⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-12 更新
Diffusion-Guided Knowledge Distillation for Weakly-Supervised Low-Light Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Chunyan Wang, Dong Zhang, Jinhui Tang
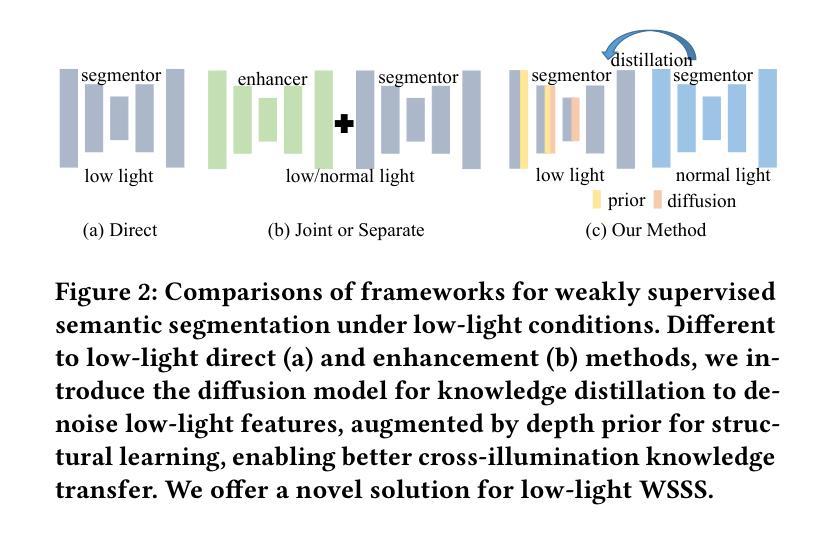
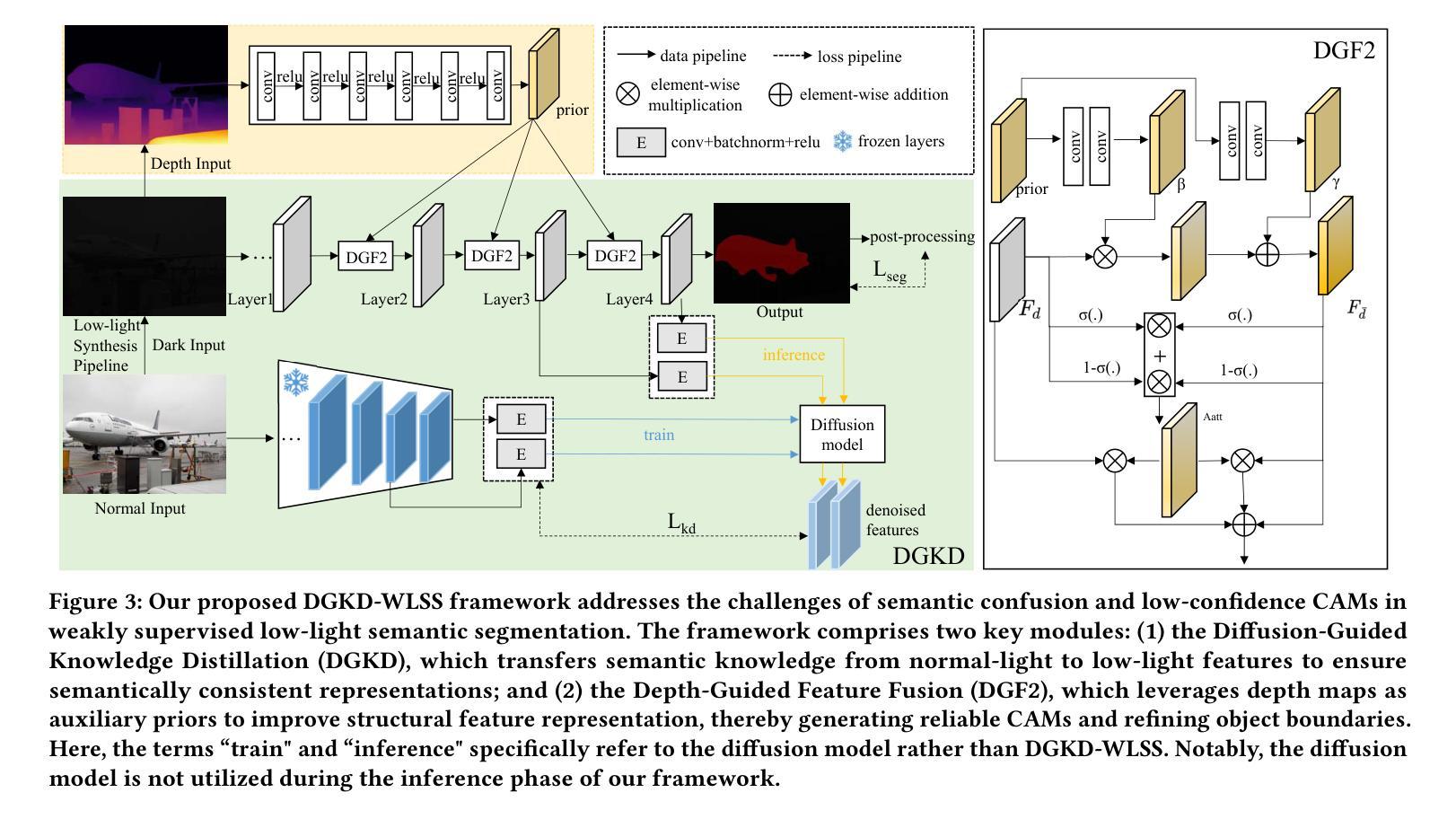
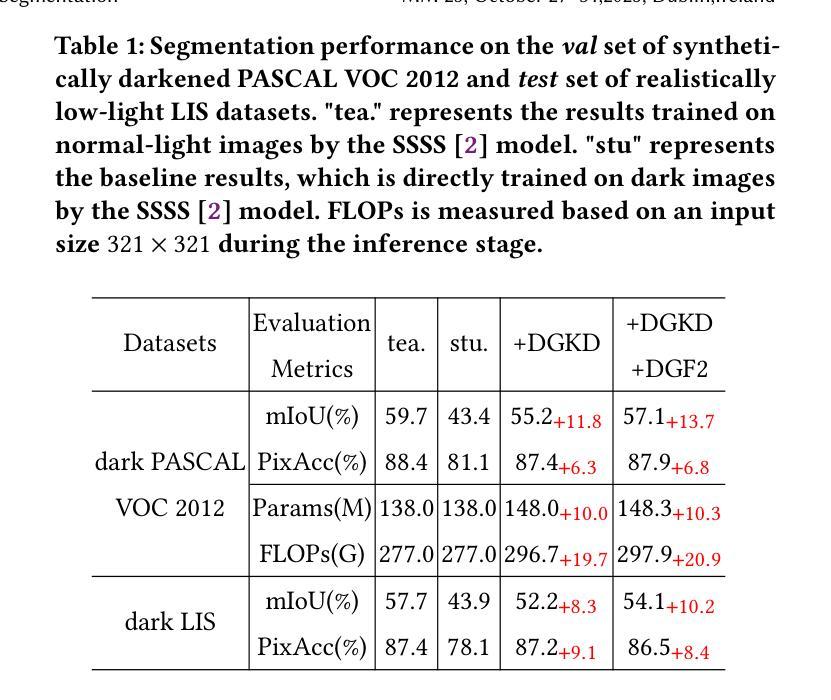
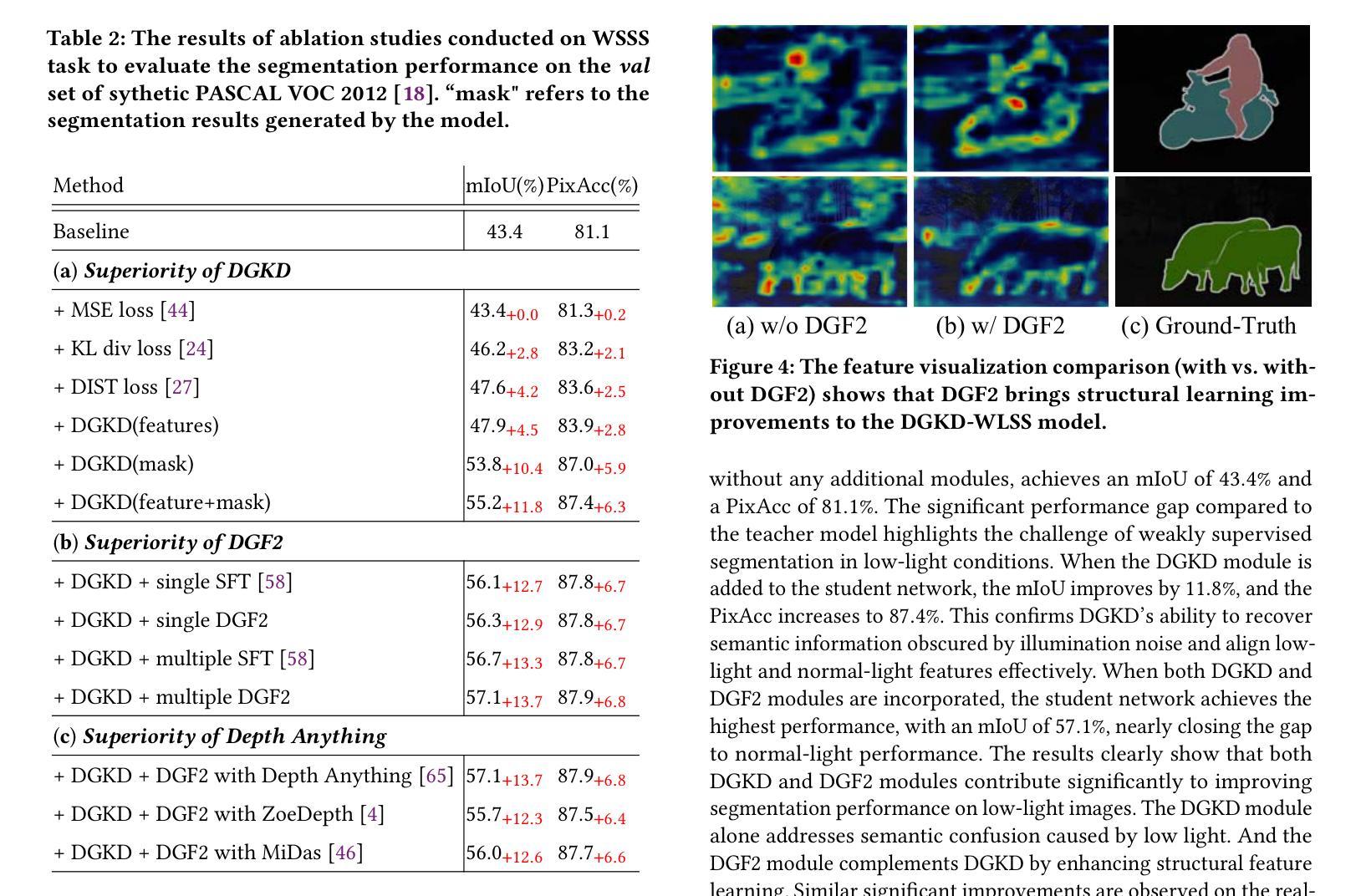
Weakly-supervised semantic segmentation aims to assign category labels to each pixel using weak annotations, significantly reducing manual annotation costs. Although existing methods have achieved remarkable progress in well-lit scenarios, their performance significantly degrades in low-light environments due to two fundamental limitations: severe image quality degradation (e.g., low contrast, noise, and color distortion) and the inherent constraints of weak supervision. These factors collectively lead to unreliable class activation maps and semantically ambiguous pseudo-labels, ultimately compromising the model’s ability to learn discriminative feature representations. To address these problems, we propose Diffusion-Guided Knowledge Distillation for Weakly-Supervised Low-light Semantic Segmentation (DGKD-WLSS), a novel framework that synergistically combines Diffusion-Guided Knowledge Distillation (DGKD) with Depth-Guided Feature Fusion (DGF2). DGKD aligns normal-light and low-light features via diffusion-based denoising and knowledge distillation, while DGF2 integrates depth maps as illumination-invariant geometric priors to enhance structural feature learning. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of DGKD-WLSS, which achieves state-of-the-art performance in weakly supervised semantic segmentation tasks under low-light conditions. The source codes have been released at:https://github.com/ChunyanWang1/DGKD-WLSS.
弱监督语义分割旨在使用弱标注为每个像素分配类别标签,从而显著降低手动标注成本。尽管现有方法在多光照场景中取得了显著进展,但在低光照环境中,由于两个基本局限因素——图像质量严重退化(例如,低对比度、噪声和颜色失真)和弱监督的固有约束,它们的性能会显著下降。这些因素共同作用导致类激活图不可靠和语义模糊的伪标签,最终损害模型学习判别特征表示的能力。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了针对弱监督低光照语义分割的扩散引导知识蒸馏(DGKD-WLSS)新框架,该框架协同结合了扩散引导知识蒸馏(DGKD)与深度引导特征融合(DGF2)。DGKD通过基于扩散的去噪和知识蒸馏对齐正常光照和低光照特征,而DGF2则利用深度图作为光照不变的几何先验来增强结构特征学习。大量实验证明了DGKD-WLSS的有效性,在低光照条件下的弱监督语义分割任务中实现了最佳性能。源代码已发布在:https://github.com/ChunyanWang1/DGKD-WLSS。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
弱监督语义分割通过利用弱标注对图像的每个像素分配类别标签,显著降低了手动标注的成本。针对低光环境下的性能下降问题,提出一种名为DGKD-WLSS的新框架,结合扩散引导知识蒸馏(DGKD)和深度引导特征融合(DGF²)来解决低光环境下的弱监督语义分割问题。DGKD通过基于扩散的去噪和知识蒸馏对齐正常光和低光特征,而DGF²则利用深度图作为光照不变的几何先验来增强结构特征学习。实验证明,DGKD-WLSS在低光条件下的弱监督语义分割任务中取得了最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 弱监督语义分割旨在利用弱标注进行像素级标签分配,降低手动标注成本。
- 低光环境对弱监督语义分割是一大挑战,存在图像质量退化和弱监督的内在限制。
- 提出的DGKD-WLSS框架结合扩散引导知识蒸馏(DGKD)和深度引导特征融合(DGF²)来解决这一问题。
- DGKD通过扩散去噪和知识蒸馏对齐正常光和低光特征。
- DGF²利用深度图作为几何先验来增强结构特征学习。
- DGKD-WLSS在低光条件下的弱监督语义分割任务中表现最佳。
- 项目的源代码已发布在https://github.com/ChunyanWang1/DGKD-WLSS。
点此查看论文截图

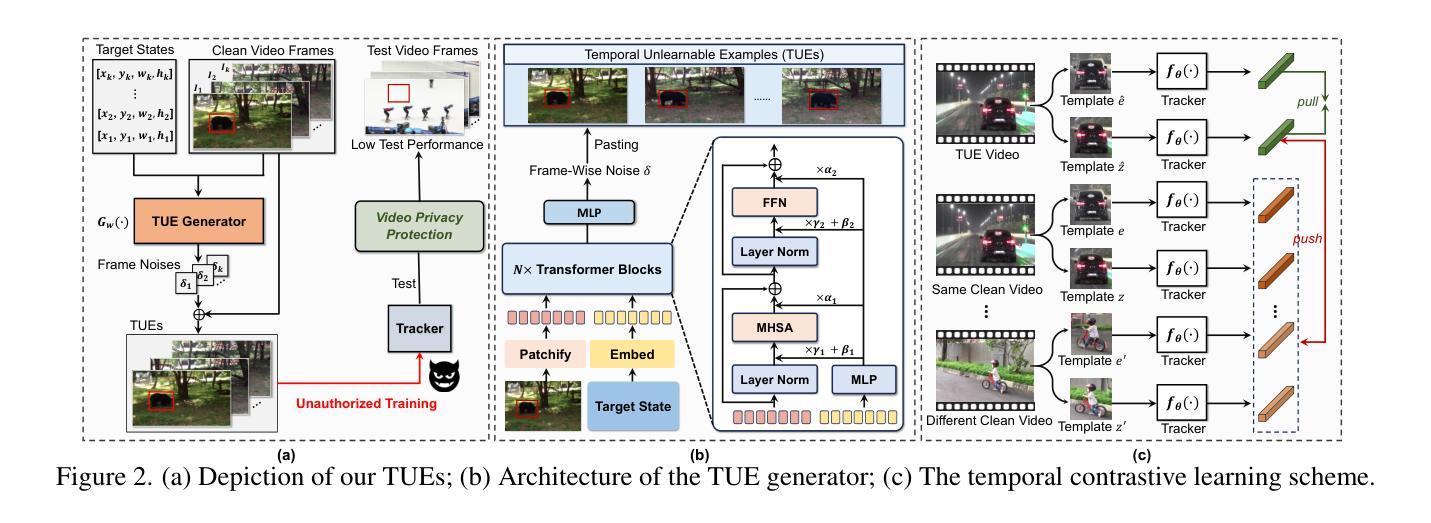
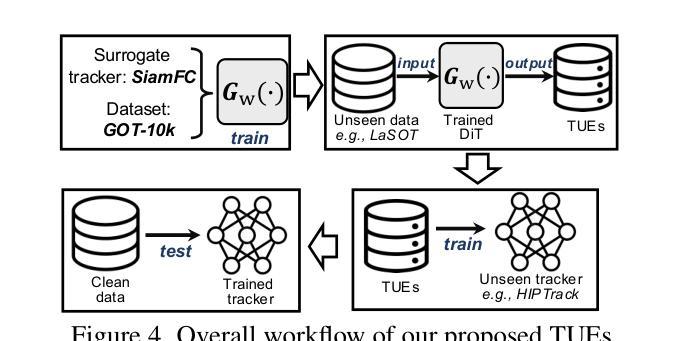
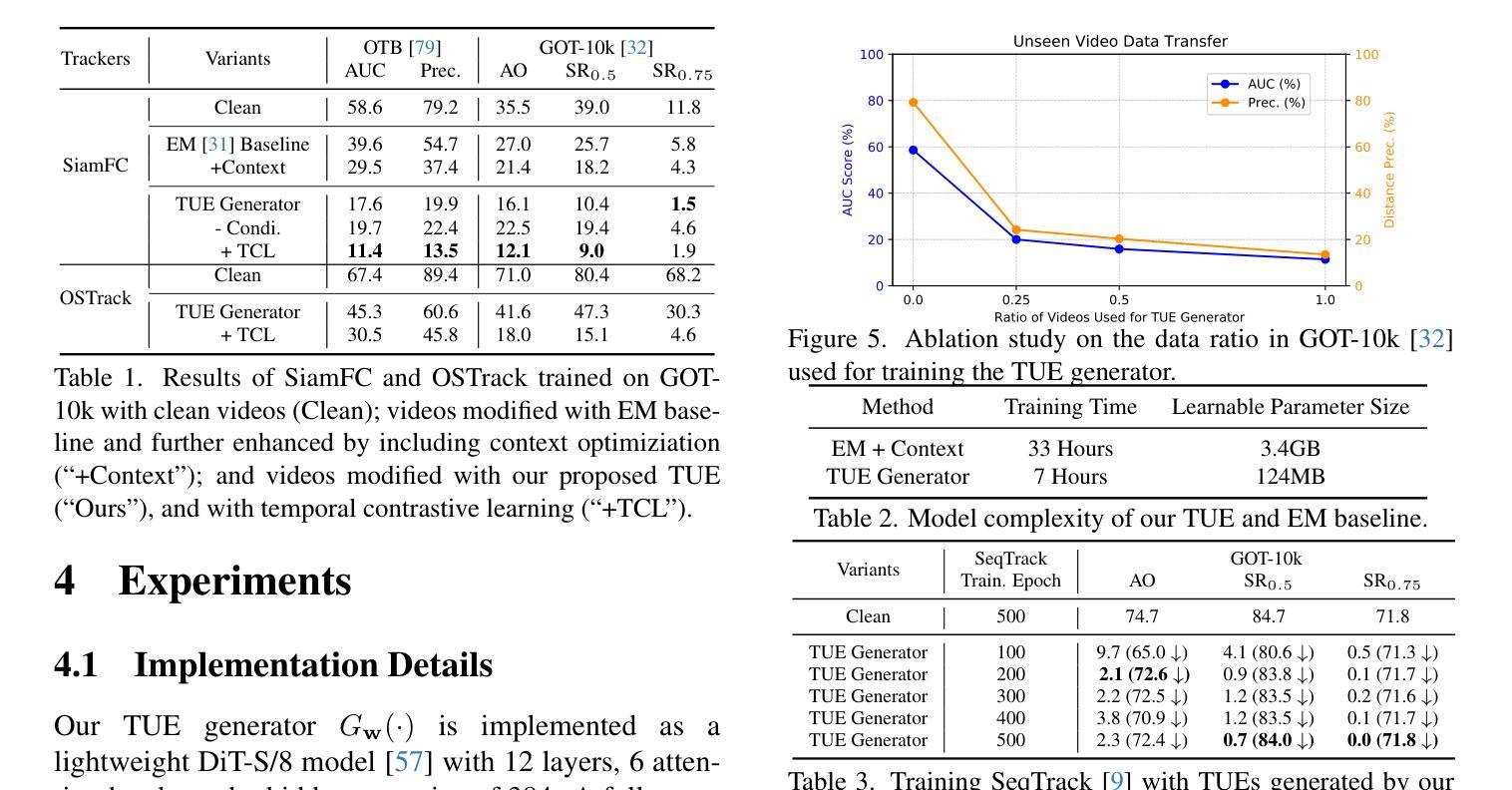
Temporal Unlearnable Examples: Preventing Personal Video Data from Unauthorized Exploitation by Object Tracking
Authors:Qiangqiang Wu, Yi Yu, Chenqi Kong, Ziquan Liu, Jia Wan, Haoliang Li, Alex C. Kot, Antoni B. Chan
With the rise of social media, vast amounts of user-uploaded videos (e.g., YouTube) are utilized as training data for Visual Object Tracking (VOT). However, the VOT community has largely overlooked video data-privacy issues, as many private videos have been collected and used for training commercial models without authorization. To alleviate these issues, this paper presents the first investigation on preventing personal video data from unauthorized exploitation by deep trackers. Existing methods for preventing unauthorized data use primarily focus on image-based tasks (e.g., image classification), directly applying them to videos reveals several limitations, including inefficiency, limited effectiveness, and poor generalizability. To address these issues, we propose a novel generative framework for generating Temporal Unlearnable Examples (TUEs), and whose efficient computation makes it scalable for usage on large-scale video datasets. The trackers trained w/ TUEs heavily rely on unlearnable noises for temporal matching, ignoring the original data structure and thus ensuring training video data-privacy. To enhance the effectiveness of TUEs, we introduce a temporal contrastive loss, which further corrupts the learning of existing trackers when using our TUEs for training. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance in video data-privacy protection, with strong transferability across VOT models, datasets, and temporal matching tasks.
随着社交媒体的兴起,大量用户上传的视频(例如YouTube)被用作视觉对象跟踪(VOT)的训练数据。然而,VOT社区在很大程度上忽视了视频数据隐私问题,许多私有视频未经授权便被收集用于训练商业模型。为了解决这些问题,本文对防止个人视频数据被深度跟踪器未经授权使用的情况进行了首次调查。现有的防止未经授权数据使用的方法主要集中在图像相关任务上(例如图像分类),将其直接应用于视频会暴露出许多局限性,包括效率低下、效果有限以及通用性不佳。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种生成时序不可学习样本(TUEs)的新型框架,其高效计算可使其在大规模视频数据集上实现使用扩展。使用TUEs训练的跟踪器严重依赖于不可学习的噪声进行时序匹配,从而忽略了原始数据结构,确保了训练视频数据的隐私。为了提高TUEs的有效性,我们引入了时序对比损失,当使用我们的TUEs进行训练时,它进一步破坏了现有跟踪器的学习。大量实验表明,我们的方法在视频数据隐私保护方面达到了最新技术水平,在VOT模型、数据集和时序匹配任务之间具有很强的可迁移性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025
Summary:
随着社交媒体的发展,大量用户上传的视频被用于视觉对象跟踪(VOT)的训练数据,但视频数据隐私问题被VOT领域所忽视。本文首次调查了防止个人视频数据未经授权被深度追踪器利用的问题。现有防止未经授权数据使用的方法主要集中在图像任务上,直接应用于视频会暴露多种局限性。为此,我们提出了一种生成时序不可学习样本(TUEs)的新型框架,其高效计算可大规模应用于大规模视频数据集。使用TUEs训练的追踪器依赖于不可学习的噪声进行时间匹配,忽略原始数据结构,从而确保训练视频数据的隐私。为提高TUEs的有效性,我们引入了时间对比损失,进一步干扰了现有追踪器的学习。实验表明,该方法在视频数据隐私保护方面达到最新性能,在不同VOT模型、数据集和时间匹配任务之间具有较强的可转移性。
Key Takeaways:
- 用户上传的大量视频被用作VOT的训练数据,但存在视频数据隐私问题。
- 现有防止数据未经授权使用的方法在视频领域存在局限性。
- 提出了一种生成时序不可学习样本(TUEs)的新型框架,用于保护视频数据隐私。
- TUEs使得追踪器依赖于不可学习的噪声进行时间匹配,忽略原始数据结构。
- 引入时间对比损失,提高TUEs的有效性,干扰现有追踪器的学习。
- 该方法在视频数据隐私保护方面达到最新性能。
点此查看论文截图


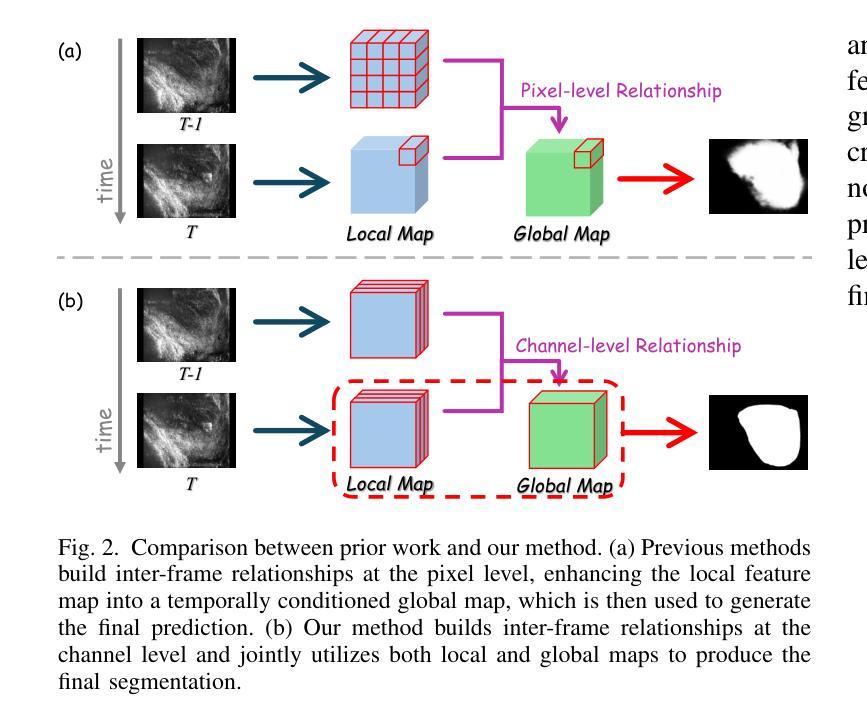
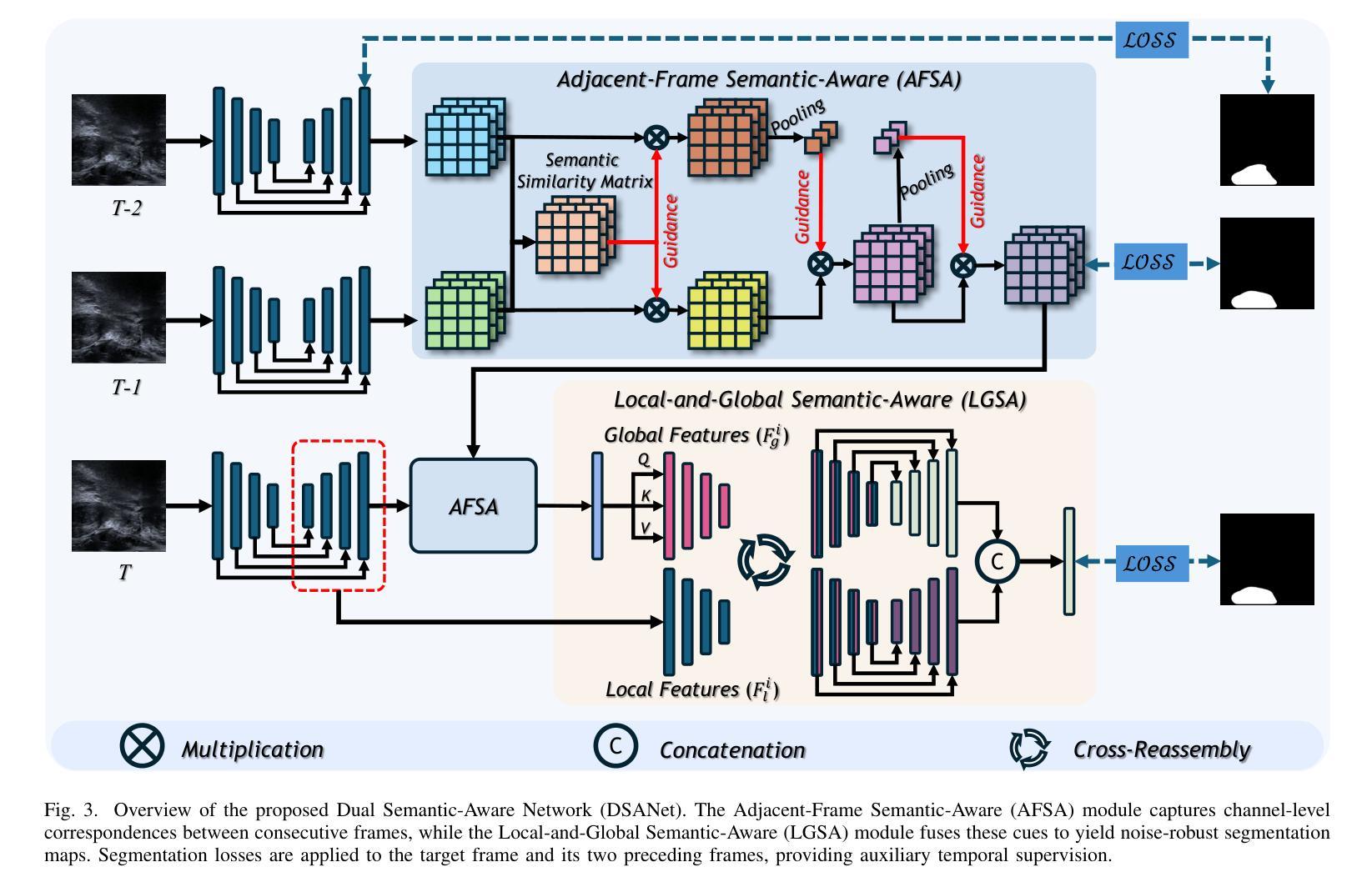
Dual Semantic-Aware Network for Noise Suppressed Ultrasound Video Segmentation
Authors:Ling Zhou, Runtian Yuan, Yi Liu, Yuejie Zhang, Rui Feng, Shang Gao
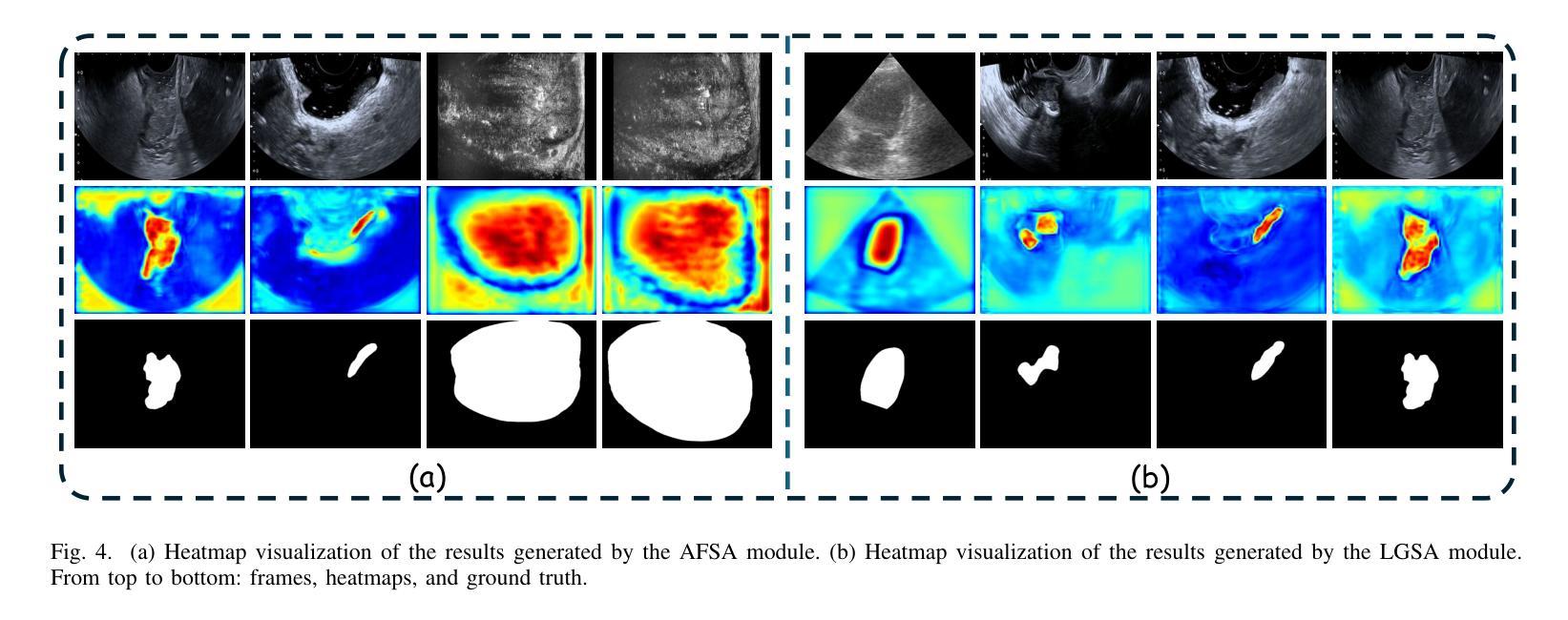
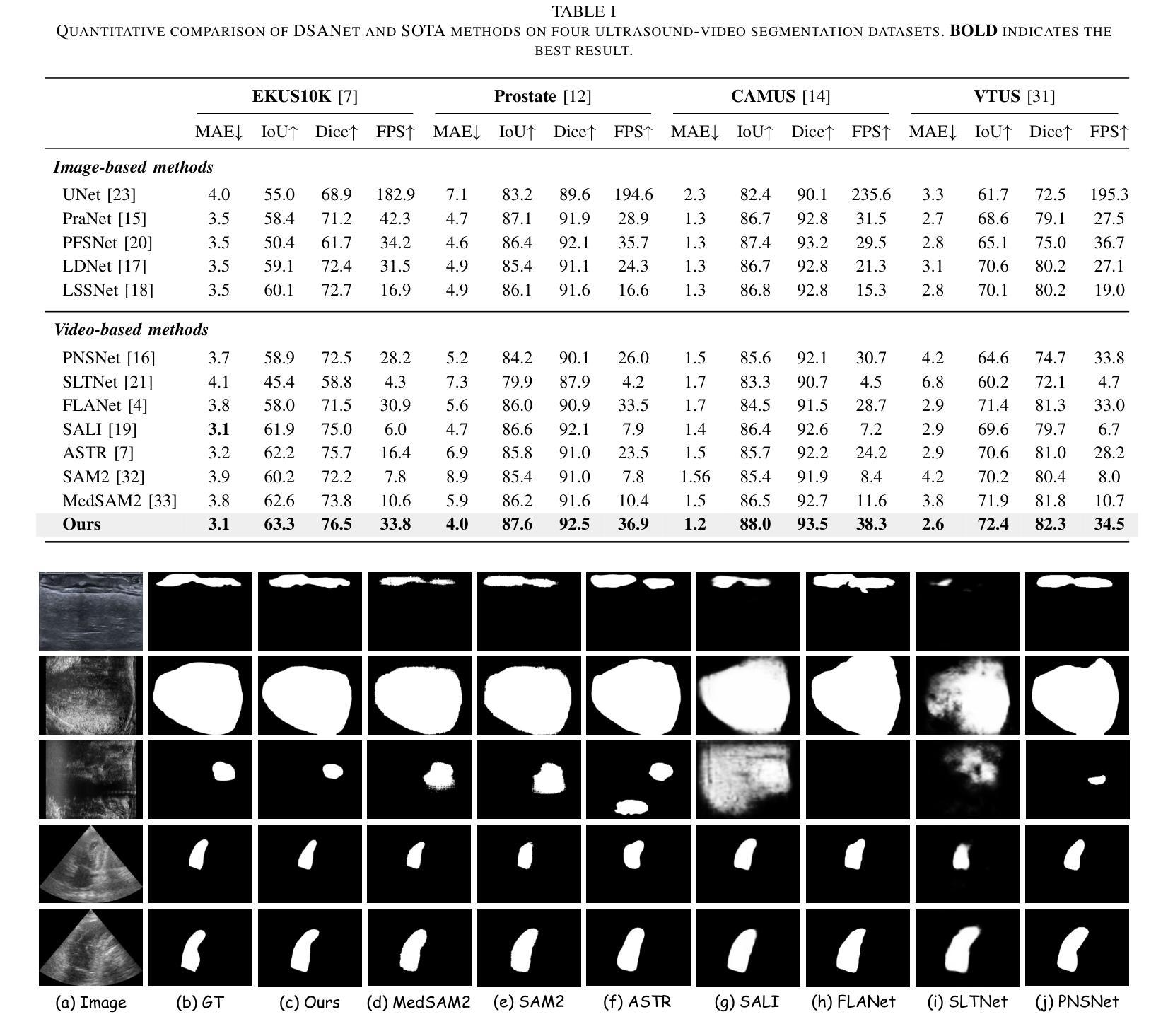
Ultrasound imaging is a prevalent diagnostic tool known for its simplicity and non-invasiveness. However, its inherent characteristics often introduce substantial noise, posing considerable challenges for automated lesion or organ segmentation in ultrasound video sequences. To address these limitations, we propose the Dual Semantic-Aware Network (DSANet), a novel framework designed to enhance noise robustness in ultrasound video segmentation by fostering mutual semantic awareness between local and global features. Specifically, we introduce an Adjacent-Frame Semantic-Aware (AFSA) module, which constructs a channel-wise similarity matrix to guide feature fusion across adjacent frames, effectively mitigating the impact of random noise without relying on pixel-level relationships. Additionally, we propose a Local-and-Global Semantic-Aware (LGSA) module that reorganizes and fuses temporal unconditional local features, which capture spatial details independently at each frame, with conditional global features that incorporate temporal context from adjacent frames. This integration facilitates multi-level semantic representation, significantly improving the model’s resilience to noise interference. Extensive evaluations on four benchmark datasets demonstrate that DSANet substantially outperforms state-of-the-art methods in segmentation accuracy. Moreover, since our model avoids pixel-level feature dependencies, it achieves significantly higher inference FPS than video-based methods, and even surpasses some image-based models. Code can be found in \href{https://github.com/ZhouL2001/DSANet}{DSANet}
超声成像是一种普遍的诊断工具,以其简单和非侵入性而闻名。然而,其固有特性往往会引入大量噪声,给超声视频序列中病变或器官的自动化分割带来了巨大的挑战。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了双语义感知网络(DSANet),这是一种新型框架,旨在通过促进局部和全局特征之间的相互语义感知,提高超声视频分割中的噪声鲁棒性。具体来说,我们引入了相邻帧语义感知(AFSA)模块,该模块构建通道相似度矩阵,以指导相邻帧之间的特征融合,在不需要依赖像素级关系的情况下有效减轻随机噪声的影响。此外,我们提出了局部和全局语义感知(LGSA)模块,该模块重新组织和融合了时间上的无条件局部特征,这些特征独立捕获每一帧的空间细节,以及与相邻帧的时间上下文相结合的条件全局特征。这种融合有助于多层次语义表示,大大提高了模型对噪声干扰的抗干扰能力。在四个基准数据集上的广泛评估表明,DSANet在分割精度上大大优于最新方法。而且,由于我们的模型避免了像素级特征依赖,因此与基于视频的方法相比,它实现了更高的推理帧率(FPS),甚至超过了某些基于图像模型的性能。代码可在DSANet的网址中找到:https://github.com/ZhouL2001/DSANet 。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:针对超声视频序列中的噪声问题,本文提出了一种名为Dual Semantic-Aware Network(DSANet)的新框架,旨在提高超声视频分割的噪声鲁棒性。通过局部和全局特征之间的互相语义感知,以及引入Adjacent-Frame Semantic-Aware(AFSA)和Local-and-Global Semantic-Aware(LGSA)模块,该框架有效减轻了噪声影响,提高了分割精度。
Key Takeaways:
- 超声成像由于其简洁性和无创性而受到广泛应用,但其中的噪声对自动化病变或器官分割带来了挑战。
- 提出了Dual Semantic-Aware Network(DSANet)框架,增强超声视频分割的噪声鲁棒性。
- DSANet通过AFSA模块构建通道相似性矩阵,实现相邻帧特征融合,减轻随机噪声影响。
- LGSA模块融合了独立的空间细节局部特征与包含时间上下文的条件全局特征,实现了多级别语义表示。
- DSANet在四个基准数据集上的评估结果表明,其在分割精度上显著优于最新方法。
- DSANet避免了像素级特征依赖,实现了较高的推理速度,超越了某些图像基方法。
点此查看论文截图

RT-OVAD: Real-Time Open-Vocabulary Aerial Object Detection via Image-Text Collaboration
Authors:Guoting Wei, Xia Yuan, Yu Liu, Zhenhao Shang, Xizhe Xue, Peng Wang, Kelu Yao, Chunxia Zhao, Haokui Zhang, Rong Xiao
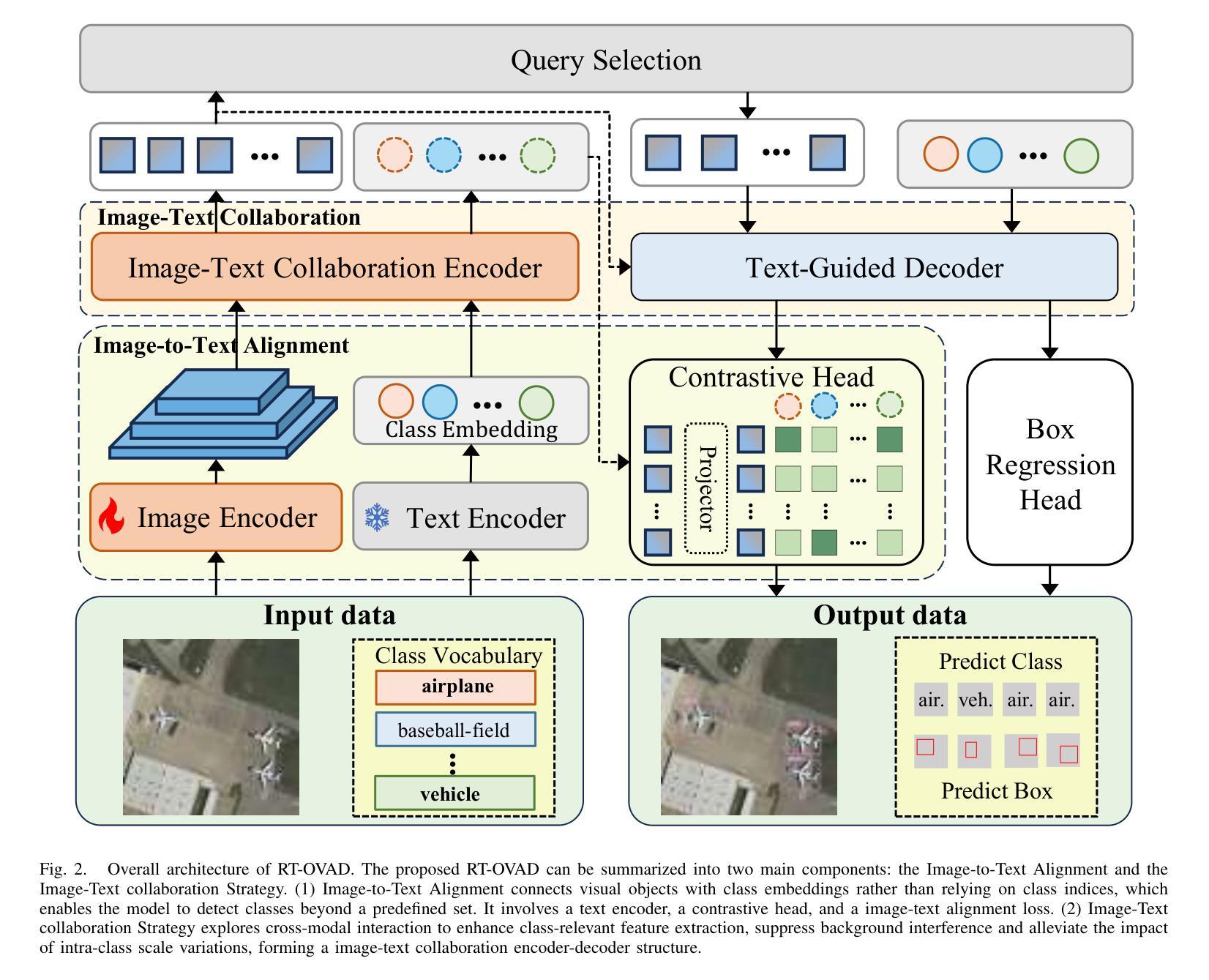
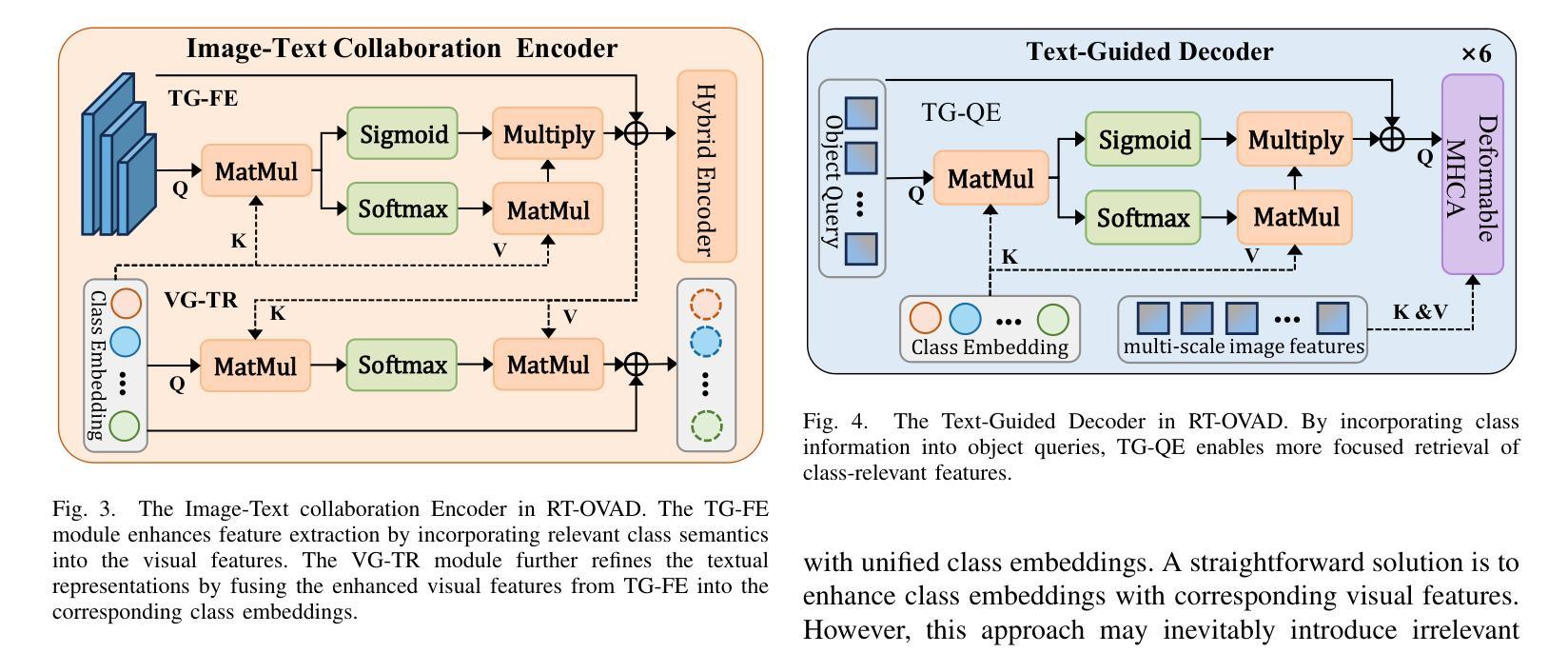
Aerial object detection plays a crucial role in numerous applications. However, most existing methods focus on detecting predefined object categories, limiting their applicability in real-world open scenarios. In this paper, we extend aerial object detection to open scenarios through image-text collaboration and propose RT-OVAD, the first real-time open-vocabulary detector for aerial scenes. Specifically, we first introduce an image-to-text alignment loss to replace the conventional category regression loss, thereby eliminating category constraints. Next, we propose a lightweight image-text collaboration strategy comprising an image-text collaboration encoder and a text-guided decoder. The encoder simultaneously enhances visual features and refines textual embeddings, while the decoder guides object queries to focus on class-relevant image features. This design further improves detection accuracy without incurring significant computational overhead. Extensive experiments demonstrate that RT-OVAD consistently outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods across open-vocabulary, zero-shot, and traditional closed-set detection tasks. For instance, on the open-vocabulary aerial detection benchmarks DIOR, DOTA-v2.0, and LAE-80C, RT-OVAD achieves 87.7 AP$_{50}$, 53.8 mAP, and 23.7 mAP, respectively, surpassing the previous state-of-the-art (LAE-DINO) by 2.2, 7.0, and 3.5 points. In addition, RT-OVAD achieves an inference speed of 34 FPS on an RTX 4090 GPU, approximately three times faster than LAE-DINO (10 FPS), meeting the real-time detection requirements of diverse applications. The code will be released at https://github.com/GT-Wei/RT-OVAD.
高空目标检测在众多应用中发挥着至关重要的作用。然而,现有的大多数方法主要关注预定目标类别的检测,限制了它们在现实开放场景中的应用。在本文中,我们通过图像文本协作将高空目标检测扩展到开放场景,并提出了RT-OVAD,即首个用于高空场景实时开放词汇检测器。具体来说,我们首先引入图像到文本的对齐损失来替换传统的类别回归损失,从而消除了类别约束。接下来,我们提出了一种轻量级的图像文本协作策略,包括图像文本协作编码器和文本引导解码器。编码器同时增强视觉特征和细化文本嵌入,而解码器引导目标查询聚焦于类别相关的图像特征。这种设计进一步提高了检测精度,且不会造成显著的计算开销。大量实验表明,RT-OVAD在开放词汇、零样本和传统的封闭集检测任务上均优于现有最先进的检测方法。例如,在开放词汇高空检测基准DIOR、DOTA-v2.0和LAE-80C上,RT-OVAD分别实现了87.7的AP50、53.8的mAP和23.7的mAP,分别超越了先前的最佳水平(LAE-DINO)2.2、7.0和3.5个点。此外,RT-OVAD在RTX 4090 GPU上的推理速度为每秒34帧,大约是LAE-DINO每秒10帧的三倍,满足了各种应用的实时检测要求。代码将在https://github.com/GT-Wei/RT-OVAD发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种用于开放场景下的实时空中目标检测的新方法。通过图像文本的协同合作,提出了首个实时开放词汇表检测器RT-OVAD。采用图像到文本的匹配损失替代传统分类回归损失,消除类别约束。提出轻量化图像文本协同策略,包含图像文本协同编码器和文本引导的解码器。实验证明,RT-OVAD在开放词汇表、零样本和传统封闭集检测任务上均优于现有先进技术。
Key Takeaways
- 论文介绍了空中目标检测在多种应用中的重要性,并指出大多数现有方法局限于预定义目标类别的检测,限制了其在现实世界的开放场景中的应用。
- 提出了一种新的实时开放词汇表检测器RT-OVAD,适用于空中场景的开放场景检测。
- 采用图像到文本的匹配损失,消除类别约束,改进了传统的类别回归损失。
- RT-OVAD采用了一种轻量级的图像文本协同策略,包括图像文本协同编码器和文本引导的解码器,提高了检测精度,同时不会增加太多计算负担。
- 实验结果显示,RT-OVAD在多个公开数据集上表现优异,包括DIOR、DOTA-v2.0和LAE-80C。
- RT-OVAD实现了快速的推理速度,达到34 FPS,满足许多实时应用的需求。
点此查看论文截图