⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-12 更新
Motion-Aware Adaptive Pixel Pruning for Efficient Local Motion Deblurring
Authors:Wei Shang, Dongwei Ren, Wanying Zhang, Pengfei Zhu, Qinghua Hu, Wangmeng Zuo
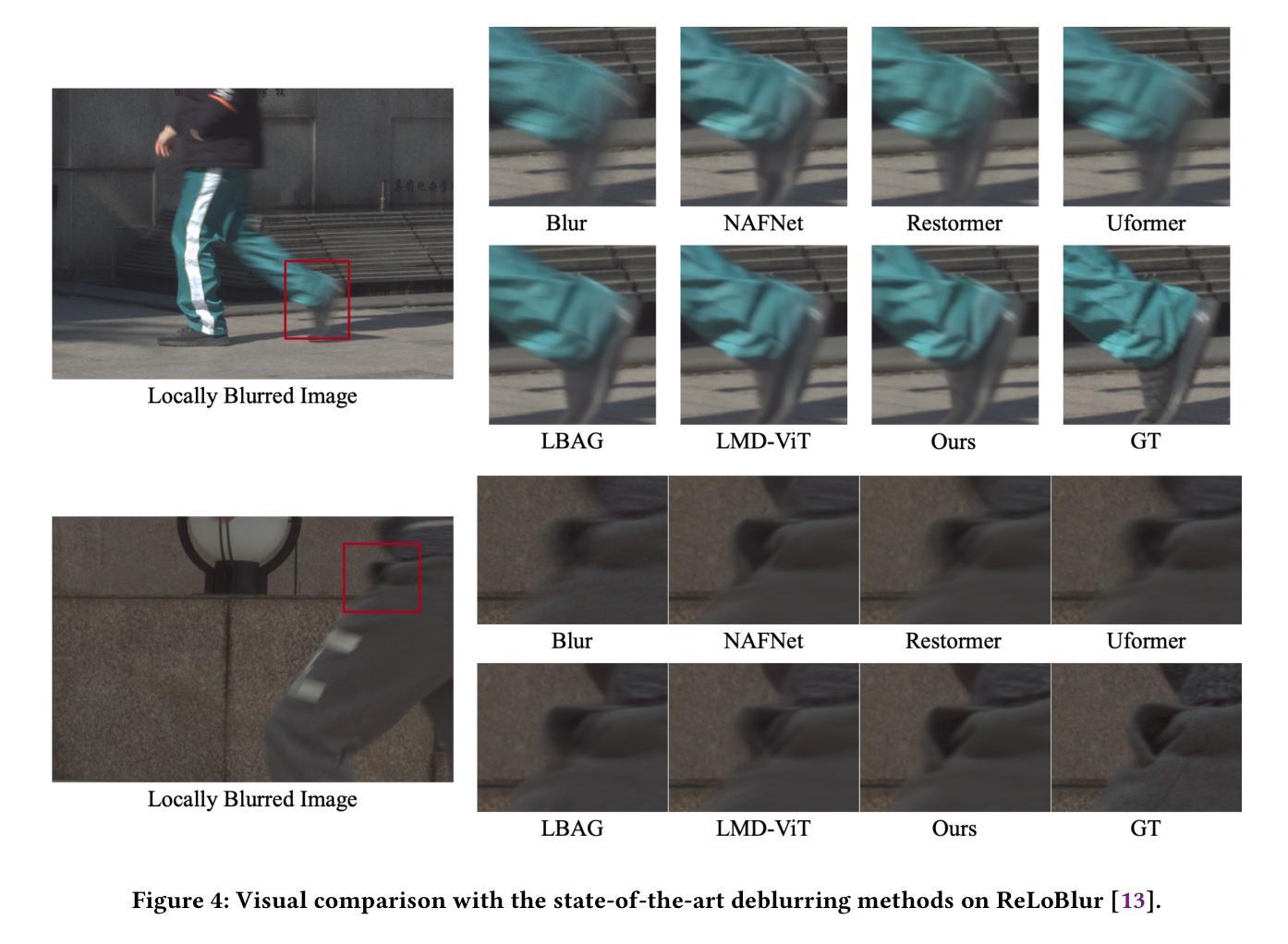
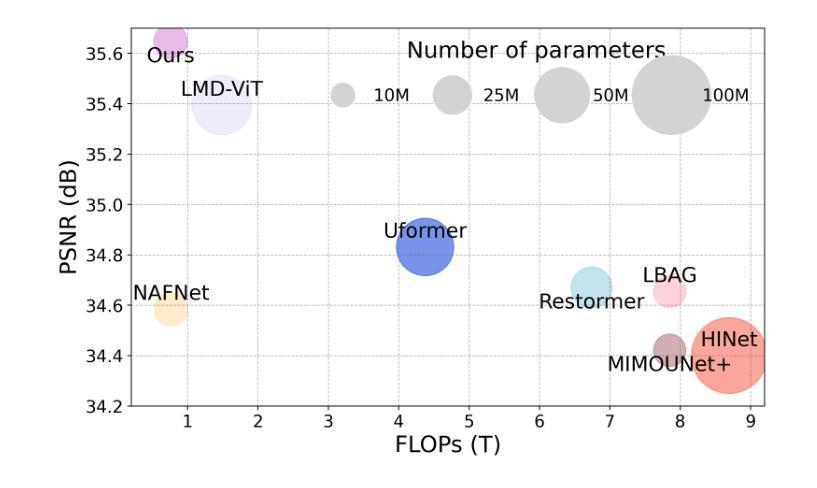
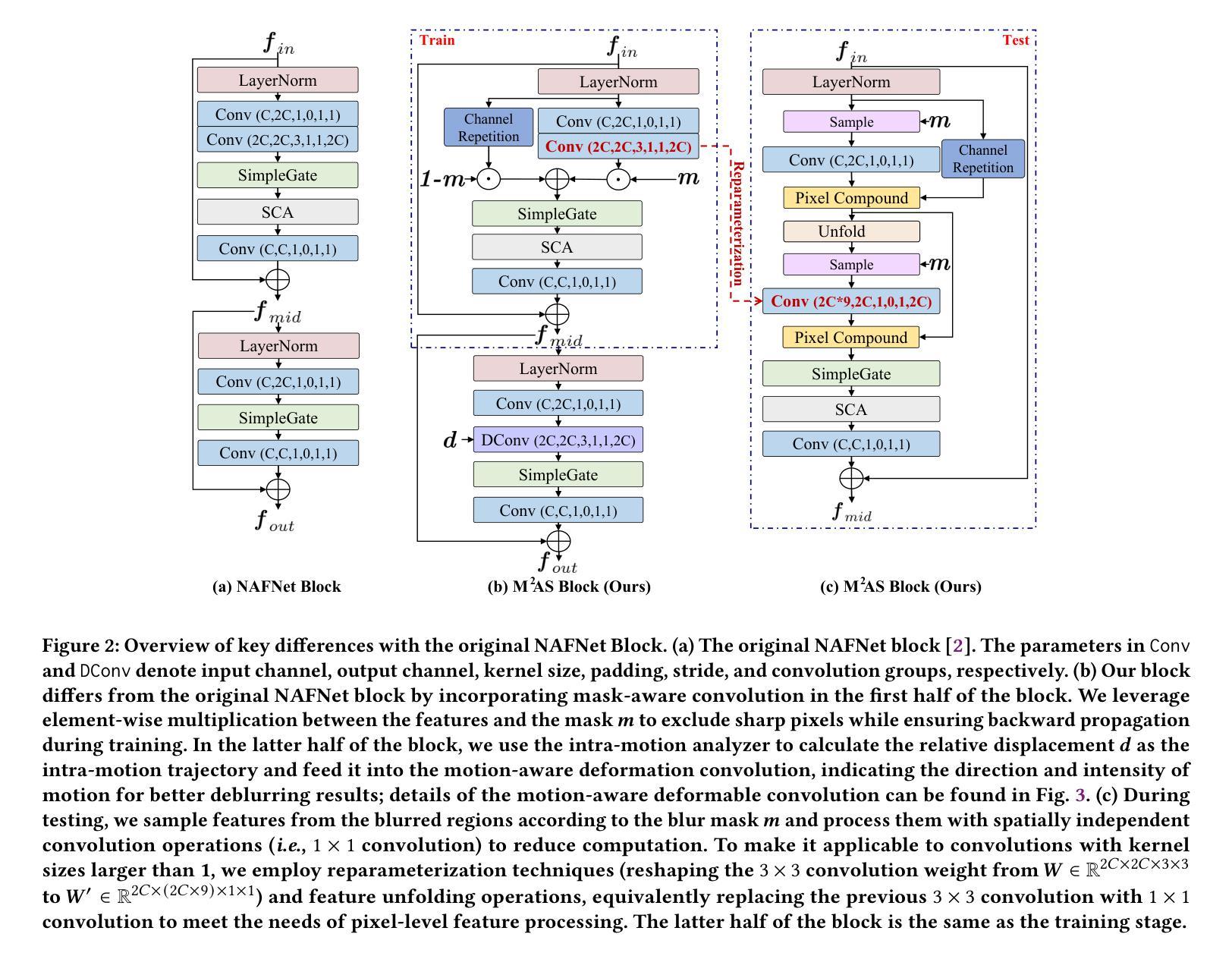
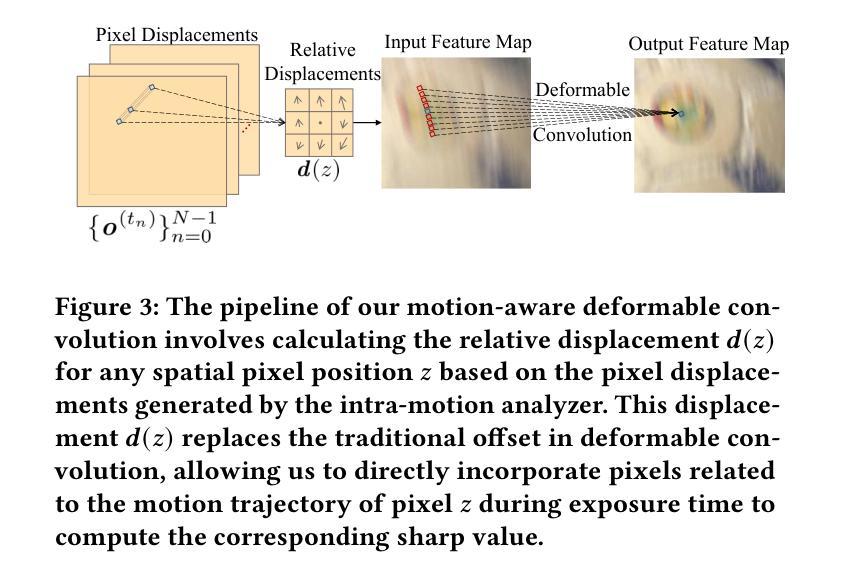
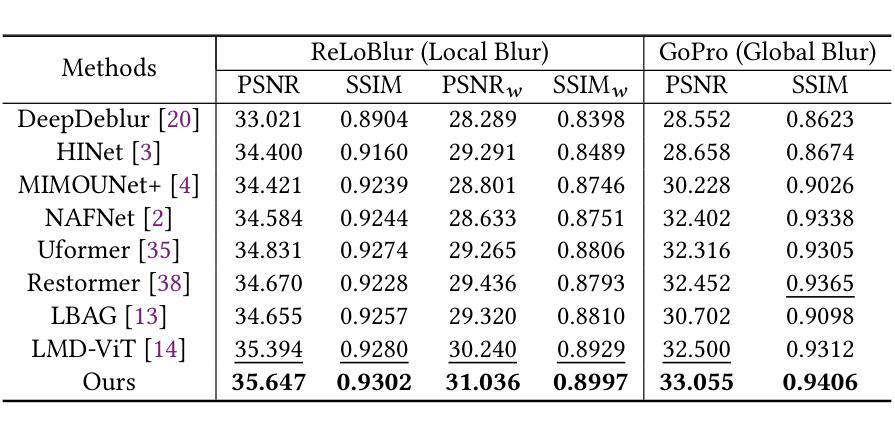
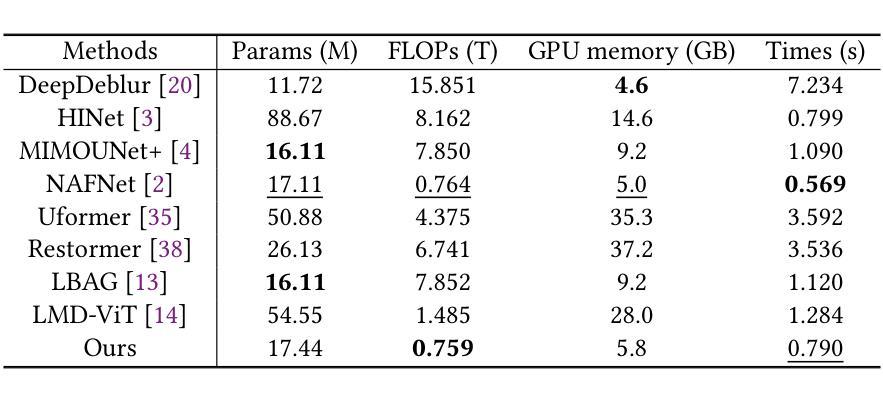
Local motion blur in digital images originates from the relative motion between dynamic objects and static imaging systems during exposure. Existing deblurring methods face significant challenges in addressing this problem due to their inefficient allocation of computational resources and inadequate handling of spatially varying blur patterns. To overcome these limitations, we first propose a trainable mask predictor that identifies blurred regions in the image. During training, we employ blur masks to exclude sharp regions. For inference optimization, we implement structural reparameterization by converting $3\times 3$ convolutions to computationally efficient $1\times 1$ convolutions, enabling pixel-level pruning of sharp areas to reduce computation. Second, we develop an intra-frame motion analyzer that translates relative pixel displacements into motion trajectories, establishing adaptive guidance for region-specific blur restoration. Our method is trained end-to-end using a combination of reconstruction loss, reblur loss, and mask loss guided by annotated blur masks. Extensive experiments demonstrate superior performance over state-of-the-art methods on both local and global blur datasets while reducing FLOPs by 49% compared to SOTA models (e.g., LMD-ViT). The source code is available at https://github.com/shangwei5/M2AENet.
数字图像中的局部运动模糊源于动态物体和静态成像系统在曝光过程中的相对运动。现有的去模糊方法由于资源分配效率低下以及对空间变化模糊模式处理不当,在解决此问题上面临重大挑战。为了克服这些局限性,我们首先提出了一种可训练的掩膜预测器,用于识别图像中的模糊区域。在训练过程中,我们采用模糊掩膜来排除清晰区域。为了进行推理优化,我们通过将3x3卷积转换为计算效率更高的1x1卷积,实现了结构重参数化,这能够在减少计算的同时实现像素级别的尖锐区域修剪。其次,我们开发了一种帧内运动分析器,将相对像素位移转化为运动轨迹,为特定区域的模糊恢复提供自适应指导。我们的方法使用重建损失、再模糊损失和由注释模糊掩膜引导的掩膜损失的组合进行端到端的训练。大量实验表明,与最新技术相比,我们的方法在局部和全局模糊数据集上的性能都更加优越,同时与最新模型相比,浮点运算减少了49%(例如LMD-ViT)。源代码可在https://github.com/shangwei5/M2AENet找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ACMMM 2025
Summary
动态物体与静态成像系统在曝光过程中的相对运动会导致数字图像出现局部运动模糊。现有去模糊方法在计算资源分配及空间变化模糊模式处理方面存在挑战。为克服这些局限性,我们提出了可训练的掩膜预测器来识别图像中的模糊区域,并利用模糊掩膜进行训练,排除清晰区域。同时,通过结构重构实现高效的卷积运算,减少计算量。此外,我们开发了帧内运动分析仪,将相对像素位移转化为运动轨迹,为特定区域的模糊恢复提供自适应指导。实验证明,我们的方法在局部和全局模糊数据集上的性能优于最新方法,同时减少了计算量。源码已公开。
Key Takeaways
- 现有去模糊方法在处理动态物体与静态成像系统相对运动导致的局部运动模糊时面临挑战。
- 提出可训练的掩膜预测器识别图像中的模糊区域,排除清晰区域进行训练。
- 通过结构重构实现高效的卷积运算,减少计算量。
- 开发帧内运动分析仪,将相对像素位移转化为运动轨迹,提供自适应的模糊恢复指导。
- 方法在局部和全局模糊数据集上的性能优于最新方法。
- 源码已公开。
- 与当前最佳模型相比,计算量减少了49%。
点此查看论文截图


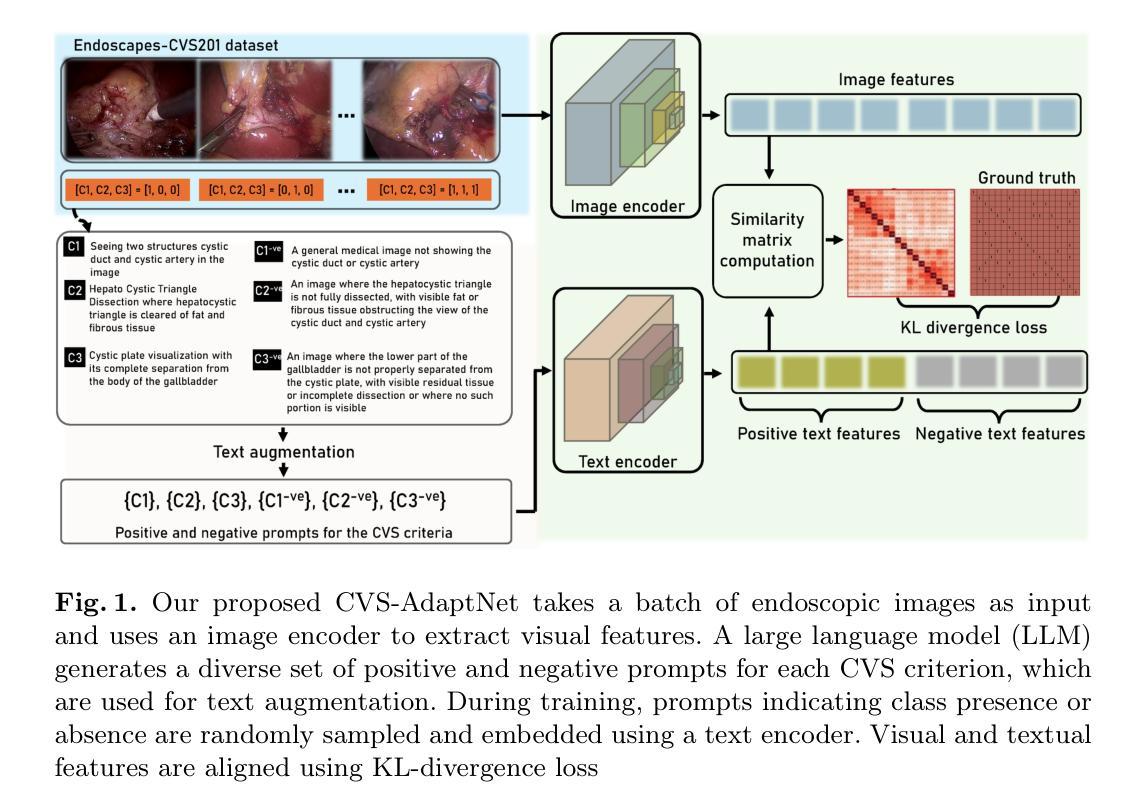
Multi-modal Representations for Fine-grained Multi-label Critical View of Safety Recognition
Authors:Britty Baby, Vinkle Srivastav, Pooja P. Jain, Kun Yuan, Pietro Mascagni, Nicolas Padoy
The Critical View of Safety (CVS) is crucial for safe laparoscopic cholecystectomy, yet assessing CVS criteria remains a complex and challenging task, even for experts. Traditional models for CVS recognition depend on vision-only models learning with costly, labor-intensive spatial annotations. This study investigates how text can be harnessed as a powerful tool for both training and inference in multi-modal surgical foundation models to automate CVS recognition. Unlike many existing multi-modal models, which are primarily adapted for multi-class classification, CVS recognition requires a multi-label framework. Zero-shot evaluation of existing multi-modal surgical models shows a significant performance gap for this task. To address this, we propose CVS-AdaptNet, a multi-label adaptation strategy that enhances fine-grained, binary classification across multiple labels by aligning image embeddings with textual descriptions of each CVS criterion using positive and negative prompts. By adapting PeskaVLP, a state-of-the-art surgical foundation model, on the Endoscapes-CVS201 dataset, CVS-AdaptNet achieves 57.6 mAP, improving over the ResNet50 image-only baseline (51.5 mAP) by 6 points. Our results show that CVS-AdaptNet’s multi-label, multi-modal framework, enhanced by textual prompts, boosts CVS recognition over image-only methods. We also propose text-specific inference methods, that helps in analysing the image-text alignment. While further work is needed to match state-of-the-art spatial annotation-based methods, this approach highlights the potential of adapting generalist models to specialized surgical tasks. Code: https://github.com/CAMMA-public/CVS-AdaptNet
批判性手术视图(CVS)对于腹腔镜胆囊切除术的安全至关重要,但评估CVS标准仍然是一个复杂且充满挑战的任务,即使是专家也是如此。传统的CVS识别模型依赖于仅视觉模型的学习,这需要昂贵的、劳动密集的空间注释。本研究探讨了文本如何成为多模态手术基础模型中用于训练和推断的强大工具,以自动化CVS识别。与许多现有的多模态模型主要适应于多类分类不同,CVS识别需要多标签框架。对现有多模态手术模型的零样本评估表明,该任务的性能存在显著差距。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了CVS-AdaptNet,这是一种多标签适应策略,通过利用正负提示将图像嵌入与每个CVS标准的文本描述对齐,增强跨多个标签的精细二进制分类。通过适应Endoscapes-CVS201数据集上的PeskaVLP这一最先进的手术基础模型,CVS-AdaptNet达到了57.6的mAP,比仅使用ResNet50图像的基线(51.5 mAP)提高了6个点。我们的结果表明,通过文本提示增强的CVS-AdaptNet的多标签、多模态框架提高了CVS识别的能力,超过了仅使用图像的方法。我们还提出了针对文本的推断方法,有助于分析图像文本对齐情况。虽然需要进一步的工作才能匹配基于空间注释的先进方法,但这种方法突显了适应通用模型以应对专业手术任务的潜力。代码地址:https://github.com/CAMMA-public/CVS-AdaptNet
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本研究了如何利用文本信息提升多模态手术基础模型在关键手术视角(CVS)识别上的性能。针对CVS识别需要精细化的多标签分类问题,提出了一种名为CVS-AdaptNet的多标签自适应策略。该策略通过图像嵌入与每个CVS标准的文本描述对齐,使用正负提示增强跨多个标签的精细化二分类。虽然仍需要进一步的工作来匹配基于空间注释的方法,但此研究展示了将通用模型适应特定手术任务的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 文中指出传统模型对关键手术视角(CVS)的识别主要依赖于视觉模型,学习成本高昂且劳动密集的空间注释。
- 研究提出了一种名为CVS-AdaptNet的多标签自适应策略,用于多模态手术基础模型中的CVS识别,实现对多个标签的精细化二分类。
- CVS-AdaptNet利用图像嵌入与文本描述对齐的方式,使用正负提示增强性能。
- 实验结果显示,CVS-AdaptNet在Endoscapes-CVS201数据集上达到了57.6 mAP的性能,相较于仅使用图像的ResNet50基础模型有6个百分点的提升。
- 文中提出了文本特定的推理方法,有助于分析图像与文本的对应关系。
- 虽然仍需进一步匹配基于空间注释的方法,但研究展示了通用模型适应特定手术任务的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

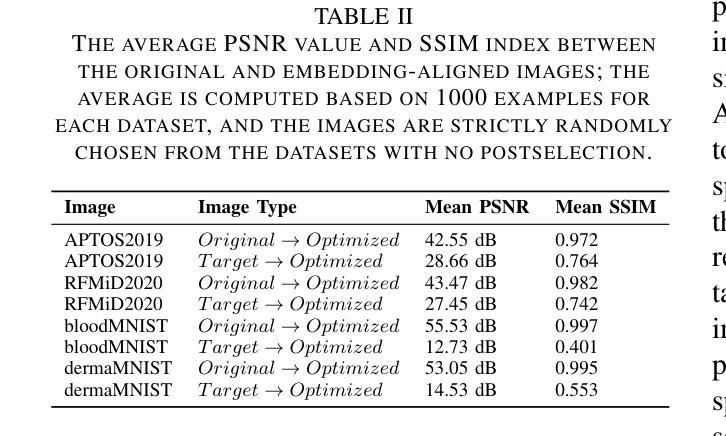
Are Vision Transformer Representations Semantically Meaningful? A Case Study in Medical Imaging
Authors:Montasir Shams, Chashi Mahiul Islam, Shaeke Salman, Phat Tran, Xiuwen Liu
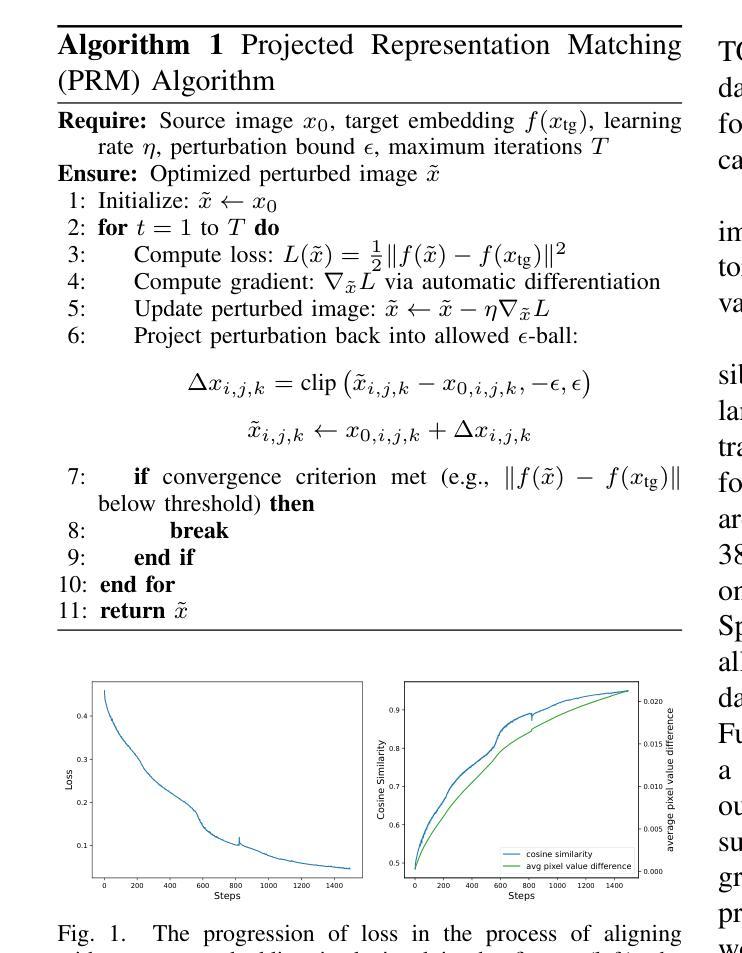
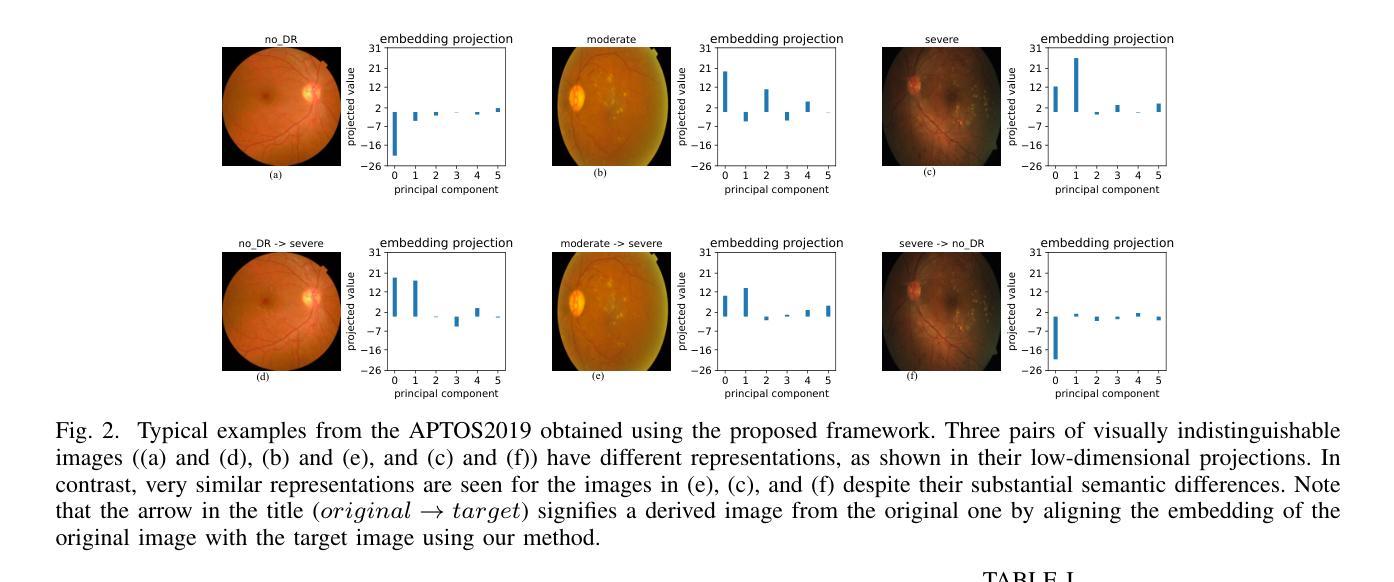
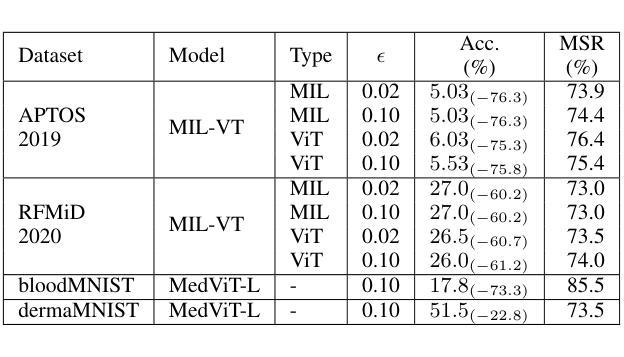
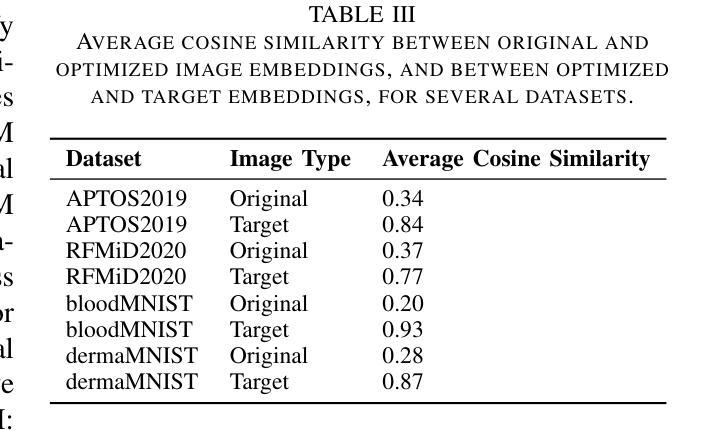
Vision transformers (ViTs) have rapidly gained prominence in medical imaging tasks such as disease classification, segmentation, and detection due to their superior accuracy compared to conventional deep learning models. However, due to their size and complex interactions via the self-attention mechanism, they are not well understood. In particular, it is unclear whether the representations produced by such models are semantically meaningful. In this paper, using a projected gradient-based algorithm, we show that their representations are not semantically meaningful and they are inherently vulnerable to small changes. Images with imperceptible differences can have very different representations; on the other hand, images that should belong to different semantic classes can have nearly identical representations. Such vulnerability can lead to unreliable classification results; for example, unnoticeable changes cause the classification accuracy to be reduced by over 60%. %. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to systematically demonstrate this fundamental lack of semantic meaningfulness in ViT representations for medical image classification, revealing a critical challenge for their deployment in safety-critical systems.
视觉转换器(ViTs)由于其相较于传统深度学习模型的卓越准确性,在疾病分类、分割和检测等医学成像任务中迅速崭露头角。然而,由于其规模以及通过自我注意机制产生的复杂交互,人们对其理解尚浅。尤其不清楚的是,此类模型产生的表示是否具有语义意义。在本文中,我们使用基于投影的梯度算法证明,它们的表示并不具有语义意义,并且本质上易于受到微小变化的影响。具有难以察觉差异的图像可能会有截然不同的表示;另一方面,本应属于不同语义类别的图像可能会有几乎相同的表示。这种脆弱性可能导致分类结果不可靠;例如,微小的、难以察觉的变化导致分类准确率降低超过60%。据我们所知,这是第一项系统证明在医学图像分类中ViT表示缺乏基本语义意义的工作,这揭示了其在安全关键系统中部署的一个关键挑战。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages
Summary
本文指出,尽管Vision Transformers(ViTs)在医疗图像分类、分割和检测等任务中表现出较高的准确性,但其表示缺乏语义意义,容易受到微小变化的影响。使用基于梯度下降算法的研究表明,ViT模型产生的图像表示存在不稳定性,细微的差别可能导致截然不同的表示,导致分类结果不可靠。这对ViT在医疗影像等安全关键系统中的应用构成重大挑战。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformers(ViTs)在医疗图像任务中表现优异,但存在语义表示不明确的问题。
- ViT模型容易受到微小变化的影响,导致图像表示不稳定。
- 细微的差别可能导致截然不同的表示,进而影响分类结果的可靠性。
- ViT模型在医疗影像等安全关键系统中部署面临重大挑战。
- 当前研究首次系统地证明了ViT在医疗图像分类中表示的语义无意义性。
- 该问题对理解ViT模型的内在工作机制提出了挑战。
点此查看论文截图