⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-12 更新
Baryonification II: Constraining feedback with X-ray and kinematic Sunyaev-Zel’dovich observations
Authors:Michael Kovač, Andrina Nicola, Jozef Bucko, Aurel Schneider, Robert Reischke, Sambit K. Giri, Romain Teyssier, Matthieu Schaller, Joop Schaye
Baryonic feedback alters the matter distribution on small and intermediate scales, posing a challenge for precision cosmology. The new, component-wise baryonification (BFC) approach provides a self-consistent framework to model feedback effects for different observables. In this paper we use this framework to fit kinematic Sunyaev-Zel’dovich (kSZ) observations from the Atacama Cosmology Telescope (ACT) alongside halo X-ray gas fractions from eROSITA, investigating baryonic feedback in a cosmological context. We first show that the kSZ data from ACT is consistent with the gas fractions from eROSITA, both suggesting a feedback model that is stronger than what is assumed in most hydrodynamical simulations. This finding is in contrast to older, pre-eROSITA gas fraction measurements that point towards weaker feedback in tension with the kSZ results. We suspect these discrepancies to be due to selection bias in the pre-eROSITA sample, or differences in halo mass estimation between the two data sets. In a further step, we use the BFC model to predict the baryonic suppression of the matter power spectrum. Based on our combined fit to data from ACT and eROSITA, we find a power spectrum suppression that exceeds the percent-level at modes above $k=0.3-0.6 ,h,\mathrm{Mpc}^{-1}$, growing to 2-8 percent at $k=1,h,\mathrm{Mpc}^{-1}$, and to 20-25 percent at $k=5,h,\mathrm{Mpc}^{-1}$, consistent with strong-feedback hydrodynamical simulations. Finally, we compare our best-fitting model to the observed gas density and pressure profiles of massive galaxy clusters from the X-COP sample, finding excellent agreement. These results show that BFC provides a self-consistent picture of feedback across mass- and length scales as well as different cosmological observables, thus making it promising for applications to multiwavelength studies to jointly constrain cosmology and baryonic effects.
重子反馈改变了小尺度和中尺度的物质分布,对精确宇宙学提出了挑战。新的逐个重子化(BFC)方法为不同的观测对象提供了模拟反馈效应的自洽框架。在本文中,我们使用这一框架来拟合来自阿塔卡马宇宙学望远镜(ACT)的动力学Sunyaev-Zel’dovich(kSZ)观测以及来自eROSITA的星系团X射线气体分数,并在宇宙学的背景下研究重子反馈。我们首先表明,ACT的kSZ数据与eROSITA的气体分数是一致的,两者都暗示反馈模型比大多数流体动力学模拟所假设的要强。这一发现与旧的、pre-eROSITA气体分数测量结果相反,后者指向较弱的反馈与kSZ结果存在张力。我们认为这些差异可能是由于pre-eROSITA样本的选择偏见,或是两组数据之间星系团质量估计的差异。进一步地,我们使用BFC模型来预测物质功率谱的重子抑制。基于我们对ACT和eROSITA数据的综合拟合,我们发现功率谱抑制在模式高于$ k=0.3-0.6 ,h,\mathrm{Mpc}^{-1} $时超过了百分之一水平,在$ k=1 ,h,\mathrm{Mpc}^{-1} $时增长到2-8%,在$ k=5 ,h,\mathrm{Mpc}^{-1} $时达到20-25%,这与强反馈流体动力学模拟相一致。最后,我们将最佳拟合模型与X-COP样本中大规模星系团观测到的气体密度和压力分布进行比较,发现吻合得很好。这些结果表明,BFC提供了跨质量和长度尺度以及不同宇宙学观测值的自洽反馈图像,因此将其应用于多波长研究以共同约束宇宙学和重子效应方面前景广阔。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 40 pages, 12 figures, 2 tables, to be submitted to JCAP
Summary
本文介绍了新的成分级重子化(BFC)方法,该方法为不同的观测值提供了模拟反馈效应的自洽框架。研究中利用此方法拟合Atacama宇宙学望远镜的动态Sunyaev-Zel’dovich(kSZ)观测与eROSITA的星系晕X射线气体分数数据,研究宇宙学背景下的重子反馈。研究结果显示kSZ数据与eROSITA气体分数数据一致,两者均支持一种比大多数流体动力学模拟中假设的更强烈的反馈模型。结合BFC模型预测物质功率谱的抑制情况,发现在一定模式下抑制超过百分之一,最高可达百分之二十五以上。最后,将最佳拟合模型与X-COP样本观察到的气体密度和压力分布进行比较,结果吻合良好。这显示出BFC方法在不同质量和长度尺度以及不同的宇宙学观测值上提供了自洽的反馈图像,因此有望应用于多波长研究,共同约束宇宙学和重子效应。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍新的成分级重子化(BFC)方法作为模拟不同观测值的反馈效应的自洽框架。
- 利用Atacama宇宙学望远镜的kSZ观测数据和eROSITA的星系晕X射线气体分数数据进行研究。
- kSZ数据和eROSITA数据均指向一种比大多数流体动力学模拟更强烈的反馈模型。
- BFC模型预测物质功率谱的抑制程度超过百分之一,最高可达百分之二十五以上。
- 研究中发现数据与模拟之间的不一致可能是由于样本选择偏见或数据集合之间在星系晕质量估计上的差异造成的。
- 最佳拟合模型与X-COP样本观测到的气体密度和压力分布比较吻合。
点此查看论文截图

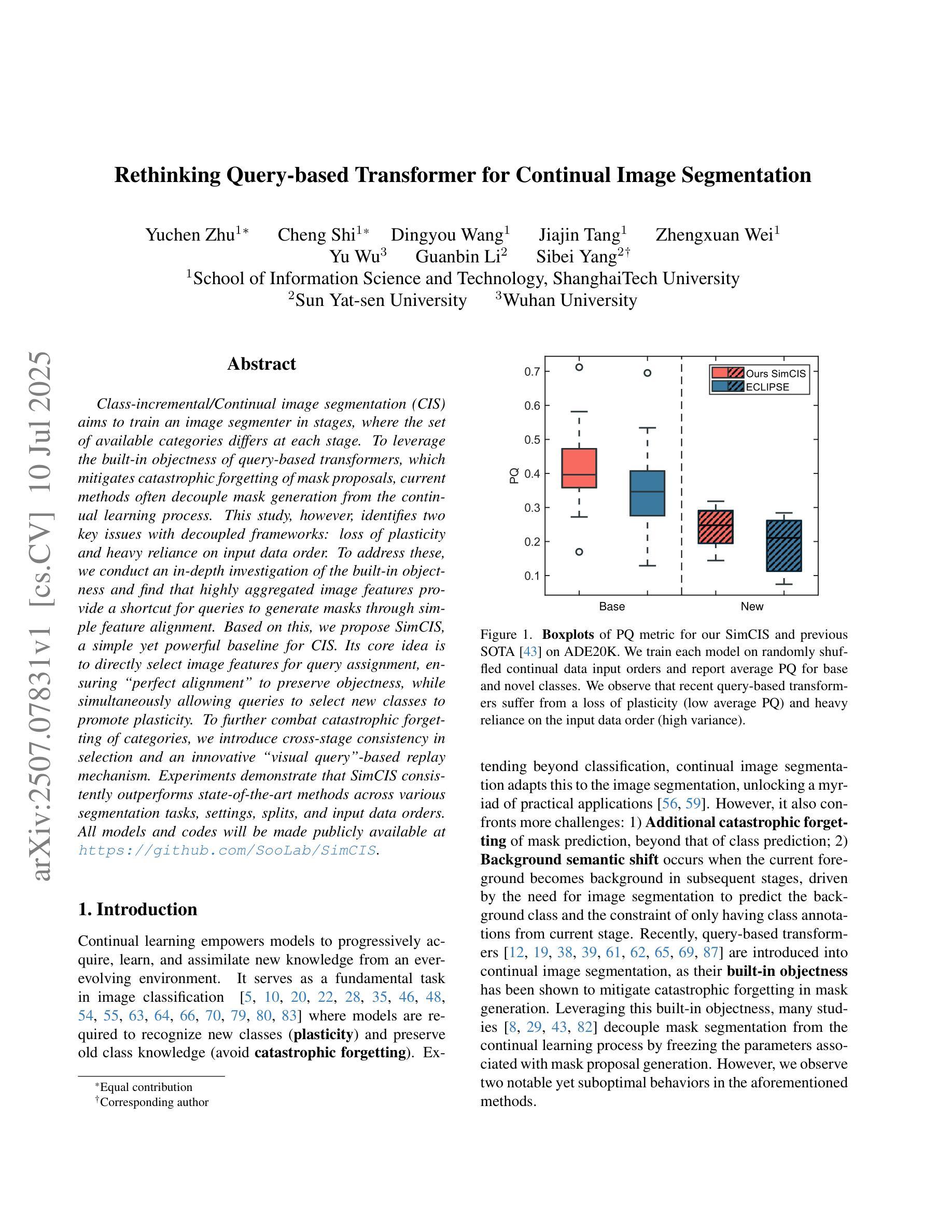
Rethinking Query-based Transformer for Continual Image Segmentation
Authors:Yuchen Zhu, Cheng Shi, Dingyou Wang, Jiajin Tang, Zhengxuan Wei, Yu Wu, Guanbin Li, Sibei Yang
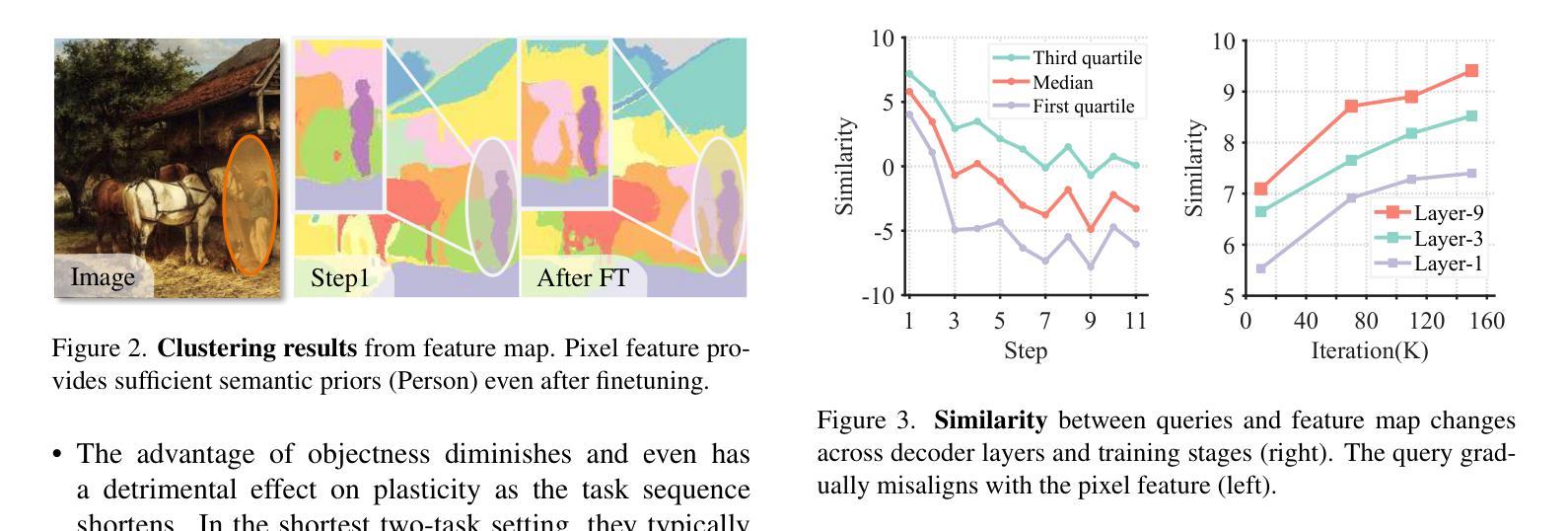
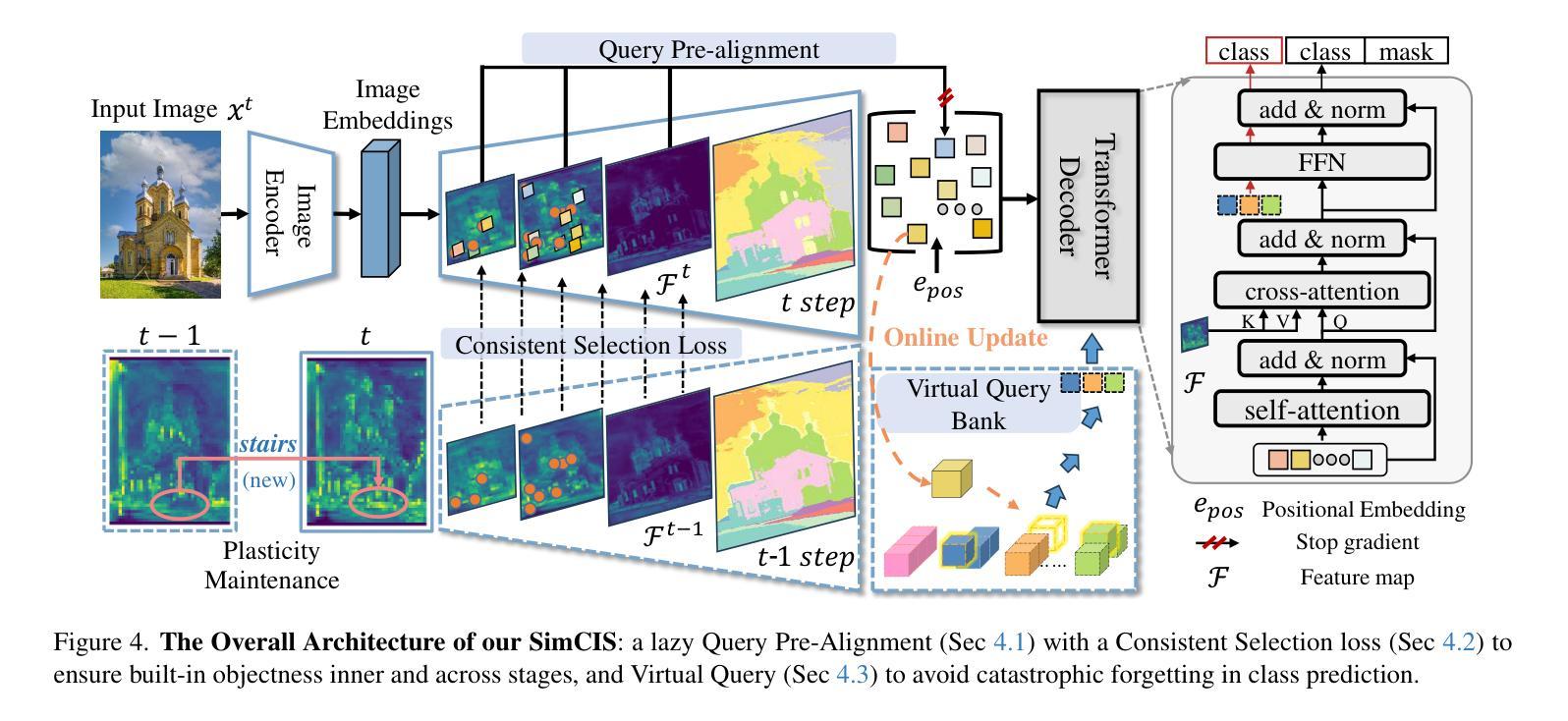
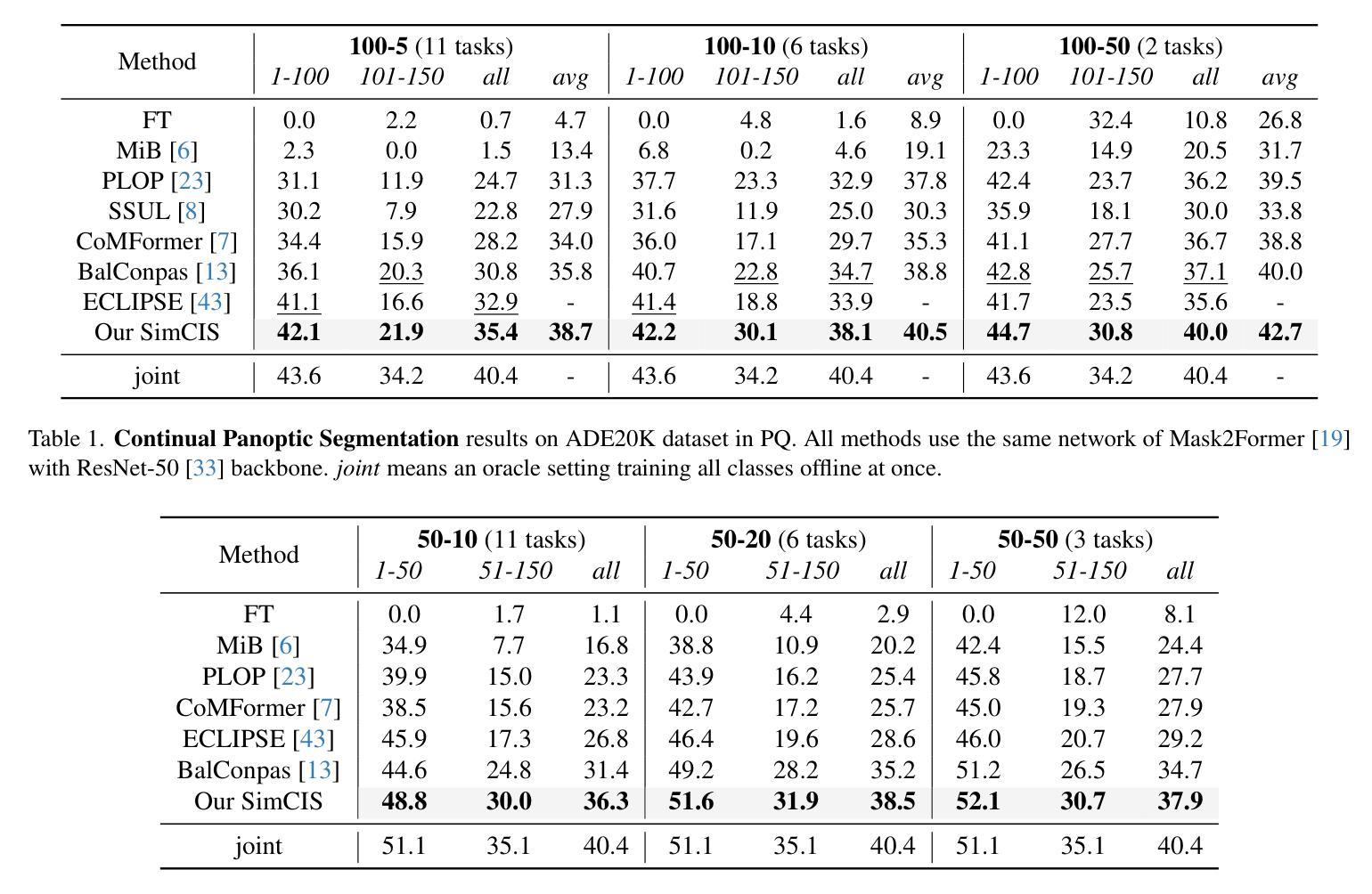
Class-incremental/Continual image segmentation (CIS) aims to train an image segmenter in stages, where the set of available categories differs at each stage. To leverage the built-in objectness of query-based transformers, which mitigates catastrophic forgetting of mask proposals, current methods often decouple mask generation from the continual learning process. This study, however, identifies two key issues with decoupled frameworks: loss of plasticity and heavy reliance on input data order. To address these, we conduct an in-depth investigation of the built-in objectness and find that highly aggregated image features provide a shortcut for queries to generate masks through simple feature alignment. Based on this, we propose SimCIS, a simple yet powerful baseline for CIS. Its core idea is to directly select image features for query assignment, ensuring “perfect alignment” to preserve objectness, while simultaneously allowing queries to select new classes to promote plasticity. To further combat catastrophic forgetting of categories, we introduce cross-stage consistency in selection and an innovative “visual query”-based replay mechanism. Experiments demonstrate that SimCIS consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods across various segmentation tasks, settings, splits, and input data orders. All models and codes will be made publicly available at https://github.com/SooLab/SimCIS.
类增量/持续图像分割(CIS)旨在分阶段训练图像分割器,每个阶段的可用类别集各不相同。为了利用基于查询的变压器(transformer)的内置对象性,减轻掩膜提案的灾难性遗忘,当前方法通常将掩膜生成与持续学习过程解耦。然而,本研究发现了基于解耦框架的两个关键问题:可塑性丧失和对输入数据顺序的严重依赖。为了解决这些问题,我们对内置的对象性进行了深入研究,并发现高度聚合的图像特征为查询生成掩膜提供了通过简单特征对齐的捷径。基于此,我们提出了SimCIS,这是CIS的简单而强大的基线。其核心思想是直接选择图像特征进行分配查询的任务,确保与对象性的“完美对齐”,同时允许查询选择新类别以促进可塑性。为了进一步克服类别的灾难性遗忘问题,我们引入了跨阶段的选型一致性以及基于“视觉查询”的回放机制。实验表明,在各种分割任务、设置、分割和输入数据顺序下,SimCIS始终优于最新方法。所有模型和代码将在https://github.com/SooLab/SimCIS公开提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This work is accepted by CVPR 2025
Summary
本文研究了基于查询的增量图像分割(CIS)技术,指出当前方法存在的两个问题并进行了改进。通过深入分析内置对象性,发现高度聚合的图像特征可作为查询生成掩码的捷径。为此,本文提出了SimCIS方案,通过直接选择图像特征进行分配来保留对象性并促进可塑性。此外,还引入了跨阶段一致性选择和基于视觉查询的回放机制来对抗类别遗忘问题。实验表明,SimCIS在各种分割任务、设置、分割和输入数据顺序上均优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 当前增量图像分割方法存在失去灵活性和依赖输入数据顺序的问题。
- 高度聚合的图像特征可以作为查询生成掩码的捷径。
- SimCIS通过直接选择图像特征进行分配来保留对象性并促进可塑性。
- SimCIS引入了跨阶段一致性选择来对抗类别遗忘问题。
- SimCIS采用基于视觉查询的回放机制来增强学习效果。
- 实验表明SimCIS在各种场景下均优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图
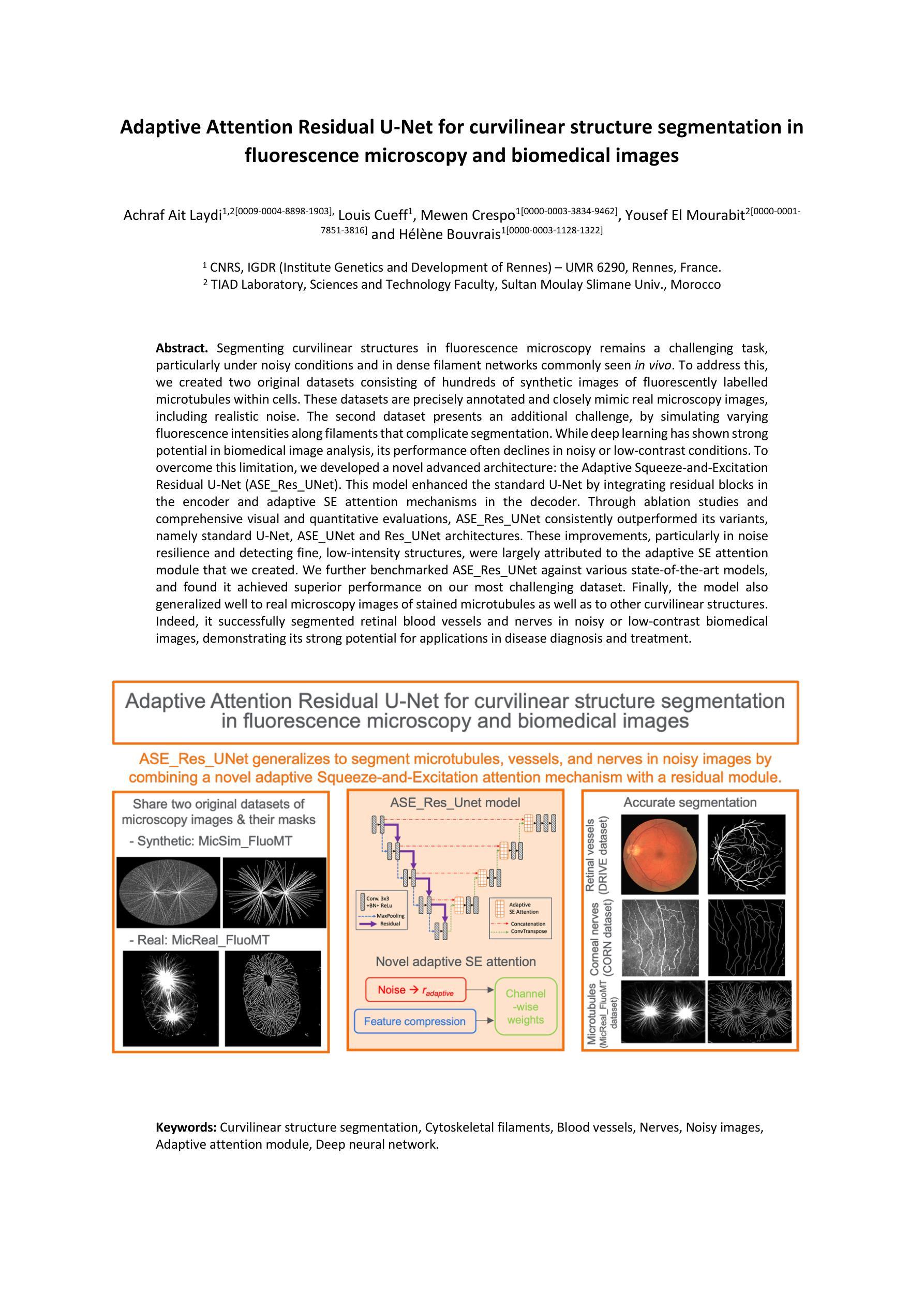
Adaptive Attention Residual U-Net for curvilinear structure segmentation in fluorescence microscopy and biomedical images
Authors:Achraf Ait Laydi, Louis Cueff, Mewen Crespo, Yousef El Mourabit, Hélène Bouvrais
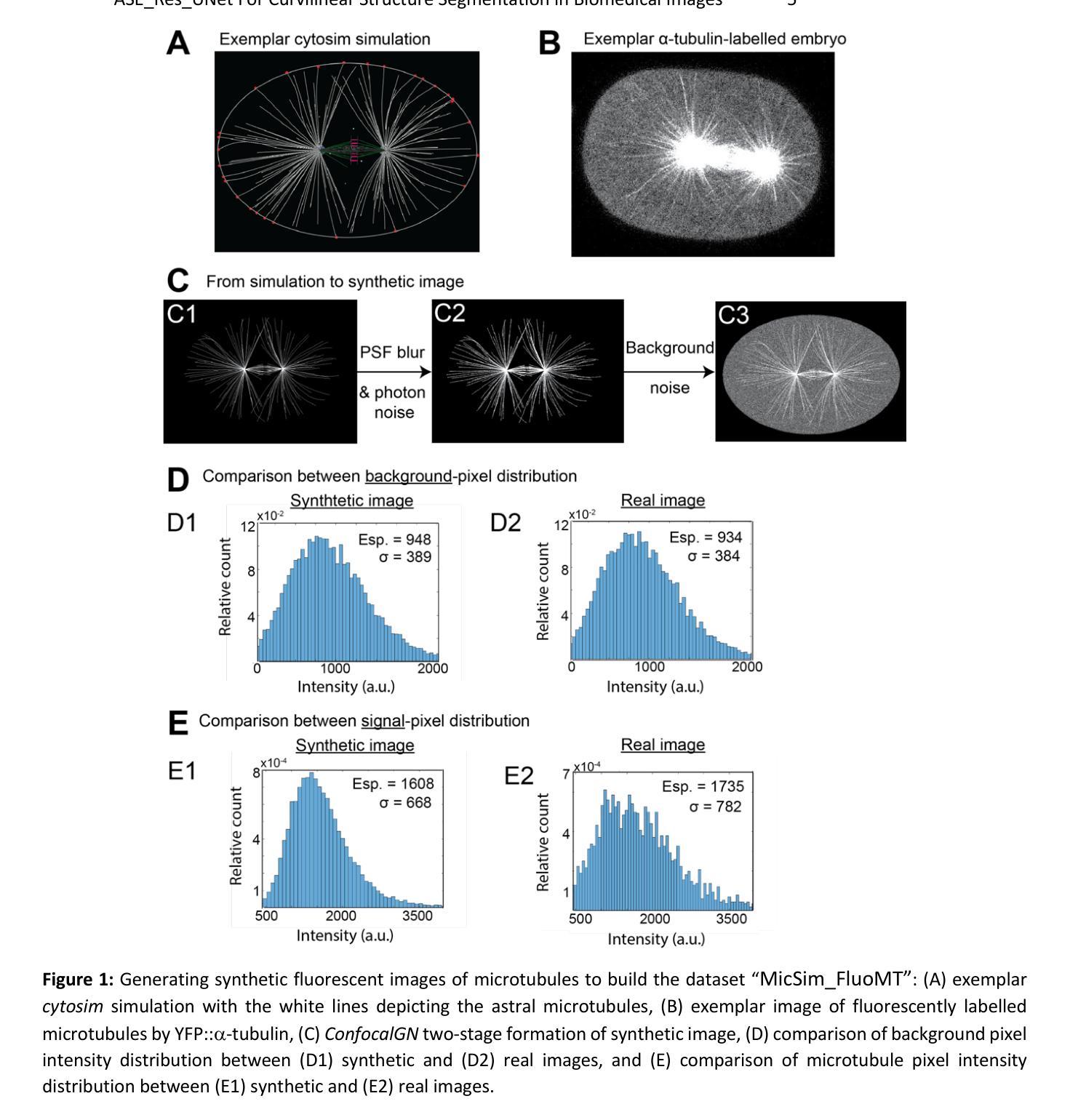
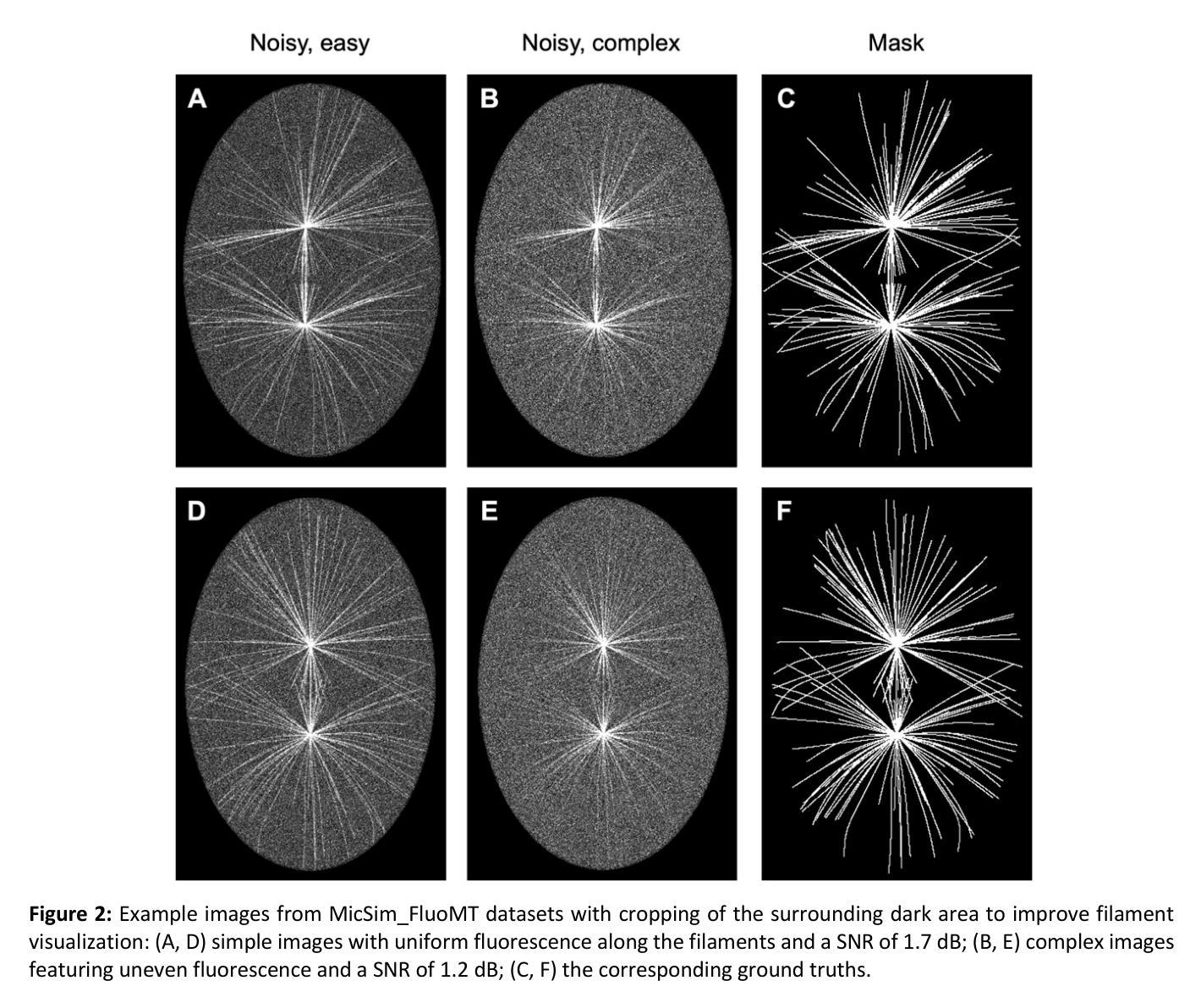
Segmenting curvilinear structures in fluorescence microscopy remains a challenging task, particularly under noisy conditions and in dense filament networks commonly seen in vivo. To address this, we created two original datasets consisting of hundreds of synthetic images of fluorescently labelled microtubules within cells. These datasets are precisely annotated and closely mimic real microscopy images, including realistic noise. The second dataset presents an additional challenge, by simulating varying fluorescence intensities along filaments that complicate segmentation. While deep learning has shown strong potential in biomedical image analysis, its performance often declines in noisy or low-contrast conditions. To overcome this limitation, we developed a novel advanced architecture: the Adaptive Squeeze-and-Excitation Residual U-Net (ASE_Res_UNet). This model enhanced the standard U-Net by integrating residual blocks in the encoder and adaptive SE attention mechanisms in the decoder. Through ablation studies and comprehensive visual and quantitative evaluations, ASE_Res_UNet consistently outperformed its variants, namely standard U-Net, ASE_UNet and Res_UNet architectures. These improvements, particularly in noise resilience and detecting fine, low-intensity structures, were largely attributed to the adaptive SE attention module that we created. We further benchmarked ASE_Res_UNet against various state-of-the-art models, and found it achieved superior performance on our most challenging dataset. Finally, the model also generalized well to real microscopy images of stained microtubules as well as to other curvilinear structures. Indeed, it successfully segmented retinal blood vessels and nerves in noisy or low-contrast biomedical images, demonstrating its strong potential for applications in disease diagnosis and treatment.
在荧光显微镜下对曲线结构进行分割仍然是一项具有挑战性的任务,特别是在噪声条件下和在体内常见的密集纤维网络中。为了解决这个问题,我们创建了两个原始数据集,包含数百张合成细胞图像中的荧光标记微管图像。这些数据集经过了精确标注,并模拟了真实的显微镜图像,包括真实噪声。第二个数据集通过模拟纤维中不同的荧光强度,增加了额外的挑战,这使得分割复杂化。深度学习在生物医学图像分析方面显示出强大的潜力,但在噪声或低对比度条件下,其性能往往会下降。为了克服这一局限性,我们开发了一种新型高级架构:自适应压缩与激发残差U-Net(ASE_Res_UNet)。此模型通过集成编码器中的残差块和解码器中的自适应SE注意力机制,增强了标准U-Net的功能。通过消融研究以及全面的视觉和定量评估,ASE_Res_UNet始终优于其变体,即标准U-Net、ASE_UNet和Res_UNet架构。这些改进在很大程度上归功于我们创建的自适应SE注意力模块,特别是在噪声韧性和检测细微、低强度结构方面。我们将ASE_Res_UNet与各种最新模型进行了基准测试,发现它在我们的最具挑战的数据集上取得了卓越的性能。最后,该模型也很好地泛化到了真实的显微镜图像染色微管和其他的曲线结构上。事实上,它能够成功分割嘈杂或低对比度的生物医学图像中的视网膜血管和神经,显示出其在疾病诊断和治疗应用中的强大潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对荧光显微镜下细胞内微管蛋白的分割问题,创建的两个合成图像数据集及提出的自适应挤压与激励残差U-Net模型(ASE_Res_UNet)。该模型通过集成残差块和自适应SE注意力机制,提高了标准U-Net的性能。实验证明,ASE_Res_UNet在噪声处理和低对比度结构检测方面表现出卓越性能,特别是在模拟不同荧光强度的微管蛋白分割问题上。该模型还具有良好的泛化能力,能够成功应用于真实显微镜图像中的微管蛋白以及其他曲率结构,如视网膜血管和神经的分割,具有疾病诊断和治疗应用的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 针对荧光显微镜下细胞内微管蛋白的分割问题,创建了两个合成图像数据集。
- 数据集模拟真实显微镜图像,包括噪声和不同的荧光强度。
- 提出了自适应挤压与激励残差U-Net模型(ASE_Res_UNet),结合了残差块和自适应SE注意力机制。
- ASE_Res_UNet在噪声处理和低对比度结构检测方面表现出卓越性能。
- 该模型在模拟不同荧光强度的微管蛋白分割问题上表现尤为出色。
- ASE_Res_UNet具有良好的泛化能力,成功应用于真实显微镜图像中的微管蛋白以及其他曲率结构(如视网膜血管和神经)的分割。
点此查看论文截图
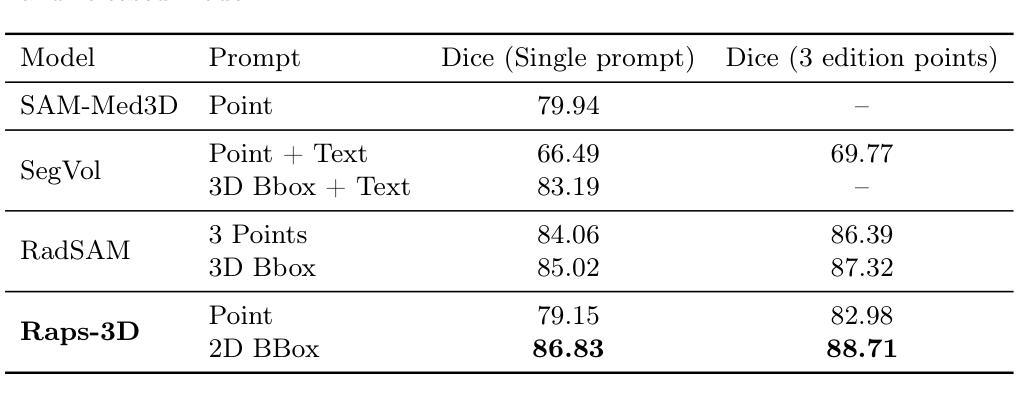
RAPS-3D: Efficient interactive segmentation for 3D radiological imaging
Authors:Théo Danielou, Daniel Tordjman, Pierre Manceron, Corentin Dancette
Promptable segmentation, introduced by the Segment Anything Model (SAM), is a promising approach for medical imaging, as it enables clinicians to guide and refine model predictions interactively. However, SAM’s architecture is designed for 2D images and does not extend naturally to 3D volumetric data such as CT or MRI scans. Adapting 2D models to 3D typically involves autoregressive strategies, where predictions are propagated slice by slice, resulting in increased inference complexity. Processing large 3D volumes also requires significant computational resources, often leading existing 3D methods to also adopt complex strategies like sliding-window inference to manage memory usage, at the cost of longer inference times and greater implementation complexity. In this paper, we present a simplified 3D promptable segmentation method, inspired by SegVol, designed to reduce inference time and eliminate prompt management complexities associated with sliding windows while achieving state-of-the-art performance.
由Segment Anything Model(SAM)引入的提示分割是医学成像的一种有前途的方法,因为它能够使临床医生以交互式方式引导和细化模型预测。然而,SAM的架构是为二维图像设计的,并不能自然地扩展到三维体积数据,如CT或MRI扫描。将二维模型适应到三维通常采用自回归策略,预测逐层传播,导致推理复杂度增加。处理大型三维体积还需要大量的计算资源,这导致现有的三维方法也采用复杂的策略,如滑动窗口推理来管理内存使用,但这会增加推理时间和实现复杂度。在本文中,我们提出了一种简化的三维提示分割方法,该方法受到SegVol的启发,旨在减少推理时间并消除与滑动窗口相关的提示管理复杂性,同时实现最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Abstract accepted at MIUA 2025
Summary
医学图像领域引入的可提示分割法,即Segment Anything Model(SAM),是一种有望用于医学成像的交互式方法,能够让临床医生对模型预测进行引导和精细调整。然而,SAM的设计初衷是针对二维图像,并不自然适用于三维体积数据如CT或MRI扫描。将二维模型适应到三维通常采用自回归策略,这种策略逐片预测并传播,增加了推理复杂性。针对处理大量三维体积数据需要大量计算资源的问题,现有的三维方法往往采用如滑动窗口推理等复杂策略以管理内存使用,但同时也牺牲了推理时间和实施复杂性。本文受SegVol启发,提出了一种简化三维可提示分割方法,旨在减少推理时间并消除与滑动窗口相关的提示管理复杂性,同时达到业界领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- SAM模型引入了一种可提示分割法用于医学成像,允许交互式地引导和精细调整模型预测。
- SAM主要适用于二维图像,对于三维体积数据的处理存在局限性。
- 将二维模型应用于三维数据通常采取自回归策略,导致推理过程复杂化。
- 处理大量三维体积数据需要大量计算资源。
- 现存的三维方法如滑动窗口推理,在管理内存使用的同时牺牲了推理时间和实施复杂性。
- 本文提出了一种简化三维可提示分割方法,旨在减少推理时间并消除与滑动窗口相关的提示管理复杂性。
点此查看论文截图

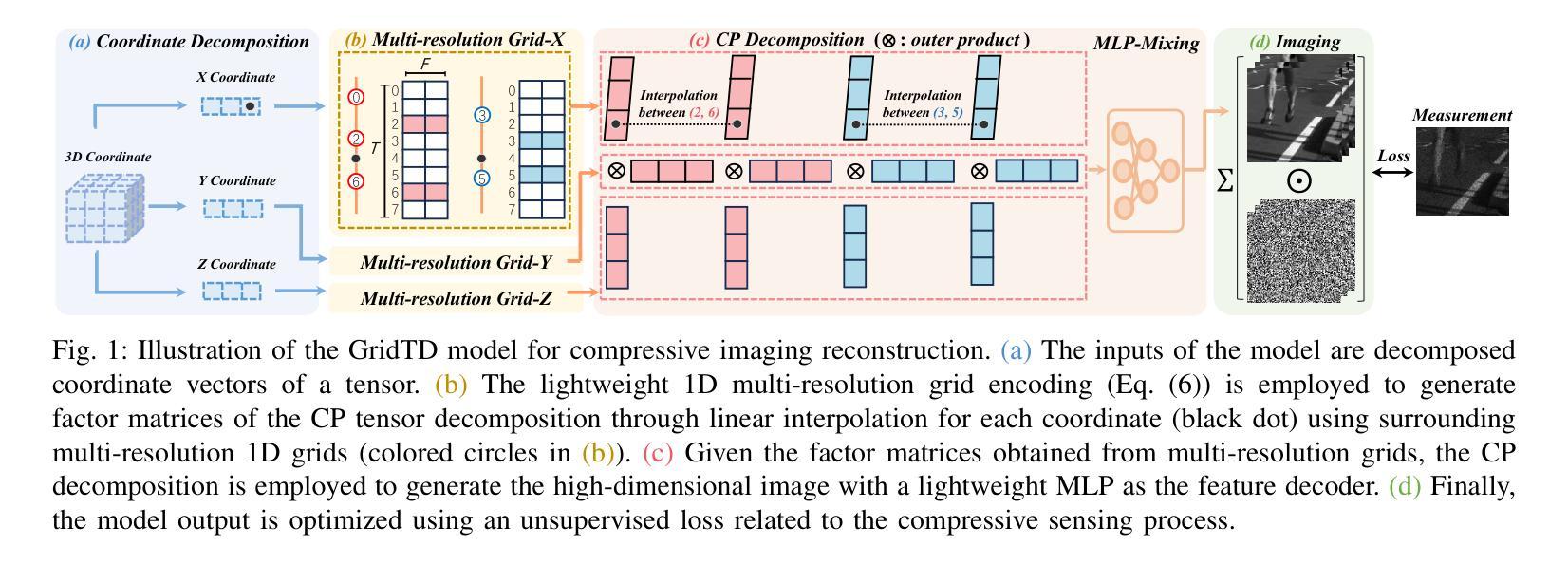
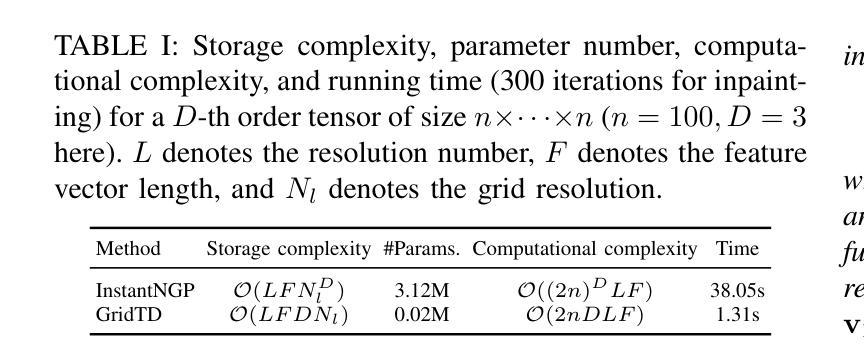
Compressive Imaging Reconstruction via Tensor Decomposed Multi-Resolution Grid Encoding
Authors:Zhenyu Jin, Yisi Luo, Xile Zhao, Deyu Meng
Compressive imaging (CI) reconstruction, such as snapshot compressive imaging (SCI) and compressive sensing magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), aims to recover high-dimensional images from low-dimensional compressed measurements. This process critically relies on learning an accurate representation of the underlying high-dimensional image. However, existing unsupervised representations may struggle to achieve a desired balance between representation ability and efficiency. To overcome this limitation, we propose Tensor Decomposed multi-resolution Grid encoding (GridTD), an unsupervised continuous representation framework for CI reconstruction. GridTD optimizes a lightweight neural network and the input tensor decomposition model whose parameters are learned via multi-resolution hash grid encoding. It inherently enjoys the hierarchical modeling ability of multi-resolution grid encoding and the compactness of tensor decomposition, enabling effective and efficient reconstruction of high-dimensional images. Theoretical analyses for the algorithm’s Lipschitz property, generalization error bound, and fixed-point convergence reveal the intrinsic superiority of GridTD as compared with existing continuous representation models. Extensive experiments across diverse CI tasks, including video SCI, spectral SCI, and compressive dynamic MRI reconstruction, consistently demonstrate the superiority of GridTD over existing methods, positioning GridTD as a versatile and state-of-the-art CI reconstruction method.
压缩成像(CI)重建,如快照压缩成像(SCI)和压缩感知磁共振成像(MRI),旨在从低维压缩测量中恢复高维图像。这一过程严重依赖于学习高维图像的正确表示。然而,现有的无监督表示可能在表示能力和效率之间难以实现平衡。为了克服这一局限性,我们提出了Tensor Decomposed多分辨率网格编码(GridTD),这是一种用于CI重建的无监督连续表示框架。GridTD优化了轻量级神经网络和输入张量分解模型,其参数通过多分辨率哈希网格编码学习。它天然地享受多分辨率网格编码的分层建模能力和张量分解的紧凑性,能够实现高维图像的有效且高效的重建。该算法的李普希茨属性、泛化误差界和定点收敛的理论分析揭示了GridTD相较于现有连续表示模型的内在优势。在包括视频SCI、光谱SCI和压缩动态MRI重建等多种CI任务的大量实验中,GridTD始终表现出优于现有方法的效果,确立了GridTD作为一种通用且最先进的CI重建方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了压缩成像(CI)重建技术,如快照压缩成像(SCI)和压缩感知磁共振成像(MRI)。文章提出了一种名为Tensor Decomposed多分辨率网格编码(GridTD)的无监督连续表示框架,用于CI重建。GridTD优化了一个轻量级神经网络和输入张量分解模型,通过多分辨率哈希网格编码学习参数。GridTD结合了多分辨率网格编码的层次建模能力和张量分解的紧凑性,能够高效、有效地重建高维图像。理论分析和在多种CI任务上的实验结果表明,GridTD相较于现有方法具有优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 压缩成像(CI)技术旨在从低维压缩测量中恢复高维图像。
- 现有无监督表示方法可能在表示能力和效率之间难以达到平衡。
- 提出的Tensor Decomposed多分辨率网格编码(GridTD)框架结合了多分辨率网格编码的层次建模能力和张量分解的紧凑性。
- GridTD通过优化轻量级神经网络和输入张量分解模型,实现了高效的高维图像重建。
- GridTD具有优异的理论性能,包括Lipschitz性质、泛化误差界和固定点收敛性分析。
- 在多种CI任务上,包括视频SCI、光谱SCI和压缩动态MRI重建,GridTD相较于现有方法表现出优越性。
点此查看论文截图

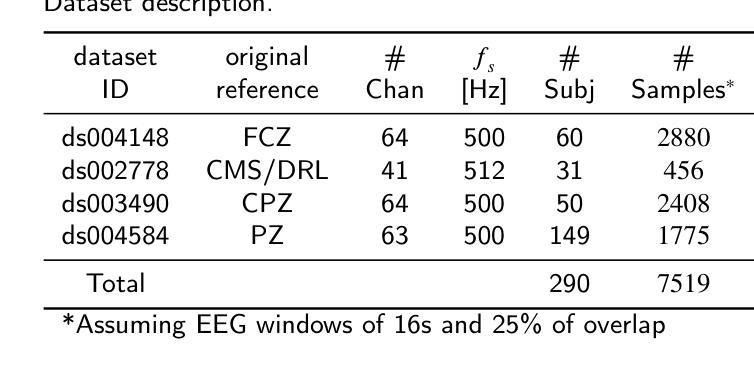
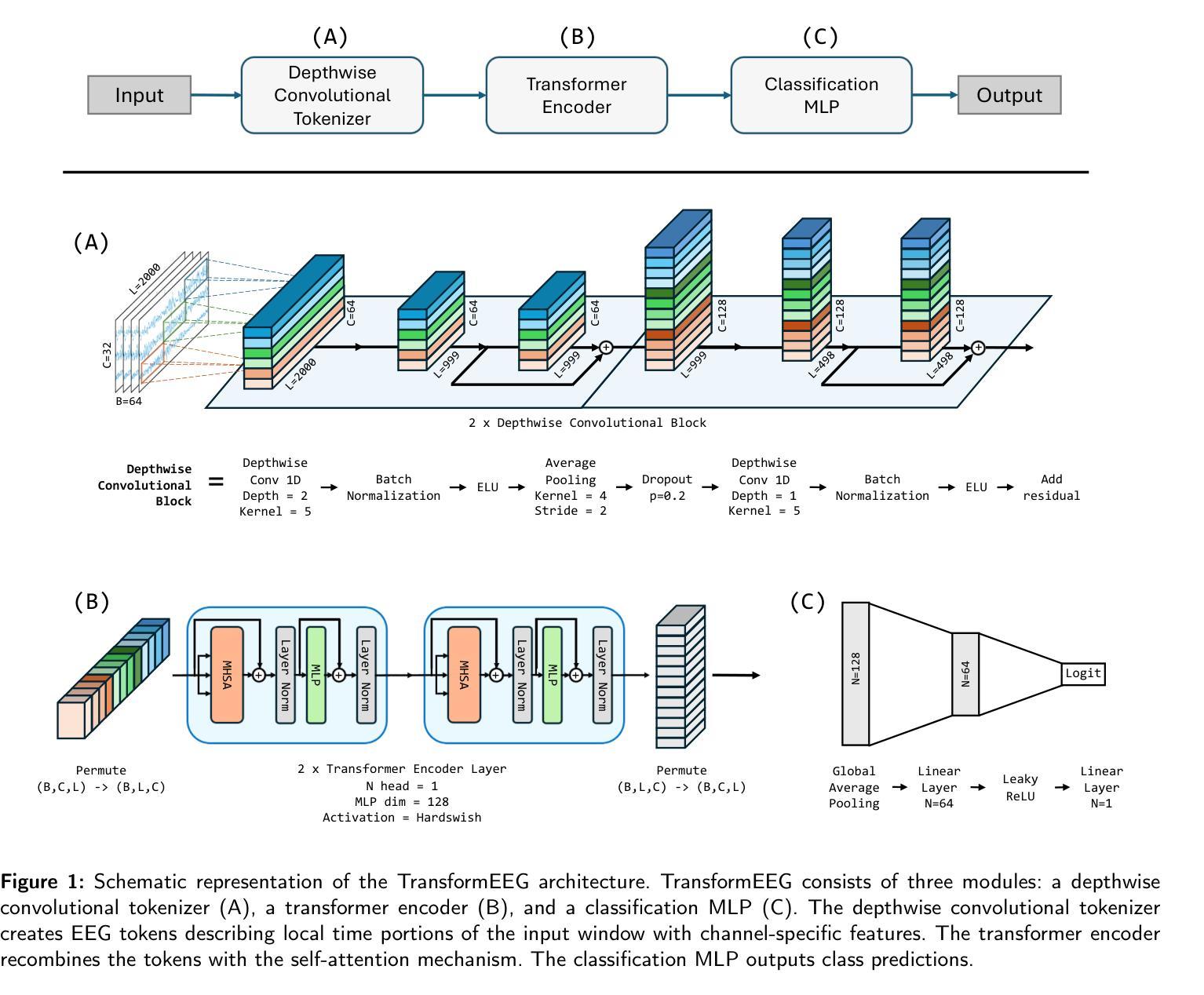
TransformEEG: Towards Improving Model Generalizability in Deep Learning-based EEG Parkinson’s Disease Detection
Authors:Federico Del Pup, Riccardo Brun, Filippo Iotti, Edoardo Paccagnella, Mattia Pezzato, Sabrina Bertozzo, Andrea Zanola, Louis Fabrice Tshimanga, Henning Müller, Manfredo Atzori
Electroencephalography (EEG) is establishing itself as an important, low-cost, noninvasive diagnostic tool for the early detection of Parkinson’s Disease (PD). In this context, EEG-based Deep Learning (DL) models have shown promising results due to their ability to discover highly nonlinear patterns within the signal. However, current state-of-the-art DL models suffer from poor generalizability caused by high inter-subject variability. This high variability underscores the need for enhancing model generalizability by developing new architectures better tailored to EEG data. This paper introduces TransformEEG, a hybrid Convolutional-Transformer designed for Parkinson’s disease detection using EEG data. Unlike transformer models based on the EEGNet structure, TransformEEG incorporates a depthwise convolutional tokenizer. This tokenizer is specialized in generating tokens composed by channel-specific features, which enables more effective feature mixing within the self-attention layers of the transformer encoder. To evaluate the proposed model, four public datasets comprising 290 subjects (140 PD patients, 150 healthy controls) were harmonized and aggregated. A 10-outer, 10-inner Nested-Leave-N-Subjects-Out (N-LNSO) cross-validation was performed to provide an unbiased comparison against seven other consolidated EEG deep learning models. TransformEEG achieved the highest balanced accuracy’s median (78.45%) as well as the lowest interquartile range (6.37%) across all the N-LNSO partitions. When combined with data augmentation and threshold correction, median accuracy increased to 80.10%, with an interquartile range of 5.74%. In conclusion, TransformEEG produces more consistent and less skewed results. It demonstrates a substantial reduction in variability and more reliable PD detection using EEG data compared to the other investigated models.
脑电图(EEG)正在成为一种重要的、低成本的、非侵入性的帕金森病(PD)早期诊断工具。在此背景下,基于脑电图的深度学习(DL)模型由于其发现信号内高度非线性模式的能力而显示出有希望的结果。然而,目前最先进的DL模型由于主体间存在高变异性而导致泛化能力较差。这种高变异性强调了通过开发更好地适应脑电图数据的新架构来提高模型泛化能力的必要性。本文介绍了TransformEEG,这是一种用于帕金森病检测的混合卷积-转换器,使用脑电图数据。与基于EEGNet结构的转换器模型不同,TransformEEG采用深度可分离卷积分词器。该分词器专门生成由通道特定特征组成的令牌,这可以在转换器编码器的自注意力层中实现更有效的特征混合。为了评估所提出的模型,四个公共数据集(包括290个受试者,其中140名为PD患者,150名为健康对照)被协调并汇总。进行了10次外部和10次内部嵌套留N个主体外(N-LNSO)的交叉验证,以与其他七个成熟的脑电图深度学习模型进行公正比较。TransformEEG在所有的N-LNSO分区中达到了最高的平衡准确率的中位数(78.45%),以及最低的四分位数范围(6.37%)。当与数据增强和阈值校正相结合时,中位数准确率提高到80.1%,四分位数范围为5.74%。总之,TransformEEG产生的结果更加一致且偏差较小。与其他调查模型相比,它显示了显著的变异性降低,并且使用脑电图数据更可靠地检测PD。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted for possible publication. GitHub repository: see https://github.com/MedMaxLab/transformeeg
Summary
本文介绍了EEG在帕金森病早期诊断中的重要作用,以及基于EEG的深度学习模型的应用前景。针对当前深度学习模型存在的泛化能力不强的问题,提出了一种新型的混合卷积-Transformer模型TransformEEG。该模型采用深度卷积分词器生成通道特定特征标记,提高了特征混合效率,并在帕金森病检测中表现出更高的准确性和一致性。
Key Takeaways
- EEG作为帕金森病早期诊断的非侵入性工具,具有低成本和重要性。
- 深度学习模型在EEG信号处理中具有发现非线性模式的能力。
- 当前深度学习模型存在泛化能力不强的问题,主要由于个体间差异大。
- TransformEEG模型引入深度卷积分词器,提高特征混合效率。
- TransformEEG模型在帕金森病检测中表现出更高的准确性。
- TransformEEG模型与其他模型相比,结果更一致、可靠性更高。
点此查看论文截图

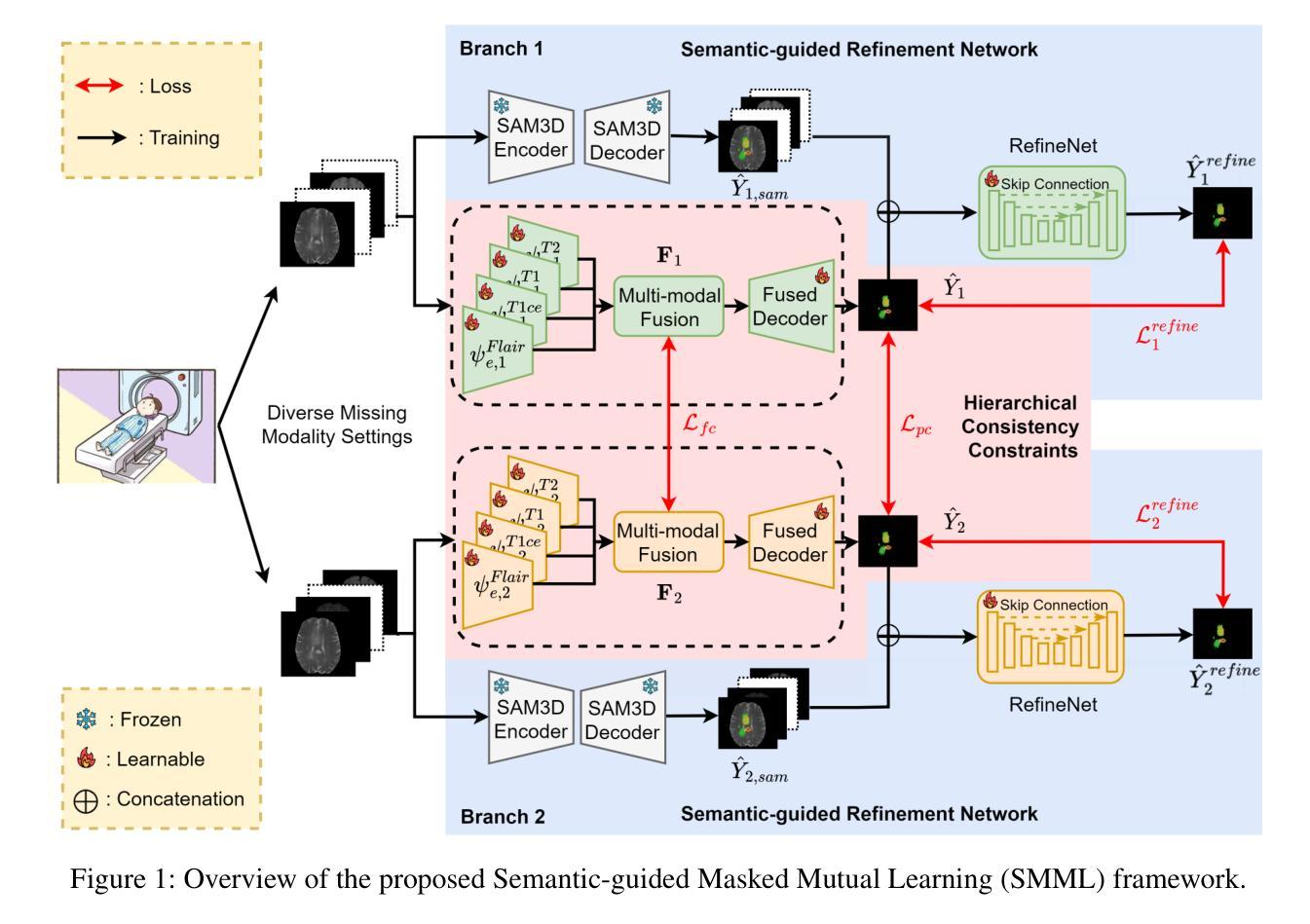
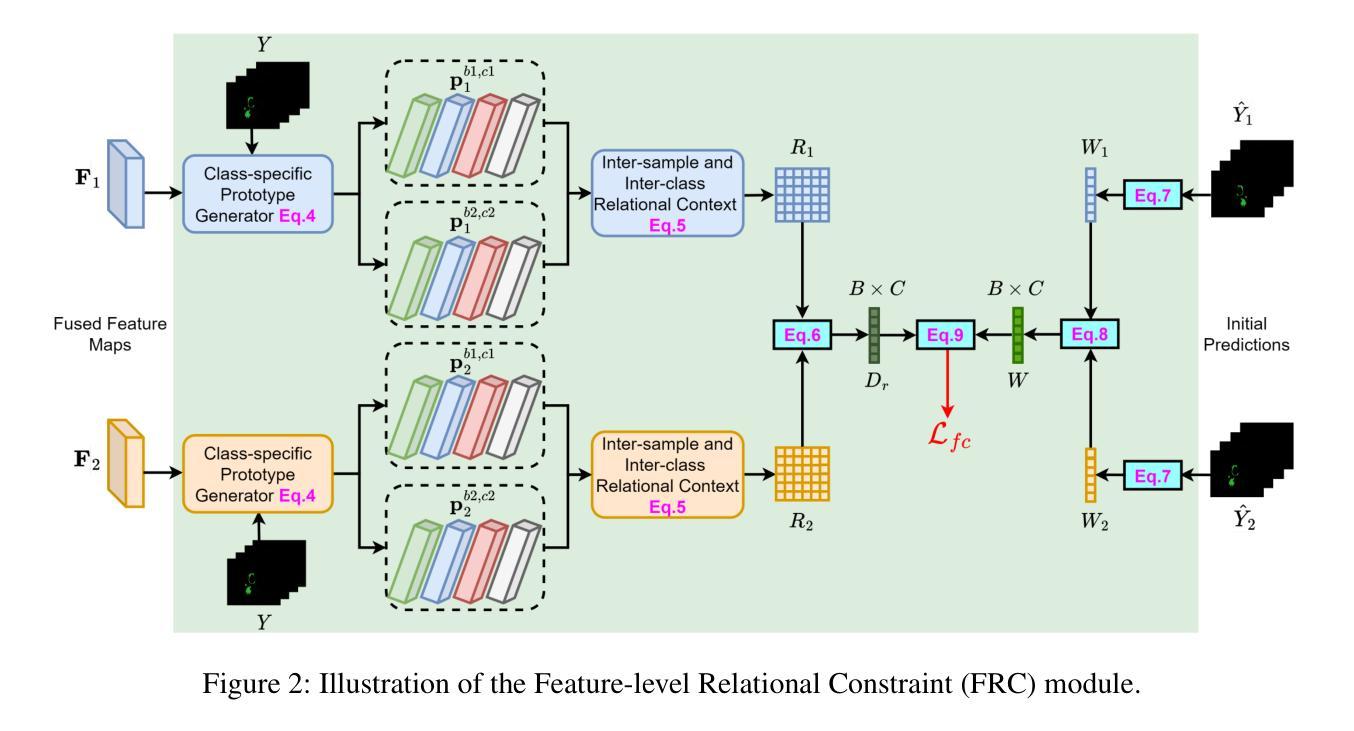
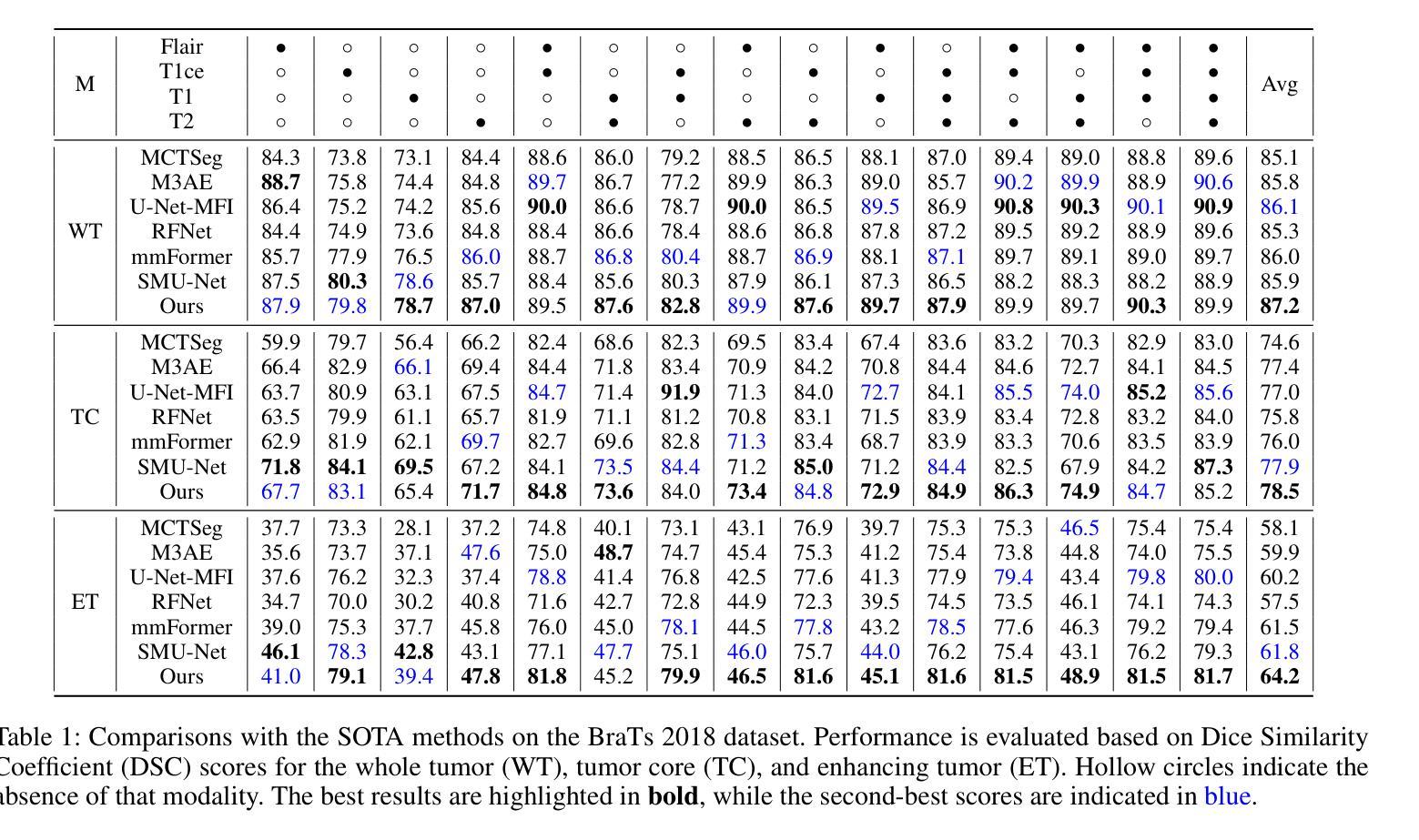
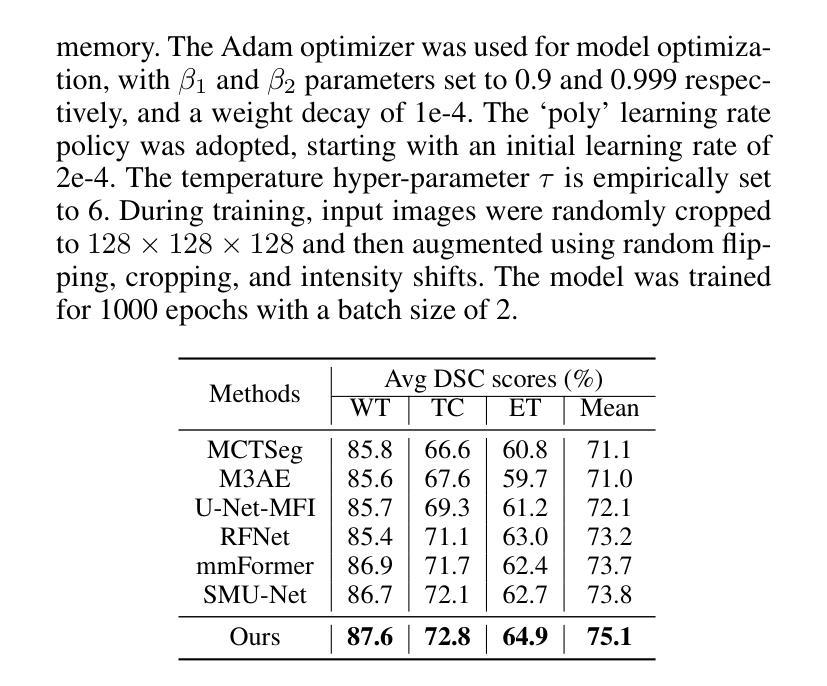
Semantic-guided Masked Mutual Learning for Multi-modal Brain Tumor Segmentation with Arbitrary Missing Modalities
Authors:Guoyan Liang, Qin Zhou, Jingyuan Chen, Bingcang Huang, Kai Chen, Lin Gu, Zhe Wang, Sai Wu, Chang Yao
Malignant brain tumors have become an aggressive and dangerous disease that leads to death worldwide.Multi-modal MRI data is crucial for accurate brain tumor segmentation, but missing modalities common in clinical practice can severely degrade the segmentation performance. While incomplete multi-modal learning methods attempt to address this, learning robust and discriminative features from arbitrary missing modalities remains challenging. To address this challenge, we propose a novel Semantic-guided Masked Mutual Learning (SMML) approach to distill robust and discriminative knowledge across diverse missing modality scenarios.Specifically, we propose a novel dual-branch masked mutual learning scheme guided by Hierarchical Consistency Constraints (HCC) to ensure multi-level consistency, thereby enhancing mutual learning in incomplete multi-modal scenarios. The HCC framework comprises a pixel-level constraint that selects and exchanges reliable knowledge to guide the mutual learning process. Additionally, it includes a feature-level constraint that uncovers robust inter-sample and inter-class relational knowledge within the latent feature space. To further enhance multi-modal learning from missing modality data, we integrate a refinement network into each student branch. This network leverages semantic priors from the Segment Anything Model (SAM) to provide supplementary information, effectively complementing the masked mutual learning strategy in capturing auxiliary discriminative knowledge. Extensive experiments on three challenging brain tumor segmentation datasets demonstrate that our method significantly improves performance over state-of-the-art methods in diverse missing modality settings.
恶性脑肿瘤已成为一种全球范围内具有侵袭性和致命性的疾病。多模态MRI数据对于准确的脑肿瘤分割至关重要,但在临床实践中的缺失模式会严重降低分割性能。虽然不完整的多模式学习方法试图解决这个问题,但从任意缺失的模式中学习稳健和具有区分性的特征仍然具有挑战性。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一种新的语义引导掩膜互学习(SMML)方法,以在多种缺失模式场景中提炼稳健和具有区分性的知识。具体来说,我们提出了一种新的由层次一致性约束(HCC)引导的双重分支掩膜互学习方案,以确保多级一致性,从而增强不完整多模式场景中的相互学习。HCC框架包括像素级约束,用于选择和交换可靠的知识以指导互学习过程。此外,它还包括特征级约束,用于揭示潜在特征空间内的稳健跨样本和跨类别关系知识。为了进一步从缺失模式数据中增强多模式学习,我们将细化网络集成到每个学生分支中。该网络利用来自分段任何模型(SAM)的语义先验信息提供补充信息,有效地补充了掩膜互学习策略在捕获辅助区分性知识方面的不足。在三个具有挑战性的脑肿瘤分割数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法在多种缺失模式设置中的性能显著优于最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 3 figures,conference
Summary
本文提出一种名为语义引导掩膜互学习(SMML)的新方法,用于在多种缺失模态场景下提炼稳健和具有区分力的知识。该方法通过双分支掩膜互学习方案,结合层次一致性约束(HCC)确保多级一致性,从而提升不完整多模态场景中的互学习效果。此外,整合精炼网络以捕获辅助区分性知识,有效补充掩膜互学习策略的不足。实验证明,该方法在多种缺失模态设置下,对脑肿瘤分割数据集的性能提升显著。
Key Takeaways
- 恶性脑肿瘤是一种全球性的致命疾病,多模态MRI数据对准确脑肿瘤分割至关重要。
- 缺失模态是临床实践中常见问题,严重影响分割性能。
- 提出一种新型的语义引导掩膜互学习(SMML)方法,以处理缺失模态场景中的稳健和区分性特征学习。
- 通过双分支掩膜互学习方案和层次一致性约束(HCC)确保多级一致性。
- HCC框架包括像素级约束和特征级约束,分别用于选择和交换可靠知识以及揭示样本和类别之间的稳健关系。
- 整合精炼网络以提供补充信息,有效补充掩膜互学习策略的不足。
点此查看论文截图

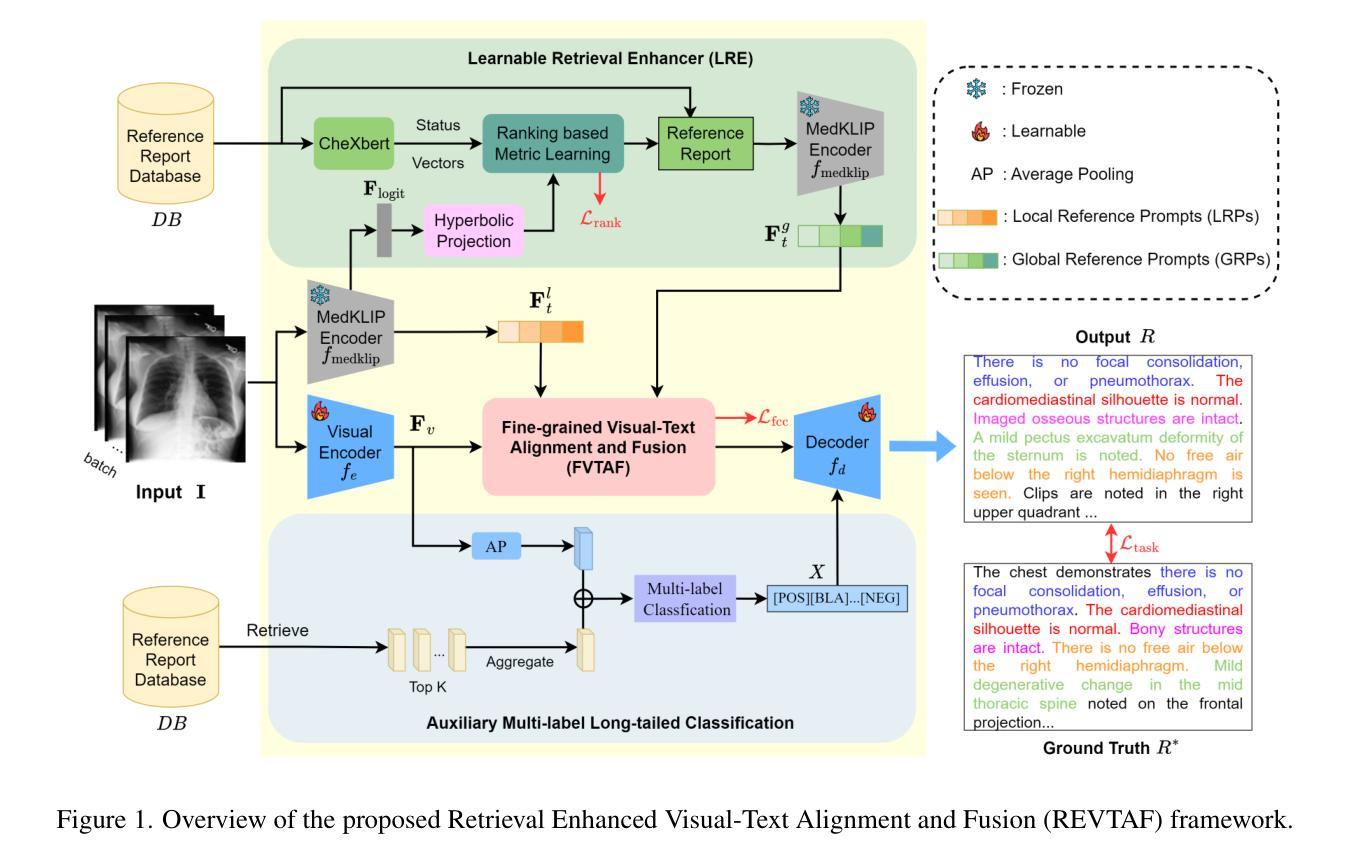
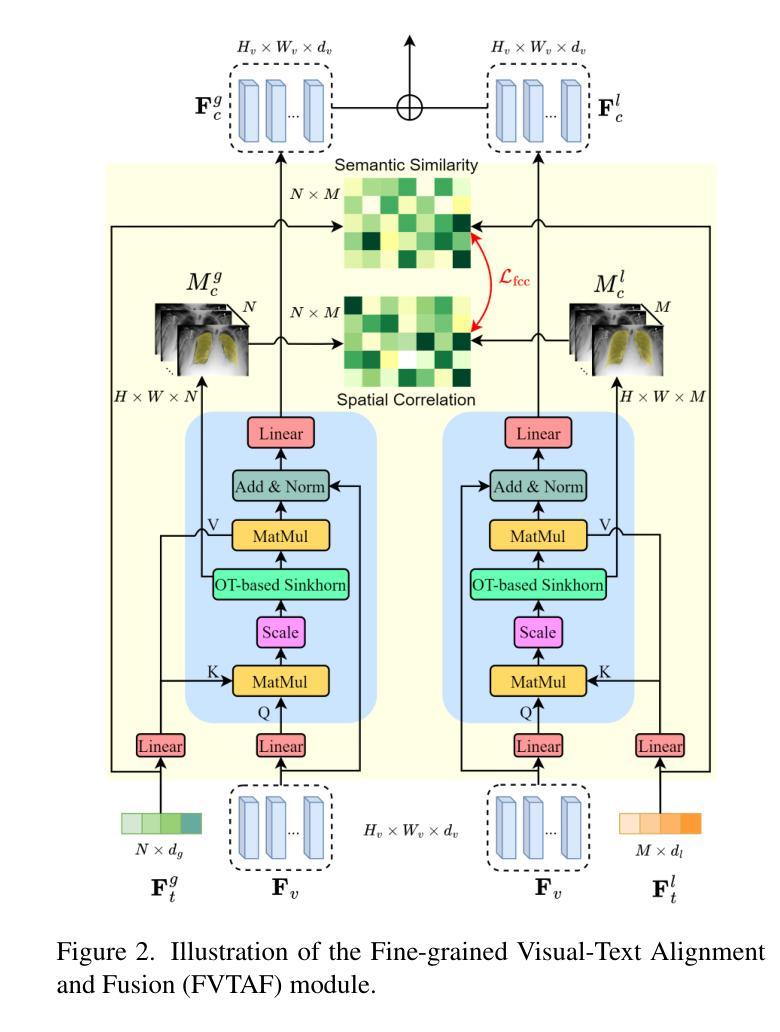
Learnable Retrieval Enhanced Visual-Text Alignment and Fusion for Radiology Report Generation
Authors:Qin Zhou, Guoyan Liang, Xindi Li, Jingyuan Chen, Wang Zhe, Chang Yao, Sai Wu
Automated radiology report generation is essential for improving diagnostic efficiency and reducing the workload of medical professionals. However, existing methods face significant challenges, such as disease class imbalance and insufficient cross-modal fusion. To address these issues, we propose the learnable Retrieval Enhanced Visual-Text Alignment and Fusion (REVTAF) framework, which effectively tackles both class imbalance and visual-text fusion in report generation. REVTAF incorporates two core components: (1) a Learnable Retrieval Enhancer (LRE) that utilizes semantic hierarchies from hyperbolic space and intra-batch context through a ranking-based metric. LRE adaptively retrieves the most relevant reference reports, enhancing image representations, particularly for underrepresented (tail) class inputs; and (2) a fine-grained visual-text alignment and fusion strategy that ensures consistency across multi-source cross-attention maps for precise alignment. This component further employs an optimal transport-based cross-attention mechanism to dynamically integrate task-relevant textual knowledge for improved report generation. By combining adaptive retrieval with multi-source alignment and fusion, REVTAF achieves fine-grained visual-text integration under weak image-report level supervision while effectively mitigating data imbalance issues. The experiments demonstrate that REVTAF outperforms state-of-the-art methods, achieving an average improvement of 7.4% on the MIMIC-CXR dataset and 2.9% on the IU X-Ray dataset. Comparisons with mainstream multimodal LLMs (e.g., GPT-series models), further highlight its superiority in radiology report generation https://github.com/banbooliang/REVTAF-RRG.
自动放射学报告生成对于提高诊断效率、减轻医疗专业人员的工作量具有重要意义。然而,现有方法面临重大挑战,如疾病类别不平衡和跨模态融合不足等。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了可学习的检索增强视觉文本对齐与融合(REVTAF)框架,该框架有效解决类别不平衡和报告生成中的视觉文本融合问题。REVTAF包含两个核心组件:(1)可学习检索增强器(LRE),它利用超球面的语义层次结构和基于排名的指标在批次内部上下文进行自适应检索。LRE能够自适应地检索最相关的参考报告,增强图像表示,特别是对于欠代表的尾部类别输入;(2)精细的视觉文本对齐与融合策略,确保跨多源交叉注意力图的一致性,以实现精确对齐。该组件进一步采用基于最优传输的交叉注意力机制,以动态集成任务相关的文本知识,改进报告生成。通过自适应检索与多源对齐和融合相结合,REVTAF在弱图像报告级别监督下实现了精细的视觉文本集成,同时有效地缓解了数据不平衡问题。实验表明,REVTAF优于最新方法,在MIMIC-CXR数据集上平均提高了7.4%,在IU X光数据集上提高了2.9%。它与主流的多模态大型语言模型(如GPT系列模型)的比较,进一步凸显其在放射学报告生成中的优越性。相关代码已上传至GitHub:https://github.com/banbooliang/REVTAF-RRG。(此处直接附上了GitHub链接)
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages,3 figures, conference
Summary
本文提出一种名为REVTAF的框架,用于解决放射学报告生成中的自动报告生成问题。它通过结合可学习的检索增强器和精细的视觉文本对齐融合策略,有效解决了疾病类别不平衡和跨模态融合的挑战。REVTAF实现了精细的视觉文本集成,并在弱图像报告级别监督下有效缓解了数据不平衡问题。实验表明,REVTAF在MIMIC-CXR和IU X-Ray数据集上的表现优于现有方法,平均提高了7.4%和2.9%。
Key Takeaways
- 自动化放射学报告生成能提高诊断效率并降低医疗专业人员的工作量。
- 当前方法面临疾病类别不平衡和跨模态融合的挑战。
- 提出的REVTAF框架包括可学习的检索增强器和精细的视觉文本对齐融合策略,有效解决上述问题。
- REVTAF通过结合自适应检索和多源对齐融合,实现了在弱图像报告级别监督下的精细视觉文本集成。
- 实验证明,REVTAF在MIMIC-CXR和IU X-Ray数据集上的表现优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

Toward All 2D-based Printed Raindrop Triboelectric Nanogenerators
Authors:Foad Ghasemi, Jonas Heirich, Dimitri Sharikow, Sebastian Klenk, Jonathan N. Coleman, Georg S. Duesberg, Claudia Backes
The raindrop triboelectric nanogenerator (RD-TENG) is an emerging technology that is designed to harvest energy from raindrops. This application requires materials with negative triboelectric effect, high surface charge density, mechanical flexibility, and a large surface area, which are key characteristics of 2D materials. However, fundamental research is necessary to understand the potential of 2D materials in this context. This study introduces all-2D-based RD-TENG devices using graphene and transition metal dichalcogenide (TMD) nanosheets. Liquid phase exfoliation (LPE) and liquid cascade centrifugation are used for nanosheet preparation and size selection. The TENGs are fabricated through a rapid, low-cost solution deposition technique based on liquid-liquid interface deposition, which allows screening of different active films and device geometries. Among the tested layered materials, medium-sized molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) nanosheets (average lateral size~160 nm, volume-fraction weighted average layer number ~9) exhibit the highest short-circuit current (microampere per drop) and voltage (mV per drop) output due to their most suited electron affinity, capacitance, and surface charge exchange properties. The variations in the performance of the TMD films were further evaluated with X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), showing the influence of oxidation differences on charge transfer and charge decay time.
雨滴静电纳米发电机(RD-TENG)是一项新兴技术,旨在从雨滴中收集能量。该应用需要具有负静电效应、高表面电荷密度、机械柔韧性和大面积等关键特性的材料,这些都是二维材料的关键特性。然而,要在此上下文中了解二维材料的潜力,基础研究是必要的。本研究引入了全二维的RD-TENG器件,使用石墨烯和过渡金属二卤化物(TMD)纳米片。液相剥离(LPE)和液体级联离心用于纳米片的制备和尺寸选择。TENG是通过快速、低成本的溶液沉积技术制造的,该技术基于液-液界面沉积,允许筛选不同的活性薄膜和器件几何形状。在测试的层状材料中,中等尺寸的硫化钼(MoS2)纳米片(平均横向尺寸约为160纳米,体积分数加权平均层数约为9)表现出最高的短路电流(微安/滴)和电压(毫伏/滴)输出,这主要得益于其适合的电子亲和力、电容和表面电荷交换特性。进一步利用X射线光电子光谱仪(XPS)评估了TMD薄膜的性能变化,显示了氧化差异对电荷转移和电荷衰减时间的影响。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
这项研究介绍了基于二维材料的全二维雨滴摩擦纳米发电机(RD-TENG)器件。该研究使用石墨烯和过渡金属二卤化物(TMD)纳米片,通过液相剥离(LPE)和液体级联离心法进行纳米片制备和尺寸选择。基于液-液界面沉积的快速、低成本溶液沉积技术用于制造TENG器件,并筛选不同的活性薄膜和器件几何形状。其中,中等尺寸的钼二硫化物(MoS₂)纳米片展现出最佳的输出性能。
Key Takeaways
- RD-TENG是一种新兴技术,用于从雨滴中收集能量。
- 二维材料在RD-TENG应用中具有关键特性,如负摩擦电效应、高表面电荷密度、机械灵活性和大表面积。
- 研究采用了全二维的RD-TENG器件,使用石墨烯和过渡金属二卤化物(TMD)纳米片。
- 液相剥离(LPE)和液体级联离心法用于纳米片的制备和尺寸选择。
- 基于液-液界面沉积的快速、低成本溶液沉积技术用于制造TENG器件。
- 中等尺寸的钼二硫化物(MoS₂)纳米片在测试中表现出最佳输出性能,这归因于其适合的电子亲和力、电容和表面电荷交换属性。
点此查看论文截图

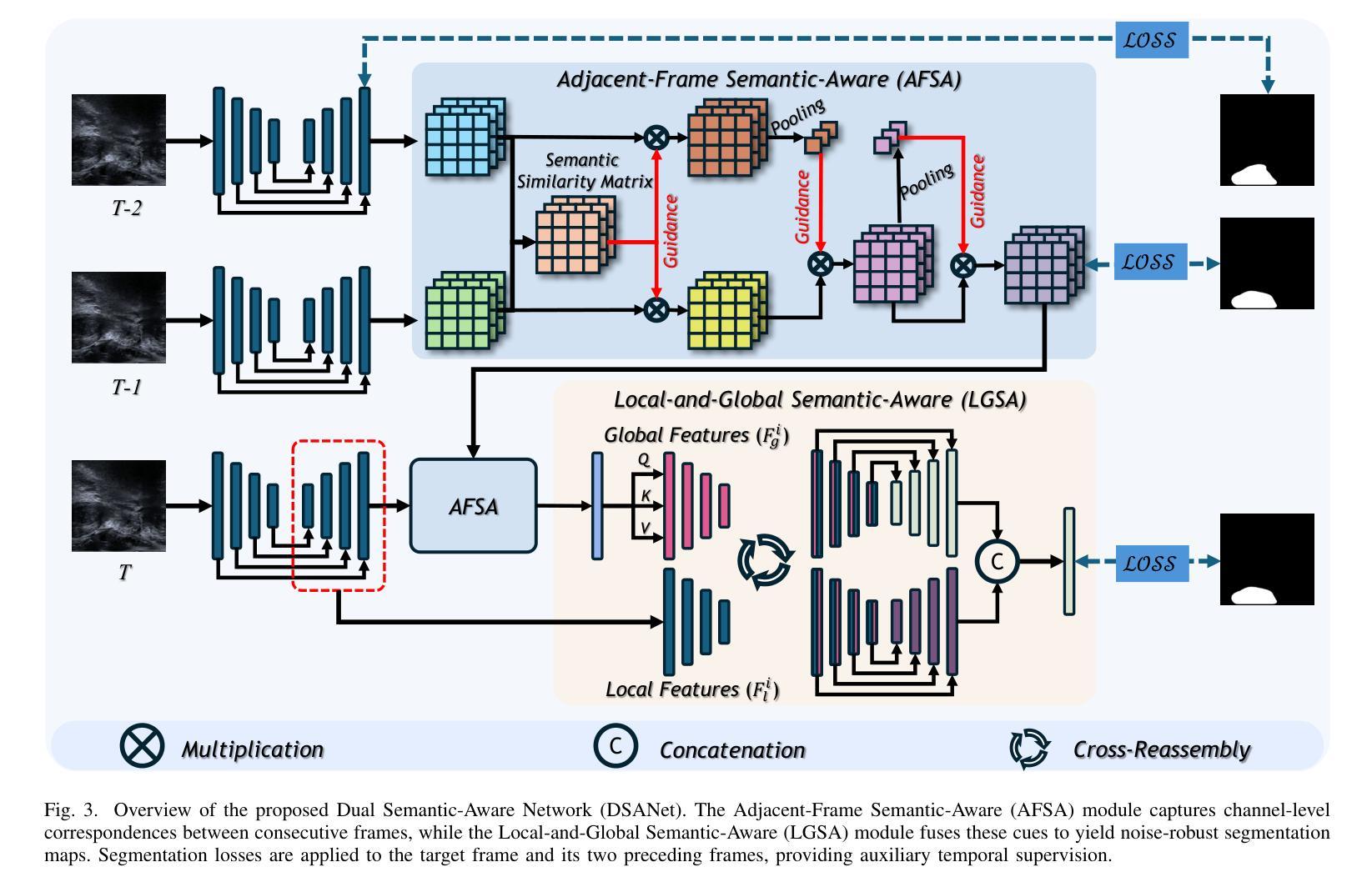
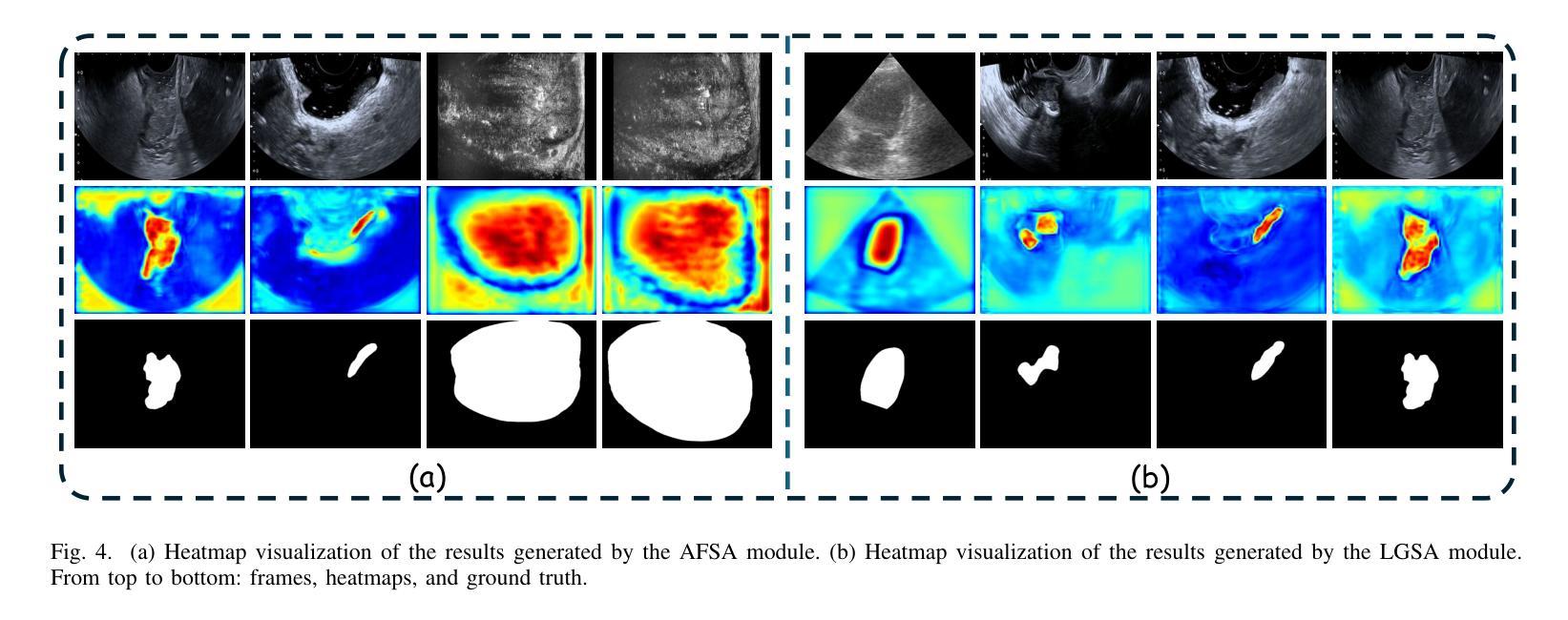
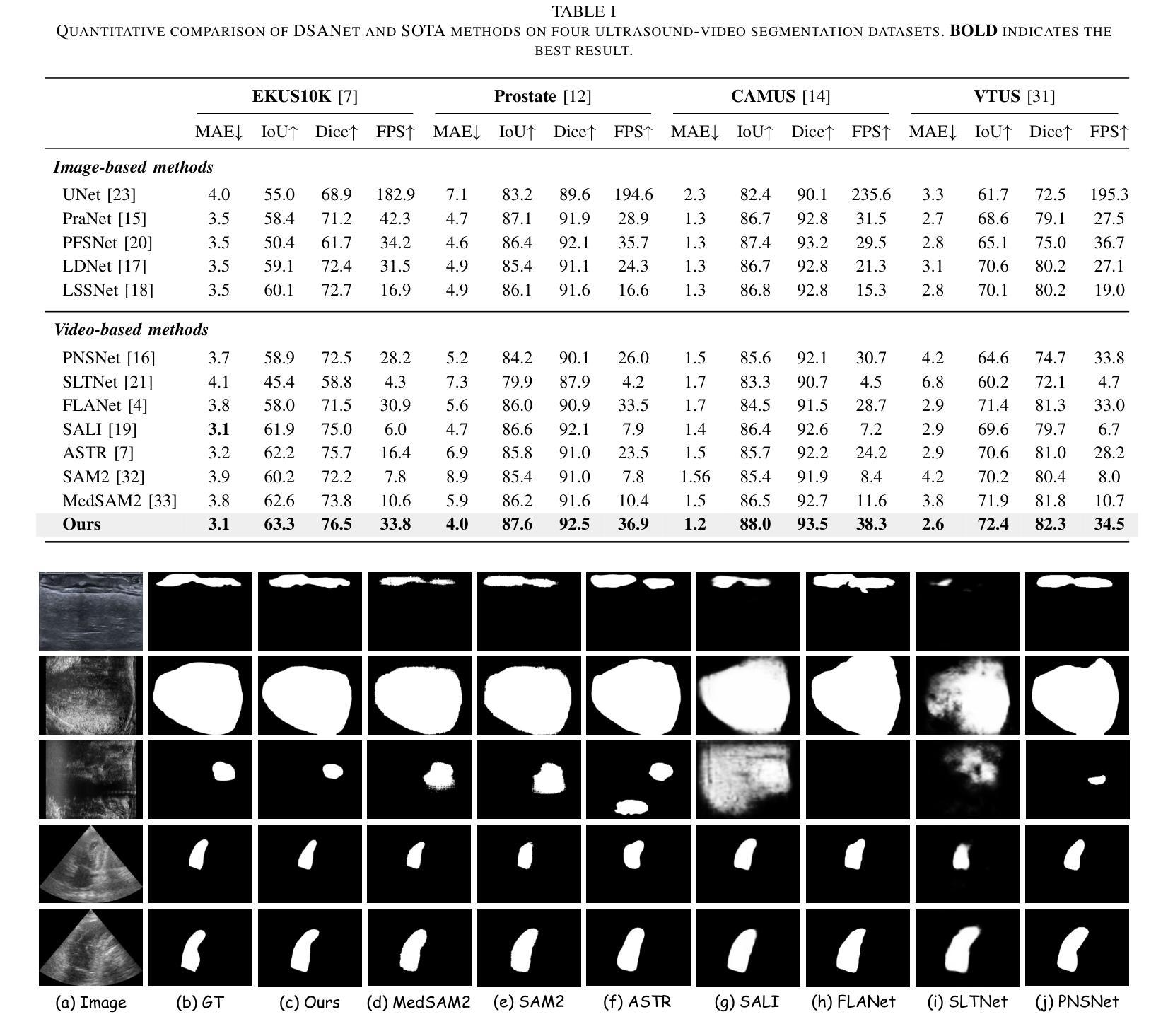
Dual Semantic-Aware Network for Noise Suppressed Ultrasound Video Segmentation
Authors:Ling Zhou, Runtian Yuan, Yi Liu, Yuejie Zhang, Rui Feng, Shang Gao
Ultrasound imaging is a prevalent diagnostic tool known for its simplicity and non-invasiveness. However, its inherent characteristics often introduce substantial noise, posing considerable challenges for automated lesion or organ segmentation in ultrasound video sequences. To address these limitations, we propose the Dual Semantic-Aware Network (DSANet), a novel framework designed to enhance noise robustness in ultrasound video segmentation by fostering mutual semantic awareness between local and global features. Specifically, we introduce an Adjacent-Frame Semantic-Aware (AFSA) module, which constructs a channel-wise similarity matrix to guide feature fusion across adjacent frames, effectively mitigating the impact of random noise without relying on pixel-level relationships. Additionally, we propose a Local-and-Global Semantic-Aware (LGSA) module that reorganizes and fuses temporal unconditional local features, which capture spatial details independently at each frame, with conditional global features that incorporate temporal context from adjacent frames. This integration facilitates multi-level semantic representation, significantly improving the model’s resilience to noise interference. Extensive evaluations on four benchmark datasets demonstrate that DSANet substantially outperforms state-of-the-art methods in segmentation accuracy. Moreover, since our model avoids pixel-level feature dependencies, it achieves significantly higher inference FPS than video-based methods, and even surpasses some image-based models. Code can be found in \href{https://github.com/ZhouL2001/DSANet}{DSANet}
超声成像是一种普遍的诊断工具,以其简单和非侵入性而闻名。然而,其固有特性常常引入大量噪声,给超声视频序列中的自动化病变或器官分割带来了巨大的挑战。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了双语义感知网络(DSANet),这是一种新型框架,旨在通过提升局部和全局特征之间的相互语义感知能力,增强超声视频分割中的噪声鲁棒性。具体来说,我们引入了邻帧语义感知(AFSA)模块,该模块构建通道相似度矩阵,以引导相邻帧之间的特征融合,有效地减轻随机噪声的影响,而无需依赖像素级关系。此外,我们提出了局部和全局语义感知(LGSA)模块,该模块重新组织和融合了时间上的无条件局部特征,这些特征能够在每个帧上独立捕捉空间细节,与考虑相邻帧时间上下文的条件全局特征相结合。这种结合促进了多级别语义表示,显著提高了模型对噪声干扰的抗性。在四个基准数据集上的广泛评估表明,DSANet在分割精度上大大优于最新方法。而且,由于我们的模型避免了像素级特征依赖性,因此与基于视频的方法相比,它实现了更高的推理FPS,甚至超过了某些基于图像模型的推理速度。代码可见于DSANet(https://github.com/ZhouL2001/DSANet)。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为Dual Semantic-Aware Network(DSANet)的新型框架,用于提高超声视频分割中的噪声鲁棒性。它通过促进局部和全局特征之间的相互语义感知,解决了超声成像中噪声带来的自动化病变或器官分割挑战。DSANet包括Adjacent-Frame Semantic-Aware(AFSA)模块和Local-and-Global Semantic-Aware(LGSA)模块,可分别通过构建通道相似度矩阵和引导特征融合来减轻噪声影响。在四个基准数据集上的广泛评估表明,DSANet在分割精度上大幅优于现有方法,并且由于避免了像素级特征依赖,其推理速度高于视频方法,甚至超越某些图像方法。
Key Takeaways
- DSANet框架旨在提高超声视频分割中的噪声鲁棒性。
- 通过促进局部和全局特征间的相互语义感知来解决超声成像中的噪声问题。
- AFSA模块构建通道相似度矩阵,指导相邻帧的特征融合。
- LGSA模块重组并融合独立的空间细节局部特征与包含时间上下文的条件全局特征。
- DSANet在四个基准数据集上的表现优于其他先进方法,显著提高分割精度。
- DSANet避免了像素级特征依赖,实现更高的推理速度。
点此查看论文截图

Label-Efficient Chest X-ray Diagnosis via Partial CLIP Adaptation
Authors:Heet Nitinkumar Dalsania
Modern deep learning implementations for medical imaging usually rely on large labeled datasets. These datasets are often difficult to obtain due to privacy concerns, high costs, and even scarcity of cases. In this paper, a label-efficient strategy is proposed for chest X-ray diagnosis that seeks to reflect real-world hospital scenarios. The experiments use the NIH Chest X-ray14 dataset and a pre-trained CLIP ViT-B/32 model. The model is adapted via partial fine-tuning of its visual encoder and then evaluated using zero-shot and few-shot learning with 1-16 labeled examples per disease class. The tests demonstrate that CLIP’s pre-trained vision-language features can be effectively adapted to few-shot medical imaging tasks, achieving over 20% improvement in mean AUC score as compared to the zero-shot baseline. The key aspect of this work is to attempt to simulate internal hospital workflows, where image archives exist but annotations are sparse. This work evaluates a practical and scalable solution for both common and rare disease diagnosis. Additionally this research is intended for academic and experimental purposes only and has not been peer reviewed yet. All code is found at https://github.com/heet007-code/CLIP-disease-xray.
现代医学成像深度学习的实现通常依赖于大量标记数据集。由于隐私担忧、高昂的成本以及病例稀缺等原因,这些数据集往往难以获取。本文提出了一种用于胸部X射线诊断的标签高效策略,旨在反映现实医院场景。实验使用NIH Chest X-ray14数据集和预训练的CLIP ViT-B/32模型。通过对视觉编码器的部分微调来适应模型,然后使用每疾病类别1-16个标记样本进行零样本和少样本学习进行评估。测试表明,CLIP的预训练视觉语言特征可以有效地适应少样本医学成像任务,与零样本基线相比,平均AUC得分提高了超过20%。这项工作的关键是尝试模拟医院内部工作流程,其中图像档案存在但注释稀疏。这项工作为常见和罕见疾病的诊断提供了实用且可扩展的解决方案。另外,本研究仅用于学术和实验目的,尚未经过同行评审。所有代码可在https://github.com/heet007-code/CLIP-disease-xray找到。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本论文针对医学影像中的深度学习应用提出了一个标签高效的策略,主要用于胸X光诊断并模拟医院实际场景。研究使用NIH Chest X-ray14数据集和预训练的CLIP ViT-B/32模型,通过部分微调视觉编码器进行模型适应,并采用零样本和少样本学习进行测试,每个疾病类别只需1-16个标签样本。实验证明CLIP的预训练视觉语言特征可有效应用于少样本医学影像任务,平均AUC得分较零样本基线提高了超过20%。本研究的关键在于模拟医院内部工作流程,图像档案丰富但标注稀缺。该研究为常见和罕见疾病的诊断提供了实用且可扩展的解决方案。此研究仅用于学术和实验目的,尚未经过同行评审。所有代码可在https://github.com/heet007-code/CLIP-disease-xray找到。
关键见解
- 论文提出了一种标签高效的策略,用于医学影像中的胸X光诊断,模拟医院实际场景。
- 研究使用预训练的CLIP模型,并通过部分微调视觉编码器进行模型适应。
- 实验采用零样本和少样本学习,展示了对少样本医学影像任务的适应性。
- 实验结果较零样本基线提高了超过20%的平均AUC得分。
- 研究重点在于模拟图像档案丰富但标注稀缺的医院内部工作流程。
- 该研究为常见和罕见疾病的诊断提供了实用且可扩展的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

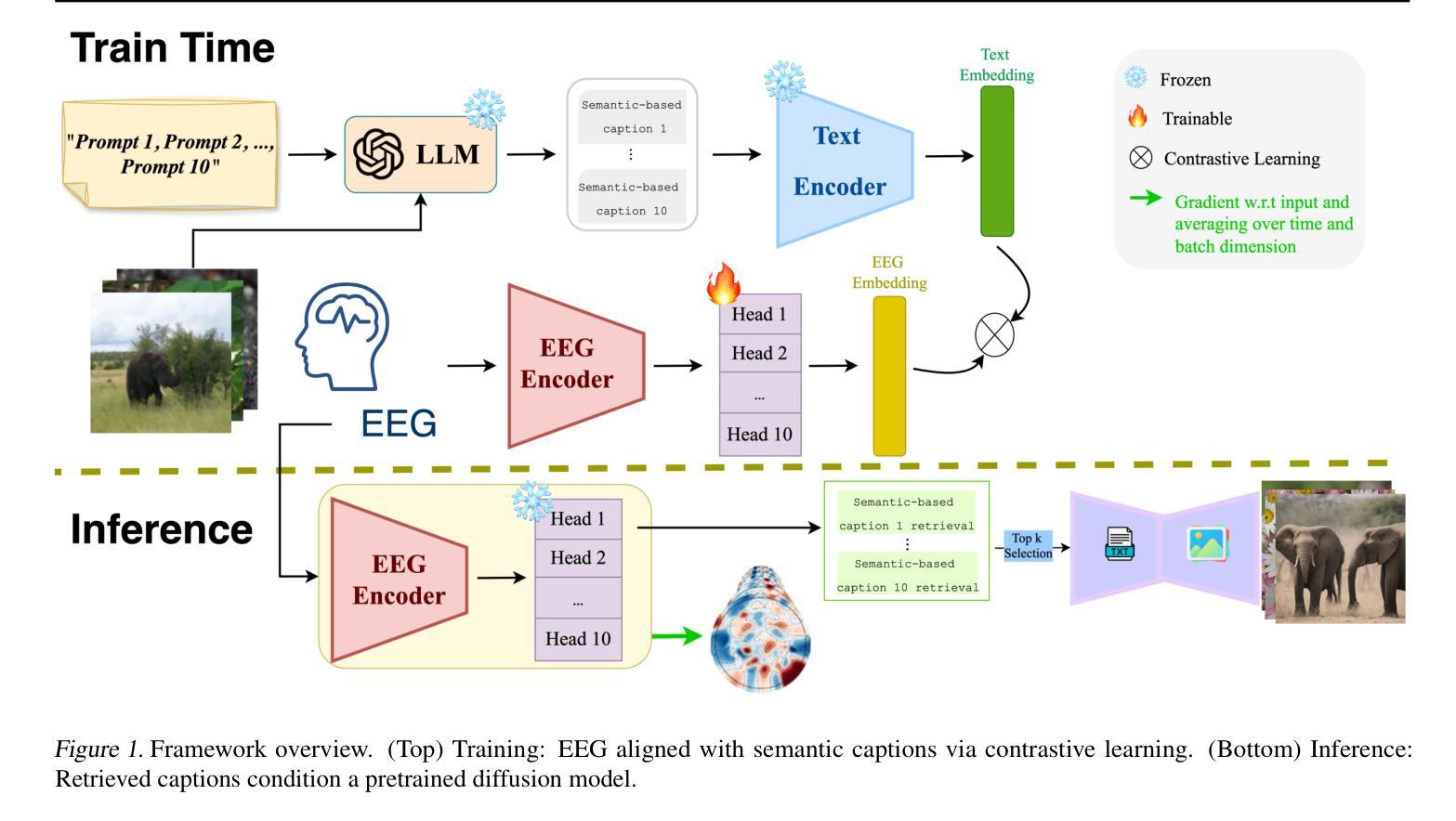
Interpretable EEG-to-Image Generation with Semantic Prompts
Authors:Arshak Rezvani, Ali Akbari, Kosar Sanjar Arani, Maryam Mirian, Emad Arasteh, Martin J. McKeown
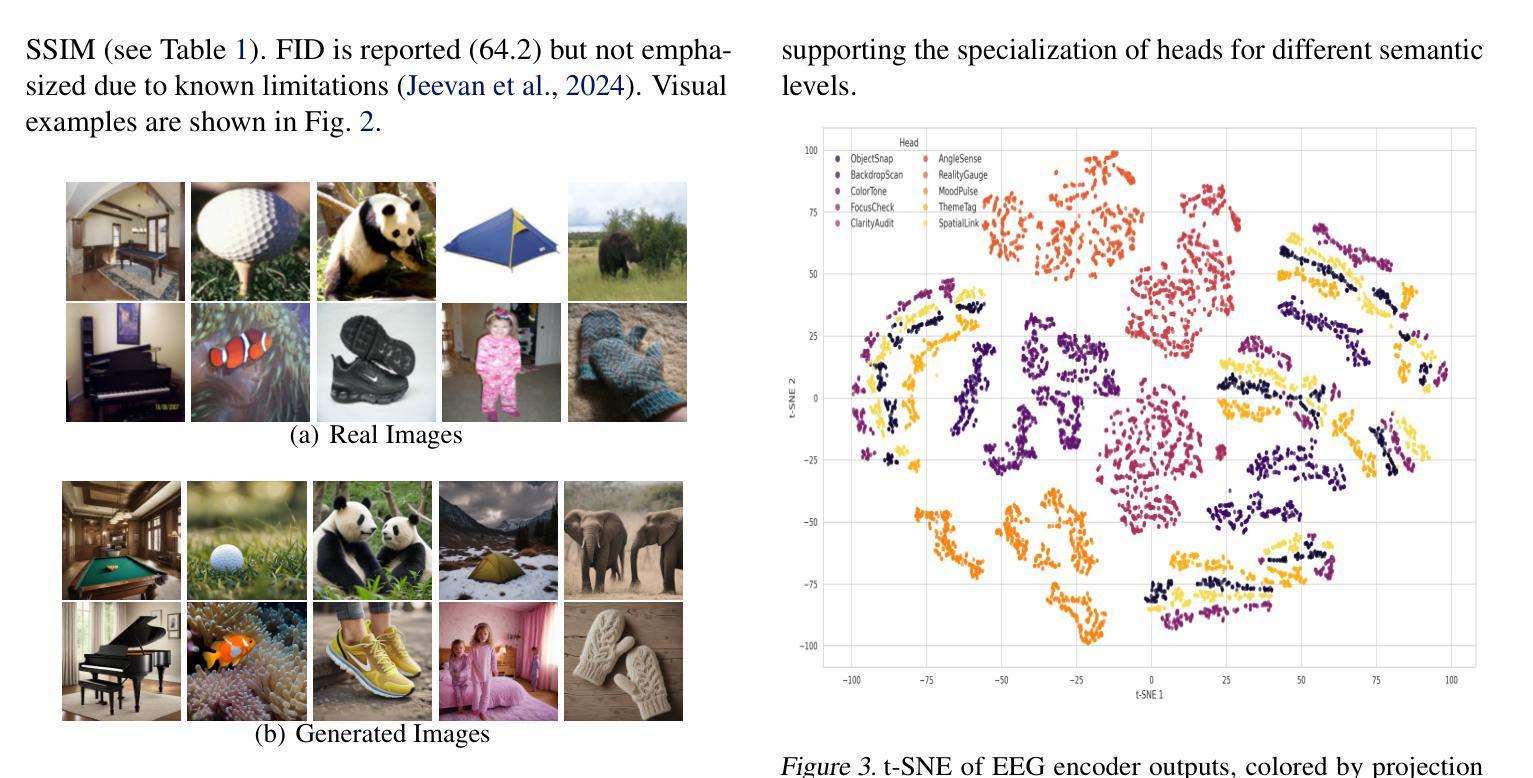
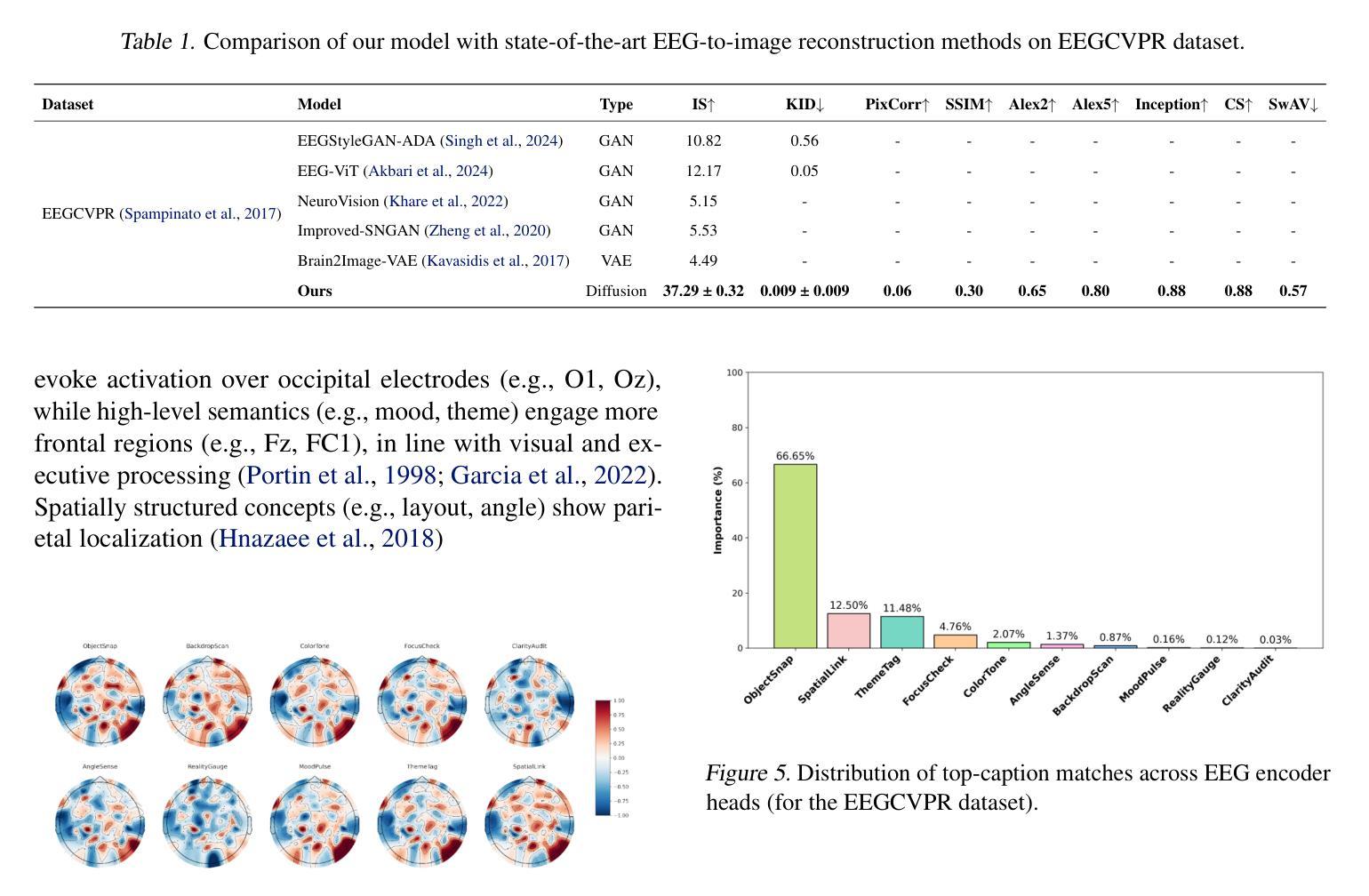
Decoding visual experience from brain signals offers exciting possibilities for neuroscience and interpretable AI. While EEG is accessible and temporally precise, its limitations in spatial detail hinder image reconstruction. Our model bypasses direct EEG-to-image generation by aligning EEG signals with multilevel semantic captions – ranging from object-level to abstract themes – generated by a large language model. A transformer-based EEG encoder maps brain activity to these captions through contrastive learning. During inference, caption embeddings retrieved via projection heads condition a pretrained latent diffusion model for image generation. This text-mediated framework yields state-of-the-art visual decoding on the EEGCVPR dataset, with interpretable alignment to known neurocognitive pathways. Dominant EEG-caption associations reflected the importance of different semantic levels extracted from perceived images. Saliency maps and t-SNE projections reveal semantic topography across the scalp. Our model demonstrates how structured semantic mediation enables cognitively aligned visual decoding from EEG.
从脑信号解码视觉经验为神经科学和可解释的AI提供了令人兴奋的可能性。脑电图是可访问的并且在时间上精确,但其空间细节上的局限性阻碍了图像重建。我们的模型通过将脑电图信号与由大型语言模型生成的多层次语义标题对齐,从而绕过直接的脑电图到图像的生成。基于变压器的脑电图编码器通过对比学习将脑活动映射到这些标题。在推理过程中,通过投影头检索的标题嵌入条件用于图像生成的预训练潜在扩散模型。这种文本介导的框架在EEGCVPR数据集上实现了最先进的视觉解码效果,并且与已知的神经认知途径有可解释的对齐性。主要的脑电图-标题关联反映了从不同语义层次中提取的视觉感知图像的重要性。显著图和时间尺度上的t-SNE投影揭示了头皮上的语义地形。我们的模型展示了如何通过结构化的语义调解实现与认知对齐的脑电图视觉解码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Actionable Interpretability Workshop (non-archival) at the 42 International Conference on Machine Learning
Summary
解码大脑信号中的视觉体验对神经科学和可解释人工智能领域具有重要意义。尽管脑电图技术易于获取且时间精确,但在空间细节方面的局限性阻碍了图像重建。本研究采用了一种基于语义标题对齐的模型,绕过直接的脑电图至图像生成过程。模型利用大型语言模型生成从对象级别到抽象主题的各级语义标题,并通过对比学习,将脑电图编码器映射到这些标题上。在推断过程中,通过投影头获取的标题嵌入用于调节预训练的潜在扩散模型以生成图像。这种文本介导的框架在EEGCVPR数据集上实现了最先进的视觉解码效果,与已知的神经认知途径具有可解释的对齐性。本研究揭示了不同语义级别在感知图像中的重要性,并展示了结构化语义调解如何促进与认知对齐的脑电图视觉解码。
Key Takeaways
- 解码大脑信号中的视觉体验对神经科学和可解释人工智能具有重要意义。
- 脑电图技术虽易于获取且时间精确,但在空间细节方面存在局限性。
- 研究采用语义标题对齐的方式绕过直接的脑电图至图像生成过程。
- 大型语言模型用于生成各级语义标题,从对象级别到抽象主题。
- 脑电图编码器通过对比学习映射到这些标题上。
- 投影头获取的标题嵌入用于调节预训练的潜在扩散模型以生成图像。
点此查看论文截图

CoPT: Unsupervised Domain Adaptive Segmentation using Domain-Agnostic Text Embeddings
Authors:Cristina Mata, Kanchana Ranasinghe, Michael S. Ryoo
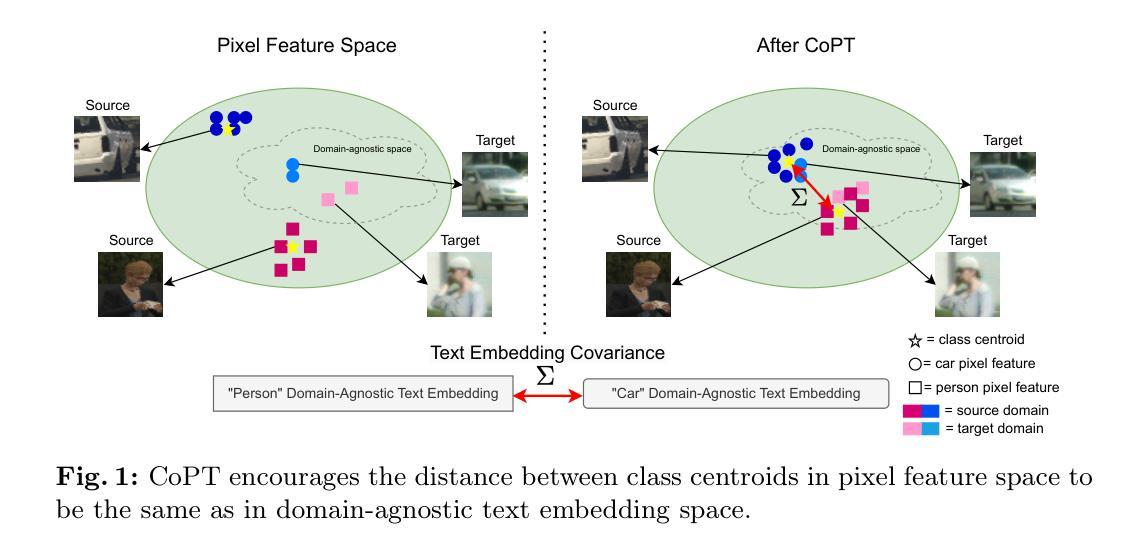
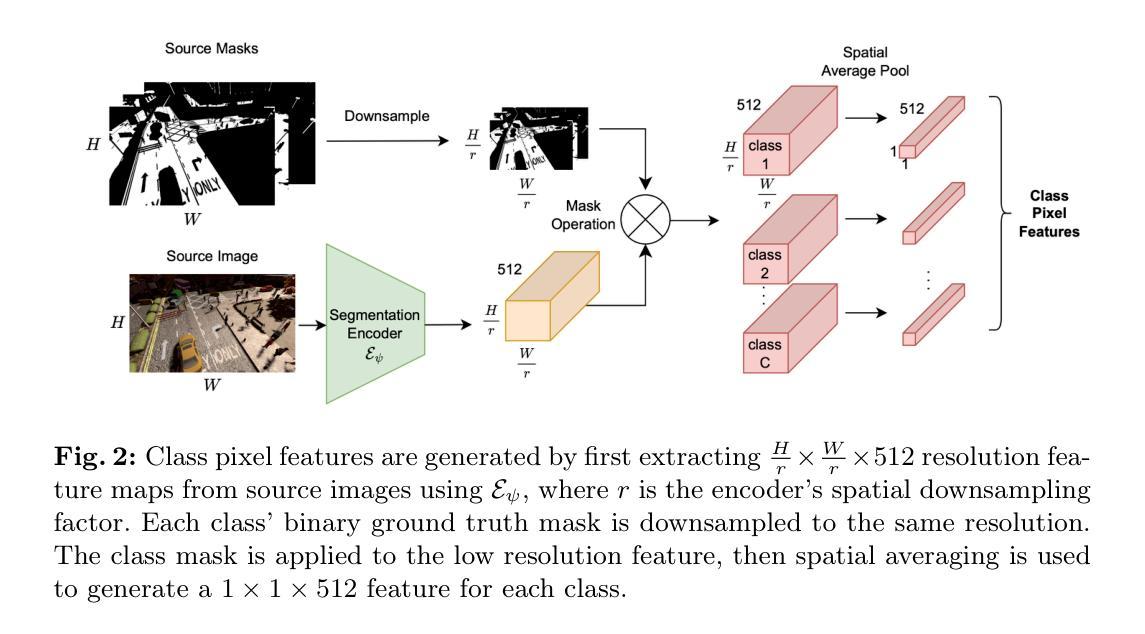
Unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) involves learning class semantics from labeled data within a source domain that generalize to an unseen target domain. UDA methods are particularly impactful for semantic segmentation, where annotations are more difficult to collect than in image classification. Despite recent advances in large-scale vision-language representation learning, UDA methods for segmentation have not taken advantage of the domain-agnostic properties of text. To address this, we present a novel Covariance-based Pixel-Text loss, CoPT, that uses domain-agnostic text embeddings to learn domain-invariant features in an image segmentation encoder. The text embeddings are generated through our LLM Domain Template process, where an LLM is used to generate source and target domain descriptions that are fed to a frozen CLIP model and combined. In experiments on four benchmarks we show that a model trained using CoPT achieves the new state of the art performance on UDA for segmentation. The code can be found at https://github.com/cfmata/CoPT.
无监督域自适应(UDA)涉及从源域中的标记数据中学习类别语义,并将其推广到未见过的目标域。UDA方法对语义分割特别有影响,因为在那里收集注释比图像分类更加困难。尽管最近在大型视觉-语言表示学习方面取得了进展,但分割的UDA方法并没有利用文本的域无关属性。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种基于协方差的新颖像素文本损失(CoPT),它使用域无关的文本嵌入来学习图像分割编码器中不变的特性。文本嵌入是通过我们的LLM域模板过程生成的,该过程使用LLM生成源和目标域的描述,然后将其输入到冻结的CLIP模型中并进行组合。在四个基准测试上的实验表明,使用CoPT训练的模型在分割UDA上达到了最新的性能水平。代码可以在 https://github.com/cfmata/CoPT 找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ECCV 2024
Summary
本文介绍了无监督域自适应(UDA)在语义分割中的应用,提出了一种基于协方差和像素文本的损失函数CoPT。该损失函数利用领域不可知的文本嵌入来在图像分割编码器中学习领域不变特征。使用大型语言模型生成源和目标域描述,结合CLIP模型生成文本嵌入。在四个基准测试上的实验表明,使用CoPT训练的模型在UDA分割任务上达到了新的最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- UDA方法用于语义分割,通过从源域的有标签数据中学习类别语义,并推广到未见过的目标域。
- 尽管大型视觉语言表示学习取得了进展,但UDA分割方法尚未利用文本的领域不可知属性。
- 提出了基于协方差和像素文本的损失函数CoPT,利用领域不可知的文本嵌入来学习图像分割中的领域不变特征。
- 使用LLM生成源和目标域描述,通过CLIP模型生成文本嵌入。
- CoPT在四个基准测试上实现了UDA分割的新最佳性能。
- CoPT损失函数可以有效地适应不同的领域,提高模型在语义分割任务上的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

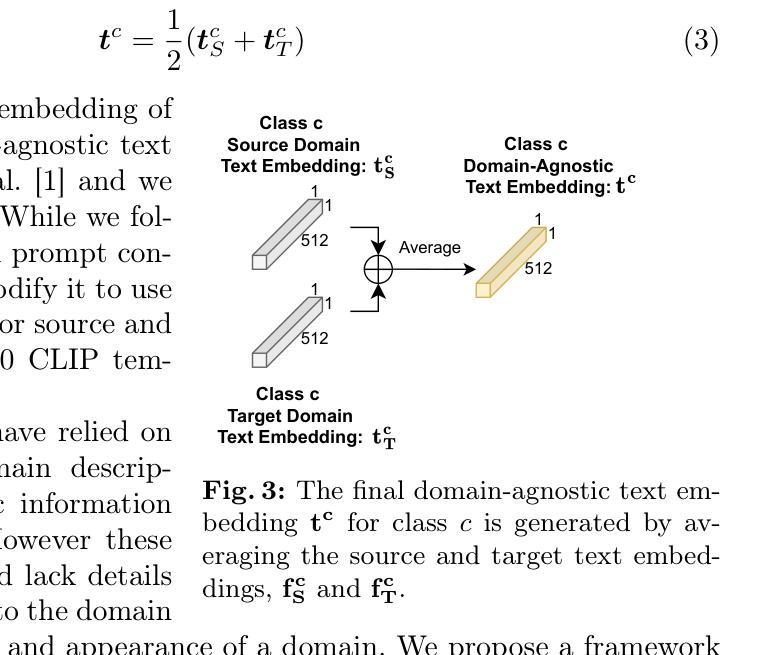
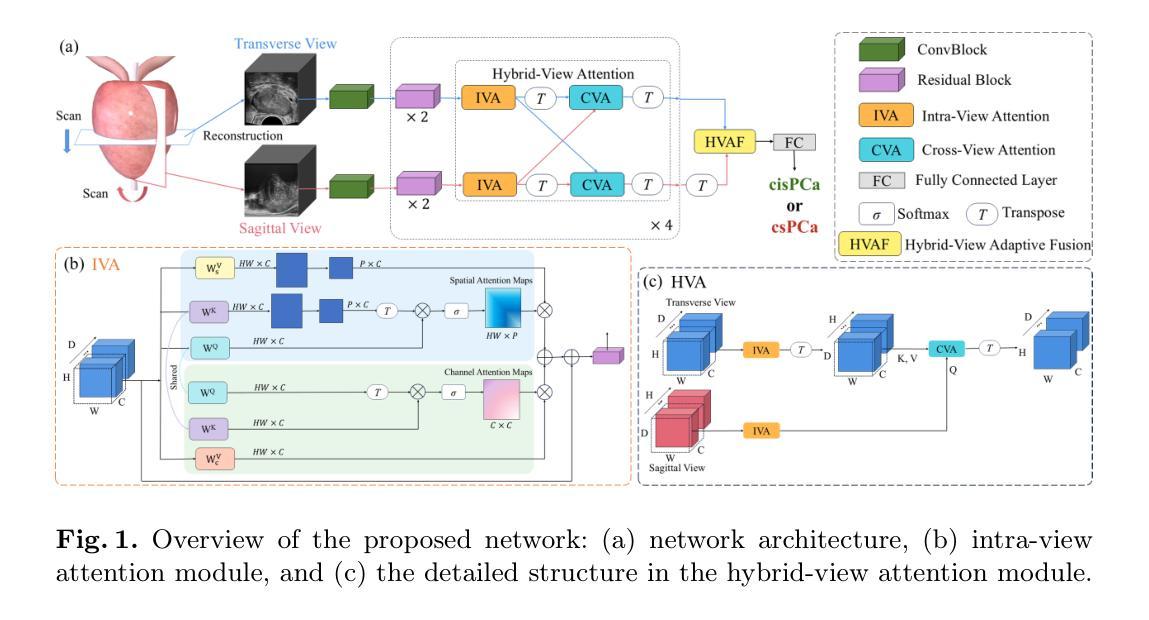
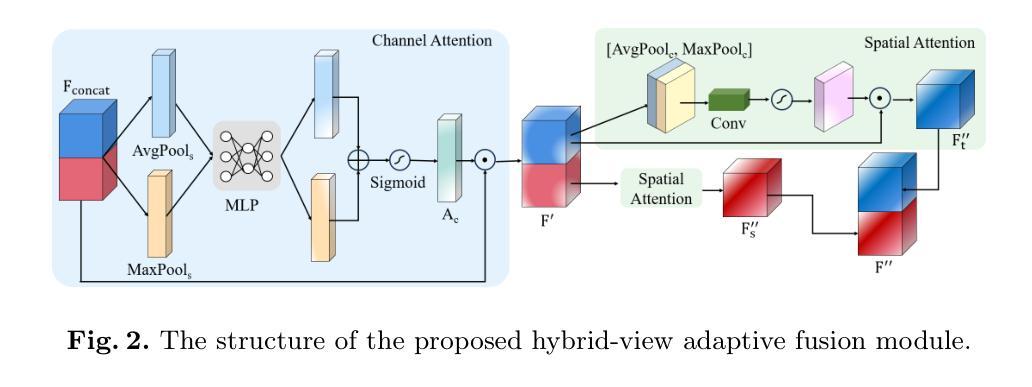
Hybrid-View Attention Network for Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer Classification in Transrectal Ultrasound
Authors:Zetian Feng, Juan Fu, Xuebin Zou, Hongsheng Ye, Hong Wu, Jianhua Zhou, Yi Wang
Prostate cancer (PCa) is a leading cause of cancer-related mortality in men, and accurate identification of clinically significant PCa (csPCa) is critical for timely intervention. Transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) is widely used for prostate biopsy; however, its low contrast and anisotropic spatial resolution pose diagnostic challenges. To address these limitations, we propose a novel hybrid-view attention (HVA) network for csPCa classification in 3D TRUS that leverages complementary information from transverse and sagittal views. Our approach integrates a CNN-transformer hybrid architecture, where convolutional layers extract fine-grained local features and transformer-based HVA models global dependencies. Specifically, the HVA comprises intra-view attention to refine features within a single view and cross-view attention to incorporate complementary information across views. Furthermore, a hybrid-view adaptive fusion module dynamically aggregates features along both channel and spatial dimensions, enhancing the overall representation. Experiments are conducted on an in-house dataset containing 590 subjects who underwent prostate biopsy. Comparative and ablation results prove the efficacy of our method. The code is available at https://github.com/mock1ngbrd/HVAN.
前列腺癌(PCa)是男性癌症相关死亡的主要原因之一,准确识别临床上重要的前列腺癌(csPCa)对于及时干预至关重要。经直肠超声(TRUS)广泛应用于前列腺活检,但其低对比度和各向异性的空间分辨率给诊断带来了挑战。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一种新型的混合视图注意力(HVA)网络,用于在3D TRUS中对csPCa进行分类,该网络利用横断面和矢状面的互补信息进行分类。我们的方法融合了CNN-transformer混合架构,其中卷积层提取精细的局部特征,而基于transformer的HVA模型全局依赖性。具体来说,HVA包括视图内注意力,用于细化单一视图内的特征,以及跨视图注意力,用于结合不同视图之间的互补信息。此外,混合视图自适应融合模块沿通道和空间维度动态聚合特征,增强了整体表示。实验是在包含590名接受前列腺活检受试者的内部数据集上进行的。对比和消融结果证明了我们的方法的有效性。代码可在https://github.com/mock1ngbrd/HVAN上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种针对三维超声成像(TRUS)中临床显著前列腺癌(csPCa)分类的混合视图注意力(HVA)网络。该网络结合卷积神经网络(CNN)和变换器(transformer)架构,旨在解决传统超声成像的低对比度和空间分辨率问题。通过利用横断面和矢状面的互补信息,该网络通过改进的单视图内注意力和跨视图注意力,实现了特征精细化并融入了多视图信息。此外,混合视图自适应融合模块能够动态聚合通道和空间维度的特征,提高整体表现。实验结果表明该方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 前列腺癌(PCa)是男性癌症死亡的主要原因之一,准确识别临床显著前列腺癌(csPCa)对及时干预至关重要。
- 目前广泛使用的经直肠超声(TRUS)成像存在低对比度和空间分辨率问题,对诊断构成挑战。
- 提出了一种名为混合视图注意力(HVA)网络的新方法,用于在三维TRUS中对csPCa进行分类。
- 该方法结合了卷积神经网络(CNN)和变换器(transformer)架构,以提取局部和全局特征。
- HVA网络包括单视图内注意力和跨视图注意力机制,能够利用不同视图的互补信息。
- 通过混合视图自适应融合模块,网络能够在通道和空间维度上动态聚合特征,增强整体性能。
点此查看论文截图

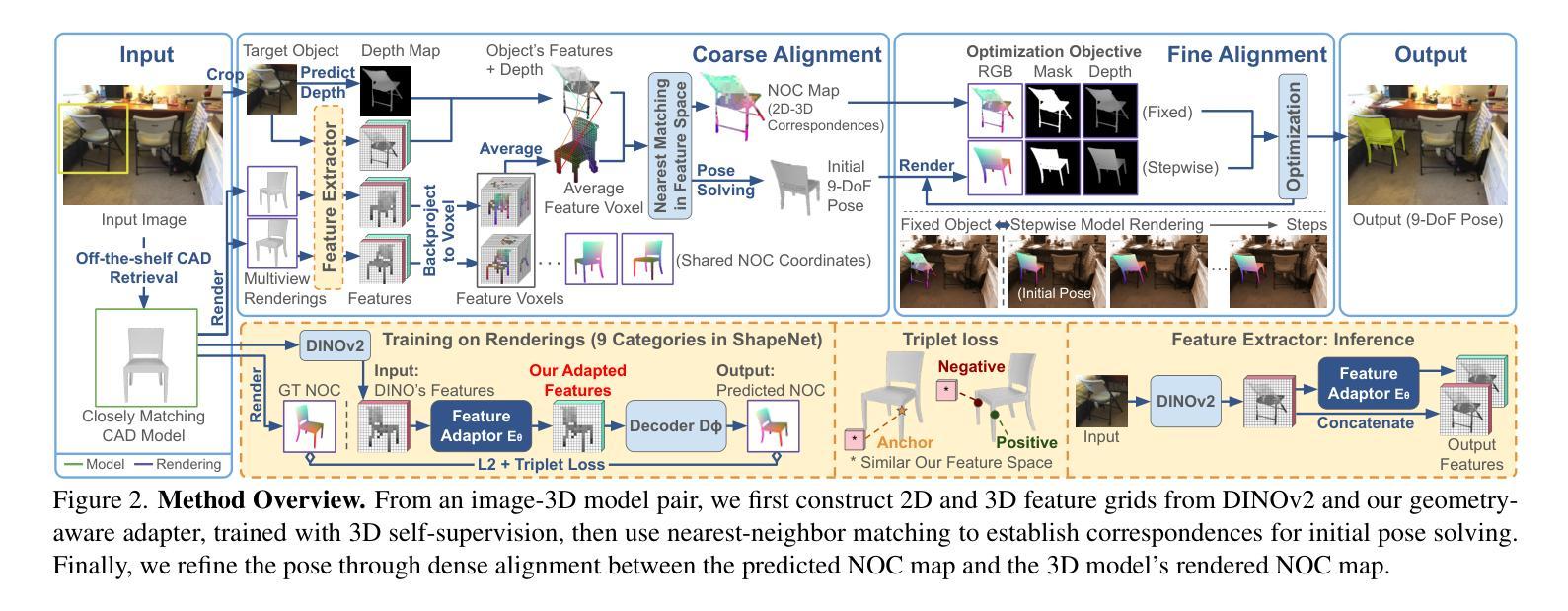
Zero-shot Inexact CAD Model Alignment from a Single Image
Authors:Pattaramanee Arsomngern, Sasikarn Khwanmuang, Matthias Nießner, Supasorn Suwajanakorn
One practical approach to infer 3D scene structure from a single image is to retrieve a closely matching 3D model from a database and align it with the object in the image. Existing methods rely on supervised training with images and pose annotations, which limits them to a narrow set of object categories. To address this, we propose a weakly supervised 9-DoF alignment method for inexact 3D models that requires no pose annotations and generalizes to unseen categories. Our approach derives a novel feature space based on foundation features that ensure multi-view consistency and overcome symmetry ambiguities inherent in foundation features using a self-supervised triplet loss. Additionally, we introduce a texture-invariant pose refinement technique that performs dense alignment in normalized object coordinates, estimated through the enhanced feature space. We conduct extensive evaluations on the real-world ScanNet25k dataset, where our method outperforms SOTA weakly supervised baselines by +4.3% mean alignment accuracy and is the only weakly supervised approach to surpass the supervised ROCA by +2.7%. To assess generalization, we introduce SUN2CAD, a real-world test set with 20 novel object categories, where our method achieves SOTA results without prior training on them.
从单一图像推断3D场景结构的一种实用方法是从数据库中检索与图像匹配度高的3D模型,并将其与图像中的对象对齐。现有方法依赖于使用图像和姿态注释进行的有监督训练,这限制了它们在特定对象类别中的使用。为解决这一问题,我们提出了一种针对不精确3D模型的弱监督9自由度对齐方法,该方法无需姿态注释,并可推广到未见过的类别。我们的方法基于基础特征构建了一个新的特征空间,确保多视图一致性,并使用自监督三元损失克服基础特征中的固有对称性歧义。此外,我们引入了一种纹理不变的姿态优化技术,在归一化对象坐标中进行密集对齐,通过增强的特征空间进行估计。我们在现实世界ScanNet25k数据集上进行了广泛评估,我们的方法较先进的弱监督基线提高了+4.3%的平均对齐精度,并且是唯一一个在未见过的类别上超越监督ROCA的弱监督方法。为了评估泛化能力,我们引入了SUN2CAD这一真实世界测试集,其中包含20个新型对象类别,我们的方法在没有事先对其进行训练的情况下取得了最先进的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025. Project page: https://zerocad9d.github.io/
Summary
该文提出了一种从单幅图像中推断三维场景结构的新方法。该方法通过从数据库中检索与图像中的对象相匹配的三维模型,并与该对象进行对齐来实现。针对现有方法依赖于图像和姿态注释进行有监督训练的局限性,该文提出了一种无需姿态注释的弱监督9自由度对齐方法,并能够对未见过的类别进行泛化。该方法基于基础特征构建了一个新的特征空间,确保多视角一致性,并利用自监督三元损失克服基础特征中的固有对称性歧义。此外,还引入了一种纹理无关的姿态优化技术,在归一化对象坐标中进行密集对齐,通过增强的特征空间进行估计。在真实世界的ScanNet25k数据集上进行的广泛评估表明,该方法在弱监督基准上的平均对齐精度提高了4.3%,并且是唯一一种在未经这些类别预先训练的情况下超越有监督ROCA方法的弱监督方法。此外,在具有20个新对象类别的真实世界测试集SUN2CAD上的评估结果表明,该方法达到了最新状态。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种从单幅图像中推断三维场景结构的新方法,即通过检索与图像中的对象相匹配的三维模型并进行对齐。
- 与现有方法不同,该方法采用弱监督方式,无需姿态注释,可以应用于未见过的对象类别。
- 通过构建新的特征空间和多视角一致性确保模型的准确性。
- 利用自监督三元损失克服基础特征中的对称性歧义问题。
- 引入了一种纹理无关的姿态优化技术,用于在归一化对象坐标中进行密集对齐。
- 在真实世界的ScanNet25k数据集上的评估结果表明,该方法在弱监督基准上优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图


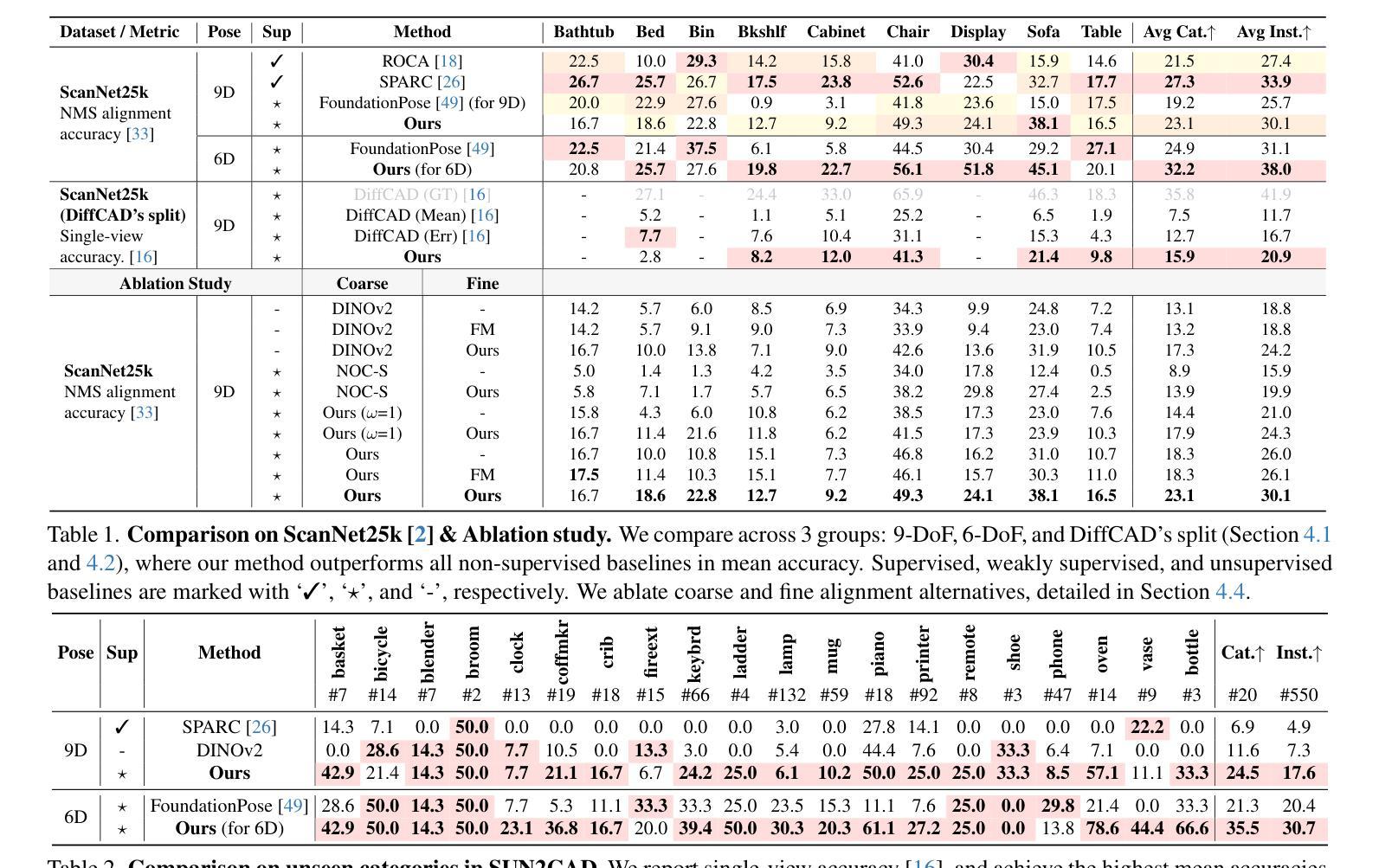
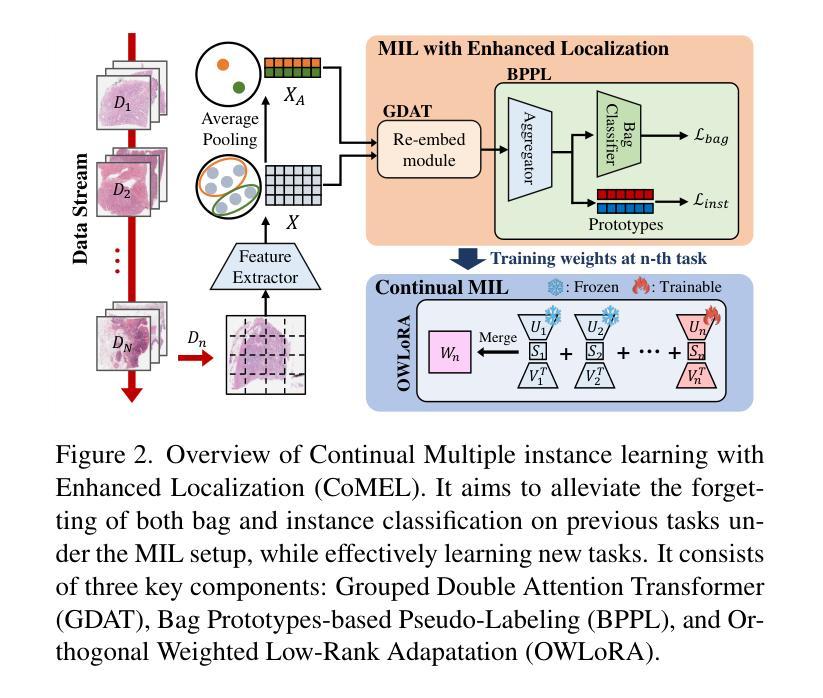
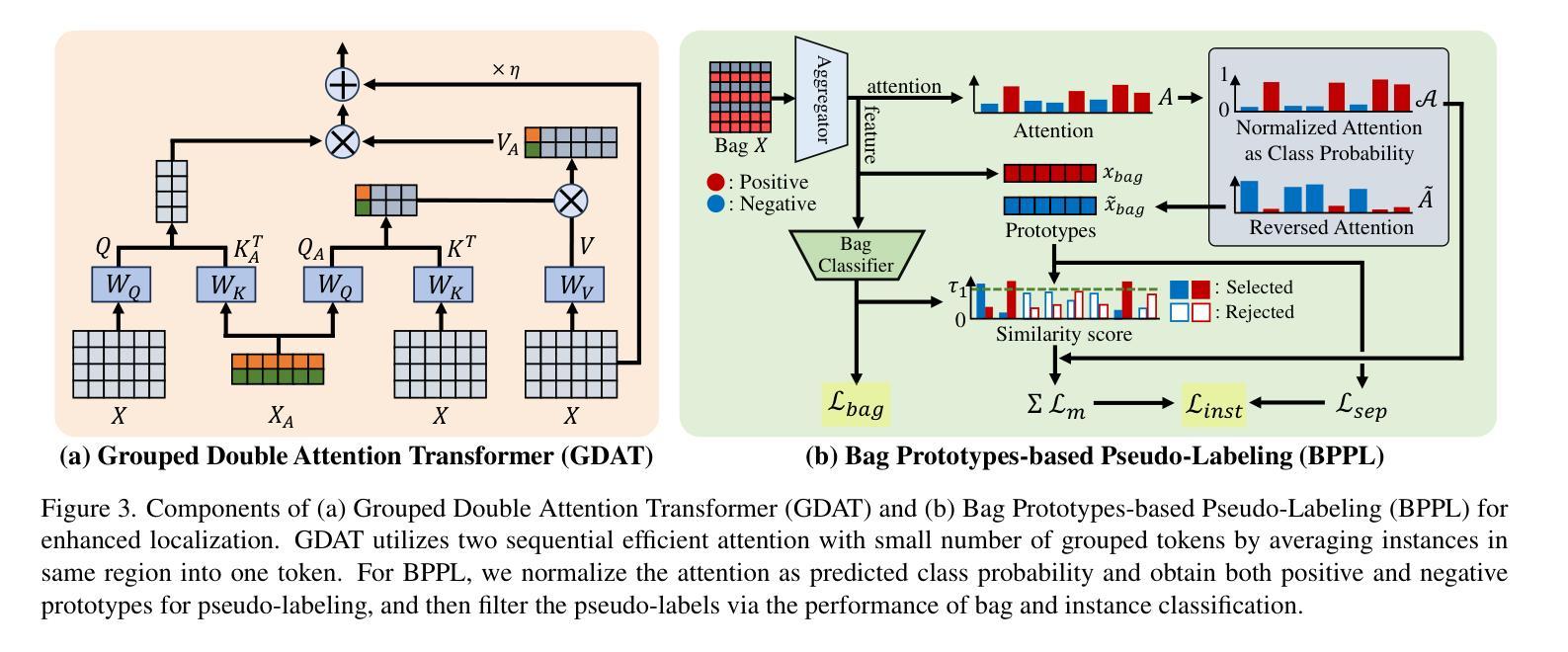
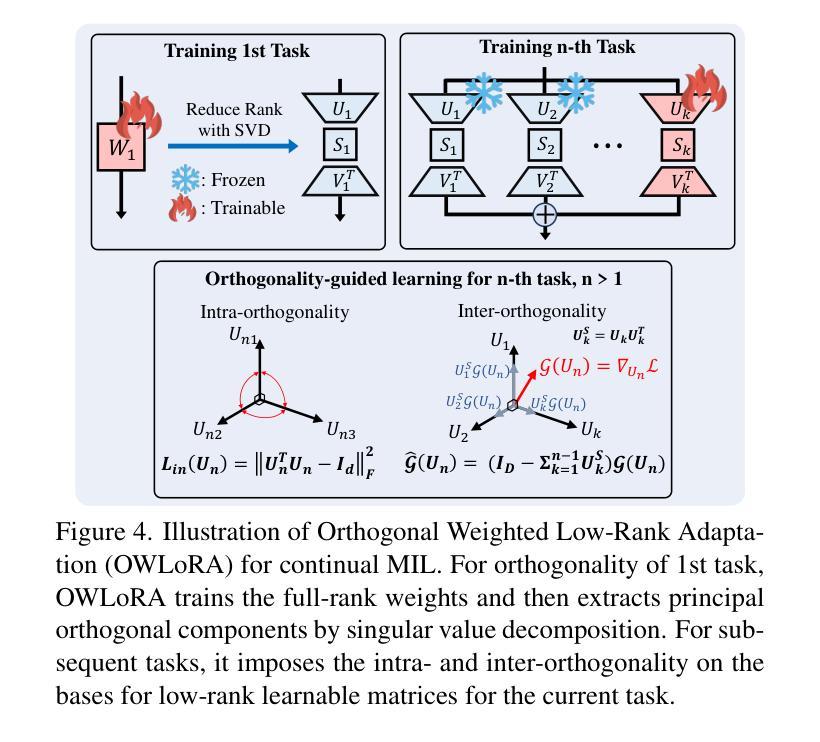
Continual Multiple Instance Learning with Enhanced Localization for Histopathological Whole Slide Image Analysis
Authors:Byung Hyun Lee, Wongi Jeong, Woojae Han, Kyoungbun Lee, Se Young Chun
Multiple instance learning (MIL) significantly reduced annotation costs via bag-level weak labels for large-scale images, such as histopathological whole slide images (WSIs). However, its adaptability to continual tasks with minimal forgetting has been rarely explored, especially on instance classification for localization. Weakly incremental learning for semantic segmentation has been studied for continual localization, but it focused on natural images, leveraging global relationships among hundreds of small patches (e.g., $16 \times 16$) using pre-trained models. This approach seems infeasible for MIL localization due to enormous amounts ($\sim 10^5$) of large patches (e.g., $256 \times 256$) and no available global relationships such as cancer cells. To address these challenges, we propose Continual Multiple Instance Learning with Enhanced Localization (CoMEL), an MIL framework for both localization and adaptability with minimal forgetting. CoMEL consists of (1) Grouped Double Attention Transformer (GDAT) for efficient instance encoding, (2) Bag Prototypes-based Pseudo-Labeling (BPPL) for reliable instance pseudo-labeling, and (3) Orthogonal Weighted Low-Rank Adaptation (OWLoRA) to mitigate forgetting in both bag and instance classification. Extensive experiments on three public WSI datasets demonstrate superior performance of CoMEL, outperforming the prior arts by up to $11.00%$ in bag-level accuracy and up to $23.4%$ in localization accuracy under the continual MIL setup.
多任务学习(MIL)通过大规模图像(如病理全切片图像)的袋级弱标签显著降低了标注成本。然而,其在连续任务中的适应性以及最小化遗忘的研究很少,特别是在实例分类定位方面的应用。针对语义分割的弱增量学习已经用于连续定位研究,但它主要集中在自然图像上,利用数百个小补丁之间的全局关系(例如,$16 \times 16$),使用预训练模型。这种方法对于多任务学习的定位似乎不可行,因为存在大量($\sim 10^5$)的大型补丁(例如,$256 \times 256$),并且没有可用的全局关系,如癌细胞等。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了增强定位的连续多任务学习(CoMEL),这是一个用于定位和适应性的多任务学习框架,具有最小的遗忘性。CoMEL包括(1)分组双重注意力转换器(GDAT)进行高效实例编码,(2)基于袋原型伪标签(BPPL)的可靠实例伪标签化,(3)正交加权低秩适应(OWLoRA)以减轻袋和实例分类中的遗忘。在三个公共WSI数据集上的广泛实验表明,CoMEL在连续多任务设置下的性能优于先前技术,袋级精度提高高达$11.00%$,定位精度提高高达$23.4%$。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICCV 2025
Summary
多实例学习(MIL)通过利用大规模图像(如病理全切片图像)的袋级弱标签大幅降低了标注成本。针对连续任务中的遗忘问题,特别是实例分类的定位问题,本文提出了面向语义分割的弱增量学习方法。然而,对于多实例学习(MIL)定位,由于其大量的大型补丁和缺乏可用的全局关系(如癌细胞),这种方法似乎并不可行。为解决这些挑战,我们提出了具有最小遗忘适应性的持续多实例学习增强定位(CoMEL)。CoMEL包括(1)分组双注意力转换器(GDAT)进行高效实例编码,(2)基于袋原型伪标签(BPPL)的可靠实例伪标签生成,以及(3)正交加权低秩适应(OWLoRA)来缓解包和实例分类中的遗忘问题。在三个公共WSI数据集上的广泛实验表明,CoMEL在连续MIL设置下表现出卓越性能,在袋级精度上比现有技术高出最多11.00%,在定位精度上高出最多23.4%。
Key Takeaways
- 多实例学习(MIL)通过利用大规模图像的袋级弱标签降低了标注成本。
- 连续任务中的遗忘问题在多实例学习定位中尤为突出。
- 提出的CoMEL框架结合了分组双注意力转换器(GDAT)、基于袋原型伪标签(BPPL)和正交加权低秩适应(OWLoRA)来解决挑战。
- GDAT用于高效实例编码。
- BPPL用于生成可靠的实例伪标签。
- OWLoRA用于缓解包和实例分类中的遗忘问题。
点此查看论文截图


Are Vision Transformer Representations Semantically Meaningful? A Case Study in Medical Imaging
Authors:Montasir Shams, Chashi Mahiul Islam, Shaeke Salman, Phat Tran, Xiuwen Liu
Vision transformers (ViTs) have rapidly gained prominence in medical imaging tasks such as disease classification, segmentation, and detection due to their superior accuracy compared to conventional deep learning models. However, due to their size and complex interactions via the self-attention mechanism, they are not well understood. In particular, it is unclear whether the representations produced by such models are semantically meaningful. In this paper, using a projected gradient-based algorithm, we show that their representations are not semantically meaningful and they are inherently vulnerable to small changes. Images with imperceptible differences can have very different representations; on the other hand, images that should belong to different semantic classes can have nearly identical representations. Such vulnerability can lead to unreliable classification results; for example, unnoticeable changes cause the classification accuracy to be reduced by over 60%. %. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to systematically demonstrate this fundamental lack of semantic meaningfulness in ViT representations for medical image classification, revealing a critical challenge for their deployment in safety-critical systems.
视觉转换器(ViTs)因其相对于传统深度学习模型的卓越准确性,在医学成像任务(如疾病分类、分割和检测)中迅速受到关注。然而,由于其规模和通过自注意力机制产生的复杂交互,人们对其理解并不充分。尤其不清楚的是,此类模型产生的表示是否具有语义意义。在本文中,我们使用基于投影的梯度算法来展示,他们的表示不具有语义意义,并且本质上容易受微小变化的影响。具有难以察觉差异的图像可以具有完全不同的表示形式;另一方面,本应属于不同语义类的图像却可以有几乎相同的表示形式。这种脆弱性可能导致分类结果不可靠;例如,不明显的变化导致分类精度降低超过60%。据我们所知,这是第一项系统展示在医学图像分类中ViT表示缺乏基本语义意义的工作,这揭示了将其部署在安全关键系统中的重大挑战。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages
Summary
ViT模型在医学图像分类、分割和检测等任务中表现出卓越准确性,但存在语义理解不足的问题。本文利用梯度投影算法显示ViT模型的表示不具有语义意义,容易受到微小变化的干扰。相同语义类别的图像可能具有不同的表示,不同语义类别的图像可能具有相似的表示,导致分类结果不可靠。
Key Takeaways
- ViT模型在医学图像任务中具有高准确性。
- ViT模型的表示缺乏语义意义。
- ViT模型容易受到微小变化的影响,导致不同的表示。
- 相同语义类别的图像可能具有不同的表示。
- 不同语义类别的图像可能具有相似的表示。
- 这种缺乏语义意义的问题会导致分类结果不可靠。
点此查看论文截图

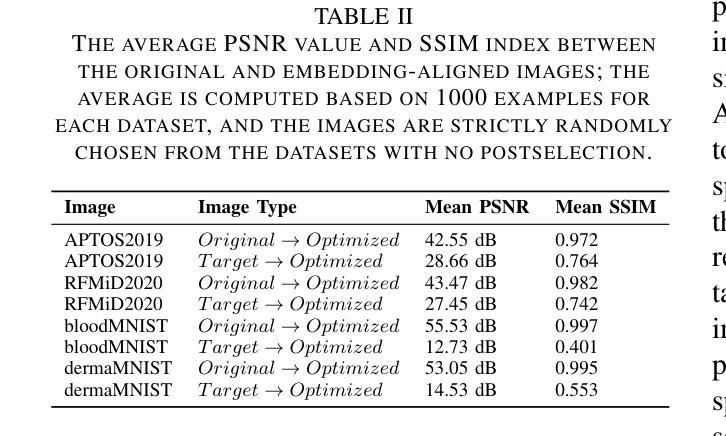
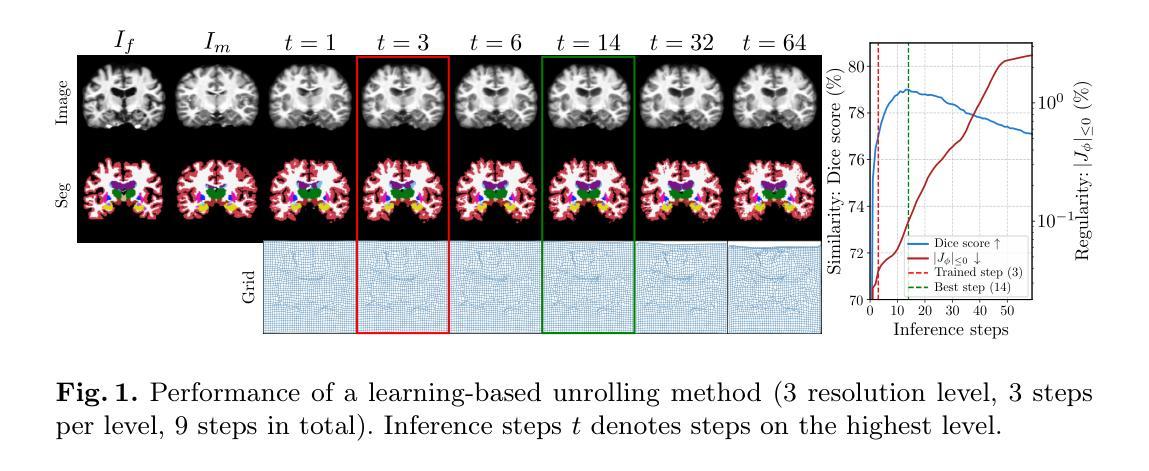
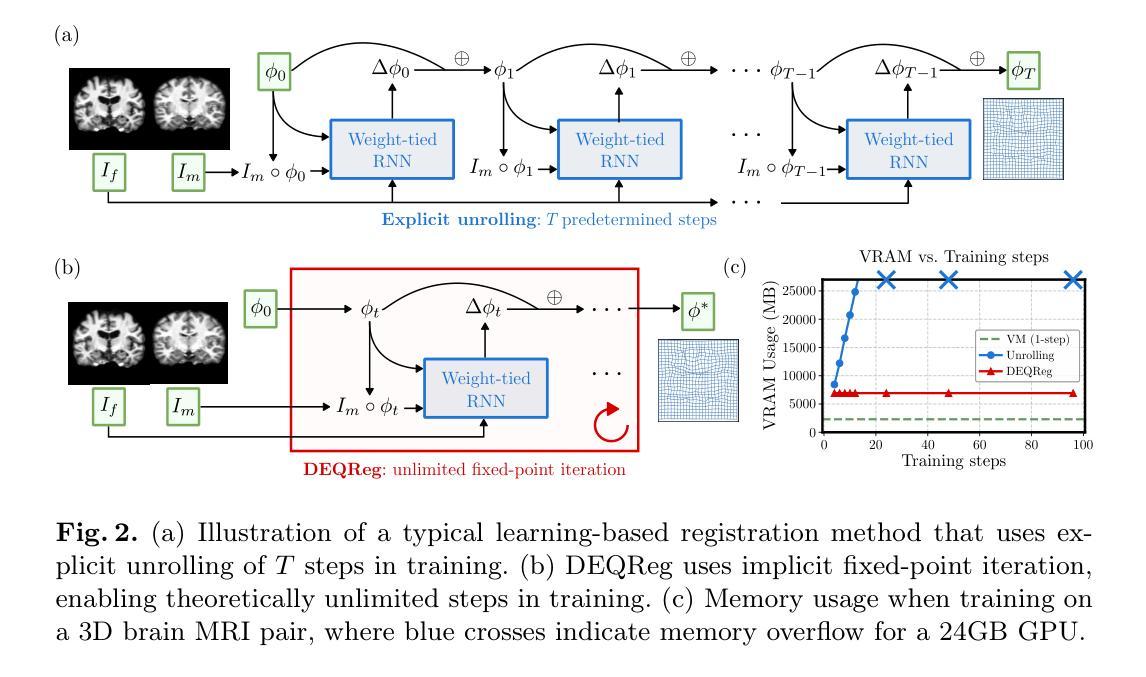
Bridging Classical and Learning-based Iterative Registration through Deep Equilibrium Models
Authors:Yi Zhang, Yidong Zhao, Qian Tao
Deformable medical image registration is traditionally formulated as an optimization problem. While classical methods solve this problem iteratively, recent learning-based approaches use recurrent neural networks (RNNs) to mimic this process by unrolling the prediction of deformation fields in a fixed number of steps. However, classical methods typically converge after sufficient iterations, but learning-based unrolling methods lack a theoretical convergence guarantee and show instability empirically. In addition, unrolling methods have a practical bottleneck at training time: GPU memory usage grows linearly with the unrolling steps due to backpropagation through time (BPTT). To address both theoretical and practical challenges, we propose DEQReg, a novel registration framework based on Deep Equilibrium Models (DEQ), which formulates registration as an equilibrium-seeking problem, establishing a natural connection between classical optimization and learning-based unrolling methods. DEQReg maintains constant memory usage, enabling theoretically unlimited iteration steps. Through extensive evaluation on the public brain MRI and lung CT datasets, we show that DEQReg can achieve competitive registration performance, while substantially reducing memory consumption compared to state-of-the-art unrolling methods. We also reveal an intriguing phenomenon: the performance of existing unrolling methods first increases slightly then degrades irreversibly when the inference steps go beyond the training configuration. In contrast, DEQReg achieves stable convergence with its inbuilt equilibrium-seeking mechanism, bridging the gap between classical optimization-based and modern learning-based registration methods.
传统上,可变形医学图像配准被制定为一个优化问题。虽然经典方法通过迭代来解决这个问题,但最近的基于学习的方法使用循环神经网络(RNN)来模拟这个过程,通过在固定数量的步骤中展开变形场的预测。然而,经典方法通常在足够的迭代后收敛,但基于展开的深度学习方法缺乏理论收敛保证,并且在经验上显示出不稳定。此外,展开方法在训练时间方面存在实际瓶颈:由于时间反向传播(BPTT),GPU内存使用量与展开步骤线性增长。为了解决理论和实践上的挑战,我们提出了基于深度均衡模型(DEQ)的新型配准框架DEQReg,它将配准制定为均衡求解问题,在经典优化和基于学习的展开方法之间建立了自然联系。DEQReg保持恒定的内存使用,支持理论上的无限迭代步骤。通过对公共脑部MRI和肺部CT数据集的广泛评估,我们证明了DEQReg可以实现具有竞争力的配准性能,同时大大降低了与最新展开方法相比的内存消耗。我们还揭示了一个有趣的现象:当推断步骤超出训练配置时,现有展开方法的性能会先略有提高然后不可逆转地下降。与此相反,DEQReg利用其内置的均衡求解机制实现了稳定的收敛,缩小了基于经典优化的现代学习和基于学习的配准方法之间的差距。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted version. Accepted by MICCAI 2025
摘要
变形医学图像配准可看作一个优化问题,传统方法是迭代解决。近年出现的基于学习的方法采用循环神经网络(RNN)模拟此过程。但现有学习方法的迭代过程缺乏理论收敛保证,且存在不稳定现象。此外,其训练时的GPU内存使用随迭代步骤线性增长,存在实际瓶颈。为解决这些问题,我们提出基于深度均衡模型(DEQ)的DEQReg框架,将配准看作一个平衡寻找问题,在经典优化与学习展开方法间建立自然联系。DEQReg保持恒定内存使用,实现理论上无限迭代步骤。在公共脑MRI和肺CT数据集上的评估显示,DEQReg可实现竞争性的配准性能,同时大幅减少内存消耗,优于最新展开方法。我们还发现一个有趣现象:现有展开方法的性能在推理步骤超出训练配置时会先略微提升然后不可逆地下降。相比之下,DEQReg凭借内置的平衡寻找机制实现了稳定的收敛,缩小了基于经典优化和现代基于学习的配准方法之间的差距。
关键见解
- 变形医学图像配准被视为优化问题,传统方法通过迭代解决。
- 基于学习的方法使用RNN模拟配准过程,但缺乏理论收敛保证且表现不稳定。
- 现有方法存在GPU内存使用随迭代步骤线性增长的实践瓶颈。
- DEQReg框架基于深度均衡模型(DEQ),将配准视为平衡寻找问题,结合了传统与优化方法。
- DEQReg实现了理论上无限的迭代步骤,同时保持恒定的内存使用。
- 在公共数据集上的评估显示DEQReg性能具有竞争力,且相比最新方法大幅减少内存消耗。
点此查看论文截图

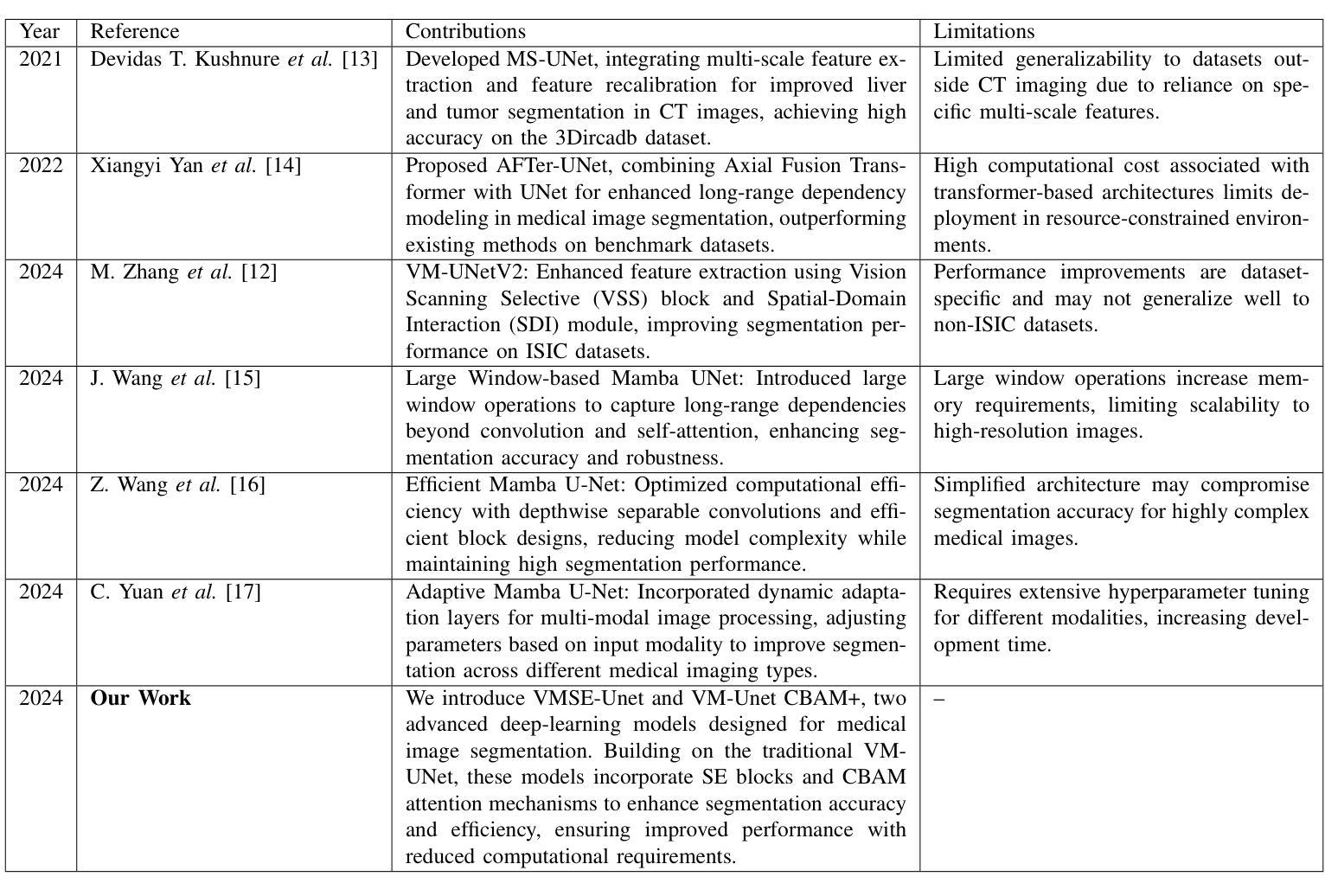
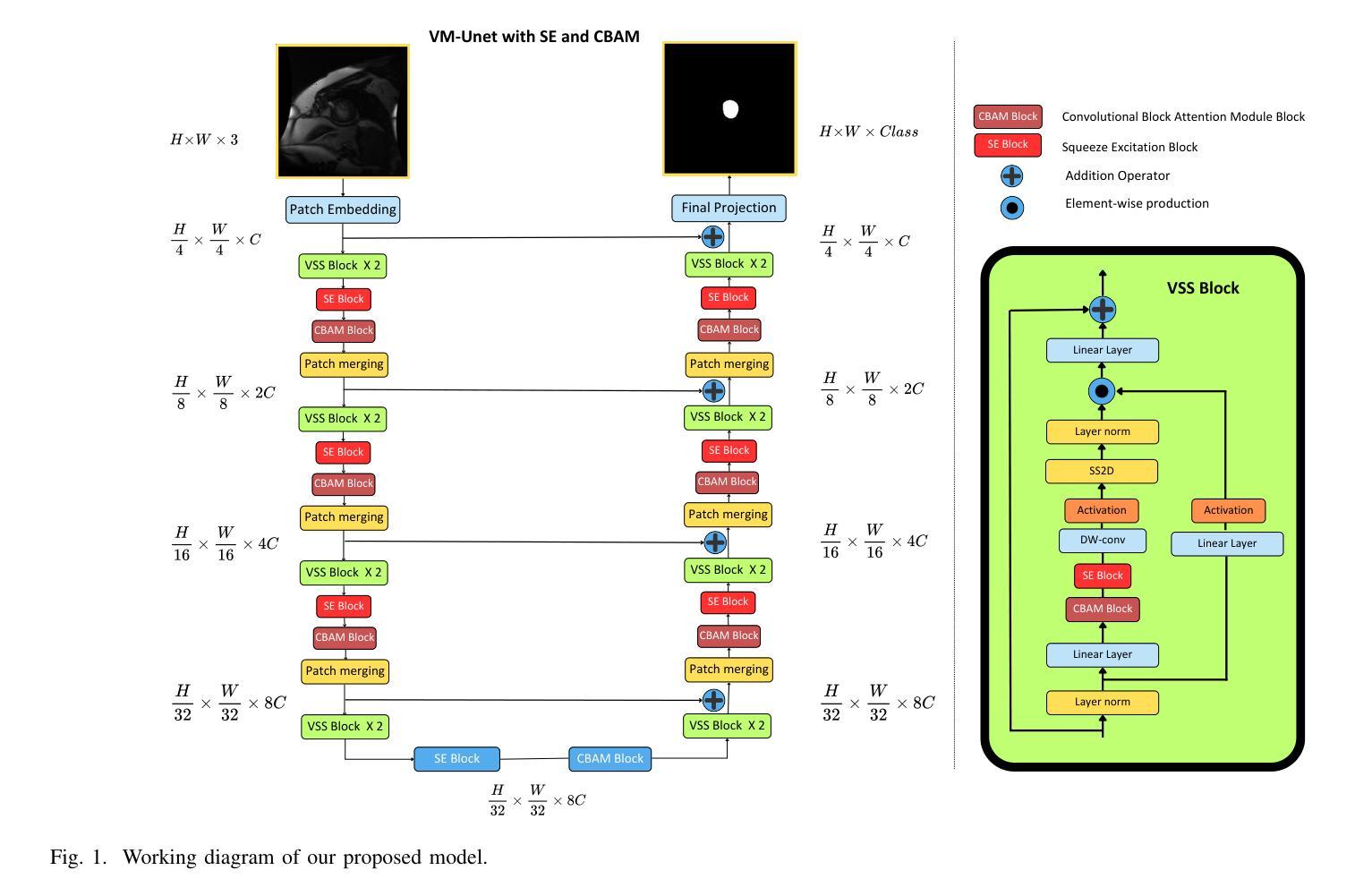
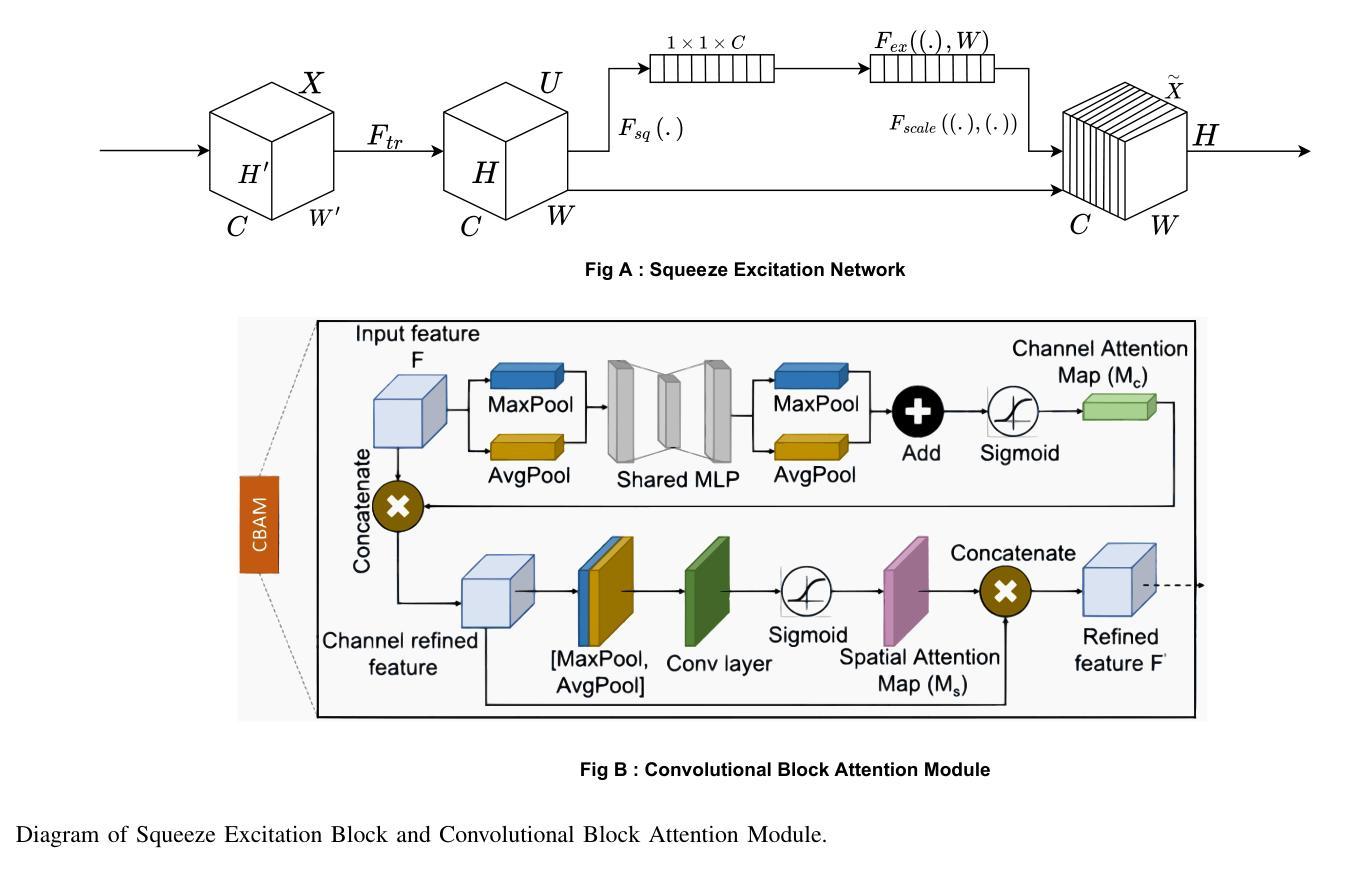
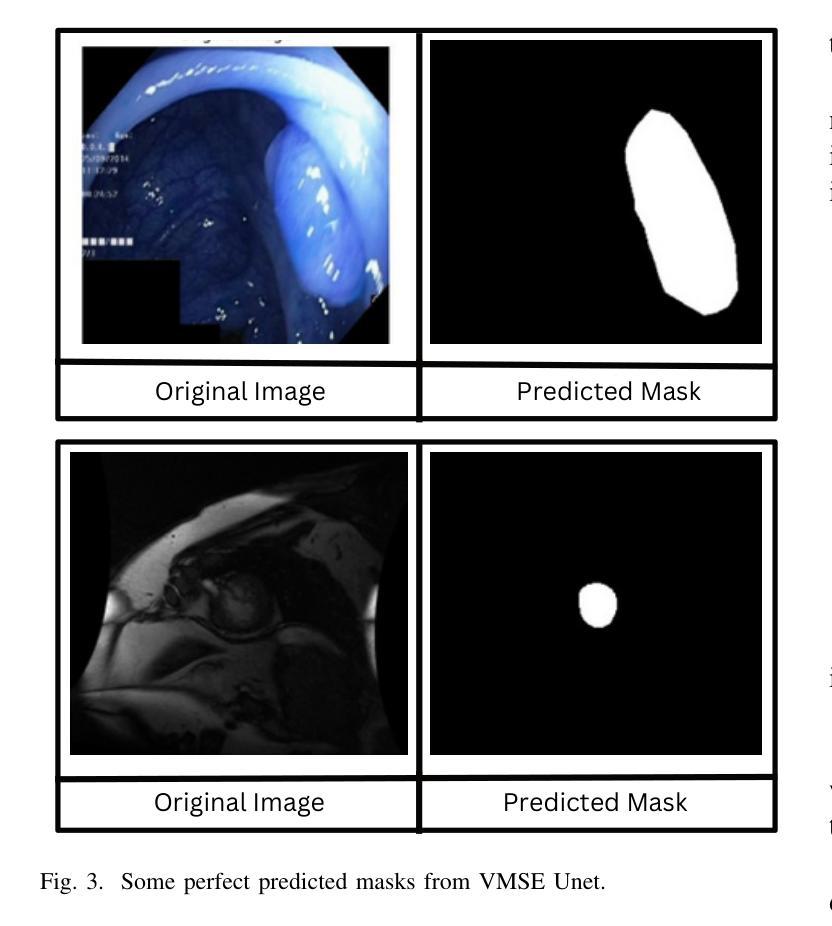
Medical Image Segmentation Using Advanced Unet: VMSE-Unet and VM-Unet CBAM+
Authors:Sayandeep Kanrar, Raja Piyush, Qaiser Razi, Debanshi Chakraborty, Vikas Hassija, GSS Chalapathi
In this paper, we present the VMSE U-Net and VM-Unet CBAM+ model, two cutting-edge deep learning architectures designed to enhance medical image segmentation. Our approach integrates Squeeze-and-Excitation (SE) and Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM) techniques into the traditional VM U-Net framework, significantly improving segmentation accuracy, feature localization, and computational efficiency. Both models show superior performance compared to the baseline VM-Unet across multiple datasets. Notably, VMSEUnet achieves the highest accuracy, IoU, precision, and recall while maintaining low loss values. It also exhibits exceptional computational efficiency with faster inference times and lower memory usage on both GPU and CPU. Overall, the study suggests that the enhanced architecture VMSE-Unet is a valuable tool for medical image analysis. These findings highlight its potential for real-world clinical applications, emphasizing the importance of further research to optimize accuracy, robustness, and computational efficiency.
在这篇论文中,我们提出了VMSE U-Net和VM-Unet CBAM+模型,这是两种先进的深度学习架构,旨在提高医学图像分割的效果。我们的方法将Squeeze-and-Excitation(SE)和卷积块注意力模块(CBAM)技术集成到传统的VM U-Net框架中,显著提高了分割精度、特征定位能力和计算效率。与基线VM-Unet相比,这两个模型在多数据集上均表现出卓越的性能。值得注意的是,VMSE U-Net在保持低损失值的同时,实现了最高的准确度、IoU、精确度和召回率。此外,它在GPU和CPU上都表现出非凡的计算效率,推理时间更快,内存使用更低。总体而言,研究结果表明,增强型架构VMSE-Unet是医学图像分析的有用工具。这些发现强调了其在真实世界临床应用中的潜力,并强调需要进一步的研究来优化准确度、稳健性和计算效率的重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了VMSE U-Net和VM-Unet CBAM+两个先进的深度学习架构,它们被设计用于提高医学图像分割的效果。通过集成Squeeze-and-Excitation(SE)和卷积块注意力模块(CBAM)技术到传统的VM U-Net框架中,显著提高了分割精度、特征定位能力和计算效率。相较于基础VM-Unet模型,两个模型在多数据集上表现出卓越性能。特别是VMSE U-Net在准确度、IoU、精确度和召回率上取得了最高成绩,同时保持较低的损失值。它在GPU和CPU上均具有出色的计算效率,推理速度快、内存占用低。总体而言,优化的VMSE U-Net架构对于医学图像分析具有重要价值,具有实际应用于临床的潜力。研究强调了进一步优化其准确性、稳健性和计算效率的必要性。
Key Takeaways
以下是本段文本的主要观点或见解:
- VMSE U-Net和VM-Unet CBAM+是设计用于医学图像分割的深度学习架构。
- 它们集成了Squeeze-and-Excitation(SE)和卷积块注意力模块(CBAM)技术,以提高分割精度、特征定位和计算效率。
- 对比基础VM-Unet模型,两种模型在多数据集上表现优越。
- VMSE U-Net在准确度、IoU、精确度和召回率等多个指标上达到最佳性能,同时具有较低损失值。
- VMSE U-Net架构在GPU和CPU上都表现出优秀的计算效率,具有快速的推理速度和低内存占用。
- 整体而言,VMSE U-Net架构对于医学图像分析具有实用价值,并有望应用于实际临床环境。
点此查看论文截图

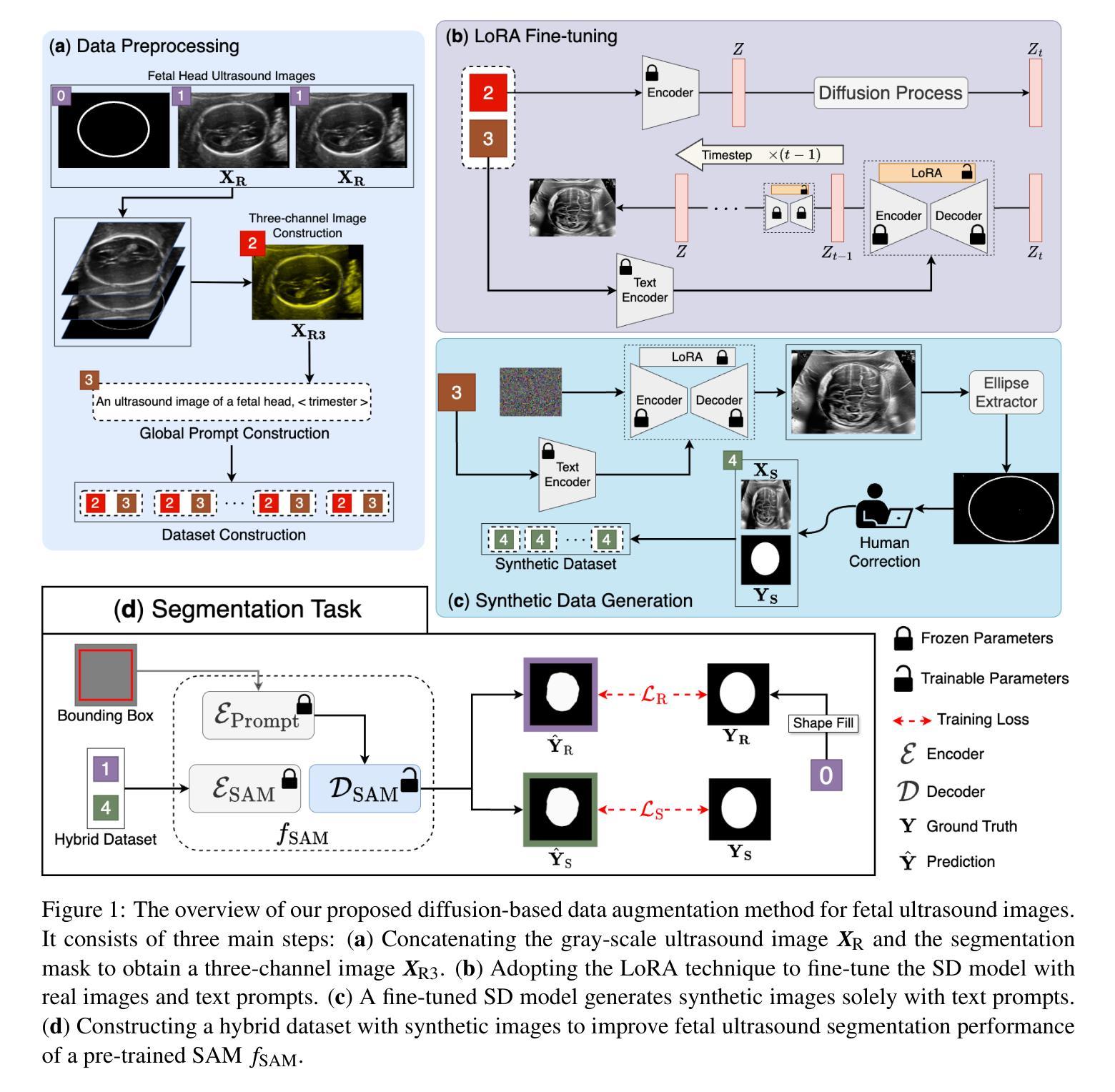
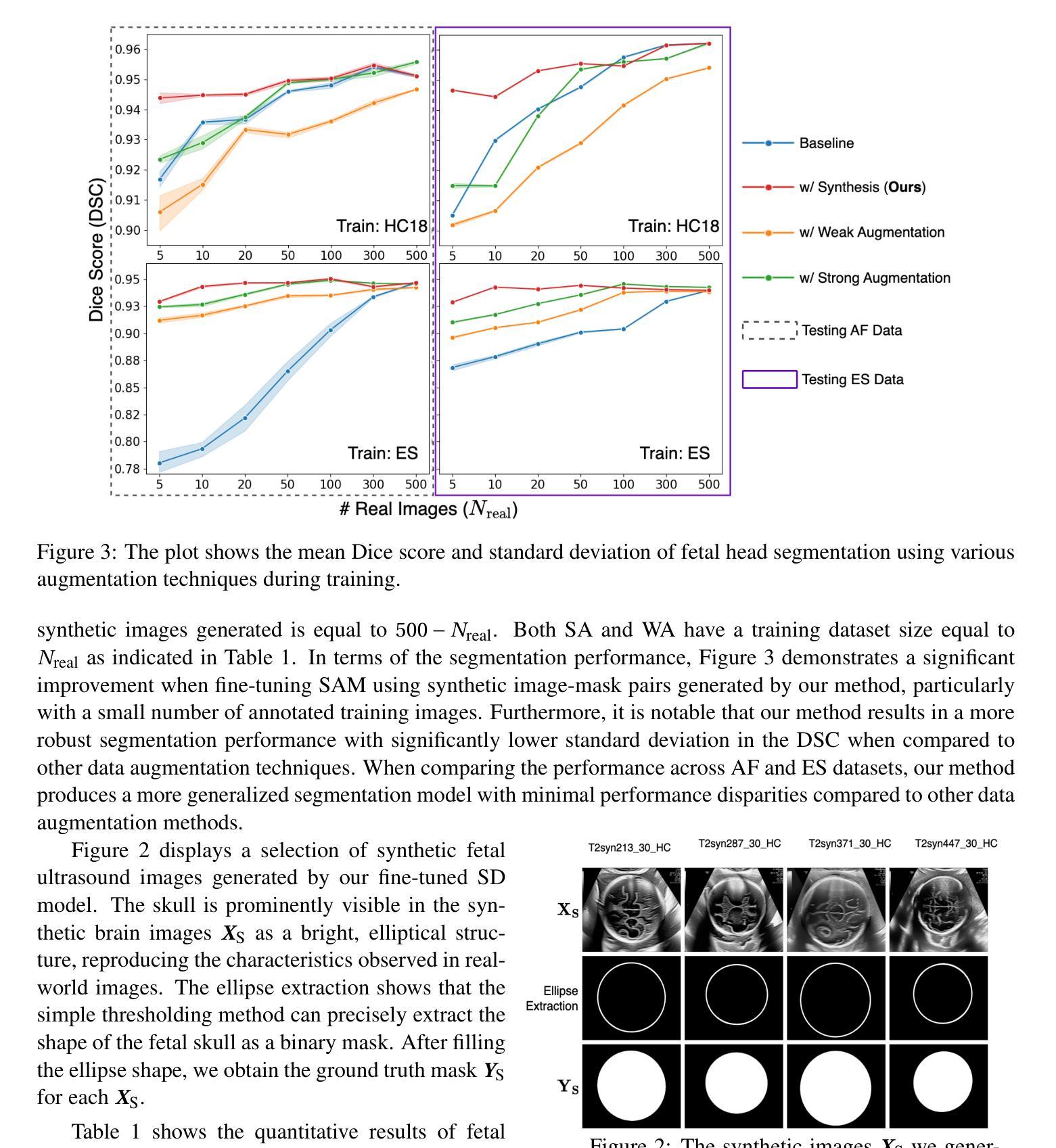
Diffusion Model-based Data Augmentation Method for Fetal Head Ultrasound Segmentation
Authors:Fangyijie Wang, Kevin Whelan, Félix Balado, Kathleen M. Curran, Guénolé Silvestre
Medical image data is less accessible than in other domains due to privacy and regulatory constraints. In addition, labeling requires costly, time-intensive manual image annotation by clinical experts. To overcome these challenges, synthetic medical data generation offers a promising solution. Generative AI (GenAI), employing generative deep learning models, has proven effective at producing realistic synthetic images. This study proposes a novel mask-guided GenAI approach using diffusion models to generate synthetic fetal head ultrasound images paired with segmentation masks. These synthetic pairs augment real datasets for supervised fine-tuning of the Segment Anything Model (SAM). Our results show that the synthetic data captures real image features effectively, and this approach reaches state-of-the-art fetal head segmentation, especially when trained with a limited number of real image-mask pairs. In particular, the segmentation reaches Dice Scores of 94.66% and 94.38% using a handful of ultrasound images from the Spanish and African cohorts, respectively. Our code, models, and data are available on GitHub.
医学图像数据由于隐私和监管限制,其可访问性比其他领域的数据要低。此外,标注需要临床专家进行昂贵且耗时的手动图像注释。为了克服这些挑战,合成医学数据生成提供了一个有前景的解决方案。采用生成式深度学习模型的生成式人工智能(GenAI)已被证明能够产生逼真的合成图像。本研究提出了一种新的基于扩散模型的mask引导GenAI方法,用于生成与分割掩膜配对的合成胎儿头部超声图像。这些合成图像对真实数据集进行了扩充,用于监督微调Segment Anything Model(SAM)。我们的结果表明,合成数据有效地捕捉了真实图像的特征,尤其是在使用有限数量的真实图像-掩膜对进行训练时,该方法达到了最先进的胎儿头部分割效果。特别是,使用来自西班牙和非洲队列的少量超声图像,分割达到Dice分数分别为94.66%和94.38%。我们的代码、模型和数据均可在GitHub上获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at Irish Machine Vision and Image Processing Conference (IMVIP) 2025
Summary
医学图像领域面临隐私和监管限制导致数据访问困难以及标注成本高昂的问题。本研究提出了一种基于扩散模型的新型生成式人工智能(GenAI)方法,能够生成带有分割掩码的合成胎儿头部超声图像。合成数据有效捕捉真实图像特征,并用于监督精细调整SAM模型。本研究在有限真实图像-掩码对的情况下取得了领先水平的胎儿头部分割效果,Dice得分达到94.66%和94.38%。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像数据由于隐私和监管限制而不易获取。
- 生成式人工智能(GenAI)可解决这一问题,通过深度学习模型生成合成医学图像。
- 本研究采用新型mask-guided GenAI方法,生成合成胎儿头部超声图像及分割掩码。
- 合成数据可有效捕捉真实图像特征。
- 此方法实现了先进的胎儿头部分割效果,特别是在真实图像-掩码对有限的情况下。
- 合成数据对提高模型的训练效果起到了重要作用。
- 代码、模型和数据已公开在GitHub上。
点此查看论文截图