⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-11 更新
A Probabilistic Approach to Uncertainty Quantification Leveraging 3D Geometry
Authors:Rushil Desai, Frederik Warburg, Trevor Darrell, Marissa Ramirez de Chanlatte
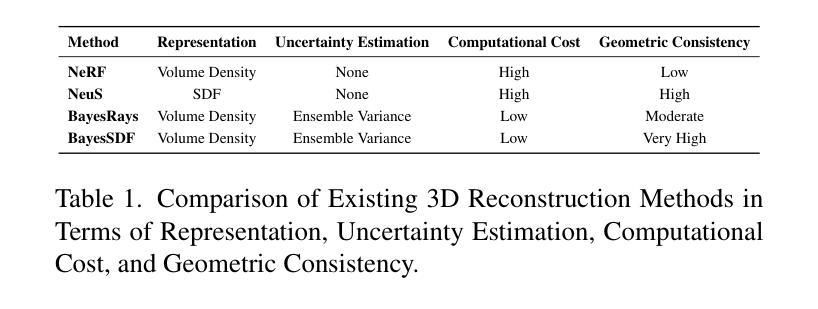
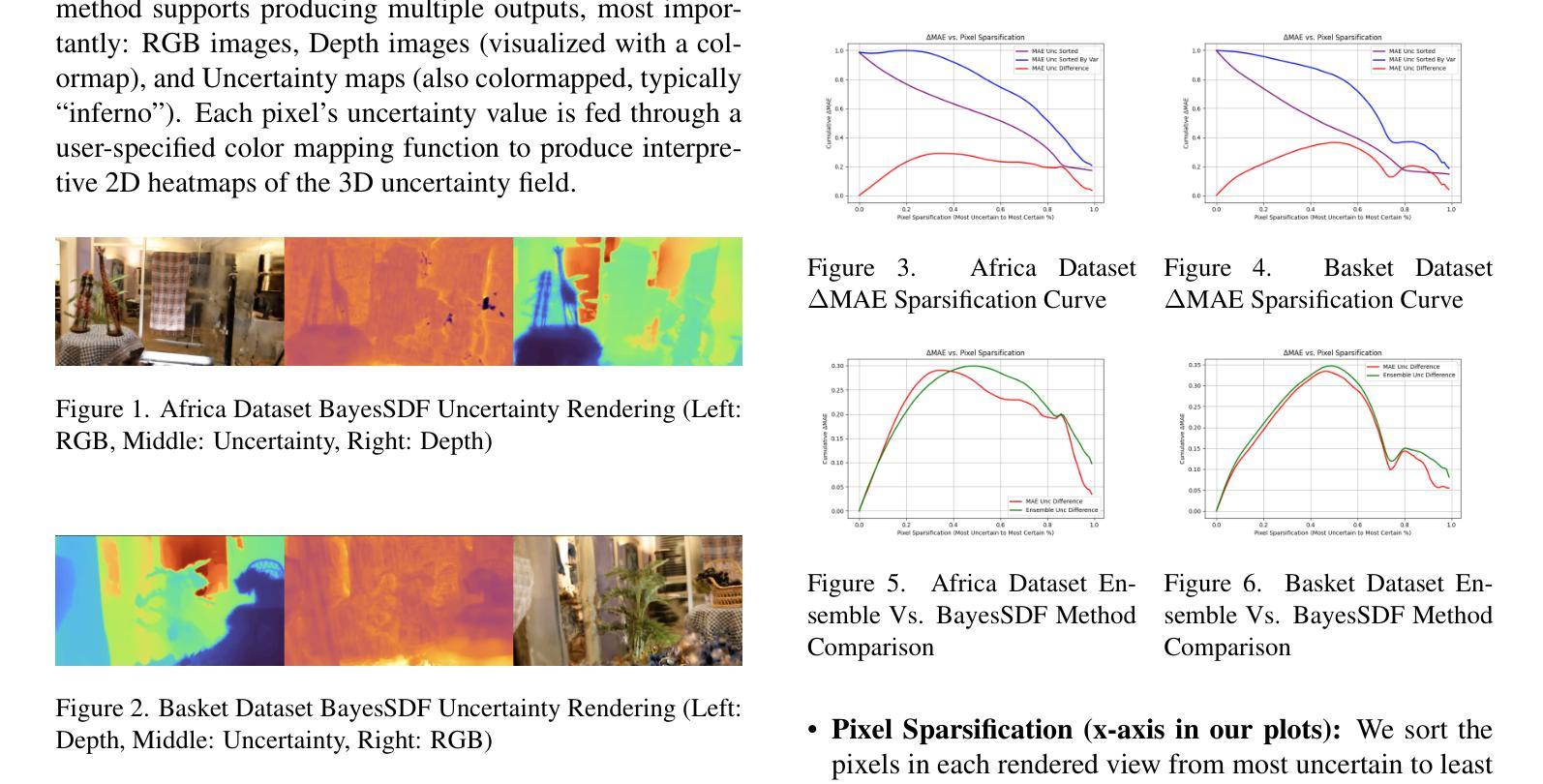
Quantifying uncertainty in neural implicit 3D representations, particularly those utilizing Signed Distance Functions (SDFs), remains a substantial challenge due to computational inefficiencies, scalability issues, and geometric inconsistencies. Existing methods typically neglect direct geometric integration, leading to poorly calibrated uncertainty maps. We introduce BayesSDF, a novel probabilistic framework for uncertainty quantification in neural implicit SDF models, motivated by scientific simulation applications with 3D environments (e.g., forests) such as modeling fluid flow through forests, where precise surface geometry and awareness of fidelity surface geometric uncertainty are essential. Unlike radiance-based models such as NeRF or 3D Gaussian splatting, which lack explicit surface formulations, SDFs define continuous and differentiable geometry, making them better suited for physical modeling and analysis. BayesSDF leverages a Laplace approximation to quantify local surface instability via Hessian-based metrics, enabling computationally efficient, surface-aware uncertainty estimation. Our method shows that uncertainty predictions correspond closely with poorly reconstructed geometry, providing actionable confidence measures for downstream use. Extensive evaluations on synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate that BayesSDF outperforms existing methods in both calibration and geometric consistency, establishing a strong foundation for uncertainty-aware 3D scene reconstruction, simulation, and robotic decision-making.
在神经隐式三维表示中,尤其是使用带符号距离函数(SDFs)的表示,量化不确定性仍然是一个巨大的挑战,这主要是由于计算效率低下、可扩展性问题以及几何不一致性。现有方法通常忽略了直接的几何集成,导致校准不良的不确定性映射。我们引入了BayesSDF,这是一种用于神经隐式SDF模型中的不确定性量化的新型概率框架,它受到三维环境科学模拟应用程序(例如森林模拟)的启发,例如在森林中模拟水流,在那里精确的表面几何和对保真度表面几何不确定性的认识至关重要。与基于辐射的模型(例如NeRF或三维高斯贴图)不同,这些模型缺乏明确的表面公式,而SDF定义了连续且可微分的几何形状,使它们更适合物理建模和分析。BayesSDF利用拉普拉斯近似来通过基于Hessian的指标来量化局部表面不稳定性,从而实现计算高效、面向表面的不确定性估计。我们的方法表明,不确定性预测与重建不良的几何形状紧密对应,为下游应用提供了可行的置信度度量。在合成和真实数据集上的广泛评估表明,BayesSDF在校准和几何一致性方面均优于现有方法,为不确定性感知的三维场景重建、模拟和机器人决策制定奠定了坚实基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025 Workshops (8 Pages, 6 Figures, 2 Tables)
Summary
本文介绍了Quantifying不确定性在神经隐式三维表示中的重要性,特别是利用Signed Distance Functions(SDFs)的模型。由于计算效率低下、可扩展性问题以及几何不一致性,现有的方法往往忽略了直接几何集成,导致不确定性映射校准不良。本文引入BayesSDF,一种用于神经隐式SDF模型的不确定性量化的新型概率框架,受到需要精确表面几何和不确定性感知的模拟应用的启发,如森林等环境中的流体流动建模。该方法使用Laplace近似通过Hessian度量局部表面不稳定来量化不确定性。广泛评估显示,在合成和真实数据集上,BayesSDF在标定和几何一致性方面都优于现有方法,为不确定感知的3D场景重建、模拟和机器人决策提供了坚实的基础。
Key Takeaways
- 神经隐式三维表示中的不确定性量化是一个重要问题,尤其是使用Signed Distance Functions(SDFs)的模型。
- 现有方法在计算效率和几何一致性方面存在挑战,往往忽视直接几何集成,导致不确定性映射校准不良。
- BayesSDF是一种新型概率框架,用于神经隐式SDF模型的不确定性量化。
- BayesSDF受到需要精确表面几何和感知的应用启发,适用于物理建模和分析。
- BayesSDF使用Laplace近似量化局部表面不稳定性的不确定性。
- 在合成和真实数据集上的评估显示,BayesSDF在不确定性的校准和几何一致性方面优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

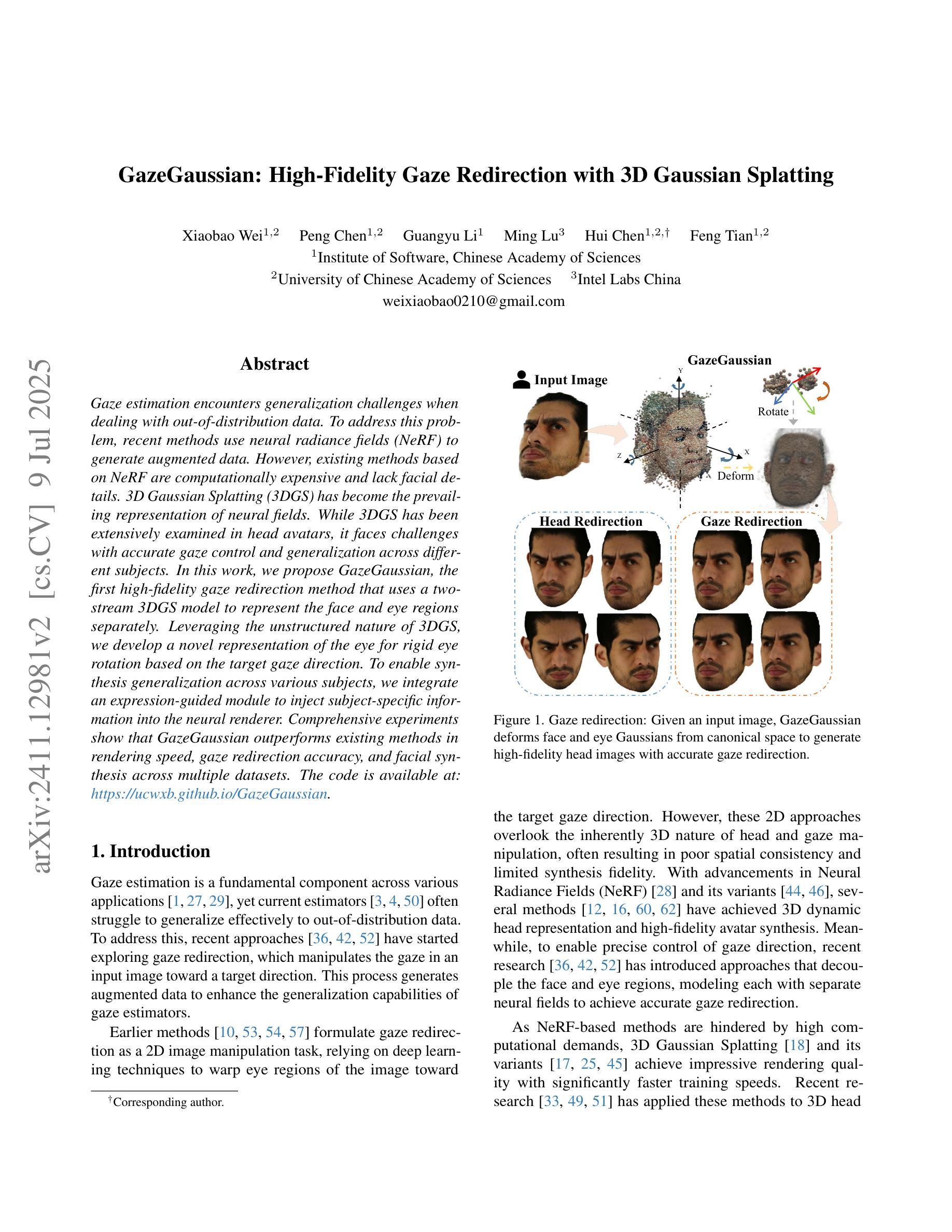
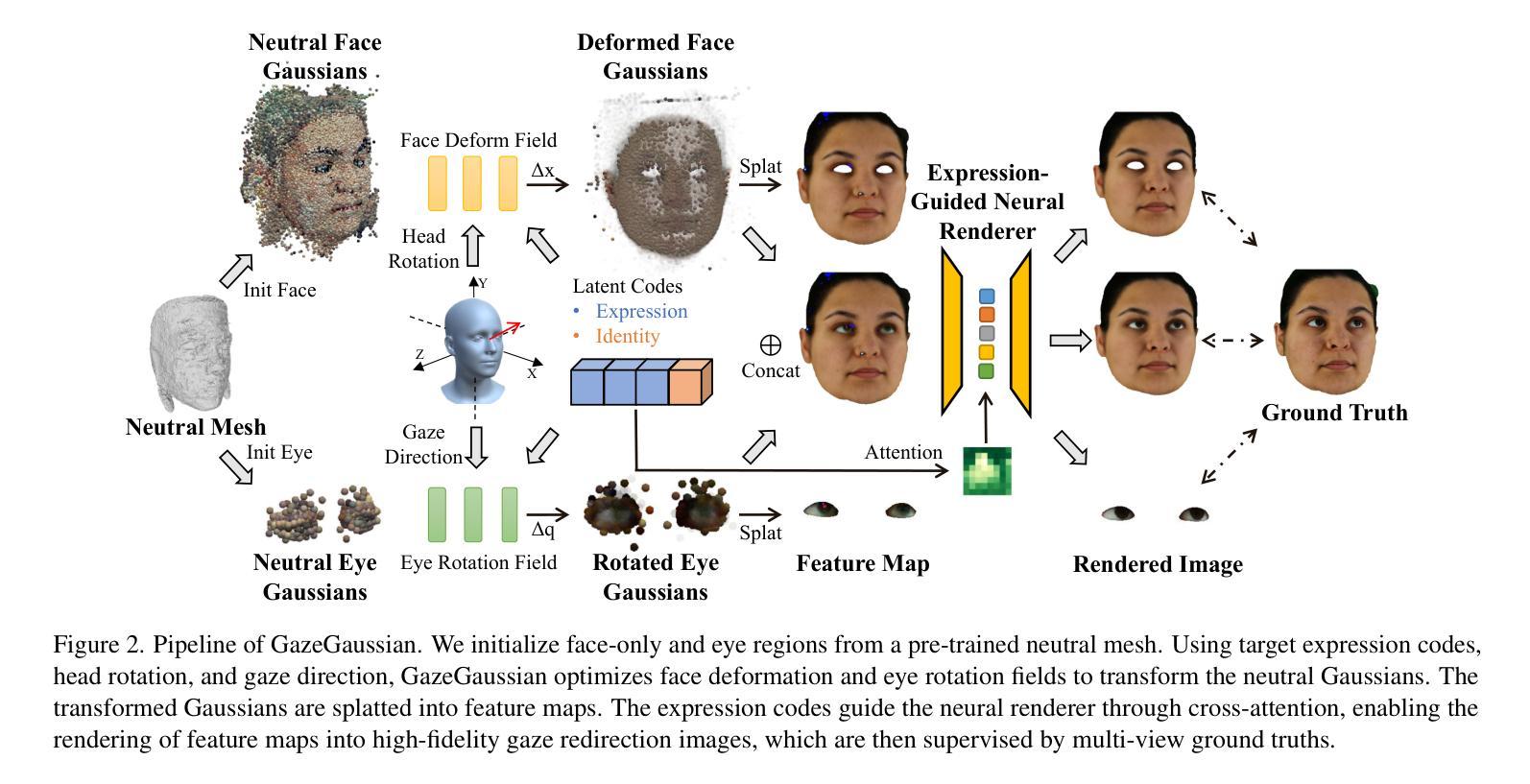
GazeGaussian: High-Fidelity Gaze Redirection with 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Xiaobao Wei, Peng Chen, Guangyu Li, Ming Lu, Hui Chen, Feng Tian
Gaze estimation encounters generalization challenges when dealing with out-of-distribution data. To address this problem, recent methods use neural radiance fields (NeRF) to generate augmented data. However, existing methods based on NeRF are computationally expensive and lack facial details. 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has become the prevailing representation of neural fields. While 3DGS has been extensively examined in head avatars, it faces challenges with accurate gaze control and generalization across different subjects. In this work, we propose GazeGaussian, the first high-fidelity gaze redirection method that uses a two-stream 3DGS model to represent the face and eye regions separately. Leveraging the unstructured nature of 3DGS, we develop a novel representation of the eye for rigid eye rotation based on the target gaze direction. To enable synthesis generalization across various subjects, we integrate an expression-guided module to inject subject-specific information into the neural renderer. Comprehensive experiments show that GazeGaussian outperforms existing methods in rendering speed, gaze redirection accuracy, and facial synthesis across multiple datasets. The code is available at: https://ucwxb.github.io/GazeGaussian.
在处理超出分布的数据时,目光估计面临着泛化挑战。为了解决这一问题,最近的方法使用神经辐射场(NeRF)来生成扩充数据。然而,基于NeRF的现有方法计算量大且缺乏面部细节。三维高斯平铺(3DGS)已成为神经场的流行表示方法。虽然3DGS在头部化身中得到了广泛的研究,但在准确的目光控制和跨不同主题的泛化方面仍然面临挑战。在这项工作中,我们提出了GazeGaussian,这是一种使用双流3DGS模型进行目光重定向的高保真方法,该模型可单独表示面部和眼部区域。利用3DGS的非结构化特性,我们基于目标目光方向开发了一种新的眼表示方法,用于进行刚性的眼球旋转。为了实现跨各种主题的合成泛化,我们整合了一个表情引导模块,将主题特定信息注入神经渲染器中。综合实验表明,GazeGaussian在渲染速度、目光重定向准确性和面部合成方面均优于现有方法,跨多个数据集表现优异。代码可在以下网址找到:GazeGaussian网址。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV2025
Summary
本文提出一种基于神经辐射场(NeRF)的高保真眼神重定向方法——GazeGaussian。针对现有技术面临的挑战,如计算成本高、面部细节缺失以及准确眼神控制等问题,GazeGaussian采用双流3D高斯贴图(3DGS)模型分别表示面部和眼部区域。通过引入表情引导模块,实现了跨不同主题的合成泛化。实验证明,GazeGaussian在渲染速度、眼神重定向精度和面部合成效果上均优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- GazeGaussian利用神经辐射场(NeRF)技术解决眼神估计中的泛化挑战。
- 采用双流3D高斯贴图(3DGS)模型分别表示面部和眼部区域,以提高渲染精度和效率。
- GazeGaussian实现了准确的眼神控制,通过引入眼神重定向技术克服现有方法的不足。
- 通过引入表情引导模块,实现跨不同主题的合成泛化。
- GazeGaussian在渲染速度、眼神重定向精度和面部合成效果上优于现有方法。
- GazeGaussian可用于处理出域数据,增强模型的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

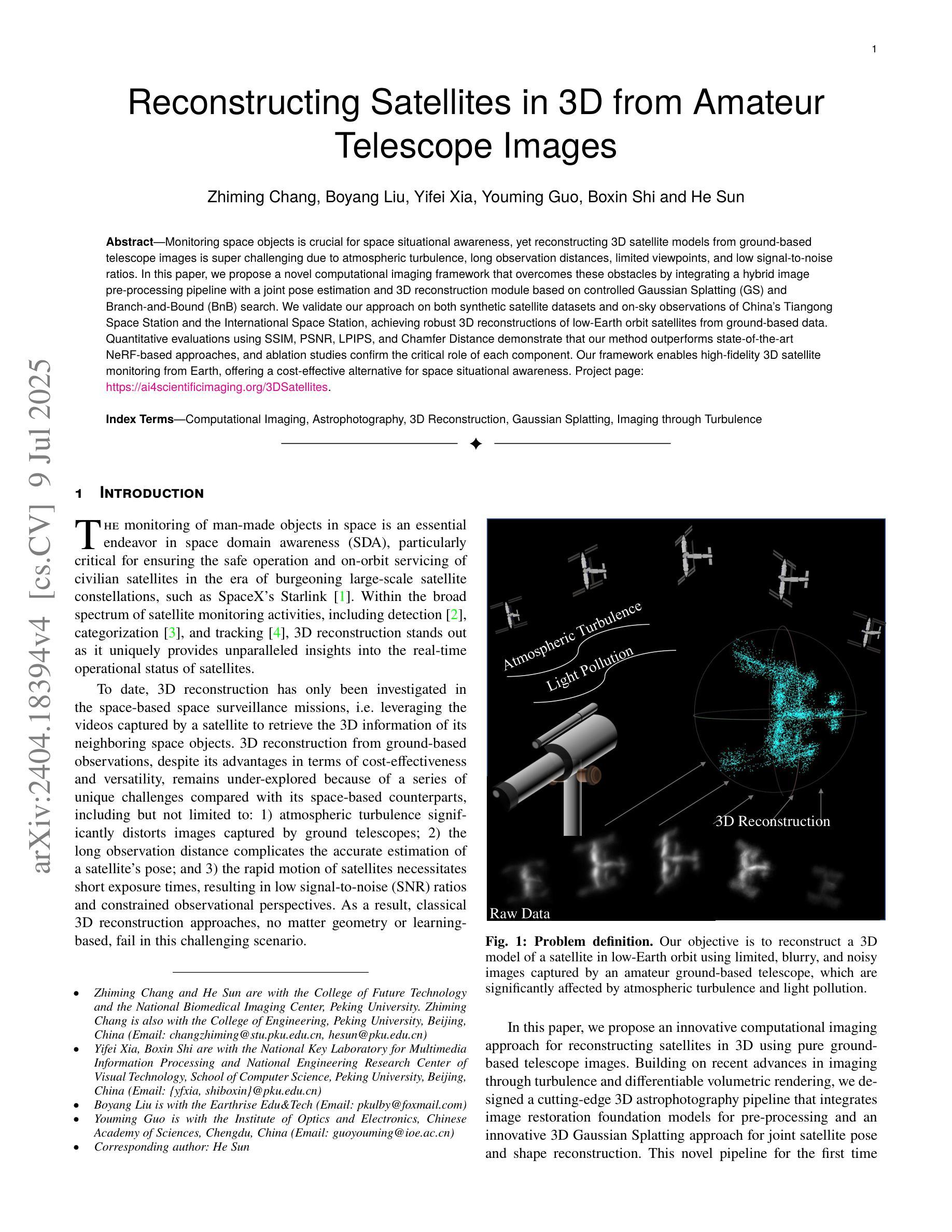
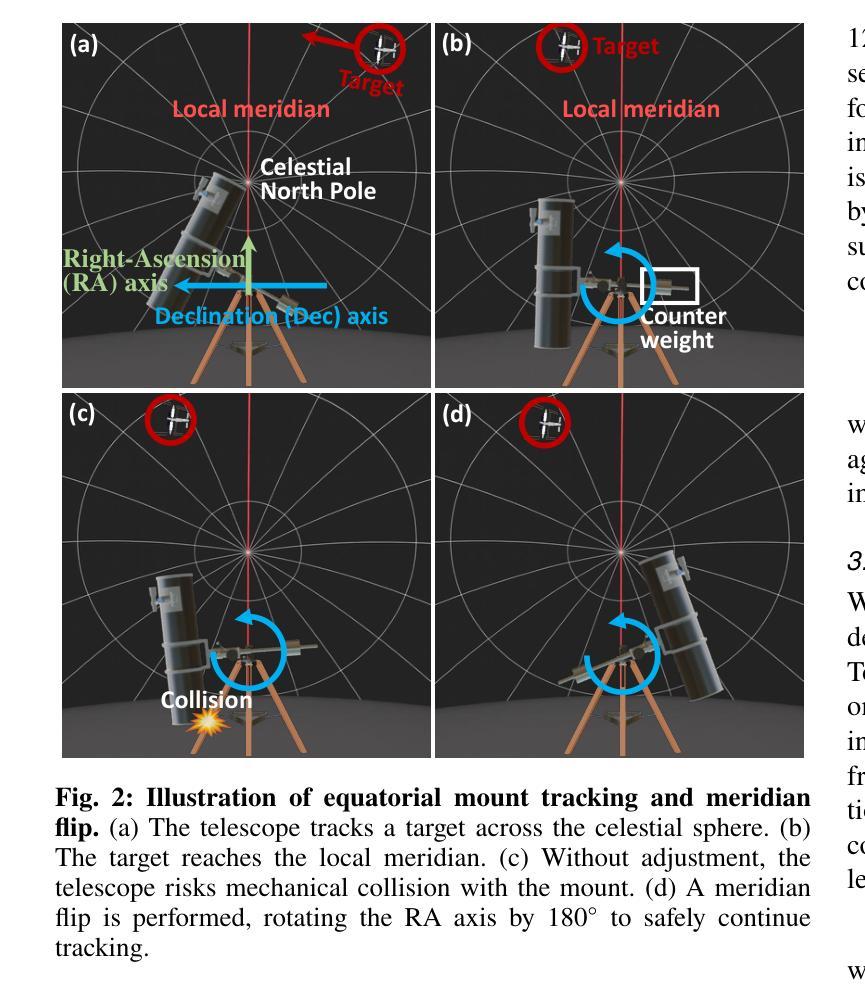
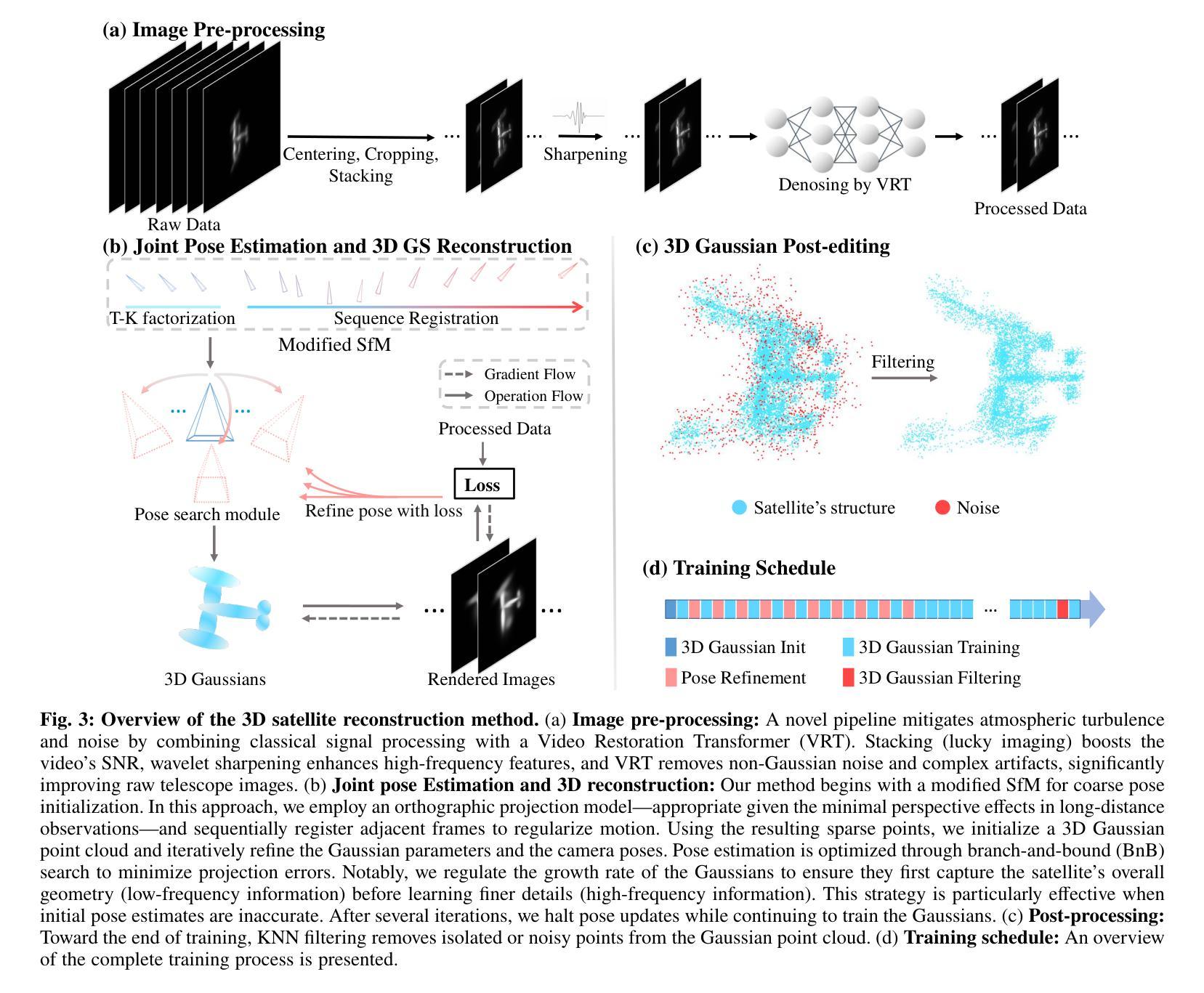
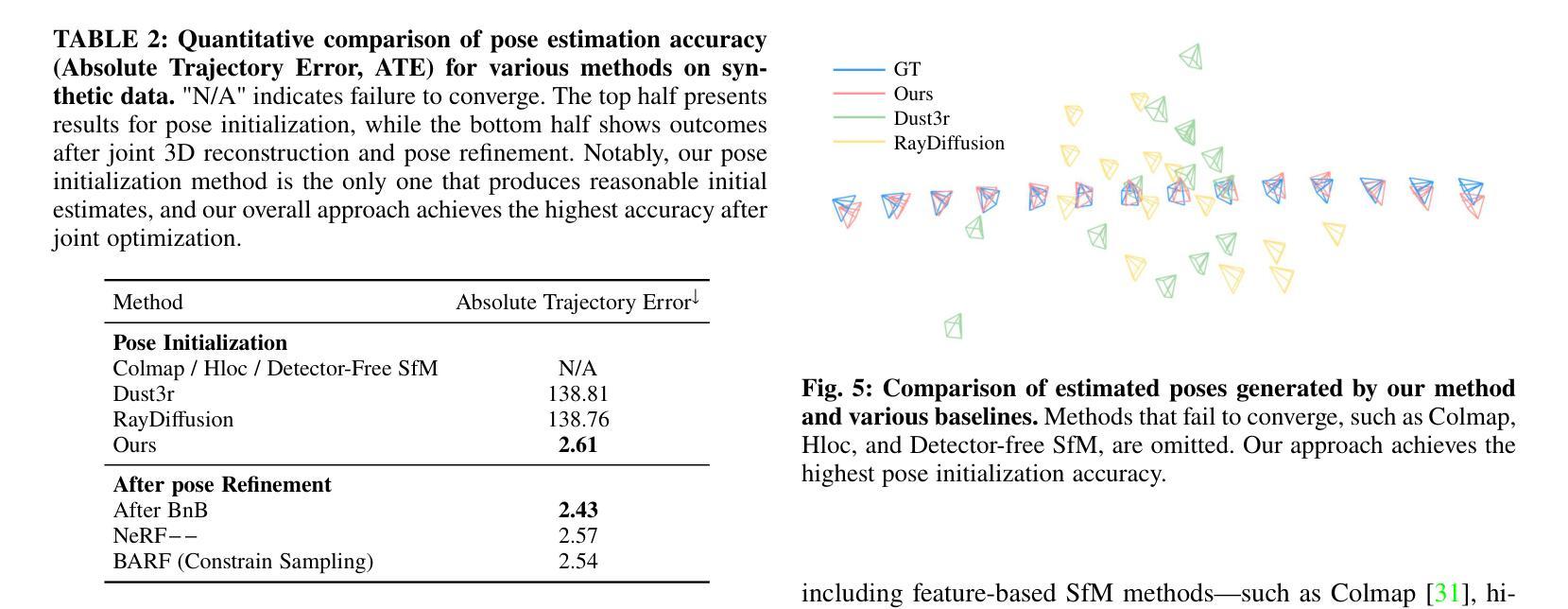
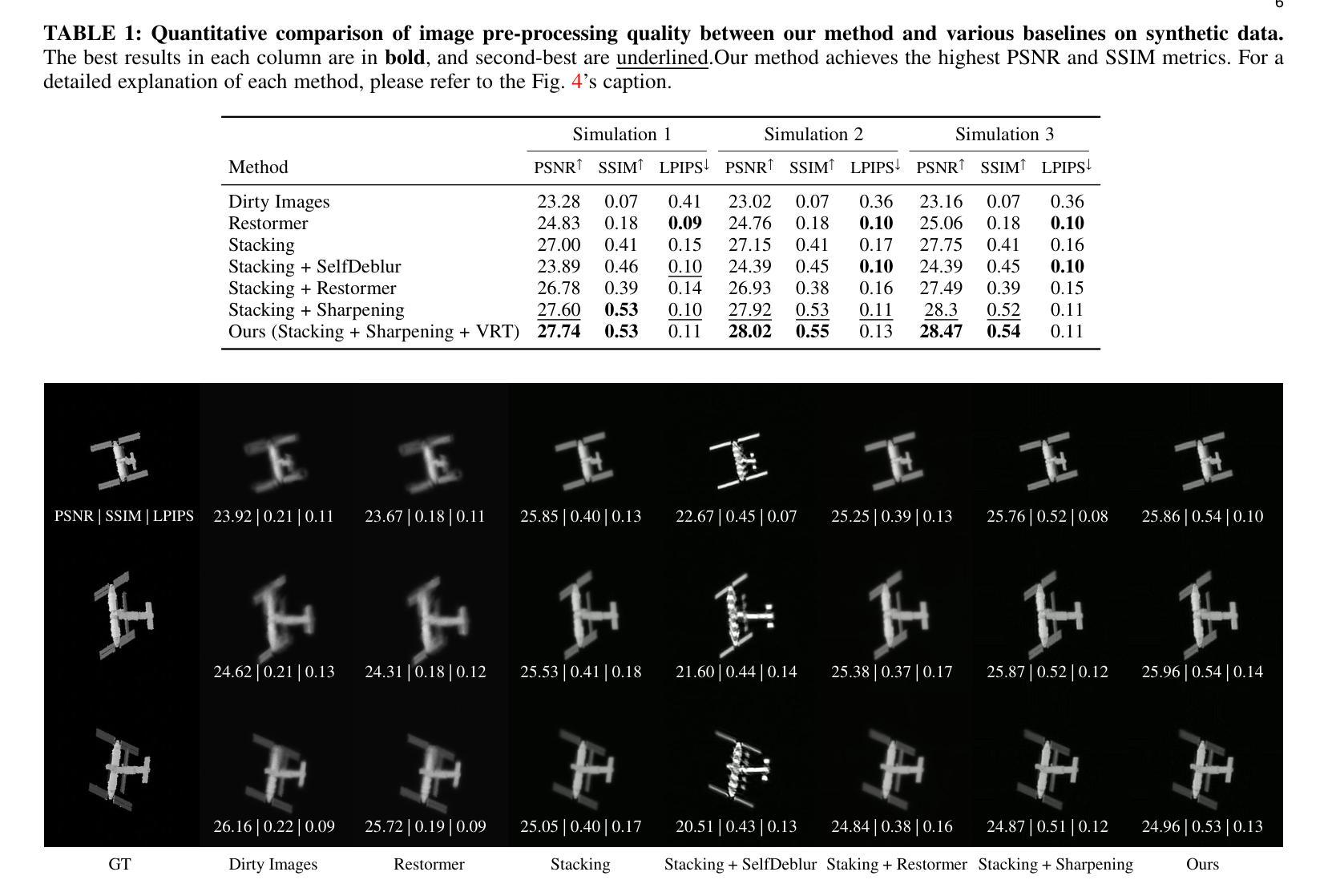
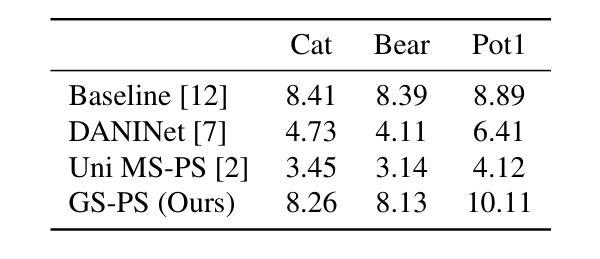
Reconstructing Satellites in 3D from Amateur Telescope Images
Authors:Zhiming Chang, Boyang Liu, Yifei Xia, Youming Guo, Boxin Shi, He Sun
Monitoring space objects is crucial for space situational awareness, yet reconstructing 3D satellite models from ground-based telescope images is challenging due to atmospheric turbulence, long observation distances, limited viewpoints, and low signal-to-noise ratios. In this paper, we propose a novel computational imaging framework that overcomes these obstacles by integrating a hybrid image pre-processing pipeline with a joint pose estimation and 3D reconstruction module based on controlled Gaussian Splatting (GS) and Branch-and-Bound (BnB) search. We validate our approach on both synthetic satellite datasets and on-sky observations of China’s Tiangong Space Station and the International Space Station, achieving robust 3D reconstructions of low-Earth orbit satellites from ground-based data. Quantitative evaluations using SSIM, PSNR, LPIPS, and Chamfer Distance demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art NeRF-based approaches, and ablation studies confirm the critical role of each component. Our framework enables high-fidelity 3D satellite monitoring from Earth, offering a cost-effective alternative for space situational awareness. Project page: https://ai4scientificimaging.org/ReconstructingSatellites
对空间目标进行监测对于空间态势感知至关重要。然而,由于大气湍流、长观测距离、有限的观测点和低信噪比等因素,从地面望远镜图像重建卫星的3D模型是一项挑战。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型的计算成像框架,通过集成混合图像预处理管道与基于受控的高斯拼贴(GS)和分治搜索(BnB)的联合姿态估计和3D重建模块来克服这些障碍。我们在合成卫星数据集和中国天宫空间站以及国际空间站的星空观测上验证了我们的方法,实现了从地面数据对低地球轨道卫星的稳健3D重建。使用结构相似性度量(SSIM)、峰值信噪比(PSNR)、局部感知图像相似性(LPIPS)和Chamfer距离进行的定量评估表明,我们的方法优于最新的基于NeRF的方法,并且消融研究证实了每个组件的关键作用。我们的框架能够实现从地球的高保真卫星监测,为空间态势感知提供了经济高效的替代方案。相关项目页面:https://ai4scientificimaging.org/ReconstructingSatellites
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种新型的计算成像框架,该框架通过整合混合图像预处理管道与基于受控高斯Splatting(GS)和分支定界(BnB)搜索的联合姿态估计和3D重建模块,克服了从地面望远镜图像重建卫星模型的诸多挑战。实验证明该框架能从地面数据实现低地球轨道卫星的稳健三维重建。研究展示了其在不同数据集上的性能优越性。本文为地球观测的高保真卫星监测提供了一种成本效益高的替代方案。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了空间物体监测的重要性以及从地面望远镜图像重建卫星模型所面临的挑战。
- 提出了一种新型的计算成像框架,整合了混合图像预处理管道和基于GS与BnB搜索的联合姿态估计与3D重建模块。
- 该框架在合成卫星数据集和在天空观测到的中国天宫空间站和国际空间站的数据上进行了验证。
- 通过定量评估,证明该框架在性能上优于现有的NeRF方法。
- 消融研究证实了框架中每个组件的关键作用。
点此查看论文截图