⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-12 更新
Motion-Aware Adaptive Pixel Pruning for Efficient Local Motion Deblurring
Authors:Wei Shang, Dongwei Ren, Wanying Zhang, Pengfei Zhu, Qinghua Hu, Wangmeng Zuo
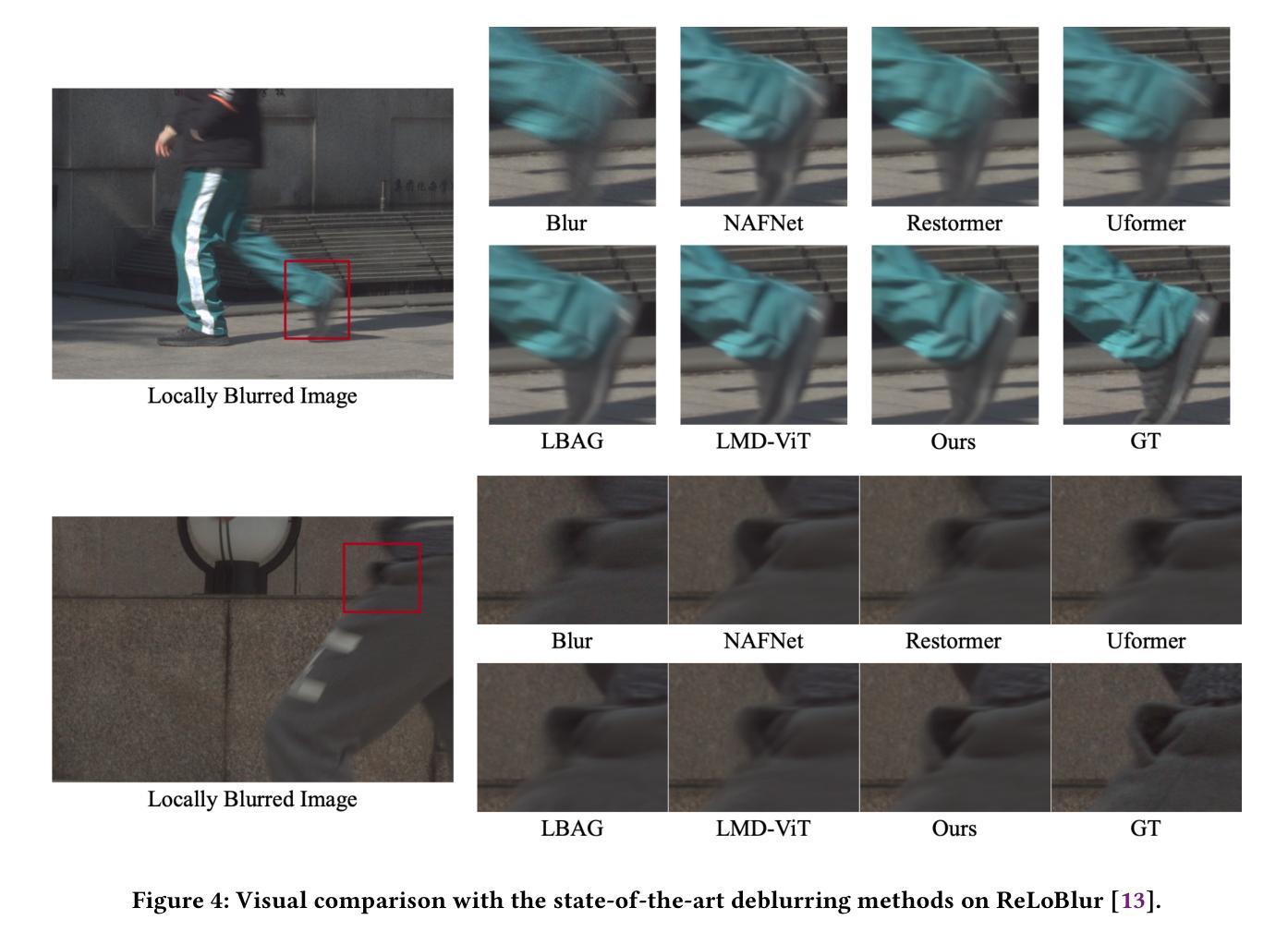
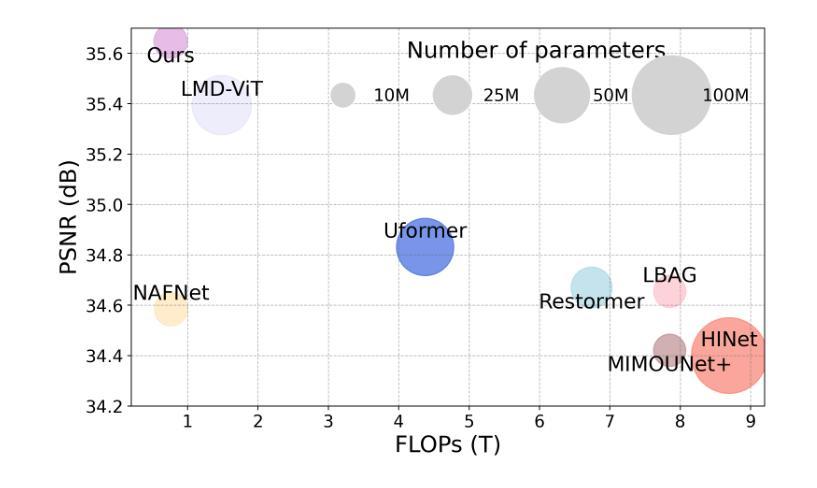
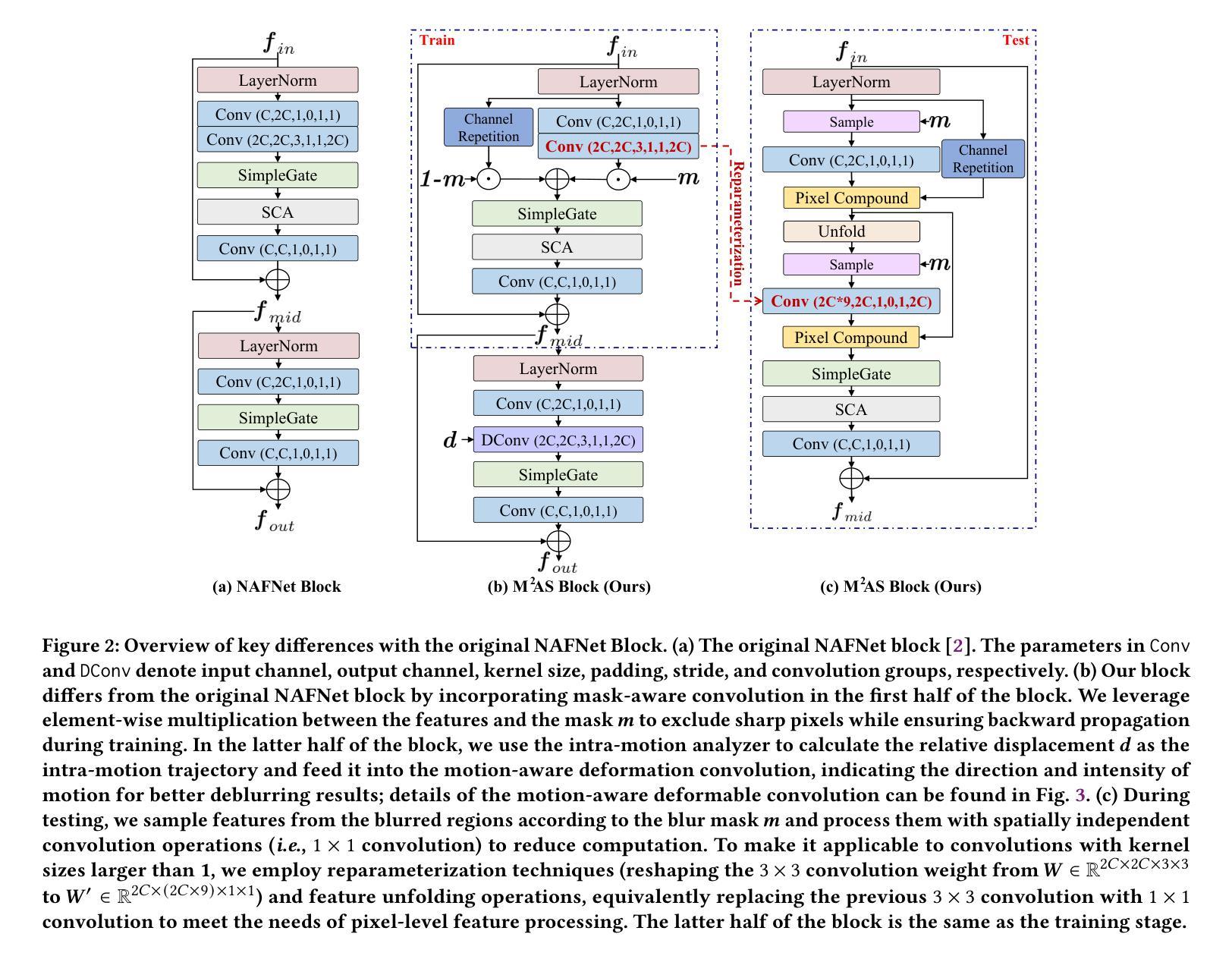
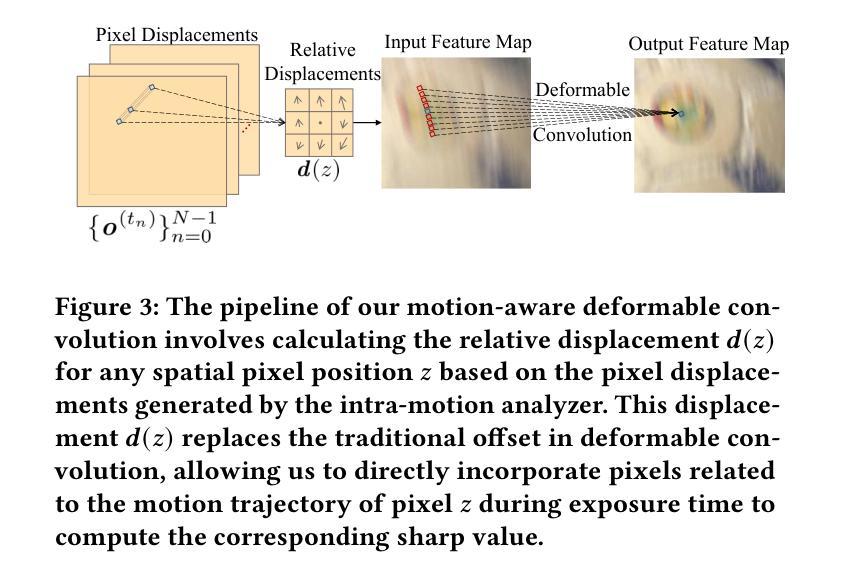
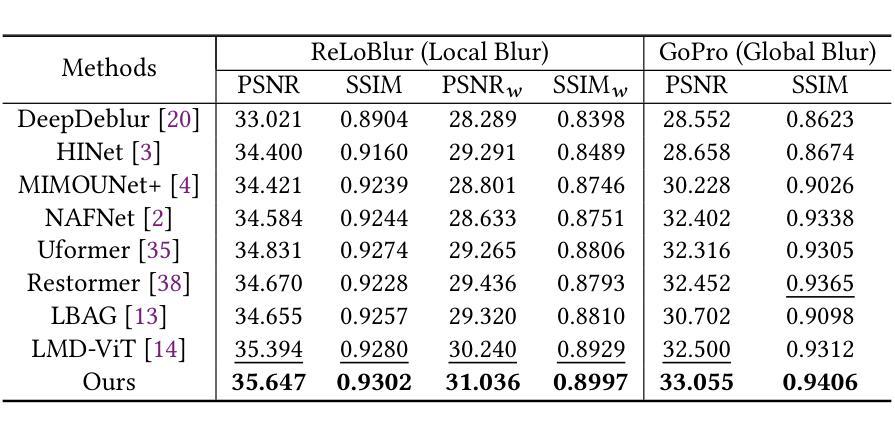
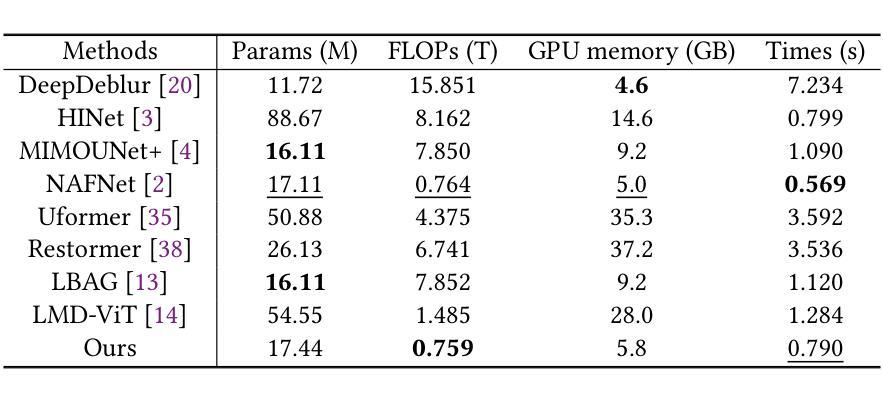
Local motion blur in digital images originates from the relative motion between dynamic objects and static imaging systems during exposure. Existing deblurring methods face significant challenges in addressing this problem due to their inefficient allocation of computational resources and inadequate handling of spatially varying blur patterns. To overcome these limitations, we first propose a trainable mask predictor that identifies blurred regions in the image. During training, we employ blur masks to exclude sharp regions. For inference optimization, we implement structural reparameterization by converting $3\times 3$ convolutions to computationally efficient $1\times 1$ convolutions, enabling pixel-level pruning of sharp areas to reduce computation. Second, we develop an intra-frame motion analyzer that translates relative pixel displacements into motion trajectories, establishing adaptive guidance for region-specific blur restoration. Our method is trained end-to-end using a combination of reconstruction loss, reblur loss, and mask loss guided by annotated blur masks. Extensive experiments demonstrate superior performance over state-of-the-art methods on both local and global blur datasets while reducing FLOPs by 49% compared to SOTA models (e.g., LMD-ViT). The source code is available at https://github.com/shangwei5/M2AENet.
数字图像中的局部运动模糊源于动态物体与静态成像系统在曝光期间的相对运动。现有的去模糊方法由于资源分配效率低下以及空间变化模糊模式处理不当,在解决此问题时面临重大挑战。为了克服这些局限性,我们首先提出了一种可训练的掩膜预测器,用于识别图像中的模糊区域。在训练过程中,我们采用模糊掩膜来排除清晰区域。为了进行推理优化,我们通过将$3\times 3$卷积转换为计算效率更高的$1\times 1$卷积,实现了结构重参数化,从而能够对清晰区域进行像素级修剪以减少计算量。其次,我们开发了一种帧内运动分析器,将相对像素位移转换为运动轨迹,为特定区域的模糊恢复提供自适应指导。我们的方法结合重建损失、再模糊损失和掩膜损失进行端对端训练,这些损失由注释的模糊掩膜指导。大量实验表明,我们的方法在局部和全局模糊数据集上的性能优于最先进的方法,与最先进模型(例如LMD-ViT)相比,浮点运算减少了49%。源代码可在https://github.com/shangwei5/M2AENet找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ACMMM 2025
Summary:
该文针对数字图像中的局部运动模糊问题,提出了一种新的去模糊方法。通过可训练的掩膜预测器识别图像中的模糊区域,并采用结构重参数化优化推断过程。同时,开发了一种帧内运动分析器,将相对像素位移转化为运动轨迹,为区域特定的去模糊恢复提供自适应指导。实验证明,该方法在局部和全局模糊数据集上的性能优于现有方法,同时降低了计算复杂度。
Key Takeaways:
- 局部运动模糊源于动态物体与静态成像系统在曝光期间的相对运动。
- 现有去模糊方法面临计算资源分配效率低下和难以处理空间变化模糊模式的问题。
- 提出了一种可训练的掩膜预测器,用于识别图像中的模糊区域,并在训练过程中使用模糊掩膜排除清晰区域。
- 通过结构重参数化优化推断过程,将3x3卷积转换为计算效率更高的1x1卷积,实现像素级修剪清晰区域以减少计算。
- 开发了一种帧内运动分析器,将相对像素位移转化为运动轨迹,为区域特定的去模糊恢复提供自适应指导。
- 该方法通过结合重建损失、重模糊损失和掩膜损失进行端到端训练。
点此查看论文截图


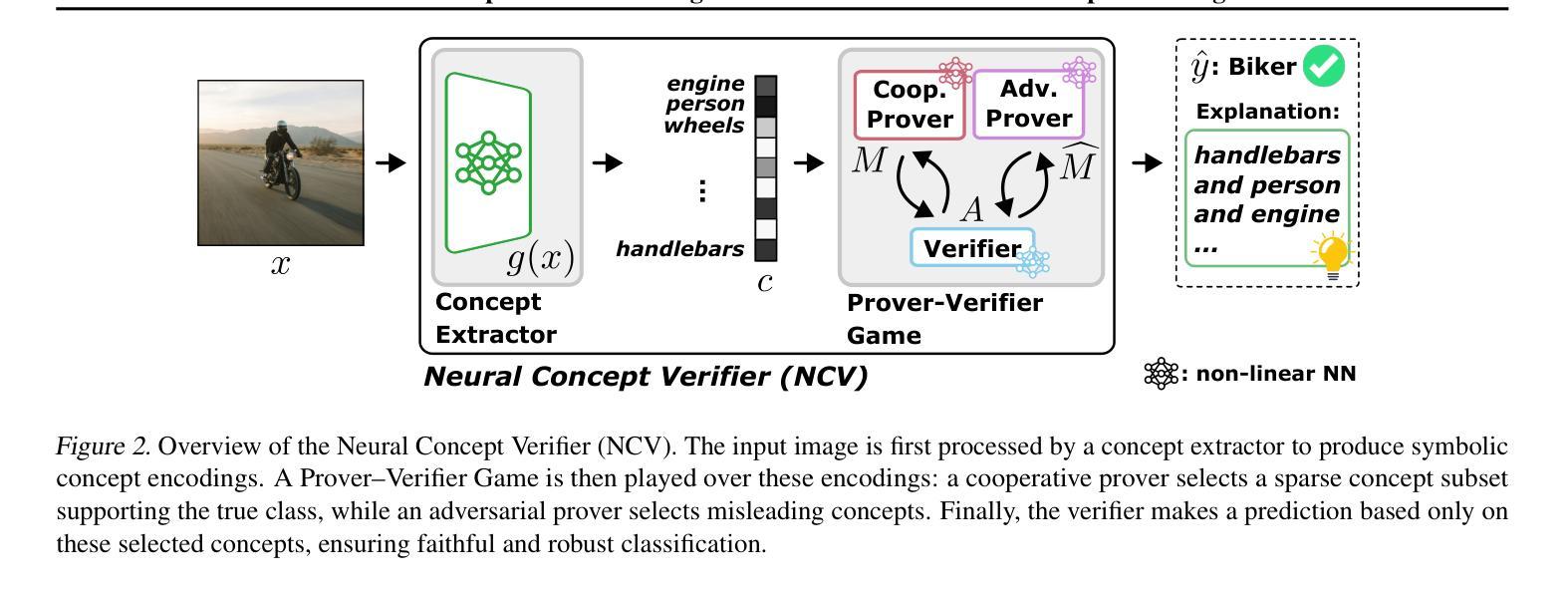
Neural Concept Verifier: Scaling Prover-Verifier Games via Concept Encodings
Authors:Berkant Turan, Suhrab Asadulla, David Steinmann, Wolfgang Stammer, Sebastian Pokutta
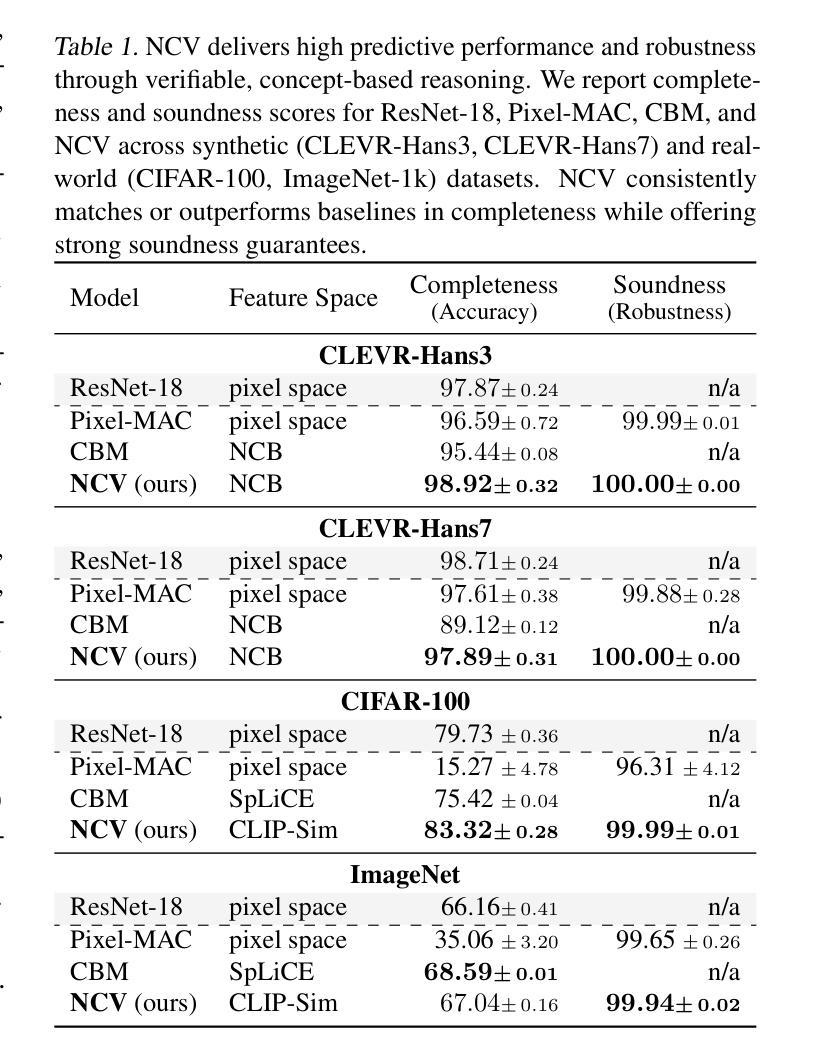
While Prover-Verifier Games (PVGs) offer a promising path toward verifiability in nonlinear classification models, they have not yet been applied to complex inputs such as high-dimensional images. Conversely, Concept Bottleneck Models (CBMs) effectively translate such data into interpretable concepts but are limited by their reliance on low-capacity linear predictors. In this work, we introduce the Neural Concept Verifier (NCV), a unified framework combining PVGs with concept encodings for interpretable, nonlinear classification in high-dimensional settings. NCV achieves this by utilizing recent minimally supervised concept discovery models to extract structured concept encodings from raw inputs. A prover then selects a subset of these encodings, which a verifier – implemented as a nonlinear predictor – uses exclusively for decision-making. Our evaluations show that NCV outperforms CBM and pixel-based PVG classifier baselines on high-dimensional, logically complex datasets and also helps mitigate shortcut behavior. Overall, we demonstrate NCV as a promising step toward performative, verifiable AI.
证明者验证者游戏(PVGs)为非线分类模型的可验证性提供了前景光明的路径,但它们尚未应用于复杂输入,如高维图像。相反,概念瓶颈模型(CBMs)能够有效地将此类数据转换为可解释的概念,但受限于其对低容量线性预测器的依赖。在这项工作中,我们引入了神经概念验证器(NCV),这是一个结合了PVGs和概念编码的统一框架,用于在高维设置中进行可解释的非线性分类。NCV通过利用最新的最小监督概念发现模型,从原始输入中提取结构化概念编码来实现这一点。证明者然后选择这些编码的一个子集,验证器(实现为非线性预测器)专门用于决策制定。我们的评估表明,在高维、逻辑复杂的数据集上,NCV的性能优于CBM和基于像素的PVG分类器基线,并有助于缓解捷径行为。总的来说,我们证明了NCV是朝着高性能、可验证的人工智能迈出的有前途的一步。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 4 figures, 8 tables
Summary
神经概念验证器(NCV)结合证明者验证器游戏(PVGs)和概念编码,在高维设置中实现可解释的非线性分类。它通过利用最新的弱监督概念发现模型从原始输入中提取结构化概念编码,证明者选择其中一部分编码供验证器进行决策。在逻辑复杂的数据集上,NCV在高维数据上的表现优于CBM和像素级PVG分类器基线,并有助于缓解捷径行为。
Key Takeaways
- NCV结合PVGs和概念编码,实现高维设置中的可解释非线性分类。
- NCV利用最新的弱监督概念发现模型从原始输入中提取结构化概念编码。
- 证明者选择概念编码的子集供验证器进行决策。
- NCV在高维、逻辑复杂的数据集上表现出优异的性能。
- NCV的表现优于CBM和像素级PVG分类器基线。
- NCV有助于缓解在分类模型中的捷径行为。
点此查看论文截图