⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-12 更新
CL-Polyp: A Contrastive Learning-Enhanced Network for Accurate Polyp Segmentation
Authors:Desheng Li, Chaoliang Liu, Zhiyong Xiao
Accurate segmentation of polyps from colonoscopy images is crucial for the early diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer. Most existing deep learning-based polyp segmentation methods adopt an Encoder-Decoder architecture, and some utilize multi-task frameworks that incorporate auxiliary tasks such as classification to enhance segmentation performance. However, these approaches often require additional labeled data and rely on task similarity, which can limit their generalizability. To address these challenges, we propose CL-Polyp, a contrastive learning-enhanced polyp segmentation network. Our method leverages contrastive learning to improve the encoder’s ability to extract discriminative features by contrasting positive and negative sample pairs derived from polyp images. This self-supervised strategy enhances visual representation without requiring additional annotations. In addition, we introduce two lightweight and effective modules: the Modified Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling (MASPP) module for better multi-scale feature fusion, and the Channel Concatenate and Element Add (CA) module to fuse low-level and upsampled features for improved boundary reconstruction. Extensive experiments on five benchmark datasets-Kvasir-SEG, CVC-ClinicDB, CVC-ColonDB, CVC-300, and ETIS-demonstrate that CL-Polyp consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods. Specifically, it improves the IoU metric by 0.011 and 0.020 on the Kvasir-SEG and CVC-ClinicDB datasets, respectively, validating its effectiveness in clinical polyp segmentation tasks.
精确地从结肠镜图像中分割息肉对于结直肠癌的早期诊断和治疗至关重要。现有的大多数基于深度学习的息肉分割方法采用编码器-解码器架构,有些则利用多任务框架,结合分类等辅助任务来提高分割性能。然而,这些方法通常需要额外的标记数据,并依赖于任务相似性,这可能会限制其泛化能力。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了CL-Polyp,一种增强对比学习的息肉分割网络。我们的方法利用对比学习来提高编码器提取判别特征的能力,通过对比来自息肉图像的正负样本对。这种自我监督的策略提高了视觉表征能力,而无需额外的注释。此外,我们引入了两个轻便有效的模块:用于更好多尺度特征融合的修改后的空洞空间金字塔池化(MASPP)模块,以及用于融合低级和上采样特征的通道合并和元素添加(CA)模块,以改进边界重建。在五个基准数据集Kvasir-SEG、CVC-ClinicDB、CVC-ColonDB、CVC 0 CVC-ClinicDB和ETIS上的广泛实验表明,CL-Polyp始终优于最先进的方法。具体而言,它在Kvasir-SEG和CVC-ClinicDB数据集上分别提高了交并比(IoU)指标0.011和0.020,验证了其在临床息肉分割任务中的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出了一种基于对比学习的结肠息肉分割网络CL-Polyp,用于结肠镜图像中的息肉精确分割。该方法利用对比学习提高编码器提取判别特征的能力,通过对比息肉图像的正负样本对实现自我监督策略,提高视觉表征能力而无需额外标注。此外,还引入了两个轻量级且有效的模块,即改进的金字塔池化模块(MASPP)和通道拼接与元素添加(CA)模块,用于更好的多尺度特征融合和边界重建。在五个基准数据集上的实验表明,CL-Polyp持续优于最新方法。具体来说,它在Kvasir-SEG和CVC-ClinicDB数据集上的IoU指标分别提高了0.011和0.020,验证了其在临床息肉分割任务中的有效性。
关键见解
- 结肠息肉的准确分割对结直肠癌的早期诊断和治疗至关重要。
- 现有深度学习方法大多采用Encoder-Decoder架构,并借助辅助任务如分类来提高分割性能,但依赖大量标注数据且泛化能力受限。
- CL-Polyp方法利用对比学习提高编码器提取判别特征的能力,通过自我监督策略增强视觉表征。
- 引入MASPP模块实现更好的多尺度特征融合。
- CA模块用于融合低级别和上采样特征,改善边界重建。
- 在五个基准数据集上的实验表明CL-Polyp性能优于最新方法。
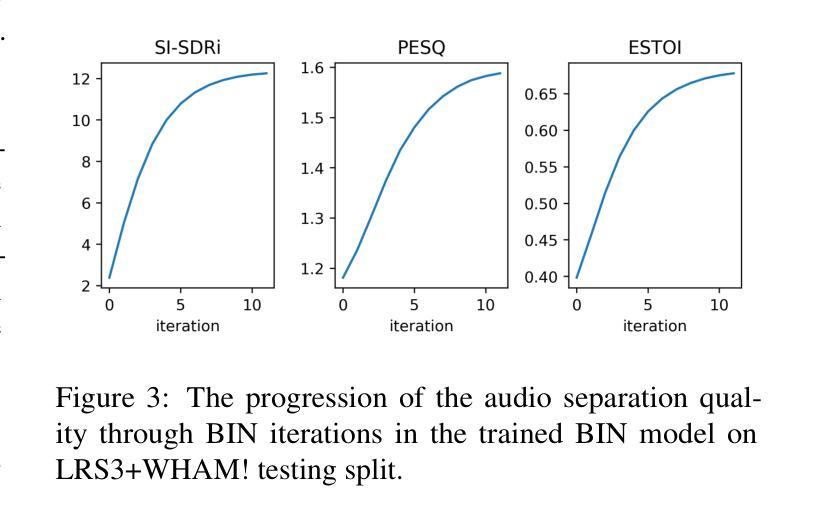
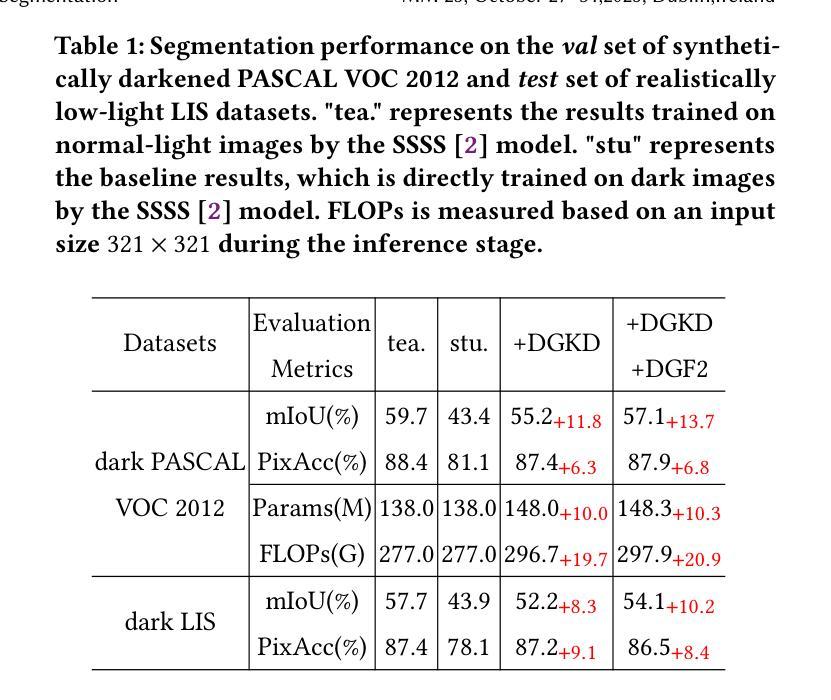
点此查看论文截图