⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-12 更新
Single-Step Latent Diffusion for Underwater Image Restoration
Authors:Jiayi Wu, Tianfu Wang, Md Abu Bakr Siddique, Md Jahidul Islam, Cornelia Fermuller, Yiannis Aloimonos, Christopher A. Metzler
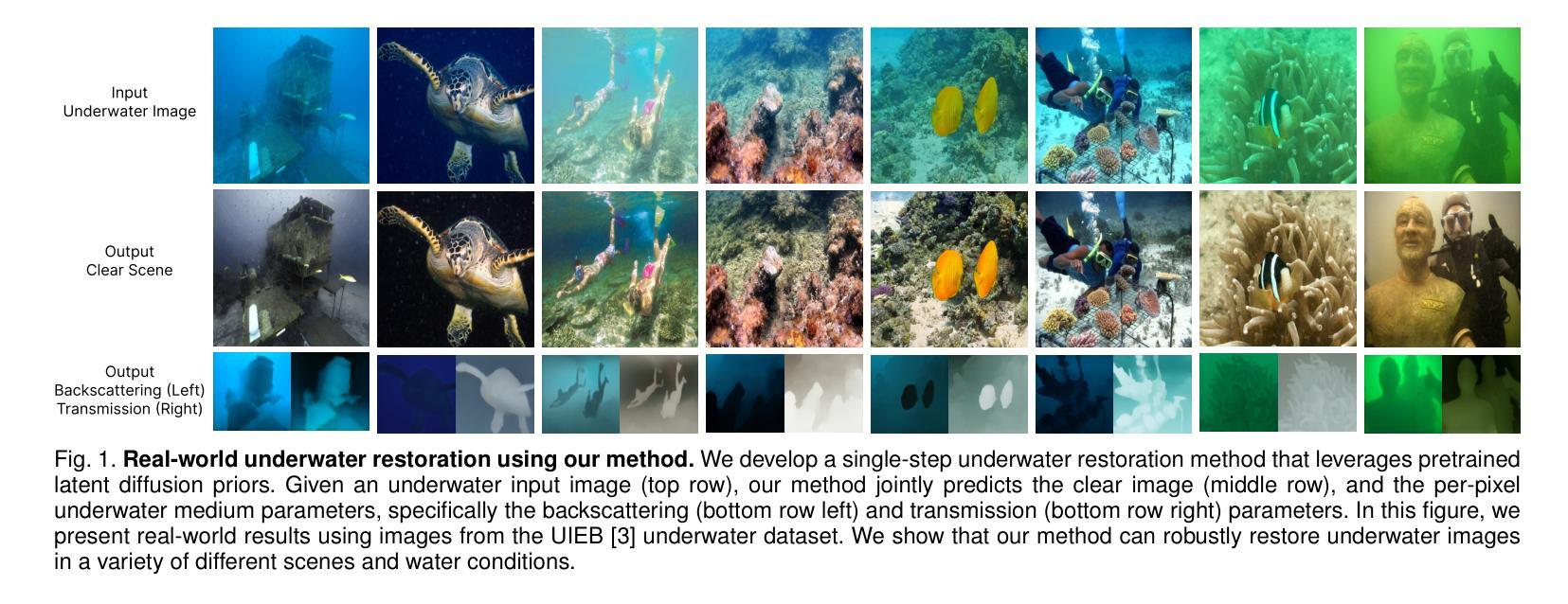
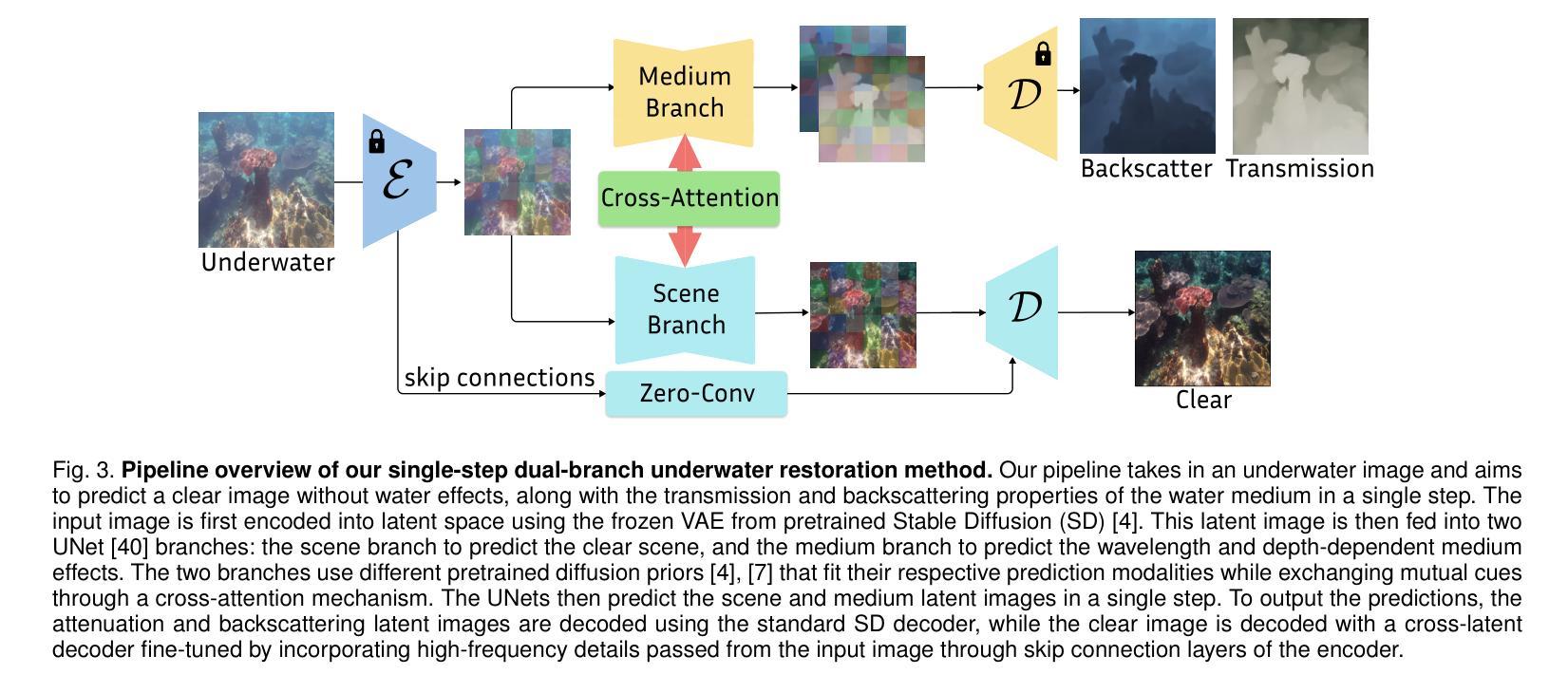
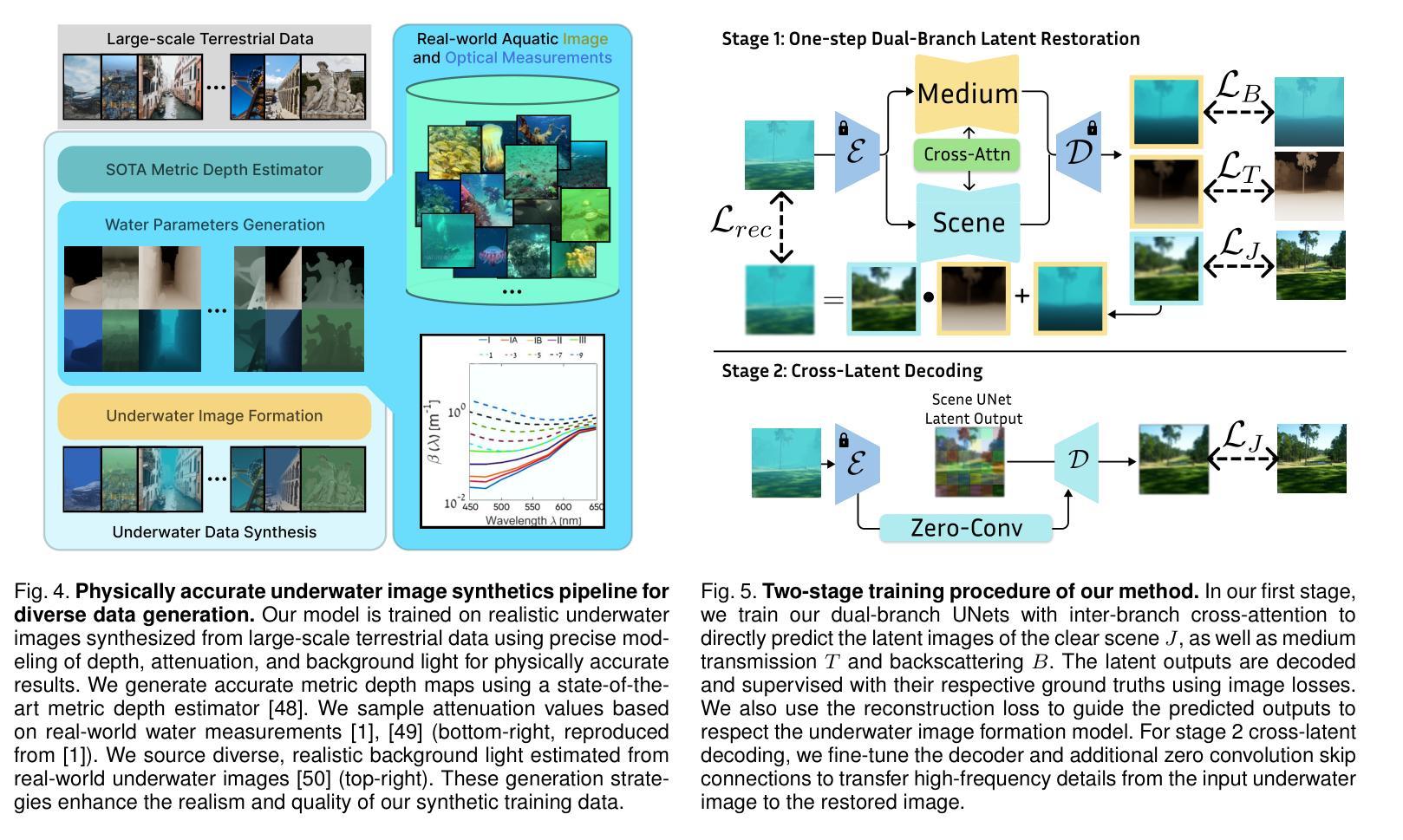
Underwater image restoration algorithms seek to restore the color, contrast, and appearance of a scene that is imaged underwater. They are a critical tool in applications ranging from marine ecology and aquaculture to underwater construction and archaeology. While existing pixel-domain diffusion-based image restoration approaches are effective at restoring simple scenes with limited depth variation, they are computationally intensive and often generate unrealistic artifacts when applied to scenes with complex geometry and significant depth variation. In this work we overcome these limitations by combining a novel network architecture (SLURPP) with an accurate synthetic data generation pipeline. SLURPP combines pretrained latent diffusion models – which encode strong priors on the geometry and depth of scenes – with an explicit scene decomposition – which allows one to model and account for the effects of light attenuation and backscattering. To train SLURPP we design a physics-based underwater image synthesis pipeline that applies varied and realistic underwater degradation effects to existing terrestrial image datasets. This approach enables the generation of diverse training data with dense medium/degradation annotations. We evaluate our method extensively on both synthetic and real-world benchmarks and demonstrate state-of-the-art performance. Notably, SLURPP is over 200X faster than existing diffusion-based methods while offering ~ 3 dB improvement in PSNR on synthetic benchmarks. It also offers compelling qualitative improvements on real-world data. Project website https://tianfwang.github.io/slurpp/.
水下图像恢复算法旨在恢复水下场景的色泽、对比度和外观。它们在海洋生态、水产养殖、水下建设和考古等应用中都是至关重要的工具。虽然现有的像素域扩散型图像恢复方法在恢复深度变化有限的简单场景时很有效,但在处理具有复杂几何和显著深度变化的场景时,它们计算量大并且常常产生不真实的伪影。在这项工作中,我们通过结合新型网络架构(SLURPP)与精准合成数据生成流程来克服这些局限。SLURPP结合了预训练的潜在扩散模型,该模型对场景的几何和深度具有强烈的先验知识,以及明确的场景分解,这允许建模和考虑光衰减和后向散射的影响。为了训练SLURPP,我们设计了一个基于物理的水下图像合成管道,该管道对现有的地面图像数据集应用多样化和现实的水下退化效果。这种方法能够生成具有密集介质/退化注释的多样化训练数据。我们在合成和实际基准测试上对我们的方法进行了广泛评估,并展示了其最先进的性能。值得注意的是,SLURPP是现有扩散方法的200倍以上,同时在合成基准测试上PSNR提高了约3分贝。它在真实世界数据上也提供了引人注目的定性改进。项目网站https://tianfwang.github.io/slurpp/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种结合新型网络架构SLURPP与精确合成数据生成流程的水下图像恢复方法。该方法通过利用预训练的潜在扩散模型与明确的场景分解,能够更有效地处理复杂场景和显著深度变化的水下图像。通过物理基础的水下图像合成管道设计训练数据,能够在陆地图像数据集上应用各种真实水下退化效应。该方法在合成和真实世界基准测试上表现出卓越性能,相较于现有扩散方法,速度提升超过200倍,同时在合成基准测试上的峰值信噪比(PSNR)提高约3分贝。
Key Takeaways
- 水下图像恢复算法旨在恢复水下场景的色泽、对比度和外观,广泛应用于海洋生态、水产养殖业、水下建设和考古等领域。
- 现有像素域扩散型图像恢复方法在处理简单场景时效果显著,但在面对复杂场景和显著深度变化时,计算量大且易产生不真实的人工痕迹。
- 本文提出的SLURPP网络架构结合了预训练的潜在扩散模型和明确的场景分解,能更有效地处理复杂的水下图像。
- 设计了基于物理的水下图像合成管道,能够在陆地图像数据集上应用各种真实水下退化效应,生成丰富的训练数据。
- SLURPP方法在合成和真实世界基准测试上表现出卓越性能,速度大幅超越现有扩散方法,同时提高了图像质量。
- SLURPP方法提供了强大的定性改进,特别是在处理真实世界数据时。
点此查看论文截图



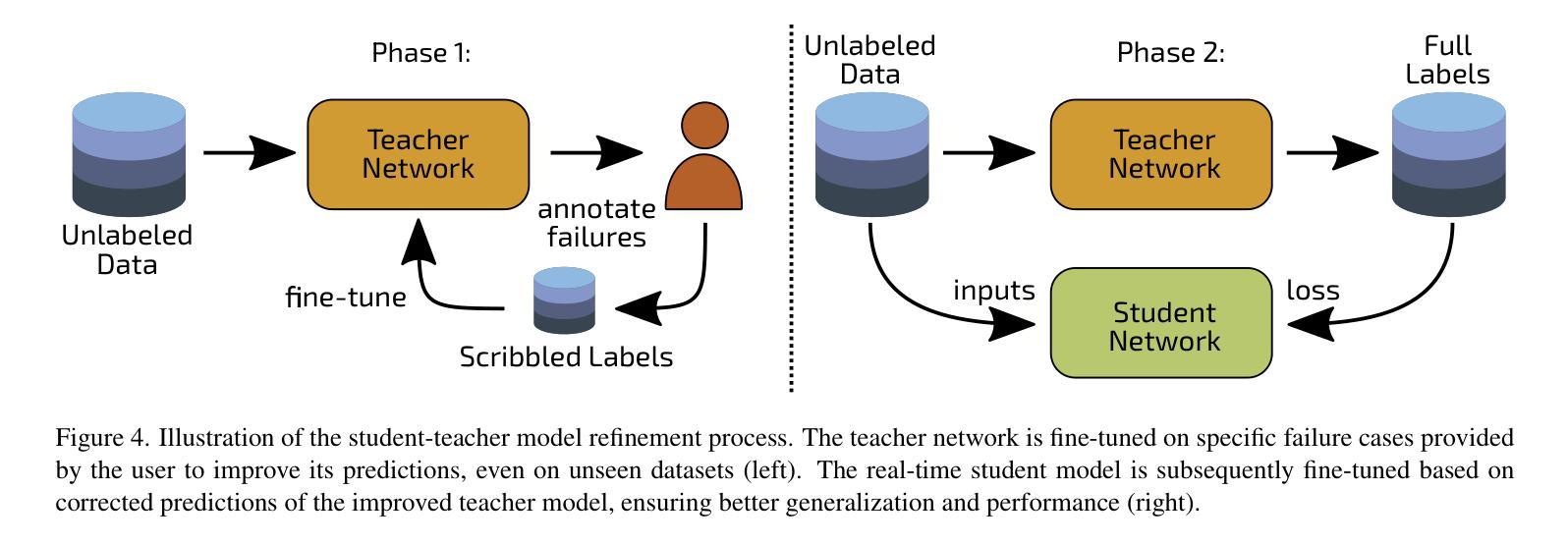
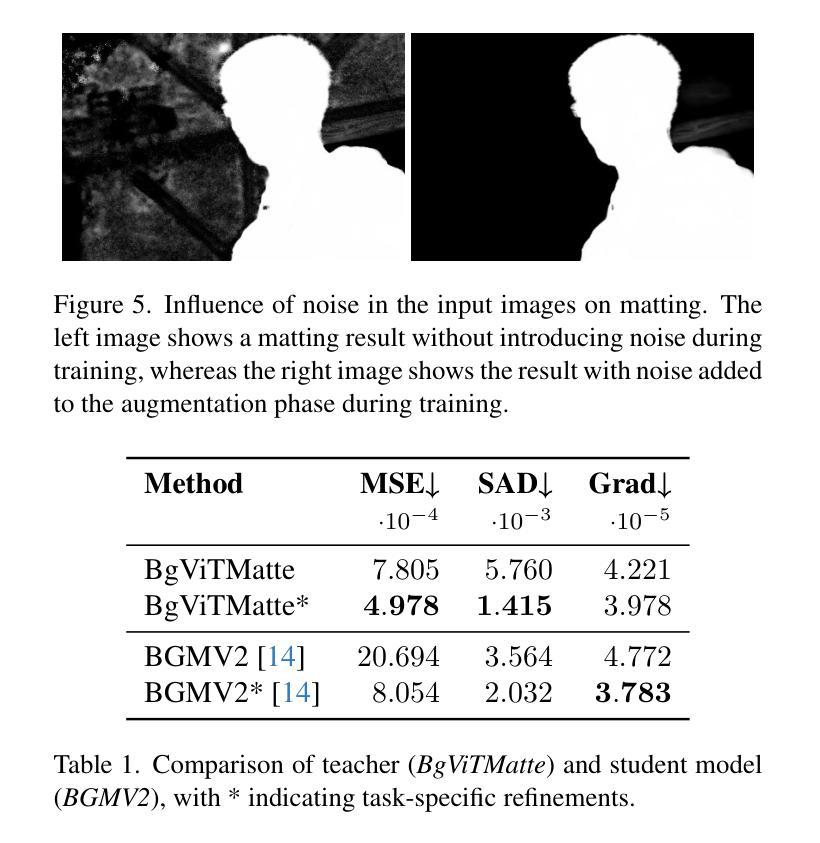
Capture Stage Environments: A Guide to Better Matting
Authors:Hannah Dröge, Janelle Pfeifer, Saskia Rabich, Markus Plack, Reinhard Klein, Matthias B. Hullin
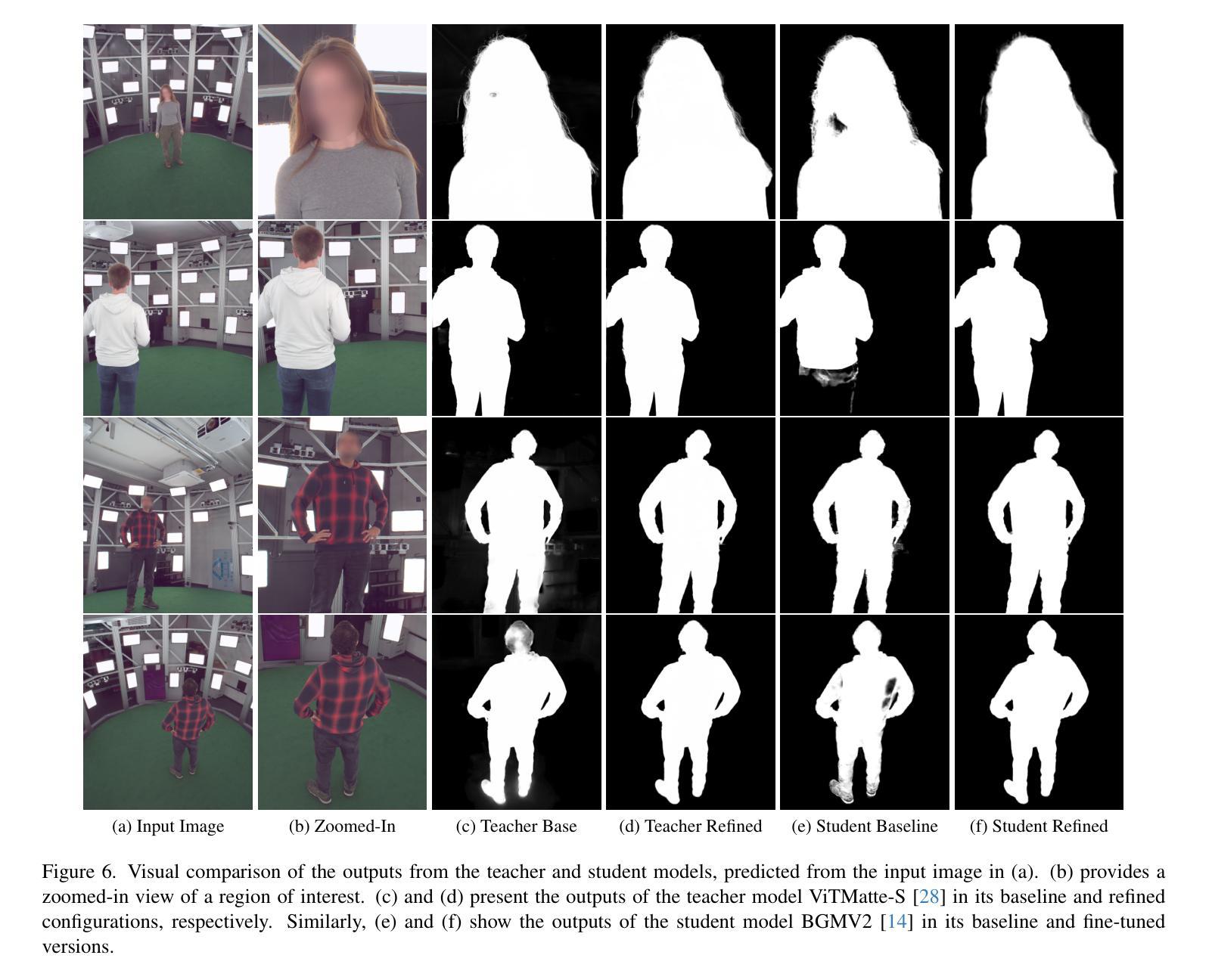
Capture stages are high-end sources of state-of-the-art recordings for downstream applications in movies, games, and other media. One crucial step in almost all pipelines is the matting of images to isolate the captured performances from the background. While common matting algorithms deliver remarkable performance in other applications like teleconferencing and mobile entertainment, we found that they struggle significantly with the peculiarities of capture stage content. The goal of our work is to share insights into those challenges as a curated list of those characteristics along with a constructive discussion for proactive intervention and present a guideline to practitioners for an improved workflow to mitigate unresolved challenges. To this end, we also demonstrate an efficient pipeline to adapt state-of-the-art approaches to such custom setups without the need of extensive annotations, both offline and real-time. For an objective evaluation, we propose a validation methodology based on a leading diffusion model that highlights the benefits of our approach.
采集阶段是为电影、游戏和其他媒体等下游应用提供最新技术录音的高端来源。在几乎所有流程中,一个至关重要的步骤是通过图像抠像技术将捕捉到的表演与背景分离。虽然常见的抠像算法在视频会议和移动娱乐等其他应用中表现出卓越的性能,但我们发现它们在应对采集阶段内容的特殊性时遇到了很大困难。我们工作的目标是分享关于这些挑战的看法,列出这些特性的精选列表,并进行建设性讨论以采取积极干预的措施,同时为从业者提供一个改进工作流程指南,以缓解未解决的挑战。为此,我们还展示了一个高效的管道,可以适应最新的技术方法来适应这种定制设置,无需大量的注释标注工作,并且适用于离线处理和实时环境。为了进行客观评估,我们提出了一种基于前沿扩散模型的验证方法,突出我们方法的优势所在。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了捕获阶段在影视、游戏等媒体下游应用中的重要性,并指出图像抠图是将捕获的表演与背景分离的关键步骤。尽管常见的抠图算法在其他应用如视频会议和手机娱乐中表现卓越,但在捕获阶段内容方面存在诸多挑战。本文旨在分享这些挑战的特性,并讨论积极应对措施,为从业者提供改进工作流程的指导。同时,展示了一种高效管道,可适应最新技术方法,无需大量标注即可应用于此类自定义设置,包括离线与实时环境。通过基于领先的扩散模型的验证方法,客观地评估了我们的方法的优势。
Key Takeaways
- 捕获阶段是影视、游戏等媒体下游应用中的高端先进技术录制重要环节。
- 图像抠图是从捕获的表演中分离背景的关键步骤。
- 常见抠图算法在捕获阶段内容方面存在挑战。
- 本文分享了对这些挑战的洞察,并讨论了积极应对措施。
- 为从业者提供了改进工作流程的指导。
- 展示了一种高效管道,可适应最新技术方法,适用于自定义设置,无需大量标注。
点此查看论文截图



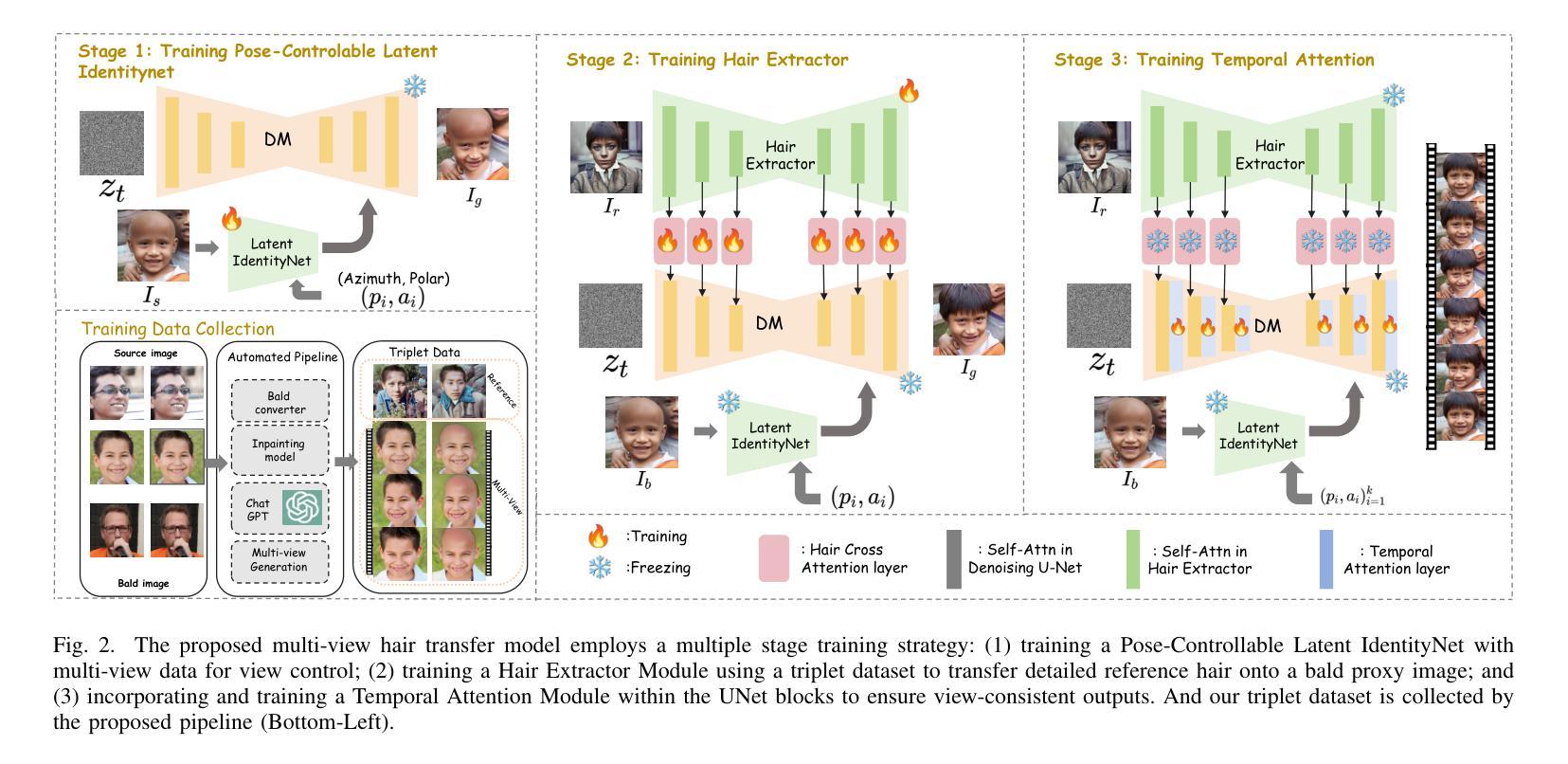
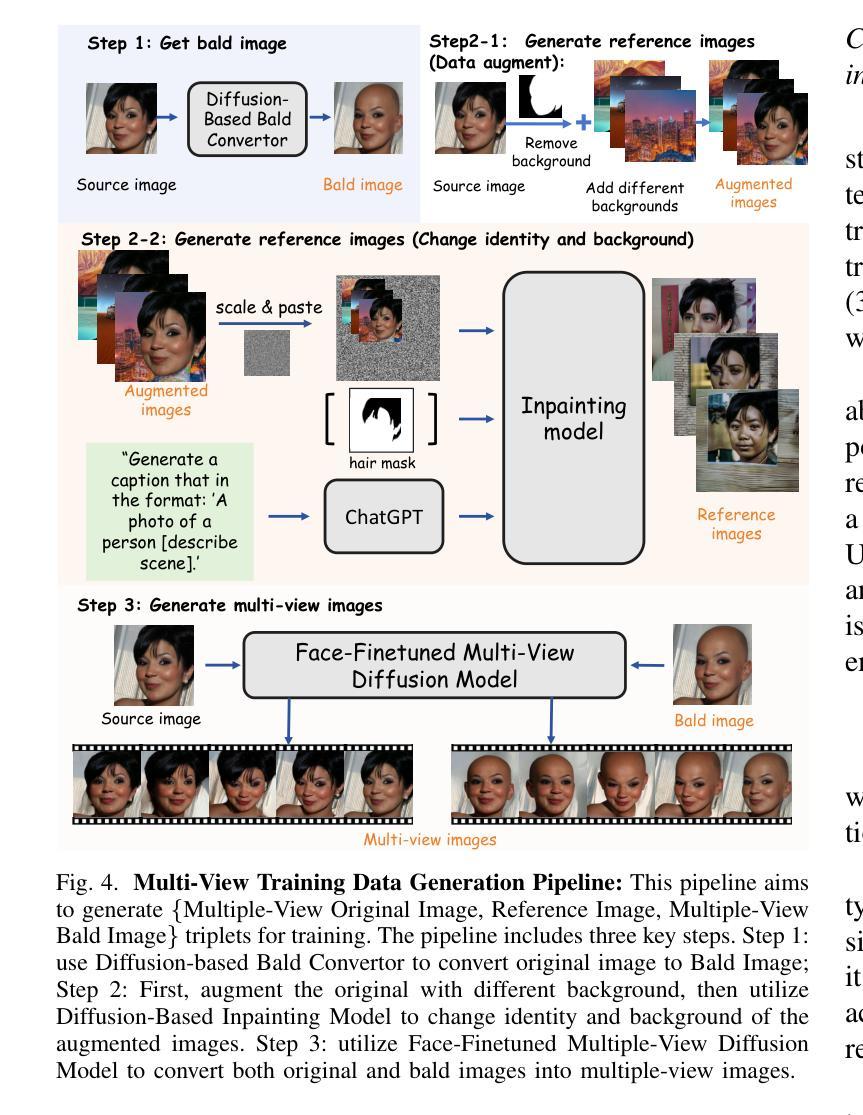
Stable-Hair v2: Real-World Hair Transfer via Multiple-View Diffusion Model
Authors:Kuiyuan Sun, Yuxuan Zhang, Jichao Zhang, Jiaming Liu, Wei Wang, Niculae Sebe, Yao Zhao
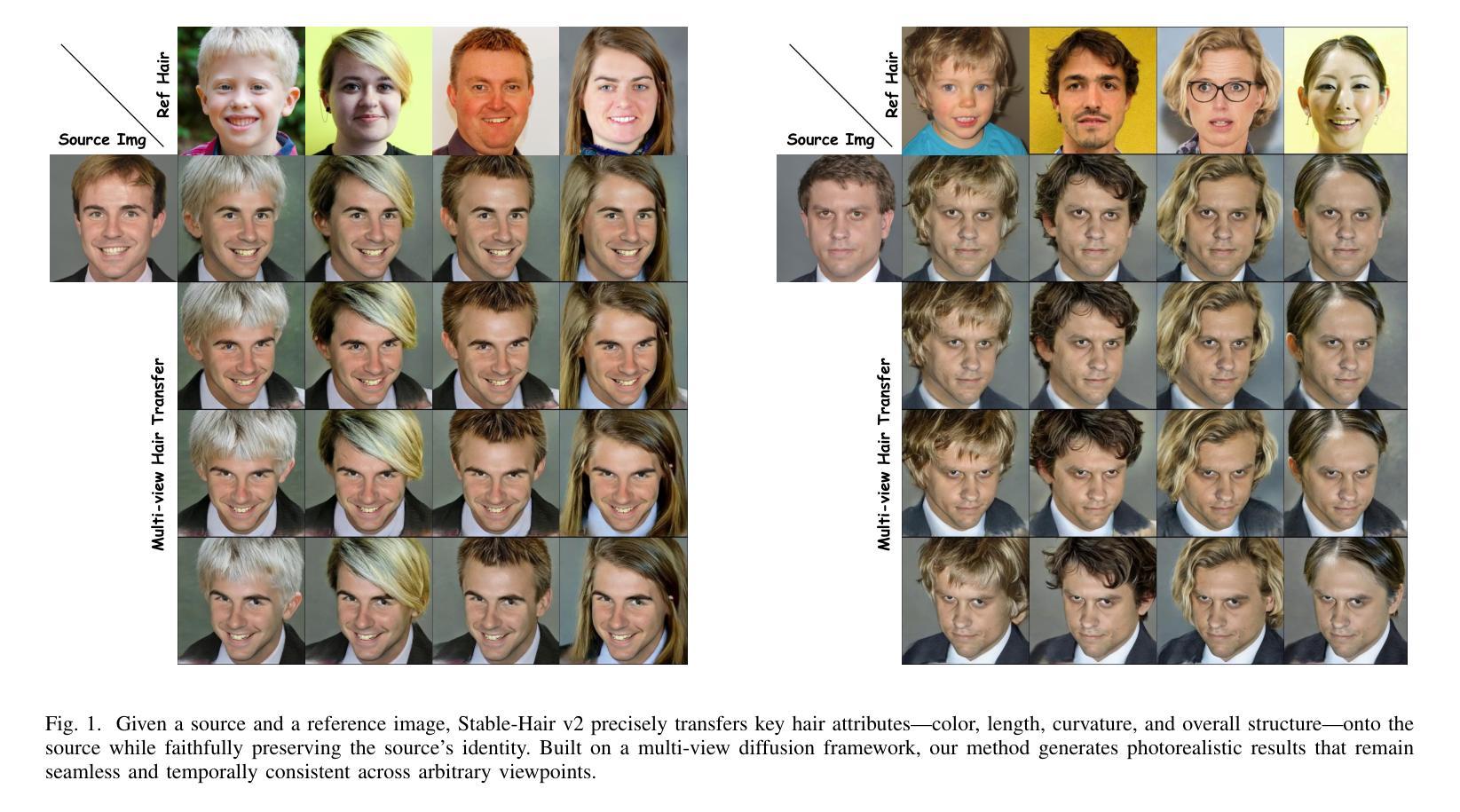
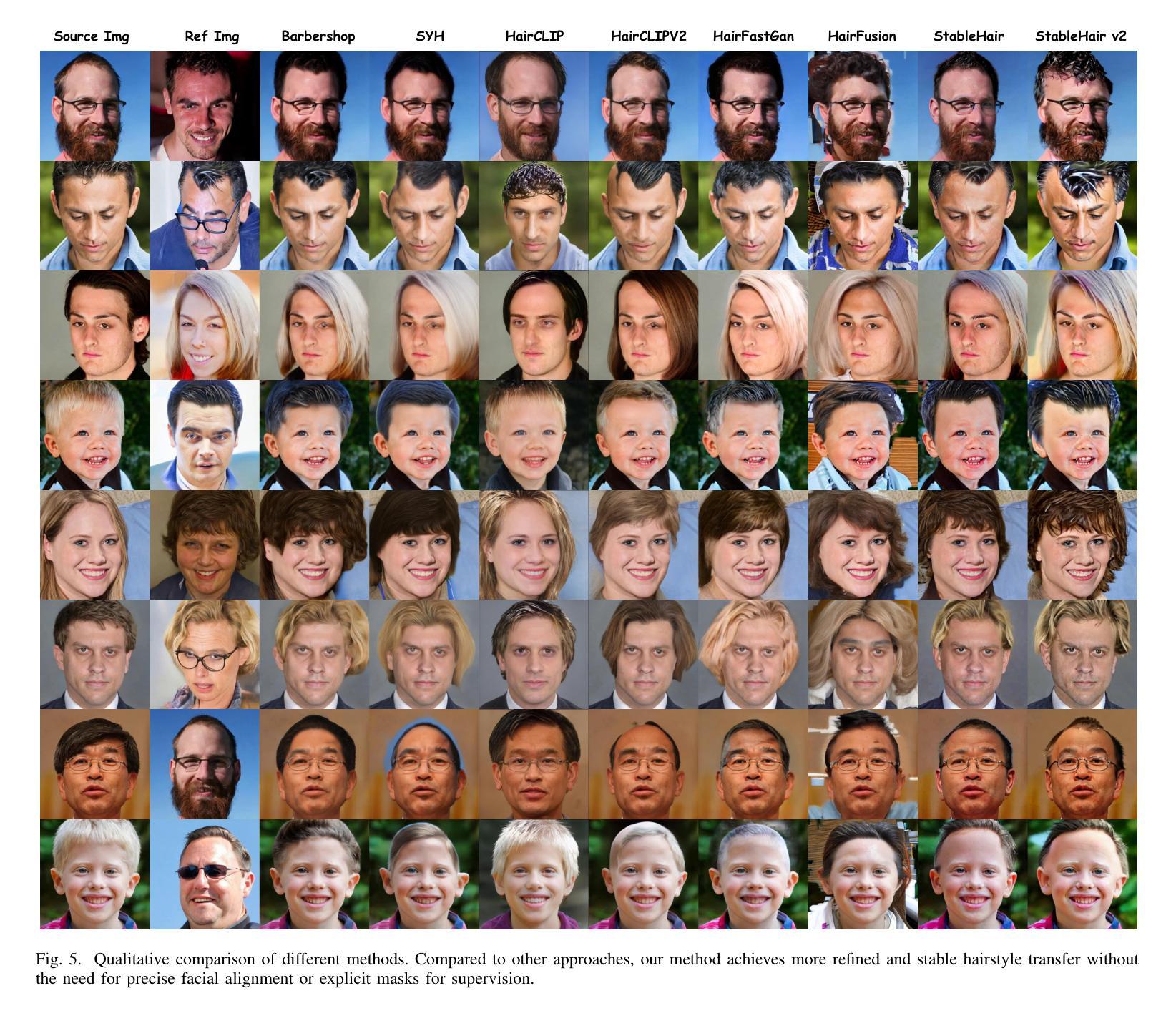
While diffusion-based methods have shown impressive capabilities in capturing diverse and complex hairstyles, their ability to generate consistent and high-quality multi-view outputs – crucial for real-world applications such as digital humans and virtual avatars – remains underexplored. In this paper, we propose Stable-Hair v2, a novel diffusion-based multi-view hair transfer framework. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to leverage multi-view diffusion models for robust, high-fidelity, and view-consistent hair transfer across multiple perspectives. We introduce a comprehensive multi-view training data generation pipeline comprising a diffusion-based Bald Converter, a data-augment inpainting model, and a face-finetuned multi-view diffusion model to generate high-quality triplet data, including bald images, reference hairstyles, and view-aligned source-bald pairs. Our multi-view hair transfer model integrates polar-azimuth embeddings for pose conditioning and temporal attention layers to ensure smooth transitions between views. To optimize this model, we design a novel multi-stage training strategy consisting of pose-controllable latent IdentityNet training, hair extractor training, and temporal attention training. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method accurately transfers detailed and realistic hairstyles to source subjects while achieving seamless and consistent results across views, significantly outperforming existing methods and establishing a new benchmark in multi-view hair transfer. Code is publicly available at https://github.com/sunkymepro/StableHairV2.
基于扩散的方法在捕捉多样且复杂的发型方面展现出了令人印象深刻的能力,但它们在生成一致且高质量的多视角输出方面的能力——对于数字人类和虚拟化身等现实世界应用至关重要——仍然未被充分探索。在本文中,我们提出了Stable-Hair v2,这是一种基于扩散的多视角头发转移框架。据我们所知,这是首次利用多视角扩散模型进行稳健、高保真、跨多个视角一致性的头发转移的工作。我们引入了一个全面的多视角训练数据生成流程,包括基于扩散的秃头转换器、数据增强填充模型,以及针对面部微调的多视角扩散模型,以生成高质量的三元组数据,包括秃头图像、参考发型和视角对齐的源秃头对。我们的多视角头发转移模型集成了极坐标方位嵌入进行姿态条件设置和临时注意力层,以确保不同视角之间的平滑过渡。为了优化这个模型,我们设计了一种新的多阶段训练策略,包括姿态可控潜在身份网训练、头发提取器训练和临时注意力训练。大量实验表明,我们的方法能够准确地将详细的现实发型转移到源主体上,同时在各视角实现无缝且一致的结果,显著优于现有方法,并在多视角头发转移方面建立了新的基准。代码已公开在:https://github.com/sunkymepro/StableHairV2。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages
Summary
本文提出了一种基于扩散模型的多视角头发转移框架Stable-Hair v2。该框架利用多视角扩散模型实现了稳健、高保真、跨不同视角的连续头发转移。为生成高质量的三元组数据,引入全面的多视角训练数据生成管道,包括基于扩散的秃顶转换器、数据增强填充模型和对脸进行微调的多视角扩散模型。该方法集成了方位嵌入用于姿态调节和临时注意力层以确保不同视角之间的平滑过渡。通过设计包含姿态可控潜在IdentityNet训练、头发提取器训练和临时注意力训练的多阶段训练策略,实现了优化模型的目的。该方法准确地将详细的现实发型转移到源主体上,同时实现跨视角的无缝和一致结果,显著优于现有方法,为多视角头发转移建立了新的基准。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文提出了Stable-Hair v2,一个基于扩散模型的多视角头发转移框架。
- 这是首次利用多视角扩散模型进行头发转移的工作,可实现稳健、高保真和连续性的头发转移。
- 引入全面的多视角训练数据生成管道,包括秃顶转换器、数据增强填充模型以及面向多视角的扩散模型。
- 集成方位嵌入用于姿态调节和临时注意力层确保不同视角间的平滑过渡。
- 通过设计多阶段训练策略优化模型,包括姿态可控的IdentityNet训练、头发提取器训练和临时注意力训练。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在将详细和现实的发型转移到源主体上表现优异,实现了跨视角的无缝和一致结果。
点此查看论文截图




Divergence Minimization Preference Optimization for Diffusion Model Alignment
Authors:Binxu Li, Minkai Xu, Meihua Dang, Stefano Ermon
Diffusion models have achieved remarkable success in generating realistic and versatile images from text prompts. Inspired by the recent advancements of language models, there is an increasing interest in further improving the models by aligning with human preferences. However, we investigate alignment from a divergence minimization perspective and reveal that existing preference optimization methods are typically trapped in suboptimal mean-seeking optimization. In this paper, we introduce Divergence Minimization Preference Optimization (DMPO), a novel and principled method for aligning diffusion models by minimizing reverse KL divergence, which asymptotically enjoys the same optimization direction as original RL. We provide rigorous analysis to justify the effectiveness of DMPO and conduct comprehensive experiments to validate its empirical strength across both human evaluations and automatic metrics. Our extensive results show that diffusion models fine-tuned with DMPO can consistently outperform or match existing techniques, specifically outperforming all existing diffusion alignment baselines by at least 64.6% in PickScore across all evaluation datasets, demonstrating the method’s superiority in aligning generative behavior with desired outputs. Overall, DMPO unlocks a robust and elegant pathway for preference alignment, bridging principled theory with practical performance in diffusion models.
扩散模型通过文本提示生成现实且多样化的图像,取得了显著的成功。受语言模型最新进展的启发,人们越来越感兴趣通过符合人类偏好来进一步改进这些模型。然而,我们从分歧最小化角度研究对齐问题,并揭示现有的偏好优化方法通常陷入次优均值寻求优化。在本文中,我们介绍了分歧最小化偏好优化(DMPO),这是一种通过最小化反向KL分歧来对齐扩散模型的新型且基于原则的方法,它渐近地享有与原始强化学习相同的优化方向。我们提供了严格的分析来证明DMPO的有效性,并进行了全面的实验来验证其在人类评估和自动指标方面的实证实力。我们的广泛结果表明,使用DMPO微调过的扩散模型可以持续超越或匹配现有技术,特别是在PickScore上,相较于所有现有扩散对齐基准测试,至少高出64.6%,这证明了该方法在将生成行为与期望输出对齐方面的优越性。总体而言,DMPO为偏好对齐解锁了稳健而优雅的途径,在理论原则与实际性能之间架起了桥梁。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 pages, 8 figures
Summary
本文探讨了扩散模型在生成图像时的偏好对齐问题。作者从分歧最小化角度进行研究,提出了Divergence Minimization Preference Optimization(DMPO)方法,该方法通过最小化反向KL分歧来实现扩散模型的偏好对齐。理论分析证明了DMPO的有效性,并通过实验验证了其在人类评估和自动指标上的优越性。使用DMPO微调后的扩散模型在所有评估数据集上的PickScore至少优于现有技术基线64.6%,展现出其在对齐生成行为与期望输出方面的优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型已成功生成与文本提示相符的真实图像。
- 随着语言模型的发展,如何进一步改善扩散模型以满足人类偏好成为研究热点。
- 本文从分歧最小化的角度研究偏好对齐问题。
- 提出了一种新的方法——Divergence Minimization Preference Optimization(DMPO),用于优化扩散模型的偏好对齐。
- DMPO方法通过最小化反向KL分歧来实现扩散模型的偏好对齐,与原始强化学习的优化方向一致。
- 实验结果显示,使用DMPO方法微调后的扩散模型在多个评估指标上表现优异,特别是PickScore。
点此查看论文截图


Degradation-Agnostic Statistical Facial Feature Transformation for Blind Face Restoration in Adverse Weather Conditions
Authors:Chang-Hwan Son
With the increasing deployment of intelligent CCTV systems in outdoor environments, there is a growing demand for face recognition systems optimized for challenging weather conditions. Adverse weather significantly degrades image quality, which in turn reduces recognition accuracy. Although recent face image restoration (FIR) models based on generative adversarial networks (GANs) and diffusion models have shown progress, their performance remains limited due to the lack of dedicated modules that explicitly address weather-induced degradations. This leads to distorted facial textures and structures. To address these limitations, we propose a novel GAN-based blind FIR framework that integrates two key components: local Statistical Facial Feature Transformation (SFFT) and Degradation-Agnostic Feature Embedding (DAFE). The local SFFT module enhances facial structure and color fidelity by aligning the local statistical distributions of low-quality (LQ) facial regions with those of high-quality (HQ) counterparts. Complementarily, the DAFE module enables robust statistical facial feature extraction under adverse weather conditions by aligning LQ and HQ encoder representations, thereby making the restoration process adaptive to severe weather-induced degradations. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed degradation-agnostic SFFT model outperforms existing state-of-the-art FIR methods based on GAN and diffusion models, particularly in suppressing texture distortions and accurately reconstructing facial structures. Furthermore, both the SFFT and DAFE modules are empirically validated in enhancing structural fidelity and perceptual quality in face restoration under challenging weather scenarios.
随着智能CCTV系统在户外环境中的部署越来越多,对于适应恶劣天气条件的面部识别系统的需求也在日益增长。恶劣天气会严重降低图像质量,进而导致识别精度下降。尽管基于生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型的面部图像恢复(FIR)模型已经取得了进展,但由于缺乏专门解决天气引起的退化的模块,其性能仍然有限。这会导致面部纹理和结构失真。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一种基于GAN的盲FIR框架,该框架包含两个关键组件:局部统计面部特征变换(SFFT)和退化无关特征嵌入(DAFE)。局部SFFT模块通过对齐低质量(LQ)面部区域的局部统计分布与高质量(HQ)对应区域的统计分布,增强面部结构和颜色保真度。互补地,DAFE模块通过对齐LQ和HQ编码器表示,实现在恶劣天气条件下的稳健统计面部特征提取,从而使恢复过程适应于由恶劣天气引起的退化。实验结果表明,所提出的退化无关SFFT模型在抑制纹理失真和准确重建面部结构方面优于现有的基于GAN和扩散模型的先进FIR方法。此外,SFFT和DAFE模块在增强结构保真度和感知质量方面也得到了实证验证,在具有挑战性的天气情况下进行面部恢复时效果显著。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
针对户外环境中智能监控系统的广泛应用,对面部识别系统在恶劣天气条件下的优化需求日益增长。恶劣天气会显著降图像质量,进而影响识别准确率。尽管基于生成对抗网络(GAN)和扩散模型的面部图像恢复(FIR)模型已取得进展,但由于缺乏专门应对天气引起的降质的模块,其性能仍然有限。为此,提出一种新颖的基于GAN的盲FIR框架,包含两个关键组件:局部统计面部特征变换(SFFT)和降质无关特征嵌入(DAFE)。SFFT模块通过对齐低质量(LQ)面部区域与高质量(HQ)区域的局部统计分布,增强面部结构和色彩保真度。同时,DAFE模块通过对齐LQ和HQ编码器表示,使面部特征提取在恶劣天气条件下更为稳健,从而使恢复过程适应严重的天气引起的降质。实验结果表明,所提出的降质无关SFFT模型在基于GAN和扩散模型的现有先进FIR方法中表现优异,尤其在抑制纹理失真和准确重建面部结构方面。此外,SFFT和DAFE模块在提高结构保真度和感知质量方面也得到了实证。
关键见解
- 恶劣天气对面部识别系统造成挑战,降低图像质量和识别准确率。
- 基于GAN和扩散模型的现有面部图像恢复(FIR)模型虽有所进展,但仍存在性能限制。
- 提出的盲FIR框架结合局部统计面部特征变换(SFFT)和降质无关特征嵌入(DAFE)两大模块以应对天气引起的图像降质。
- SFFT模块通过局部统计分布对齐增强面部结构和色彩保真度。
- DAFE模块使面部特征提取在恶劣天气下更为稳健,适应严重天气引起的降质。
- 实证结果显示,所提出模型在抑制纹理失真和面部结构重建方面表现优异。
- SFFT和DAFE模块在提高结构保真度和感知质量方面得到验证。
点此查看论文截图

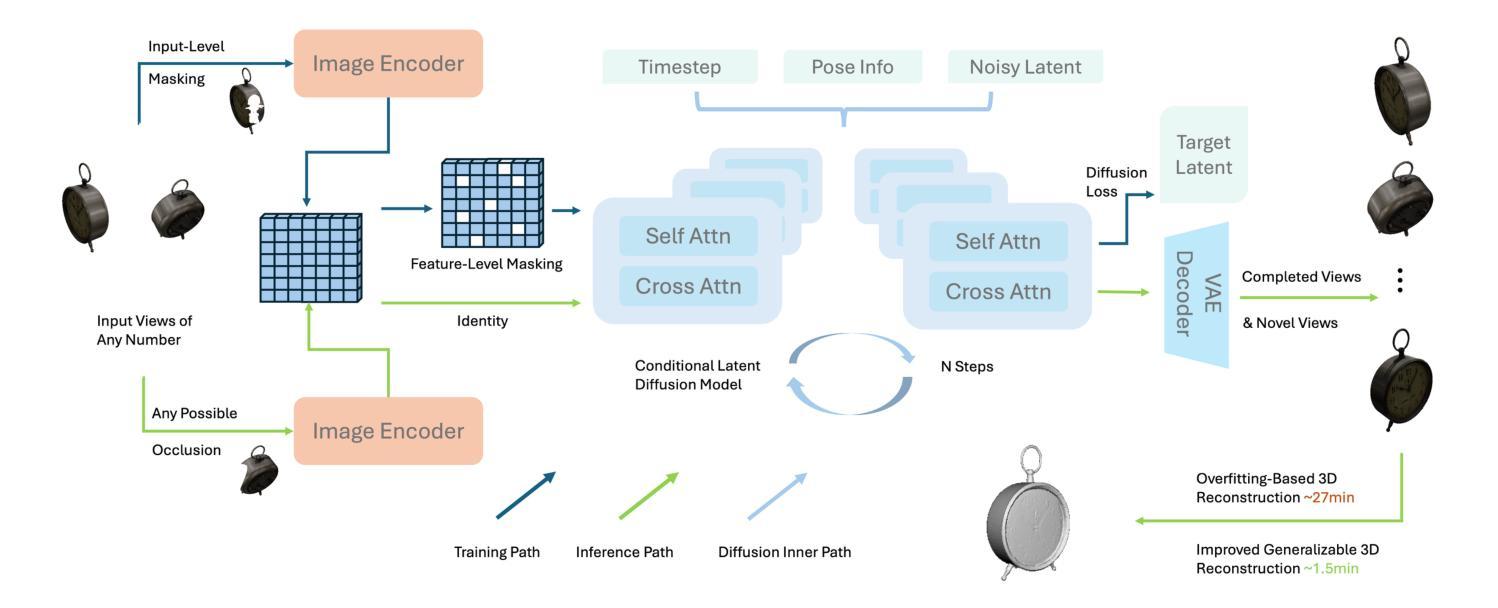
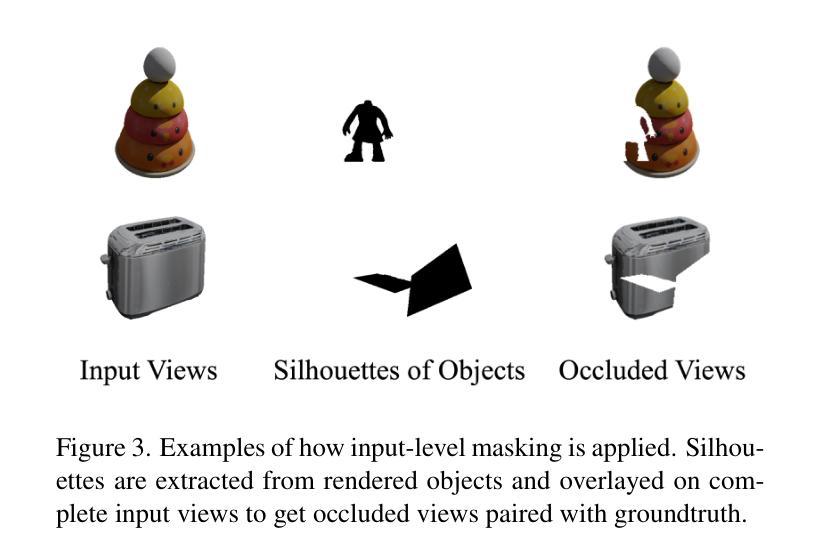
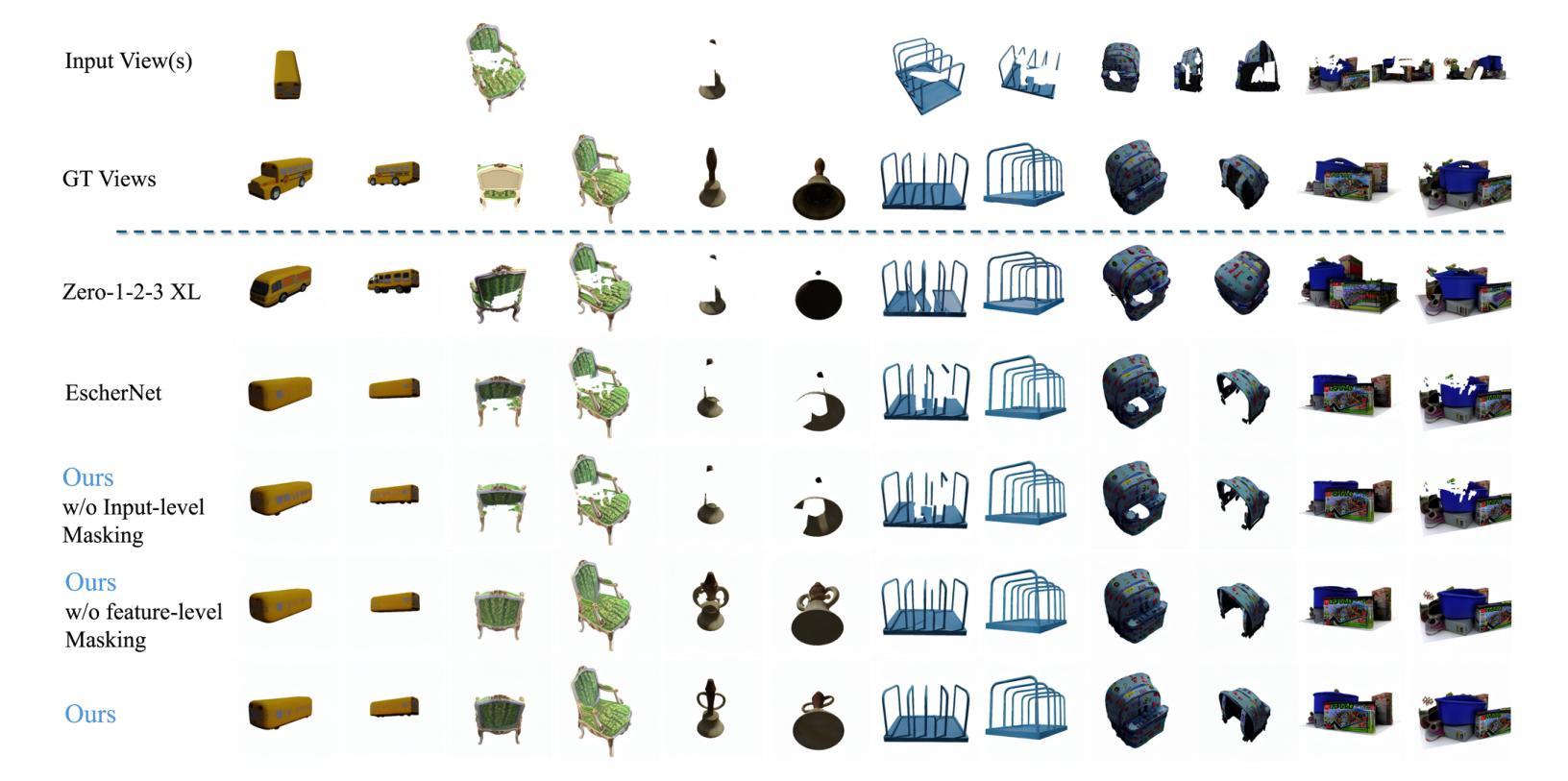
EscherNet++: Simultaneous Amodal Completion and Scalable View Synthesis through Masked Fine-Tuning and Enhanced Feed-Forward 3D Reconstruction
Authors:Xinan Zhang, Muhammad Zubair Irshad, Anthony Yezzi, Yi-Chang Tsai, Zsolt Kira
We propose EscherNet++, a masked fine-tuned diffusion model that can synthesize novel views of objects in a zero-shot manner with amodal completion ability. Existing approaches utilize multiple stages and complex pipelines to first hallucinate missing parts of the image and then perform novel view synthesis, which fail to consider cross-view dependencies and require redundant storage and computing for separate stages. Instead, we apply masked fine-tuning including input-level and feature-level masking to enable an end-to-end model with the improved ability to synthesize novel views and conduct amodal completion. In addition, we empirically integrate our model with other feed-forward image-to-mesh models without extra training and achieve competitive results with reconstruction time decreased by 95%, thanks to its ability to synthesize arbitrary query views. Our method’s scalable nature further enhances fast 3D reconstruction. Despite fine-tuning on a smaller dataset and batch size, our method achieves state-of-the-art results, improving PSNR by 3.9 and Volume IoU by 0.28 on occluded tasks in 10-input settings, while also generalizing to real-world occluded reconstruction.
我们提出了EscherNet++,这是一种经过掩码微调(fine-tuning)的扩散模型,能够以零样本方式合成对象的新视角,并具有模态完成能力。现有方法采用多阶段和复杂的流水线,首先虚构图像缺失的部分,然后进行新视角合成,这种方法忽略了跨视角依赖性,需要针对各个阶段进行冗余存储和计算。相反,我们应用包括输入级别和特征级别的掩码进行掩码微调,使端到端模型能够合成新视角并具备模态完成能力。此外,我们通过实证将我们的模型与其他前馈图像到网格模型相结合,无需额外训练,由于模型能够合成任意查询视角,重建时间减少了95%。我们方法的可扩展性进一步加强了快速三维重建。尽管在较小的数据集和批次大小上进行微调,我们的方法取得了最先进的成果,在遮挡任务的PSNR指标上提高了3.9,体积IoU提高了0.28的10输入设置上,同时推广到真实世界的遮挡重建任务。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一个名为EscherNet++的扩散模型改进方案,通过采用掩码微调技术,能够零样本方式合成对象的新视角并具有无模态完成能力。现有方法采用多阶段和复杂的流水线来先模拟图像缺失部分,然后进行新视角合成,这种方法忽略了跨视角的依赖关系,并需要冗余的存储和计算资源。相比之下,EscherNet++通过输入级和特征级的掩码微调,实现了端到端的模型,提高了合成新视角和无模态完成的能力。此外,该模型还可以与其他前馈图像到网格模型进行实证集成,无需额外训练,由于能够合成任意查询视角,重建时间减少了95%。该方法的可扩展性进一步提高了快速三维重建。即使在较小的数据集和批量大小上进行微调,该方法也达到了最先进的成果,在遮挡任务的PSNR指标上提高了3.9,体积IoU提高了0.28的10输入设置中,而且还能够推广到真实世界的遮挡重建。
Key Takeaways
- EscherNet++是一个通过掩码微调优化的扩散模型,可零样本方式合成对象的新视角。
- 与多阶段和复杂流水线方法相比,EscherNet++实现了端到端的模型,提高了新视角合成和无模态完成能力。
- EscherNet++通过输入级和特征级掩码微调技术来提升性能。
- 该模型可与其他前馈图像到网格模型集成,无需额外训练。
- EscherNet++能够合成任意查询视角,大大降低了三维重建的时间。
- EscherNet++具有可扩展性,在遮挡任务中表现出色,并在PSNR和体积IoU指标上达到了先进水准。
点此查看论文截图

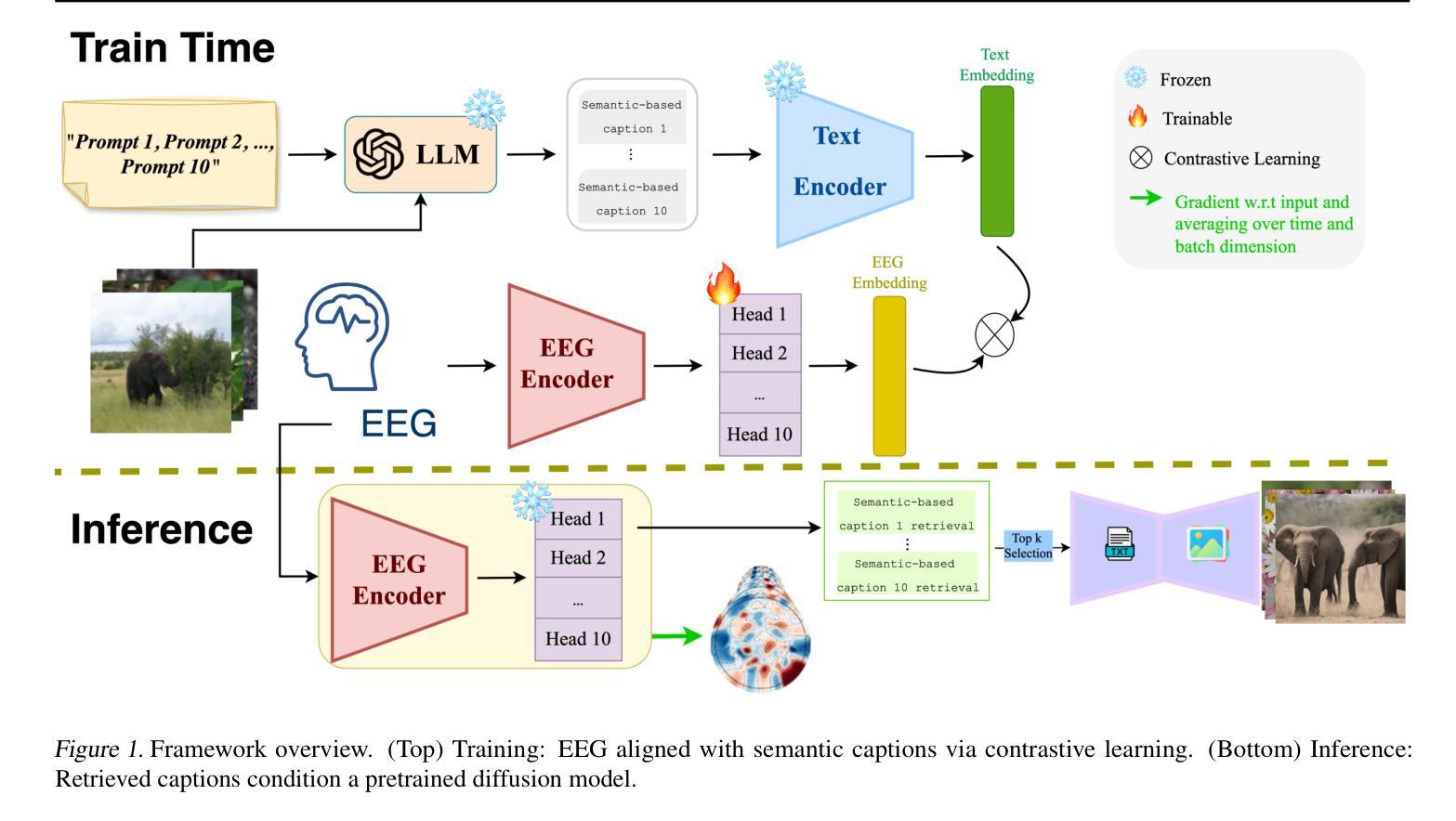
Interpretable EEG-to-Image Generation with Semantic Prompts
Authors:Arshak Rezvani, Ali Akbari, Kosar Sanjar Arani, Maryam Mirian, Emad Arasteh, Martin J. McKeown
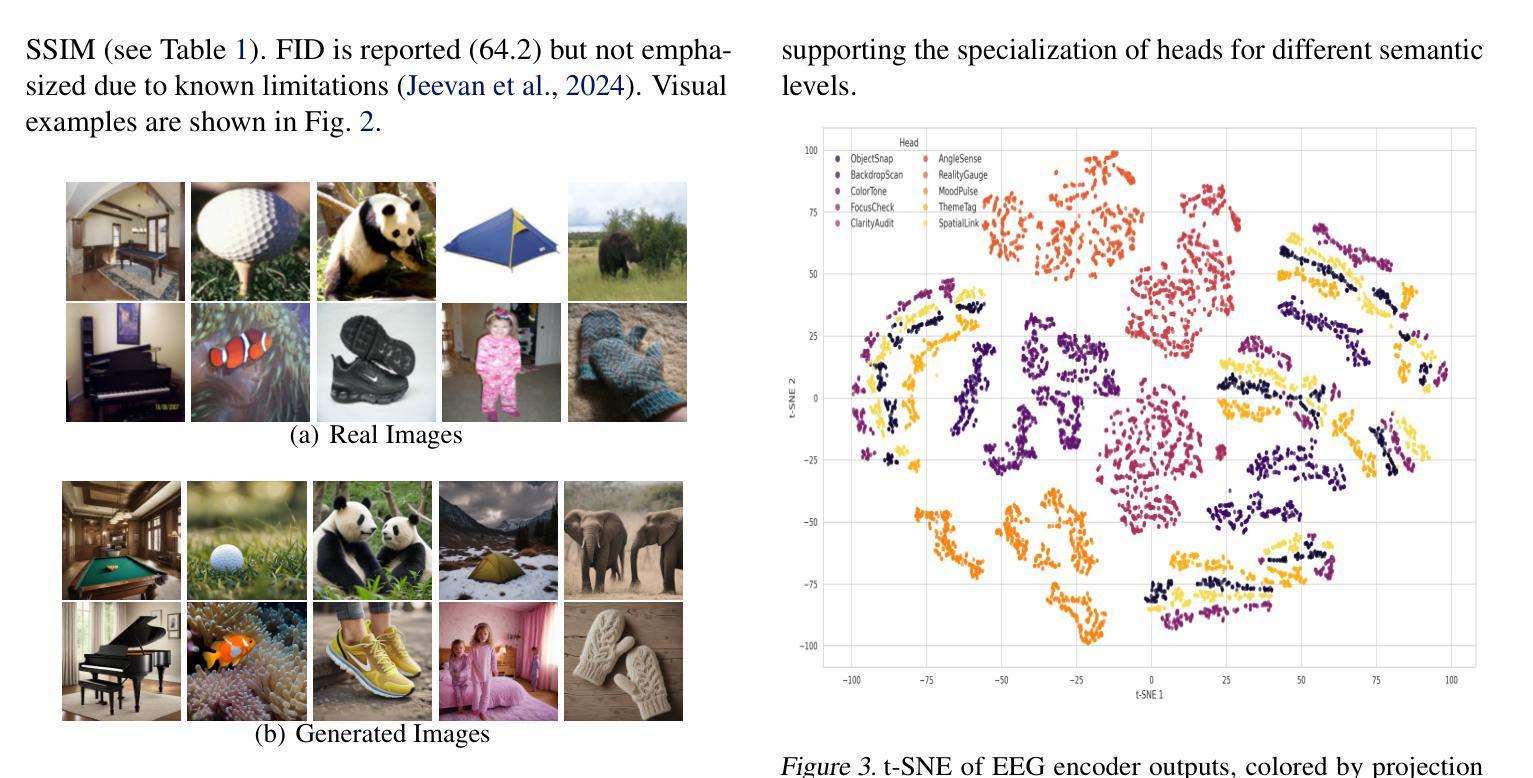
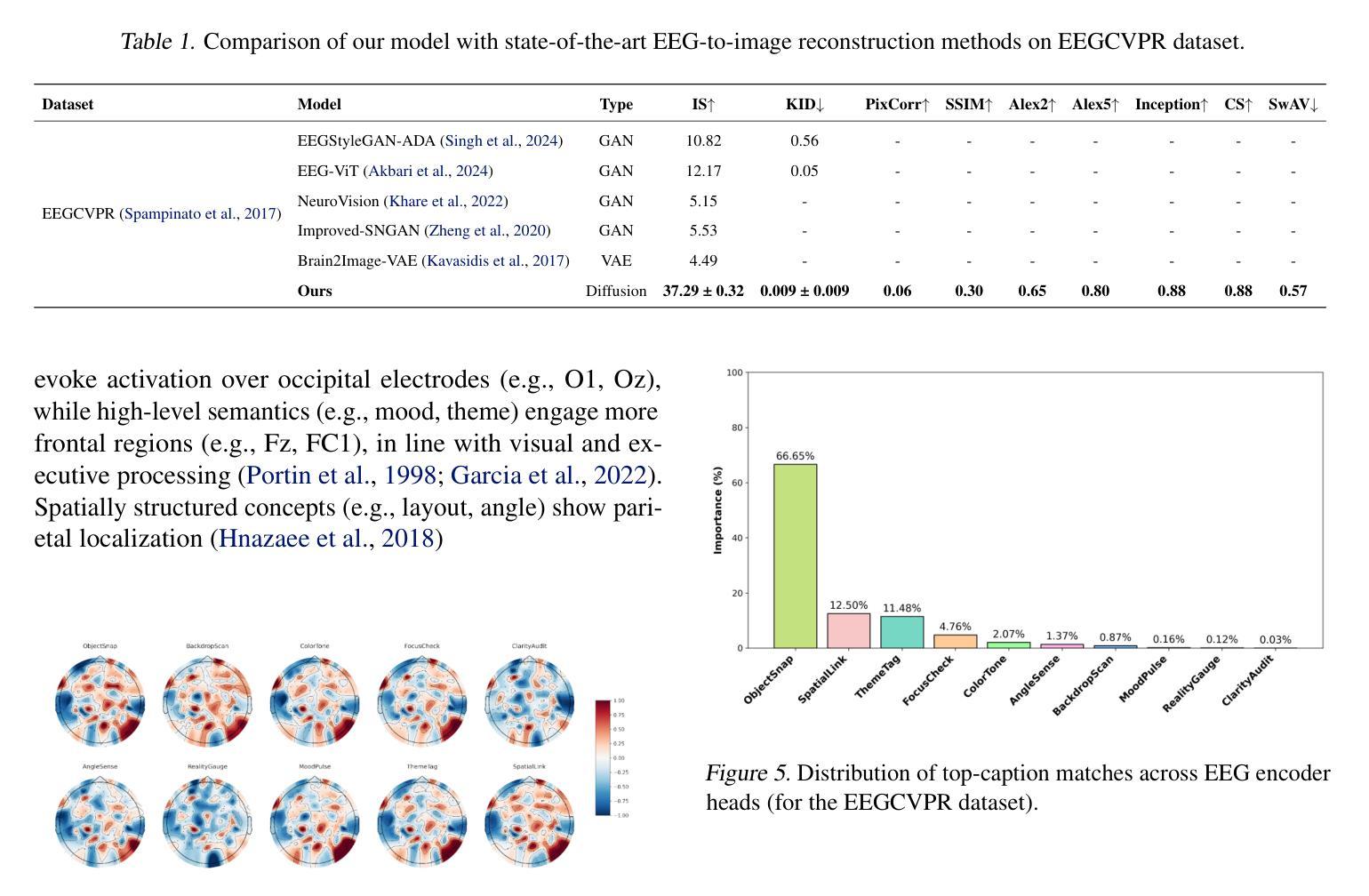
Decoding visual experience from brain signals offers exciting possibilities for neuroscience and interpretable AI. While EEG is accessible and temporally precise, its limitations in spatial detail hinder image reconstruction. Our model bypasses direct EEG-to-image generation by aligning EEG signals with multilevel semantic captions – ranging from object-level to abstract themes – generated by a large language model. A transformer-based EEG encoder maps brain activity to these captions through contrastive learning. During inference, caption embeddings retrieved via projection heads condition a pretrained latent diffusion model for image generation. This text-mediated framework yields state-of-the-art visual decoding on the EEGCVPR dataset, with interpretable alignment to known neurocognitive pathways. Dominant EEG-caption associations reflected the importance of different semantic levels extracted from perceived images. Saliency maps and t-SNE projections reveal semantic topography across the scalp. Our model demonstrates how structured semantic mediation enables cognitively aligned visual decoding from EEG.
从脑信号解码视觉经验为神经科学和可解释的AI提供了令人兴奋的可能性。脑电图(EEG)易于获取且时间精确,但其空间细节的局限性阻碍了图像重建。我们的模型通过使脑电图信号与大型语言模型生成的多层次语义标题(从对象级别到抽象主题)对齐,从而绕过了直接的脑电图到图像生成过程。基于变压器的脑电图编码器通过对比学习将这些标题映射到大脑活动上。在推理过程中,通过投影头检索的标题嵌入为图像生成提供了预训练的潜在扩散模型的先验条件。这种文本介导的框架在EEGCVPR数据集上实现了最先进的视觉解码效果,并与已知的神经认知途径具有可解释的对齐性。主导的脑电图标题关联反映了从感知图像中提取的不同语义级别的重要性。显著图(saliency maps)和t-SNE投影揭示了头皮上的语义地形。我们的模型展示了结构化语义中介如何使脑电图的认知对齐视觉解码成为可能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Actionable Interpretability Workshop (non-archival) at the 42 International Conference on Machine Learning
Summary
基于脑电信号解码视觉体验对于神经科学和可解释人工智能领域具有巨大潜力。本文提出一种新方法,通过语义字幕将EEG信号与图像生成相联系,避免了直接生成EEG图像的技术难题。该方法使用对比学习训练基于变压器的EEG编码器,将脑活动与语义字幕相对应,语义字幕涵盖从对象级别到抽象主题的不同层次。通过投影头检索字幕嵌入,进而在预训练的潜在扩散模型中生成图像。该文本介导框架在EEGCVPR数据集上实现了最先进的视觉解码效果,与已知神经认知途径的对齐解释性较强。EEG与字幕的主要关联反映了从感知图像中提取的不同语义层次的重要性。显著性图和t-SNE投影揭示了头皮表面的语义地形。该研究展示了结构化语义调解如何实现与认知对齐的EEG视觉解码。
Key Takeaways
- EEG在视觉解码方面具有巨大潜力,可以通过语义字幕与图像生成相联系。
- 使用对比学习训练基于变压器的EEG编码器,将脑活动与不同层次的语义字幕相对应。
- 通过投影头检索字幕嵌入,在预训练的潜在扩散模型中生成图像。
- 文本介导框架在EEGCVPR数据集上实现了先进的视觉解码效果。
- EEG与字幕的主要关联反映了从感知图像中提取的不同语义层次的重要性。
- 显著性图和t-SNE投影揭示了语义在头皮表面的分布。
点此查看论文截图

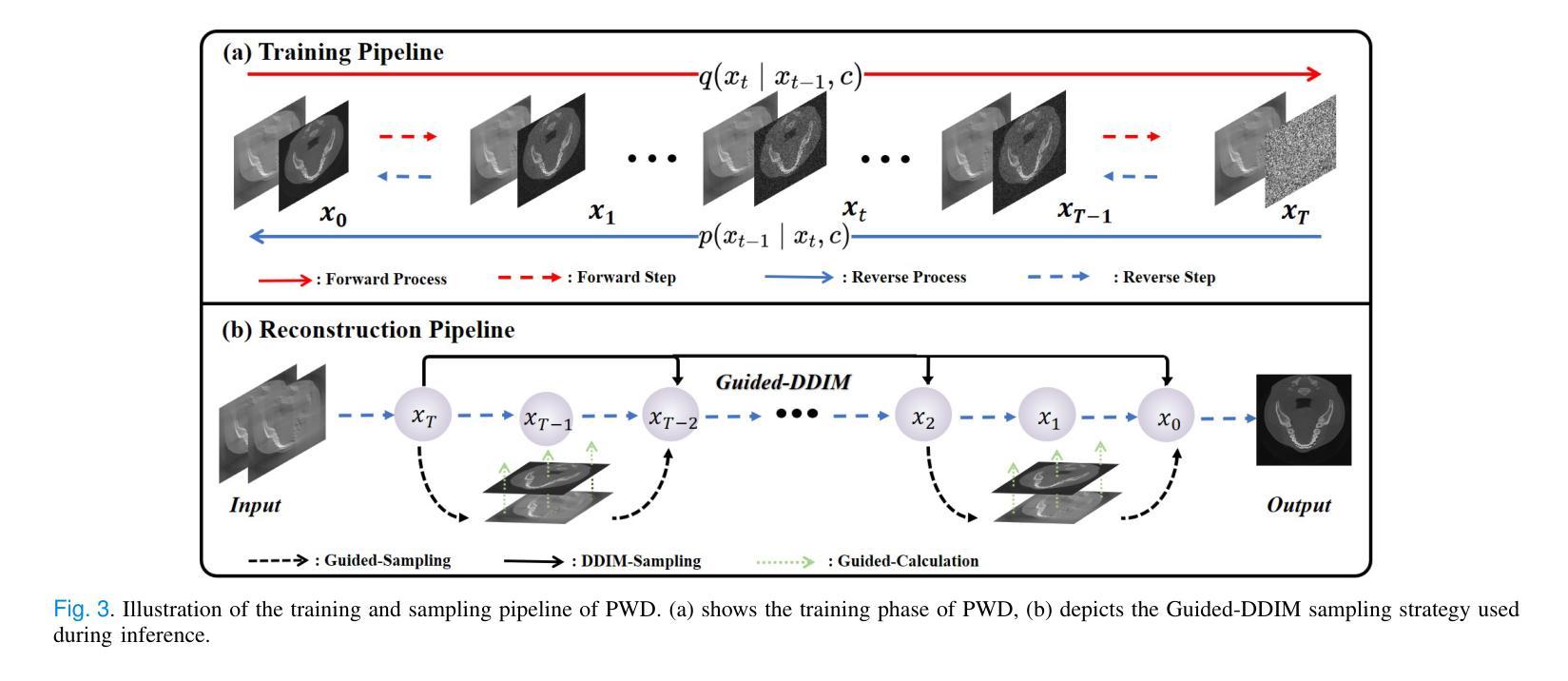
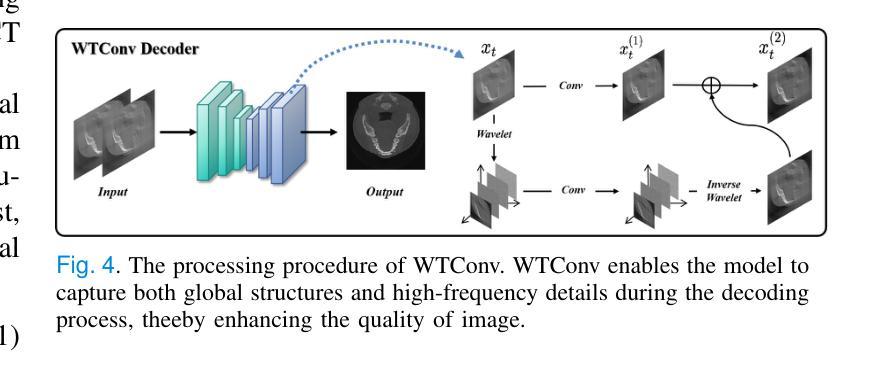
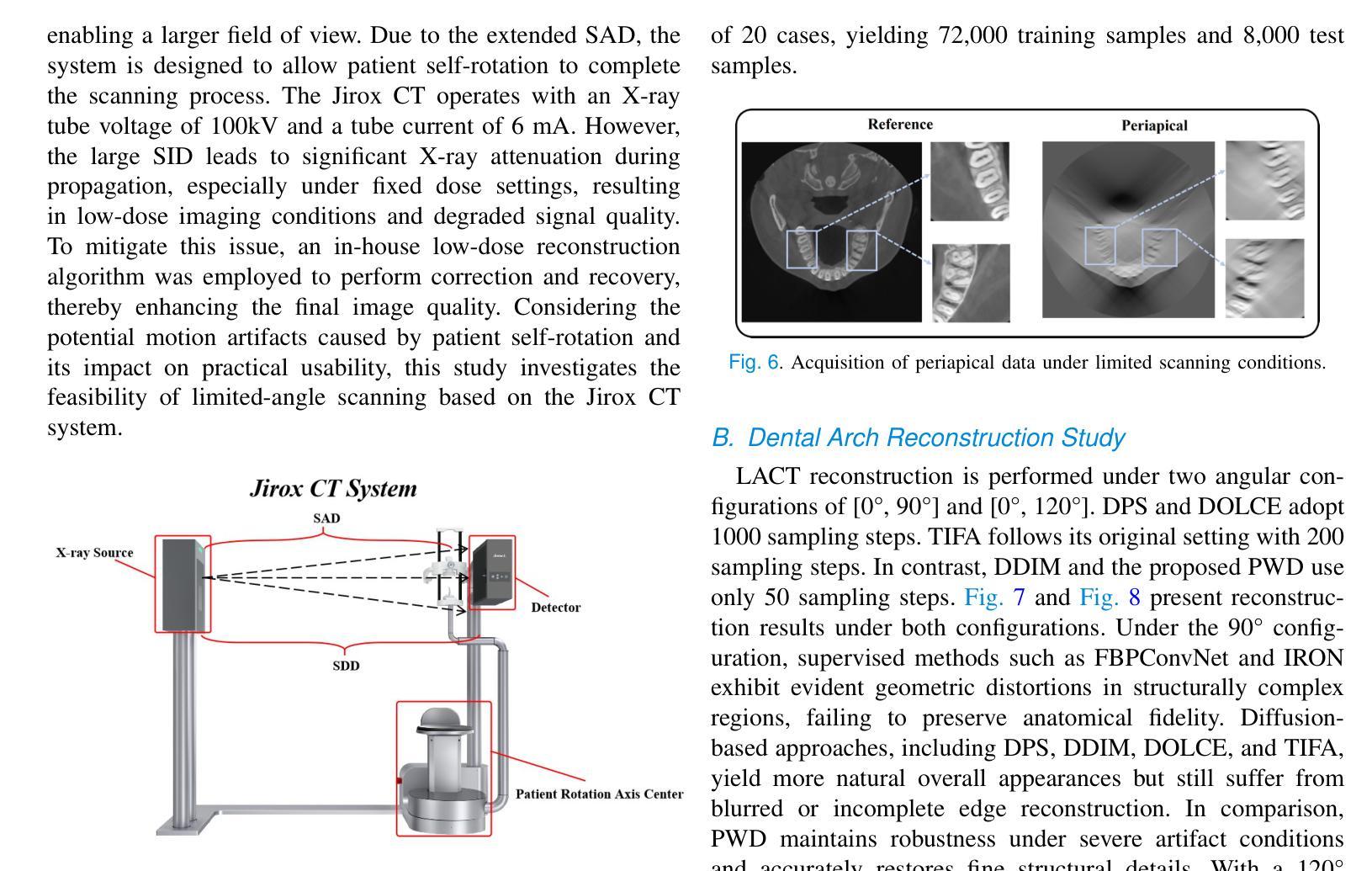
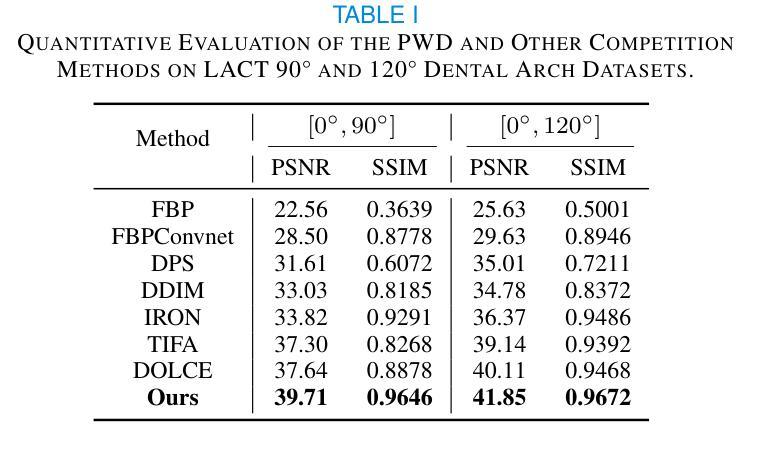
PWD: Prior-Guided and Wavelet-Enhanced Diffusion Model for Limited-Angle CT
Authors:Yi Liu, Yiyang Wen, Zekun Zhou, Junqi Ma, Linghang Wang, Yucheng Yao, Liu Shi, Qiegen Liu
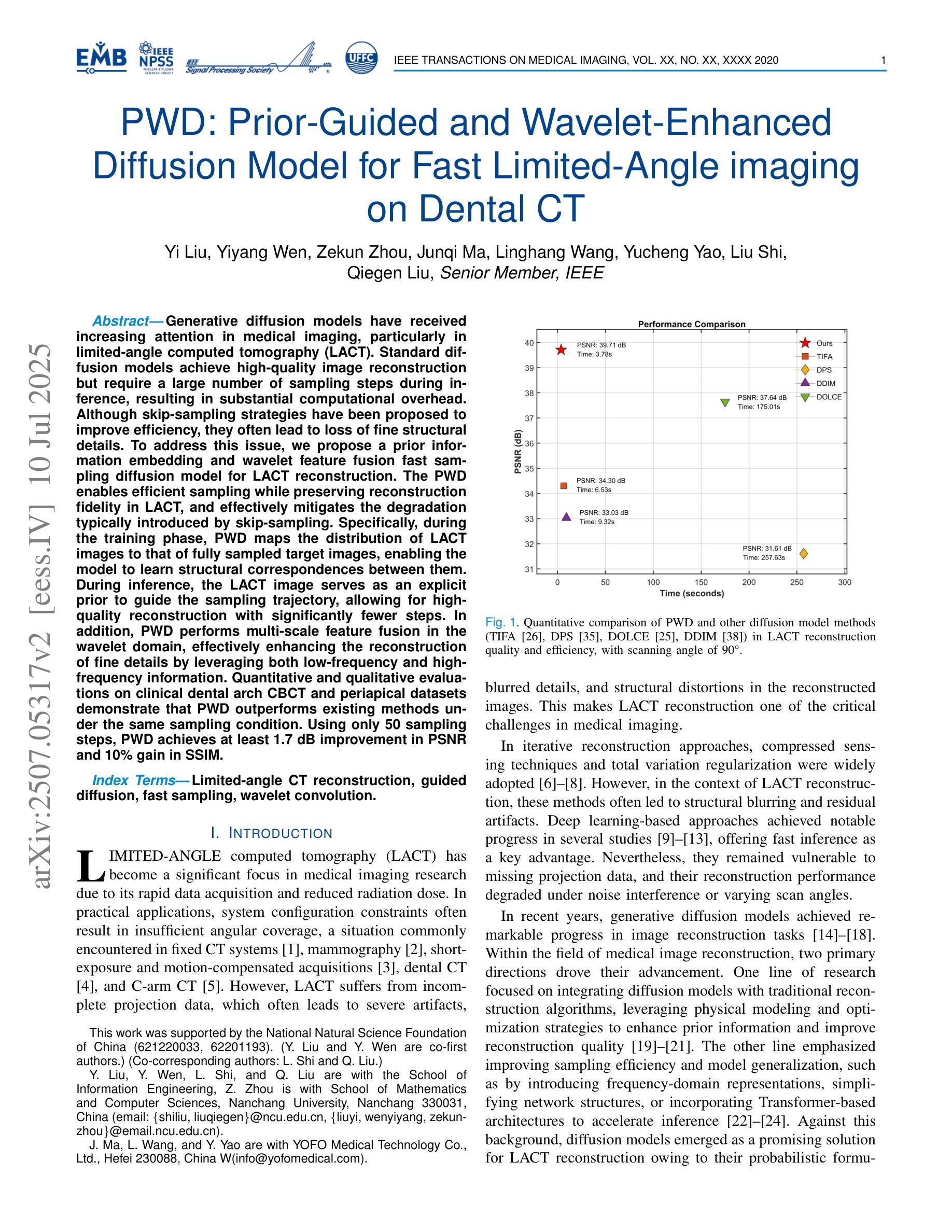
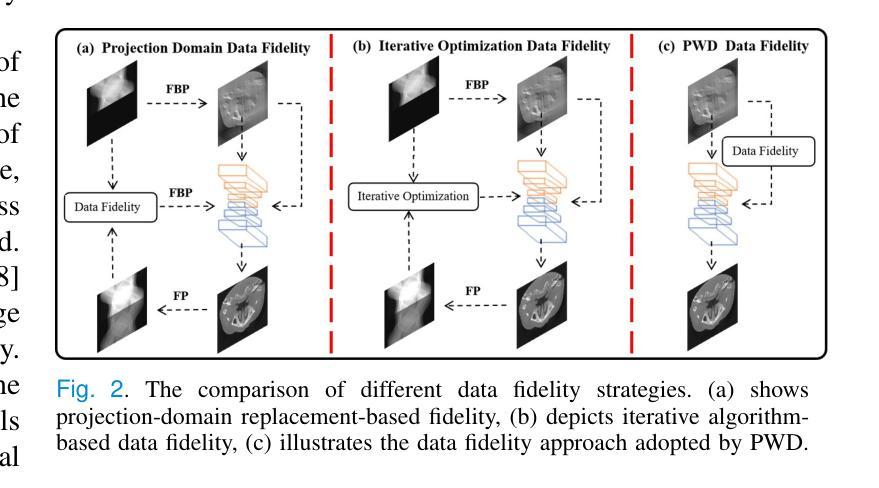
Generative diffusion models have received increasing attention in medical imaging, particularly in limited-angle computed tomography (LACT). Standard diffusion models achieve high-quality image reconstruction but require a large number of sampling steps during inference, resulting in substantial computational overhead. Although skip-sampling strategies have been proposed to improve efficiency, they often lead to loss of fine structural details. To address this issue, we propose a prior information embedding and wavelet feature fusion fast sampling diffusion model for LACT reconstruction. The PWD enables efficient sampling while preserving reconstruction fidelity in LACT, and effectively mitigates the degradation typically introduced by skip-sampling. Specifically, during the training phase, PWD maps the distribution of LACT images to that of fully sampled target images, enabling the model to learn structural correspondences between them. During inference, the LACT image serves as an explicit prior to guide the sampling trajectory, allowing for high-quality reconstruction with significantly fewer steps. In addition, PWD performs multi-scale feature fusion in the wavelet domain, effectively enhancing the reconstruction of fine details by leveraging both low-frequency and high-frequency information. Quantitative and qualitative evaluations on clinical dental arch CBCT and periapical datasets demonstrate that PWD outperforms existing methods under the same sampling condition. Using only 50 sampling steps, PWD achieves at least 1.7 dB improvement in PSNR and 10% gain in SSIM.
生成扩散模型在医学成像中得到了越来越多的关注,特别是在有限角度计算机断层扫描(LACT)中。标准扩散模型能够实现高质量图像重建,但在推理过程中需要大量采样步骤,导致计算开销大。虽然提出了跳过采样策略来提高效率,但它们往往会导致精细结构细节的丢失。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种基于先验信息嵌入和小波特征融合的快速采样扩散模型,用于LACT重建。PWD(Prior Wavelet Diffusion)能够在保持LACT重建保真度的同时实现高效采样,并有效缓解跳过采样通常引起的退化。具体而言,在训练阶段,PWD将LACT图像的分布映射到完全采样目标图像的分布,使模型能够学习两者之间的结构对应关系。在推理阶段,LACT图像作为明确的先验来引导采样轨迹,允许以较少的步骤实现高质量重建。此外,PWD在小波域执行多尺度特征融合,通过利用低频和高频信息有效地增强了精细细节的重建。在临床牙科全景CBCT和根尖周数据集上的定量和定性评估表明,在相同的采样条件下,PWD优于现有方法。仅使用50个采样步骤,PWD在PSNR上实现了至少1.7 dB的提升,在SSIM上获得了10%的增益。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对有限角度计算机断层扫描(LACT)的重构问题,提出了一种基于先验信息嵌入和小波特征融合的快速采样扩散模型。该模型在训练阶段将LACT图像分布映射到完全采样的目标图像分布,学习两者之间的结构对应关系。在推理阶段,LACT图像作为显式先验引导采样轨迹,实现高质量重构并大大减少采样步骤。同时,该模型利用小波域多尺度特征融合,有效增强精细细节的重构。实验证明,该模型在相同采样条件下优于现有方法,50步采样即可实现至少1.7 dB的峰值信噪比(PSNR)提升和10%的结构相似性指数(SSIM)增长。
Key Takeaways
- 生成性扩散模型在医学成像领域,特别是在有限角度计算机断层扫描(LACT)中受到关注。
- 标准扩散模型需要大量采样步骤,计算开销大,而跳过采样策略可能导致细节损失。
- 提出的模型利用先验信息嵌入和小波特征融合进行快速采样扩散。
- 在训练阶段,模型学习LACT图像与完全采样目标图像之间的结构对应关系。
- 在推理阶段,LACT图像作为显式先验引导采样轨迹,实现高效高质量重构。
- 模型利用小波域多尺度特征融合,增强细节重构能力。
点此查看论文截图
Diffusion Model-based Data Augmentation Method for Fetal Head Ultrasound Segmentation
Authors:Fangyijie Wang, Kevin Whelan, Félix Balado, Kathleen M. Curran, Guénolé Silvestre
Medical image data is less accessible than in other domains due to privacy and regulatory constraints. In addition, labeling requires costly, time-intensive manual image annotation by clinical experts. To overcome these challenges, synthetic medical data generation offers a promising solution. Generative AI (GenAI), employing generative deep learning models, has proven effective at producing realistic synthetic images. This study proposes a novel mask-guided GenAI approach using diffusion models to generate synthetic fetal head ultrasound images paired with segmentation masks. These synthetic pairs augment real datasets for supervised fine-tuning of the Segment Anything Model (SAM). Our results show that the synthetic data captures real image features effectively, and this approach reaches state-of-the-art fetal head segmentation, especially when trained with a limited number of real image-mask pairs. In particular, the segmentation reaches Dice Scores of 94.66% and 94.38% using a handful of ultrasound images from the Spanish and African cohorts, respectively. Our code, models, and data are available on GitHub.
医学图像数据由于隐私和监管限制,其可访问性比其他领域的数据要低。此外,标注需要临床专家进行昂贵且耗时的手动图像标注。为了克服这些挑战,合成医学数据生成提供了一个有前景的解决方案。采用生成式深度学习模型的生成式人工智能(GenAI)在生成逼真的合成图像方面已证明是有效的。本研究提出了一种使用扩散模型的新型掩膜引导GenAI方法,生成合成胎儿头部超声图像及其分割掩膜配对。这些合成配对数据增强了真实数据集,用于监督微调Segment Anything Model(SAM)。结果表明,合成数据有效地捕捉了真实图像的特征,尤其是在使用有限数量的真实图像-掩膜配对进行训练时,该方法达到了最先进的胎儿头部分割效果。尤其是,使用来自西班牙和非洲队列的少量超声图像,分割达到迪克分数(Dice Scores)分别为94.66%和94.38%。我们的代码、模型和数据均可在GitHub上获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at Irish Machine Vision and Image Processing Conference (IMVIP) 2025
Summary
本研究提出一种使用扩散模型生成带有分割掩膜合成胎儿头部超声图像的新方法。这种方法克服了医学图像数据难以获取和标注成本高昂的问题,通过生成合成数据增强真实数据集,用于监督微调SAM模型。结果显示合成数据有效捕捉真实图像特征,并在有限真实图像-掩膜对训练下达到先进胎儿头部分割效果,Dice得分分别为94.66%和94.38%。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像数据因隐私和监管限制而难以获取。
- 手工标注医学图像耗时且成本高昂。
- 生成式AI(GenAI)采用深度生成模型可有效生成逼真的合成图像。
- 本研究提出一种新颖的mask-guided GenAI方法,使用扩散模型生成配对的合成胎儿头部超声图像和分割掩膜。
- 合成数据增强现实数据集,用于监督微调SAM模型。
- 合成数据有效捕捉真实图像特征,在有限真实图像-掩膜对训练下达到先进胎儿头部分割效果。
点此查看论文截图

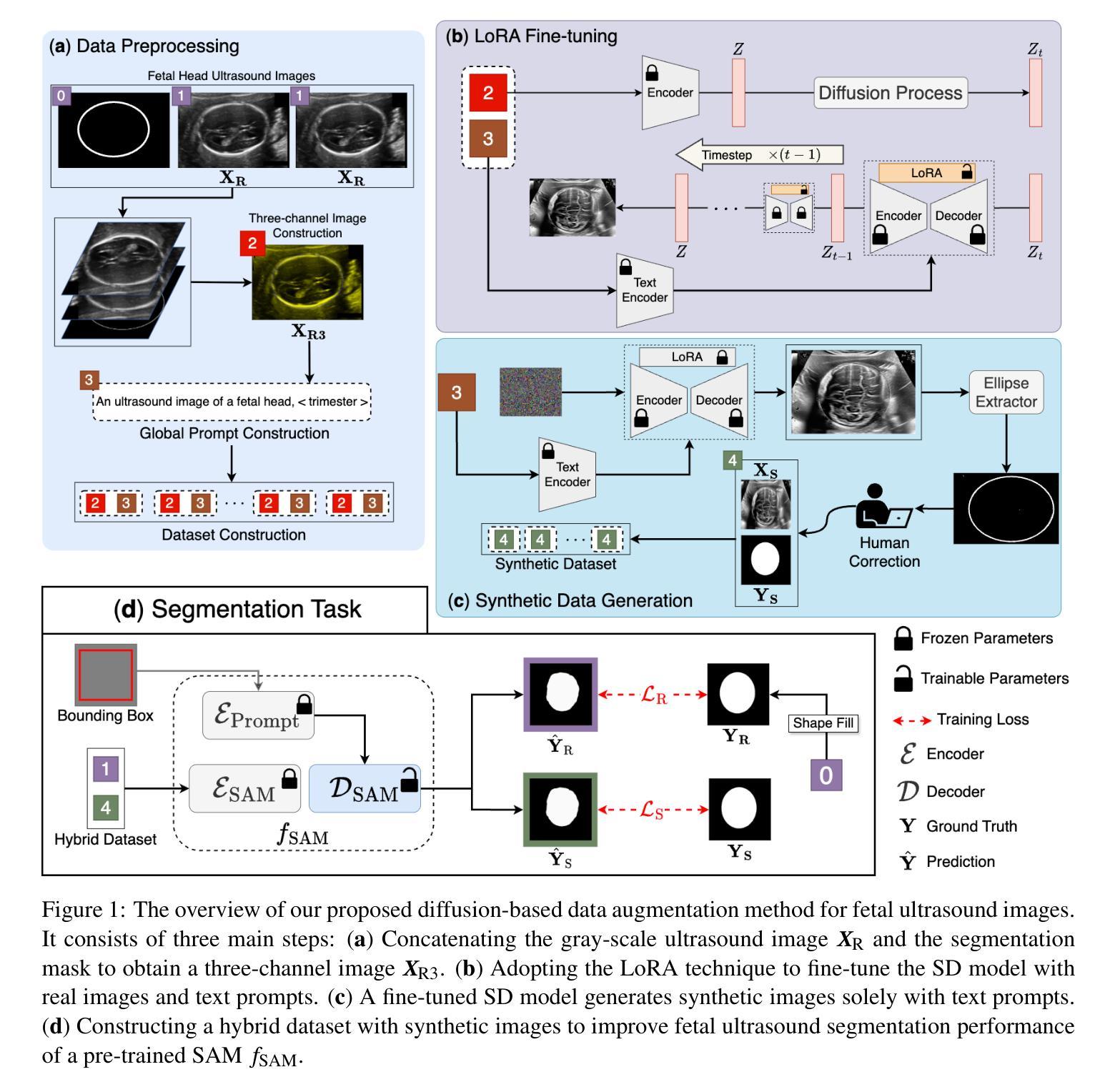
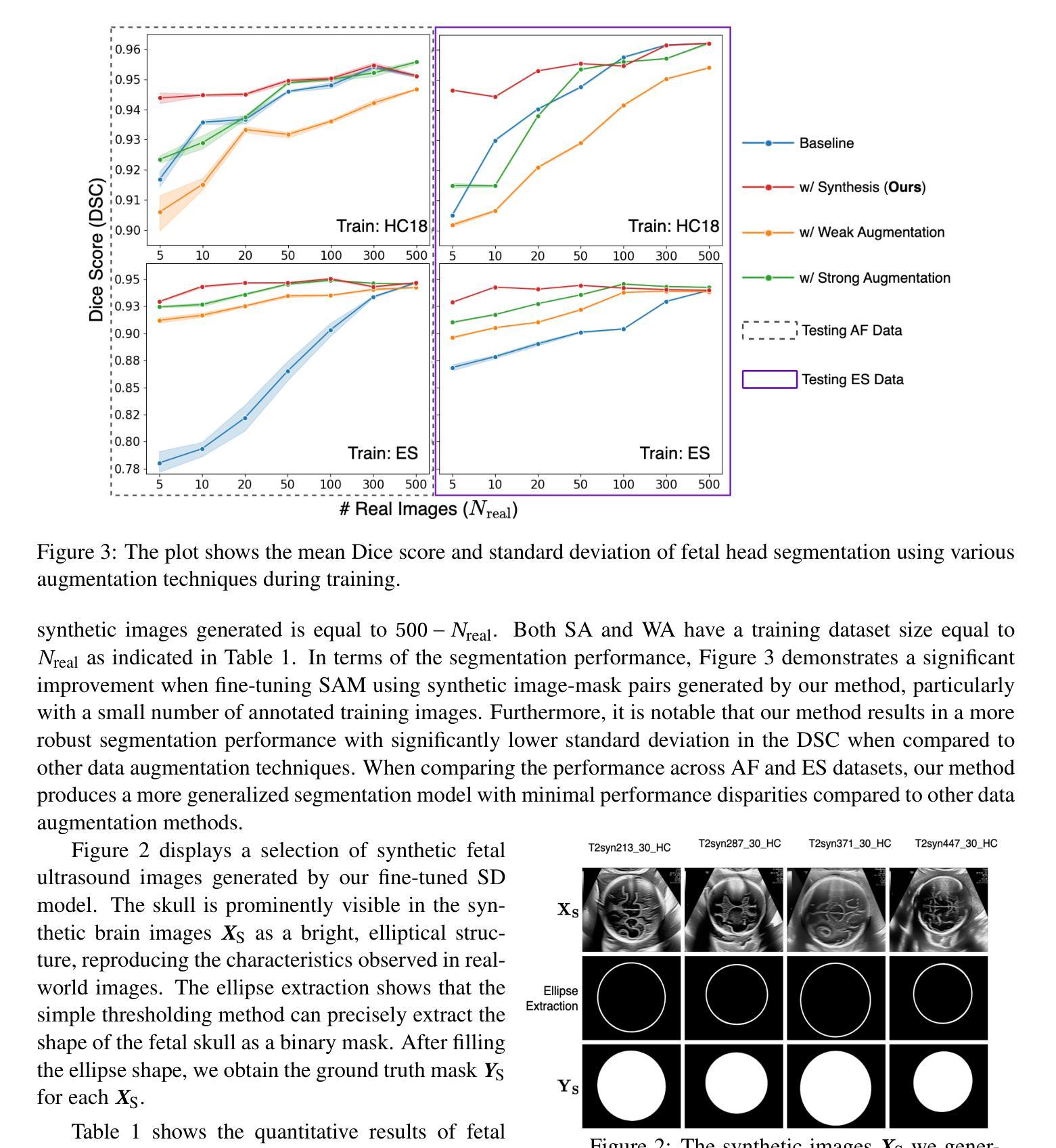
HadaNorm: Diffusion Transformer Quantization through Mean-Centered Transformations
Authors:Marco Federici, Riccardo Del Chiaro, Boris van Breugel, Paul Whatmough, Markus Nagel
Diffusion models represent the cutting edge in image generation, but their high memory and computational demands hinder deployment on resource-constrained devices. Post-Training Quantization (PTQ) offers a promising solution by reducing the bitwidth of matrix operations. However, standard PTQ methods struggle with outliers, and achieving higher compression often requires transforming model weights and activations before quantization. In this work, we propose HadaNorm, a novel linear transformation that extends existing approaches by both normalizing channels activations and applying Hadamard transforms to effectively mitigate outliers and enable aggressive activation quantization. We demonstrate that HadaNorm consistently reduces quantization error across the various components of transformer blocks, outperforming state-of-the-art methods.
扩散模型是图像生成领域的前沿技术,但其对内存和计算资源的高需求限制了其在资源受限设备上的部署。后训练量化(PTQ)通过降低矩阵操作的位宽提供了一种有前景的解决方案。然而,标准PTQ方法难以处理异常值,为实现更高的压缩,通常需要在量化前对模型权重和激活进行转换。在这项工作中,我们提出了HadaNorm,这是一种新型线性转换,它通过标准化通道激活和应用哈达玛变换来有效缓解异常值问题,从而实现激烈的激活量化。我们证明,HadaNorm在变压器块的各种组件中一致地减少了量化误差,超越了最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 Pages, 6 Figures
Summary
本文介绍了扩散模型在图像生成领域的最新进展,但其高内存和计算需求限制了其在资源受限设备上的应用。为解决这一问题,研究人员提出了采用后训练量化(PTQ)方法降低矩阵操作位宽的策略。然而,标准PTQ方法面临处理异常值的问题,并且为了在量化前变换模型权重和激活值来实现更高的压缩率。本研究提出了HadaNorm,一种新型线性变换方法,它通过归一化通道激活和采用Hadamard变换来有效减轻异常值问题,从而实现激烈的激活量化。实验证明,HadaNorm在变压器块的各个组件中一致降低了量化误差,优于现有最先进的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型是图像生成的前沿技术,但其在资源受限设备上的部署受限。
- 后训练量化(PTQ)是解决扩散模型高内存和计算需求的有效方法。
- 标准PTQ方法面临处理异常值的问题。
- HadaNorm是一种新型线性变换方法,用于在量化过程中有效减轻异常值问题。
- HadaNorm通过归一化通道激活和采用Hadamard变换来实现激活量化的优化。
- HadaNorm在不同组件的变压器块中一致降低了量化误差。
点此查看论文截图
Revisiting Likelihood-Based Out-of-Distribution Detection by Modeling Representations
Authors:Yifan Ding, Arturas Aleksandraus, Amirhossein Ahmadian, Jonas Unger, Fredrik Lindsten, Gabriel Eilertsen
Out-of-distribution (OOD) detection is critical for ensuring the reliability of deep learning systems, particularly in safety-critical applications. Likelihood-based deep generative models have historically faced criticism for their unsatisfactory performance in OOD detection, often assigning higher likelihood to OOD data than in-distribution samples when applied to image data. In this work, we demonstrate that likelihood is not inherently flawed. Rather, several properties in the images space prohibit likelihood as a valid detection score. Given a sufficiently good likelihood estimator, specifically using the probability flow formulation of a diffusion model, we show that likelihood-based methods can still perform on par with state-of-the-art methods when applied in the representation space of pre-trained encoders. The code of our work can be found at $\href{https://github.com/limchaos/Likelihood-OOD.git}{\texttt{https://github.com/limchaos/Likelihood-OOD.git}}$.
在深度学习的可靠性保障方面,尤其是在关键安全应用中,超出分布范围的检测(Out-of-Distribution Detection,简称OOD)是非常关键的。基于可能性的深度生成模型在历史中因其对超出分布范围检测的欠佳表现而受到批评。当应用于图像数据时,这些模型往往会对超出分布范围的数据分配更高的可能性,高于对内部分布样本的分配可能性。在这项工作中,我们证明了可能性并非天生存在问题。相反,图像空间中的某些属性阻止了可能性作为一个有效的检测分数。给定一个足够好的可能性估计器,特别是使用扩散模型的概率流公式,我们展示了在预训练编码器的表示空间中应用时,基于可能性的方法仍然可以与最先进的方法表现相当。我们工作的代码可以在https://github.com/limchaos/Likelihood-OOD.git找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Scandinavian Conference on Image Analysis 2025 (oral)
Summary
基于似然的方法在进行异常检测(OOD检测)时能够表现良好,但需要选择正确的图像特征空间并使用合适的预训练编码器。本工作指出,利用扩散模型的概率流公式构建似然估计器,可以在预训练编码器的特征空间上实现与最新技术相当的性能。
Key Takeaways
- OOD检测对于确保深度学习系统的可靠性至关重要,特别是在安全关键应用中。
- 传统上基于似然的深度生成模型在OOD检测中表现不佳,容易对OOD数据赋予较高的似然值。
- 在图像空间中,某些特性阻碍了似然作为有效的检测分数。
- 使用良好的似然估计器,特别是基于扩散模型的概率流公式,可以改善基于似然的方法的性能。
- 在预训练编码器的特征空间上应用基于似然的方法,可以达到与最新技术相当的效果。
- 该工作的代码已公开,可供进一步研究参考。
点此查看论文截图

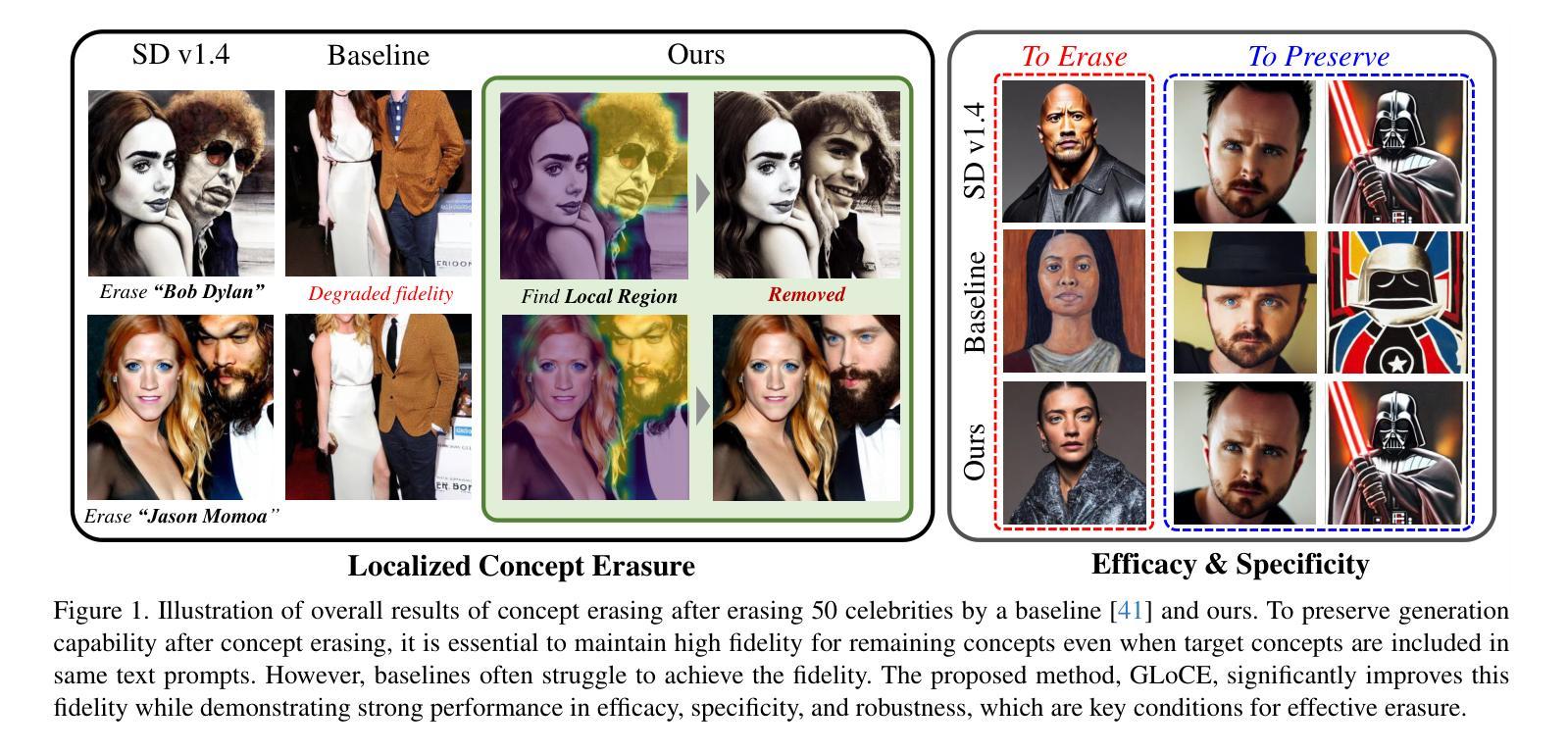
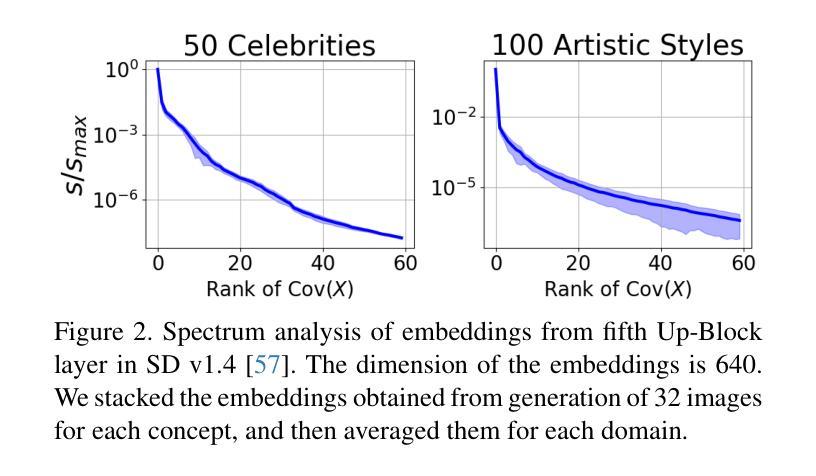
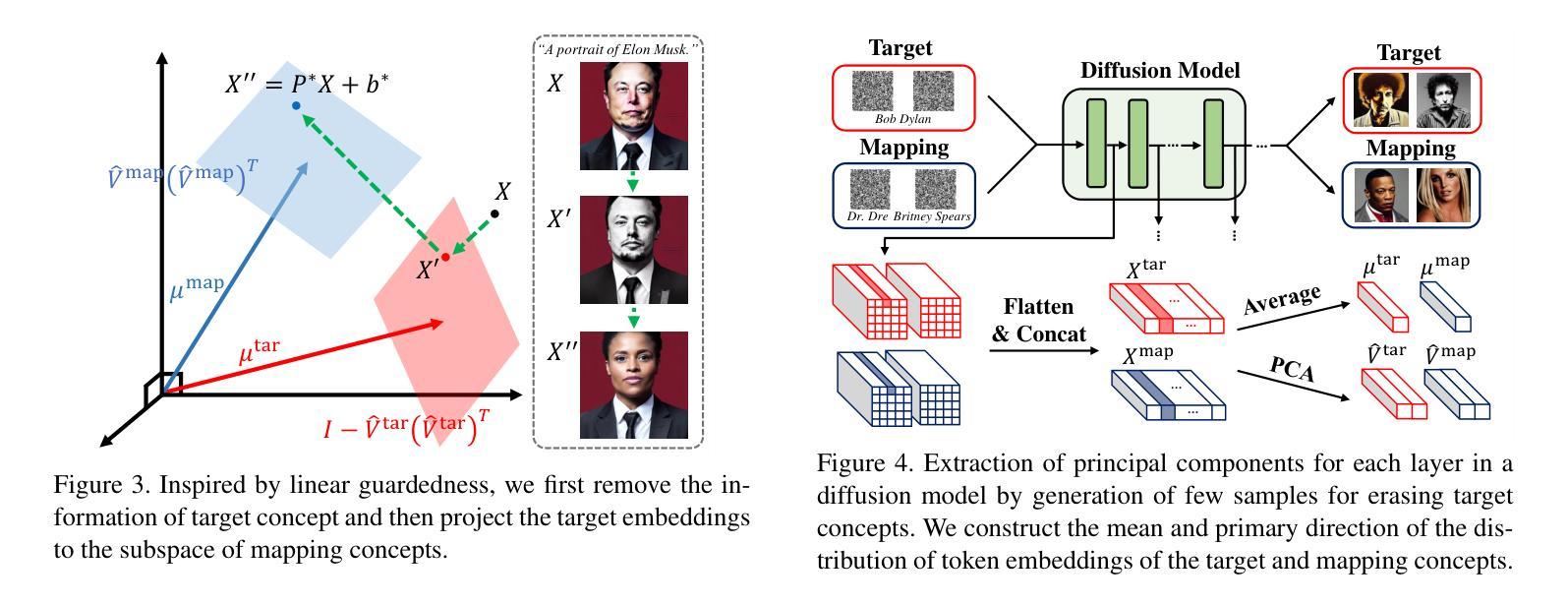
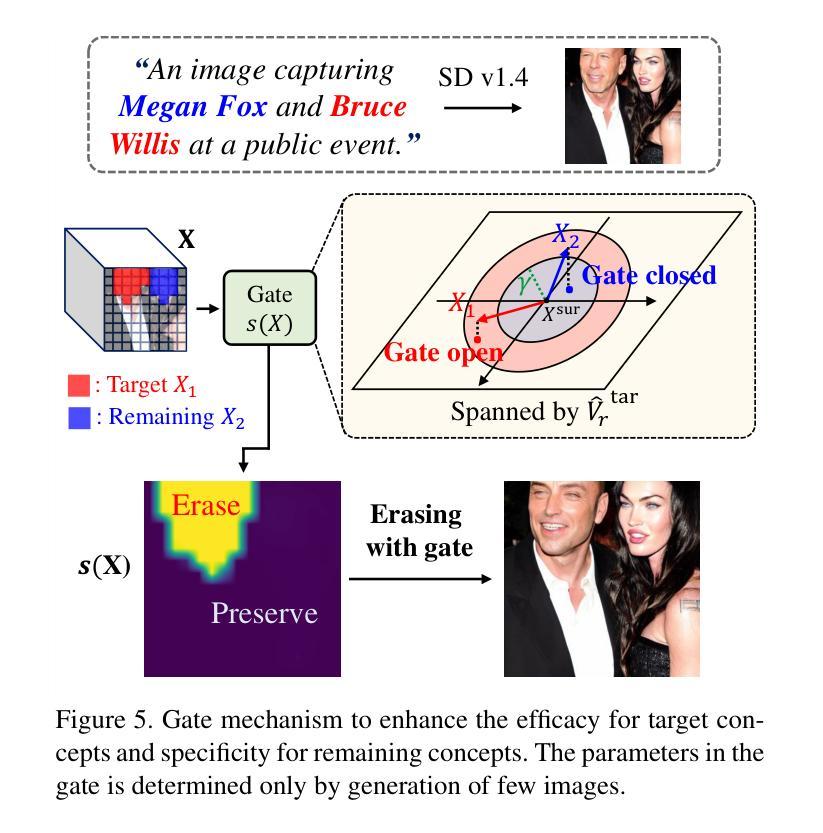
Localized Concept Erasure for Text-to-Image Diffusion Models Using Training-Free Gated Low-Rank Adaptation
Authors:Byung Hyun Lee, Sungjin Lim, Se Young Chun
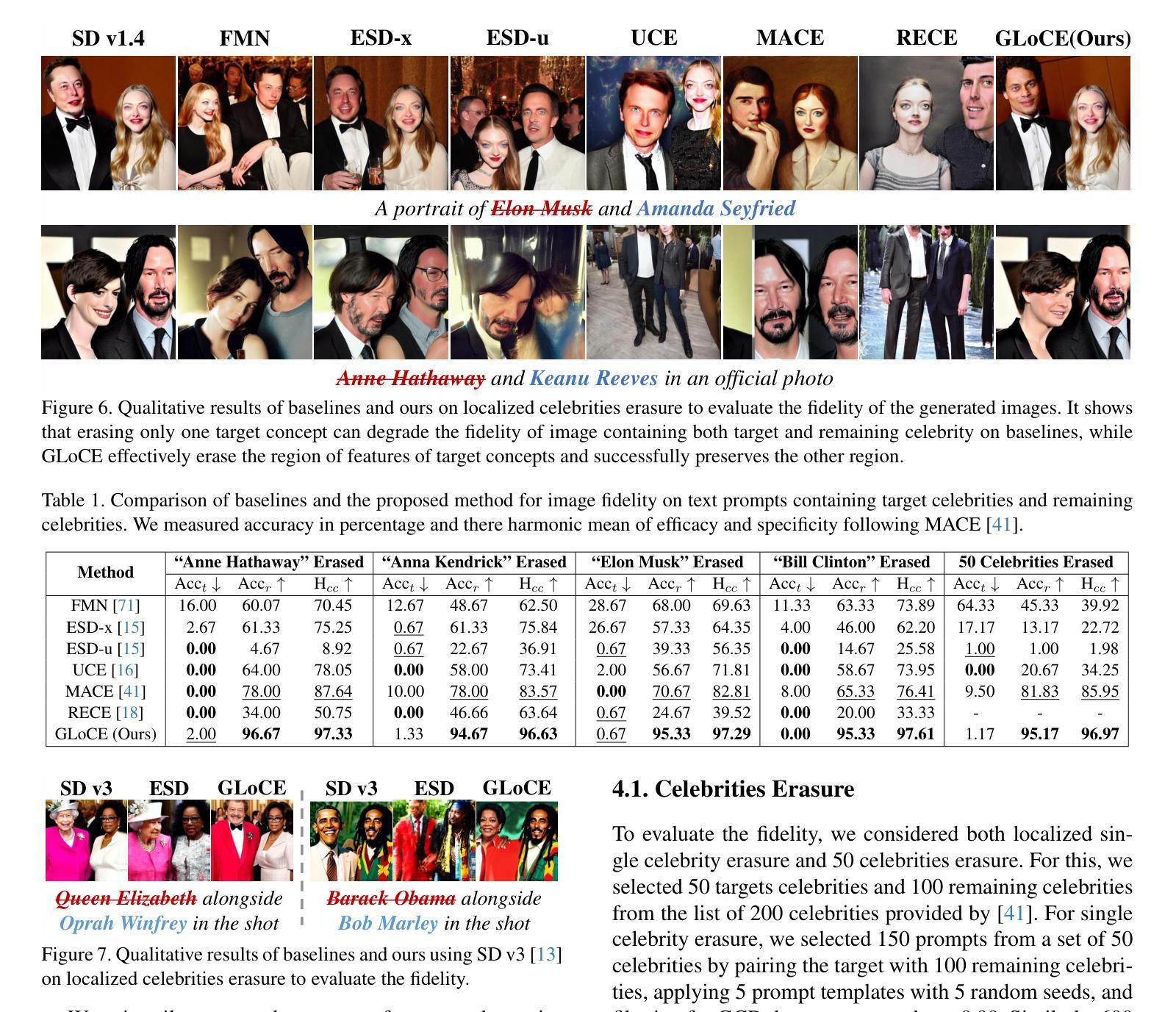
Fine-tuning based concept erasing has demonstrated promising results in preventing generation of harmful contents from text-to-image diffusion models by removing target concepts while preserving remaining concepts. To maintain the generation capability of diffusion models after concept erasure, it is necessary to remove only the image region containing the target concept when it locally appears in an image, leaving other regions intact. However, prior arts often compromise fidelity of the other image regions in order to erase the localized target concept appearing in a specific area, thereby reducing the overall performance of image generation. To address these limitations, we first introduce a framework called localized concept erasure, which allows for the deletion of only the specific area containing the target concept in the image while preserving the other regions. As a solution for the localized concept erasure, we propose a training-free approach, dubbed Gated Low-rank adaptation for Concept Erasure (GLoCE), that injects a lightweight module into the diffusion model. GLoCE consists of low-rank matrices and a simple gate, determined only by several generation steps for concepts without training. By directly applying GLoCE to image embeddings and designing the gate to activate only for target concepts, GLoCE can selectively remove only the region of the target concepts, even when target and remaining concepts coexist within an image. Extensive experiments demonstrated GLoCE not only improves the image fidelity to text prompts after erasing the localized target concepts, but also outperforms prior arts in efficacy, specificity, and robustness by large margin and can be extended to mass concept erasure.
基于概念擦除的微调在防止文本到图像扩散模型生成有害内容方面显示出良好的前景。它通过消除目标概念同时保留剩余概念来实现这一点。为了保持扩散模型在概念擦除后的生成能力,有必要只移除图像中包含目标概念的区域,同时保持其他区域不变。然而,现有的技术往往为了消除特定区域中出现的局部目标概念而牺牲了其他图像区域的保真度,从而降低了图像生成的总体性能。为了解决这些局限性,我们首先引入了一个名为局部概念擦除的框架,它允许只删除图像中包含目标概念的特定区域,同时保留其他区域。作为局部概念擦除的解决方案,我们提出了一种无需训练的方法,称为用于概念擦除的带门控的低秩自适应(GLoCE),它将一个轻量级模块注入到扩散模型中。GLoCE由低秩矩阵和简单门组成,仅由几代的生成步骤决定概念,无需训练。通过将GLoCE直接应用于图像嵌入并设计仅在目标概念出现时激活的门,GLoCE可以仅选择性地删除目标概念的区域,即使目标概念和剩余的概念共存于图像中也是如此。大量实验表明,GLoCE不仅在擦除局部目标概念后对文本提示的图像保真度有所提高,而且在有效性、特异性和稳健性方面大大超越了现有技术,并且可以扩展到大规模的概念擦除。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025
Summary:
基于概念擦除的微调在防止文本到图像扩散模型生成有害内容方面展现出良好效果。为了维护扩散模型在概念擦除后的生成能力,只需删除包含目标概念的图像区域,同时保留其他区域。为解决现有技术在擦除特定区域目标概念时损害其他图像区域保真度的问题,本文引入了一个名为局部概念擦除的框架,并提出了一种无需训练的解决方案——GLoCE(门控低秩适应概念擦除)。GLoCE通过在扩散模型中注入轻量级模块来实现选择性擦除目标概念区域,即使目标概念和剩余概念共存于图像中也是如此。实验表明,GLoCE不仅能提高擦除目标概念后的图像对文本提示的保真度,而且在有效性、特异性和稳健性方面大大优于现有技术,并可扩展到大规模概念擦除。
Key Takeaways:
- 概念擦除在防止文本到图像扩散模型生成有害内容方面至关重要。
- 局部概念擦除框架允许仅删除图像中包含目标概念的特定区域,同时保持其他区域的完整性。
- GLoCE是一种无需训练的解决方案,通过注入轻量级模块到扩散模型中实现选择性擦除目标概念区域。
- GLoCE通过直接在图像嵌入上应用并设计仅针对目标概念的门来控制激活,实现选择性擦除。
- 实验表明,GLoCE在擦除局部目标概念后提高了图像对文本提示的保真度。
- GLoCE在有效性、特异性和稳健性方面显著优于现有技术。
- GLoCE可扩展到大规模概念擦除。
点此查看论文截图

Solving Inverse Problems using Diffusion with Iterative Colored Renoising
Authors:Matt C. Bendel, Saurav K. Shastri, Rizwan Ahmad, Philip Schniter
Imaging inverse problems can be solved in an unsupervised manner using pre-trained diffusion models, but doing so requires approximating the gradient of the measurement-conditional score function in the diffusion reverse process. We show that the approximations produced by existing methods are relatively poor, especially early in the reverse process, and so we propose a new approach that iteratively reestimates and “renoises” the estimate several times per diffusion step. This iterative approach, which we call Fast Iterative REnoising (FIRE), injects colored noise that is shaped to ensure that the pre-trained diffusion model always sees white noise, in accordance with how it was trained. We then embed FIRE into the DDIM reverse process and show that the resulting “DDfire” offers state-of-the-art accuracy and runtime on several linear inverse problems, as well as phase retrieval. Our implementation is at https://github.com/matt-bendel/DDfire
使用预训练的扩散模型以无监督的方式解决成像反问题,需要在扩散反向过程中近似测量条件得分函数的梯度。我们显示现有方法产生的近似值相对较差,尤其是在反向过程的早期,因此,我们提出了一种新方法,该方法在每个扩散步骤中多次重新估计和“增加噪声”。我们称这种迭代方法为快速迭代重新噪声化(FIRE),它注入有色噪声,以确保预训练的扩散模型始终看到白噪声,符合其训练方式。然后,我们将FIRE嵌入到DDIM反向过程中,并证明由此产生的“DDfire”在几个线性反问题以及相位检索方面提供了最先进的准确性和运行时。我们的实现位于https://github.com/matt-bendel/DDfire。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:利用预训练的扩散模型以无监督的方式解决成像反问题,需要估计测量条件分数函数的梯度。现有方法产生的近似值在早期逆向过程中相对较差,因此提出了一种新的方法——快速迭代去噪(FIRE),在每个扩散步骤中多次重新估计和“加入噪声”。将FIRE嵌入DDIM逆向过程,得到的DDfire在多个线性反问题以及相位检索方面具有最佳精度和运行时效率。
Key Takeaways:
- 扩散模型可以无监督地解决成像反问题。
- 现有方法估计测量条件分数函数的梯度时存在不足。
- 提出了快速迭代去噪(FIRE)方法,以提高估计的准确性。
- FIRE方法通过注入彩色噪声,确保预训练的扩散模型始终看到白噪声。
- DDfire方法将FIRE嵌入DDIM逆向过程。
- DDfire在多个线性反问题和相位检索方面具有最佳性能和效率。
点此查看论文截图


Diffusion Augmented Retrieval: A Training-Free Approach to Interactive Text-to-Image Retrieval
Authors:Zijun Long, Kangheng Liang, Gerardo Aragon-Camarasa, Richard Mccreadie, Paul Henderson
Interactive Text-to-image retrieval (I-TIR) is an important enabler for a wide range of state-of-the-art services in domains such as e-commerce and education. However, current methods rely on finetuned Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), which are costly to train and update, and exhibit poor generalizability. This latter issue is of particular concern, as: 1) finetuning narrows the pretrained distribution of MLLMs, thereby reducing generalizability; and 2) I-TIR introduces increasing query diversity and complexity. As a result, I-TIR solutions are highly likely to encounter queries and images not well represented in any training dataset. To address this, we propose leveraging Diffusion Models (DMs) for text-to-image mapping, to avoid finetuning MLLMs while preserving robust performance on complex queries. Specifically, we introduce Diffusion Augmented Retrieval (DAR), a framework that generates multiple intermediate representations via LLM-based dialogue refinements and DMs, producing a richer depiction of the user’s information needs. This augmented representation facilitates more accurate identification of semantically and visually related images. Extensive experiments on four benchmarks show that for simple queries, DAR achieves results on par with finetuned I-TIR models, yet without incurring their tuning overhead. Moreover, as queries become more complex through additional conversational turns, DAR surpasses finetuned I-TIR models by up to 7.61% in Hits@10 after ten turns, illustrating its improved generalization for more intricate queries.
交互式文本到图像检索(I-TIR)是电子商务和教育等领域先进服务广泛应用的重要推动者。然而,当前的方法依赖于微调的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs),这些模型训练和更新的成本很高,并且通用性较差。后者的问题尤其值得关注,因为:1)微调会缩小MLLMs的预训练分布,从而降低其通用性;2)I-TIR引入了日益增长的查询多样性和复杂性。因此,I-TIR解决方案很可能会遇到任何训练数据集中表示不佳的查询和图像。为了解决这一问题,我们提出利用扩散模型(DMs)进行文本到图像的映射,以避免对MLLMs进行微调,同时在复杂查询上保持稳健的性能。具体来说,我们引入了扩散增强检索(DAR)框架,该框架通过基于LLM的对话精炼和DMs生成多个中间表示,从而提供更丰富的用户信息需求的描述。这种增强的表示有助于更准确地识别语义和视觉相关的图像。在四个基准测试上的大量实验表明,对于简单查询,DAR在不产生额外的微调开销的情况下,实现了与微调过的I-TIR模型相当的结果。此外,随着查询通过额外的对话回合变得更为复杂,DAR在十回合后的命中率提高了高达7.61%,这证明了其在更复杂的查询中具有更好的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了Interactive Text-to-image Retrieval(I-TIR)的重要性及其在电子商务和教育等领域的应用。然而,当前的方法依赖于微调的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs),训练成本高且通用性较差。为解决这一问题,本文提出利用Diffusion Models(DMs)进行文本到图像的映射,避免微调MLLMs,同时在复杂查询上保持稳健性能。实验表明,对于简单查询,新提出的方法与微调I-TIR模型结果相当,而对于复杂查询,则表现出更好的泛化能力和性能提升。
Key Takeaways
- I-TIR对于电子商务和教育等领域至关重要。
- 当前I-TIR方法依赖昂贵的训练成本且通用性差的微调多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)。
- 利用Diffusion Models(DMs)进行文本到图像的映射可以避免微调MLLMs并保持对复杂查询的稳健性能。
- 新方法通过引入Diffusion Augmented Retrieval(DAR)框架生成多个中间表示,通过LLM基于对话的细化修正和DMs产生更丰富用户信息需求的描述。
- 对于简单查询,DAR与微调的I-TIR模型结果相当。
- 对于复杂查询,DAR在多次对话回合后超越调参模型,在Hits@10上提高了7.61%,显示出更好的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图


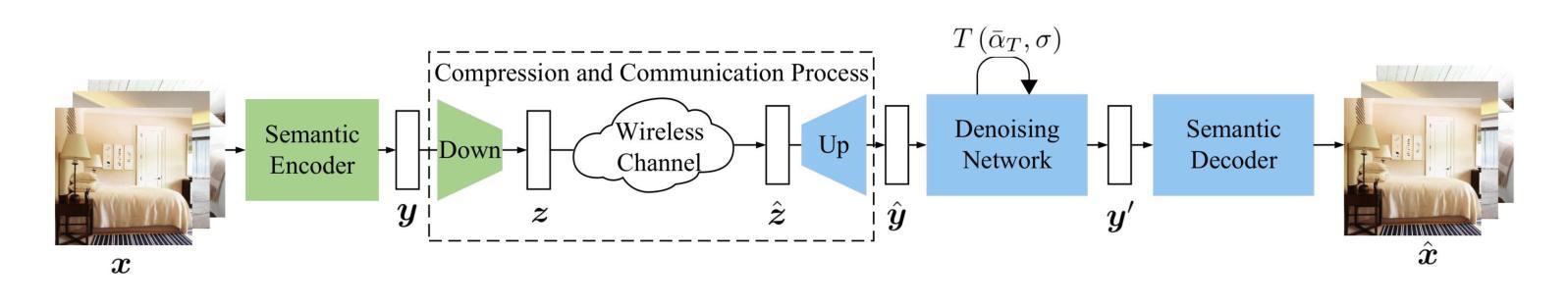
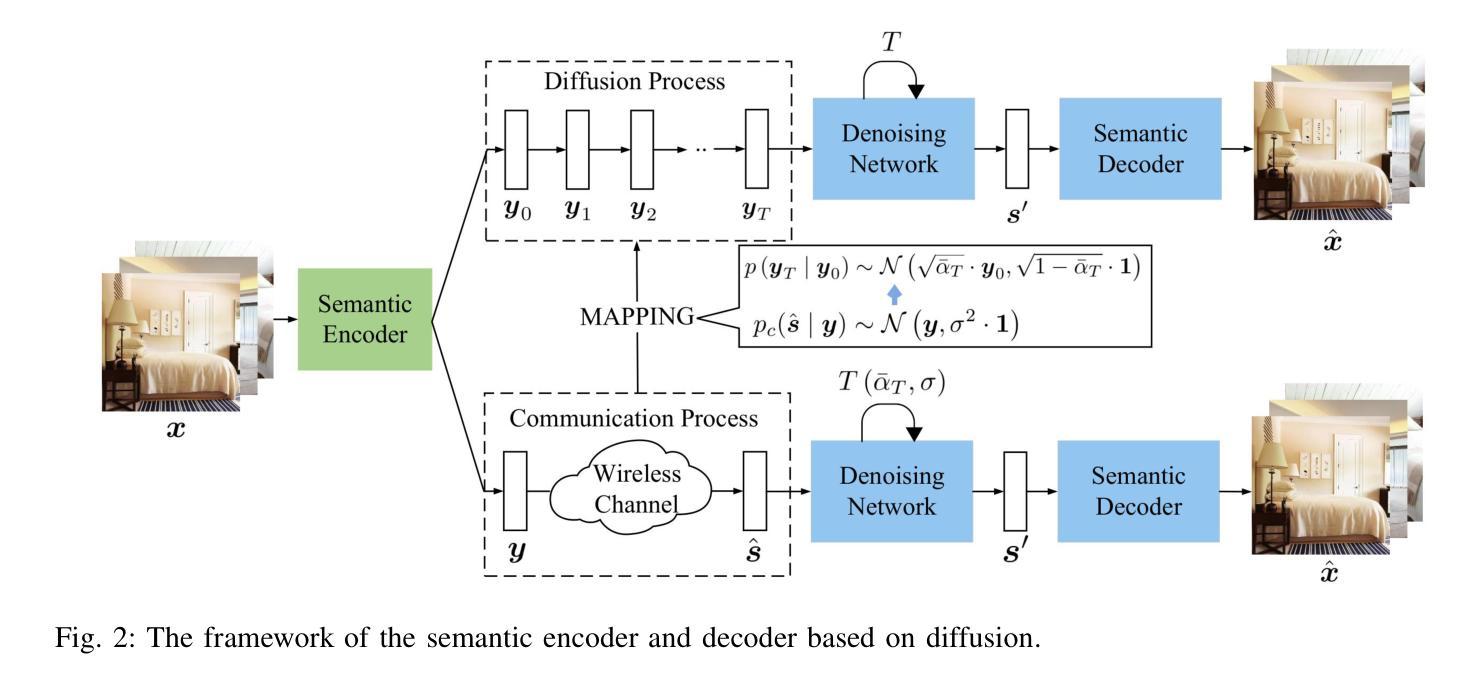
Diffusion-Driven Semantic Communication for Generative Models with Bandwidth Constraints
Authors:Lei Guo, Wei Chen, Yuxuan Sun, Bo Ai, Nikolaos Pappas, Tony Q. S. Quek
Diffusion models have been extensively utilized in AI-generated content (AIGC) in recent years, thanks to the superior generation capabilities. Combining with semantic communications, diffusion models are used for tasks such as denoising, data reconstruction, and content generation. However, existing diffusion-based generative models do not consider the stringent bandwidth limitation, which limits its application in wireless communication. This paper introduces a diffusion-driven semantic communication framework with advanced VAE-based compression for bandwidth-constrained generative model. Our designed architecture utilizes the diffusion model, where the signal transmission process through the wireless channel acts as the forward process in diffusion. To reduce bandwidth requirements, we incorporate a downsampling module and a paired upsampling module based on a variational auto-encoder with reparameterization at the receiver to ensure that the recovered features conform to the Gaussian distribution. Furthermore, we derive the loss function for our proposed system and evaluate its performance through comprehensive experiments. Our experimental results demonstrate significant improvements in pixel-level metrics such as peak signal to noise ratio (PSNR) and semantic metrics like learned perceptual image patch similarity (LPIPS). These enhancements are more profound regarding the compression rates and SNR compared to deep joint source-channel coding (DJSCC). We release the code at https://github.com/import-sudo/Diffusion-Driven-Semantic-Communication.
扩散模型因其出色的生成能力,近年来在人工智能生成内容(AIGC)中得到了广泛应用。结合语义通信,扩散模型被用于去噪、数据重建和内容生成等任务。然而,现有的基于扩散的生成模型并未考虑严格的带宽限制,这限制了其在无线通信中的应用。本文介绍了一个扩散驱动的语义通信框架,该框架具有先进的基于VAE的压缩技术,适用于带宽受限的生成模型。我们设计的架构利用扩散模型,其中通过无线信道传输信号的过程作为扩散的前向过程。为了减少带宽要求,我们融入了下采样模块和基于变分自动编码器的配对上采样模块,并在接收器处进行重参数化,以确保恢复的特征符合高斯分布。此外,我们推导了所提出系统的损失函数,并通过综合实验评估了其性能。实验结果证明,在像素级指标(如峰值信噪比)和语义指标(如学习感知图像补丁相似性)方面,我们的系统有显著改进。与深度联合源信道编码相比,我们的系统在压缩率和信噪比方面获得了更显著的改进。我们在https://github.com/import-sudo/Diffusion-Driven-Semantic-Communication上发布了代码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted to IEEE for possible publication
Summary
扩散模型结合语义通信,用于去噪、数据重建和内容生成等任务。针对现有扩散生成模型在带宽限制方面的应用瓶颈,本文提出一种基于变分自编码器压缩的扩散驱动语义通信框架。设计架构利用扩散模型,通过无线信道传输信号的过程作为扩散中的正向过程。通过引入下采样模块和配对上采样模块,减少带宽要求,并在接收器处采用重参数化确保恢复的特征符合高斯分布。实验结果在像素级和语义度量上都有显著提高。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在AI生成内容(AIGC)中广泛应用,具有出色的生成能力。
- 扩散模型与语义通信结合,用于去噪、数据重建和内容生成。
- 现有扩散生成模型在无线通信中面临带宽限制的挑战。
- 本文提出一种基于变分自编码器压缩的扩散驱动语义通信框架,以适应带宽限制。
- 设计架构利用无线信道传输信号的扩散模型,引入下采样和上采样模块以减少带宽需求。
- 通过实验,该框架在像素级度量(如峰值信噪比PSNR)和语义度量(如学习感知图像补丁相似性LPIPS)上表现出显著改进。
点此查看论文截图
QuEST: Low-bit Diffusion Model Quantization via Efficient Selective Finetuning
Authors:Haoxuan Wang, Yuzhang Shang, Zhihang Yuan, Junyi Wu, Junchi Yan, Yan Yan
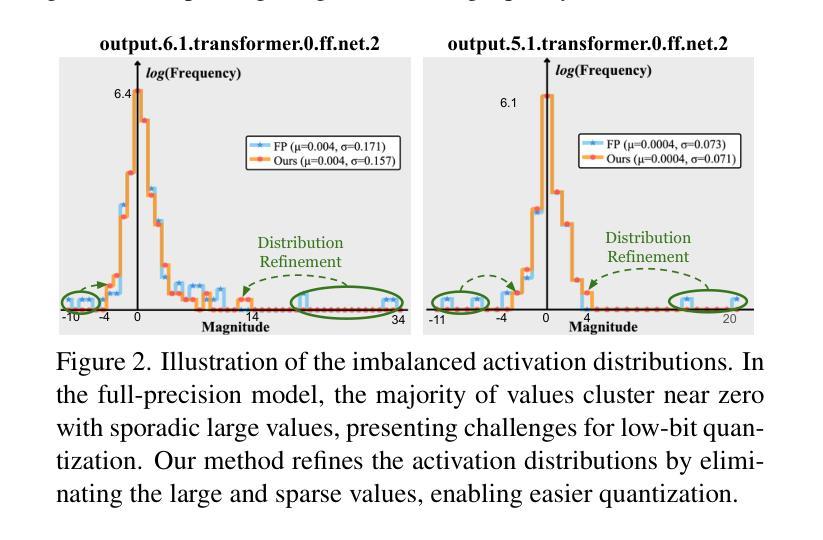
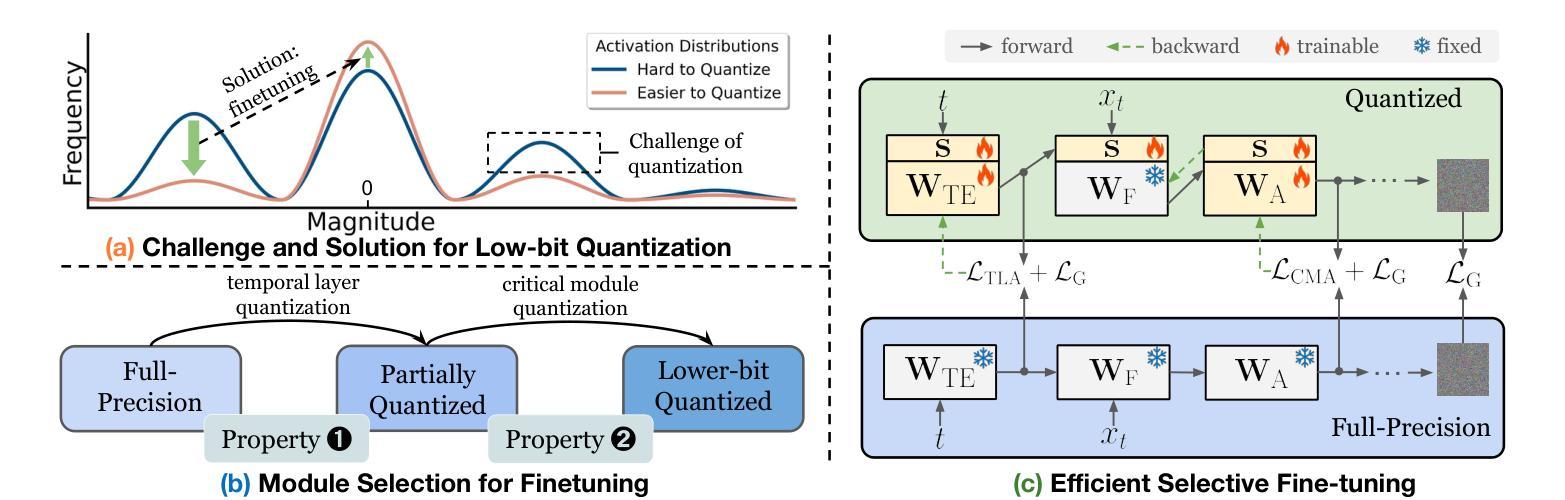
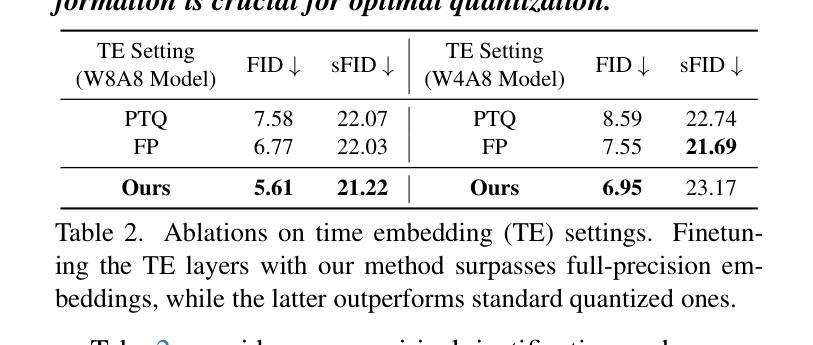
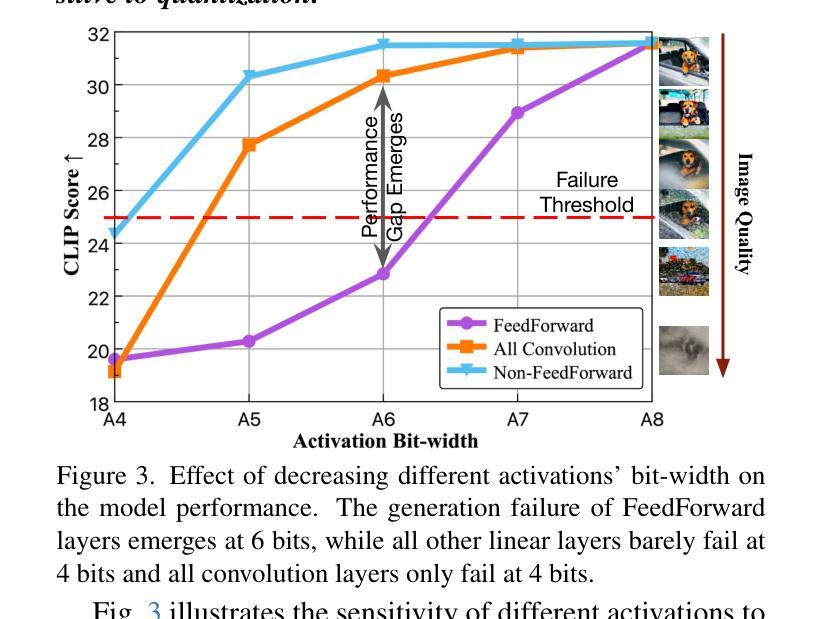
The practical deployment of diffusion models is still hindered by the high memory and computational overhead. Although quantization paves a way for model compression and acceleration, existing methods face challenges in achieving low-bit quantization efficiently. In this paper, we identify imbalanced activation distributions as a primary source of quantization difficulty, and propose to adjust these distributions through weight finetuning to be more quantization-friendly. We provide both theoretical and empirical evidence supporting finetuning as a practical and reliable solution. Building on this approach, we further distinguish two critical types of quantized layers: those responsible for retaining essential temporal information and those particularly sensitive to bit-width reduction. By selectively finetuning these layers under both local and global supervision, we mitigate performance degradation while enhancing quantization efficiency. Our method demonstrates its efficacy across three high-resolution image generation tasks, obtaining state-of-the-art performance across multiple bit-width settings.
扩散模型的实际应用仍然受到高内存和计算开销的阻碍。尽管量化可以为模型压缩和加速铺平道路,但现有方法在实现低位量化时面临挑战。在本文中,我们将激活分布不平衡作为量化的主要困难来源,并提出通过权重微调调整这些分布,使其更利于量化。我们提供了理论和实证证据,支持微调作为一种实用且可靠的解决方案。在此基础上,我们进一步区分了两种关键的量化层:那些负责保留重要时间信息的层和那些对位宽减少特别敏感的层。通过局部和全局监督下有选择地微调这些层,我们在提高量化效率的同时缓解了性能下降。我们的方法在三个高分辨率图像生成任务中证明了其有效性,并在多个位宽设置下达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025. Code is available at https://github.com/hatchetProject/QuEST
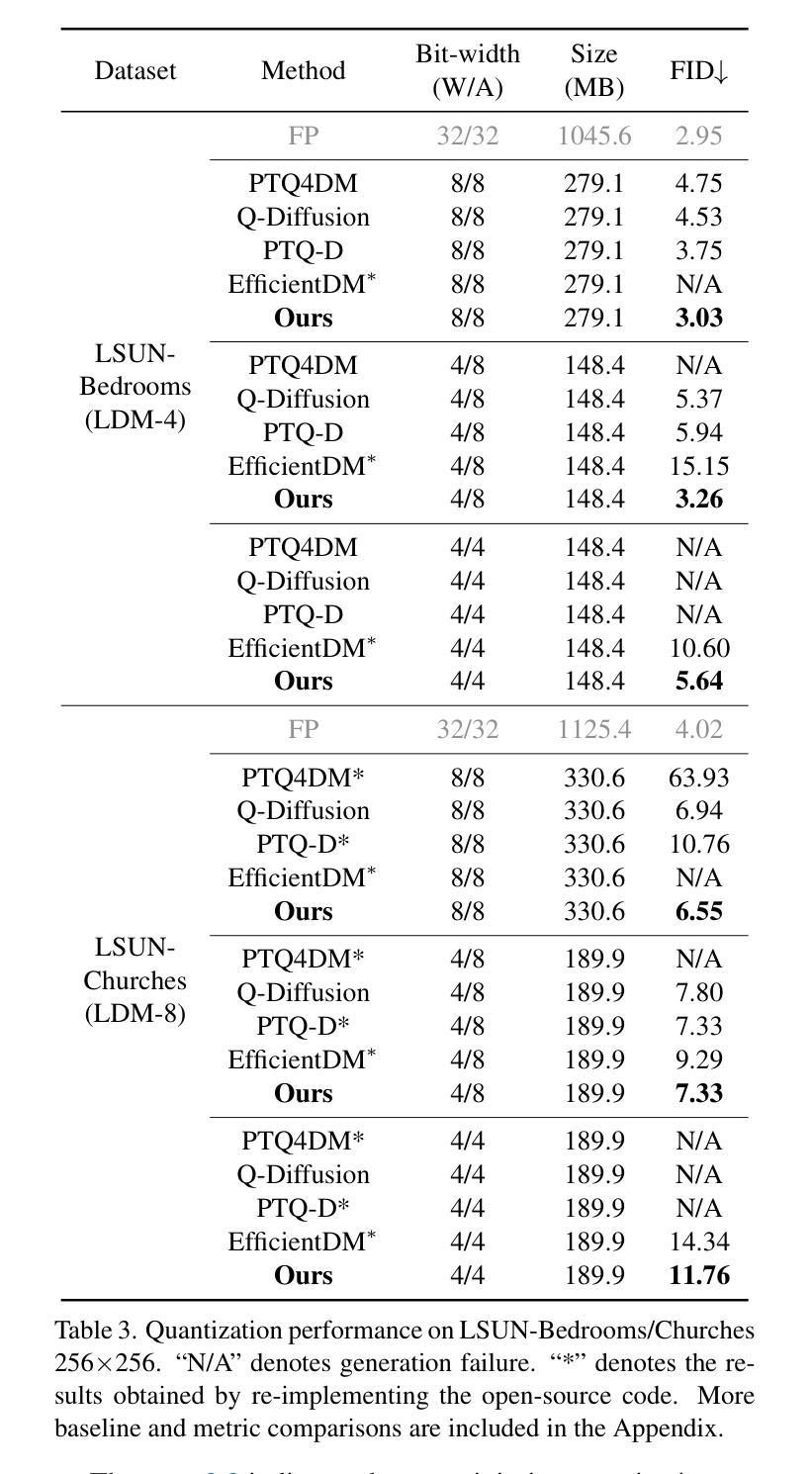
Summary
本文探讨了扩散模型在实际部署中遇到的内存和计算开销问题。针对量化压缩和加速的需求,本文识别出激活分布不平衡是量化困难的主要原因,并提出通过权重微调来调整这些分布,使其更利于量化。同时,本文还区分了两种关键的量化层类型,并通过局部和全局监督下的选择性微调来增强量化效率,同时在高分辨率图像生成任务中取得了先进性能。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在实际部署中面临高内存和计算开销的挑战。
- 量化是模型压缩和加速的一种可行方法,但现有方法在实现低位量化时面临挑战。
- 激活分布不平衡被识别为量化的主要困难。
- 通过权重微调调整激活分布,使其更利于量化。
- 区分了两种关键的量化层类型:保留重要时间信息的层和对比特宽度减少敏感的层。
- 通过局部和全局监督下的选择性微调,缓解了性能下降,提高了量化效率。
点此查看论文截图