⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-14 更新
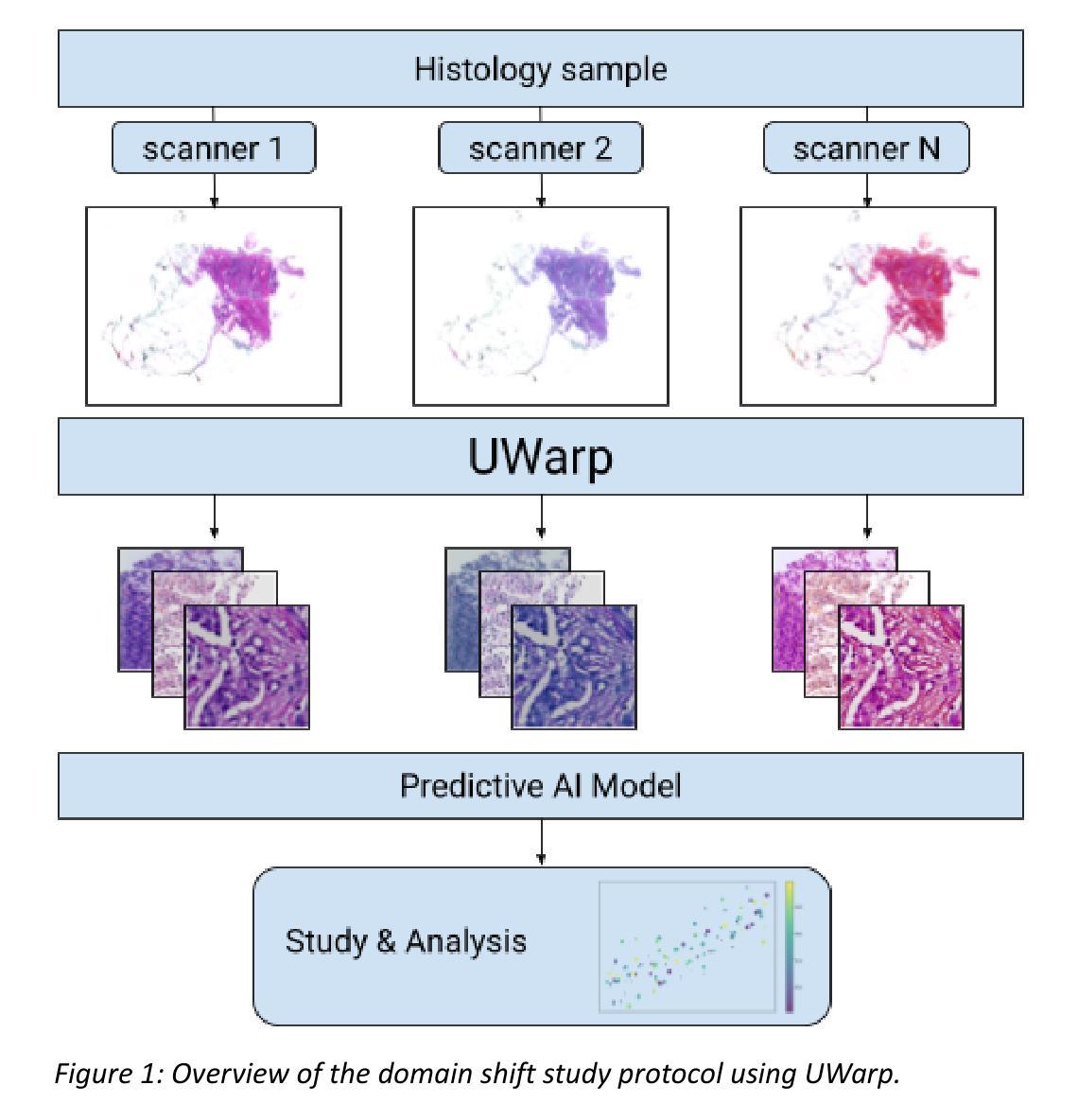
UWarp: A Whole Slide Image Registration Pipeline to Characterize Scanner-Induced Local Domain Shift
Authors:Antoine Schieb, Bilal Hadjadji, Natalia Fernanda Valderrama, Daniel Tshokola Mweze, Valentin Derangère, Laurent Arnould, Sylvain Ladoire, Alain Lalande, Alessio Fiorin, Carlos López Pablo, Noèlia Gallardo Borràs, Shrief Abdelazeez, Vincenzo Della Mea, Anna Korzynska, Nathan Vinçon, Louis-Oscar Morel
Histopathology slide digitization introduces scanner-induced domain shift that can significantly impact computational pathology models based on deep learning methods. In the state-of-the-art, this shift is often characterized at a broad scale (slide-level or dataset-level) but not patch-level, which limits our comprehension of the impact of localized tissue characteristics on the accuracy of the deep learning models. To address this challenge, we present a domain shift analysis framework based on UWarp, a novel registration tool designed to accurately align histological slides scanned under varying conditions. UWarp employs a hierarchical registration approach, combining global affine transformations with fine-grained local corrections to achieve robust tissue patch alignment. We evaluate UWarp using two private datasets, CypathLung and BosomShieldBreast, containing whole slide images scanned by multiple devices. Our experiments demonstrate that UWarp outperforms existing open-source registration methods, achieving a median target registration error (TRE) of less than 4 pixels (<1 micrometer at 40x magnification) while significantly reducing computational time. Additionally, we apply UWarp to characterize scanner-induced local domain shift in the predictions of Breast-NEOprAIdict, a deep learning model for breast cancer pathological response prediction. We find that prediction variability is strongly correlated with tissue density on a given patch. Our findings highlight the importance of localized domain shift analysis and suggest that UWarp can serve as a valuable tool for improving model robustness and domain adaptation strategies in computational pathology.
病理切片数字化引入了由扫描仪引起的领域偏移,这可能会显著影响基于深度学习方法的计算病理学模型。目前,这种偏移通常在大规模(幻灯片级别或数据集级别)上进行表征,而不是在补丁级别上进行,这限制了我们对局部组织特性对深度学习模型精度影响的理解。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了一个基于UWarp的领域偏移分析框架,UWarp是一种新型注册工具,旨在准确对齐在不同条件下扫描的组织切片。UWarp采用分层注册方法,结合全局仿射变换和精细的局部校正,实现稳健的组织补丁对齐。我们使用两个私有数据集CypathLung和BosomShieldBreast(包含由多台设备扫描的整个幻灯片图像)对UWarp进行了评估。实验表明,UWarp在目标注册误差(TRE)方面的表现优于现有的开源注册方法,实现了不到4像素的中值目标注册误差(在40倍放大时小于1微米),并大大减少了计算时间。此外,我们将UWarp应用于表征扫描仪引起的局部领域偏移对乳腺癌病理反应预测模型Breast-NEOprAIdict的预测影响。我们发现预测变量与给定补丁上的组织密度有很强的相关性。我们的研究结果表明局部领域偏移分析的重要性,并表明UWarp可以作为提高计算病理学中的模型稳健性和领域适应策略的有用工具。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF preprint
Summary
病理切片数字化引入扫描器引起的领域偏移,影响深度学习模型在病理学上的应用。为解决挑战,提出基于UWarp的域偏移分析框架,采用层次注册方法,实现稳健的组织斑块对齐。实验证明UWarp优于现有开源注册方法,可显著降低预测变异性,并为提升模型稳健性和领域适应策略提供重要工具。
Key Takeaways
- 病理切片数字化中扫描器引起的领域偏移对深度学习模型有重要影响。
- UWarp是一种新型注册工具,能准确对齐在不同条件下扫描的组织切片。
- UWarp采用层次注册方法,结合全局仿射变换和局部精细校正,实现稳健的组织斑块对齐。
- 实验证明UWarp在图像注册误差和计算时间方面优于现有开源注册方法。
5.UWarp能降低深度学习模型的预测变异性,有助于分析扫描器引起的局部领域偏移。 - 组织密度对深度学习模型的预测结果有重要影响。
点此查看论文截图

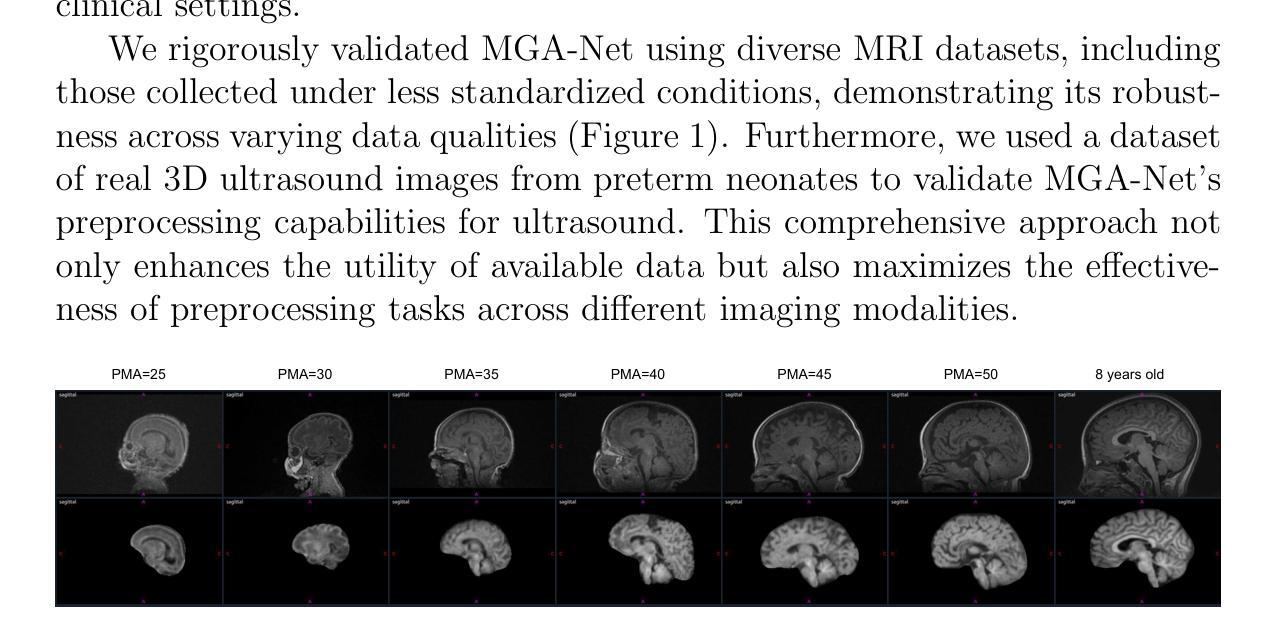
Mask-Guided Attention U-Net for Enhanced Neonatal Brain Extraction and Image Preprocessing
Authors:Bahram Jafrasteh, Simon Pedro Lubian-Lopez, Emiliano Trimarco, Macarena Roman Ruiz, Carmen Rodriguez Barrios, Yolanda Marin Almagro, Isabel Benavente-Fernandez
In this study, we introduce MGA-Net, a novel mask-guided attention neural network, which extends the U-net model for precision neonatal brain imaging. MGA-Net is designed to extract the brain from other structures and reconstruct high-quality brain images. The network employs a common encoder and two decoders: one for brain mask extraction and the other for brain region reconstruction. A key feature of MGA-Net is its high-level mask-guided attention module, which leverages features from the brain mask decoder to enhance image reconstruction. To enable the same encoder and decoder to process both MRI and ultrasound (US) images, MGA-Net integrates sinusoidal positional encoding. This encoding assigns distinct positional values to MRI and US images, allowing the model to effectively learn from both modalities. Consequently, features learned from a single modality can aid in learning a modality with less available data, such as US. We extensively validated the proposed MGA-Net on diverse datasets from varied clinical settings and neonatal age groups. The metrics used for assessment included the DICE similarity coefficient, recall, and accuracy for image segmentation; structural similarity for image reconstruction; and root mean squared error for total brain volume estimation from 3D ultrasound images. Our results demonstrate that MGA-Net significantly outperforms traditional methods, offering superior performance in brain extraction and segmentation while achieving high precision in image reconstruction and volumetric analysis. Thus, MGA-Net represents a robust and effective preprocessing tool for MRI and 3D ultrasound images, marking a significant advance in neuroimaging that enhances both research and clinical diagnostics in the neonatal period and beyond.
在这项研究中,我们引入了MGA-Net,这是一种新型的面罩引导注意力神经网络,它扩展了U-net模型,用于精密新生儿脑成像。MGA-Net旨在从其他结构中提取大脑并重建高质量的大脑图像。该网络采用通用编码器和两个解码器:一个用于大脑掩膜提取,另一个用于大脑区域重建。MGA-Net的关键功能是其高级面罩引导注意力模块,该模块利用大脑掩膜解码器的特征以增强图像重建。为了使相同的编码器和解码器能够处理MRI和超声(US)图像,MGA-Net集成了正弦位置编码。这种编码为MRI和超声图像分配了不同的位置值,使得模型可以有效地从这两种模式中进行学习。因此,从单一模式中学到的特征可以帮助学习可用数据较少的模式,例如超声。我们在来自不同临床环境和新生儿年龄组的多种数据集上广泛验证了所提出的MGA-Net。评估所使用的指标包括用于图像分割的DICE相似系数、召回率和准确度;用于图像重建的结构相似性;以及用于从3D超声图像估计总脑体积的均方根误差。我们的结果表明,MGA-Net显著优于传统方法,在大脑提取和分割方面表现出卓越的性能,同时在图像重建和体积分析方面达到高精度。因此,MGA-Net是一个稳健有效的MRI和3D超声图像的预处理工具,在新生儿期及其之后的神经影像学研究及临床诊断中具有重要的进步意义。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究介绍了一种新型掩膜引导注意力神经网络MGA-Net,该网络基于U-net模型,用于精准新生儿脑成像。MGA-Net旨在从其他结构中提取大脑并重建高质量的大脑图像。该网络采用一个通用编码器和两个解码器:一个用于大脑掩膜提取,另一个用于大脑区域重建。MGA-Net的关键功能是其高级掩膜引导注意力模块,该模块利用大脑掩膜解码器的特征以增强图像重建。此外,为了处理MRI和超声图像,MGA-Net集成了正弦位置编码,使得同一编码器解码器能够处理MRI和超声图像。因此,从一个模态学习的特征可以帮助学习数据较少的模态,如超声。在多种数据集和临床环境中验证了MGA-Net的有效性,评估指标包括DICE相似系数、召回率、图像分割的准确性、图像重建的结构相似性、以及从3D超声图像估计总脑体积的均方根误差。结果表明,MGA-Net显著优于传统方法,在大脑提取和分割方面表现出卓越性能,同时在图像重建和体积分析方面达到高精度。因此,MGA-Net是MRI和3D超声图像的稳健有效预处理工具,在新生儿期及以后神经影像研究及临床诊断中具有重要意义。
Key Takeaways
- MGA-Net是一种基于U-net的新型神经网络,用于新生儿脑成像。
- 该网络能够提取大脑并重建高质量的大脑图像。
- MGA-Net具备高级掩膜引导注意力模块,可提高图像重建的质量。
- 网络采用正弦位置编码,以处理MRI和超声图像。
- MGA-Net在多种数据集和临床环境中经过验证,表现卓越。
- 评估指标包括DICE相似系数、召回率、图像分割准确性等。
点此查看论文截图