⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-11 更新
Integrated Structural Prompt Learning for Vision-Language Models
Authors:Jiahui Wang, Qin Xu, Bo Jiang, Bin Luo
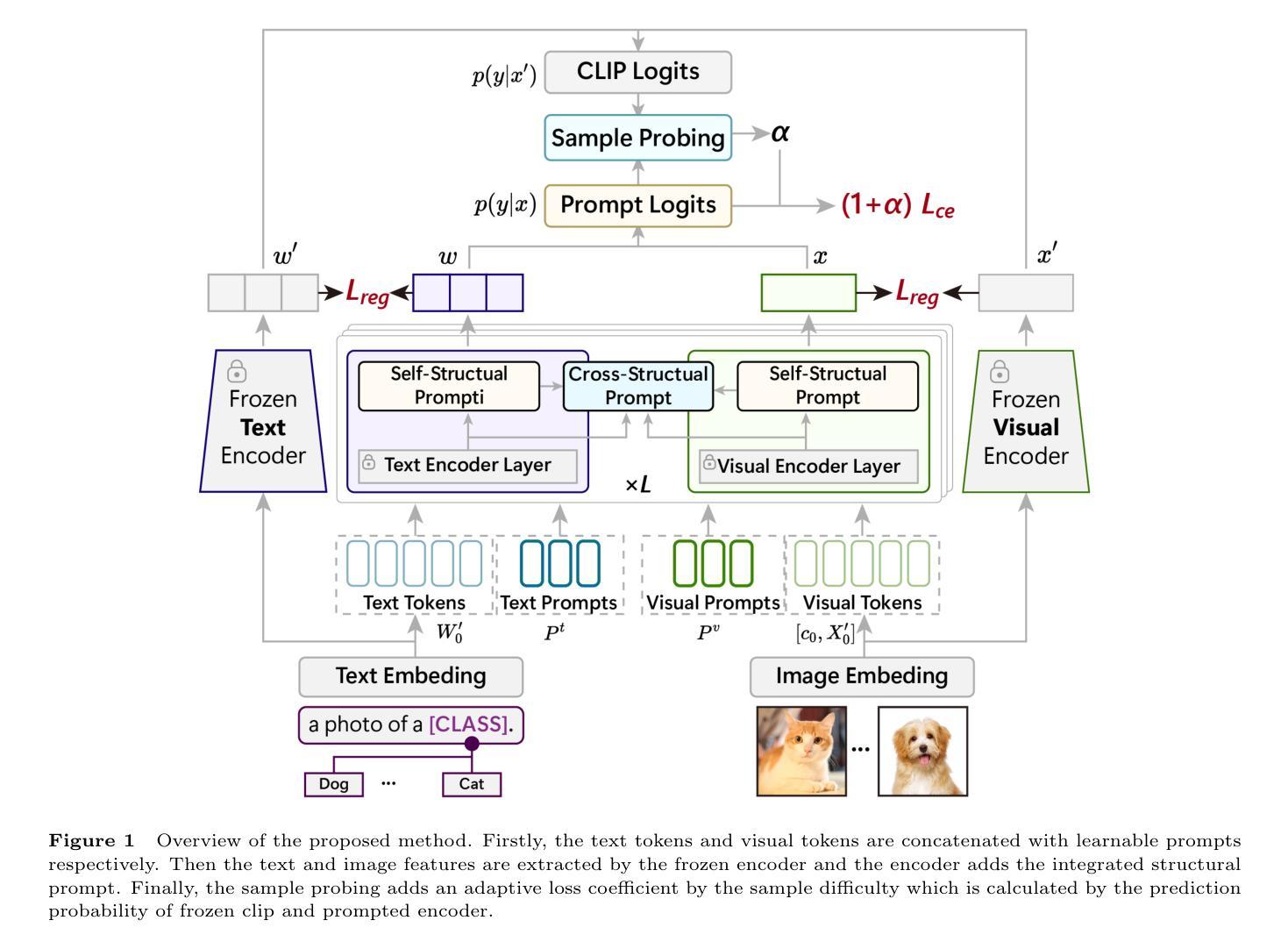
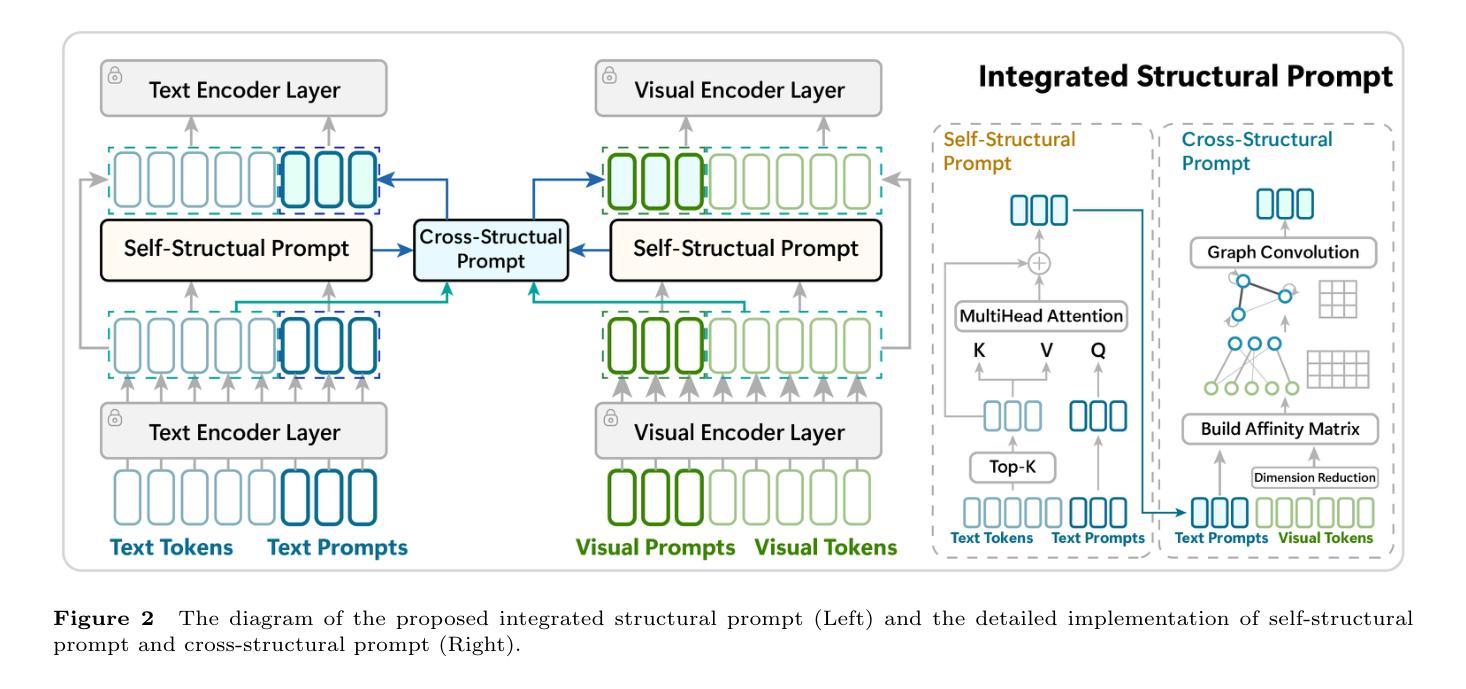
Prompt learning methods have significantly extended the transferability of pre-trained Vision-Language Models (VLMs) like CLIP for various downstream tasks. These methods adopt handcraft templates or learnable vectors to provide text or image instructions in fine-tuning VLMs. However, most existing works ignore the structural relationships between learnable prompts and tokens within and between modalities. Moreover, balancing the performance of base and new classes remains a significant challenge. In this paper, we propose an Integrated Structural Prompt (ISP) for VLMs to enhance the interaction of information representations between the text and image branches. ISP introduces self-structural and cross-structural prompt modules to model the structural relationships between learnable prompts and frozen tokens within and across modalities. This enables efficient information transfer while preserving feature stability. Additionally, we propose a sample probing module that dynamically adjusts loss coefficients based on sample difficulty, preventing the mode from overfitting to simple samples and improving generalization ability to new classes. Extensive experiments on three widely used settings: base-to-new generalization, cross-dataset evaluation, and domain generalization demonstrate that the proposed ISP achieves competitive performance against state-of-the-art methods.
提示学习方法已显著扩展了预训练视觉语言模型(如CLIP)对于各种下游任务的迁移能力。这些方法采用手工模板或可学习向量来在微调VLMs时提供文本或图像指令。然而,大多数现有工作忽略了可学习提示与模态内和模态间标记之间的结构关系。此外,平衡基础类别和新类别的性能仍然是一个重大挑战。在本文中,我们提出了用于VLMs的集成结构提示(ISP),以增强文本和图像分支之间信息表示的交互。ISP引入了自我结构提示和跨结构提示模块,以建模可学习提示与模态内和跨模态冻结标记之间的结构关系。这可以在保持特征稳定性的同时实现有效的信息传输。此外,我们提出了一个样本探测模块,该模块根据样本难度动态调整损失系数,防止模型对简单样本过度拟合,提高对新类别的泛化能力。在广泛使用的三种设置:基础到新类别的泛化、跨数据集评估和域泛化上的实验表明,所提出的ISP在性能上达到了最新技术水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
预训练视觉语言模型(VLMs)如CLIP在各种下游任务中的可迁移性已通过提示学习方法得到显著扩展。然而,现有方法忽视了可学习提示与模态内和模态间标记之间的结构关系。本文提出了一种集成结构提示(ISP)方法,通过引入自结构和跨结构提示模块,增强文本和图像分支之间信息表示的交互作用。此外,还提出了一种样本探测模块,根据样本难度动态调整损失系数,防止模型过度拟合简单样本,提高对新类别的泛化能力。实验表明,ISP在多种设置下实现了与最新技术相当的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 提示学习方法增强了预训练视觉语言模型(VLMs)的可迁移性,用于各种下游任务。
- 现有方法忽略了可学习提示与模态内和模态间标记之间的结构关系。
- 集成结构提示(ISP)方法通过引入自结构和跨结构提示模块,增强文本和图像分支之间信息表示的交互。
- ISP通过样本探测模块根据样本难度动态调整损失系数,提高模型泛化能力。
- ISP在基础到新类别的推广、跨数据集评估和领域推广等多种设置下实现了具有竞争力的性能。
- ISP方法在提高信息转移效率的同时保持了特征稳定性。
点此查看论文截图

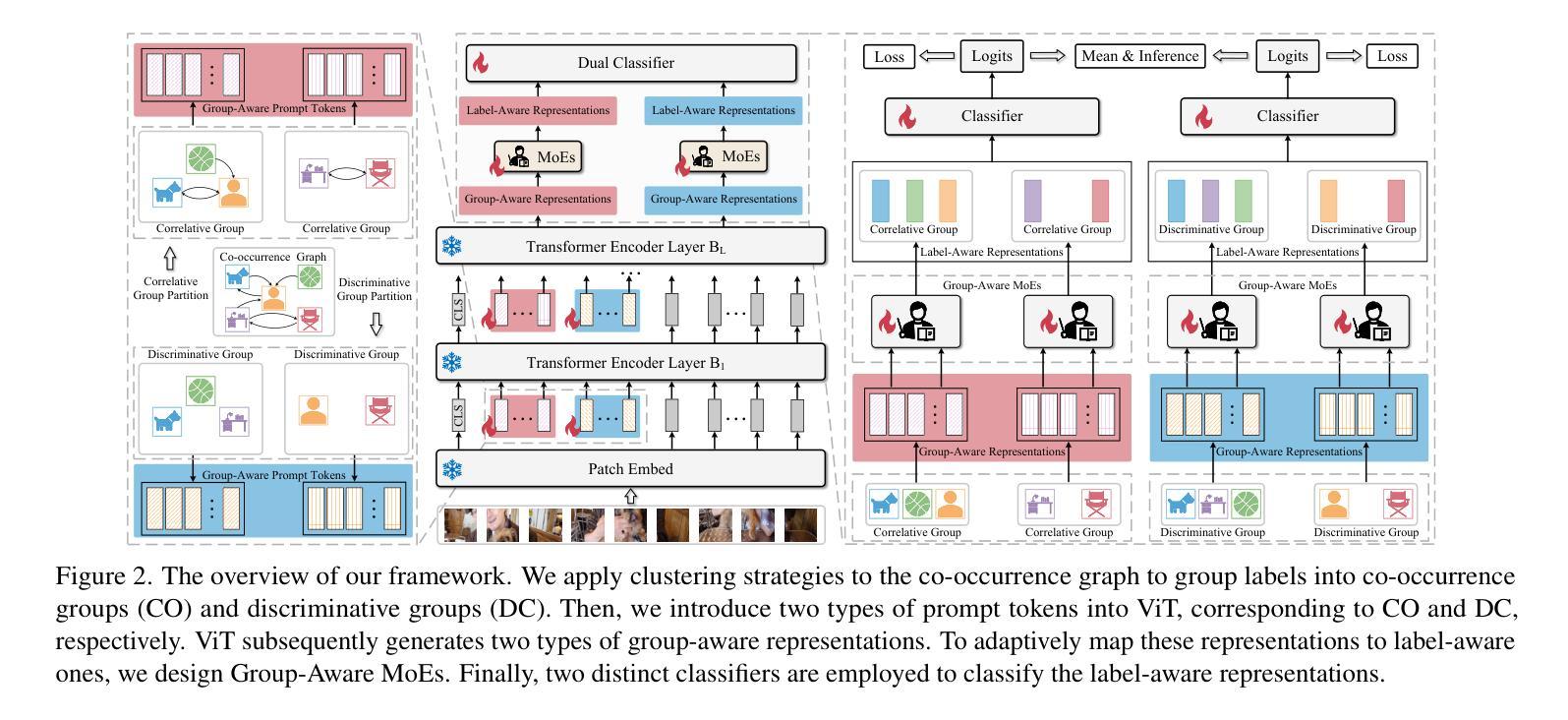
Correlative and Discriminative Label Grouping for Multi-Label Visual Prompt Tuning
Authors:LeiLei Ma, Shuo Xu, MingKun Xie, Lei Wang, Dengdi Sun, Haifeng Zhao
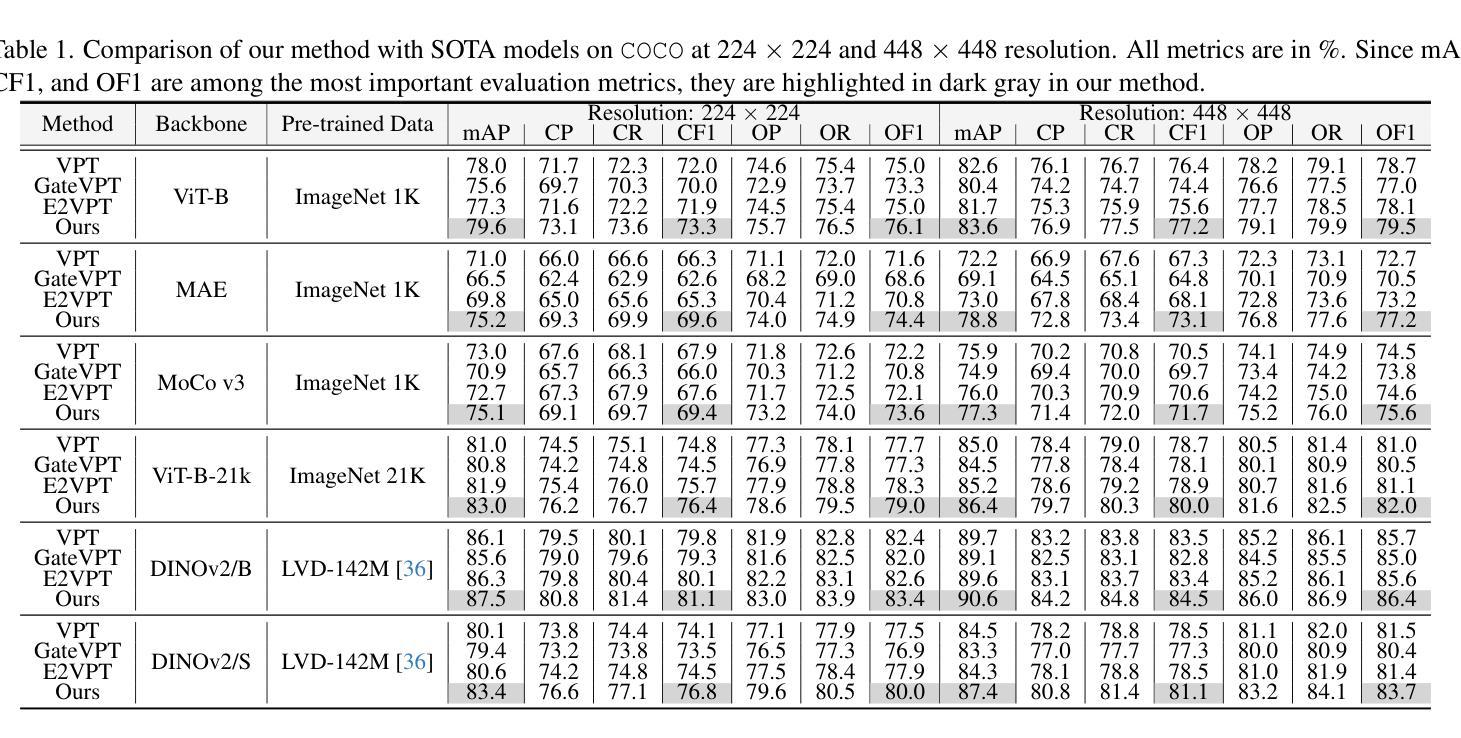
Modeling label correlations has always played a pivotal role in multi-label image classification (MLC), attracting significant attention from researchers. However, recent studies have overemphasized co-occurrence relationships among labels, which can lead to overfitting risk on this overemphasis, resulting in suboptimal models. To tackle this problem, we advocate for balancing correlative and discriminative relationships among labels to mitigate the risk of overfitting and enhance model performance. To this end, we propose the Multi-Label Visual Prompt Tuning framework, a novel and parameter-efficient method that groups classes into multiple class subsets according to label co-occurrence and mutual exclusivity relationships, and then models them respectively to balance the two relationships. In this work, since each group contains multiple classes, multiple prompt tokens are adopted within Vision Transformer (ViT) to capture the correlation or discriminative label relationship within each group, and effectively learn correlation or discriminative representations for class subsets. On the other hand, each group contains multiple group-aware visual representations that may correspond to multiple classes, and the mixture of experts (MoE) model can cleverly assign them from the group-aware to the label-aware, adaptively obtaining label-aware representation, which is more conducive to classification. Experiments on multiple benchmark datasets show that our proposed approach achieves competitive results and outperforms SOTA methods on multiple pre-trained models.
在多标签图像分类(MLC)中,建模标签相关性始终扮演着至关重要的角色,吸引了研究人员的广泛关注。然而,最近的研究过分强调了标签之间的共现关系,这可能导致因过度关注共现关系而产生的过拟合风险,从而导致模型表现不佳。为了解决这个问题,我们主张平衡标签之间的相关性和判别性关系,以减轻过拟合的风险并提高模型性能。为此,我们提出了多标签视觉提示调整框架,这是一种新颖且参数效率高的方法,根据标签的共现和相互排斥关系将类别分为多个类别子集,然后分别对其进行建模,以平衡这两种关系。在这项工作中,由于每个组包含多个类别,因此在视觉转换器(ViT)中使用多个提示令牌来捕获每个组内的相关性或判别性标签关系,并有效地学习类别子集的相关性或判别性表示。另一方面,每个组包含多个组感知视觉表示,它们可能对应于多个类别,而混合专家(MoE)模型可以巧妙地将它们从组感知分配给标签感知,自适应地获得标签感知表示,这更有助于分类。在多个基准数据集上的实验表明,我们提出的方法取得了具有竞争力的结果,并在多个预训练模型上优于最新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) 2025
Summary
多标签图像分类中标签关联建模至关重要,但过度强调标签间的共现关系可能导致模型过拟合。为解决这个问题,我们提出平衡标签间关联与区分关系,并提出Multi-Label Visual Prompt Tuning框架。该框架根据标签共现和互斥关系将类别分为多个子集,并分别建模。在Vision Transformer中,采用多个提示标记来捕捉每个分组内的标签关联或区分关系,学习子集的相关性或区分表示。此外,使用MoE模型将分组感知的视觉表示转换为标签感知表示,有助于分类。实验证明,该方法在多个预训练模型上表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 多标签图像分类中标签关联建模重要,但需平衡,避免过度强调共现关系导致过拟合。
- 提出Multi-Label Visual Prompt Tuning框架,根据标签关系分组建模,提高模型性能。
- 采用Vision Transformer中的多个提示标记捕捉每个分组内的标签关联和区分关系。
- 使用MoE模型将分组感知的视觉表示转换为标签感知表示,增强分类效果。
- 框架在多个预训练模型上表现优异,具有竞争力。
- 框架适用于多种基准数据集,具有广泛的应用前景。
点此查看论文截图