三个关键模块,TDRI提高了图像生成的质量和用户满意度。
- TDRI实现了与GPT-4增强的对比优势,取得了更高的人类偏好率(33.6%对比6.2%)。
- TDRI获得了较高的CLIP和BLIP对齐分数(0.338和0.336)。
- 在迭代反馈任务中,用户满意度随着迭代轮次的增加而提高,在8轮后达到88%,但超过6轮后的回报逐渐减小。
点此查看论文截图