⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-12 更新
RTR-GS: 3D Gaussian Splatting for Inverse Rendering with Radiance Transfer and Reflection
Authors:Yongyang Zhou, Fang-Lue Zhang, Zichen Wang, Lei Zhang
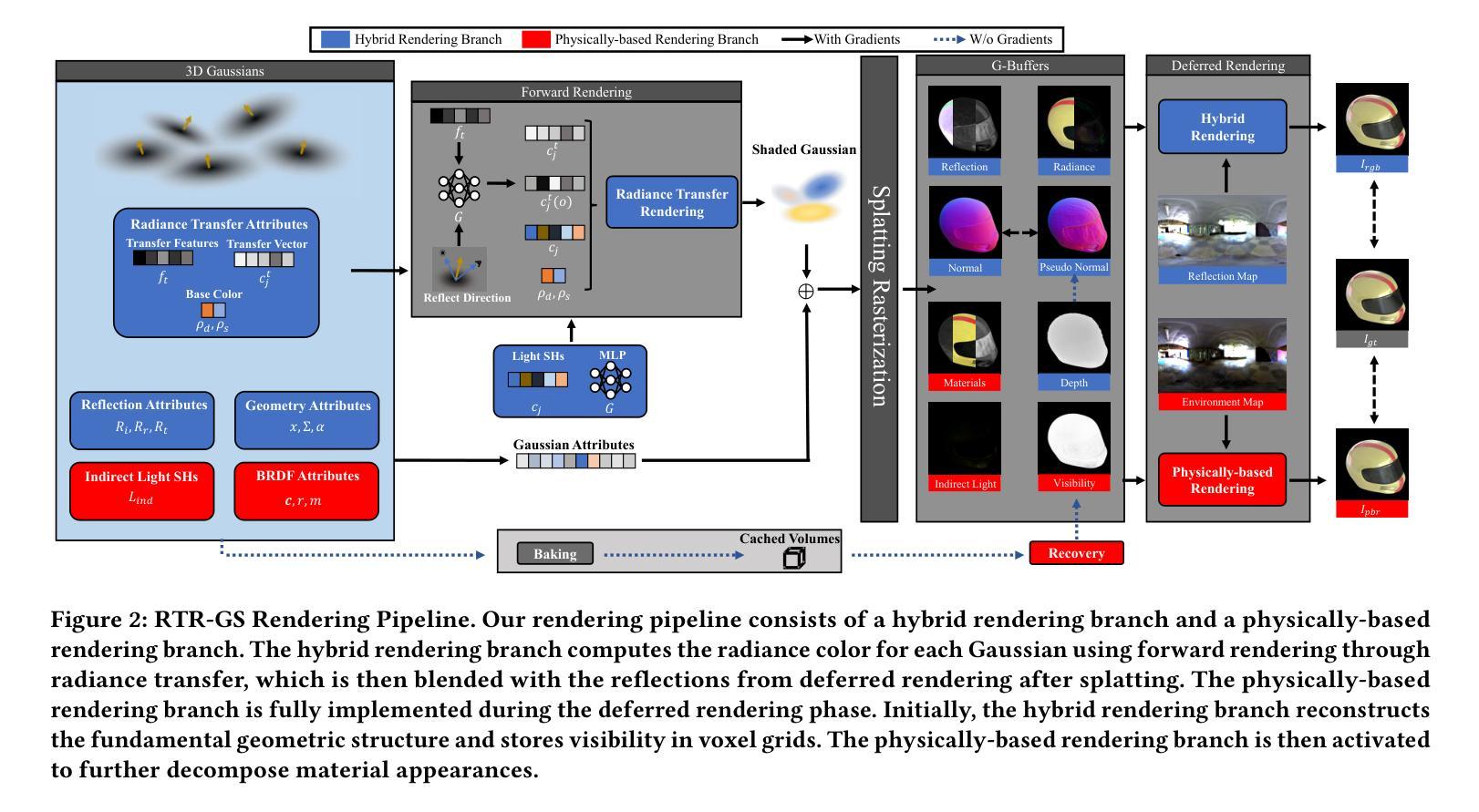
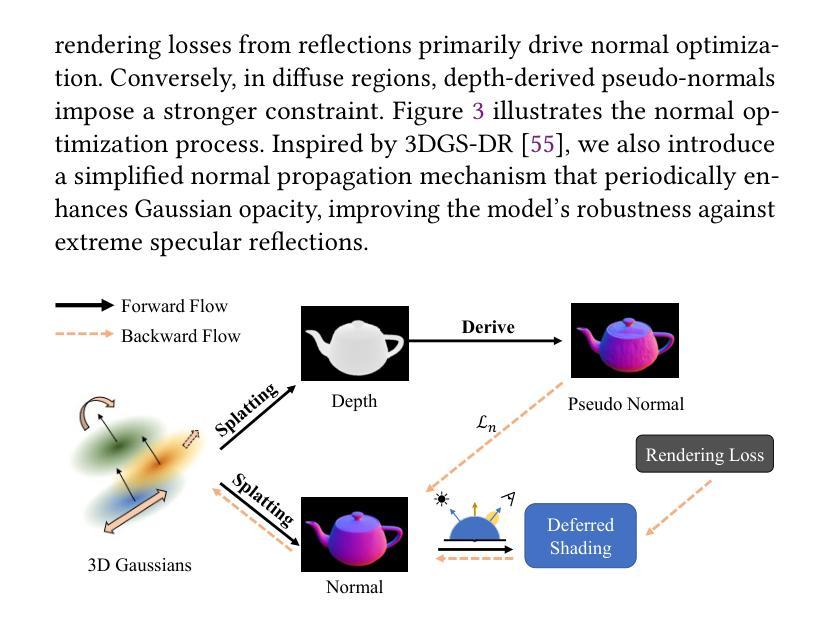
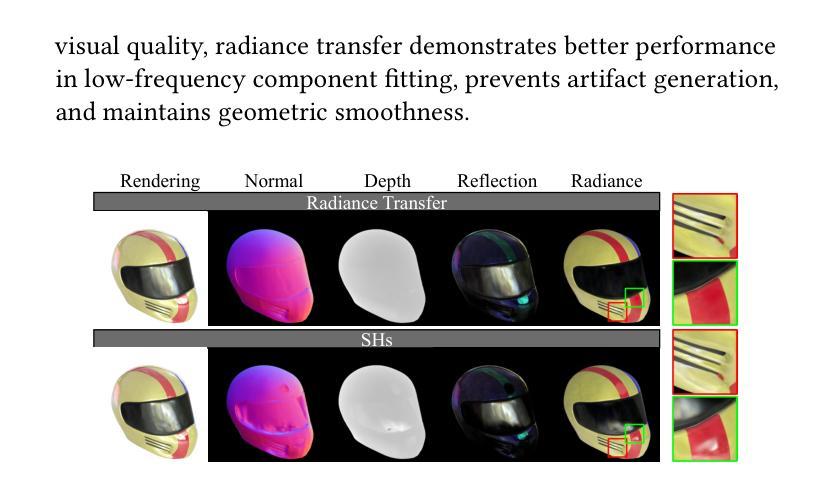
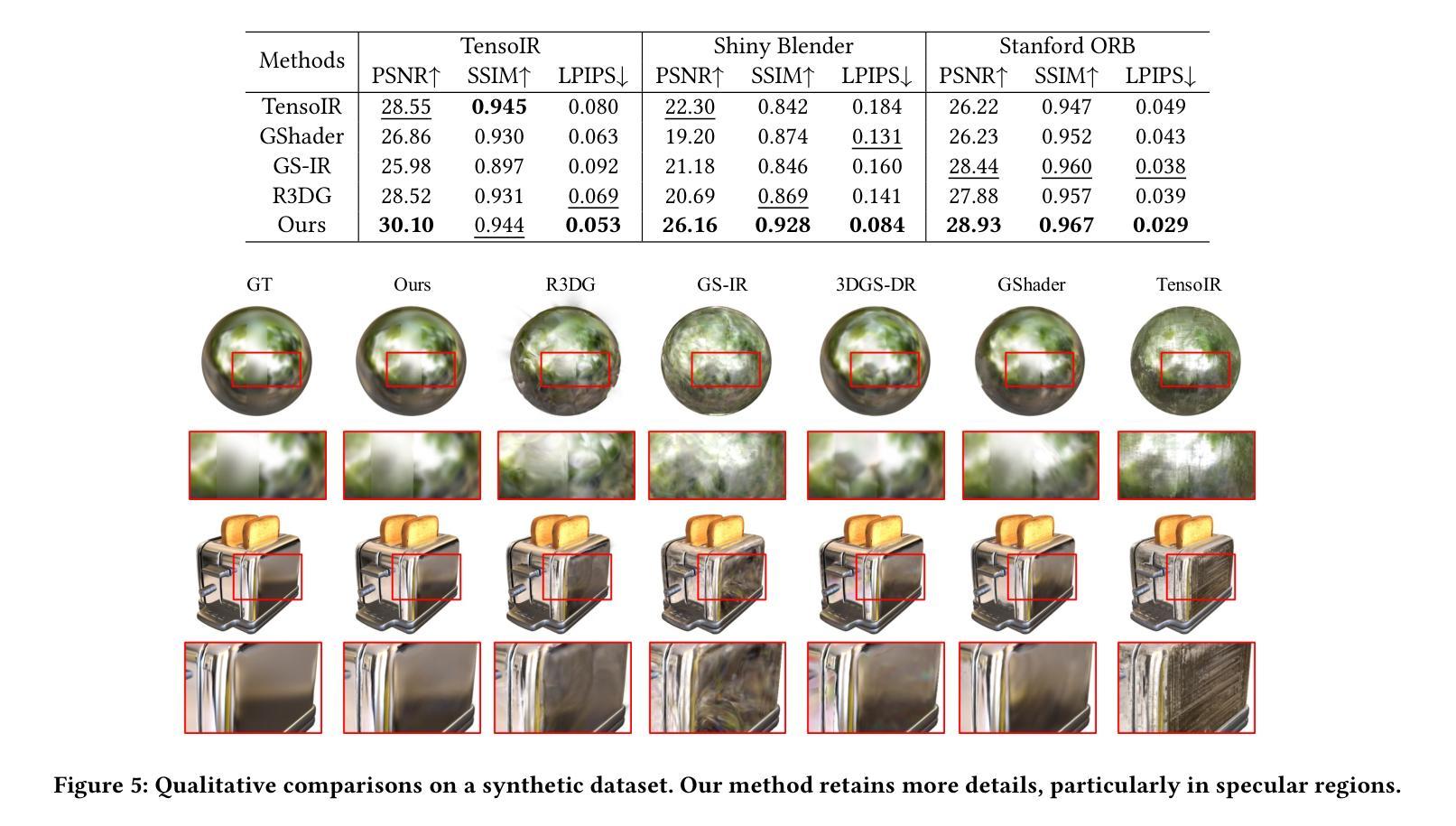
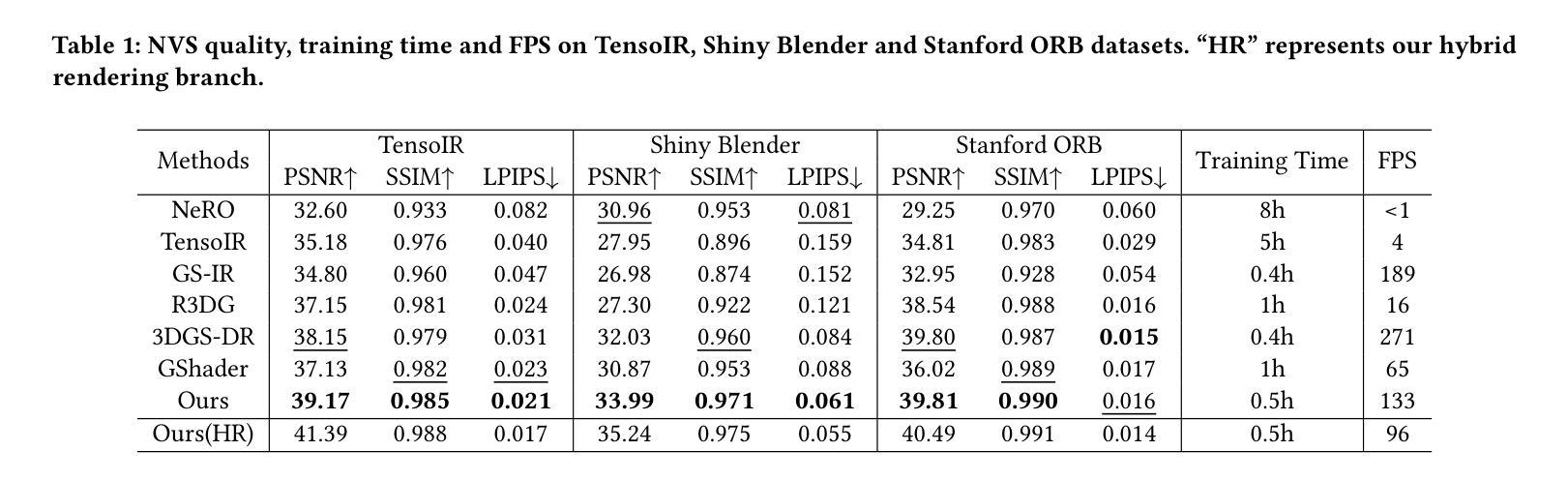
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has demonstrated impressive capabilities in novel view synthesis. However, rendering reflective objects remains a significant challenge, particularly in inverse rendering and relighting. We introduce RTR-GS, a novel inverse rendering framework capable of robustly rendering objects with arbitrary reflectance properties, decomposing BRDF and lighting, and delivering credible relighting results. Given a collection of multi-view images, our method effectively recovers geometric structure through a hybrid rendering model that combines forward rendering for radiance transfer with deferred rendering for reflections. This approach successfully separates high-frequency and low-frequency appearances, mitigating floating artifacts caused by spherical harmonic overfitting when handling high-frequency details. We further refine BRDF and lighting decomposition using an additional physically-based deferred rendering branch. Experimental results show that our method enhances novel view synthesis, normal estimation, decomposition, and relighting while maintaining efficient training inference process.
3D高斯溅出(3DGS)在新视角合成方面展现出了令人印象深刻的能力。然而,渲染反射物体仍然是一个巨大的挑战,特别是在逆向渲染和重新照明方面。我们引入了RTR-GS,这是一种新型的逆向渲染框架,能够稳健地呈现具有任意反射特性的物体,分解BRDF和照明,并提供可靠的重新照明结果。给定一组多视角图像,我们的方法通过一个混合渲染模型有效地恢复几何结构,该模型结合了用于辐射量传递的前向渲染和用于反射的延迟渲染。这种方法成功地分离了高频和低频外观,在处理高频细节时缓解了由于球面谐波过度拟合导致的浮动伪影。我们进一步使用基于物理的附加延迟渲染分支来完善BRDF和照明分解。实验结果表明,我们的方法提高了新视角合成、法线估计、分解和重新照明的效果,同时保持了高效的训练推理过程。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages
Summary
3DGS在新型视角合成方面展现出卓越性能,但在处理反射物体时存在挑战。提出RTR-GS新型逆向渲染框架,具备稳健渲染任意反射物体能力,可分解BRDF和照明,实现可信的重新照明效果。结合正向渲染辐射传输与延迟渲染反射的混合渲染模型,有效恢复几何结构,分离高频和低频外观,减轻球形谐波过度拟合导致的高频细节浮动伪影。使用基于物理的延迟渲染分支进一步精细BRDF和照明分解。实验结果显示,该方法提升新型视角合成、法线估计、分解和重新照明效果,同时保持高效训练推理过程。
Key Takeaways
- RTR-GS框架能有效处理反射物体的渲染,具有任意反射物体的稳健渲染能力。
- 提出的混合渲染模型结合正向渲染和延迟渲染,以恢复几何结构并分离高频和低频外观。
- 该方法能够分解BRDF(双向反射分布函数)和照明,实现可信的重新照明效果。
- 通过物理延迟渲染分支进一步精细BRDF和照明分解,提高性能。
- 该方法改善了球形谐波过度拟合引起的高频细节浮动伪影问题。
- 实验结果显示,该方法在多个方面(如视角合成、法线估计等)表现优越。
点此查看论文截图

MUVOD: A Novel Multi-view Video Object Segmentation Dataset and A Benchmark for 3D Segmentation
Authors:Bangning Wei, Joshua Maraval, Meriem Outtas, Kidiyo Kpalma, Nicolas Ramin, Lu Zhang
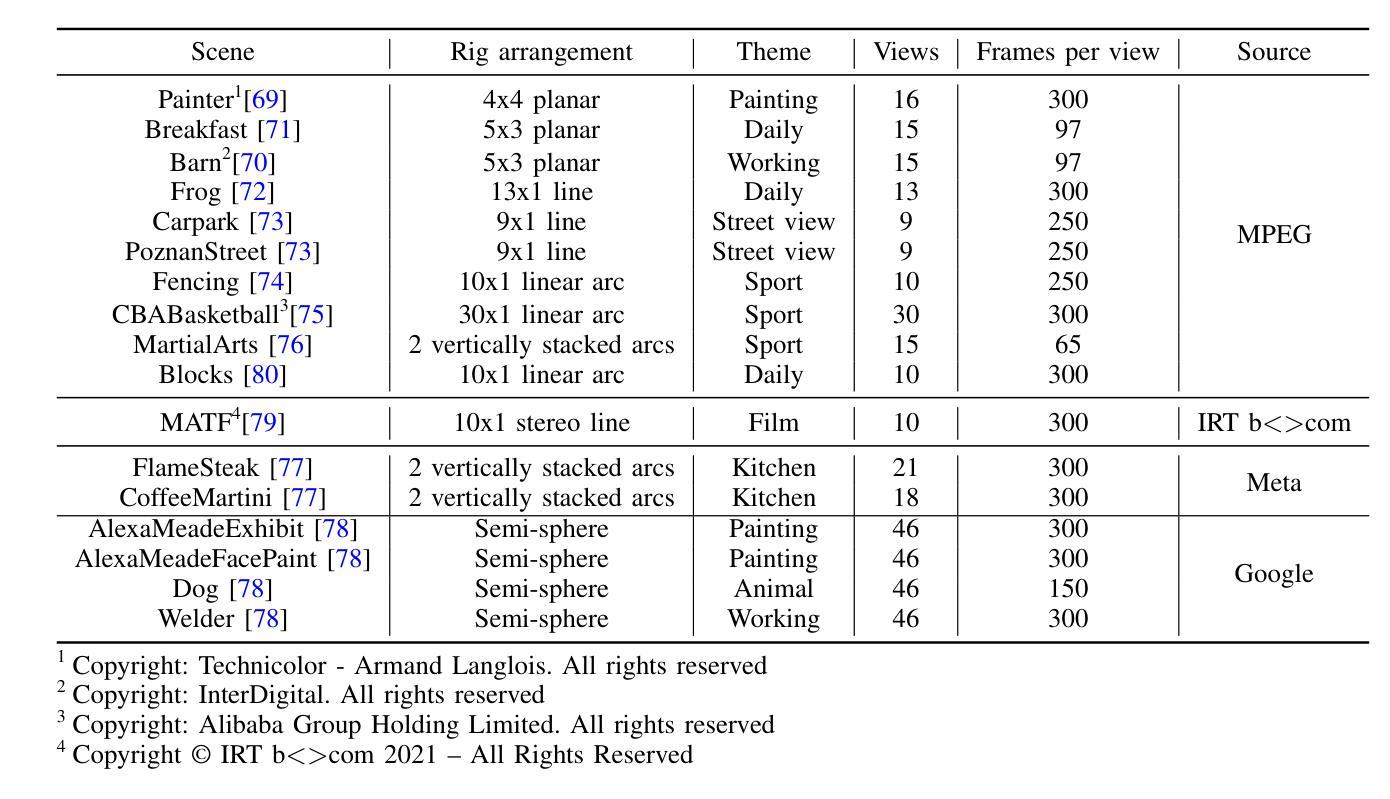
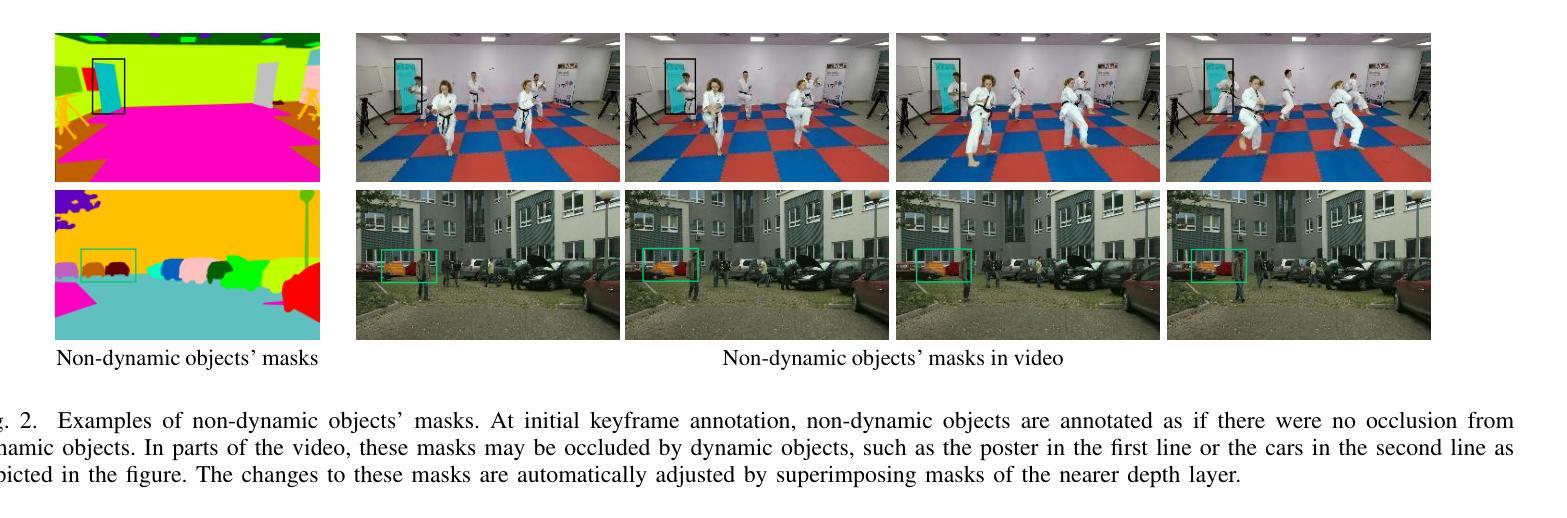
The application of methods based on Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D GS) have steadily gained popularity in the field of 3D object segmentation in static scenes. These approaches demonstrate efficacy in a range of 3D scene understanding and editing tasks. Nevertheless, the 4D object segmentation of dynamic scenes remains an underexplored field due to the absence of a sufficiently extensive and accurately labelled multi-view video dataset. In this paper, we present MUVOD, a new multi-view video dataset for training and evaluating object segmentation in reconstructed real-world scenarios. The 17 selected scenes, describing various indoor or outdoor activities, are collected from different sources of datasets originating from various types of camera rigs. Each scene contains a minimum of 9 views and a maximum of 46 views. We provide 7830 RGB images (30 frames per video) with their corresponding segmentation mask in 4D motion, meaning that any object of interest in the scene could be tracked across temporal frames of a given view or across different views belonging to the same camera rig. This dataset, which contains 459 instances of 73 categories, is intended as a basic benchmark for the evaluation of multi-view video segmentation methods. We also present an evaluation metric and a baseline segmentation approach to encourage and evaluate progress in this evolving field. Additionally, we propose a new benchmark for 3D object segmentation task with a subset of annotated multi-view images selected from our MUVOD dataset. This subset contains 50 objects of different conditions in different scenarios, providing a more comprehensive analysis of state-of-the-art 3D object segmentation methods. Our proposed MUVOD dataset is available at https://volumetric-repository.labs.b-com.com/#/muvod.
基于神经辐射场(NeRF)和3D高斯拼贴(3D GS)的方法在静态场景的3D对象分割领域逐渐流行起来。这些方法在各种3D场景理解和编辑任务中表现出有效性。然而,由于缺少足够广泛和精确标注的多视角视频数据集,动态场景的4D对象分割仍然是一个未被充分探索的领域。在本文中,我们介绍了MUVOD,这是一个用于训练和评估重建现实世界场景中的对象分割的多视角视频数据集。所选择的17个场景描述了各种室内或室外活动,是从不同类型相机装置的不同数据源集中收集的。每个场景包含至少9个视角,最多46个视角。我们提供了7830张RGB图像(每段视频30帧)及其相应的4D运动分割掩膜,这意味着场景中的任何感兴趣的对象都可以在给定视角的时间帧内或在属于同一相机装置的不同视角中被追踪。这个包含73类459个实例的数据集旨在作为多视角视频分割方法评估的基本基准。我们还介绍了一种评估指标和一种基准分割方法,以鼓励和评估这一不断发展的领域的进展。此外,我们从MUVOD数据集中选择了一部分标注的多视角图像,提出了一个新的3D对象分割任务的基准。这个子集包含了不同场景下50个不同条件下的对象,为最新的3D对象分割方法提供了更全面的分析。我们提出的MUVOD数据集可在https://volumetric-repository.labs.b-com.com/#/muvod获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种新的多视角视频数据集MUVOD,用于训练和评价重建现实场景中对象分割的技术。数据集包含多个室内外活动场景,至少包含9个视角,最多包含46个视角。它包含具有相应分割掩码的RGB图像,旨在成为多视角视频分割方法的基准测试数据集。此外,还提出了一个针对特定子集的新三维物体分割任务基准。该数据集用于评估静态场景三维物体分割和动态场景四维度物体分割技术性能优劣的关键评估资源。对数据的收集和构成进行了详细阐述,并提供了数据访问链接。
Key Takeaways
- 方法基于NeRF和3D GS的NeRF技术应用于三维物体分割逐渐被大众所重视并广受欢迎。该技术可在各类重建三维场景的静态画面分析中获得实效和应用于内容编辑的便捷工作等环节中显现效用优势。
点此查看论文截图


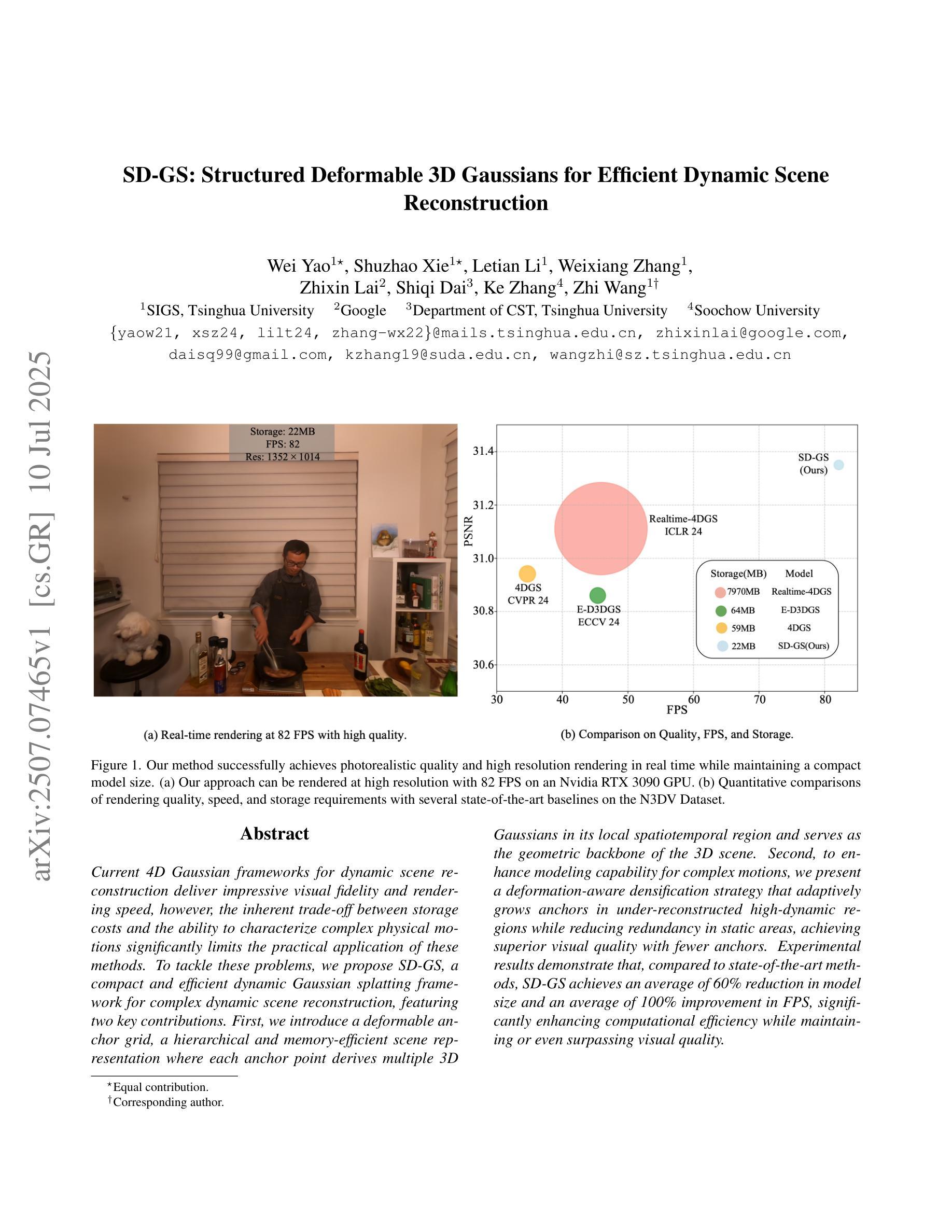
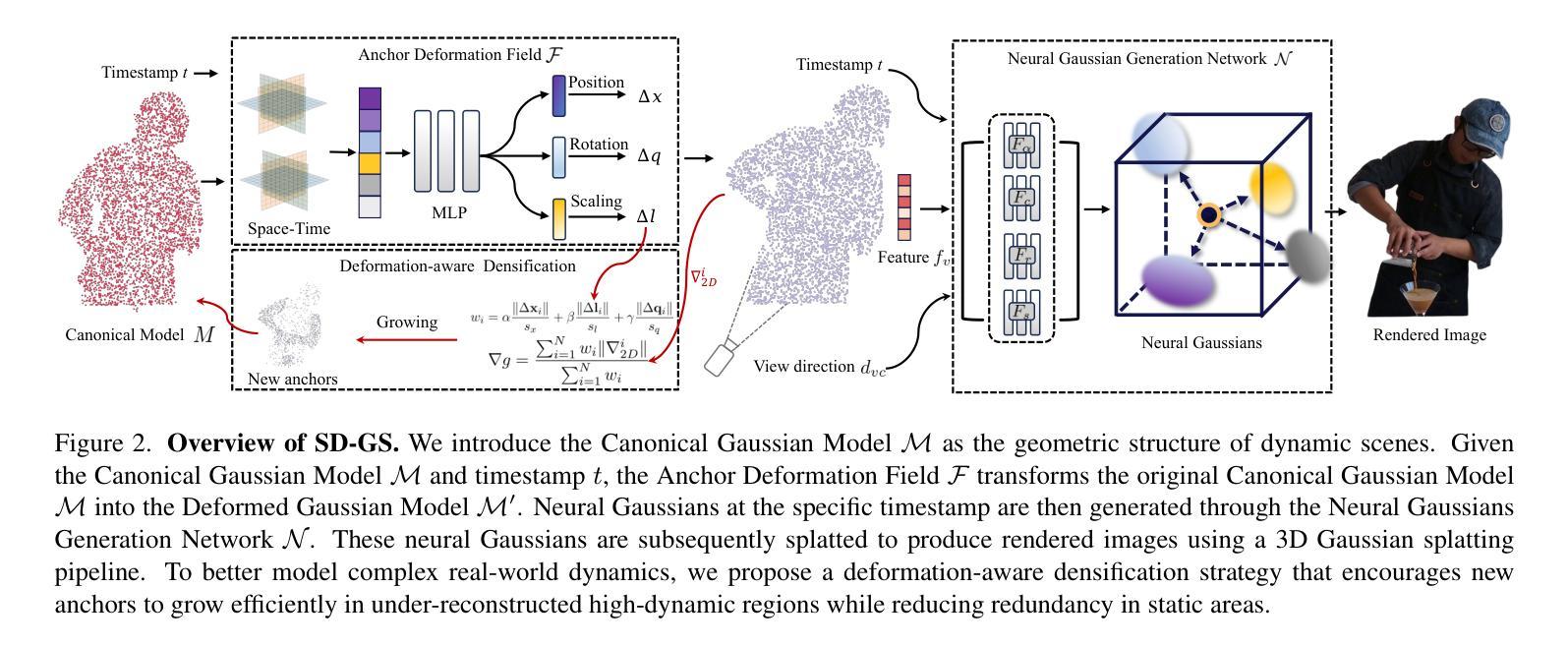
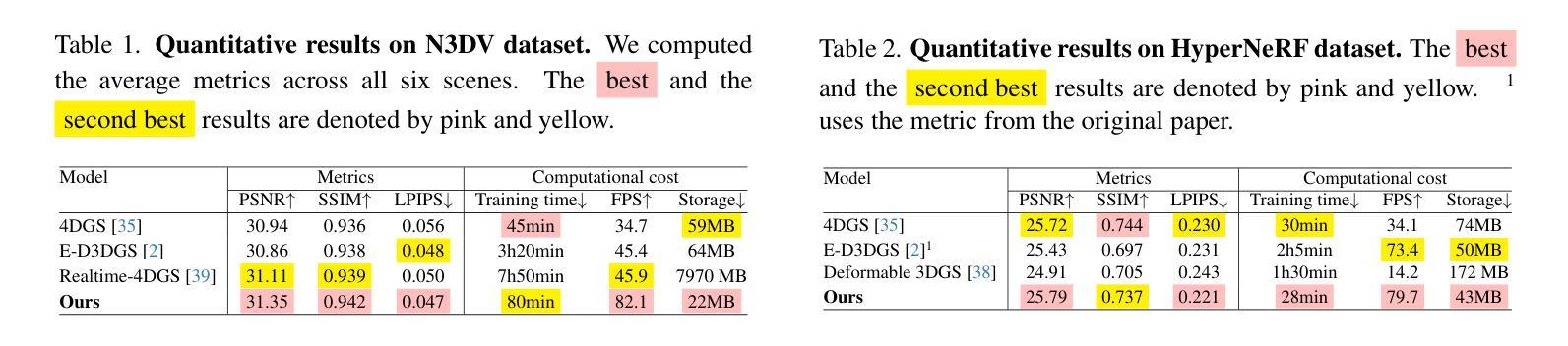
SD-GS: Structured Deformable 3D Gaussians for Efficient Dynamic Scene Reconstruction
Authors:Wei Yao, Shuzhao Xie, Letian Li, Weixiang Zhang, Zhixin Lai, Shiqi Dai, Ke Zhang, Zhi Wang
Current 4D Gaussian frameworks for dynamic scene reconstruction deliver impressive visual fidelity and rendering speed, however, the inherent trade-off between storage costs and the ability to characterize complex physical motions significantly limits the practical application of these methods. To tackle these problems, we propose SD-GS, a compact and efficient dynamic Gaussian splatting framework for complex dynamic scene reconstruction, featuring two key contributions. First, we introduce a deformable anchor grid, a hierarchical and memory-efficient scene representation where each anchor point derives multiple 3D Gaussians in its local spatiotemporal region and serves as the geometric backbone of the 3D scene. Second, to enhance modeling capability for complex motions, we present a deformation-aware densification strategy that adaptively grows anchors in under-reconstructed high-dynamic regions while reducing redundancy in static areas, achieving superior visual quality with fewer anchors. Experimental results demonstrate that, compared to state-of-the-art methods, SD-GS achieves an average of 60% reduction in model size and an average of 100% improvement in FPS, significantly enhancing computational efficiency while maintaining or even surpassing visual quality.
当前用于动态场景重建的4D高斯框架提供了令人印象深刻的视觉保真度和渲染速度。然而,存储成本与表征复杂物理运动的能力之间的固有折衷,极大地限制了这些方法的实际应用。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了SD-GS,这是一种紧凑且高效的动态高斯喷射框架,用于复杂的动态场景重建,具有两个主要贡献。首先,我们引入了一种可变形锚点网格,这是一种分层且内存高效的场景表示,其中每个锚点在其局部时空区域中衍生出多个3D高斯,并作为3D场景的结构骨架。其次,为了提高对复杂运动的建模能力,我们提出了一种基于变形的加密策略,该策略在重建不足的高动态区域中自适应地增加锚点数量,同时减少静态区域的冗余性,以实现使用更少锚点达到卓越视觉质量的效果。实验结果表明,与最新方法相比,SD-GS实现了模型大小平均减少60%,每秒帧数(FPS)平均提高100%,在保持甚至超越视觉质量的同时,显著提高了计算效率。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
新一代四维高斯框架在动态场景重建中展现出卓越的视觉保真度和渲染速度。然而,存储成本与复杂物理运动表征能力之间的固有权衡限制了其实际应用。为解决这些问题,我们提出了SD-GS,这是一种紧凑且高效的动态高斯飞溅框架,用于复杂动态场景重建。其两大贡献为:引入可变形锚点网格,一种分层且内存高效的场景表示方法,每个锚点在其局部时空区域内衍生多个三维高斯,作为三维场景几何骨架;并提出变形感知加密策略,自适应增长在重建不足的高动态区域中的锚点,同时减少静态区域的冗余,以更少锚点实现优越视觉质量。实验结果表明,与最新方法相比,SD-GS模型大小平均减少60%,帧率(FPS)平均提高100%,在计算效率提高的同时,维持甚至超越视觉品质。
Key Takeaways
- 当前四维高斯框架在动态场景重建中具有高视觉保真度和渲染速度。
- 存储成本与表征复杂物理运动能力之间的权衡限制了其实际应用。
- SD-GS框架被提出以解决这些问题,具有紧凑且高效的特点。
- SD-GS引入可变形锚点网格,作为场景的三维几何骨架。
- 变形感知加密策略被提出,以自适应增长高动态区域的锚点并减少静态区域的冗余。
- 实验结果表明SD-GS在模型大小和帧率上有显著提高,同时维持或超越视觉质量。
点此查看论文截图

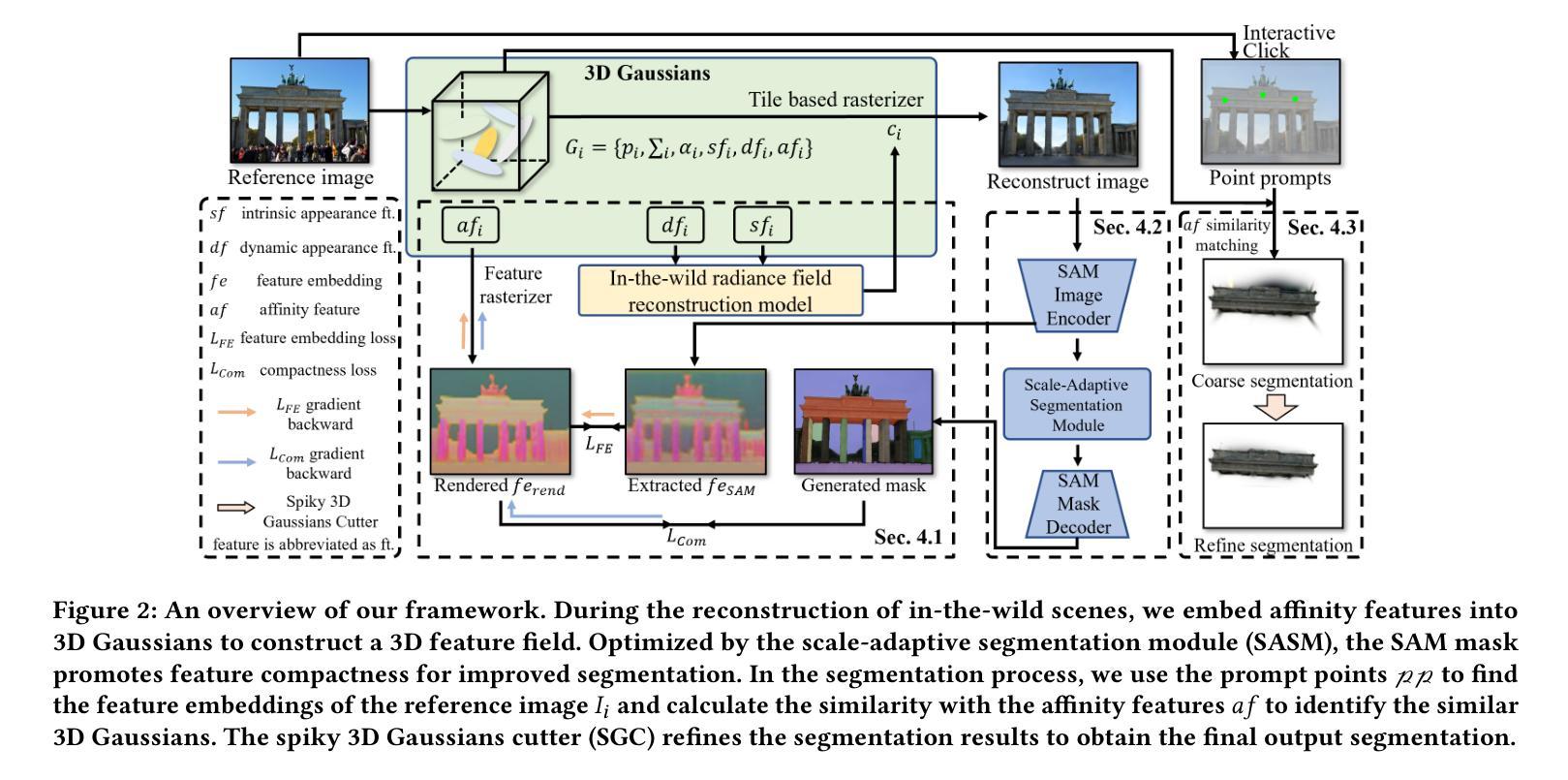
Seg-Wild: Interactive Segmentation based on 3D Gaussian Splatting for Unconstrained Image Collections
Authors:Yongtang Bao, Chengjie Tang, Yuze Wang, Haojie Li
Reconstructing and segmenting scenes from unconstrained photo collections obtained from the Internet is a novel but challenging task. Unconstrained photo collections are easier to get than well-captured photo collections. These unconstrained images suffer from inconsistent lighting and transient occlusions, which makes segmentation challenging. Previous segmentation methods cannot address transient occlusions or accurately restore the scene’s lighting conditions. Therefore, we propose Seg-Wild, an interactive segmentation method based on 3D Gaussian Splatting for unconstrained image collections, suitable for in-the-wild scenes. We integrate multi-dimensional feature embeddings for each 3D Gaussian and calculate the feature similarity between the feature embeddings and the segmentation target to achieve interactive segmentation in the 3D scene. Additionally, we introduce the Spiky 3D Gaussian Cutter (SGC) to smooth abnormal 3D Gaussians. We project the 3D Gaussians onto a 2D plane and calculate the ratio of 3D Gaussians that need to be cut using the SAM mask. We also designed a benchmark to evaluate segmentation quality in in-the-wild scenes. Experimental results demonstrate that compared to previous methods, Seg-Wild achieves better segmentation results and reconstruction quality. Our code will be available at https://github.com/Sugar0725/Seg-Wild.
从互联网上获取的无约束照片集进行场景重建和分割是一项新颖且具有挑战性的任务。无约束照片集比拍摄良好的照片集更容易获得。这些无约束的图像受到光照不一致和瞬时遮挡的影响,使得分割更具挑战性。以往的分割方法无法处理瞬时遮挡或准确恢复场景的照明条件。因此,我们提出了Seg-Wild,这是一种基于3D高斯拼贴的无约束图像集合的交互式分割方法,适用于自然场景。我们对每个3D高斯进行多维特征嵌入,并计算特征嵌入与分割目标之间的特征相似性,以实现3D场景中的交互式分割。此外,我们引入了尖峰3D高斯切割器(SGC)来平滑异常的3D高斯。我们将3D高斯投影到2D平面上,并计算需要使用SAM蒙版切割的3D高斯的比例。我们还设计了一个基准测试来评估自然场景中的分割质量。实验结果表明,与以往的方法相比,Seg-Wild实现了更好的分割效果和重建质量。我们的代码将在https://github.com/Sugar0725/Seg-Wild上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
针对互联网上获取的无约束图片集合的场景重建和分割是一项新颖且具挑战性的任务。由于光照不一致和瞬时遮挡,无约束图像给分割带来了困难。为此,我们提出了基于3D高斯拼贴技术的交互式分割方法Seg-Wild,适用于自然场景。该方法整合了多维特征嵌入,通过计算特征嵌入与分割目标之间的特征相似性实现交互式分割。此外,我们还引入了尖峰型三维高斯切割器(SGC)来平滑异常的三维高斯。实验结果表明,与以往方法相比,Seg-Wild在分割效果和重建质量上表现更佳。代码将在https://github.com/Sugar0725/Seg-Wild上公开。
Key Takeaways:
- 无约束图片集合的场景重建和分割是一项挑战,因为图片的光照不一致和瞬时遮挡。
- Seg-Wild是一种针对无约束图像集合的交互式分割方法,基于3D高斯拼贴技术。
- Seg-Wild整合多维特征嵌入,通过计算特征相似度实现交互式分割。
- 引入尖峰型三维高斯切割器(SGC)以平滑异常的三维高斯。
- 建立了一个用于评估自然场景分割质量的基准测试。
点此查看论文截图

LangSplatV2: High-dimensional 3D Language Gaussian Splatting with 450+ FPS
Authors:Wanhua Li, Yujie Zhao, Minghan Qin, Yang Liu, Yuanhao Cai, Chuang Gan, Hanspeter Pfister
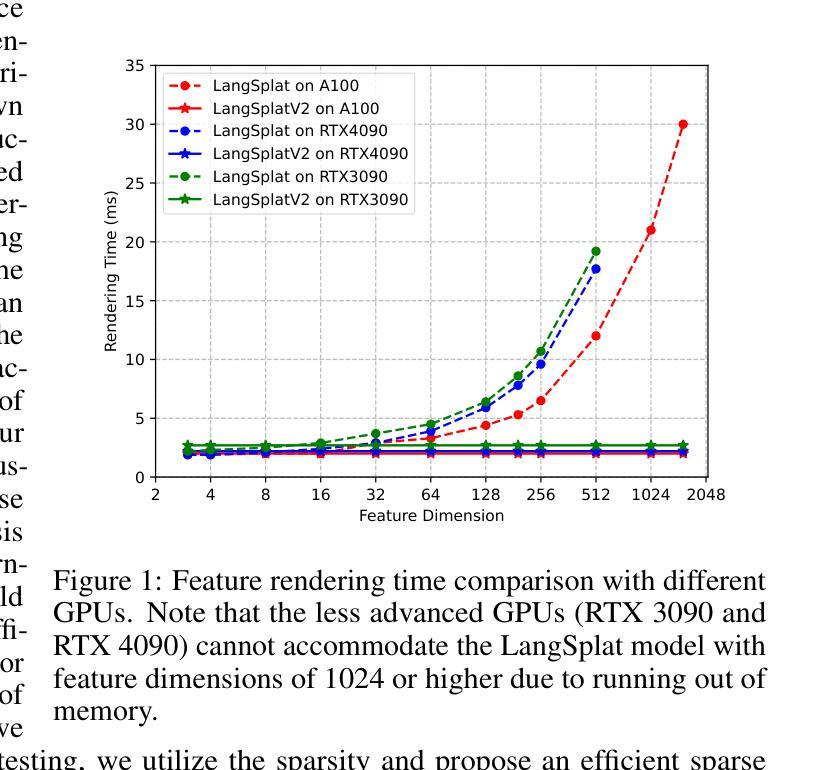
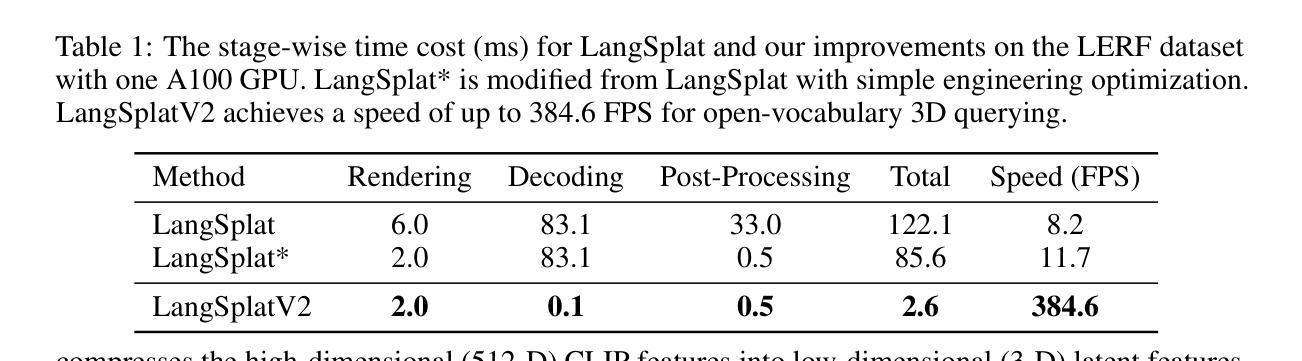
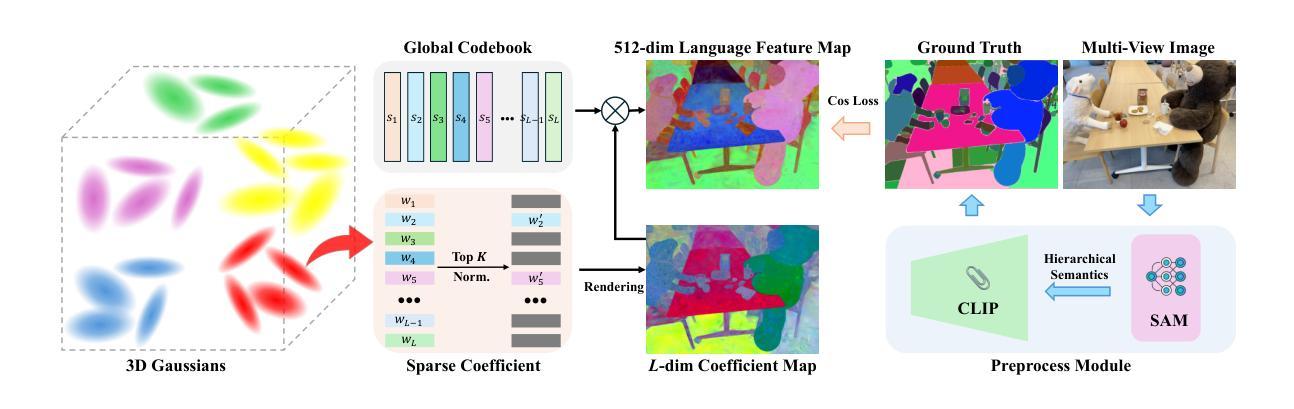
In this paper, we introduce LangSplatV2, which achieves high-dimensional feature splatting at 476.2 FPS and 3D open-vocabulary text querying at 384.6 FPS for high-resolution images, providing a 42 $\times$ speedup and a 47 $\times$ boost over LangSplat respectively, along with improved query accuracy. LangSplat employs Gaussian Splatting to embed 2D CLIP language features into 3D, significantly enhancing speed and learning a precise 3D language field with SAM semantics. Such advancements in 3D language fields are crucial for applications that require language interaction within complex scenes. However, LangSplat does not yet achieve real-time inference performance (8.2 FPS), even with advanced A100 GPUs, severely limiting its broader application. In this paper, we first conduct a detailed time analysis of LangSplat, identifying the heavyweight decoder as the primary speed bottleneck. Our solution, LangSplatV2 assumes that each Gaussian acts as a sparse code within a global dictionary, leading to the learning of a 3D sparse coefficient field that entirely eliminates the need for a heavyweight decoder. By leveraging this sparsity, we further propose an efficient sparse coefficient splatting method with CUDA optimization, rendering high-dimensional feature maps at high quality while incurring only the time cost of splatting an ultra-low-dimensional feature. Our experimental results demonstrate that LangSplatV2 not only achieves better or competitive query accuracy but is also significantly faster. Codes and demos are available at our project page: https://langsplat-v2.github.io.
本文介绍了LangSplatV2,它在高分辨率图像上实现了高达476.2 FPS的高维特征平铺和高达384.6 FPS的3D开放词汇文本查询,与LangSplat相比,分别提供了42倍和47倍的速度提升,同时提高了查询准确性。LangSplat采用高斯平铺技术将二维CLIP语言特征嵌入到三维空间中,大大提高了速度,并学习了具有SAM语义的精确三维语言场。这种三维语言场的进步对于需要在复杂场景中进行语言交互的应用至关重要。然而,即使使用先进的A100 GPU,LangSplat尚未实现实时推理性能(每秒仅处理8.2帧),这严重限制了其更广泛的应用。本文首先详细分析了LangSplat的时间消耗情况,确定了重量级解码器是主要的速度瓶颈。我们的解决方案是LangSplatV2,它假设每个高斯在全球词典中作为一个稀疏代码出现,从而学习一个三维稀疏系数场,完全消除了对重量级解码器的需求。通过利用这种稀疏性,我们进一步提出了高效的稀疏系数平铺方法,并使用CUDA进行优化,以高质量渲染高维特征图,同时只产生超低维特征平铺的时间成本。实验结果表明,LangSplatV2不仅具有更好的或竞争力的查询准确性,而且速度也更快。相关代码和演示可在我们的项目页面查看:https://langsplat-v2.github.io。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://langsplat-v2.github.io
Summary
论文介绍了LangSplatV2技术,该技术实现了高维特征展铺,提高了查询准确性,并在高分辨率图像上实现了高速的3D开放词汇查询。通过采用高斯展铺嵌入技术,将二维CLIP语言特征嵌入到三维中,增强了速度和精确的三维语言场学习能力。论文详细分析了LangSplat的时间瓶颈,并提出了LangSplatV2解决方案,通过利用稀疏系数场和高效的稀疏系数展铺方法,实现了显著的速度提升。
Key Takeaways
- LangSplatV2实现了高维特征展铺,提高了查询准确性。
- LangSplatV2在3D开放词汇查询方面实现了显著的速度提升,相对于LangSplat分别实现了42倍和47倍的速度提升。
- LangSplat采用高斯展铺嵌入技术,将二维CLIP语言特征嵌入到三维中,增强了速度和精确的三维语言场学习能力。
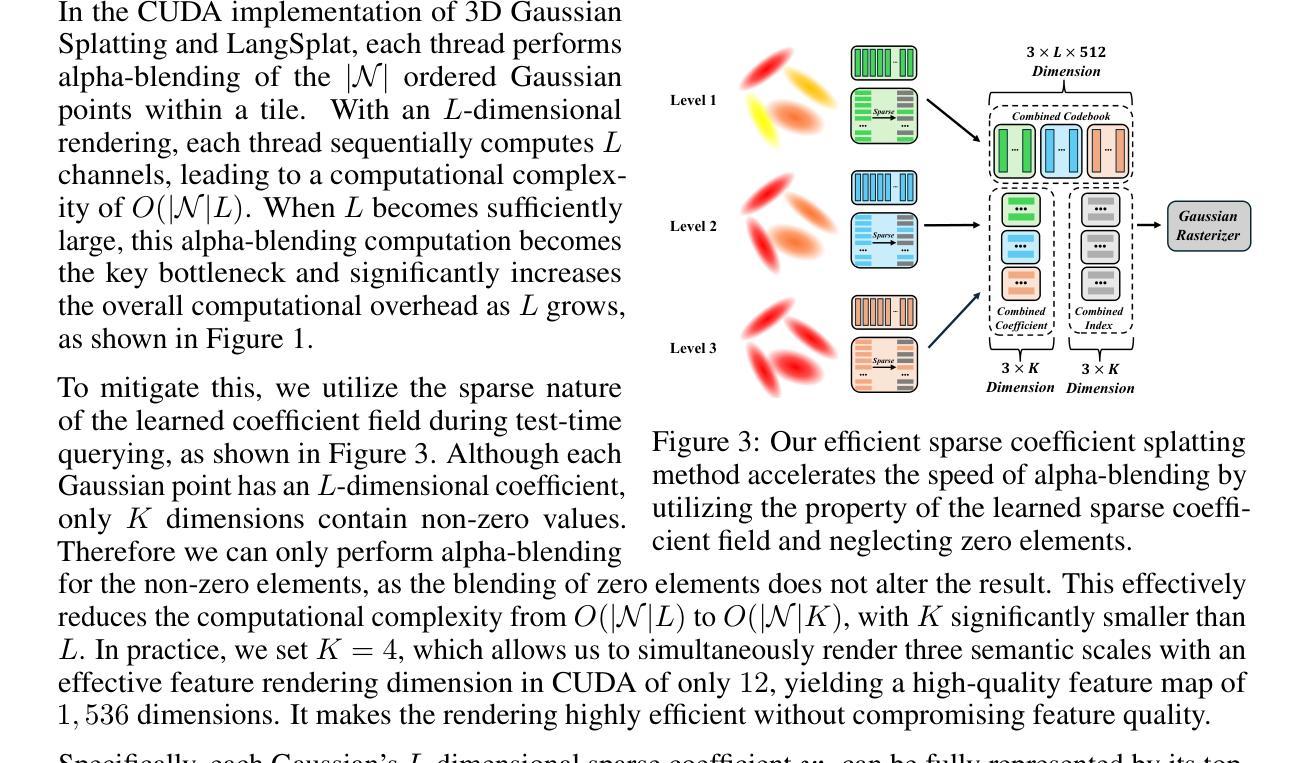
- LangSplat的主要速度瓶颈在于重量级解码器,LangSplatV2通过假设每个高斯在全球词典中作为稀疏代码来消除这一瓶颈。
- LangSplatV2利用稀疏系数场提出了高效稀疏系数展铺方法,只花费超低维度特征的时间成本即可呈现高质量的高维特征图。
- LangSplatV2不仅实现了更好的查询准确性,而且速度更快。
点此查看论文截图