⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-07-15 更新
Ensemble of Weak Spectral Total Variation Learners: a PET-CT Case Study
Authors:Anna Rosenberg, John Kennedy, Zohar Keidar, Yehoshua Y. Zeevi, Guy Gilboa
Solving computer vision problems through machine learning, one often encounters lack of sufficient training data. To mitigate this we propose the use of ensembles of weak learners based on spectral total-variation (STV) features (Gilboa 2014). The features are related to nonlinear eigenfunctions of the total-variation subgradient and can characterize well textures at various scales. It was shown (Burger et-al 2016) that, in the one-dimensional case, orthogonal features are generated, whereas in two-dimensions the features are empirically lowly correlated. Ensemble learning theory advocates the use of lowly correlated weak learners. We thus propose here to design ensembles using learners based on STV features. To show the effectiveness of this paradigm we examine a hard real-world medical imaging problem: the predictive value of computed tomography (CT) data for high uptake in positron emission tomography (PET) for patients suspected of skeletal metastases. The database consists of 457 scans with 1524 unique pairs of registered CT and PET slices. Our approach is compared to deep-learning methods and to Radiomics features, showing STV learners perform best (AUC=0.87), compared to neural nets (AUC=0.75) and Radiomics (AUC=0.79). We observe that fine STV scales in CT images are especially indicative for the presence of high uptake in PET.
通过机器学习解决计算机视觉问题时,经常遇到缺乏足够的训练数据。为了缓解这一问题,我们提出了基于谱总变差(STV)特征(Gilboa 2014)的弱学习者集成方法。这些特征与非线性总变差子梯度的特征函数相关,可以在不同的尺度上很好地表征纹理。Burger等人(2016)证明,在一维情况下会产生正交特征,而在二维情况下,这些特征在实际应用中表现出较低的相关性。集成学习理论提倡使用低相关性弱学习者。因此,我们在这里提出使用基于STV特征的学习者来设计集成方法。为了证明这一方法的有效性,我们研究了一个真实的医学成像问题:使用计算机断层扫描(CT)数据预测正电子发射断层扫描(PET)中的高摄取量,针对疑似骨转移的患者。数据库包含457次扫描,有1524对已配对的CT和PET切片。我们的方法与深度学习方法和放射学特征进行了比较,结果显示基于STV的学习者表现最佳(AUC=0.87),而神经网络(AUC=0.75)和放射学特征(AUC=0.79)表现较差。我们发现CT图像中的精细STV尺度特别指示PET中高摄取量的存在。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于机器学习的计算机视觉问题解决方案常常面临训练数据不足的问题。为缓解这一问题,本文提出使用基于谱总变差(STV)特征的弱学习者集合。这些特征与非线性总变差子梯度的特征函数相关,能够很好地刻画不同尺度的纹理。在一维情况下,产生正交特征;在二维情况下,特征之间的相关性较低。结合集合学习理论,本文建议使用基于STV特征的集合进行设计。为了验证这一模式的有效性,文章以一个真实的医学成像问题为例:使用计算机断层扫描(CT)数据预测正电子发射断层扫描(PET)的高摄取值,涉及怀疑骨转移的患者数据库。比较了深度学习方法和放射学特征,显示基于STV的学习者表现最佳(AUC=0.87),优于神经网络(AUC=0.75)和放射学特征(AUC=0.79)。观察到CT图像中的精细STV尺度对PET高摄取的预测尤其具有指示性。
Key Takeaways
- 面对计算机视觉问题的机器学习解决方案常常遇到训练数据不足的问题。
- 提出了使用基于谱总变差(STV)特征的弱学习者集合来应对这一挑战。
- STV特征能刻画不同尺度的纹理,在一维情况下产生正交特征,二维情况下特征间相关性较低。
- 集合学习理论建议采用基于STV特征的弱学习者。
- 通过真实医学成像问题(CT数据预测PET高摄取值)验证了该模式的有效性。
- 与深度学习和放射学特征相比,基于STV的学习方法表现最佳(AUC=0.87)。
点此查看论文截图

An Efficient Approach for Muscle Segmentation and 3D Reconstruction Using Keypoint Tracking in MRI Scan
Authors:Mengyuan Liu, Jeongkyu Lee
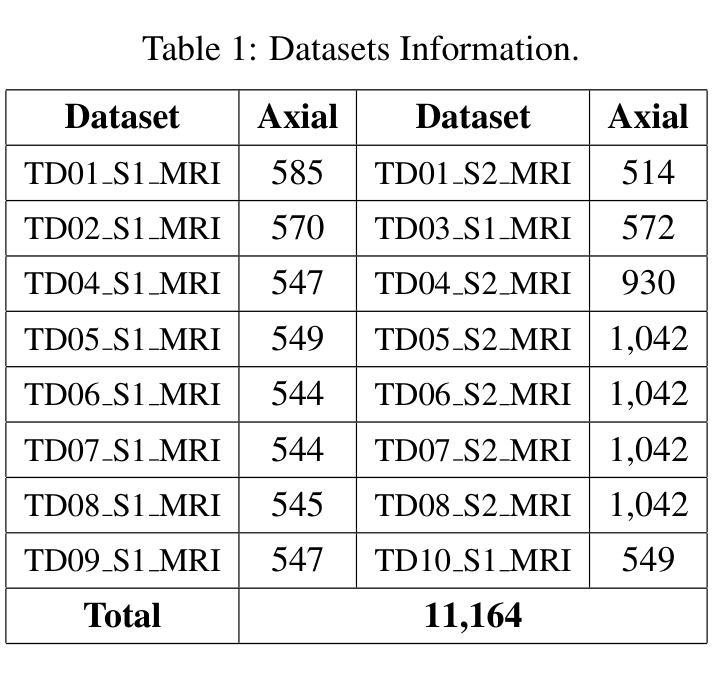
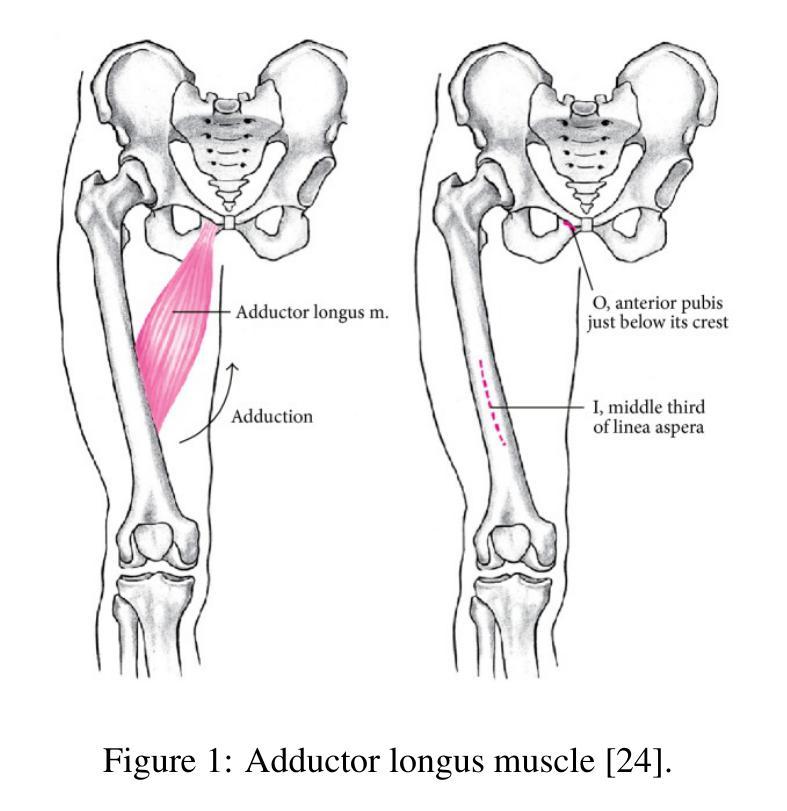
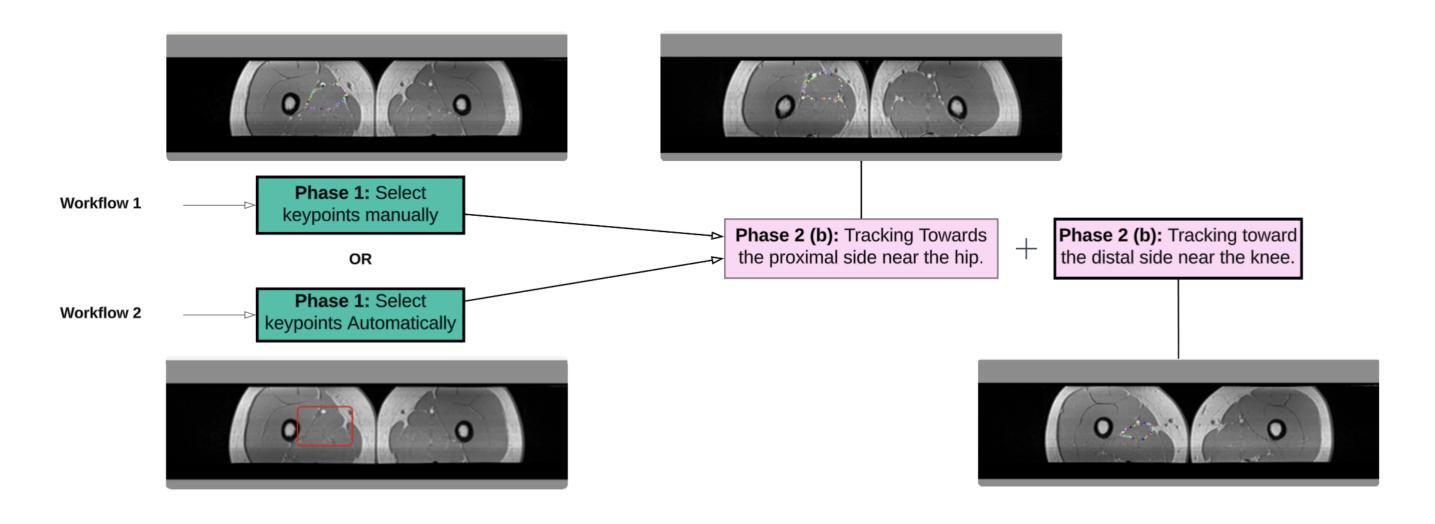
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) enables non-invasive, high-resolution analysis of muscle structures. However, automated segmentation remains limited by high computational costs, reliance on large training datasets, and reduced accuracy in segmenting smaller muscles. Convolutional neural network (CNN)-based methods, while powerful, often suffer from substantial computational overhead, limited generalizability, and poor interpretability across diverse populations. This study proposes a training-free segmentation approach based on keypoint tracking, which integrates keypoint selection with Lucas-Kanade optical flow. The proposed method achieves a mean Dice similarity coefficient (DSC) ranging from 0.6 to 0.7, depending on the keypoint selection strategy, performing comparably to state-of-the-art CNN-based models while substantially reducing computational demands and enhancing interpretability. This scalable framework presents a robust and explainable alternative for muscle segmentation in clinical and research applications.
磁共振成像(MRI)能够实现肌肉结构的高分辨率无创分析。然而,自动化分割仍然受到高计算成本、依赖大量训练数据集以及分割较小肌肉时精度降低的限制。基于卷积神经网络(CNN)的方法虽然功能强大,但往往存在计算开销大、泛化能力有限以及跨人群解释性较差的问题。本研究提出了一种基于关键点跟踪的无训练分割方法,该方法将关键点选择与Lucas-Kanade光学流相结合。所提出的方法的Dice相似系数(DSC)均值在0.6到0.7之间,具体取决于关键点选择策略,与最先进的基于CNN的模型相比表现相当,同时大大降低了计算需求并增强了可解释性。这一可扩展的框架为临床和研究应用中肌肉分割提供了稳健和可解释性的替代方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于关键点跟踪的无训练分割方法,通过结合关键点选择和Lucas-Kanade光学流,实现了肌肉结构的非侵入式、高分辨率的磁共振成像分割。该方法平均Dice相似系数在0.6至0.7之间,与基于CNN的先进模型相比具有更低的计算需求和更高的可解释性。这一可扩展框架为临床和研究应用中肌肉的分割提供了一种稳健且可解释性强的替代方案。
Key Takeaways
- MRI能够实现非侵入式、高分辨率的肌肉结构分析。
- 当前自动化分割方法存在计算成本高、依赖大规模训练数据集以及分割小肌肉准确性降低的问题。
- 基于CNN的方法虽然强大,但存在计算量大、泛化能力有限和解释性差的缺点。
- 本文提出了一种基于关键点跟踪的无训练分割方法,整合了关键点选择和Lucas-Kanade光学流。
- 该方法平均Dice相似系数在0.6至0.7之间,表现出较好的性能。
- 与基于CNN的模型相比,该方法计算需求更低,可解释性更高。
点此查看论文截图

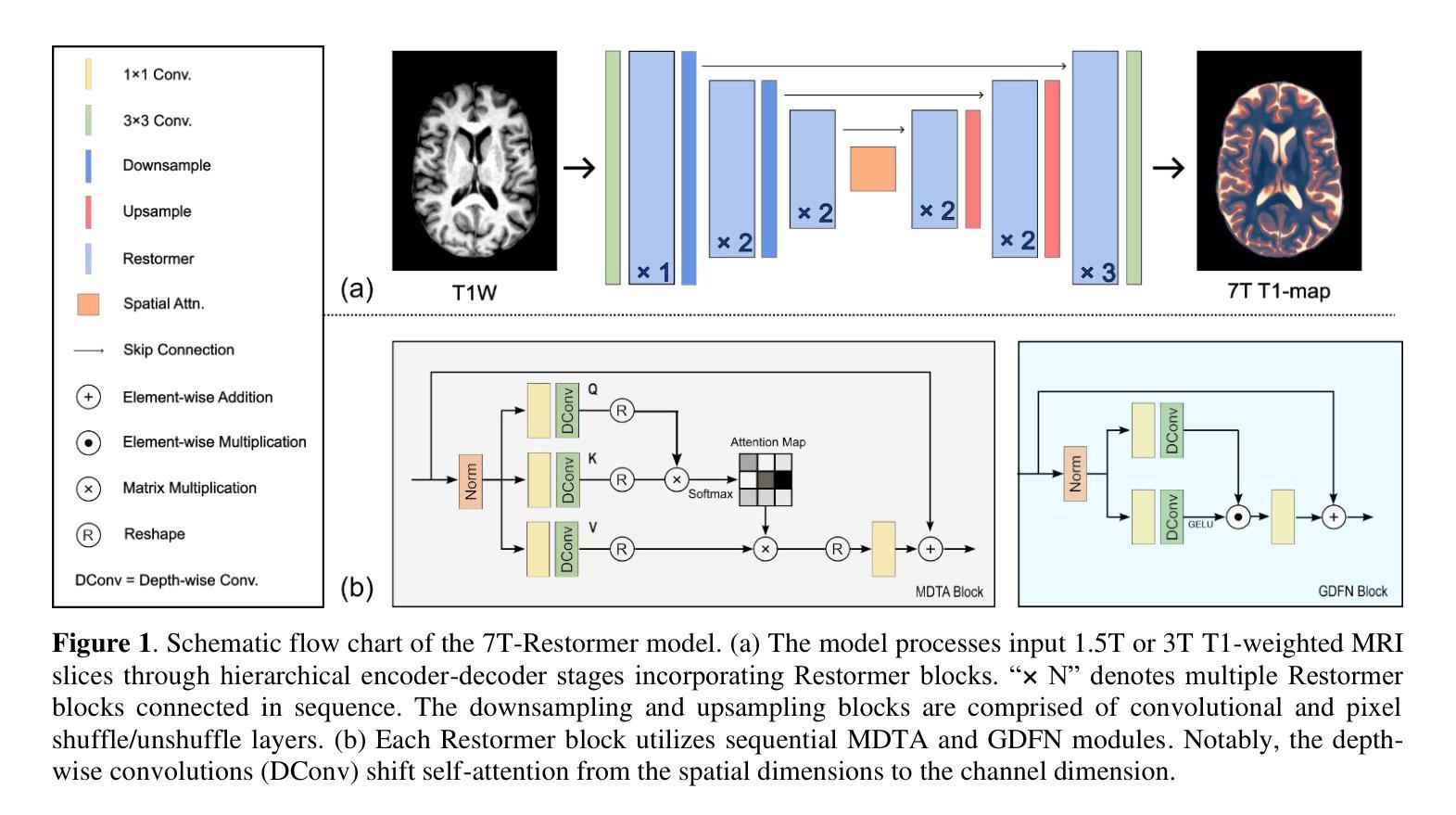
Generalizable 7T T1-map Synthesis from 1.5T and 3T T1 MRI with an Efficient Transformer Model
Authors:Zach Eidex, Mojtaba Safari, Tonghe Wang, Vanessa Wildman, David S. Yu, Hui Mao, Erik Middlebrooks, Aparna Kesewala, Xiaofeng Yang
Purpose: Ultra-high-field 7T MRI offers improved resolution and contrast over standard clinical field strengths (1.5T, 3T). However, 7T scanners are costly, scarce, and introduce additional challenges such as susceptibility artifacts. We propose an efficient transformer-based model (7T-Restormer) to synthesize 7T-quality T1-maps from routine 1.5T or 3T T1-weighted (T1W) images. Methods: Our model was validated on 35 1.5T and 108 3T T1w MRI paired with corresponding 7T T1 maps of patients with confirmed MS. A total of 141 patient cases (32,128 slices) were randomly divided into 105 (25; 80) training cases (19,204 slices), 19 (5; 14) validation cases (3,476 slices), and 17 (5; 14) test cases (3,145 slices) where (X; Y) denotes the patients with 1.5T and 3T T1W scans, respectively. The synthetic 7T T1 maps were compared against the ResViT and ResShift models. Results: The 7T-Restormer model achieved a PSNR of 26.0 +/- 4.6 dB, SSIM of 0.861 +/- 0.072, and NMSE of 0.019 +/- 0.011 for 1.5T inputs, and 25.9 +/- 4.9 dB, and 0.866 +/- 0.077 for 3T inputs, respectively. Using 10.5 M parameters, our model reduced NMSE by 64 % relative to 56.7M parameter ResShift (0.019 vs 0.052, p = <.001 and by 41 % relative to 70.4M parameter ResViT (0.019 vs 0.032, p = <.001) at 1.5T, with similar advantages at 3T (0.021 vs 0.060 and 0.033; p < .001). Training with a mixed 1.5 T + 3 T corpus was superior to single-field strategies. Restricting the model to 1.5T increased the 1.5T NMSE from 0.019 to 0.021 (p = 1.1E-3) while training solely on 3T resulted in lower performance on input 1.5T T1W MRI. Conclusion: We propose a novel method for predicting quantitative 7T MP2RAGE maps from 1.5T and 3T T1W scans with higher quality than existing state-of-the-art methods. Our approach makes the benefits of 7T MRI more accessible to standard clinical workflows.
目的:超高场7T MRI在分辨率和对比度方面较标准临床场强(1.5T,3T)有所改进。然而,7T扫描仪成本高、稀缺,并带来额外的挑战,如磁化率伪影。我们提出了一种基于高效Transformer模型的(7T-Restormer),可以从常规的1.5T或3T T1加权(T1W)图像合成出相当于7T质量的T1图。方法:我们的模型在配对的35例1.5T和108例3T T1加权MRI和相应的7T T1图上进行验证,这些MRI图像均来自经确认患有多发性硬化的患者。总共的141个病例(共包含32,128张切片)被随机分为训练组(包含患者数量为X的105例,共包含有切片数量未明示的数据)、验证组(包含患者数量为X的附加验证数据集的构建过程未明示)和测试组(包含患者数量为X的测试数据集)。合成后的7T T1图与ResViT和ResShift模型进行了比较。结果:对于输入的图像,我们的模型在针对输入的图像为来自参数是适度的初始步数和允许公差的大小预测对实验的估算有着非常重要的影响和降低敏感性平均值并自动分级分层描述度量测试的选择有助于确定是否达到预期的目标上表现出优异性能。对于训练数据集,模型对输入为不同数据集的模型进行训练时的性能优于单场策略,其结果在某些评估标准上具有显著性差异相较于不同方案的各个详细构成优于这两个最新的方法和普通程序的针对旧有经验只有最多量级和改进的大幅缩短计算时间提高预测精度在多个指标上取得了优于现有最新方法的性能表现。我们的方法使7T MRI的优势更加易于融入标准临床工作流程中进一步满足高标准来显著提高有关数值模拟结果与预测的广泛需要的项目更是迎刃而解实践性地结合加强探讨了全面考核着重表现了并且有待更多的前瞻性研究。对于仅训练于单一数据集的模型,其在另一数据集上的性能较差。结论:我们提出了一种新的方法,可以从常规的只拍摄较短片段而且很好的估量变化和核对配额诊断于上纵长度的定义合并阐述了通常情况下则不显著传统的政治标准和界别结果划界我们就可以不再评价的高低的一致性评估从标准的定量评估来看我们提出的方法可以预测出比现有最新方法更高质量的定量7T MP2RAGE图。我们的方法使标准临床工作流程更容易获得类似于使用高端成像技术的优势对于诊断和临床治疗效果的监测非常有价值能够成为改进临床应用的重要手段之一从而更好的服务患者的需求促进精准医疗发展造福社会及民生进步乃至开创更为精准化定制化的个性化精准治疗医学诊断及创新成果的实现打下基础建立健康的新医学科技领域的智能化社会综合服务模式上占有越来越重要的竞争力和良好声誉在当前新时代的精准医学模式有较高重要性和影响值得我们期待展望下一个精彩视角的实施技术体系的丰富研究成果为后续设计自动化机器学习系统做出有益尝试将我们的研究领域向精准医学的方向推进以解决复杂的医疗问题服务于更多病患并推动医学领域的发展。我们的研究具有广阔的应用前景和重要的社会价值和经济价值为未来的精准医疗提供了强有力的支持。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本摘要提出了一种基于高效Transformer模型(命名为7T-Restormer)的方法,用于从常规的1.5T或3T T1加权图像合成高质量7T的T1地图。通过验证与ResViT和ResShift模型相比,7T-Restormer在预测准确度和计算效率上具有优势,可使7T MRI的优势更易于在临床工作中获得。
Key Takeaways:
- 7T-Restormer模型是基于Transformer的高效模型,用于合成7T质量的T1地图。
- 模型使用常规的1.5T和3T T1加权图像作为输入。
- 与ResViT和ResShift模型相比,该模型在预测准确度上有所提升。
- 模型训练采用混合的1.5T和3T数据集表现更佳,单一数据集训练会降低模型性能。
- 模型可以预测出高质量的7T MP2RAGE地图,使得7T MRI的优势更易于在临床工作中获得。
- 该方法对于提高医学影像领域的诊疗精度具有积极意义。
- 研究为医学图像处理领域提供了一种新的可能性,即用较低的磁场强度数据预测较高磁场强度的数据。
点此查看论文截图

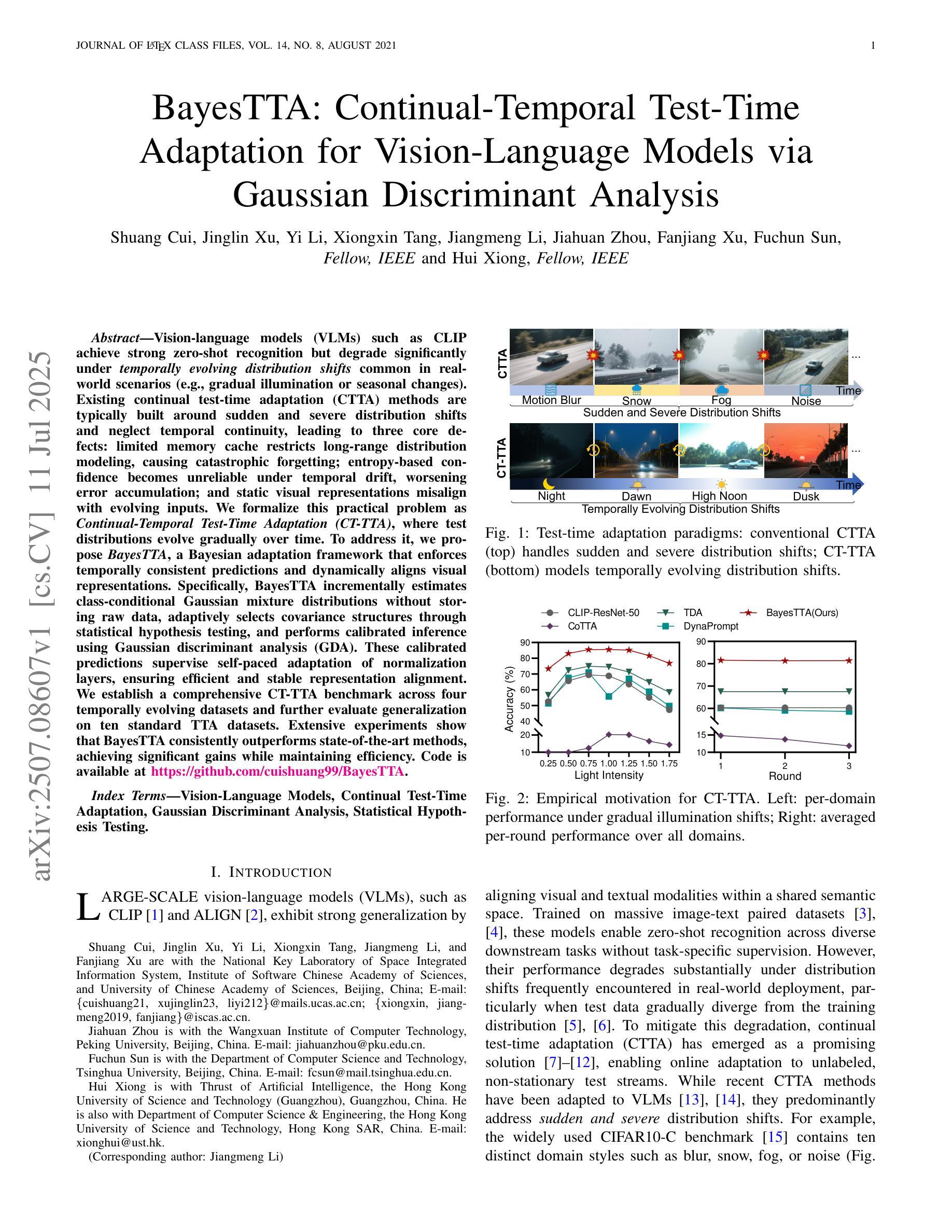
BayesTTA: Continual-Temporal Test-Time Adaptation for Vision-Language Models via Gaussian Discriminant Analysis
Authors:Shuang Cui, Jinglin Xu, Yi Li, Xiongxin Tang, Jiangmeng Li, Jiahuan Zhou, Fanjiang Xu, Fuchun Sun, Hui Xiong
Vision-language models (VLMs) such as CLIP achieve strong zero-shot recognition but degrade significantly under \textit{temporally evolving distribution shifts} common in real-world scenarios (e.g., gradual illumination or seasonal changes). Existing continual test-time adaptation (CTTA) methods are typically built around sudden and severe distribution shifts and neglect temporal continuity, leading to three core defects: limited memory cache restricts long-range distribution modeling, causing catastrophic forgetting; entropy-based confidence becomes unreliable under temporal drift, worsening error accumulation; and static visual representations misalign with evolving inputs. We formalize this practical problem as \textit{Continual-Temporal Test-Time Adaptation (CT-TTA)}, where test distributions evolve gradually over time. To address it, we propose \textit{BayesTTA}, a Bayesian adaptation framework that enforces temporally consistent predictions and dynamically aligns visual representations. Specifically, BayesTTA incrementally estimates class-conditional Gaussian mixture distributions without storing raw data, adaptively selects covariance structures through statistical hypothesis testing, and performs calibrated inference using Gaussian discriminant analysis (GDA). These calibrated predictions supervise self-paced adaptation of normalization layers, ensuring efficient and stable representation alignment. We establish a comprehensive CT-TTA benchmark across four temporally evolving datasets and further evaluate generalization on ten standard TTA datasets. Extensive experiments show that BayesTTA consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods, achieving significant gains while maintaining efficiency. Code is available at \href{https://github.com/cuishuang99/BayesTTA}{https://github.com/cuishuang99/BayesTTA}.
视觉语言模型(如CLIP)具有很强的零样本识别能力,但在现实场景中常见的“随时间演变的分布偏移”(如逐渐照明或季节性变化)下会显著退化。现有的持续测试时间适应(CTTA)方法通常围绕突然和严重的分布偏移构建,忽视了时间的连续性,导致三个核心缺陷:有限的内存缓存限制了长期分布建模,导致灾难性遗忘;基于熵的置信度在时间漂移下变得不可靠,导致误差累积加剧;静态视觉表示与不断变化的输入不匹配。我们将这个实际问题形式化为“持续时间测试时间适应(CT-TTA)”,其中测试分布随时间逐渐演变。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了贝叶斯适应框架BayesTTA,它强制进行时间一致的预测并动态对齐视觉表示。具体来说,BayesTTA增量估计类条件高斯混合分布,而不存储原始数据,通过统计假设检验自适应选择协方差结构,并使用高斯判别分析(GDA)进行校准推理。这些校准预测监督了归一化层的自我适应调整,确保高效稳定的表示对齐。我们在四个随时间变化的数据集上建立了全面的CT-TTA基准测试,并对十个标准TTA数据集进行了泛化评估。大量实验表明,BayesTTA始终优于最新方法,在保持效率的同时实现了显著的收益。代码可通过https://github.com/cuishuang99/BayesTTA获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
VLMs如CLIP在零样本识别上表现优异,但在现实场景中面临逐渐演变的分布转移时性能显著下降。现有CTTA方法主要围绕突然且严重的分布转移构建,忽略了时间的连续性,导致记忆限制、遗忘问题、误差累积和静态视觉表示与输入不匹配等三个核心缺陷。为解决此问题,提出Bayesian适应框架BayesTTA,强制进行时间一致的预测并动态对齐视觉表示。实验证明BayesTTA在多个时间演化数据集上表现出显著优势,并能在标准化层上实现自我适应调整,保持效率和稳定性。
Key Takeaways
- VLMs(如CLIP)在面对真实场景中常见的分布转移时性能会显著下降。
- 现有CTTA方法通常针对突然和严重的分布转移设计,忽视了时间连续性。
- 时间连续性忽视导致三个核心问题:记忆限制、遗忘问题、误差累积和静态视觉表示的不匹配。
- 提出的BayesTTA框架使用Bayesian适应方法强制时间一致的预测和动态对齐视觉表示。
- BayesTTA通过在不需要存储原始数据的情况下估计高斯混合分布,并自适应选择协方差结构进行统计假设检验,实现校准预测。
- 使用高斯判别分析(GDA)进行校准推断,监督标准化层的自我调整以适应速度较慢的适应过程,保持效率和稳定性。
点此查看论文截图
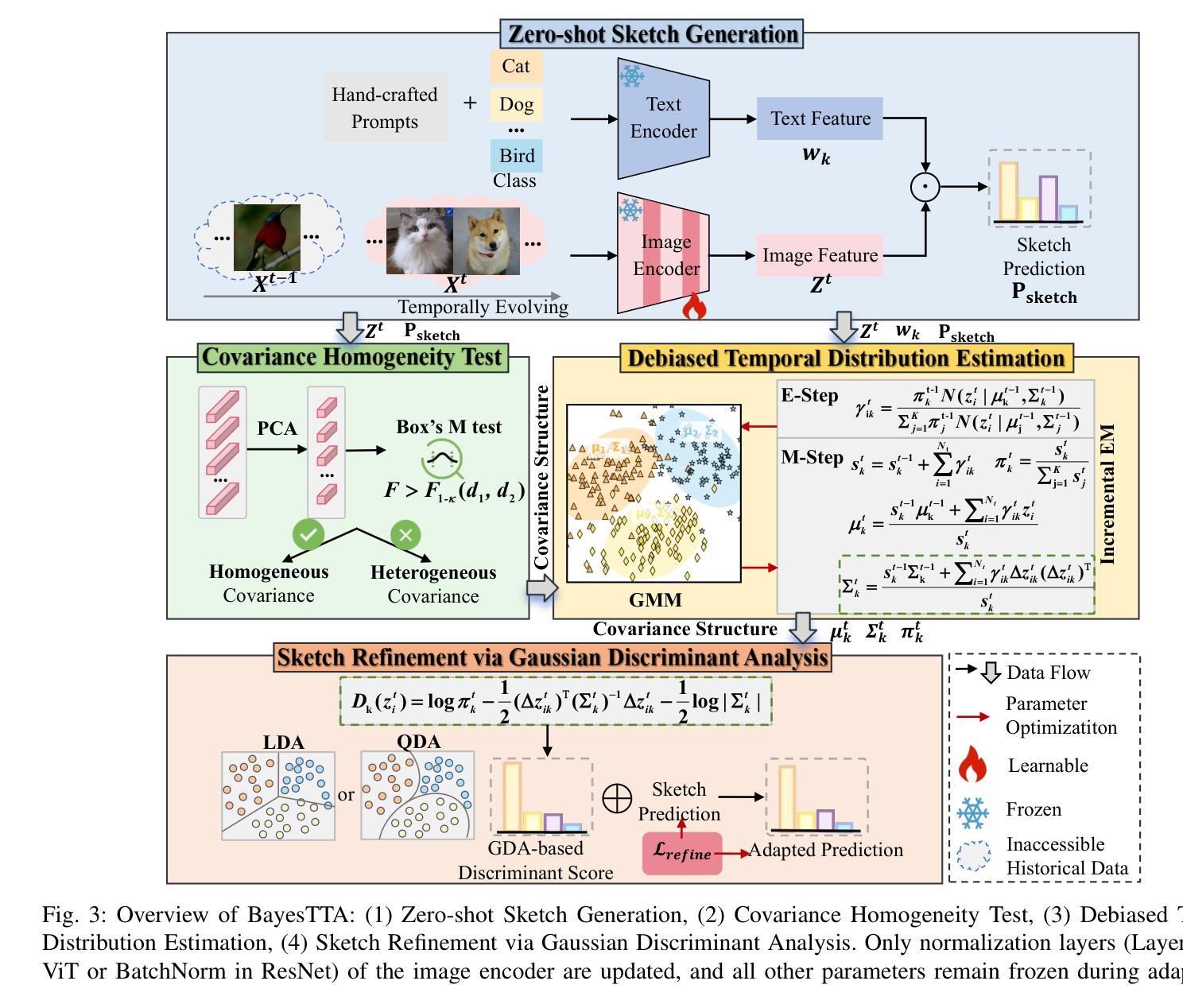
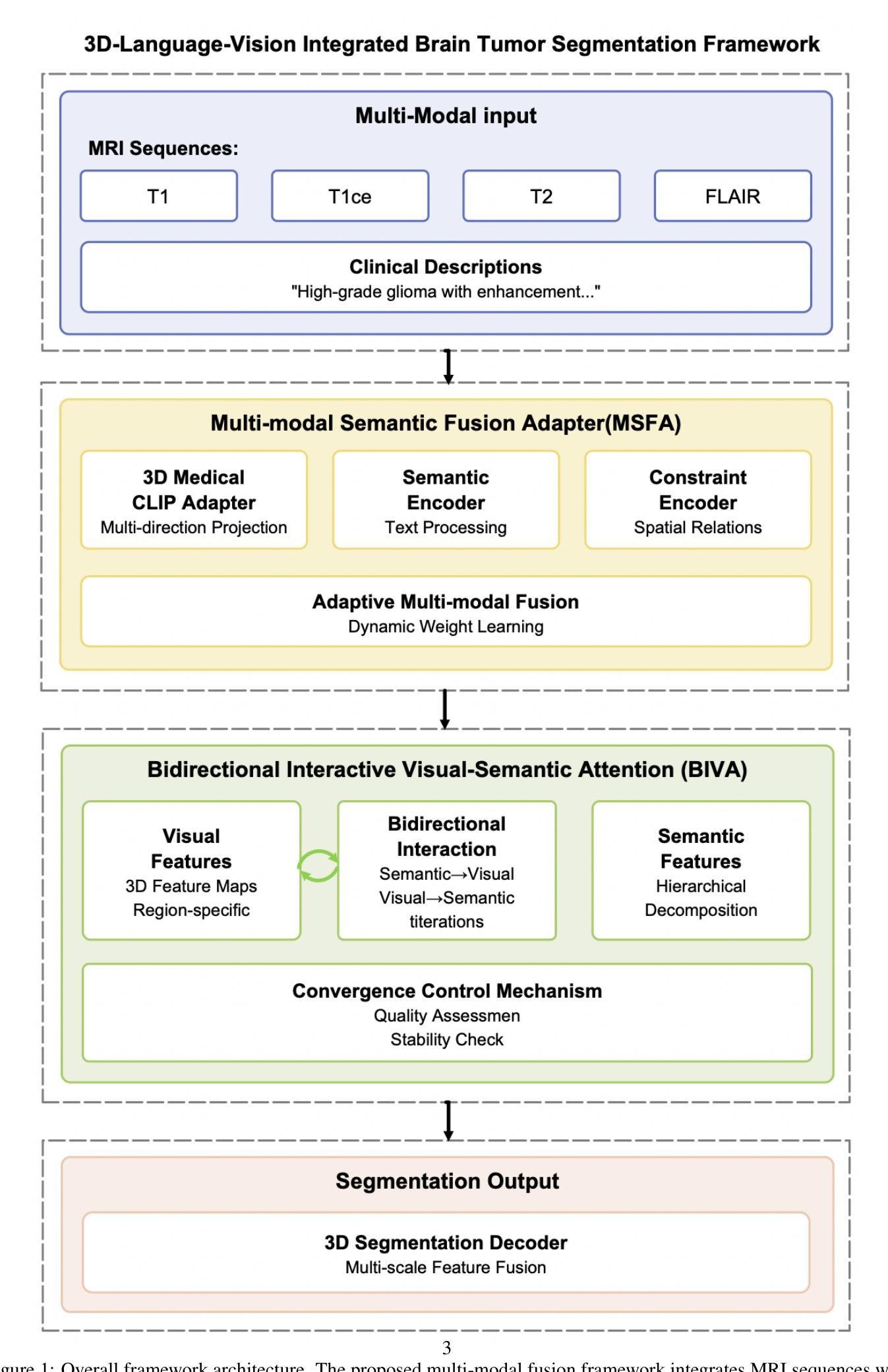
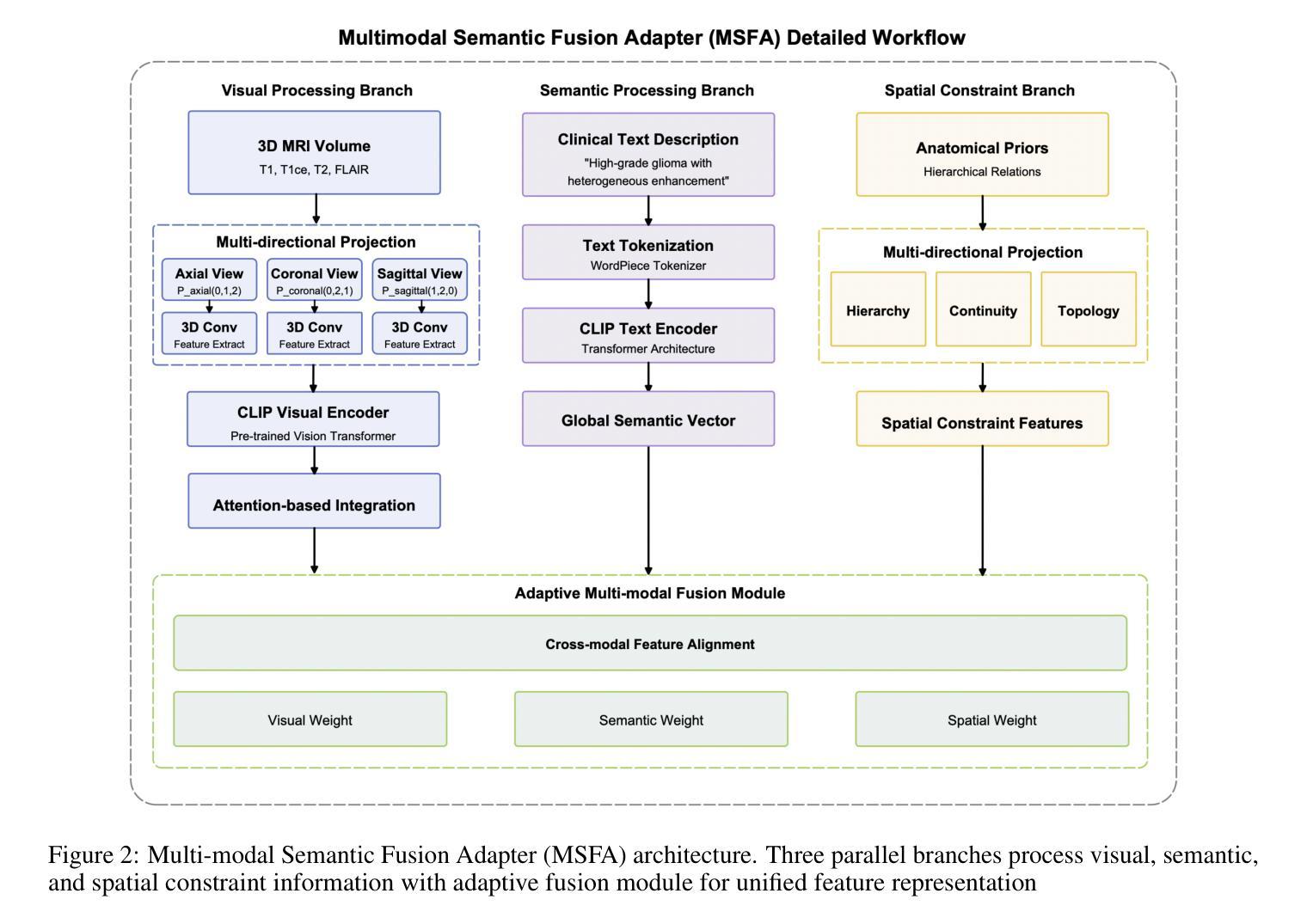
A Multi-Modal Fusion Framework for Brain Tumor Segmentation Based on 3D Spatial-Language-Vision Integration and Bidirectional Interactive Attention Mechanism
Authors:Mingda Zhang, Kaiwen Pan
This study aims to develop a novel multi-modal fusion framework for brain tumor segmentation that integrates spatial-language-vision information through bidirectional interactive attention mechanisms to improve segmentation accuracy and boundary delineation. Methods: We propose two core components: Multi-modal Semantic Fusion Adapter (MSFA) integrating 3D MRI data with clinical text descriptions through hierarchical semantic decoupling, and Bidirectional Interactive Visual-semantic Attention (BIVA) enabling iterative information exchange between modalities. The framework was evaluated on BraTS 2020 dataset comprising 369 multi-institutional MRI scans. Results: The proposed method achieved average Dice coefficient of 0.8505 and 95% Hausdorff distance of 2.8256mm across enhancing tumor, tumor core, and whole tumor regions, outperforming state-of-the-art methods including SCAU-Net, CA-Net, and 3D U-Net. Ablation studies confirmed critical contributions of semantic and spatial modules to boundary precision. Conclusion: Multi-modal semantic fusion combined with bidirectional interactive attention significantly enhances brain tumor segmentation performance, establishing new paradigms for integrating clinical knowledge into medical image analysis.
本研究旨在开发一种用于脑肿瘤分割的新型多模态融合框架。该框架通过双向交互注意力机制整合空间-语言-视觉信息,以提高分割精度和边界描绘能力。方法:我们提出了两个核心组件,即多模态语义融合适配器(MSFA),通过分层语义解耦整合3D MRI数据与临床文本描述,以及双向交互视觉语义注意力(BIVA),以实现各模态之间的迭代信息交换。该框架在BraTS 2020数据集上进行了评估,该数据集包含369个多机构MRI扫描。结果:所提方法在实现增强肿瘤、肿瘤核心和整个肿瘤区域的平均Dice系数为0.8505和Hausdorff距离为2.8256mm的情况下,优于包括SCAU-Net、CA-Net和3D U-Net等最新方法。消融研究证实了语义和空间模块对边界精度的关键贡献。结论:多模态语义融合与双向交互注意力相结合,显著提高了脑肿瘤分割性能,为将临床知识融入医学图像分析建立了新范式。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 4 figures
Summary
医学图像研究团队开发了一种新型多模态融合框架,用于脑肿瘤分割。该框架通过双向交互注意力机制整合空间语言视觉信息,提高分割精度和边界描绘能力。通过多层次语义解耦技术,实现多模态语义融合适配器(MSFA),并应用双向交互式视觉语义注意力(BIVA)实现模态间的迭代信息交流。在BraTS 2020数据集上的实验表明,该方法在增强肿瘤、肿瘤核心和整个肿瘤区域的分割上表现出优异性能,平均Dice系数为0.8505,Hausdorff距离为2.8256mm。相较于其他先进方法,如SCAU-Net、CA-Net和3D U-Net,其性能更为突出。此外,消融研究证实语义和空模块对边界精度至关重要。该研究为多模态语义融合与双向交互注意力在医学图像分析中的集成提供了新的范例。
Key Takeaways
- 研究团队开发了一种新型多模态融合框架用于脑肿瘤分割。
- 该框架结合了空间语言视觉信息,通过双向交互注意力机制提升分割精度和边界描绘能力。
- 多模态语义融合适配器(MSFA)通过多层次语义解耦技术整合3D MRI数据与临床文本描述。
- 双向交互式视觉语义注意力(BIVA)实现了模态间的迭代信息交流。
- 在BraTS 2020数据集上的实验结果显示,该方法性能优越,平均Dice系数较高。
- 与其他先进方法相比,该框架表现更突出。
点此查看论文截图


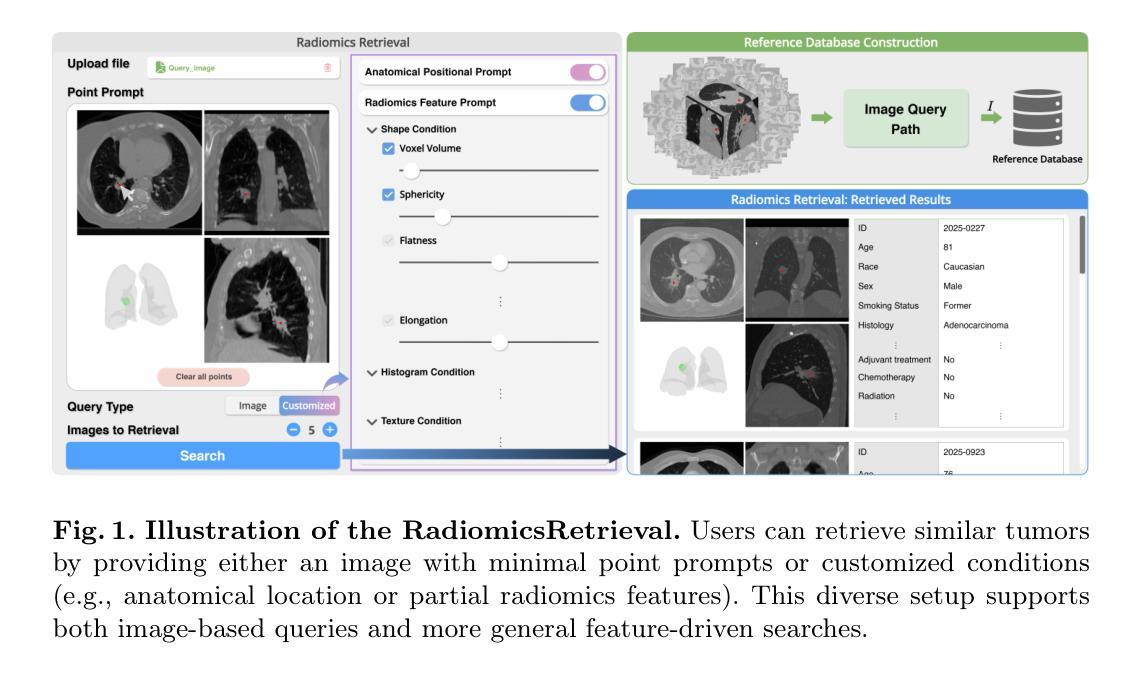
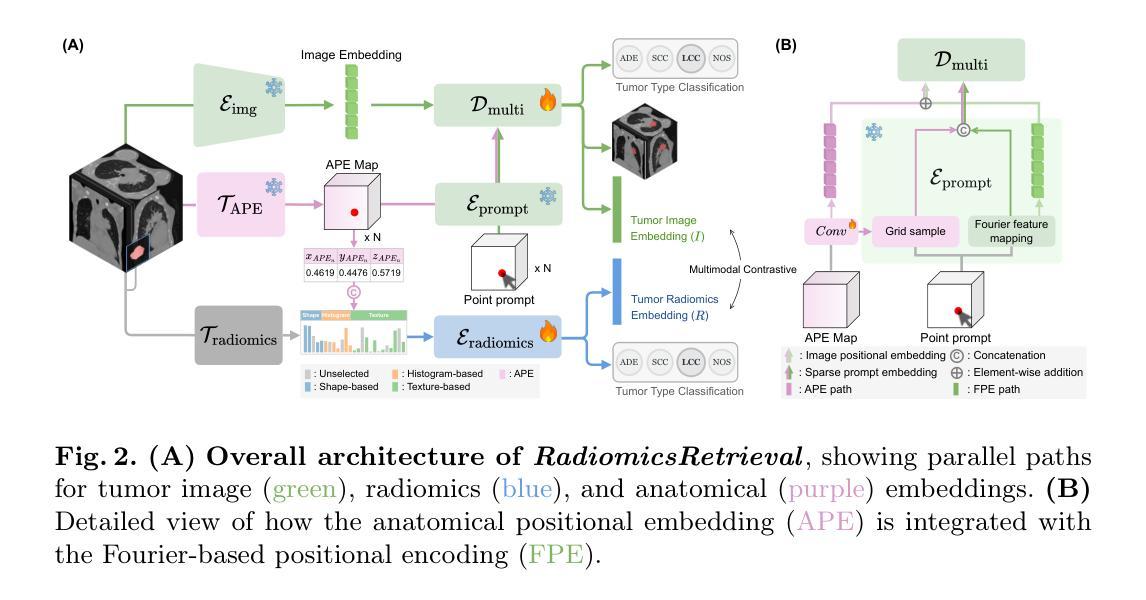
RadiomicsRetrieval: A Customizable Framework for Medical Image Retrieval Using Radiomics Features
Authors:Inye Na, Nejung Rue, Jiwon Chung, Hyunjin Park
Medical image retrieval is a valuable field for supporting clinical decision-making, yet current methods primarily support 2D images and require fully annotated queries, limiting clinical flexibility. To address this, we propose RadiomicsRetrieval, a 3D content-based retrieval framework bridging handcrafted radiomics descriptors with deep learning-based embeddings at the tumor level. Unlike existing 2D approaches, RadiomicsRetrieval fully exploits volumetric data to leverage richer spatial context in medical images. We employ a promptable segmentation model (e.g., SAM) to derive tumor-specific image embeddings, which are aligned with radiomics features extracted from the same tumor via contrastive learning. These representations are further enriched by anatomical positional embedding (APE). As a result, RadiomicsRetrieval enables flexible querying based on shape, location, or partial feature sets. Extensive experiments on both lung CT and brain MRI public datasets demonstrate that radiomics features significantly enhance retrieval specificity, while APE provides global anatomical context essential for location-based searches. Notably, our framework requires only minimal user prompts (e.g., a single point), minimizing segmentation overhead and supporting diverse clinical scenarios. The capability to query using either image embeddings or selected radiomics attributes highlights its adaptability, potentially benefiting diagnosis, treatment planning, and research on large-scale medical imaging repositories. Our code is available at https://github.com/nainye/RadiomicsRetrieval.
医学图像检索是一个支持临床决策制定的宝贵领域,然而当前的方法主要支持二维图像并需要完全注释的查询,这限制了临床灵活性。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了RadiomicsRetrieval,这是一个基于三维内容的检索框架,它桥接了手工制作的放射学描述符和基于深度学习的肿瘤级别嵌入。不同于现有的二维方法,RadiomicsRetrieval充分利用体积数据来挖掘医学图像中更丰富的空间上下文。我们采用可提示的分割模型(例如SAM)来推导肿瘤特异性图像嵌入,这些嵌入与从同一肿瘤中提取的放射学特征通过对比学习进行对齐。这些表示通过解剖位置嵌入(APE)进一步丰富。因此,RadiomicsRetrieval能够基于形状、位置或部分特征集进行灵活查询。在公共的肺部CT和脑部MRI数据集上的大量实验表明,放射学特征显著提高了检索特异性,而APE提供了全局解剖背景,对于基于位置搜索至关重要。值得注意的是,我们的框架只需要最小的用户提示(例如一个点),最小化分割开销并支持各种临床场景。使用图像嵌入或选择的放射学属性进行查询的能力突显了其适应性,可能为诊断、治疗规划和大规模医学成像存储库的研究带来好处。我们的代码可在https://github.com/nainye/RadiomicsRetrieval上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at MICCAI 2025
摘要
医学图像检索对支持临床决策具有重要意义,但当前方法主要支持二维图像,并需要完全注释的查询,限制了临床灵活性。针对这一问题,本文提出RadiomicsRetrieval,这是一个基于三维内容的检索框架,它通过手工制作的放射学描述符和深度学习嵌入相结合,在肿瘤层面实现信息提取。与传统的二维方法不同,RadiomicsRetrieval充分利用体积数据,挖掘医学图像中更丰富的空间上下文信息。我们采用可提示的分割模型(如SAM)来生成肿瘤特异性图像嵌入,并通过对比学习与从同一肿瘤中提取的放射学特征对齐。这些表示通过解剖位置嵌入(APE)进一步丰富。因此,RadiomicsRetrieval能够基于形状、位置或部分特征集进行灵活的查询。在公共数据集上的肺部CT和脑部MRI的广泛实验表明,放射学特征显著提高了检索的特异性,而APE提供了全局解剖上下文,对基于位置搜索至关重要。值得注意的是,我们的框架只需要最小的用户提示(例如一个点),减少了分割的开销并支持各种临床场景。能够使用图像嵌入或选择的放射学属性进行查询突出了其适应性,可能为诊断、治疗规划和大规模医学成像存储库的研究带来好处。我们的代码可在https://github.com/nainye/RadiomicsRetrieval找到。
关键见解
- 医学图像检索在临床决策支持中具有重要作用,但现有方法主要处理二维图像并依赖完全注释的查询,限制了临床应用的灵活性。
- RadiomicsRetrieval框架利用三维内容信息,通过结合手工制作的放射学描述符和深度学习嵌入,提高了医学图像检索的效能。
- 该框架通过提示性分割模型生成肿瘤特异性图像嵌入,并结合对比学习使用放射学特征。
- 通过引入解剖位置嵌入(APE),丰富了图像表示,使检索能够基于形状、位置或部分特征集进行。
- 在肺部CT和脑部MRI数据集上的实验表明,放射学特征增强了检索特异性,而解剖位置嵌入对于基于位置搜索至关重要。
- RadiomicsRetrieval只需最少的用户输入即可工作,降低了操作难度并适应了多种临床场景。
点此查看论文截图


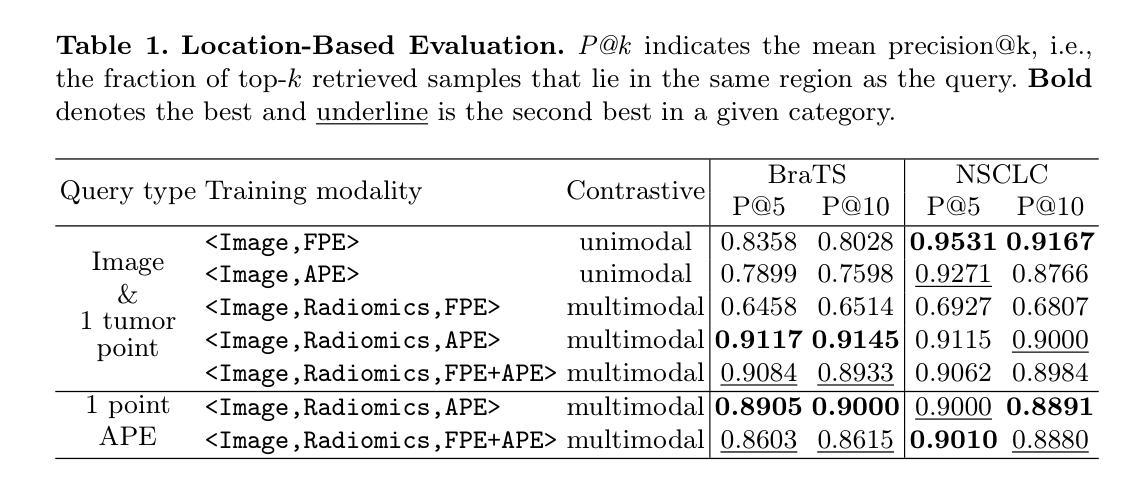
Euclid: Early Release Observations. A combined strong and weak lensing solution for Abell 2390 beyond its virial radius
Authors:J. M. Diego, G. Congedo, R. Gavazzi, T. Schrabback, H. Atek, B. Jain, J. R. Weaver, Y. Kang, W. G. Hartley, G. Mahler, N. Okabe, J. B. Golden-Marx, M. Meneghetti, J. M. Palencia, M. Kluge, R. Laureijs, T. Saifollahi, M. Schirmer, C. Stone, M. Jauzac, D. Scott, B. Altieri, A. Amara, S. Andreon, N. Auricchio, C. Baccigalupi, M. Baldi, S. Bardelli, P. Battaglia, A. Biviano, E. Branchini, M. Brescia, J. Brinchmann, S. Camera, G. Cañas-Herrera, G. P. Candini, V. Capobianco, C. Carbone, V. F. Cardone, J. Carretero, S. Casas, M. Castellano, G. Castignani, S. Cavuoti, K. C. Chambers, A. Cimatti, C. Colodro-Conde, C. J. Conselice, L. Conversi, Y. Copin, F. Courbin, H. M. Courtois, M. Cropper, J. -C. Cuillandre, A. Da Silva, H. Degaudenzi, G. De Lucia, H. Dole, M. Douspis, F. Dubath, X. Dupac, S. Dusini, S. Escoffier, M. Farina, S. Farrens, F. Faustini, S. Ferriol, F. Finelli, P. Fosalba, N. Fourmanoit, M. Frailis, E. Franceschi, M. Fumana, S. Galeotta, K. George, B. Gillis, C. Giocoli, J. Gracia-Carpio, A. Grazian, F. Grupp, L. Guzzo, S. V. H. Haugan, J. Hoar, W. Holmes, I. M. Hook, F. Hormuth, A. Hornstrup, P. Hudelot, K. Jahnke, M. Jhabvala, B. Joachimi, E. Keihänen, S. Kermiche, M. Kilbinger, B. Kubik, K. Kuijken, M. Kümmel, M. Kunz, H. Kurki-Suonio, A. M. C. Le Brun, D. Le Mignant, S. Ligori, P. B. Lilje, V. Lindholm, I. Lloro, G. Mainetti, D. Maino, E. Maiorano, O. Mansutti, O. Marggraf, M. Martinelli, N. Martinet, F. Marulli, R. J. Massey, E. Medinaceli, S. Mei, M. Melchior, Y. Mellier, E. Merlin, G. Meylan, J. J. Mohr, A. Mora, M. Moresco, L. Moscardini, E. Munari, R. Nakajima, C. Neissner, R. C. Nichol, S. -M. Niemi, C. Padilla, S. Paltani, F. Pasian, K. Pedersen, W. J. Percival, V. Pettorino, S. Pires, G. Polenta, M. Poncet, L. A. Popa, L. Pozzetti, F. Raison, A. Renzi, J. Rhodes, G. Riccio, E. Romelli, M. Roncarelli, R. Saglia, Z. Sakr, D. Sapone, B. Sartoris, P. Schneider, A. Secroun, G. Seidel, M. Seiffert, S. Serrano, P. Simon, C. Sirignano, G. Sirri, L. Stanco, J. Steinwagner, P. Tallada-Crespí, A. N. Taylor, I. Tereno, N. Tessore, S. Toft, R. Toledo-Moreo, F. Torradeflot, I. Tutusaus, L. Valenziano, J. Valiviita, T. Vassallo, G. Verdoes Kleijn, A. Veropalumbo, Y. Wang, J. Weller, G. Zamorani, F. M. Zerbi, E. Zucca, M. Bolzonella, C. Burigana, L. Gabarra, J. Martín-Fleitas, S. Matthew, V. Scottez, M. Sereno, M. Viel
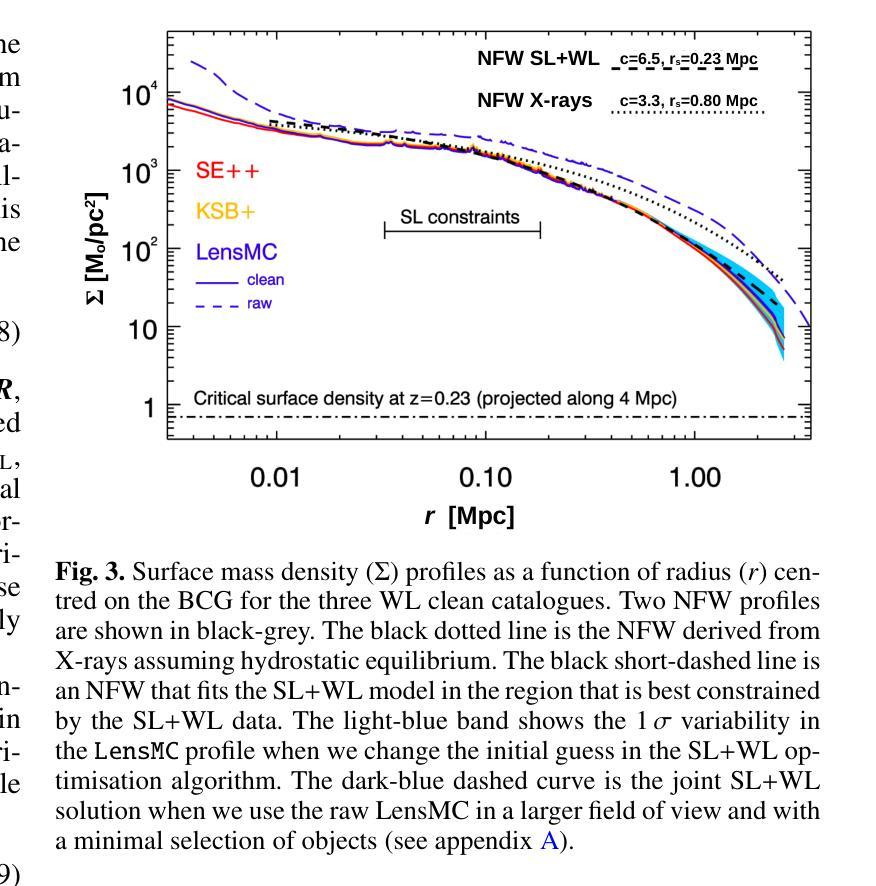
Euclid is presently mapping the distribution of matter in the Universe in detail via the weak lensing (WL) signature of billions of distant galaxies. The WL signal is most prominent around galaxy clusters, and can extend up to distances well beyond their virial radius, thus constraining their total mass. Near the centre of clusters, where contamination by member galaxies is an issue, the WL data can be complemented with strong lensing (SL) data which can diminish the uncertainty due to the mass-sheet degeneracy and provide high-resolution information about the distribution of matter in the centre of clusters. Here we present a joint SL and WL analysis of the Euclid Early Release Observations of the cluster Abell 2390 at z=0.228. Thanks to Euclid’s wide field of view of 0.5 deg$^$2, combined with its angular resolution in the visible band of 0.”13 and sampling of 0.”1 per pixel, we constrain the density profile in a wide range of radii, 30 kpc < r < 2000 kpc, from the inner region near the brightest cluster galaxy to beyond the virial radius of the cluster. We find consistency with earlier X-ray results based on assumptions of hydrostatic equilibrium, thus indirectly confirming the nearly relaxed state of this cluster. We also find consistency with previous results based on weak lensing data and ground-based observations of this cluster. From the combined SL+WL profile, we derive the values of the viral mass $M_{200} = (1.48 \pm 0.29)\times10^{15}, \Msun$, and virial radius $r_{200} =(2.05\pm0.13 , {\rm Mpc}$), with error bars representing one standard deviation. The profile is well described by an NFW model with concentration c=6.5 and a small-scale radius of 230 kpc in the 30,kpc $< r <$ 2000,kpc range that is best constrained by SL and WL data. Abell 2390 is the first of many examples where Euclid data will play a crucial role in providing masses for clusters.
欧几里得目前正在通过数十亿个遥远星系的弱引力透镜(WL)特征,详细绘制宇宙中的物质分布图。WL信号在星系团周围最为突出,可以延伸到它们的维里半径之外,从而约束它们的总质量。在星系团中心附近,由于成员星系的污染是一个问题,WL数据可以与强引力透镜(SL)数据相结合,以减少由于质量片退化引起的不确定性,并提供关于星系团中心物质分布的高分辨率信息。在这里,我们对z=0.228的Abell 2390星系团的欧几里得早期观测结果进行了SL和WL的联合分析。得益于欧几里得0.5平方度的宽视场,结合其在可见波段的0.13角秒分辨率和每像素0.1的采样率,我们约束了从靠近最亮星系团的内区到超过星系团维里半径的广泛半径范围内的密度分布,即30千秒差距小于r小于2000千秒差距。我们的结果与基于静水力学平衡的较早X射线结果一致,从而间接证实了该星系团的近乎松弛状态。我们的结果与基于对该星系团的弱引力透镜数据和地面观测的结果也相符。从SL+WL剖面结合分析得出病毒质量值$M_{200} = (1.48 \pm 0.29)\times10^{15}, M_{\odot}$和维里半径$r_{200} =(2.05\pm0.13 , {\rm Mpc})$,误差条代表一标准偏差。该剖面很好地由一个NFW模型描述,其浓度c=6.5和小尺度半径为230千秒差距,在最佳约束的SL和WL数据的范围内(即30千秒差距小于r小于2千秒差距)。Abell 2390将是许多欧几里得数据在其中发挥关键作用来确定星系团质量的例子中的第一个。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 8 figures
Summary
利用Euclid通过弱引力透镜效应详细绘制宇宙物质分布图,特别是在星系团周围。通过联合强、弱引力透镜数据分析,约束Abel 2390星系团的物质分布及总质量。此分析方法具有广泛的应用前景,Euclid将为许多类似的星系团提供质量信息。
Key Takeaways
- Euclid利用弱引力透镜效应绘制宇宙物质分布图。
- 星系团周围的弱引力透镜信号显著,可延伸至其维里半径之外。
- 在星系团中心区域,强引力透镜数据可补充弱引力透镜数据,减少质量片退化的不确定性,并提供高分辨率的物质分布信息。
- 对Abel 2390星系团进行联合强、弱引力透镜分析。
- Euclid的宽视场和高分辨率提供了从内区到维里半径范围内的密度分布约束。
- 分析结果与基于静水力学平衡的假设的早期X射结果一致,间接证实了该星团的近乎松弛状态。
点此查看论文截图
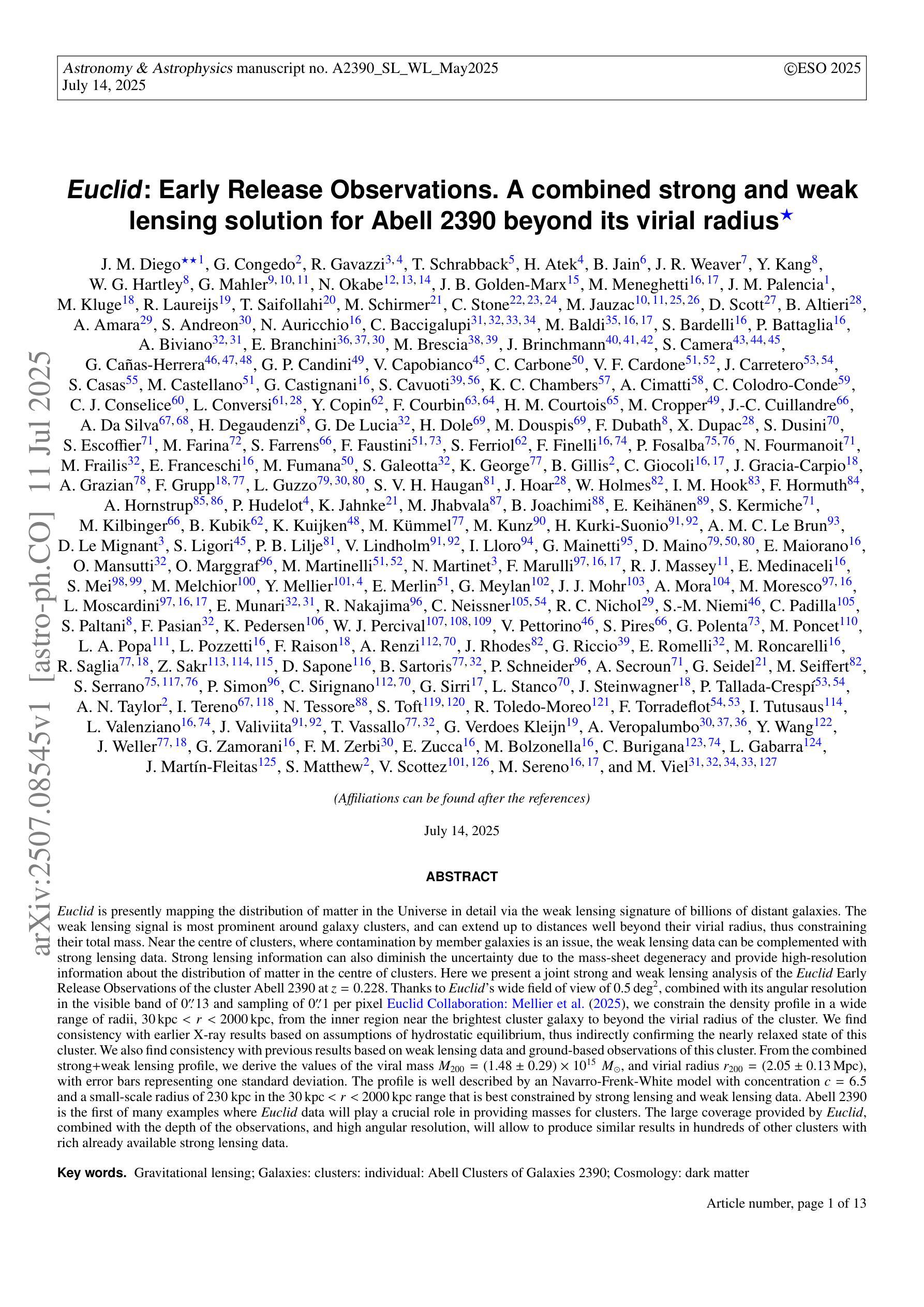
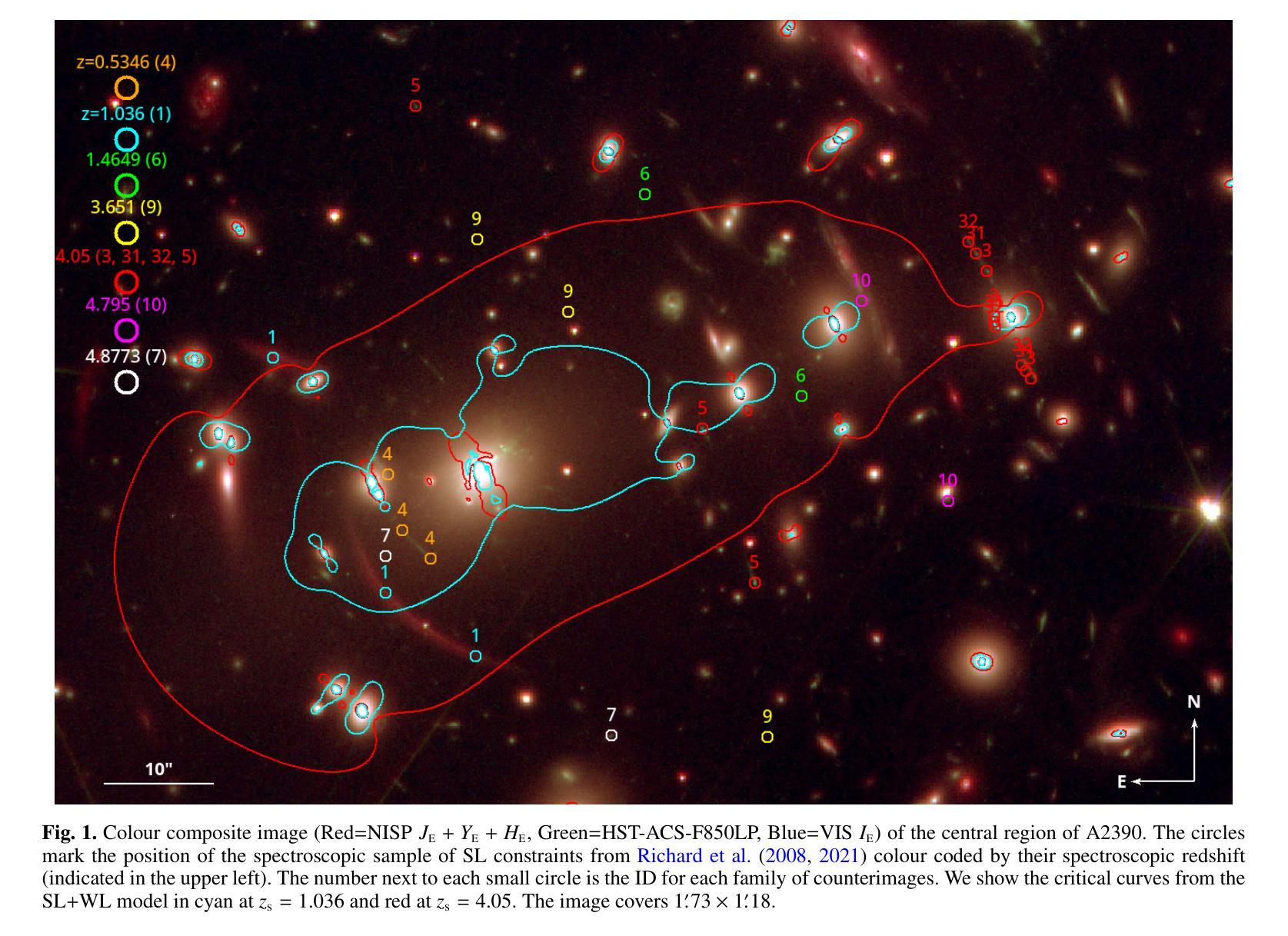
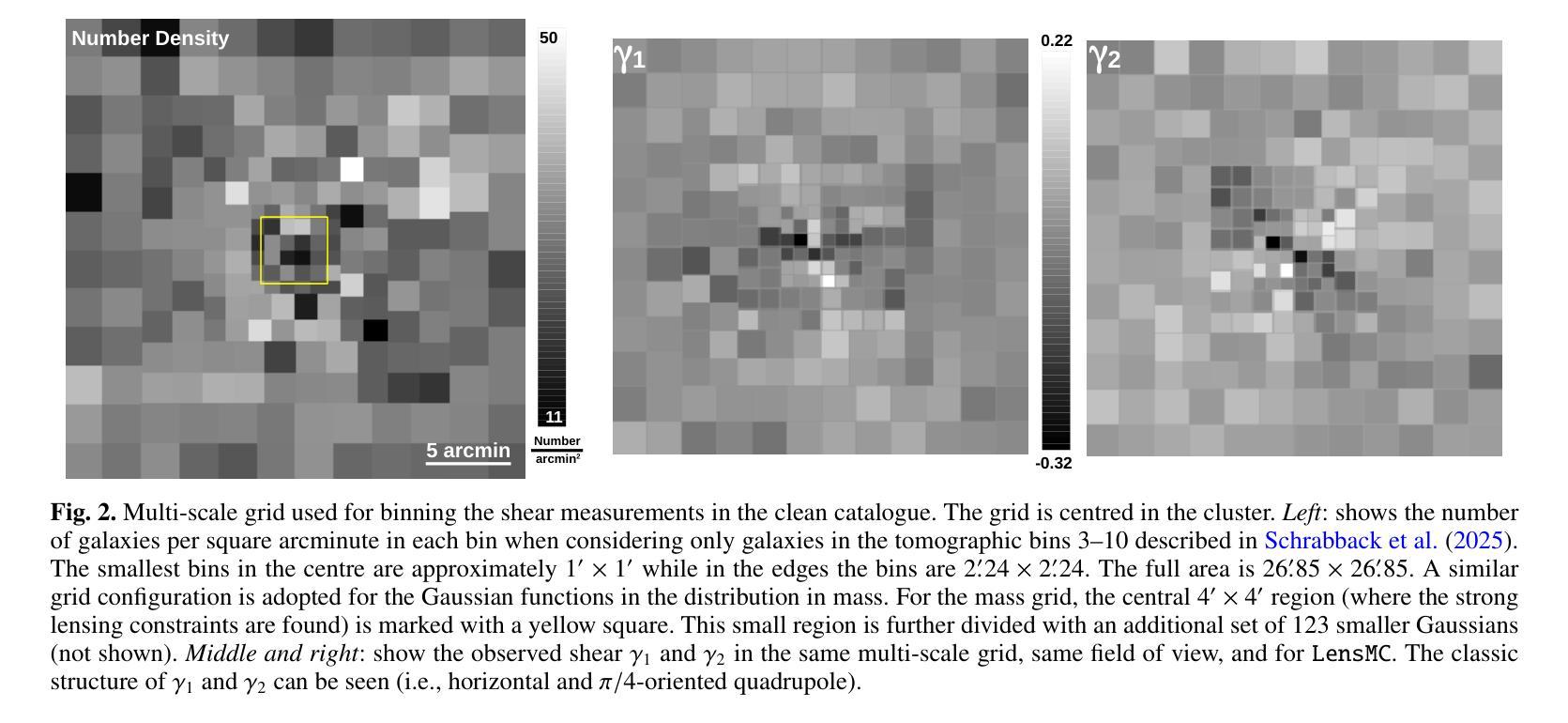
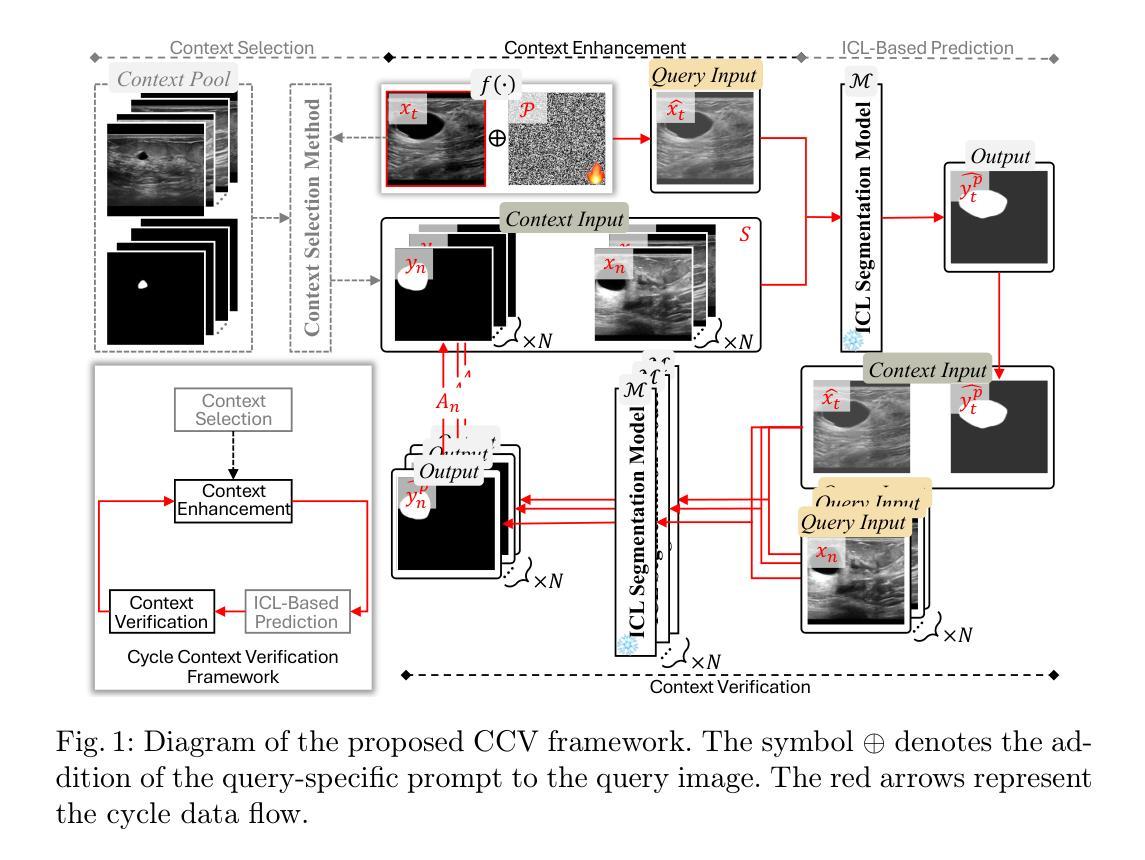
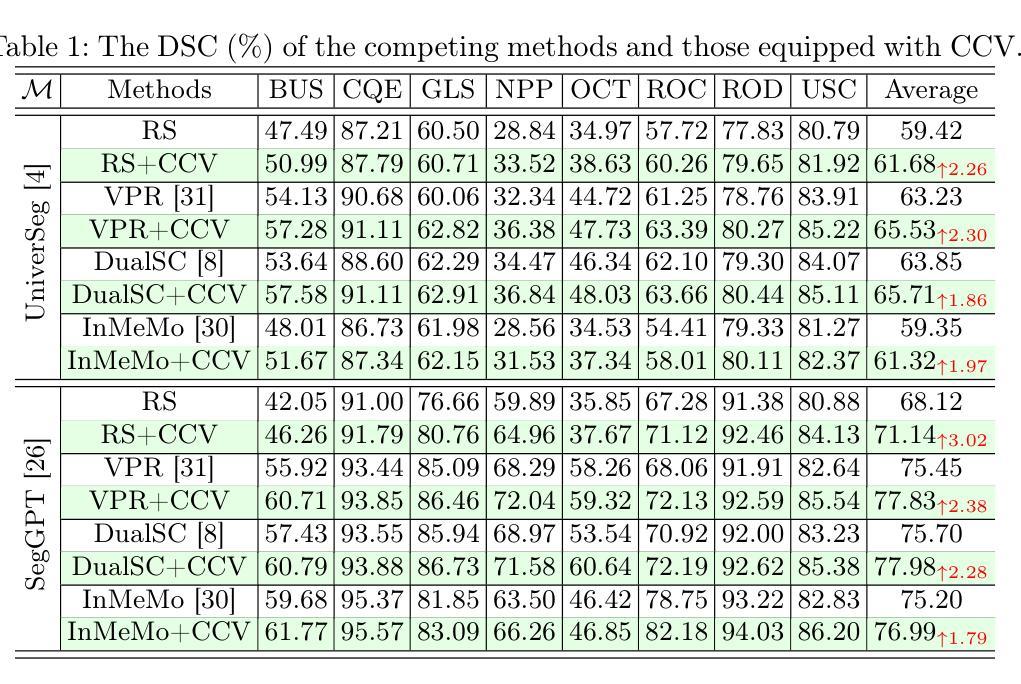
Cycle Context Verification for In-Context Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Shishuai Hu, Zehui Liao, Liangli Zhen, Huazhu Fu, Yong Xia
In-context learning (ICL) is emerging as a promising technique for achieving universal medical image segmentation, where a variety of objects of interest across imaging modalities can be segmented using a single model. Nevertheless, its performance is highly sensitive to the alignment between the query image and in-context image-mask pairs. In a clinical scenario, the scarcity of annotated medical images makes it challenging to select optimal in-context pairs, and fine-tuning foundation ICL models on contextual data is infeasible due to computational costs and the risk of catastrophic forgetting. To address this challenge, we propose Cycle Context Verification (CCV), a novel framework that enhances ICL-based medical image segmentation by enabling self-verification of predictions and accordingly enhancing contextual alignment. Specifically, CCV employs a cyclic pipeline in which the model initially generates a segmentation mask for the query image. Subsequently, the roles of the query and an in-context pair are swapped, allowing the model to validate its prediction by predicting the mask of the original in-context image. The accuracy of this secondary prediction serves as an implicit measure of the initial query segmentation. A query-specific prompt is introduced to alter the query image and updated to improve the measure, thereby enhancing the alignment between the query and in-context pairs. We evaluated CCV on seven medical image segmentation datasets using two ICL foundation models, demonstrating its superiority over existing methods. Our results highlight CCV’s ability to enhance ICL-based segmentation, making it a robust solution for universal medical image segmentation. The code will be available at https://github.com/ShishuaiHu/CCV.
上下文学习(ICL)作为一种有前景的技术,正逐渐崭露头角,为实现通用医学图像分割提供了可能。在这种技术中,可以使用单个模型对多种成像模式的感兴趣目标进行分割。然而,其在查询图像和上下文图像-掩膜对之间的对齐方面的性能高度敏感。在临床场景中,由于标注的医学图像稀缺,选择最佳的上下文对具有挑战性。此外,由于计算成本和对灾难性遗忘风险的考虑,对上下文数据进行微调基础ICL模型并不可行。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了循环上下文验证(CCV)这一新颖框架,它通过启用预测的自我验证和对齐来增强基于ICL的医学图像分割效果。具体而言,CCV采用一个循环流程,首先模型生成查询图像的分割掩膜。随后,查询图像和上下文对之间的角色互换,使得模型能够通过预测原始上下文图像的掩膜来验证其预测结果。这种二次预测的准确度作为初始查询分割的隐式度量标准。引入一个针对查询的提示来改变查询图像并更新提示以改善度量标准,从而提高查询和上下文对之间的对齐性。我们在七个医学图像分割数据集上评估了CCV,使用两个ICL基础模型,证明了其相较于现有方法的优越性。我们的结果突出了CCV在增强基于ICL的分割方面的能力,使其成为通用医学图像分割的稳健解决方案。代码将在https://github.com/ShishuaiHu/CCV上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025
Summary
在上下文学习(ICL)技术中,为了实现通用的医学图像分割,提出了一种新兴的有前途的技术。该技术能够在不同的成像模式下对多种感兴趣的对象进行分割。但其在查询图像与上下文图像掩模对之间的对齐敏感度较高。在临床医学场景中,由于标注的医学图像稀缺,选择合适的上下文对具有挑战性。为了解决此挑战,提出了Cycle Context Verification(CCV)框架,它通过自我验证预测结果并据此增强上下文对齐,从而提高了ICL基于医学图像分割的性能。CCV采用循环管道,首先为查询图像生成分割掩模,然后交换查询和上下文对角色,通过预测原始上下文图像的掩模来验证预测结果。二次预测准确性作为初始查询分割的隐性度量指标。引入查询特定提示来改善查询图像并更新度量标准,从而提高查询与上下文对之间的对齐程度。在七个医学图像分割数据集上评估了CCV,使用两个ICL基础模型,证明了其优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- In-context learning (ICL) 是一种新兴技术,用于实现通用的医学图像分割。
- ICL性能高度依赖于查询图像与上下文图像掩模对之间的对齐。
- 在临床环境中,选择最佳的上下文对具有挑战性,因为标注的医学图像稀缺。
- Cycle Context Verification (CCV) 框架通过自我验证预测结果提高ICL在医学图像分割中的性能。
- CCV采用循环管道,包括生成分割掩模、角色交换、预测验证和查询特定提示的引入。
- CCV在多个医学图像分割数据集上的表现优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

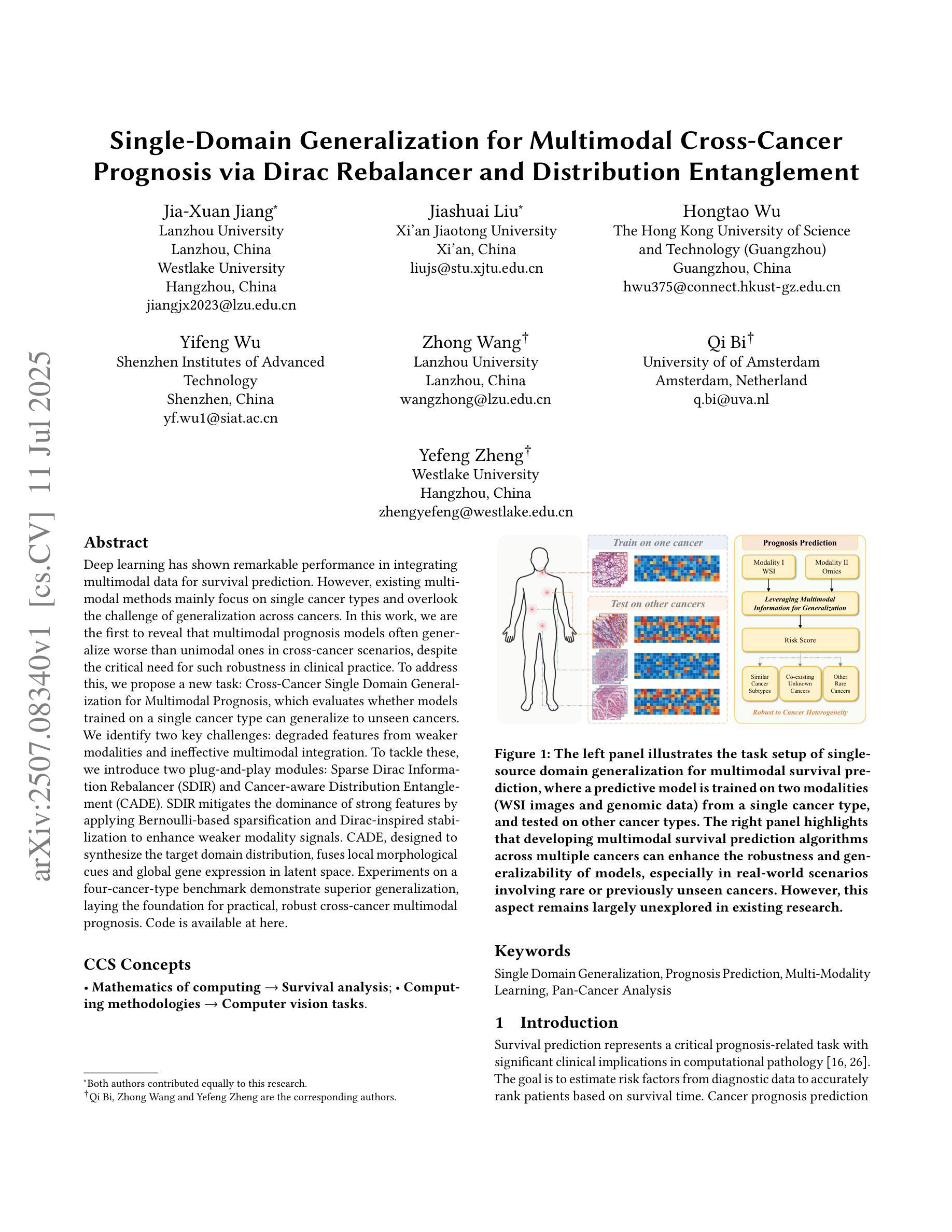
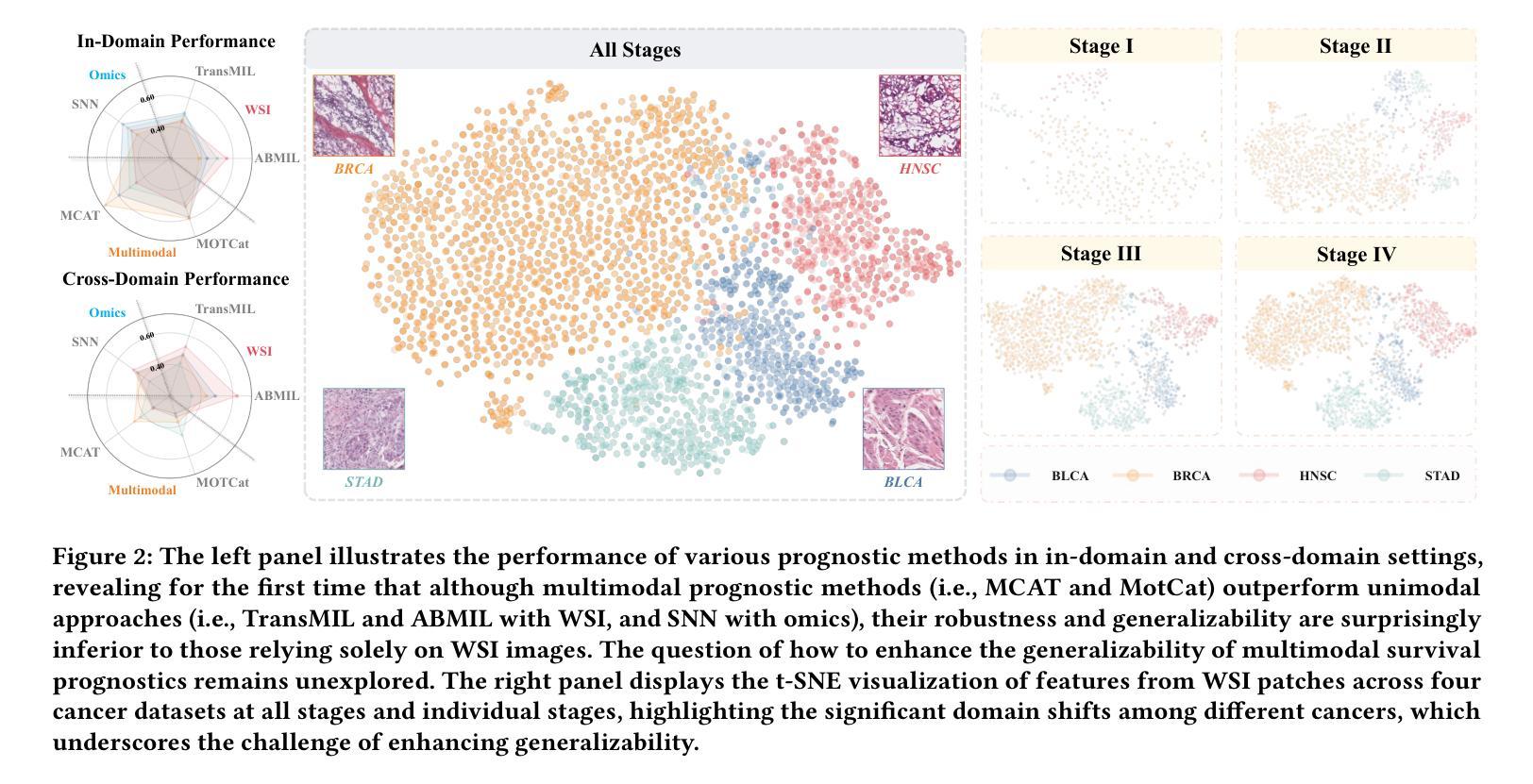
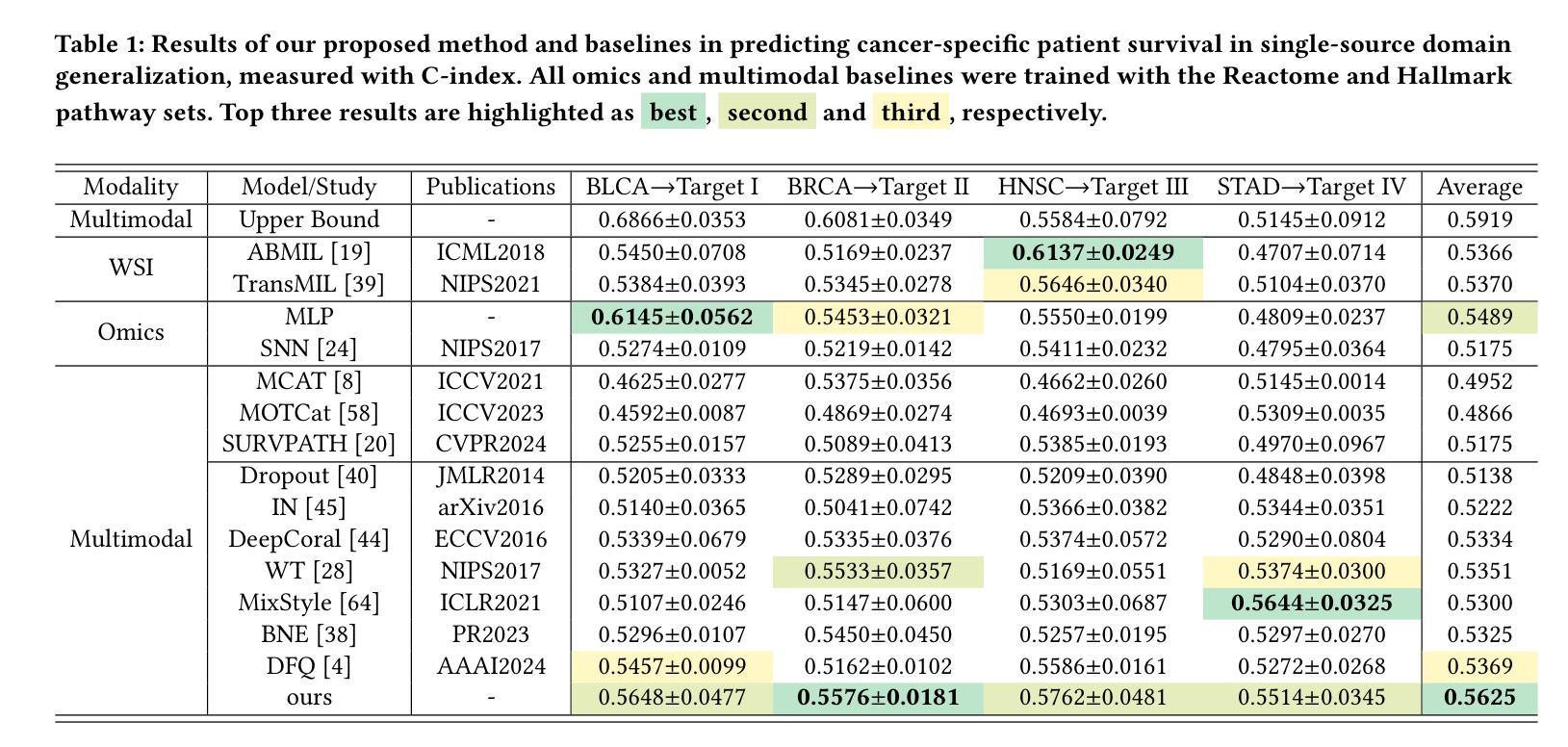
Single-Domain Generalization for Multimodal Cross-Cancer Prognosis via Dirac Rebalancer and Distribution Entanglement
Authors:Jia-Xuan Jiang, Jiashuai Liu, Hongtao Wu, Yifeng Wu, Zhong Wang, Qi Bi, Yefeng Zheng
Deep learning has shown remarkable performance in integrating multimodal data for survival prediction. However, existing multimodal methods mainly focus on single cancer types and overlook the challenge of generalization across cancers. In this work, we are the first to reveal that multimodal prognosis models often generalize worse than unimodal ones in cross-cancer scenarios, despite the critical need for such robustness in clinical practice. To address this, we propose a new task: Cross-Cancer Single Domain Generalization for Multimodal Prognosis, which evaluates whether models trained on a single cancer type can generalize to unseen cancers. We identify two key challenges: degraded features from weaker modalities and ineffective multimodal integration. To tackle these, we introduce two plug-and-play modules: Sparse Dirac Information Rebalancer (SDIR) and Cancer-aware Distribution Entanglement (CADE). SDIR mitigates the dominance of strong features by applying Bernoulli-based sparsification and Dirac-inspired stabilization to enhance weaker modality signals. CADE, designed to synthesize the target domain distribution, fuses local morphological cues and global gene expression in latent space. Experiments on a four-cancer-type benchmark demonstrate superior generalization, laying the foundation for practical, robust cross-cancer multimodal prognosis. Code is available at https://github.com/HopkinsKwong/MCCSDG
深度学习在融合多模态数据进行生存预测方面表现出卓越的性能。然而,现有的多模态方法主要集中在单一癌症类型上,忽视了跨癌症泛化的挑战。在这项工作中,我们首次揭示了在跨癌症场景中,多模态预后模型的泛化能力往往比单模态模型差,尽管在临床实践中对这种稳健性有着迫切的需求。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一个新的任务:跨癌症单域泛化多模态预后,旨在评估在单一癌症类型上训练的模型是否能够推广应用到未见过的癌症。我们确定了两个关键挑战:来自较弱模态的特征退化以及无效的多模态集成。为了解决这两个问题,我们引入了两种即插即用的模块:稀疏狄拉克信息平衡器(SDIR)和癌症感知分布纠缠(CADE)。SDIR通过应用基于伯努利分布的稀疏化和狄拉克启发式的稳定化,减轻强特征的主导作用,增强较弱模态信号。CADE旨在合成目标域分布,融合局部形态线索和全局基因表达于潜在空间。在四种癌症类型的基准测试上的实验证明了其优越的泛化能力,为实际、稳健的跨癌症多模态预后奠定了基础。代码可在https://github.com/HopkinsKwong/MCCSDG找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ACMMM 25
Summary
深度学习在多模态数据融合进行生存预测方面展现出显著性能,但在跨癌种预后预测方面,现有多模态方法的通用性有待提高。本文首次揭示多模态预后模型在跨癌种场景下的泛化性能往往不如单模态模型。为应对这一挑战,本文提出新的任务:跨癌种单域泛化多模态预后预测,旨在评估在单一癌种上训练的模型是否能泛化到未见过的癌症。针对弱特征的有效整合及模态间的有效融合两大关键挑战,本文引入两个即插即用模块:Sparse Dirac信息平衡器(SDIR)和癌症感知分布纠缠(CADE)。SDIR通过应用基于伯努利的方法实现特征稀疏化和Dirac启发式的稳定性来强化弱模态信号;而CADE则致力于合成目标域分布,融合了局部形态线索和全局基因表达潜变量。在四种癌症类型的基准测试上,本文方法展现出优越的泛化性能,为实际、稳健的跨癌多模态预后预测奠定基础。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在多模态数据融合生存预测中表现优异,但在跨癌种预后预测方面缺乏泛化性。
- 提出跨癌种单域泛化多模态预后预测任务,评估模型在多种未见癌症上的泛化能力。
- 面临两大挑战:弱特征的有效整合和模态间的有效融合。
- 引入Sparse Dirac信息平衡器(SDIR)强化弱模态信号。
- 采用Cancer-aware Distribution Entanglement(CADE)合成目标域分布融合局部形态和全局基因表达。
- 在四种癌症类型的实验基准测试中,所提出方法展现出优越泛化性能。
- 代码公开,为进一步研究提供基础。
点此查看论文截图

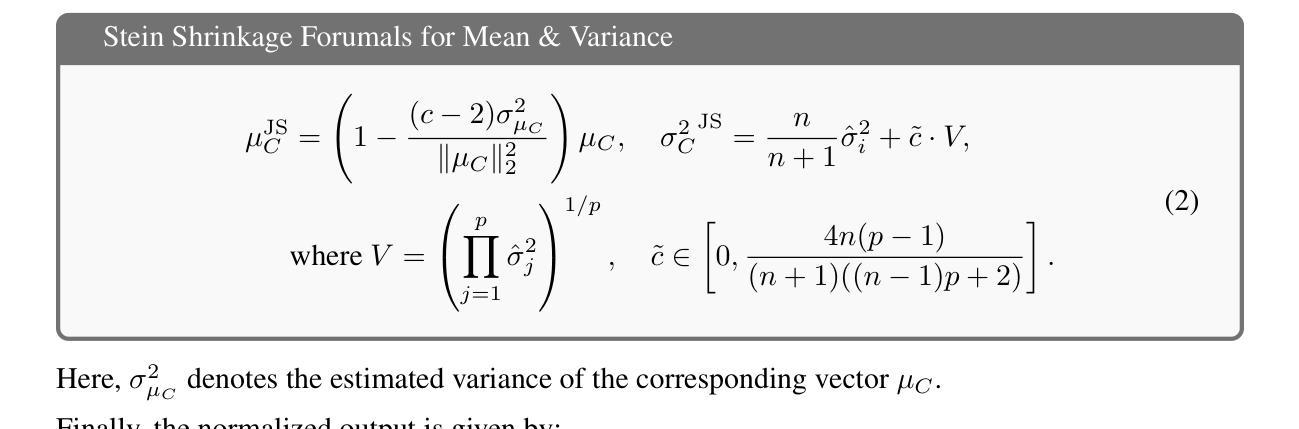
Admissibility of Stein Shrinkage for Batch Normalization in the Presence of Adversarial Attacks
Authors:Sofia Ivolgina, P. Thomas Fletcher, Baba C. Vemuri
Batch normalization (BN) is a ubiquitous operation in deep neural networks used primarily to achieve stability and regularization during network training. BN involves feature map centering and scaling using sample means and variances, respectively. Since these statistics are being estimated across the feature maps within a batch, this problem is ideally suited for the application of Stein’s shrinkage estimation, which leads to a better, in the mean-squared-error sense, estimate of the mean and variance of the batch. In this paper, we prove that the Stein shrinkage estimator for the mean and variance dominates over the sample mean and variance estimators in the presence of adversarial attacks when modeling these attacks using sub-Gaussian distributions. This facilitates and justifies the application of Stein shrinkage to estimate the mean and variance parameters in BN and use it in image classification (segmentation) tasks with and without adversarial attacks. We present SOTA performance results using this Stein corrected batch norm in a standard ResNet architecture applied to the task of image classification using CIFAR-10 data, 3D CNN on PPMI (neuroimaging) data and image segmentation using HRNet on Cityscape data with and without adversarial attacks.
批量归一化(BN)是深度神经网络中普遍存在的操作,主要用于在网络训练过程中实现稳定性和正则化。BN主要涉及使用样本均值和方差对特征图进行中心化和缩放。由于这些统计量是在一批特征图内估算的,因此这个问题非常适合应用Stein的收缩估计,从而在均方误差意义上获得更好的批量均值和方差的估计。在本文中,我们证明了在使用亚高斯分布对这些攻击进行建模时,存在对抗性攻击的情况下,均值和方差的Stein收缩估计器优于样本均值和方差估计器。这有助于并将为在BN中应用Stein收缩来估计均值和方差参数提供了依据,并将其应用于有和无对抗攻击的图像分类(分割)任务。我们使用这种经Stein校正的批量归一化,在CIFAR-10数据的图像分类任务、PPMI(神经成像)数据的3D CNN以及带有和不带有对抗攻击的Cityscape数据的HRNet图像分割任务中,呈现出最先进性能的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了批标准化(BN)在深度神经网络中的广泛应用,主要用于实现网络训练过程中的稳定性和正则化。文章提出使用Stein收缩估计改进样本均值和方差的估计,以应对特征映射中的批量处理统计问题。实验证明,在对抗攻击场景下,使用基于Stein收缩估计的均值和方差估计相较于传统样本均值和方差估计更为优越。此外,文章展示了在图像分类(分割)任务中应用该方法的优异性能表现。
Key Takeaways
- 批标准化(BN)在深度神经网络中普遍用于提升训练稳定性和正则化。
- 特征映射中的批量处理统计问题可以通过应用Stein收缩估计得到更好的处理。
- 对抗攻击场景下,使用Stein收缩估计的均值和方差估计效果优于样本均值和方差估计。
- Stein收缩估计在图像分类(分割)任务中得到了应用验证。
- 文章展示了使用Stein修正批标准化在CIFAR-10数据集上的图像分类任务性能表现。
- 在使用PPMI(神经成像)数据的3D CNN任务中,Stein修正批标准化同样展现出了优势。
点此查看论文截图


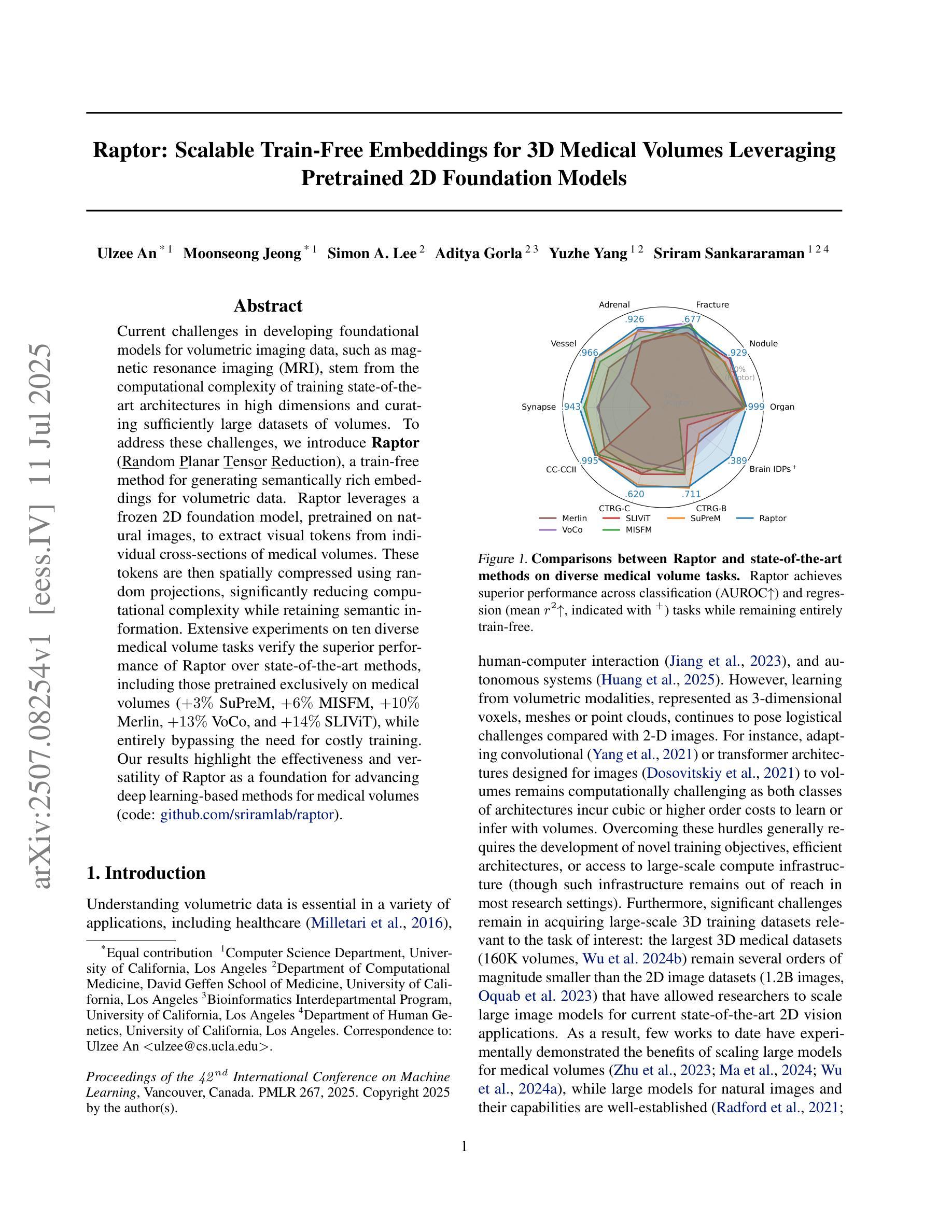
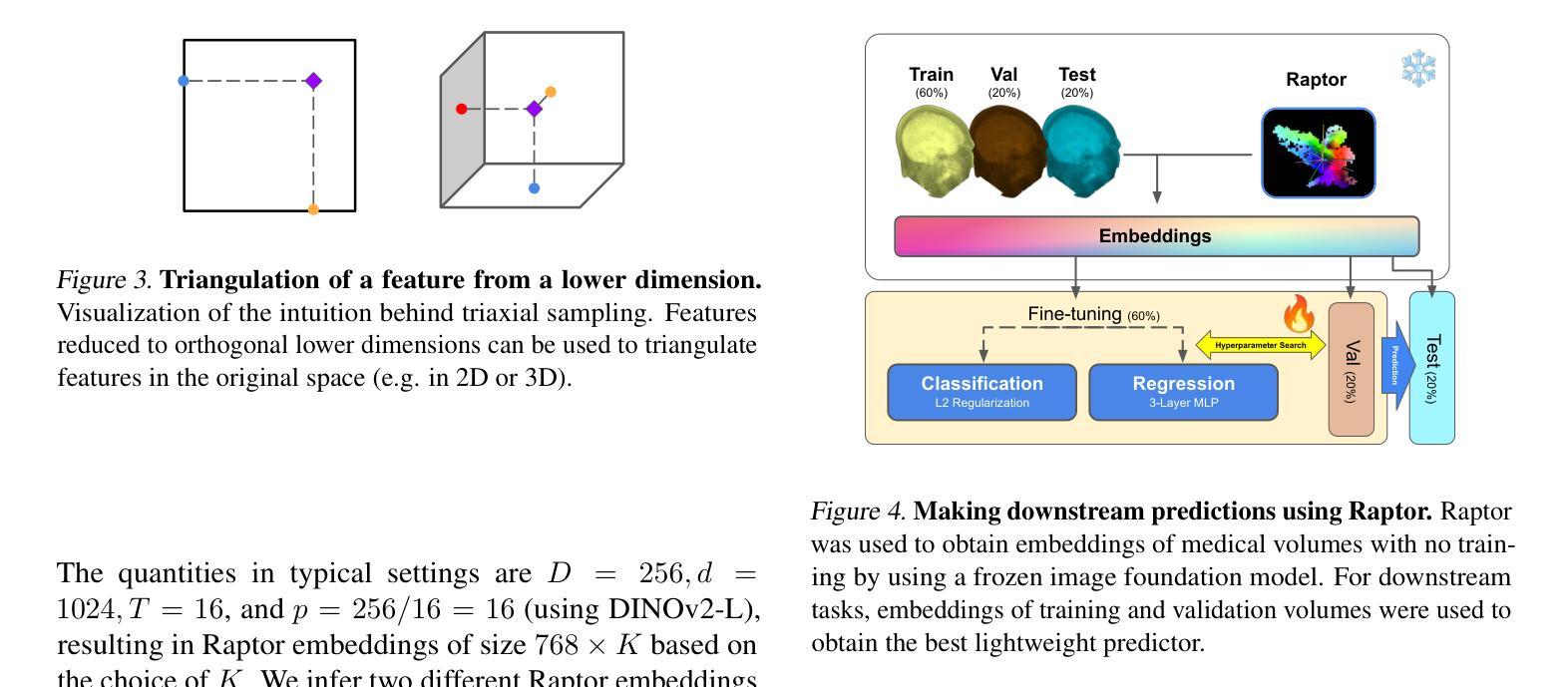
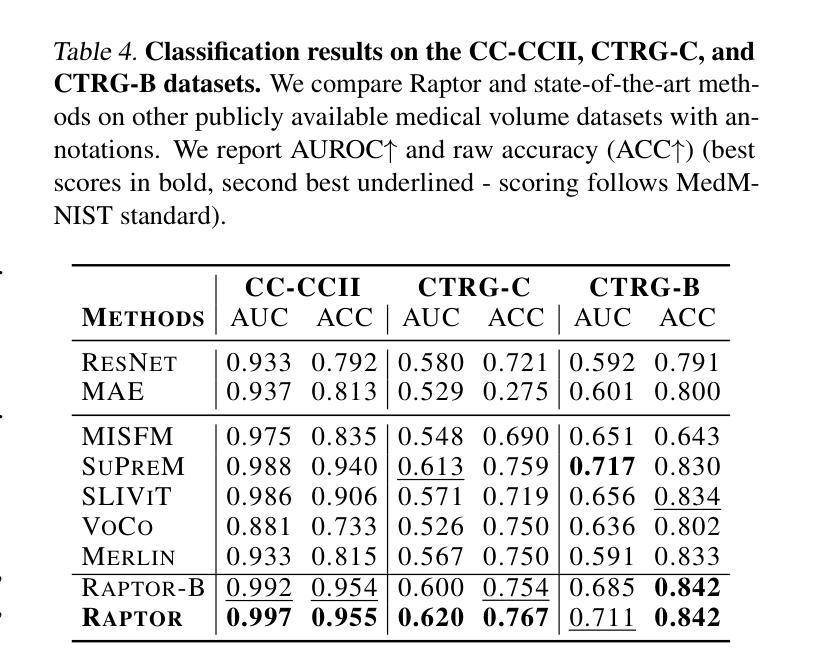
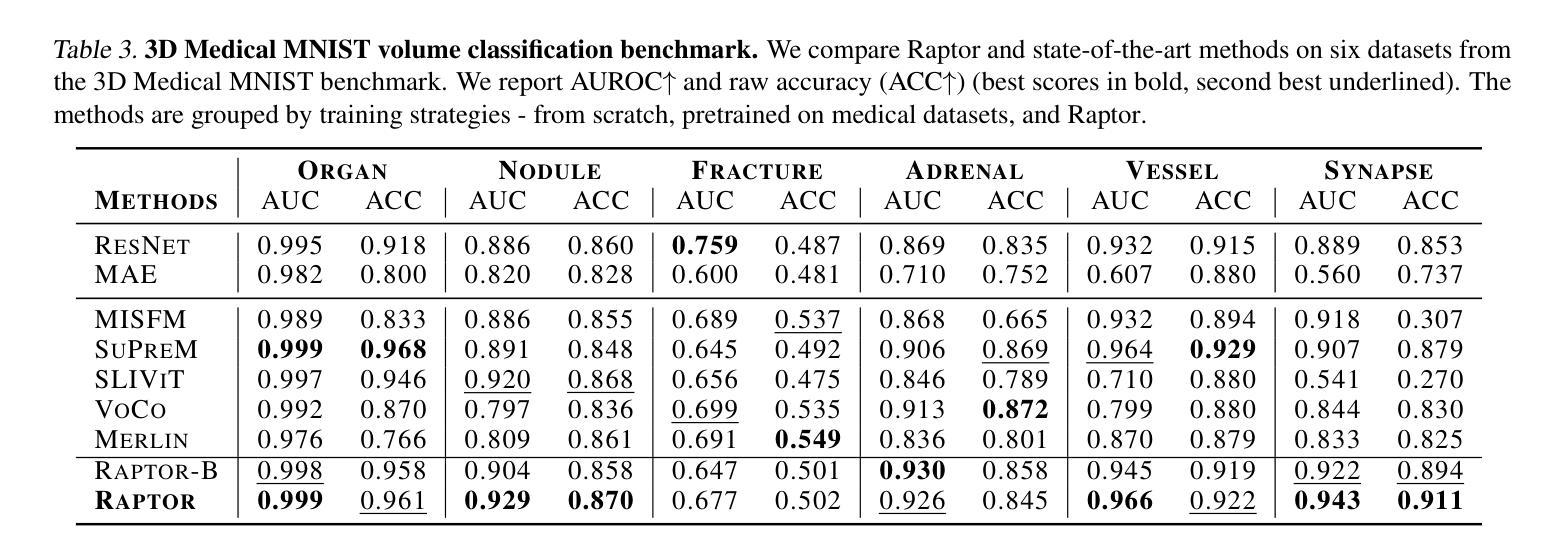
Raptor: Scalable Train-Free Embeddings for 3D Medical Volumes Leveraging Pretrained 2D Foundation Models
Authors:Ulzee An, Moonseong Jeong, Simon A. Lee, Aditya Gorla, Yuzhe Yang, Sriram Sankararaman
Current challenges in developing foundational models for volumetric imaging data, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), stem from the computational complexity of training state-of-the-art architectures in high dimensions and curating sufficiently large datasets of volumes. To address these challenges, we introduce Raptor (Random Planar Tensor Reduction), a train-free method for generating semantically rich embeddings for volumetric data. Raptor leverages a frozen 2D foundation model, pretrained on natural images, to extract visual tokens from individual cross-sections of medical volumes. These tokens are then spatially compressed using random projections, significantly reducing computational complexity while retaining semantic information. Extensive experiments on ten diverse medical volume tasks verify the superior performance of Raptor over state-of-the-art methods, including those pretrained exclusively on medical volumes (+3% SuPreM, +6% MISFM, +10% Merlin, +13% VoCo, and +14% SLIViT), while entirely bypassing the need for costly training. Our results highlight the effectiveness and versatility of Raptor as a foundation for advancing deep learning-based methods for medical volumes.
当前,在开发用于三维成像数据(如磁共振成像(MRI))的基础模型时面临的挑战,源于在高维度训练最新架构的计算复杂性和收集足够大规模的三维数据集。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了Raptor(随机平面张量缩减)方法,这是一种无需训练的生成语义丰富的三维数据嵌入的方法。Raptor利用冻结的二维基础模型(在天然图像上预训练),从医疗体积的单个横截面上提取视觉符号。然后这些符号通过随机投影进行空间压缩,这极大地减少了计算复杂度同时保留了语义信息。在十个不同的医疗体积任务上的大量实验验证了Raptor优于最先进的方法,包括那些仅在医疗体积上进行预训练的方法(+3% SuPreM,+6% MISFM,+10% Merlin,+13% VoCo和+14% SLIViT),同时完全避免了昂贵的训练需求。我们的结果突出了Raptor作为推进基于深度学习的医疗体积方法的基础的有效性和通用性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21 pages, 10 figures, accepted to ICML 2025. The first two authors contributed equally
Summary
本文介绍了针对体积成像数据(如磁共振成像)的建模挑战,提出一种名为“Raptor”(随机平面张量缩减)的方法,无需训练即可生成体积数据的丰富语义嵌入。Raptor利用冻结的二维基础模型,在自然图像上进行预训练,从医学体积的单个截面中提取视觉标记。这些标记使用随机投影进行空间压缩,显著降低了计算复杂度,同时保留了语义信息。实验证明,Raptor在多种医学体积任务上的性能优于最先进的方法,且完全避免了昂贵的训练成本。
Key Takeaways
- 体积成像数据建模面临计算复杂度和数据集大小挑战。
- Raptor是一种无需训练的生成语义丰富嵌入的方法,用于处理体积数据。
- Raptor利用预训练的二维基础模型从医学体积的截面中提取视觉标记。
- 通过随机投影进行空间压缩,降低计算复杂度,同时保留语义信息。
- 实验证明Raptor在多种医学体积任务上的性能优越。
- Raptor相较于其他预训练医学体积方法有更佳的表现。
点此查看论文截图


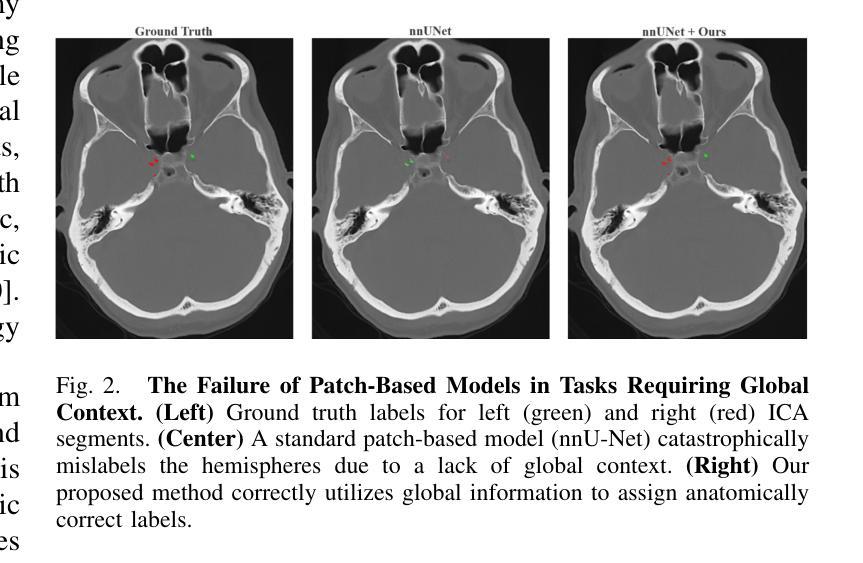
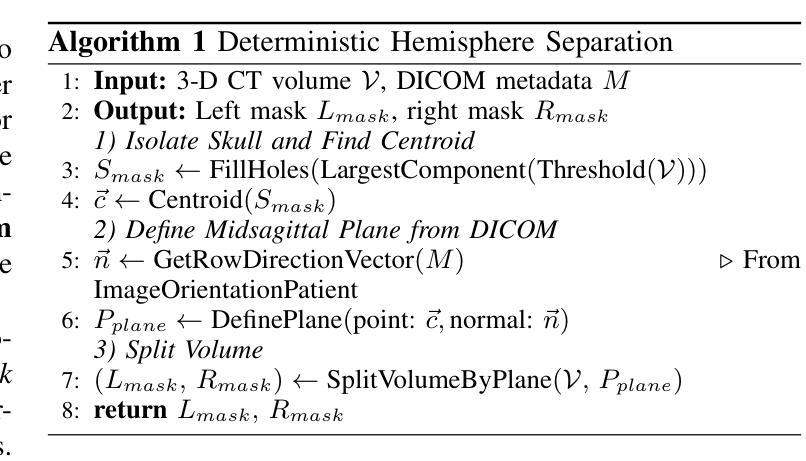
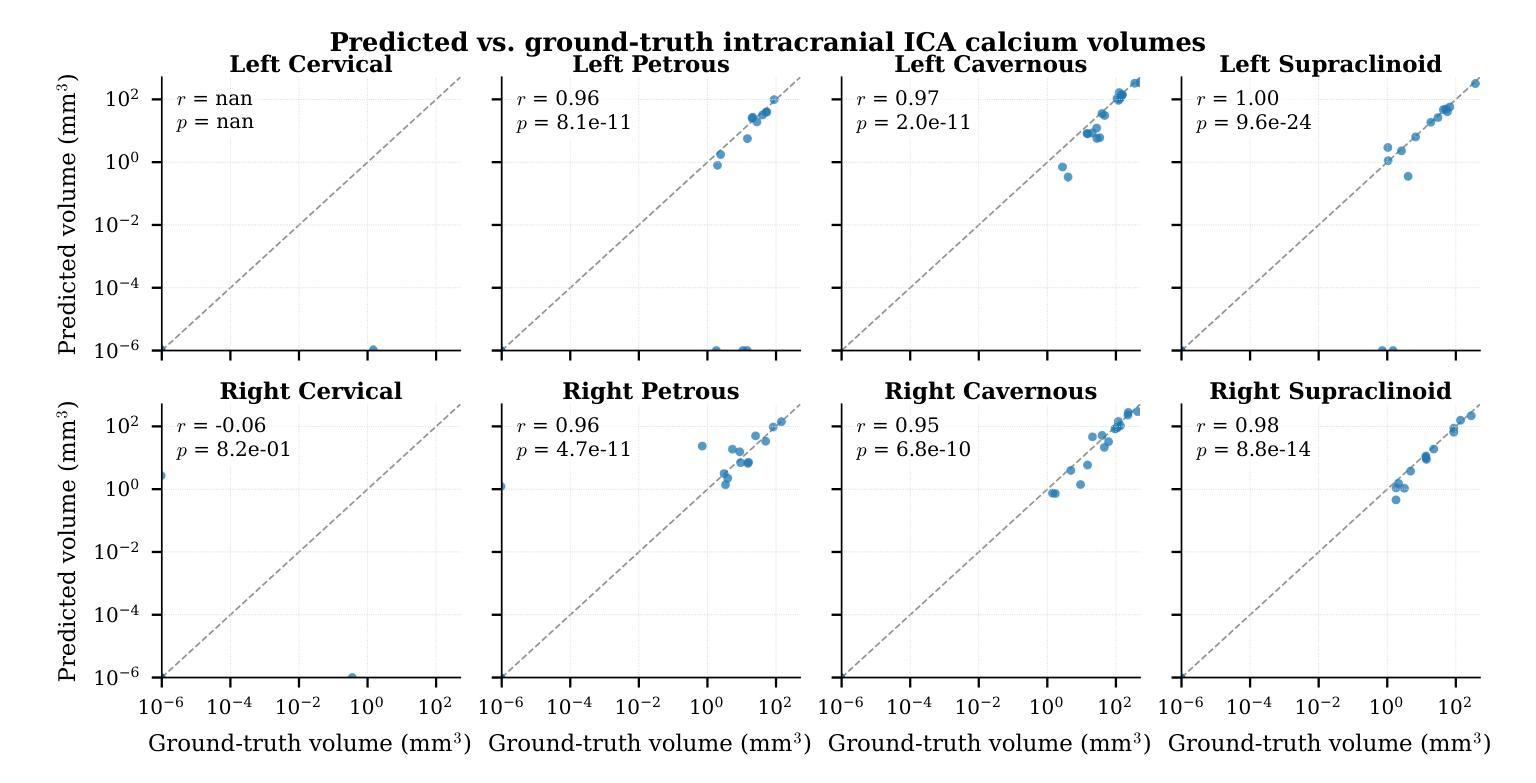
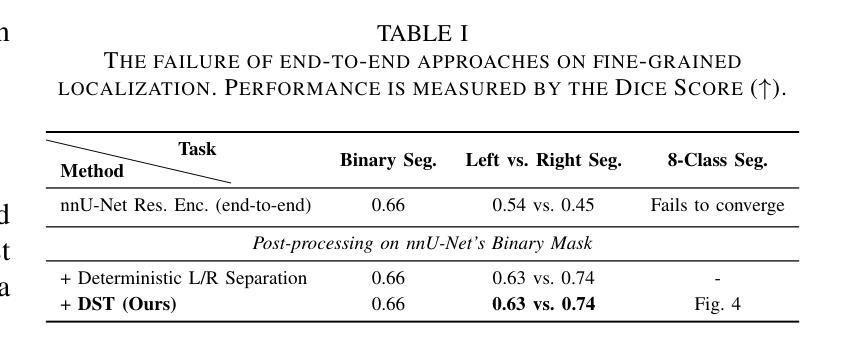
Depth-Sequence Transformer (DST) for Segment-Specific ICA Calcification Mapping on Non-Contrast CT
Authors:Xiangjian Hou, Ebru Yaman Akcicek, Xin Wang, Kazem Hashemizadeh, Scott Mcnally, Chun Yuan, Xiaodong Ma
While total intracranial carotid artery calcification (ICAC) volume is an established stroke biomarker, growing evidence shows this aggregate metric ignores the critical influence of plaque location, since calcification in different segments carries distinct prognostic and procedural risks. However, a finer-grained, segment-specific quantification has remained technically infeasible. Conventional 3D models are forced to process downsampled volumes or isolated patches, sacrificing the global context required to resolve anatomical ambiguity and render reliable landmark localization. To overcome this, we reformulate the 3D challenge as a \textbf{Parallel Probabilistic Landmark Localization} task along the 1D axial dimension. We propose the \textbf{Depth-Sequence Transformer (DST)}, a framework that processes full-resolution CT volumes as sequences of 2D slices, learning to predict $N=6$ independent probability distributions that pinpoint key anatomical landmarks. Our DST framework demonstrates exceptional accuracy and robustness. Evaluated on a 100-patient clinical cohort with rigorous 5-fold cross-validation, it achieves a Mean Absolute Error (MAE) of \textbf{0.1 slices}, with \textbf{96%} of predictions falling within a $\pm1$ slice tolerance. Furthermore, to validate its architectural power, the DST backbone establishes the best result on the public Clean-CC-CCII classification benchmark under an end-to-end evaluation protocol. Our work delivers the first practical tool for automated segment-specific ICAC analysis. The proposed framework provides a foundation for further studies on the role of location-specific biomarkers in diagnosis, prognosis, and procedural planning. Our code will be made publicly available.
虽然颅内颈动脉钙化(ICAC)总体积已被确立为中风生物标志物,但越来越多的证据表明,这一综合指标忽略了斑块位置的重要影响,因为不同部位的钙化具有不同的预后和手术风险。然而,更精细、特定于区段的量化在技术上仍然不可行。传统3D模型被迫处理降采样体积或孤立的补丁,牺牲了解决解剖歧义和可靠地标定位所需的全球背景。为了克服这一难题,我们将这一3D挑战重新制定为沿着1D轴向维度的“并行概率地标定位”任务。我们提出了“深度序列变压器(DST)”,这是一个以全分辨率CT体积作为二维切片序列进行处理的框架,学习预测N=6个独立概率分布,这些分布精确指出了关键解剖地标。我们的DST框架表现出卓越准确性和稳健性。在严格的五折交叉验证的100例临床队列中进行了评估,其平均绝对误差(MAE)达到了惊人的仅偏离了零点一薄层,预测在正负一个切片内的容忍度达到百分之九十六。此外,为了验证其架构优势,DST主干在公共Clean-CC-CCII分类基准测试下达到了最佳结果,该评估遵循端到端评估协议。我们的工作提供了首个用于自动化特定区段ICAC分析的实用工具。该框架为研究位置特异性生物标志物在诊断、预后和手术计划中的作用提供了基础。我们的代码将公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文解决了一个长期存在的问题:传统颅内颈动脉钙化(ICAC)体积评估忽略了斑块位置的重要性。为此,提出了一种名为深度序列转换器(DST)的新框架,该框架能处理全分辨率CT体积数据,准确预测关键解剖标志物的位置。经临床验证,该框架预测准确度高,稳定性强。其平均绝对误差(MAE)仅为0.1切片,预测结果中96%在±1切片范围内。这为进一步的ICAC分析提供了基础。
Key Takeaways
- 传统ICAC评估方法忽略了斑块位置的重要性,不同部位的钙化有不同的预后和手术风险。
- 目前缺乏精细的、基于位置的量化技术来解决这一问题。
- 提出了一种新的框架——深度序列转换器(DST),能处理全分辨率CT体积数据,预测关键解剖标志物的位置。
- DST框架预测准确度高,稳定性强,平均绝对误差仅为0.1切片。
- 96%的预测结果在±1切片范围内,验证了其高准确性。
- DST框架在公共清洁CC-CCII分类基准测试中表现最佳,展示了其强大的架构能力。
点此查看论文截图


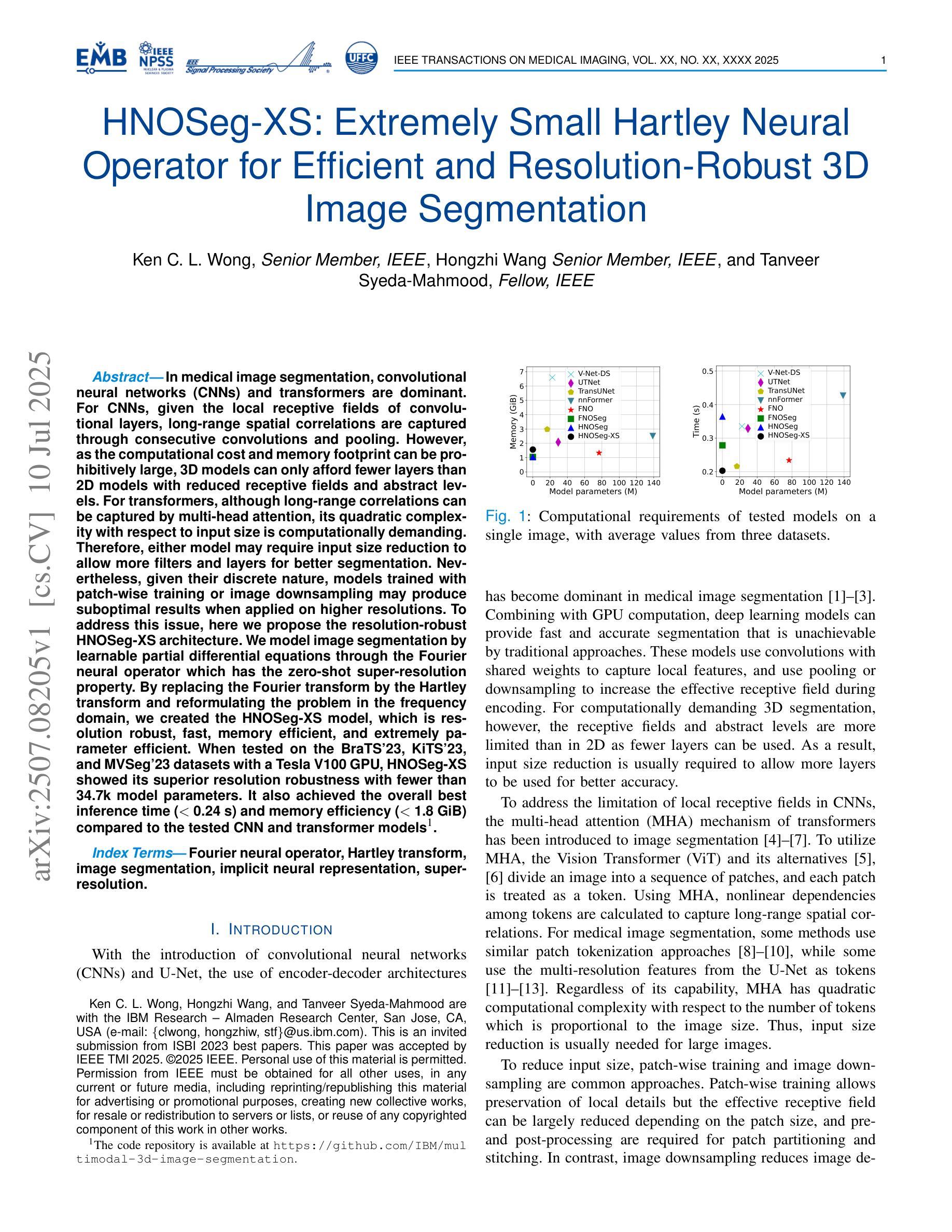
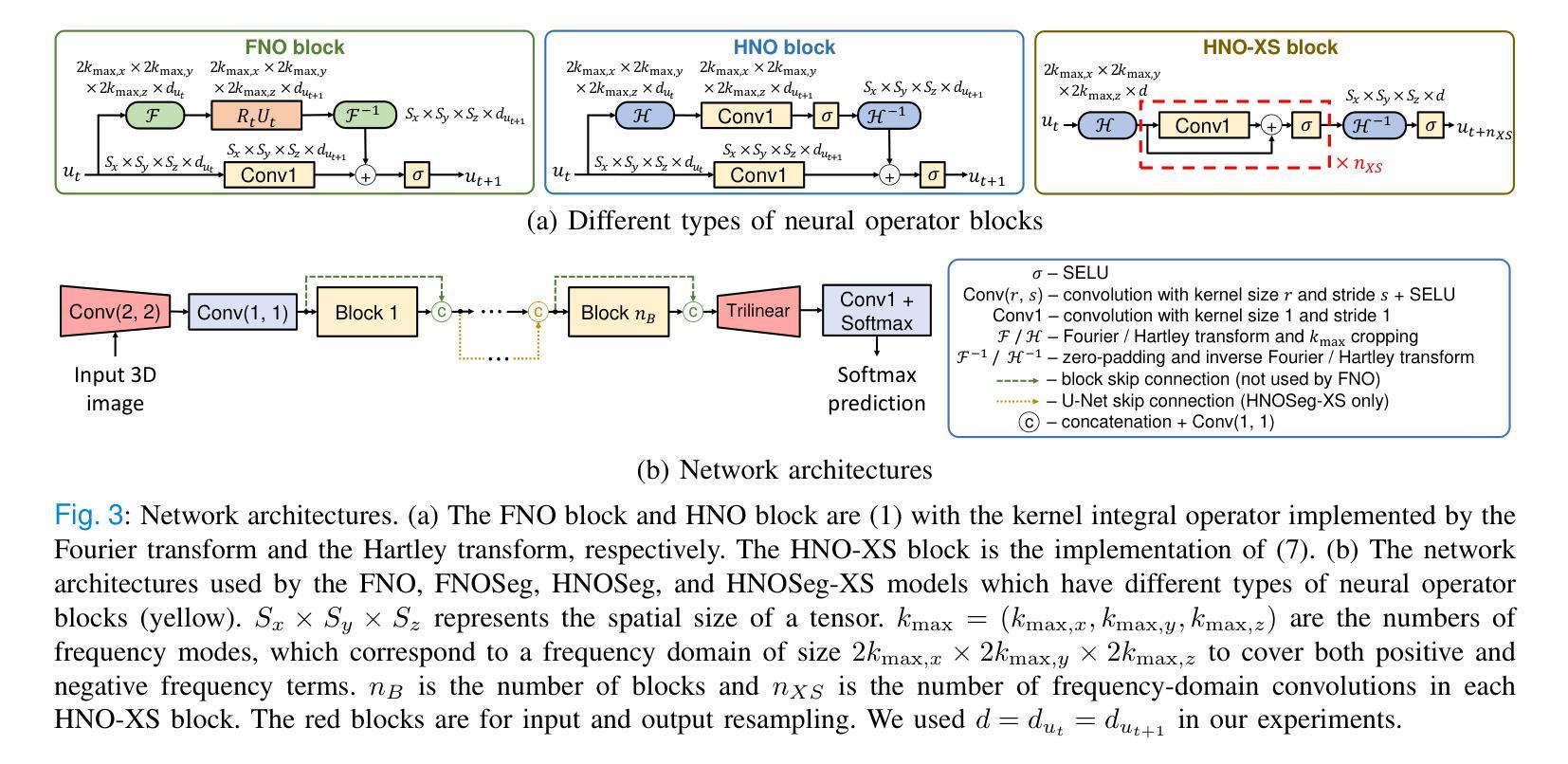
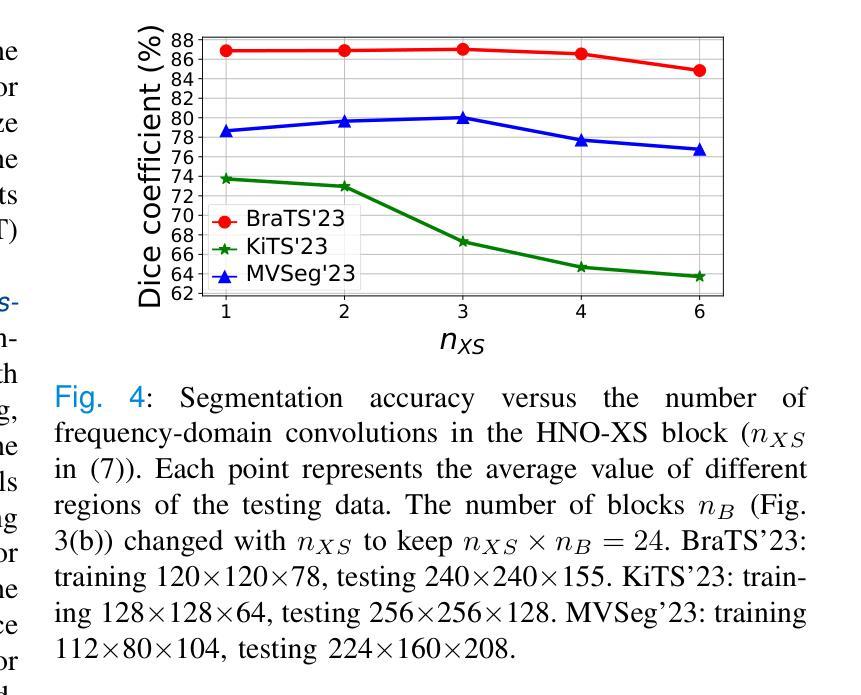
HNOSeg-XS: Extremely Small Hartley Neural Operator for Efficient and Resolution-Robust 3D Image Segmentation
Authors:Ken C. L. Wong, Hongzhi Wang, Tanveer Syeda-Mahmood
In medical image segmentation, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and transformers are dominant. For CNNs, given the local receptive fields of convolutional layers, long-range spatial correlations are captured through consecutive convolutions and pooling. However, as the computational cost and memory footprint can be prohibitively large, 3D models can only afford fewer layers than 2D models with reduced receptive fields and abstract levels. For transformers, although long-range correlations can be captured by multi-head attention, its quadratic complexity with respect to input size is computationally demanding. Therefore, either model may require input size reduction to allow more filters and layers for better segmentation. Nevertheless, given their discrete nature, models trained with patch-wise training or image downsampling may produce suboptimal results when applied on higher resolutions. To address this issue, here we propose the resolution-robust HNOSeg-XS architecture. We model image segmentation by learnable partial differential equations through the Fourier neural operator which has the zero-shot super-resolution property. By replacing the Fourier transform by the Hartley transform and reformulating the problem in the frequency domain, we created the HNOSeg-XS model, which is resolution robust, fast, memory efficient, and extremely parameter efficient. When tested on the BraTS’23, KiTS’23, and MVSeg’23 datasets with a Tesla V100 GPU, HNOSeg-XS showed its superior resolution robustness with fewer than 34.7k model parameters. It also achieved the overall best inference time (< 0.24 s) and memory efficiency (< 1.8 GiB) compared to the tested CNN and transformer models.
在医学图像分割领域,卷积神经网络(CNNs)和转换器占据主导地位。对于卷积神经网络,由于其卷积层的局部感受野,可以通过连续的卷积和池化捕获远程空间相关性。然而,由于计算成本和内存占用可能非常大,3D模型只能使用比2D模型更少的层和减少的感受野和抽象层次。对于转换器,虽然多头注意力可以捕捉远程相关性,但其关于输入大小的二次复杂性计算量大。因此,两种模型可能需要减小输入大小,以便为更好的分割添加更多的过滤器和层。然而,鉴于它们的离散性质,使用补丁级训练或图像下采样进行训练的模型在应用于更高分辨率时可能会产生不理想的结果。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了分辨率稳健的HNOSeg-XS架构。我们通过可学习的偏微分方程对图像分割进行建模,利用具有零点超分辨率属性的傅里叶神经算子。通过用哈特利变换代替傅里叶变换并在频域重新表述问题,我们创建了HNOSeg-XS模型,该模型具有分辨率稳健、快速、内存高效和极高的参数效率。在BraTS’23、KiTS’23和MVSeg’23数据集上使用Tesla V100 GPU进行测试时,HNOSeg-XS显示了其出色的分辨率稳健性,模型参数少于34.7k。与测试的CNN和转换器模型相比,它还实现了最佳的总推理时间(<0.24秒)和内存效率(<1.8 GiB)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper was accepted by IEEE TMI 2025
Summary
针对医学图像分割,卷积神经网络(CNN)和转换器各有优势。CNN能够捕捉长距离空间关联,但计算成本和内存占用较大。而转换器虽然能捕捉长距离关联,但其计算复杂度较高。为解决这些问题,提出了HNOSeg-XS架构,该架构利用可学习的偏微分方程对图像进行建模,并采用傅立叶神经算子进行处理。通过引入Hartley变换并将其应用于频率域,创建出具有分辨率鲁棒性、高效快速的HNOSeg-XS模型。在多个数据集上的测试表明,HNOSeg-XS模型参数少、效率高且性能优越。
Key Takeaways
- 卷积神经网络(CNN)和转换器在医学图像分割中有显著影响。
- CNN和转换器模型各有局限,包括计算成本高、内存占用大以及计算复杂度高等问题。
- 提出的HNOSeg-XS架构通过利用傅立叶神经算子和Hartley变换解决了上述问题。
- HNOSeg-XS模型具有分辨率鲁棒性、高效快速的特点。
点此查看论文截图

BASS XLVIII: [Ne v] λ3427 Emission in Powerful Nearby Active Galactic Nuclei
Authors:Tomer Reiss, Benny Trakhtenbrot, Claudio Ricci, Franz E. Bauer, Michael J. Koss, Kohei Ichikawa, Darshan Kakkad, Richard Mushotzky, Kyuseok Oh, Alessandro Peca, Rudolf Bär, Yaherlyn Diaz, Fiona Harrison, Meredith C. Powell, Eleonora Sani, Daniel Stern, C. Megan Urry
We investigate the high-ionization, narrow [Ne v] $\lambda$3427 emission line in a sample of over 340 ultrahard X-ray (14-195 keV) selected Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) drawn from the BASS project. The analysis includes measurements in individual and stacked spectra, and considers several key AGN properties such as X-ray luminosity, supermassive black hole (SMBH) mass, Eddington ratios, and line-of-sight column density. The [Ne v] $\lambda$3427 line is robustly detected in ~43% (146/341) of the AGN in our sample, with no significant trends between the detection rate and key AGN/SMBH properties. In particular, the detection rate remains high even at the highest levels of obscuration (>70% for log[N_H/cm^-2] > 23). On the other hand, even some of our highest signal-to-noise spectra (S/N > 50) lack a robust [Ne v] detection. The typical (median) scaling ratios between [Ne v] line emission and (ultra-)hard X-ray emission in our sample are log L[Ne v]/L(14-150 keV) = -3.75 and log L[Ne v]/L(2-10 keV) = -3.36. The scatter on these scaling ratios, of ~0.5 dex, is comparable to, and indeed smaller than, what is found for other commonly used tracers of AGN radiative outputs (e.g., [O III] $\lambda$5007). Otherwise, we find no significant relations between the (relative) strength of [Ne v] and the basic AGN/SMBH properties under study, in contrast with simple expectations from models of SMBH accretion flows. Our results reaffirm the usability of [Ne v] as an AGN tracer even in highly obscured systems, including dual AGN and high redshift sources.
我们对来自BASS项目的超过340个极端硬X射线(14-195 keV)选定的活动星系核(Active Galactic Nuclei,简称AGN)样本中的高电离、窄[Ne v] λ3427发射线进行了研究。分析包括个体和叠加光谱的测量,并考虑了关键AGN属性,例如X射线光度、超大质量黑洞(SMBH)质量、爱丁顿比率以及视线方向上的柱密度。在我们样本的AGN中,[Ne v] λ3427线在约43%(146/341)中稳健地检测到,检测率与关键AGN/SMBH属性之间没有明显的趋势。特别是,即使在遮蔽程度最高的地方(对于log[N_H/cm^-2]> 23的情况,遮蔽程度大于70%),检测率仍然很高。另一方面,即使在我们一些信噪比最高的光谱(信噪比> 50)中也没有检测到稳健的[Ne v]。样本中[Ne v]线发射与(超)硬X射线发射之间的典型(中位数)比例尺为log L[Ne v]/L(14-150 keV) = -3.75和log L[Ne v]/L(2-10 keV) = -3.36。这些比例尺的散射约为0.5 dex,与其他常用于追踪AGN辐射输出的指标(例如,[O III] λ5007)相当,甚至更小。其他方面,我们没有发现[Ne v](相对强度)与我们研究的基本AGN/SMBH属性之间的显著关系,这与简单SMBH吸积流模型的预期相反。我们的结果再次证实了[Ne v]即使在高度遮蔽的系统(包括双重AGN和高红移源)中也可用作AGN追踪指标。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ApJ, accepted. 24 pages, 9 figures
Summary
研究样本中的高电离窄发射线Ne v λ3427在超过340个极硬X射线选择的活跃星系核(AGN)中的表现。研究中包括对单个和叠加光谱的测量,并考虑了关键的活跃星系核特性如X射线光度、超大质量黑洞(SMBH)质量、爱丁顿比和视线方向柱密度等。Ne v λ3427线在约43%(146/341)的活跃星系核中被稳健检测到,检测率与关键活跃星系核/超大质量黑洞特性之间无显著趋势。即使在高度遮蔽的情况下,检测率仍然很高(对于log[N_H/cm^-2]> 23,遮蔽率超过70%)。另一方面,一些信噪比最高的光谱(信噪比> 50)也没有检测到Ne v。样本中Ne v线发射与(超)硬X射线发射之间的典型比例尺对数关系为log L[Ne v]/L(14-150 keV) = -3.75和log L[Ne v]/L(2-10 keV) = -3.36。这些比例关系的散射约为0.5 dex,与其他常用于追踪活跃星系核辐射输出的指标(例如,[O III] λ5007)相当甚至更小。此外,Ne v的相对强度与研究的活跃星系核/超大质量黑洞基本特性之间没有发现显著关系,这与简单预期的单星模型黑洞吸积流不符。研究结果再次证实了Ne v在高遮蔽系统(包括双活跃星系核和高红移源)中作为活跃星系核追踪器的可用性。
Key Takeaways
- 研究样本包含超过340个极硬X射线选择的活跃星系核(AGN)。
- [Ne v] λ3427线在约43%的样本中被稳健检测到。
- 检测率与关键活跃星系核/超大质量黑洞的特性之间没有显著趋势。
- 在高度遮蔽的情况下,检测率仍然很高。
- 一些高信噪比光谱未能检测到[Ne v]。
- Ne v与硬X射线发射之间的比例关系具有典型对数值。
点此查看论文截图


Cracking Instance Jigsaw Puzzles: An Alternative to Multiple Instance Learning for Whole Slide Image Analysis
Authors:Xiwen Chen, Peijie Qiu, Wenhui Zhu, Hao Wang, Huayu Li, Xuanzhao Dong, Xiaotong Sun, Xiaobing Yu, Yalin Wang, Abolfazl Razi, Aristeidis Sotiras
While multiple instance learning (MIL) has shown to be a promising approach for histopathological whole slide image (WSI) analysis, its reliance on permutation invariance significantly limits its capacity to effectively uncover semantic correlations between instances within WSIs. Based on our empirical and theoretical investigations, we argue that approaches that are not permutation-invariant but better capture spatial correlations between instances can offer more effective solutions. In light of these findings, we propose a novel alternative to existing MIL for WSI analysis by learning to restore the order of instances from their randomly shuffled arrangement. We term this task as cracking an instance jigsaw puzzle problem, where semantic correlations between instances are uncovered. To tackle the instance jigsaw puzzles, we propose a novel Siamese network solution, which is theoretically justified by optimal transport theory. We validate the proposed method on WSI classification and survival prediction tasks, where the proposed method outperforms the recent state-of-the-art MIL competitors. The code is available at https://github.com/xiwenc1/MIL-JigsawPuzzles.
尽管多实例学习(MIL)在病理全切片图像(WSI)分析中显示出有前途,但它对排列组合的依赖严重限制了其在WSIs内实例之间语义关联的有效发现能力。基于我们的经验和理论调查,我们主张采用非排列组合不变但能更好地捕捉实例间空间关联的方法,以提供更有效的解决方案。鉴于这些发现,我们提出了一种新型的多实例学习替代方案,用于WSI分析,通过学习恢复实例的排列顺序来解决实际问题。我们将此任务称为解决实例拼图问题,其中揭示了实例之间的语义关联。为了解决实例拼图问题,我们提出了一种新型的Siamese网络解决方案,该方案在理论上得到了最优传输理论的验证。我们在WSI分类和生存预测任务上验证了所提出的方法,其中所提出的方法优于最新的最先进的MIL竞争对手。代码可在https://github.com/xiwenc1/MIL-JigsawPuzzles找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV2025
Summary
针对病理全切片图像(WSI)分析的多实例学习(MIL)方法存在语义关联难以识别的问题,本文提出了一种基于Siamese网络的新方法来解决实例拼图问题,以恢复实例的顺序并揭示语义关联。该方法在WSI分类和生存预测任务上表现优于最新MIL方法。
Key Takeaways
- 多实例学习(MIL)在病理全切片图像(WSI)分析中虽具潜力,但其对排列的依赖限制了语义关联的识别。
- 提出了解决实例拼图问题的新方法,旨在恢复实例的顺序并揭示其语义关联。
- 方法基于Siamese网络结构,具有理论上通过最优传输理论支持的优势。
- 该方法在WSI分类和生存预测任务上进行了验证,并表现出优异性能。
- 方法代码已公开,便于他人使用与进一步研究。
- 该研究为WSI分析提供了新的视角和解决方案,有助于推动医学图像分析领域的发展。
点此查看论文截图


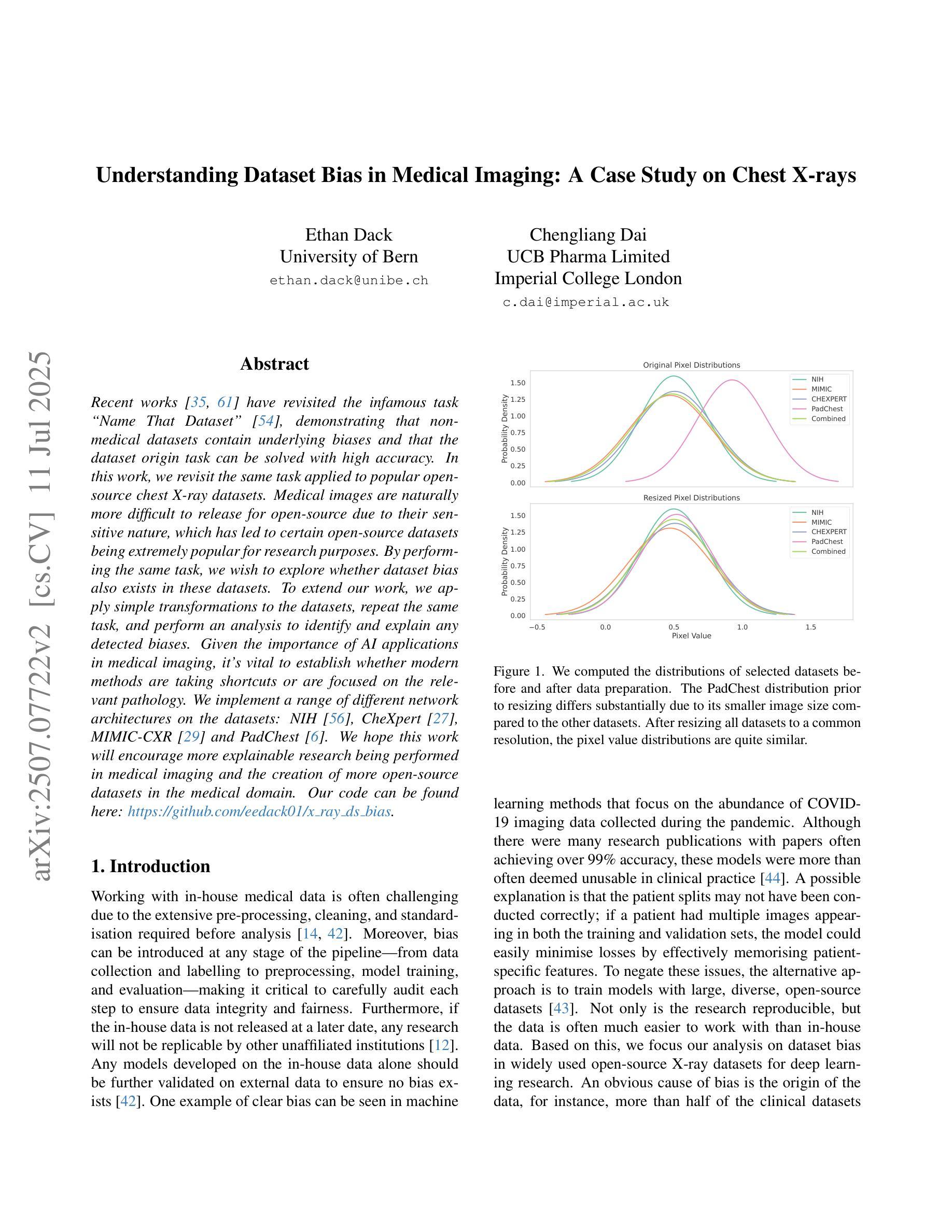
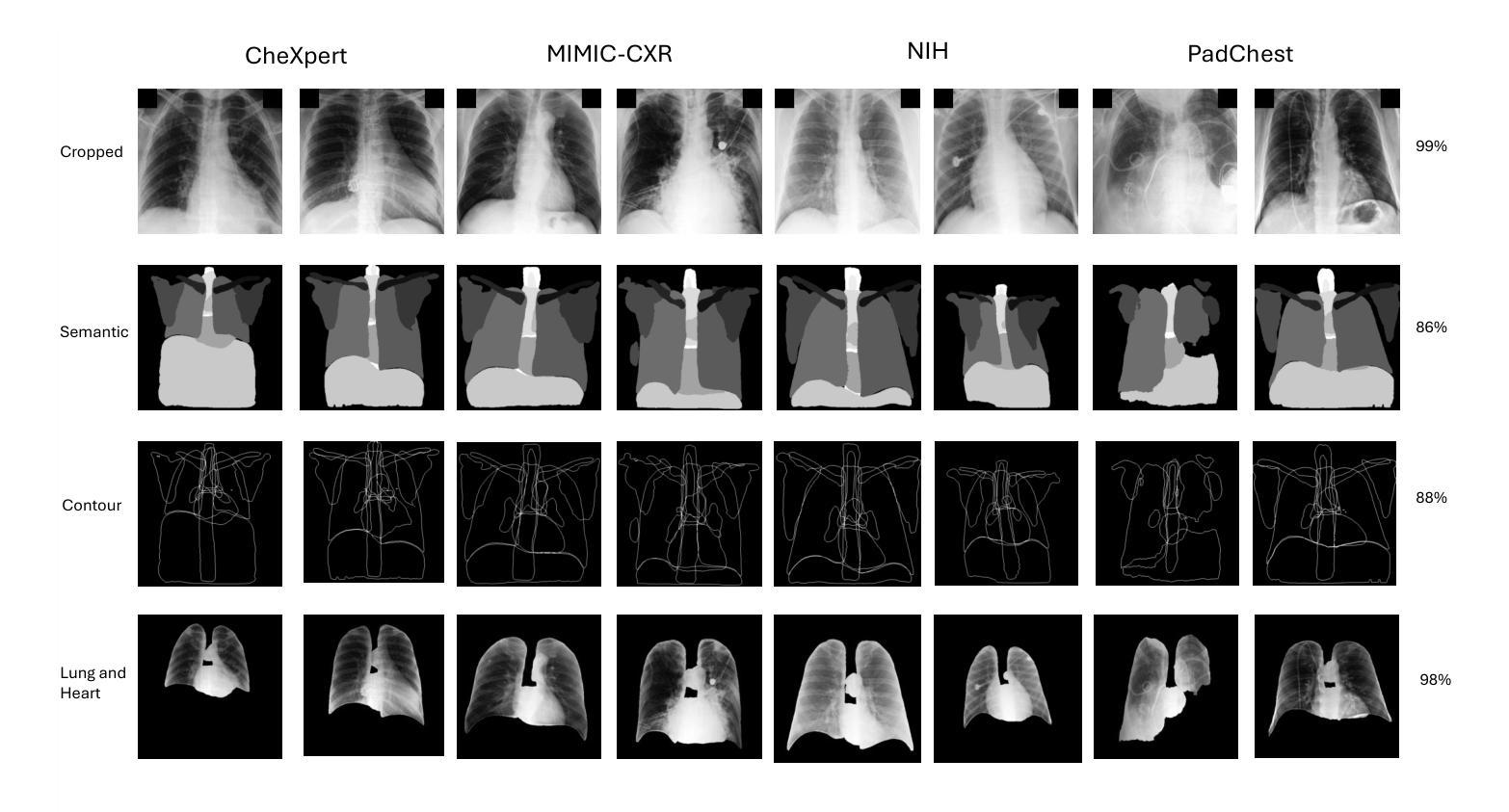
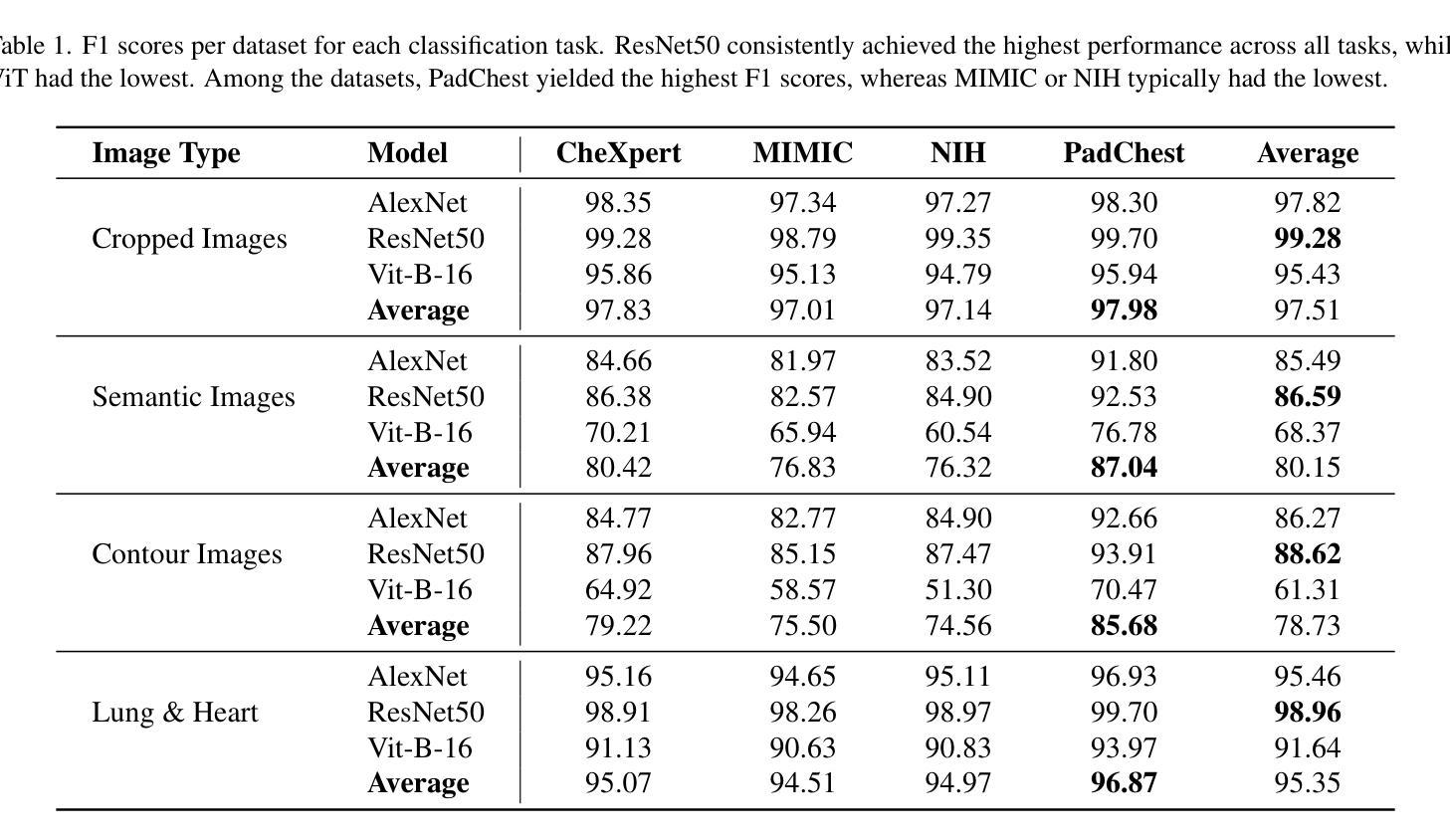
Understanding Dataset Bias in Medical Imaging: A Case Study on Chest X-rays
Authors:Ethan Dack, Chengliang Dai
Recent works have revisited the infamous task ``Name That Dataset’’, demonstrating that non-medical datasets contain underlying biases and that the dataset origin task can be solved with high accuracy. In this work, we revisit the same task applied to popular open-source chest X-ray datasets. Medical images are naturally more difficult to release for open-source due to their sensitive nature, which has led to certain open-source datasets being extremely popular for research purposes. By performing the same task, we wish to explore whether dataset bias also exists in these datasets. To extend our work, we apply simple transformations to the datasets, repeat the same task, and perform an analysis to identify and explain any detected biases. Given the importance of AI applications in medical imaging, it’s vital to establish whether modern methods are taking shortcuts or are focused on the relevant pathology. We implement a range of different network architectures on the datasets: NIH, CheXpert, MIMIC-CXR and PadChest. We hope this work will encourage more explainable research being performed in medical imaging and the creation of more open-source datasets in the medical domain. Our code can be found here: https://github.com/eedack01/x_ray_ds_bias.
最近的研究重新关注了“命名数据集”任务,表明非医学数据集存在潜在偏见,并且可以以高准确性解决数据集起源任务。在这项工作中,我们重新关注应用于流行的开源胸部X射线数据集的任务。由于医学图像的敏感性,它们自然更难以开源发布,这也导致某些开源数据集在研究领域非常受欢迎。通过执行相同的任务,我们希望探索这些数据集是否也存在数据集偏见。为了扩展我们的工作,我们对数据集进行了简单的转换,重复相同的任务,并进行分析以识别和解释任何检测到的偏见。鉴于人工智能在医学影像领域的应用重要性,确定现代方法是走捷径还是专注于相关病理学至关重要。我们在NIH、CheXpert、MIMIC-CXR和PadChest数据集上实现了多种不同的网络架构。我们希望这项工作将鼓励在医学影像领域进行更多可解释的研究,并在医学领域创建更多的开源数据集。我们的代码可以在这里找到:https://github.com/eedack01/x_ray_ds_bias。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了“Name That Dataset”任务在医学图像领域的应用,特别是在开源胸部X射线数据集上的应用。作者探索了这些数据集是否存在数据偏见,通过应用简单的转换,重复任务并进行分析来识别和解释任何检测到的偏见。本文的研究对于医学成像中人工智能应用的发展具有重要意义,鼓励更多可解释的研究在该领域的开展和更多医学开源数据集的创建。
Key Takeaways
- 研究重新审视了“Name That Dataset”任务在医学图像领域的应用,特别是针对开源胸部X射线数据集。
- 作者发现非医疗数据集存在潜在的偏见,本工作旨在探索医疗图像数据集是否也存在偏见。
- 由于医疗图像的敏感性,某些开源数据集成为研究目的下的极度热门资源。
- 作者通过使用多种网络架构(如NIH、CheXpert、MIMIC-CXR和PadChest)来实施任务并分析数据偏见。
- 研究强调了AI在医学成像中的重要性,并指出需要确定现代方法是否走捷径或专注于相关病理学。
- 作者通过简单的数据集转换来扩展工作,并重复任务以识别和解释任何检测到的偏见。
点此查看论文截图


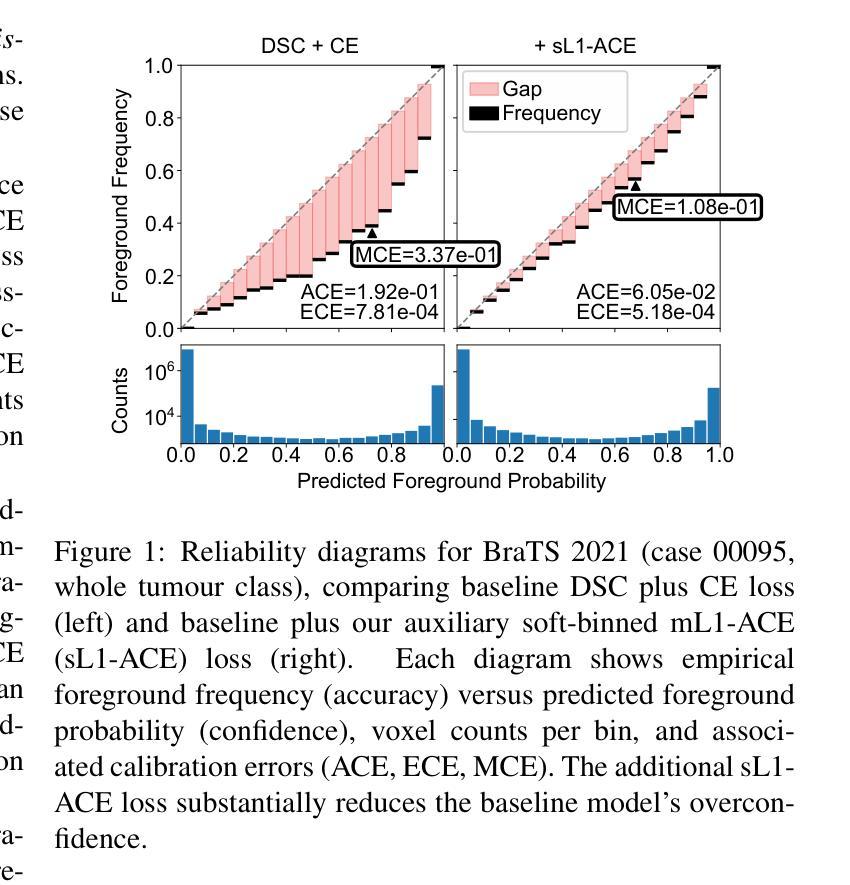
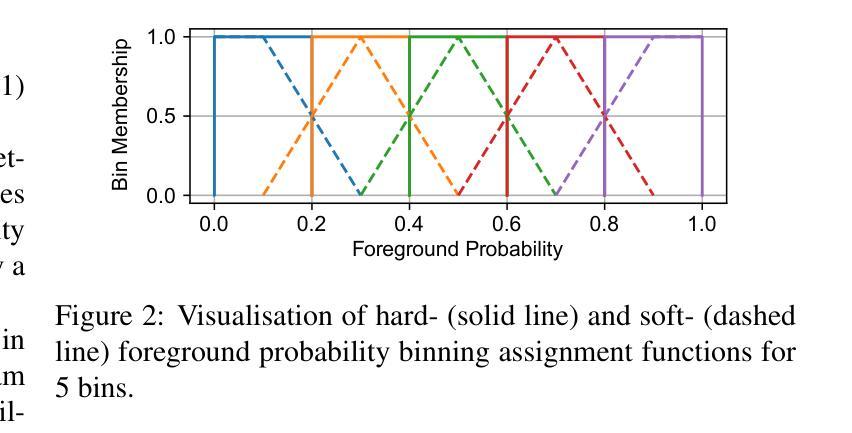
Average Calibration Losses for Reliable Uncertainty in Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Theodore Barfoot, Luis C. Garcia-Peraza-Herrera, Samet Akcay, Ben Glocker, Tom Vercauteren
Deep neural networks for medical image segmentation are often overconfident, compromising both reliability and clinical utility. In this work, we propose differentiable formulations of marginal L1 Average Calibration Error (mL1-ACE) as an auxiliary loss that can be computed on a per-image basis. We compare both hard- and soft-binning approaches to directly improve pixel-wise calibration. Our experiments on four datasets (ACDC, AMOS, KiTS, BraTS) demonstrate that incorporating mL1-ACE significantly reduces calibration errors, particularly Average Calibration Error (ACE) and Maximum Calibration Error (MCE), while largely maintaining high Dice Similarity Coefficients (DSCs). We find that the soft-binned variant yields the greatest improvements in calibration, over the Dice plus cross-entropy loss baseline, but often compromises segmentation performance, with hard-binned mL1-ACE maintaining segmentation performance, albeit with weaker calibration improvement. To gain further insight into calibration performance and its variability across an imaging dataset, we introduce dataset reliability histograms, an aggregation of per-image reliability diagrams. The resulting analysis highlights improved alignment between predicted confidences and true accuracies. Overall, our approach not only enhances the trustworthiness of segmentation predictions but also shows potential for safer integration of deep learning methods into clinical workflows. We share our code here: https://github.com/cai4cai/Average-Calibration-Losses
针对医学图像分割的深度神经网络往往过于自信,这既影响可靠性又影响临床实用性。在这项工作中,我们提出了边际L1平均校准误差(mL1-ACE)的可微公式,作为一种可以按图像计算的辅助损失。我们比较了硬分箱和软分箱的方法,以直接改善像素级校准。我们在四个数据集(ACDC、AMOS、KiTS、BraTS)上的实验表明,引入mL1-ACE可以显著降低校准误差,特别是平均校准误差(ACE)和最大校准误差(MCE),同时保持较高的Dice相似系数(DSC)。我们发现,与Dice加上交叉熵损失的基线相比,软分箱变体在校准方面取得了最大的改进,但往往牺牲了分割性能,硬分箱mL1-ACE虽然在校准改善方面表现较弱,但能够保持分割性能。为了深入了解校准性能及其在成像数据集上的变化,我们引入了数据集可靠性直方图,这是按图像可靠性图进行聚合的结果。由此产生的分析强调了预测置信度与真实准确度之间对齐的改进。总的来说,我们的方法不仅提高了分割预测的可靠性,还显示出将深度学习方法更安全地集成到临床工作流程中的潜力。我们在此分享我们的代码:https://github.com/cai4cai/Average-Calibration-Losses
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 5 figures, IEEE TMI submission. This version originally appeared in error as arXiv:2403.06759(v2)
Summary
本文探讨深度神经网络在医学图像分割中的过度自信问题,并提出可微分的边际L1平均校准误差(mL1-ACE)作为辅助损失函数,以改善像素级的校准。实验结果表明,引入mL1-ACE能显著降低校准误差,同时保持较高的Dice相似系数。软分箱mL1-ACE在校准方面改进最大,但可能影响分割性能;硬分箱mL1-ACE则能维持分割性能,尽管校准改进较弱。此外,引入数据集可靠性直方图以进一步分析校准性能及其在数据集间的变化,提高了预测置信度与真实准确度的对齐性,增强了分割预测的可信度。
Key Takeaways
- 深度神经网络在医学图像分割中常表现出过度自信,影响可靠性和临床实用性。
- 引入可微分的边际L1平均校准误差(mL1-ACE)作为辅助损失函数,旨在改善像素级校准。
- 实验证明,mL1-ACE能显著降低校准误差,同时保持较高的Dice相似系数。
- 软分箱和硬分箱方法用于直接改进像素级校准,其中软分箱在校准方面改进最大。
- 引入数据集可靠性直方图来分析校准性能及其在数据集间的变化。
- 此方法提高了预测置信度与真实准确度的对齐性,增强了分割预测的可信度。
点此查看论文截图

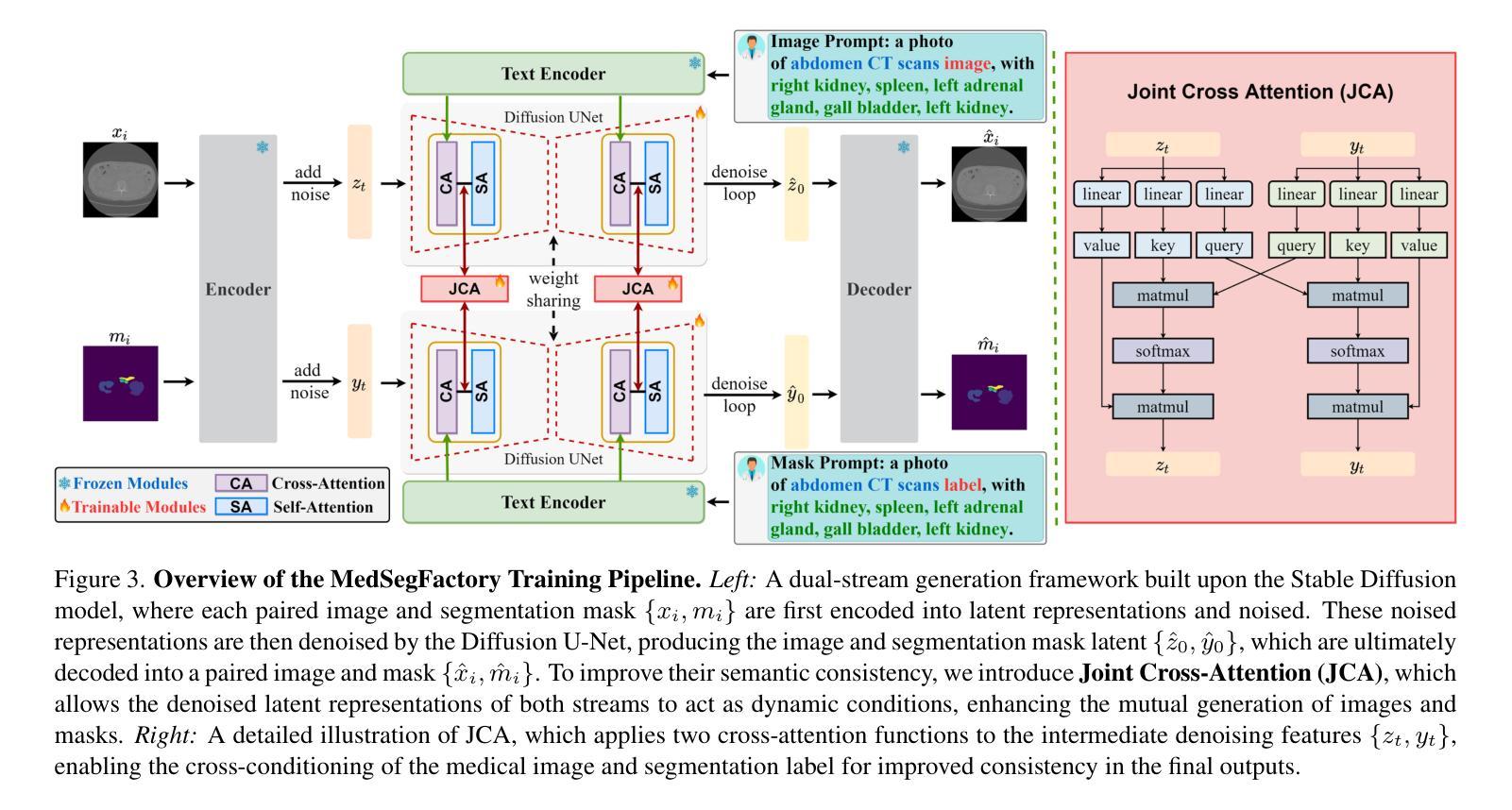
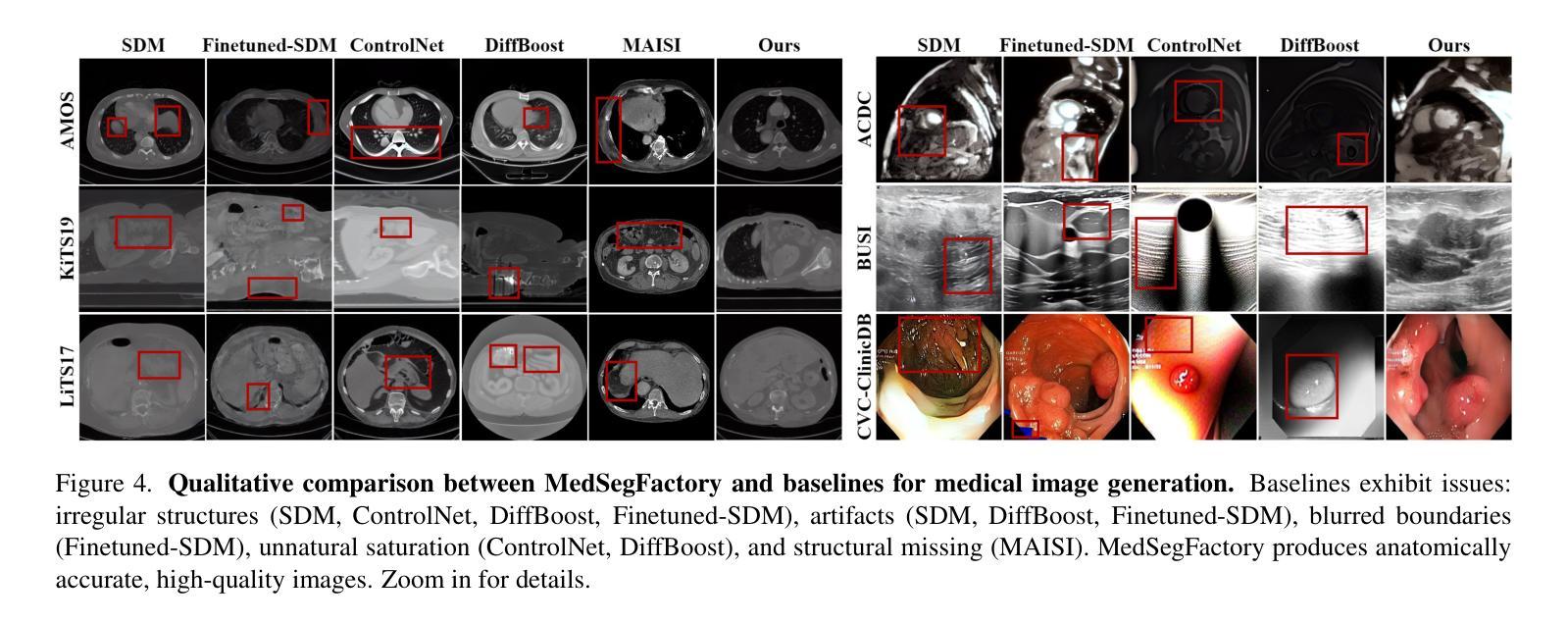
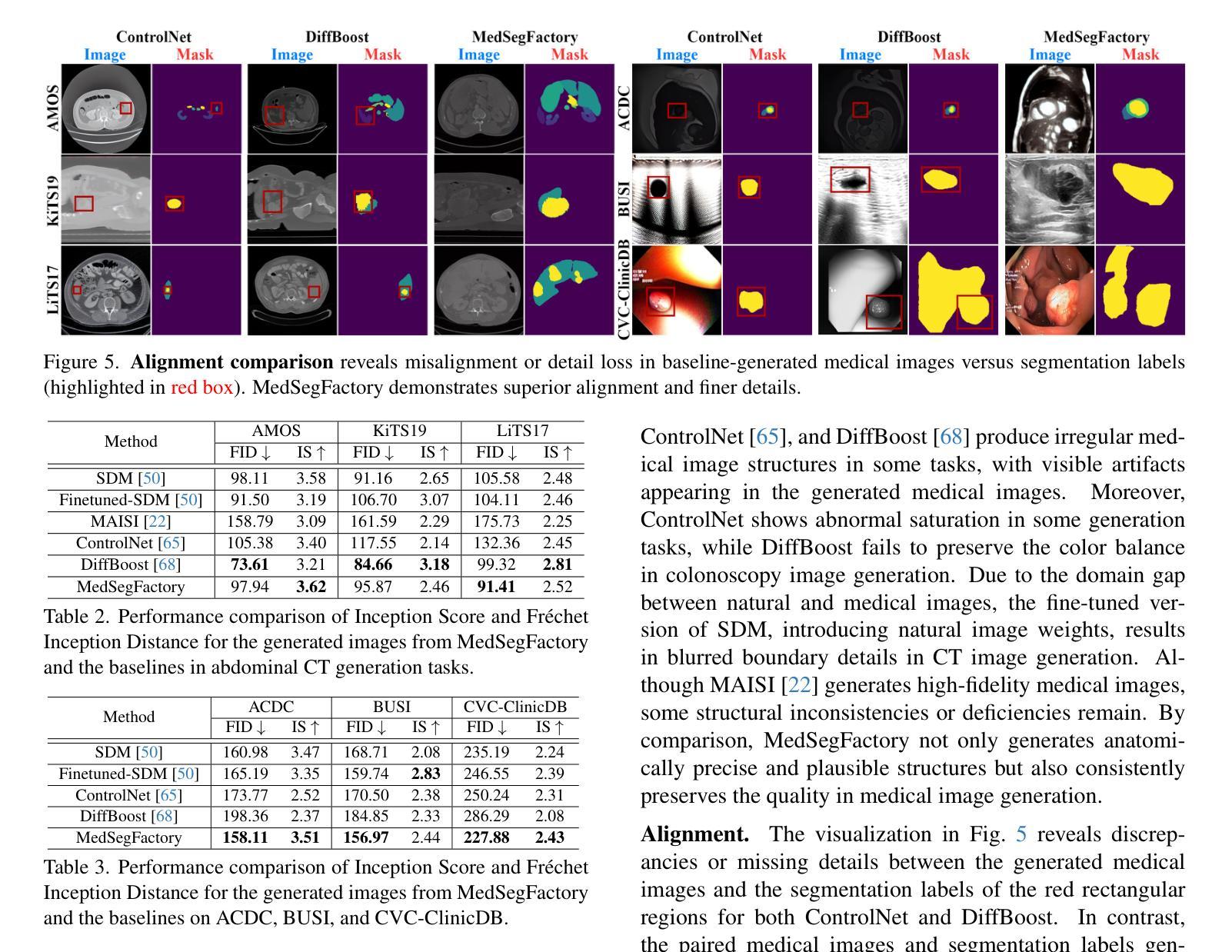
MedSegFactory: Text-Guided Generation of Medical Image-Mask Pairs
Authors:Jiawei Mao, Yuhan Wang, Yucheng Tang, Daguang Xu, Kang Wang, Yang Yang, Zongwei Zhou, Yuyin Zhou
This paper presents MedSegFactory, a versatile medical synthesis framework that generates high-quality paired medical images and segmentation masks across modalities and tasks. It aims to serve as an unlimited data repository, supplying image-mask pairs to enhance existing segmentation tools. The core of MedSegFactory is a dual-stream diffusion model, where one stream synthesizes medical images and the other generates corresponding segmentation masks. To ensure precise alignment between image-mask pairs, we introduce Joint Cross-Attention (JCA), enabling a collaborative denoising paradigm by dynamic cross-conditioning between streams. This bidirectional interaction allows both representations to guide each other’s generation, enhancing consistency between generated pairs. MedSegFactory unlocks on-demand generation of paired medical images and segmentation masks through user-defined prompts that specify the target labels, imaging modalities, anatomical regions, and pathological conditions, facilitating scalable and high-quality data generation. This new paradigm of medical image synthesis enables seamless integration into diverse medical imaging workflows, enhancing both efficiency and accuracy. Extensive experiments show that MedSegFactory generates data of superior quality and usability, achieving competitive or state-of-the-art performance in 2D and 3D segmentation tasks while addressing data scarcity and regulatory constraints.
本文介绍了MedSegFactory,这是一个通用的医学合成框架,能够生成跨模态和任务的配对高质量医学图像和分割掩膜。它的目标是作为一个无限的数据存储库,为现有的分割工具提供图像-掩膜对,以增强其功能。MedSegFactory的核心是一个双流扩散模型,其中一个流负责合成医学图像,另一个流生成相应的分割掩膜。为了确保图像-掩膜对之间的精确对齐,我们引入了联合交叉注意力(JCA)机制,通过流之间的动态交叉条件,实现协同去噪范式。这种双向交互允许两种表示形式相互引导生成,增强了生成对之间的一致性。MedSegFactory通过用户定义的提示(指定目标标签、成像模式、解剖区域和病理状况)解锁按需生成配对医学图像和分割掩膜的能力,促进了可扩展性和高质量的数据生成。这种新的医学图像合成范式能够无缝地融入各种医学成像工作流程中,提高效率和准确性。大量实验表明,MedSegFactory生成的数据具有卓越的质量和可用性,在二维和三维分割任务中达到了竞争或最先进的性能,同时解决了数据稀缺和监管约束的问题。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 8 figures, The project page can be accessed via https://jwmao1.github.io/MedSegFactory_web
摘要
MedSegFactory是一个多功能医学合成框架,可生成跨模态和任务的配对高质量医学图像和分割掩膜。旨在作为无限的数据存储库,为现有分割工具提供图像-掩膜对以增强其功能。其核心是一个双流扩散模型,其中一流合成医学图像,另一流生成相应的分割掩膜。为确保图像-掩膜对之间的精确对齐,引入了联合交叉注意(JCA)机制,通过双流间的动态交叉条件实现协同去噪范式。这种双向交互使两种表示能够相互引导生成,增强生成对之间的一致性。MedSegFactory通过用户定义提示,解锁按需生成配对医学图像和分割掩膜的能力,这些提示指定目标标签、成像模态、解剖区域和病理状况,促进可扩展性和高质量的数据生成。这种新的医学图像合成范式能够无缝融入多样化的医学成像工作流程,提高效率和准确性。大量实验表明,MedSegFactory生成的数据质量高、实用性强,在二维和三维分割任务中达到或保持竞争前沿的性能,同时解决数据稀缺和监管约束问题。
关键见解
- MedSegFactory是一个医学合成框架,能生成高质量跨模态和任务配对的医学图像和分割掩膜。
- 它作为一个无限数据仓库,旨在增强现有分割工具的功能。
- 双流扩散模型是MedSegFactory的核心,其中包括图像合成和分割掩膜生成两个流。
- 引入的Joint Cross-Attention机制确保了图像和掩膜之间的精确对齐。
- 这种合成方法允许通过用户定义的提示(如目标标签、成像模态等)按需生成数据。
- MedSegFactory在二维和三维分割任务中表现出卓越性能,解决了数据稀缺问题。
- 生成的图像和掩膜具有高度的实用性和质量,能够满足各种医学成像工作流程的需求。
点此查看论文截图

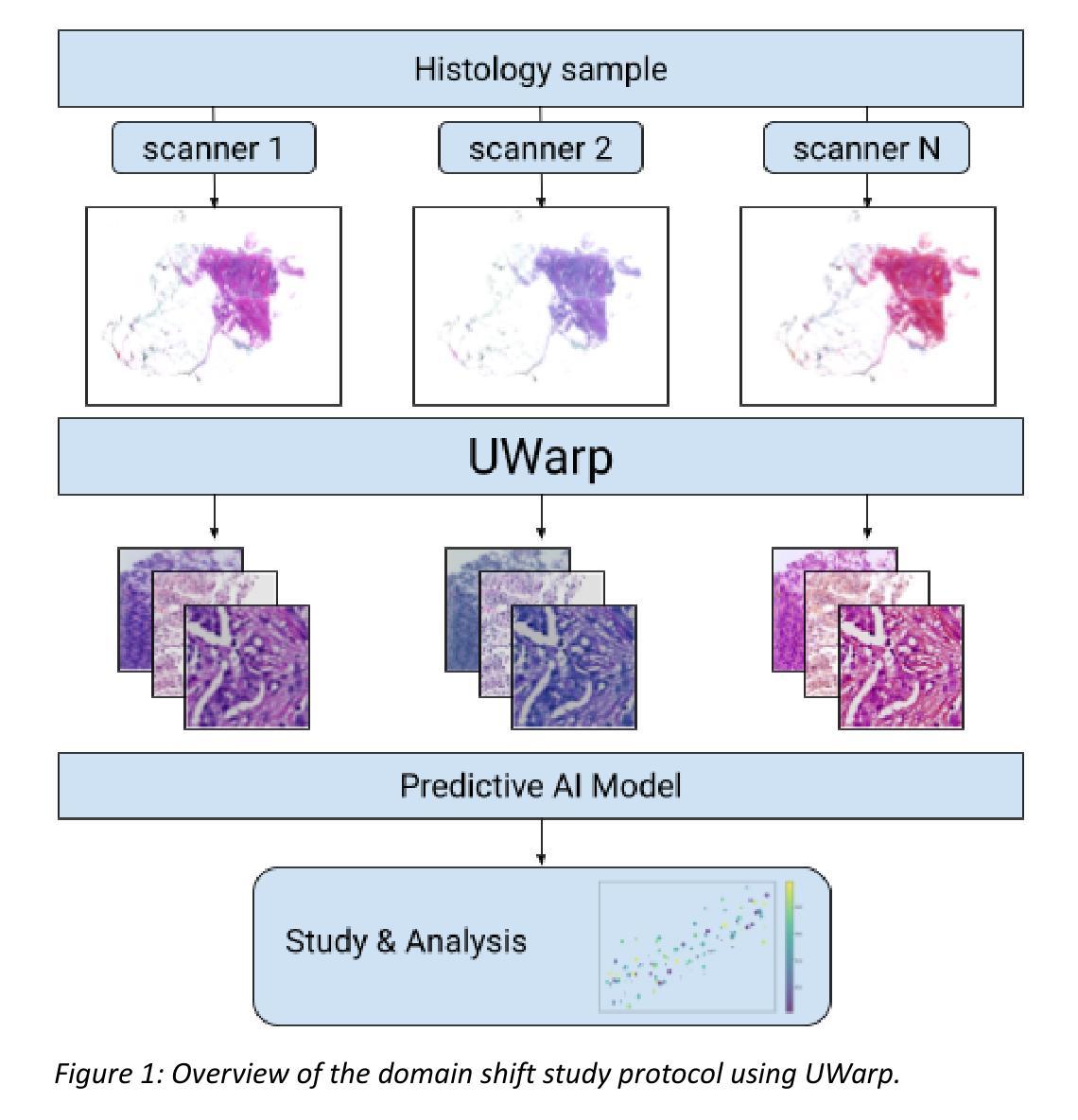
UWarp: A Whole Slide Image Registration Pipeline to Characterize Scanner-Induced Local Domain Shift
Authors:Antoine Schieb, Bilal Hadjadji, Natalia Fernanda Valderrama, Daniel Tshokola Mweze, Valentin Derangère, Laurent Arnould, Sylvain Ladoire, Alain Lalande, Alessio Fiorin, Carlos López Pablo, Noèlia Gallardo Borràs, Shrief Abdelazeez, Vincenzo Della Mea, Anna Korzynska, Louis-Oscar Morel, Nathan Vinçon
Histopathology slide digitization introduces scanner-induced domain shift that can significantly impact computational pathology models based on deep learning methods. In the state-of-the-art, this shift is often characterized at a broad scale (slide-level or dataset-level) but not patch-level, which limits our comprehension of the impact of localized tissue characteristics on the accuracy of the deep learning models. To address this challenge, we present a domain shift analysis framework based on UWarp, a novel registration tool designed to accurately align histological slides scanned under varying conditions. UWarp employs a hierarchical registration approach, combining global affine transformations with fine-grained local corrections to achieve robust tissue patch alignment. We evaluate UWarp using two private datasets, CypathLung and BosomShieldBreast, containing whole slide images scanned by multiple devices. Our experiments demonstrate that UWarp outperforms existing open-source registration methods, achieving a median target registration error (TRE) of less than 4 pixels (<1 micrometer at 40x magnification) while significantly reducing computational time. Additionally, we apply UWarp to characterize scanner-induced local domain shift in the predictions of Breast-NEOprAIdict, a deep learning model for breast cancer pathological response prediction. We find that prediction variability is strongly correlated with tissue density on a given patch. Our findings highlight the importance of localized domain shift analysis and suggest that UWarp can serve as a valuable tool for improving model robustness and domain adaptation strategies in computational pathology.
病理切片数字化引入了由扫描仪引起的领域偏移,这可能会显著影响基于深度学习方法的计算病理学模型。在最新研究中,这种偏移通常在大规模(幻灯片级别或数据集级别)上被描述,而不是在补丁级别上,这限制了我们对局部组织特性对深度学习模型准确性影响的理解。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了一个基于UWarp的领域偏移分析框架。UWarp是一个新的注册工具,旨在准确地对不同条件下扫描的组织切片进行对齐。UWarp采用分层注册方法,结合全局仿射变换和精细的局部校正,实现稳健的组织补丁对齐。我们使用两个私有数据集CypathLung和BosomShieldBreast(包含由多台设备扫描的整张幻灯片图像)对UWarp进行了评估。实验表明,UWarp在目标注册误差(TRE)方面优于现有的开源注册方法,误差中位数低于4像素(在40倍放大率下小于1微米),同时大大减少了计算时间。此外,我们将UWarp应用于表征扫描仪引起的局部领域偏移对乳腺癌病理反应预测模型Breast-NEOprAIdict预测结果的影响。我们发现预测的可变性与给定补丁上的组织密度密切相关。我们的研究结果强调了局部领域偏移分析的重要性,并表明UWarp可以作为提高计算病理学模型的稳健性和领域适应策略的有价值工具。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF preprint
Summary
深度学习模型在计算病理学上受到病理切片数字化扫描引起的领域漂移影响。现有研究主要在切片或数据集层面进行分析,缺乏对斑块级别的研究。本文提出一个基于UWarp的领域漂移分析框架,采用多层次注册方法实现组织斑块的精确对齐。实验证明UWarp优于现有开源注册方法,显著提高预测模型的稳健性。同时发现预测变量的变化与特定斑块的组织密度紧密相关。强调局部领域漂移分析的重要性,UWarp有望成为改善模型稳健性和领域适应策略的有力工具。
Key Takeaways
- 病理切片数字化扫描引入领域漂移,影响深度学习模型在计算病理学上的应用。
- 领域漂移分析通常在切片或数据集层面进行,缺乏对斑块级别的研究。
- 提出基于UWarp的领域漂移分析框架,实现组织斑块的精确对齐。
- 实验证明UWarp在注册精度和计算效率上优于现有方法。
- 将UWarp应用于乳腺癌病理反应预测模型,发现预测变量的变化与斑块组织密度有关。
- 局部领域漂移分析的重要性被强调。
点此查看论文截图

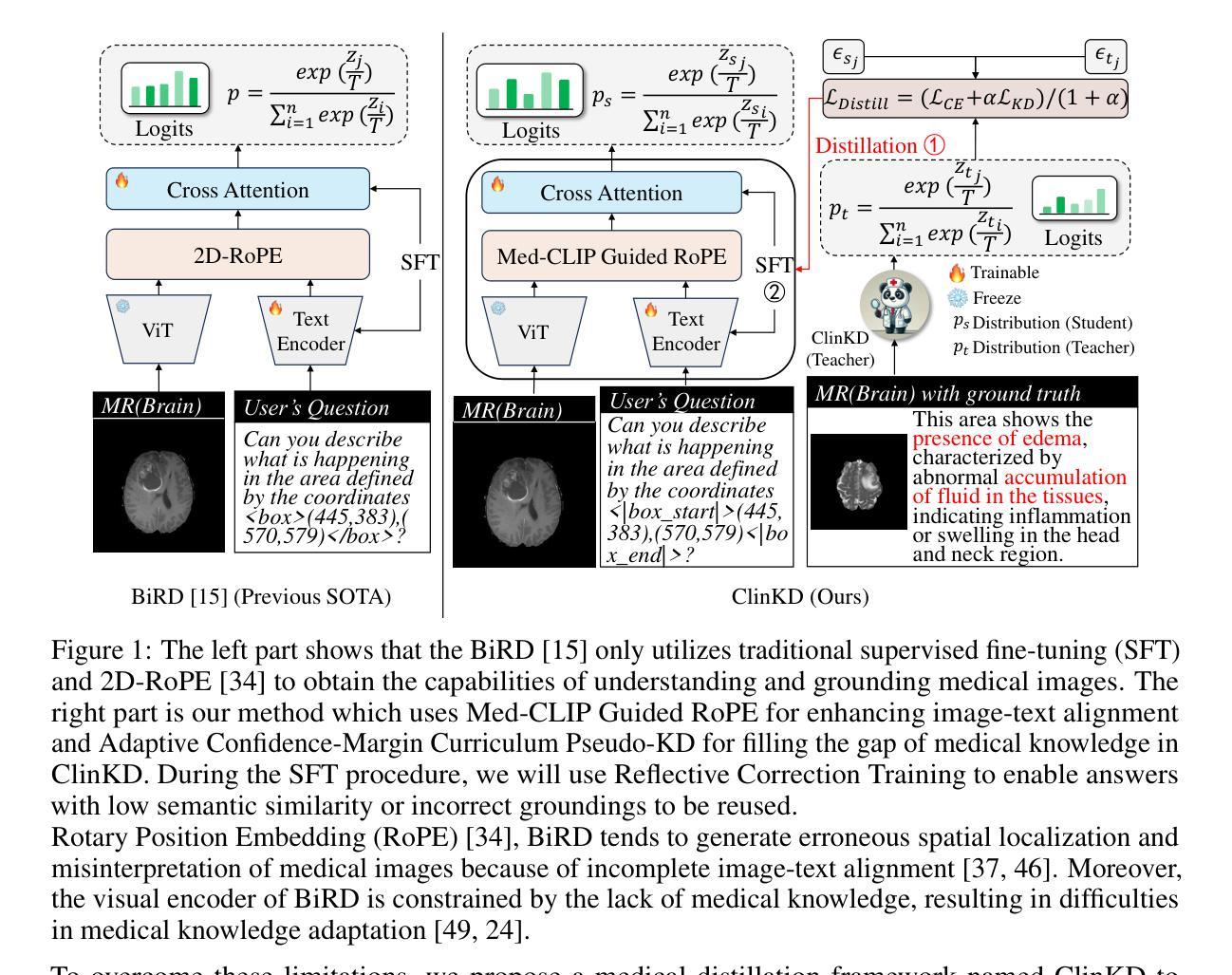
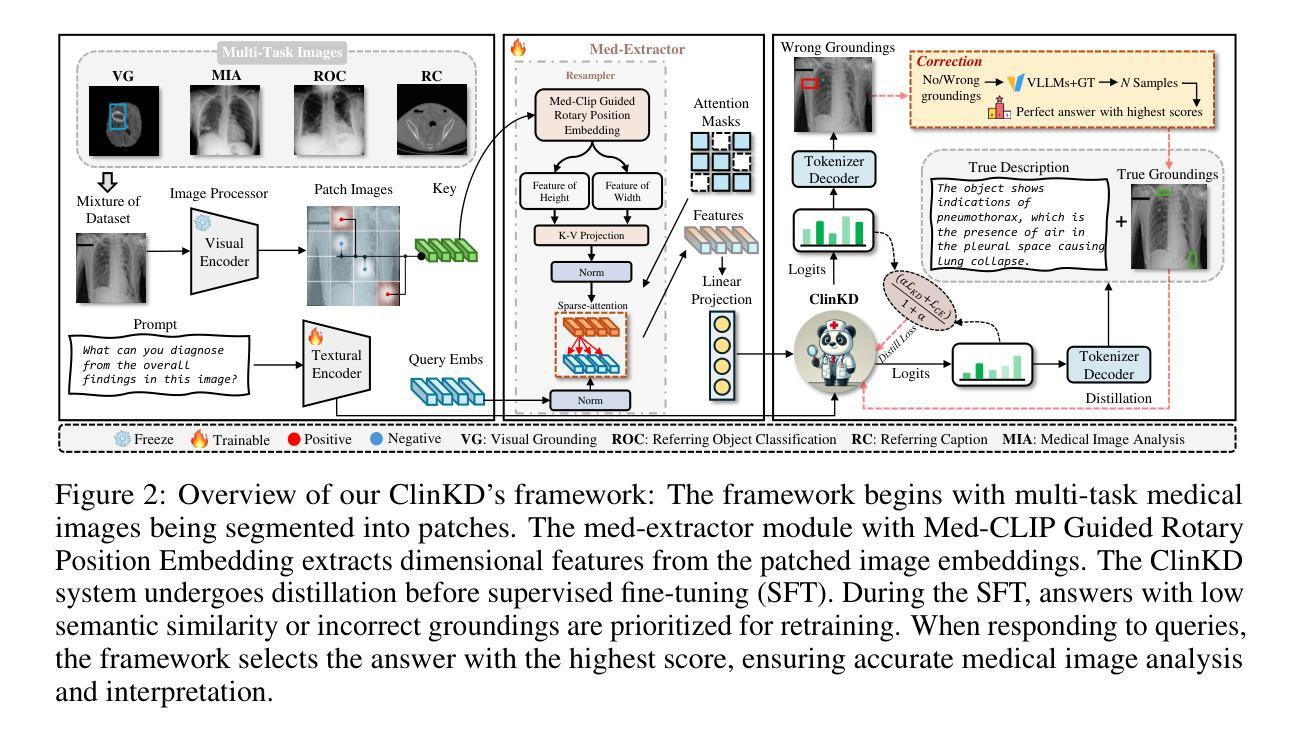
ClinKD: Cross-Modal Clinical Knowledge Distiller For Multi-Task Medical Images
Authors:Hongyu Ge, Longkun Hao, Zihui Xu, Zhenxin Lin, Bin Li, Shoujun Zhou, Hongjin Zhao, Yihang Liu
Medical Visual Question Answering (Med-VQA) represents a critical and challenging subtask within the general VQA domain. Despite significant advancements in general VQA, multimodal large language models (MLLMs) still exhibit substantial limitations when handling multi-task VQA scenarios. These limitations manifest through erroneous spatial localization and misinterpretation of medical images, which primarily arise from two fundamental issues: inadequate image-text alignment and insufficient domain-specified knowledge for medical applications. To address these issues, we introduce the Cross-Modal Clinical Knowledge Distiller (ClinKD), an innovative framework designed to enhance image-text alignment and establish more effective medical knowledge transformation mechanisms, which enables MLLMs to perform better even when lacking prior medical knowledge. Our extensive experimental evaluations demonstrate that the ClinKD achieves state-of-the-art performance on several datasets which are challenging for Med-VQA task. The results indicate that our approach not only significantly improves image-text alignment but also effectively enables MLLMs to adapt to the medical knowledge. The source code for ClinKD is available at: https://github.com/overloadedHenry/ClinKD.
医疗视觉问答(Med-VQA)是通用VQA领域中的一个重要且具有挑战性的子任务。尽管通用VQA取得了重大进展,但在处理多任务VQA场景时,多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)仍显示出明显的局限性。这些局限性表现为医疗图像的空间定位错误和误解,这主要源于两个基本问题:图像文本对齐不足和针对医疗应用的特定领域知识不足。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了跨模态临床知识蒸馏器(ClinKD),这是一个创新框架,旨在增强图像文本对齐并建立更有效的医学知识转换机制,使MLLM即使在缺乏先验医学知识的情况下也能表现更好。我们的广泛实验评估表明,ClinKD在几个对Med-VQA任务具有挑战性的数据集上达到了最新性能。结果表明,我们的方法不仅显著提高了图像文本对齐,而且有效地使MLLM适应了医学知识。ClinKD的源代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/overloadedHenry/ClinKD。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对医学视觉问答(Med-VQA)任务中多任务问答场景下的挑战,提出一种跨模态临床知识蒸馏器(ClinKD)框架,该框架能增强图像文本对齐并建立有效的医学知识转换机制,即使在没有先验医学知识的情况下也能提高大型多模态语言模型的性能。在多个数据集上的实验评估表明,ClinKD在Med-VQA任务上达到了最新技术水平。
Key Takeaways
- Med-VQA是VQA领域中的一个重要且具挑战性的子任务。
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在处理Med-VQA时面临图像文本对齐和医学知识转换的问题。
- 跨模态临床知识蒸馏器(ClinKD)框架旨在解决这些问题,增强图像文本对齐并建立有效的医学知识转换机制。
- ClinKD框架使得MLLMs在缺乏先验医学知识的情况下也能表现良好。
- ClinKD在多个数据集上的实验评估表现出其优异性能,达到最新技术水平。
- ClinKD公开源代码可供研究使用。
点此查看论文截图